Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 48(1); 2014 > Article
-
Review
Guideline Recommendations for Testing ofALK Gene Rearrangement in Lung Cancer: A Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group - Hyojin Kim, Hyo Sup Shim1, Lucia Kim2, Tae-Jung Kim3, Kun Young Kwon4, Geon Kook Lee5, Jin-Haeng Chung, Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
-
Korean Journal of Pathology 2014;48(1):1-9.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.1
Published online: February 25, 2014
Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
1Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Pathology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
3Department of Pathology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Department of Pathology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
5Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
-
Corresponding Author: Jin-Haeng Chung, M.D. Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 82 Gumi-ro 173beon-gil, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 463-707, Korea. Tel: +82-31-787-7713, Fax: +82-31-787-4012, chungjh@snu.ac.kr
Corresponding Author: Geon Kook Lee, M.D. Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang 410-769, Korea. Tel: +82-31-920-1746, Fax: +82-31-920-1369, gklee@ncc.re.kr
© 2014 The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- Rearrangement of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene is the best predictor of response to crizotinib, an ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor. However, the prevalence of the ALK fusion is low, so accurate patient identification is crucial for successful treatment using ALK inhibitors. Furthermore, most patients with lung cancer present with advanced-stage disease at the time of diagnosis, so it is important for pathologists to detect ALK-rearranged patients while effectively maximizing small biopsy or cytology specimens. In this review, we propose a guideline recommendation for ALK testing approved by the Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists.
- Clinical characteristics associated with the ALK gene rearrangement are known to be adenocarcinoma histology, never/light smoking history, and younger age.6,13-15 However, not all ALK-rearranged patients demonstrate these characteristics. ALK fusion has also been detected in older patients (over 70 years old) with a smoking history, and in patients with squamous cell carcinoma.12,16 Therefore, clinical characteristics alone are not the determinant of ALK testing. Guidelines from the College of American Pathologists (CAP), the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC), and the Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) also state that clinical characteristics (age, sex, ethnicity, smoking history, etc.) are not sufficiently sensitive or specific to be used to select or exclude patients for treatment or testing for ALK gene rearrangement.17
- Recent published guidelines recommend histological type as the most important factor for determining whether ALK testing should be performed. Patients who are diagnosed with adenocarcinoma, large cell carcinoma, or non-small cell carcinoma with an adenocarcinoma component are recommended for ALK testing.17,18 Thus, accurate histological diagnosis is the first step for molecular testing. Pathologists should try to further classify poorly differentiated NSCLCs into more specific types using immunohistochemistry (IHC), such as thyroid transcription factor-1, napsin A, p63, p40, and cytokeratin5/6.19-24 There have been a few reports about squamous cell carcinoma harboring ALK gene rearrangement, but the frequency is very low.6,16 Thus, the CAP-IASLC-AMP guideline does not recommend ALK testing in lung cancer cases without any adenocarcinoma component, such as pure squamous cell carcinomas, pure small cell carcinomas, or large cell carcinomas lacking any IHC evidence of adenocarcinoma differentiation.17
- Actually, about two-thirds of lung cancer patients present with advanced stage at the time of diagnosis, and small biopsies or cytology specimens are the only available samples for diagnosis and molecular testing. In these cases, histological sub-typing may not be always feasible, the biopsy or cytology specimens may not be representative of the whole tumor, and any adenocarcinoma component cannot be completely excluded. For these cases, ALK testing is recommended and the clinical features, such as young age and/or lack of smoking history, may be used to select patients for testing.17
PATIENT ELIGIBILITY
- Specimen type
- Various biopsy specimens obtained by different techniques including endoscopic biopsies, core-needle biopsies, biopsies guided by endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) or endoscopic esophageal ultrasound, mediastinoscopy, and thoracotomy can be used for ALK testing. Recent studies have shown that cytology specimens are suitable for ALK testing, and that the results are highly concordant with those of corresponding histological specimens, thus cytology specimens such as EBUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA), transthoracic FNA, bronchial secretions or brushes, bronchoalveolar lavages, and pleural effusions can be used for ALK testing.25-28 Thus, both histological and cytological specimens are acceptable for ALK testing, if appropriately processed and validated.
