Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Pathol Transl Med > Volume 57(4); 2023 > Article
-
Review
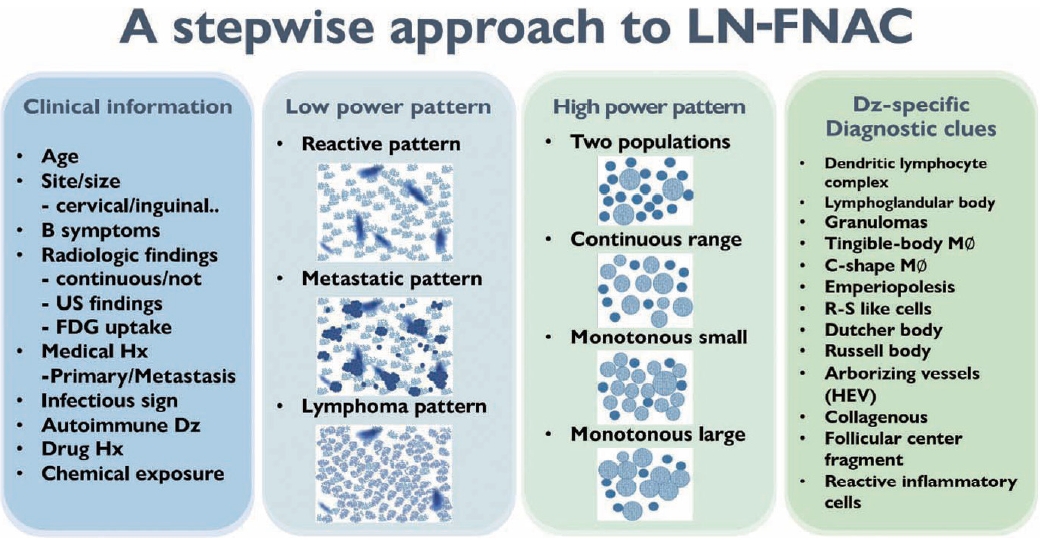
A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes -
Yosep Chong1
 , Gyeongsin Park1
, Gyeongsin Park1 , Hee Jeong Cha2
, Hee Jeong Cha2 , Hyun-Jung Kim3
, Hyun-Jung Kim3 , Chang Suk Kang4, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar1
, Chang Suk Kang4, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar1 , Seung-Sook Lee5
, Seung-Sook Lee5 -
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2023;57(4):196-207.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.12
Published online: July 11, 2023
1Department of Hospital Pathology, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Pathology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea
3Department of Pathology, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea
4Department of Pathology, Samkwang Medical Laboratories, Seoul, Korea
5Department of Pathology, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Yosep Chong, MD, PhD, Department of Hospital Pathology, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 271 Cheonbo-ro, Uijeongbu 11765, Korea Tel: +82-32-820-3160, Fax: +82-32-820-3877, E-mail: ychong@catholic.ac.kr
