Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: two case reports with targeted next-generation sequencing analysis
- Yoo Jin Lee, Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):119-122. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30
- 6,546 View
- 137 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
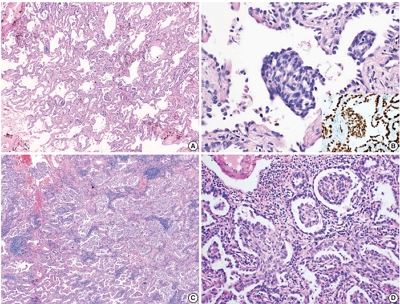
PDF - Morules, or morule-like features, can be identified in benign and malignant lesions in various organs. Morular features are unusual in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with only 26 cases reported to date. Here, we describe two cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with morule-like features in Korean women. One patient had a non-mucinous-type adenocarcinoma in situ and the other had an acinarpredominant adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component. Both patients showed multiple intra-alveolar, nodular, whorled proliferative foci composed of atypical spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of the tumors. Results showed unusual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, which are associated with drug resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, revealing the importance of identifying morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and the need for additional study, since there are few reported cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Mitsuteru Yosida, Mitsuru Tomita, Naoya Kawakita, Teruki Shimizu, Ryou Yamada, Hiromitsu Takizawa, Hisanori Uehara
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2024; 48: 102008. CrossRef - Clinicopathological, Radiological, and Molecular Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma with Morule-Like Components
Li-Li Wang, Li Ding, Peng Zhao, Jing-Jing Guan, Xiao-Bin Ji, Xiao-Li Zhou, Shi-Hong Shao, Yu-Wei Zou, Wei-Wei Fu, Dong-Liang Lin, Dong Pan
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
- Adenocarcinoma Arising in an Ectopic Hamartomatous Thymoma with HER2 Overexpression
- Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Yoo Jin Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):403-406. Published online August 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.06.23
- 5,791 View
- 116 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Branchioma: immunohistochemical and molecular genetic study of 23 cases highlighting frequent loss of retinoblastoma 1 immunoexpression
Martina Bradová, Lester D. R. Thompson, Martin Hyrcza, Tomáš Vaněček, Petr Grossman, Michael Michal, Veronika Hájková, Touraj Taheri, Niels Rupp, David Suster, Sunil Lakhani, Dimitar Hadži Nikolov, Radim Žalud, Alena Skálová, Michal Michal, Abbas Agaimy
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 103. CrossRef - Adenocarcinoma arising in branchioma with a KRAS and TP53 mutation
Natsuki Taniguchi, Akira Satou, Takanori Ito, Masato Nakaguro, Toyonori Tsuzuki
Pathology International.2023; 73(7): 317. CrossRef - Two Ectopic Hamartomatous Thymomas of Suprasternal Region of the Neck in A Single Patient: A Case Report
Wei WANG, Manmei LONG, Zhichao WANG
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.2021; 3(1): 51. CrossRef
- Branchioma: immunohistochemical and molecular genetic study of 23 cases highlighting frequent loss of retinoblastoma 1 immunoexpression
- Human Papillomavirus–Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma with Late Recurrence
- Bokyung Ahn, Eojin Kim, Harim Oh, Yang-Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Youngseok Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Yoo Jin Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):337-340. Published online April 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.04.02
- 7,444 View
- 117 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinicopathological Profile of HPV-related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
João Paulo Gonçalves de Paiva, Daniela Giraldo Roldán, Ricardo Anderson de Oliveira Vasconcelos, Luiz Miguel Ferreira, Isaac Santos Araújo, Ana Lúcia Carrinho Ayroza Rangel, Maíra Medeiros Pacheco de Andrade, Igor Lima Fernandes, Lucas Faria Abrahao-Macha
Head and Neck Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV-related multiphenotypic sinonasal carcinoma: Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characterization of 3 cases with comprehensive literature review and emphasis on differential diagnosis
Gabriella C. Speakman, Paul E. Wakely, Prokopios P. Argyris
Human Pathology.2025; : 105961. CrossRef - HPV-Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Clinicoradiological Series of 3 Cases With Full Endoscopic Surgical Outcome
Catherine Beaumont, Sylvie Nadeau, Pierre-Olivier Champagne, Michel Beauchemin, Noémie Villemure-Poliquin
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case of Human Papillomavirus-Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma Resected by Endoscopic Surgery
Keigo Nakamura, Ichiro Tojima, Yoshihito Kubo, Kento Kawakita, Takuya Murao, Yuichiro Oe, Hiroyuki Arai, Koji Matsumoto, Hideaki Kouzaki, Takeshi Shimizu
Practica oto-rhino-laryngologica. Suppl..2024; 164: 61. CrossRef - Human papillomavirus-related multiphenotypic sinonasal carcinoma: A report of two patients and review of the literature
Satoru Miyamaru, Tetsuji Sanuki, Yusuke Miyamoto, Kohei Nishimoto, Masako Masuda, Yumi Honda, Yoshiki Mikami, Yorihisa Orita
Auris Nasus Larynx.2023; 50(3): 473. CrossRef - Malignant Sinonasal Tumors: Update on Histological and Clinical Management
Alessandra Bracigliano, Fabiana Tatangelo, Francesco Perri, Giuseppe Di Lorenzo, Roberto Tafuto, Alessandro Ottaiano, Ottavia Clemente, Maria Luisa Barretta, Nunzia Simona Losito, Mariachiara Santorsola, Salvatore Tafuto
Current Oncology.2021; 28(4): 2420. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus-Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma—An Even Broader Tumor Entity?
Mark Zupancic, Anders Näsman
Viruses.2021; 13(9): 1861. CrossRef - A Case of Human Papillomavirus-related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma Resected by Endonasal Endoscopic En Bloc Resection
Satoru Miyamaru, Yu Shimoda, Kohei Nishimoto, Hiroyuki Ueda, Masako Masuda, Taro Okazaki, Tetsuji Sanuki, Yumi Honda, Yoshiki Mikami, Yorihisa Orita
Nihon Bika Gakkai Kaishi (Japanese Journal of Rhinology).2021; 60(4): 531. CrossRef - Don't stop the champions of research now: a brief history of head and neck pathology developments
Lester D.R. Thompson, James S. Lewis, Alena Skálová, Justin A. Bishop
Human Pathology.2020; 95: 1. CrossRef - HPV-Related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: Four Cases that Expand the Morpho-Molecular Spectrum and Include Occupational Data
Niels J. Rupp, Ulrike Camenisch, Kati Seidl, Elisabeth J. Rushing, Nanina Anderegg, Martina A. Broglie, David Holzmann, Grégoire B. Morand
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(3): 623. CrossRef
- Clinicopathological Profile of HPV-related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
- Combined Adenosquamous and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
- Jiyoon Jung, Yang-Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Youngseok Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Dong-Sik Kim, Young-Dong Yu, Joo Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):121-125. Published online October 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.20
- 8,854 View
- 155 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) of the gallbladder is extremely rare and usually combined with other type of malignancy, mostly adenocarcinoma. We report an unusual case of combined adenosquamous carcinoma and LCNEC of the gallbladder in a 54-year-old woman. A radical cholecystectomy specimen revealed a 4.3×4.0 cm polypoid mass in the fundus with infiltration of adjacent liver parenchyma. Microscopically, the tumor consisted of two distinct components. Adenosquamous carcinoma was predominant and abrupt transition from adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma was observed. LCNEC showed round cells with large, vesicular nuclei, abundant mitotic figures, and occasional pseudorosette formation. The patient received adjuvant chemotherapy. However, multiple liver metastases were identified at 3-month follow-up. Metastatic nodules were composed of LCNEC and squamous cell carcinoma components. Detecting LCNEC component is important in gallbladder cancer, because the tumor may require a different chemotherapy regimen and show early metastasis and poor prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postoperative gastric cancer accompanied by large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report
Zhiqin Chen, Jiang Liu, Jin Liu, Yinhang Wu, Jian Liu
Medicine.2025; 104(41): e44367. CrossRef - Does the size of the neuroendocrine-carcinoma component determine the prognosis of gallbladder cancer?
