Abstract
- Inflammatory and reactive lesions of the breast are relatively uncommon among benign breast lesions and can be the source of an abnormality on imaging. Such lesions can simulate a malignant process, based on both clinical and radiographic findings, and core biopsy is often performed to rule out malignancy. Furthermore, some inflammatory processes can mimic carcinoma or other malignancy microscopically, and vice versa. Diagnostic difficulty may arise due to the small and fragmented sample of a core biopsy. This review will focus on the pertinent clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic features of the more commonly encountered inflammatory lesions of the breast that can be characterized in a core biopsy sample. These include fat necrosis, mammary duct ectasia, granulomatous lobular mastitis, diabetic mastopathy, and abscess. The microscopic differential diagnoses for these lesions when seen in a core biopsy sample will be discussed.
-
Keywords: Breast; Core biopsy; Inflammatory; Mammogram
Inflammatory and reactive conditions of the breast are relatively uncommon among benign breast lesions, and may present with clinical and radiologic abnormalities akin to malignant processes. As such, core biopsy may be performed to exclude the possibility of malignancy. In most cases, the diagnosis based on microscopy is clear, but in fragmented core biopsy samples, some conditions may mimic malignancy. Conversely, some malignancies can also simulate benign inflammatory or reactive conditions.
The clinical, radiographic, and histologic features of commonly encountered inflammatory and reactive breast lesions, namely, fat necrosis, mammary duct ectasia, granulomatous lobular mastitis, diabetic mastopathy, and abscess will be reviewed (Table 1). In addition, we will discuss the histologic features on core biopsy that distinguish the items on this differential.
FAT NECROSIS
- Fat necrosis is most often seen in traumatized breast tissue, particularly in areas of prior surgery or biopsy. Radiation therapy can also lead to fat necrosis in breast [1-3] and has been seen in up to 50% of patients following balloon-based brachytherapy [4]. Clinically, fat necrosis can present as a palpable mass with or without skin retraction, or it can be asymptomatic [5].
- On mammography, oil or lipid cysts, which are often calcified, are characteristic of fat necrosis (Fig. 1A). Calcifications in fat necrosis may be clustered, pleomorphic, and linear, simulating ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) [6,7]. Fat necrosis can also appear as a stellate mass with irregular margins on mammography and ultrasound [8-10].
- Microscopically, fat necrosis is characterized by infiltration of foamy histiocytes and foreign body type giant cells around necrotic fat cells and lipid vacuoles (Fig. 1B). Cysts lined by foamy histiocytes are often present (Fig. 1C). Lymphocytic infiltration, often accompanied by plasma cells, can be present to varying degrees. As fat necrosis evolves, fibrosis develops within the lesion, forming a scar and fibrous walled cysts that can calcify (Fig. 1D–F). Adjacent glandular structures in a biopsied sample may show changes indicative of radiation therapy, such as cytologic atypia, squamous metaplasia, and thickened basement membranes.
- The differential diagnosis for fat necrosis includes less common types of invasive carcinoma, including the lipid-rich variant and carcinomas with “histiocytoid” morphology, such as apocrine carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. A broad-spectrum cytokeratin can be used to exclude the presence of carcinoma. Some histiocytic processes, although rare, should also be included in the differential diagnosis of fat necrosis. Rosai-Dorfman disease is a histiocytic proliferation that rarely involves the breast and is characterized by large histiocytes accompanied by a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate [11]. Histiocytes show emperipolesis and positive immunohistochemical staining for S100 and CD68, but negative staining for CD1a. Erdheim-Chester disease is an even rarer form of histiocytosis which may involve the breast, showing positive immunohistochemical staining for CD68 and negative staining for CD1a and S100. Patients with Erdheim-Chester disease will have involvement of other sites, most commonly the long bones, before breast involvement [12].
- Fat necrosis does not need to be excised when diagnosed via a core biopsy, unless features on imaging are suspicious for malignancy or are discordant with the pathologic diagnosis of fat necrosis.
MAMMARY DUCT ECTASIA
- Mammary duct ectasia is an inflammatory condition characterized by dilatation of the central ducts with associated fibrosis and chronic inflammation. Perimenopausal and postmenopausal women are most often affected [13-15]. Duct ectasia presents as unilateral or bilateral non-bloody nipple discharge, nipple retraction, or a palpable mass that is typically subareolar and sometimes associated with pain. On mammography, duct ectasia appears as branching calcifications, ductal dilatation, or a stellate mass [16]. Ultrasound shows dilated subareolar ducts or a mass-like lesion filled with echogenic material, which may not be evident on mammography [17]. On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), duct ectasia can present with a pattern of enhancement that can mimic DCIS.
- The microscopic appearance of duct ectasia is variable and depends on the disease stage. In early stages, mild ductal dilatation with luminal histiocytes is seen (Fig. 2A, B). Ductal epithelium is not hyperplastic and may be flattened or completely absent. Sloughed epithelium may be seen in ductal lumens (Fig. 2C). Lipid-laden foamy histiocytes can be seen within the duct lumen and in adjacent stroma. Intraepithelial histiocytes can also be seen. “Ochrocytes” refers to histiocytes in periductal stroma that show accumulation of lipofuscin pigment, which imparts a brown color to the cells (Fig. 2D) [18]. A periductal chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells is also present, particularly when leakage of duct contents into the surrounding stroma has occurred. In the later stages of duct ectasia, fibrosis of duct walls, sometimes accompanied by elastosis, is the predominant histologic feature. The fibrotic wall of the duct may calcify, and can result in calcifications within duct lumens (Fig. 2E). A small portion of a fibrotic duct, with or without accompanying inflammation, may be the only finding in a limited core biopsy sample. Cholesterol granulomas, or “cholesterolomas,” may form within ducts and rupture, spilling contents into the surrounding stroma (Fig. 2F).
- The differential diagnosis for duct ectasia includes cysts associated with fibrocystic change. Cysts are seen in terminal duct lobular units, in contrast to the subareolar duct involvement seen in duct ectasia. Making this distinction is not critical, as both lesions are typically managed conservatively. Juvenile papillomatosis is an uncommon localized lesion showing a constellation of histologic findings, including ductal stasis with luminal histiocytes. Florid ductal hyperplasia, apocrine metaplasia, papillary proliferations, and sclerosis are other characteristic findings in juvenile papillomatosis. Ductal hyperplasia and papillary epithelial hyperplasia are not seen in duct ectasia. Finally, duct ectasia occur because of duct obstruction due to an intraductal mass. If an intraductal mass is suspected and not represented in the core biopsy, excisional biopsy is necessary.
- When duct ectasia is diagnosed in a screening core biopsy, excisional biopsy is not necessary, provided there is radiologic-pathologic concordance. Symptomatic cases of duct ectasia are treated by excision of the involved ducts. Duct ectasia is not associated with an elevated risk for breast carcinoma.
