Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 54(2); 2020 > Article
-
Review
Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology -
Soojeong Nam1,*
 , Yosep Chong2,*
, Yosep Chong2,* , Chan Kwon Jung2
, Chan Kwon Jung2 , Tae-Yeong Kwak3
, Tae-Yeong Kwak3 , Ji Youl Lee4
, Ji Youl Lee4 , Jihwan Park5,6
, Jihwan Park5,6 , Mi Jung Rho5
, Mi Jung Rho5 , Heounjeong Go1
, Heounjeong Go1
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2020;54(2):125-134.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.12.31
Published online: February 13, 2020
1Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Hospital Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
3Deep Bio Inc., Seoul, Korea
4Department of Urology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
5Catholic Cancer Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
6Department of Biomedicine & Health Sciences, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Heounjeong Go, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Seoul 05505, Korea Tel: +82-2-3010-5888, Fax: +82-2-472-7898, E-mail: damul37@amc.seoul.kr
- *Soojeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, and Tae-Yeong Kwak contributed equally to this work.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Deep learning model to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis from haematoxylin/eosin-stained myocardial tissue
Takeshi Tohyama, Takeshi Iwasaki, Masataka Ikeda, Masato Katsuki, Tatsuya Watanabe, Kayo Misumi, Keisuke Shinohara, Takeo Fujino, Toru Hashimoto, Shouji Matsushima, Tomomi Ide, Junji Kishimoto, Koji Todaka, Yoshinao Oda, Kohtaro Abe
European Heart Journal - Imaging Methods and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The current landscape of artificial intelligence in oral and maxillofacial surgery– a narrative review
Rushil Rajiv Dang, Balram Kadaikal, Sam El Abbadi, Branden R. Brar, Amit Sethi, Radhika Chigurupati
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the quality of whole slide images in cytology from nuclei features
Paul Barthe, Romain Brixtel, Yann Caillot, Benoît Lemoine, Arnaud Renouf, Vianney Thurotte, Ouarda Beniken, Sébastien Bougleux, Olivier Lézoray
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 17: 100420. CrossRef - An update on applications of digital pathology: primary diagnosis; telepathology, education and research
Shamail Zia, Isil Z. Yildiz-Aktas, Fazail Zia, Anil V. Parwani
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence–driven digital pathology in urological cancers: current trends and future directions
Inyoung Paik, Geongyu Lee, Joonho Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hong Koo Ha
Prostate International.2025; 13(4): 181. CrossRef - Label-free optical microscopy with artificial intelligence: a new paradigm in pathology
Chiho Yoon, Eunwoo Park, Donggyu Kim, Byullee Park, Chulhong Kim
Biophotonics Discovery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - EPIIC: Edge-Preserving Method Increasing Nuclei Clarity for Compression Artifacts Removal in Whole-Slide Histopathological Images
Julia Merta, Michal Marczyk
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4450. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of a 5G campus network and existing networks for real-time consultation in remote pathology
Ilgar I. Guseinov, Arnab Bhowmik, Somaia AbuBaker, Anna E. Schmaus-Klughammer, Thomas Spittler
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 18: 100444. CrossRef - The Evolution of Digital Pathology in Infrastructure, Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Impact
Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 6. CrossRef - Role of Telepathology, Artificial Intelligence, and Emerging Technologies in Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
Yugeshwari R. Tiwade, Obaid Noman, Pratibha Dawande, Nandkishor J Bankar, Sweta Bahadure, Praful Patil
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2025; 8(2): 115. CrossRef - Analysis of system and scanner downtime in a digital pathology–predominant institution: A 6-year experience
