Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 46(2); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
Significance of Electron Dense Deposits in Patients with Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome - Sae Yoon Kim, Sang Su Lee, Myoung Uk Kim, Jae Min Lee, Seok Jeong Kang, Yong Jin Kim1, Yong Hoon Park
-
Korean Journal of Pathology 2012;46(2):137-141.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.137
Published online: April 25, 2012
1Department of Pediatirics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
2Department of Pathology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Yong Hoon Park, M.D. Department of Pediatirics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 705-717, Korea. Tel: +82-53-620-3532, Fax: +82-53-629-2252, yhpark@med.yu.ac.kr
© 2012 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 7,569 Views
- 42 Download
Abstract
-
Background
- Minimal change nephritic syndrome (MCNS) is characterized by a lack of obvious abnormalities on light microscopy, but its electron microscopic findings include the negative immunofluorescence findings and the diffuse effacement of the epithelial cell foot processes. Rarely the presence of electron dense deposits (EDDs) has been reported, but its clinical significance remains obscure.
-
Methods
- Eleven patients with MCNS who had the EDD deposited were enrolled in the current study. We compared the clinical characteristics, laboratory results and response to steroid treatment between the two group: the EDD group (n=11; the male-to-female ratio, 8:3) and the non-EDD group (n=13, 8:5).
-
Results
- There were no significant differences in most of the laboratory results or response to steroid treatment between the two groups. The frequency of relapses per year was significantly higher in the EDD group (1.1±0.7 times vs. 0.5±0.6 times; p=0.023). These EDDs were found in the mesangium or paramesangium. With no respect to the characteristics of EDDs, our results showed that they did not cause poor treatment outcomes except for the annual frequency of relapse.
-
Conclusions
- Further large-scale studies are warrented to determine the immunologic and prognostic significance of EDDs in patients with MCNS.
- In the current study, we reviewed 307 cases of renal biopsies that had been performed in 234 adults and 73 children, both of whom were diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome, during the same period. In addition, a diagnosis of MCNS was established in 23 adults and 39 children. Of total patients who were diagnosed with MCNS at Yeungnam University Hospital from February of 2000 to April of 2010, those who had EDDs on electron microscopy and for whom medical records were available were enrolled in the current study. A total of 11 patients were assigned to the EDD group (n=11). Besides, there were 13 age- and sex-matched patients who had no EDDs on electron microscopy during the same period. These 13 patients were assigned to the non-EDD group (n=13), served as the control group. We excluded patients with so-called IgM nephropathy from the current analysis.
- At the time of diagnosis, we evaluated the clinical characteristics such as age, gender, main symptoms, disease duration, and blood pressure. We also compared clinical laboratory findings associated with the renal function such as complete blood counts, protein, cholesterol, complement and immunoglobulins between the two groups. Besides, on urinalysis, we also evaluated hematuria, glucose, protein and creatinine. To analyze the treatment response, we also compared medications for early stage, a period until a remission of the disease and the frequency of recurrence between the two groups.
- Based on criteria of Valentini and Smoyer,1 according to the onset of primary nephrotic syndrome and its remission and the pattern of its response to steroid therapy, the nephrotic syndrome was divided into the frequent relapse nephrotic syndrome (FRNS), the steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS) and the steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). In children of each group, high blood pressure was defined as systolic and/or diastolic pressure over the 95 percentile. In addition, it was also defined as the systolic pressure of >140 mm Hg and the diastolic pressure of >90 mm Hg in adults of each group.1
- At the time of diagnosis, for steroid treatment, patients were daily given prednisolone (PDS) 60 mg/m2/day (maximum dose for children, 60 mg/day; adult, 80 mg/day) via an oral route three times in divided doses for four weeks every day. Thereafter, patients were given at a dose of 40 mg/m2/day every other day for another four weeks. If patients had a recurrence after remission, patients were daily given PDS at a dose of 60 mg/m2/day until three days after the remission. Thereafter, patients were given at a dose of 40 mg/m2/day once every two days for additional four weeks. Then, the dosage was decreased dosage and then eventually stopped. In patients with a dependency on or a resistance to the PDS treatment, the secondary drugs were administered and they include cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and methylprednisolone pulse.