© 2023The Korean Society of Pathologists/The Korean Society for Cytopathology
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Abstract
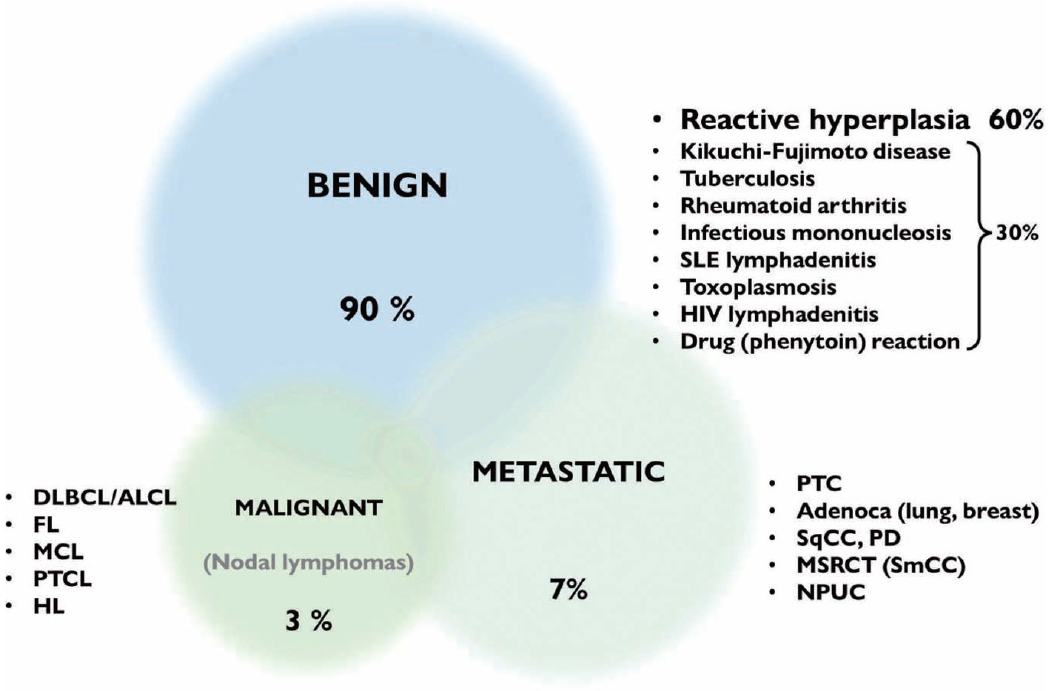
- CLINICAL FINDINGS
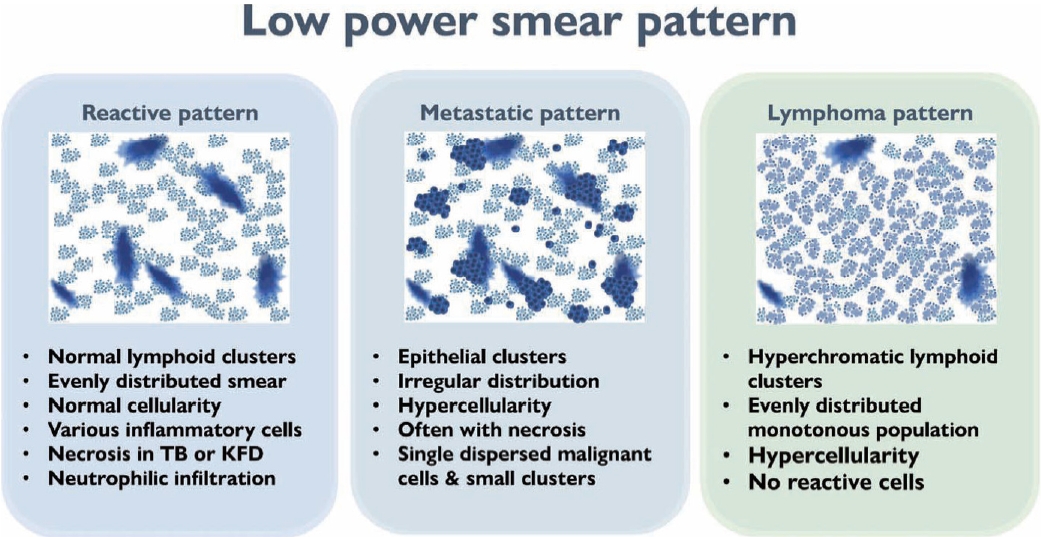
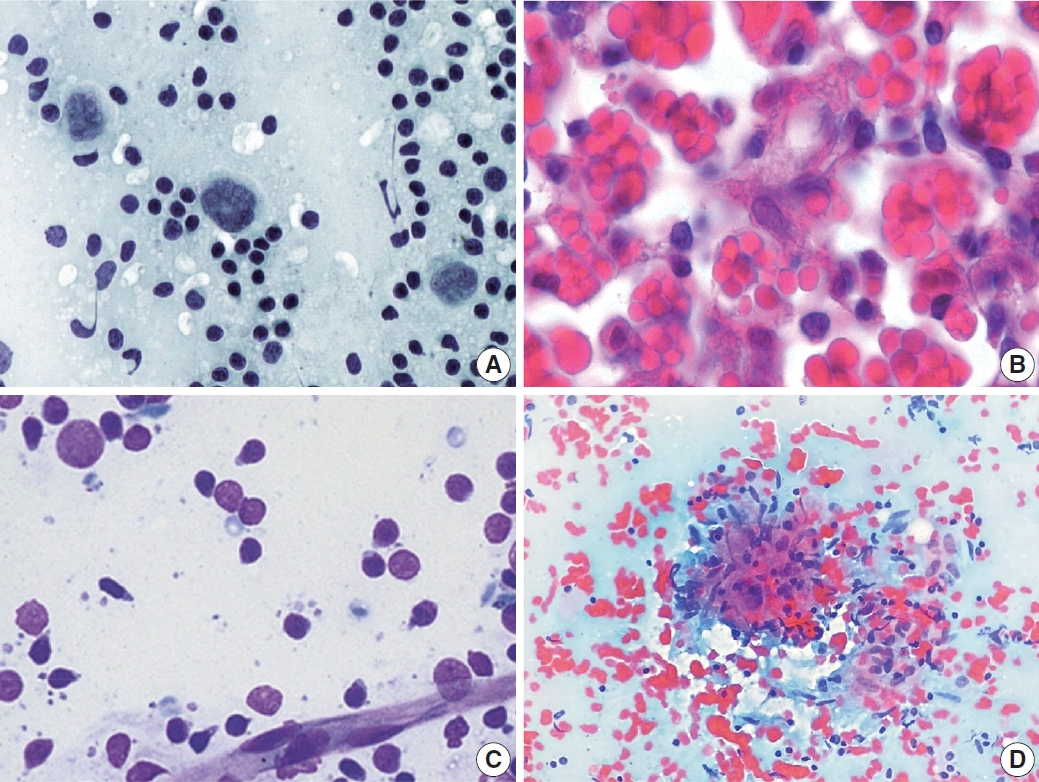
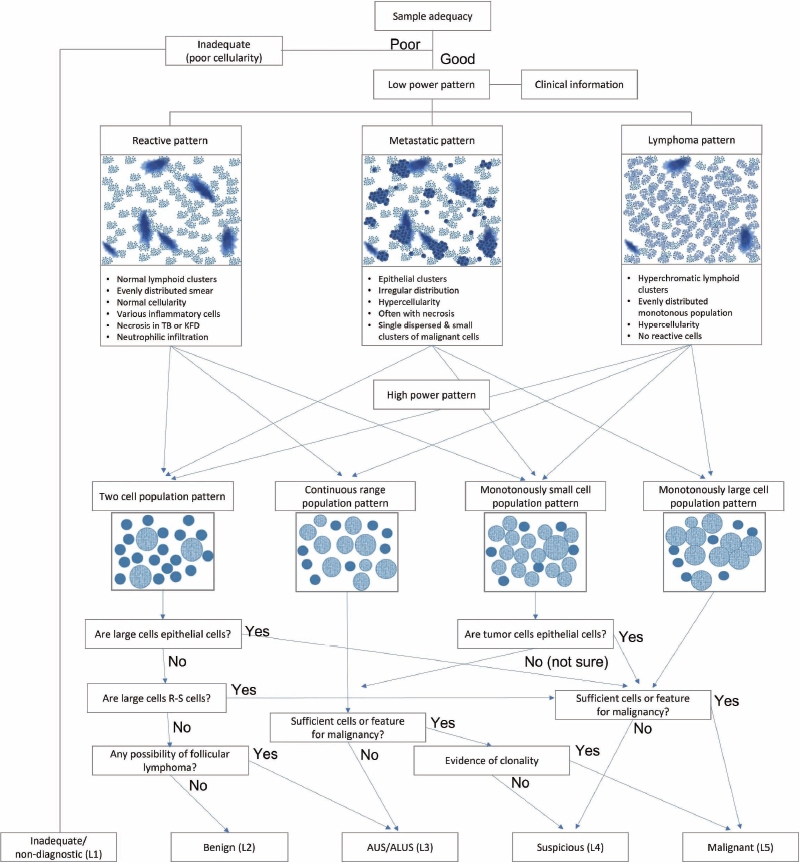
- LOW-POWER PATTERN OF LYMPH NODE FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY
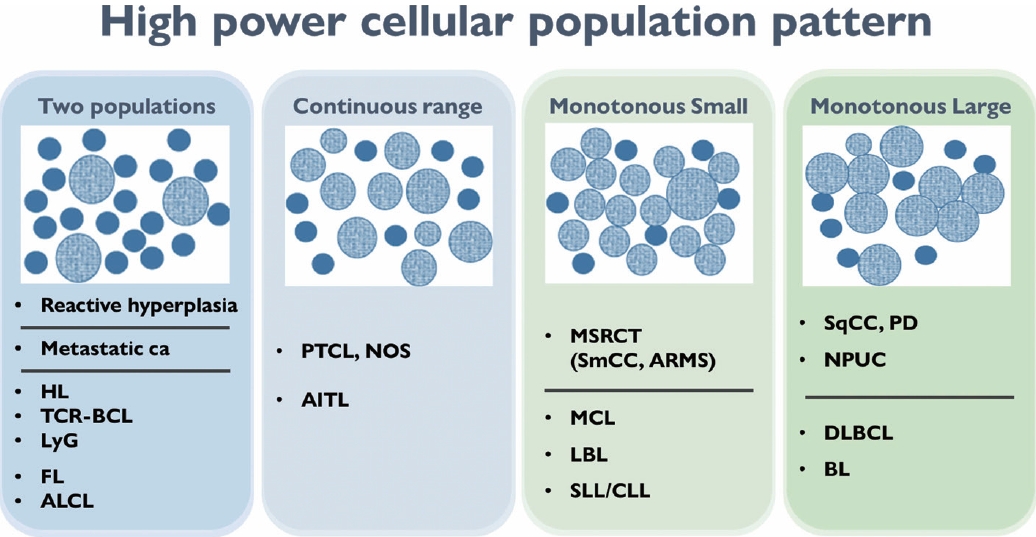
- HIGH-POWER PATTERN OF LYMPH NODE FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY
- DISEASE-SPECIFIC DIAGNOSTIC CLUES
- SYDNEY CLASSIFICATION
- SUGGESTED DIAGNOSTIC ALGORITHM FOR LYMPH NODE FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY
- CONCLUSION
- Supplementary Information
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Development and Validation of Explainable Artificial Intelligence System for Automatic Diagnosis of Cervical Lymphadenopathy From Ultrasound Images
Ming Xu, Yubiao Yue, Zhenzhang Li, Yinhong Li, Guoying Li, Haihua Liang, Di Liu, Xiaohong Xu, Mohamadreza (Mohammad) Khosravi
