Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 57(2); 2023 > Article
-
Case Study
Unusual biclonal IgA plasma cell myeloma with aberrant expression of high-risk immunophenotypes: first report of a new diagnostic and clinical challenge -
Carlos A. Monroig-Rivera1
 , Clara N. Finch Cruz2,3
, Clara N. Finch Cruz2,3
-
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2023;57(2):132-137.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.02.07
Published online: March 14, 2023
1School of Medicine, Ponce Health Sciences University, Ponce, Puerto Rico, USA
2Department of Basic Sciences, School of Medicine - Ponce Health Sciences University, Ponce, Puerto Rico, USA
3Southern Pathology Services, Inc., Ponce, Puerto Rico, USA
- Corresponding Author: Clara N. Finch Cruz, MD, Department of Basic Sciences, School of Medicine - Ponce Health Sciences University, 388 Zona Industrial Reparada 2 Ponce, Puerto Rico 00716-2347, USA Tel: +1-787-840-2575, Fax: +1-787-844-3865, E-mail: cfinch@psm.edu
© 2023The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 4,662 Views
- 140 Download
Abstract
- IgA plasma cell myeloma (PCM) has been linked to molecular abnormalities that confer a higher risk for adverse patient outcomes. However, since IgA PCM only accounts for approximately 20% of all PCM, there are very few reports on high-risk IgA PCM. Moreover, no such reports are found on the more infrequent biclonal IgA PCM. Hence, we present a 65-year-old Puerto Rican female with acute abdominal pain, concomitant hypercalcemia, and acute renal failure. Protein electrophoresis with immunofixation found high IgA levels and detected a biclonal IgA gammopathy with kappa specificity. Histomorphologically, bone marrow showed numerous abnormal plasma cells (32%) replacing over 50% of the marrow stroma. Immunophenotyping analysis detected CD45-negative plasma cells aberrantly expressing CD33, CD43, OCT-2, and c-MYC. Chromosomal analysis revealed multiple abnormalities including the gain of chromosome 1q. Thus, we report on an unusual biclonal IgA PCM and the importance of timely diagnosing aggressive plasma cell neoplasms.
- A 65-year-old female, Hispanic (from Puerto Rico) presented to the Emergency Department with a history of abdominal pain of 6 hours’ duration, a day after receiving the second dose of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine. The patient denied fever, chills, dizziness, chest pain, trauma, and changes in urine or stool. Her past medical history included: obesity, hypertension, adult-onset diabetes, and status post cholecystectomy, but no history of smoking, alcohol intake, or of COVID-19 infection. She had a family history of diabetes and hypertension. Physical examination revealed mild tachycardia but was otherwise unremarkable. Subsequently, she was transferred and admitted to the hospital due to laboratory tests showing hypercalcemia with calcium level greater than 15.0 mg/dL (reference range, 8.3 to 10.6 mg/dL), increased blood urea nitrogen 36 mg/dL (reference range, 9 to 23 mg/dL) and creatinine levels 2.40 mg/dL (reference range, 0.6 to 1.1 mg/dL). Additionally, initial complete blood count results detected leukocytosis of 19.7× 103 cells/μL (4.3–10.3×103 cells/μL) with an increase in the absolute counts of all leukocyte subtypes in the blood and morphologic findings suggestive of infection. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 testing detected IgG antibody (positive), but not IgM or antigen.
- During her hospitalization, peripheral blood evaluations showed resolving leukocytosis, but worsening normocytic anemia with hemoglobin levels dropping from an initial 10.8 to 7.8 g/dL (11.3–14.8 g/dL) that required blood transfusions. Also, rouleaux formation and slight leukoerythroblastosis were noted. Serum protein electrophoresis with immunofixation (PEP/IFx) found significantly high IgA levels at 3,410 mg/dL (87–352 mg/dL) and detected two M-protein bands in the beta region confirming the presence of a biclonal IgA gammopathy with kappa specificity (Table 1). Serum levels of IgG and IgM were decreased. Urine PEP/IFx detected increased Ig in the IgA region without a well-defined band. Additionally, serum beta-2 microglobulin was markedly increased at 8.4 mg/L (0.6–2.4 mg/L).
- Imaging studies including computed tomography scans of the abdomen, pelvis, and brain were done and did not find abdominal or extraosseous mass lesions. However, a whole-body bone scan identified several nonspecific lesions suspicious of metastatic infiltration or post-trauma involving the left sacroiliac joint, sternum, and the right knee lateral femoral component.
