Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Histopathological characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated encephalitis and colitis in chronic active EBV infection
- Betty A Kasimo, James J Yahaya, Sun Och Yoon, Se Hoon Kim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):188-194. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.02.21
- 3,993 View
- 164 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
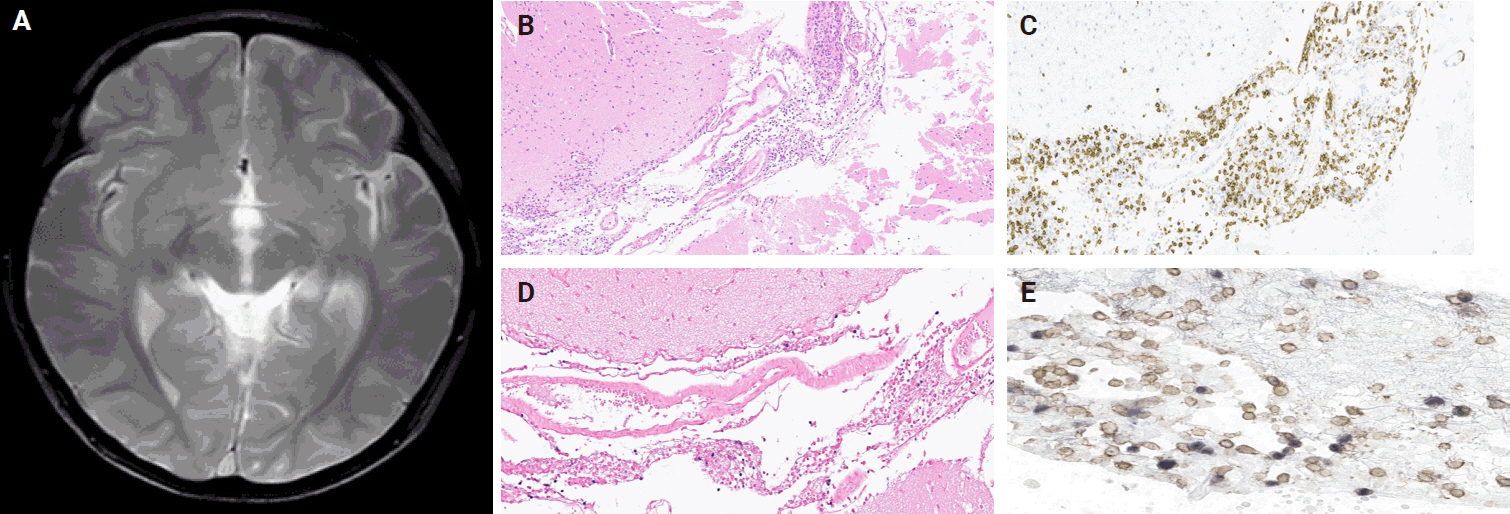
PDF - Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus (CAEBV) can induce complications in various organs, including the brain and gastrointestinal tract. A 3-year-old boy was referred to the hospital with a history of fever and seizures for 15 days. A diagnosis of encephalitis based on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging findings and clinical correlation was made. Laboratory tests showed positive serology for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and negative for Rotavirus antigen and IgG and IgM antibodies for cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and varicella zoster virus, respectively. Abdominal CT showed diffuse wall thickening with fluid distension of small bowel loops, lower abdomen wall thickening, and a small amount of ascites. The biopsy demonstrated positive Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization in cells within the crypts and lamina propria. The patient was managed with steroids and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). This case showed histopathological characteristics of concurrent EBV-associated encephalitis and colitis in CAEBV infection. The three-step strategy of immunosuppressive therapy, chemotherapy, and allogeneic HSCT should be always be considered for prevention of disease progression.
- Clinicopathological differences in radiation-induced organizing hematomas of the brain based on type of radiation treatment and primary lesions
- Myung Sun Kim, Se Hoon Kim, Jong-Hee Chang, Mina Park, Yoon Jin Cha
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(1):16-21. Published online October 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.30
- 6,983 View
- 239 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Radiation-induced organizing hematoma (RIOH) is a sporadic form of cavernous hemangioma (CH) that occurs after cerebral radiation. RIOH lesions are distinct histologically from de novo CH; however, detailed research on this subject is lacking. In the present study, the clinical and histological features of RIOHs were evaluated based on causative lesions.
Methods
The present study included 37 RIOHs confirmed by surgical excision from January 2009, to May 2020, in Yonsei Severance Hospital. All cases were divided into subgroups based on type of radiation treatment (gamma knife surgery [GKS], n = 24 vs. conventional radiation therapy [RT], n = 13) and pathology of the original lesion (arteriovenous malformation, n = 14; glioma, n = 12; metastasis, n = 4; other tumors, n = 7). The clinicopathological results were compared between the groups.
Results
Clinical data of multiplicity, latency, and size and wall thickness of the original tumors and RIOHs were analyzed. The GKS group showed shorter latency (5.85 ± 4.06 years vs. 11.15 ± 8.27 years, p = .046) and thicker tumor wall (693.7 ± 565.7 μm vs. 406.9 ± 519.7 μm, p = .049) than the conventional RT group. Significant difference was not found based on original pathology.
Conclusions
RIOH is more likely to occur earlier with thick tumor wall in subjects who underwent GKS than in patients who underwent conventional RT. These results indicate the clinical course of RIOH differs based on type of treatment and might help determine the duration of follow-up. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiation-Induced Cavernous Malformation in the Cerebellum: Clinical Features of Two Cases
Hyoung Soo Choi, Chae-Yong Kim, Byung Se Choi, Seung Hyuck Jeon, In Ah Kim, Joo-Young Kim, Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe
Brain Tumor Research and Treatment.2025; 13(2): 58. CrossRef - End-stage ADPKD with a low-frequency PKD1 mosaic variant accelerated by chemoradiotherapy
Hiroaki Hanafusa, Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Naoya Morisada, Ming Juan YE, Riki Matsumoto, Hiroaki Nagase, Kandai Nozu
Human Genome Variation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recapitulating the Key Advances in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of High-Grade Gliomas: Second Half of 2021 Update
Guido Frosina
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6375. CrossRef - Earlier Age at Surgery for Brain Cavernous Angioma-Related Epilepsy May Achieve Complete Seizure Freedom without Aid of Anti-Seizure Medication
Ayataka Fujimoto, Hideo Enoki, Keisuke Hatano, Keishiro Sato, Tohru Okanishi
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(3): 403. CrossRef
- Radiation-Induced Cavernous Malformation in the Cerebellum: Clinical Features of Two Cases
- Adjunctive markers for classification and diagnosis of central nervous system tumors: results of a multi-center neuropathological survey in Korea
- Yoon Jin Cha, Se Hoon Kim, Na Rae Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):165-170. Published online February 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.02.04
- 8,184 View
- 224 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The revised 4th 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumors of the central nervous system (CNS) classification has adopted integrated diagnosis encompassing the histology and molecular features of CNS tumors. We aimed to investigate the immunohistochemistry, molecular testing, and testing methods for diagnosis of CNS tumors in pathological labs of tertiary centers in Korea, and evaluate the adequacy of tests for proper diagnosis in daily practice.
