Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The evolving role of TRPS1 in dermatopathology: insights from the past 4 years
- Mokhtar H. Abdelhammed, Woo Cheal Cho
- Received September 11, 2025 Accepted November 25, 2025 Published online January 29, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.11.25 [Epub ahead of print]
- 51 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Over the past 4 years, trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) has rapidly gained attention among practicing pathologists, with numerous studies emerging that both support and question its diagnostic utility. Initially regarded as a highly specific marker for tumors of mammary origin, TRPS1 is now recognized to have broader expression patterns, including in a variety of cutaneous neoplasms. This is likely due to embryologic parallels between breast tissue and skin adnexal structures, an overlap that was underappreciated in early investigations. Although TRPS1 lacks absolute specificity—even among cutaneous neoplasms—it can still offer meaningful diagnostic value when interpreted alongside conventional immunohistochemical markers and within the appropriate morphologic context. Noteworthy diagnostic applications include mammary Paget disease, primary extramammary Paget disease, rare adnexal neoplasms such as endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and primary cutaneous NUT adnexal carcinoma, and cutaneous metastases from breast carcinoma. In this review, we present the most comprehensive and up-to-date evaluation of the utility and limitations of TRPS1 immunohistochemistry in dermatopathology. Our aim is to deepen understanding of this emerging marker and provide practical guidance on its optimal integration with established immunohistochemical panels to enhance diagnostic accuracy in routine practice.
- Drug-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney suspected to be caused by atomoxetine
- Sung-Eun Choi, Kee Hyuck Kim, Minsun Jung, Jeong Hae Kie
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):124-128. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.10
- 528 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIP) is characterized by intracellular accumulation of phospholipids with lamellar body formation secondary to drug-altered lipid metabolism, which can trigger inflammation and histopathological changes. Fabry disease and DIP both exhibit zebra bodies on electron microscopy, complicating differential diagnosis. A 17-year-old male with microscopic hematuria and proteinuria had received atomoxetine (40 mg) for 11 months to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Light microscopy showed one glomerulus with perihilar sclerosis and periglomerular fibrosis. Kidney biopsy revealed zebra bodies in podocytes, initially suggesting Fabry disease. However, α-galactosidase A enzyme activity was normal on tandem mass spectrometry. Next-generation sequencing of GLA identified only three benign variants. This represents the first reported case of atomoxetine-induced DIP. When zebra bodies are observed, clinicians should consider DIP caused by cationic amphiphilic drugs alongside Fabry disease. Atomoxetine meets the structural criteria for inducing DIP, and awareness of this potential complication is essential.
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 3,868 View
- 195 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
- Paricalcitol prevents MAPK pathway activation and inflammation in adriamycin-induced kidney injury in rats
- Amanda Lima Deluque, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Beatriz Magalhães Oliveira, Cláudia Silva Souza, Ana Lívia Dias Maciel, Heloísa Della Coletta Francescato, Cleonice Giovanini, Roberto Silva Costa, Terezila Machado Coimbra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):219-228. Published online August 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.12
- 3,719 View
- 221 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway induces uncontrolled cell proliferation in response to inflammatory stimuli. Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (ADRN) in rats triggers MAPK activation and pro-inflammatory mechanisms by increasing cytokine secretion, similar to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) plays a crucial role in suppressing the expression of inflammatory markers in the kidney and may contribute to reducing cellular proliferation. This study evaluated the effect of pre-treatment with paricalcitol on ADRN in renal inflammation mechanisms.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an osmotic minipump containing activated vitamin D (paricalcitol, Zemplar, 6 ng/day) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%). Two days after implantation, ADR (Fauldoxo, 3.5 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) was injected. The rats were divided into four experimental groups: control, n = 6; paricalcitol, n = 6; ADR, n = 7 and, ADR + paricalcitol, n = 7.
Results
VDR activation was demonstrated by increased CYP24A1 in renal tissue. Paricalcitol prevented macrophage infiltration in the glomeruli, cortex, and outer medulla, prevented secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, increased arginase I and decreased arginase II tissue expressions, effects associated with attenuation of MAPK pathways, increased zonula occludens-1, and reduced cell proliferation associated with proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Paricalcitol treatment decreased the stromal cell-derived factor 1α/chemokine C-X-C receptor type 4/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions
Paricalcitol plays a renoprotective role by modulating renal inflammation and cell proliferation. These results highlight potential targets for treating CKD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Ana Checa-Ros, Antonella Locascio, Owahabanun-Joshua Okojie, Pablo Abellán-Galiana, Luis D’Marco
BMC Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating amiodarone-induced lung toxicity by the vitamin D receptor activator paricalcitol in rats: targeting TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Aamal G. El-Waseif, Mahmoud Elshal, Dalia H. El-Kashef, Nashwa M. Abu-Elsaad
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
- Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
- Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):251-264. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.17
- 7,663 View
- 339 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Korean Society for Cytopathology introduced a digital proficiency test (PT) in 2021. However, many doubtful opinions remain on whether digitally scanned images can satisfactorily present subtle differences in the nuclear features and chromatin patterns of cytological samples.
Methods
We prepared 30 whole-slide images (WSIs) from the conventional PT archive by a selection process for digital PT. Digital and conventional PT were performed in parallel for volunteer institutes, and the results were compared using feedback. To assess the quality of cytological assessment WSIs, 12 slides were collected and scanned using five different scanners, with four cytopathologists evaluating image quality through a questionnaire.
Results
Among the 215 institutes, 108 and 107 participated in glass and digital PT, respectively. No significant difference was noted in category C (major discordance), although the number of discordant cases was slightly higher in the digital PT group. Leica, 3DHistech Pannoramic 250 Flash, and Hamamatsu NanoZoomer 360 systems showed comparable results in terms of image quality, feature presentation, and error rates for most cytological samples. Overall satisfaction was observed with the general convenience and image quality of digital PT.
Conclusions
As three-dimensional clusters are common and nuclear/chromatin features are critical for cytological interpretation, careful selection of scanners and optimal conditions are mandatory for the successful establishment of digital quality assurance programs in cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Chang Gok Woo, Seung‐Myoung Son, Hye‐Kyung Hwang, Jung‐Sil Bae, Ok‐Jun Lee, Ho‐Chang Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(1): 35. CrossRef - Integration of AI‐Assisted in Digital Cervical Cytology Training: A Comparative Study
Yihui Yang, Dongyi Xian, Lihua Yu, Yanqing Kong, Huaisheng Lv, Liujing Huang, Kai Liu, Hao Zhang, Weiwei Wei, Hongping Tang
Cytopathology.2025; 36(2): 156. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Focus Quality in Whole-Slide Imaging of Thyroid Liquid-Based Cytology Using Laplacian Variance
Chan Kwon Jung, Chankyung Kim, Sora Jeon, Andrey Bychkov
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of digital image slides for diagnosis in cervico-vaginal cytology
Francisco Tresserra, Gemma Fabra, Olga Luque, Miriam Castélla, Carla Gómez, Carmen Fernández-Cid, Ignacio Rodríguez
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(3): 182. CrossRef - Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yujin Lee, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Hongsik Park, Kwangil Yim, Kyung Jin Seo, Gisu Hwang, Dahyeon Kim, Yeonsoo Chung, Gyungyub Gong, Nam Hoon Cho, Chong Woo Yoo, Yosep Chong, Hyun Joo Choi
Thyroid®.2024; 34(6): 723. CrossRef
- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
- Postmortem lung and heart examination of COVID-19 patients in a case series from Jordan
- Maram Abdaljaleel, Isra Tawalbeh, Malik Sallam, Amjad Bani Hani, Imad M. Al-Abdallat, Baheth Al Omari, Sahar Al-Mustafa, Hasan Abder-Rahman, Adnan Said Abbas, Mahmoud Zureigat, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):102-112. Published online March 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.01.30
- 6,950 View
- 170 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has emerged as a pandemic for more than 2 years. Autopsy examination is an invaluable tool to understand the pathogenesis of emerging infections and their consequent mortalities. The aim of the current study was to present the lung and heart pathological findings of COVID-19–positive autopsies performed in Jordan.
Methods
The study involved medicolegal cases, where the cause of death was unclear and autopsy examination was mandated by law. We included the clinical and pathologic findings of routine gross and microscopic examination of cases that were positive for COVID-19 at time of death. Testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was confirmed through molecular detection by real-time polymerase chain reaction, serologic testing for IgM and electron microscope examination of lung samples.
Results
Seventeen autopsies were included, with male predominance (76.5%), Jordanians (70.6%), and 50 years as the mean age at time of death. Nine out of 16 cases (56.3%) had co-morbidities, with one case lacking such data. Histologic examination of lung tissue revealed diffuse alveolar damage in 13/17 cases (76.5%), and pulmonary microthrombi in 8/17 cases (47.1%). Microscopic cardiac findings were scarcely detected. Two patients died as a direct result of acute cardiac disease with limited pulmonary findings.
Conclusions
The detection of SARS-CoV-2 in postmortem examination can be an incidental or contributory finding which highlights the value of autopsy examination to determine the exact cause of death in controversial cases.
- Development of quality assurance program for digital pathology by the Korean Society of Pathologists
- Yosep Chong, Jeong Mo Bae, Dong Wook Kang, Gwangil Kim, Hye Seung Han
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):370-382. Published online November 15, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.30
- 6,600 View
- 162 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Digital pathology (DP) using whole slide imaging is a recently emerging game changer technology that can fundamentally change the way of working in pathology. The Digital Pathology Study Group (DPSG) of the Korean Society of Pathologists (KSP) published a consensus report on the recommendations for pathologic practice using DP. Accordingly, the need for the development and implementation of a quality assurance program (QAP) for DP has been raised.
Methods
To provide a standard baseline reference for internal and external QAP for DP, the members of the Committee of Quality Assurance of the KSP developed a checklist for the Redbook and a QAP trial for DP based on the prior DPSG consensus report. Four leading institutes participated in the QAP trial in the first year, and we gathered feedback from these institutes afterwards.
Results
The newly developed checklists of QAP for DP contain 39 items (216 score): eight items for quality control of DP systems; three for DP personnel; nine for hardware and software requirements for DP systems; 15 for validation, operation, and management of DP systems; and four for data security and personal information protection. Most participants in the QAP trial replied that continuous education on unfamiliar terminology and more practical experience is demanding.
Conclusions
The QAP for DP is essential for the safe implementation of DP in pathologic practice. Each laboratory should prepare an institutional QAP according to this checklist, and consecutive revision of the checklist with feedback from the QAP trial for DP needs to follow. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An equivalency and efficiency study for one year digital pathology for clinical routine diagnostics in an accredited tertiary academic center
Viola Iwuajoku, Kübra Ekici, Anette Haas, Mohammed Zaid Khan, Azar Kazemi, Atsuko Kasajima, Claire Delbridge, Alexander Muckenhuber, Elisa Schmoeckel, Fabian Stögbauer, Christine Bollwein, Kristina Schwamborn, Katja Steiger, Carolin Mogler, Peter J. Schüf
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(1): 3. CrossRef - Quality Assurance of the Whole Slide Image Evaluation in Digital Pathology: State of the Art and Development Results
Miklós Vincze, Béla Molnár, Miklós Kozlovszky
Electronics.2025; 14(10): 1943. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(5): 251. CrossRef
- An equivalency and efficiency study for one year digital pathology for clinical routine diagnostics in an accredited tertiary academic center
- Recommendations for pathologic practice using digital pathology: consensus report of the Korean Society of Pathologists
- Yosep Chong, Dae Cheol Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong-chul Kim, Sang Yong Song, Hee Jae Joo, Sang-Yeop Yi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(6):437-452. Published online October 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.08.27
- 12,313 View
- 339 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Digital pathology (DP) using whole slide imaging (WSI) is becoming a fundamental issue in pathology with recent advances and the rapid development of associated technologies. However, the available evidence on its diagnostic uses and practical advice for pathologists on implementing DP remains insufficient, particularly in light of the exponential growth of this industry. To inform DP implementation in Korea, we developed relevant and timely recommendations. We first performed a literature review of DP guidelines, recommendations, and position papers from major countries, as well as a review of relevant studies validating WSI. Based on that information, we prepared a draft. After several revisions, we released this draft to the public and the members of the Korean Society of Pathologists through our homepage and held an open forum for interested parties. Through that process, this final manuscript has been prepared. This recommendation contains an overview describing the background, objectives, scope of application, and basic terminology; guidelines and considerations for the hardware and software used in DP systems and the validation required for DP implementation; conclusions; and references and appendices, including literature on DP from major countries and WSI validation studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Commercially Available Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Gynaecologic Cytology Screening and Their Integration Into Clinical Workflow
Yosep Chong, Andrey Bychkov
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 24. CrossRef - An equivalency and efficiency study for one year digital pathology for clinical routine diagnostics in an accredited tertiary academic center
Viola Iwuajoku, Kübra Ekici, Anette Haas, Mohammed Zaid Khan, Azar Kazemi, Atsuko Kasajima, Claire Delbridge, Alexander Muckenhuber, Elisa Schmoeckel, Fabian Stögbauer, Christine Bollwein, Kristina Schwamborn, Katja Steiger, Carolin Mogler, Peter J. Schüf
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(1): 3. CrossRef - An adapted & improved validation protocol for digital pathology implementation
Ying-Han R. Hsu, Iman Ahmed, Juliana Phlamon, Charlotte Carment-Baker, Joyce Yin Tung Chan, Ioannis Prassas, Karen Weiser, Shaza Zeidan, Blaise Clarke, George M. Yousef
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 42(4): 150905. CrossRef - Transforming pathology into digital pathology: highway to hell or stairway to heaven?
Rainer Grobholz, Andrew Janowczyk, Inti Zlobec
Diagnostic Histopathology.2025; 31(7): 410. CrossRef - The Evolution of Digital Pathology in Infrastructure, Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Impact
Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 6. CrossRef - Current Trends and Future Directions of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence in Dermatopathology: A Scientometric-Based Review
Iuliu Gabriel Cocuz, Raluca Niculescu, Maria-Cătălina Popelea, Maria Elena Cocuz, Adrian-Horațiu Sabău, Andreea-Cătălina Tinca, Andreea Raluca Cozac-Szoke, Diana Maria Chiorean, Corina Eugenia Budin, Ovidiu Simion Cotoi
Diagnostics.2025; 15(17): 2196. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Focus Quality in Whole-Slide Imaging of Thyroid Liquid-Based Cytology Using Laplacian Variance
Chan Kwon Jung, Chankyung Kim, Sora Jeon, Andrey Bychkov
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance of externally validated machine learning models based on histopathology images for the diagnosis, classification, prognosis, or treatment outcome prediction in female breast cancer: A systematic review
Ricardo Gonzalez, Peyman Nejat, Ashirbani Saha, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Andrew P. Norgan, Cynthia Lokker
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100348. CrossRef - Swiss digital pathology recommendations: results from a Delphi process conducted by the Swiss Digital Pathology Consortium of the Swiss Society of Pathology
Andrew Janowczyk, Inti Zlobec, Cedric Walker, Sabina Berezowska, Viola Huschauer, Marianne Tinguely, Joel Kupferschmid, Thomas Mallet, Doron Merkler, Mario Kreutzfeldt, Radivoje Gasic, Tilman T. Rau, Luca Mazzucchelli, Isgard Eyberg, Gieri Cathomas, Kirst
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(1): 13. CrossRef - ChatGPT as an aid for pathological diagnosis of cancer
Shaivy Malik, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 154989. CrossRef - Possible benefits, challenges, pitfalls, and future perspective of using ChatGPT in pathology
Durre Aden, Sufian Zaheer, Sabina Khan
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(3): 198. CrossRef - Remote Placental Sign-Out: What Digital Pathology Can Offer for Pediatric Pathologists
Casey P. Schukow, Jacqueline K. Macknis
Pediatric and Developmental Pathology.2024; 27(4): 375. CrossRef - Digital Validation in Breast Cancer Needle Biopsies: Comparison of Histological Grade and Biomarker Expression Assessment Using Conventional Light Microscopy, Whole Slide Imaging, and Digital Image Analysis
Ji Eun Choi, Kyung-Hee Kim, Younju Lee, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 312. CrossRef - Pathologists light level preferences using the microscope—study to guide digital pathology display use
Charlotte Jennings, Darren Treanor, David Brettle
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100379. CrossRef - Eye tracking in digital pathology: A comprehensive literature review
Alana Lopes, Aaron D. Ward, Matthew Cecchini
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100383. CrossRef - Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Frozen Tissue Section Analysis in Women with Breast Cancer
Young-Gon Kim, In Hye Song, Seung Yeon Cho, Sungchul Kim, Milim Kim, Soomin Ahn, Hyunna Lee, Dong Hyun Yang, Namkug Kim, Sungwan Kim, Taewoo Kim, Daeyoung Kim, Jonghyeon Choi, Ki-Sun Lee, Minuk Ma, Minki Jo, So Yeon Park, Gyungyub Gong
Cancer Research and Treatment.2023; 55(2): 513. CrossRef - Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable development goals applied to digital pathology and artificial intelligence applications in low- to middle-income countries
Sumi Piya, Jochen K. Lennerz
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(5): 251. CrossRef - Real-World Implementation of Digital Pathology: Results From an Intercontinental Survey
Daniel Gomes Pinto, Andrey Bychkov, Naoko Tsuyama, Junya Fukuoka, Catarina Eloy
Laboratory Investigation.2023; 103(12): 100261. CrossRef - National digital pathology projects in Switzerland: A 2023 update
Rainer Grobholz, Andrew Janowczyk, Ana Leni Frei, Mario Kreutzfeldt, Viktor H. Koelzer, Inti Zlobec
Die Pathologie.2023; 44(S3): 225. CrossRef - Understanding the ethical and legal considerations of Digital Pathology
Cheryl Coulter, Francis McKay, Nina Hallowell, Lisa Browning, Richard Colling, Philip Macklin, Tom Sorell, Muhammad Aslam, Gareth Bryson, Darren Treanor, Clare Verrill
The Journal of Pathology: Clinical Research.2022; 8(2): 101. CrossRef - Current Trend of Artificial Intelligence Patents in Digital Pathology: A Systematic Evaluation of the Patent Landscape
Muhammad Joan Ailia, Nishant Thakur, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Chan Kwon Jung, Kwangil Yim, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2400. CrossRef - Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence from Histopathologic Image-Based Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Solid Cancers: A Systematic Review
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Nishant Thakur, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(11): 2590. CrossRef - Automated Hybrid Model for Detecting Perineural Invasion in the Histology of Colorectal Cancer
Jiyoon Jung, Eunsu Kim, Hyeseong Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Sangjeong Ahn
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(18): 9159. CrossRef - Development of quality assurance program for digital pathology by the Korean Society of Pathologists
Yosep Chong, Jeong Mo Bae, Dong Wook Kang, Gwangil Kim, Hye Seung Han
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 370. CrossRef - Improving quality control in the routine practice for histopathological interpretation of gastrointestinal endoscopic biopsies using artificial intelligence
Young Sin Ko, Yoo Mi Choi, Mujin Kim, Youngjin Park, Murtaza Ashraf, Willmer Rafell Quiñones Robles, Min-Ju Kim, Jiwook Jang, Seokju Yun, Yuri Hwang, Hani Jang, Mun Yong Yi, Anwar P.P. Abdul Majeed
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0278542. CrossRef - What is Essential is (No More) Invisible to the Eyes: The Introduction of BlocDoc in the Digital Pathology Workflow
Vincenzo L’Imperio, Fabio Gibilisco, Filippo Fraggetta
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 32. CrossRef
- Commercially Available Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Gynaecologic Cytology Screening and Their Integration Into Clinical Workflow
- Inconspicuous longitudinal tears of the intracranial vertebral artery in traumatic basal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Seongho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):179-183. Published online November 8, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.15
- 10,185 View
- 208 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Blunt force trauma to the head or neck region can cause traumatic basal subarachnoid hemorrhage (TBSAH), which can result in rapid loss of consciousness and death; however, detecting such a vascular injury is difficult. Posterior neck dissection was performed to investigate the bleeding focus in TBSAH cases 2018 and 2019. In all four cases, autopsies revealed a longitudinal tear in the midsection of the vertebral artery’s intracranial portion. The midportion of the intracranial vertebral artery appears to be most vulnerable to TBSAH. Interestingly, three of the cases showed only a vaguely visible longitudinal fissure in the artery without a grossly apparent tear; rupture was confirmed by microscopic examination. Longitudinal fissures of the intracranial vertebral artery, which are difficult to identify without detailed examination, may be overlooked in some cases of TBSAH. Thus, careful gross and microscopic examination of the vertebral artery is recommended in cases of TBSAH.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Traumatic vertebrobasilar pseudoaneurysms: diagnostic pitfalls on CT angiography with forensic implications — two case reports
Numfon Tweeatsani, Kana Unuma, Yukiko Uemura, Hirotaro Iwase, Yohsuke Makino
Emergency Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ginseng Extract Ginsenoside Rg1 on Mice with Intracerebral Injury
Zixin Zhuang, Jinman Chen, Hao Xu, Yongjun Wang, Qianqian Liang
Chinese Medicine and Culture.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Traumatic vertebrobasilar pseudoaneurysms: diagnostic pitfalls on CT angiography with forensic implications — two case reports
- MicroRNA-374a Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Yeseul Kim, Jongmin Sim, Hyunsung Kim, Seong Sik Bang, Seungyun Jee, Sungeon Park, Kiseok Jang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):354-360. Published online October 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.01
- 6,675 View
- 130 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related death, and adenocarcinoma is the most common histologic subtype. MicroRNA is a small non-coding RNA that inhibits multiple target gene expression at the post-transcriptional level and is commonly dysregulated in malignant tumors. The purpose of this study was to analyze the expression of microRNA-374a (miR-374a) in lung adenocarcinoma and correlate its expression with various clinicopathological characteristics.