International Journal of Intelligent Systems.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of the Sydney system for classification and reporting lymph node cytopathology: a retrospective analysis at a tertiary centre
Ashok Teja Kummari, Pramod Kumar Pamu, Krishna Kiran Ganna, Param Jyothi, Sadashivudu
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic approach to FNA biopsy of cystic lesions of the head and neck
Stefen Andrianus, Olivia Leung, Zubair Baloch
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applicability of Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes Using WHO Reporting System: Comparison between Pediatric and Adult Brazilian Populations
Leonardo Fávaro Ficoto, Deolino João Camilo Júnior, Gustavo Resende Nora, Vitor Bonetti Valente, Daniel Galera Bernabé, José Cândido Caldeira Xavier-Júnior
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Intraoperative cytological assessment of sentinel lymph nodes in gynecologic cancer: diagnostic accuracy and limitations
O. V. Pankova, S. V. Vtorushin, M. V. Klimova, D. S. Pismenny, M. O. Ochirov, L. A. Kolomiets, V. M. Perelmuter
Siberian journal of oncology.2025; 24(5): 72. CrossRef - Immunocytochemical markers, molecular testing and digital cytopathology for aspiration cytology of metastatic breast carcinoma
Joshua J. X. Li, Gary M. Tse
Cytopathology.2024; 35(2): 218. CrossRef - Response to comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 43. CrossRef - Comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Elisabetta Maffei, Valeria Ciliberti, Pio Zeppa, Alessandro Caputo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 40. CrossRef - The Incidence of Thyroid Cancer in Bethesda III Thyroid Nodules: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Endocrine Surgery Center
Iyad Hassan, Lina Hassan, Nahed Balalaa, Mohamad Askar, Hussa Alshehhi, Mohamad Almarzooqi
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 1026. CrossRef - Efficiency of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) in Relation to Tru-Cut Biopsy of Lateral Neck Swellings
Mohammed S Al Olaimat, Fahad S Al Qooz, Zaid R Alzoubi, Elham M Alsharaiah, Ali S Al Murdif, Mohammad O Alanazi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls in the Cytological Diagnosis of Nodal Hodgkin Lymphoma
