Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases: from Averill A. Liebow to artificial intelligence
- Eunhee S. Yi, Paul Wawryko, Jay H. Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):1-11. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.17
- 7,860 View
- 438 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histopathologic criteria of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) were defined over the years and endorsed by leading organizations decades after Dr. Averill A. Liebow first coined the term UIP in the 1960s as a distinct pathologic pattern of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Novel technology and recent research on interstitial lung diseases with genetic component shed light on molecular pathogenesis of UIP/IPF. Two antifibrotic agents introduced in the mid-2010s opened a new era of therapeutic approaches to UIP/IPF, albeit contentious issues regarding their efficacy, side effects, and costs. Recently, the concept of progressive pulmonary fibrosis was introduced to acknowledge additional types of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases with the clinical and pathologic phenotypes comparable to those of UIP/IPF. Likewise, some authors have proposed a paradigm shift by considering UIP as a stand-alone diagnostic entity to encompass other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases that manifest a relentless progression as in IPF. These trends signal a pendulum moving toward the tendency of lumping diagnoses, which poses a risk of obscuring potentially important information crucial to both clinical and research purposes. Recent advances in whole slide imaging for digital pathology and artificial intelligence technology could offer an unprecedented opportunity to enhance histopathologic evaluation of interstitial lung diseases. However, current clinical practice trends of moving away from surgical lung biopsies in interstitial lung disease patients may become a limiting factor in this endeavor as it would be difficult to build a large histopathologic database with correlative clinical data required for artificial intelligence models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
Nathan Hennion, Corentin Bedart, Léonie Vandomber, Frédéric Gottrand, Sarah Humez, Cécile Chenivesse, Jean-Luc Desseyn, Valérie Gouyer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Insights into UIP Pattern: A Comparison Between IPF and Non-IPF Patients
Stefano Palmucci, Miriam Adorna, Angelica Rapisarda, Alessandro Libra, Sefora Fischetti, Gianluca Sambataro, Letizia Antonella Mauro, Emanuele David, Pietro Valerio Foti, Claudia Mattina, Corrado Spatola, Carlo Vancheri, Antonio Basile
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4162. CrossRef
- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
- Morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: two case reports with targeted next-generation sequencing analysis
- Yoo Jin Lee, Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):119-122. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30
- 6,720 View
- 138 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Morules, or morule-like features, can be identified in benign and malignant lesions in various organs. Morular features are unusual in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with only 26 cases reported to date. Here, we describe two cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with morule-like features in Korean women. One patient had a non-mucinous-type adenocarcinoma in situ and the other had an acinarpredominant adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component. Both patients showed multiple intra-alveolar, nodular, whorled proliferative foci composed of atypical spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of the tumors. Results showed unusual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, which are associated with drug resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, revealing the importance of identifying morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and the need for additional study, since there are few reported cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Mitsuteru Yosida, Mitsuru Tomita, Naoya Kawakita, Teruki Shimizu, Ryou Yamada, Hiromitsu Takizawa, Hisanori Uehara
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2024; 48: 102008. CrossRef - Clinicopathological, Radiological, and Molecular Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma with Morule-Like Components
Li-Li Wang, Li Ding, Peng Zhao, Jing-Jing Guan, Xiao-Bin Ji, Xiao-Li Zhou, Shi-Hong Shao, Yu-Wei Zou, Wei-Wei Fu, Dong-Liang Lin, Dong Pan
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
- Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia with Mass-Formation: Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Nine Cases and Review of the Literature
- Jongmin Sim, Hyun Hee Koh, Sangjoon Choi, Jinah Chu, Tae Sung Kim, Hojoong Kim, Joungho Han
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):211-218. Published online June 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.27
- 13,782 View
- 393 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia (PNLH) is a non-neoplastic pulmonary lymphoid disorder that can be mistaken for malignancy on radiography. Herein, we present nine cases of PNLH, emphasizing clinicoradiological findings and histological features.
Methods
We analyzed radiological and clinicopathological features from the electronic medical records of nine patients (eight females and one male) diagnosed with PNLH. IgG and IgG4 immunohistochemical staining was performed in three patients.
Results
Two of the nine patients had experienced tuberculosis 40 and 30 years prior, respectively. Interestingly, none were current smokers, although two were ex-smokers. Three patients complaining of persistent cough underwent computed tomography of the chest. PNLH was incidentally discovered in five patients during examination for other reasons. The remaining patient was diagnosed with the disease following treatment for pneumonia. Imaging studies revealed consolidation or a mass-like lesion in eight patients. First impressions included invasive adenocarcinoma and mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue‒type lymphoma. Aspergillosis was suspected in the remaining patient based on radiological images. Resection was performed in all patients. Microscopically, the lesions consisted of nodular proliferation of reactive germinal centers accompanied by infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages in various degrees and surrounding fibrosis. Ultimately, all nine patients were diagnosed with PNLH and showed no evidence of recurrence on follow-up.
Conclusions
PNLH is an uncommon but distinct entity with a benign nature, and understanding the radiological and clinicopathological characteristics of PNLH is important. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Imaging Features of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Dong-Lei Nie, Yan-Hong Shi, Xin-Min Li, Xiao-Jiang Wang, Bao-Li Han, Guo-Fu Zhang
Journal of Thoracic Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathologic Findings of Pulmonary Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Yoshiaki Zaizen, Junya Fukuoka
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2025; 46(4): 272. CrossRef - Utilizing Immunoglobulin G4 Immunohistochemistry for Risk Stratification in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated with Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Faridul Haq, Gyeongsin Park, Sora Jeon, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(3): 468. CrossRef - Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia Evaluated with Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Findings: A Case Report and Review of the Literature on Japanese Patients
Sakiko Moriyama, Takashi Kido, Noriho Sakamoto, Mai Fuchigami, Takatomo Tokito, Daisuke Okuno, Takuto Miyamura, Shota Nakashima, Atsuko Hara, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Yoshitaka Imaizumi, Kazuto Tsuruda, Katsunori Yanagihara, Junya Fukuoka, Hiroshi Mukae
Internal Medicine.2023; 62(1): 95. CrossRef - A Case of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia Responding to Corticosteroid Treatment
Jonathan Teow Koon Goh, Issam Al Jajeh, Jessica Han Ying Tan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as cavitating lung mass
Aqeel Alameer, Chary Duraikannu, Avinash Kumar Kanodia, David Dorward
BMJ Case Reports.2023; 16(8): e254121. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Characteristics and Curative Effect of Lymphoma Based on Sampling Theory
Shuxiang Ding, Leipo Liu
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as multifocal subsolid nodules: A case report and literature review
Yoon Jin Cha, Duk Hwan Moon, Ji Hyun Park, Sungsoo Lee, Ji Ae Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Chul Hwan Park
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2022; 36: 101581. CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia in a 53-year-old man with malignant sign: a case report
Zhen Yang, Lianshuang Wei, Xu Li, Xin Liu
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The diagnostic challenge of adenocarcinoma in pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia
Anita Savić Vuković, Melita Kukuljan, Morana Dinter, Ksenija Jurinović, Nives Jonjić
SAGE Open Medical Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical and Imaging Features of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia
- Sclerosing Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Lung: A Case Report with Cytologic Findings
- Ha Yeon Kim, Jin Hyuk Choi, Hye Seung Lee, Yoo Jin Choi, Aeree Kim, Han Kyeom Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):238-242. Published online April 11, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.19
- 10,424 View