Methods
A survey, composed of eight questions concerning molecular testing for diagnosis of CNS tumors, was sent to 10 neuropathologists working in tertiary centers in Korea.
Results
For diagnosis of astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors, all 10 centers performed isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations testing and 1p/19q loss of heterozygosity. For glioneuronal tumors, immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays for synaptophysin (n = 9), CD34 (n = 7), BRAF(VE1) (n = 5) were used. For embryonal tumors, particularly in medulloblastoma, four respondents used IHC panel (growth factor receptor bound protein 2-associated protein 1, filamin A, and yes-associated protein 1) for molecular subclassification. Regarding meningioma, all respondents performed Ki-67 IHC and five performed telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation.
Conclusions
Most tertiary centers made proper diagnosis in line with 2016 WHO classification. As classification of CNS tumors has evolved to be more complex and more ancillary tests are required, these should be performed considering the effect of necessity and justification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the role of epidermal growth factor receptor variant III in meningeal tumors
Rashmi Rana, Vaishnavi Rathi, Kirti Chauhan, Kriti Jain, Satnam Singh Chhabra, Rajesh Acharya, Samir Kumar Kalra, Anshul Gupta, Sunila Jain, Nirmal Kumar Ganguly, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Timir Tripathi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0255133. CrossRef
- Exploring the role of epidermal growth factor receptor variant III in meningeal tumors
- Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor of the Thyroid Gland, a Diagnostic Challenge in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology: Case Report
- Ye-Young Rhee, Hong Kyu Jung, Se Hoon Kim, Soo Hee Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):252-256. Published online June 11, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.28
- 11,030 View
- 185 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyalinizing trabecular tumor (HTT) is a rare thyroid tumor with low to minimal malignant potential. HTT is often misinterpreted as other thyroid tumors, including papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), on fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology, because of its overlapping cytologic features, such as nuclear grooves and intranulcear pseudoinclusions. Although cytopathologists cannot definitely conclude HTT by FNA cytology, suspicion of HTT is necessary to avoid misdiagnosing HTT as PTC or MTC and to avoid unnecessary aggressive treatment. Here, we report a case of HTT with novel cytologic features in CellPrep liquid based cytology that was diagnosed as suspicious for papillary carcinoma by FNA and finally diagnosed as HTT in the surgical specimen.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hyalinizing trabecular tumor of the thyroid: A comprehensive review of clinicopathological features, diagnostic dilemmas, and emerging molecular insights
Yinghe Huang, Shanshan Liu, Yilei Wen
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152539. CrossRef - Cytomorphological traits of fine-needle aspirates of hyalinizing trabecular tumor of the thyroid gland: A brief report
Fei Wang, Yufei Liu
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2024; 67(1): 128. CrossRef - Total thyroidectomy can still remain the method of choice in some Bethesda III cases
Jindrich Lukas, Barbora Hintnausova, Vlasta Sykorova, Martin Syrucek, Marek Maly, Jaroslava Duskova
Biomedical Papers.2023; 167(1): 61. CrossRef - Diagnostic clues for hyalinizing trabecular tumor on fine needle aspiration cytology
Lone Nielsen, Ana María Colino Gallardo, Pablo Pérez Alonso, Luis Ortega Medina, Esthefanía Latorre García, Cristina Díaz del Arco, Reyes Bergillos Jiménez, Lorenzo Alarcón García, Marta Cruz Blanco, Jesús Vega González, Montserrat De la Torre Serrano, Ma
Cytojournal.2023; 20: 19. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of the Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor
Byung-Chang Kim, Shin Jeong Pak, Jae Won Cho, Won Woong Kim, Yu-mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jung Hwan Baek, Ki-Wook Chung
Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2022; 22(4): 116. CrossRef - A Case of Multifocal Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumors of the Thyroid
Gland
Suhwan Jeong, Hanaro Park
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2021; 32(3): 308. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor: A Difficult and Controversial Thyroid Entity
Esther Diana Rossi, Mauro Papotti, William Faquin, Luigi Maria Larocca, Liron Pantanowitz
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(3): 778. CrossRef - A large series of hyalinizing trabecular tumors: Cytomorphology and ancillary techniques on fine needle aspiration
Marco Dell’Aquila, Carmen Gravina, Alessandra Cocomazzi, Sara Capodimonti, Teresa Musarra, Stefania Sfregola, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Luca Revelli, Maurizio Martini, Guido Fadda, Liron Pantanowitz, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Diana Rossi
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(6): 390. CrossRef - GLIS rearrangements in thyroid nodules: A key to preoperative diagnosis of hyalinizing trabecular tumor
Marina N. Nikiforova, Yuri E. Nikiforov, N. Paul Ohori
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(9): 560. CrossRef
- Hyalinizing trabecular tumor of the thyroid: A comprehensive review of clinicopathological features, diagnostic dilemmas, and emerging molecular insights
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to Pleural Fluid: A Case Report
- Ye-Young Rhee, Soo Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):206-209. Published online November 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.11.10
- 8,133 View