Uma Handa, Rasheeda Mohamedali, Rajpal Singh Punia, Simrandeep Singh, Ranjeev Bhagat, Phiza Aggarwal, Manveen Kaur
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(12): 715. CrossRef - Rapid 3D imaging at cellular resolution for digital cytopathology with a multi-camera array scanner (MCAS)
Kanghyun Kim, Amey Chaware, Clare B. Cook, Shiqi Xu, Monica Abdelmalak, Colin Cooke, Kevin C. Zhou, Mark Harfouche, Paul Reamey, Veton Saliu, Jed Doman, Clay Dugo, Gregor Horstmeyer, Richard Davis, Ian Taylor-Cho, Wen-Chi Foo, Lucas Kreiss, Xiaoyin Sara J
npj Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link-
 Cite this Article
Cite this Article
- Cite this Article
-
- Close
- Download Citation
- Close
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Primary thyroid diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: fine needle aspiration and histological correlation
- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
- Erratum: Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Response to comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”










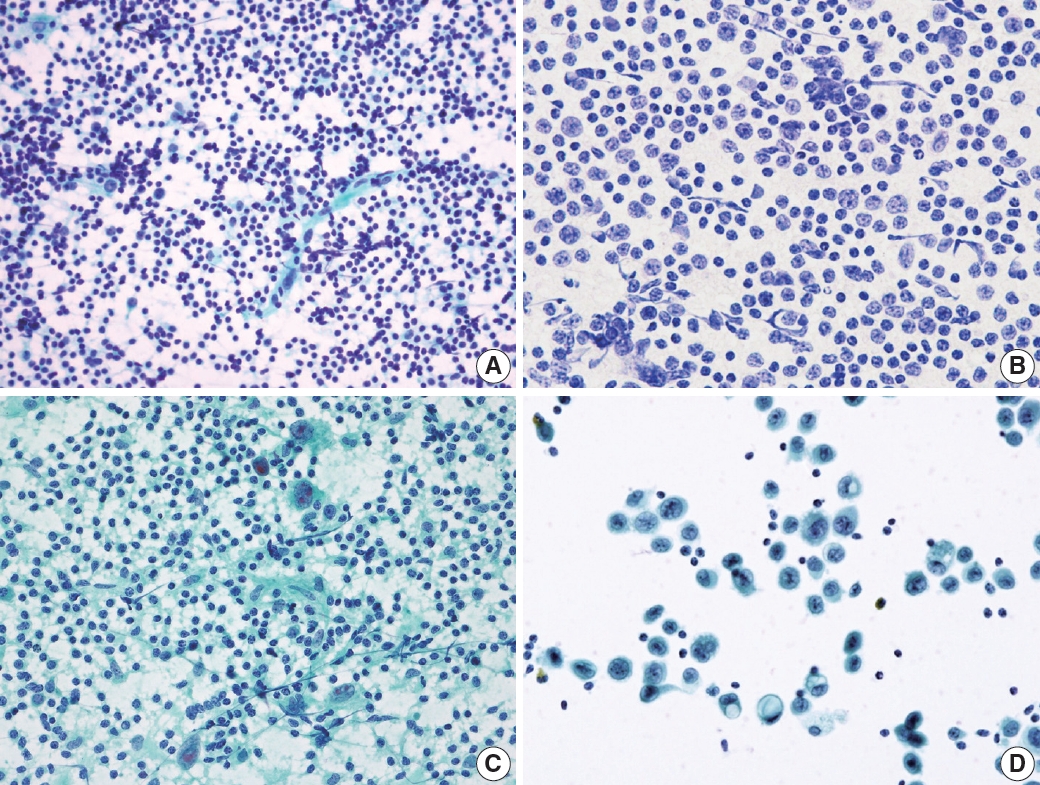
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
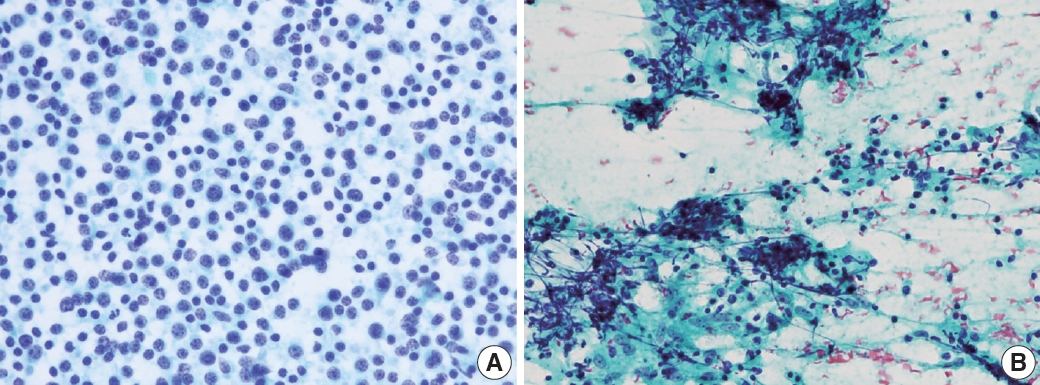
Fig. 5.
