Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 55(5); 2021 > Article
-
Case Study
Appendiceal actinomycosis mimicking appendiceal tumor, appendicitis or inflammatory bowel disease -
You-Na Sung
 , Jihun Kim
, Jihun Kim
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2021;55(5):349-354.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.05.17
Published online: June 26, 2020
Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Jihun Kim, MD, PhD, Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, 88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 05505, Korea Tel: +82-2-3010-4556, Fax: +82-2-472-7898, E-mail: jihunkim@amc.seoul.kr
© 2021 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- Appendiceal actinomycosis is very rare and its diagnosis is often difficult even in surgically resected specimens. Here we report two cases of appendiceal actinomycosis confirmed by pathologic examination of surgically resected specimens. Characteristic histologic features included transmural chronic inflammation with Crohn-like lymphoid aggregates and polypoid mucosal protrusion into cecal lumen through fibrous expansion of the submucosa. Chronic active inflammation involved the mucosa of the appendix and cecum around the appendiceal orifice. Crohn’s disease with predominant cecal involvement and inflammatory pseudotumor were considered as differential diagnoses. Careful examination revealed a few actinomycotic colonies in the mucosa, confirming the diagnosis. A high index of suspicion with awareness of the characteristic histologic features might prompt careful inspection for the actinomycotic colonies, leading to the appropriate diagnosis of this rare disease.
- Case 1
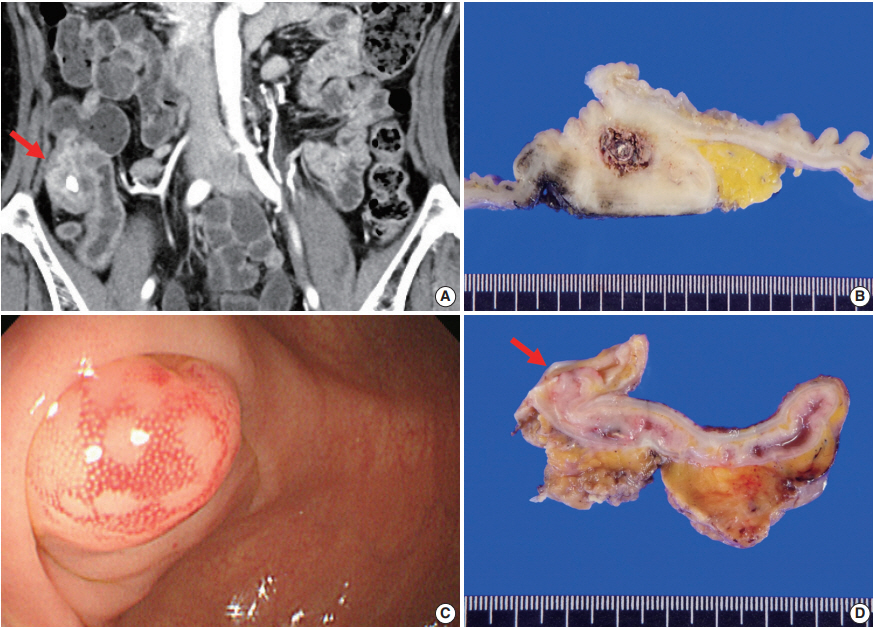
- A 61-year-old woman presented with a mass-like lesion on imaging studies during health screening without any specific symptom. She had been diagnosed with breast cancer 9 years ago. Laboratory tests revealed mild leukocytosis (11.1×102/μL) and increased C-reactive protein (3.41 mg/dL). Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) revealed appendicolith, periappendiceal fat infiltration with prominent wall thickening, and arterial enhancement in the appendiceal base (Fig. 1A). No mural thickening or contrast enhancement was found in the small intestine or other parts of the colon. Based on these findings, appendicitis with peri-appendiceal abscess or other inflammatory mass was suspected, but a primary appendiceal neoplasm could not be completely excluded. Colonofiberscopy (CFS) showed cecal contraction with multiple small polyps and scars in the large intestine. Intestinal tuberculosis was added to the list of differential diagnoses. Colonoscopic biopsy showed a focal active colitis pattern only and no actinomycotic colonies were found (data not shown).