Ya-Fei Hu, Jun-Ke Wang, Wen-Jie Ma, Hai-Jie Hu, Han-Fei Gu, Fei Liu, Tian-Run Lv, Si-Qi Yang, Yu-Shi Dai, Rui-Qi Zou, Yan-Wen Jin, Fu-Yu Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Az epehólyag adenosquamosus daganata
Fanni Hegedűs, Anita Sejben
Orvosi Hetilap.2024; 165(49): 1945. CrossRef - Comparison of Metastatic Patterns Among Neuroendocrine Tumors, Neuroendocrine Carcinomas, and Nonneuroendocrine Carcinomas of Various Primary Organs
Hyung Kyu Park, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical features and outcomes analysis of Gallbladder neuroendocrine carcinoma
Man Jiang, Yijing Zhang
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(4): 910. CrossRef - Primary mixed large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder: A case report and literature review
Tingting Yu, Shike Li, Zhuo Zhang
Asian Journal of Surgery.2022; 45(11): 2336. CrossRef - Mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasm of the gallbladder: case report and literature review
Xu Ren, Hong Jiang, Kan Sun, Xufu Qin, Yongping Qu, Tian Xia, Yan Chen
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Gallbladder: A Clinicopathological Analysis of 13 Patients and a Review of the Literature
Pengyan Wang, Jingci Chen, Ying Jiang, Congwei Jia, Junyi Pang, Shan Wang, Xiaoyan Chang, Oronzo Brunetti
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Gallbladder Mixed Neuroendocrine-Non-neuroendocrine Neoplasm (MiNEN) Arising in Intracholecystic Papillary Neoplasm: Clinicopathologic and Molecular Analysis of a Case and Review of the Literature
Amedeo Sciarra, Edoardo Missiaglia, Mounir Trimech, Emmanuel Melloul, Jean-Philippe Brouland, Christine Sempoux, Stefano La Rosa
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(1): 84. CrossRef - Mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine carcinoma of gallbladder: case report
Adam Skalický, Lucie Vištejnová, Magdaléna Dubová, Tomáš Malkus, Tomáš Skalický, Ondřej Troup
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Postoperative gastric cancer accompanied by large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report
- Hyalinizing Cholecystitis and Associated Carcinoma: A Case Report
- Youngjin Kang, Yang-Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Youngseok Lee, Dong-Sik Kim, Young-Dong Yu, Joo Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):64-66. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.11.04
- 11,149 View
- 216 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unexpected intraoperative finding of a hyalinizing cholecystitis in a patient with gallbladder calculi
Klaudia Gjinoska, Andrej Nikolovski, Emil Stoicovski, Zan Mitrev
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 18F-FDG PET/CT in Hyalinized Cholecystitis
Esra Arslan, Aytül Hande Yardimci, Enver Yarikkaya, Göksel Alçin, Tevfik Fikret Çermik
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2021; 46(4): e228. CrossRef - Gallbladder Carcinoma and Its Differential Diagnosis at MRI: What Radiologists Should Know
Camila Lopes Vendrami, Michael J. Magnetta, Pardeep K. Mittal, Courtney C. Moreno, Frank H. Miller
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(1): 78. CrossRef - A simple method for diagnosing gallbladder malignant tumors with subserosa invasion by endoscopic ultrasonography
Mitsuru Sugimoto, Hiroki Irie, Mika Takasumi, Minami Hashimoto, Yuka Oka, Tadayuki Takagi, Rei Suzuki, Naoki Konno, Hiroyuki Asama, Yuki Sato, Jun Nakamura, Tsunetaka Kato, Ryoichiro Kobashi, Yuko Hashimoto, Shigeru Marubashi, Takuto Hikichi, Hiromasa Ohi
BMC Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - KRONİK KOLESİSTİTİN NADİR VE MALİGNİTE POTANSİYELİ YÜKSEK OLAN ALT TİPİ; HYALİNİZE KOLESİSTİT: OLGU SUNUMU
Leymune PARLAK, Bahar MEMİŞ
Balıkesir Medical Journal.2019; 3(3): 129. CrossRef
- Unexpected intraoperative finding of a hyalinizing cholecystitis in a patient with gallbladder calculi
- Comparison of the Mismatch Repair System between Primary and Metastatic Colorectal Cancers Using Immunohistochemistry
- Jiyoon Jung, Youngjin Kang, Yoo Jin Lee, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Eunjung Lee, Joo Young Kim, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Chul Hwan Kim, Yang-Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):129-136. Published online February 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.12.09
- 12,442 View
- 330 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Approximately 10%–15% of the CRC cases have defective DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Although the high level of microsatellite instability status is a predictor of favorable outcome in primary CRC, little is known about its frequency and importance in secondary CRC. Immunohistochemical staining (IHC) for MMR proteins (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2) has emerged as a useful technique to complement polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analyses. Methods: In this study, comparison between the MMR system of primary CRCs and paired liver and lung metastatic lesions was done using IHC and the correlation with clinical outcomes was also examined. Results: Based on IHC, 7/61 primary tumors (11.4%) showed deficient MMR systems, while 13/61 secondary tumors (21.3%) showed deficiencies. In total, 44 cases showed proficient expression in both the primary and metastatic lesions. Three cases showed deficiencies in both the primary and paired metastatic lesions. In 10 cases, proficient expression was found only in the primary lesions, and not in the corresponding metastatic lesions. In four cases, proficient expression was detected in the secondary tumor, but not in the primary tumor. Conclusions: Although each IHC result and the likely defective genes were not exactly matched between the primary and the metastatic tumors, identical results for primary and metastatic lesions were obtained in 77% of the cases (47/61). These data are in agreement with the previous microsatellite detection studies that used PCR and IHC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immunotherapy-induced microsatellite instability status shift in recurrent perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A case report
Hailing Yu, Tan Deng, Hongbing Liu
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic and Predictive Value of Microsatellite Instability Analysis in Circulating Tumor DNA Using Digital Droplet PCR for Patients With Microsatellite Instability Colorectal Cancers
Camille Evrard, Tristan Rochelle, Marine Martel, Anis Al Achkar, Aurélie Ferru, Violaine Randrian, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, David Tougeron
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(8): 104176. CrossRef - HER2, HER3, and Mismatch Repair Protein Expression in Stage IV Small Bowel Adenocarcinoma: Results From a Multicenter Series
Alessandro Vanoli, Tommaso Colella, Paola Parente, Giuseppe De Lisi, Federica Grillo, Erica Quaquarini, Salvatore Corallo, Rondell Patrell Graham, Marc Ferrante, Annick Moens, Gert De Hertogh, Camilla Guerini, Roberta Riboni, Paola Alberizzi, Luca Mastrac
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(11): 100825. CrossRef - Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Current Status of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Dandan Cao, Aiping Zhou
Current Oncology.2025; 32(9): 493. CrossRef - MMR profile and microsatellite instability status in colorectal mucinous adenocarcinoma with synchronous metastasis: a new clue for the clinical practice
Paola Parente, Umberto Malapelle, Valentina Angerilli, Mariangela Balistreri, Sara Lonardi, Salvatore Pucciarelli, Caterina De Luca, Francesco Pepe, Gianluca Russo, Elena Vigliar, Angela Danza, Fabio Scaramuzzi, Giancarlo Troncone, Paolo Graziano, Matteo
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2023; 76(7): 492. CrossRef - Histomorphological and molecular genetic characterization of different intratumoral regions and matched metastatic lymph nodes of colorectal cancer with heterogenous mismatch repair protein expression
Jing Zhang, Xin Zhang, Qian Wang, Yu-yin Xu, Qian-lan Yao, Dan Huang, Wei-qi Sheng, Xiao-li Zhu, Xiao-yan Zhou, Qian-ming Bai
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(7): 3423. CrossRef - Intraindividual Tumor Heterogeneity of Mismatch Repair Status in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Qianpeng Huang, Tao Yu, Lei Li, Qi Zhang, Shiyao Zhang, Baosong Li, Xiaoping Li, Wanyi Xiao, Gang Liu
