Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A single-institution demographic study of pathologically proven kidney disease in South Korea over the last 33 years
- Hyejin Noh, Jiyeon Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):306-319. Published online September 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.18
- 1,661 View
- 84 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
To date, epidemiological studies on the entire spectrum of kidney disease based on pathology have been rarely reported. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on patients diagnosed with kidney disease at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital between 1991 and 2023. Results: Among 7,803 patients with native kidney disease, glomerular disease (70.3%) was the most common, followed by tubulointerstitial (15.1%) and vascular disease (8.8%). In kidney biopsy, glomerular disease (77.8%) showed the highest frequency, particularly in those under 20s (95.6%) (p = .013). Primary glomerulonephritis (GN) (72.8%) was the predominant glomerular disease, with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) (47.3%) being the most common one. Tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased with age, showing the highest prevalence in those over 60 years (p = .008 and p = .032, respectively). Glomerular disease was diagnosed at a younger age (39.7 ± 16.7 years) than tubulointerstitial (49.1 ± 16.2) and vascular (48.1 ± 15.3) diseases (p < .001). When glomerular diseases were classified morphologically, proliferative GN (57.9%) was the most common, followed by non-proliferative (39.6%) and sclerosing (1.6%). When classified by etiology, primary GN accounted for the most (72.8%), followed by secondary (19.3%) and hereditary GN (5.7%). In nephrectomy, tubulointerstitial disease (64.6%) was the most common. Those with a tubulointerstitial disease had a higher mean age than those with a glomerular disease (p < .001). In cases where nephrectomy was performed for glomerular diseases, IgAN (34.1%) was the most common diagnosis. Conclusions: Kidney disease has been increasing in South Korea for 33 years. Glomerular disease was the most common across all age groups, tubulointerstitial and vascular diseases increased over 60 years.
- EWSR1 rearranged primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma: a diagnostic conundrum
- Nilay Nishith, Zachariah Chowdhury
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):284-288. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.08.08
- 4,153 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma is an exceedingly rare neoplasm with an aggressive phenotype and Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) rearrangement in a small fraction of cases. In addition to its rarity, the diagnosis can be challenging for the pathologist due to morphologic heterogeneity, particularly on the biopsy specimen. At times, immunohistochemistry may be indecisive; therefore, molecular studies should be undertaken for clinching the diagnosis. We aim to illustrate a case of primary myoepithelial carcinoma of the kidney with EWSR1-rearrangement in a 67-year-old male patient who presented with right supraclavicular mass, which was clinically diagnosed as carcinoma of an unknown primary. An elaborate immunohistochemical work-up aided by fluorescent in-situ hybridization allowed us to reach a conclusive diagnosis. This unusual case report advocates that one should be aware of the histological mimickers and begin with broad differential diagnoses alongside sporadic ones and then narrow them down with appropriate ancillary studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney
João Lobo, Huiying He, Raheel Ahmed, Bassel Zein-Sabatto, Thomas Winokur, Shi Wei, Shuko Harada, Jesse K. McKenney, Jonathan L. Myles, Jane K. Nguyen, Christopher G. Przybycin, Sean R. Williamson, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Reza Alaghehbandan
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 49(10): 1078. CrossRef
- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney
- Post-mortem assessment of vimentin expression as a biomarker for renal tubular regeneration following acute kidney injury
- Juan Carlos Alvarez Moreno, Hisham F. Bahmad, Christopher A. Febres-Aldana, Andrés Pirela, Andres Azuero, Ali Salami, Robert Poppiti
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):369-379. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.03
- 7,072 View
- 150 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality. It mainly targets the renal tubular epithelium with pathological changes, referred to as acute tubular injury. The latter is followed by a regenerative response that is difficult to visualize on routine hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains. In this study, we examined the regenerative capacity of renal tubules by correlating vimentin (VIM) immunohistochemical (IHC) expression and pathological findings of AKI and renal tubular regeneration (RTR) on H&E.
Methods
We reviewed 23 autopsies performed in the clinical setting of AKI and RTR. VIM expression was scored in the renal cortical tubular epithelium using a statistical cutoff ≥ 3% for high expression and < 3% for low expression.
Results
Of the 23 kidney tissues examined, seven (30.4%) had low VIM expression, and 16 (69.6%) had high VIM expression. Kidney tissues with evidence of AKI and RTR had significantly higher VIM expression. Renal peritubular microenvironment features showing regenerative changes on H&E were associated with high VIM expression. In the univariate model, kidney tissues with RTR were 18-fold more likely to have high VIM expression.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings suggest that VIM could serve as an IHC marker for RTR following AKI. However, correlation with H&E findings remains critical to excluding chronic tubular damage. Collectively, our preliminary results pave the way for future studies including a larger sample size to validate the use of VIM as a reliable biomarker for RTR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myocardial Infarction Injury Is Exacerbated by Nicotine in Vape Aerosol Exposure
Clarissa Savko, Carolina Esquer, Claudia Molinaro, Sophie Rokaw, Abraham G. Shain, Faid Jaafar, Morgan K. Wright, Joy A. Phillips, Tyler Hopkins, Sama Mikhail, Abigail Rieder, Ariana Mardani, Barbara Bailey, Mark A. Sussman
Journal of the American Heart Association.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatio-temporal transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct nephrotoxicity, DNA damage, and regeneration response after cisplatin
Lukas S. Wijaya, Steven J. Kunnen, Panuwat Trairatphisan, Ciarán P. Fisher, Meredith E. Crosby, Kai Schaefer, Karen Bodié, Erin E. Vaughan, Laura Breidenbach, Thomas Reich, Diana Clausznitzer, Sylvestre Bonnet, Sipeng Zheng, Chantal Pont, James L. Stevens
Cell Biology and Toxicology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization of macrophages in ischemia–reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury based on single-cell RNA-Seq and bulk RNA-Seq analysis
Qin Wang, Yuxing Liu, Yan Zhang, Siyuan Zhang, Meifang Zhao, Zhangzhe Peng, Hui Xu, Hao Huang
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 130: 111754. CrossRef - Renal tubular necrosis associated with anagrelide administration: a case report
Atsushi Sawase, Mineaki Kitamura, Misato Morimoto, Haruka Fukuda, Tadashi Uramatsu, Eisuke Katafuchi, Hiroshi Yamashita, Toshiyuki Nakayama, Hiroshi Mukae, Tomoya Nishino
CEN Case Reports.2024; 13(6): 510. CrossRef - Morin attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by regulating inflammatory responses, oxidative stress and tubular regeneration (morin and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury)
Aya M. Shehata, Nagui H. Fares, Basma H. Amin, Asmaa A. Mahmoud, Yomna I. Mahmoud
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2024; 111: 104543. CrossRef
- Myocardial Infarction Injury Is Exacerbated by Nicotine in Vape Aerosol Exposure
- Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the kidney in an adult with loss of INI1 expression and mutation in the SMARCB1 gene
- Eunkyung Han, Jiyoon Kim, Min Jung Jung, Susie Chin, Sang Wook Lee, Ahrim Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):145-153. Published online March 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.01.26
- 5,923 View
- 112 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 57-year-old man with left flank pain was referred to our institute. Computed tomography scans revealed two enhancing masses in the left kidney. The clinical diagnosis was renal cell carcinoma (RCC). He underwent a radical nephrectomy with an adrenalectomy. Two well-circumscribed solid masses in the hilum and the lower pole (4.5 × 3.5 cm and 7.0 × 4.1 cm) were present. Poorly cohesive uniform round to polygonal epithelioid cells making solid sheets accounted for most of the tumor area. The initial diagnosis was RCC, undifferentiated with rhabdoid features. As the tumor showed loss of INI1 expression and a mutation in the SMARCB1 gene on chromosome 22, the revised diagnosis was a malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT) of the kidney. To date, only a few cases of renal MRT in adults have been reported. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of MRT in the native kidney of an adult demonstrating a SMARCB1 gene mutation, a hallmark of MRT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cancer epigenetic therapy: recent advances, challenges, and emerging opportunities
Rajita Vatapalli, Alex P. Rossi, Ho Man Chan, Jingwen Zhang
Epigenomics.2025; 17(1): 59. CrossRef - Navigating the complexity of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (ATRT) in pediatric neuro-oncology: Insights from clinical spectrum to therapeutic challenges
Ali Msheik, Mohamad Yazbeck, Abdulla Illeyan, Youssef Comair
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2025; 131: 111354. CrossRef - French recommendations on multi-gene panel testing in renal cell carcinoma
Sophie Giraud, Pascaline Berthet, Caroline Abadie, Nadine Andrieu, Patrick R. Benusiglio, Valérie Bonadona, Olivier Caron, Carole Corsini, Isabelle Coupier, Louise Crivelli, Capucine Delnatte, Pierre Devulder, Antoine DE Pauw, Sophie Dussart, Anne-Paule G
European Journal of Medical Genetics.2025; 78: 105062. CrossRef - Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the kidney in a 27-Year-Old adult: a rare case with favorable outcomes following surgery and adjuvant radiotherapy
Dimitri Paillusson, Stéphane De Vergie, Jérome Rigaud, Gaëlle Le Quellennec, Stéphane Supiot
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Supratentorial ATRT in a young Infant: Expanding the diagnostic spectrum beyond medulloblastoma
Ali Msheik, Mohamad Aoun, Youssef Fares
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2024; 35: 101857. CrossRef - Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
Adebowale J. Adeniran, Brian Shuch, Peter A. Humphrey
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(7): e65. CrossRef - Malignant rhabdoid tumor of kidney in an adult patient with positive family history of rhabdoid tumor: A case report and review of literature
Farhood Khaleghi mehr, Nasrollah Abian, Mandana Rahimi, Yasaman Moradi
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2023; 113: 109053. CrossRef
- Cancer epigenetic therapy: recent advances, challenges, and emerging opportunities
- Renal intravascular large B cell lymphoma: the first case report in Korea and a review of the literature
- Moonsik Kim, Haerim Chung, Woo Ick Yang, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):426-431. Published online August 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.18
- 6,198 View
- 121 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Herein, we describe the first case of renal intravascular large B cell lymphoma in Korea occurring in a 66-year-old female. She presented with mild fever and dyspnea. On physical and laboratory evaluations, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis was suspected, but the bone marrow biopsy results were unremarkable. During the work-up, massive proteinuria developed, which led to a renal biopsy. The renal architecture was relatively well-preserved, but the glomeruli were hypercellular with the infiltration of atypical, large lymphoid cells with increased nucleus-cytoplasm ratio and clumped chromatin. Similar cells were also present in the peritubular capillaries. The tumor cells exhibited membranous staining for CD20 and CD79a. After the diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma, the patient received rituximab-based chemotherapy under close follow-up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system with renal involvement: a case report and literature review
Jun Li, Zhaojiao Li, Yifeng Shi, Jiajie Chen, Heng Zhao, Xueye Mao, Shan Li, Huiying Wang, Qiang Meng, Lingchun Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - EBV-Positive Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the Small Intestine: A Case Report and Literature Review
Chenglong Pan, Xiaoling Ma, Yanfei Yao, Chunyan Wang
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(3): 586. CrossRef - Intravascular large B‐cell lymphoma in renal cell carcinoma incidentally detected by robot‐assisted partial nephrectomy
Michio Noda, Yutaka Enomoto, Yukari Shirasugi, Sumiyo Ando, Yukimasa Matsuzawa, Haruki Kume
IJU Case Reports.2022; 5(3): 191. CrossRef - Case Report: Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of Four Cases With Review of Additional 331 Cases in the Literature
Yingying Han, Qingjiao Li, Dan Wang, Lushan Peng, Tao Huang, Chunlin Ou, Keda Yang, Junpu Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renal Involvement of CD20-Negative Intravascular Large B Cell Lymphoma with Neurological Manifestations
Faten Aqeel, Serena M. Bagnasco, Duvuru Geetha, Yoshihide Fujigaki
Case Reports in Nephrology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system with renal involvement: a case report and literature review
- Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Intratumoral Granulomatous Reaction: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hayeon Kim, Jong Wook Kim, Aeree Kim, Hyeyoon Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):325-328. Published online March 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.08
- 9,696 View
- 122 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Granulomatous reaction associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is a rare finding, and only a few cases have been described in the literature. It is postulated to occur due to cancer- related antigenic factors such as cancer cells themselves or soluble tumor antigens shed into the blood. Herein, we describe a case of a 56-year-old male patient diagnosed with CCRCC with intratumoral granulomatous inflammation.