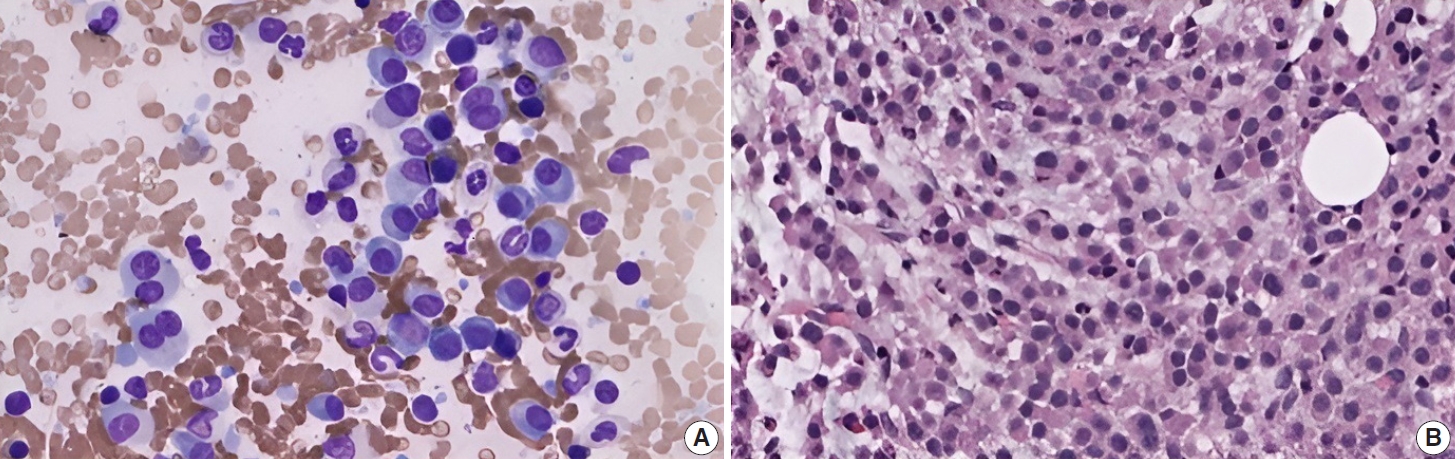
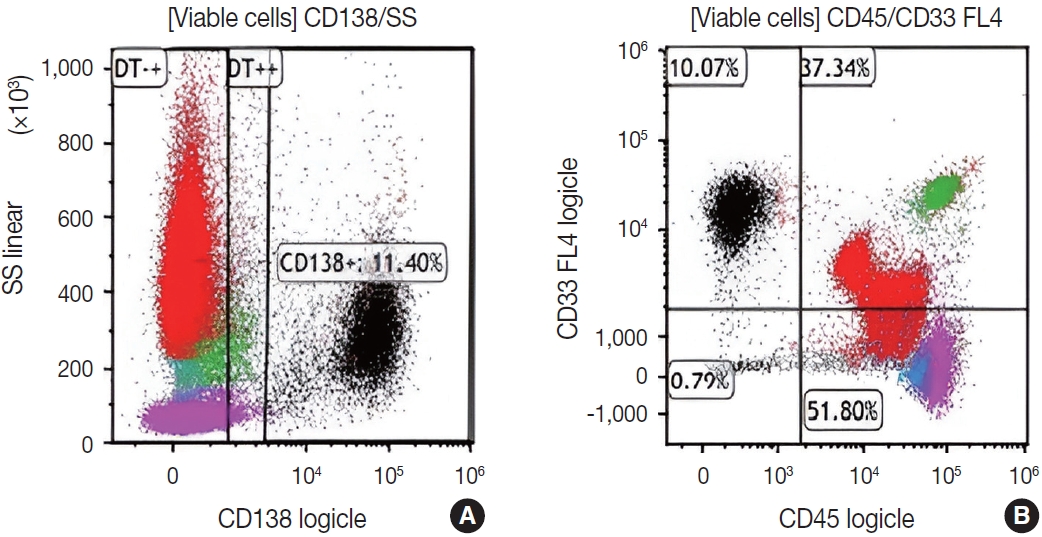
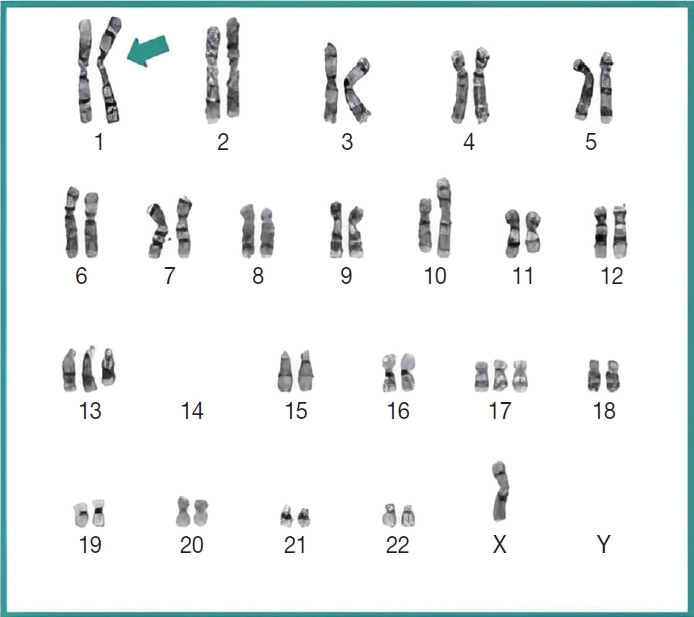
- Subsequently, a bone marrow sampling was obtained from her right iliac crest. Morphological and histological evaluations of bone marrow aspirate and biopsy samples showed the following: hypercellularity (85%–95% cellularity); increase proportion of abnormal plasma cells (32%), predominantly of intermediate-type morphology with features between immature and mature plasma cells; and replacement of over 50% of the marrow stroma by the neoplastic infiltrate (Fig. 1A, B). Additionally, using reticulin and collagen stains, the presence of myelofibrosis and osteosclerosis was identified within the focal areas replaced by sheets of plasma cells and graded as MF2 of 3 [5]. No myelofibrosis was observed in the uninvolved marrow areas. Semiquantitative morphometric analysis using immunohistochemical stains were performed and revealed that a significant proportion of the marrow plasma cells expressed CD138 (>90%) and MUM1 (>95%) with a high kappa/lambda ratio of ~49.5. Additionally, CD43 (>95%, a T-cell marker), OCT-2 (70%–80%), and c-MYC (15%– 25%, low expression) were aberrantly expressed (Fig. 2A–D). These plasma cells did not appear to significantly express (<20% positivity) CD10, CD56, CD79a, CD117/c-KIT, IgG, IgM, PAX5, SOX-10, cyclin D1/BCL1, Epstein-Barr virus, or myeloid markers (CD11c, CD15, and myeloperoxidase). However, flow cytometry studies detected CD45-negative, CD19-positive plasma cells aberrantly expressing CD33, a myeloid marker (Fig. 3A, B). Cytogenetics studies showed an abnormal complex karyotype including odd-number trisomies, and gain of chromosome 1q (Fig. 4). Then, a final diagnosis was rendered of biclonal IgA PCM with aberrant expression of multiple high-risk markers such as CD33, CD43, OCT-2, c-MYC, and gain of chromosome 1q.