- For a biopsy of the renal tissue, we prepared the paraffin-embedded blocks into the tissue sections at a thickness of 2 µm. This was followed by staining with hematoxylin and eosin, periodic acid-Schiff, trichrome and periodic acid-methenamine-silver stains for microscopic examination. For immunohistochemistry, we prepared a frozen tissue section and then stained it with anti-human IgG, A, M and complements 3 and 1q. For an electron microscopy, the fresh tissue was double fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and OsO4 embedded in an epon mixture, ultrathin sectioned and stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. This was followed by an electron microscopy using a Hitachi H-7000 transmission electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Statistical analysis was done using SPSS ver. 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) for which a chi-square test and a Mann-Whitney test were performed. A p<0.05 was considered statistically.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
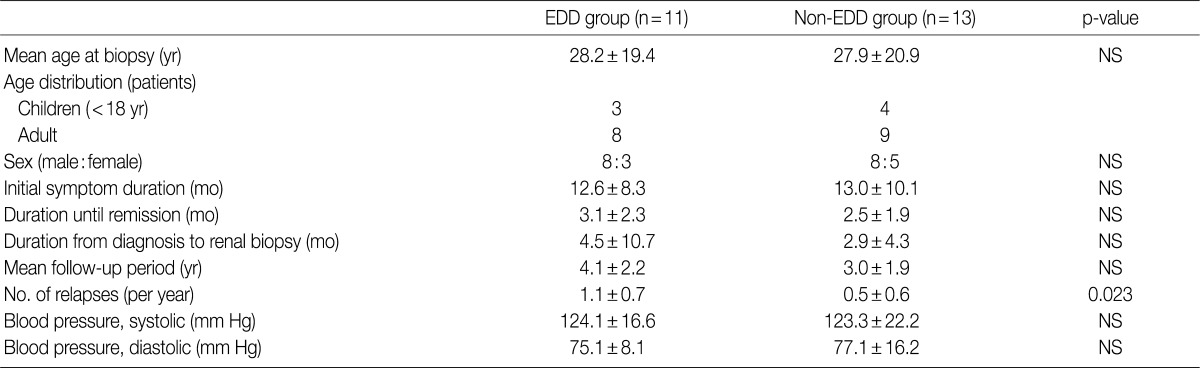
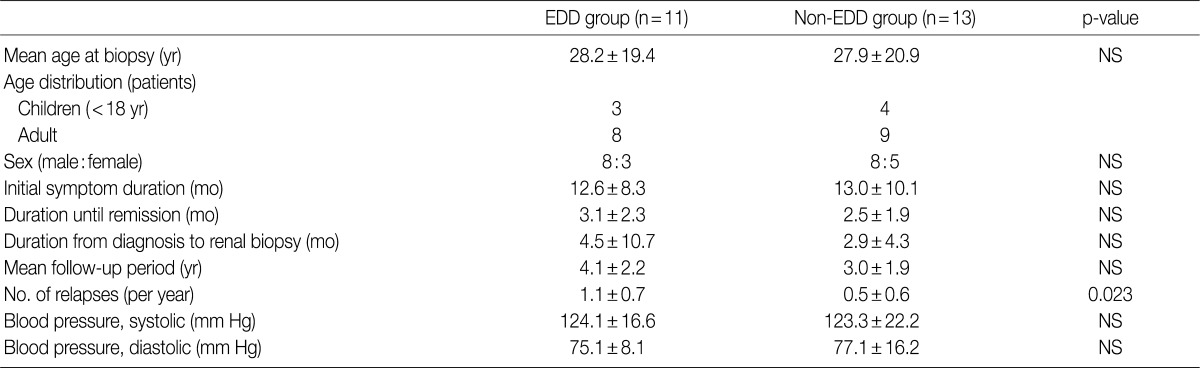
- The mean age at the time of diagnosis was 28.2±19.4 years old in the EDD group and 27.9±20.9 years in the non-EDD group. In the EDD group, there were 11 patients (n=11) who were composed of eight men and three women. In the non-EDD group, there were 13 patients (n=13) who were composed of eight men and five women. These results indicate that there was no significant difference in the male-to-female ratio between the two groups.
- At the time of diagnosis, chief complaints were edema in our clinical series of patients. In addition, the disease duration was 12.6±8.3 days in the EDD group and 13.0±10.1 days in the non-EDD group. These results indicate that there was no significant difference in the disease duration between the two groups.