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(2): 84. CrossRef - Patterns of DNA mismatch repair protein expression for primary and recurrent colorectal cancer at an advanced surgical unit: A retrospective audit
Charles Risbey, Timothy Fielder, Daniel Steffens, Joo‐Shik Shin, Michael Solomon
Colorectal Disease.2023; 25(3): 369. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Genomic and Immunohistochemical Profiling with Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analysis of 17 Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution
Hyun-Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Biomedicines.2023; 11(8): 2269. CrossRef - Multilevel Heterogeneity of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Hao Chen, Chongya Zhai, Xian Xu, Haidong Wang, Weidong Han, Jiaying Shen
Cancers.2023; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - Heterogeneity of Mismatch Repair Status and Microsatellite Instability between Primary Tumour and Metastasis and Its Implications for Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancers
Camille Evrard, Stéphane Messina, David Sefrioui, Éric Frouin, Marie-Luce Auriault, Romain Chautard, Aziz Zaanan, Marion Jaffrelot, Christelle De La Fouchardière, Thomas Aparicio, Romain Coriat, Julie Godet, Christine Silvain, Violaine Randrian, Jean-Chri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4427. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Factors Associated with Mismatch Repair Status Among Filipino Patients with Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Dennis Lee Sacdalan, Reynaldo L Garcia, Michele H Diwa, Danielle Benedict Sacdalan
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 2105. CrossRef - Recommendations for Specimen and Therapy Selection in Colorectal Cancer
Snehal B. Patel, Robert Bookstein, Navid Farahani, Myriam Chevarie-Davis, Andy Pao, Angela Aguiluz, Christian Riley, Jennelle C. Hodge, Serhan Alkan, Zhenqui Liu, Nan Deng, Jean R. Lopategui
Oncology and Therapy.2021; 9(2): 451. CrossRef - Evaluating Mismatch Repair/Microsatellite Instability Status Using Cytology Effusion Specimens to Determine Eligibility for Immunotherapy
Elizabeth M. Jacobi, Gene Landon, Russell R. Broaddus, Sinchita Roy-Chowdhuri
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(1): 46. CrossRef - Médecine de précision et immunoradiothérapie
C. Chargari, C. Robert, C. Genestie, E. Deutsch
Cancer/Radiothérapie.2021; 25(6-7): 570. CrossRef - Identificación del fenotipo de inestabilidad microsatelital en carcinoma colorrectal mediante el análisis de la expresión de proteínas reparadoras del ADN: Revisión narrativa
Orlando Rodas-Pernillo, Edith Oregón
Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud.2021; 8(2): 232. CrossRef - Japan Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion for the diagnosis and use of immunotherapy in patients with deficient DNA mismatch repair tumors, cooperated by Japanese Society of Medical Oncology, First Edition
Saori Mishima, Hiroya Taniguchi, Kiwamu Akagi, Eishi Baba, Yutaka Fujiwara, Akira Hirasawa, Masafumi Ikeda, Osamu Maeda, Kei Muro, Hiroshi Nishihara, Hiroyki Nishiyama, Tadao Takano, Katsuya Tsuchihara, Yasushi Yatabe, Yasuhiro Kodera, Takayuki Yoshino
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2020; 25(2): 217. CrossRef - Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer With an Immunogenic Phenotype: Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
James Saller, Dahui Qin, Seth Felder, Domenico Coppola
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2020; 19(2): 123. CrossRef - Should you repeat mismatch repair testing in cases of tumour recurrence? An evaluation of repeat mismatch repair testing by the use of immunohistochemistry in recurrent tumours of the gastrointestinal and gynaecological tracts
John J Aird, Michael J Steel, Christine Chow, Julie Ho, Robert Wolber, C Blake Gilks, Lynn N Hoang, David F Schaeffer
Histopathology.2020; 76(4): 521. CrossRef - Microsatellite instability as a unique characteristic of tumors and a predictor of response to immune therapy
A. A. Tryakin, M. Yu. Fedyanin, A. S. Tsukanov, Yu. A. Shelygin, I. A. Pokataev, E. O. Ignatova, G. G. Khakimova, M. A. Frolova, S. A. Tjulandin
Malignant tumours.2020; 9(4): 59. CrossRef - Spontaneous regression of transverse colon cancer with high-frequency microsatellite instability: a case report and literature review
Nozomi Karakuchi, Manabu Shimomura, Kazuhiro Toyota, Takao Hinoi, Hideki Yamamoto, Seiji Sadamoto, Koichi Mandai, Hiroyuki Egi, Hideki Ohdan, Tadateru Takahashi
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomarker concordance between primary colorectal cancer and its metastases
D.S. Bhullar, J. Barriuso, S. Mullamitha, M.P. Saunders, S.T. O'Dwyer, O. Aziz
EBioMedicine.2019; 40: 363. CrossRef - Identification of novel pathogenic MSH2 mutation and new DNA repair genes variants: investigation of a Tunisian Lynch syndrome family with discordant twins
Amira Jaballah-Gabteni, Haifa Tounsi, Maria Kabbage, Yosr Hamdi, Sahar Elouej, Ines Ben Ayed, Mouna Medhioub, Moufida Mahmoudi, Hamza Dallali, Hamza Yaiche, Nadia Ben Jemii, Afifa Maaloul, Najla Mezghani, Sonia Abdelhak, Lamine Hamzaoui, Mousaddak Azzouz,
Journal of Translational Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mismatch repair status between primary colorectal tumor and metastatic tumor, a retrospective consistent study
Zheng Wang, Xiaoli Tang, Xiaoqing Wu, Meiyuan Yang, Daorong Wang
Bioscience Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Heterogeneity of mismatch repair defect in colorectal cancer and its implications in clinical practice
Gaelle Tachon, Eric Frouin, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Luce Auriault, Julie Godet, Valerie Moulin, Qing Wang, David Tougeron
European Journal of Cancer.2018; 95: 112. CrossRef - DNA mismatch repair in cancer
Marina Baretti, Dung T. Le
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 189: 45. CrossRef - Discordant loss of mismatch repair proteins in advanced endometrial endometrioid carcinoma compared to paired primary uterine tumors
Robert M. Ta, Jonathan L. Hecht, Douglas I. Lin
Gynecologic Oncology.2018; 151(3): 401. CrossRef - The CpG island methylator phenotype is concordant between primary colorectal carcinoma and matched distant metastases
Stacey A. Cohen, Ming Yu, Kelsey Baker, Mary Redman, Chen Wu, Tai J. Heinzerling, Ralph M. Wirtz, Elpida Charalambous, George Pentheroudakis, Vassiliki Kotoula, Konstantine T. Kalogeras, George Fountzilas, William M. Grady
Clinical Epigenetics.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Immunotherapy-induced microsatellite instability status shift in recurrent perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A case report
- Does Polymerase Chain Reaction of Tissue Specimens Aid in the Diagnosis of Tuberculosis?
- Yoo Jin Lee, Seojin Kim, Youngjin Kang, Jiyoon Jung, Eunjung Lee, Joo-Young Kim, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang-seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):451-458. Published online October 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.04
- 13,904 View
- 258 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mycobacterial culture is the gold standard test for diagnosing tuberculosis (TB), but it is time-consuming. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a highly sensitive and specific method that can reduce the time required for diagnosis. The diagnostic efficacy of PCR differs, so this study determined the actual sensitivity of TB-PCR in tissue specimens.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 574 cases. The results of the nested PCR of the IS6110 gene, mycobacterial culture, TB-specific antigen-induced interferon-γ release assay (IGRA), acid-fast bacilli (AFB) staining, and histological findings were evaluated.
Results
The positivity rates were 17.6% for PCR, 3.3% for the AFB stain, 22.2% for mycobacterial culture, and 55.4% for IGRA. PCR had a low sensitivity (51.1%) and a high specificity (86.3%) based on the culture results of other studies. The sensitivity was higher (65.5%) in cases with necrotizing granuloma but showed the highest sensitivity (66.7%) in those with necrosis only. The concordance rate between the methods indicated that PCR was the best method compared to mycobacterial culture, and the concordance rate increased for the methods using positive result for PCR or histologic features.