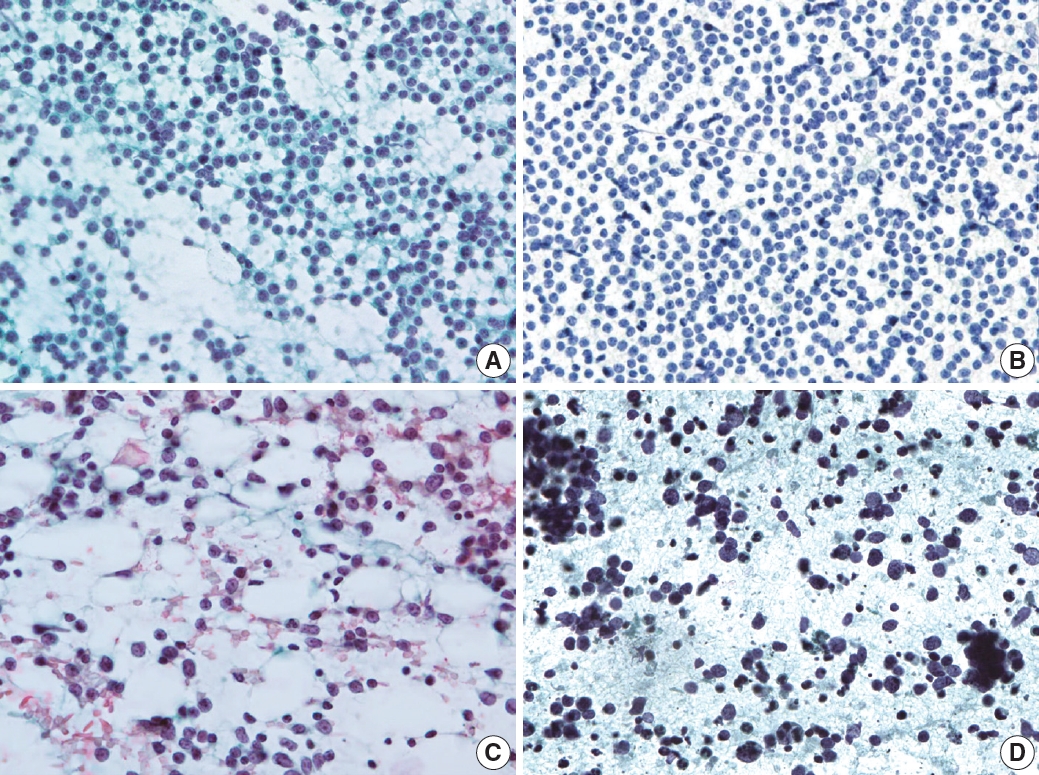
Fig. 6.
Fig. 7.