- We evaluated a period until a remission of the disease, the length of time elapsed until a renal biopsy since a diagnosis was made and the mean follow-up period. But there were no significant differences in these parameters between the two groups. In addition, at the time of diagnosis, mean blood pressure (systolic blood pressure/diastolic blood pressure) was 124.1±16.6/75.1±8.1 mm Hg in the EDD group and 123.3±22.2/77.1±16.2 mm Hg in the non-EDD group. These results indicate that there were no significant differences in the mean blood pressure (systolic blood pressure/diastolic blood pressure) between the two groups (Table 1). High blood pressure was found in two adults of the EDD group and five adults of the non-EDD group. But there were no children who had a high blood pressure. Based on a retrospective analysis of the medical records at the latest follow-up, there was one adult woman who was diagnosed with hypertension. This patient was found to use loop diuretics and angiotensin receptor blockers for blood pressure control. The rate of recurrence was 90.9% in the EDD group and 58.8% in the non-EDD group. The annual frequency of relapse was 1.1±0.7 times/yr in the EDD group and 0.5±0.6 times/yr in the non-EDD group. This difference reached a statistical significance (p=0.023).
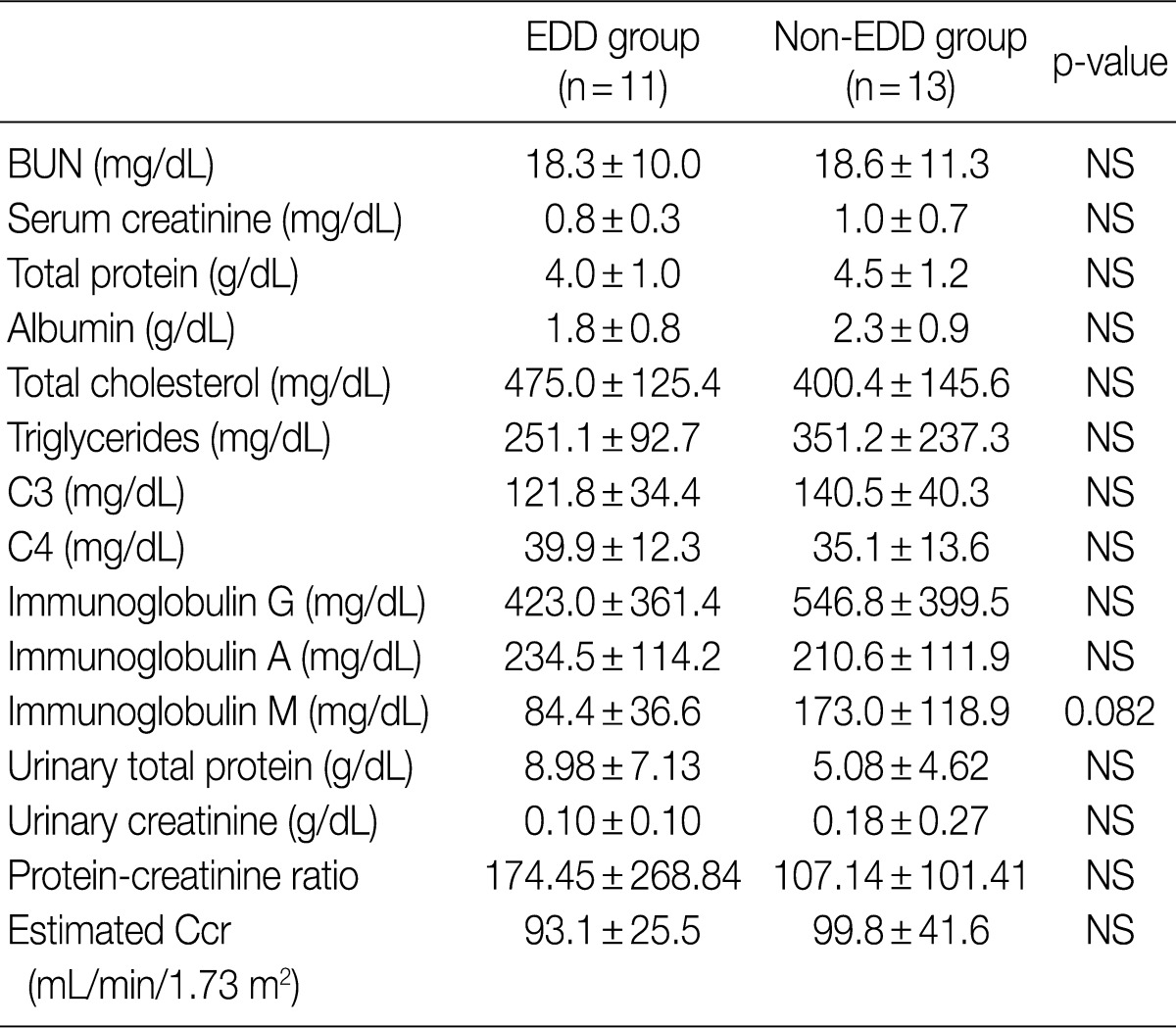
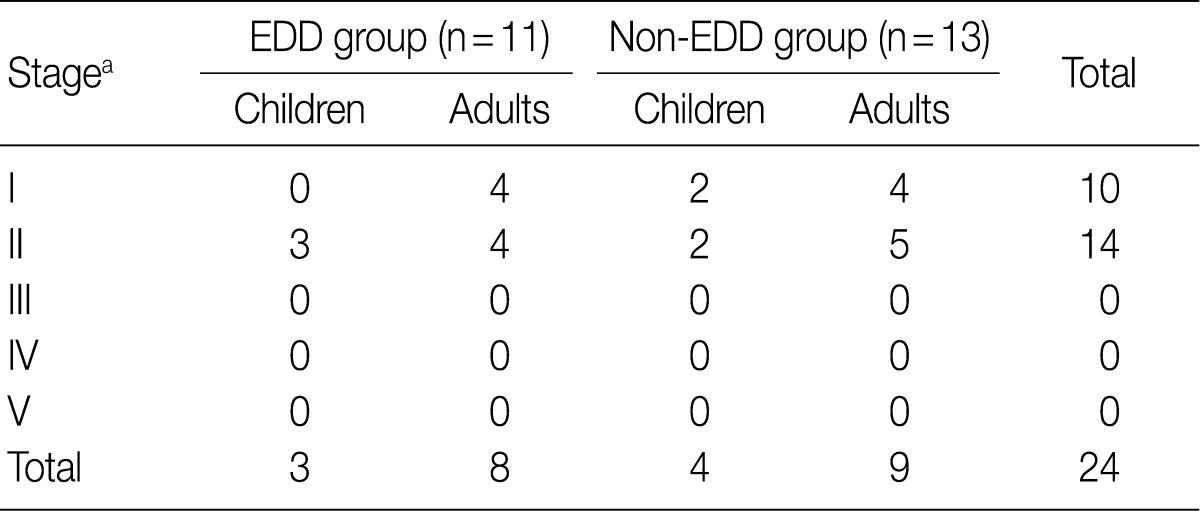
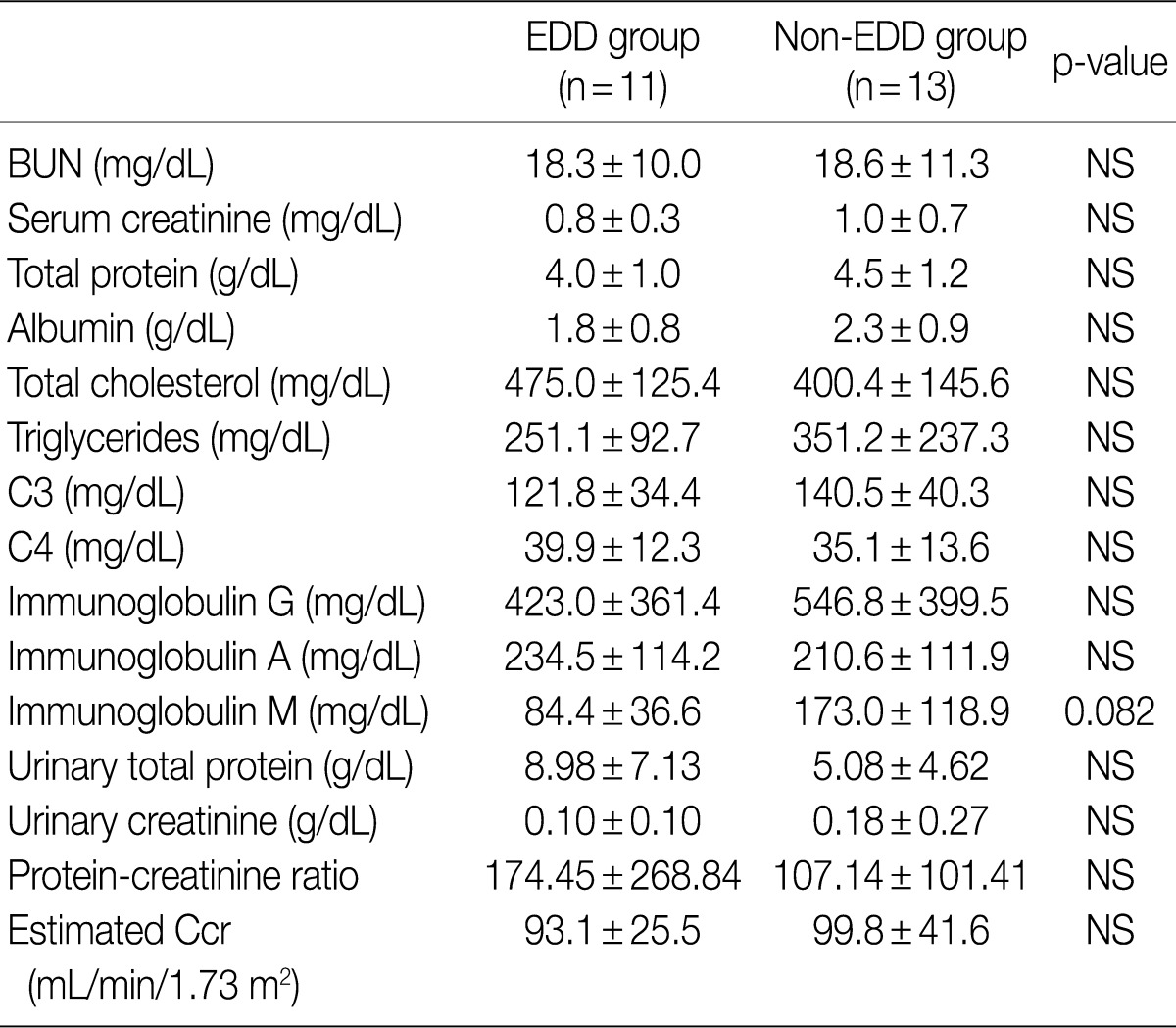
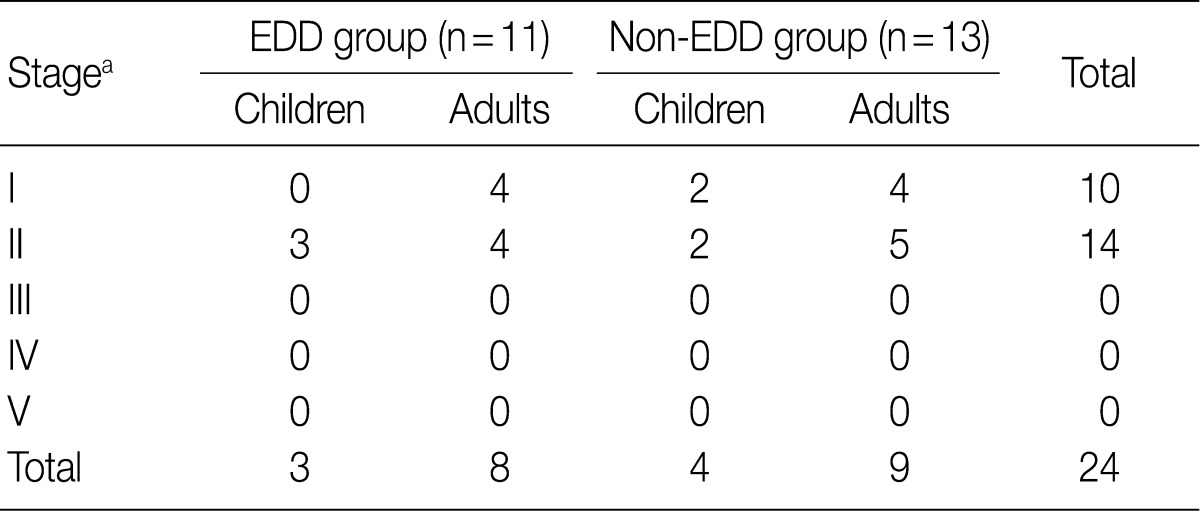
- Regarding the kidney function, mean serum level of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) was 18.3±10.0 in the EDD group and 18.6±11.3 mg/dL in the non-EDD group. But this difference reached no statistical significance. Mean serum creatinine level was 0.8±0.3 mg/dL in the EDD group and 1.0±0.7 mg/dL in the non-EDD group. But this difference reached no statistical significance. Besides, mean creatinine clearance was 93.1±25.5 mL/min in the EDD group and 99.8±41.6 mL/min in the non-EDD group. But this difference reached no statistical significance (Table 2). In addition, there were no significant differences