Ryan Reagans, Lokman Cevik, Himani Kumar, David Kellough, Abberly Lott Limbach, Giovanni Lujan, Anil Parwani, Hamza N Gokozan
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(4): 634. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Telepathology for Consultation in the Military Health System: An Evaluation of Pathologists’ Impressions of Facilitators and Barriers Prior to Implementation
Victoria Mahar, Zachary Colburn, Joshua Sakai
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(11): 104236. CrossRef - Online histostereometric analysis in digital forensic pathology: a technical report
Vladimir G. Nedugiv, Anna V. Zhukova, German V. Nedugov
Russian Journal of Forensic Medicine.2025; 11(2): 145. CrossRef - Latent representation of H&E images retains biological information in a breast cancer cohort
Chloé Benmussa, Esther Sanfeliu, Anabel Martínez-Romero, Blanca González-Farré, Tomás Pascual, Joaquín Gavilá, Alona Levy-Jurgenson, Ariel Shamir, Fara Brasó-Maristany, Aleix Prat, Zohar Yakhini, Amgad Muneer
PLOS One.2025; 20(9): e0329221. CrossRef - Modernizing Colorectal Cancer Care With Artificial Intelligence: Real-Time Detection, Radiomics, and Digital Pathology
Elmoatazbellah Nasr, Zaid Al-Hamid, Mina H Younan, Mohamed Omran, Maan Sarsam, Mohamed Abdellatif
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A multi-task learning model for evaluating non-tumor gastric diseases indicators in whole slide images
Mingxi Fu, Liming Liu, Fanglei Fu, Jingli Ouyang, Xueying Shi, Song Duan, Tian Guan, Yonghong He, Zhiqiang Cheng, Lianghui Zhu
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance Evaluation of MambaVision in Breast Cancer Detection from Histopathology Images
Hasan Zan
Dicle Üniversitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Mühendislik Dergisi.2025; 16(4): 879. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence for automatic detection of basal cell carcinoma from frozen tissue tangential biopsies
Dennis H Murphree, Yong-hun Kim, Kirk A Sidey, Nneka I Comfere, Nahid Y Vidal
Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.2024; 49(7): 719. CrossRef - Performance of externally validated machine learning models based on histopathology images for the diagnosis, classification, prognosis, or treatment outcome prediction in female breast cancer: A systematic review
Ricardo Gonzalez, Peyman Nejat, Ashirbani Saha, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Andrew P. Norgan, Cynthia Lokker
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100348. CrossRef - Invisible for a few but essential for many: the role of Histotechnologists in the establishment of digital pathology
Gisela Magalhães, Rita Calisto, Catarina Freire, Regina Silva, Diana Montezuma, Sule Canberk, Fernando Schmitt
Journal of Histotechnology.2024; 47(1): 39. CrossRef - Using digital pathology to analyze the murine cerebrovasculature
Dana M Niedowicz, Jenna L Gollihue, Erica M Weekman, Panhavuth Phe, Donna M Wilcock, Christopher M Norris, Peter T Nelson
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism.2024; 44(4): 595. CrossRef - PATrans: Pixel-Adaptive Transformer for edge segmentation of cervical nuclei on small-scale datasets
Hexuan Hu, Jianyu Zhang, Tianjin Yang, Qiang Hu, Yufeng Yu, Qian Huang
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2024; 168: 107823. CrossRef - CNAC-Seg: Effective segmentation for cervical nuclei in adherent cells and clusters via exploring gaps of receptive fields
Hexuan Hu, Jianyu Zhang, Tianjin Yang, Qiang Hu, Yufeng Yu, Qian Huang
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2024; 90: 105833. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: Current State and Future Implications
Swati Satturwar, Anil V. Parwani
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2024; 31(2): 136. CrossRef - Ensemble Deep Learning Model to Predict Lymphovascular Invasion in Gastric Cancer
Jonghyun Lee, Seunghyun Cha, Jiwon Kim, Jung Joo Kim, Namkug Kim, Seong Gyu Jae Gal, Ju Han Kim, Jeong Hoon Lee, Yoo-Duk Choi, Sae-Ryung Kang, Ga-Young Song, Deok-Hwan Yang, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Sangjeong Ahn, Kyoung Min Moon, Myung-Giun Noh