- Aberrant Blood Vessel Formation Connecting the Glomerular Capillary Tuft and the Interstitium Is a Characteristic Feature of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis-like IgA Nephropathy
- Beom Jin Lim, Min Ju Kim, Soon Won Hong, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):211-216. Published online April 11, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.01
- 9,818 View
- 75 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Segmental glomerulosclerosis without significant mesangial or endocapillary proliferation is rarely seen in IgA nephropathy (IgAN), which simulates idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). We recently recognized aberrant blood vessels running through the adhesion sites of sclerosed tufts and Bowman’s capsule in IgAN cases with mild glomerular histologic change.
Methods
To characterize aberrant blood vessels in relation to segmental sclerosis, we retrospectively reviewed the clinical and histologic features of 51 cases of FSGS-like IgAN and compared them with 51 age and gender-matched idiopathic FSGS cases.
Results
In FSGS-like IgAN, aberrant blood vessel formation was observed in 15.7% of cases, 1.0% of the total glomeruli, and 7.3% of the segmentally sclerosed glomeruli, significantly more frequently than in the idiopathic FSGS cases (p = .009). Aberrant blood vessels occasionally accompanied mild cellular proliferation surrounding penetrating neovessels. Clinically, all FSGS-like IgAN cases had hematuria; however, nephrotic range proteinuria was significantly less frequent than idiopathic FSGS.
Conclusions
Aberrant blood vessels in IgAN are related to glomerular capillary injury and may indicate abnormal repair processes in IgAN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Twin Glomeruli: a Newly Discovered Marker of Neonephrogenesis in the Ischemia–Reperfusion Injured Adult Mouse Kidney
Hanguk Hwang, Dongju Woo, You Ri Park, Min Jung Kong, Heedong Lee, Kwon Moo Park, Yong Seok Nam, Je-Yong Choi, Sungwook Nam, Eon Jung Nam, Sun-Hee Park, Hongtae Kim, Sang Yeon Lee, Soo Ho Lee, Jeong Ok Lim, Mae Ja Park
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - IgA nephropathy
Maria F. Soares, Ian S.D. Roberts
Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension.2017; 26(3): 165. CrossRef
- Twin Glomeruli: a Newly Discovered Marker of Neonephrogenesis in the Ischemia–Reperfusion Injured Adult Mouse Kidney
- Silent Colonic Malakoplakia in a Living-Donor Kidney Transplant Recipient Diagnosed during Annual Medical Examination
- Go Eun Bae, Nara Yoon, Ha Young Park, Sang Yun Ha, Junhun Cho, Yunkyung Lee, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Cheol Keun Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):163-166. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.163
- 8,246 View
- 61 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Malakoplakia is a characteristic inflammatory condition, which is usually seen in the urogenital tract, and less frequently in the gastrointestinal tract. We present a case of colonic malakoplakia in an immunocompromised patient. A 55-year-old female visited the outpatient clinic for routine cancer surveillance. Her past medical history was significant for kidney transplantation 11 years ago, and she had been taking immunosuppressants. A colonoscopy revealed several depressed flat lesions and elevated polyps, which were 0.3 to 0.4 cm in size and accompanied by whitish exudates. A biopsy revealed an infiltration of histiocytes with ample granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, with some lymphocytes and plasma cells. Many histiocytes had the characteristic morphology, described as Michaelis-Gutmann bodies: one or several round basophilic structures of approximately 1 to 10 µm in size with some being laminated, some appearing homogeneous, and others having a dense central core with a targetoid appearance. These Michaelis-Gutmann bodies were positively stained on von Kossa stain, and were diagnostic for malakoplakia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Malakoplakia in kidney transplant recipients: Three case reports
Prathap Kumar Simhadri, Renish Contractor, Deepak Chandramohan, Matthew McGee, Udit Nangia, Mohammad Atari, Syed Bushra, Sanjana Kapoor, Ramya Krishna Velagapudi, Pradeep K Vaitla
World Journal of Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Caecal malakoplakia: a rare mimic of malignancy
Jeffrey Li Voon Chong, Noor Ali
BMJ Case Reports.2024; 17(1): e257130. CrossRef - A Surgical Challenge Generated by Colonic Malakoplakia in Disguise as a Locally Advanced Colonic Malignancy—A Case Report
Cristina Șerban, Alexandra Toma, Dragoș Cristian Voicu, Constantin Popazu, Dorel Firescu, George Țocu, Raul Mihailov, Laura Rebegea
Medicina.2023; 59(1): 156. CrossRef - Colonic malakoplakia in a cardiac transplant recipient: A case report
Sadiya Shafijan
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2020; 63(2): 322. CrossRef - Immunosuppressive drugs and the gastrointestinal tract in renal transplant patients
Merel M. Tielemans, Gerben A.J. van Boekel, Teun van Gelder, Eric T. Tjwa, Luuk B. Hilbrands
Transplantation Reviews.2019; 33(2): 55. CrossRef - Malakoplakia of the colon following renal transplantation in a 73 year old woman: report of a case presenting as intestinal perforation
Andrew Mitchell, Alexandre Dugas
Diagnostic Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Colonic malakoplakia in a liver transplant recipient: A case report
Rana Ajabnoor, Mohammad Mawardi, Abdulmonem Almutawa
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2019; 18: 200323. CrossRef - Malakoplakia after kidney transplantation: Case report and literature review
John Fredy Nieto‐Ríos, Isabel Ramírez, Mónica Zuluaga‐Quintero, Lina María Serna‐Higuita, Federico Gaviria‐Gil, Alejandro Velez‐Hoyos
Transplant Infectious Disease.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Megalocytic Interstitial Nephritis Following Acute Pyelonephritis with Escherichia coli Bacteremia: A Case Report
Hee Jin Kwon, Kwai Han Yoo, In Young Kim, Seulkee Lee, Hye Ryoun Jang, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(1): 110. CrossRef
- Malakoplakia in kidney transplant recipients: Three case reports
- Castleman's Disease of the Renal Sinus Presenting as a Urothelial Malignancy: A Brief Case Report
- Se Min Jang, Hulin Han, Ki-Seok Jang, Young Jin Jun, Tchun Yong Lee, Seung Sam Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):503-506. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.503
- 8,510 View
- 48 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Castleman's disease is a rare benign lymphoproliferative disorder that frequently affects lymph nodes of the mediastinal thorax and the neck. It very rarely affects the renal sinus. We report a case of Castleman's disease arising in the renal sinus in a 64-year-old man. The patient visited the hospital with the chief complaint of hematuria. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a homogeneous mass in the sinus of the left kidney, radiologically interpreted as a malignant urothelial tumor. Subsequently, nephroureterectomy was performed, after which microscopic examination of the specimen revealed a diffuse lymphoproliferative lesion with reactive lymphoid follicles of various sizes and prominent plasma cell infiltration of interfollicular spaces, highlighted by immunohistochemical staining for CD138. The lesion was diagnosed as Castleman's disease of the plasma cell type. Although preoperative diagnosis of Castleman's disease is difficult and the incidence is exceedingly rare, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of renal sinus tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Misdiagnosis of renal pelvic unicentric Castleman disease: a case report
Dian Fu, Bo Yang, Ming Yang, Zhenyu Xu, Wen Cheng, Zhijia Liu, Liming Zhang, Zhiguo Mao, Cheng Xue
Frontiers in Surgery.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Castleman’s disease involving the renal sinus resembling renal cell carcinoma
Enlong Zhang, Yuan Li, Ning Lang
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiologic features of Castleman’s disease involving the renal sinus: A case report and review of the literature
Xiao-Wan Guo, Xu-Dong Jia, Shan-Shan Shen, Hong Ji, Ying-Min Chen, Qian Du, Shu-Qian Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2019; 7(8): 1001. CrossRef - Castleman’s Disease: a Suprarenal Surprise!