Methods
The expression level of miR-374a was measured in 111 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded lung adenocarcinoma tissues using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays. The correlation between miR-374a expression and clinicopathological parameters, including clinical outcome, was further analyzed.
Results
High miR-374 expression was correlated with advanced pT category (chi-square test, p=.004) and pleural invasion (chi-square test, p=.034). Survival analysis revealed that patients with high miR-374a expression had significantly shorter disease-free survival relative to those with low miR-374a expression (log-rank test, p=.032).
Conclusions
miR-374a expression may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for predicting recurrence in early stage lung adenocarcinoma after curative surgery. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Upregulated miR-374a-5p drives psoriasis pathogenesis through WIF1 downregulation and Wnt5a/NF-κB activation
Jing Ma, Lu Gan, Hongying Chen, Lihao Chen, Yu Hu, Chao Luan, Kun Chen, Jiaan Zhang
Cellular Signalling.2024; 119: 111171. CrossRef - Association between the expression level of miRNA‑374a and TGF‑β1 in patients with colorectal cancer
Noha El Din, Reem El‑Shenawy, Rehab Moustafa, Ahmed Khairy, Sally Farouk
World Academy of Sciences Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cell-free plasma miRNAs analysis for low invasive lung cancer diagnostics
M. Yu. Konoshenko, P. P. Laktionov, Yu. A. Lancuhaj, S. V. Pak, S. E. Krasilnikov, O. E. Bryzgunova
Advances in Molecular Oncology.2023; 10(2): 78. CrossRef - MicroRNA‑mediated regulation in lung adenocarcinoma: Signaling pathways and potential therapeutic implications (Review)
Jiye Liu, Fei Zhang, Jiahe Wang, Yibing Wang
Oncology Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysregulation of miR-374a is involved in the progression of diabetic retinopathy and regulates the proliferation and migration of retinal microvascular endothelial cells
Zhanhong Wang, Xiao Zhang, Yanjun Wang, Dailing Xiao
Clinical and Experimental Optometry.2022; 105(3): 287. CrossRef - MicroRNA Profile for Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Seon-Kyu Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan-Kwon Jung, Yong-Sung Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 632. CrossRef
- Upregulated miR-374a-5p drives psoriasis pathogenesis through WIF1 downregulation and Wnt5a/NF-κB activation
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- Hye Yoon Chang, Chan Kwon Jung, Junwoo Isaac Woo, Sanghun Lee, Joonyoung Cho, Sun Woo Kim, Tae-Yeong Kwak
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):1-12. Published online December 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.12.16
- 32,537 View
- 1,285 Download
- 128 Web of Science
- 142 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As in other domains, artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important in medicine. In particular,deep learning-based pattern recognition methods can advance the field of pathology byincorporating clinical, radiologic, and genomic data to accurately diagnose diseases and predictpatient prognoses. In this review, we present an overview of artificial intelligence, the brief historyof artificial intelligence in the medical domain, recent advances in artificial intelligence applied topathology, and future prospects of pathology driven by artificial intelligence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
Shuangshuang Li, Kaiwen Zhao, Wen Li, Qingsheng Lu, Jian Zhou, Jia He
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2026; 122: 895. CrossRef - An automatic, rapid and accurate method for the annotation of tumor components on whole slide images
Hong Tang, Xiaodong Wang, Xiaolin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Xinyue Tang, Yaqiong Ma, Ying Chen, Guanzhen Yu
Journal of Histotechnology.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Exploring the status of artificial intelligence for healthcare research in Africa: a bibliometric and thematic analysis
Tabu S. Kondo, Salim A. Diwani, Ally S. Nyamawe, Mohamed M. Mjahidi
AI and Ethics.2025; 5(1): 117. CrossRef - Prioritize Threat Alerts Based on False Positives Qualifiers Provided by Multiple AI Models Using Evolutionary Computation and Reinforcement Learning
Anup Sharma, V. G. Kiran Kumar, Asmita Poojari
Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B.2025; 106(4): 1305. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence versus human analysis: Interpreting data in elderly fat reduction study
Piotr Sporek, Mariusz Konieczny
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2025; 12(1): 13. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare applications targeting cancer diagnosis—part I: data structure, preprocessing and data organization
Anna Luíza Damaceno Araújo, Marcelo Sperandio, Giovanna Calabrese, Sarah S. Faria, Diego Armando Cardona Cardenas, Manoela Domingues Martins, Cristina Saldivia-Siracusa, Daniela Giraldo-Roldán, Caique Mariano Pedroso, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2025; 140(1): 79. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence–driven digital pathology in urological cancers: current trends and future directions
Inyoung Paik, Geongyu Lee, Joonho Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hong Koo Ha
Prostate International.2025; 13(4): 181. CrossRef - Optimizing deep learning for accurate blood cell classification: A study on stain normalization and fine-tuning techniques
Mohammed Tareq Mutar, Jaffar Nouri Alalsaidissa, Mustafa Majid Hameed, Ali Almothaffar
Iraqi Journal of Hematology.2025; 14(1): 60. CrossRef - Structural imbalance of medical resources amid population mobility and digital empowerment: a study of national and port-developed provinces in China
Haiwei Fu, Junjie Lu
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of artificial intelligence in pathology: a bibliometric and network analysis
Burcu Sanal Yılmaz
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2025; 6(3): 224. CrossRef - ШТУЧНИЙ ІНТЕЛЕКТ У СУЧАСНІЙ СТОМАТОЛОГІЇ
О. І. Бульбук, О. В. Бульбук, О. В. Шутак, Ю. І. Сухоребський
Art of Medicine.2025; : 101. CrossRef - Natural language processing in veterinary pathology: A review
Lev Stimmer, Raoul V. Kuiper, Laura Polledo, Lorenzo Ressel, Josep M. Monné Rodriguez, Inês B. Veiga, Jonathan Williams, Vanessa Herder
Veterinary Pathology.2025; 62(6): 829. CrossRef - Impact of Magnification, Image Type, and Number on Convolutional Neural Network Performance in Differentiating Canine Large Cell Lymphoma From Non‐Lymphoma via Lymph Node Cytology
Christina Pacholec, Hehuang Xie, Julianne Curnin, Amy Lin, Kurt Zimmerman
Veterinary Clinical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology image-based predictive model for individual survival time of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma patients
Vi Thi-Tuong Vo, Hyung-Jeong Yang, Taebum Lee, Soo-Hyung Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Artificial Intelligence's Potential to Enhance Conventional Anticancer Drug Development
Sorin‐Ștefan Bobolea, Miruna‐Ioana Hinoveanu, Andreea Dimitriu, Miruna‐Andrada Brașoveanu, Cristian‐Nicolae Iliescu, Cristina‐Elena Dinu‐Pîrvu, Mihaela Violeta Ghica, Valentina Anuța, Lăcrămioara Popa, Răzvan Mihai Prisada
Drug Development Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicability of PD-L1 expression in cancer cells based solely on H&E-stained sections
Gavino Faa, Matteo Fraschini, Pina Ziranu, Andrea Pretta, Giuseppe Porcu, Luca Saba, Mario Scartozzi, Nazar Shokun, Massimo Rugge
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 19: 100524. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
Umur Karan, Osman Elbek
Thoracic Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole Slide Imaging Technology and Its Applications: Current and Emerging Perspectives
Ekta Jain, Ankush Patel, Anil V. Parwani, Saba Shafi, Zoya Brar, Shivani Sharma, Sambit K. Mohanty
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(3): 433. CrossRef - ChatGPT as an aid for pathological diagnosis of cancer
Shaivy Malik, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 154989. CrossRef - Computational pathology: A survey review and the way forward
Mahdi S. Hosseini, Babak Ehteshami Bejnordi, Vincent Quoc-Huy Trinh, Lyndon Chan, Danial Hasan, Xingwen Li, Stephen Yang, Taehyo Kim, Haochen Zhang, Theodore Wu, Kajanan Chinniah, Sina Maghsoudlou, Ryan Zhang, Jiadai Zhu, Samir Khaki, Andrei Buin, Fatemeh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100357. CrossRef - Applications of artificial intelligence in the field of oral and maxillofacial pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Nishath Sayed Abdul, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Sunila Bukanakere Sangappa, Marco Di Blasio, Salvatore Crimi, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine-learning models are superior to severity scoring systems for the prediction of the mortality of critically ill patients in a tertiary medical center
Ruey-Hsing Chou, Benny Wei-Yun Hsu, Chun-Lin Yu, Tai-Yuan Chen, Shuo-Ming Ou, Kuo-Hua Lee, Vincent S. Tseng, Po-Hsun Huang, Der-Cherng Tarng
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2024; 87(4): 369. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Technology for the Differentiation of Fresh Human Blood Cells From Other Species Blood in the Investigation of Crime Scenes
Syed Sajid Hussain Shah, Ekramy Elmorsy, Rashad Qasem Ali Othman, Asmara Syed, Syed Umar Armaghan, Syed Usama Khalid Bokhari, Mahmoud E Elmorsy, Abdulhakim Bawadekji
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of Diagnostic and Immunohistochemical Workup and Literature Review Capabilities of Online Artificial Intelligence Assistance Models in Pathology
Johnika Dougan, Netra Patel, Svetoslav Bardarov
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - ChatENT: Augmented Large Language Model for Expert Knowledge Retrieval in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery
Cai Long, Deepak Subburam, Kayle Lowe, André dos Santos, Jessica Zhang, Sang Hwang, Neil Saduka, Yoav Horev, Tao Su, David W.J. Côté, Erin D. Wright
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2024; 171(4): 1042. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in forensic medicine and related sciences – selected issues = Sztuczna inteligencja w medycynie sądowej i naukach pokrewnych – wybrane zagadnienia
Michał Szeremeta, Julia Janica, Anna Niemcunowicz-Janica
Archives of Forensic Medicine and Criminology.2024; 74(1): 64. CrossRef - Unveiling the landscape of pathomics in personalized immunotherapy for lung cancer: a bibliometric analysis
Lei Yuan, Zhiming Shen, Yibo Shan, Jianwei Zhu, Qi Wang, Yi Lu, Hongcan Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PathEX: Make good choice for whole slide image extraction
Xinda Yang, Ranze Zhang, Yuan Yang, Yu Zhang, Kai Chen, Alberto Marchisio
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0304702. CrossRef - Automatic point detection on cephalograms using convolutional neural networks: A two-step method
Miki HORI, Makoto JINCHO, Tadasuke HORI, Hironao SEKINE, Akiko KATO, Ken MIYAZAWA, Tatsushi KAWAI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 701. CrossRef - The use of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in teaching and assessment of postgraduate students in pathology and microbiology
Dipmala Das, Asitava Deb Roy, Subhayan Dasgupta, Rohon Das Roy
Indian Journal of Microbiology Research.2024; 11(3): 140. CrossRef - Inteligencia artificial: desafíos éticos y futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence: ethical and future challenges
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inteligência artificial: desafios éticos e futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Constrained-Disorder Principle Assists in Overcoming Significant Challenges in Digital Health: Moving from “Nice to Have” to Mandatory Systems
Noa Hurvitz, Yaron Ilan
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(4): 994. CrossRef - Building a nonclinical pathology laboratory of the future for pharmaceutical research excellence
D.G. Rudmann, L. Bertrand, A. Zuraw, J. Deiters, M. Staup, Y. Rivenson, J. Kuklyte
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103747. CrossRef - Automated image analysis of keratin 7 staining can predict disease outcome in primary sclerosing cholangitis
Nelli Sjöblom, Sonja Boyd, Anniina Manninen, Sami Blom, Anna Knuuttila, Martti Färkkilä, Johanna Arola
Hepatology Research.2023; 53(4): 322. CrossRef - Application of convolutional neural network for analyzing hepatic fibrosis in mice
Hyun-Ji Kim, Eun Bok Baek, Ji-Hee Hwang, Minyoung Lim, Won Hoon Jung, Myung Ae Bae, Hwa-Young Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Toxicologic Pathology.2023; 36(1): 21. CrossRef - Machine Learning Techniques for Prognosis Estimation and Knowledge Discovery From Lab Test Results With Application to the COVID-19 Emergency
Alfonso Emilio Gerevini, Roberto Maroldi, Matteo Olivato, Luca Putelli, Ivan Serina
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 83905. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in dentistry—A review
Hao Ding, Jiamin Wu, Wuyuan Zhao, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Michael F. Burrow, James K. H. Tsoi
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Age Estimation Using the Demirjian Method: Statistical Analysis Using Neural Networks
Byung-Yoon Roh, Jong-Seok Lee, Sang-Beom Lim, Hye-Won Ryu, Su-Jeong Jeon, Ju-Heon Lee, Yo-Seob Seo, Ji-Won Ryu, Jong-Mo Ahn
Korean Journal of Legal Medicine.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence in health care. Problems of identification of patients' conditions in the processes of detailing the diagnosis
Mintser O
Artificial Intelligence.2023; 28(AI.2023.28): 8. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation for Mature White Blood Cell Image Classification in Deep Learning — Selection of an Optimal Technique for Hematological Morphology Recognition —
Hiroyuki NOZAKA, Kosuke KAMATA, Kazufumi YAMAGATA
IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems.2023; E106.D(5): 707. CrossRef - Rectal Cancer Stages T2 and T3 Identification Based on Asymptotic Hybrid Feature Maps
Shujing Sun, Jiale Wu, Jian Yao, Yang Cheng, Xin Zhang, Zhihua Lu, Pengjiang Qian
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences.2023; 137(1): 923. CrossRef - How to use AI in pathology
Peter Schüffler, Katja Steiger, Wilko Weichert
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2023; 62(9): 564. CrossRef - Cutting-Edge Technologies for Digital Therapeutics: A Review and Architecture Proposals for Future Directions
Joo Hun Yoo, Harim Jeong, Tai-Myoung Chung
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6929. CrossRef - A convolutional neural network STIFMap reveals associations between stromal stiffness and EMT in breast cancer
Connor Stashko, Mary-Kate Hayward, Jason J. Northey, Neil Pearson, Alastair J. Ironside, Johnathon N. Lakins, Roger Oria, Marie-Anne Goyette, Lakyn Mayo, Hege G. Russnes, E. Shelley Hwang, Matthew L. Kutys, Kornelia Polyak, Valerie M. Weaver
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based PTEN Loss Assessment as an Early Predictor of Prostate Cancer Metastasis After Surgery: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Palak Patel, Stephanie Harmon, Rachael Iseman, Olga Ludkowski, Heidi Auman, Sarah Hawley, Lisa F. Newcomb, Daniel W. Lin, Peter S. Nelson, Ziding Feng, Hilary D. Boyer, Maria S. Tretiakova, Larry D. True, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Peter R. Carroll, Matthew R. Co
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(10): 100241. CrossRef - Minimum resolution requirements of digital pathology images for accurate classification
Lydia Neary-Zajiczek, Linas Beresna, Benjamin Razavi, Vijay Pawar, Michael Shaw, Danail Stoyanov
Medical Image Analysis.2023; 89: 102891. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in the Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Sangjoon Choi, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 410. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Based Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms
Jin-Seok Park, Seok Jeong
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2023; 28(3): 53. CrossRef - Framework for Classifying Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Algorithms in Clinical Medicine
Thomas Gniadek, Jason Kang, Talent Theparee, Jacob Krive
Online Journal of Public Health Informatics.2023; 15: e50934. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Future of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Oral Pathology, and Oral Surgery in the Hands of Technology
Ishita Singhal, Geetpriya Kaur, Dirk Neefs, Aparna Pathak
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - AI-Powered Biomolecular-Specific and Label-Free Multispectral Imaging Rapidly Detects Malignant Neoplasm in Surgically Excised Breast Tissue Specimens
Rishikesh Pandey, David Fournier, Gary Root, Machele Riccio, Aditya Shirvalkar, Gianfranco Zamora, Noel Daigneault, Michael Sapack, Minghao Zhong, Malini Harigopal
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(11): 1298. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence for patient scheduling in the real-world health care setting: A metanarrative review
Dacre R.T. Knight, Christopher A. Aakre, Christopher V. Anstine, Bala Munipalli, Parisa Biazar, Ghada Mitri, Jose Raul Valery, Tara Brigham, Shehzad K. Niazi, Adam I. Perlman, John D. Halamka, Abd Moain Abu Dabrh
Health Policy and Technology.2023; 12(4): 100824. CrossRef - Towards Autonomous Healthcare: Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Personalized Medicine and Disease Prediction
Nitin Rane, Saurabh Choudhary, Jayesh Rane
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical imaging and multimodal artificial intelligence models for streamlining and enhancing cancer care: opportunities and challenges