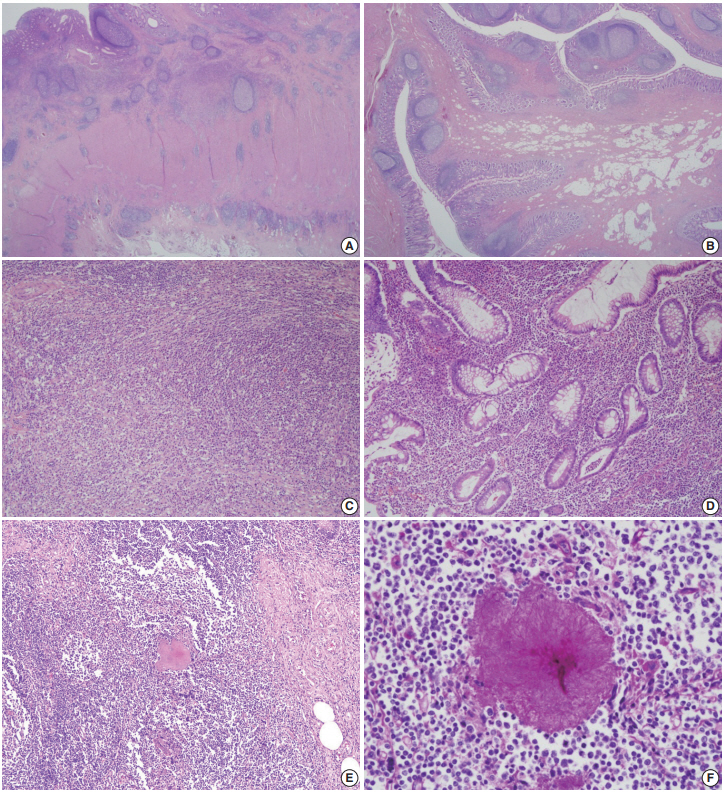
- Ileocecal resection was performed for histologic confirmation. Upon surgery, a mass-like lesion was observed in the appendiceal orifice and regional ileocolic lymph nodes were enlarged. On gross examination, the base of the appendiceal wall was markedly thickened and fibrotic (Fig. 1B). The appendiceal lumen was filled with fecal materials. On microscopy, the most striking features under low magnification were transmural chronic inflammation with Crohn-like lymphoid aggregates and marked mural thickening (Fig. 2A). The thickened appendiceal and peri-appendiceal cecal wall showed multiple foci of mixed chronic inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis reminiscent of inflammatory pseudotumor (Fig. 2C). The mucosa showed chronic active inflammation, including cryptitis, crypt abscess, crypt distortion, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in the lamina propria (Fig. 2D). Fibrous thickening of the subserosa and reactive regional lymph node hyperplasia were observed but there was no neutrophilic infiltration in the proper muscle. A few colonies of filamentous micro-organism of about 150 µm were found within the mucosa as well as in the appendiceal lumen (Fig. 2E), and the filamentous nature of the colonies were better appreciated on periodic acid–Schiff staining (Fig. 2F). The patient was diagnosed with appendiceal actinomycosis and was discharged without any complications. No additional antibiotics were taken, and until 6 months after surgery, there were no complications or recurrence of actinomycosis.
- Case 2
- A previously healthy 45-year-old man was incidentally found to have a submucosal mass in the periappendiceal orifice during routine CFS screening. An approximately 1.0 cm-sized hyperemic mucosal bulging was observed around the appendiceal orifice (Fig. 1C). Like case No. 1, the causative organisms were not found in the colonoscopic biopsy specimen. Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT showed intraluminal calcification and enhancing wall thickening in the appendix. Physical examination and laboratory investigation were unremarkable. Based on these findings, both chronic appendicitis and appendiceal malignancy were considered.