GRANULOMATOUS LOBULAR MASTITIS
- Granulomatous mastitis have various etiologies, including infection (bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial), sarcoidosis, and other systemic granulomatous disease. After such causes are excluded, idiopathic “granulomatous lobular mastitis” describes a condition causing chronic, destructive non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation of lobules. The etiology of granulomatous lobular mastitis is unknown, though some cases are associated with Corynebacterium infection (described below). Oral contraceptive use, smoking, and autoimmune disease do not appear to predispose women to granulomatous lobular mastitis [19].
- Most cases of granulomatous lobular mastitis occur in women of reproductive age (20s–40s). Most women have been pregnant at least once prior to presentation, though the condition does not usually occur during pregnancy or lactation [20-23]. Patients present with a unilateral palpable mass that is often accompanied by skin or nipple retraction and pain. Symptoms may be accompanied by axillary lymphadenopathy [19,21,22]. On imaging, granulomatous lobular mastitis is often suggestive of malignancy. A spiculated mass or multiple nodular masses may be seen on mammography [22,24,25]. Ultrasound often shows an irregular hypoechoic mass, fluid collection, tubular structures, or parenchymal mixed echogenicity [21,22,24-26].
- Microscopically, granulomatous lobular mastitis is characterized by non-necrotizing granulomas concentrated in lobules. The granulomas contain epithelioid histiocytes, Langhans giant cells, and lymphoplasmacytic inflammation (Fig. 3A, B). Neutrophilic microabscesses may also be seen. Granulomatous lobular mastitis may be complicated by frank abscess formation and draining skin sinuses. Cystic vacuoles, representing dissolved lipid, are often present within the granulomas, and can be lined by neutrophils; this has been termed “cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis” (Fig. 3C) [27-29]. In such cases, gram-positive bacilli representing Corynebacterium can be seen within the cystic vacuoles (Fig. 3D). The bacteria show “coryneform” features, such as arrangement into palisades and “V” shapes, as well as clubbing of the organisms. These bacteria are not readily identifiable on hematoxylin and eosin examination, and in most cases only rare (<10) bacteria may be present in one or two vacuoles in one core biopsy sample. In fact, gram stains and microbial cultures of these samples are often negative in these cases, in part due to the fastidious nature of these organisms [27]. We recently reported on a series of twelve patients with histologically identified cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis [29]. All patients presented with a unilateral breast mass that was painful in six of twelve cases. Imaging was either suspicious (BI-RADS 4) or highly suggestive of malignancy (BI-RADS 5) in over half of the studied cases. Gram-positive bacilli were identified in five of twelve cases, and all microbial cultures were negative for bacterial growth. Patients showed a variable response to treatment, with time to resolution of symptoms ranging from two weeks to six months.
- Granulomatous lobular mastitis is often initially encountered in a core biopsy sample, with the differential including other causes of granulomatous lobular inflammation. Special stains should be performed to rule out infection with fungi and acid-fast bacilli as the cause of the granulomatous process. Sarcoidosis should be excluded based on clinical, imaging, and laboratory findings. Sarcoidosis involvement of the breast is uncommon, and rarely the initial site of disease detection. Sarcoid granulomas tend to show less inflammation and are not associated with abscess or microabscess formation, as in granulomatous lobular mastitis. Schaumann bodies and asteroid bodies may be identified within granulomas. In cases where cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis is seen, gram stains should be performed to identify gram-positive bacilli. At our institution, when this pattern is seen on biopsy, we include a note in the pathology report stating its known association with Corynebacterium infection, in order to help guide treatment. Microbial cultures should be obtained in all cases of granulomatous lobular mastitis to rule out infection.
- Patients with granulomatous lobular mastitis are typically treated using a combination of antibiotics and surgery. Steroids have also been shown to be effective when added to the treatment regimen or used alone [22,23,28,30,31]. Despite various treatments options, patients often experience persistent and recurrent disease, with complications including draining sinuses and abscess formation. Patients often have to undergo multiple surgical procedures and courses of antibiotics.
DIABETIC MASTOPATHY
- Diabetic mastopathy, also known as “lymphocytic mastopathy” or “sclerosing lymphocytic lobulitis” is an uncommon mass-forming lesion seen in patients with insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus, particularly in those who have long-standing disease with microvascular complications [32-34]. The characteristic histologic findings seen in diabetic mastopathy can also be seen in lesions of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and even those with no history of diabetes or autoimmune disease [34,35]. The cause of diabetic mastopathy is not known. One theory is that hyperglycemia leads to stromal matrix expansion and accumulation of advanced glycosylation end products, leading ultimately to an inflammatory B-cell response [32]. It has also been suggested that diabetic mastopathy develops as a result of an immunologic response to exogenous insulin; however, this is unlikely the sole cause, as the lesion also develops in patients who have not taken exogenous insulin [36].
- Diabetic mastopathy most often occurs in premenopausal women, although rare cases have been reported in men [32,34,35,37]. The typical presentation is a palpable unilateral mass, though screening mammography may detect the first changes. In some instances, multiple masses or ill-defined nodules are clinically detectable. The mammographic and sonographic features of diabetic mastopathy may be suspicious for malignancy: mammography may reveal an ill-defined mass, distortion, or dense glandular breast tissue [38]; ultrasound may show an irregular hypoechoic mass with posterior shadowing [38-40]. MRI shows nonspecific enhancement [40-42].
- Tomaszewski et al. [32] were the first to put forth criteria for the microscopic diagnosis of diabetic mastopathy. The characteristic constellation of findings includes lymphocytic lobulitis and ductitis, lymphocytic perivasculitis, and stromal fibrosis with epithelioid fibroblasts [32]. Lymphocytic infiltrates, which can be fairly dense, surround ducts, lobules, and small vessels, and may sometimes be associated with plasma cells (Fig. 4A–C). Immunohistochemical characterization of these infiltrates reveals mature B-lymphocytes with a small population of T cells [43]. Germinal centers are not typically seen here. Involved lobules may be atrophic or unremarkable. The stroma in diabetic mastopathy is dense and has a keloidal appearance. Intra-stromal epithelioid fibroblasts appear as plump cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (Fig. 4B–D). Nuclei are oval to round with vesicular nuclei. Neither significant nuclear atypia nor mitotic figures are seen. The distribution of fibroblasts within the stroma can be heterogeneous, and show a whorled or nodular growth pattern [35]. These distinctive fibroblasts are not present in all cases of diabetic mastopathy. In a series by Ely et al. [35], epithelioid fibroblasts were absent in five of 19 (26%) cases, including the two cases occurring in men. However, these fibroblasts were present in all three non-diabetic patients in their study.