- Tumor tissues from either primary tumors or metastatic lesions are equally suitable for ALK testing according to biopsy accessibility. Although discordance in ALK status between primary and metastatic disease has been reported,29 data are insufficient regarding which one is better for ALK testing.17 For patients with multiple, synchronous primary lung adenocarcinomas, each tumor may be tested. However, testing of multiple different areas within a single tumor is not necessary, because heterogeneity of ALK gene status does not seem to be related to the presence of a different histological pattern or biology, but is more likely due to technical problems.17
- Sample selection
- A sufficient number of tumor cells are crucial for successful molecular testing. The number of tumor cells required for IHC assessment of ALK protein remains undefined, as IHC can be performed as long as there are at least a few clusters of viable tumor cells. Regarding ALK FISH, a minimum of 50 to 100 assessable tumor cells are required. Unlike EGFR mutation testing, cells are analyzed individually, so tumor percentage is not as critical. However, it is necessary to choose slides or regions of slides in which the tumor cells do not overlap, and to distinguish them from the adjacent non-neoplastic cells. If the tumor component is very focal within the sample, it is recommended that the area examined be marked on the slide so that it may be readily identifiable under a dark field fluorescence microscope. In this step, the pathologist has the responsibility to determine if the selected sample contains a sufficient number and quality of tumor cells to ensure the quality of the analysis.
- Sample processing
- Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues are routinely used for molecular testing. The diagnostic kits for ALK testing were developed and validated only on FFPE histological samples.18 The first and most important step in tissue processing is immediate fixation, preferably within one hour after the sample is removed from the patient.30,31 It is widely recognized that 10% neutral-buffered formalin is ideal for preparing FFPE samples, whereas the optimal fixation time ranges from six to 48 hours.18,31-33 Specimens treated with decalcifying solution (e.g., bone biopsy) are usually suboptimal for molecular studies, because the solution may interfere with IHC and can frequently compromise FISH testing, so the reliability of molecular testing is reduced.
- Regarding cytological specimens, most sample types, including conventional smears, cytospins, or liquid-based preparations (e.g., ThinPrep, Hologic, or SurePath, BD Diagnostics) regardless of fixation type (air-dried and alcohol-based fixatives) can be used for ALK testing. Cytology specimens should be fixed immediately by the usual alcohol-based methods. For FISH analysis, the use of adhesive-coated or positively charged slides in lung cytology is recommended, as these slides improve the adherence of the cells. FISH works equally well on unstained specimens as well as those processed with Papanicolaou, hematoxylin, or a modified Giemsa stain, and a separate procedure is not usually required. However, in case of a modified Giemsa stain, de-staining with an acid-alcohol technique is recommended before FISH analysis.25 Cell blocks are regarded as appropriate for molecular testing and can be handled in the same way as histological FFPE specimens.
SPECIMEN TYPE AND PROCESSING FOR ALK TESTING
- Several methods are currently available to assess ALK gene rearrangement, including FISH, IHC, and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
- Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- FISH is currently the standard method to detect ALK rearrangements because it was used previously in clinical trials, and is the only test correlated with clinical response. The FDA has approved crizotinib with a companion diagnostic FISH test for ALK-rearranged NSCLC using the certified commercial kit, Abbott Vysis (ALK Break Apart FISH Probe Kit, Abbott Molecular Inc.). The kit includes red (3') and green (5')-colored break-apart probes, which overlap in a fused signal without ALK gene rearrangement (Fig. 1A). Although the break-apart FISH assay requires experience for interpretation, patience, high cost, and technical expertise, this assay is highly sensitive and specific for the detection of ALK gene rearrangement regardless of ALK fusion partners.
- Interpretation should be performed in areas of the slide with good signal, in which at least 50% of all nuclei are easily analyzable, with minimal background or nuclear fluorescent "noise." Areas where the borders of individual nuclei are not clearly identifiable and/or high cell density causes excessive nuclear overlap are easily misinterpreted, and should be avoided. Criteria that must be met for a break-apart FISH assay to be considered positive for ALK rearrangement include: at least 50 cells counted and at least 15% of the counted cells demonstrating separated green and red signals by at least two signal diameters (Fig. 1B), and/or an isolated red signal (Fig. 1C).34 There have been several reports in which a few cases showed "borderline" ALK FISH positivity that approached the 15% cutoff point or less than two signal diameter distances. These cases were regarded as negative with the current criteria and suggest alternative ALK diagnostic techniques and/or an assessment of their response to ALK inhibitors would be required. There are also rare instances when FISH showed atypical signal patterns, such as for an isolated 5' signal that does not fulfill current positive criteria. Such unusual patterns require confirmation of ALK status using a different secondary assay or examination of the effects of crizotinib therapy.
