Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification
- Hye Ju Kang, Sun Young Kwon, Ahrong Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Soo Kee Min, So Young Park, Sun Hee Sung, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Hyang Im Lee, Ho Chang Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Sun Young Jun, Min Jung Jung, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Hye Jeong Choi, So Yeon Park, Jee Yeon Kim, In Ae Park, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):380-387. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
- 7,331 View
- 226 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
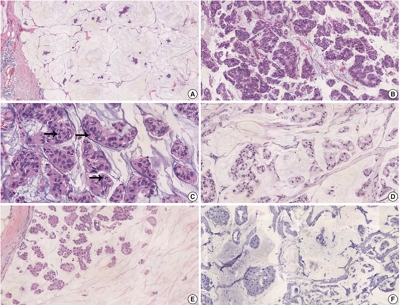
Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
Methods
Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
Results
On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
Conclusions
Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
- Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
- Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):95-102. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.24
- 10,836 View
- 293 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pure mucinous carcinoma (PMC) is a rare type of breast cancer, estimated to represent 2% of invasive breast cancer. PMC is typically positive for estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive PMC have not been investigated.
Methods
Pathology archives were searched for PMC diagnosed from January 1999 to April 2018. Clinicopathologic data and microscopic findings were reviewed and compared between HER2-positive PMC and HER2-negative PMC. We also analyzed the differences in disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival according to clinicopathologic parameters including HER2 status in overall PMC cases.
Results
There were 21 HER2-positive cases (4.8%) in 438 PMCs. The average tumor size of HER2-positive PMC was 32.21 mm (± 26.55). Lymph node metastasis was present in seven cases. Compared to HER2-negative PMC, HER2-positive PMC presented with a more advanced T category (p < .001), more frequent lymph node metastasis (p = .009), and a higher nuclear and histologic grade (p < .001). Microscopically, signet ring cells were frequently observed in HER2-positive PMC (p < .001), whereas a micropapillary pattern was more frequent in HER2-negative PMC (p = .012). HER2-positive PMC was more frequently negative for ER (33.3% vs. 1.2%) and PR (28.6% vs. 7.2%) than HER2-negative PMC and showed a high Ki-67 labeling index. During follow-up, distant metastasis and recurrence developed in three HER2-positive PMC patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that only HER2-positivity and lymph node status were significantly associated with DFS.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that HER2-positive PMC is a more aggressive subgroup of PMC. HER2 positivity should be considered for adequate management of PMC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
Sunayana Misra, Mihir Gudi, Kimberly H Allison, Edi Brogi, Cecily Quinn, Hannah Y Wen, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of a 6-years study from national cancer center in Vietnam
Thi Huyen Phung, Thanh Tung Pham, Huu Thang Nguyen, Dinh Thach Nguyen, Thanh Long Nguyen, Thi Hoai Hoang
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(3): 667. CrossRef - Poor response of HER2-positive mucinous carcinomas of breast to neoadjuvant HER2-targeted therapy: A study of four cases
Min Han, Daniel Schmolze, Javier A. Arias-Stella, Christina H. Wei, Joanne Mortimer, Fang Fan
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 74: 152396. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Mesonephric Marker Expression in Low-grade Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma
Yurimi Lee, Sangjoon Choi, Hyun-Soo Kim
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(3): 221. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of circ-FOXO3 and miR-23a in radiosensitivity of breast cancer
Elahe Abdollahi, Hossein Mozdarani, Behrooz Z. Alizadeh
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(5): 714. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Spectrum of Mucin-containing Lesions of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Review with Pathologic Correlation
Janice N. Thai, Melinda F. Lerwill, Shinn-Huey S. Chou
RadioGraphics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Metastasis of the Mucionous adenocarcinoma of breast to the mandibular gingiva: Rare case report
Ivana Mijatov, Aleksandra Fejsa Levakov, Aleksandar Spasić, Jelena Nikolić, Saša Mijatov
Medicine.2022; 101(38): e30732. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Carcinoma mucosecretor de mama HER2-positivo, un caso clínico
A.M. González Aranda, E. Martínez Gómez, A. Santana Costa, F. Arnanz Velasco, M.H. González de Diego, A. Zapico Goñi
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2021; 48(4): 100685. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of unexpectedly HER2 positive breast carcinomas: An institutional experience
Carissa LaBoy, Kalliopi P. Siziopikou, Lauren Rosen, Luis Z. Blanco, Jennifer L. Pincus
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153441. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef
- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
- The Prognostic Impact of Synchronous Ipsilateral Multiple Breast Cancer: Survival Outcomes according to the Eighth American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging and Molecular Subtype
- Jinah Chu, Hyunsik Bae, Youjeong Seo, Soo Youn Cho, Seok-Hyung Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):396-403. Published online October 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.03
- 8,289 View
- 102 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the current American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system of breast cancer, only tumor size determines T-category regardless of whether the tumor is single or multiple. This study evaluated if tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and can be used to subclassify breast cancer.
Methods
We included 5,758 patients with invasive breast cancer who underwent surgery at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, from 1995 to 2012.
Results
Patients were divided into two groups according to multiplicity (single, n = 4,744; multiple, n = 1,014). Statistically significant differences in lymph node involvement and lymphatic invasion were found between the two groups (p < .001). Patients with multiple masses tended to have luminal A molecular subtype (p < .001). On Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, patients with multiple masses had significantly poorer disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .016). The prognostic significance of multiplicity was seen in patients with anatomic staging group I and prognostic staging group IA (p = .019 and p = .032, respectively). When targeting patients with T1-2 N0 M0, hormone receptor–positive, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative cancer, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis also revealed significantly reduced DFS with multiple cancer (p = .031). The multivariate analysis indicated that multiplicity was independently correlated with worse DFS (hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.03 to 1.47; p = .025). The results of this study indicate that tumor multiplicity is frequently found in luminal A subtype, is associated with frequent lymph node metastasis, and is correlated with worse DFS.