Conclusions
PCR of tissue specimens is a good alternative to detect tuberculosis, but it may not be as sensitive as previously suggested. Its reliability may also be influenced by some histological features. Our data showed a higher sensitivity when specimens contained necrosis, which indicated that only specimens with necrosis should be used for PCR to detect tuberculosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
The Need for Persistence in the Diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mono-arthritis: A Unique Case Presentation
T. Bekoulis, P. Christodoulou, K. Dogramatzis, E. Markopoulou, Emmanouel Antonogiannakis, E. Kokkinakis, Alexandros P. Apostolopoulos, A. Manimanaki
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants.2024; 34(1): 35. CrossRef - A Case Report on Scrofuloderma: A Cutaneous Manifestation of Tuberculosis
Soham R Meghe, Adarshlata Singh, Drishti M Bhatt, Shreya N Gupta, Varun Hanumanthaiah, Shree Ramya Talasila
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An overview of infectious disease laboratory methods: an update for the histopathologist
Daniel R. Stevenson
Diagnostic Histopathology.2024; 30(10): 534. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Biplex/Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction in Infectious Granulomatous Dermatitis in North Indian Population
Mayur Parkhi, Mukin Kumar S, Dipankar De, Rakesh Yadav, Sunil Sethi, Bishan Dass Radotra, Uma Nahar Saikia
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2021; 43(8): 567. CrossRef - Reduction of turnaround time for non-tuberculous mycobacteria detection in heater–cooler units by propidium monoazide–real-time polymerase chain reaction
S. Ditommaso, M. Giacomuzzi, G. Memoli, R. Cavallo, A. Curtoni, M. Avolio, C. Silvestre, C.M. Zotti
Journal of Hospital Infection.2020; 104(3): 365. CrossRef - Ergonomic Diagnostic Tool based on Chip Mini RT-PCR for Diagnosis of Pulmonary and Extra Pulmonary Tuberculosis
V Mangayarkarasi, Sneka P, Sujith R, Jayaprakash Jayaprakash
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2019; 13(2): 1185. CrossRef - Cutaneous Tuberculosis: Clinicopathologic Arrays and Diagnostic Challenges
Priyatam Khadka, Soniya Koirala, Januka Thapaliya
Dermatology Research and Practice.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Utility of Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction in DetectingMycobacterium tuberculosis
Zhongquan Lv, Mingxin Zhang, Hui Zhang, Xinxin Lu
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Primary Appendicular Tuberculosis
Vipul D Yagnik
Gastroenterology & Hepatology: Open Access.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
-
The Need for Persistence in the Diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mono-arthritis: A Unique Case Presentation
- Intramuscular Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor, Diffuse-Type
- Yoo Jin Lee, Youngjin Kang, Jiyoon Jung, Seojin Kim, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):306-308. Published online January 11, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.11.15
- 10,537 View
- 116 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intramuscular Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor Harboring a Novel CSF1-CD96 Fusion Transcript
Haider Mejbel, Gene P. Siegal, Shi Wei
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(3): 335. CrossRef - Diffuse-Type Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor of the Tendon Sheath in Both Wrists
Sunah Heo, Sun-Young Park, Jinwon Seo, Sung Hye Koh, In Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2021; 82(1): 250. CrossRef - Limited usefulness of classic MR findings in the diagnosis of tenosynovial giant cell tumor
Julia Crim, Samantha L Dyroff, James Derek Stensby, Andrea Evenski, Lester J Layfield
Skeletal Radiology.2021; 50(8): 1585. CrossRef - Hot shoulder PET/CT lesion: Unusual presentation of tenosynovial giant cell tumor
Steven Lewis, Lance Edmonds, Ely Wolin
Radiology Case Reports.2018; 13(3): 559. CrossRef
- Intramuscular Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor Harboring a Novel CSF1-CD96 Fusion Transcript
- Myxoid Liposarcoma with Cartilaginous Differentiation: A Case Study with Cytogenetical Analysis
- Hyunchul Kim, Won Hwangbo, Sangjeong Ahn, Suhjin Kim, Insun Kim, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):284-288. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.284
- 9,414 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Myxoid liposarcoma is a subtype of liposarcoma. This specific subtype can be identified based on its characteristic histological and cytogenetical features. The tumor has a fusion transcript of the
CHOP andTLS genes, which is caused by t(12;16)(q13;p11). Most of the fusion transcripts that have been identified fall into three categories, specifically type I (exons 7-2), type II (exons 5-2), and type III (exons 8-2). A total of seven myxoid liposarcomas associated with the rare phenomenon of cartilaginous differentiation have been documented in the literature. Currently, only one of these cases has been cytogenetically analyzed, and the analysis indicated that it was a type IITLS-CHOP fusion transcript in both the typical myxoid liposarcoma and cartilaginous areas. This study presents a second report of myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation, and includes a cytogenetical analysis of both the myxoid and cartilaginous areas.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
Naoki Kojima, Takashi Kubo, Taisuke Mori, Kaishi Satomi, Yuko Matsushita, Shintaro Iwata, Yasushi Yatabe, Koichi Ichimura, Akira Kawai, Hitoshi Ichikawa, Akihiko Yoshida
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 71. CrossRef - The Conundrum of Dedifferentiation in a Liposarcoma at a Peculiar Location: A Case Report and Literature Review
Ana-Maria Ciongariu, Adrian-Vasile Dumitru, Cătălin Cîrstoiu, Bogdan Crețu, Maria Sajin, Dana-Antonia Țăpoi, Aminia-Diana Ciobănoiu, Adrian Bejenariu, Andrei Marin, Mariana Costache
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 967. CrossRef - Myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation showing DDIT3 rearrangement
Kayo Suzuki, Taketoshi Yasuda, Kenta Watanabe, Takeshi Hori, Masahiko Kanamori, Tomoatsu Kimura
Oncology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
- Naked Cuticle Drosophila 1 Expression in Histologic Subtypes of Small Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- Sangjeong Ahn, Won Hwangbo, Hyunchul Kim, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):211-218. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.211
- 7,985 View
- 28 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Naked cuticle Drosophila 1 (NKD1) has been related to non-small cell lung cancer in that decreased NKD1 levels have been associated with both poor prognosis and increased invasive quality.
Methods Forty cases of lung adenocarcinoma staged as Tis or T1a were selected. Cases were subclassified into adenocarcinoma
in situ (AIS), minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), and small adenocarcinoma (SAD). Immunohistochemical studies for NKD1 were performed.Results Forty samples comprised five cases of AIS (12.5%), eight of MIA (20.0%), and 27 of SAD (67.5%). AIS and MIA showed no lymph node metastasis and 100% disease-free survival, whereas among 27 patients with SAD, 2 (7.4%) had lymph node metastasis, and 3 (11.1%) died from the disease. Among the 40 cases, NKD1-reduced expression was detected in 8 (20%) samples, whereas normal expression was found in 15 (37.5%) and overexpression in 17 (42.5%). Loss of NKD1 expression was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (p=0.001). All cases with predominant papillary pattern showed overexpression of NKD1 (p=0.026).