- Immunohistochemistry
- ALK protein represents a potential marker for indicating ALK gene rearrangement, and immunohistochemical detection of ALK protein can be a rapid screening method with low cost for detection of ALK-rearranged NSCLC. When the ALK1 antibody, which has been used for the diagnosis of anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is applied, detection of ALK protein in NSCLCs is difficult because the protein expression level is usually lower in NSCLCs than in ALCL.35 Therefore, several factors including antigen retrieval, primary antibodies with high affinity and sufficient concentration, incubation time and temperature, and strong amplification of the signal should be applied to improve the sensitivity of ALK IHC. There are three ALK antibodies (ALK1, 5A4, and D5F3) that have been studied in depth for NSCLC. D5F3 and 5A4 appeared to be both more sensitive and more specific than the ALK1 antibody.35-38 For a detection system, there are various systems with a substantial degree of signal amplification (Leica/Novocastra Novolink, Dako Advance, Tyramide, Envision+, Ventana i-view). Using highly sensitive detection methods in combination with high affinity antibodies, IHC can effectively detect ALK fusion protein with high sensitivity and specificity. However, so far, there is no qualified guideline for the selection of primary antibodies or the detection system.
- There are still several considerations regarding the use of ALK IHC as a screening method for ALK rearrangement. First of all, there is no accepted standard criterion for IHC interpretation. IHC scoring has been proposed by several publications, including a representatively binary system (positive/negative)9,37,39,40 and a scoring system in the range of 0 to 3 by signal intensity and percentage (Fig. 2).11,35,36,38,41-44 As a screening tool, IHC score is an important criterion for the selection of patients for ALK FISH testing or crizotinib therapy. Paik et al.11 showed good correlations between IHC score and FISH results: cases assigned an ALK IHC score of 3 showed FISH-positivity, while ALK IHC scores of 0 and 1 showed FISH-negativity. However, there are arguments that a four-tiered scoring system creates higher inter-observer variability, so a binary system is more than clear cut for the selection of ALK-positive patients.44 Thus, we recommend that tumors that are positive for ALK IHC, either weakly or strongly, should still be referred to FISH analysis for confirmation of a rearrangement, regardless of primary antibody or detection system.
- Another consideration is the lack of clinical validation for crizotinib treatment in ALK IHC positive and FISH negative cases. Although there was a report that showed a FISH negative, IHC positive patient who showed better response to crizotinib,45 this single instance is insufficient to develop a specific recommendation regarding the use of ALK IHC as a sole determinant of ALK TKI therapy.
- If the IHC method is eventually proven to be accurate in detecting ALK rearrangements and variability, and interpretation can be standardized, IHC assays hold the potential to facilitate the routine identification of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma. Many studies have investigated and reported the high concordance between IHC and FISH results.11,35,39-44,46,47 The CAP-IASLC-AMP guideline also recommends that a properly validated IHC method be used as a screening modality, and that tumors that fail to demonstrate ALK immunoreactivity with a sensitive IHC method need not be tested for ALK rearrangement by FISH.17
- Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- ALK rearrangement generates a unique sequence and the PCR primer that hybridizes with the fusion transcript is responsible for the high sensitivity of the RT-PCR test.48-50 However, RT-PCR requires ALK fusion variants to be known so that primers to all variants should be included in the reaction.51-53 Although, despite an ever-expanding list of ALK fusion variants, all the reported variants require skillful application. In addition, the majority of current ALK fusion variants were detected by RT-PCR in fresh frozen tumor tissue. However, in daily clinical practice, most of the tumor tissues available for molecular profiling are FFPE samples,53 where the integrity of RNAs is likely to be greatly compromised compared with fresh frozen tissue. Thus, at the present time, RT-PCR is not recommended as a first-line diagnostic method for determining ALK fusion status.