- The patient underwent ileocecal resection. On gross examination, mucosal bulging (about 1.0 cm in the greatest dimension) was observed in the appendiceal orifice (Fig. 1D). The entire appendiceal wall was fibrotic and the periappendiceal soft tissue was rough and hemorrhagic. A few actinomycotic colonies with surrounding active inflammation were observed in the mucosa. In contrast to case No. 1, additional gross examination and step sectioning were required for identification of the organisms. Prominent transmural reactive lymphoid hyperplasia was also present mainly in the appendix. Mucosal bulging, which looked like a mass lesion on CFS, turned out to be reactive fibroadipose tissue hypertrophy due to chronic inflammation (Fig. 2B). The patient was diagnosed with appendiceal actinoymycosis and discharged with oral antibiotics (amoxicillin) for 2 months. Ten months after the surgery, the patient had no other complications or recurrence of actinomycosis.
CASE REPORT
- The purpose of this report is to further define the pathologic features of appendiceal actinomycosis so that an accurate pathologic diagnosis can be made. Both cases had localized chronic transmural inflammation with scattered Crohn-like lymphoid aggregates or follicles across the base of the appendix and the cecum around the appendiceal orifice. In addition, there was reactive fibroadipose tissue hypertrophy that appeared as a bulging mass in the appendiceal orifice. Actinomycotic colonies, which are critical for the diagnosis, were relatively hard to find and only a few colonies were observed in the superficial lamina propria and appendiceal lumen. The appendiceal tip had fibrosis similar to chronic appendicitis, and active inflammation was rarely observed. Although a confirmatory diagnosis through colonoscopic biopsy is usually limited, awareness of these pathologic features might lead to an accurate diagnosis of this rare inflammatory mass-like lesion.
- To date, there have been a few reports in the literature describing appendiceal actinomycosis, and their clinicopathologic features are summarized in Table 1 [1,5,7-13]. Among the 10 cases, six cases were initially diagnosed with appendicitis, while atypical inflammatory condition was suspected in four cases, and one case was suspected to have a malignant tumor on imaging studies. In our series, both patients were asymptomatic, and a wide range of preoperative differential diagnoses including neoplasm, chronic appendicitis, inflammatory mass-like lesion, and tuberculosis were considered. Radiologically, the appendiceal actinomycosis can mimic a malignant neoplasm because it can show contrast enhancement and infiltration into the surrounding tissue. Although these are actually granulation tissue and fibrotic reaction associated with actinomycosis [6], complete exclusion of malignancy is often impossible. Furthermore, goblet cell adenocarcinoma of the appendix may frequently mimic an inflammatory lesion on abdominal CT [14], and tumor cells may not reach the appendiceal orifice in many of them. For these reasons, surgical exploration is frequently required for confirmatory diagnosis.
- In pathological perspective, Crohn’s disease is histologically quite similar to the actinomycosis in that chronic transmural inflammation is evident. In such cases, it is more suggestive of Crohn’s disease when the lesion is not limited to the appendix and histologic features such as patchy lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, non-caseating granulomas, fissure or fistula are observed in bowel segments other than the appendix. Thus, integration of colonoscopic findings and pathologic features is required to exclude Crohn’s disease in most cases.
- While acute appendicitis should be treated by surgical removal of the appendix [15,16], asymptomatic appendiceal actinomycosis as in our cases might be amenable to medical treatment with antibiotics [5]. Surgery is reserved for patients who fail to respond to antibiotic therapy, or for those with complicated disease as a therapeutic adjunct [4,5,8]. When patients do not show a progressive clinical course, and malignancy is not in the top list of radiologic differential diagnosis, antibiotic therapy might be carefully tried in the presence of microscopic proof of actinomycotic colonies. If patients respond to medical treatment, surveillance endoscopic biopsy along with radiologic test can be used afterwards. If not, pathologic confirmation after surgical resection is required [4,5,7].