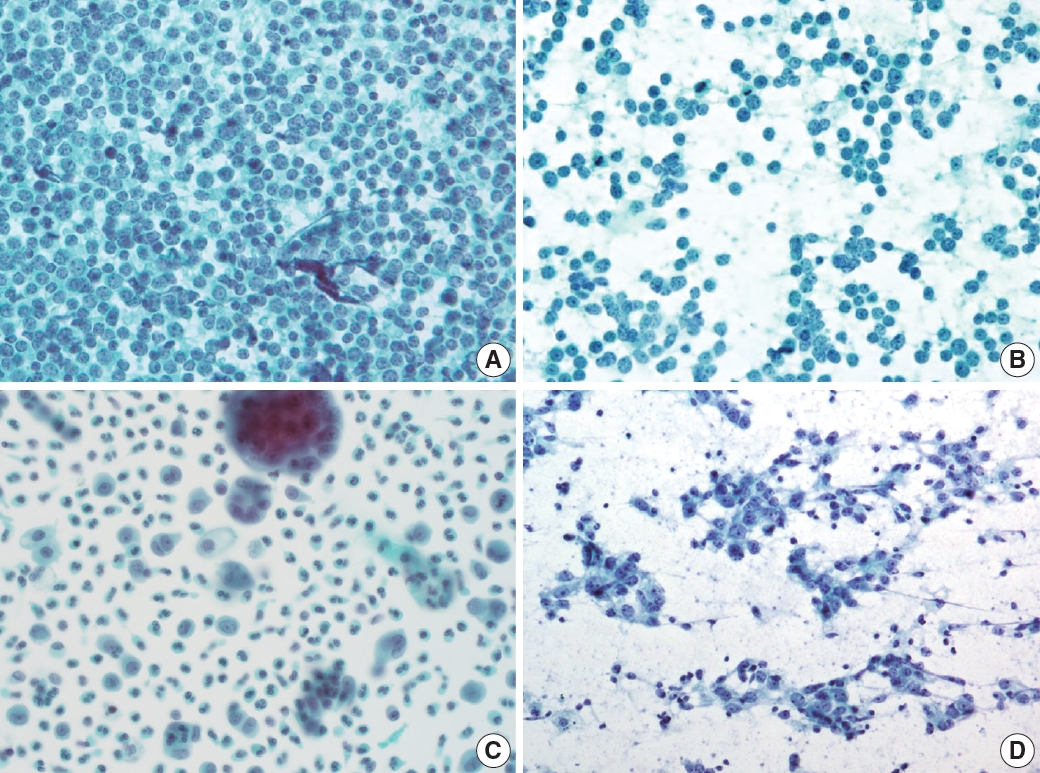
Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
Fig. 10.
| Diagnostic reporting categories | Explanation | Post–LN-FNAC management recommendations | Exemplary findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inadequate/non-diagnostic (L1) | Low cellularity | LN-FNAC repetition and/or CNB or excision | - |
| Benign (L2) | Reactive hyperplasia | Clinical F/U or specific Tx depending on the Dx | - |
| Benign lymphadenitis | |||
| AUS/ALUS (L3) | Possibly benign, not fully supported by cytology and ancillary technique | LN-FNAC repetition with acquisition of material for ancillary studies and/or CNB or excision | Two-cell population that cannot exclude follicular lymphoma |
| Monotonously small cell population that cannot exclude low-grade B-cell lymphomas such as marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, small cell lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia, mantle cell lymphoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma | |||
| Suspicious (L4) | Possibly malignant, not fully supported by cytology and ancillary technique | LN-FNAC repetition with acquisition of material for appropriate ancillary studies and/or CNB or excision | Monotonously small and/or medium-sized, monomorphic atypical lymphoid cells suspicious of lymphoma, but cytomorphology alone is not sufficient for diagnosis, polymorphous lymphoid smears in which few Reed-Sternberg-like cells are detected, large cell or Burkitt lymphomas with scantly cellular, and smears in which atypical cells suspicious for metastasis are detected but are too scant to be diagnostic |
| Malignant (L5) | (NHL, HL, metastases) | Histological biopsy requested (not requested for HL/NHL relapses or metastasis from known or clearly indicated primary tumor, etc.) | Small-to-medium-sized cells of non-Hodgkin lymphomas supported by evidence of clonality and all the entities in which cytopathological features alone are sufficient to identify malignancy as large cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. This category also includes Hodgkin’s lymphoma in which there is an appropriate cellular background and diagnostic Reed-Sternberg cells as well as metastatic neoplasms |
LN-FNAC, lymph node fine needle aspiration cytology; CNB, core needle biopsy; F/U, follow-up; Tx, therapy; Dx, diagnosis; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

 E-submission
E-submission