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS FOR ALK GENE REARRANGEMENT
- Based on the advantages and characteristics of individual methods for detecting ALK gene status, several investigator groups have proposed diagnostic algorithms for ALK testing.11,18,36,54,55 Considering the trends that the histological types are usually determined by only small biopsy materials or cytological specimens in advanced NSCLC patients, we recommend that ALK rearrangement testing should be done simultaneously with EGFR/K-ras mutation testing for eligible patients (Fig. 3). We also propose that validated IHC can be used as a screening method to detect the ALK rearrangement and ALK FISH can be a confirmative method for all cases showing positive ALK IHC results. If the consensus between pathologists and institutional clinicians can be established, 'reflex molecular testing' is recommended to minimize the exhaustion of small biopsy tissue samples for the necessary molecular tests, and to provide a rapid determination of the genetic characteristics of NSCLC patients.
DIAGNOSTIC ALGORITHM
- Molecular testing reports should contain the following information: 1) identification of the patient including pathologic number, age, sex, hospital unit number, and requesting physician/department, 2) material used for the analysis including biopsy site and sample source, 3) methodology used for analysis and the type of commercial test used, and 4) test results, expressed in terms of negativity or positivity for the rearrangement of the ALK gene. We recommend reporting the following details: total number of counted nuclei, percentage of the nuclei showing gene rearrangements (break-apart and isolated red signal), as well as atypical pattern (e.g., isolated green signal), and copy number gain if observed, 5) receipt day and report day, 6) comments, and 7) names of testing technician and corresponding pathologist.
REPORTING THE RESULTS
- For optimal ALK testing in NSCLC, the quality of the sample, validation status of the analytical procedure, and reliable reporting of the test results are crucial. There are several accessible external quality assessment (EQA) programs for the quality assessment of molecular testing (e.g., http://lung.eqascheme.org; http://kras.eqascheme.org; http://www.ukneqas.org.uk; http://www.emqn.org/emqn/schemes; http://www.quip-ringversuche.de). At this time, no external quality control program for ALK testing exists. To improve the reliability of assays for detecting ALK positivity, as well as optimal information regarding patient selection for ALK inhibitors, further studies should be performed to compare and validate these different diagnostic assays. Quality control programs used in HER-2 testing in Spain, the United Kingdom, and Scandinavia would be a good role model.33
PROPOSAL FOR AN EXTERNAL QUALITY ASSESSMENT PROGRAM
- Molecular testing for targetable mutation has emerged as the standard of care in the management of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Standardization and optimization of diagnostic molecular testing methods using clinical samples have become increasingly important. However, because most lung cancer patients present with an advanced tumor stage at the time of diagnosis, the diagnosis of lung cancer is often based on small specimens from a biopsy or cytology alone. Therefore, it is important that the pathologists handle specimens carefully for further molecular profiling, including EGFR and ALK tests, and do their best to obtain rapid and accurate determination of the patients who are candidates for targeted therapy. Each pathology department must fully validate the detection methods and develop a strategy to manage clinical samples and closely collaborate with clinicians. As a professional group, pathologists should take the lead in determining laboratory references, based on a balance between patient care and resource availability.