- To try medical treatment in a patient with suspected appendiceal actinomycosis, detection of the organisms in colonoscopic material is essential. There is a report on an appendiceal actinomycosis case diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy [17]. In the report, the patient had a past history of prior surgical resection for colon adenocarcinoma, and follow up colonoscopic biopsy on a nodular lesion in the anastomosis site revealed actinomycotic colonies. However, in general, diagnostic actinomycotic colonies are seldom detected in biopsy material like the present series. Regarding the diagnostic sensitivity for the actinomycotic colonies, there is no consensus upon how many pieces of biopsy are recommended for detection of the causative organisms. In general, a greater number of biopsies would lead to a better diagnostic yield. However, abdominal actinomycosis cannot be easily diagnosed without surgical intervention and colonoscopic approach is often limited in terms of specimen size and accessibility to the lesion especially for that in the appendix. Thus, ultrasound or CT guided aspiration or biopsy, or explorative laparotomy may be a more realistic diagnostic option [5,9-11]. Furthermore, if there is a past history of previous surgical procedure, bowel preparation, trauma, or prolonged use of intrauterine devices, more aggressive preoperative diagnostic approach might be needed.
- In conclusion, integration of clinical, colonoscopic, and radiological features with pathologic findings is necessary to diagnose appendiceal actinomycosis. Awareness of these characteristic clinicopathologic features might lead to suspect and accurately diagnose this uncommon, but clinically important disease. Because the causative organisms are often very hard to find, serial sectioning is advised in colonoscopic biopsy material and extensive sampling is advised in surgically resected specimen.
DISCUSSION
Ethics Statement
Formal written informed consents were waived by the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (2019-1213).
Author contributions
Conceptualization: JK. Data curation: YNS, JK. Investigation: YNS, JK. Writing—original draft: YNS, JK. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
No funding to declare.
| Case | Study | Age (yr)/Sex | Symptom | Radiologic or colonoscopic finding | Initial diagnosis | Pathologic feature | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atalaia-Martins et al. (2018) [8] | 66/F | Abdominal pain | Subepithelial luminal protrusion in the region of the appendiceal orifice with a whitish liquid material discharge | Uncertain | Polymorphic cell infiltrate and erosion with appendiceal fibrosis | Right hemicolectomy |
| 2 | Gomez-Torres et al. (2017) [5] | 39/M | Abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting | Non compressible enlarged cecal appendix (58 mm) with peri-appendiceal edema | Appendicitis | Chronic fistulized appendicitis with transmural lymphoid infiltration | Appendectomy |
| 3 | Liu et al. (2016) [7] | 53/M | Abdominal pain, fever | Distended appendix (9 mm) with surrounding mesenteric stranding | Appendicitis | Lymphoid hyperplasia and chronic inflammatory cells in muscularis propria and serosa | Appendectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (6 months) |
| 4 | Liu et al. (2016) [7] | 54/F | Abdominal pain, fever | Markedly thickened appendix (18 mm) with periappendiceal fat stranding | Appendicitis | Suppurative granulomatous inflammation | Preoperative antibiotics and drainage with elective appendectomy |
| 5 | Ng et al. (2014) [12] | 19/F | Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting | Markedly swollen appendix (2.3 cm) with a calcified appendicolith | Uncertain | Extensive chronic inflammation and eosinophilic infiltration within the wall of appendix | Ileocecectomy |
| 6 | Karakus et al. (2014) [13] | 14/M | Abdominal pain and vomiting | Increased (10 mm) thickness of the appendix with nonperistaltic ileocecal region on ultrasonography | Appendicitis | Vermiform appendix with neutrophilic infiltration | Appendectomy |