Praveen Sundar, Priyank Bijalwan, Ginil Kumar Pooleri
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2018; 9(2): 254. CrossRef
- Misdiagnosis of renal pelvic unicentric Castleman disease: a case report
- Pigmented Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa) of the Kidney: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hyeyoon Chang, Wonkyung Jung, Youngran Kang, Woon Yong Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):499-502. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.499
- 10,109 View
- 74 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Heavily pigmented perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComa) are rare, only eight cases of which have been reported. Unlike typical epithelioid angiomyolipoma, most of these tumors have been encountered in female patients without tuberous sclerosis. The long-term prognosis thereof is undetermined. Cytological similarity and heavy melanin pigment make it difficult for pigmented PEComa to be differentiated from pigmented clear cell renal cell carcinoma or malignant melanoma. The immunoprofile of tumor cells, such as human melanoma black-45 expression, as well as the absence or presence of other melanocytic or epithelial markers, are helpful in determining a differential diagnosis. Here we report a case of heavily pigmented PEComa of the right kidney and review the literature describing this tumor. In this case, the immunoprofile and clinical features corresponded well to those described in the literature. Since the prognosis of such disease has not yet been established, close follow-up of this patient was recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pigmented Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
Quinn Rainer, Li Lei, Yue Sun
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor de células epitelioides perivasculares (PEComa) primário do rim: uma revisão sistemática
Eric Lima Freitas Mota, Mariana Macambira Noronha, Letícia Pinheiro Amorim, João Luiz Lima Pinheiro, Eduarda Severo Alvarenga, Paulo Eduardo de Oliveira, Fabrícia Cardoso Marques, Emmanuel Apollo de Macedo Ferreira
Cuadernos de Educación y Desarrollo.2024; 16(12 Edição ): e6498. CrossRef - Malignant Pigmented Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of the Kidney in a Child with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Thu Dang Anh Phan, Nhi Thuy To, Diem Thi Nhu Pham
Fetal and Pediatric Pathology.2023; 42(2): 285. CrossRef - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the cystic duct
Takeshi Okamoto, Takashi Sasaki, Yu Takahashi, Manabu Takamatsu, Hiroaki Kanda, Makiko Hiratsuka, Masato Matsuyama, Masato Ozaka, Naoki Sasahira
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 16(1): 87. CrossRef - PEComa of the Adrenal Gland
Craig B. Wakefield, Peter M. Sadow, Jason L. Hornick, Christopher D.M. Fletcher, Justine A. Barletta, William J. Anderson
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 47(11): 1316. CrossRef - Recurrence of Pigmented Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of the Kidney With Xp11 Translocation: A Case Report
Mahmoud D Srour, Andrew Harris
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pigmented perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) arising from kidney
Hexi Du, Jun Zhou, Lingfan Xu, Cheng Yang, Li Zhang, Chaozhao Liang
Medicine.2016; 95(44): e5248. CrossRef - PEComas of the kidney and of the genitourinary tract
Guido Martignoni, Maurizio Pea, Claudia Zampini, Matteo Brunelli, Diego Segala, Giuseppe Zamboni, Franco Bonetti
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(2): 140. CrossRef - Pigmented Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Skin
Pooja Navale, Masoud Asgari, Sheng Chen
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2015; 37(11): 866. CrossRef - Clear Cell Melanoma: A Cutaneous Clear Cell Malignancy
Maria A. Pletneva, Aleodor Andea, Nallasivam Palanisamy, Bryan L. Betz, Shannon Carskadon, Min Wang, Rajiv M. Patel, Douglas R. Fullen, Paul W. Harms
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2014; 138(10): 1328. CrossRef - Extrapulmonary Lymphangioleiomyoma: Clinicopathological Analysis of 4 Cases
Dae Hyun Song, In Ho Choi, Sang Yun Ha, Kang Min Han, Jae Jun Lee, Min Eui Hong, Yoon-La Choi, Kee-Taek Jang, Sang Yong Song, Chin A Yi, Joungho Han
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(3): 188. CrossRef
- Pigmented Renal Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Ki Yong Na, Hyun-Soo Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Sung-Goo Chang, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):382-386. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.382
- 10,486 View
- 77 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney (ADPKD) is rare. To date, 54 cases of RCC in ADPKD have been reported. Among these, only 2 cases have different histologic types of RCC. Here we describe a 45-year-old man who received radical nephrectomy for multifocal RCC with synchronous papillary and clear cell histology in ADPKD and chronic renal failure under regular hemodialysis. The case reported herein is another example of the rare pathological finding of RCC arising in a patient with ADPKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
Consolato M. Sergi, Luis Guerra, Josef Hager
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(9): 3965. CrossRef - Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Patients Requiring Nephrectomy: Characteristics and Surgical Considerations
Joel Ern Zher Chan, Kate S. Olakkengil, Shantanu Bhattacharjya, Santosh Antony Olakkengil
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2025; 95(7-8): 1605. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Background of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
Poorva Vias, Shikha Goyal, Renu Madan, Nandita Kakkar, Ridhi Sood, Kannan Periasamy, Rajender Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024; 45(02): 188. CrossRef - Detection of two synchronous histologically different renal cell carcinoma subtypes in the same kidney: a case report and review of the literature
Mohamed Sakr, Merhan Badran, Sarah Ahmed Hassan, Mohamed Elsaqa, Mohamed Anwar Elwany, Nevine M. F. El Deeb, Mohamed Sharafeldeen
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Importance of Genetic Testing in the Differential Diagnosis of Atypical TSC2-PKD1 Contiguous Gene Syndrome—Case Series
Petronella Orosz, Zita Kollák, Ákos Pethő, András Fogarasi, György Reusz, Kinga Hadzsiev, Tamás Szabó
Children.2023; 10(3): 420. CrossRef - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease coming up with an unusual presentation of renal cell carcinoma on its first encounter
Asma Shoukat Masumdar, Anitha Padmanabhan, Nitin Gadgil, Gargi Padalkar
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2023; 10(4): 417. CrossRef - Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review
Yuji Hakozaki, Kiyotaka Uchiyama, Akane Yanai, Daisuke Yamada, Yuka Kamijo, Yoshitaka Ishibashi
CEN Case Reports.2021; 10(2): 199. CrossRef - CT and MRI findings of cystic renal cell carcinoma: comparison with cystic collecting duct carcinoma
Qingqiang Zhu, Jun Ling, Jing Ye, Wenrong Zhu, Jingtao Wu, Wenxin Chen
Cancer Imaging.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental occurrence of papillary renal cell carcinoma in the native kidney with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease after renal transplantation: A case report
Mahmoud Abbas, Melanie Pätzel, Angelika Thurn, Olaf Brinkmann, Olaf Bettendorf
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patient with preserved renal function
Hyuk Huh, Hyung Ah Jo, YongJin Yi, Seung Hyup Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Curie Ahn, Hayne Cho Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 1108. CrossRef - The Association between Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and Renal Cell Carcinoma
Chase C. Hansen, Michael Derrick, Irfan Warriach, James Thomas Cammack, James Thomas Cammack, Werner de Riese
Open Journal of Urology.2015; 05(06): 84. CrossRef - The MSCT and MRI findings of collecting duct carcinoma
Q. Zhu, J. Wu, Z. Wang, W. Zhu, W. Chen, S. Wang
Clinical Radiology.2013; 68(10): 1002. CrossRef - Thyroid-like follicular carcinoma of the kidney in a patient with nephrolithiasis and polycystic kidney disease: a case report
Metka Volavšek, Margareta Strojan-Fležar, Gregor Mikuz
Diagnostic Pathology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
- Hyaline Vascular Castleman Disease Involving Renal Parenchyma and a Lymph Node: A Case Report
- Ji Hyun Kwon, Soo Kee Min, Mi Kyung Shin, Yong Seong Lee, Young-Goo Lee, Young Hyeh Ko
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):79-82. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.79
- 9,528 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Castleman disease is a rare lymphoproliferative lesion that is predominantly found in the mediastinum. Retroperitoneal and pararenal localizations are very rare. We describe a 36-year-old man with a hyaline vascular type of Castleman disease involving renal parenchyma and a paraaortic lymph node. Most reported renal Castleman disease was plasma cell type with systemic symptoms. Herein, we report the first Korean case of the hyaline vascular type of Castleman disease involving the renal parenchyma and the paraaortic lymph node simultaneously.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hiding in the kidney: a series of 13 lymphoid proliferations clinically mimicking renal carcinoma
Jihoon William Lee, Marie E. Perrone, Daniel E. Sabath, Daniel W. Lin, George R. Schade, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Maria Tretiakova
Virchows Archiv.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary hyaline vascular Castleman disease in the kidney: a report and brief literature review
Ibrahim Elsharawi, Sorin Selegean
Journal of Hematopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Castleman Disease of the Kidney in Computed Tomography Urography
Kai Wang, Fengjuan Xing, Heng Ma, Wenjuan Li
Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2022; 18(1): 74. CrossRef - Primary hyaline vascular Castleman disease of the kidney: case report and literature review
Yunzhu Li, Haixia Zhao, Bingyin Su, Chan Yang, Shurong Li, Wanlei Fu
Diagnostic Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Castleman’s Disease of the Kidney Mimicking Renal Cell Carcinoma on FDG PET/CT
Yang Wang, Aisheng Dong, Bo Yang, Jianping Lu
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2018; 43(5): e160. CrossRef - Unicentric hyaline vascular type of castleman disease of the renal hilum with diagnostic dilemma: A case report and review of literature
AmitKumar Adhya, ManasRanjan Pradhan
Oncology Journal of India.2018; 2(4): 96. CrossRef
- Hiding in the kidney: a series of 13 lymphoid proliferations clinically mimicking renal carcinoma
- Prognostic Significance and Nature of Rhabdoid Features in Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Misun Choe, Ji Young Park, Ilseon Hwang, Sang Pyo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):371-378.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.371
- 4,732 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Recent reports have indicated that renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with rhabdoid features follows an aggressive clinical course. We investigated the prognostic significance and nature of the rhabdoid component.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed the incidence and clinicopathologic characteristics of RCC with rhabdoid features in 174 radical nephrectomy cases. The specimens were examined histologically and immunohistochemically.