- Ultimately, the revised International Staging System (R-ISS) was used to estimate the patient’s prognosis [4]. Based on the Cytogenetics and other key laboratory results, the patient’s predicted R-ISS score placed her in the stage III (of III) category. This information confirming the presence of an aggressive biclonal IgA myeloma was also reported and discussed with her treating physician to help guide treatment options. However, upon being discharged, the patient was lost to follow-up.
CASE REPORT
- Studies of newly-diagnosed patients with biclonal IgA PCM are uncommon. A possible explanation for this apparent underreporting could be that IgA PCM is a rare entity and difficult to diagnose [6,7]. Until recently, no major differences in clinical presentation, prognosis, and treatment of plasma cell neoplasms were identified among patients diagnosed with IgA or the most common IgG isotype, whether expressing monoclonal or biclonal M-protein(s) [8]. However, PCM is now recognized as a genetically heterogenous neoplasm with a subset of patients targeted to develop high-risk disease [9]. Moreover, Habermehl et al. [1] reported on the poorer long-term survival of a cohort of patients with IgA gammopathy when compared to IgG patients. This recently recognized higher risk for adverse outcomes is potentially due to a decreased genomic stability in IgA neoplasms; and favors that IgA be considered in a separate diagnostic category from other PCMs. Further, their study demonstrates the importance of reporting unusual features, biomarkers, molecular abnormalities, and prognostic factors to further characterize high-risk, aggressive IgA PCM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of a biclonal IgA PCM with an unusual clinical presentation in which a combination of multiple high-risk molecular phenotypes is detected.