Conclusions Among MIA and SAD, MIA had better outcomes than SAD. Down-regulated NKD1 expression was closely associated with nodal metastasis, and overexpression was associated with papillary predominant adenocarcinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Challenges of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for pathologists focusing on early stage lung adenocarcinoma
Yu‐Ting Wang, Il‐Chi Chang, Chih‐Yi Chen, Jiun‐Yi Hsia, Frank Cheau‐Feng Lin, Wan‐Ru Chao, Tuan‐Ying Ke, Ya‐Ting Chen, Chih‐Jung Chen, Min‐Shu Hsieh, Shiu‐Feng Huang
Thoracic Cancer.2023; 14(6): 592. CrossRef - Clinical Significance of NKD Inhibitor of WNT Signaling Pathway 1 (NKD1) in Glioblastoma
Lijun Li, Ruiying Gao, Weizhong Huangfu, Fang Zhang, Ruixia Wang, Hongda Liu
Genetics Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Naked cuticle homolog 1 prevents mouse pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin and oxidative stress
Shanwu Wei, Lu Lin, Wen Jiang, Jie Chen, Gu Gong, Daming Sui
Aging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA‐195‐5p suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing naked cuticle homolog 1
Qiang Qu, Xiangdong Chu, Peng Wang
Cell Biology International.2017; 41(3): 287. CrossRef - Downregulation of NKD1 in human osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
Xiang Chen, Ping Xu, Jianwei Zhu, Fan Liu
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung Adenocarcinoma Staging Using the 2011 IASLC/ATS/ERS Classification: A Pooled Analysis of Adenocarcinoma In Situ and Minimally Invasive Adenocarcinoma
Madhusmita Behera, Taofeek K. Owonikoko, Anthony A. Gal, Conor E. Steuer, Sungjin Kim, Rathi N. Pillai, Fadlo R. Khuri, Suresh S. Ramalingam, Gabriel L. Sica
Clinical Lung Cancer.2016; 17(5): e57. CrossRef - The NKD1/Rac1 feedback loop regulates the invasion and migration ability of hepatocarcinoma cells
Jie Li, Sheng Zhang, Qing Hu, Kang Zhang, Jianbin Jin, Xuqing Zheng, Zhenyu Yin, Xiaomin Wang
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - NKD1 correlates with a poor prognosis and inhibits cell proliferation by inducing p53 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
Sheng Zhang, Jie Li, Xiaomin Wang
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(10): 14059. CrossRef - Expression pattern and clinicopathologic significance of NKD1 in human primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Sheng Zhang, Jie Li, Zhen‐Yu Yin, Ping‐Guo Liu, Wen‐Xiu Zhao, Cheng‐Rong Xie, Bi‐Xin Zhao, Xiao‐Min Wang
APMIS.2015; 123(4): 315. CrossRef - Early lung cancer with lepidic pattern
Wilko Weichert, Arne Warth
Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine.2014; 20(4): 309. CrossRef - Altered Expression of PTEN and Its Major Regulator MicroRNA-21 in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Hyoun Wook Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 17. CrossRef - The New 2011 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma in Resected Specimens: Clinicopathologic Relevance and Emerging Issues
Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(4): 316. CrossRef
- Challenges of the eighth edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for pathologists focusing on early stage lung adenocarcinoma
EGFR Gene Amplification and Protein Expression in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast- Won Hwangbo, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Sangjeong Ahn, Seojin Kim, Kyong Hwa Park, Chul Hwan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):107-115. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.107
- 14,043 View
- 82 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a surrogate marker for basal-like breast cancer. A recent study suggested that EGFR may be used as a target for breast cancer treatment.
Methods A total of 706 invasive ductal carcinomas (IDC) of the breast were immunophenotyped, and 82 cases with EGFR protein expression were studied for
EGFR gene amplification.Results EGFR protein was expressed in 121 of 706 IDCs (17.1%); 5.9% were of luminal type, 25.3% of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) type, and 79.3% of basal-like tumors.
EGFR gene amplification and high polysomy (fluorescentin situ hybridization [FISH]-positive) were found in 18 of 82 cases (22.0%); 41.2% of the HER-2+, EGFR+, cytokeratin 5/6- (CK5/6-) group, 11.2% of the HER-2-, EGFR+, CK5/6- group, and 19.1% of the HER-2-, EGFR+, CK5/6+ group. FISH-positive cases were detected in 8.3% of the EGFR protein 1+ expression cases, 15.9% of 2+ expression cases, and 38.5% of 3+ expression cases. In group 2, the tumors had a high Ki-67 labeling (>60%), but the patients showed better disease-free survival than those with tumors that co-expressed HER-2 or CK5/6.Conclusions EGFR-directed therapy can be considered in breast cancer patients with EGFR protein overexpression and gene amplification, and its therapeutic implication should be determined in HER-2 type breast cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An overview of phenylsulfonylfuroxan-based nitric oxide donors for cancer treatment
Chao Gao, Xingyu Li, Tong Liu, Wanning Wang, Jianhui Wu
Bioorganic Chemistry.2025; 154: 108020. CrossRef - Identification of a cross-talk between EGFR and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in HepG2 liver cancer cells
Gurjinder Singh, Md Mehedi Hossain, Aadil Qadir Bhat, Mir Owais Ayaz, Nasima Bano, Rafiqa Eachkoti, Mohd Jamal Dar
Cellular Signalling.2021; 79: 109885. CrossRef - Blocking c-MET/ERBB1 Axis Prevents Brain Metastasis in ERBB2+ Breast Cancer
Shailendra K. Gautam, Ranjana K. Kanchan, Jawed A. Siddiqui, Shailendra K. Maurya, Sanchita Rauth, Naveenkumar Perumal, Pranita Atri, Ramakanth C. Venkata, Kavita Mallya, Sameer Mirza, Moorthy P. Ponnusamy, Vimla Band, Sidharth Mahapatra, Maneesh Jain, Su
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 2838. CrossRef - Evaluation of lapatinib cytotoxicity and genotoxicity on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line
Mona A.M. Abo-Zeid, Mahmoud T. Abo-Elfadl, Amira M. Gamal-Eldeen
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2019; 71: 103207. CrossRef - Improved characterization of the relationship between long intergenic non‐coding RNA Linc00152 and the occurrence and development of malignancies
Jiasheng Xu, Jingjing Guo, Yangkai Jiang, Yujun Liu, Kaili Liao, Zhonghua Fu, Zhenfang Xiong
Cancer Medicine.2019; 8(10): 4722. CrossRef - Relationship between EGFR expression and subcellular localization with cancer development and clinical outcome
Ge Yan, Mohamed E.M. Saeed, Sebastian Foersch, Jose Schneider, Wilfried Roth, Thomas Efferth
Oncotarget.2019; 10(20): 1918. CrossRef - A novel matrine derivative WM622 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
Xiao Sun, Xiao-bin Zhuo, Yi-ping Hu, Xuan Zheng, Qing-jie Zhao
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2018; 449(1-2): 47. CrossRef - lncRNA LINC00152 knockdown had effects to suppress biological activity of lung cancer via EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway
Yan Zhang, Cheng Xiang, Yuling Wang, Yuanyuan Duan, Ci Liu, Yongli Jin, Yajing Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2017; 94: 644. CrossRef - Copy Number Profiling of MammaPrint™ Genes Reveals Association with the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Patients
Areej Fatima, Fomaz Tariq, Muhammad Faraz Arshad Malik, Muhammad Qasim, Farhan Haq
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(3): 246. CrossRef - Evaluation of serum epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in correlation to circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer
Malgorzata Banys-Paluchowski, Isabell Witzel, Sabine Riethdorf, Brigitte Rack, Wolfgang Janni, Peter A. Fasching, Erich-Franz Solomayer, Bahriye Aktas, Sabine Kasimir-Bauer, Klaus Pantel, Tanja Fehm, Volkmar Müller
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - EGFR Is Regulated by TFAP2C in Luminal Breast Cancer and Is a Target for Vandetanib
James P. De Andrade, Jung M. Park, Vivian W. Gu, George W. Woodfield, Mikhail V. Kulak, Allison W. Lorenzen, Vincent T. Wu, Sarah E. Van Dorin, Philip M. Spanheimer, Ronald J. Weigel
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2016; 15(3): 503. CrossRef - Prognostic and predictive values of EGFR overexpression and EGFR copy number alteration in HER2-positive breast cancer
H J Lee, A N Seo, E J Kim, M H Jang, Y J Kim, J H Kim, S-W Kim, H S Ryu, I A Park, S-A Im, G Gong, K H Jung, H J Kim, S Y Park
British Journal of Cancer.2015; 112(1): 103. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor protein overexpression and gene amplification are associated with aggressive biological behaviors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
GANG LIN, XIAO-JIANG SUN, QIAN-BO HAN, ZHUN WANG, YA-PING XU, JIA-LEI GU, WEI WU, GU ZHANG, JIN-LIN HU, WEN-YONG SUN, WEI-MIN MAO
Oncology Letters.2015; 10(2): 901. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Classification of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas
Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyung Han Nam, An Na Seo, Sumi Yun, Kyung Ju Kim, Hwa Jin Cho, Sung Hye Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(6): 541. CrossRef - A Comparison of Tumor Biology in Primary Ductal CarcinomaIn SituRecurring as Invasive Carcinoma versus a NewIn Situ
Wenjing Zhou, Christine Johansson, Karin Jirström, Anita Ringberg, Carl Blomqvist, Rose-Marie Amini, Marie-Louise Fjallskog, Fredrik Wärnberg
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
- An overview of phenylsulfonylfuroxan-based nitric oxide donors for cancer treatment
- Type and Incidence of Soft Tissue Sarcomas in Korea: 2001-2007.
