Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 46(5); 2012 > Article
-
Case Report
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report - Zhi-Yu Zhu, Zhi-Gang Chu1, Yu Chen, Wei-Ping Zhang, Di Lv, Ning Geng, Ming-Zhong Yang
-
Korean Journal of Pathology 2012;46(5):478-482.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.478
Published online: October 25, 2012
Department of Pathology, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Sichuan, China.
1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Sichuan, China.
- Corresponding Author: Yu Chen, M.D. Department of Pathology, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Sichuan 610041, China. Tel: +86-28-61153399, Fax: +86-28-61153399, chen_yuhx@163.com
• Received: December 9, 2010 • Revised: November 24, 2011 • Accepted: November 30, 2011
© 2012 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma (GCOC) is an exceptionally rare and malignant odontogenic tumor with aggressive growth characteristics. We describe a case of GCOC which was considerably derived from a previously resected calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor (CCOT). Cellular atypia, mitotic activity, Ki-67 labeling index and matrix metalloprotease-9 positive expression rate were all increased in the currently resected specimen compared to the initial one. This is a rare case of malignant transformation of CCOT to GCOC with respect to its histopathological and immunohistochemical findings.
- The patient was referred to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, West China College of Stomatology, Sichuan University with a one-year history of a slowly growing, painful mass in the right maxillary region. Physical examination revealed a tender, soft, palpable mass measuring 3×3×1.5 cm with clear borders, adjacent to the right upper lip and nasal ala. Oral examination revealed a thickened vestibular groove between the right upper central incisor and the first molar, a swollen right maxilla and sensitivity of the adjacent teeth to percussion. Panoramic X-ray film revealed an oval, radiolucent lesion with clear borders located between the right upper central incisor and the first molar. Enlarged cervical lymph nodes were not found on physical examination, and both lungs were clear on chest X-ray.
- Curettage of the cystic lesion was subsequently performed. The gross appearance of the resected specimen showed a cyst measuring 3×3×3 cm with a thin wall (0.2 cm). Histopathological examination (Fig. 1A) demonstrated the epithelial lining to be composed of a well-defined basal layer consisting of columnar or cubical cells, with nuclei in the barrier range situated away from the basilar membrane. An overlying layer of sparsely distributed polygonal or asteroid cells resembled a stellate reticulum. Sporadic or conglobate ghost cells were trapped in the epithelium. Immunohistochemistry showed that Ki-67 was sparsely expressed in the epithelial cells with a positive expression rate of 12.2% (Fig. 1B), whereas matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) was sporadically expressed in both cells and mesenchyma (Fig. 1C). Based on these findings, the tumor was diagnosed as a CCOT.
- One year after the operation, the patient returned to our hospital with a painful and rapidly growing mass in the formerly operated region of the right maxilla. Oral examination revealed a mass measuring 3×2.5×2 cm located on the inner surface between the cuspid teeth and the first molar of the right maxilla. The mass was solid and tender with a smooth surface and clear borders. Panoramic X-ray film revealed a nonopaque lesion with clear borders. Root apices of the involved teeth showed absorption (Fig. 2). Based on the patient's medical history, we suspected recurrence of CCOT.
- Sub-total resection of the right maxilla was performed. The resected specimen was a solid tumor measuring 3×3×2.5 cm, with interior necrotic areas and devoid of an integrated envelope. Histopathological examination (Fig. 3A) showed that the tumor was composed of epithelial cell nests. The neoplastic cells showed cytological atypia, manifested mainly as hyperchromatic cells with variably sized nuclei, raised nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and an increased number of mitotic figures (Fig. 3B). Clusters of ghost cells were diffusely distributed in the tumor nests. This tumor showed aggressive behaviour (Fig. 3C). Immunohistochemical staining revealed that Ki-67 was strongly expressed in the epithelial cells with a positive expression rate of 61.8% (Fig. 3D). MMP-9 was weakly expressed in the epithelial cells, but was strongly expressed in the tumor mesenchyma and was occasionally found in ghost cells (Fig. 3E). Pathologically, the tumor was diagnosed as GCOC.
- Postoperatively, the patient survived and showed no evidence of recurrence or metastasis at the time of follow-up (i.e., a year after the second operation).
CASE REPORT
- GCOC is a rare malignant tumor with no more than 30 cases reported in the English language medical literature. Among these cases nearly one-third of GCOCs were derived from a preexisting CCOT.6 In some cases, DGCT also occasionally combines with other odontogenic tumors, such as ameloblastoma to form GCOCs.7 With regard to newly developed tumors, most had certain similar characteristics such as rapid growth and infiltration or destruction of the surrounding tissues and structures. In our case, however, we observed only bony absorption of the teeth adjacent to the lesion due to early detection.