RESULTS
Twelve of the 174 RCC cases (6.9%) showed rhabdoid features. Histologically, all the tumors with rhabdoid features were of the clear cell type. The presence of rhabdoid features was significantly associated with higher Fuhrman's nuclear grade and higher pathologic tumor stage at presentation. Among the 12 patients who showed the rhabdoid component, nine (75%) developed metastasis and seven (58.3%) died of disease-related causes. The presence of rhabdoid features was independently associated with metastasis and disease-related mortality. The rhabdoid cells were positive for vimentin; variably positive for pan-cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen, and CD10; and negative for cytokeratin 7, smooth muscle actin, desmin, E-cadherin, and c-Kit. No case showed loss of integrase interactor-1; one was p53 positive, and five were insulin-like growth factor mRNA binding protein 3 positive. The Ki-67 labeling index was 1-25% (mean, 5.5%).
CONCLUSIONS
The rhabdoid component is an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of RCC; therefore, identification of this component is critical.
- Comparison of Detecting Methods of BK Virus Infection in Patients with Renal Allograft Recipients.
- Sung Hak Lee, Youn Jun Park, Chul Woo Yang, Yong Soo Kim, In Sung Moon, Chang Suk Kang, Yeong Jin Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(6):636-641.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.6.636
- 4,405 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) is an emerging problem as a consequence of the use of potent immunosuppressive agents. Because optimal detection methods for the diagnosis of BKVN are required clinically, we compared the results of renal allograft biopsy, urine cytology, and urine and blood viral loads.
METHODS
Four hundred sixty two case notes from 2004 to 2009 at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital were reviewed. During that period, 286 cases of urine cytology for decoy cells, 938 cases of urine BKV reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and 1,029 cases of blood BKV RT-PCR were performed. All diagnostic methods were performed in 85 cases.
RESULTS
A histological diagnosis of BKVN was made in 2.4% of cases (11/462). Urine cytology for decoy cells was positive in 26.2% (75/286). BKV RT-PCR revealed viruria in positivity of 22.1% (207/938) and viremia in 5.2% (54/1,029). In cases of BKVN, the sensitivities of urine and blood BKV RT-PCR were all 100% and the specificities were 69% and 94.5%, respectively. In cases with positive urine decoy cells, the sensitivities of urine and blood BKV RT-PCR were 50% and 27.7%, with specificities of 77.7% and 100%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
BKV screening by RT-PCR assays may be a clinically useful noninvasive test to identify renal recipients with concurrent BKVN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of BK Virus among Iranian Renal Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mohsen Ebrahimi, Alireza Mohebbi, Mohammad Mostakhdem Hashemi, Mobina Ashrafi Shahmirzadi
Journal of Clinical and Basic Research.2020; 4(4): 50. CrossRef - Asymptomatic hematuria associated with urinary polyomavirus infection in immunocompetent patients
Sung Hak Lee, Sung Hoo Hong, Ji Youl Lee, Tae Kon Hwang, Kyoung Suk Kim, Hyoungnam Lee, Yeong Jin Choi
Journal of Medical Virology.2014; 86(2): 347. CrossRef
- Prevalence of BK Virus among Iranian Renal Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Practical Standardization in Renal Biopsy Reporting.
- So Young Jin, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Sun Hee Sung, Beom Jin Lim, Jee Young Han, Soon Won Hong, Hyun Ee Yim, Yeong Jin Choi, Yong Mee Cho, Myoung Jae Kang, Kyung Chul Moon, Hee Jeong Cha, Seung Yeon Ha, Mi Seon Kang, Mee Young So, Kwang Sun Suh, Jong Eun Joo, Yong Jin Kim, Nam Hee Won, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(6):613-622.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.6.613
- 5,683 View
- 185 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To standardize renal biopsy reporting and diagnosis, The Renal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists (RPSKSP) has developed a renal pathology reporting format for the native and allograft kidney.
METHODS
A consensus checklist of a provisional renal biopsy format was sent to all members of the RPSKSP. Feed back opinions regarding the practical application of the checklist to the diagnostic work were received.
RESULTS
Kidney biopsies require three essential examinations: by light microscopy, immunofluorescence (IF), and electron microscopy (EM). A final report of a renal biopsy should include information on specimen adequacy and a description of the morphologic change using a systematic semiquantitative method for each of the compartments, with optional separate IF and EM reports.
CONCLUSIONS
A standard renal biopsy report format is important in establishing clinicopathologic correlations, making reliable prognostic considerations, comparing the findings in sequential biopsies and evaluating the effects of therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional antihypertensive effect of magnesium supplementation with an angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypomagnesemic rats
Kyubok Jin, Tae Hee Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Yang Wook Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2013; 28(2): 197. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Features of IgA-Dominant Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis
Tai Yeon Koo, Gheun-Ho Kim, Hyang Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(2): 105. CrossRef
- Additional antihypertensive effect of magnesium supplementation with an angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypomagnesemic rats
- Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney: A Report of Two Cases with Review of Literature.
- Sun A Kim, Jung Eun Hwang, Jae Y Ro, Kyung Ja Cho, Cheryn Song, Mi Jung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):420-425.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.420
- 4,502 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a benign mesenchymal neoplasm usually occurring in the pleura. Kidney is one of the rarest sites for SFT. We report here on two cases of renal SFT found in 30-year-old and 33-year-old men with review of the literatures. Both cases manifested as well-enhanced solid masses in kidney and radical nephrectomies were done. The tumors consisted of bland-looking spindle cells arranged in short, ill-defined fascicles and storiform pattern with characteristic hemangiopericytoma-like blood vessels. The tumor cells were strongly positive for CD34 and CD99, focally positive for bcl-2, and negative for cytokeratin and human melanoma black-45 on immunohistochemical stainings. Possibility of SFT should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a renal mass which consists of benign-looking spindle cells and hemangiopericytomatous blood vessels. Immunohistochemical staining for CD34 is essential to confirm the renal solitary fibrous tumor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Solitary fibrous tumor located in the sella turcica: A report of two cases and review of the literature
XIAO YANG, QINGJUN JIANG, BINGBING YU
Oncology Letters.2015; 10(1): 354. CrossRef - Pediatric Renal Solitary Fibrous Tumor
William W. Wu, Julia T. Chu, Stephen G. Romansky, Lisa Shane
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 23(1): 34. CrossRef
- Solitary fibrous tumor located in the sella turcica: A report of two cases and review of the literature
- Mucinous Tubular and Spindle Cell Carcinoma of the Kidney with Aggressive Behavior: An Unusual Renal Epithelial Neoplasm: A Case Report.
- Ji Hye Lee, Mee Hye Oh, Hyun Deuk Cho, Young Sik Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):211-215.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.211
- 4,432 View
- 31 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma is a rare low-grade renal cell carcinoma, which was first described as a new entity in the World Health Organization 2004 classification. We report here on a case of this tumor with very unusual aggressive behavior. A 73-year-old man presented with gross hematuria. A computed tomography scan demonstrated a 5 cm sized low density mass in the left kidney. The radical nephrectomy specimen grossly showed a well demarcated tumor confined to the renal parenchyma. Histologically, the tumor consisted of elongated tubules or trabeculae of oval to cuboidal cells with a low nuclear grade, and these tubules/trabeculae were separated by abundant acidic mucinous stroma. In some areas, spindle cell components were mixed with parallel tubules. Neither significant atypia nor mitosis was seen. The patient developed multiple metastatic pulmonary nodules 2 months later. Four months after the surgery, the left supraclavicular, right hilar and right subcarinal lymph nodes were also enlarged by metastasis. The patient died of respiratory failure 13 months after the operation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell carcinoma: analysis of chromosomal aberration pattern of low-grade, high-grade, and overlapping morphologic variant with papillary renal cell carcinoma
Kvetoslava Peckova, Petr Martinek, Maris Sperga, Delia Perez Montiel, Ondrej Daum, Pavla Rotterova, Kristýna Kalusová, Milan Hora, Kristýna Pivovarcikova, Boris Rychly, Semir Vranic, Whitney Davidson, Josef Vodicka, Magdaléna Dubová, Michal Michal, Ondrej
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 19(4): 226. CrossRef
- Mucinous spindle and tubular renal cell carcinoma: analysis of chromosomal aberration pattern of low-grade, high-grade, and overlapping morphologic variant with papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Malignant Glomus Tumors of the Stomach: A Report of 2 Cases with Multiple Metastases.
- Hyunjoo Lee, Yoon Seok Choi, Sang Cheul Oh, Jong Jae Park, Chul Whan Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):358-363.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.358
- 4,868 View
- 97 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Glomus tumors are mesenchymal neoplasms usually developing in the dermis or subcutis of the extremities. The majority of glomus tumors are entirely benign, and malignant glomus tumors are very rare, especially those arising in the visceral organs. Here, we are presenting two cases of malignant glomus tumor, initially diagnosed in the stomach by endoscopic biopsy. Case 1 was found in the stomach, right kidney, brain and humerus of a 65-year-old woman, and Case 2 in the stomach and liver of a 63-year-old man. Histologically, the tumor was composed of solid sheets and nests of round and short-spindle shaped tumor cells with vesicular nucleus and prominent nucleolus. The tumor cells were closely admixed with blood vessels of varying size. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells showed diffuse and strong positive staining for smooth muscle actin and paranuclear, dot-like staining for synaptophysin, but negative for desmin, c-kit, CD34 and S-100 protein. These two are rare cases of a malignant glomus tumor with widespread metastases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Malignant gastric glomus tumor with heterochronous liver metastases: a case report and review of the literature
Shining Xu, Teng Xu, Yihao Zhi, Feng Dong, Chao Wu, Minhua Zheng
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of gastric glomus tumor: A report of 15 cases and literature review
Minying Deng, Rongkui Luo, Jie Huang, Yuanlong Luo, Qi Song, Huaiyu Liang, Chen Xu, Wei Yuan, Yingyong Hou
Pathology and Oncology Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Glomus Tumor of the Stomach: A Systematic Review and Illustrative Case Report
Andrea Pansa, Laura Samà, Laura Ruspi, Federico Sicoli, Ferdinando Carlo Maria Cananzi, Vittorio Quagliuolo
Digestive Diseases.2023; 41(1): 17. CrossRef - Locally Advanced Glomus Tumor of the Stomach With Synchronous Liver Metastases: Case Report and Literature Review
Fabio Frosio, Carmine Petruzziello, Elia Poiasina, Michele Pisano, Alessandro Lucianetti
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gastric Glomus Tumor: A Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Study of 21 Cases
Jun Lin, Juan Shen, Hao Yue, Qiongqiong Li, Yuqing Cheng, Mengyun Zhou, Yujiang Fang
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignant glomus tumor of the gastric antrum with hepatic metastases: a case report and literature review
Adina A. Bodolan, Rebecca Wilcox, Michelle X. Yang
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2018; 14: 81. CrossRef
- Malignant gastric glomus tumor with heterochronous liver metastases: a case report and review of the literature
- Primary Synovial Sarcoma of the Kidney: A Case Report and Literature Review.
