Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Reviews
- Post-transplant liver biopsies: a concise and practical approach for beginners
- Mohamad Besher Ourfali, David Hirsch, Marianna Scranton, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):1-10. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.15
- 4,489 View
- 381 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Exposure to post-transplant liver biopsies varies among pathology residencies and largely depends on the institution's training program, particularly if the hospital has a liver transplant program. The interpretation of biopsies from transplanted livers presents its own set of challenges, even for those with a solid understanding of non-transplant medical liver biopsies. In this review, we aim to provide a succinct, step-by-step approach to help you interpret liver transplant biopsies. This article may be beneficial for residents interested in liver pathology, gastrointestinal and liver pathology fellows in the early stages of training, clinical gastroenterology and hepatology fellows, hepatologists and general pathologists who are curious about this niche.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7729. CrossRef
- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
- Professional biobanking education in Korea based on ISO 20387
- Jong Ok Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Sangyong Song, Eunah Shin, Ji-Sun Song, Mee Sook Roh, Dong-chul Kim, Han-Kyeom Kim, Joon Mee Kim, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):11-25. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.04
- 5,676 View
- 182 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To ensure high-quality bioresources and standardize biobanks, there is an urgent need to develop and disseminate educational training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, which was developed in 2018. The standardization of biobank education programs is also required to train biobank experts. The subdivision of categories and levels of education is necessary for jobs such as operations manager (bank president), quality manager, practitioner, and administrator. Essential training includes programs tailored for beginner, intermediate, and advanced practitioners, along with customized training for operations managers. We reviewed and studied ways to develop an appropriate range of education and training opportunities for standard biobanking education and the training of experts based on KS J ISO 20387. We propose more systematic and professional biobanking training programs in accordance with ISO 20387, in addition to the certification programs of the National Biobank and the Korean Laboratory Accreditation System. We suggest various training programs appropriate to a student’s affiliation or work, such as university biobanking specialized education, short-term job training at unit biobanks, biobank research institute symposiums by the Korean Society of Pathologists, and education programs for biobankers and researchers. Through these various education programs, we expect that Korean biobanks will satisfy global standards, meet the needs of users and researchers, and contribute to the advancement of science.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
Yun Seon Im, Seol Whan Oh, Ki Hoon Kim, Wona Choi, In Young Choi
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 398. CrossRef
- Development of a big data platform for collecting and utilizing clinical information from the Korea Biobank Network
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Ahrong Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):26-38. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.01
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(2):147
- 12,141 View
- 426 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has long been recognized as a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for breast lesions. However, with the advent of core-needle biopsy (CNB), the role of FNAC has diminished in some clinical settings. This review aims to re-evaluate the diagnostic value of FNAC in the current era, focusing on its complementary use alongside CNB, the adoption of new approaches such as the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System, and the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation to reduce inadequate sample rates. Advances in liquid-based cytology, receptor expression testing, molecular diagnostics, and artificial intelligence are discussed, highlighting their potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of FNAC. Despite challenges, FNAC remains a valuable diagnostic method, particularly in low-resource settings and specific clinical scenarios, and its role continues to evolve with technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Daniella Serafin Couto Vieira, Laura Otto Walter, Maria Eduarda Cunha da Silva, Lisandra de Oliveira Silva, Heloísa Zorzi Costa, Chandra Chiappin Cardoso, Fernando Carlos de Lander Schmitt, Maria Cláudia Santos-Silva
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(23): 4771. CrossRef
- Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Original Articles
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):39-49. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
- 4,150 View
- 322 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Methods
We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
Results
We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
- The combination of CDX2 expression status and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density as a prognostic factor in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal cancers
- Ji-Ae Lee, Hye Eun Park, Hye-Yeong Jin, Lingyan Jin, Seung Yeon Yoo, Nam-Yun Cho, Jeong Mo Bae, Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):50-59. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.26
- 3,603 View
- 279 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) loss are recognized to pursue an aggressive behavior but tend to be accompanied by a high density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). However, little is known about whether there is an interplay between CDX2 loss and TIL density in the survival of patients with CRC.
Methods
Stage III CRC tissues were assessed for CDX2 loss using immunohistochemistry and analyzed for their densities of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial (iTILs) and stromal areas using a machine learning-based analytic method.