CONCLUSION: ROLE OF PATHOLOGISTS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
- 1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69-90. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2129-2139. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004; 304: 1497-1500. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from "never smokers" and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101: 13306-13311. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007; 448: 561-566. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 1693-1703. PubMedPMC
- 7. Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Solomon BJ, et al. Effect of crizotinib on overall survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring ALK gene rearrangement: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol 2011; 12: 1004-1012. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Koivunen JP, Mermel C, Zejnullahu K, et al. EML4-ALK fusion gene and efficacy of an ALK kinase inhibitor in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 4275-4283. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Boland JM, Erdogan S, Vasmatzis G, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase immunoreactivity correlates with ALK gene rearrangement and transcriptional up-regulation in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Hum Pathol 2009; 40: 1152-1158. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Inamura K, Takeuchi K, Togashi Y, et al. EML4-ALK fusion is linked to histological characteristics in a subset of lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol 2008; 3: 13-17. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Paik JH, Choe G, Kim H, et al. Screening of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement by immunohistochemistry in non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 466-472. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, et al. Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 5216-5223. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M, et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4247-4253. PubMedPMC
- 14. Inamura K, Takeuchi K, Togashi Y, et al. EML4-ALK lung cancers are characterized by rare other mutations, a TTF-1 cell lineage, an acinar histology, and young onset. Mod Pathol 2009; 22: 508-515. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Sun Y, Ren Y, Fang Z, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma from East Asian never-smokers is a disease largely defined by targetable oncogenic mutant kinases. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 4616-4620. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Kim H, Park E, Kim YJ, Chung JH. ALK rearrangement in a pure squamous cell carcinoma: the challenge of detection of ALK rearrangement. Virchows Arch 2013; 462: 597-599. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J Thorac Oncol 2013; 8: 823-859. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Marchetti A, Ardizzoni A, Papotti M, et al. Recommendations for the analysis of ALK gene rearrangements in non-small-cell lung cancer: a consensus of the Italian Association of Medical Oncology and the Italian Society of Pathology and Cytopathology. J Thorac Oncol 2013; 8: 352-358. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 244-285. PubMedPMC
- 20. Rekhtman N, Ang DC, Sima CS, Travis WD, Moreira AL. Immunohistochemical algorithm for differentiation of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma based on large series of whole-tissue sections with validation in small specimens. Mod Pathol 2011; 24: 1348-1359. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Kargi A, Gurel D, Tuna B. The diagnostic value of TTF-1, CK 5/6, and p63 immunostaining in classification of lung carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2007; 15: 415-420. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Wu M, Wang B, Gil J, et al. p63 and TTF-1 immunostaining: a useful marker panel for distinguishing small cell carcinoma of lung from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of lung. Am J Clin Pathol 2003; 119: 696-702. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Rossi G, Pelosi G, Graziano P, Barbareschi M, Papotti M. A reevaluation of the clinical significance of histological subtyping of non-small-cell lung carcinoma: diagnostic algorithms in the era of personalized treatments. Int J Surg Pathol 2009; 17: 206-218. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Rossi G, Papotti M, Barbareschi M, Graziano P, Pelosi G. Morphology and a limited number of immunohistochemical markers may efficiently subtype non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: e141-e142. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Betz BL, Dixon CA, Weigelin HC, Knoepp SM, Roh MH. The use of stained cytologic direct smears for ALK gene rearrangement analysis of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cytopathol 2013; 121: 489-499. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Savic S, Bode B, Diebold J, et al. Detection of ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancers on cytological specimens: high accuracy of immunocytochemistry with the 5A4 clone. J Thorac Oncol 2013; 8: 1004-1011. ArticlePubMed