- The differential diagnosis for diabetic mastopathy as seen in core biopsy sample depends on which components of the lesion are present in the limited sample. If dense keloidal fibrosis is the predominant finding, fibrocystic change should be considered. It would be atypical for fibrosis to occur in diabetic mastopathy without coexisting perilobular or perivascular lymphocytic infiltrates, unless the sample is quite limited. The most diagnostically relevant caveat would be to avoid misclassifying the epithelioid fibroblasts as neoplastic proliferations. Further, care should be taken to exclude carcinomas with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, such as pleomorphic lobular carcinomas that exhibit “histiocytoid” and/or apocrine features. These carcinomas, as in diabetic mastopathy, may not be associated with desmoplastic stroma; a broad-spectrum cytokeratin stain can be performed to rule out carcinoma in such cases. Granular cell tumors are composed of cells with abundant pink granular cytoplasm and bland nuclear features (Fig. 4E). These tumors stain positive for S100 and CD68, which helps to distinguish them from diabetic mastopathy. Multinucleated stromal giant cells, a benign incidental finding in breast tissue, can be distinguished from cells of diabetic mastopathy by their multiple hyperchromatic nuclei and scant, versus abundant, cytoplasm (Fig. 4F). Multinucleated stromal giant cells are incidental microscopic findings, while diabetic mastopathy is a mass-forming proliferation. Other mass-forming lesions with lymphoid infiltrates should be considered when lymphocytic ductitis, lobulitis, and perivasculitis are present in the absence of epithelioid fibroblasts. Lymphoma in the breast tends to diffusely infiltrate the stroma, a pattern of inflammation distinct from that seen in diabetic mastopathy. Additionally, immunostaining and molecular analysis will reveal a clonal proliferation of lymphocytes in lymphoma, but not in diabetic mastopathy.
- Diabetic mastopathy is a benign condition, and patients can be managed with routine mammographic surveillance. In patients who have undergone excision of the lesion, recurrences may be ipsilateral or contralateral [35]. In a series reported by Dorokhova et al. [40], five of 34 cases (15%) of diabetic mastopathy recurred (2 ipsilateral, 3 bilateral). Patients with diabetic mastopathy are not at increased risk for subsequent development of breast carcinoma. Further, the lymphocytes in diabetic mastopathy do not show evidence of clonality by immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement studies, and patients also do not appear to be at risk for developing lymphoma [43].
ABSCESS
- Breast abscesses occur most commonly during lactation, but may also occur in the subareolar breast tissue of non-lactating breasts. Abscess formation is a consequence of ductal stasis in both lactational and non-lactational breasts. Though most patients with mastitis or breast abscess are treated with empiric antibiotics, core biopsy is indicated in some cases to rule out malignancy.
- Lactational abscess can develop as a complication of mastitis, which occurs in up to 10% of lactating women, most commonly during the initiation and weaning phases of breastfeeding [44-47]. The most common organism isolated from these abscesses is S. aureus, identified approximately 50% of the time [46,48-50]. Primiparity, prior lactational mastitis, and improper nursing technique are risk factors for the development of mastitis and abscesses [44-46]. Cracking of the nipple skin may facilitate the entry of bacteria into the ductal system. In a series reported by Dener and Inan [46], 22 out of 128 patients (17%) with lactational abscess or mastitis had cracked nipples. Bacteria that enter the ducts are supplied with a lactose-rich environment from milk within the ductal lumen. Patients with lactational mastitis and abscess can present with redness, swelling, tenderness, or a palpable mass. Fever may additionally be present in some cases.
- Subareolar, or non-puerperal abscesses, most often develop as a consequence of squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts. Squamous metaplasia of ducts leads to keratin accumulation with eventual rupture and spillage of duct contents into the surrounding stroma, which leads to abscess formation. This may be complicated abscess rupture and the formation of a sinus tract. The clinical scenario of recurring subareolar abscesses and sinus formation has been referred to as Zuska’s Disease or periductal mastitis [51]. Patients with subareolar abscesses are typically premenopausal, though older women and men may also be affected [49,52]. Cigarette smoking is a strong risk factor for the development of subareolar abscesses, with approximately 70%–90% of patients reporting a history of smoking [50,53,54]. Diabetes and obesity are other associated risk factors [54]. Patients present with a painful subareolar or periareolar mass, with or without nipple retraction [55]. Nipple discharge, if present, may have a pasty consistency. Most cases are unilateral, but bilateral disease can also occur. In a series of 152 patients reported by Habif et al. [49], 40 (26%) presented with bilateral abscesses. In contrast with lactational mastitis, the bacteria isolated from non-puerperal abscesses are most commonly mixed and predominantly anaerobic [54]. In one study, coagulase-negative staphylococci was the most common aerobic organism isolated [56].
- Mammographic features of abscesses are non-specific and may include a mass, architectural distortion, or skin thickening [44,45]. Ultrasound shows a hypoechoic mass or a multiloculated fluid collection with a thick, echogenic rim [45,55].
- Microscopically, an abscess shows a mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed mainly of neutrophils in breast tissue, which may additionally show lactational changes in a lactational abscess. In abscess resolution, neutrophilic inflammation is replaced by granulation tissue and chronic inflammatory changes. In some cases, subareolar abscesses may show dilated ducts that contain squamous metaplasia; a foreign body giant cell reaction to keratin may also be seen within the abscess. The differential diagnosis for breast abscess includes duct ectasia and granulomatous lobular mastitis, both of which can be associated with abscess formation.
- Lactational mastitis can be adequately treated with antibiotics, though surgical drainage may be necessary in unresponsive cases [57]. Nursing should be continued throughout treatment, and may in fact help resolve the infection. Treatment of subareolar abscess involves a combination of antibiotics and surgery, involving excision of the abscess and adjacent lactiferous duct. Significantly lower rates of recurrence are seen when the infected duct is also excised, compared excision of abscess alone [50,53]. Subareolar abscesses are often chronic and recurring, with longer time to resolution and higher rates of recurrence, when compared to lactational abscesses [45,50,57].
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Fig. 1.Mammographic and microscopic features of fat necrosis in core biopsy samples. (A) Mammography shows a calcified lipid cyst, a characteristic feature of fat necrosis. (B) Core biopsy shows foamy histiocytes in adipose tissue. (C) Chronic inflammation is present and histiocyte-lined cysts are evident (right). (D) Necrotic adipocytes, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis are seen. (E, F) Fat necrosis is seen in stereotactic core biopsies obtained due to calcifications. (E) Calcifications formed within necrotic fat. (F) Calcified fibrous wall of a lipid cyst.

