Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Original Articles
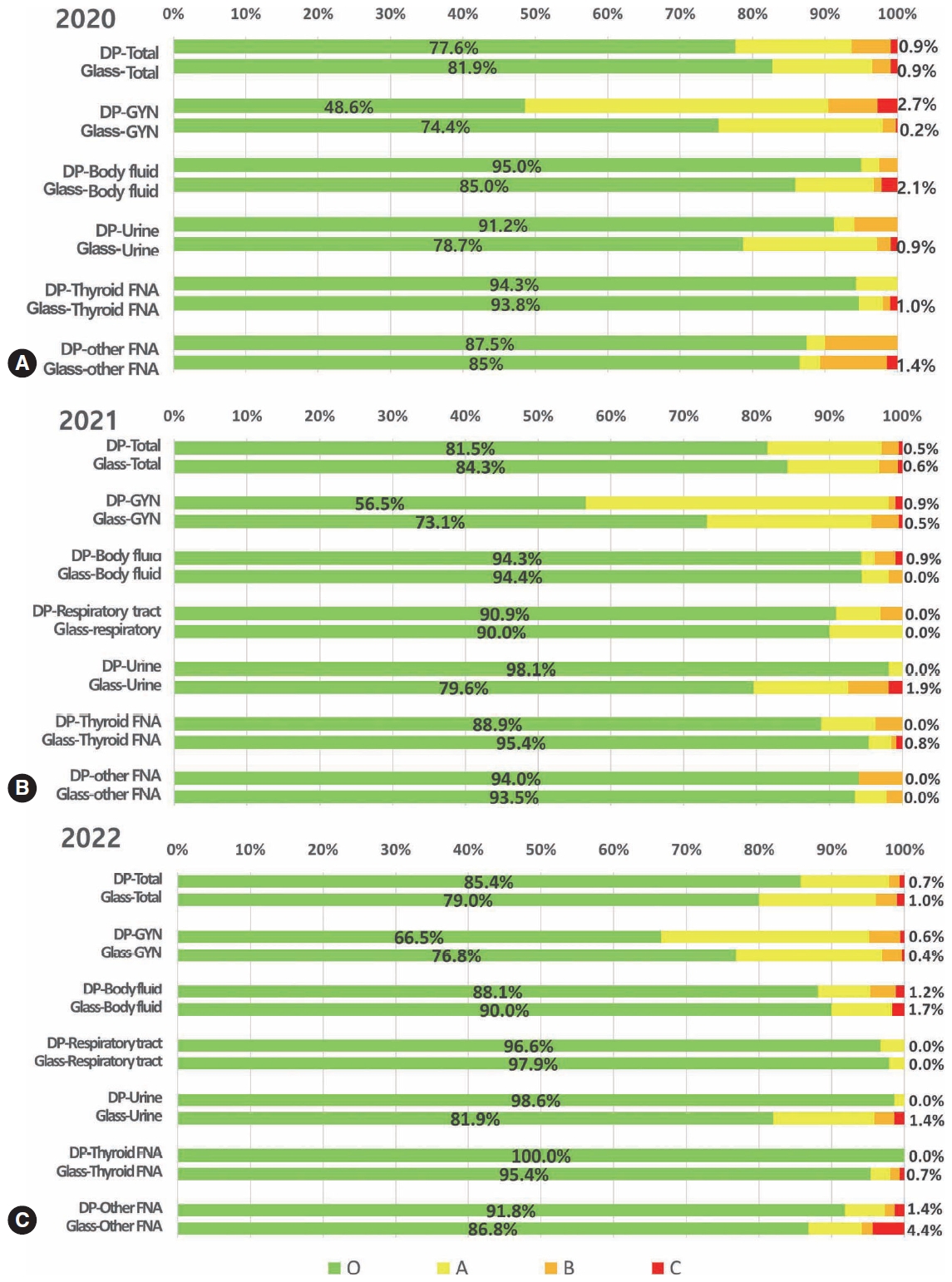
- Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
- Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):251-264. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.17
- 7,201 View
- 339 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Korean Society for Cytopathology introduced a digital proficiency test (PT) in 2021. However, many doubtful opinions remain on whether digitally scanned images can satisfactorily present subtle differences in the nuclear features and chromatin patterns of cytological samples.
Methods
We prepared 30 whole-slide images (WSIs) from the conventional PT archive by a selection process for digital PT. Digital and conventional PT were performed in parallel for volunteer institutes, and the results were compared using feedback. To assess the quality of cytological assessment WSIs, 12 slides were collected and scanned using five different scanners, with four cytopathologists evaluating image quality through a questionnaire.