- 109 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Benign perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the lung is a rare benign neoplasm, a sclerosing variant of which is even rarer. We present a case of 51-year-old man who was diagnosed with benign sclerosing PEComa by percutaneous fine needle aspiration cytology and biopsy. The aspirate revealed a few cell clusters composed of bland-looking polygonal or spindle cells with fine granular or clear cytoplasm. Occasional fine vessel-like structures with surrounding hyalinized materials were seen. The patient later underwent wedge resection of the lung. The histopathological study of the resected specimen revealed sheets of polygonal cells with clear vacuolated cytoplasm, variably sized thin blood vessels, and densely hyalinized stroma. In immunohistochemical studies, reactivity of tumor cells for human melanoma black 45 and Melan-A further supported the diagnosis of benign sclerosing PEComa. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of benign sclerosing PEComa described in lung.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of pulmonary perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm
Maolin Xu, Xiaofang Guo
Asian Journal of Surgery.2026; 49(3): 1492. CrossRef - Renal sclerosing AML/PEComa in a male - A case report and literature review
Zoe Williams, Paul Kim, James Kovacic, Andrew Shepherd, Krishan Rasiah, Ankur Dhar, Kathleen Young
Urology Case Reports.2026; 65: 103326. CrossRef - Robotic Treatment of Adrenal Sclerosing PEComa: A Case Report with 13 Years of Follow-Up and a Literature Review
Alessio Paladini, Raffaele La Mura, Michele Del Zingaro, Luca Lepri, Andrea Vitale, Jessica Pagnotta, Matteo Mearini, Guido Massa, Ettore Mearini, Giovanni Cochetti
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(16): 9161. CrossRef - Cytopathology of rare gastric mesenchymal neoplasms: A series of 25 cases and review of literature
Carla Saoud, Peter B. Illei, Momin T. Siddiqui, Syed Z. Ali
Cytopathology.2023; 34(1): 15. CrossRef - Retroperitoneal Sclerosing Angiomyolipoma with Long-Term Follow up: A Case Report with Unique Clinicopathologic and Genomic Profile
Liwei Jia, Vandana Panwar, Michelle Parmley, Elena Lucas, Ivan Pedrosa, Payal Kapur
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(1): 86. CrossRef - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the lung: A case report and literature review
Shaofu Yu, Shasha Zhai, Qian Gong, Xiaoping Hu, Wenjuan Yang, Liyu Liu, Yi Kong, Lin Wu, Xingxiang Pu
Thoracic Cancer.2022; 13(17): 2542. CrossRef - Cytopathology of extra-renal perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): a series of 7 cases and review of the literature
Sintawat Wangsiricharoen, Tatianna C. Larman, Paul E. Wakely, Momin T. Siddiqui, Syed Z. Ali
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2021; 10(2): 175. CrossRef - Clear cell sugar tumour: a rare tumour of the lung
Sarah Page, Matthew S. Yong, Alka Sinha, Pankaj Saxena
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors (PEComas) of the Orbit
Panagiotis Paliogiannis, Giuseppe Palmieri, Francesco Tanda, Antonio Cossu
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(1): 7. CrossRef
- A rare case of pulmonary perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm
- Therapeutic Effects of Umbilical Cord Blood Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats
- Jae Chul Lee, Choong Ik Cha, Dong-Sik Kim, Soo Young Choe
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(6):472-480. Published online October 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.09.11
- Retraction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2016;50(4):325
- 17,079 View
- 82 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
- Indolent CD56-Positive Clonal T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of the Stomach Mimicking Lymphomatoid Gastropathy
- Mineui Hong, Won Seog Kim, Young Hyeh Ko
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):430-433. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.430
- 10,803 View
- 70 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indolent T- and Natural Killer-Cell Lymphomas and Lymphoproliferative Diseases—Entities in Evolution
Chi Sing Ng
Lymphatics.2025; 3(4): 41. CrossRef - Case Report: Primary Indolent Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease Involving the Central Nervous System
Kun Wang, Jinjian Li, Xuehui Zhou, Junhui Lv, Yirong Wang, Xinwei Li
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Indolent NK cell proliferative lesion mimicking NK/T cell lymphoma in the gallbladder
Su Hyun Hwang, Joon Seong Park, Seong Hyun Jeong, Hyunee Yim, Jae Ho Han
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2016; 5: 39. CrossRef
- Indolent T- and Natural Killer-Cell Lymphomas and Lymphoproliferative Diseases—Entities in Evolution
- Usual Interstitial Pneumonia with Lung Cancer: Clinicopathological Analysis of 43 Cases
- Dae Hyun Song, In Ho Choi, Sang Yun Ha, Kang Min Han, Jae Jun Lee, Min Eui Hong, Kyeongman Jeon, Man Pyo Chung, Jhingook Kim, Joungho Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):10-16. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.10
- 11,306 View
- 79 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Previous studies have suggested an association between usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and lung cancer (Ca). However, clinical and histological information is not enough to determine such an association, due to the low incidence and short survival time of patients with both conditions.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the clinical and histological records of Ca patients with UIP between January 1999 and August 2013 at the Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. We found 43 patients who had Ca with UIP (UIP-Ca). Previously reported data of eighty-four patients with UIP-only were included as a comparison group.
Results Smoking is related to poor prognosis in patients with UIP-Ca, and the number of patients with a high smoking index of more than 30 pack-years significantly increased in UIP-Ca patients compared with UIP-only patients. There is no significant prognostic differentiation between UIP-Ca patients and UIP-only patients. Microscopically, UIP-Ca patients showed characteristically heterogeneous histological patterns and degrees of differentiation. There were many foci of squamous metaplasia or dysplasia at the peripheral area of squamous cell carcinomas.
Conclusions We report 43 cases of UIP-Ca. Our results suggest that smoking is related to cancer occurrence in UIP patients and poor prognosis in UIP-Ca patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatable traits in interstitial lung disease: a narrative review
Megan Harrison, Chloe Lawler, Fiona Lake, Vidya Navaratnam, Caitlin Fermoyle, Yuben Moodley, Tamera J. Corte
Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Usual Interstitial Pneumonia and Lung Cancer
Lamiyae Senhaji, Meryem Karhate, Abir Bouhamdi, Mounia Serraj, Mohamed ElBiaze, Mohammed Chakib Benjelloun, Badreddine Alami, Bouchra Amara
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis without anti-fibrotic therapy: a systematic review
Yet H. Khor, Yvonne Ng, Hayley Barnes, Nicole S.L. Goh, Christine F. McDonald, Anne E. Holland
European Respiratory Review.2020; 29(157): 190158. CrossRef - Linfoma difuso de células B grandes pulmonar en paciente con neumonía intersticial no específica
Luis Gorospe Sarasúa, Paola Arrieta, Anabelle Chinea-Rodríguez, Carlos de la Puente-Bujidos
Reumatología Clínica.2019; 15(6): e151. CrossRef - Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma of the Lung in a Patient With Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia
Luis Gorospe Sarasúa, Paola Arrieta, Anabelle Chinea-Rodríguez, Carlos de la Puente-Bujidos
Reumatología Clínica (English Edition).2019; 15(6): e151. CrossRef - Characteristics of lung cancer among patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial lung disease – analysis of institutional and population data
Joo Heung Yoon, Mehdi Nouraie, Xiaoping Chen, Richard H Zou, Jacobo Sellares, Kristen L Veraldi, Jared Chiarchiaro, Kathleen Lindell, David O Wilson, Naftali Kaminski, Timothy Burns, Humberto Trejo Bittar, Samuel Yousem, Kevin Gibson, Daniel J Kass
Respiratory Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Genomic profiles of lung cancer associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Ji An Hwang, Deokhoon Kim, Sung‐Min Chun, SooHyun Bae, Joon Seon Song, Mi Young Kim, Hyun Jung Koo, Jin Woo Song, Woo Sung Kim, Jae Cheol Lee, Hyeong Ryul Kim, Chang‐Min Choi, Se Jin Jang
The Journal of Pathology.2018; 244(1): 25. CrossRef - Survival after repeated surgery for lung cancer with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a retrospective study
Seijiro Sato, Yuki Shimizu, Tatsuya Goto, Akihiko Kitahara, Terumoto Koike, Hiroyuki Ishikawa, Takehiro Watanabe, Masanori Tsuchida
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar Squamous Cell Metaplasia: Preneoplastic Lesion?
Adriana Handra-Luca
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(6): 355. CrossRef - Low expression of long noncoding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis predicts lung cancer by regulating the p53-signaling pathway
Yufeng Du, Xiaoyan Hao, Xuejun Liu
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A clinicopathological study of surgically resected lung cancer in patients with usual interstitial pneumonia
Yasutaka Watanabe, Yoshinori Kawabata, Nobuyuki Koyama, Tomohiko Ikeya, Eishin Hoshi, Noboru Takayanagi, Shinichiro Koyama
Respiratory Medicine.2017; 129: 158. CrossRef - Risk of the preoperative underestimation of tumour size of lung cancer in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
Mariko Fukui, Kazuya Takamochi, Takeshi Matsunaga, Shiaki Oh, Katsutoshi Ando, Kazuhiro Suzuki, Atsushi Arakawa, Toshimasa Uekusa, Kenji Suzuki
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.2016; 50(3): 428. CrossRef - The Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Histology and Imaging
Diane C. Strollo, Teri J. Franks, Jeffrey R. Galvin
Seminars in Roentgenology.2015; 50(1): 8. CrossRef - Do Chest Expansion Exercises Aid Re‐shaping the Diaphragm Within the First 72 Hours Following Lung Transplantation in a Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Patient?