Fig. 2.Mammary duct ectasia. (A) Core biopsy performed for an “intraductal mass” shows a portion of a fibrotic duct wall lined with foamy histiocytes. (B) Disrupted/ruptured duct wall with histiocytes in periductal stroma. (C) Flattened epithelium and fragments within the proteinacious luminal contents. The sample lacks prominent inflammatory features. (D) Brown histiocytes, or “ochrocytes,” are seen in the periductal stroma. Intraepithelial foamy histiocytes are also present. (E) An older lesion shows intraductal calcification. (F) Intraductal “cholesteroloma” formed within a duct with rupture into surrounding stroma.
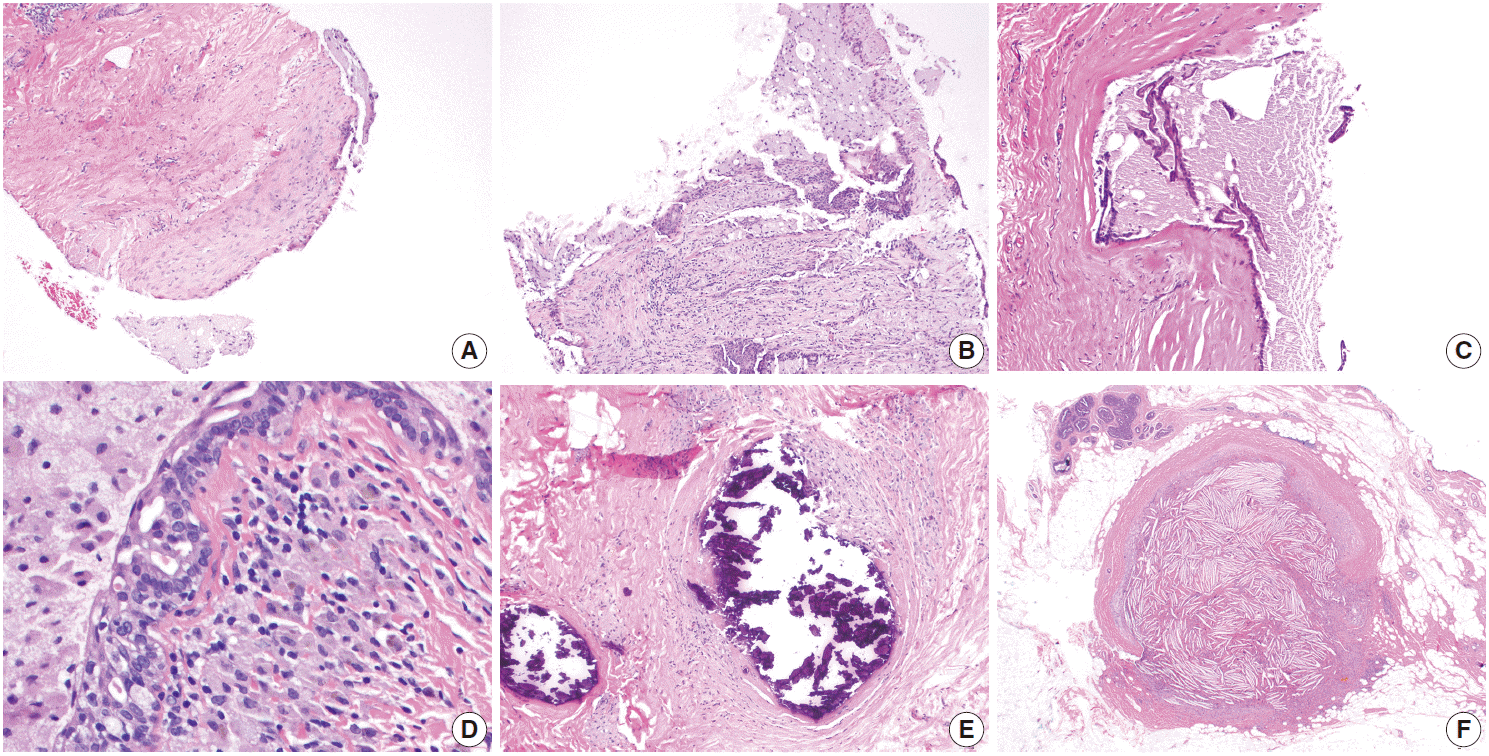
Fig. 3.Granulomatous lobular mastitis. (A, B) Non-necrotizing granulomas are centered within lobules. Granulomas contain Langhans giant cells, and are associated with lymphocytes and plasma cells. (C) Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis showing neutrophil-lined cysts within granulomas. (D) Gram-positive coryneform bacilli are present within the cysts.

Fig. 4.Diabetic mastopathy. (A) Lymphoid infiltrates surround ducts, lobules, and small vessels. The stroma has a hyalinized appearance. (B, C) Plump epithelioid fibroblasts are present in the stroma (C inset, high power). Perilobular (B) and perivascular (C) chronic inflammation is seen. (D) Fibroblasts in diabetic mastopathy compared with granular cell tumor (E) and multinucleated stromal giant cells (F).