- 130 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare aggressive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin that shows locoregional or distant metastasis. Metastasis of MCC to body cavity effusion is extremely rare; only three cases have been reported so far. Metastatic MCC in effusion cytology shows small blue round cells with fine stippled chromatin like other small blue round cell tumors such as small cell lung carcinoma or lymphoma. The diagnosis of metastatic MCC can grant patients good chances at recently advanced therapeutic options. Here, we present a case of metastatic MCC to pleural effusion with characteristic single file-like pattern.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pleural Metastasis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Sina Maghsoudlou, Marc Pusztaszeri, Mauro Saieg
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(6): 308. CrossRef - Merkel cell carcinoma presenting as a malignant pleural effusion post‐COVID‐19 hospitalization: A case report and literature review
Joel Lanceta, Mesut Toprak, Oana C. Rosca
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology coupled with immunocytochemistry identifies Merkel cell carcinoma: A rare intruder in the cerebrospinal fluid
Reetu Kundu, Brijdeep Singh, Pranab Dey
Cytopathology.2022; 33(4): 530. CrossRef - Derrame pleural por carcinoma de células de Merkel
María J. Soler-Sempere, María O. Alvárez-Fernández, Isabel Padilla-Navas, María Cabezas-Macián, Jose F. Sánchez-Hernández, Eduardo García-Pachón
Archivos de Bronconeumología.2021; 57(11): 715. CrossRef - A rare case of pleural localisation of both metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Elise Kaspi, Shirley Fritz, Julien Colle, Florent Amatore, Diane Frankel, Patrice Roll
Cytopathology.2021; 32(3): 367. CrossRef - Merkel cell carcinoma with pleural effusion
María J. Soler-Sempere, María O. Alvárez-Fernández, Isabel Padilla-Navas, María Cabezas-Macián, Jose F. Sánchez-Hernández, Eduardo García-Pachón
Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition).2021; 57(11): 715. CrossRef
- Pleural Metastasis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Liquid-Based Cytology of the Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Case of Cryptococcal Meningitis
- Jiwoon Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):61-63. Published online October 26, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.06.13
- 10,400 View
- 197 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cryptococcus neoformans is the most common microorganism found in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytology and causes life-threatening infections in immunocompromised hosts. Although its cytomorphologic features in conventional smear cytology have been well described, those in liquid-based cytology have rarely been. A 73-year-old woman with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presented with mental confusion and a spiking fever. To rule out infectious conditions, CSF examination was performed. A cytology slide that was prepared using the ThinPrep method showed numerous spherical yeast-form organisms with diameters of 4–11 μm and thick capsules. Occasional asymmetrical, narrow-based budding but no true hyphae or pseudohyphae were observed. Gomori methenamine silver staining was positive. Cryptococcosis was confirmed in blood and CSF through the cryptococcal antigen test and culture. Liquid-based cytology allows for a clean background and additional slides for ancillary testing, facilitating the detection of microorganisms in CSF specimens, particularly when the number of organisms is small.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unraveling Capsule Biosynthesis and Signaling Networks in Cryptococcus neoformans
Eun-Ha Jang, Ji-Seok Kim, Seong-Ryong Yu, Yong-Sun Bahn, Teresa R. O’Meara
Microbiology Spectrum.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis in immunocompromised patients: Can it be Cryptococcus
Ridhi Sood, Ruchita Tyagi, Pavneet Selhi, Harpreet Kaur, Neena Sood
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(2): 164. CrossRef - Special Staining of the Liquid-Based Cytopathology Test in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Diagnosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis with Nonneutropenic Patients
Yue Hu, Lin Zheng, Deng Pan, Lei Shao, Xianfa Xu, Yiming Yu, Qidong Zhuang, Zaichun Deng, Zhongbo Chen
Canadian Respiratory Journal.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Sensitivity of Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytology for the Diagnosis of Cryptococcal Infections
Kelsey E McHugh, Melanie Gersey, Daniel D Rhoads, Gary W Procop, Yaxia Zhang, Christine N Booth, Charles D Sturgis
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2019; 151(2): 198. CrossRef - Cryptococcal Capsules in Cerebrospinal Fluid Visible on Hemocytometer
Zen Kobayashi, Yuriko Hirota, Shuzo Shintani
Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Journal Canadien des Sciences Neurologiques.2018; 45(6): 700. CrossRef
- Unraveling Capsule Biosynthesis and Signaling Networks in Cryptococcus neoformans
- A Rare Case of Aggressive Melanotic Schwannoma Occurred in Spinal Nerve of a 59-Year-Old Male
- Sung-eun Choi, Yoon Jin Cha, Jisup Kim, Hyunseo Cha, Jayeong Seo, Sung-Uk Kuh, Sung-Jun Kim, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):505-508. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.04
- 14,741 View
- 221 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Melanotic schwannoma (MS) is a rare variant of nerve sheath neoplasm that shows ultrastructural and immunophenotypical features of Schwann cells but also has cytoplasmic melanosomes and is reactive for melanocytic markers as well. Unlike conventional schwannoma, which is totally benign, MS has an unpredictable prognosis and is thought to have low-malignant potential. Herein, we present a rare case of recurrent MS in lumbar spine of a 59-year-old male.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The “Pigmented Side” of Nerve Sheaths: Malignant Melanotic Nerve Sheath Tumor
Raduan Ahmed Franca, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Lorenzo Ugga, Rosa Della Monica, Elena D'Avella
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 33(4): 1068. CrossRef - Case Report: Cutaneous melanocytic schwannoma with concomitant melanocytoma in a canine
Olwam H. Monakali, Nicolize O'Dell, Louise van der Weyden
Wellcome Open Research.2024; 8: 364. CrossRef - Intradural Melanotic Schwannoma of the Sacral Spine: An Illustrated Case Report of Diagnostic Conundrum