Massimiliano Polastri, Erika Venturini, Saverio Pastore, Andrea Dell'Amore
Physiotherapy Research International.2015; 20(3): 191. CrossRef - Scrotal wall metastasis from a primary lung adenocarcinoma
Marie-Louise M. Coussa-Koniski, Pia A. Maalouf, Nehme E. Raad, Noha A. Bejjani
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2015; 15: 77. CrossRef - The Ratio KL-6 to SLX in Serum for Prediction of the Occurrence of Drug-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease in Lung Cancer Patients with Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias Receiving Chemotherapy
Kosuke Kashiwabara, Hiroshi Semba, Shinji Fujii, Shinsuke Tsumura, Ryota Aoki
Cancer Investigation.2015; 33(10): 516. CrossRef - Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis will increase the risk of lung cancer
Li Junyao, Yang Ming, Li Ping, Su Zhenzhong, Gao Peng, Zhang Jie
Chinese Medical Journal.2014; 127(17): 3142. CrossRef
- Treatable traits in interstitial lung disease: a narrative review
- Morphologic Analysis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Seung Seok Lee, Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk An, Mee Sook Roh, Chang Won Ha, Jungho Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):16-20. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.16
- 7,986 View
- 52 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Few studies on how to diagnose pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors through morphometric analysis have been reported. In this study, we measured and analyzed the characteristic parameters of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors using an image analyzer to aid in diagnosis.
Methods Sixteen cases of typical carcinoid tumor, 5 cases of atypical carcinoid tumor, 15 cases of small cell carcinoma, and 51 cases of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma were analyzed. Using an image analyzer, we measured the nuclear area, perimeter, and the major and minor axes.
Results The mean nuclear area was 0.318±0.101 µm2 in typical carcinoid tumors, 0.326±0.119 µm2 in atypical carcinoid tumors, 0.314±0.107 µm2 in small cell carcinomas, and 0.446±0.145 µm2 in large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. The mean nuclear circumference was 2.268±0.600 µm in typical carcinoid tumors, 2.408±0.680 µm in atypical carcinoid tumors, 2.158±0.438 µm in small cell carcinomas, and 3.247±1.276 µm in large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. All parameters were useful in distinguishing large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma from other tumors (p=0.001) and in particular, nuclear circumference was the most effective (p=0.001).
Conclusions Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors showed nuclear morphology differences by subtype. Therefore, evaluation of quantitative nuclear parameters improves the accuracy and reliability of diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Significance of Persistent Tumor in Bone Marrow during Treatment of High-risk Neuroblastoma
Young Bae Choi, Go Eun Bae, Na Hee Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(8): 1062. CrossRef - Morphologic Alteration of Metastatic Neuroblastic Tumor in Bone Marrow after Chemotherapy
Go Eun Bae, Yeon-Lim Suh, Ki Woong Sung, Jung-Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(5): 433. CrossRef
- Clinical Significance of Persistent Tumor in Bone Marrow during Treatment of High-risk Neuroblastoma
- Mimicry of Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules to Metastatic Deposits in a Patient with Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hala Kfoury, Maria A. Arafah, Maha M. Arafah, Sami Alnassar, Waseem Hajjar
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):87-91. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.87
- 10,398 View
- 66 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules (MPMNs) are incidentally found lesions in lung resection specimens and autopsies. MPMNs have been associated with neoplastic and non-neoplastic pulmonary conditions and occasionally with extrapulmonary diseases. We report a case of a female patient presenting with invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast and MPMNs, masquerading as metastatic deposits. We describe the morphological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural features of MPMNs and emphasize the importance of their recognition for proper staging and treatment of patients. To our knowledge, this is the first case in the English literature describing this coexistence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis with pan-TRK expression by immunohistochemistry: a novel finding and potential pitfall
Cansu Karakas, Michael A. Nead, Moises J. Velez
Diagnostic Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diffuse Pulmonary Meningotheliomatosis: Clinic-Pathologic Entity or Indolent Metastasis from Meningioma (or Both)?
Laura Melocchi, Giulio Rossi, Mirca Valli, Maria Cecilia Mengoli, Michele Mondoni, Luigi Lazzari-Agli, Giacomo Santandrea, Fabio Davoli, Chiara Baldovini, Alberto Cavazza, Thomas V. Colby
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 802. CrossRef - Pathological diagnosis and immunohistochemical analysis of minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: A case report
Xin Ruan, Liu-Sheng Wu, Zheng-Yang Fan, Qi Liu, Jun Yan, Xiao-Qiang Li
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(33): 8022. CrossRef - Benign disease prone to be misdiagnosed as malignant pulmonary nodules: Minute meningothelioid nodules
Xiao‐Xiao Peng, Li‐Xu Yan, Chao Liu, Si‐Yun Wang, Wen‐Feng Li, Xing Gao, Xue‐Wu Wei, Qing Zhou
Thoracic Cancer.2019; 10(5): 1182. CrossRef - Atypical finding of meningothelial-like inclusions in cervical lymph nodes
Rebecca Donkin, Andrew Dettrick, Penelope Wyche, Sarah Grigg
Pathology.2018; 50(7): 785. CrossRef - Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-Like Nodules Simulating Hematogenous Lung Metastasis: A Case Report
Sang Kook Lee, Gi Jeong Kim, Young Jae Kim, Ah Young Leem, Eu Dong Hwang, Se Kyu Kim, Joon Chang, Young Ae Kang, Song Yee Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2013; 75(2): 67. CrossRef - Diffuse Pulmonary Meningotheliomatosis Diagnosed by Transbronchial Lung Biopsy
Roberto Bernabeu Mora, Juan Miguel Sánchez Nieto, Chunshao Hu, Eduardo Alcaraz Mateos, Alberto Giménez Bascuñana, Manuel Rodríguez Rodríguez
Respiration.2013; 86(2): 145. CrossRef
- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis with pan-TRK expression by immunohistochemistry: a novel finding and potential pitfall
- Congenital Pulmonary Lymphangiectasia, Associated with Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return.
- Seong Wook Hwang, Mee Seon Kim, Po Eun Park, Tae In Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):650-653.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.650
- 3,882 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Congenital pulmonary lymphangiectasia (CPL) is very rare. It shows diffuse pulmonary lymphatic dilatation without lymphatic proliferation. CPL can occur as a primary disorder or arise secondarily from other diseases such as the obstruction of pulmonary veins or lymphatics. The prognosis of CPL is very poor. Approximately 50% of infants are stillborn and most others usually die within the first day of life. The present case showed diffuse lymphangiectasia in the subpleural, interlobular, and peribronchovascular areas. The flat lining cells were immunohistochemically positive for D2-40 and CD31. CPL is usually diagnosed by clinicoradiological or postmortem examinations. However, our case was diagnosed by an antemortem lung biopsy. We report a case of CPL with total anomalous pulmonary venous return.
- Pulmonary Vascular Sarcomas: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 14 Cases.
- Na Rae Kim, Jhingook Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Joungho Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):132-138.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.132
- 4,977 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Pulmonary vessel sarcomas are rare, and their pathogenesis is still unclear.
METHODS
We focus on the pathologic findings of fourteen pulmonary artery and/or vein sarcomas along with clinical prognosis.
RESULTS
Nine patients were male and five were female, and they ranged in age from 26 to 72 years (mean, 47 years). There were ten cases of pulmonary artery sarcoma, three cases of pulmonary artery and vein sarcoma, and one case of pure pulmonary vein sarcoma. Ten out of the fourteen cases were associated with pulmonary thromboembolism. Microscopically, all the tumors showed an undifferentiated sarcomatous portion. There were leiomyosarcoma portions in 8 cases, malignant fibrous histiocytomatous portions in 7 cases, angiosarcomatous differentiation in 3 cases, and osteosarcomatous portion in 1 case. All but two patients died during the follow up period (range, 1 to 78 months). The mean survival time of the patients who died was 14 months and the longest survival time was 78 months after surgical resection.