Kevin Pierre, Manas Gupta, Abheek Raviprasad, Seyedeh Mehrsa Sadat Razavi, Anjali Patel, Keith Peters, Bruno Hochhegger, Anthony Mancuso, Reza Forghani
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2023; 23(12): 1265. CrossRef - Automated differential diagnostics of respiratory diseases using an electronic stethoscope
Diana Arhypenko, Denis Panaskin, Dmytro Babko
Polish Journal of Medical Physics and Engineering.2023; 29(4): 208. CrossRef - Application of machine learning in identification of pathogenic microbes
Lakshmi Venkata S Kutikuppala, Kanishk K Adhit, Reewen George D Silva
Digital Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Beginning of a New Era
C Nandini, Shaik Basha, Aarchi Agarawal, R Parikh Neelampari, Krishna P Miyapuram, R Jadeja Nileshwariba
Advances in Human Biology.2023; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Respiratory Medicine
K Kalaiyarasan, R Sridhar
Journal of Association of Pulmonologist of Tamil Nadu.2023; 6(2): 53. CrossRef - Automated abstraction of myocardial perfusion imaging reports using natural language processing
Parija Sharedalal, Ajay Singh, Neal Shah, Diwakar Jain
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.2022; 29(3): 1188. CrossRef - Polyploid giant cancer cell characterization: New frontiers in predicting response to chemotherapy in breast cancer
Geetanjali Saini, Shriya Joshi, Chakravarthy Garlapati, Hongxiao Li, Jun Kong, Jayashree Krishnamurthy, Michelle D. Reid, Ritu Aneja
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 81: 220. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Markov Random Field and Conditional Random Field Approaches in Pathology Image Analysis
Yixin Li, Chen Li, Xiaoyan Li, Kai Wang, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Changhao Sun, Hao Chen, Xinran Wu, Hong Zhang, Qian Wang
Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering.2022; 29(1): 609. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology: From bench to clinic
Jamal Elkhader, Olivier Elemento
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 84: 113. CrossRef - Yeast‐like organisms phagocytosed by circulating neutrophils: Evidence of disseminated histoplasmosis
Yue Zhao, Jenna McCracken, Endi Wang
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2022; 44(1): 51. CrossRef - Whole-slide imaging, tissue image analysis, and artificial intelligence in veterinary pathology: An updated introduction and review
Aleksandra Zuraw, Famke Aeffner
Veterinary Pathology.2022; 59(1): 6. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of computer-aided whole-slide image analysis: from datasets to feature extraction, segmentation, classification and detection approaches
Xintong Li, Chen Li, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Hongzan Sun, Xiaoqi Li, Jian Wu, Yudong Yao, Marcin Grzegorzek
Artificial Intelligence Review.2022; 55(6): 4809. CrossRef - Liquid Biopsy and Artificial Intelligence as Tools to Detect Signatures of Colorectal Malignancies: A Modern Approach in Patient’s Stratification
Octav Ginghina, Ariana Hudita, Marius Zamfir, Andrada Spanu, Mara Mardare, Irina Bondoc, Laura Buburuzan, Sergiu Emil Georgescu, Marieta Costache, Carolina Negrei, Cornelia Nitipir, Bianca Galateanu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated bone marrow cytology using deep learning to generate a histogram of cell types
Rohollah Moosavi Tayebi, Youqing Mu, Taher Dehkharghanian, Catherine Ross, Monalisa Sur, Ronan Foley, Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Clinton J. V. Campbell
Communications Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risultati di esami di laboratorio per intelligenza artificiale e "machine learning"
Marco PRADELLA
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Deception of Certainty: how Non-Interpretable Machine Learning Outcomes Challenge the Epistemic Authority of Physicians. A deliberative-relational Approach
Florian Funer
Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy.2022; 25(2): 167. CrossRef - Deep discriminative learning model with calibrated attention map for the automated diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Sautami Basu, Ravinder Agarwal, Vishal Srivastava
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2022; 76: 103728. CrossRef - Question and Answer Techniques for Financial Audits in Universities Based on Deep Learning
Qiang Li, Hangjun Che
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Noninvasive Screening Tool for Hyperkalemia Using a Single-Lead Electrocardiogram and Deep Learning: Development and Usability Study
Erdenebayar Urtnasan, Jung Hun Lee, Byungjin Moon, Hee Young Lee, Kyuhee Lee, Hyun Youk
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(6): e34724. CrossRef - Impact of artificial intelligence on pathologists’ decisions: an experiment
Julien Meyer, April Khademi, Bernard Têtu, Wencui Han, Pria Nippak, David Remisch
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2022; 29(10): 1688. CrossRef - Rapid Screening Using Pathomorphologic Interpretation to Detect BRAFV600E Mutation and Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer
Satoshi Fujii, Daisuke Kotani, Masahiro Hattori, Masato Nishihara, Toshihide Shikanai, Junji Hashimoto, Yuki Hama, Takuya Nishino, Mizuto Suzuki, Ayatoshi Yoshidumi, Makoto Ueno, Yoshito Komatsu, Toshiki Masuishi, Hiroki Hara, Taito Esaki, Yoshiaki Nakamu
Clinical Cancer Research.2022; 28(12): 2623. CrossRef - Using Deep Learning to Predict Final HER2 Status in Invasive Breast Cancers That are Equivocal (2+) by Immunohistochemistry
Sean A. Rasmussen, Valerie J. Taylor, Alexi P. Surette, Penny J. Barnes, Gillian C. Bethune
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(10): 668. CrossRef - Deep Neural Network for the Prediction of KRAS Genotype in Rectal Cancer
Waleed M Ghareeb, Eman Draz, Khaled Madbouly, Ahmed H Hussein, Mohammed Faisal, Wagdi Elkashef, Mona Hany Emile, Marcus Edelhamre, Seon Hahn Kim, Sameh Hany Emile
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 235(3): 482. CrossRef - Next Generation Digital Pathology: Emerging Trends and Measurement Challenges for Molecular Pathology
Alex Dexter, Dimitrios Tsikritsis, Natalie A. Belsey, Spencer A. Thomas, Jenny Venton, Josephine Bunch, Marina Romanchikova
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2022; 3(3): 168. CrossRef - Animation Design of Multisensor Data Fusion Based on Optimized AVOD Algorithm
Li Ding, Guobing Wei, Kai Zhang, Gengxin Sun
Journal of Sensors.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Study on Machine Translation Teaching Model Based on Translation Parallel Corpus and Exploitation for Multimedia Asian Information Processing
Yan Gong
ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and Estimation of Pathological Data and Findings with Deep Learning Methods
Ahmet Anıl ŞAKIR, Ali Hakan IŞIK, Özlem ÖZMEN, Volkan İPEK
Veterinary Journal of Mehmet Akif Ersoy University.2022; 7(3): 175. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Pathology: Friend or Enemy?
Selim Sevim, Ezgi Dicle Serbes, Murat Bahadır, Mustafa Said Kartal, Serpil Dizbay Sak
Journal of Ankara University Faculty of Medicine.2022; 75(1): 13. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding artificial intelligence in histopathology: A cross-sectional study among oral pathologists in India
M. Indu, Vidya Gurram Shankar, Latha Mary Cherian, Revathi Krishna, Sabu Paul, Pradeesh Sathyan
Saudi Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 9(3): 157. CrossRef - Evaluation Challenges in the Validation of B7-H3 as Oral Tongue Cancer Prognosticator
Meri Sieviläinen, Anna Maria Wirsing, Aini Hyytiäinen, Rabeia Almahmoudi, Priscila Rodrigues, Inger-Heidi Bjerkli, Pirjo Åström, Sanna Toppila-Salmi, Timo Paavonen, Ricardo D. Coletta, Elin Hadler-Olsen, Tuula Salo, Ahmed Al-Samadi
Head and Neck Pathology.2021; 15(2): 469. CrossRef - Amsterdam International Consensus Meeting: tumor response scoring in the pathology assessment of resected pancreatic cancer after neoadjuvant therapy
Boris V. Janssen, Faik Tutucu, Stijn van Roessel, Volkan Adsay, Olca Basturk, Fiona Campbell, Claudio Doglioni, Irene Esposito, Roger Feakins, Noriyoshi Fukushima, Anthony J. Gill, Ralph H. Hruban, Jeffrey Kaplan, Bas Groot Koerkamp, Seung-Mo Hong, Alyssa
Modern Pathology.2021; 34(1): 4. CrossRef - Fabrication of ultra-thin 2D covalent organic framework nanosheets and their application in functional electronic devices
Weikang Wang, Weiwei Zhao, Haotian Xu, Shujuan Liu, Wei Huang, Qiang Zhao
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2021; 429: 213616. CrossRef - Generalizability of Deep Learning System for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Various Cancers
Hyun-Jong Jang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 808. CrossRef - Integrated digital pathology at scale: A solution for clinical diagnostics and cancer research at a large academic medical center
Peter J Schüffler, Luke Geneslaw, D Vijay K Yarlagadda, Matthew G Hanna, Jennifer Samboy, Evangelos Stamelos, Chad Vanderbilt, John Philip, Marc-Henri Jean, Lorraine Corsale, Allyne Manzo, Neeraj H G Paramasivam, John S Ziegler, Jianjiong Gao, Juan C Peri
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2021; 28(9): 1874. CrossRef - Translational Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Diagnostic Pathology in Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Comprehensive and Evolutive Analysis
Julia Moran-Sanchez, Antonio Santisteban-Espejo, Miguel Angel Martin-Piedra, Jose Perez-Requena, Marcial Garcia-Rojo
Biomolecules.2021; 11(6): 793. CrossRef - Development and operation of a digital platform for sharing pathology image data
Yunsook Kang, Yoo Jung Kim, Seongkeun Park, Gun Ro, Choyeon Hong, Hyungjoon Jang, Sungduk Cho, Won Jae Hong, Dong Un Kang, Jonghoon Chun, Kyoungbun Lee, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Kyoung Chul Moon, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyu Sang Lee, Jeong Hwan Park, Won-Ki Jeong, Se Yo
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sliding window based deep ensemble system for breast cancer classification
Amin Alqudah, Ali Mohammad Alqudah
Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology.2021; 45(4): 313. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and computational pathology
Miao Cui, David Y. Zhang
Laboratory Investigation.2021; 101(4): 412. CrossRef - Effects of Image Quantity and Image Source Variation on Machine Learning Histology Differential Diagnosis Models
Elham Vali-Betts, Kevin J. Krause, Alanna Dubrovsky, Kristin Olson, John Paul Graff, Anupam Mitra, Ananya Datta-Mitra, Kenneth Beck, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Cynthia Loomis, Antonio Galvao Neto, Esther Adler, Hooman H. Rashidi
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 5. CrossRef - Feasibility of deep learning‐based fully automated classification of microsatellite instability in tissue slides of colorectal cancer
Sung Hak Lee, In Hye Song, Hyun‐Jong Jang
International Journal of Cancer.2021; 149(3): 728. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare
Yamini D Shah, Shailvi M Soni, Manish P Patel
Indian Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2021; 8(2): 102. CrossRef - Proof of Concept for a Deep Learning Algorithm for Identification and Quantification of Key Microscopic Features in the Murine Model of DSS-Induced Colitis
Agathe Bédard, Thomas Westerling-Bui, Aleksandra Zuraw
Toxicologic Pathology.2021; 49(4): 897. CrossRef - An empirical analysis of machine learning frameworks for digital pathology in medical science
S.K.B. Sangeetha, R Dhaya, Dhruv T Shah, R Dharanidharan, K. Praneeth Sai Reddy
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2021; 1767(1): 012031. CrossRef - Application of Single-Cell Approaches to Study Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Biology
Daniel Royston, Adam J. Mead, Bethan Psaila
Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America.2021; 35(2): 279. CrossRef - Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) and Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI): Diagnostic Algorithm Based on the Quantitative Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM)
Rolf Teschke, Gaby Danan
Diagnostics.2021; 11(3): 458. CrossRef - Searching Images for Consensus
Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Phedias Diamandis, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Amir Safarpoor, Shivam Kalra, Danial Maleki, Abtin Riasatian, Morteza Babaie
The American Journal of Pathology.2021; 191(10): 1702. CrossRef - Automated Classification and Segmentation in Colorectal Images Based on Self‐Paced Transfer Network
Yao Yao, Shuiping Gou, Ru Tian, Xiangrong Zhang, Shuixiang He, Zhiguo Zhou
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and sleep: Advancing sleep medicine
Nathaniel F. Watson, Christopher R. Fernandez
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2021; 59: 101512. CrossRef - Prospective Of Artificial Intelligence: Emerging Trends In Modern Biosciences Research
Pradeep Kumar, Ajit Kumar Singh Yadav, Abhishek Singh
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1020(1): 012008. CrossRef - Use and Control of Artificial Intelligence in Patients Across the Medical Workflow: Single-Center Questionnaire Study of Patient Perspectives
Simon Lennartz, Thomas Dratsch, David Zopfs, Thorsten Persigehl, David Maintz, Nils Große Hokamp, Daniel Pinto dos Santos
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(2): e24221. CrossRef - HEAL: an automated deep learning framework for cancer histopathology image analysis
Yanan Wang, Nicolas Coudray, Yun Zhao, Fuyi Li, Changyuan Hu, Yao-Zhong Zhang, Seiya Imoto, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Geoffrey I Webb, Roger J Daly, Jiangning Song, Zhiyong Lu
Bioinformatics.2021; 37(22): 4291. CrossRef - A Review of Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Gastroenterology
Khalid Nawab, Ravi Athwani, Awais Naeem, Muhammad Hamayun, Momna Wazir
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Cancer-Related Biomarkers Based on Pathological Images: A Systematic Review
Xiaoliang Xie, Xulin Wang, Yuebin Liang, Jingya Yang, Yan Wu, Li Li, Xin Sun, Pingping Bing, Binsheng He, Geng Tian, Xiaoli Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based histopathological segmentation for whole slide images of colorectal cancer in a compressed domain
Hyeongsub Kim, Hongjoon Yoon, Nishant Thakur, Gyoyeon Hwang, Eun Jung Lee, Chulhong Kim, Yosep Chong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Ex Vivo Fluorescent Confocal Microscopy Data: A Feasibility Study
Veronika Shavlokhova, Sameena Sandhu, Christa Flechtenmacher, Istvan Koveshazi, Florian Neumeier, Víctor Padrón-Laso, Žan Jonke, Babak Saravi, Michael Vollmer, Andreas Vollmer, Jürgen Hoffmann, Michael Engel, Oliver Ristow, Christian Freudlsperger
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(22): 5326. CrossRef - A Pathologist-Annotated Dataset for Validating Artificial Intelligence: A Project Description and Pilot Study
Sarah N. Dudgeon, Si Wen, Matthew G. Hanna, Rajarsi Gupta, Mohamed Amgad, Manasi Sheth, Hetal Marble, Richard Huang, Markus D. Herrmann, Clifford H. Szu, Darick Tong, Bruce Werness, Evan Szu, Denis Larsimont, Anant Madabhushi, Evangelos Hytopoulos, Weijie
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 45. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: A Multinational Multi-Center Survey on the Medical and Dental Students' Perception
Sotirios Bisdas, Constantin-Cristian Topriceanu, Zosia Zakrzewska, Alexandra-Valentina Irimia, Loizos Shakallis, Jithu Subhash, Maria-Madalina Casapu, Jose Leon-Rojas, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Dilys Miriam Andrews, Claudia Zeicu, Ahmad Mohammad Bouhuwaish
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital/Computational Technology for Molecular Cytology Testing: A Short Technical Note with Literature Review
Robert Y. Osamura, Naruaki Matsui, Masato Kawashima, Hiroyasu Saiga, Maki Ogura, Tomoharu Kiyuna
Acta Cytologica.2021; 65(4): 342. CrossRef - Advances in Digital Pathology: From Artificial Intelligence to Label-Free Imaging
Frederik Großerueschkamp, Hendrik Jütte, Klaus Gerwert, Andrea Tannapfel
Visceral Medicine.2021; 37(6): 482. CrossRef - Feasibility of fully automated classification of whole slide images based on deep learning
Kyung-Ok Cho, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2020; 24(1): 89. CrossRef - Same same but different: A Web‐based deep learning application revealed classifying features for the histopathologic distinction of cortical malformations
Joshua Kubach, Angelika Muhlebner‐Fahrngruber, Figen Soylemezoglu, Hajime Miyata, Pitt Niehusmann, Mrinalini Honavar, Fabio Rogerio, Se‐Hoon Kim, Eleonora Aronica, Rita Garbelli, Samuel Vilz, Alexander Popp, Stefan Walcher, Christoph Neuner, Michael Schol
Epilepsia.2020; 61(3): 421. CrossRef - Segmentation and Classification in Digital Pathology for Glioma Research: Challenges and Deep Learning Approaches
Tahsin Kurc, Spyridon Bakas, Xuhua Ren, Aditya Bagari, Alexandre Momeni, Yue Huang, Lichi Zhang, Ashish Kumar, Marc Thibault, Qi Qi, Qian Wang, Avinash Kori, Olivier Gevaert, Yunlong Zhang, Dinggang Shen, Mahendra Khened, Xinghao Ding, Ganapathy Krishnamu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology
B. Acs, M. Rantalainen, J. Hartman
Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 288(1): 62. CrossRef - Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology
Soojeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(2): 125. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine
Zeeshan Ahmed, Khalid Mohamed, Saman Zeeshan, XinQi Dong
Database.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Scoring pleurisy in slaughtered pigs using convolutional neural networks
Abigail R. Trachtman, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Angelo Porrello, Andrea Capobianco Dondona, Ercole Del Negro, Andrea Paolini, Giorgio Vignola, Simone Calderara, Giuseppe Marruchella