Conclusions
Tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and could be used to subclassify invasive breast cancer at early stages. Adjuvant chemotherapy would be necessary for multiple masses of T1–2 N0 M0, hormone-receptor-positive, and HER2-negative cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
Neyaz Ahmad, Khushboo Rani, Zenith Kerketta, Krishna Murari, Anish Baxla, Ujala Murmu, Amit Nishant, Shreya .
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Large Format Histology in Diagnosis of Breast Carcinoma
Hari Shankar Pandey, Sanya Bhasin, Suman Kumari Pandey
NMO Journal.2025; 19(2): 189. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Multiple Synchronous T1 Breast Cancer
Hongki Gwak, Sung Hoo Jung, Young Jin Suh, Seok Jin Nam, Jai Hong Han, Se Jeong Oh, Eun Hwa Park, Seong Hwan Kim
Cancers.2024; 16(23): 4019. CrossRef - Deep learning-based system for automatic prediction of triple-negative breast cancer from ultrasound images
Alexandre Boulenger, Yanwen Luo, Chenhui Zhang, Chenyang Zhao, Yuanjing Gao, Mengsu Xiao, Qingli Zhu, Jie Tang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2023; 61(2): 567. CrossRef - Multicentre prospective cohort study of unmet supportive care needs among patients with breast cancer throughout their cancer treatment trajectory in Penang: a PenBCNeeds Study protocol
Noorsuzana Mohd Shariff, Nizuwan Azman, Rohayu Hami, Noor Mastura Mohd Mujar, Mohammad Farris Iman Leong Bin Abdullah
BMJ Open.2021; 11(3): e044746. CrossRef - The subgross morphology of breast carcinomas: a single-institution series of 2033 consecutive cases documented in large-format histology slides
Tibor Tot, Maria Gere, Syster Hofmeyer, Annette Bauer, Ulrika Pellas
Virchows Archiv.2020; 476(3): 373. CrossRef - Editorial for “Synchronous Breast Cancer: Phenotypic Similarities on MRI”
Uma Sharma
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2020; 52(1): 309. CrossRef - Synchronous Multiple Breast Cancers—Do We Need to Reshape Staging?
Minodora Onisâi, Adrian Dumitru, Iuliana Iordan, Cătălin Aliuș, Oana Teodor, Adrian Alexandru, Daniela Gheorghiță, Iulian Antoniac, Adriana Nica, Alexandra-Ana Mihăilescu, Sebastian Grădinaru
Medicina.2020; 56(5): 230. CrossRef - Molecular mechanism of triple‑negative breast cancer‑associated BRCA1 and the identification of signaling pathways
Feng Qi, Wen‑Xing Qin, Yuan‑Sheng Zang
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
- TFE3-Expressing Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Breast
- Hyunjin Kim, Jimin Kim, Se Kyung Lee, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):62-65. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.30
- 9,436 View
- 157 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) is a very rare mesenchymal tumor with a distinctive morphology and immunophenotype. PEComas usually harbor TSC2 alterations, although TFE3 translocations, which occur in MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma, are also possible. We recently experienced a case of PEComa with TFE3 expression arising in the breast. An 18-year-old female patient presented with a right breast mass. Histologically, the tumor consisted of epithelioid cells with alveolar structure and showed a diffuse strong expression of HMB45 and TFE3. TSC2 was preserved. Melan A and smooth muscle actin were negative. To our knowledge, this is the first Korean case of PEComa of the breast that intriguingly presented with TFE3 expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
Anuradha Sharma, Reetika Sharma, Jyoti Bala, Monika Sharma
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(1): 107. CrossRef - Malignant lung PEComa (clear cell tumor): rare case report and literature review
Marcos Adriano Garcia Campos, Lucas Fernandes Vasques, Rafael Goulart de Medeiros, Érico Murilo Monteiro Cutrim, Ana Júlia Favarin, Sarah Rebecca Machado Silva, Gyl Eanes Barros Silva, Marcelo Padovani de Toledo Moraes, Mariana Lopes Zanatta, Diego Aparec
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cathepsin K: A Versatile Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Various Cancers
Die Qian, Lisha He, Qing Zhang, Wenqing Li, Dandan Tang, Chunjie Wu, Fei Yang, Ke Li, Hong Zhang
Current Oncology.2022; 29(8): 5963. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef - Invasive Lobular Carcinoma With Extensive Clear Cells: A Pitfall in Diagnosis
Mark H. Kavesh, Daniel Sanchez, Jaya Ruth Asirvatham
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2020; 28(2): 169. CrossRef - Glycogen-rich Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review
Semir Vranic, Faruk Skenderi, Vanesa Beslagic, Zoran Gatalica
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2020; 28(9): 655. CrossRef - TFE3-expressing primary perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the Lymph node mimicking nodal relapse of rectal cancer
Jongmin Park, An Na Seo
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2019; 59(C): 46. CrossRef
- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
- Secretory Carcinoma Arising in a Fibroadenoma: A Brief Case Report
- Sharon Lim, Min Keun Shim, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):198-201. Published online October 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.01
- 7,447 View
- 118 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Breast Carcinoma within Fibroadenoma: A Systematic Review
Abdulwahid M. Salih, Lana R.A. Pshtiwan, Mohammed Gh. Hamasaeed, Sami S. Omar, Shaban Latif, Shadi H. Sidiq, Bushra O. Hussein, Hunar A. Hassan, Diyar A. Omar, Sarhang S. Abdalla, Hemn A. Hassan, Yousif M. Mahmood, Marwan N. Hassan, Dahat A.