CONCLUSIONS
The current study is one of the largest single institutional reviews of pulmonary artery and/or vein sarcoma. Regardless of the histological components and macroscopic growth patterns, these rare tumors have a grave prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Therapeutic Use of Bee Venom and Potential Applications in Veterinary Medicine
Roberto Bava, Fabio Castagna, Vincenzo Musella, Carmine Lupia, Ernesto Palma, Domenico Britti
Veterinary Sciences.2023; 10(2): 119. CrossRef - Intimal Sarcoma of the Great Vessels
Alan M. Ropp, Allen P. Burke, Seth J. Kligerman, Jay S. Leb, Aletta A. Frazier
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(2): 361. CrossRef - Incidence of pulmonary non-epithelial tumors: 18 years’ experience at a single institute
In Ho Choi, Dae Hyun Song, Kang Min Han, Yong Soo Choi, Joungho Han
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(4): 210. CrossRef - Pleomorphic Malignant Histiocytoma of Pulmonary Arteries Presenting as Pulmonary Aneurysms
Gustavo Armando De La Cerda Belmont, Carlos Alberto Lezama Urtecho
The Annals of Thoracic Surgery.2013; 95(3): 1091. CrossRef
- Therapeutic Use of Bee Venom and Potential Applications in Veterinary Medicine
- Complex Bronchopulmonary Foregut Malformation: Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration Communicating with an Esophageal Duplication Cyst: A Case Report.
- Soyoung Im, Sun Mi Lee, Ji Han Jung, Jinyoung Yoo, Kyu Do Cho, Seok Jin Kang, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):207-210.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.207
- 4,592 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a case of a rare, complex bronchopulmonary foregut malformation (BPFM) that was composed of an extralobar pulmonary sequestration communicating with an esophageal duplication cyst. A 33-year-old female presented with an incidentally detected chest mass. The computed tomography revealed a 7.5 x 4.0 cm sized heterogeneous, solid and cystic lesion in the right superior mediastinum. Surgical resection demonstrated the solid portion to be isolated lung tissue invested in its own pleura. A unilocular cyst was communicating with the bronchus of the sequestrated lung, and microscopically the cyst was lined by squamous epithelium overlying the thick layers of smooth muscle. This case is important for understanding the spectrum of BPFMs and for differentiating a mediastinal mass, especially one at the unusual location.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prenatal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and therapeutic options for fetal thoracic anomalies: a pictorial essay
Pablo Caro-Domínguez, Teresa Victoria, Pierluigi Ciet, Estrella de la Torre, Ángel Chimenea Toscano, Lutgardo García Diaz, José Antonio Sainz-Bueno
Pediatric Radiology.2023; 53(10): 2106. CrossRef - Concurrent bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: a rare case of right-sided extralobar pulmonary sequestration and bronchogenic cyst
Carolyn Hanna, Priya G. Sharma, Moiz M. Mustafa, Jennifer Reppucci, Archana Shenoy, Dhanashree Rajderkar
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prenatal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and therapeutic options for fetal thoracic anomalies: a pictorial essay
- eNOS Gene Polymorphisms in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy.
- Min Cho, Kwang Sun Hyun, David Chanwook Chung, In Young Choi, Myeung Ju Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):306-311.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.306
- Retraction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2019;53(5):345
- 65,535 View
- 15,434 Download
- 1 Crossref
- A Morphological Study of the Pulmonary Endothelium and Neuroendocrine Cells in Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
- Woo Ick Yang, Sang Ho Cho, In Joon Choi, Yoo Bock Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(6):582-592.
- 1,884 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To investigate the mechanism of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension, authors performed immunohistochemical study using antibody to von Willebrand factor(vWF), cell kinetic study using 5-bromodeoxyuridine and ultrastructural study after single subcutaneous injection of monocrotaline(MCT) to Wistar rats. The results of this study demonstrated that the expression of vWF by pulmonary endothelial cells was markedly increased from day 3 until 2 months after MCT injection. The labeling index of pulmonary microvessel endothelium began to increase after six days and was maximal on the third weeks, and thereafter it remained slightly increased above basal level. Electron microscopic study revealed attachment of inflammatory cells an platelets to endothelium from 6 hours and degranulation of attached platelets 24 hours after MCT injection. Evidences of endothelial injury began to appear from 12 hours after MCT injection. Evidences of endothelial injury began to appear from 12 hours and was maximal after 48 hours. From the third day, ultrastructural change of cell regeneration and hypertrophy began to appear and was continuosly observed until 2 months. In addition, we evaluated the changes in the number of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells using antibody to gastrin releasing peptide but it demonstrated no change until 2 months suggesting no role of neuroendocrine cells in the development of pulmonary hypertension of Wistar rats at early stage. In conclusion, the results indicate that pulmonary hypertension by MCT injection is due to increased vascular resistance caused by vasoconstriction and hyperplasia of endothelium with musculariz ation of the pulmonary arterioles induced by endothelial dysfunction and some biologic substances released form endothelium and platelets.
- Pulmonary Blastoma with Rhabdomyoblastic Differentiation: A case report with immunohistochemical and electron microscopic examination.
- Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(6):620-626.
- 2,209 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary blastoma is a rare lung tumor composed of epithelial and mesenchymal element : the latter element may show various pattern of differentiation toward mature tissue, such as cartilage, smooth muscle, and bone. Rhabdomyoblastic differentiation in pulmonary blastoma is quire rare. In th literature, only seven cases have been reported. We report a case of pulmonary blastoma with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation which occured in a 3 year old girl. Microscopically, cytoplasmic cross-striation was present. Immunohistochemically, strong positivity for vimentin and desmin was observed. Electron microscopy demonstrated A and I bands which documented rhabdomyoblastic differentiation.
- Mucous Gland Adenoma Presenting as a Peripheral Lung Mass: A Brief Case Report.
- Ji Eun Kwon, Gou Young Kim, Joungho Han, Tae Sung Kim, Kwanmien Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(2):126-128.
- 2,247 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mucous gland adenoma (MGA) of the lung is an uncommon, benign tumor that histologically resembles the mucus-secreting component of the tracheobronchial gland. The majority arises within the main, lobar or segmental bronchi. MGA presenting as a peripheral lung mass is extremely rare. We herein report a case of MGA that uniquely arose from the peripheral territory of the superior segmental bronchus of the left lower lobe in a 73-year-old male. Chest computed tomography showed a 13 mm-sized, subpleural nodule, which was easily enucleated by video-assisted thoracotomy. The mass was round and gray-tan in color with mucoid material. The tumor was composed of cysts, tubules, and glands lined by bland columnar, cuboidal or flattened, mucus secreting cells.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pulmonary Hamartoma: 3 cases.
- Na Hye Myong, Kyung Ja Cho, Ja June Jang
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(3):355-358.
- 2,230 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine needle aspiration cytology of three cases of pulmonary hamartoma is presented. Case 1 was in a 67-year-old man with a 7 cm-sized left lung mass. Case 2 and 3 were in 47 and 53 year old females and consisted of 3 cm and 2 cm-sized right lung nodules, respectively. Fine needle aspiration of the masses revealed several fragments of irregularly shaped mature hyaline cartilage or fibromyxoid mesenchyme and sheets of benign epithelial cells in scanty to acellular background. Also scattered were inflammatory cells including lymphocytes, neutrophils and histiocytes and mature fat cells. These features were diagnostic for pulmonary hamartoma and case 1 was histologically confirmed by following surgical excision of the mass. Differential diagnoses about pulmonary hamartoma in the respect of conditions capable of producing cartilage on fine needle aspiration, were discussed.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pulmonary Carcinosarcoma.
- Tae Jung Jang, Kwang Gil Lee, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1990;1(2):164-169.
- 2,620 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Carcinosarcoma is an uncommon pulmonary malignancy characterized by carcinomatous parenchyma and sarcomatous stroma. The cytologic, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural features of a case of pulmonary carcinosarcoma suspected by fine needle aspiration cytology is presented. Only bizarre spindle cells arranged in loose groups, in microtissue fragments and in a dissociate fashion were present in the aspiration smears. They were markedly positive for vimentin. The epithelial component was not found, which was probably due to marked paucity of carcinomatous component that was proved by histologic examination of the resected tumor. The diagnosis of pulmonary carcinosarcoma should be considered whenever poorly differentiated epithelial cell groups with a malignant mesenchymal component set in a myxoid background are seen in a pulmonary cytology specimen.