Veterinary Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status of Computational Intelligence Applications in Dermatological Clinical Practice
Carmen Rodríguez-Cerdeira, José Luís González-Cespón, Roberto Arenas
The Open Dermatology Journal.2020; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - New unified insights on deep learning in radiological and pathological images: Beyond quantitative performances to qualitative interpretation
Yoichi Hayashi
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2020; 19: 100329. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology: Present and Future
Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, Zachi Attia, Adelaide M. Arruda-Olson, Rickey Carter, Panithaya Chareonthaitawee, Hayan Jouni, Suraj Kapa, Amir Lerman, Christina Luong, Jose R. Medina-Inojosa, Peter A. Noseworthy, Patricia A. Pellikka, Margaret M. Redfield, Vero
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(5): 1015. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology
Hideyuki Shimizu, Keiichi I. Nakayama
Cancer Science.2020; 111(5): 1452. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and the future of global health
Nina Schwalbe, Brian Wahl
The Lancet.2020; 395(10236): 1579. CrossRef - The future of pathology is digital
J.D. Pallua, A. Brunner, B. Zelger, M. Schirmer, J. Haybaeck
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153040. CrossRef - Weakly-supervised learning for lung carcinoma classification using deep learning
Fahdi Kanavati, Gouji Toyokawa, Seiya Momosaki, Michael Rambeau, Yuka Kozuma, Fumihiro Shoji, Koji Yamazaki, Sadanori Takeo, Osamu Iizuka, Masayuki Tsuneki
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in oncologic histopathology
Ahmed S. Sultan, Mohamed A. Elgharib, Tiffany Tavares, Maryam Jessri, John R. Basile
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2020; 49(9): 849. CrossRef - Convergence of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Tools in Anatomic Pathology Practice: Current Landscape and Future Directions
Anil V. Parwani, Mahul B. Amin
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2020; 27(4): 221. CrossRef - Advances in tissue-based imaging: impact on oncology research and clinical practice
Arman Rahman, Chowdhury Jahangir, Seodhna M. Lynch, Nebras Alattar, Claudia Aura, Niamh Russell, Fiona Lanigan, William M. Gallagher
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2020; 20(10): 1027. CrossRef - Current Trends of Artificial Intelligence for Colorectal Cancer Pathology Image Analysis: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Hongjun Yoon, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1884. CrossRef - Explainable Machine Learning Model for Predicting GI Bleed Mortality in the Intensive Care Unit
Farah Deshmukh, Shamel S. Merchant
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 115(10): 1657. CrossRef - Prediction of clinically actionable genetic alterations from colorectal cancer histopathology images using deep learning
Hyun-Jong Jang, Ahwon Lee, J Kang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 26(40): 6207. CrossRef - Application of system analysis methods for modeling the development of hand-arm vibration syndrome: problems and approaches to solution
M P Diakovich, M V Krivov
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1661(1): 012029. CrossRef - Histo-ELISA technique for quantification and localization of tissue components
Zhongmin Li, Silvia Goebel, Andreas Reimann, Martin Ungerer
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of artificial intelligence in diagnostic oral pathology-A modern approach
Ayinampudi Bhargavi Krishna, Azra Tanveer, Pancha Venkat Bhagirath, Ashalata Gannepalli
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2020; 24(1): 152. CrossRef - Applications of deep learning for the analysis of medical data
Hyun-Jong Jang, Kyung-Ok Cho
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2019; 42(6): 492. CrossRef - PROMISE CLIP Project: A Retrospective, Multicenter Study for Prostate Cancer that Integrates Clinical, Imaging and Pathology Data
Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Yong Hyun Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong, Choung-Soo Kim, Heounjeong Go, Seong Soo Jeon, Minyong Kang, Hak Jong Lee, Sung Il Hwang, Ji Youl Lee
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(15): 2982. CrossRef - Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence
Christopher J. Kelly, Alan Karthikesalingam, Mustafa Suleyman, Greg Corrado, Dominic King
BMC Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning for Whole Slide Image Analysis: An Overview
Neofytos Dimitriou, Ognjen Arandjelović, Peter D. Caie
Frontiers in Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers to Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Healthcare Management: A Systematic Review
Mir Mohammed Assadullah
SSRN Electronic Journal .2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
- An Immunohistochemical and Polarizing Microscopic Study of the Tumor Microenvironment in Varying Grades of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Aeman Khalid, Safia Siddiqui, Bharadwaj Bordoloi, Nafis Faizi, Fahad Samadi, Noora Saeed
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):314-322. Published online July 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.07.17
- 9,066 View
- 164 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Invasion of epithelial cells into the connective tissue brings about massive morphological and architectural changes in the underlying stroma. Myofibroblasts reorganize the stroma to facilitate the movement of tumor cells leading to metastasis. The aim of this study was to determine the number and pattern of distribution of myofibroblasts and the qualitative and quantitative change that they cause in the collagen present in the stroma in various grades of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods
The study was divided into two groups with group I (test group, 65 cases) consisting of 29 cases of well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, 25 moderately differentiated SCC, and 11 poorly differentiated SCC, and group II (control group) consisting of 11 cases of normal mucosa. Sections from each sample were stained with anti–α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) antibodies, hematoxylin and eosin, and Picrosirius red. Several additional sections from each grade of OSCC were stained with Masson’s trichrome to observe the changes in collagen. For the statistical analysis, Fisher’s exact test, Tukey’s post hoc honest significant difference test, ANOVA, and the chi-square test were used, and p < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
As the tumor stage progressed, an increase in the intensity α-SMA expression was seen, and the network pattern dominated in more dedifferentiated carcinomas. The collagen fibers became thin, loosely packed, and haphazardly aligned with progressing cancer. Additionally, the mean area fraction decreased, and the fibers attained a greenish yellow hue and a weak birefringence when observed using polarizing light microscopy.
Conclusions
Myofibroblasts bring about numerous changes in collagen. As cancer progresses, there isincrease in pathological collagen,which enhances the movement of cells within the stroma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifractal Alterations in Oral Sub-Epithelial Connective Tissue During Progression of Pre-Cancer and Cancer
Debaleena Nawn, Sawon Pratiher, Subhankar Chattoraj, Debjani Chakraborty, Mousumi Pal, Ranjan Rashmi Paul, Srimonti Dutta, Jyotirmoy Chatterjee
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2021; 25(1): 152. CrossRef
- Multifractal Alterations in Oral Sub-Epithelial Connective Tissue During Progression of Pre-Cancer and Cancer
- Primary Cutaneous Mucinous Carcinoma with Extramammary Paget’s Disease: Eccrine or Apocrine?
- Sun-Ju Oh, Young-Ok Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):238-242. Published online January 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.11.21
- 9,752 View
- 146 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma (PCMC) is an uncommon tumor of the sweat gland origin. The occurrence of PCMC is mostly in middle-aged and older patients, with a slight male predominance. Most cases of PCMC arise on the head, with a preference for eyelids. The histogenesis of PCMC, whether eccrine or apocrine, remains controversial. We report a rare case of PCMC with secondary extramammary Paget’s disease in the groin of a 75-year-old man, which favored an apocrine origin. Furthermore, based on a review of the literature, we provide several histologic clues that can be used to differentiate PCMC from metastatic mucinous carcinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma of the scalp masquerading as a benign dermatological mass – A case report
Fadi Alnehlaoui, Nafad Mohamed Lotfy Elhadidi, Shafik Fwakhrji, Shekhar V. Shikare, Majid Hassan Alhammadi, Salman Yousuf Guraya
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2024; 114: 109175. CrossRef - Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma in a periorbital lesion: two case reports and literature review
Jun Woo Kim, Sung Eun Kim
Archives of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 25(2): 90. CrossRef - Primary Cutaneous Mucinous Carcinoma: A Review of the Literature
Timothy Freeman, Aaron J. Russell, M. Laurin Council
Dermatologic Surgery.2023; 49(12): 1091. CrossRef - A Case of Eccrine Mucinous Carcinoma Involving Scalp
Ramsha Saleem, Sachin Vaidya
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma of the scalp masquerading as a benign dermatological mass – A case report
- Morphological and Functional Changes in the Thyroid Follicles of the Aged Murine and Humans
- Junguee Lee, Shinae Yi, Yea Eun Kang, Hyeon-Woo Kim, Kyong Hye Joung, Hae Joung Sul, Koon Soon Kim, Minho Shong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):426-435. Published online October 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.19
- 18,549 View
- 468 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although both thyroid histology and serum concentrations of hormones are known to change with age, only a few reports exist on the relationship between the age-related structural and functional changes of the thyroid follicles in both mice and humans. Our objectives were to investigate age-related histological changes of the thyroid follicles and to determine whether these morphological changes were associated with the functional activity of the follicles.
Methods
The thyroid glands of mice at 18 weeks and at 6, 15, and 30 months of age were histologically examined, and the serum levels of thyroid hormones were measured in 11-week-old and 20-month-old mice. Samples of human thyroid tissue from 10 women over 70 years old and 10 women between 30 and 50 years of age were analyzed in conjunction with serum thyroid hormone level.
Results
The histological and functional changes observed in the thyroid follicles of aged mice and women were as follows: variable sizing and enlargement of the follicles; increased irregularity of follicles; Sanderson’s polsters in the wall of large follicles; a large thyroglobulin (Tg) globule or numerous small fragmented Tg globules in follicular lumens; oncocytic change in follicular cells; and markedly dilated follicles empty of colloid. Serum T3 levels in 20-month-old mice and humans were unremarkable.
Conclusions
Thyroid follicles of aged mice and women show characteristic morphological changes, such as cystic atrophy, empty colloid, and Tg globules. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of donor–recipient age differences in allogenic rat thyroid transplantation
Ayumi Arauchi, Katsuhisa Matsuura, Tatsuya Shimizu
Regenerative Therapy.2026; 31: 101047. CrossRef - Characterization of primary cilia in different epithelial cells of thyroid gland
B. Pérez-Fernández, V. Vázquez-Román, J. M. Fernández-Santos, I. Martín-Lacave
Histochemistry and Cell Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterizing thyroid follicles histogenesis in the human fetuses: A morphological approach
Chacchu Bhattarai, Phanindra Prasad Poudel, Mahendra Raj Pandey, Chandni Gupta, Sneha Guruprasad Kalthur
Tissue and Cell.2025; 93: 102710. CrossRef - Effect of a Low-Molecular-Weight Allosteric Agonist of the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor on Basal and Thyroliberin-Stimulated Activity of Thyroid System in Diabetic Rats
Kira V. Derkach, Alena S. Pechalnova, Viktor N. Sorokoumov, Inna I. Zorina, Irina Y. Morina, Elizaveta E. Chernenko, Egor A. Didenko, Irina V. Romanova, Alexander O. Shpakov
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(2): 703. CrossRef - Human Relevance of Pharmaceutical Drug‐Induced Thyroid Tumors in Rats, Labeling Implications, and Carcinogenicity Study Requirements
B. D. Hollingshead, Z. A. Radi
Journal of Applied Toxicology.2025; 45(8): 1426. CrossRef - Early developmental exposure to sodium perchlorate disrupts thyroid, liver, and testicular development in mice
Kyle Bouten, Roman Parpart, Marielle Calanza, Michael Minicozzi
Integrative And Comparative Biology.2025; 65(1): 11. CrossRef - OCT-Based Differentiation of papillary thyroid carcinoma through quantitative optical attenuation and microstructural characterization
Zengming Li, Chao Zhao, Weizheng Mao, Xiaofeng Shi, Hang Zhao, Jun Ma
Journal of Modern Optics.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Experimental induction of hypothyroidism and goitre in goat kids: Clinical, pathological and histomorphometric findings
Luis Adrián Colque-Caro, Claudio Gustavo Barbeito, Dadín Prando Moore, Juan Francisco Micheloud
Research in Veterinary Science.2025; 197: 105926. CrossRef - The role of the primary cilium in thyroid function and dysfunction with implications for thyroid disease
Inés Martín-Lacave, Victoria Vázquez-Román, Beatriz Pérez-Fernández, José María Fernández-Santos
Histochemistry and Cell Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic Rescue of a Subset of Thyroid Follicular Cells Restores Thyroid Function in Dyshormonogenic Duoxa−/− Mice
Sami Djerbib, Helmut Grasberger, Steven Goossens, Jody Haigh, Lieven Haenebalcke, Tim Pieters, Jukka Kero, Françoise Miot, Xavier De Deken
Thyroid®.2025; 35(11): 1230. CrossRef - Arsenic-Induced Thyroid Hormonal Alterations and Their Putative Influence on Ovarian Follicles in Balb/c Mice
Nandheeswari K, Jayapradha P, Sree Vaishnavi Nalla, Itishree Dubey, Sapana Kushwaha
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(9): 4087. CrossRef - Histological evidence of hypothyroidism in mice chronically exposed to conventional farming
Nádia Coelho, Ricardo Camarinho, Patrícia Garcia, Armindo S. Rodrigues
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2024; 106: 104387. CrossRef - Optimizing decellularization protocols for human thyroid tissues: a step towards tissue engineering and transplantation
Özge Karabıyık Acar, Gülnihal Bozdağ, Ezgi Hacıhasanoğlu, A Alperen Tuncer, Erhan Aysan, Gamze Torun Köse
Biomedical Materials.2024; 19(4): 045034. CrossRef - A comparative cross-sectional study on the quality of life in Grave’s disease patients: urban vs. rural perspectives
Shivang Mishra, Anurag Kumar Singh, Sumit Rajotiya, Sourav Debnath, Sachin Kumar, Pratima Singh, Snehpreet, Preeti Raj, Mahaveer Singh, Hemant Bareth, Deepak Nathiya, Balvir Singh Tomar
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of thyroid disruption on ovarian development following maternal exposure to Bisphenol S
Lina Chouchene, Sana Boughammoura, Mariem Ben Rhouma, Rania Mlouka, Mohamed Banni, Imed Messaoudi, Kaouthar Kessabi
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2024; 31(39): 52596. CrossRef - Fish collagen peptides supplementation ameliorates skeletal muscle injury in high-fat diet mice associated with thyroid function recovery
Yuhui Yang, Hao Yang, Xu Tian, Wenhan Jian, Nazish Muzaffar, Guowei Le, Yanli Xie, Peng Li, Yuncong Xu
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 123: 106612. CrossRef - Thyroid‐on‐a‐Chip: An Organoid Platform for In Vitro Assessment of Endocrine Disruption
Daniel J. Carvalho, Anna M. Kip, Mírian Romitti, Marta Nazzari, Andreas Tegel, Matthias Stich, Christian Krause, Florian Caiment, Sabine Costagliola, Lorenzo Moroni, Stefan Giselbrecht
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Serious lesions in Green turtles (Chelonia mydas) afflicted by fatal Spirorchiidiasis found stranded in south and southeastern Brazil
Hassan Jerdy, Bruna Barreto, Max Werneck, Rachel Ann Hauser-Davis, Paula Baldassin, Patrick Gabriel, Aline Luize de Moraes Souza, Maria Aparecida da Silva, Aline Felix, Rachel Ribeiro Rodrigues, Mariah Bianchi, Carla Barbosa, Gessica Gomes Vieira, Lara Ri
International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife.2023; 20: 73. CrossRef - 基于光学相干层析技术的甲状腺乳头状癌图像识别
李增鸣 Li Zengming, 赵潮 Zhao Chao, 张旭 Zhang Xu, 毛伟征 Mao Weizheng, 赵航 Zhao Hang, 史晓凤 Shi Xiaofeng, 马君 Ma Jun
Laser & Optoelectronics Progress.2023; 60(4): 0417002. CrossRef - Differentiating Thyroid Follicular Adenoma from Follicular Carcinoma via G-Protein Coupled Receptor-Associated Sorting Protein 1 (GASP-1)
Yuan Rong, Cesar Torres-Luna, George Tuszynski, Richard Siderits, Frank N. Chang
Cancers.2023; 15(13): 3404. CrossRef - The effects of glyphosate-based herbicide on the hypothalamic-pituitary thyroid axis are tissue-specific and dependent on age exposure
Jeane Maria Oliveira, Jamilli Zenzeluk, Paula Bargi-Souza, Raphael Escorsim Szawka, Marco Aurelio Romano, Renata Marino Romano
Environmental Pollution.2023; 334: 122216. CrossRef - Borealin/CDCA8 deficiency alters thyroid development and results in papillary tumor-like structures
Hortense Didier-Mathon, Athanasia Stoupa, Dulanjalee Kariyawasam, Sonny Yde, Beatrix Cochant-Priollet, Lionel Groussin, Frédéric Sébag, Nicolas Cagnard, Patrick Nitschke, Dominique Luton, Michel Polak, Aurore Carré