Barw Medical Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Breast Carcinoma within Fibroadenoma: A Systematic Review
- Evaluation of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Experience in a Single Institution over a 10-Year Period
- Misun Choi, Yeon Hee Park, Jin Seok Ahn, Young-Hyuck Im, Seok Jin Nam, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):69-78. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.05
- 12,996 View
- 269 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has been associated with favorable clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. However, the possibility that the prognostic significance of pCR differs among various definitions has not been established. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated the pathologic response after NAC in 353 breast cancer patients and compared the prognoses after applying the following different definitions of pCR: ypT0/is, ypT0, ypT0/is ypN0, and ypT0 ypN0. Results: pCR was significantly associated with improved distant disease-free survival (DDFS) regardless of the definition (ypT0/is, p = .002; ypT0, p = .008; ypT0/is ypN0, p < .001; ypT0 ypN0, p = .003). Presence of tumor deposits of any size in the lymph nodes (LNs; ypN ≥ 0(i+)) was associated with worse DDFS (ypT0 ypN0 vs ypT0 ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .036 and ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .015), and presence of isolated tumor cells was associated with decreased overall survival (OS; ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN0(i+), p = .013). Residual ductal carcinoma in situ regardless of LN status showed no significant difference in DDFS or OS (DDFS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .373 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .462; OS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .441 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .758). In subsequent analysis using ypT0/is ypN0, pCR was associated with improved DDFS and OS in triple-negative tumors (p < .001 and p = .003, respectively). Conclusions: Based on our study results, the prognosis and rate of pCR differ according to the definition of pCR and ypT0/is ypN0 might be considered a more preferable definition of pCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
Christine Hong Ngoc Che Thai, Selena J. An, Conner R. Haase, Julia M. Selfridge, Chris B. Agala, Philip M. Spanheimer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(2): 315. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Study on Response Rate and Toxicity
Matt Galloway, Paula Barlow, Jody Jordan, Edward Lo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(20): 7362. CrossRef - Association of residual ductal carcinoma in situ with breast cancer treatment outcomes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to hormone receptor status
Eunju Shin, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Jisun Kim, Il Yong Chung, Beom Seok Ko, Hee Jeong Kim, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son, Sae Byul Lee
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mammographic Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection in Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Ga Eun Park, Bong Joo Kang, Sung Hun Kim, Han Song Mun
Life.2024; 14(11): 1449. CrossRef - Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment – How to assess residual disease
Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
The Breast.2022; 62: S25. CrossRef - Pathological examination of breast cancer samples before and after neoadjuvant therapy: recommendations from the Italian Group for the Study of Breast Pathology - Italian Society of Pathology (GIPaM-SIAPeC)
Nicola Fusco, Antonio Rizzo, Leopoldo Costarelli, Alfredo Santinelli, Bruna Cerbelli, Cristian Scatena, Ettore Macrì, Francesca Pietribiasi, Giulia d’Amati, Anna Sapino, Isabella Castellano
Pathologica.2022; 114(2): 104. CrossRef - Pathological complete response as a surrogate to improved survival in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Ferdia Browne, Nicola Miller, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neoadjuvant therapy with doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by weekly paclitaxel in early breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of 200 consecutive patients treated in a single center with a median follow-up of 9.5 years
Lisi M. Dredze, Michael Friger, Samuel Ariad, Michael Koretz, Bertha Delgado, Ruthy Shaco-Levy, Margarita Tokar, Michael Bayme, Ravit Agassi, Maia Rosenthal, Victor Dyomin, Olga Belochitski, Shai Libson, Tamar Mizrahi, David B. Geffen
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 193(3): 597. CrossRef - “No Ink on Tumor” in Breast-Conserving Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Giulia Atzori, Marco Gipponi, Chiara Cornacchia, Raquel Diaz, Marco Sparavigna, Maurizio Gallo, Tommaso Ruelle, Federica Murelli, Simonetta Franchelli, Francesca Depaoli, Daniele Friedman, Piero Fregatti
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1031. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models and Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Carmen Herrero Vicent, Xavier Tudela, Paula Moreno Ruiz, Víctor Pedralva, Ana Jiménez Pastor, Daniel Ahicart, Silvia Rubio Novella, Isabel Meneu, Ángela Montes Albuixech, Miguel Ángel Santamaria, María Fonfria, Almudena Fuster-Matanzo, Santiago Olmos Antó
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3508. CrossRef - Applying artificial intelligence technology to assist with breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction
Meredith A. Jones, Warid Islam, Rozwat Faiz, Xuxin Chen, Bin Zheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemotherapy response score as a prognostic tool in patients with advanced stage endometrial carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ina Jani, Ricardo R Lastra, Katherine S Brito, Chuanhong Liao, Isabel Lazo, Nita Karnik Lee, S Diane Yamada, Katherine C Kurnit
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2021; 31(6): 852. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with anlotinib in occult breast cancer: A case report and review of literature
Yu Zhang, Di Wu, Bo Zhao, Xue-Liang Tian, Tian-Cheng Yao, Feng Li, Wei-Fang Liu, Ai-Ping Shi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(4): 919. CrossRef - Pathologic Complete Response and Its Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Patient’s Survival after Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Hui Liu, Liqiong Lv, Hui Gao, Ming Cheng, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Impact of Surgical Margins in Breast Cancer After Preoperative Systemic Chemotherapy on Local Recurrence and Survival
K. Wimmer, M. Bolliger, Z. Bago-Horvath, G. Steger, D. Kauer-Dorner, R. Helfgott, C. Gruber, F. Moinfar, M. Mittlböck, F. Fitzal
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2020; 27(5): 1700. CrossRef - Predictive factors for omitting lymphadenectomy in patients with node‐positive breast cancer treated with neo‐adjuvant systemic therapy
Sergi Fernandez‐Gonzalez, Catalina Falo, Maria J. Pla, Paula Verdaguer, Diana Nuñez, Anna Guma, Teresa Soler, Andrea Vethencourt, Silvia Vázquez, Maria Eulalia Fernandez‐Montoli, Miriam Campos, Sonia Pernas, Miguel Gil, Jordi Ponce, Amparo Garcia‐Tejedor
The Breast Journal.2020; 26(5): 888. CrossRef - Is There a Role for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy for T1-2N1 Breast Cancers With Node-Positive Pathology After Patients Become Node-Negative Pathology Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?