Jiunn-Kai Chong, Navneet Kumar Dubey, Wen-Cheng Lo
Reports.2024; 7(3): 56. CrossRef - Rare giant retroperitoneal melanotic schwannoma: a case report and literature review
Pan Chen, Junfeng Cheng, Lin Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Case of Melanotic Schwannoma Occurred Intraosseous of Sacrum: A Literature Review
Xiaobo Yan, Keyi Wang, Nong Lin, Xin Huang, YanBiao Fu, Zhaoming Ye
Orthopaedic Surgery.2023; 15(2): 655. CrossRef - Sporadic spinal psammomatous malignant melanotic nerve sheath tumor: A case report and literature review
Giulio Bonomo, Alessandro Gans, Elio Mazzapicchi, Emanuele Rubiu, Paolo Alimonti, Marica Eoli, Rosina Paterra, Bianca Pollo, Guglielmo Iess, Francesco Restelli, Jacopo Falco, Francesco Acerbi, Marco Paolo Schiariti, Paolo Ferroli, Morgan Broggi
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Case Report: Cutaneous melanocytic schwannoma with concomitant melanocytoma in a canine
Olwam H. Monakali, Nicolize O'Dell, Louise van der Weyden
Wellcome Open Research.2023; 8: 364. CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration cytology of melanotic schwannoma in the submandibular gland
Yu‐Hua Huang, Ying‐Chou Lu, Hsuan‐Ying Huang, Chien‐Chin Chen
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(1): 142. CrossRef - Checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy in refractory malignant melanocytic schwannoma with Carney complex: first evidence of efficacy
Jyoti Bajpai, Akhil Kapoor, Rakesh Jalali, Mrinal M Gounder
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(5): e240296. CrossRef - 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for aggressive melanotic schwannoma of the L3 spinal root
Xun-Ze Shen, Wei Wang, Zhou-Ye Luo
Medicine.2021; 100(8): e24803. CrossRef - Hemorrhagic spinal melanotic schwannoma presenting as acute chest pain: A case report and literature review
Dallas J. Soyland, Dylan R. Goehner, Kayla M. Hoerschgen, Troy D. Gust, Shawn M. Vuong
Surgical Neurology International.2021; 12: 164. CrossRef - Retroperitoneal Recurrence of Melanotic Schwannoma on 18F-FDG PET/CT
Xiangliu OuYang, Lichun Zheng, Xiaoming Zhang
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2021; 46(12): 991. CrossRef - Schwannoma originating from the common iliac artery: a case report
Seung-Myoung Son, Chang Gok Woo
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous Melanotic Schwannoma in the Sacrum Mimicking Primary Bone Tumor
Yoshitaka Nagashima, Yusuke Nishimura, Kaoru Eguchi, Takayuki Awaya, Satoshi Yoshikawa, Shoichi Haimoto, Toshihiko Wakabayashi, Masahito Hara
NMC Case Report Journal.2020; 7(3): 107. CrossRef - Extramedullary melanotic schwannoma recurrence in the cervical vertebral arch: a case report and review of the literature
Zongbin Hou, Teng Shi, Guangrun Li, Lin Tian, Xinna Li, Xiaoyang Liu
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Extramedullary malignant melanotic schwannoma of the spine: Case report and an up to date systematic review of the literature
Georgios Solomou, Adikarige Haritha Dulanka Silva, Adrianna Wong, Ute Pohl, Nikolaos Tzerakis
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2020; 59: 217. CrossRef - Melanotic Schwannoma of the Vagina: A Report of a Very Rare Tumor and Review of the Literature
Kofi Effah, Stefan Seidl, Edith Gorges, Patrick Kafui Akakpo
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Melanotic Schwannomas Are Rarely Seen Pigmented Tumors with Unpredictable Prognosis and Challenging Diagnosis
Elif Keskin, Sumeyye Ekmekci, Ozgur Oztekin, Gulden Diniz
Case Reports in Pathology.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- The “Pigmented Side” of Nerve Sheaths: Malignant Melanotic Nerve Sheath Tumor
- History of the Official Journal Published by the Korean Society of Pathologists: From the Korean Journal of Pathology to the Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine
- Se Hoon Kim, Chong Jai Kim, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):1-6. Published online January 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.07
- 11,398 View
- 135 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advancing pathology through sixty volumes: reflections and future directions
Chan Kwon Jung, So Yeon Park, Soon Won Hong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2026; 60(1): 1. CrossRef - A Multistakeholder Approach to the Airport Gate Assignment Problem: Application of Fuzzy Theory for Optimal Performance Indicator Selection
Haonan Li, Xu Wu, Yinghui Liang, Chen Zhang, Yu-Ting Bai
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advancing pathology through sixty volumes: reflections and future directions
- Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor Arising in the Sacrum: A Case Report
- Yoon Sung Bae, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(4):331-334. Published online August 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.4.331
- 7,831 View
- 45 Download
- Diagnostic Accuracy of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology in Metastatic Tumors: An Analysis of Consecutive CSF Samples
- Yoon Sung Bae, June-Won Cheong, Won Seok Chang, Sewha Kim, Eun Ji Oh, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):563-568. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.563
- 9,849 View
- 69 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination can be used to verify the presence of primary malignancies as well as cases of central nervous system (CNS) metastasis. Because of its importance, there have been several studies concerning the sensitivity of CSF cytology. To determine the practical use and reproducibility of diagnoses based on CSF cytology, we evaluated this test by analyzing cytology results from consecutive CSF samples.
Methods Between July 2010 and June 2013, 385 CSF cytology samples from 42 patients were collected. The samples were gathered using a ventricular catheter and reservoir. CSF cytology of all patients was examined more than two times with immunocytochemistry for cytokeratin.
Results Primary neoplastic sites and histologic types of patients' metastatic cancer were diverse. The overall sensitivity for detecting malignancy was 41.3%. Even within short-term intervals, diagnoses frequently changed.