- GCOC can occur at any age, with a predominance of male patients around 40 years old. More frequently, it occurs in the maxilla than the mandible.8 Jaw expansion with or without pain is the most common clinical presentation, which may also be associated with local paraesthesia, tooth mobility or displacement. Few patients had enlarged neck lymph nodes, but metastasis was extremely rare.3,9 With regard to CCOT, the tumor mainly manifested as gradual expansion of the jaw with occasional pain, probably on account of increased periosteal tension and compression of adjacent nerves and vessels by the expanding mass. Plain X-ray usually demonstrate CCOT manifesting as a single radiolucent shadow with clear borders, while GCOC is usually seen as a unicameral or multilocular radiolucent shadow without clear borders and associated with different degrees of bony destruction and infiltration of adjacent structures. As seen in our case, all tooth apices involved showed absorption.
- Ward and Cohen10 suggested three possible explanations for the histogenesis of a cyst with lining epithelium and its associated carcinoma in jaws. Firstly, carcinomas and cysts have different origins, the former possibly originating from adjacent epithelium or by distant metastasis of a primary tumor. Secondly, the primary lesion was a carcinoma which partially underwent cystic degeneration. Thirdly, the primary lesion was a cyst, and the lining epithelium subsequently underwent malignant transformation. In our case, the two tumors occurred at the same site successively. The pathological characteristics of the first tumor corresponded with those of CCOT, and no malignant epithelium was found. However, the pathological characteristics of the second tumor corresponded with those of GCOC. Thus, the diagnosis of GCOC in our case agreed with the third theory mentioned above. We did not find any remnant of CCOT in the GCOC, which may imply that the earlier benign tumor had been completely removed.
- According to the 2005 World Health Organization guidelines,11 GCOC usually exhibits prominent mitotic activity, nuclear atypia and cellular pleomorphism, groups of ghost cells and necrosis, and has an infiltrative growth pattern which presents locally aggressive and destructive behaviour. At times, metastatic deposits can also be found. Ki-67 is a sensitive biomarker of cell proliferation activity, which can be used to predict the severity and prognosis of tumor, while MMP-9 is another biomarker closely related to tumor invasion and metastasis.12 In our case, the positive expression rate of Ki-67 in CCOT and GCOC was 12.2% and 61.8%, respectively, which indicates that cell proliferation activity of GCOC was significantly higher than that of CCOT. In our study, whether tumor parenchyma or mesenchyma was involved, the positive expression rate of MMP-9 in GCOC was higher than that in CCOT. In both tumors, only a few ghost cells were positive for MMP-9 while all were negative for Ki-67.
- GCOC has a low incidence. Most cases are sporadic, with different biological characteristics ranging from relatively indolent growth to an aggressive and potentially fatal course. However, distant metastases are uncommon. The recommended treatment for GCOC is wide surgical excision because of high recurrence rates in patients who had undergone local surgical resection or curettage. In this study, any other additional therapy was not performed after surgery because of the controversy regarding postoperative adjuvant irradiation with or without chemotherapy.1,3 With regard to the prognosis of GCOC, the overall five-year survival rate has been reported to be as high as 73%.13 However, in view of the fact that the biological behaviour of this tumor is unpredictable, long-term follow-up is highly recommended following therapy.14
- In summary, the pathological characteristics of CCOT and GCOC show similarities but also significant differences which are helpful in predicting their malignant potential. Furthermore, measuring the expression of the biomarkers, Ki-67 and MMP-9, associated with tumor proliferation and invasion, is helpful in evaluating the prognosis of GCOC.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Goldenberg D, Sciubba J, Koch W, Tufano RP. Malignant odontogenic tumors: a 22-year experience. Laryngoscope 2004; 114: 1770-1774. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Ledesma-Montes C, Gorlin RJ, Shear M, et al. International collaborative study on ghost cell odontogenic tumours: calcifying cystic odontogenic tumour, dentinogenic ghost cell tumour and ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 2008; 37: 302-308. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Goldenberg D, Sciubba J, Tufano RP. Odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2004; 26: 378-381. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Tanaka N, Iwaki H, Yamada T, Amagasa T. Carcinoma after enucleation of a calcifying odontogenic cyst: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993; 51: 75-78. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Ellis GL, Shmookler BM. Aggressive (malignant?) epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1986; 61: 471-478. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Motosugi U, Ogawa I, Yoda T, et al. Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma arising in calcifying odontogenic cyst. Ann Diagn Pathol 2009; 13: 394-397. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Kim TJ, Lee YS, Kim BK, Lee KY. Ameloblastoma associated with dentinogenic ghost cell tumor: a case report. Korean J Pathol 2006; 40: 297-302.