Cancers.2024; 16(2): 430. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence’s impact on breast cancer pathology: a literature review
Amr Soliman, Zaibo Li, Anil V. Parwani
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated Analysis of Nuclear Parameters in Oral Exfoliative Cytology Using Machine Learning
Shubhangi Mhaske, Karthikeyan Ramalingam, Preeti Nair, Shubham Patel, Arathi Menon P, Nida Malik, Sumedh Mhaske
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing AI Research for Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Datasets
Alessio Fiorin, Carlos López Pablo, Marylène Lejeune, Ameer Hamza Siraj, Vincenzo Della Mea
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine.2024; 37(6): 2996. CrossRef - Current Developments in Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Tumors: From Structure to Artificial Intelligence
Alexandra Corina Faur, Roxana Buzaș, Adrian Emil Lăzărescu, Laura Andreea Ghenciu
Life.2024; 14(6): 727. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN) diagnosis in rat kidneys using an artificial intelligence deep learning model
Yeji Bae, Jongsu Byun, Hangyu Lee, Beomseok Han
Toxicological Research.2024; 40(4): 551. CrossRef - A Pan-Cancer Patient-Derived Xenograft Histology Image Repository with Genomic and Pathologic Annotations Enables Deep Learning Analysis
Brian S. White, Xing Yi Woo, Soner Koc, Todd Sheridan, Steven B. Neuhauser, Shidan Wang, Yvonne A. Evrard, Li Chen, Ali Foroughi pour, John D. Landua, R. Jay Mashl, Sherri R. Davies, Bingliang Fang, Maria Gabriela Raso, Kurt W. Evans, Matthew H. Bailey, Y
Cancer Research.2024; 84(13): 2060. CrossRef - Non-contrasted computed tomography (NCCT) based chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) automatic diagnosis using cascaded network with multiple instance learning
Mayang Zhao, Liming Song, Jiarui Zhu, Ta Zhou, Yuanpeng Zhang, Shu-Cheng Chen, Haojiang Li, Di Cao, Yi-Quan Jiang, Waiyin Ho, Jing Cai, Ge Ren
Physics in Medicine & Biology.2024; 69(18): 185011. CrossRef - MR_NET: A Method for Breast Cancer Detection and Localization from Histological Images Through Explainable Convolutional Neural Networks
Rachele Catalano, Myriam Giusy Tibaldi, Lucia Lombardi, Antonella Santone, Mario Cesarelli, Francesco Mercaldo
Sensors.2024; 24(21): 7022. CrossRef - Advances in AI-Enhanced Biomedical Imaging for Cancer Immunology
Willa Wen-You Yim, Felicia Wee, Zheng Yi Ho, Xinyun Feng, Marcia Zhang, Samuel Lee, Inti Zlobec, Joe Yeong, Mai Chan Lau
World Scientific Annual Review of Cancer Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Blockchain: A safe digital technology to share cancer diagnostic results in pandemic times—Challenges and legacy for the future
Bruno Natan Santana Lima, Lucas Alves da Mota Santana, Rani Iani Costa Gonçalo, Carla Samily de Oliveira Costa, Daniel Pitanga de Sousa Nogueira, Cleverson Luciano Trento, Wilton Mitsunari Takeshita
Oral Surgery.2023; 16(3): 300. CrossRef - Pathologists’ acceptance of telepathology in the Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Hospitals in Saudi Arabia: A survey study
Raneem Alawashiz, Sharifah Abdullah AlDossary
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Atrous Convolved Hybrid Seg-Net Model with residual and attention mechanism for gland detection and segmentation in histopathological images
Manju Dabass, Jyoti Dabass
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2023; 155: 106690. CrossRef - Validation of a Machine Learning Expert Supporting System, ImmunoGenius, Using Immunohistochemistry Results of 3000 Patients with Lymphoid Neoplasms
Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kyung Jin Seo, Hye-Ra Jung, Gyeongsin Park, Seung-Sook Lee, Yosep Chong
Diagnostics.2023; 13(7): 1308. CrossRef - Diagnosing Infectious Diseases in Poultry Requires a Holistic Approach: A Review
Dieter Liebhart, Ivana Bilic, Beatrice Grafl, Claudia Hess, Michael Hess
Poultry.2023; 2(2): 252. CrossRef - Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Canine Mammary Tumor Histopathological Image Classification via Computer-Aided Pathology: An Available Dataset for Imaging Analysis