- Clinically, PCM presenting with abdominal pain as the initial symptom, like in our patient, is unusual and seldom reported. Upon review of the biomedical literature, we found only four reports of patients with IgA PCM presenting with abdominal pain (Table 2) [10-13]. In all four reports, a single monoclonal IgA paraprotein was identified. Interestingly, three of these four cases of IgA PCM presenting with abdominal pain occurred in adults of a younger age (39, 49, 57 years) [10-12] than the reported average age for IgA patients (66.5 years) [1]. Our 65-year-old patient would be the first report of an aggressive biclonal IgA PCM presenting as new-onset abdominal pain. Hence, findings such as non-localized abdominal pain in the adult population should alert clinicians to evaluate their patients for unsuspected malignancy and should prompt the ordering of imaging studies that could lead to an early diagnosis of PCM presenting with atypical symptoms.
- Histologically, the bone marrow findings together with the patient’s clinical history and key laboratory results, including biclonal IgA gammopathy, were most consistent with bone marrow involvement by an IgA PCM, following the diagnostic guidelines of the International Myeloma Working Group [2,3]. In addition, a kappa/lambda ratio of ~50 supported the presence of PCM in the patient. Moreover, since over 50% of the marrow stroma was replaced by sheets of clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow biopsy, this finding met the criteria of histologic Stage III of III, as per the proposed Histopathology-based staging system [2]. According to McKenna et al. [2], there appears to be a good correlation between the histologic stage, clinical stage, and prognosis. Therefore, these histologic findings predicted an aggressive, high-risk IgA PCM in the patient.
- Immunophenotypically, the patient’s clonal plasma cells aberrantly expressed CD33 (a myeloid marker) and CD43 (a T-cell marker), and overexpressed transcription factors OCT-2 and MYC. The detection of any of these abnormal immunophenotypes in PCM is now associated with high-risk disease and poor survival [14-17]. Moreover, as published by Kodali et al. [17], MYC protein expression may serve as a potential predictor for prognosis and to assess residual disease in PCM. Based on their criteria, our patient fits in the low-MYC-expressing group (MYC <30%) and could benefit from targeted treatment for high-risk myeloma.
- Importantly, molecular cytogenetic studies in the patient identified several chromosomal abnormalities of known prognostic value in PCM. Based on the reported copy number abnormalities, her PCM could be categorized as non-hyperdiploid or hypodiploid (45 chromosomes) of complex karyotype including the loss of chromosomes14, odd-number trisomies (chromosomes 13 and 17), and gain of 1q [9]. These results highlight the degree of genomic instability in her neoplastic plasma cells. According to Cardona-Benavides et al. [9], PCM patients with hypodiploid karyotypes and those with gain of 1q tend to have more aggressive clinical presentations and worse outcomes. Further, the R-ISS was used to estimate the patient’s prognosis. Her predicted R-ISS score placed her in Stage III of III category with a median overall survival of 43 months and a median progression-free survival of 29 months [4]. Therapeutic options for these newly-diagnosed R-ISS/Stage III PCM patients with gain of 1q chromosomal abnormality are limited [9].
- The translational relevance of identifying these high-risk IgA PCM could be significant for PCM patients, especially in Puerto Rico. Although PCM survival has improved due to new treatment modalities, the majority (~72%) of Puerto Ricans diagnosed with PCM are still likely to die from PCM [18]. Also, for unknown reasons, the decline in PCM-specific mortality in Puerto Rico is less than in other comparable US populations [18]. Future studies are needed to identify additional PCM patients with potential high-risk phenotypes such as biclonality, IgA subtype, MYC overexpression, gain of chromosome 1q. These studies should establish a definitive association between these high-risk markers and aggressive PCM. This could lead to improve medical care including the use of targeted therapies, which could result in a further decline in PCM-specific mortality in Puerto Rico.
DISCUSSION
Ethics Statement
Formal written informed consent was not required with a waiver granted by the Institutional Review Board of Ponce Health Sciences University (IRB No. 2110075611).