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Notch signaling in thyrocytes is essential for adult thyroid function and mammalian homeostasis
Lluc Mosteiro, Thi Thu Thao Nguyen, Simona Hankeova, Daniel Alvarez-Sierra, Mike Reichelt, Shannon M. Vandriel, Zijuan Lai, Feroza K. Choudhury, Dewakar Sangaraju, Binita M. Kamath, Alexis Scherl, Ricardo Pujol-Borrell, Robert Piskol, Christian W. Siebel
Nature Metabolism.2023; 5(12): 2094. CrossRef - Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - Сравнение морфологических изменений щитовидной железы крыс послевлияния разных видов алиментарной депривации
Р. В. Янко
Biological Journal of Armenia.2022; : 24. CrossRef - Zinc Depletion Inhibits the Synthesis and Secretion of Thyroglobulin by Inducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in PCCL3 Thyroid Cells
Kisang Kwon, Eun-Ryeong Lee, Kyung-Hee Kang, Tae-Sik Hwang, Seung-Whan Kim, Hyewon Park, O-Yu Kwon
International Journal of Biology and Biomedical Engineering.2022; 16: 290. CrossRef - Metimazol ile Oluşturulan Sıçan Hipotiroidi Modelinde Kognitif Fonksiyonlar, Anksiyete ve Depresyon Benzeri Davranışların Değerlendirilmesi: Pilot Çalışma
Oğuzhan Ekin EFE, Selda EMRE AYDINGÖZ, Karl Michael LUX, Eda ÖZER, Ayşegül SÜZER, Meral TUNCER
Uludağ Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2022; 48(2): 147. CrossRef - Loss of thyroid gland circadian PER2 rhythmicity in aged mice and its potential association with thyroid cancer development
Junguee Lee, Hae Joung Sul, Hyunsu Choi, Dong Hyun Oh, Minho Shong
Cell Death & Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HISTOTOPOGRAPHIC AND STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF CANINE THYROID GLAND FOLLICLES UNDER SINGLE DYNAMIC MOTOR LOADS
Andrey V. Bezdenezhnykh, Sofia S. Kolodezhnaya, Daria E. Nazarova, Anna P. Bavrina
Morphological newsletter.2022; 30(4): 22. CrossRef - Thyroid hormone receptor β sumoylation is required for thyrotropin regulation and thyroid hormone production
Sujie Ke, Yan-Yun Liu, Rajendiran Karthikraj, Kurunthachalam Kannan, Jingjing Jiang, Kiyomi Abe, Anna Milanesi, Gregory A. Brent
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid Gland Alterations in Old-Aged Wistar Rats: A Comprehensive Stereological, Ultrastructural, Hormonal, and Gene Expression Study
Marko Miler, Vladimir Ajdžanović, Jasmina Živanović, Jelena Marković Filipović, Branka Šošić-Jurjević, Verica Milošević
Microscopy and Microanalysis.2021; 27(2): 437. CrossRef - Age-dependent effects on radiation-induced carcinogenesis in the rat thyroid
Mutsumi Matsuu-Matsuyama, Kazuko Shichijo, Katsuya Matsuda, Nariaki Fujimoto, Hisayoshi Kondo, Shiro Miura, Tomomi Kurashige, Yuji Nagayama, Masahiro Nakashima
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Relevant dose of the environmental contaminant, tributyltin, promotes histomorphological changes in the thyroid gland of male rats
Paula Rodrigues-Pereira, Sofia Macedo, Tiago Bordeira Gaspar, Sule Canberk, Samia Selmi-Ruby, Valdemar Máximo, Paula Soares, Leandro Miranda-Alves
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2020; 502: 110677. CrossRef - Morphological and functional changes in neonatally X-irradiated thyroid gland in rats
Nariaki Fujimoto, Mutsumi Matsuu-Matsuyama, Masahiro Nakashima
Endocrine Journal.2020; 67(2): 231. CrossRef - Optical coherence tomography for thyroid pathology: 3D analysis of tissue microstructure
Iulian Emil Tampu, Michaela Maintz, Daniela Koller, Kenth Johansson, Oliver Gimm, Arrigo Capitanio, Anders Eklund, Neda Haj-Hosseini
Biomedical Optics Express.2020; 11(8): 4130. CrossRef - Thyroid surgery in the elderly
Nicole Ruszkay, David Goldenberg, Guy Slonimsky
Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2020; 31(3): 206. CrossRef - Liver X Receptor β Related to Tumor Progression and Ribosome Gene Expression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Seonhyang Jeong, In-Kyu Kim, Hyunji Kim, Moon Jung Choi, Jandee Lee, Young Suk Jo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 656. CrossRef - A historical excursus of diagnostic methods for Hashimoto thyroiditis and Graves' disease
Maria Trovato
Gazzetta Medica Italiana Archivio per le Scienze Mediche.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross‐sectional comparison of health‐span phenotypes in young versus geriatric marmosets
Corinna N. Ross, Jessica Adams, Olga Gonzalez, Edward Dick, Luis Giavedoni, Vida L. Hodara, Kimberley Phillips, Anna D Rigodanzo, Balakuntalam Kasinath, Suzette D. Tardif
American Journal of Primatology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of nonylphenols on embryonic development and metamorphosis of Xenopus laevis: FETAX and amphibian metamorphosis toxicity test (OECD TG231)
Yang Xu, Sun Jung Park, Myung Chan Gye
Environmental Research.2019; 174: 14. CrossRef - Basal Autophagy Deficiency Causes Thyroid Follicular Epithelial Cell Death in Mice
Tomomi Kurashige, Yasuyo Nakajima, Mika Shimamura, Mutsumi Matsuyama, Masanobu Yamada, Masahiro Nakashima, Yuji Nagayama
Endocrinology.2019; 160(9): 2085. CrossRef - Aging Is Associated with Low Thyroid State and Organ-Specific Sensitivity to Thyroxine
Helena Rakov, Meri De Angelis, Kostja Renko, Georg Sebastian Hönes, Denise Zwanziger, Lars Christian Moeller, Karl-Werner Schramm, Dagmar Führer
Thyroid.2019; 29(12): 1723. CrossRef - High-fat, simple-carbohydrate diet intake induces hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis dysregulation in C57BL/6J male mice
Nagaraj Banavara Swarnalatha, Neena Roy, Mahesh Manjunath Gouda, Rajeish Moger, Asha Abraham
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2018; 43(4): 371. CrossRef - Biomarker Sensitivity to Vehicle Exhaust in Experimentally Exposed European Starlings
Michelle A. North, Jaime Rodriguez-Estival, Judit E. G. Smits
Environmental Science & Technology.2017; 51(22): 13427. CrossRef
- Influence of donor–recipient age differences in allogenic rat thyroid transplantation
- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyekyung Lee, Tae Hwa Baek, Meeja Park, Seung Yun Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Dong Wook Kang, Joo Heon Kim, Soo Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):355-360. Published online August 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.05.19
- 8,275 View
- 90 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
There is subjective disagreement regarding nuclear clearing in papillary thyroid carcinoma. In this study, using digital instruments, we were able to quantify many ambiguous pathologic features and use numeric data to express our findings.
Methods
We examined 30 papillary thyroid carcinomas. For each case, we selected representative cancer cells showing clear nuclei and surrounding non-neoplastic follicular epithelial cells and evaluated objective values of green light intensity (GLI) for quantitative analysis of nuclear clearing in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Results
From 16,274 GLI values from 600 cancer cell nuclei and 13,752 GLI values from 596 non-neoplastic follicular epithelial nuclei, we found a high correlation of 94.9% between GLI and clear nuclei. GLI between the cancer group showing clear nuclei and non-neoplastic follicular epithelia was statistically significant. The overall average level of GLI in the cancer group was over two times higher than the non-neoplastic group despite a wide range of GLI. On a polygonal line graph, there was a fluctuating unique difference between both the cancer and non-neoplastic groups in each patient, which was comparable to the microscopic findings.
Conclusions
Nuclear GLI could be a useful factor for discriminating between carcinoma cells showing clear nuclei and non-neoplastic follicular epithelia in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer: Review Article from a Pathologist’s Point of View
- Sophia K. Apple
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):83-95. Published online January 12, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.11.23
- 25,912 View
- 493 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Breast cancer staging, in particular N-stage changed most significantly due to the advanced technique of sentinel lymph node biopsy two decades ago. Pathologists have more thoroughly examined and scrutinized sentinel lymph node and found increased number of small volume metastases. While pathologists use the strict criteria from the Tumor Lymph Node Metastasis (TNM) Classification, studies have shown poor reproducibility in the application of American Joint Committee on Cancer and International Union Against Cancer/TNM guidelines for sentinel lymph node classification in breast cancer. In this review article, a brief history of TNM with a focus on N-stage is described, followed by innate problems with the guidelines, and why pathologists may have difficulties in assessing lymph node metastases uniformly. Finally, clinical significance of isolated tumor cells, micrometastasis, and macrometastasis is described by reviewing historical retrospective data and significant prospective clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Out-of-distribution generalization for segmentation of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
Yiannis Varnava, Kiran Jakate, Richard Garnett, Dimitrios Androutsos, Pascal N. Tyrrell, April Khademi
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen section analysis in community settings: Diagnostic challenges and key considerations
Rashna Meunier, Kisong Kim, Noureldien Darwish, Syed M. Gilani
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 42(3): 150903. CrossRef - Axillary lymph node dissection offers no survival benefit in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node micrometastases after neoadjuvant therapy
Jianing Zhang, Yudong Zhou, Lizhe Zhu, Jiaqi Zhang, Chenglong Duan, Jinsui Du, Yi Pan, Yalong Wang, Danni Li, Yu Ren, Bin Wang
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between postoperative pathological results and non-sentinel nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node-positive breast cancer
Lingguang Dong, Suosu Wei, Zhen Huang, Fei Liu, Yujie Xie, Jing Wei, Chongde Mo, Shengpeng Qin, Quanqing Zou, Jianrong Yang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clonal dominance defines metastatic dissemination in pancreatic cancer
I-Lin Ho, Chieh-Yuan Li, Fuchenchu Wang, Li Zhao, Jingjing Liu, Er-Yen Yen, Charles A. Dyke, Rutvi Shah, Zhaoliang Liu, Ali Osman Çetin, Yanshuo Chu, Francesca Citron, Sergio Attanasio, Denise Corti, Faezeh Darbaniyan, Edoardo Del Poggetto, Sara Loponte,
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognosis of isolated tumor cells and use of molecular classification in early stage endometrioid endometrial cancer
Eric Rios-Doria, Nadeem R Abu-Rustum, Kaled M Alektiar, Vicky Makker, Ying L Liu, Dmitriy Zamarin, Claire F Friedman, Carol Aghajanian, Lora H Ellenson, Sarah Chiang, Britta Weigelt, Jennifer J Mueller, Mario M Leitao
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2024; 34(9): 1373. CrossRef - Predictive factors for dissection-free sentinel node micrometastases in early oral squamous cell carcinoma
Takashi Matsuzuka, Kiyoaki Tsukahara, Seiichi Yoshimoto, Kazuaki Chikamatsu, Akihiro Shiotani, Isao Oze, Yoshiko Murakami, Takeshi Shinozaki, Yuichiro Enoki, Shinichi Ohba, Daisuke Kawakita, Nobuhiro Hanai, Yusuke Koide, Michi Sawabe, Yusuke Nakata, Yujir
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Nodes and Nodal Assessment in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prediction in ER+, Node-Positive Breast Cancer
Charlene Kay, Carlos Martinez-Perez, J. Michael Dixon, Arran K. Turnbull
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(10): 1476. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Personalized Medicine
Jong Seok Ahn, Sangwon Shin, Su-A Yang, Eun Kyung Park, Ki Hwan Kim, Soo Ick Cho, Chan-Young Ock, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Breast Cancer.2023; 26(5): 405. CrossRef - Clinicopathological predictors of finding additional inguinal lymph node metastases in penile cancer patients after positive dynamic sentinel node biopsy: a European multicentre evaluation
Hielke M. de Vries, Hack Jae Lee, Wayne Lam, Rosa S. Djajadiningrat, Sarah R. Ottenhof, Eduard Roussel, Bin Klaas Kroon, Igle Jan de Jong, Pedro Oliveira, Hussain M. Alnajjar, Maarten Albersen, Asif Muneer, Vijay Sangar, Arie Parnham, Benjamin Ayres, Nick
BJU International.2022; 130(1): 126. CrossRef - Fast Segmentation of Metastatic Foci in H&E Whole-Slide Images for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Muhammad-Adil Khalil, Yu-Ching Lee, Huang-Chun Lien, Yung-Ming Jeng, Ching-Wei Wang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 990. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Postoperative Complications of Sentinel Node Identification Using the SentiMag® Method and the Use of a Radiotracer in Patients with Breast Cancer
Andrzej Lorek, Katarzyna Steinhof-Radwańska, Wojciech Zarębski, Joanna Lorek, Zoran Stojčev, Jacek Zych, Aleksandra Syrkiewicz, Paweł Niemiec, Karol Szyluk
Current Oncology.2022; 29(5): 2887. CrossRef - Improving Cancer Metastasis Detection via Effective Contrastive Learning
Haixia Zheng, Yu Zhou, Xin Huang
Mathematics.2022; 10(14): 2404. CrossRef - Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images
Haixia Zheng, Yu Zhou, Xin Huang
Mathematics.2022; 10(15): 2657. CrossRef - Independent assessment of a deep learning system for lymph node metastasis detection on the Augmented Reality Microscope
David Jin, Joseph H. Rosenthal, Elaine E. Thompson, Jared Dunnmon, Arash Mohtashamian, Daniel Ward, Ryan Austin, Hassan Tetteh, Niels H. Olson
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2022; 13: 100142. CrossRef - Generalization of Deep Learning in Digital Pathology: Experience in Breast Cancer Metastasis Detection
Sofia Jarkman, Micael Karlberg, Milda Pocevičiūtė, Anna Bodén, Péter Bándi, Geert Litjens, Claes Lundström, Darren Treanor, Jeroen van der Laak
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5424. CrossRef - Assessment of cellular and humoral immunity in sentinel lymph node in breast cancer
A. D. Neryakhin, A. U. Gallyamov, D. N. Kamilianov, E. H. Sunagatullina, R. U. Kamalov, L. A. Sharafutdinova
Ural Medical Journal.2022; 21(6): 13. CrossRef - Lessons Learned from Designing an AI-Enabled Diagnosis Tool for Pathologists
Hongyan Gu, Jingbin Huang, Lauren Hung, Xiang 'Anthony' Chen
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2021; 5(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Deep Regional Metastases Segmentation for Patient-Level Lymph Node Status Classification
Lu Wang, Tian Song, Takafumi Katayama, Xiantao Jiang, Takashi Shimamoto, Jenq-Shiou Leu
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 129293. CrossRef - Isolated tumor cells in the regional lymph nodes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus are rarely observed but often represent part of a true metastasis
Dea Natalie Munch Jepsen, Anne-Marie Kanstrup Fiehn, Bonnie Svendsen, Michael Patrick Achiam, Birgitte Federspiel
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 45: 151478. CrossRef - Independent risk factors for axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with one or two positive sentinel lymph nodes
Wei Zhang, Jing Xu, Ke Wang, Xiao-Jiang Tang, Hua Liang, Jian-Jun He
BMC Women's Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The spectrum of pathological diagnoses in non-sentinel axillary lymph node biopsy: A single institution's experience
Wei Huang, Xiaoyu Tang, Jozef Malysz, Bing Han, Zhaohai Yang
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 49: 151646. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic Algorithm for the Assessment of Sentinel Lymph Nodes That Drain the Mammary Carcinomas in Female Dogs
Florin Stan, Alexandru Gudea, Aurel Damian, Adrian Florin Gal, Ionel Papuc, Alexandru Raul Pop, Cristian Martonos
Animals.2020; 10(12): 2366. CrossRef - Prognostic Value of EndoPredict in Women with Hormone Receptor–Positive, HER2-Negative Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer
Ivana Sestak, Martin Filipits, Richard Buus, Margaretha Rudas, Marija Balic, Michael Knauer, Ralf Kronenwett, Florian Fitzal, Jack Cuzick, Michael Gnant, Richard Greil, Mitch Dowsett, Peter Dubsky
Clinical Cancer Research.2020; 26(17): 4682. CrossRef - Performance of Molecular Lymphosonography for Detection and Quantification of Metastatic Involvement in Sentinel Lymph Nodes
Kibo Nam, Robert Stapp, Ji‐Bin Liu, Maria Stanczak, Flemming Forsberg, Patrick L. O'Kane, Zhou Lin, Ziyin Zhu, Jingzhi Li, Charalambos C. Solomides, John R. Eisenbrey, Andrej Lyshchik
Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2019; 38(8): 2103. CrossRef - Application of Circulation Tumor Cells Detection in Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Tumors
Fengfeng Cai, Chunmei Cen, Lu Cai, Manuel Antonio Falar Luis, Ewelina Biskup
Rejuvenation Research.2019; 22(6): 498. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence–Based Breast Cancer Nodal Metastasis Detection: Insights Into the Black Box for Pathologists
Yun Liu, Timo Kohlberger, Mohammad Norouzi, George E. Dahl, Jenny L. Smith, Arash Mohtashamian, Niels Olson, Lily H. Peng, Jason D. Hipp, Martin C. Stumpe
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(7): 859. CrossRef - Isolated tumor cells in regional lymph nodes in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction might represent part of true metastases
Anne-Marie Kanstrup Fiehn, Dea Natalie Munch Jepsen, Michael Patrick Achiam, Heidi Ugleholdt, Birgitte Federspiel
Human Pathology.2019; 93: 90. CrossRef - Impact of Deep Learning Assistance on the Histopathologic Review of Lymph Nodes for Metastatic Breast Cancer
David F. Steiner, Robert MacDonald, Yun Liu, Peter Truszkowski, Jason D. Hipp, Christopher Gammage, Florence Thng, Lily Peng, Martin C. Stumpe
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 42(12): 1636. CrossRef - One-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA): where do we go with it?