- 27. Neat MJ, Foot NJ, Hicks A, et al. ALK rearrangements in EBUS-derived transbronchial needle aspiration cytology in lung cancer. Cytopathology 2013; 24: 356-364. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Tanaka H, Tone K, Hayashi A, et al. Clinical application of immunocytochemical detection of ALK rearrangement on cytology slides for detection or screening of lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2013; 80: 289-292. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Kim H, Xu X, Yoo SB, et al. Discordance between anaplastic lymphoma kinase status in primary non-small-cell lung cancers and their corresponding metastases. Histopathology 2013; 62: 305-314. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Boldrini L, Gisfredi S, Ursino S, et al. Mutational analysis in cytological specimens of advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a sensitive method for molecular diagnosis. J Thorac Oncol 2007; 2: 1086-1090. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Pirker R, Herth FJ, Kerr KM, et al. Consensus for EGFR mutation testing in non-small cell lung cancer: results from a European workshop. J Thorac Oncol 2010; 5: 1706-1713. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Eberhard DA, Giaccone G, Johnson BE. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Working Group. Biomarkers of response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Working Group: standardization for use in the clinical trial setting. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 983-994. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Garrido P, de Castro J, Concha Á, et al. Guidelines for biomarker testing in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. A national consensus of the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology (SEOM) and the Spanish Society of Pathology (SEAP). Clin Transl Oncol 2012; 14: 338-349. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 34. Camidge DR, Kono SA, Flacco A, et al. Optimizing the detection of lung cancer patients harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements potentially suitable for ALK inhibitor treatment. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 5581-5590. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. Mino-Kenudson M, Chirieac LR, Law K, et al. A novel, highly sensitive antibody allows for the routine detection of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas by standard immunohistochemistry. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 1561-1571. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Conklin CM, Craddock KJ, Have C, Laskin J, Couture C, Ionescu DN. Immunohistochemistry is a reliable screening tool for identification of ALK rearrangement in non-small-cell lung carcinoma and is antibody dependent. J Thorac Oncol 2013; 8: 45-51. ArticlePMC
- 37. Minca EC, Portier BP, Wang Z, et al. ALK status testing in non-small cell lung carcinoma: correlation between ultrasensitive IHC and FISH. J Mol Diagn 2013; 15: 341-346. PubMed
- 38. Selinger CI, Rogers TM, Russell PA, et al. Testing for ALK rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma: a multicenter comparison of immunohistochemistry and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Mod Pathol 2013; 26: 1545-1553. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Hofman P, Ilie M, Hofman V, et al. Immunohistochemistry to identify EGFR mutations or ALK rearrangements in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Oncol 2012; 23: 1738-1743. ArticlePubMed
- 40. Martinez P, Hernández-Losa J, Montero MÁ, et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry as diagnostic methods for ALK positive non-small cell lung cancer patients. PLoS One 2013; 8: e52261.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Yi ES, Boland JM, Maleszewski JJ, et al. Correlation of IHC and FISH for ALK gene rearrangement in non-small cell lung carcinoma: IHC score algorithm for FISH. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 459-465. ArticlePubMed
- 42. McLeer-Florin A, Moro-Sibilot D, Melis A, et al. Dual IHC and FISH testing for ALK gene rearrangement in lung adenocarcinomas in a routine practice: a French study. J Thorac Oncol 2012; 7: 348-354. ArticlePubMed
- 43. Wang Z, Zhang X, Bai H, et al. EML4-ALK rearrangement and its clinical significance in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology 2012; 83: 248-256. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 44. Ying J, Guo L, Qiu T, et al. Diagnostic value of a novel fully automated immunochemistry assay for detection of ALK rearrangement in primary lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Oncol 2013; 24: 2589-2593. ArticlePubMed