in total protein, albumin, total blood cholesterol and triglyceride between the two groups. There were no differences in the mean serum levels of IgG and IgA between the two groups. Overall, however, the mean serum level of IgM was 84.4±36.6 mg/dL in the EDD group and 173.0±118.9 mg/dL in the non-EDD group. These results showed that it was significantly higher in the non-EDD group as compared with the EDD group (p=0.082) (Table 2). At the time of diagnosis, on urinalysis, there was one case of microscopic hematuria in the EDD group and three cases in the non-EDD group. But this difference reached no statistical significance. There were no patients who presented with the symptoms that are suggestive of diabetes. When categorized according to the kidney function steps of the National Kidney Foundation-Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-K/DOQI) categorization, there was no case that seemed to have a low kidney function of above stage III (Table 3).5
- On a biopsy of the renal tissue, followed by a light microscopy, there were no such findings as glomerular cell proliferation, glomerulosclerosis, tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis (Fig. 1). Besides, there was no infiltration of the interstitial inflammatory cells. In the non-EDD group, two cases were positive for IgM but only at a trace amount. We excluded cases of strong positive for IgM from the current analysis. Of these cases, one had whole glomerulus in paraffin-embedded blocks and all the remaining ones showed a loss of foot processes under an electron microscopy. Besides, we incidentally detected EDDs from the mesangium in nine cases and around the mesangium (paramesangium) in two cases, all of which were small and discrete (Figs. 2, 3).
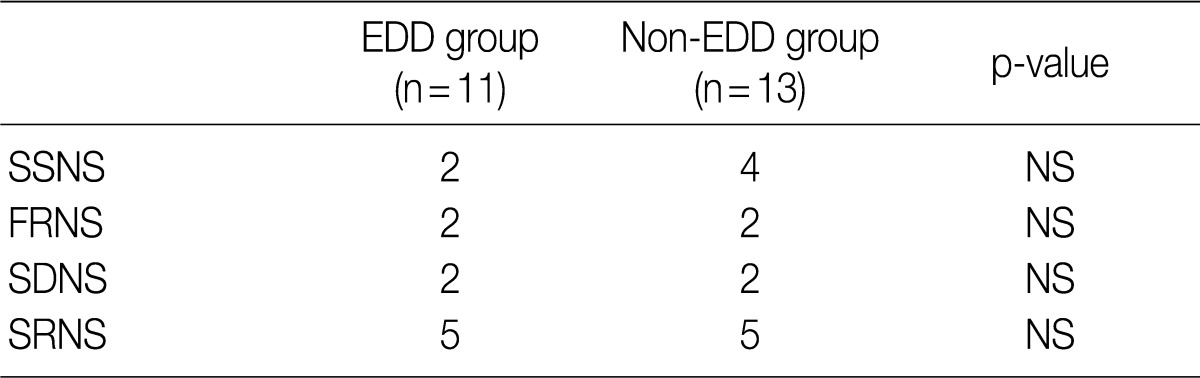
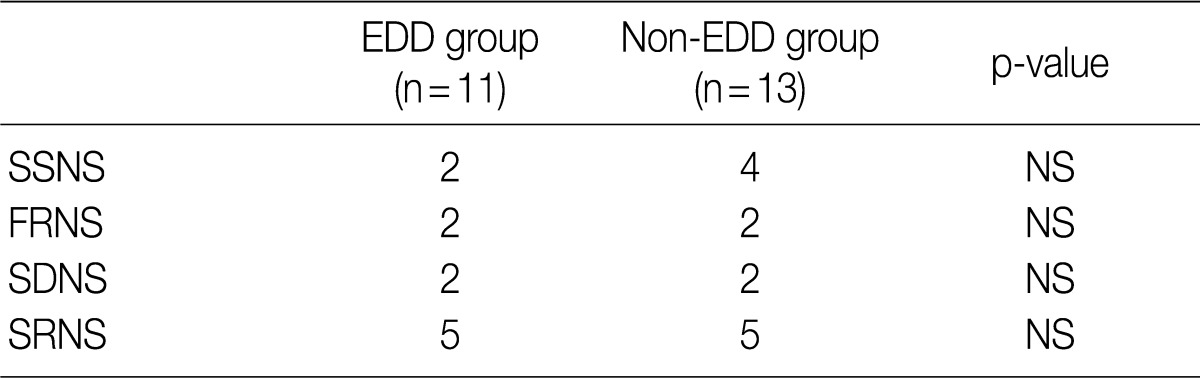
- Based on the classification into the FRNS, the SDNS and the SRNS according to the degree of response to steroid treatment, the progression to SDNS was seen in five patients of each group. But this difference reached no statistical significance (Table 4).