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: CNFC. Formal analysis: CNFC. Funding acquisition: CNFC. Investigation: CAMR, CNFC. Methodology: CNFC. Project administration: CNFC. Resources: CNFC. Supervision: CNFC. Validation: CAMR, CNFC. Visualization: CAMR, CNFC. Writing—original draft: CAMR, CNFC. Writing—review & editing: CAMR, CNFC.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
No funding to declare.
Acknowledgments

| Test | Result | Reference range | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgG | 465 L | 586–1,602 mg/d | Quantitative immunoglobulin (Ig) serum levels |
| IgM | 7 L | 26–217 mg/dL | |
| IgA | 3410 H | 87–352 mg/dL | |
| Albumin | 3.4 | 2.9–4.4 g/dL | Serum protein electrophoresis |
| Alpha-1-globulin | 0.2 | 0.0–0.4 g/dL | |
| Alpha-2-globulin | 0.7 | 0.4–1.0 g/dL | |
| Beta globulin | 4.5 H | 0.7–1.3 g/dL | |
| Gamma globulin | 0.4 | 0.4–1.8 g/dL | |
| M-spike | 3.9 H | 0.01 g/dL | |
| Beta 1 | 3.2 H | - | |
| Beta 2 | 0.7 H | - | |
| IgA, total | 3.9 H | - | |
| Immunofixation, serum | Biclonal IgA with kappa specificity | - | Confirmatory test |
| Beta-2 microglobulin | 8.4 H | 0.6–2.4 mg/L | High-risk factor, when ≥ 5.5 mg/La |
L, low; H, high.
aAccording to the Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma (R-ISS) [4], and The Multiple Myeloma Prognosis (R-ISS) calculator created by QxMD.
| Case | Age (yr), sex | Clinical feature | Ig specificity | M-protein clonality | Location | Microscopic findings | Immunophenotyping/Cytogenetics/Molecular studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annibali et al. (2009) [10] | 39, female | Abdominal pain, and obstructive jaundice 7 yr after ASCT | IgA-lambda | Monoclonal | Head of the pancreas, pleural effusion | US-guided FNA cytology of the pancreatic mass and cytology of pleural effusion revealed myeloma plasma cells | Unknown |
| Age at the time of initial diagnosis | Extramedullary relapse | ||||||
| Cerqueira et al. (2020) [11] | 49, female | Presented with abdominal pain, biliary vomiting of 6 days duration | IgA-kappa | Monoclonal | Kidney, bone marrow | Kidney biopsy demonstrating myeloma kidney | Immunophenotyping: 60% of bone marrow monoclonal plasma cells with 100% CD138+, 100% CD38+, and 45% CD20+ |
| Admitted to ICU for acute kidney failure | |||||||
| Suo et al. (2020) [12] | 57, male | History of liver cirrhosis presenting with abdominal pain and pancytopenia | IgA-kappa | Monoclonal | Liver, MRI- left hepatic mass | Abundant plasmacytoid cells, kappa restricted neoplastic plasma cells | Plasmacytoid cells showed CD138+, kappa+, lambda– |
| Extramedullary involvement | Cytogenetics and FISH suggestive of advanced disease progression | ||||||
| Yamane et al. (2021) [13] | 73, male | Acute left lower abdominal pain | IgA-type | Monoclonal | Left vertebral arch of the 10th thoracic vertebra | Bone marrow biopsy: plasma cell neoplasm with 26.0% of plasma cells | Flow cytometry: CD38+, CD56+, CD138+, MPC-1+. |
| Chromosomal analysis: 45,X,-Y,+5,+6,+7,-8,+9, +11,-13, and +21 | |||||||
| Current case | 65, female | Acute abdominal pain | IgA-kappa | Biclonal | Bone marrow | Hypercellularity (85%–95%), abnormal plasma cells (32%) | Immunophenotyping: CD138+, CD33+, MUM-1+, CD43+, OCT-2+, c-MYC+ |
| Chromosomal analysis: gain of 1q,13,17, loss of 14 |
- 1. Habermehl GK, Nakashima MO, Cotta CV. IgA plasma cell neoplasms are characterized by poorer long-term survival and increased genomic complexity compared to IgG neoplasms. Ann Diagn Pathol 2020; 44: 151449.ArticlePubMed
- 2. McKenna RW, Kroft SH, Linden MA. Plasma cell neoplasms. In: Jaffe ES, Arber DA, Campo E, Harris NL, Quintanilla-Martinez L, eds. Hematopathology. 2nd. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2017; 473-506.