Conclusions Our results were inconsistent, with low sensitivity, when compared to the results of previous studies. However, CSF evaluation can still provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic information because adjuvant treatments are now routinely performed in patients with CNS metastasis. Negative CSF cytology results should not be ignored, and continuous CSF follow-up is essential for following the clinical course of patients with metastatic cancer involving the CNS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analytical validation of the Belay Vantage™ assay for evaluation of MGMT promoter methylation using enzymatically converted tumorDNA from cerebrospinal fluid
Kala F Schilter, Qian Nie, Jennifer N Adams, Rakshitha Jagadish, Anthony Acevedo, Alexandra Larson, Samantha A Vo, Brett A Domagala, Kyle M Hernandez, Christopher Douville, Yuxuan Wang, Brian Coe, Chetan Bettegowda, Honey V Reddi
Cancer Genetics.2025; 294-295: 94. CrossRef - Analytical Validation and Clinical Sensitivity of the Belay Summit Assay for the Detection of DNA Variants in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Primary and Metastatic Central Nervous System Cancer
Qian Nie, Kala F. Schilter, Kyle M. Hernandez, Jennifer N. Adams, Rakshitha Jagadish, Anthony Acevedo, Alexandra Larson, Brett A. Domagala, Samantha A. Vo, Sakshi Khurana, Kathleen Mitchell, Dean Ellis, Baymuhammet Muhammedov, Yuxuan Wang, Christopher Dou
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2025; 27(7): 615. CrossRef - Demonstrating the clinical utility of genomic profiling using cerebrospinal fluid to inform management of central nervous system tumors – a meta analysis of the literature
Sakshi Khurana, Qian Nie, Kala F. Schilter, Honey V. Reddi
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 9: 100317. CrossRef - Application of the International System for Serous Fluid Cytopathology in Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytology
Ioannina Vidali, Konstantinos Christofidis, Georgia Bairaktari, Maria Sevastiadou, Alexandros Pergaris, Aglaia Dimitrakopoulou, Panagiota Keramari, Panagiota Mikou
Cytopathology.2025; 36(6): 589. CrossRef - The Spectrum of Malignant Diagnoses in Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology in Both Pediatric and Adult Populations: A Single‐Institutional Retrospective Review
Nida Babar, Asif Loya, Sajid Mushtaq, Maryam Hameed, Usman Hassan, Mudassar Hussain
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(12): 620. CrossRef - Molecular Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Tumor-Derived DNA to Aid in the Diagnosis and Targeted Treatment of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis
Michael Youssef, Alexandra Larson, Vindhya Udhane, Viriya Keo, Kala F. Schilter, Qian Nie, Honey V. Reddi
Diseases.2025; 13(10): 336. CrossRef - Numb cheek syndrome in breast cancer: a case report
Zhibin Tan, Si Ying Tan
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility and performance of cell blocks in cerebrospinal fluid cytology: Experience at two teaching hospitals
Hyeji Yoon, Constance V. Chen, Vimal Krishnan, Jill Grochowski, Gioia Iezza, Poonam Vohra, Ronald Balassanian, Nancy Y. Greenland
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(10): 621. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy for evaluating mutations and chromosomal aberrations in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with primary or metastatic CNS tumors
Ahmad Charifa, Sally Agersborg, Arash Mohtashamian, Andrew Ip, Andre Goy, Maher Albitar
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2024; 6: 100281. CrossRef - Body fluids
Shyam H. Nemade, Meherbano M. Kamal
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2023; 66(1): 75. CrossRef - Standardizing a volume benchmark for cerebrospinal fluids for optimal diagnostic accuracy
David Kim, Susan A. Alperstein, Momin T. Siddiqui
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(2): 258. CrossRef - Evaluating Infectious, Neoplastic, Immunological, and Degenerative Diseases of the Central Nervous System with Cerebrospinal Fluid-Based Next-Generation Sequencing
Konstantinos I. Tsamis, Hercules Sakkas, Alexandros Giannakis, Han Suk Ryu, Constantina Gartzonika, Ilias P. Nikas
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2021; 25(2): 207. CrossRef - Imaging of Intraspinal Tumors
Luke N. Ledbetter, John D. Leever
Radiologic Clinics of North America.2019; 57(2): 341. CrossRef - Isolated leptomeningeal carcinomatosis and possible fungal meningitis as late sequelae of oesophageal adenocarcinoma
Richard Dumbill, Sanja Thompson, Heiko Peschl, GDH Turner, Charles Woodrow
BMJ Case Reports.2019; 12(11): e230117. CrossRef - Cytomorphological and immunocytochemical examinations of cerebrospinal fluid in primary and metastatic brain lesions
M. V. Savostikova, L. Ya. Fomina, E. S. Fedoseeva, E. Yu. Furminskaya
Onkologiya. Zhurnal imeni P.A.Gertsena.2018; 7(1): 28. CrossRef - Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Cytopathological Review of 15 Cases
Rema Rao, Syed A. Hoda, Alan Marcus, Rana S. Hoda
The Breast Journal.2017; 23(4): 456. CrossRef - Clinicocytological analysis of cases with positive cerebrospinal fluid in our hospital
Nozomi IWAMOTO, Mitsuaki ISHIDA, Akiko KAGOTANI, Nozomi KASUGA, Muneo IWAI, Yuji HAYASHI, Namie ARITA, Yoshimitsu MIYAHIRA, Ryoji KUSHIMA
The Journal of the Japanese Society of Clinical Cytology.2016; 55(5): 291. CrossRef
- Analytical validation of the Belay Vantage™ assay for evaluation of MGMT promoter methylation using enzymatically converted tumorDNA from cerebrospinal fluid
- Cytologic Features of Giant Cell Ependymoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Myoung Ju Koh, Sun Och Yoon, Hyae Min Jeon, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Soon Won Hong, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):507-513. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.507
- 10,335 View
- 71 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Here, we present a case of anaplastic giant cell ependymoma (GCE) occurring in a 15-year-old woman. Squash smear slides for intraoperative frozen section diagnosis revealed oval to round cell clusters with a papillary structure in a fibrillary background. This was occasionally accompanied by the presence of bizarre pleomorphic giant cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and prominent intranuclear inclusions. These intranuclear inclusions were a key clue to diagnosis of ependymoma. Histologic analysis revealed features of a high-grade tumor with perivascular pseudorosettes and bizarre pleomorphic giant cells, which established the diagnosis of GCE. We performed a review of literatures about the cytologic features of GCE, including our case, thus proposing that intraoperative frozen diagnosis of GCE would be established by squash smear preparations featuring the mitosis and necrosis, as well as the high cellularity, and the presence of giant cells showing hyperchromatic nuclei with eosinophilic cytoplasm and intranuclear inclusions/pseudoinclusions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of myxopapillary ependymoma with predominant giant cell morphology: A rare entity with comprehensive genomic profiling and review of literature
Bryan Morales‐Vargas, Hassan Saad, Daniel Refai, Matthew Schniederjan, Zied Abdullaev, Kenneth Aldape, Malak Abedalthagafi
Neuropathology.2025; 45(1): 13. CrossRef - Report of a case of giant cell ependymoma with unusual clinical and pathological presentation
Mónica B. Mezmezian, Victor Del Caño, Liliana G. Olvi
Neuropathology.2019; 39(4): 313. CrossRef - Giant Cell Ependymoma of Cervicomedullary Junction: A Case Report of a Long-Term Survivor and Literature Review
Martina Cappelletti, Andrea G. Ruggeri, Giorgia Iacopino, Roberto Delfini
World Neurosurgery.2018; 116: 121. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical features of giant cell ependymoma of the filum terminale with unusual clinical and radiological presentation
Fernando Candanedo-Gonzalez, Cindy Sharon Ortiz-Arce, Samuel Rosales-Perez, Ana Lilia Remirez-Castellanos, Candelaria Cordova-Uscanga, Armando Gamboa-Dominguez
Diagnostic Pathology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Giant Cell Ependymoma of Lateral Ventricle: Case Report, Literature Review, and Analysis of Prognostic Factors and Genetic Profile
Hirokazu Takami, Christopher S. Graffeo, Avital Perry, Aditya Raghunathan, Robert B. Jenkins, Caterina Giannini, Terry C. Burns
World Neurosurgery.2017; 108: 997.e9. CrossRef
- A case of myxopapillary ependymoma with predominant giant cell morphology: A rare entity with comprehensive genomic profiling and review of literature
- Value of Additional Immunocytochemical Stain for Cytokeratin in the Diagnosis of Leptomeningeal Involvement of Metastatic Carcinoma.