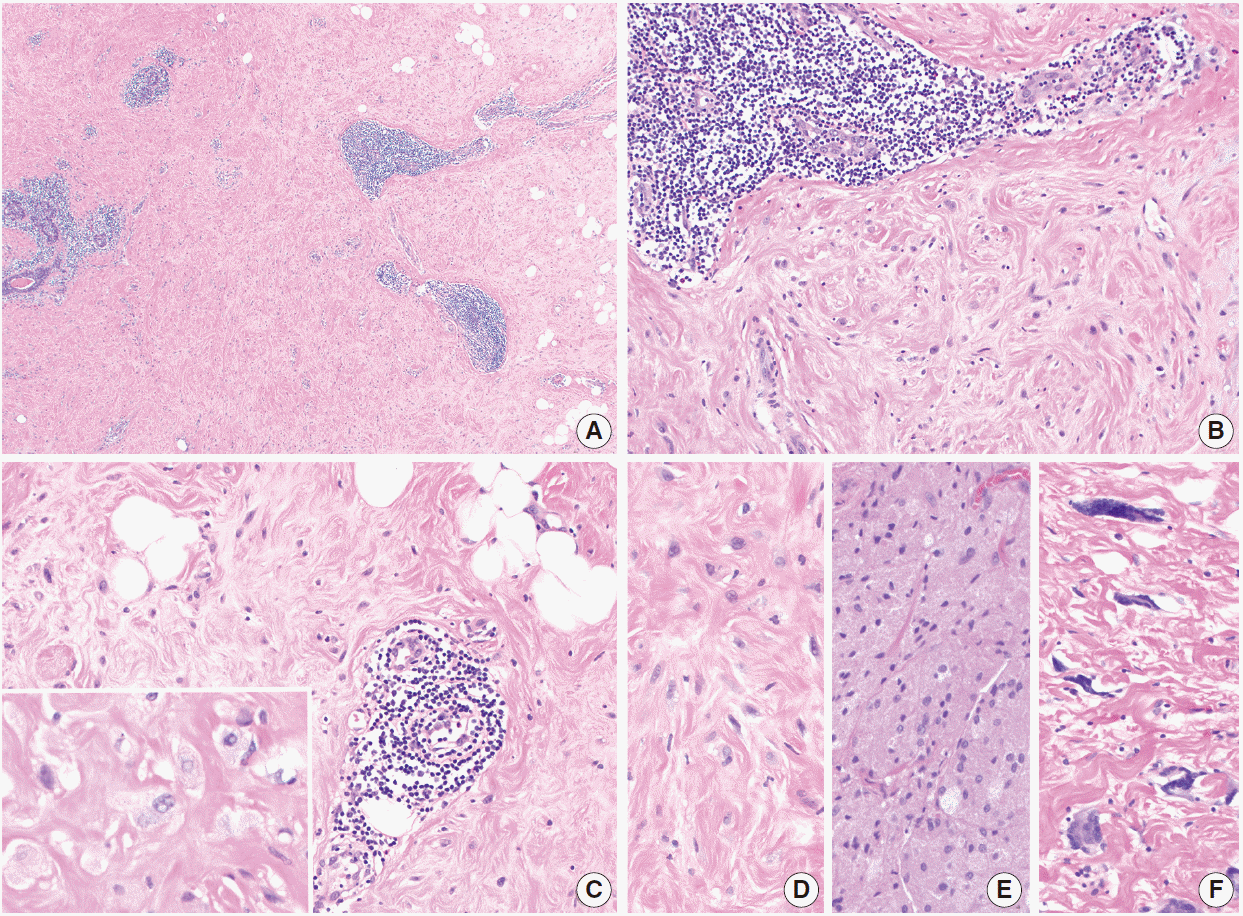
Table 1.Pertinent features of inflammatory lesions of the breast
|
Clinical |
Etiology and associations |
Imaging |
Microscopic features |
Differential diagnosis |
|
Fat necrosis |
Mass
Nipple/skin retraction |
Trauma
Surgery/biopsy
Radiation |
MMG: oil cyst; calcifications; spiculated mass
US: oil cyst; solid mass; complex cyst |
Lipid vacuoles and necrotic adipocytes surrounded by foamy histiocytes and foreign body giant cells
Chronic inflammation
Fibrosis, calcification |
Invasive carcinoma
- “Histiocytoid”
- Lobular
- Apocrine
- Lipid-rich
Erdheim-Chester (rare) |
|
Duct ectasia |
Unilateral or bilateral non-bloody nipple discharge
Nipple/skin retraction
Mass |
- |
MMG: branching calcifications; stellate mass
US: dilated subareolar ducts; mass |
Dilated ducts with luminal histiocytes
Periductal fibrosis
Periductal chronic inflammation
Intraepithelial histiocytes
Calcifications in duct lumen or duct wall |
Ruptured cyst
Ductal dilatation due to intraductal mass |
|
Granulomatous lobular mastitis |
Mass
Erythema
Nipple/skin retraction
Pain
Draining sinus |
Idiopathic
Corynebacterim spp. |
Often suspicious for malignancy
MMG: ill-defined mass
US: irregular hypoechoic mass; dilated ducts |
Non-necrotizing granulomatous inflammation in lobules
Microabscesses
Suppurative granulomas with cystic vacuoles: “cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis” |
Granulomatous mastitis secondary to:
- Infection (TB, fungal)
- Sarcoidosis
- Other systemic granulomatous disease |
|
Diabetic mastopathy |
Palpable mass or nodularity |
Diabetes mellitus (types I > II)
Autoimmune dx.
Endocrine dx.(i.e., thyroid dx.) |
MMG: ill-defined mass; architectural distortion
US: irregular hypoechoic solid mass
MRI: non-specific |
Does not form well-defined mass
Stromal fibrosis: dense with keloidal features and epithelioid fibroblasts
Lymphocytic infiltrates in periductal, perilobular, perivascular distribution |
Invasive carcinoma (apocrine or lobular)
Granular cell tumor
Multinucleated stromal giant cells
Lymphoma
Vasculitis |
|
Breast abscess |
Tender mass with redness, warmth, swelling
± Fever
± Draining sinus
± Nipple discharge |
Lactational/puerperal abscess:
- S. aureus
Subareolar/non-puerperal abscess:
- SMOLD
- Smoking
- Trauma
- Mixed flora |
MMG: asymmetric mass; skin thickening
US: multiloculated mass/collection |
Mixed inflammatory infiltrate, mainly neutrophils
Granulation tissue and chronic inflammation with resolution
± Gram-positive cocci in clusters (i.e., S. aureus) |
Abscess secondary to granulomatous lobular mastitis or duct ectasia |
REFERENCES
- 1. Clarke D, Curtis JL, Martinez A, Fajardo L, Goffinet D. Fat necrosis of the breast simulating recurrent carcinoma after primary radiotherapy in the management of early stage breast carcinoma. Cancer 1983; 52: 442-5. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Rivera R, Smith-Bronstein V, Villegas-Mendez S, et al. Mammographic findings after intraoperative radiotherapy of the breast. Radiol Res Pract 2012; 2012: 758371.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Shah C, Badiyan S, Ben Wilkinson J, et al. Treatment efficacy with accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI): final analysis of the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite((R)) breast brachytherapy registry trial. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: 3279-85. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Paryani NN, Vallow L, Magalhaes W, et al. The incidence of fat necrosis in balloon-based breast brachytherapy. J Contemp Brachytherapy 2015; 7: 29-34. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Aqel NM, Howard A, Collier DS. Fat necrosis of the breast: a cytological and clinical study. Breast 2001; 10: 342-5. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Hogge JP, Robinson RE, Magnant CM, Zuurbier RA. The mammographic spectrum of fat necrosis of the breast. Radiographics 1995; 15: 1347-56. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Taboada JL, Stephens TW, Krishnamurthy S, Brandt KR, Whitman GJ. The many faces of fat necrosis in the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009; 192: 815-25. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Bilgen IG, Ustun EE, Memis A. Fat necrosis of the breast: clinical, mammographic and sonographic features. Eur J Radiol 2001; 39: 92-9. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Atasoy MM, Oren NC, Ilica AT, Güvenç İ, Günal A, Mossa-Basha M. Sonography of fat necrosis of the breast: correlation with mammography and MR imaging. J Clin Ultrasound 2013; 41: 415-23. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Soo MS, Kornguth PJ, Hertzberg BS. Fat necrosis in the breast: sonographic features. Radiology 1998; 206: 261-9. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Morkowski JJ, Nguyen CV, Lin P, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease confined to the breast. Ann Diagn Pathol 2010; 14: 81-7. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Guo S, Yan Q, Rohr J, Wang Y, Fan L, Wang Z. Erdheim-Chester disease involving the breast: a rare but important differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol 2015; 46: 159-64. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Rahal RM, de Freitas-Junior R, Paulinelli RR. Risk factors for duct ectasia. Breast J 2005; 11: 262-5. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Thomas WG, Williamson RC, Davies JD, Webb AJ. The clinical syndrome of mammary duct ectasia. Br J Surg 1982; 69: 423-5. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Dixon JM. Periductal mastitis/duct ectasia. World J Surg 1989; 13: 715-20. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Sweeney DJ, Wylie EJ. Mammographic appearances of mammary duct ectasia that mimic carcinoma in a screening programme. Australas Radiol 1995; 39: 18-23. ArticlePubMed
- 17. An HY, Kim KS, Yu IK, Kim KW, Kim HH. Image presentation. The nipple-areolar complex: a pictorial review of common and uncommon conditions. J Ultrasound Med 2010; 29: 949-62. PubMed