Giovanni P. Burrai, Andrea Gabrieli, Marta Polinas, Claudio Murgia, Maria Paola Becchere, Pierfranco Demontis, Elisabetta Antuofermo
Animals.2023; 13(9): 1563. CrossRef - Rapid digital pathology of H&E-stained fresh human brain specimens as an alternative to frozen biopsy
Bhaskar Jyoti Borah, Yao-Chen Tseng, Kuo-Chuan Wang, Huan-Chih Wang, Hsin-Yi Huang, Koping Chang, Jhih Rong Lin, Yi-Hua Liao, Chi-Kuang Sun
Communications Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Applied machine learning in hematopathology
Taher Dehkharghanian, Youqing Mu, Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Clinton J. V. Campbell
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2023; 45(S2): 87. CrossRef - Automated diagnosis of 7 canine skin tumors using machine learning on H&E-stained whole slide images
Marco Fragoso-Garcia, Frauke Wilm, Christof A. Bertram, Sophie Merz, Anja Schmidt, Taryn Donovan, Andrea Fuchs-Baumgartinger, Alexander Bartel, Christian Marzahl, Laura Diehl, Chloe Puget, Andreas Maier, Marc Aubreville, Katharina Breininger, Robert Klopf
Veterinary Pathology.2023; 60(6): 865. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in the Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Sangjoon Choi, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 410. CrossRef - Efficient Convolution Network to Assist Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Target Therapy
Ching-Wei Wang, Kai-Lin Chu, Hikam Muzakky, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
Cancers.2023; 15(15): 3991. CrossRef - Multi-Configuration Analysis of DenseNet Architecture for Whole Slide Image Scoring of ER-IHC
Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Md Jahid Hasan, Zaka Ur Rehman, Jenny Tung Hiong Lee, See Yee Khor, Lai-Meng Looi, Fazly Salleh Abas, Afzan Adam, Elaine Wan Ling Chan, Sei-Ichiro Kamata
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 79911. CrossRef - Digitization of Pathology Labs: A Review of Lessons Learned
Lars Ole Schwen, Tim-Rasmus Kiehl, Rita Carvalho, Norman Zerbe, André Homeyer
Laboratory Investigation.2023; 103(11): 100244. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration/Biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) for Solid Pancreatic Lesions: Opportunities and Challenges
Xianzheng Qin, Taojing Ran, Yifei Chen, Yao Zhang, Dong Wang, Chunhua Zhou, Duowu Zou
Diagnostics.2023; 13(19): 3054. CrossRef - Deep Learning for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cholangiocarcinoma, and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Hyun-Jong Jang, Jai-Hyang Go, Younghoon Kim, Sung Hak Lee
Cancers.2023; 15(22): 5389. CrossRef - AIR-UNet++: a deep learning framework for histopathology image segmentation and detection
Anusree Kanadath, J. Angel Arul Jothi, Siddhaling Urolagin
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2023; 83(19): 57449. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Dermatological Condition Detection: A Systematic Review With Recent Methods, Datasets, Challenges, and Future Directions
Stephanie S. Noronha, Mayuri A. Mehta, Dweepna Garg, Ketan Kotecha, Ajith Abraham
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 140348. CrossRef - Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice
Vipul Baxi, Robin Edwards, Michael Montalto, Saurabh Saha
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(1): 23. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Toxicological Pathology: Quantitative Evaluation of Compound-Induced Follicular Cell Hypertrophy in Rat Thyroid Gland Using Deep Learning Models
Valeria Bertani, Olivier Blanck, Davy Guignard, Frederic Schorsch, Hannah Pischon
Toxicologic Pathology.2022; 50(1): 23. CrossRef - Investigating the genealogy of the literature on digital pathology: a two-dimensional bibliometric approach
Dayu Hu, Chengyuan Wang, Song Zheng, Xiaoyu Cui
Scientometrics.2022; 127(2): 785. CrossRef - Digital Dermatopathology and Its Application to Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Yeongjoo Oh, Hye Min Kim, Soon Won Hong, Eunah Shin, Jihee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(Suppl): S112. CrossRef - Assessment of parathyroid gland cellularity by digital slide analysis