- Junjeong Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):516-519.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.516
- 3,647 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to describe potential pitfalls in the diagnosis of metastatic adenocarcinoma in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and to suggest additional work in association with cytokeratin immunocytochemistry for the proper diagnosis, especially in the specimens with low cellularity.
METHODS
We collected 267 cytologic specimens of CSF from patients, who were diagnosed over a 9-month period. Each of the individual samples were divided into half the sample size and processed via both, ThinPrep (TP) with Papanicolau stain and cytocentrifugation-based preparation (cytospin, CP) with immunocytochemical stain for cytokeratin.
RESULTS
Amongst the 267 cases, 45 cases from 22 patients were diagnosed to be positive for metastasis adenocarcinoma in CSF. TP with Papanicolau stain showed satisfactory cytomorphology when compared with specimen of CP preparation and cytokeratin immunocytochemical staining. All the TP processed cases belonged to satisfactory/superior categories based on the assessment of technical artifact, which potentially helps in decreasing diagnositc errors. However, in 10 out of 45 cases, diagnostic atypical cells were present only in one of the two slides.
CONCLUSIONS
Immunocytochemical stain for cytokeratin along with TP processed specimen helps in decreasing potential diagnostic errors in the cytological diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma in CSF specimen.
- Multiple Glomus Tumors of the Ankle with Prominent Intranuclear Pseudoinclusions.
- Jae Yeon Seok, Se Hoon Kim, Tae jung Kwon, Jieun Kwon, Yoon Hee Lee, Kyoo Ho Shin, Woo Ick Yang
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(5):337-342.
- 2,374 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Glomus tumors are neoplasms that are composed of modified smooth muscle cells of the glomus body. Here, we report a case of multiple glomus tumors of the ankle that showed various histologic types, including the solid type (glomus tumor proper) and angiomatous type (glomangioma). The tumor cells observed in this case also showed prominent intranuclear inclusions, which has not yet been reported in glomus tumors. Ultrastructural examination demonstrated that the nuclear inclusions were not true inclusion bodies but were intranuclear cytoplasmic pseudoinclusions formed by cytoplasmic invaginations that formed as a result of the deep and complex nuclear contours.
- Pleomorphic Variant of Pineocytoma: A Case Report.
- Eunah Shin, Haeryoung Kim, Tae Seung Kim, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(4):265-267.
- 2,125 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We herein present a rare case of pineocytoma in a 23-year-old female exhibiting distinct histomorphological features. The tumor contained highly pleomorphic, often multinucleated giant cells in the background of otherwise benign pineocytomatous architecture, which at first led to an erroneous diagnosis of a high grade malignancy. However, the worrisome histological findings turned out to be constituents of a distinct subtype of pineocytoma previously described as pleomorphic variant of pineocytoma. Although it is rare, pathologists should be aware of this entity since the tumor takes on a benign clinical course like any other classic pineocytomas.
- Isolated Polypoid Ganglioneuroma in the Rectum.
- Se Hoon Kim, Chang Hwan Choi, Yong Han Paik, Won Ho Kim, Hoguen Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(4):344-346.
- 2,333 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gastrointestinal ganglioneuroma is a rare benign neoplasm, composed of ganglion cells, nerve fibers, and supporting cells. Ganglioneuromas are presented as isolated polypoid ganglioneuroma, ganglioneuromatous polyposis, and diffuse ganglioneuromas. We have experienced a case of an isolated ganglioneuromatous polyp in the rectum. The patient was a 58-year-old female who had experienced low abdominal discomfort and tenesmus for 6 to 7 months. Colonoscopic examination revealed a polypoid tumor in the rectum. Microscopically, the tumor showed cystic glands, expanded lamina propria, and smooth surface epithelium. Many proliferated ganglion cells with nerve fibers were evident in the lamina propria which was extended to the submucosa.
- The Expression of Extracellular Signal Regulated Kinase (ERK) in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.
- Se Hoon Kim, Hyung Jung Kim, Young Nyun Park, Sang Ho Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(5):361-367.
- 2,012 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although it was suggested that constitutive extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) activation plays a pivotal role in intracellular signal transduction related to oncogenesis, a consistent relationship between constitutive ERK activation and oncogenesis has not yet been clearly demonstrated. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the expression frequencies and pattern of phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK) in the non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and to evaluate whether p-ERK is a useful prognostic factor.
METHODS
One hundred sixty cases of NSCLC tissue specimens were investigated by immunohistochemical staining for p-ERK. Clinicopathologic values (tumor stage, cell type, differentiation and presence of metastasis) and p-ERK expression of normal alveolar pneumocytes around NSCLC were compared with the incidence of tumor p-ERK expression.
RESULTS
Fifty-three out of 160 cases (33%) of NSCLC showed expression of p-ERK. There was no statistical correlation between the expression of p-ERK in the NSCLC neoplastic cells and the corresponding tumor stage, cell type and presence of metastasis. There was statistical significance between the expressions of p-ERK in alveolar pneumocytes around NSCLC (odds ratio: 6.130).
CONCLUSIONS
Based on these results, we suggest that p-ERK expression is not useful in predicting the prognosis of NSCLC. In regard to the theory of "field cancerization" and the phenomenon of "allele-specific loss or allele-specific mutations", the statistically significant p-ERK expression in alveolar pneumocytes around NSCLC suggests that constitutive ERK activation is involved in the early stage of NSCLC carcinogenesis rather than in proliferation, differentiation or metastasis of NSCLC.