- Kyung Un Choi, Hae Youn Kang, Heasoo Koo, Mi Seon Kwon, Dong Hoon Kim, Mi Jung Kim, Su Jin Kim, Young Sill Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Yong Koo Park, Hye Rim Park, Seung Sam Paik, Jin Young Yoo, Anhi Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hyekyung Lee, Kyu Yun Jang, Young Chae Chu, Joon Hyuk Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):557-563.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.557
- 4,710 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The Korean Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists conducted a nationwide retrospective analysis of soft tissue sarcoma (STS) to provide the clinicopathologic characteristics of STS within the population of the Republic of Korea.
METHODS
The cases of STS were collected during a 7-year period (2001-2007) from 19 institutes in Korea. All cases were classified according to the histologic criteria proposed by the World Health Organization. Clinicopathologic data were reviewed.
RESULTS
Data from 722 patients (median age, 50 years) were collected. Data showed a slight male predominance. The most frequent types of STS in decreasing order were liposarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, leiomyosarcoma, and synovial sarcoma. STS occurred throughout the body, although approximately half (47.8%) were located in the extremities. The majority of STS was histologically classified as high grade with a large tumor size (>5 cm). The overall survival rate for the patients was 76.3% (median follow-up time, 26 months; range, 1 to 89 months). Histologic grade, tumor size, American Joint Committee on Cancer stage, tumor site, and resection status were prognostic. Significant independent adverse prognostic factors were large tumor size (>5 cm) and tumor site other than extremities.
CONCLUSIONS
We reported the distribution and characteristics of STS in the Republic of Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distribution and survival of primary sarcoma in Korea: A single center analysis of 2017 cases
Sung Jun Jo, Kyeong Sik Kim, Kyo Won Lee, Jae Berm Park, Yoon-La Choi, Jeong Il Yu, Su Jin Lee, Dong Il Choi, Sung Joo Kim
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2018; 14(1): 30. CrossRef
- Distribution and survival of primary sarcoma in Korea: A single center analysis of 2017 cases
- Association of CD57+ Natural Killer Cells with Better Overall Survival in DLBCL Patients.
- Jeong Hyeon Lee, Yoon Jin Kwak, Chul Hwan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):361-370.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.361
- 3,622 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Malignant tumor cells may evoke the innate and adaptive immune systems. Various immune cells are involved in this immune reaction, and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells are associated with patient prognosis for solid tumors.
METHODS
Seventy-eight patients who were diagnosed with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) between 2001 and 2009 were selected. CD57+ NK cells, CD68+ tumor associated macrophages (TAMs), and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were evaluated in tissue sections using immunohistochemical staining and compared with clinical parameters including age, gender, performance status, clinical stage, serum lactic dehydrogenase level, number of extranodal sites, international prognostic index score, chemotherapy response, and survival.
RESULTS
Patients with high numbers of CD57+ NK cells had a significantly higher overall survival rate than patients with low numbers of CD57+ NK cells. However, no significant difference was observed between the number of CD57+ NK cells and other prognostic parameters. The number of CD68+ TAMs and CD4+ or CD8+ T cells was not significantly correlated with prognostic factors in patients with DLBCL.
CONCLUSIONS
An evaluation of tumor infiltrating CD57+ NK cells is recommended as a prognostic indicator in patients with DLBCL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The prognostic value of tumor-associated macrophages detected by immunostaining in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
Mei Lin, Shupei Ma, Lingling Sun, Zhiqiang Qin
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The prognostic value of tumor-associated macrophages detected by immunostaining in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- The Significance of MicroRNA Let-7b, miR-30c, and miR-200c Expression in Breast Cancers.
- Sung Min Chun, Hee Jung Park, Chul Hwan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):354-360.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.354
- 4,294 View
- 50 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a class of noncoding protein RNA as a promising biomarker for various diseases. In this study, the expression of let-7b, miR-30c, and miR-200c was studied in breast cancer tissues to evaluate the potential relationship with known clinicopathological parameters.
METHODS
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to determine the expression level of three miRNAs in 37 pairs of noncancerous normal and cancer tissues and an additional 38 cancer tissues from patients with invasive ductal carcinoma.
RESULTS
miR-200c expression was higher in cancer tissues compared to noncancerous normal tissues, and its ratio was correlated with patient age at surgery, type of surgery, and Ki-67 expression. The expression level of let-7b in cancer tissues was inversely correlated with lymph node metastasis, histological grade, and Ki-67 expression but positively correlated with estrogen and progesterone receptor expression. miR-200c expression level was positively correlated with Her-2 expression. The miR-30c expression level in breast cancer was not correlated with any parameters.
CONCLUSIONS
miR-200c and let-7b could be used as biomarkers in patients with breast cancer, but its pathological mechanism should be determined. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating MicroRNAs as diagnostic tools for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: Findings from a systematic review and meta-analysis
Coral González Martínez, Stavros Therapontos, Jose A. Lorente, Miriam Alcaide Lucena, F.Gabriel Ortega, M.Jose Serrano
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2025; 207: 104598. CrossRef - High DRC Levels Are Associated with Let-7b Overexpression in Women with Breast Cancer
Jarline Encarnación, Carmen Ortiz, Ralphdy Vergne, Wanda Vargas, Domenico Coppola, Jaime Matta
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(6): 865. CrossRef
- Evaluating MicroRNAs as diagnostic tools for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: Findings from a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effect of Selective Cyclooxygenase 2 Inhibitor in TCDD Pre-exposed Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma Cell Line.
- Hae Sung Kim, Kwang Sung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):1-8.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.1
- 4,184 View
- 41 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) is related to carcinogenesis and progression of cancer. COX-2 has been detected in thyroid cancer. This suggests that COX-2 inhibitor may be useful to control the growth of thyroid cancer cells as well as the progression of thyroid cancer. Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD), acting as an inflammatory cytokine, directly induces the expression of COX-2. We examine whether TCDD controls the effect of COX-2 inhibitor on thyroid cancer cells.
METHODS
The effects of TCDD and celecoxib on thyroid papillary carcinoma cell line (SNU790) were examined using cell proliferation and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Western blot analysis was performed to determine the expressed COX-2 levels and the cell cycle-related proteins. The matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) expression and gelatinolytic activity were examined using real time-polymerase chain reaction and zymography.
RESULTS
TCDD directly induced the growth of SNU790 and the expression of cyclin D1, cyclin A, cyclin E, p21 and COX-2. Celecoxib suppressed the growth of SNU790 and the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E. Celecoxib reduced the MMP-2 expression and the gelatinolytic activity, but those effects were decreased in the SNU790 by either pre-treatment with TCDD or co-treatment with TCDD and celecoxib.
CONCLUSIONS
Celocoxib effect is directly reduced depending on the exposure to TCDD. TCDD exposure should be considered in the treatment with Celecoxib. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histone H3 phosphorylation, immediate-early gene expression, and the nucleosomal response: a historical perspective1This article is part of Special Issue entitled Asilomar Chromatin and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process.
Shannon Healy, Protiti Khan, Shihua He, James R. Davie
Biochemistry and Cell Biology.2012; 90(1): 39. CrossRef
- Histone H3 phosphorylation, immediate-early gene expression, and the nucleosomal response: a historical perspective1This article is part of Special Issue entitled Asilomar Chromatin and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process.