Rotem Sagiv, Bertha Delgado, Oleg Lavon, Vladislav Osipov, Re'em Sade, Sagi Shashar, Ksenia M. Yegodayev, Moshe Elkabets, Ben-Zion Joshua
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 58: 151907. CrossRef - PancreaSys: An Automated Cloud-Based Pancreatic Cancer Grading System
Muhammad Nurmahir Mohamad Sehmi, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Elaine Wan Ling Chan
Frontiers in Signal Processing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Classification of Mouse Lung Metastatic Tumor with Deep Learning
Ha Neul Lee, Hong-Deok Seo, Eui-Myoung Kim, Beom Seok Han, Jin Seok Kang
Biomolecules & Therapeutics.2022; 30(2): 179. CrossRef - Techniques for digital histological morphometry of the pineal gland
Bogdan-Alexandru Gheban, Horaţiu Alexandru Colosi, Ioana-Andreea Gheban-Roșca, Carmen Georgiu, Dan Gheban, Doiniţa Crişan, Maria Crişan
Acta Histochemica.2022; 124(4): 151897. CrossRef - Current Trend of Artificial Intelligence Patents in Digital Pathology: A Systematic Evaluation of the Patent Landscape
Muhammad Joan Ailia, Nishant Thakur, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Chan Kwon Jung, Kwangil Yim, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2400. CrossRef - Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence from Histopathologic Image-Based Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Solid Cancers: A Systematic Review
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Nishant Thakur, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(11): 2590. CrossRef - Development of a prognostic prediction support system for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia using artificial intelligence-based diagnosis
Takayuki Takahashi, Hikaru Matsuoka, Rieko Sakurai, Jun Akatsuka, Yusuke Kobayashi, Masaru Nakamura, Takashi Iwata, Kouji Banno, Motomichi Matsuzaki, Jun Takayama, Daisuke Aoki, Yoichiro Yamamoto, Gen Tamiya
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Applications in Pathology
Heounjeong Go
Brain Tumor Research and Treatment.2022; 10(2): 76. CrossRef - Mass spectrometry imaging to explore molecular heterogeneity in cell culture
Tanja Bien, Krischan Koerfer, Jan Schwenzfeier, Klaus Dreisewerd, Jens Soltwisch
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrating artificial intelligence in pathology: a qualitative interview study of users' experiences and expectations
Jojanneke Drogt, Megan Milota, Shoko Vos, Annelien Bredenoord, Karin Jongsma
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1540. CrossRef - Deep Learning on Basal Cell Carcinoma In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy Data
Veronika Shavlokhova, Michael Vollmer, Patrick Gholam, Babak Saravi, Andreas Vollmer, Jürgen Hoffmann, Michael Engel, Christian Freudlsperger
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1471. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Classification of Uterine Cervical and Endometrial Cancer Subtypes from Whole-Slide Histopathology Images
JaeYen Song, Soyoung Im, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2623. CrossRef - A self-supervised contrastive learning approach for whole slide image representation in digital pathology
Parsa Ashrafi Fashi, Sobhan Hemati, Morteza Babaie, Ricardo Gonzalez, H.R. Tizhoosh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2022; 13: 100133. CrossRef - A Matched-Pair Analysis of Nuclear Morphologic Features Between Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Specimen in Thyroid Tumors Using a Deep Learning Model
Faridul Haq, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(4): 472. CrossRef - Development of quality assurance program for digital pathology by the Korean Society of Pathologists
Yosep Chong, Jeong Mo Bae, Dong Wook Kang, Gwangil Kim, Hye Seung Han
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 370. CrossRef - Machine learning in renal pathology
Matthew Nicholas Basso, Moumita Barua, Julien Meyer, Rohan John, April Khademi
Frontiers in Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole Slide Image Quality in Digital Pathology: Review and Perspectives
Romain Brixtel, Sebastien Bougleux, Olivier Lezoray, Yann Caillot, Benoit Lemoine, Mathieu Fontaine, Dalal Nebati, Arnaud Renouf