Qian Wang, Jingjing Zhao, Xiaowei Han, Puchun Er, Xiangying Meng, Jinyan Shi, Huiru Sun, Jingyang Zhu, Li Zhu, Shikai Wu, Wencheng Zhang, Bing Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic role of microRNA 182 and microRNA 18a in locally advanced triple negative breast cancer
Rajat Bajaj, Rupal Tripathi, T. S. Sridhar, Aruna Korlimarla, Kumardeep Dutta Choudhury, Moushumi Suryavanshi, Anurag Mehta, Dinesh Chandra Doval, Elda Tagliabue
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242190. CrossRef - Association of Pathologic Complete Response with Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Min Huang, Joyce O'Shaughnessy, Jing Zhao, Amin Haiderali, Javier Cortés, Scott D. Ramsey, Andrew Briggs, Peter Hu, Vassiliki Karantza, Gursel Aktan, Cynthia Z. Qi, Chenyang Gu, Jipan Xie, Muhan Yuan, John Cook, Michael Untch, Peter Schmid, Peter A. Fasch
Cancer Research.2020; 80(24): 5427. CrossRef - Multiparametric MR imaging to assess response following neoadjuvant systemic treatment in various breast cancer subtypes: Comparison between different definitions of pathologic complete response
G Santamaría, X Bargalló, S Ganau, I Alonso, M Muñoz, M Mollà, PL Fernández, A Prat
European Journal of Radiology.2019; 117: 132. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of residual nodal burden using lymph node ratio in locally advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Reshu Agarwal, Arun Philip, Keechilat Pavithran, Anupama Rajanbabu, Gaurav Goel, DK Vijaykumar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2019; 56(3): 228. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in occult breast cancer
Haisong Yang, Ling Li, Mengmeng Zhang, Shiyong Zhang, Shu Xu, Xiaoxia Ma
Medicine.2017; 96(40): e8200. CrossRef - Wnt7a Deficiency Could Predict Worse Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Kijong Yi, Kyueng-Whan Min, Young Chan Wi, Yeseul Kim, Su-Jin Shin, Min Sung Chung, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(4): 361. CrossRef
- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
- Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor: A Case Study and Literature Review
- Yuil Kim, Ha Young Park, Junhun Cho, Joungho Han, Eun Yoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):172-176. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.172
- 9,600 View
- 61 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor (CPMT) is a benign pulmonary spindle cell neoplasm of intrauterine and perinatal period, which is thought to arise from primitive peribronchial mesenchyme. We present a case detected incidentally in a one-month-old infant. The solid and partially necrotic tumor involved the right middle and lower lobes of the lung with extension to the diaphragm. Histologically, the tumor was composed of fasciculated monotonous spindle cells, proliferating peribronchiolar cartilage and round cells with rich vasculature, and high mitotic activity was identified in the round cell area. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies showed that the spindle cells were myofibroblastic in phenotype. Although the tumor showed several malignant pathological features, recurrence was not observed in the two-year follow-up period, consistent with the benign clinical behavior of CPMT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor: Clinical Features, Pathology, and Surgical Considerations
Kavya Rajesh, Drew Bolster, Mariam Naqvi, Sonya Fabricant, Raghavendra Pillappa, Andrew Brownlee, Carlos Pelayo, Eugene Kim, David Bliss, Eveline Shue
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumors Harbor a Recurrent EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication
Sheren Younes, Carlos J. Suarez, Jennifer Pogoriler, Tricia Bhatti, Archana Shenoy, Raya Saab, Lea F. Surrey, Serena Y. Tan
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(2): 100661. CrossRef - EGFR‐KDD Myofibroblastic Neoplasm or Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor (CPMT)? Report of a Congenital Myofibroblastic Neoplasm With Unusual Histologic Features
Emma Rullo, Sabina Barresi, Sabrina Rossi, Sara Patrizi, Evelina Miele, Marta Barisella, Michela Casanova, Andrea Ferrari, Stefano Chiaravalli, Gloria Pelizzo, Rita Alaggio
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor (CPMT): a case report with long term follow-up and next-generation sequencing (NGS)
Ping Zhou, Shuang Li, Weiya Wang, Yuan Tang, Lili Jiang
BMC Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neonatal congenital lung tumors — the importance of mid-second-trimester ultrasound as a diagnostic clue
Stephan L. Waelti, Laurent Garel, Dorothée Dal Soglio, Françoise Rypens, Michael Messerli, Josée Dubois
Pediatric Radiology.2017; 47(13): 1766. CrossRef - Congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor: Case report and review of literature
Jolanta Jedrzkiewicz, Eric Scaife, Bo Hong, Sarah South, Mouied Alashari
Journal of Pediatric Surgery Case Reports.2015; 3(4): 154. CrossRef - Perinatal Thoracic Mass Lesions: Pre- and Postnatal Imaging
Evan J. Zucker, Monica Epelman, Beverley Newman
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2015; 36(6): 501. CrossRef - Prenatal imaging and immunohistochemical analysis of congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor
Y.‐A. Tu, W.‐C. Lin, H.‐J. Chen, J.‐C. Shih
Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology.2015; 46(2): 247. CrossRef - A Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor Detected in a Premature Infant at 28 Weeks but That Resolved in the Late Stage of Pregnancy
Bo Xia, Gang Yu, Chun Hong, Lei Zhang, Jing Tang, Cuifen Liu
Medicine.2015; 94(42): e1842. CrossRef - Congenital peribronchial myofibroblastic tumor
Yuka Hotokebuchi, Kenichi Kohashi, Satoshi Toyoshima, Naoko Matsumoto, Toshinori Nakashima, Yoshinao Oda
Pathology International.2014; 64(4): 189. CrossRef
- Congenital Peribronchial Myofibroblastic Tumor: Clinical Features, Pathology, and Surgical Considerations
- Methylation and Immunoexpression of
p16INK4a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Primary Breast Cancer Tissue and Their Quantitativep16INK4a Hypermethylation in Plasma by Real-Time PCR - Jae Jun Lee, Eunkyung Ko, Junhun Cho, Ha Young Park, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Jin Nam, Duk-Hwan Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):554-561. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.554
- 9,728 View
- 56 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The