- 8. Lu Y, Xuan M, Takata T, et al. Odontogenic tumors: a demographic study of 759 cases in a Chinese population. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998; 86: 707-714. PubMed
- 9. Roh GS, Jeon BT, Park BW, et al. Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma of the mandible: a case report demonstrating expression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) and vitronectin receptor. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2008; 36: 419-423. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Ward TG, Cohen B. Squamous carcinoma in a mandibular cyst. Br J Oral Surg 1963; 1: 8-12. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. 2005; Lyon: IARC Press, 293.
- 12. Hidalgo M, Eckhardt SG. Development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93: 178-193. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Lu Y, Mock D, Takata T, Jordan RC. Odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma: report of four new cases and review of the literature. J Oral Pathol Med 1999; 28: 323-329. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Kim HJ, Choi SK, Lee CJ, Suh CH. Aggressive epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumor in the mandible: CT and MR imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001; 22: 175-179. PubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Fig. 1Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor. (A) Histopathologic examination shows the epithelial lining is composed of columnar or cubical cells, and the nuclei of which are barrier-ranged. Sporadic or conglobate ghost cells are seen in the lining epithelium. (B) Immunohistochemistry shows the Ki-67 is sparsely expressed in tumor cells but negatively in ghost cells, and (C) matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) is sparsely expressed in tumor cells and interstitium but negatively in ghost cells (Ki-67 and MMP-9 marker).
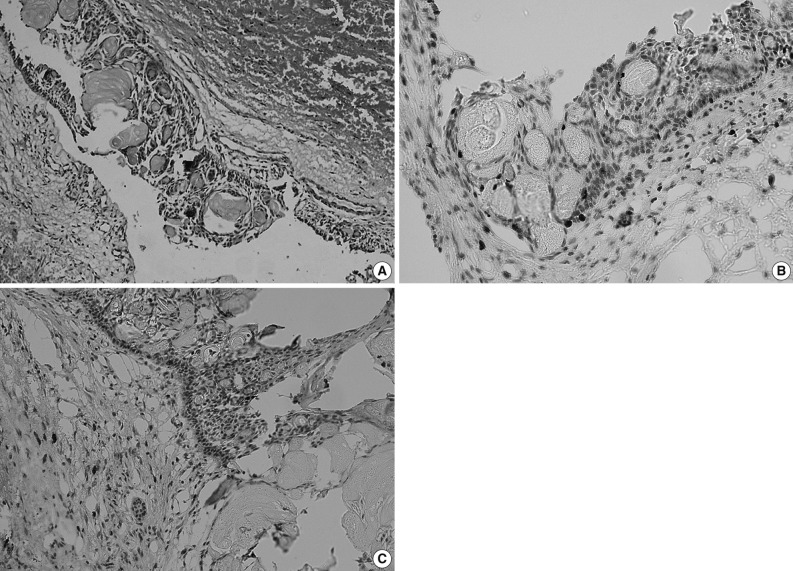

Fig. 2Panoramic X-ray film shows a nonopaque lesion located between the right upper lateral incisor and second premolar. The absorption of the root apex could be detected in the involved teeth.
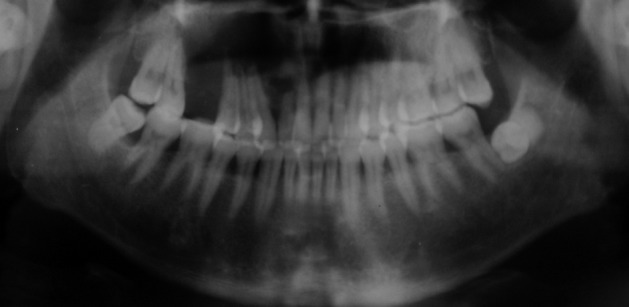

Fig. 3Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma. (A) Histopathologic examination shows epithelial cell nests in tumor tissue. (B) Tumor cells are admixed with anucleate ghost cells. Inset: Several tumor cells show atypical mitoses. (C) The tumor cells invade the surrounding vessel. The tumor cells infiltrate into the adjacent fibro-vascular tissue. The clusters of ghost cells are diffusely distributed in the tumor nests. (D) Immunohistochemistry shows the Ki-67 is strongly expressed in the tumor cells but negatively in ghost cells, and (E) matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) is strongly expressed in interstitium, weakly in the tumor cells but sparsely in ghost cells (Ki-67 and MMP-9 marker).