- Transthoracic Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: Review of 213 cases.
- Kyung Ja Cho, Na Hye Myong, Ja June Jang, Soo Yil Chin, Ki Hwan Kim, Hong Sik Byun, Duk Lim
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(4):455-460.
- 2,139 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A total of 213 fine needle aspirations from pulmonary lesions in 193 patients performed from January, 1986 to March, 1989 were analyzed. The cytologic diagnoses were unsatisfactory in 10, negative in 60, atypical in 6, suspicious in 11 and malignant in 126 cases. The cytologic types of the malignant cases were 47 squamous cell carcinomas, 40 adenocarcinomas, 10 small cell carcinomas, 6 large cell carcinomas and 10 metastatic tumors. They were verified by the histologic confirmation in 31 cases and by the clinical data in the remainder. There were 5 false-negative cases and none was false-positive, representing 96% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Primary lung cancers were accurately typed in 73% of histologically confirmed case. Cell blocks, prepared in 99 cases, were helpful in tumor typing of 11 cases.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pulmonary Hamartoma.
- Tae Jin Lee, Jin Sook Lee, Gyung Yub Gong, Shin Kwang Khang, Jae Y Ro
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2000;11(1):19-24.
- 2,285 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary hamartomas are uncommon benign tumors, usually discovered radiologically as a solitary coin lesion in asymptomatic individual. The approach to the patient with a peripheral lung nodule has changed with the increasing acceptance of fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC) as a rapid, safe, inexpensive, and highly accurate diagnostic tool. However, a few reports describing the FNAC findings of pulmonary hamartoma have appeared in the cytologic literature and the experience of FNAC is limited. We reviewed all 9 cases of pulmonary hamartoma with histologic confirmation after FNAC seen at Asan Medical Center since 1995 to evaluate cytologic findings and to determine the value of FNAC in identifying that lesion. Originally, seven of nine patients were diagnosed as pulmonary hamartoma, while two patients were diagnosed as inflammatory lesion and adenocarcinoma of each. On review, eight of nine patients were considered as diagnostic of pulmonary hamartoma. The diagnostic findings in FNAC of pulmonary hamartoma were the presence of fibrillary myxoid tissue with spindle cells as well as hyaline cartilage.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pulmonary Hamartoma: A Report of Two Cases.
- Jeana Kim, Kyoung Mee Kim, Young Sill Kim, An hi Lee, Sang In Shim, Byung Kee Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2000;11(1):31-34.
- 2,283 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary hamartoma is an uncommon benign tumor consisting of a mixture of loose fibromyxoid tissue, cartilage, fat, and cleft-like spaces lined by cuboidal or ciliated epithelium. Cytologically, the presence of a mesenchymal component is essential for the diagnosis of pulmonary hamartoma. We report the fine needle aspiration cytologic findings of two cases of pulmonary hamartoma. Case 1 was a 71-year-old woman with a mass, measuring 1.8X1.5 cm in the upper lobe of the right lung. Case 2 was a 51-year-old woman with a mass, measuring 2.3 x 2.0 cm in the lower lobe of the right lung. Fine needle aspiration cytology of both pulmonary masses revealed several sheets of loose fibromyxoid tissue fragments with focal cartilaginous differentiation and a few clusters of bland cuboidal epithelial cells on the bloody background. The diagnosis was histologically confirmed by needle biopsy.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Primary Pulmonary Amyloidosis: A Case Report .
- Hyuni Cho, Seung Yeon Ha, Young Ha Oh, Seong Hwan Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2000;11(2):99-102.
- 2,191 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary amyloid deposition generally occurs with concurrent primary systemic amyloidosis. Localized forms of pulmonary amyloidosis are rare and appear most frequently as an incidental finding on chest radiographs. We present a case of nodular pulmonary amyloid tumor suggested by fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) and confirmed by histologic examination with the polarizing light microscopy. A 41-year-old woman presented with ill-defined nodules in the middle and lower lobes of both lungs. FNAC of the nodules revealed waxy, acellular amorphous fragments. Thoracotomy for diagnosis may be avoided by FNAC diagnosis of this unusual lesion.
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: A Case Report with Diagnostic Features in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Specimen .
- Seung Yeon Ha, Hyuni Cho, Young Ha Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2000;11(2):103-108.
- 2,369 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis(PAP) is a rare disease in which the alveolar spaces are filled with an eosinophilic, PAS-positive material, whereas the interstitial architecture of the lung usually remains unaffected. Although a definitive diagnosis is usually made by an open lung biopsy, bronchoalveolar lavage(BAL) cytology may play a decisive role in the diagnosis and therapy of these patients and may spare a patient a more invasive diagnostic procedure. The author presents a patient in whom BAL cytology specimen contained the characteristic globules of amorphous proteinaceous PAS-positive material accompanied by background of rare macrophages and inflammatory cells. Ultrastructural study using BAL specimen can confirm the diagnosis of PAP.
- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study on Microvascular Changes in the Monocrotaline-induced Rat Lung by Corrosion Casting Method.
- Na Hye Myong, Eui Keun Ham
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):644-659.
- 1,990 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- To investigate the microvascular changes in primary pulmonary hypertension, the lungs of 24 Sprague-Dawley rats were treated by an intraperitoneal injection of 2% monocrotaline(MCT) solution and then examined with scanning electron microscopy(SEM) after microvascular corrosion casting. Histologic examination revealed significant medial thickening in the small to medium-sized pulmonary arteries. Scanning electron microscopic findings of the normal lungs showed two kinds of microvascular structures. One showed a well-fortned three-dimensional basket structure of uniform flat-tubular alveolar capillaries, which were connected to each other in a T or Y shape or at right angles. The other revealed a two-dimensional reticular sheet of round tubular branches mainly in the bronchial artery-supplying regions. The MCT-treated groups(remodelling) showed apparent changes in both kinds of microvasculatures in comparison to the normal group but the more prominent change was found in Lbe bronchial artery microvasculature showing the dense thick encasement around large pulmonary arteries. Alveolar microvasculature of the pulmonary artery revealed individually enlarged angular appearance, with generally deformed alveolar architecture. Quantitatively, the significant enlargement of diameter and intercapillary distance appeared in both microvasculatures of MCT-induced rat lungs, but the density was increased only in the bronchial artery microvasculature. In conclusion, our three-dimensional microvascular study of the MCT-treated rat lungs demonstrates a new morphologic finding of vascular remodeling in primary puhnonary hypertension, which is thought to play an important vascular role in the pathogenesis in addition to interstitial fibrosis.
- Primary Pulmonary Glomus Tumor, Diagnosed by Preoperative Needle Biopsy: Report of One Case and Literature Review.
- Mi Jin Kim, Woo Jung Sung
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):37-40.
- 2,159 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Glomus tumors commonly occur in dermal and subcutaneous tissue in the subungal region of a finger. Some glomus tumors occur extracutaneously, including lung. Only 15 cases of primary pulmonary glomus tumor have been described in literature. In this report, we describe a case of primary pulmonary glomus tumor, which is the first case diagnosed before surgical resection. A 51-year-old man underwent a needle biopsy of a well defined coin-like mass in left lower lobe of the lung on chest radiography. Microscopic examination revealed a tumor composed of perivascularly arranged round to ovoid epithelioid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Tumor cells are immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin and vimentin, but negative for desmin, cytokeratin (AE1/AE3), chromogranin, or synaptophysin. A diagnosis of glomus tumor was then made. The lung mass was resected by wedge resection after being diagnosed by preoperative lung needle biopsy. Although primary pulmonary glomus tumor is rare, most cases follows a benign course. For proper treatment of the patient, glomus tumor should be considered as a differential diagnosis of solitary lung mass.
- Malignant Small Cell Tumor of the Thoracopulmonary Region (Askin Tumor): Report of a case.
- Young Im Han, Hye Jin Lee, Kang Suek Suh, Sun Kyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):687-690.