p16INK4a gene methylation has been reported to be a major tumorigenic mechanism.Methods We evaluated the methylation status of the
p16INK4a genes in 231 invasive breast cancer and 90 intraductal carcinoma specimens using a methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and p16 protein expression using immunohistochemistry. The quantity of cell-free methylatedp16INK4a DNA in the plasma samples of 200 patients with invasive breast cancer was also examined using a fluorescence-based real-time polymerase chain reaction assay.Results The frequencies of
p16INK4a methylation in invasive and intraductal tumors were 52.8% (122/231) and 57.8% (52/90), respectively. The p16 protein was overexpressed in 145 of the 231 invasive carcinomas (62.8%) and 63 of the 90 intraductal carcinomas (70%). High p16 expression in invasive carcinomas correlated significantly with a high histologic grade, a negative estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status, p53 immunoreactivity and high Ki-67 expression with immunohistochemistry. In addition, the methylation index ofp16INK4a was significantly higher in the cancer patients than the normal controls (p<0.001).Conclusions High p16 immunoreactivity correlated with a loss of differentiation in breast carcinomas and high frequency of
p16INK4a promoter methylation in both invasive and intraductal carcinomas, suggesting it may be involved in the pathogenesis of breast cancer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s
Hua Yang, Yu Fang, Haijuan Wang, Ting Lu, Qihua Chen, Hui Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epigenetic Silencing of p16INK4a gene in Sporadic Breast Cancer
Satya P. Singh, Mallika Tewari, Alok K. Singh, Raghvendra R. Mishra, Hari S. Shukla
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2023; 14(4): 822. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Chia-Jung Li, Yen-Dun Tony Tzeng, Yi-Han Chiu, Hung-Yu Lin, Ming-Feng Hou, Pei-Yi Chu
Cancers.2021; 13(12): 2978. CrossRef - Mechanisms of resistance to estrogen receptor modulators in ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancer
Jin Zhang, Qianying Wang, Qing Wang, Jiangran Cao, Jiafu Sun, Zhengmao Zhu
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2020; 77(4): 559. CrossRef - Aberrantly Methylated cfDNA in Body Fluids as a Promising Diagnostic Tool for Early Detection of Breast Cancer
Igor Stastny, Pavol Zubor, Karol Kajo, Peter Kubatka, Olga Golubnitschaja, Zuzana Dankova
Clinical Breast Cancer.2020; 20(6): e711. CrossRef - Epigenetic modulation of BRCA‐1 and MGMT genes, and histones H4 and H3 are associated with breast tumors
Parisa Paydar, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Hamid Zeynali Nejad, Hamed Akbari, Moslem Abolhassani, Vahid Moazed, Mohammad Hadi Nematollahi, Ghasem Ebrahimi, Hossein Fallah
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(8): 13726. CrossRef - The 9p21 locus: A potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker in breast cancer
Mahdi Rivandi, Mohammad‐Sadegh Khorrami, Hamid Fiuji, Soodabeh Shahidsales, Malihe Hasanzadeh, Mir Hadi Jazayeri, Seyed Mahdi Hassanian, Gordon A. Ferns, Nafiseh Saghafi, Amir Avan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(7): 5170. CrossRef - p16INK4a overexpression as a predictor of survival in ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Sheetal Chauhan, Seema Sen, Anjana Sharma, Seema Kashyap, Radhika Tandon, Mandeep S Bajaj, Neelam Pushker, Murugesan Vanathi, Shyam S Chauhan
British Journal of Ophthalmology.2018; 102(6): 840. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer
Ju-Han Lee, Hoiseon Jeong, Jung-Woo Choi, Hwa Eun Oh, Young-Sik Kim
Medicine.2018; 97(42): e12862. CrossRef - EZH2 inhibition sensitizes tamoxifen‑resistant breast cancer cells through cell cycle regulation
Si Chen, Fan Yao, Qinghuan Xiao, Qiannan Liu, Yikun Yang, Xuejuan Li, Guanglie Jiang, Takayoshi Kuno, Yue Fang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Aberrant promoter methylation of cancer-related genes in human breast cancer
Liang Wu, Ye Shen, Xianzhen Peng, Simin Zhang, Ming Wang, Guisheng Xu, Xianzhi Zheng, Jianming Wang, Cheng Lu
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(6): 5145. CrossRef - Centrosome aberrations in human mammary epithelial cells driven by cooperative interactions between p16INK4a deficiency and telomere-dependent genotoxic stress
Daniel Domínguez, Purificación Feijoo, Aina Bernal, Amaia Ercilla, Neus Agell, Anna Genescà, Laura Tusell
Oncotarget.2015; 6(29): 28238. CrossRef - Relationships Betweenp16Gene Promoter Methylation and Clinicopathologic Features of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 27 Cohort Studies
Yan-Zhi Chen, Dan Liu, Yu-Xia Zhao, He-Tong Wang, Ya Gao, Ying Chen
DNA and Cell Biology.2014; 33(10): 729. CrossRef - Endocrine disruption of the epigenome: a breast cancer link
Kevin C Knower, Sarah Q To, Yuet-Kin Leung, Shuk-Mei Ho, Colin D Clyne
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2014; 21(2): T33. CrossRef - Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p16 and p27, demonstrate different expression patterns in thymoma and thymic carcinoma
Mutsuko Omatsu, Toshiaki Kunimura, Tetsuya Mikogami, Akira Shiokawa, Atsuko Masunaga, Tomoko Nagai, Akihiko Kitami, Takashi Suzuki, Mitsutaka Kadokura
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2014; 62(11): 678. CrossRef - Limoniastrum guyonianum aqueous gall extract induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells involving p16INK4A re-expression related to UHRF1 and DNMT1 down-regulation
Mounira Krifa, Mahmoud Alhosin, Christian D Muller, Jean-Pierre Gies, Leila Chekir-Ghedira, Kamel Ghedira, Yves Mély, Christian Bronner, Marc Mousli
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating tumor-related DNA in cancer patients
Diego M Marzese, Hajime Hirose, Dave S B Hoon
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2013; 13(8): 827. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and trichostatin A synergistically inhibit human lymphoma cell proliferation through epigenetic modification of p16INK4a
DAN-SEN WU, JIAN-ZHEN SHEN, AI-FANG YU, HAI-YING FU, HUA-RONG ZHOU, SONG-FEI SHEN
Oncology Reports.2013; 30(6): 2969. CrossRef
- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s
- Comparative Study of Metaplastic Breast Carcinoma and Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma Using Histologic and Immunohistochemical Analyses.