- 3. Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 2020; 95: 548-67. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Palumbo A, Avet-Loiseau H, Oliva S, et al. Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma: a report from International Myeloma Working Group. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 2863-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM, Facchetti F, Franco V, van der Walt J, Orazi A. European consensus on grading bone marrow fibrosis and assessment of cellularity. Haematologica 2005; 90: 1128-32. PubMed
- 6. Willrich MA, Katzmann JA. Laboratory testing requirements for diagnosis and follow-up of multiple myeloma and related plasma cell dyscrasias. Clin Chem Lab Med 2016; 54: 907-19. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Keren DF, Schroeder L. Challenges of measuring monoclonal proteins in serum. Clin Chem Lab Med 2016; 54: 947-61. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Rossi F, Petrucci MT, Guffanti A, et al. Proposal and validation of prognostic scoring systems for IgG and IgA monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 4439-45. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Cardona-Benavides IJ, de Ramon C, Gutierrez NC. Genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Cells 2021; 10: 336.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Annibali O, Marchesi F, Petrucci MT, Tirindelli MC, Avvisati G. Relapse of IgA lambda multiple myeloma presenting as obstructive jaundice and abdominal pain. Onkologie 2009; 32: 119-21. PubMed
- 11. Cerqueira A, Seco T, Paiva D, Martins H, Cotter J. Acute kidney failure: when multiple myeloma doesn’t give additional clues. Cureus 2020; 12: e7664. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Suo L, Liu S, Vega I, Thrall M. Extramedullary multiple myeloma involving the liver and periportal lymph node, diagnosed by EUSFNA in a patient with cirrhosis. Diagn Cytopathol 2020; 48: 657-61. PubMed