- Adequate Microsatellite Markers for 1p/19q Loss of Heterozygosity of Oligodendroglial Tumors in Korean Patients.
- Se Hoon Kim, Hoguen Kim, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(1):23-33.
- 2,145 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is well known that oligodendrogliomas can be divided into two groups according to the 1p/19q or 1p loss of heterozygosity (LOH) status because oligodendrogliomas with the 1p/19q LOH or the 1p LOH have a better prognosis and chemosensitivity. In this study, we investigated the adequate microsatellite markers for 1p/19q LOH of oligodendroglial tumors in Korean patients.
METHODS
We performed PCR that was based on the LOH test with the 1p (D1S508, D1S199, D1S2734, D1S186 & D1S312) and 19q (D19S219, D19S112, D19S412 & D19S596) microsatellite markers; these were the markers that were recommended by other researchers. We performed this PCR on microdissected paraffin embedded tissue blocks of 67 tumors from 56 cases.
RESULTS
The PCR based LOH analysis revealed that 3 microsatellite markers (D1S508, D1S2734 & D1S186) of 1p and 2 markers (D19S219 & D19S412) of 19q had higher heterozygosity scores than other markers. In addition, chromosomal LOH status using these selective markers showed a statistically significant difference of prognosis for oligodendroglial tumors.
CONCLUSIONS
We can suggest that the microsatellite markers with high heterozygosity scores (D1S508, D1S2734, D1S186, D19S219 and D19S412) would be adequate microsatellite markers for a PCR based LOH test of oligodendroglial tumors in Korean patients.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Kimura's Disease of Parotid Gland: Report of A Case Cytologically Failed to Diagnose as Kimura's Disease.
- Se Hoon Kim, Haeryoung Kim, Sung Eun Kim, Woo Ick Yang, Soon Won Hong, Kwang Gil Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2003;14(2):86-90.
- 2,123 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Kimura's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder of unknown cause and is most prevalent among Asians. The cytologic findings of Kimura's disease are significant numbers of eosinophils in a background of lymphoid cells, occasional fragments of collagenous tissue, proliferation of vessels, and Warthin-Finkeldey polykaryocytes. Among these features, the most important cytologic feature of Kimura's disease is a significant numbers of eosinophils. We experienced a case of Kimura's disease in the parotid gland which we failed to recognize on cytology due to the apparent paucity of eosinophils. On careful retrograde reviewing of the cytologic findings, a few scattered leukocytes, previously interpreted as polymorphous leukocytes, had bilobed nuclei and coarse green but granular cytoplasm on Papanicolaou preparation. These leukocytes showed obvious orange-red intracytoplasmic granules as in eosionophils on Giemsa stain. The paucity of eosinophils may be due to the thick fibrosis around lymphoid follicles or any technical error during aspiration. Whereas the Warthin-Finkeldey type giant cell is not a sensitive cytologic marker of Kimura's disease, it may be a helpful cytologic feature. To reach a correct cytologic diagnosis of Kimura's disease, it is important to keep in mind that searching for Warthin-Finkeldey type giant cells and evaluation of Giemsa stain for detection of eosinophils would be helpful.
- Symptomatic Graular Cell Tumor Involving Intra- and Suprasellar Area: A case report.
- Se Hoon Kim, Sun Ho Kim, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):745-750.
- 1,947 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Symptomatic parasellar granular cell tumor is a very rare tumor. To the best of our knowledge, 43 cases was be found in the English literatures. We recently experienced a case of a parasellar granular cell tumor in a 61-year-old female who had bilateral temporal hemianopsia and severe panhypopituitarism. The tumor was composed of diffuse sheets of polygonal cells with abundant eosinophilic PAS positive granular cytoplasm. In the immunohistochemical and ultrastructural examinations, the tumor failed to show any evidence of Schwann cell or glial differentiation. These findings suggest that granular cell tumor has heterogenous cell types of origin.
- Cytologic Features of Secretory Meningioma in Squash Preparation: A Case Report.
- Se Hoon Kim, Kwang Gil Lee, Tai Seung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2004;15(1):52-55.
- 2,245 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Secretory meningioma is a distinct subtype of meningioma. We describe the cytologic features of a secretory meningioma on squash preparations, in comparision with other cytologic mimickers. A 54-year-old woman presented with hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus, and headache for seven years. A brain MRI study revealed a 4.5 cm sized mass in the cerebellopontine angle, which showed homogenous signal intensity in T2-weighted image. The intraoperative squash smear showed some well-defined, thin rimmed intracytoplasmic inclusions, containing a finely granular eosinophilic core among less cohesive meningiomatous cells. Histologic sections revealed a meningothelial meningioma with scattered inclusions, with periodic acid-Schiff, carcinoembryonic antigen, and cytokeratin positivity. Identification of characteristic intracytoplasmic inclusions is helpful for diagnosing secretory meningiomas. On squash preparations, differential diagnoses included tumors with inclusions or cytoplasmic vacuolizations, such as metastatic mammary infiltrating ductal carcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and clear cell ependymoma, oligodendroglioma, hemangioblastoma, chordoma, and other variants of meningiomas (clear cell, xanthomatous, microcytic, and chordoid variants). In addition, the possibilities of glioma with eosinophilic granular body, and metastatic tumors from mammary infiltrating ductal carcinoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma in meningioma should be considered.
- Williams Syndrome in an Infant An autopsy case report .
- Jeong Hae Kie, Se Hoon Kim, Jae Young Choi, Sang Ho Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(11):1090-1093.
- 2,016 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Williams syndrome is a congenital disorder characterized by mental retardation, loquacious personalities, dysmorphic face, and vascular and valvular abnormalities. The etiology of this syndrome was one allelic loss of elastin gene, exhibiting a submicroscopic deletion, at 7q11.23. Sudden death is an infrequently recognized complication. The mechanism of sudden death is explained by myocardial ischemia, decreased cardiac output, and arrhythmia by anatomical abnormality of coronary artery stenosis and severe biventricular outflow tract obstruction. We report an autopsy case of a 80 day-old male with Williams syndrome. Five days before admission, cardiac murmur was detected incidentally on ascultation at a local clinic during a visit for vaccination. He was transferred to our hospital and cardiac catheterization was done. He died suddenly next day. Postmortem examination revealed a dysmorphic face and multiple cardiovascular abnormalities including supravalvular aortic stenosis with narrowed coronary artery ostia, supravalvular pulmonic stenosis, secundum type of atrial septal defect, right ventricular hypertrophy, and renal artery stenosis. Histologically, aorta and pulmonary, bronchial, and renal arteries showed markedly hyperplastic medial elastic laminae approximately three times thick compared to those of age-matched normal artery. The elastic fibers of the innermost two thirds of media were disposed in a normal orderly parallel fashion. In outer third of the media, the elastic fibers had lost the normal orderly arrangement.