- Mee Ja Park, Tae Hwa Baek, Joo Heon Kim, Dong Wook Kang, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Jin Son
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):274-278.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.274
- 4,401 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Synovial sarcoma is a rare renal neoplasm that is not easy to diagnose unless SYT-SSX fusion transcripts are identified. We report here on a case of primary renal synovial sarcoma in a 35-year-old woman. A mass was discovered by accident in the lower part of the right kidney when ultrasonography was performed, and it was removed via radical nephrectomy. Grossly, the tumor was a homogeneously tan-brown soft mass that measured 4.5x3.2x3.0 cm, and it was encircled by a well-defined cystic space. The lesion exhibited hypercellularity of the oval or short spindle cells that were arranged in various solid sheets or intersecting fascicles. Immunohistochemically, the tumor showed diffuse positivity for vimentin, bcl-2 and CD99, and it showed focal positivity for epithelial membrane antigen. The SYT-SSX fusion transcripts were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Synovial sarcoma should be considered in the differential diagnosis when a spindle cell neoplasm is encountered in the kidney.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma and Clinical and Pathological Findings: a Systematic Review
Leandro Blas, Javier Roberti
Current Urology Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma - A rare histology
Premkumar Krishnappa, Mohan keshavamurthy, Shakir Tabrez, Sreeharsha Harinatha, Mohan Balaiah Aswathaiya
Urology Case Reports.2020; 33: 101402. CrossRef
- Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma and Clinical and Pathological Findings: a Systematic Review
- Giant Cell Tumor-like Proliferation Associated with Renal Staghorn Calculi: A Case Report.
- Han Seong Kim, Mee Joo, Sun Hee Chang, Ji Eun Kwak, Sang Hwa Shim, Sung Yong Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(2):182-184.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.2.182
- 4,038 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 62-year-old man with left flank pain and hematuria was shown to have a staghorn stone in left renal pelvis. Grossly, renal pelvis and calyces were markedly dilated with cystic and hemorrhagic degeneration and renal parenchyma was atrophied. A tumor-like mass was located in a hemorrhagic cyst of the renal upper pole. This mass consisted of giant cells and stromal cells mimicking a giant cell tumor of bone. This giant cell tumor-like proliferation may represent a response to hemorrhage into a cystic cavity. Recognition of this finding is important to avoid the over-diagnosis of neoplastic lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Imaged guided surgery during arteriovenous malformation of gastrointestinal stromal tumor using hyperspectral and indocyanine green visualization techniques: A case report
Tristan Wagner, Onur Mustafov, Marielle Hummels, Anders Grabenkamp, Michael N Thomas, Lars Mortimer Schiffmann, Christiane J Bruns, Dirk L Stippel, Roger Wahba
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(23): 5530. CrossRef
- Imaged guided surgery during arteriovenous malformation of gastrointestinal stromal tumor using hyperspectral and indocyanine green visualization techniques: A case report
- The Morphologic Patterns of Diabetic Nephropathy in Koreans.
- Si Hyong Jang, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(1):36-42.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.1.36
- 4,110 View
- 31 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diabetic nephropathy is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease and it has various pathologic features. We investigated the clinicopathologic differences between the histologic classes of diabetic nephropathy.
METHODS
A total of 46 patients with diabetic nephropathy were evaluated. Morphologically, the renal lesions were divided into three categories: class 1, diffuse or nodular glomerulosclerosis: class 2, vascular change without evidence of glomerulosclerosis: and class 3, non-diabetic renal disease superimposed on diabetic glomerulosclerosis. We evaluated the laboratory findings and the histologic findings, including mesangial expansion, interstitial fibrosis and inflammation, arteriolar hyalinosis and tubular atrophy.
RESULTS
The proportion of each class was 32 cases (70%), 4 cases (9%) and 10 cases (21%), respectively. The clinical and laboratory data showed no significant difference among the classes. For the groups of class 1, the group with nodular sclerosis showed a higher serum creatinine level than did the diffuse group (p=0.003). IgA nephropathy was the most common non-diabetic renal disease superimposed on diabetic glomerulosclerosis in our study.
CONCLUSIONS
The patients with nodular glomerulosclerosis presented with a more progressed clinicopathological features than did the patients with class 1 diffuse glomerulosclerosis. We also found 21% of all the patients with diabetic nephropathy had superimposed non-diabetic renal disease in a Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Renal biopsy pattern in diabetes mellitus patients and their correlation with clinical parameters
G. Singh, B. Naik, U. Singh, A. Modi, R. Dave
Nephrology (Saint-Petersburg).2023; 27(3): 53. CrossRef - Non-diabetic renal disease in Croatian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ivica Horvatic, Miroslav Tisljar, Patricia Kacinari, Ivana Matesic, Stela Bulimbasic, Danica Galesic Ljubanovic, Tina Katic, Darko Kristovic, Kresimir Galesic
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2014; 104(3): 443. CrossRef - Clinical versus histological diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy--is renal biopsy required in type 2 diabetic patients with renal disease?
G. Biesenbach, G. Bodlaj, H. Pieringer, M. Sedlak
QJM.2011; 104(9): 771. CrossRef
- Renal biopsy pattern in diabetes mellitus patients and their correlation with clinical parameters
- Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Early Stage of Aging Rat Kidney.
- Kye Won Kwon, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(2):86-92.
- 2,100 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) has been suggested to have a role in renal injury of aging rats.
METHODS
Renal function and histology were compared between 12 month-and 7-9 week-old rats. Proliferating activity and cell death were evaluated by PCNA index and apoptosis. Three isoforms of NOS (eNOS, iNOS, and nNOS) were stained by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
Serum creatinine level was increased in old rats (1.0 mg/dL vs 0.5 mg/dL, p=0.000). 24 h proteinuria and urinary NO were comparable between the two groups. The percentage of global and segmental glomerulosclerosis increased in old rats. PCNA index decreased in the glomeruli (0.1 vs 0.6/glomerulus, p=0.005) and the tubulointerstitium (10.2 vs 19.2/mm2, p=0.019) of old rats compared to that of young rats. However, no difference was observed in the number of TUNEL positive cells. eNOS was not stained in young and old rat kidney, whereas iNOS was stained in the interstitial inflammatory cells of old rats (0.3 vs 0.0 of young rats/mm2, p=0.188). Macula densa nNOS staining significantly decreased in old rats compared to young rats (5.6 vs 9.5/mm2, p=0.009).
CONCLUSIONS
Proliferating activity is more affected than cell death with aging. Decreased nNOS expression without alteration of eNOS and iNOS expressions may implicate nNOS as a marker of renal injury in the early stage of aging.
- Pseudosarcomatous Variant of Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis.
- Yun Kyung Kang, Ta Jin Kim, Yong Il Kim, Si Whang Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(6):610-614.
- 1,974 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of pseudosarcomatous variant of transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis which showed grossly and microscopically the distinct biphasic growth patterns. Grossly, most part of the tumor showed solid growth protruding into the renal pelvic cavity as well as infiltrating into the parenchyma of lower pole. The overlying pelvic mucosa was replaced by a diffuse, papillary transitional cell carcinoma, and the solid mass was composed of pleomorphic spindle cell sarcomatoid component with frequent myxoid change and a few foci of osteoid deposit. Ultrastructural study of the spindle cells revealed epithelial differentiation featured with rich cytoplasmic organelles, basal lamina and basement membrane-like structures, although immunohistochemistry failed to detect epithelial differentiation.
- Liesegang Structure in Simple Hemorrhagic Cyst Incidentally Found in Donor Kidney: A case report.
- Dong Hoon Kim, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(2):133-136.
- 2,164 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Liesegang rings (LRs) are peculiar structure of periodic precipitation zones from supersaturated solution in colloidal system. LRs are formed by a process referred to as "the Liesegang phenomenon". Here we describe LRs in renal hemorrhagic cyst from the donor kidney of a 59-year-old man. His general condition was good. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed a simple cyst in the left kidney. After donor nephrectomy for renal transplantation, a 3x2 cm sized cyst containing the brownish necrotic fluid was noted in the upper pole of left kidney. Frozen section from the relatively thickened cystic wall was performed. During frozen section examination, round concentric rings with double-layered outer wall, striations and amorphous central nidus admixed with the foamy macrophages were found and the lesion was originally interpreted as xanthogranulomatous inflammation with unusual crystalline structures in the cytoplasm of macrophages or freely in the interstitium. Macrophages with calcium crystals or malakoplakia were also considered at that time. Additional specimen for the permanent sections showed a simple hemorrhagic renal cyst with areas of small or large aggregates of LRs along the cyst wall. Multiple round ring-like structures ranging from 11 to 42 micrometer in diameter had uniform, pale eosinophilic, radially striated double wall. Histochemical and immunohistochemical stainings for iron, calcium, mucopolysaccharide, amyloid, cytokeratin were negative in these structures. They were highlighted by CD68 immunostaining as well as PAS and Masson's trichrome stainings. Awareness of Liesegang phenomenon in cystic lesions will decrease the possibility of erroneous diagnosis as another type of pathologic process, such as parasitic worms or eggs.
- Polyomavirus Renal Infection Confirmed by Electron Microscopy in a Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome: An Autopsy Case Report.
- Na Rae Kim, Byoung Kwon Kim, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(2):168-171.
- 1,820 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Polyomavirus infection commonly occurs in childhood and adolescence, remaining in a latent status and reactivated in an immunocompromised status. We report herein an autopsy case of HIV-positive 41-year-old male, who succumbed to disseminated Kaposi sarcoma and cytomegalovirus infection involving the gastrointestinal tract, lung and brain. The involved kidney showed minimal inflammatory infiltrates and tubular injury: the nuclei of tubular epithelial cells were markedly enlarged with central clearing and peripheral chromatin margination or bore basophilic nuclear inclusions. Inclusion-bearing tubular epithelial cells were negative for the viral immunostains including herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus and adenovirus. Electron microscopy disclosed 42 nm intranuclear viral particles compatible with the BK polyomavirus. The viral particles were icosahedral in paracrystalline array and nonenveloped.