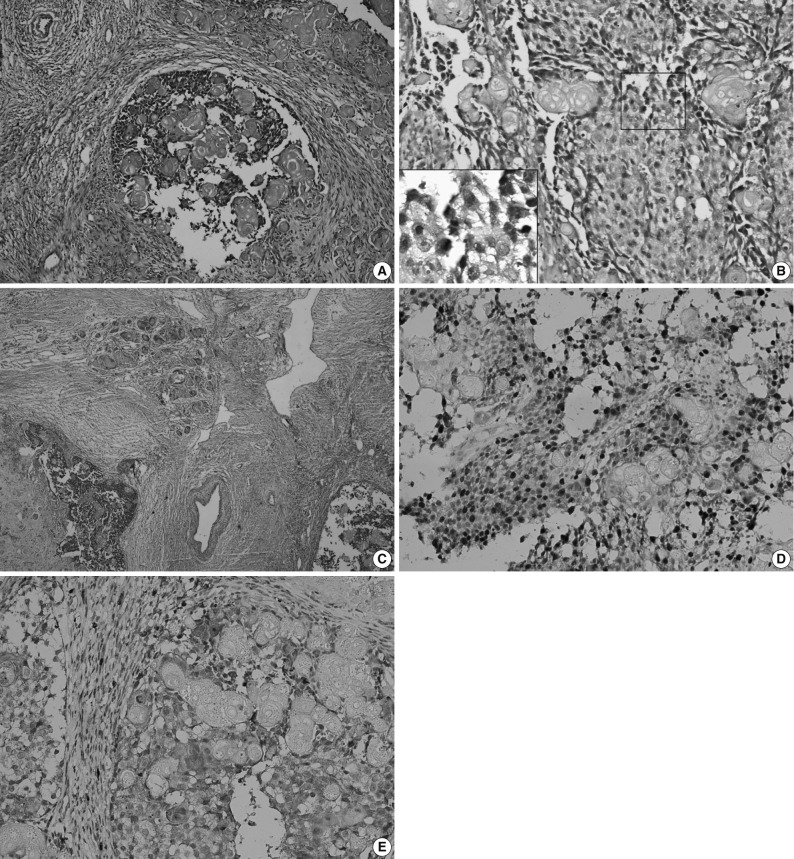

Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma of the Anterior Maxilla with ARID1A Mutation: A Case Report and Literature Review
Nasser Mohammed Almadan, Doaa Alghamdi, Meshal AlOrf, Hamed Alali, Mohammed Mohajrye
Head and Neck Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma: Case Series and Literature Review
Dalja Parks, Nancy J. Zhou, Danny A. Vazquez, Matthew Fisher, Sakar Budhathoki, Jergin Chen, Shawn Iganej, Onita Bhattasali, Lester D. R. Thompson
Head and Neck Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Late recurrence of calcifying odontogenic cyst: Report of a rare case and review of the literature
Paris Tamiolakis, Maria Georgaki, Panagiotis Christopoulos, Nikolaos G. Nikitakis
Oral Surgery.2024; 17(3): 258. CrossRef - Treatment challenges of persistent ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma: a case report and literature review
Ali Al-Sammak, Othman Rezki, Michael Pennington, Frances Manosca, Maria Cuevas-Nunez, Mohammed Qaisi, Even Greenbaum, James Murphy
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2023; 136(4): e123. CrossRef - Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma: A rare case report and review of literature
Yong Xia, Zongchang Song, Xinlei Zhang, Xinhong Guan, Guifang Tan, Yi Le, Shuang Liu, Hui Xue, Jing Li, Yajun Zhang, Jing Chen, Huajuan Jiang, Xia Jiang, Yanxia Cheng, Chuchu Zhou, Xu Sha, Jin-Xin Lou
Medicine.2023; 102(38): e35225. CrossRef - A novel parotid carcinoma with a prominent ghost cell population: a masquerading tumor or “salivary ghost cell carcinoma”?