- 2,199 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Malignant small cell tumor(MSCT) of the thoracopulmonary region(Askin tumor) is extremely rare and is seen predominantly in children and adolescents. This tumor represents a distinct clinicopathologic entity of neuroectodertnal origin, arising from the soft tissues of the chest wall or peripheral lung. This tumor tends to recur locally, but does not seem to disseminate widely. The overall survival is poor. Recently, we experienced a case of the MSCT of the thoracopulmonary region of a 12-year-old female. She was admitted because of a chest wall mass on radiographic examination, and a complaint of intermittent chest pain. Grossly, the mass was lobulated, round and had a solid appearance with focal necrosis and hemorrhage on the cut surface. Histologically, small round to oval cells were arranged in compact sheets, nests and lobular patterns with intervening fibrovascular stroma. Ultrastructurally, the presence of loose-fitting membrane-bound neurosecretory granules was noted.
- Imprint Cytologic Feature of Pleuropulmonary Blastoma: A Case Report .
- Mee Sook Roh, Ji Young Seo, Gi Yeong Huh, Pill Jo Choi, Sook Hee Hong, Jin Sook Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2001;12(1):39-43.
- 1,890 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB) is an unusual intrathoracic blastoma presenting in childhood and characterized by a biphasic neoplastic population of undifferentiated, small round blastemal cells and larger spindle-shaped sarcomatous cells with entrapped benign epithelial-lined structures. We experienced the cytologic features of PPB in imprint smear from the pleural-based huge mass of the middle lobe of the right lung in a 4-year-old boy. The smears showed high cellularity composed of small ovoid blastemal elements and scattered spindle mesenchymal tumor cells. Lobectomy and pathologic investigation confirmed the diagnosis. PPB seems to be a tumor in which accurate diagnosis may be achieved by cytology if appropriate clinical information were given. Timely and accurate diagnosis of PPB by cytology paves the way for attempting preoperative treatment in future cases.
- IgA Nephropathy Associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis.
- Mi Kyung Kim, Hyun Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(3):215-226.
- 2,208 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There have been a few reports suggesting that the imune response to pulmonary tuberculosis provides the appropriate setting for the development of IgA nephropathy (IgAN). To define better the relation between pulmonary tuberculosis and IgAN, we evaluated the prevalence of pulmonary tuberculosis among 386 Korean patients with IgAN. Seventeen cases (4.4%) showed abnormal chest X-ray findings suggestive of pulmonary tuberculosis. Ten patients were male and seven were female. Only one case was a child. Urinary abnormalities were detected during the course of antituberculous medication in 11 patients, and after completion of chemotherapy in 2. Chest abnormalities were noted in the remaining 4 patient after IgAN had been diagnosed. Clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis was made mainly based on the chest X-ray findings, but sputum Acid-Fast Bacilli were detected in one patient and pulmonary granulomo was noted in 2. The patients presented various clinical manifestations such as gross hematuris (5 cases), nephrotic syndrome (5 cases), asymptomatic urinary abnormalities (4 cases) and pyuris (1 case) at time of biopsy. Histologic grading of the glomerular lesions was made with modified Meadow classification (1972): one had grade I lesion, 8 grade II, 5 GRADE III and 3 showed grade IV. Follow-up studies were made in 7 patients. Six showed resolution of urinary abnormalities after completion f antituberculous medication, while one pursued chronic renal failure 20 days after the onset. The above clinical and morphologic features suggest that pulmonary tuberculosis may be partly related to the occurrence of IgAN in some Korean patients.
- Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma of Fetal Type: Report of a case.
- Nam Hoon Cho, Kwang Gil Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(3):287-293.
- 2,299 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary adenocarcinoma of fetal type is a very uncommon tumor of the lung which simulates an early stage of lung differentiation. This is a primitive appearing epithelial tumor similar to the epithelial component of pulmonary blastoma but lacking the sarcomatous features. Since the report of Kradin et al, 8 more cases have been reported by a variety of name. These tumors are composed of glycogen-rich, non-ciliated tubular epithelial cells forming irregularly shaped tubules or arranged in a papillary pattern. A very remarkable findings of this tumor is the presence of endocrine cells which is confirmed by argyrophilia, immunohistochemistry or electron microscopy. We experienced a case of this tumor which showed hepatocytoid differentiation in addition to the characteristic histologic findings. Immunohistochemical studies performed on a resected tumor tissue showed immunoreactivity for alpha-fetoprotein, neuron-specific enolase and somatostatin, and endocrine type granules were found ultrastructurally. Although this tumor seems to have a relation with pulmonary blastoma in its histology, immunohistochemistry and ontogeny, a distinction between these should be attained because the average survival of the former group is longer as 23 months, while that of the latter is only 4 months.
- Congenital Bronchopulmonary Foregut Malformation: Analysis of the surgical and autopsy cases.
- Sung Hye Park, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(5):459-467.
- 2,137 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Because early embryonic development of the tracheobronchial tree and foregut are closely associated, there is a wide spectrum of congenital anomalies involving either one or both organ systems. We analysed a total of 89 surgical and autopsy cases that are assumed to belong to congenital bronchopulmonary foregut malformation from the files of Seoul National University Hospital and Children's Hospital during the periord of 1961~1990. We also reviewed the serial sections of the embryos and fetuses from 3 weeks to fifteen weeks fertilization age for the observation of tracheobronchial and esophageal trees. Intralobar sequestrations(25 cases) and extralobar pulmonary sequestrations(4 cases) with patent, involuted-partial or complete-communication with the alimentary tract, tracheoesophageal fistula(30 cases) with or without esophageal atresia, esophageal atresia, esophageal stenosis due to tracheobroncheal remnant(4 cases), foregut duplication cysts(3 cases), esophageal or gastric diverticulum(1 cases), and bronchogenic cysts(22 cases) are included in this analysis(Table 1). Through this study, we confirmed the unifying concept of "bronchopulmonary forgut malformations". We believe a common embryologic pathogenesis leads to the formation of a previously described spectrum of malformations.
- Expression of TGF-beta and PDGF in Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats.
- Min Sun Cho, Sang Ho Cho, Woo Ick Yang, Woon Sup Han
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(8):545-554.
- 2,239 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary vascular hypertension is characterized by migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells accompanying abnormal synthesis and accumulation of extracellular proteins in vascular wall. The aim of this study is to define the role of endogneous TGF-betas and PDGF in the process of remodeling vessels through determining the temporal and spatial distribution of these growth factors in hypertensive pulmonary vessels in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rat. Sprague-Dawley rats were sacrificed 12 hours, 1, 2, 4, 7, 10, 14, 21, 28, and 56 days after treatment. The morphometric analysis of medial thickening and immunohistochemical study using antibodies to TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, TGF-beta3, and PDGF were performed. Immunoreactivities for TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3 were increased from the 14th day in the medial smooth muscle cells and PDGF showed increased expression from the 21st day in the medial smooth muscle cells. No difference in TGF-beta2 immunoreactivity was found between control and experimental groups. The expression of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta3 and PDGF increased in medial layers with the progressive thickening of pulmonary arteries which was considered to have close relation to medial hypertrophy of pulmonary arterioles. In the case of PDGF, however, the morphologic change occurred before increase in immunoreactivity was observed in the medial layer of pulmonary arterioles. Moreover, the function of isoforms of TGF-beta has yet to be completely elucidated; the different affinity to receptors and the degree of expression of these receptors that are supposed to affect the function of growth factors. Thus, further studies are needed.
- Unilateral Pulmonary Agenesis Combined with other Unusual Anomalies: An autopsy report.
- Ik Su Kim, Sang Han Lee, In Soo Shu
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(2):166-168.
- 1,956 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary agenesis is a very rare anomaly. It is defined as total absence of the pulmonary parenchyma, vascular structures, and bronchi beyond the carina. We experienced a case of right pulmonary agenesis in association with other congenital defects who died at 1 day of age. The other defects included: esophageal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula, cardiac malformation, anal atresia and a malformed left thumb. The cardiac malformations were a type of Pentalogy of Fallot, composed of right ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular septal defect, an overiding of aorta, pulmonary atresia, and an atrial septal defect. Hand roentgenograms of the malformed left thumb showed an unarticulated metacarpopharyngeal joint. This unique combination of anomalies is extremely rare.
- Placental Transmogrification of the Lung: A Brief Case Report.
- Eun Su Park, Joungho Han, Won Jung Koh, Kyung Soo Lee, Jhingook Kim, Jinwon Seo, Jiyoung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(5):308-310.