- 45. Sun JM, Choi YL, Won JK, et al. A dramatic response to crizotinib in a non-small-cell lung cancer patient with IHC-positive and FISH-negative ALK. J Thorac Oncol 2012; 7: e36-e38. ArticlePubMed
- 46. Jokoji R, Yamasaki T, Minami S, et al. Combination of morphological feature analysis and immunohistochemistry is useful for screening of EML4-ALK-positive lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol 2010; 63: 1066-1070. ArticlePubMed
- 47. Han XH, Zhang NN, Ma L, et al. Immunohistochemistry reliably detects ALK rearrangements in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Virchows Arch 2013; 463: 583-591. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Soda M, et al. Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for EML4-ALK fusion transcripts. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 6618-6624. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 49. Sanders HR, Li HR, Bruey JM, et al. Exon scanning by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for detection of known and novel EML4-ALK fusion variants in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Genet 2011; 204: 45-52. ArticlePubMed
- 50. Wong DW, Leung EL, So KK, et al. The EML4-ALK fusion gene is involved in various histologic types of lung cancers from nonsmokers with wild-type EGFR and KRAS. Cancer 2009; 115: 1723-1733. ArticlePubMed
- 51. Horn L, Pao W. EML4-ALK: honing in on a new target in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4232-4235. ArticlePubMed
- 52. Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Togashi Y, et al. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 3143-3149. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 53. Togashi Y, Soda M, Sakata S, et al. KLC1-ALK: a novel fusion in lung cancer identified using a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue only. PLoS One 2012; 7: e31323.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Kim H, Yoo SB, Choe JY, et al. Detection of ALK gene rearrangement in non-small cell lung cancer: a comparison of fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromogenic in situ hybridization with correlation of ALK protein expression. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 1359-1366. ArticlePubMed
- 55. Thunnissen E, Bubendorf L, Dietel M, et al. EML4-ALK testing in non-small cell carcinomas of the lung: a review with recommendations. Virchows Arch 2012; 461: 245-257. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
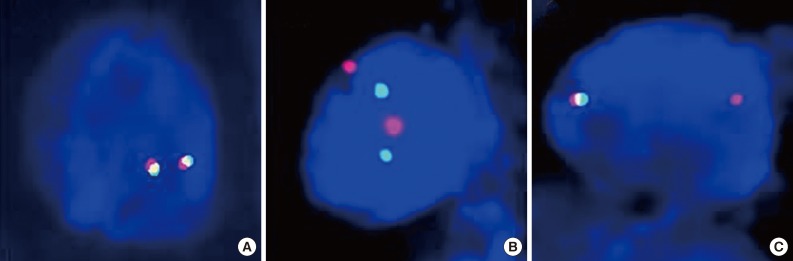

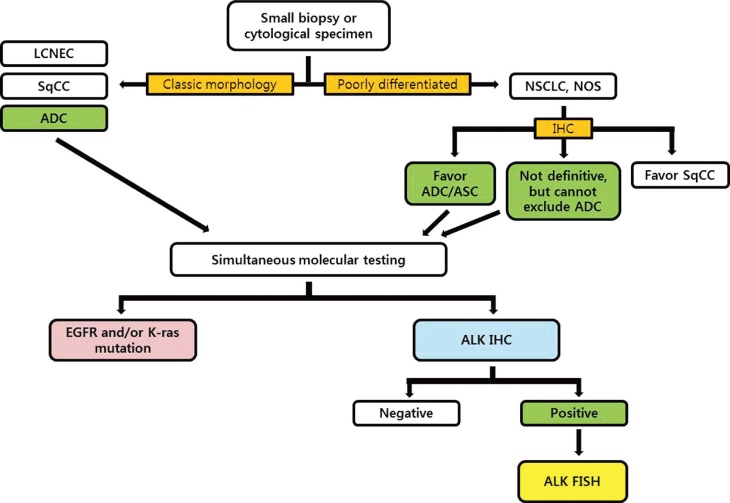
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Molecular Characteristics of Radon Associated Lung Cancer Highlights MET Alterations
Gabriele Gamerith, Marcel Kloppenburg, Finn Mildner, Arno Amann, Sabine Merkelbach-Bruse, Carina Heydt, Janna Siemanowski, Reinhard Buettner, Michael Fiegl, Claudia Manzl, Georg Pall
Cancers.2022; 14(20): 5113. CrossRef -
ALK Translocation in ALK-Positive Mesenchymal Tumors: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Insights
Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon, Jeongmo Bae, Tae Min Kim, Miso Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Cheol Lee
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2022; 146(12): 1460. CrossRef - Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 181. CrossRef - Testing for EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Considerations for Countries in Emerging Markets
Mercedes L Dalurzo, Alejandro Avilés-Salas, Fernando Augusto Soares, Yingyong Hou, Yuan Li, Anna Stroganova, Büge Öz, Arif Abdillah, Hui Wan, Yoon-La Choi
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4671. CrossRef - Molecular testing for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Malaysia: Consensus statement from the College of Pathologists, Academy of Medicine Malaysia, the Malaysian Thoracic Society, and the Malaysian Oncological Society
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Phaik Leng Cheah, Soon Hin How, Chong Kin Liam, Muhammad Azrif Ahmad Annuar, Norhayati Omar, Noriah Othman, Nurhayati Mohd Marzuki, Yong Kek Pang, Ros Suzanna Ahmad Bustamam, Lye Mun Tho
Lung Cancer.2019; 136: 65. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2018; 13(3): 323. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2018; 20(2): 129. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benja
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(3): 321. CrossRef - 5′/ 3′ imbalance strategy to detect ALK fusion genes in circulating tumor RNA from patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Yongqing Tong, Zhijun Zhao, Bei Liu, Anyu Bao, Hongyun Zheng, Jian Gu, Mary McGrath, Ying Xia, Bihua Tan, Chunhua Song, Yan Li