Results
CDX2 loss was significantly associated with a higher density of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial and stromal areas. Both CDX2 loss and a high CD8 iTIL density were found to be prognostic parameters and showed hazard ratios of 2.314 (1.050–5.100) and 0.378 (0.175–0.817), respectively, for cancer-specific survival. A subset of CRCs with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs showed the best clinical outcome (hazard ratio of 0.138 [0.023–0.826]), whereas a subset with CDX2 loss and a high density of CD8 iTILs exhibited the worst clinical outcome (15.781 [3.939–63.230]).
Conclusions
Altogether, a high density of CD8 iTILs did not make a difference in the survival of patients with CRC with CDX2 loss. The combination of CDX2 expression and intraepithelial CD8 TIL density was an independent prognostic marker in adjuvant chemotherapy-treated patients with stage III CRC.
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Yoon Kyung Kang, Dong Hoon Shin, Joon Young Park, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, JooYoung Na
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):60-67. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.01
- 4,684 View
- 197 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutation testing is crucial for the administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors to treat non–small cell lung cancer. In addition to traditional tissue-based tests, liquid biopsies using plasma are increasingly utilized, particularly for detecting T790M mutations. This study compared tissue- and plasma-based EGFR testing methods.
Methods
A total of 248 patients were tested for EGFR mutations using tissue and plasma samples from 2018 to 2023 at Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital. Tissue tests were performed using PANAmutyper, and plasma tests were performed using the Cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2.
Results
All 248 patients underwent tissue-based EGFR testing, and 245 (98.8%) showed positive results. Of the 408 plasma tests, 237 (58.1%) were positive. For the T790M mutation, tissue biopsies were performed 87 times in 69 patients, and 30 positive cases (38.6%) were detected. Plasma testing for the T790M mutation was conducted 333 times in 207 patients, yielding 62 positive results (18.6%). Of these, 57 (27.5%) were confirmed to have the mutation via plasma testing. Combined tissue and plasma tests for the T790M mutation were positive in nine patients (13.4%), while 17 (25.4%) were positive in tissue only and 12 (17.9%) in plasma only. This mutation was not detected in 28 patients (43.3%).
Conclusions
Although the tissue- and plasma-based tests showed a sensitivity of 37.3% and 32.8%, respectively, combined testing increased the detection rate to 56.7%. Thus, neither test demonstrated superiority, rather, they were complementary.
- PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Ranran Feng, Yilin Guo, Meilin Chen, Ziying Tian, Yijun Liu, Su Jiang, Jieyu Zhou, Qingluan Liu, Xiayu Li, Wei Xiong, Lei Shi, Songqing Fan, Guiyuan Li, Wenling Zhang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):68-83. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.27
- 3,389 View
- 135 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is characterized by high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and abundant infiltration of non-malignant lymphocytes, which renders patients potentially suitable candidates for immune checkpoint blockade therapies. Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) inhibit the growth of NPC cells and enhance cellular apoptosis and differentiation. Currently, the relationship between PLUNC (as a tumor-suppressor) and PD-L1 in NPC is unclear.
Methods
We collected clinical samples of NPC to verify the relationship between PLUNC and PD-L1. PLUNC plasmid was transfected into NPC cells, and the variation of PD-L1 was verified by western blot and immunofluorescence. In NPC cells, we verified the relationship of PD-L1, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), and β-catenin by western blot and immunofluorescence. Later, we further verified that PLUNC regulates PD-L1 through β-catenin. Finally, the effect of PLUNC on β-catenin was verified by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP).
Results
We found that PLUNC expression was lower in NPC tissues than in paracancer tissues. PD-L1 expression was opposite to that of PLUNC. Western blot and immunofluorescence showed that β-catenin could upregulate ATF3 and PD-L1, while PLUNC could downregulate ATF3/PD-L1 by inhibiting the expression of β-catenin. PLUNC inhibits the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. Co-IP experiments demonstrated that PLUNC inhibited the interaction of DEAD-box helicase 17 (DDX17) and β-catenin.