Hiroshi Harada, Mitsuo P. Sato, Naoki Otsuki, Mao Kawamura, Akira Kurose, Takao Satou
Medical Molecular Morphology.2022; 55(1): 76. CrossRef - Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor with focal atypical features suggesting ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma: Report of a challenging diagnosis
Danielle Castex Conde, Gustavo de Souza Vieira, Pâmella de Pinho Montovani, João Pedro Roque Beserra, Mauro César Gaspar Ribeiro, Rafaela Elvira Rozza-de-Menezes, Karin Soares Cunha
Oral Oncology.2022; 124: 105524. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis Between Dentinogenic Ghost Cell Tumor and Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
Gustavo de Souza Vieira, Pâmella de Pinho Montovani, Rafaela Elvira Rozza-de-Menezes, Karin Soares Gonçalves Cunha, Danielle Castex Conde
Head and Neck Pathology.2021; 15(4): 1265. CrossRef - Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma of anterior mandible
Gopikrishnan Vijayakumar, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(Suppl 1): S99. CrossRef - Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma of the jaws: Report of two cases and a literature review
Meng-Qi Jia, Jun Jia, Li Wang, Hai-Xiao Zou
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2019; 7(3): 357. CrossRef - Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma with suspected cholesterol granuloma of the maxillary sinus in a patient treated with combined modality therapy
You Qin, Yanwei Lu, Liduan Zheng, Hong Liu
Medicine.2018; 97(7): e9816. CrossRef - A lesion categorized between ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma and dentinogenic ghost cell tumor with CTNNB1 mutation
Yae Ohata, Kou Kayamori, Akane Yukimori, Kanako Sumikura, Toshimitsu Ohsako, Hiroyuki Harada, Kei Sakamoto, Tohru Ikeda
Pathology International.2018; 68(5): 307. CrossRef - A case of large ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma arising in the mandible
Daisuke ARAKI, Shunichi YOSHIDA, Keisuke KOYAMA, Shuutarou ISHII, Toshihiro HASEGAWA, Sadao OOYAMA
Japanese Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 64(12): 708. CrossRef - Three-dimensional volumetric analysis of ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma using 3-D reconstruction software: a case report
João Pedro Perez Gomes, Andre Luiz Ferreira Costa, Carlos Takahiro Chone, Albina Messias de Almeida Milani Altemani, João Maurício Carrasco Altemani, Carmen Silvia Passos Lima
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2017; 123(5): e170. CrossRef - Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma transformed from dentinogenic ghost cell tumor of the maxilla after recurrences
Sase Miwako, Itoh Hiroto, Nakano Takahumi, Hayasaka Junichi, Noguchi Tadahide, Jinbu Yoshinori, Mori Yoshiyuki
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2017; 29(5): 438. CrossRef - Ki-67 and p53 expression in ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma: a case report and literature review
G. Del Corso, M. L. Tardio, D. B. Gissi, C. Marchetti, L. Montebugnoli, A. Tarsitano
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2015; 19(1): 85. CrossRef - Integrative genomic analysis of ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma
Pinaki Bose, Erin D. Pleasance, Martin Jones, Yaoqing Shen, Carolyn Ch’ng, Caralyn Reisle, Jacqueline E. Schein, Andrew J. Mungall, Richard Moore, Yussanne Ma, Brandon S. Sheffield, Thomas Thomson, Steven Rasmussen, Tony Ng, Stephen Yip, Christopher W. Le
Oral Oncology.2015; 51(9): e71. CrossRef - Pediatric Metastatic Odontogenic Ghost Cell Carcinoma: A Multimodal Treatment Approach
Safia K. Ahmed, Masayo Watanabe, Daphne E. deMello, Thomas B. Daniels
Rare Tumors.2015; 7(2): 73. CrossRef - Predictive Factors of Potential Malignant Transformation in Recurrent Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Review of the Literature
Sepideh Mokhtari, Zhaleh Mohsenifar, Maedeh Ghorbanpour
Case Reports in Pathology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report



Fig. 1 Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor. (A) Histopathologic examination shows the epithelial lining is composed of columnar or cubical cells, and the nuclei of which are barrier-ranged. Sporadic or conglobate ghost cells are seen in the lining epithelium. (B) Immunohistochemistry shows the Ki-67 is sparsely expressed in tumor cells but negatively in ghost cells, and (C) matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) is sparsely expressed in tumor cells and interstitium but negatively in ghost cells (Ki-67 and MMP-9 marker).
Fig. 2 Panoramic X-ray film shows a nonopaque lesion located between the right upper lateral incisor and second premolar. The absorption of the root apex could be detected in the involved teeth.
Fig. 3 Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma. (A) Histopathologic examination shows epithelial cell nests in tumor tissue. (B) Tumor cells are admixed with anucleate ghost cells. Inset: Several tumor cells show atypical mitoses. (C) The tumor cells invade the surrounding vessel. The tumor cells infiltrate into the adjacent fibro-vascular tissue. The clusters of ghost cells are diffusely distributed in the tumor nests. (D) Immunohistochemistry shows the Ki-67 is strongly expressed in the tumor cells but negatively in ghost cells, and (E) matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) is strongly expressed in interstitium, weakly in the tumor cells but sparsely in ghost cells (Ki-67 and MMP-9 marker).
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report

 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader Cite this Article
Cite this Article