- Carcinoid Tumor Arising from A Normal Kidney: A Case Report.
- Seo Young Sohn, Han seong Kim, Mee Joo, Min Kyung Kim, Sung Hye Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(3):196-199.
- 1,949 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary carcinoid tumor of the kidney is a very rare disease. Until now, only 41 cases have been reported worldwide, and nine of these arose in a horseshoe kidney. In Korea, 3 cases have been reported to date, and all of these arose in a horseshoe kidney. We present a case of primary carcinoid tumor occurring in a normal kidney of a 45 year old man. A tumor was incidentally found close to the hilum of the left kidney. Histologically, the tumor exhibited trabecular and ribbon-like pattern of cuboidal or columnar cells. Mitotic activity was rarely seen. The tumor cells were positive for synaptophysin and chromogranin A. Numerous dense-core neurosecretary granules were observed by the electron microscopic examination. To our knowledge, the present case is the first report of primary renal carcinoid tumor arising in a normal kidney in Korea.
- Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney: A case report.
- Soon Ae Oak, Bang Hur, Man Ha Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):81-84.
- 2,159 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney(CCSK) is a rare malignant childhood tumor which is distinguished from Wilms tumor by its pathologic features, clinical presentation and frequent occurrence of metastasis to bone. We report a case of CCSK from a 2 year-old girl in the right kidney, followed by metastasis to thoracic vertebrae and left temporal lobe. Histogenesis of this tumor is controversial, although some studies suggest primitive mesenchymal origin. This case was studied with the aids of immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy in an effort to verify the histogenesis of the tumor. Vimentin was reactive in tumor cell, but cytokeratin, GFAP, S-100 protein and desmin were not stained, which confirmed the previous reports by others. Ultrastructural observation of the tumor cells showed neither features of epithelial cell nor differentiated mesenchymal cells.
- Localized Cystic Disease of the Kidney: A case report.
- Wan Seop Kim, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(3):210-213.
- 1,826 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Localized cystic disease of the kidney is a rare entity with the gross and microscopic features of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease localized to only a portion of a kidney, and negative family history. We report a case of localized cystic disease of the kidney in a 38-year-old woman who complained of intermittent right flank pain for 1 year. The resected kidney showed multiple cysts measuring up to 4.0 3.5 3.0 cm, which were scattered throughout the mid- and lower poles of the kidney. Microscopically, the cystic lesion was composed of numerous cysts of variable size, lined by flattened epithelium. The intervening septa of the cysts contained normal or compressed renal tubules and glomeruli. Neither dysgenetic tissue such as immature cartilage or primitive mesenchymal tissue nor malignant cells was identified. Localized cystic disease should be included in the differential diagnosis of cystic lesions in the kidney.
- A Study on the Pathogenesis of Renal Papillary Necrosis Induced by Endotoxin.
- Kyung Rak Sohn, Tae Joong Sohn
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(4):416-454.
- 2,023 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The author carried out an experimentation to clarify a possible pathogenesis of renal papillary necrosis induced by an univisceral Shwartzman reaction. The experimental animals were healthy white rabbits in weighing between 1.7 kg and 3.0 kg. Under the condition of ureterostomy, animals were pretreated with 0.5 cc of 50% ethyl alcohol and followed by administration of 0.2 ~ 1.5 mg endotoxin (E. coli 026 : B6, bacto lipopolysaccharide B. Difco, U.S.A.) as preparation in the renal pelvis. And then sacrificed at 10 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, 6 hours and 24 hours after intravenous injection of 0.2 mg or 0.6 mg endotoxin through the ear veins, subjection to examine light and electron microscopically. The obtained results were summarized as follows: Papillary necrosis was developed in 88% among 18 cases excluding 6 cases died before sacrification. There were two types of necrosis, namely papillary and medullary type, but the former and combined forms of both types were the most common findings. Initial main target site of injury in renal papilla induced by endotoxiin was the endothelium of vasa recta and then followed by the Henle's loop, interstitial cell and collecting tubule respectively. Vascular injuries such as swelling and detachment of endothelium were observed since 10 minutes after endotoxin injection. Henle's loop showed stratification of basement membrane without consistent features with time lapses and initially observed fatty vaculoes at 1 hour after endotoxin injection were more eminent in 24 hours group. Main changes of interstitial cells were decrease of lipid droplets while increase of fatty vacuoles; the latter were initially observed in 1 hour group and more eminent in 24 hours group. Collecting tubule showed many fatty vacuoles especially in 24 hours group. It is thought that emergence of fatty vacuoles seems to be a kind of immature lipid droplets to compensate the increased demand of PC release due to continuous ischemic condition. In conclusion, it is thought that ischemic injury due to the vascular changes is pathogenic mechanism producing renal papillary necrosis. Endotoxin induced univisceral Shwartzman reaction in the kidney may be a good experimental model in studying renal papillary necrosis.
- Potter's Syndrome with Adult Polycystic Renal Disease: An autopsy case report.
- Hwa Sook Jeong, Beom Soo Park, Geon Kook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):361-365.
- 2,337 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Potter's syndrome including bilateral renal agenesis or polycystic renal disease, bilateral pulmonary hypoplasia and characteristic face was first described in 1946. Although a great number of cases of Potter's syndrome was reported, Potter's syndrome with adult polycystic kidney disease(Potter type III) was very rarely found. In this report, we described an autopsy case of Potter's syndrome having adult polycystic kidneys disease, bilateral pulmonary hypoplasia and characteristic face in conjunction with multiple hepatic cysts, features of congenital hepatic fibrosis and a pancreatic cyst. Microscopically, all cysts were lined by cuboidal epithelial cells, showing positive for epithelial membrane antigen and cytokeratins.
- Image Analysis of Glomerular Changes in Patients with Post-transplant IgA Nephropathy.
- Kye Won Kwon, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):206-211.
- 2,038 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
IgA nephropathy after renal transplantation (post-transplant IgAN) may recapitulate the IgAN of native kidneys, however, little has been reported about the histologic characteristics. The aim of this study is to apply glomerular morphometry using an image analyser to examine the histologic characteristics of post-transplant IgAN.
METHODS
The outer margin of the glomerulus (Bowman's area, BA) and glomerular tuft area (GA) were traced manually. The measured area were automatically calculated by KS300 image analysis system (Kontron, Munchen, Germany). The mesangial area (MA) was calculated with a summing each manually traced mesangial area. The total number of glomerular (GC) and mesangial cells (MC) were counted. Eight cases of renal section obtained by nephrectomy due to renal cell carcinoma (normal control: N-CTRL) and nineteen cases of renal section obtained from post-transplantation patients without IgAN (transplantation control: Tx-CTRL) served as controls.
RESULTS
A total of 35 biopsies were finally selected for measurement. BA and GA of post-transplant IgAN were 1.6 and 1.4 times larger than the N-CTRL, respectively, and were not significantly different from Tx-CTRL. MA was 1.4 times significantly larger than that of the Tx-CTRL. As compared to that of the N-CTRL, it was 1.2 times larger, but this difference was not statistically significant. The GC and MC of post-transplant IgAN and the Tx-CTRL were significantly lower than the N-CTRL. There were no significant correlations between glomerular hypertrophy and duration after renal transplantation, mesangial changes, segmental sclerosis, or degree of renal cortical interstitial fibrosis in post-transplant IgAN.
CONCLUSIONS
Prominent glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion suggest a hyperfiltration injury in post-transplant IgAN and a possible way to glomerulosclerosis.
- Congenital Mesoblastic Nephroma.
- Seok Hoon Jeon, Seung Sam Paik, Nam Hoon Kim, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):375-378.
- 2,055 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mesoblastic nephroma is an important differential diagnosis of a renal mass occurring in the neonatal period or in early childhood. It is a rare monomorphous congenital renal neoplasm most commonly recognized during the first 3 months of life. With the widespread application of ultrasound imaging, many cases are recognized prior to birth. We report a case of mesoblastic nephroma detected by ultrasonograph at 36 weeks of intrauterine fetal life and removed after birth. It showed a well circumscribed, grayish white, solid mass measuring 4x3x2 cm. The tumor was predominantly a classic type with a focal cellular pattern. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies were done.
- Epidermal Cyst in the Renal Pelvis: A Case Report with Review of the Literature.
- Sun Zoo Kim, Tae In Park, Sang Han Lee, Jung Sik Kwak
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(4):270-272.
- 1,995 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a case of an epidermal cyst arising in the kidney. This cyst occurred in a 61-year-old woman with a past history of several attacks of ureteral stones and she received treatments of extracoporeal shock wave lithotripsy and open nephrolithostomy. On the intravenous pyelogram, a relatively well demarcated, 5x5 cm-sized lesion with calcification was detected in the renal pelvis and calices. The lesion was removed by percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Histologically, the lesion had the same morphologic feature as a typical epidermal cyst arising in the skin. It has been postulated that the intrarenal epidermal cyst arises either from epidermal remnants or it results from traumatic implantation of transformed epithelium. Considering the past history of the patient, it might well be suspected that the present case occurred as a result of traumatic implantation of metaplastic squamous epithelial cells. We report here on a very interesting case of an epidermal cyst in the renal pelvis with a review of the relevant literatures.
- An Unusual Type of Acute Renal Failure due to Extensive Crystal Deposition in the Renal Tubular Epithelium and Interstitium: A Case Report.
- Ja Seung Koo, Eunah Shin, Shin Woo Kang, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(5):337-340.
- 2,012 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute tubular necrosis is a major cause of acute renal failure. Acute renal failure that is caused by crystal deposition can result from drug toxicity, lymphoplasmacytic neoplasms, ingestion of industrial organic solvents, or intratubular obstruction due to degenerated red blood cells and red blood cell casts. We herein present an uncommon case of acute renal failure in a 57-year-old woman showing an unusually massive accumulation of variable-sized, round, ellipsoid or rhomboid, pale-pink, refractile bodies in the proximal and distal tubular epithelial cells, interstitial macrophages and Bowman's spaces. These bodies were electron dense with a maximum diameter of 3 micrometer. The information we gathered from the patient history, the laboratory data and the various histochemical and immunohistochemical analyses failed to reveal the exact nature of these crystal-like structures.