Yasuhiro Tamaki
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 22(1): 3. CrossRef
- Out-of-distribution generalization for segmentation of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
- Rare Case of Anal Canal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma Associated with Perianal and Vulvar Pagetoid Spread
- Na Rae Kim, Hyun Yee Cho, Jeong-Heum Baek, Juhyeon Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Jae Yeon Seok, Sung Won Park, Sun Jin Sym, Kyu Chan Lee, Dong Hae Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):231-237. Published online October 8, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.08.08
- 13,583 View
- 141 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 61-year-old woman was referred to surgery for incidentally found colonic polyps during a health examination. Physical examination revealed widespread eczematous skin lesion without pruritus in the perianal and vulvar area. Abdominopelvic computed tomography showed an approximately 4-cm-sized, soft tissue lesion in the right perianal area. Inguinal lymph node dissection and Mils’ operation extended to perianal and perivulvar skin was performed. Histologically, the anal canal lesion was composed of mucin-containing signet ring cells, which were similar to those found in Pagetoid skin lesions. It was diagnosed as an anal canal signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) with perianal and vulvar Pagetoid spread and bilateral inguinal lymph node metastasis. Anal canal SRCC is rare, and the current case is the third reported case in the English literature. Seven additional cases were retrieved from the world literature. Here, we describe this rare case of anal canal SRCC with perianal Pagetoid spread and provide a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Carcinomas of the Episiotomy Scar Site: A Systematic Literature Review
Andrea Palicelli, Federica Torricelli, Gabriele Tonni, Alessandra Bisagni, Eleonora Zanetti, Magda Zanelli, Venus Damaris Medina-Illueca, Beatrice Melli, Maurizio Zizzo, Andrea Morini, Maria Paola Bonasoni, Giacomo Santandrea, Giuseppe Broggi, Rosario Cal
Current Oncology.2025; 32(2): 65. CrossRef - Metastatic Carcinomas at the Episiotomy Site: A Systematic Literature Review
Andrea Palicelli, Gabriele Tonni, Federica Torricelli, Beatrice Melli, Vincenza Ylenia Cusenza, Sandra Martinelli, Eleonora Zanetti, Alessandra Bisagni, Magda Zanelli, Maria Paola Bonasoni, Teresa Rossi, Lucia Mangone, Venus Damaris Medina-Illueca, Mauriz
Cancers.2025; 17(17): 2801. CrossRef - A Case of Prostatic Signet-Ring Cell-like Carcinoma with Pagetoid Spread and Intraductal Carcinoma and Long-Term Survival: PD-L1 and Mismatch Repair System Proteins (MMR) Immunohistochemical Evaluation with Systematic Literature Review
Nektarios Koufopoulos, Argyro-Ioanna Ieronimaki, Andriani Zacharatou, Alina Roxana Gouloumis, Danai Leventakou, Ioannis Boutas, Dionysios T. Dimas, Adamantia Kontogeorgi, Kyparissia Sitara, Lubna Khaldi, Magda Zanelli, Andrea Palicelli
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(6): 1016. CrossRef - Anal canal adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine features accompanying secondary extramammary Paget disease, successfully treated with modified FOLFOX6: a case report
Masamichi Yamaura, Takeshi Yamada, Rei Watanabe, Hitomi Kawai, Suguru Hirose, Hiroki Tajima, Masashi Sato, Yuichi Uchida, Daisuke Suganuma, Yoshiyuki Yamamoto, Toshikazu Moriwaki, Ichinosuke Hyodo
BMC Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Solitary left axillary lymph node metastasis after curative resection of carcinoma at the colostomy site: a case report
Ken Imaizumi, Shigenori Homma, Tadashi Yoshida, Tatsushi Shimokuni, Hideyasu Sakihama, Norihiko Takahashi, Hideki Kawamura, Emi Takakuwa, Akinobu Taketomi
Surgical Case Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Primary Carcinomas of the Episiotomy Scar Site: A Systematic Literature Review
- Cytology Specimen Management, Triage and Standardized Reporting of Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsies of the Pancreas
- Won Jae Yoon, Martha Bishop Pitman
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):364-372. Published online August 10, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.19
- 15,265 View
- 148 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The recent advances in pancreas cytology specimen sampling methods have enabled a specific cytologic diagnosis in most cases. Proper triage and processing of the cytologic specimen is pivotal in making a diagnosis due to the need for ancillary testing in addition to cytological evaluation, which is especially true in the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Newly proposed terminology for pancreaticobiliary cytology offers a standardized language for reporting that aims to improve communication among patient caregivers and provide for increased flexibility in patient management. This review focuses on these updates in pancreas cytology for the optimal evaluation of solid and cystic lesions of the pancreas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue sampling: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical and Technology Review
Antonio Facciorusso, Marianna Arvanitakis, Stefano Francesco Crinò, Carlo Fabbri, Adele Fornelli, John Leeds, Livia Archibugi, Silvia Carrara, Jahnvi Dhar, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, Beate Haugk, Julio Iglesias Garcia, Bertrand Napoleon, Ioannis S. Papanikolao
Endoscopy.2025; 57(04): 390. CrossRef - Imaging of pancreatic serous cystadenoma and common imitators
Camila Lopes Vendrami, Nancy A. Hammond, David J. Escobar, Zachary Zilber, Meaghan Dwyer, Courtney C. Moreno, Pardeep K. Mittal, Frank H. Miller
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(10): 3666. CrossRef - “Evolving Trends in Pancreatic Cystic Tumors: A 3-Decade Single-Center Experience With 1290 Resections”
Jorge Roldán, Jon M. Harrison, Motaz Qadan, Louisa Bolm, Taisuke Baba, William R. Brugge, Brenna W. Casey, Kumar Krishnan, Mari Mino-Kenudson, Martha B. Pitman, Avinash Kambadakone, Cristina R. Ferrone, Andrew L. Warshaw, Keith D. Lillemoe, Carlos Fernánd
Annals of Surgery.2023; 277(3): 491. CrossRef - Role of fluorescence confocal microscopy for rapid evaluation of EUS fine-needle biopsy sampling in pancreatic solid lesions
Serena Stigliano, Anna Crescenzi, Chiara Taffon, Francesco Covotta, Cesare Hassan, Giulio Antonelli, Martina Verri, Dario Biasutto, Roberto Mario Scarpa, Francesco Maria Di Matteo
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2021; 94(3): 562. CrossRef - Towards optimal pancreatic cyst fluid management: the need for standardisation
Giacomo Puppa, Yann Christinat, Thomas Alexander McKee
Gut.2019; 68(10): 1906. CrossRef - It is necessary to exam bottom and top slide smears of EUS-FNA for pancreatic cancer
Jong-chan Lee, Haeryoung Kim, Hyoung Woo Kim, Jongchan Lee, Kyu-hyun Paik, Jingu Kang, Jin-Hyeok Hwang, Jaihwan Kim
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2018; 17(6): 553. CrossRef - Rationale and feasibility of mucin expression profiling by qRT-PCR as diagnostic biomarkers in cytology specimens of pancreatic cancer
Milosz Wiktorowicz, Damian Mlynarski, Radoslaw Pach, Romana Tomaszewska, Jan Kulig, Piotr Richter, Marek Sierzega
Pancreatology.2018; 18(8): 977. CrossRef - Variations in cancer centers’ use of cytology for the diagnosis of unresectable pancreatic cancer in the National Cancer Data Base
Ted Gansler, Stacey A. Fedewa, Chun Chieh Lin, Ahmedin Jemal, Elizabeth M. Ward
Cancer Cytopathology.2016; 124(11): 791. CrossRef - Pancreatic Cytopathology
Jennifer A. Collins, Syed Z. Ali, Christopher J. VandenBussche
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2016; 9(4): 661. CrossRef
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue sampling: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical and Technology Review
- Pathology Reporting of Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy: A Proposal of the Korean Endocrine Pathology Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Study Group
- Chan Kwon Jung, Hye Sook Min, Hyo Jin Park, Dong Eun Song, Jang Hee Kim, So Yeon Park, Hyunju Yoo, Mi Kyung Shin, Korean Endocrine Pathology Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Study Group
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(4):288-299. Published online June 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.06.04
- 20,810 View
- 491 Download
- 108 Web of Science
- 103 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years throughout Korea, the use of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy (CNB) has become common for the preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules. However, there is no consensus on the pathology reporting system for thyroid CNB. The Korean Endocrine Pathology Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Study Group held a conference on thyroid CNB pathology and developed guidelines through contributions from the participants. This article discusses the outcome of the discussions that led to a consensus on the pathology reporting of thyroid CNB.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive US findings for differentiating between malignant and benign thyroid nodules: Doppler and microvascular imaging according to the TI-RADS and pathologic subtypes of malignancy
Younghee Yim, Hye Shin Ahn, Min Ji Hong, Hyun Jeong Park, Sung Bin Park
Ultrasonography.2026; 45(1): 38. CrossRef - Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules Diagnosed as Follicular Neoplasm on Core Needle Biopsy
Byeong-Joo Noh, Won Jun Kim, Jin Yub Kim, Ha Young Kim, Jong Cheol Lee, Myoung Sook Shim, Yong Jin Song, Kwang Hyun Yoon, In-Hye Jung, Hyo Sang Lee, Wooyul Paik, Dong Gyu Na
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(4): 610. CrossRef - Diagnostic performances of five US risk stratification systems for malignancy in focal [18F]FDG-PET/CT thyroid incidentalomas
Chae Young Shin, Hye Shin Ahn, Dong Gyu Na, Hyo Sang Lee, Eon-Woo Shin
European Radiology.2025; 35(12): 7701. CrossRef - Malignancy risk in AUS thyroid lesions: comparison between FNA and CNB with implications for NIFTP diagnosis
Yeseul Kim, Jae Ho Shin, You-Na Sung, Dawon Park, Harim Oh, Hyo Seon Ryu, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hyun Joo Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Hoon Yub Kim, Kwang Yoon Jung, Seung-Kuk Baek, Sangjeong Ahn
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Diagnostic Role of Repeated Biopsy of Thyroid Nodules with Atypia of Undetermined Significance with Architectural Atypia on Core-Needle Biopsy
Hye Hyeon Moon, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(2): 300. CrossRef - Core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules assessment-a new horizon?
David D Dolidze, Serghei Covantsev, Grigorii M Chechenin, Natalia V Pichugina, Anastasia V Bedina, Anna Bumbu
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2024; 15(5): 580. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic features and diagnostic accuracy of FNA and CNB in secondary thyroid malignancies: A retrospective study
Zhen Xia, Xiaochen Huang, Ting Zhang, Zhigang Gao, Xiuliang Tang, Wei Zhang, Qing Miao
Heliyon.2024; 10(16): e36305. CrossRef - Current role of interventional radiology in thyroid nodules
Onur Taydas, Erbil Arik, Omer Faruk Sevinc, Ahmet Burak Kara, Mustafa Ozdemir, Hasret Cengiz, Zulfu Bayhan, Mehmet Halil Ozturk
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A simplified four-tier classification for thyroid core needle biopsy
M. Paja, J. L. Del Cura, R. Zabala, I. Korta, Mª T. Gutiérrez, A. Expósito, A. Ugalde
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024; 48(4): 895. CrossRef - Follow-up of benign thyroid nodules confirmed by ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy after inconclusive cytology on fine-needle aspiration biopsy
Yoon Ji Hwang, Hye Ryoung Koo, Jeong Seon Park
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(1): 121. CrossRef - Subcategorization of intermediate suspicion thyroid nodules based on suspicious ultrasonographic findings
Haejung Kim, Jung Hee Shin, Ka Eun Kim, Myoung Kyoung Kim, Jiyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(2): 307. CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - Cytological and Ultrasound Features of Thyroid Nodules Correlate With Histotypes and Variants of Thyroid Carcinoma
Daniele Sgrò, Alessandro Brancatella, Giuseppe Greco, Liborio Torregrossa, Paolo Piaggi, Nicola Viola, Teresa Rago, Fulvio Basolo, Riccardo Giannini, Gabriele Materazzi, Rossella Elisei, Ferruccio Santini, Francesco Latrofa
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(11): e1186. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - Contrast Enhancement Ultrasound Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Jianming Li, Jianping Dou, Huarong Li, Fan Xiao, Jie Yu, Mingxing Xie, Ping Zhou, Lei Liang, Guiming Zhou, Ying Che, Cun Liu, Zhibin Cong, Fangyi Liu, Zhiyu Han, Ping Liang
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Core needle biopsy and ultrasonography are superior to fine needle aspiration in the management of follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas
Ji-Ye Kim, Sunhee Chang, Ah-Young Kwon, Eun Young Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sangjoon Choi, Minju Lee, Young Lyun Oh
Endocrine.2022; 75(2): 437. CrossRef - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology vs. Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective, Experimental Study Using Surgical Specimen
Hyuk Kwon, Jandee Lee, Soon Won Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Jin Young Kwak, Jung Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2022; 83(3): 645. CrossRef - Diagnostic efficacy, performance and safety of side-cut core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules: comparison of automated and semi-automated biopsy needles
Ji Yeon Park, Seong Yoon Yi, Soo Heui Baek, Yu Hyun Lee, Heon-Ju Kwon, Hee Jin Park
Endocrine.2022; 76(2): 341. CrossRef - Approach to Bethesda system category III thyroid nodules according to US-risk stratification
Jieun Kim, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Soo Yeon Hahn, Ko Woon Park
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(1): 67. CrossRef - Quantitative analysis of vascularity for thyroid nodules on ultrasound using superb microvascular imaging
Min Ji Hong, Hye Shin Ahn, Su Min Ha, Hyun Jeong Park, Jiyun Oh
Medicine.2022; 101(5): e28725. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Using the Revised Reporting System: Comparison with Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 159. CrossRef - A Matched-Pair Analysis of Nuclear Morphologic Features Between Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Specimen in Thyroid Tumors Using a Deep Learning Model
Faridul Haq, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(4): 472. CrossRef - Role of echogenic foci in ultrasonographic risk stratification of thyroid nodules: Echogenic focus scoring in the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System
Renxu Li, Zhenwei Liang, Xiangyu Wang, Luzeng Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasonographic characteristics of medullary thyroid carcinoma according to nodule size: application of the Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System and American Thyroid Association guidelines
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Ko Woon Park
Acta Radiologica.2021; 62(4): 474. CrossRef - Malignancy risk of thyroid nodules with nonshadowing echogenic foci
Yu-Mee Sohn, Dong Gyu Na, Wooyul Paik, Hye Yun Gwon, Byeong-Joo Noh
Ultrasonography.2021; 40(1): 115. CrossRef - Assessing the diagnostic performance of thyroid biopsy with recommendations for appropriate interpretation
Su Min Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Gyu Na, Chan-Kwon Jung, Chong Hyun Suh, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Jeong Hyun Lee
Ultrasonography.2021; 40(2): 228. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of the American Thyroid Association Guidelines and American College of Radiology TI-RADS
Jinghua Liu, Yajun Guo, Jiangxi Xiao, Luzeng Chen, Zhenwei Liang
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(7): 661. CrossRef - Malignancy Rate of Bethesda Class III Thyroid Nodules Based on the Presence of Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis in Surgical Patients
Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung, Hee Sung Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Differential Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Shear Wave Elastography—the Stiffness Map
Myung Hi Yoo, Hye Jeong Kim, In Ho Choi, Suyeon Park, Sumi Yun, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of thyroid nodule size on malignancy risk according to histological type of thyroid cancer
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Acta Radiologica.2020; 61(5): 620. CrossRef - Concordance of Three International Guidelines for Thyroid Nodules Classified by Ultrasonography and Diagnostic Performance of Biopsy Criteria
Younghee Yim, Dong Gyu Na, Eun Ju Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji-hoon Kim, Won-Jin Moon
Korean Journal of Radiology.2020; 21(1): 108. CrossRef - 2019 Practice guidelines for thyroid core needle biopsy: a report of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association
Chan Kwon Jung, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Gyu Na, Young Lyun Oh, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 64. CrossRef - Core-Needle Biopsy Does Not Show Superior Diagnostic Performance to Fine-Needle Aspiration for Diagnosing Thyroid Nodules
Ilah Shin, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Vivian Youngjean Park, Si Eun Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Jin Young Kwak
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(2): 161. CrossRef - Ultrasound‐guided fine‐needle aspiration or core needle biopsy for diagnosing follicular thyroid carcinoma?