- Ji Yeon Kim, Taeeun Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(6):605-612.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.6.605
- 4,317 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare subtype of breast cancer, which is characterized by estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor and HER2 negativity.
METHODS
Tissue specimens from 60 metaplastic breast cancer and 60 triple-negative breast cancer patients diagnosed at a single institution between 1995 and 2009 were analyzed. Immunohistochemistry for caveolin-1 (CAV-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), c-kit, p53, Ki-67, breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1), cytokeratin (CK)14, and CK17 were performed on both retained tissue sets.
RESULTS
Of the 60 metaplastic carcinomas, 15 tumors (25%) exhibited spindle cell component, 27 (45%) exhibited chondroid differentiation, and 18 (30%) exhibited squamous areas. Compared to triple-negative carcinomas, metaplastic carcinomas significantly more frequently expressed CK14 (p < 0.0001), CK17 (p = 0.002), EGFR (p < 0.0001), CAV-1 (p < 0.0001), and VEGF (p = 0.029). However, expressions of BRCA1, p53, c-kit, and Ki-67 were not significantly different between both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The expression profile of metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is more homogeneous than that of other triple-negative tumors and frequently over-expresses basal markers, CAV-1, and VEGF. A typical "basal-like" phenotype and frequent expressions of CAV-1 and VEGF may justify specific therapeutic approaches. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast with Squamous Differentiation: A Case Report from the University Teaching Hospital of Kigali (CHUK), Rwanda
Delphine Uwamariya, Carine Nyampinga, Anne Yvette Nsenguwera, Belson Rugwizangoga, Piero Tosi
Case Reports in Pathology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef
- Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast with Squamous Differentiation: A Case Report from the University Teaching Hospital of Kigali (CHUK), Rwanda
- Comparison of Liqui-PREP(TM) and Conventional Preparations in Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration.
- Eun Su Park, Eun Yoon Cho, In Gu Do, Soon Jae Kim, Jung Hee Shin, Boo Kyung Han, Young Lyun Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(6):550-556.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.6.550
- 5,470 View
- 28 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Liqui-PREP(TM) (LP) is a new liquid-based cytologic preparation that produces a thin layer of cells.
METHODS
Thyroid aspirates were obtained from 189 patients and divided to prepare pairs of conventional preparation (CP) and LP slides. The CP slides were routinely diagnosed by attending staffs and classified into the six categories. LP slides were independently evaluated by three cytopathologists and classified in an identical manner. Agreements between CP and LP diagnoses were investigated and interobserver variability of thyroid aspiration cytology results obtained using the LP method was determined using kappa values. RESULTS: CP and LP slides from 155 patients (83%) were identically classified by all of three cytopathologists. Concurrences between CP and LP diagnoses for the three cytopathologists were 89% (kappa=0.78), 92% (kappa=0.87), and 85% (kappa=0.70), respectively. Interobserver agreement among the three cytopathologists for LP slides ranged from substantial to almost perfect (kappa=0.84, 0.74 and 0.84). However, a lack of interobserver agreement was found for LP slides of the undetermined category as determined by original CP-based diagnoses. Moreover, cytomorphological alterations in the benign category appeared more worrisome for LP slides.
CONCLUSIONS
An awareness of the novel cytomorphologic changes induced by the LP method is needed to avoid misinterpretations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liquid base cytology in evaluation of thyroid nodules
Elahe Keyhani, Sasan A Sharghi, Rana Amini, Sina A Sharghi, Masoud Karimlou, Fatemeh A Moghaddam, Bagher Larijani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic value of liquid‐based (Liqui‐PREP) preparations and interobserver reproducibility in fine needle aspiration cytology of the nodular thyroid lesions
U. S. Tetikkurt, F. Oz Puyan, F. Oz, N. Erdogan, S. Ceylan, A. Yakupoglu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2012; 40(5): 388. CrossRef - Application of Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Aspiration Cytology
Kyungji Lee, Chan-Kwon Jung, Kyo-Young Lee, Ja-Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So-Lyung Jung
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2010; 44(5): 521. CrossRef
- Liquid base cytology in evaluation of thyroid nodules
- Expression of pS2/TFF1 Protein in Normal Colonic Mucosa, Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma.
- Seoung Wan Chae, Eun Yoon Cho, Eo Jin Kim, Jin Hee Sohn, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(5):324-329.
- 2,143 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The trefoil factor 1 protein (pS2/TFF1) is a candidate tumor-suppressor protein, and it is a pleiotropic factor involved in the organization and homeostasis of the gastrointestinal tract and various inflammatory or neoplastic diseases. The purpose of this study was to assess the expression of pS2/TFF1 and its clinicopathologic relationship, including the p53 and Ki-67 labeling index, in colorectal carcinogenesis.
METHODS
The expression of pS2/TFF1 protein was evaluated immunohistochemically in 45 samples of normal colonic mucosa, 43 samples of adenoma and 186 samples of colorectal carcinoma.
RESULTS
pS2/TFF1 protein was expressed weakly in 37.8% of normal colonic mucosa samples, and it had a weak to strong expression in 48.8% of adenomas and 28% of colorectal adenocarcinomas. pS2/TFF1 expression in carcinoma was slightly increased in the poorly differentiated group compared with the well to moderately differentiated group (p=0.059). Interestingly, mucinous carcinoma (4/4) and signet ring cell carcinoma (2/3) showed significant increase of pS2/TFF1 expression. pS2/TFF1 expression was inversely correlated with the p53 protein expression and the Ki-67 labelling index (p<0.05). There was no significant correlation with the tumor size, metastasis or pathologic staging.