- 13. Yamane F, Ohta R, Sano C. Left lower abdominal pain as an initial symptom of multiple myeloma. Cureus 2021; 13: e20652. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Muchtar E, Gertz MA. The colorful landscape of multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 2019; 60: 2099-100. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Ning X, Wei Y, Wei X, et al. CD43 expression is an adverse prognostic factor in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 2021; 138(Suppl 1):4753.ArticlePDF
- 16. Toman I, Loree J, Klimowicz AC, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of Oct2 and Bob1 in multiple myeloma: implications for targeted therapeutics. Leuk Lymphoma 2011; 52: 659-67. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Kodali S, Yu H, Cerny J. Assessing MYC expression in multiple myeloma. J Hematol Thrombo Dis 2015; 3: e119.
- 18. Castaneda-Avila MA, Ortiz-Ortiz KJ, Torres-Cintron CR, Birmann BM, Epstein MM. Trends in cause of death among patients with multiple myeloma in Puerto Rico and the United States SEER population, 1987-2013. Int J Cancer 2020; 146: 35-43. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure

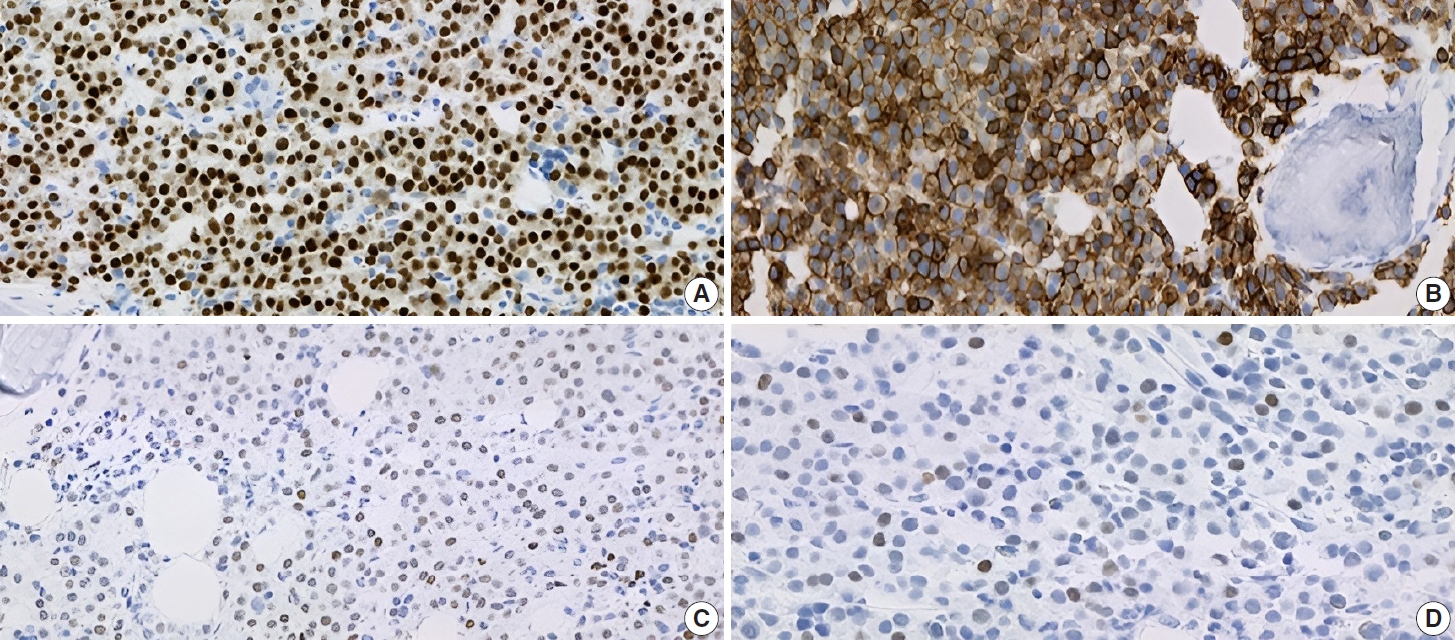
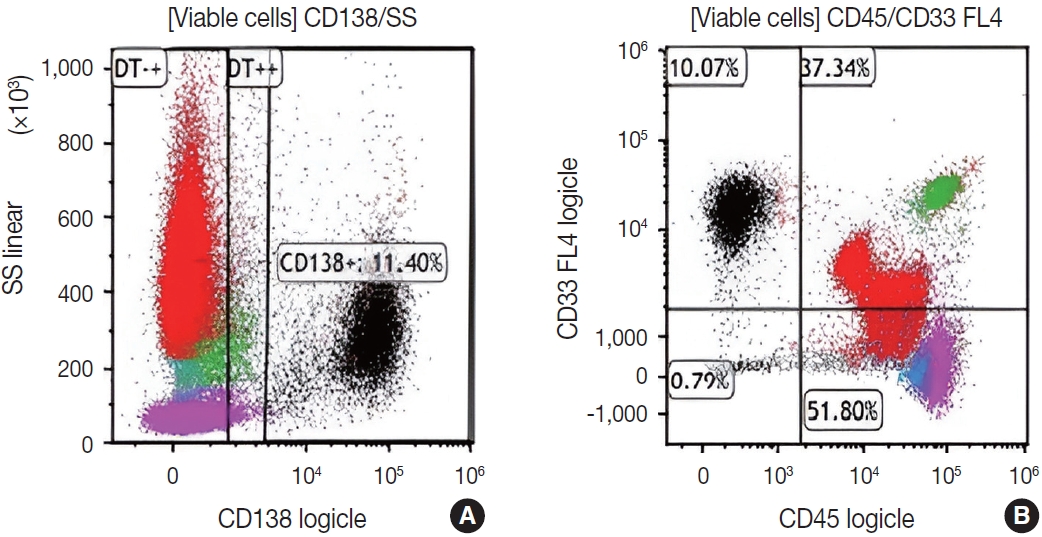
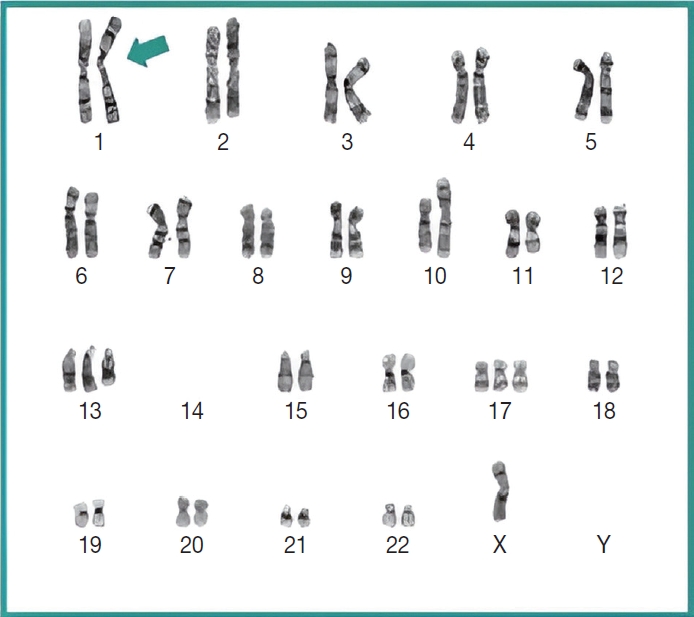
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
| Test | Result | Reference range | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgG | 465 L | 586–1,602 mg/d | Quantitative immunoglobulin (Ig) serum levels |
| IgM | 7 L | 26–217 mg/dL | |
| IgA | 3410 H | 87–352 mg/dL | |
| Albumin | 3.4 | 2.9–4.4 g/dL | Serum protein electrophoresis |
| Alpha-1-globulin | 0.2 | 0.0–0.4 g/dL | |
| Alpha-2-globulin | 0.7 | 0.4–1.0 g/dL | |
| Beta globulin | 4.5 H | 0.7–1.3 g/dL | |
| Gamma globulin | 0.4 | 0.4–1.8 g/dL | |
| M-spike | 3.9 H | 0.01 g/dL | |
| Beta 1 | 3.2 H | - | |
| Beta 2 | 0.7 H | - | |
| IgA, total | 3.9 H | - | |
| Immunofixation, serum | Biclonal IgA with kappa specificity | - | Confirmatory test |
| Beta-2 microglobulin | 8.4 H | 0.6–2.4 mg/L | High-risk factor, when ≥ 5.5 mg/L |