RESULTS
- The MCNS is one of the most common causes of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome, for which the standard initial treatment is corticosteroid therapy at the present in children in particular.6 The most important prognostic indicator in nephrotic syndrome is a responsiveness to the steroid therapy.7 This is because the initial attack of MCNS is very sensitive to prednisone treatment.8 Renal biopsies are generally limited to patients with SRNS and are recommended before starting nephrotoxic treatments such as cyclosporin to identify the reason for the lack of a clinical response.7
- In cases of MCNS, the glomeruli appear to be normal or show a minimal increase in mesangial cells and matrix.9 In addition, they are negative for deposits on immunofluorescent microscopy or occasionally show small amounts of IgM in the mesangium.10 An electron microscopy consistently demonstrates the effacement of the foot processes of podocytes.10 Additionally, there are some minor abnormalities on light microscopy and they are considered to be MCNS variants. Some authors have reported that the IgM deposition in the mesangium and mesangial hypercellularity are related to the response to steroid therapy and the long-term course of MCNS.6 In the current study, there were two cases of IgM deposits in the non-EDD group but only at a trace amount on immunofluorescence microscopy. We excluded so-called IgM nephropathy that is characterized by strong IgM deposition. In our series, the mean serum level of IgM was significantly lower in the EDD group compared with the non-EDD group (p=0.082).
- On immunofluorescence microscopy, there were several glomeruli at a mean number of 4.5 in the EDD group. We detected very little deposition of immunoglobulin or complement, being less than a trace or on 1+. This may be due to a very small amount of antibodies available to detect or to other types of immunoglobulin or complement compared with the conventional staining items.
- According to Jeong et al.,11 of a total of 60 patients with MCD, 25 (15 adults and 10 children) had a mesangial IgA deposition and 24 of them (14 adults and 10 children) had the EDD deposited in the mesangium. Similarly, most of our clinical series of patients had the EDD deposited in the mesangium or paramesangium with no additional changes.
- Regarding kidney function, mild azotemia is usual in children with nephrotic syndrome and the serum creatinine is elevated in 32% of total cases.12 Nevertheless, our results showed that there were no differences in the estimated creatinine clearance and serum creatinine levels between the two groups. Furthermore, there were also no differences in the BUN and other laboratory findings (total protein, serum albumin, total blood cholesterol and triglycerides) between the two groups. It has been reported that the microscopic hematuria is found in 25% of the children with MCNS at the time of diagnosis.2 In our series, however, on urinalysis at the time of diagnosis, there was one case of microscopic hematuria in the EDD group and three cases in the non-EDD group. But this difference reached no statistical significance.
- A large-scale study of MCNS found a gradual tendency toward an increase in the number of non-relapsing patients over time, reaching 80% at 8 years after onset of the disease.13 A majority of children (60%) with nephrotic syndrome experience one or more relapses, and most patients experience a gradual decrease in the frequency of relapses over time.1 Allen et al.14 reported that eight of 25 patients with immune deposits on the initial renal biopsy were steroid non-responsive, whereas only one of 43 patients without immune deposits was steroid non-responsive (p<0.01). Of 44 patients with normal mesangial cellularity, 31 experienced fewer than three relapses a year, whereas only six of 15 patients with mesangial hypercellularity experienced fewer than three relapses a year (p=0.035).13
- In the current study, the number of relapses per year was also significantly higher in the EDD group (p=0.023) as compared with the non-EDD group. But it could not predict the clinical course or responsiveness to steroid therapy. Because the current study was conducted in a small number of patients (n=11), however, further studies are warranted to indentify the importance of electron dense deposition in the mesangium and mesangial hypercellularity in a large series of patients with MCNS.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Valentini RP, Smoyer WE. In: Kher KK, Schnaper HW, Makker SP, eds. Nephrotic syndrome. Clinical pediatric nephrology. 2007; 2nd ed. London: Informa UK Ltd, 155-194. Article
- 2. Meyers KE, Kaplan BS. In: Kaplan BS, Meyers KE, eds. Minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric nephrology and urology. 2004; Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby, 163-171. Article
- 3. Alpers CE. In: Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T, eds. The kidney. Robbins pathologic basis of disease. 1999; 6th ed. Philidelphia: W. B. Saunders, 930-996. Article
- 4. Yoshikawa N, Cameron AH, White RH. Ultrastructure of the non-sclerotic glomeruli in childhood nephrotic syndrome. J Pathol 1982; 136: 133-147. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Hogg RJ, Furth S, Lemley KV, et al. National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Pediatrics 2003; 111(6 Pt 1):1416-1421. ArticlePDF
- 6. Swartz SJ, Eldin KW, Hicks MJ, Feig DI. Minimal change disease with IgM+ immunofluorescence: a subtype of nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2009; 24: 1187-1192. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Eddy AA, Symons JM. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 2003; 362: 629-639. Article
- 8. Brodehl J. The treatment of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: lessons learned from multicentre co-operative studies. Eur J Pediatr 1991; 150: 380-387. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Vogt BA, Avner ED. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, eds. Nephrotic syndrome. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2007; 18th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2190-2195.