IEEE Access.2022; 10: 131005. CrossRef - Generalizability of Deep Learning System for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Various Cancers
Hyun-Jong Jang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 808. CrossRef - Recent advances in the use of stimulated Raman scattering in histopathology
Martin Lee, C. Simon Herrington, Manasa Ravindra, Kristel Sepp, Amy Davies, Alison N. Hulme, Valerie G. Brunton
The Analyst.2021; 146(3): 789. CrossRef - Preference and Demand for Digital Pathology and Computer-Aided Diagnosis among Korean Pathologists: A Survey Study Focused on Prostate Needle Biopsy
Soo Jeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(16): 7380. CrossRef - An SVM approach towards breast cancer classification from H&E-stained histopathology images based on integrated features
M. A. Aswathy, M. Jagannath
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2021; 59(9): 1773. CrossRef - Diagnosis prediction of tumours of unknown origin using ImmunoGenius, a machine learning-based expert system for immunohistochemistry profile interpretation
Yosep Chong, Nishant Thakur, Ji Young Lee, Gyoyeon Hwang, Myungjin Choi, Yejin Kim, Hwanjo Yu, Mee Yon Cho
Diagnostic Pathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning for Automatic Subclassification of Gastric Carcinoma Using Whole-Slide Histopathology Images
Hyun-Jong Jang, In-Hye Song, Sung-Hak Lee
Cancers.2021; 13(15): 3811. CrossRef - A novel evaluation method for Ki-67 immunostaining in paraffin-embedded tissues
Eliane Pedra Dias, Nathália Silva Carlos Oliveira, Amanda Oliveira Serra-Campos, Anna Karoline Fausto da Silva, Licínio Esmeraldo da Silva, Karin Soares Cunha
Virchows Archiv.2021; 479(1): 121. CrossRef - Assessment of Digital Pathology Imaging Biomarkers Associated with Breast Cancer Histologic Grade
Andrew Lagree, Audrey Shiner, Marie Angeli Alera, Lauren Fleshner, Ethan Law, Brianna Law, Fang-I Lu, David Dodington, Sonal Gandhi, Elzbieta A. Slodkowska, Alex Shenfield, Katarzyna J. Jerzak, Ali Sadeghi-Naini, William T. Tran
Current Oncology.2021; 28(6): 4298. CrossRef - Prediction of genetic alterations from gastric cancer histopathology images using a fully automated deep learning approach
Hyun-Jong Jang, Ahwon Lee, Jun Kang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(44): 7687. CrossRef - Clustered nuclei splitting based on recurrent distance transform in digital pathology images
Lukasz Roszkowiak, Anna Korzynska, Dorota Pijanowska, Ramon Bosch, Marylene Lejeune, Carlos Lopez
EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Trends of Artificial Intelligence for Colorectal Cancer Pathology Image Analysis: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Hongjun Yoon, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1884. CrossRef - A bird’s-eye view of deep learning in bioimage analysis
Erik Meijering
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2020; 18: 2312. CrossRef - Pathomics in urology
Victor M. Schuettfort, Benjamin Pradere, Michael Rink, Eva Comperat, Shahrokh F. Shariat
Current Opinion in Urology.2020; 30(6): 823. CrossRef - Model Fooling Attacks Against Medical Imaging: A Short Survey
Tuomo Sipola, Samir Puuska, Tero Kokkonen
Information & Security: An International Journal.2020; 46(2): 215. CrossRef - Recommendations for pathologic practice using digital pathology: consensus report of the Korean Society of Pathologists
Yosep Chong, Dae Cheol Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong-chul Kim, Sang Yong Song, Hee Jae Joo, Sang-Yeop Yi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 437. CrossRef - A machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosis prediction of lymphoid neoplasms using a probabilistic decision-tree algorithm and immunohistochemistry profile database
Yosep Chong, Ji Young Lee, Yejin Kim, Jingyun Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Gyeongsin Park, Mee Yon Cho, Nishant Thakur
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 462. CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


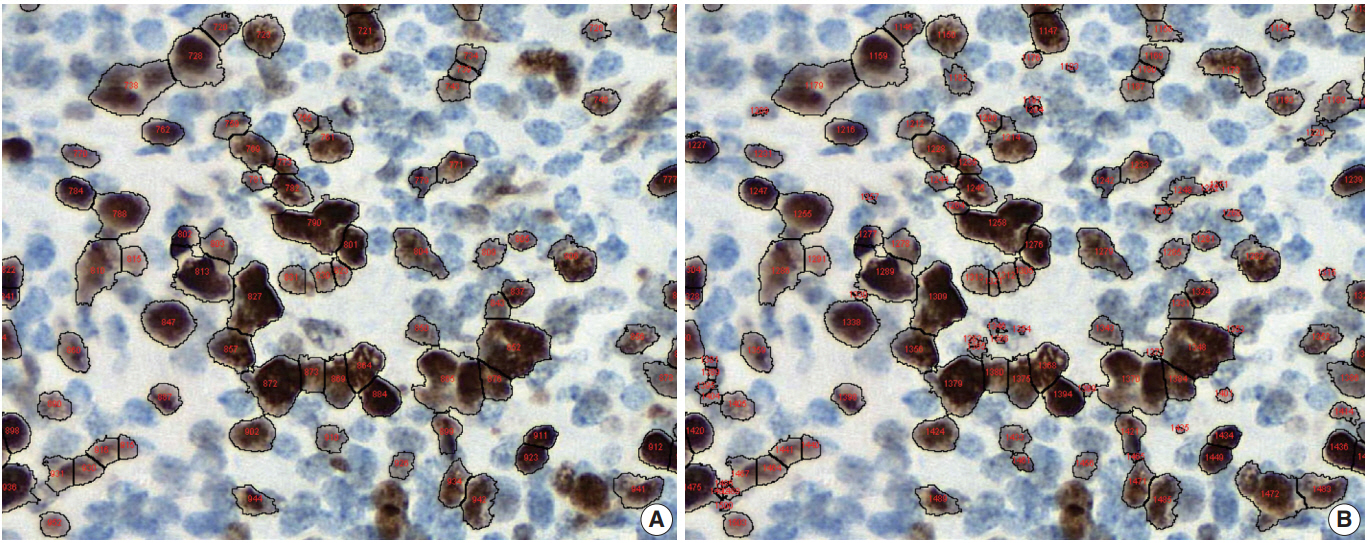
Fig. 1.