Results
Among the 215 institutes, 108 and 107 participated in glass and digital PT, respectively. No significant difference was noted in category C (major discordance), although the number of discordant cases was slightly higher in the digital PT group. Leica, 3DHistech Pannoramic 250 Flash, and Hamamatsu NanoZoomer 360 systems showed comparable results in terms of image quality, feature presentation, and error rates for most cytological samples. Overall satisfaction was observed with the general convenience and image quality of digital PT.
Conclusions
As three-dimensional clusters are common and nuclear/chromatin features are critical for cytological interpretation, careful selection of scanners and optimal conditions are mandatory for the successful establishment of digital quality assurance programs in cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Chang Gok Woo, Seung‐Myoung Son, Hye‐Kyung Hwang, Jung‐Sil Bae, Ok‐Jun Lee, Ho‐Chang Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(1): 35. CrossRef - Integration of AI‐Assisted in Digital Cervical Cytology Training: A Comparative Study
Yihui Yang, Dongyi Xian, Lihua Yu, Yanqing Kong, Huaisheng Lv, Liujing Huang, Kai Liu, Hao Zhang, Weiwei Wei, Hongping Tang
Cytopathology.2025; 36(2): 156. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of digital image slides for diagnosis in cervico-vaginal cytology
Francisco Tresserra, Gemma Fabra, Olga Luque, Miriam Castélla, Carla Gómez, Carmen Fernández-Cid, Ignacio Rodríguez
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(3): 182. CrossRef - Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yujin Lee, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Hongsik Park, Kwangil Yim, Kyung Jin Seo, Gisu Hwang, Dahyeon Kim, Yeonsoo Chung, Gyungyub Gong, Nam Hoon Cho, Chong Woo Yoo, Yosep Chong, Hyun Joo Choi
Thyroid®.2024; 34(6): 723. CrossRef
- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
- Establishing molecular pathology curriculum for pathology trainees and continued medical education: a collaborative work from the Molecular Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists
- Jiwon Koh, Ha Young Park, Jeong Mo Bae, Jun Kang, Uiju Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Haeyoun Kang, Min Eui Hong, Jae Kyung Won, Youn-La Choi, Wan-Seop Kim, Ahwon Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):265-272. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.08.26
- 4,964 View
- 207 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The importance of molecular pathology tests has increased during the last decade, and there is a great need for efficient training of molecular pathology for pathology trainees and as continued medical education.
Methods
The Molecular Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists appointed a task force composed of experienced molecular pathologists to develop a refined educational curriculum of molecular pathology. A 3-day online educational session was held based on the newly established structure of learning objectives; the audience were asked to score their understanding of 22 selected learning objectives before and after the session to assess the effect of structured education.
Results
The structured objectives and goals of molecular pathology was established and posted as a web-based interface which can serve as a knowledge bank of molecular pathology. A total of 201 pathologists participated in the educational session. For all 22 learning objectives, the scores of self-reported understanding increased after educational session by 9.9 points on average (range, 6.6 to 17.0). The most effectively improved items were objectives from next-generation sequencing (NGS) section: ‘NGS library preparation and quality control’ (score increased from 51.8 to 68.8), ‘NGS interpretation of variants and reference database’ (score increased from 54.1 to 68.0), and ‘whole genome, whole exome, and targeted gene sequencing’ (score increased from 58.2 to 71.2). Qualitative responses regarding the adequacy of refined educational curriculum were collected, where favorable comments dominated.