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular testing and treatment patterns for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: PIvOTAL observational study
Dae Ho Lee, Ming-Sound Tsao, Karl-Otto Kambartel, Hiroshi Isobe, Ming-Shyan Huang, Carlos H. Barrios, Adnan Khattak, Filippo de Marinis, Smita Kothari, Ashwini Arunachalam, Xiting Cao, Thomas Burke, Amparo Valladares, Javier de Castro, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0202865. CrossRef - Microfluidics-based immunofluorescence for fast staining of ALK in lung adenocarcinoma
Saška Brajkovic, Benjamin Pelz, Maria-Giuseppina Procopio, Anne-Laure Leblond, Grégoire Repond, Ariane Schaub-Clerigué, Diego G Dupouy, Alex Soltermann
Diagnostic Pathology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanded Circulating Tumor Cells from a Patient with ALK- Positive Lung Cancer Present with EML4-ALK Rearrangement Along with Resistance Mutation and Enable Drug Sensitivity Testing: A Case Study
Zhuo Zhang, Hiroe Shiratsuchi, Nallasivam Palanisamy, Sunitha Nagrath, Nithya Ramnath
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(2): 397. CrossRef - Molecular Testing of Lung Cancers
Hyo Sup Shim, Yoon-La Choi, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Tae-Jung Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jin-Haeng Chung, Se Jin Jang, Geon Kook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 242. CrossRef - Novel ALK fusion partners in lung cancer
Aglaya G. Iyevleva, Grigory A. Raskin, Vladislav I. Tiurin, Anna P. Sokolenko, Natalia V. Mitiushkina, Svetlana N. Aleksakhina, Aigul R. Garifullina, Tatiana N. Strelkova, Valery O. Merkulov, Alexandr O. Ivantsov, Ekatherina Sh. Kuligina, Kazimir M. Pozha
Cancer Letters.2015; 362(1): 116. CrossRef - Strategic management of transthoracic needle aspirates for histological subtyping and EGFR testing in patients with peripheral lung cancer: An institutional experience
Choonhee Son, Eun‐Ju Kang, Mee Sook Roh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2015; 43(7): 532. CrossRef - Current and future molecular diagnostics in non-small-cell lung cancer
Chun Man Li, Wing Ying Chu, Di Lun Wong, Hin Fung Tsang, Nancy Bo Yin Tsui, Charles Ming Lok Chan, Vivian Wei Wen Xue, Parco Ming Fai Siu, Benjamin Yat Ming Yung, Lawrence Wing Chi Chan, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2015; 15(8): 1061. CrossRef - Role of biopsy sampling for diagnosis of early and progressed hepatocellular carcinoma
Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology.2014; 28(5): 813. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions
Mee Sook Roh
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2014; 77(2): 49. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangements in lung cancer with nodular ground-glass opacity
Sung-Jun Ko, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young-Jae Cho, Ho Il Yoon, Jin-Haeng Chung, Tae Jung Kim, Kyung Won Lee, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon, Hyojin Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef



Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
| Recommendation | |
|---|---|
| Patient eligibility | Histologic type is the most important factor: patients diagnosed with adenocarcinoma, large cell carcinoma or non-small cell carcinoma with adenocarcinoma component should be tested for ALK rearrangement. |
| Clinical criteria might be considered, when adenocarcinoma component cannot be completely excluded. | |
| Specimen type | Histological and cytological specimens are both acceptable. |
| Either primary tumors or metastatic lesions are equally suitable. | |
| In cases with multiple, synchronous primary lung adenocarcinomas, each tumor may be tested. | |
| Sample selection | A minimum of 50-100 assessable tumor cells are required for ALK FISH test. |
| ALK IHC can be performed as long as there are at least a few clusters of viable tumor cells. | |
| Sample processing | Fixative: 10% neutral-buffered formalin, immediately after the sample is removed from the patient. |
| Fixation time: from 6 to 48 hours. | |
| Avoid decalcified tissue. | |
| Routine preparation for cytology is acceptable, if fully validated. | |
| Diagnostic method | FISH is a companion diagnostic test for detection of ALK rearrangement. |
| IHC can be a potential screening method with high sensitive detection method. | |
| RT-PCR is highly sensitive but not recommended as a first-line diagnostic method for determining ALK fusion status. | |
| The pathologist should consider the pros and cons of each method and combination of more than one technique may be useful in equivocal cases. | |
| Reporting format | Patients and sample information, type of detection method, results of the test, comments. |
ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; FISH, fluorescence

 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader Cite this Article
Cite this Article