- 2,562 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Placental transmogrification (PT) is an unusual condition in which the alveoli develop a peculiar villous configuration that resembles the placental villi. We report a rare case of pulmonary PT in a 46-year-old man who presented with multiple cystic lesions and nodules on radiography. The patient was treated with a surgical excision. The cut surface of the lung lesion had a villous spongiform manifestation with a partly yellow granular appearance. Microscopically, multiple papillary cores mimicking the villous structures of the placenta were observed within the bullous airspaces. These papillary cores contained many vascular structures, lymphoid aggregates, interstitial clear cells, mature fat and dystrophic calcification. This case was solitary and not associated with other pulmonary or systemic diseases. The etiology is unknown, and further studies will be needed to understand the pathogenesis of the lesion.
- A Case Report of Pleuropulmonary Blastoma in Childhood.
- Hye Rim Park, Jin Hee Sohn, Ki Woo Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(4):351-354.
- 2,092 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Classic pulmonary blastoma is a variant of carcinosarcoma which is seen almost exclusively in adults. By contrast, most cases of pulmonary blastoma in children have been described as having an exclusive mesenchymal composition, which was proposed as pleuropulmonary blastoma. Recently we experienced a case of pleuropulmonary blastoma, type 1. This 27-month-old male baby was transferred to our hospital due to the left tension pneumothorax. Chest CT revealed a subpleural pulmonary cystic lesion on the left upper lung and an open cystectomy was performed. Histologically the lesion was composed of variable-sized cystic structures lined with a single layer of respiratory-type epithelium. the underlying stroma was composed of sheets of small, round to oval, primitive tumor cells. Some of them had eccentric, eosinophilic cytoplasm, suggestive of rhabdomyoblastic differentiation. These rhabdomyoblastic cells were fuchsinophilic and positive with desmin and vimentin on immunohistochemistry.
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: A case report.
- Chang Ho Cho, Yoon Kyung Sohn, Jyung Sik Kwak, Jung Yoon Choi, Won Sik Lee, Tae Hoon Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(3):263-268.
- 2,041 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A case of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is reported. Most of the alveolar spaces were filled with amorphous deep eosinohilic material which revealed strong positive reaction to periodic acid-Schiff staining. Electron microscopic observation of this material showed numerous lamellar bodies in the alveolar spaces and cytoplasms of alveolar macrophages. A part of them were concentric multilamellated type A lamellar bodies and the other were finger printlike type B bodies. Combined type A and type B lamellar bodies were rarely present. From the above features it is suggested that both type A and B lamellar bodies could be transformed one another and those lamellar bodies may be originated from pulmonary surfactant.
- Pulmonary Cavernous Hemangioma: A case report.
- Seung Yeon Ha, Sang Ae Yoon, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(2):203-205.
- 2,256 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pulmonary cavernous hemangioma is usually from birth and there may be without symptoms until adulthood. Larger or multiple pulmonary angiomata with considerable pulmonary arteriovenous shunts may cause cyanosis, finger clubbing, dyspnea and frequently accompanyingbruit. Recently, we experienced a case of cavernous hemangioma of the lung. A 34-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital for surgical evaluation of a 4 cm solitary, round nodule in the right upper lobe on the chest X-ray and CT scan. She had no symptoms. Laboratory findings are within normal limits except for elevated glucose levels. At surgery, the mass was well encapsulated and easily excised from the peripheral portion of the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. Grossly, it consisted of a 4 cm in diameter, round, soft, sponge-like, hemorrhagic, slightly lobulated mass with a smooth external surface. Microscopically, the mass was composed of vessels, which were thin walled, dilated and filled with blood. The wall of the abnormal vessels was thin and composed of endothelium and fibrous connective tissue with only a little smooth muscle. Immunohistochemically, the wall of the dilated abnormal vessesls showed negative reaction for cytokeratin(low and high) and epithelial membrane antigen but weakly positive reaction for UEA-1 in focal areas.
- A Cytopathologic Analysis of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Lung: A Six-year Correlation Study in 322 Cases.
- Sook Kim, Dong Won Kim, So Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1995;6(2):140-147.
- 1,834 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In a six-year period (from May 1988 to April 1994), fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of 322 pulmonary lesions from 296 patients were performed at Soonchunhyang University Hospital. Of these 322, malignancy was diagnosed cytologically in 139 (43.2%), suspicious malignancy in 7 (2.2%), negative in 164 (50.8%), and insufficient material in 12 (3.8%). Malignant lesion consisted of 54 cases of adenocarcinoma, 50 cases of squamous cell carcinoma, 18 cases of small cell carcinoma. They were verified by histologic confirmation in 70 cases. There were 2 (0.6%) false positive cases due to florid bronchoalveolar hyperplasia and atypical bronchial epithelial cells associated with granulomatous lesion. Overall accuracy rate was 90%, the sensitivity 84.3% and the specificity 94.7%.
- Plexogenic Pulmonary Arteriopathy in Congenital Heart Disease: A Report of Two Cases.
- Seung Yeon Ha, Kook Yang Park, Hyun Yee Cho, Young Ha Oh, Jae Gul Chung, Dong Hae Chung, Chung Yeul Kim, Han Kyeom Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(6):412-415.
- 2,285 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease can develop in those cases of congenital cardiac shunt in which critical levels of pulmonary artery pressure and flow are reached and exceeded. We have experienced two cases of plexogenic arteriopathy in complex congenital heart disease and tried to evaluate of distribution of arterial lesions by total mapping of the explanted lung. Case 1 and 2 were 12-year-old boy and 36 year-old man. They were treated with combined heart-lung transplantation. Mapping of the both lungs was done, and graded according to Heath and Edward's grading scheme. The elastic pulmonary artery was tortuous, dilated and aortic configuration. Both lungs showed mostly grade 3. Plexiform lesion or veinlike branches of hypertrophied muscular arteries arosed in a lateral branch of a muscular artery that might be proximal to an area of occlusion. Comprising the right and left lung, the right was more severe than the left. By getting closer to the distal part, the grade tended to increase to 4 to 5. By analyzing the pulmonary lobe, severe pulmonary hypertension of grade 4 or 5 was comparatively disseminated throughout the right lung. On the other hand, in the left lung, the grade of the lower lobe was higher than that of the upper lobe, and within the upper lobe, there was a tendency for the grade of inferior segment to be higher than that of the corresponding apical segment.
- Four Cases of Intrapulmonary Hamartoma: An ultrastructural study.
- Ho Jong Chun, Keun Hong Kee, Chae Hong Suh, Jang Sihn Sohn, Chung Hee Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(1):70-81.
- 1,929 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tumors of the lung and bronchi containing cartilage were known by a variety of names, chondroma, adenochondroma, chondromatous hamartoma and mixed tumor. This variation in nomenclatures explain the difference of illustration on the nature of these tumor. The concept pulmonary harmatomas are benign neoplasm and not developmental malformations, has gained wide acceptance in recent years. We have experienced four cases of intrapulmonary hamartoma which were all discovered during routine chest film check up for certificate of health and evaluation of other disease. One case is added further detailed histologic examination by electron microscopy. The age at time of the detection were 53 (male), 23 (male), 39 (female), and 56 (female) years old. The mean size is 4.3x3.7x3.4 cm. The locations were three left upper lobes and one right upper lobe. Lobectomy and wedge resecions were done. Cut surface showed promiment lobular structures, papillary configuration and multiple cleft like spaces. Predominant cellular components were cartilage but fat tissue in one of the four cases. Microscopic findings showed abundant hyaline cartilages bearing lobular configuration and overlying pseudostratified ciliated columnar and cuboidal epithelium. Fibromyxoid and undifferentiated cells were seen in myxoid and fatty tissue. Electron microscopic findings revealed stellate, undifferentiated mesenchymal cells bearing collagen formation, stellate smooth muscle and transition areas between undifferentiated mesenchymal cells and mature cartilage. Epithelial components were similar to terminal bronchiole and alveolar epithelium. These findings suggest the concept that intrapulmonary hamartoma represent a histologic specturm of benign mesenchymal neoplasms, which originate in peribronchial connective tissue.
- Pulmonary Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Pathologic Analysis of Eight Korean Cases.
- Seung Sook Lee, Jeong Wook Seo, Eul Keun Ham, Yong Il Kim, Nam Hee Won, Jung Gi Im, Young Soo Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(4):358-367.