CONCLUSIONS
Overexpression of pS2/TFF1 expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma was inversely correlated with the Ki-67 labelling index and the p53 expression in cancer. These results suggest that pS2/TFF1 protein may contribute as tumor suppressor factor in colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Diagnostic Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Clonality Analysis for Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene and T-cell Receptor Gamma Chain Gene Rearrangement in Lymphoid Neoplasms.
- Eun Yoon Cho, Young Hyeh Ko, Dae Shick Kim, Jae Joon Han, Howe J Ree
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):461-469.
- 2,046 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The clonality of lymphoid infiltrates determined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) or T cell receptor (TCR) genes is not only useful in confirming the diagnosis of malignant lymphoma but also in establishing the lineage of a clonal lymphoid proliferation. We analyzed the efficiency of PCR analyses for IgH and TCRgenes that have been routinely applied for the diagnosis of malignant lymphoma in our laboratory.
METHODS
Paraffin sections of 200 cases were analyzed by seminested PCR. Primers were FRIIIA-LJH/VLJH consensus primer for IgH gene and V-J consensus primer for TCR gene. The cases showing negative results by PCR for TCR gene were further analyzed by multiplex V family primers with heteroduplex analysis.
RESULTS
PCR approach for IgH gene allowed detection of clonality in 100% of cases with false positive rate of 0.3% and false negative rate of 0%. The combination of PCR for TCR consensus primers with multiplex V family primers allowed detection of clonality in 91% of cases with false positive rate of 0.6% and false negative rate of 10.3%.
CONCLUSIONS
Combined analysis of IgH and TCR gene rearragnements by the PCR technique followed by heteroduplex analysis can be a useful diagnostic adjunct to determine the clonality of various lymphoproliferative diseases with high sensitivity. But clinical, morphological and immunophenotypical correlation should be considered to reach the final diagnosis due to a few false positive cases.
- Primary Nodal Marginal Zone B-cell Lymphoma: Clincopathologic Analysis of Splenic and Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Type.
- Jae Joon Han, Young Hyeh Ko, Eun Yoon Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Nam Hun Kim, Howe J Ree
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):470-476.
- 2,148 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Primary nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MZBL) is recently divided into mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) type and splenic type. Herein, we analyzed clinicopathologic differences of those two types of nodal MZBL.
METHODS
Histologic and clinical findings of eleven cases of primary nodal MZBL lymphoma were reviewed. Immunohistochemical stains for IgD, Ki-67, CD3, and CD20 were performed.
RESULTS
The cases were classified as splenic type in four, MALT type in five, and unclassified in two. The age at presentation was 36.7 years old (range: 16-73) in splenic type and 48 years old (range: 31-68) in MALT type. Two patients with splenic type and one with MALT type had a long history of lymphadenopathy up to 9 years. Whereas tumors of splenic type showed nodular infiltration of tumor cells with follicular colonization and hyperplastic germinal center, tumors of MALT type showed mainly sinusoidal or parafollicular infiltration and atrophic germinal centers. All the patients with splenic type were alive at last follow-up and one patient with MALT type died of disease at 5 months after diagnosis.
CONCLUSIONS
Although the number of cases we analyzed was small, splenic type seems to be distinct from MALT type and lower grade neoplasm.
- Diagnostic Correlation and Accuracy Between Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Histopathologic Examination.
- Jin Hee Sohn, Seoung Wan Chae, Eun Yoon Cho, Eo Jin Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2003;14(2):53-59.
- 2,311 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has been known as a very sensitive and effective method for preoperative diagnosis. We studied cases preoperatively diagnosed by FNAC and confirmed by the histopathologic examination to define the effectiveness of FNAC. A total of 567 cases including breast, thyroid gland, lymph node, and soft tissue confirmed histologically after FNAC were enrolled, among 2,844 FNAC cases from January 1996 to March 2000. Overall sensitivity and specificity of FNAC were 93% and 100%, respectively. Sensitivity and specificity of FNAC by sites or organs were 91% and 100% in breast, 100% and 100% in thyroid, 97% and 100% in lymph node, and 71% and 100% in soft tissue, respectively. Nine cases showed diagnostic discrepancy; eight cases of sampling error and one case of interpretation error. Five cases, diagnosed as fibrocystic change at FNAC but invasive ductal carcinoma after the histopathologic examination, were categorized as sampling error due to the presence of diffuse fibrosis or deep seated location. One case of breast, diagnosed descriptively as atypical ductal and stromal cells suggesting invasive ductal carcinoma at FNAC but malignant phyllodes tumor histologically, was categorized as interpretation error. Other cases of sampling errors were two cases of soft tissue, a case of lymph node, and a case of salivary gland.
- Expression of Actin-bundling Protein Fascin and its Relationship with Altered E-cadherin and beta-catenin Expressions in Ovarian Serous Neoplasms.
- Eun Yoon Cho, YoonLa Choi, Seoung Wan Chae, Eo Jin Kim, Kyehyun Kim, Geung Hwan Ahn, Jin Hee Sohn
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(4):258-264.
- 2,228 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
: Fascin, an actin-bundling protein, has been found in specialized normal cells, including the neuronal, endothelial and dendritic cells, and its expression is known to be greatly increased in various human neoplasms. Methods : Immunohistochemical stainings for fascin, betacatenin, and E-cadherin were performed in normal ovary tissue (n=13), and in benign (n=14), borderline (n=32), and malignant (n=74) ovarian serous neoplasms. We evaluated the fascin expression, and its relationship with the betacatenin and E-cadherin expressions, as well as the clinicopathologic factors. Results : Fascin expression was detected in the majority of the borderline (100%, 32/32) and malignant tumors (90.5%, 67/74), but it was not seen in the normal ovarian surface epithelial cells and the benign tumors (p<0.001). Fascin expression was significantly correlated with the occurrence of peritoneal metastases in the carcinomas (p=0.043). A significant relationship between the expressions of fascin and betacatenin (p=0.046), as well as E-cadherin (p=0.035) was noted. There was no significant correlation with the tumor grade of carcinoma, the FIGO stage, tumor recurrence, tumor-related death and the survival rate. Conclusions : In ovarian serous neoplasms, the fascin expression may be closely linked with tumor progression and metastasis, and it was associated with the up-regulation of betacatenin and E-cadherin.