- Hepatoid Thymic Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Jeong Hyeon Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(6):562-565.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.6.562
- 4,292 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a rare case of hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a 34-year-old man. The patient complained of a high fever and headache, and a 6.6cm-sized anterior mediastinal mass was found on chest computed tomography (CT). There was no hepatic mass seen on abdominal CT. The resected mass consisted of epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, pleomorphic vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli, and the mass was surrounded by thymic tissue. The tumor cells were immunopositive for cytokeratin 7, alpha-1-antitrypsin, hepatocyte staining, and epithelial membrane antigen, but they were negative for CD5, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and placental alkaline phosphatase, and this all led to a diagnosis of hepatoid thymic carcinoma rather than hepatoid yolk sac tumor. This entity should be included in the differential diagnosis of epithelioid thymic tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a polycythemia vera patient treated with ropeginterferon Alfa-2b: Clinical, histopathological and molecular correlates
Giuseppe G. Loscocco, Margherita Vannucchi, Raffaella Santi, Andrea Amorosi, Stefania Scarpino, Maria Chiara Siciliano, Paola Guglielmelli, Claudio Tripodo, Arianna Di Napoli, Alessandro M. Vannucchi
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155648. CrossRef
- Hepatoid thymic carcinoma in a polycythemia vera patient treated with ropeginterferon Alfa-2b: Clinical, histopathological and molecular correlates
- Metastatic Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid to Breast; A Case Initially Diagnosed as Primary Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Youngseok Lee, Jungsuk An, Chul Hwan Kim, Bom Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(6):412-415.
- 2,290 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Metastasis to the breast from medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is extremely rare. We report a case of metastatic medullary carcinoma of the thyroid which presented as multiple breast masses with ipsilateral axillary lymphadenopathy in a 48-year-old woman. Six years ago, she underwent total thyroidectomy and neck dissection because of palpable neck masses, with a diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Histological features of breast masses showed single- file or linear-cord arrangements, with plasmacytoid appearance, and the initial diagnosis was invasive lobular carcinoma. She underwent modified radical mastectomy. The tumor cells were diffusely positive for E-cadherin, calcitonin and thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) and were metastatic medullary carcinoma of thyroid. In the patients with a history of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, a careful examination is necessary for a breast mass composed of solid and cord-like clusters of small round to ovoid cells with plasmacytoid appearance. Immunohistochemical staining for E-cadherin, calcitonin and TTF-1 could be helpful for differential diagnosis.
- Primary Undifferentiated Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Small Cell and Trophoblastic Differentiation.
- Chul Hwan Kim, Seoung Hye Park, In Sun Kim, Seung Yong Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(1):58-64.
- 2,113 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This report describes a very rare case of primary undifferentiated carcinoma of the endometrium with small cell and trophoblastic differentiation. The patient was 54-year-old woman with complaints of vaginal bleeding and palpable lower abdominal mass. The light microscopic findings revealed predominantly small cells with round nuclei, spindle cells, and large cells with hyperchromatic bizarre nuclei. Foci of syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells are scattered, especially in the hemorrhagic areas. Immunohistochemical stainging for neuron specific enolase and beta-hCG showed positive reactions to small cells and syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells, respectively. Argentaffin and argyrophil stains, however, showed negative reactions to small cells. The histogenesis of small cell undifferentiated carcinoma of the endometrium remains unclear; however, it may arise from epithelial precursors instead of neuroendocrine cells, and syncytiotrophoblastic cells may be differentiated or dedifferentiated from the undifferentiated carcinoma cells.
- Expression of Cancer-Related Genes in Epstein Barr Virus-Infected Burkitt's Lymphoma Cell Line Treated with Mitomycin C.
- Woo Bom Yeom, Seol Hee Park, Min Kyung Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, In Sun Kim, Dale Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(4):271-277.
- 2,138 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Infection of Epstein Barr virus (EBV) into B cells drives the infected cells into the cell cycle and frequently results in lymphoblastoid cells. Mitomycin C inhibits DNA synthesis of epithelial cells as well as lymphoid cells by cross-linking with DNA. Many of the cancer cells have various pathways for escaping the responsiveness to the negative growth-regulatory effects of mitomycin C and gaining the immortalized property. The auther performed a cell culture of an EBV infected Jijoye lymphoma cell line, and compared the cell cycle and cancer related genes between the mitomycin treated- and non-treated group.
METHODS
DNA and RNA were extracted from the Jijoye cells; and EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA)-1, 2 and latent membrane protein (LMP) of EBV and p53 and p21 mRNA analyse was performed.
RESULTS
Mitomycin C blocked G2/M phase, however, mitomycin did not affect the expression of EBNA-1, 2 and LMP. Mitomycin C also increased the p21 mRNA expression without p53 mRNA increase.
CONCLUSIONS
Mitomycin C induces B cell apoptosis by blocking the G2/M phase and by increasing p21 mRNA independent to p53, which reveals the presence of an alternative pathway of p21 induction by mitomycin C in EBV positive lymphoma cells
- Paleopathologic Analysis of a Mummified Pregnant Woman of Papyung Yoon's Family.
- Woon Yong Jeong, Bong Kyung Shin, Chul Hwan Kim, Insun Kim, Woo Rim Kim, Kwang Sik Choe, Chang Sub Uhm, Juck Joon Hwang, Han Kyeom Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(6):394-400.
- 3,049 View
- 63 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A mummy is a dead body of a human being or an animal that has been preserved artificially or naturally from decaying. Because the natural environment of Korea isn't appropriate for mummification and Korean people haven't artificially made mummies, mummies were rarely studied in Korea.
METHODS
On September 6, 2002, a well-preserved female mummy was found in the grave of a family in Kyunggi-do. She was submitted to a thorough autopsy examination along with the review of genealogical documents.
RESULTS
The mummy died in winter. She was pregnant and the fetal head was observed at the vaginal orifice. The uterine wall was ruptured, and the peritoneum was discolored, probably by hemorrhage. Histologically, the gastric mucosa was well preserved. On the smear cytology of gastrointestinal material and the fluid from the coffin, pollens and parasitic eggs were observed. The woman seemed to be death from hypovolemic shock due to uterine rupture during the 2nd phase of labor.
CONCLUSION
From this case, we concluded the causes of the woman's mummification included the cold and dry circumstance at the time of her death, and the thick mortared wall of the grave that completely isolated the body from the outside.
- An Immunohistochemical Study of PNA (peaunt agglutinin) Binding in Transitional Cell Carcinomas of the Urinary Bladder.
- Chul Hwan Kim, Nam Hee Won, Kap No Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(3):227-235.
- 1,928 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, extensive uses of lectins as cytochemical markers have made of studies for various epithelial and nonepithelial neoplasia, however, investigations of epithelial cell surface of transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder have been few. Thus, the atuhors performed a study of PNA binding in the authors performed a study of PNA binding in transitional cell carcinomas with comparision with that in normal mucosa of the urinary bladder to allow more accurate diagnosis and histological grade or degree of differentiation. The results of this study are as follows: 1) PNA shows negative reactions on all ten normal mucosae of the urinary bladder but positive staining at the glycocalyx of umbrellar cells in two cases. 2) PNA shows negative reactions on all four cases of von Brun'n nests and cystitis cystica. 3) PNA shows positive reactions on thirty (50%) of total sixty-one cases of transitional cell carcinomas and reveals two (20%), nine (41%), eleven (55%) and eight (88%) cases in grade I, II, III and IV, respectively. 4) PNA shows positive reactions on the intracytoplasm and/or degree of PNA binding activity in grade I to IV transitional cell carcinomas is not statistically significantly different (p>0.05). In summary, PNA did not react with normal nucosa and metaplastic lesions such as von Brunn's nests and cystitis cystica, however, it reacted with 50% (30/61 cases) of transitional cell carcinoma and its positivity is significantly increased with gradings of transitional cell carcinomas (p<0.05).
- Primary Spinal Oncocytic Paraganglioma.