Ko Woon Park, Jung Hee Shin, Soo Yeon Hahn, Young Lyun Oh, Sun Wook Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Clinical Endocrinology.2020; 92(5): 468. CrossRef - Distribution and malignancy risk of six categories of the pathology reporting system for thyroid core-needle biopsy in 1,216 consecutive thyroid nodules
Hye Min Son, Ji-hoon Kim, Soo Chin Kim, Roh-Eul Yoo, Jeong Mo Bae, Hyobin Seo, Dong Gyu Na
Ultrasonography.2020; 39(2): 159. CrossRef - CT features of thyroid nodules with isolated macrocalcifications detected by ultrasonography
Wooyul Paik, Dong Gyu Na, Hye Yun Gwon, Jinna Kim
Ultrasonography.2020; 39(2): 130. CrossRef - Contribution of cytologic examination to diagnosis of poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Na Rae Kim, Jae Yeon Seok, Yoo Seung Chung, Joon Hyop Lee, Dong Hae Chung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(2): 171. CrossRef - Comparison Between Fine Needle Aspiration and Core Needle Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules: Effective Indications According to US Findings
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Ko Woon Park, Yaeji Lim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid Nodules with Isolated Macrocalcifications: Malignancy Risk of Isolated Macrocalcifications and Postoperative Risk Stratification of Malignant Tumors Manifesting as Isolated Macrocalcifications
Hye Yun Gwon, Dong Gyu Na, Byeong-Joo Noh, Wooyul Paik, So Jin Yoon, Soo-Jung Choi, Dong Rock Shin
Korean Journal of Radiology.2020; 21(5): 605. CrossRef - Diagnostic Efficacy and Safety of Core Needle Biopsy as a First-Line Diagnostic Method for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Cohort Study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Hunkyung Lee
Thyroid.2020; 30(8): 1141. CrossRef - Re: The 2019 core-needle biopsy practice guidelines
Ji-hoon Kim
Ultrasonography.2020; 39(3): 313. CrossRef - Cytopathologic criteria and size should be considered in comparison of fine-needle aspiration vs. core-needle biopsy for thyroid nodules: results based on large surgical series
Jung Hyun Yoon, Hye Sun Lee, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Vivian Youngjean Park, Jin Young Kwak
Endocrine.2020; 70(3): 558. CrossRef - Preoperative diagnostic categories of fine needle aspiration cytology for histologically proven thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma, and Hurthle cell adenoma and carcinoma: Analysis of cause of under- or misdiagnoses
Hee Young Na, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241597. CrossRef - The Role of Core Needle Biopsy for the Evaluation of Thyroid Nodules with Suspicious Ultrasound Features
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Radiology.2019; 20(1): 158. CrossRef - Pathological diagnosis of thyroid nodules based on core needle biopsies: comparative study between core needle biopsies and resected specimens in 578 cases
Yan Xiong, Limin Yan, Lin Nong, Yalin Zheng, Ting Li
Diagnostic Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Histologic Classification of Thyroid Cancer
Sylvia L. Asa
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2019; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Core-needle biopsy in thyroid nodules: performance, accuracy, and complications
Miguel Paja, Jose Luis del Cura, Rosa Zabala, Igone Korta, Aitziber Ugalde, José I. López
European Radiology.2019; 29(9): 4889. CrossRef - Ultrasound‐guided needle biopsy of large thyroid nodules: Core needle biopsy yields more reliable results than fine needle aspiration
Hyeon Jin Lee, Young Joong Kim, Hye Yeon Han, Jae Young Seo, Cheol Mog Hwang, KeumWon Kim
Journal of Clinical Ultrasound.2019; 47(5): 255. CrossRef - Tumor Volume Doubling Time in Active Surveillance of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ki-Wook Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2019; 29(5): 642. CrossRef - Role of Immunohistochemistry in Fine Needle Aspiration and Core Needle Biopsy of Thyroid Nodules
Seulki Song, Hyojin Kim, Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2019; 12(2): 224. CrossRef - Echogenic foci in thyroid nodules: diagnostic performance with combination of TIRADS and echogenic foci
Su Min Ha, Yun Jae Chung, Hye Shin Ahn, Jung Hwan Baek, Sung Bin Park
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Malignancy According to the Sub-classification of Atypia of Undetermined Significance and Suspicious Follicular Neoplasm Categories in Thyroid Core Needle Biopsies
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(2): 146. CrossRef - Thyroid core needle biopsy: patients’ pain and satisfaction compared to fine needle aspiration
Hyo Jin Kim, Yeo Koon Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Sang Il Choi
Endocrine.2019; 65(2): 365. CrossRef - Does Radiofrequency Ablation Induce Neoplastic Changes in Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Preliminary Study
Su Min Ha, Jun Young Shin, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Eun Song, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(2): 169. CrossRef - Differential Diagnosis of Thyroid Follicular Neoplasm from Nodular Hyperplasia by Shear Wave Elastography
Myung Hi Yoo, Hye Jeong Kim, In Ho Choi, Ji-Oh Mok, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh
Soonchunhyang Medical Science.2019; 25(1): 10. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy Techniques for Intermediate or Low Suspicion Thyroid Nodules: Which Method is Effective for Diagnosis?
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Ko Woon Park
Korean Journal of Radiology.2019; 20(10): 1454. CrossRef - Preoperative Diagnostic Categories of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features in Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy and Its Impact on Risk of Malignancy
Hee Young Na, Ji Won Woo, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(4): 329. CrossRef - Utility of a formatted pathologic reporting system in thyroid core needle biopsy: A validation study of 1998 consecutive cases
Ji‐Young Choe, Yoonjin Kwak, Mimi Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Hyun Jeong Kim, Yeo Koon Kim, So Yeon Park
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 88(1): 96. CrossRef - Nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Comparison of Core needle biopsy and thyroidectomy specimens
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Younghye Kim, Seung Yeon Ha
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2018; 32: 35. CrossRef - Prevention of total thyroidectomy in noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features (NIFTP) based on combined interpretation of ultrasonographic and cytopathologic results
Sung‐Hye You, Kyu Eun Lee, Roh‐Eul Yoo, Hye Jeong Choi, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jae‐Kyung Won, Koung Mi Kang, Tae Jin Yoon, Seung Hong Choi, Chul‐Ho Sohn, Ji‐hoon Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 88(1): 114. CrossRef - Statement and Recommendations on Interventional Ultrasound as a Thyroid Diagnostic and Treatment Procedure
Christoph F. Dietrich, Thomas Müller, Jörg Bojunga, Yi Dong, Giovanni Mauri, Maija Radzina, Manjiri Dighe, Xin-Wu Cui, Frank Grünwald, Andreas Schuler, Andre Ignee, Huedayi Korkusuz
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2018; 44(1): 14. CrossRef - Core needle biopsy of thyroid nodules: outcomes and safety from a large single-center single-operator study
Jooae Choe, Jung Hwan Baek, Hye Sun Park, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Acta Radiologica.2018; 59(8): 924. CrossRef - Improvement of diagnostic performance of pathologists by reducing the number of pathologists responsible for thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology: An institutional experience
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(7): 561. CrossRef - Comparison of Immunohistochemistry and Direct Sanger Sequencing for Detection of theBRAFV600EMutation in Thyroid Neoplasm
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Jene Choi, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparison of the Diagnostic Efficacy of Ultrasound‐Guided Core Needle Biopsy With 18‐ Versus 20‐Gauge Needles for Thyroid Nodules
Hye Shin Ahn, Mirinae Seo, Su Min Ha, Hee Sung Kim
Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2018; 37(11): 2565. CrossRef - Impact of Nodule Size on Malignancy Risk Differs according to the Ultrasonography Pattern of Thyroid Nodules
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji-Hoon Kim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2018; 19(3): 534. CrossRef - Web‐based thyroid imaging reporting and data system: Malignancy risk of atypia of undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance thyroid nodules calculated by a combination of ultrasonography features and biopsy results
Young Jun Choi, Jung Hwan Baek, Jung Hee Shin, Woo Hyun Shim, Seon‐Ok Kim, Won‐Hong Lee, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Ki‐Wook Chung, Jeong Hyun Lee
Head & Neck.2018; 40(9): 1917. CrossRef - Thyroid Incidentalomas Detected on18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography: Malignant Risk Stratification and Management Plan
Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Chong Hyun Suh, Hwa Jung Kim, Jong Jin Lee, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yon Sung, Yu-mi Lee, Dong Eun Song, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hwan Baek
Thyroid.2018; 28(6): 762. CrossRef - The role of core needle biopsy in the diagnosis of initially detected thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sae Rom Chung, Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
European Radiology.2018; 28(11): 4909. CrossRef - The History of Korean Thyroid Pathology
Soon Won Hong, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 15. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic Echogenicity and Histopathologic Correlation of Thyroid Nodules in Core Needle Biopsy Specimens
Ji-hoon Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Hunkyung Lee
Korean Journal of Radiology.2018; 19(4): 673. CrossRef - Evaluation of Modified Core-Needle Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
Soomin Ahn, Sejin Jung, Ji-Ye Kim, Jung Hee Shin, Soo Yeon Hahn, Young Lyun Oh
Korean Journal of Radiology.2018; 19(4): 656. CrossRef - Role of core needle biopsy as a first-line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules: a retrospective cohort study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Soo Jin Kim, Dae Sik Kim
Ultrasonography.2018; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Active Surveillance of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
Hye-Seon Oh, Jeonghoon Ha, Hye In Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jae Hoon Chung, Jung Hwan Baek
Thyroid.2018; 28(12): 1587. CrossRef - Risk of malignancy according to sub‐classification of the atypia of undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance (AUS/FLUS) category in the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology
S. J. Kim, J. Roh, J. H. Baek, S. J. Hong, Y. K. Shong, W. B. Kim, D. E. Song
Cytopathology.2017; 28(1): 65. CrossRef - Fine-needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy for diagnosis of thyroid malignancy and neoplasm: a matched cohort study
Soo-Yeon Kim, Hye Sun Lee, Jieun Moon, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Jin Young Kwak
European Radiology.2017; 27(2): 801. CrossRef - Follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: comparison of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy and ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in a multicentre study
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Hyun Kyung Lim, So Lyung Jung
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(1): 113. CrossRef - Core‐needle biopsy versus repeat fine‐needle aspiration for thyroid nodules initially read as atypia/follicular lesion of undetermined significance
Young Jun Choi, Jung Hwan Baek, Chong Hyun Suh, Woo Hyun Shim, Boseul Jeong, Jae Kyun Kim, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Ki‐Wook Chung, Jeong Hyun Lee
Head & Neck.2017; 39(2): 361. CrossRef - Preoperative differentiation between noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) and non-NIFTP
Soo Yeon Hahn, Jung Hee Shin, Hyun Kyung Lim, So Lyung Jung, Young Lyun Oh, In Ho Choi, Chan Kwon Jung
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 86(3): 444. CrossRef - Core Needle Biopsy of the Thyroid: 2016 Consensus Statement and Recommendations from Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology
Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, So Lyung Jung, Ji-hoon Kim, Jin Yong Sung, Kyu Sun Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hee Shin, Yoon Jung Choi, Eun Ju Ha, Hyun Kyung Lim, Soo Jin Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Kwang Hwi Lee, Young Jun Choi, Inyoung Youn, Young Joong Kim, Hye Sh
Korean Journal of Radiology.2017; 18(1): 217. CrossRef - First-Line Use of Core Needle Biopsy for High-Yield Preliminary Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
H.C. Kim, Y.J. Kim, H.Y. Han, J.M. Yi, J.H. Baek, S.Y. Park, J.Y. Seo, K.W. Kim
American Journal of Neuroradiology.2017; 38(2): 357. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Pathology Discordant Nodules on Core-Needle Biopsy: Malignancy Risk and Management Strategy
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Hye Sun Park, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Thyroid.2017; 27(5): 707. CrossRef - Current status of core needle biopsy of the thyroid
Jung Hwan Baek
Ultrasonography.2017; 36(2): 83. CrossRef - Cytology-Ultrasonography Risk-Stratification Scoring System Based on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and the Korean-Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji-Hoon Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 953. CrossRef - Preoperative clinicopathological characteristics of patients with solitary encapsulated follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinomas
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim, Dong Eun Song
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2017; 116(6): 746. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Patients With Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Single Center’s Experience in Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Jung Hwan Baek, Ki-Wook Chung, Tae Yong Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(6): 1917. CrossRef - Comparison of Consecutive Results from Fine Needle Aspiration and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules
Soon-Hyun Ahn, So-Yeon Park, Sang Il Choi
Endocrine Pathology.2017; 28(4): 332. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of core-needle biopsy in initially detected thyroid nodules via propensity score analysis
Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Tae Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Jeong Hyun Lee
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Core-Needle Biopsy and Fine-Needle Aspiration for Evaluating Thyroid Incidentalomas Detected by 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography: A Propensity Score Analysis
Chong Hyun Suh, Young Jun Choi, Jong Jin Lee, Woo Hyun Shim, Jung Hwan Baek, Han Cheol Chung, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yon Sung, Jeong Hyun Lee
Thyroid.2017; 27(10): 1258. CrossRef - Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology Practice in Korea
Yoon Jin Cha, Ju Yeon Pyo, SoonWon Hong, Jae Yeon Seok, Kyung-Ju Kim, Jee-Young Han, Jeong Mo Bae, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Yeejeong Kim, Kyueng-Whan Min, Soonae Oak, Sunhee Chang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 521. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules
Chan Kwon Jung, Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(4): 407. CrossRef - Core-needle biopsy for the preoperative diagnosis of follicular neoplasm in thyroid nodule screening: A validation study
Sung Hak Lee, Gyeong Sin Park, So Lyung Jung, Min-Hee Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Dong Jun Lim, Chan Kwon Jung
Pathology - Research and Practice.2016; 212(1): 44. CrossRef - The Role of Core-Needle Biopsy as a First-Line Diagnostic Tool for Initially Detected Thyroid Nodules
Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Young Jun Choi, Jae Kyun Kim, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Young Kee Shong
Thyroid.2016; 26(3): 395. CrossRef - Thyroid nodules with minimal cystic changes have a low risk of malignancy
Dong Gyu Na, Ji-hoon Kim, Dea Sik Kim, Soo Jin Kim
Ultrasonography.2016; 35(2): 153. CrossRef - Thyroid nodules with isolated macrocalcification: malignancy risk and diagnostic efficacy of fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy
Dong Gyu Na, Dae Sik Kim, Soo Jin Kim, Jae Wook Ryoo, So Lyung Jung
Ultrasonography.2016; 35(3): 212. CrossRef - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules: Categorization Based on Solidity and Echogenicity
Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji-Hoon Kim, Jae Kyun Kim, Young Jun Choi, Hyobin Seo
Thyroid.2016; 26(4): 562. CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration and core needle biopsy: An update on 2 common minimally invasive tissue sampling modalities
Paul A. VanderLaan
Cancer Cytopathology.2016; 124(12): 862. CrossRef - The role of core-needle biopsy in the diagnosis of thyroid malignancy in 4580 patients with 4746 thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Young Jun Choi, Kyung Won Kim, Jayoun Lee, Ki-Wook Chung, Young Kee Shong
Endocrine.2016; 54(2): 315. CrossRef - The Role of Core-Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Nondiagnostic Fine-Needle Aspiration Results: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chong Hyun Suh, Jung Hwan Baek, Kyung Won Kim, Tae Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Dong Eun Song, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrine Practice.2016; 22(6): 679. CrossRef - Should Core Needle Biopsy be Used in the Evaluation of Thyroid Nodules?