- Nephroblastomatosis Associated with Wilms' Tumor.
- Kyeong Cheon Jung, Sang Yong Song, Yeon Lim Suh, Je G Chi, Hwang Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):274-278.
- 2,280 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In contrast to the nodular renal blastema which is defined by nests of primitive metanephric cells after 36 weeks of gestation, the nephroblastomatosis is characterized by neoplastic proliferation of the primitive cells. This lesion is presumed to be closely related to the development of Wilms' tumor. We report a case of bilateral nephroblastomatosis associated with Wilms' tumor in a child. This 4 1/2 year-old girl was admitted because of a 10 cm-sized round mass in the right kidney, and smaller nodules in the left kidney and the lung. After three cycles of chemotherapy and subsequent disappearance of the nodules in the left kidney and lung, she underwent a right nephrectomy and a wedge resection of the left kidney. A round Wilms' tumor mass was seen in the lower pole of the right kidney. Remaining right renal cortex showed multiple, slightly depressed gray-white nodules associated with multiple samll cysts. They were comprised of multifocal subcapsular nests of primitive nephrogenic cells with focal tubular or glomerular differentiation. They resembled fetal renal tissue. In the left kidney, similar nests of primitive cells were also noted. These lesions were interpreted as multifocal perilobar type of nephroblastomatosis.
- Cholesteatoma of the Renal Pelvis: A case report.
- Nam Hoon Kim, Young Chun Moon, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):691-693.
- 2,035 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Cholesteatoma in the kidney and ureter are accumulations of waxy, gray flakes of keratin materials, secondary to squamous metaplasia of the transitional epithelium. Herein, we describe a case of cholesteatoma in the renal pelvis of a 69-year-old woman, and give a brief review of the literature. In the upper pole of the left kidney was a 6 cm cystic lesion filled with a thick, flaky, grayish, comified material. Microscopically, the cystic area showed calyceal and pelvic structures being replaced by keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium. The surrounding renal parenchyma was atrophic with features of chronic pyelonephritis.
- Mucinous Tubular and Spindle Cell Carcinoma of Kidney Occurring in a Patient with Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma.
- Seog Yun Park, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Jae Y Ro, Jennifer Black, Jinsoo Chung, Kang Hyun Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Weon Seo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):54-59.
- 1,987 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma (MTSCC) is a rare type of kidney tumor that has only been recently described. Furthermore, a case of MTSCC associated with a simultaneous lung cancer in the same patient has never been reported in the literature. In this paper, we describe a kidney tumor that was detected during staging work-up in a 72-year-old lung cancer patient. The kidney tumor was removed and shown to exhibit histological and immunophenotypic features of MTSCC, completely distinct from the pulmonary adenocarcinoma. In addition, this case was unique because it was characterized by neuroendocrine differentiation as well as p53 and Ki-67 overexpression in tumor cells. Therefore, we report a case of MTSCC diagnosed in a patient with pulmonary adenocarcinoma and describe the detailed histologic and immunohistochemical features of MTSCC.
- Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in a Horseshoe Kidney.
- Man Hoon Han, Sang Chul Nam, Bup Wan Kim, Ghil Suk Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):60-62.
- 1,930 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a case of mucinous adenocarcinoma that probably originated in the renal pelvis of a horseshoe kidney. A 61-year-old woman presented with a palpable mass in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen, and this mass had been present for several months. Computed tomography (CT) revealed a left renal pelvic tumor in the horseshoe kidney. Grossly, a 10x9x8 cm unilocular cystic mass filled with chocolate colored mucinous fluid was seen. A connection between the cystic mass and the renal pelvis was demonstrated on retrograde pyelography. Microscopically, the cyst contained anaplastic columnar mucosecretory epithelial cells. Some atypical cell clusters were freely floating in the mucinous lakes. The histopathological findings were consistent with mucinous adenocarcinoma. In addition, glandular metaplasia was noted in the cystic wall. Immunohistochemical assessment of the pelvic adenocarcinoma revealed the positive expressions of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin 20 (CK20) and a weak positive expression of cytokeratin 7 (CK7).
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Kidney.
- Hwa Eun Oh, Jeong Seok Moon, Sung Jin Cho, Nam Hee Won
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(6):592-594.
- 2,123 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor, originally described in the lung, is a relatively rare tumor-like lesion that occurs in various organs and tissues. It is usually well demarcated from the surrounding tissue, however it can be unfortunately resected as a malignant tumor. A few inflammtory pseudotumor in the kidney have been reported in English literature, but there have been no reports in Korea. We report a case with inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. A 48 year old woman had an intermittent flank pain on the right side. An ultrasonographic study suggested a renal cell carcinoma and a nephrectomy was done. Grossly, there were two separate masses with a well demarcated yellowish appearance, measuring 2.3 cm and 1.3 cm in diameter, respectively. Histologically, they were composed of smooth muscle actin positive spindle cells and a large number of foamy histiocytes, lymphocytes, and plasma cells in the fibrotic backgound.
- Apoptosis in Renal Hypertrophy after Uninephrectomy in the Rats.
- Chan Pil Park, Jung Woo Noh, Joo Seob keum, Myung Sook Kim, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(6):513-523.
- 1,916 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Glomerular compensatory hypertrophy maintains decreased renal function after uninephrectomy (UNX). Proliferation and apoptosis of renal cells may be involved in hypertrophy.
METHODS
In small and large male Sprague-Dawley rats, contralateral kidneys were harvested 1, 7, 14 and 30 days after UNX. Apoptosis was assessed by the Tdt-mediated dUTP-digoxigenin nick end labelling method. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and Fas ligand (FasL) expression was determined by immunohistochemically.
RESULTS
Morphometrically, glomerular hypertrophy was observed in both small and large rats after UNX, and it was more significant in the small rats. The glomerular proliferation index (PI) was gradually increased from day 7 but decreased on day 30 in the small rats. Glomerular PI was significantly increased from day 7 in large rats and peaked at day 14. Apoptotic cells in the glomeruli were slightly increased on day 1 and on day 7 in both groups of rats. The expression of FasL was gradually increased in the distal tubular epithelium in both groups.
CONCLUSIONS
These results demonstrate different profiles regarding the compensatory growth of the kidney, cell proliferation, and apoptosis during the period of compensatory hypertrophy in uninephrectomized rats of different weight and age. Apoptosis may play a role in regressing a number of proliferated cells during renal compensatory hypertrophy.
- A Case Report of Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Polycystic Kidney: A case report.
- Kyoung Chan Choi, Joon Hyuk Choi, Won Hee Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(1):57-60.
- 2,022 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A forty-nine-year-old woman with polycystic disease had a right nephrectomy for what was preoperatively thought to be a polycystic disease, but at surgery turned out to be a tumor based on frozen section. Microscopic examination revealed papillary type, renal cell carcinoma with classical features of adult polycystic kidneys. Radiologic findings revealed multiple cysts in the liver. The clinical recognition of a carcinoma developing in polycystic kidneys is often difficult because of the presence of preexisting large renal masses and occasional hematuria. Renal cell carcinoma should be thought of when confronted with abdominal pain or back pain, severe hematuria, sudden dysuria or a new renal mass occurring in a patient with polycystic kidneys.
- Cyclosporine Toxicity on Cultured Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells.
- Jung Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(4):423-429.
- 2,115 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nephrotoxicity is the most common dose-limiting factor of cyclosporine A (CSA) in clinical usage. But the mechanism of CSA-induced nephrotoxicity still remains unresolved. Many authors insisted that CSA induced renal proximal tubular cell injury is due to the secondary effects following hemodynamic changes or endothelial cell damage, instead of direct toxicity by CSA. To find out that CSA has a direct toxicity to the proximal tubular cells, the author used primary cultures of human proximal tubular cells to eliminate the hemodynamic or endothelial influences that could be produced in in vivo model. In the present study, the viability against CSA was tested by the neutral red assay method with modulation of Ca2+ amount in incubating media and observed electron microscopically. The viability test showed direct toxic effect of CSA on human proximal tubular cells and this was enhanced by Ca2+ depletion in incubating media. Morphologically noted are accumulation of lipid droplets and polyribosomal dispersion, which may be association with inhibition of cellular synthetic activity. These results suggest the toxixity is a direct effect of cyclosporine and that toxic mechanism may be due to inhibition of cellular synthetic activity. And this experiment also showed that primary cultures of human renal proximal tubular cells can be a good in in vivo model for investigating CSA nephrotoxicity.
- Kinetics of Cyclosporine uptake on Cultured Human Proximal Tubular Cells.
- Jung Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(4):430-435.
- 2,010 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cyclosporine A (CSA), a lipophilic cyclic undecapeptide, is not accumulated evently in all tissues and has a high affinity to several tissues such as lymphoid organs, liver, and kidneys. From this point of view, it is reasonable to assume that the amount of CSA uptake would be correlated with the extent of cell injury. On the other hand, verapamil, a Ca2+ channel blocker, bas been shown to ameliorate CSA nephrotoxicity. Since proximal tubule is the major site of drug transport and CSA uptake and its interaction with verapamil in isolated human renal proximal tubular cells. The CSA uptake rapidly increased over the first 5 min and then achieved almost steady-state after 10 min at all concentrations (0.5-10 uM). Kinetic analysis yielded that the Km and Vmax values of CSA were 5.6 uM and 86.2 p mol/mg cell protein/min, respectively. And Ca2+ depletion in media enhanced CSA uptake significantly but verapamil reduced it. These results suggest that the Ca2+ channels and CSA transporting sites on cell membrane are closely associated and that Ca2+ and CSA might be taken up competitively by proximal tubular cells.
- Ultrastructural Changes in Rat Kidney after Lead Acetate Administration.
- Hyun Chul Kim, Seung Pil Kim, Kwan Kyu Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(2):73-88.