Conclusions
Approach toward the education of molecular pathology was refined, which would greatly benefit the future trainees. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Presence of RB1 or Absence of LRP1B Mutation Predicts Poor Overall Survival in Patients with Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
In Hye Song, Bokyung Ahn, Young Soo Park, Deok Hoon Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 57(2): 492. CrossRef
- Presence of RB1 or Absence of LRP1B Mutation Predicts Poor Overall Survival in Patients with Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
Case Studies
- Hepatic small vessel neoplasm: not totally benign, not yet malignant
- Madison Miranda, David Howell, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):273-277. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.19
- 4,636 View
- 277 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic small vessel neoplasm (HSVN) is a rare vascular tumor with few reports in the literature. While imaging findings may show characteristic enhancement patterns, limited available literature may not reveal the full potential for image-based diagnosis. Histologically, HSVN mimics other entities, though certain morphologic and immunohistochemical findings provide clues for diagnosis. However, HSVN still provides diagnostic challenges, especially on core biopsies with limited material for morphologic and molecular evaluation. While current recommendations are surgical resection and close observation, the long-term course of the tumor is unknown. We report a case of HSVN in a liver with additional feature of organized lymphoid aggregates necessitating additional hematopathology consultation and workup to rule out concurrent entities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef - Revisiting Hepatic Small Vessel Neoplasms and Anastomosing Hemangiomas as a Unique Capillary Liver Neoplasm: A 25-Case Series With Pathomolecular Correlations
Aurélie Beaufrère, Astrid Laurent-Bellue, Antoinette Lemoine, Agnès Bourillon, Nathalie Sturm, Pierre Gosset, Virginie Cahn, Valérie Vilgrain, Maité Lewin, Valérie Paradis, Catherine Guettier
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(10): 100835. CrossRef - Imaging features of recently identified low-grade vascular neoplasia of the liver: hepatic small vessel neoplasm and anastomosing hemangioma
Maïté Lewin, Rauda Aldhaheri, Aurélie Beaufrère, Christophe Desterke, Anita Paisant, Ivan Bricault, Paul Borde, Gabriel Simon, Mickaël Lesurtel, Daniel Cherqui, Clara Prud’Homme, Valérie Vilgrain, Astrid Laurent-Bellue
European Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
- Diagnostic conundrums of schwannomas: two cases highlighting morphological extremes and diagnostic challenges in biopsy specimens of soft tissue tumors
- Chankyung Kim, Yang-Guk Chung, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):278-283. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.13
- 5,002 View
- 264 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing peripheral nerve sheath tumors commonly occurring in the head, neck, and flexor regions of the extremities. Although most schwannomas are easily diagnosable, their variable morphology can occasionally create difficulty in diagnosis. Reporting pathologists should be aware that schwannomas can exhibit a broad spectrum of morphological patterns. Clinical and radiological examinations can show correlation and should be performed, in conjunction with ancillary tests, when appropriate. Furthermore, deferring a definitive diagnosis until excision may be necessary for small biopsy specimens and frozen sections. This report underscores these challenges through examination of two unique schwannoma cases, one predominantly cellular and the other myxoid, both of which posed significant challenges in histological interpretation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plexiform Schwannoma Over the Anterior Chest Wall: A Clinicopathological Review
Debojyoti Sasmal, Saswata Barenya, Hinglaj Saha, Pankaj Kumar Halder
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2025; 21(2): 95. CrossRef - Giant Retroperitoneal Schwannoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Magdalena Alexieva, Evgeni V Mekov, Silvia Ivanova, Alexandrina Vlahova, Georgi Yankov
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 353. CrossRef - Oral and Maxillofacial Schwannoma (OMSCH): an institutional study of 102 patients
Lingli Huang, Wenya Zhu, Qicheng Ye, Shengwen Liu, Hao Lu, Wenjun Yang, Wanlin Xu
Journal of Stomatology Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025; : 102678. CrossRef
- Plexiform Schwannoma Over the Anterior Chest Wall: A Clinicopathological Review
- EWSR1 rearranged primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma: a diagnostic conundrum
- Nilay Nishith, Zachariah Chowdhury
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):284-288. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.08.08
- 3,865 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma is an exceedingly rare neoplasm with an aggressive phenotype and Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) rearrangement in a small fraction of cases. In addition to its rarity, the diagnosis can be challenging for the pathologist due to morphologic heterogeneity, particularly on the biopsy specimen. At times, immunohistochemistry may be indecisive; therefore, molecular studies should be undertaken for clinching the diagnosis. We aim to illustrate a case of primary myoepithelial carcinoma of the kidney with EWSR1-rearrangement in a 67-year-old male patient who presented with right supraclavicular mass, which was clinically diagnosed as carcinoma of an unknown primary. An elaborate immunohistochemical work-up aided by fluorescent in-situ hybridization allowed us to reach a conclusive diagnosis. This unusual case report advocates that one should be aware of the histological mimickers and begin with broad differential diagnoses alongside sporadic ones and then narrow them down with appropriate ancillary studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney
João Lobo, Huiying He, Raheel Ahmed, Bassel Zein-Sabatto, Thomas Winokur, Shi Wei, Shuko Harada, Jesse K. McKenney, Jonathan L. Myles, Jane K. Nguyen, Christopher G. Przybycin, Sean R. Williamson, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Reza Alaghehbandan
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 49(10): 1078. CrossRef
- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney

 E-submission
E-submission







 First
First Prev
Prev