| 7 | Lee et al. (2010) [1] | 50/F | Incidental finding (routine screening) | Well defined mass (2 cm) at the origin of appendix | Appendiceal neoplasm of mucosal origin | Localized abscess formation of the appendiceal wall | Appendectomy |
| 8 | Nissotakis et al. (2008) [9] | 31/M | Abdominal pain | No sign of appendicitis on X-ray and ultrasonography | Appendicitis | Transmural inflammatory cell infiltrate with lymphoid hyperplasia and fibrosis | Appendectomy with oral antibiotics (6 months) |
| 9 | Karagulle et al. (2008) [10] | 51/F | Abdominal pain, fever and vomiting | 3 × 2-cm-sized enhancing mass near cecum | Appendicitis | Chronic active inflammation around sulfur granules | Appendectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (3 months) |
| 10 | Koren et al. (2002) [11] | 83/F | Abdominal pain | Lobular mass (5 m) attached to the cecum | Uncertain | Dense inflammatory cell infiltration within muscularis and fibro- purulent reaction over the serosa | Right hemicolectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (6 months) |
- 1. Lee SY, Kwon HJ, Cho JH, et al. Actinomycosis of the appendix mimicking appendiceal tumor: a case report. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16: 395-7. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Yeguez JF, Martinez SA, Sands LR, Hellinger MD. Pelvic actinomycosis presenting as malignant large bowel obstruction: a case report and a review of the literature. Am Surg 2000; 66: 85-90. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Cintron JR, Del Pino A, Duarte B, Wood D. Abdominal actinomycosis. Dis Colon Rectum 1996; 39: 105-8. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Garner JP, Macdonald M, Kumar PK. Abdominal actinomycosis. Int J Surg 2007; 5: 441-8. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Gomez-Torres GA, Ortega-Garcia OS, Gutierrez-Lopez EG, et al. A rare case of subacute appendicitis, actinomycosis as the final pathology reports: a case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep 2017; 36: 46-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Lee IJ, Ha HK, Park CM, et al. Abdominopelvic actinomycosis involving the gastrointestinal tract: CT features. Radiology 2001; 220: 76-80. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Liu K, Joseph D, Lai K, Kench J, Ngu MC. Abdominal actinomycosis presenting as appendicitis: two case reports and review. J Surg Case Rep 2016; 2016: rjw068.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Atalaia-Martins C, Cotrim I, Alves P. Appendiceal tumor or something more? Gastroenterology 2018; 154: e14-5. Article
- 9. Nissotakis C, Sakorafas GH, Koureta T, Revelos K, Kassaras G, Peros G. Actinomycosis of the appendix: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Int J Infect Dis 2008; 12: 562-4. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Karagulle E, Turan H, Turk E, Kiyici H, Yildirim E, Moray G. Abdominal actinomycosis mimicking acute appendicitis. Can J Surg 2008; 51: E109-10. PubMedPMC
- 11. Koren R, Dekel Y, Ramadan E, Veltman V, Dreznik Z. Periappendiceal actinomycosis mimicking malignancy report of a case. Pathol Res Pract 2002; 198: 441-3. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Ng N, Ng G, Davis BR, Meier DE. Actinomyces appendicitis: diagnostic dilemma--malignancy or infection? Am Surg 2014; 80: E33-5. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Karakus E, Mambet E, Azili MN, Gulhan B, Tiryaki T, Tezer H. Actinomycosis of the appendix in childhood- an unusual cause of appendicitis. APSP J Case Rep 2014; 5: 26.PubMedPMC
- 14. Lee KS, Tang LH, Shia J, et al. Goblet cell carcinoid neoplasm of the appendix: clinical and CT features. Eur J Radiol 2013; 82: 85-9. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Maternini M, Saucy F, Sandmeier D, Vuilleumier H. Simple appendicitis? Can J Surg 2008; 51: E54-5. PubMedPMC
- 16. DeKoning EP. Simple appendicitis?. In: Tintinalli JE, Stapczynski JS, Ma OJ, eds. Tintinalli’s emergency medicine: a comprehensive study guide. 7th ed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2011; 574-8.