Conclusions
PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in NPC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Aurelius Scheer, Lars Bräuer, Markus Eckstein, Heinrich Iro, Friedrich Paulsen, Fabian Garreis, Martin Schicht, Antoniu-Oreste Gostian
Biomedicines.2025; 13(5): 1240. CrossRef - Role of DEAD/DEAH-box helicases in immunity, infection and cancers
Rex Devasahayam Arokia Balaya, Saptami Kanekar, Shreya Kumar, Richard K. Kandasamy
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CHIP modulates Wnt/β-catenin signalling in colorectal cancer through proteasomal degradation of DDX17
Sunny Kumar, Sayani Ghosh, Malini Basu, Mrinal K. Ghosh
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2025; 1872(8): 120049. CrossRef
- The Potential Role of SP-G and PLUNC in Tumor Pathogenesis and Wound Healing in the Human Larynx
Case Study
- Primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a female patient: case report
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):84-90. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.30
- 4,766 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
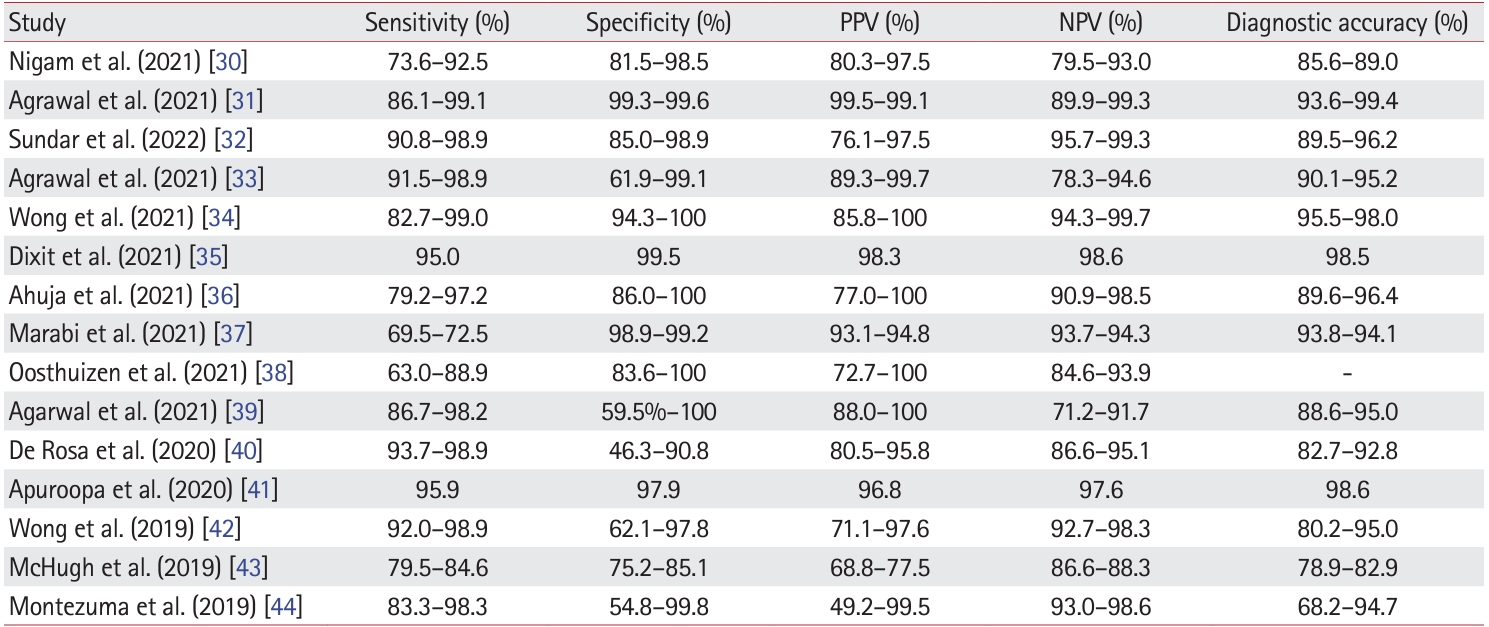
PDF - BCOR-rearranged sarcoma was classified by the World Health Organization in 2020 as a new subgroup of undifferentiated small round-cell sarcoma. It is known to occur very rarely in the kidney. This report presents the first case of a primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a 22-year-old woman. An 8-cm cystic mass was identified in the left kidney by abdominal pelvic computed tomography. Histopathologic examination revealed the mass to be composed of small round to oval or spindle cells with fibrous septa and a delicate vascular network. A BCOR::CCNB3 fusion was detected by next-generation sequencing–based molecular testing. BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma presents diagnostic difficulties, highlighting the importance of recognizing its histological features. Immunohistochemical markers are helpful for diagnosis, but genetic molecular testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis. These tumors have a very poor and aggressive prognosis, and an optimal therapeutic regimen has not yet been defined. Therefore, further studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
Jungo Imanishi, Kenji Sato, Yoshinao Kikuchi, Asako Yamamoto, Shiori Watabe, Taisuke Matsuyama, Chiaki Sato, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Hirotaka Kawano
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology.2025; 55(10): 1097. CrossRef
- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma

 E-submission
E-submission









 First
First Prev
Prev