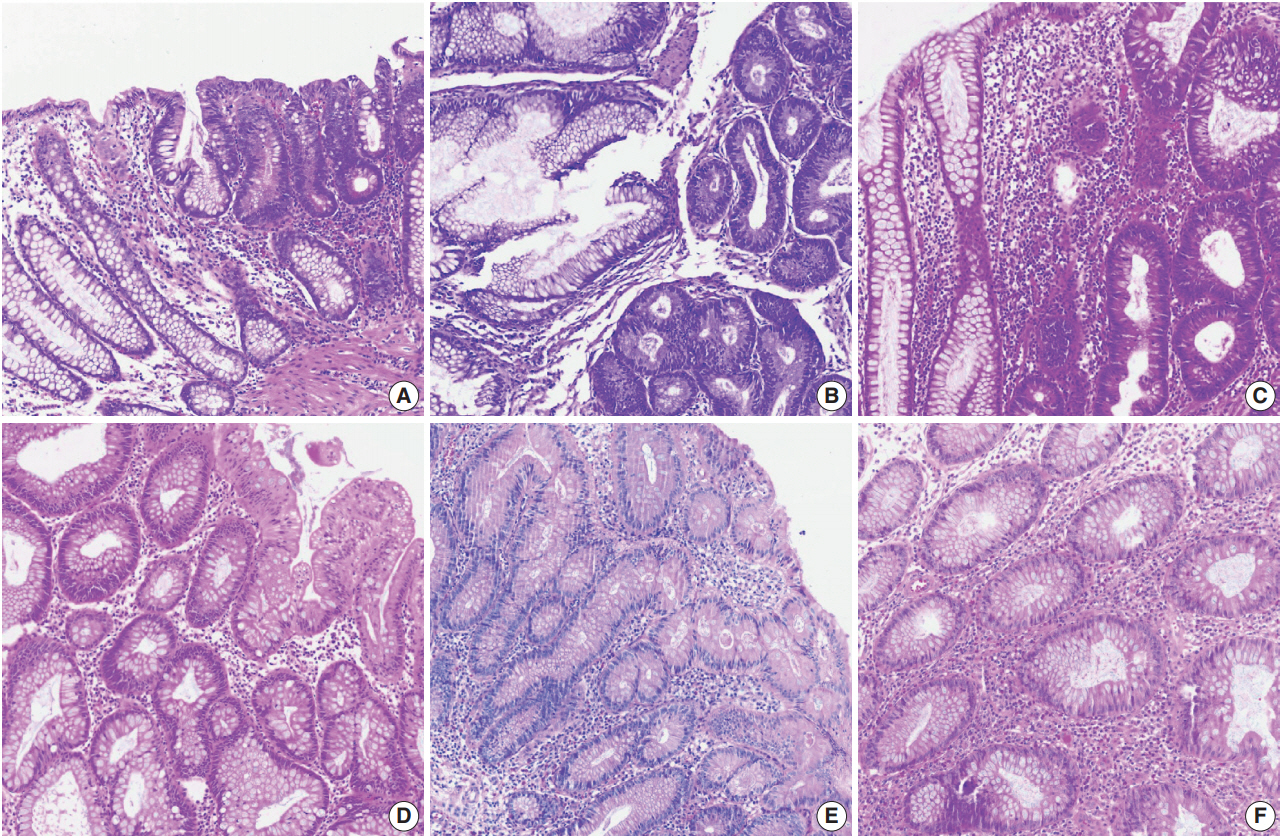
Fig. 2.
| Limitations |
|---|
| Lack of confidence in diagnostic results |
| Opacity of the diagnostic process |
| Lack of interpretability of diagnostic results |
| Opacity in the AI development process |
| Insufficient validation of AI |
| Inconvenience in practical use |
| Slow execution time of AI |
| Lack of clinical workflow integration |
| Simplicity of function |
| Limited to certain data and specific tasks |
AI, artificial intelligence.

 E-submission
E-submission