- 17. Piper MH, Schaberg DR, Ross JM, Shartsis JM, Orzechowski RW. Endoscopic detection and therapy of colonic actinomycosis. Am J Gastroenterol 1992; 87: 1040-2. PubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Persistent intra-abdominal abscess with intestinal obstruction following seven failed drainage procedures over 3.5 years: a case report
Ayman Shemes, Salma Samra, Ahmed Mohamed, Amr A. Elgharib
BMC Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Appendicular actinomycosis: The first reported case of an uncommon finding of a common ailment from Nepal
Sujan Bohara, Manoj Khadka, Pawan Singh Bhat, Prajwal Syangtang, Badal Karki, Bhagawan Shrestha, Shoshan Arja Acharya, Khusbhu Khetan, Jyoti Rayamajhi, Sushil Bahadur Rawal
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Abdominopelvic actinomycosis: An unexpected diagnosis in an elderly female with a destructive-appearing soft tissue mass
Elise Hyser, Drashti Antala, Harvey Friedman, Jonathan Stake
IDCases.2022; 28: e01479. CrossRef - Diagnosing granulomatous disease during appendectomy
Atilla Şenaylı
Clinical Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure


Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
| Case | Study | Age (yr)/Sex | Symptom | Radiologic or colonoscopic finding | Initial diagnosis | Pathologic feature | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atalaia-Martins et al. (2018) [8] | 66/F | Abdominal pain | Subepithelial luminal protrusion in the region of the appendiceal orifice with a whitish liquid material discharge | Uncertain | Polymorphic cell infiltrate and erosion with appendiceal fibrosis | Right hemicolectomy |
| 2 | Gomez-Torres et al. (2017) [5] | 39/M | Abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting | Non compressible enlarged cecal appendix (58 mm) with peri-appendiceal edema | Appendicitis | Chronic fistulized appendicitis with transmural lymphoid infiltration | Appendectomy |
| 3 | Liu et al. (2016) [7] | 53/M | Abdominal pain, fever | Distended appendix (9 mm) with surrounding mesenteric stranding | Appendicitis | Lymphoid hyperplasia and chronic inflammatory cells in muscularis propria and serosa | Appendectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (6 months) |
| 4 | Liu et al. (2016) [7] | 54/F | Abdominal pain, fever | Markedly thickened appendix (18 mm) with periappendiceal fat stranding | Appendicitis | Suppurative granulomatous inflammation | Preoperative antibiotics and drainage with elective appendectomy |
| 5 | Ng et al. (2014) [12] | 19/F | Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting | Markedly swollen appendix (2.3 cm) with a calcified appendicolith | Uncertain | Extensive chronic inflammation and eosinophilic infiltration within the wall of appendix | Ileocecectomy |
| 6 | Karakus et al. (2014) [13] | 14/M | Abdominal pain and vomiting | Increased (10 mm) thickness of the appendix with nonperistaltic ileocecal region on ultrasonography | Appendicitis | Vermiform appendix with neutrophilic infiltration | Appendectomy |
| 7 | Lee et al. (2010) [1] | 50/F | Incidental finding (routine screening) | Well defined mass (2 cm) at the origin of appendix | Appendiceal neoplasm of mucosal origin | Localized abscess formation of the appendiceal wall | Appendectomy |
| 8 | Nissotakis et al. (2008) [9] | 31/M | Abdominal pain | No sign of appendicitis on X-ray and ultrasonography | Appendicitis | Transmural inflammatory cell infiltrate with lymphoid hyperplasia and fibrosis | Appendectomy with oral antibiotics (6 months) |
| 9 | Karagulle et al. (2008) [10] | 51/F | Abdominal pain, fever and vomiting | 3 × 2-cm-sized enhancing mass near cecum | Appendicitis | Chronic active inflammation around sulfur granules | Appendectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (3 months) |
| 10 | Koren et al. (2002) [11] | 83/F | Abdominal pain | Lobular mass (5 m) attached to the cecum | Uncertain | Dense inflammatory cell infiltration within muscularis and fibro- purulent reaction over the serosa | Right hemicolectomy with IV/oral antibiotics (6 months) |

 E-submission
E-submission