- 18. Davies JD. Pigmented periductal cells (ochrocytes) in mammary dysplasias: their nature and significance. J Pathol 1974; 114: 205-16. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Oran EŞ, Gürdal SÖ, Yankol Y, et al. Management of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis diagnosed by core biopsy: a retrospective multicenter study. Breast J 2013; 19: 411-8. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Going JJ, Anderson TJ, Wilkinson S, Chetty U. Granulomatous lobular mastitis. J Clin Pathol 1987; 40: 535-40. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Ocal K, Dag A, Turkmenoglu O, Kara T, Seyit H, Konca K. Granulomatous mastitis: clinical, pathological features, and management. Breast J 2010; 16: 176-82. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Hovanessian Larsen LJ, Peyvandi B, Klipfel N, Grant E, Iyengar G. Granulomatous lobular mastitis: imaging, diagnosis, and treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009; 193: 574-81. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Pandey TS, Mackinnon JC, Bressler L, Millar A, Marcus EE, Ganschow PS. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a prospective study of 49 women and treatment outcomes with steroid therapy. Breast J 2014; 20: 258-66. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Ozturk M, Mavili E, Kahriman G, Akcan AC, Ozturk F. Granulomatous mastitis: radiological findings. Acta Radiol 2007; 48: 150-5. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Al-Khawari HA, Al-Manfouhi HA, Madda JP, Kovacs A, Sheikh M, Roberts O. Radiologic features of granulomatous mastitis. Breast J 2011; 17: 645-50. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Joseph KA, Luu X, Mor A. Granulomatous mastitis: a New York public hospital experience. Ann Surg Oncol 2014; 21: 4159-63. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Renshaw AA, Derhagopian RP, Gould EW. Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis: an underappreciated pattern strongly associated with gram-positive bacilli. Am J Clin Pathol 2011; 136: 424-7. PubMed
- 28. Taylor GB, Paviour SD, Musaad S, Jones WO, Holland DJ. A clinicopathological review of 34 cases of inflammatory breast disease showing an association between corynebacteria infection and granulomatous mastitis. Pathology 2003; 35: 109-19. ArticlePubMed
- 29. D’Alfonso T, Moo TA, Arleo E, Cheng E, Antonio L, Hoda S. Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous lobular mastitis: further clinical and pathological characterization of an under-recognized entity based on eleven cases. Mod Pathol 2015; 28 Suppl 2: 40A-41A.
- 30. Jorgensen MB, Nielsen DM. Diagnosis and treatment of granulomatous mastitis. Am J Med 1992; 93: 97-101. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Akbulut S, Yilmaz D, Bakir S. Methotrexate in the management of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: review of 108 published cases and report of four cases. Breast J 2011; 17: 661-8. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Tomaszewski JE, Brooks JS, Hicks D, Livolsi VA. Diabetic mastopathy: a distinctive clinicopathologic entity. Hum Pathol 1992; 23: 780-6. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Camuto PM, Zetrenne E, Ponn T. Diabetic mastopathy: a report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Surg 2000; 135: 1190-3. ArticlePubMed
- 34. Soler NG, Khardori R. Fibrous disease of the breast, thyroiditis, and cheiroarthropathy in type I diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1984; 1: 193-5. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Ely KA, Tse G, Simpson JF, Clarfeld R, Page DL. Diabetic mastopathy: a clinicopathologic review. Am J Clin Pathol 2000; 113: 541-5. PubMed
- 36. Seidman JD, Schnaper LA, Phillips LE. Mastopathy in insulin-requiring diabetes mellitus. Hum Pathol 1994; 25: 819-24. ArticlePubMed
- 37. Logan WW, Hoffman NY. Diabetic fibrous breast disease. Radiology 1989; 172: 667-70. ArticlePubMed
- 38. Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Triggiani V, et al. Diabetic mastopathy: a diagnostic challenge in breast sonography. J Clin Ultrasound 2015; 43: 113-7. ArticlePubMed
- 39. Chan CL, Ho RS, Shek TW, Kwong A. Diabetic mastopathy. Breast J 2013; 19: 533-8. ArticlePubMed
- 40. Dorokhova O, Fineberg S, Koenigsberg T, Wang Y. Diabetic mastopathy, a clinicopathological correlation of 34 cases. Pathol Int 2012; 62: 660-4. ArticlePubMed
- 41. Tuncbilek N, Karakas HM, Okten O. Diabetic fibrous mastopathy: dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging findings. Breast J 2004; 10: 359-62. ArticlePubMed
- 42. Wong KT, Tse GM, Yang WT. Ultrasound and MR imaging of diabetic mastopathy. Clin Radiol 2002; 57: 730-5. ArticlePubMed
- 43. Valdez R, Thorson J, Finn WG, Schnitzer B, Kleer CG. Lymphocytic mastitis and diabetic mastopathy: a molecular, immunophenotypic, and clinicopathologic evaluation of 11 cases. Mod Pathol 2003; 16: 223-8. ArticlePubMed
- 44. Mahoney MC, Ingram AD. Breast emergencies: types, imaging features, and management. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 202: W390-9. ArticlePubMed
- 45. Trop I, Dugas A, David J, et al. Breast abscesses: evidence-based algorithms for diagnosis, management, and follow-up. Radiographics 2011; 31: 1683-99. ArticlePubMed
- 46. Dener C, Inan A. Breast abscesses in lactating women. World J Surg 2003; 27: 130-3. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Scott-Conner CE, Schorr SJ. The diagnosis and management of breast problems during pregnancy and lactation. Am J Surg 1995; 170: 401-5. ArticlePubMed
- 48. Dabbas N, Chand M, Pallett A, Royle GT, Sainsbury R. Have the organisms that cause breast abscess changed with time? Implications for appropriate antibiotic usage in primary and secondary care. Breast J 2010; 16: 412-5. ArticlePubMed
- 49. Habif DV, Perzin KH, Lipton R, Lattes R. Subareolar abscess associated with squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts. Am J Surg 1970; 119: 523-6. ArticlePubMed
- 50. Versluijs-Ossewaarde FN, Roumen RM, Goris RJ. Subareolar breast abscesses: characteristics and results of surgical treatment. Breast J 2005; 11: 179-82. ArticlePubMed
- 51. Zuska JJ, Crile G Jr, Ayres WW. Fistulas of lactifierous ducts. Am J Surg 1951; 81: 312-7. PubMed
- 52. Johnson SP, Kaoutzanis C, Schaub GA. Male Zuska’s disease. BMJ Case Rep 2014; 2014: bcr2013201922.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 53. Meguid MM, Oler A, Numann PJ, Khan S. Pathogenesis-based treatment of recurring subareolar breast abscesses. Surgery 1995; 118: 775-82. ArticlePubMed
- 54. Gollapalli V, Liao J, Dudakovic A, Sugg SL, Scott-Conner CE, Weigel RJ. Risk factors for development and recurrence of primary breast abscesses. J Am Coll Surg 2010; 211: 41-8. ArticlePubMed