- 2,026 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histopathology of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis(LAM) is studied using four new cases and six previously reported cases, which include two cases without definite evidence of LAM. The important diagnostic features of this lesion were nodular proliferation of immature smooth muscle and cleft or cyst formation within the nodules of smooth muscle cells. The nuclei of the smooth muscle cells were bigger than those of blood vessels or fibrotic lung, and the direction of nuclei was irregular. The lung parenchyma showed little inflammatory change but there were multiple air cysts with smooth muscle nodules at their margin. There were two cases with exuberant proliferation of smooth muscle nodules and two cases with papilliferous projections of the cells into lymphatic lumen. Whereas, three cases had only a few small slender nodules of smooth muscle cells at the margin of air cyst. The lymphatic lumen with smooth muscle nodules is dilated in four cases but other four cases show collapsed lumen. Pulmonary hemorrhage and hemosiderosis were prominent in three cases. There were variety of histology in terms of the cellularity of smooth muscle nodules, the size of the lymphatic lumen and the degree of pulmonary destruction, which may have significance on the clinical presentation and prognostication.
- An Ultrastructural Study of Bleomycin-Induced Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Rat.
- Seung Che Cho, Kwan Kyu Park, Kun Young Kwon, Eun Sook Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(6):539-550.
- 2,266 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was carried out to investigate the mechanisms of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis of rats after the intratracheal administration of bleomycin. Both lungs after bleomycin injection were examined by light and electron microscopy. The results are as follows: Light microscopically, 1 or 2 weeks after bleomycin injection acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrates and edema in the interstitium and alveolar spaces were observed. Proliferation of alveolar type II pneumocytes was also found at 4 to 6 weeks after bleomycin injection, chronic inflammatory infiltrates with interstitial fibrous thickening were noted. Electron microscopically, the number of type II pneumocytes and irregular lamellar bodies were increased and blunted microvilli were noted at 2 weeks. 4 to 8 weeks, proliferation of fibroblasts with deposition of abundant collagen fibrils in the thickened interstitium revealing irregular or collapsed alveolar spaces were observed. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary fibrosis is considered to pass from an early acute inflammation of the interstitium and alveolar spaces to an interstitial fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition to the length of the period after injection.
- Intrauterine Infection as a Cause of the Neonatal Pulmonary Injury and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.
- Jin Haeng Chung, Jeong Wook Seo
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(6):431-436.
- 1,920 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pathogenetic role of intrauterine infection to the neonatal pulmonary injury and bronchopulmonary dysplasia was assessed by studying the interleukin-6 (IL-6) level in the umbilical cord blood and the early morphologic changes of the neonatal lung. Patients were grouped into bronchopulmonary dysplasia (4 cases), chorioamnionitis without chronic lung injury (4 cases), and 6 cases without morphologic evidence of chronic lung injury or placental inflammation. IL-6 level of umbilical cord blood was higher in babies with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (17.7 pg/ml) compared to those with chorioamnionitis (4.7 pg/ml) or those with morphologically normal lung and placenta (6.2 pg/ml). Morphologic parameters of neonatal pulmonary injury were hyaline membrane, terminal bronchiole inflammation, terminal bronchiole regeneration, alveolar collapse and fibroblastic proliferation. Bronchiolar regeneration was the most peculiar feature seen in the lung with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Alveolar collapse and interstitial fibroblastic reaction were commonly seen in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The postnatal age at death was higher in those with bronchopulmonary dysplasia, although the occurrence of the morphologic changes was related with the chronicity of those lesions. These findings suggest that intrauterine infection is an aggravating factor for the neonatal pulmonary injury and bronchopulmonary dysplasia, although the early stage of the lung injury is not a definitive indicator for the progressive pulmonary damage leading to the bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis accompanied by Osseous Metaplasia: A case report.
- Ae Ree Kim, Hyun I Cho, Han Kyeom Kim, Jong Sang Choi, In Sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(5):547-549.
- 1,901 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors experienced a case of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A 58-year-old woman presented with 6 months duration of cough sputum and multiple patch mottled densities in both lung fields. Major histologic finding was filling of the alveoli by Periodic-Acid-Schiff-positive proteinaceous material with maintenance of normal alveolar architecture. Osseous metaplasia was seen in the alveolar space, focally. Ultrastructural study revealed numerous lamellar bodies in alveolar spaces. The immunohistochemical study using antibody to surfactant apoprotein revealed positive reaction in proteinaceous material.
- Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma of Fetal Type: Report of a case.
- Soon Bong Chung, Il Seon Lee, Hee Kyung Chang, Bang Hur, Man Ha Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(2):186-190.
- 2,115 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adenocarcionma of fetal type is in lung is a newly recognized malignant tumor sharing morphologic features with the epithelial component of the pulmonary blastoma devoid of sarcomatous component. We present a case of adenocarcinoma of fetal type in a 28-year-old female, consisting of numerous branching tubules or glands and morula-like epithelial complexes. Histologically, the tubules and glands were composed of glycogne-rich nonciliated epithelial cells showing in part argyrophilia. Some of tubular and morula-like epithelial cells revealed immunoreactivity for neuron-specific enolase. We report this case with a review of literatures with special references on the histogenisis. This report is the pathologically confirmed second case of the pulmonary adenocarcinoma of fetal type in Korea, following the report of Cho and Lee, 1990.
- Comparison between Transthoracic Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologyand Gun Biopsy of Pulmonary Mass.
- Eun Sook Nam, Duck Hwan Kim, Hyung Sik Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1998;9(1):55-62.
- 2,153 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To compare the diagnostic yields and complication rates of transthoracic fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC) and gun biopsy in the diagnosis of pulmonary mass, a retrospective review was performed in 125 cases. Under the fluoroscopic guide, FNAC was performed by 20G Chiba needle in 91 cases, core biopsy was done by 18.5 G vaccum needle attached with automated biopsy gun in 74 cases and both procedures were done together in 37 cases. Overall sensitivity was 88.4% in FNAC and 87.5% in gun biopsy. For malignant pulmonary tumors, correct type correlation with final diagnosis was obtained in 33(76.7%) out of 43 cases by FNAC and 30(75.0%) out of 40 cases by gun biopsy. For benign pulmonary lesions, there were correct type correlation in 14(35.0%) out of 40 cases by FNAC and 14(53.8%) out of 26 cases by gun biopsy. The complication was pneumothorax and hemoptysis. Pneumothorax occured in 11.1% of FNAC, 10.9% of gun biopsy and 10.9% of both technique, among which chest tube drainages were necessary in one patient by gun biopsy and in three patients by both technique. Although no significant difference of diagnositc accuracy and complication rate was found between FNAC and gun biopsy, gun biopsy was more helpful in the diagnosis of pulmonary benign lesions than FNAC.
- Dendriform Pulmonary Ossification: A case report.
- Chan Kwon Jung, Kyo Young Lee, Chang Suk Kang, Sang In Shim, Byung Kee Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(11):950-952.
- 2,387 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The dendriform pulmonary ossification (DPO) is a rare condition of unknown origin in which branching mature bony spicules, usually containing marrow, are found within the alveolar septa. DPO manifests slow progression over many years or may remain unchanged; spontaneous regression has not been recorded. Most patients have no symptoms directly attributed to the ossification, although they may have symptoms due to the underlying fibrotic process. We experienced a case of DPO in 38 year-old-man who presented with cough and sputum for a month. The chest X-ray showed marked coarsened interstitial lung markings in both lungs, especially in the lower lobes. Open lung biopsy was done. Grossly, there were significant dendriform osseous structures. Histologically, branching arrays of mature bone were found in the interstitium and occasionally in alveolar spaces. Some bony trabeculae contained fatty or cellular marrow. The alveolar septa showed fibrous thickening with chronic inflammation. The transition between fibrosis and bone tissue was observed. Our case suggests that dendriform pulmonary ossification may be a rare special manifestation of chronic fibrosing interstitial inflammation of the lung. Osseous structures seem to derive from metaplastic bone formation in the vicinity of undergoing fibrous process.

 E-submission
E-submission


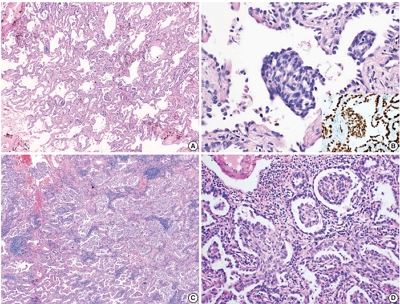
 First
First Prev
Prev