- 10. Lewis JB, Neilson EG. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Kasper DL, eds. Glomerular diseases. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2008; 17th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Co. Inc., 1782-1797.
- 11. Jeong HJ, Jung SH, Choi IJ. Electron microscopic study of the cases of minimal change nephrotic syndrome with mesangial IgA deposition. Yonsei Med J 1992; 33: 351-356. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. A report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Kidney Int 1978; 13: 159-165.
- 13. Tarshish P, Tobin JN, Bernstein J, Edelmann CM Jr. Prognostic significance of the early course of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. J Am Soc Nephrol 1997; 8: 769-776. PubMed
- 14. Allen WR, Travis LB, Cavallo T, Brouhard BH, Cunningham RJ 3rd. Immune deposits and mesangial hypercellularity in minimal change nephrotic syndrome: clinical relevance. J Pediatr 1982; 100: 188-191. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
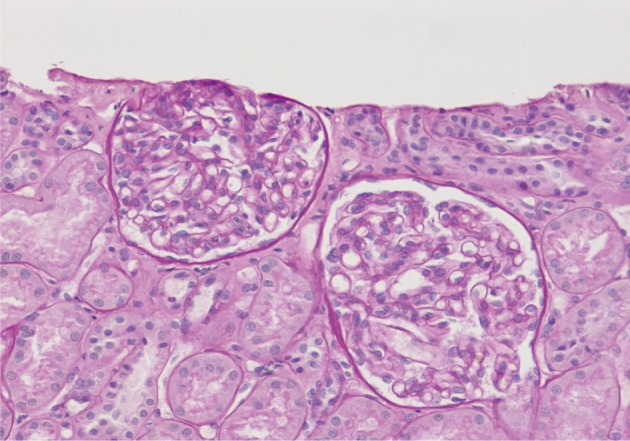
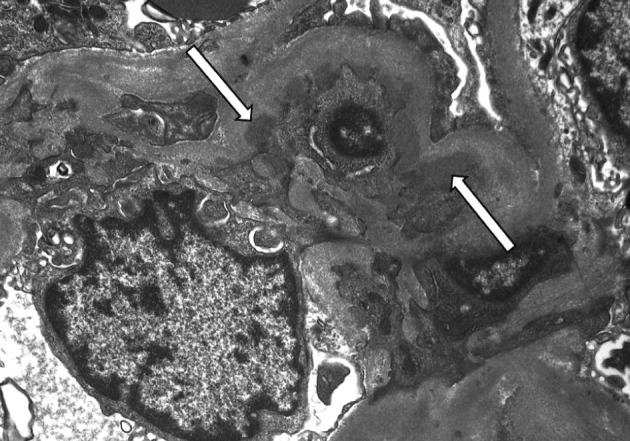

Figure & Data
References
Citations




Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
EDD, electron dense deposits; NS, not significant.
EDD, electron dense deposits; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; NS, not significant; Ccr, creatinine clearance.
NKF-K/DOQI, National Kidney Foundation-Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative; EDD, electron dense deposits. aStage: I, ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; II, 60-89; III, 30-59; IV, 15-29; V, <15.
EDD, electron dense deposits; SSNS, steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome; NS, not significant; FRNS, frequent-relapse nephrotic syndrome; SDNS, steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome; SRNS, steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome.

 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader Cite this Article
Cite this Article