- Salivary Duct Carcinoma with Mucin Containing Cells: Report of a Case Misdiagnosed as Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology.
- Haeryoung Kim, Hyunki Kim, Hoguen Kim, Jin Kim, Soon Won Hong, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(1):56-62.
- 2,320 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) is a rare primary salivary gland malignancy characterized by histological features similar to those of ductal carcinomas of the breast. It is regarded as a high-grade malignancy associated with frequent local recurrences and early distant metastases that require aggressive treatment. The typical fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) findings in SDC include cellular smears showing tumor cells with eccentric pleomorphic nuclei and a granular cytoplasm arranged in flat sheets or cribriform patterns against a necrotic background. However, the presence of mucin-containing cells in SDC has been rarely described. We report the FNAC findings in a patient with histologically confirmed SDC that demonstrated numerous mucin-containing cells and was subsequently misdiagnosed as a high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Here we discuss the problems involved in distinguishing SDC from high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma on the basis of cytologic findings alone.
- Comparision of Effectiveness between the ThinPrep(R) and the Cytospin Preparations of the Repeated Urine Cytology.
- Soon Won Hong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoonhee Lee, Woo Hee Jung, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2007;18(1):55-61.
- 2,343 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Once diagnosed as "cell paucity" or "atypia" by the cytospin (CS) preparation, this CS preparation does not secure a precise diagnosis by repeated testing alone. Although the ThinPrep(R) (TP) preparation is acknowledged to show increased cellularity, performing the screening tests for the cases that have enough cellularity, according to CS, raises issues for the cost-effectiveness. To obtain a more precise diagnosis through increasing the cellularity by performing TP, we selected the cases that were diagnosed as "cell paucity" or "atypia" by CS, but they required a more precise diagnosis, and the samples were processed via both CS and TP to compare the results. 11 patients diagnosed as "cell paucity" and 22 patients diagnosed as "atypia" by CS participated in this study. When the detection rate of atypical cells in both preparations with repeated urine cytology was compared, the overall detection rate of TP (16cases, 48.5%) was superior than that of CS (11cases, 33.3%), with statistical significance. The cellularity of both preparations was compared on repeated urine cytology; the general cellularity of TP (29cases, 87.9%) was higher than that of CS (20cases, 60.6%), but there was no statistical significance. Particularly, we repeated the TP for the 1 case that was diagnosed as "atypia" and we performed polyoma virus immunohistochemical staining, which confirmed polyoma virus. In conclusion, we can avoid obtaining negative diagnosis from cases with uncertain "atypia" or "cell paucity" by performing repeated TP testing.
- Hepatic Veno-occlusive Disease Developed after Irradiation: A report of three cases .
- Kyoungsoo Har, Se Hoon Kim, Young Nyun Park, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(5):381-385.
- 1,830 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) is a rare disease due to occlusion of the terminal hepatic venules and/or sublobular veins, which is a result of endothelial damage from pyrrolizidine alkaloids in herbal teas, irradiation of the liver, or chemotherapy particularly in association with bone marrow transplantation. We recently experienced three cases of VOD developed after radiation therapy. Two cases occurred in hepatocellular carcinoma patients of a 37-year-old man with B viral chronic hepatitis and a 22-year-old man with B viral cirrhosis and the other in a 64-year-old patient with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. For the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, chemoembolization with lipiodol and adriamycin, and external irradiation on the liver mass were done. The total radiation dose was 5400 cGy and 3000 cGy in each case. Five months and 3 months after irradiation, respectively, the resected liver masses showed extensive necrosis due to pre-operative treatment. To treat esophageal carcinoma, pre-operative concurrent chemotherapy of 5-FU and radiation of 4500 cGY were done. One month after irradiation, the radical esophgectomy and wedge biopsy of the liver were done. The liver of all 3 cases showed a dark red appearance with severe congestion in contrast to the pale brown normal liver, which was not included in the radiation field. On micoscopic examination, the terminal hepatic venules and sublobular veins showed subintimal edema, fibrin deposition, and partial or total luminal occlusion by loose fibrous tissue. The centrizonal sinusoids were markedly dilatated and congested with atrophy of hepatocytes.
- Vimentin and Survivin Expression Rates as Prognostic Factors in Medulloblastoma.
- Jae Yeon Seok, Se Hoon Kim, Yoon Hee Lee, Jieun Kwon, Tai Seung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(2):87-94.
- 2,392 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A medulloblastoma is a primitive neuroepithelial tumor of the cerebellum that occurs in children and metastasizes through the cerebrospinal fluid. It is highly malignant and invasive, and the 5-year survival rate is only 60%. Surgical resection techniques, radiation, and chemotherapy have improved the overall survival but the patients suffer life-long cognitive dysfunctions or endocrine abnormalities as the side effects of treatment. Therefore it is essential to identify prognostic markers to determine the appropriate treatment strategy in order to minimize the side effects.
METHODS
This study evaluated the immunohistochemical differentiation and survival rate with synaptophysin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, epithelial membrane antigen, vimentin and primitive neuroepithelial marker nestin of 55 paraffin-embedded medulloblastomas, using a tissue microarray. The expression of survivin, the apoptotic inhibitor, and the survival rate with regard to the proliferation index of Ki-67 were also investigated.
RESULTS
The group testing positive to vimentin, a mesenchymal differentiation marker, had a worse prognosis and there was a strong correlation between vimentin expression and nestin expression. Patients with a survivin expression rate >35% had a significantly poorer clinical course and there was a correlation between the survivin expression rate and Ki-67 expression rate.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, vimentin and survivin are negative prognostic markers in medulloblastomas.

 E-submission
E-submission


 First
First Prev
Prev