- 55. Lo G, Dessauvagie B, Sterrett G, Bourke AG. Squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts (SMOLD). Clin Radiol 2012; 67: e42-6. ArticlePubMed
- 56. Walker AP, Edmiston CE Jr, Krepel CJ, Condon RE. A prospective study of the microflora of nonpuerperal breast abscess. Arch Surg 1988; 123: 908-11. ArticlePubMed
- 57. Kasales CJ, Han B, Smith JS Jr, Chetlen AL, Kaneda HJ, Shereef S. Nonpuerperal mastitis and subareolar abscess of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014; 202: W133-9. ArticlePubMed
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Clinical-radiologic-pathologic characterization of diabetic mastopathy: an analysis of 21 cases
Juan Chen, Chao Zhang, Zhilong Liu, Zhuojun Qi, Lele Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of fatty acid composition in mammary adipose tissue using deep neural network with unsupervised training
Suneeta Chaudhary, Elizabeth G. Lane, Allison Levy, Anika McGrath, Eralda Mema, Melissa Reichmann, Katerina Dodelzon, Katherine Simon, Eileen Chang, Marcel Dominik Nickel, Linda Moy, Michele Drotman, Sungheon Gene Kim
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.2025; 93(5): 2163. CrossRef - Society of surgical oncology medical student & trainee primer for breast surgical oncology
Marissa K. Boyle, Julia M. Selfridge, Rachel E. Sargent, Y. Everett Warren, Julia M. Chandler, Christopher P. Childers
Surgical Oncology Insight.2025; 2(1): 100129. CrossRef - An update on multimodal imaging strategies for nipple discharge: from detection to decision
Mireia Pitarch, Rodrigo Alcantara, Laura Comerma, Ivonne Vázquez de Las Heras, Javier Azcona, Antonia Wiedemann, Maja Prutki, Eva Maria Fallenberg
Insights into Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign Breast Lesions: Diagnostic Utility and Drawbacks of Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology
Shirish S. Chandanwale, Kumar Roushan, Mallika Agarwal, Madhuri Singh, Abhishek Tambile, Ranjana Roy
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Health Care.2025; 17(1): 39. CrossRef - Squamous Metaplasia of Lactiferous Ducts (SMOLD) in a Male Patient: Clinical, Dermoscopic, and Histopathological Insights
Beata Zagórska, Przemysław Miłosz, Jakub Żółkiewicz, Urszula Maińska, Martyna Sławińska
Diagnostics.2025; 15(19): 2489. CrossRef - Ductal carcinoma in situ: Current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Jelena Petrović, Stefan Stevanović
Srpski medicinski casopis Lekarske komore.2025; 6(3): 318. CrossRef - The diagnostic dilemma of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with an emphasis on histopathologic findings
Kiana Anousha, Behnaz Jahanbin, Farid Azmoudeh Ardalan, Vahid Soleimani, Maryam Azizi, Amin Rezvani
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical profiles, imaging findings and antituberculosis treatment outcome in granulomatous mastitis: An Indian scenario
R. Mithen, R.R. Mahin Nallasivam, Dhanasekar Thangaswamy, T. Mohanapriya
Indian Journal of Tuberculosis.2024; 71(2): 163. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis: A diagnostic challenge—3 year single institutional experience
Adil Aziz Khan, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer, Charanjeet Ahluwalia, Mukul Singh, Sachin Kolte, Sunil Ranga
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(1): 50. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of rifampicin-based triple therapy for non-puerperal mastitis: A single-arm, open-label, prospective clinical trial
Fei Zhou, Huanjie Li, Fei Wang, Liyuan Liu, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhigang Yu
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2024; 140: 25. CrossRef - Periductal Mastitis, a Disease with Distinct Clinicopathological Features from Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis
Fei Zhou, Liyuan Liu, Fei Wang, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhen Yang, Zhigang Yu
Journal of Inflammation Research.2024; Volume 17: 3815. CrossRef - MASTITE GRANULOMATOSA E O DIFÍCIL MANEJO DA DOENÇA: UMA REVISÃO SISTEMÁTICA DE LITERATURA
Samara Alves Messias Viana, Laís Barbosa de Azevedo Bulsoni
REVISTA FOCO.2024; 17(6): e5136. CrossRef - Autoimmune Mastitis in a Patient with Behcet’s Syndrome: A Case Report with Rapid Changes in Radiologic Features and Characteristic Pathologic Findings
Yun Hwa Chang, Suk Jin Park, Joo Heon Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(6): 1221. CrossRef - Possibilities of MRI in the differential diagnosis of non-lactative mastitis and cancer
S. V. Serebryakova, T. A. Shumakova, E. A. Yukhno, O. B. Safronova, A. L. Serebryakov
Medical Visualization.2023; 27(2): 36. CrossRef - Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis in seventy seven-female patients: Management, follow up of an overlooked immune-mediated disease, and review of literature
Amira A. Shahin, Emad Khallaf, Lamiaa A. Salaheldin, Somia A.M. Soliman, Yosra S. Rezk, Marwa H. Niazy
The Egyptian Rheumatologist.2023; 45(3): 183. CrossRef - Increased breast cancer mortality due to treatment delay and needle biopsy type: a retrospective analysis of SEER-medicare
Rashmi Pathak, Macall Leslie, Priya Dondapati, Rachel Davis, Kenichi Tanaka, Elizabeth Jett, Inna Chervoneva, Takemi Tanaka
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(4): 627. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and therapeutic strategy of granulomatous mastitis accompanied by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: a retrospective cohort study
ShunBo Li, Qian Huang, PeiPei Song, XiaoRong Han, ZeYu Liu, Lin Zhou, Ping Ning
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano Uncaria gambir as Chemopreventive Agent Against Breast Cancer
Andika Pramudya Wardana, Nanik Siti Aminah, Alfinda Novi Kristanti, Mochamad Zakki Fahmi, Haninda Iffatuz Zahrah, W Widiyastuti, Hendrix Abdul Ajiz, Ummi Zubaidah, Priangga Adi Wiratama, Yoshiaki Takaya
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 4471. CrossRef - Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
Gulisa Turashvili, Xiaoxian Li
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(10): 1133. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Inflammatory granulomatous mastitis caused by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: A clinical challenge