- Ji Hye Lee, Seong Hwan Park, Duk Hyun Cho, Bum Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim, Yeon Lim Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):561-564.
- 2,087 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Paraganglioma is a generic term applied to tumors of paraganglia, regardless of location, and composed largely of paraganglionic chief cells. It is a rare tumor, especially in the spinal region. When it appears in the craniospinal axis, it is restricted to the cauda equina or filum terminale, and less commonly, the spinal nerve root. We report a case of oncocytic paraganglioma in the spinal nerve root of 13-year-old girl. The tumor was located in intradural and extramedullary areas from the 12th thoracic to the 1st lumbar vertebra. Histologically, the tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasms show diffuse compact clusters, which are surrounded by fibers in a reticulin stain, like a nested pattern. The nuclei are round to ovoid in shape with mild atypia. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells are positive for synaptophysin, neuron-specific enolase and vimentin but are negative for cytokeratin, chromogranin and glial fibrillary acidic protein. Some cells are positive for S-100 protein. The MIB-1 labeling index is low. Ultrastructurally, dense core neurosecretory granules are not found but mitochondrias are commonly noted.
- Liposclerosing Myxofibrous Tumor in Tibia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
- Jung Woo Choi, Young Seok Lee, Ju Han Lee, Han Kyeom Kim, Bom Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Hong Chul Lim, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(3):207-210.
- 2,613 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor (LSMFT) is a benign fibro-osseous lesion that is characterized by a complex mixture of histologic elements, including its fibrous dysplasia-like features and its lipoma, myxofibroma, xanthoma and pseudo-Paget's bone patterns. However, this lesion is considered by some researchers as a variant of fibrous dysplasia or as the non-specific end result of degenerative change, while it is considered by others as a definite clinicopathologic entity. Here, we report on a case of LSMFT occurring in tibia, which is a very uncommon location for this tumor, and we review the related literatures. The case presented here shares features with those described for LSMFT, except for the location of this tumor. We believe that more studies on a larger scale that compare LSMFT with other benign bone lesions, including fibrous dysplasia, are required to clarify the origin and behavior of this lesion.
- Cytodiagnosis of Primary Small Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Hye Sun Kim, Aee Ree Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(2):167-171.
- 1,830 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Samll cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare tumor which occurs in about 0.48% of all bladder tumors. We report cytologic features of small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder in a 66-year-old man who had painless total gross hematuria, which was confirmed by partial cystectomy. In urine cytology, abundant tumor cells appeared in scattered and clustered forms in a bloody background. The tumor cells were small and uniform in size with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. The nuclei of the tumor cells were hyperchromatic, characteristically molded and showed inconspicuous nucleoli. The cytoplasms were scanty and plae blue.
- The Usefulness of Concomitant High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Test and Colposcopy in Combination with the Papanicolaou Test in ASCUS Patients.
- Min Kyung Kim, Jin Hee Sohn, Chul Hwan Kim, Jong Sang Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2005;16(1):18-24.
- 2,031 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to ascertain whether or not the high-risk human papillomavirus(HPV) test, when coupled with Papanicolaou(Pap) smears, would prove useful in the screening and management of patients in whom abnormal Pap smear results had been obtained. Concomitant high-risk HPV detection using the hybrid capture II test and colposcopy with a Pap smear were performed with 176 patients, all of whom had been screened for both cervical carcinoma and precancerous lesions. We concomitantly performed colposcopies on these patients. Upon the follow-ups, the histologic diagnoses of these patients were confirmed via either biopsy or hysterectomy. The rate of high-risk HPV detection was correlated with cytologic diagnoses and colposcopic findings. The group composed of the high-risk HPV-positive ASCUS patients exhibited a 55.7% rate of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia(CIN), a significantly higher rate than the 7.5% result obtained in the high-risk HPV- negative ASCUS group. HPV test showed high sensitivity(87%) and low specificity (62.6%) in detection of CIN and colposcopy also showed high sensitivity (88%) and low specificity(22%). Any combination of these tests improve sensitivity, but not specificity. High-risk HPV tests, when coupled with Pap smears, constituted a useful triage approach with regard to colposcopy-directed biopsies in patients in whom a cytologic diagnosis of ASCUS had been rendered.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Extranodal Marginal Zone B cell Lymphoma with Abundant Plasma Cells and Eosinophilic Histiocytes in Parotid Gland.
- Youngseok Lee, Jungsuk An, Yang Seok Chae, Bom Woo Yeom, Jong Sang Choi, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2007;18(2):165-169.
- 2,046 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors present the fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) cytologic findings of a case of extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma (MZBCL), which featured abundant plasma cells and eosinophilic histiocytes arising in both parotid glands. A 49-year-old female presented with palpable masses in both parotid glands. She had been suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. The lesions were evaluated by FNAC and smears showed a small number of clusters of oncocytic cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and small nuclei, intermixed with small to medium-sized lymphoid cells containing round to lobulated nuclei, which suggested Warthin's tumor. Some of lymphoid cells had a plasmacytoid appearance, and some scattered large cells contained a large amount of eosinophilic cytoplasm. Bilateral superficial parotidectomy was performed and a histopathologic study indicated MZBCL with abundant plasma cells, intermixed with eosinophilic histiocytes. The presence of oncocytic cells and a mixture of lymphoid and plasma cells indicates Warthin's tumor, but the cytologic features of a relatively monotonous small to medium-sized lymphoid infiltrate suggest the possibility of MZBCL in the clinical setting of an FNAC study performed on a patient suffering from a connective tissue disease.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland.
- Jeong Seok Moon, Hwa Eun Oh, Joo Han Lee, Aee Ree Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Mee Ja Park, Nam Hee Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1997;8(2):135-142.
- 2,535 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE: There is no specific treatment guidelines for Henoch-Schonlein (HS) nephritis. Therefore we performed this study to observe the effect of long term steroid therapy combined with azathioprine METHODS: Treatment protocols; 1) Steroid pulse therapy: methylprednisolon 30 mg/kg/dose, maximum 1 gm, intravenously 6 times for alternate day. 2) Oral steroid was given 2 mg/kg/day for 1 month, 1 mg/kg/day for following I month and alternate day oral steroid combined with azathioprine 2 mg/kg/day for 2 years. RESULTS: Time period from HSP to onset of HS nephritis was between 2 weeks to 5 months with mean 7.4+/-7.4 weeks. Clinical remission were seen in 4 cases out of 5 (80%). Mean time period with disappearance of proteinuria and microscopic hematuria were 5+/-2.4 month and 13.3+/-2.9 month respectively. On pathologic findings by ISKDC, 3 cases were grade IIIb, 2 cases were grade IV in first kidney biopsies and showed pathologic improvement in follow up kidney biopsies after 2 years treatment. CONCLUSION: As there no definitive treatment for HS nephritis so far, our study of long term oral steroid therapy with azathioprine was effective in clinical and histologic aspect. Therefore further study in HS nephritis with in a large group will be needed in the future.
- Pregnancy Luteoma of the Ovary in a Primiparous Woman: A case report.
- Chul Hwan Kim, Han Kyeom Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(4):417-419.
- 2,065 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pregnancy luteoma is composed of a single or multiple nodules of large lutenized cells that develop during pregnancy but involute during the puerperium. This lesion is usually an incidental finding at the time of cesarean section or postpartum tubal ligation. Microscopically, this tumor is difficult to be differentiated from various types of sex-cord stromal tumors including Leydig cell tumor, luteinized thecoma, adult or juvenile granulosa cell tumors with luteinization, and lipoid cell tumor. We report a case of pregnancy luteoma in a 34-year-old primipara without virilizing symptoms at the time of cesarean section in the right ovary. The mass measured 5x4.5x3.5 cm and 60 gm in weight. The cut surface was homogeneously yellow-orange with mulitple hemorrhagic spots. Microscopically, the tumor revealed solid, trabecular, or microcystic pattern of large granular eosinophilic luteinized cells and somewhat large nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Differentiation from Leydig cell tumor and juvenile granulosa cell tumor was difficult in this case.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