- Usefulness of Sputum Cytology as a Diagnostic Tool of Lung Cancer.
- Eun Yoon Cho, Hee Dae Park, Sun Hee Kim, Woon Sun Park, Seoung Wan Chae, Eo Jin Kim, Jin Hee Sohn
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2004;15(2):75-80.
- 3,368 View
- 63 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To analyze the accuracy and usefulness of sputum cytology as a screening method, 103 cases of histologically proven lung cancer registered from 1998 to 2000 at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital were retrospectively examined. We reviewed the original cytologic and surgical diagnoses for the cases, and the cytology slides of all cytologically negative cases. The overall sensitivity of sputum cytology was 0.83 ; the sensitivity of prebronchoscopy sputum cytology for bronchogenic carcinoma was 0.87. Central tumor location (P=0.002), tumor size (>2.4 cm), (P=0.027) and the number of sputum samples (> or =3) (P=0.001) were associated with a positive cytologic diagnosis. Of the 18 cytologically negative cases, 9 cases (38% of smears) were determined to be insufficient for diagnosis, due strictly to low cellularity and saliva. After a review of the cytology slides of cytologically negative cases, we identified several atypical clusters in one case of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. This negativity was thus attributed to an interpretation error (1/18, 5.6%). Our results suggest that its sensitivity is more strongly related to the specimen adequacy and the times of sampling than to interpretation error. In terms of sensitivity, specificity, accessibility, cost, and morbidity associated with the screening tests, sputum cytology was found to be an accurate effective screening method for lung cancer.
- The Loss of Expression of Caveolin-1 in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors.
- Eo Jin Kim, Jin Hee Sohn, Min Kyung Kim, Seoung Wan Chae, Hye Seung Lee, Eun Yoon Cho, Woo Ho Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(5):338-344.
- 2,391 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The down-regulation of caveolin-1, a putative tumor suppressor gene, has been demonstrated in several types of sarcomas. However, it's not known whether or not the gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) express caveolin-1. We carried out this study to investigate the caveolin-1 expression in GISTs and to determine the correlation between the clinicopathologic profiles of GISTs and the expression of caveolin-1.
METHODS
One hundred eight cases of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues of GISTs were immunohistochemically evaluated for the expression of caveolin-1 by using the tissue-array method. Survival data of 98 cases of primary GISTs was analysed according to the expression status of caveolin-1.
RESULTS
Ninety three cases (86.1%) of 108 GISTs did not express caveolin-1 protein. There was no correlation between the caveolin-1 expression status and any of the clinicopathologic variables, including mitosis (p=0.948) and tumor grade (p=0.334). The expression of caveolin-1 was not correlated with other immunohistochemical marker proteins including, c-kit (p=0.373), CD34 (p=0.437) and SMA (p=0.831). On the univariate analysis, the caveolin-1 expression status (p=0.635) was not a significant predictor of the disease-free survival for GIST patients.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of this study suggest that caveolin-1 might act as a tumor suppressor gene in the GIST oncogenesis, but it has no function as a prognostic marker for disease free survival.
- Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Cytokeratin 7 Expression: A Case Report.
- Mi Jung Kim, Eun Yoon Cho, Mi Sun Choe, Eun Sil Yu
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(5):344-347.
- 2,276 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) is a rare variant of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A 26-year-old female presented a hepatic mass and mild elevation of liver enzymes. Viral markers were negative, and levels of tumor markers were normal. Radiologically, the mass was well demarcated with central dot-like calcification and hypervascularity. Under the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma, right lobectomy was performed. The tumor was grayish yellow with central fibrosis and focal hemorrhage and invaded a septal bile duct. Non-neoplastic liver was unremarkable. Microscopically, the tumor consisted of large polygonal cells in sheets, cords, and pseudoglands that were interwound by dense collagenous stroma. Tumor cells had abundant deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm and large nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Intracellular bile pigments and pale bodies were present. Tumor cells were diffusely immunostained for cytokeratin 7 (CK7), but not for cytokeratin 20 (CK20). Strong expression of CK7 in the present case suggests dual differentiation of FLC.
- Analysis of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Ultrasonography of Metastatic Tumors to the Thyroid.
- Eun Yoon Cho, Young Lyun Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2007;18(2):133-142.
- 2,003 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cytologic diagnosis of the metastatic tumors to the thyroid is important in the management of the patients. There have been rare reports analyzing fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology of metastatic tumors to the thyroid. This study examines comprehensive cytologic findings of metastatic tumors to the thyroid with radiologic findings. The FNA cytology slides obtained from 12 cases with metastatic tumors of the thyroid; lung cancer (n=5), tongue and tonsil cancer (n=3), esophageal cancer (n=2), and breast cancer (n=2) were reviewed. Radiological study showed single mass with heterogeneous texture or multiple masses without calcification. Metastatic tumor was easily considered in a differential diagnosis of FNA cytology because they had peculiar cytological features which were not seen in primary thyroid tumor. The smear background varied from predominantly necrotic, bloody, and inflammatory to colloid. The aspirates exhibited a mixture of benign follicular cells and malignant cells in 6 cases. The characteristic cytoplasmic features of the tumor cells, such as keratin, mucin and melanin, were found in 9 cases. Although some cases mimic primary thyroid neoplasm, a careful examination of the cytological characteristics may help cytopathologists to recognize a metastatic tumor in the thyroid by FNA, and may help the clinicians to establish a proper treatment plan.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