| Case | Age (yr), sex | Clinical feature | Ig specificity | M-protein clonality | Location | Microscopic findings | Immunophenotyping/Cytogenetics/Molecular studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annibali et al. (2009) [10] | 39, female | Abdominal pain, and obstructive jaundice 7 yr after ASCT | IgA-lambda | Monoclonal | Head of the pancreas, pleural effusion | US-guided FNA cytology of the pancreatic mass and cytology of pleural effusion revealed myeloma plasma cells | Unknown |
| Age at the time of initial diagnosis | Extramedullary relapse | ||||||
| Cerqueira et al. (2020) [11] | 49, female | Presented with abdominal pain, biliary vomiting of 6 days duration | IgA-kappa | Monoclonal | Kidney, bone marrow | Kidney biopsy demonstrating myeloma kidney | Immunophenotyping: 60% of bone marrow monoclonal plasma cells with 100% CD138+, 100% CD38+, and 45% CD20+ |
| Admitted to ICU for acute kidney failure | |||||||
| Suo et al. (2020) [12] | 57, male | History of liver cirrhosis presenting with abdominal pain and pancytopenia | IgA-kappa | Monoclonal | Liver, MRI- left hepatic mass | Abundant plasmacytoid cells, kappa restricted neoplastic plasma cells | Plasmacytoid cells showed CD138+, kappa+, lambda– |
| Extramedullary involvement | Cytogenetics and FISH suggestive of advanced disease progression | ||||||
| Yamane et al. (2021) [13] | 73, male | Acute left lower abdominal pain | IgA-type | Monoclonal | Left vertebral arch of the 10th thoracic vertebra | Bone marrow biopsy: plasma cell neoplasm with 26.0% of plasma cells | Flow cytometry: CD38+, CD56+, CD138+, MPC-1+. |
| Chromosomal analysis: 45,X,-Y,+5,+6,+7,-8,+9, +11,-13, and +21 | |||||||
| Current case | 65, female | Acute abdominal pain | IgA-kappa | Biclonal | Bone marrow | Hypercellularity (85%–95%), abnormal plasma cells (32%) | Immunophenotyping: CD138+, CD33+, MUM-1+, CD43+, OCT-2+, c-MYC+ |
| Chromosomal analysis: gain of 1q,13,17, loss of 14 |
L, low; H, high. According to the Revised International Staging System for Multiple Myeloma (R-ISS) [
ASCT, autologous stem cell transplant; US, ultrasound; FNA, fine-needle aspiration; ICU; intensive care unit; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.

 E-submission
E-submission