- 1,983 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to investigate the ultrastructural findings of rats after administration of 0.5% lead acetate with drinking water. The Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into control and experimental groups. The control group was composed of 12 rats and was orally administered with 0.5% sodium acetate. The experimental group was composed of 36 rats and orally administered with 0.5% lead acetate. Two rats in the control group and four rats in the experimental group were sacrificed on day 2, and week 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8 after administration. The kidney was extirpated and examined by electron microscopy. The results obtained were as follows: The blood lead concentration in the experimental group began to increase from the second day after administration and it increased gradually until the 6th week and it decreased at the 8 week. The urinary excretion of delta-ALA also increased from the secondary and gradually increased up to the 8th week. On electron microscopic examination, the proximal tubular cells showed fat droplets, dilatation of the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrial swelling, increased numbers of secondary lysosomes and myelin figure-like residual bodies and intranuclear inclusion bodies. All these findings peaked at the eighth week after administration. Ultrastructural findings after Timm sulphide silver reaction revealed the lead granules in the proximal tubular lumen and between the microvilli of the proximal tubular cells without membrane-bounded. It can be concluded that most of the changes of micro-organelles are compatible with degenerative changes of lead exposure and passive diffusion of lead granules are involved in the proximal tubular cells.
- Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: A Report of 4 Cases.
- Sunhee Chang, Jooryung Hugh, Kyung Mo Kim, Duck Jong Han, Seung Kyu Lee, Eunsil Yu
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(1):45-50.
- 2,407 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is a proliferation of B-cells associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection as a complication of immunosuppression, especially by FK506. We investigated four cases of PTLD which developed either in allografts or in other organs.
Case
1 was a 38-year-old woman, who developed monomorphic PTLD in a kidney 7 years and 7 months after renal transplantation. Case 2 was a 37-year-old man, who developed monomorphic PTLD in the right submandibular lymph node 4 months after liver transplantation. Case 3 was a 60-year-old man, who developed monomorphic PTLD in the liver 8 months after liver transplantation. Case 4 was a 2-year-old female child, who developed polymorphic PTLD in the colon, liver, and mesenteric lymph node 10 months after liver transplantation. FK506 was administered to case 4. EBV was identified in the tissues of all cases by immunohistochemistry and/or in situ hybridization.
- The Expression of C4d and HLA-DR in Renal Allografts with the Histologic Features of Antibody-Mediated Rejection.
- Young Soo Song, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(5):260-269.
- 2,036 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Deposition of C4d along the peritubular capillaries is generally associated with an antibody-mediated response. We evaluated, with performing C4d immunostaining, the diagnostic accuracy of the cases that were previously diagnosed as antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) when based only on the histologic findings, and we examined possible correlation of C4d with HLA-DR.
METHODS
Forty-five renal transplantation biopsies, which showed ABMR-like histology, were obtained. The expressions of C4d and HLA-DR in the transplant rejection cases were investigated using immunofluorescent and/or immunohistochemical staining. RESULTS: There were 14 discordant cases among a total of 45 cases when C4d was used as a diagnostic marker and the original slides were reviewed. These total cases consisted of the C4d negative cases in two cases of hyperacute rejection and all the cases of ABMR and ABMR with chronic/sclerosing allograft nephropathy (CAN) and two C4d positive cases (one each of acute cellular rejection (ACR) and CAN according to their original diagnosis) and all these cases were then revised according to Banff 07. The expression of HLA-DR tended to be correlated with the log-transformed duration of grafts until three years after the transplantation. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that C4d together with the histologic findings should be used for making the diagnosis of ABMR. The tubular HLA-DR expression over time should be studied to further understand the mechanism of graft rejection.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Renal Angiomyolipoma.
- Yong Hee Lee, Dong Won Min, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Kwang Gil Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(1):65-70.
- 2,099 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We describe a case of fine needle aspiration cytologyof renal angiomyolipoma which was not associated with the clinical complex of tuberous sclerosis and was incidentally found. It was a solitary lesion and the clinical impression before needle aspiration was renal cell carcinoma. The aspirated specimen showed mature fat cells, clusters of renal tubular epithelial cells and sheets of pleomorphic smooth muscle cells with fibrillary cytoplasm. The nuclei of smooth muscle cells varied in size and shape. Since the treatment of renal angiomyolipoma differs from that of renal cell carcinoma, the preoperative cytological diagnosis is of great value.
- Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Myoung Jin Ju, Kee Tac Jang, Je Geun Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(11):1240-1243.
- 1,919 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma is a distinct subtype of renal cell carcinoma with its pathological characteristics and good prognosis. Multilocular renal cysts and renal cell carcinoma with cystic change are important differential diagnoses. We report a case of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma in a 37-year-old woman who came to the hospital because of the right renal mass. The removed right kidney showed a 6x4 cm well defined cystic mass in the lower pole. On cut section there were multiple cavities in the mass, filled with serosanguineous fluid and focal yellowish solid area. Microscopically, these cysts were lined by a single layer of flat or cuboidal cells consisted of clear cytoplasm with small central nuclei. In some portions of the tumor, the clear neoplastic cells formed sheets within the septa or walls of the cysts.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Collecting Duct Carcinoma of the Kidney: A Case Report.
- Sang Yeop Yi, Kwang Gil Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(2):160-166.
- 1,831 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney is an unusual variety of renal carcinoma considered to arise from the epithelium of the collecting ducts. We recently experienced an case of fine needle aspiration cytology of collecting duct carcinoma of the kidney in a 17 year-old girl. The smear revealed many cellular clusters of ordinary papillary pattern, characterized by clumping of cells with nuclear overlapping, in a slightly necrotic background. The tumor cells had abundant delicate granular cytoplasm with some having vacuolation. The nuclei were only slightly pleomorphic with somethat coarse chromatin and one or more small nucleoli. Some nuclei showed irregular nuclear membrane and nuclear groove. A few polmorphs were also present.
- Teratoid Wilms' Tumor: A Case Report.
- Seong Rim Kim, Sang Yong Song, Yeon Lim Suh, Ki Woong Sung, Suk Koo Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(3):187-190.
- 1,866 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Teratoid Wilms' tumor is a rare renal tumor. Fourteen cases have been reported. A 14-month-old girl was presented to us. She had a right renal mass which was diagnosed as a Wilms' tumor in another hospital. She had been treated with chemotherapy but failed to respond to it. The nephrectomy specimen revealed an encapsulated mass of which the cut surface was solid, firm, gray to yellow tan. Microscopically, the stromal elements were predominant, especially comparing with few blastemal element, but the degree of heterologous differentiation was sufficient to warrant the diagnosis of teratoid Wilms' tumor.

 E-submission
E-submission
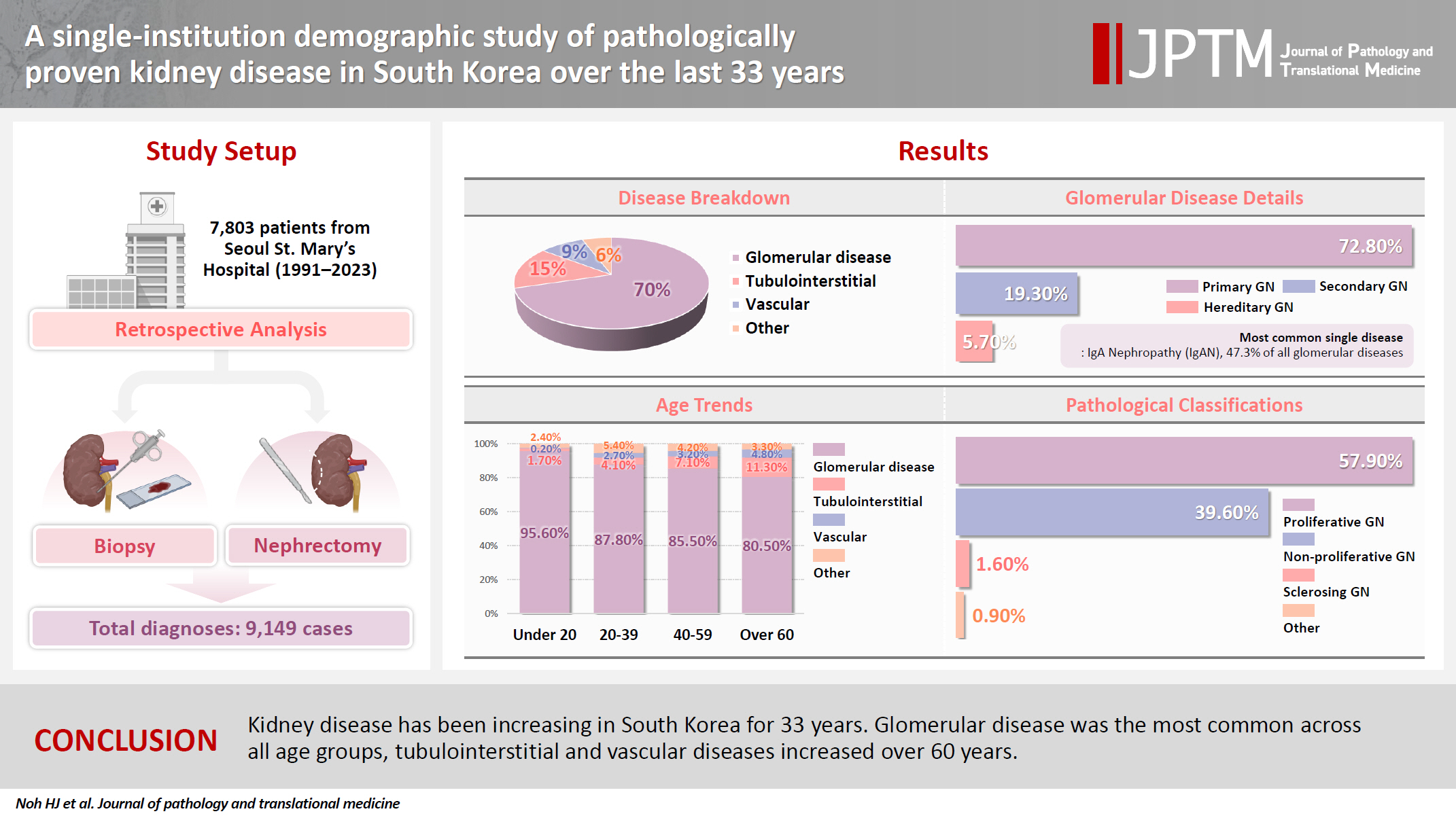





 First
First Prev
Prev