I.M. Brouwer de Koning, A. Lemson, N.H.M. Renders, M. Bessems, P.T.G.A. Nooijen, W.A. Draaisma, K. Bosscha
Clinical Infection in Practice.2022; 15: 100147. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Exocrine gland structure-function relationships
Sameed Khan, Sarah Fitch, Sarah Knox, Ripla Arora
Development.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision pathology as applied to breast core needle biopsy evaluation: implications for management
Laura C. Collins
Modern Pathology.2021; 34: 48. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis, watch and wait is a good option
Gökay Çetinkaya, Ramazan Kozan, Ahmet Cihangir Emral, Ekmel Tezel
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2021; 190(3): 1117. CrossRef - Mammary duct ectasia in adult females; risk factors for the disease, a case control study
Ayad Ahmad Mohammed
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2021; 62: 140. CrossRef - Palpable Lumps after Mastectomy: Radiologic-Pathologic Review of Benign and Malignant Masses
Rend Al-Khalili, Ali Alzeer, Giang-Kimthi Nguyen, Erin P. Crane, Judy H. Song, Janice L. Jeon, Michael Nellamattathil, Erini V. Makariou, Victoria L. Mango
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(4): E967. CrossRef - A case report of TB versus idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with erythema nodosum, reactive arthritis, cough, and headache
Fatma Ben Abid, Hussam Abdel Rahman S. Al Soub
The Aging Male.2020; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Imaging features of granulomatous mastitis in 36 patients with new sonographic signs
Afsaneh Alikhassi, Fahimeh Azizi, Fereshteh Ensani
Journal of Ultrasound.2020; 23(1): 61. CrossRef - Secreciones mamarias
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Ginecología-Obstetricia.2020; 56(1): 1. CrossRef - Mastitis in Autoimmune Diseases: Review of the Literature, Diagnostic Pathway, and Pathophysiological Key Players
Radjiv Goulabchand, Assia Hafidi, Philippe Van de Perre, Ingrid Millet, Alexandre Thibault Jacques Maria, Jacques Morel, Alain Le Quellec, Hélène Perrochia, Philippe Guilpain
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 958. CrossRef - Factors associated with treatment duration and recurrence rate of complicated mastitis
Ming-Jui Tsai, Wei-Chia Huang, Jann-Tay Wang, Ming-Yang Wang, Yi-Hsuan Lee, Shu-Wen Lin, Sung-Ching Pan, Shan-Chwen Chang
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.2020; 53(6): 875. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis: an update
Jessie M Wu, Gulisa Turashvili
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 73(8): 445. CrossRef - Coryneform Bacteria in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis: Morphological Diagnosis in Breast Biopsies
David Oddó, Angeles Stefanelli, Alejandra Villarroel, Gonzalo P. Méndez
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 27(4): 380. CrossRef - Sonographic features of inflammatory conditions of the breast
Alice Febery, Ian Bennett
Australasian Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2019; 22(3): 165. CrossRef - Écoulements mamelonnaires
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Gynécologie.2019; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Etiología de la mastitis crónica: propuesta de secuencia diagnóstica
A. García-Vilanova Comas, J. Galbis Caravajal, V. Sabater Marco, C.A. Fuster Diana, F. Villalba Ferrer, M. Bruna Esteban, C. Zaragozá Fernández
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2018; 45(3): 98. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Manifestations at Multimodality Imaging and Pitfalls
Cedric W. Pluguez-Turull, Jennifer E. Nanyes, Cristina J. Quintero, Hamza Alizai, Daniel D. Mais, Kenneth A. Kist, Nella C. Dornbluth
RadioGraphics.2018; 38(2): 330. CrossRef - Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii in granulomatous mastitis: Analysis of formalin‐fixed, paraffin‐embedded biopsy specimens by immunostaining using low‐specificity bacterial antisera and real‐time polymerase chain reaction
Mari Fujii, Yasuyoshi Mizutani, Takahiko Sakuma, Kouichiro Tagami, Kiichiro Okamoto, Yasushi Kuno, Michihiko Harada, Koichi Kubouchi, Yutaka Tsutsumi
Pathology International.2018; 68(7): 409. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis Presenting as a Breast Pseudotumor: Case Reports with Review of the Literature
Nour Abdul Halim, Imad Uthman, Rayan Rammal, Hazem I. Assi
Case Reports in Rheumatology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - UTILITY OF FNAC IN UNCOMMON INFLAMMATORY AND REACTIVE LESIONS OF BREAST: AN UNSUSPECTED CLINICAL SCENARIO
Rallapalli Rajyalakshmi, Mohammad Akhtar, Rani Vijaya Bhaskar, Kada Venkataramana, Guttikonda Nageswararao, Rayachoti Sridhar
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2018; 5(44): 3070. CrossRef - Inflammatory breast disease: A pictorial essay with radiological‐pathological correlation
Rusiru P Gunawardena, Deepika Gunawardena, Cecily Metcalf, Donna Taylor, Liz Wylie
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2017; 61(1): 70. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis associated with Corynebacterium including Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii
Kate J. Johnstone, Jennifer Robson, Sarah G. Cherian, Jenny Wan Sai Cheong, Kris Kerr, Judith F. Bligh
Pathology.2017; 49(4): 405. CrossRef - Is contrast‐enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) helpful in differentiating diabetic mastopathy from breast carcinoma?
María del Mar Travieso Aja, Gloria Santana López, Mario Rodríguez Rodríguez, Octavio P Luzardo
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2016; 60(5): 639. CrossRef - Lesiones inflamatorias mamarias benignas
Andrés García-Vilanova Comas, Vicente Sabater Marco, Carlos Fuster Diana, Francisco Villalba Ferrer, José Medrano González, Ramón Gómez Contreras
Revista Española de Patología.2016; 49(3): 169. CrossRef - Granulomatous lobular mastitis
Fei Zhou, Li‐Xiang Yu, Zhong‐Bing Ma, Zhi‐Gang Yu
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2016; 2(1): 17. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Cytologic and Histologic Study of 65 Egyptian Patients
Thanaa El A. Helal, Lobna S. Shash, Somaia A. Saad El-Din, Sally M. Saber
Acta Cytologica.2016; 60(5): 438. CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite this Article
Cite this Article





 E-submission
E-submission