Beril Guler, Tugce Kiran, Dilek Sema Arici, Erhan Aysan, Fatma Cavide Sonmez
Endocrine Pathology.2016; 27(4): 352. CrossRef - A Multicenter Prospective Validation Study for the Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System in Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Eun Ju Ha, Won-Jin Moon, Dong Gyu Na, Young Hen Lee, Nami Choi, Soo Jin Kim, Jae Kyun Kim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2016; 17(5): 811. CrossRef - Impact of Reclassification on Thyroid Nodules with Architectural Atypia: From Non-Invasive Encapsulated Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas to Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features
Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Chan Kwon Jung, Won Gu Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki-Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim, Rafael Rosell
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0167756. CrossRef
- Predictive US findings for differentiating between malignant and benign thyroid nodules: Doppler and microvascular imaging according to the TI-RADS and pathologic subtypes of malignancy
- Cancers with Higher Density of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Were Associated with Poor Survival Rates
- Kyong Yeun Jung, Sun Wook Cho, Young A Kim, Daein Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(4):318-324. Published online June 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.06.01
- 17,113 View
- 252 Download
- 157 Web of Science
- 148 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Macrophages are a component of a tumor’s microenvironment and have various roles in tumor progression and metastasis. This study evaluated the relationships between tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) density and clinical outcomes in 14 different types of human cancers. Methods: We investigated TAM density in human tissue microarray sections from 14 different types of human cancers (n = 266) and normal thyroid, lung, and breast tissues (n = 22). The five-year survival rates of each cancer were obtained from the 2011 Korea Central Cancer Registry. Results: Among 13 human cancers, excluding thyroid cancer, pancreas, lung, and gallbladder cancers had the highest density of CD163-positive macrophages (7.0±3.5%, 6.9±7.4%, and 6.9 ± 5.5%, respectively). The five-year relative survival rates of these cancers (pancreas, 8.7%; lung, 20.7%; gallbladder, 27.5%) were lower than those of other cancers. The histological subtypes in thyroid cancer exhibited significantly different CD163-positive macrophages densities (papillary, 1.8 ± 1.6% vs anaplastic, 22.9 ± 17.1%; p < .001), but no significant difference between histological subtypes was detected in lung and breast cancers. Moreover, there was no significant difference in CD163-positive macrophages densities among the TNM stages in lung, breast, and thyroid cancers. Conclusions: Cancers with higher TAM densities (pancreas, lung, anaplastic thyroid, and gallbladder) were associated with poor survival rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immune cells in thyroid adenoma and carcinoma: uncovering a hidden value of assessing tumor-host interplay and its potential application in thyroid cytopathology
Iryna Omelianenko, Nazarii Kobyliak, Tetyana Falalyeyeva, Oleksii Seleznov, Pavlina Botsun, Lyudmila Ostapchenko, Oleksandr Korotkyi, Liudmyla Domylivska, Olena Tsyryuk, Galyna Mykhalchyshyn, Tetiana Shapochka, Oksana Sulaieva
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on the Immunological Correlation Between Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Digui Fang, Limei Zhou, Biao Zheng, Ran Wang
Journal of Immunology Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumour-associated macrophages in human meningiomas
Rahmina Meta, Henrik Sahlin Pettersen, Sofie Eline Tollefsen, Borgny Ytterhus, Øyvind Olav Salvesen, Wenche Sjursen, Sverre Helge Torp, Jianhong Zhou
PLOS One.2025; 20(5): e0319960. CrossRef - Turning tumor microenvironmental foes to friends: A new opportunity for thyroid cancer therapy and redifferentiation
Liya Zhu, Xiuli Jing, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
Oral Oncology.2025; 168: 107513. CrossRef - Unveiling Macrophage Content as a Predictive Biomarker for Intraoperative ICG Imaging Efficacy in Lung Cancer
Yue Yan, Jiahui Mi, Yun Li, Guanchao Jiang, Yimeng Zhang, Yanguo Liu, Hui Zhao, Jianfeng Li, Xing Yang, Jun Wang, Fan Yang, Kezhong Chen, Yiguang Wang, Jian Zhou
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique
Nisan Atiya, Amir Shemer, Ariel Schwarz, Yevgeny Beiderman, Yossef Danan
Sensors.2025; 25(16): 4977. CrossRef - Molecular landscape of colorectal cancer liver metastasis: Tumor microenvironment heterogeneity and driver inference
Ailing Zhang, Yi Zhang, Jiayue Xu, Rui Zhu, Tingming Liang, Li Guo
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2025; 216: 104946. CrossRef - Precision engineering of macrophage reprogramming with RNA interference-loaded lipid nanoparticles: a game-changer in cancer immunotherapy
Sezen Gül, Juliette Vergnaud, François Fay, Elias Fattal
Drug Delivery and Translational Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncogenic mutation-driven metabolism-immunity regulatory axis: Potential prospects for thyroid cancer precision therapy
Tingting Zhang, Hengtong Han, Tianying Zhang, Yating Zhang, Libin Ma, Ze Yang, Yong-xun Zhao
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2025; 1880(6): 189459. CrossRef - Impact of the tumor microenvironment on survival in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
Chanchal Rana, Prabhakar Mishra, Kulranjan Singh, Pooja Ramakant, Anand Mishra, Sumaira Qayoom, Gulshan Kumar, Jyoti Mishra, Komal Verma
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chimeric antigen receptor cells as a tool for localized delivery of TNFα in solid cancer treatment
Zhenqiang Yao, Chutamath Sittplangkoon
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Defining Gene Signature of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma as Target for Immunotherapy Using Single Cell and Bulk RNA Sequencing
Joshua S. Badshah, Ryan M. Lee, Andrea Reitsma, Marc L. Melcher, Olivia M. Martinez, Sheri M. Krams, Daniel J. Delitto, Varvara A. Kirchner
Livers.2025; 5(4): 53. CrossRef - Therapeutic Strategies Targeting CD163 and CD169 in Macrophages for Cancer
Yukio Fujiwara, Yoshihiro Komohara
Pathology International.2025; 75(11): 551. CrossRef - Circulating immunophenotypes are potentially prognostic in follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer
Anupam Kotwal, Michael P. Gustafson, Svetlana Bornschlegl, Allan B. Dietz, Danae Delivanis, Mabel Ryder
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano-enhanced immunotherapy: Targeting the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment
Yuzhi Jin, Yangyue Huang, Hui Ren, Huanhuan Huang, Chunyu Lai, Wenjun Wang, Zhou Tong, Hangyu Zhang, Wei Wu, Chuan Liu, Xuanwen Bao, Weijia Fang, Hongjun Li, Peng Zhao, Xiaomeng Dai
Biomaterials.2024; 305: 122463. CrossRef - Tumor microenvironment in thyroid cancer: Immune cells, patterns, and novel treatments
Beatriz Febrero, Juan José Ruiz‐Manzanera, Inmaculada Ros‐Madrid, Antonio Miguel Hernández, Esteban Orenes‐Piñero, José Manuel Rodríguez
Head & Neck.2024; 46(6): 1486. CrossRef - Research progress of immunotherapy against anaplastic thyroid cancer
Jiaqian Chen, Zuixuan Xiao, Hongyan Wu
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor‐associated macrophages impair NK cell IFN‐γ production and contribute to tumor progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Sol Yanel Núñez, Aldana Trotta, María Victoria Regge, María Sofía Amarilla, Florencia Secchiari, Jessica Mariel Sierra, María Cecilia Santilli, Mariana Gantov, Agustín Rovegno, Nicolás Richards, Carlos Ameri, Hernando Ríos Pita, Luis Rico, Mauro Mieggi, G
European Journal of Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Monocytes in leukapheresis products affect the outcome of CD19–targeted CAR T-cell therapy in patients with lymphoma
Cristiana Carniti, Nicole M. Caldarelli, Luca Agnelli, Tommaso Torelli, Silva Ljevar, Sadhana Jonnalagadda, Giada Zanirato, Eugenio Fardella, Federico Stella, Daniele Lorenzini, Silvia Brich, Flavio Arienti, Anna Dodero, Annalisa Chiappella, Martina Magni
Blood Advances.2024; 8(8): 1968. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Features and Molecular Signatures of Lateral Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Jinsun Lim, Han Sai Lee, Jin-Hyung Heo, Young Shin Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(2): 324. CrossRef - Relaxin-2 is a novel biomarker for differentiated thyroid carcinoma in humans
Anupam Kotwal, Ronda Simpson, Nicholas Whiteman, Benjamin Swanson, Ana Yuil-Valdes, Madelyn Fitch, Joshua Nguyen, Salma Elhag, Oleg Shats, Whitney Goldner, Robert Bennett
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 225: 116323. CrossRef - Emerging therapeutic options for follicular-derived thyroid cancer in the era of immunotherapy
Naimah Turner, Sarah Hamidi, Rim Ouni, Rene Rico, Ying C. Henderson, Maria Puche, Sayan Alekseev, Jocelynn G. Colunga-Minutti, Mark E. Zafereo, Stephen Y. Lai, Sang T. Kim, Maria E. Cabanillas, Roza Nurieva
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering the performance of macrophages in tumour microenvironment: a call for precision immunotherapy
Belén Toledo, Linrui Zhu Chen, María Paniagua-Sancho, Juan Antonio Marchal, Macarena Perán, Elisa Giovannetti
Journal of Hematology & Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization of Immune Infiltrate Along the Leading Edge of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Anupam Kotwal, Krysten Vance, Kemal Hajric, Ana Yuil-Valdes, Benjamin Swanson, Ernesto Martinez Duarte, Oleg Shats, Michael Hollingsworth, Hamid Band, Whitney Goldner
Thyroid®.2024; 34(8): 999. CrossRef - Leveraging molecular targeted drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors treat advanced thyroid carcinoma to achieve thyroid carcinoma redifferentiation
Jing-Yang Su
American Journal of Cancer Research.2024; 14(2): 407. CrossRef - Harnessing the tumor microenvironment to boost adoptive T cell therapy with engineered lymphocytes for solid tumors
Martina Spiga, Elisa Martini, Maria Chiara Maffia, Fabio Ciceri, Eliana Ruggiero, Alessia Potenza, Chiara Bonini
Seminars in Immunopathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anaplastic thyroid cancer cell-secreted TGFβ1 plays a key role in inducing macrophage polarization of human monocytes
Agustina Jaroszewski
American Journal of Cancer Research.2024; 14(7): 3626. CrossRef - Therapeutic treatments targeting communication between angiogenic and immune microenvironments in thyroid cancers
Alessandro Prete, Carmelo Nucera
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research.2024; 37: 100544. CrossRef - Immune microenvironment in papillary thyroid carcinoma: roles of immune cells and checkpoints in disease progression and therapeutic implications
Xun Zheng, Ruonan Sun, Tao Wei
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis on the tumor microenvironment in papillary thyroid cancer: insights from single-cell analysis
Hongzhe Ma, Guoqi Li, Diwei Huo, Yangguang Su, Qing Jin, Yangxu Lu, Yanyan Sun, Denan Zhang, Xiujie Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Unconventional p65/p52 NF-κB module regulates key tumor microenvironment-related genes in breast tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)
Veronica De Paolis, Virginia Troisi, Antonella Bordin, Francesca Pagano, Viviana Caputo, Chiara Parisi
Life Sciences.2024; 357: 123059. CrossRef - Revolutionizing prognostic predictions in colorectal cancer: Macrophage‑driven transcriptional insights from single‑cell RNA sequencing and gene co‑expression network analysis
Yang Feng, Zhuo Cheng, Jingyuan Gao, Tao Huang, Jun Wang, Qian Tang, Ke Pu, Chang Liu
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Aggressive Types of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms
Maria Boudina, Eleana Zisimopoulou, Persefoni Xirou, Alexandra Chrisoulidou
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(20): 6119. CrossRef - Unravelling the Reasons Behind Limited Response to Anti-PD Therapy in ATC: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Checkpoints
Monikongkona Boruah, Shipra Agarwal, Riyaz Ahmad Mir, Saumitra Dey Choudhury, Kapil Sikka, Sameer Rastogi, Nishikant Damle, Mehar C. Sharma
Endocrine Pathology.2024; 35(4): 419. CrossRef - Imaging tumor and ascites-associated macrophages in a mouse model of metastatic ovarian cancer
Catherine A. Foss, Flonné Wildes, Delia Mezzanzanica, Franca Podo, Chien-Fu Hung, Santosh Yadav, Marie-France Penet Vidaver
EJNMMI Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - From ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer: the prognostic value of the extracellular microenvironment
Taylor S. Hulahan, Peggi M. Angel
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Combinatory actions of cytokines induce M2-like macrophages in anaplastic thyroid cancer
Takahito Kimura
American Journal of Cancer Research.2024; 14(12): 5812. CrossRef - The ratio of adaptive to innate immune cells differs between genders and associates with improved prognosis and response to immunotherapy
Johanne Ahrenfeldt, Ditte S. Christensen, Andreas B. Østergaard, Judit Kisistók, Mateo Sokač, Nicolai J. Birkbak, Albert Rübben
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(2): e0281375. CrossRef - Current Landscape of Immunotherapy for Advanced Sarcoma
Víctor Albarrán, María Luisa Villamayor, Javier Pozas, Jesús Chamorro, Diana Isabel Rosero, María San Román, Patricia Guerrero, Patricia Pérez de Aguado, Juan Carlos Calvo, Coral García de Quevedo, Carlos González, María Ángeles Vaz
Cancers.2023; 15(8): 2287. CrossRef - Iron-mediated oxidative stress induces PD-L1 expression via activation of c-Myc in lung adenocarcinoma
Anna Martina Battaglia, Alessandro Sacco, Ilenia Aversa, Gianluca Santamaria, Camillo Palmieri, Cirino Botta, Roberto De Stefano, Maurizio Bitetto, Lavinia Petriaggi, Emanuele Giorgio, Concetta Maria Faniello, Francesco Costanzo, Flavia Biamonte
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of immunotherapy resistance in triple-negative breast cancer
Yiwen Zheng, Shujin Li, Hongchao Tang, Xuli Meng, Qinghui Zheng
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Modeling the tumor microenvironment of anaplastic thyroid cancer: an orthotopic tumor model in C57BL/6 mice
Zhen Xu, Hyo Shik Shin, Yoo Hyung Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Jae-Kyung Won, Su-jin Kim, Young Joo Park, Sareh Parangi, Sun Wook Cho, Kyu Eun Lee
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A new approach to overcoming resistance to immunotherapy: nanotechnology
Jiangbo Shao, Ying Jin, Chunxiang Jin
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals immune suppressive landscape in the anaplastic thyroid cancer
Chao Feng, Yujia Tao, Chao Yu, Lirui Wang, Xiao Liu, Yuan Cao
Cancer Gene Therapy.2023; 30(12): 1598. CrossRef - Tumor-associated macrophages as a potential therapeutic target in thyroid cancers
Liya Zhu, Xiu Juan Li, Prakash Gangadaran, Xiuli Jing, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2023; 72(12): 3895. CrossRef - Influence of Macrophages on Vascular Invasion of Inflammatory Breast Cancer Emboli Measured Using an In Vitro Microfluidic Multi-Cellular Platform
Manasa Gadde, Melika Mehrabi-Dehdezi, Bisrat G. Debeb, Wendy A. Woodward, Marissa Nichole Rylander
Cancers.2023; 15(19): 4883. CrossRef - The Prognosis of Cancer Depends on the Interplay of Autophagy, Apoptosis, and Anoikis within the Tumor Microenvironment
Shweta Gulia, Prakash Chandra, Asmita Das
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2023; 81(4): 621. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of BTNL9 as a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltrations in thyroid cancer
Luyao Zhang, Shuang Yu, Shubin Hong, Xi Xiao, Zhihong Liao, Yanbing Li, Haipeng Xiao
BMC Medical Genomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - FF-10850, a Novel Liposomal Topotecan Achieves Superior Antitumor Activity via Macrophage- and Ammonia-Mediated Payload Release in the Tumor Microenvironment
Susumu Shimoyama, Ken Okada, Toshifumi Kimura, Yasushi Morohashi, Shinji Nakayama, Sayaka Kemmochi, Keiko Makita-Suzuki, Ursula A. Matulonis, Mikinaga Mori
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2023; 22(12): 1454. CrossRef - Estrogen-related genes for thyroid cancer prognosis, immune infiltration, staging, and drug sensitivity
Leiying Zhang, Man Zhou, Xiaoni Gao, Yang Xie, Junqi Xiao, Tao Liu, Xiangtai Zeng
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Harnessing Immunity to Treat Advanced Thyroid Cancer
Hiroki Komatsuda, Michihisa Kono, Risa Wakisaka, Ryosuke Sato, Takahiro Inoue, Takumi Kumai, Miki Takahara
Vaccines.2023; 12(1): 45. CrossRef - Are third-generation active-targeting nanoformulations definitely the best? In vitro and in vivo comparisons of pixantrone-loaded liposomes modified with different sialic acid derivatives
Yanzhi Song, Zhennan She, Zhenjun Huang, Shuo Wang, Xinrong Liu, Qi Zhang, Jing Sun, Donghua Di, Yihui Deng
Drug Delivery and Translational Research.2022; 12(3): 647. CrossRef - Synergistic nanoassemblies constructed from a STAT3 inhibitor and a cabazitaxel prodrug with enhanced cancer chemo-immunotherapy
X. Shi, L. Shu, Y. Qiao, J. Yao, H. Xie, L. Zhou, H. Wang, S. Zheng
Materials Today Nano.2022; 17: 100155. CrossRef - Polypharmacologic Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages toward an Inflammatory Phenotype
Nao Nishida-Aoki, Taranjit S. Gujral
Cancer Research.2022; 82(3): 433. CrossRef - Role of Suprabasin in the Dedifferentiation of Follicular Epithelial Cell-Derived Thyroid Cancer and Identification of Related Immune Markers
Hao Tan, Lidong Wang, Zhen Liu
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Macrophage C/EBPδ Drives Gemcitabine, but Not 5-FU or Paclitaxel, Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cells in a Deoxycytidine-Dependent Manner
C. Arnold Spek, Hella L. Aberson, JanWillem Duitman
Biomedicines.2022; 10(2): 219. CrossRef - Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: An Update
Arnaud Jannin, Alexandre Escande, Abir Al Ghuzlan, Pierre Blanchard, Dana Hartl, Benjamin Chevalier, Frédéric Deschamps, Livia Lamartina, Ludovic Lacroix, Corinne Dupuy, Eric Baudin, Christine Do Cao, Julien Hadoux
Cancers.2022; 14(4): 1061. CrossRef - LC3-associated phagocytosis in bone marrow macrophages suppresses acute myeloid leukemia progression through STING activation
Jamie A. Moore, Jayna J. Mistry, Charlotte Hellmich, Rebecca H. Horton, Edyta E. Wojtowicz, Aisha Jibril, Matthew Jefferson, Thomas Wileman, Naiara Beraza, Kristian M. Bowles, Stuart A. Rushworth
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of chemokine signaling with non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment and heterogeneity in different cancers
Shweta Arora, Salman Khan, Almaz Zaki, Gulnaz Tabassum, Mohd Mohsin, Humaira Naaz Bhutto, Tanveer Ahmad, Tasneem Fatma, Mansoor Ali Syed
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 86: 720. CrossRef - BRAFV600E Induction in Thyrocytes Triggers Important Changes in the miRNAs Content and the Populations of Extracellular Vesicles Released in Thyroid Tumor Microenvironment
Ophélie Delcorte, Catherine Spourquet, Pascale Lemoine, Jonathan Degosserie, Patrick Van Der Smissen, Nicolas Dauguet, Axelle Loriot, Jeffrey A. Knauf, Laurent Gatto, Etienne Marbaix, James A. Fagin, Christophe E. Pierreux
Biomedicines.2022; 10(4): 755. CrossRef - Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment in Cranial Meningiomas: Clinical Implications and Intraindividual Reproducibility
Johannes Wach, Tim Lampmann, Ági Güresir, Hartmut Vatter, Ulrich Herrlinger, Albert Becker, Marieta Toma, Michael Hölzel, Erdem Güresir
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 853. CrossRef - Roles and new Insights of Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment of Thyroid Cancer
Qi Liu, Wei Sun, Hao Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fucoxanthin Is a Potential Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
Tsz-Ying Lau, Hiu-Yee Kwan
Marine Drugs.2022; 20(6): 370. CrossRef - Dissecting Immunosuppressive Cell Communication Patterns Reveals JunB Proto-Oncogene (JUNB) Shaping a Non-Inflamed Tumor Microenvironment
Hualin Chen, Gang Chen
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - LIMK1: A promising prognostic and immune infiltration indicator in colorectal cancer
Xin Liu, Qiang Song, Daohan Wang, Yubiao Liu, Zhixiang Zhang, Weihua Fu
Oncology Letters.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unusual Association of NF-κB Components in Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) Promotes HSPG2-Mediated Immune-Escaping Mechanism in Breast Cancer
Veronica De Paolis, Fabio Maiullari, Maila Chirivì, Marika Milan, Chiara Cordiglieri, Francesca Pagano, Alessandra Rita La Manna, Elena De Falco, Claudia Bearzi, Roberto Rizzi, Chiara Parisi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7902. CrossRef - Crosstalk between angiogenesis and immune regulation in the tumor microenvironment
Hei Jung Kim, Young Rae Ji, You Mie Lee
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(6): 401. CrossRef - Cancer Resistance to Immunotherapy: Molecular Mechanisms and Tackling Strategies
Son Hai Vu, Preethi Vetrivel, Jongmin Kim, Myeong-Sok Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10906. CrossRef - Transcription Factor MAFB as a Prognostic Biomarker for the Lung Adenocarcinoma
Omar Samir, Naohiro Kobayashi, Teppei Nishino, Mennatullah Siyam, Manoj Kumar Yadav, Yuri Inoue, Satoru Takahashi, Michito Hamada
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9945. CrossRef - Construction and Validation of a CNV-Driven Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma
Yanqing Wang, Yi Zhao, Yong Li, Zemin Luo, Hongzhu Chen, Yuan Li
Journal of Sensors.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - CXCL12 derived from CD248-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates M2-polarized macrophages to promote nonsmall cell lung cancer progression
Jieheng Wu, Xinlei Liu, Jiangwei Wu, Chunju Lou, Qiaoling Zhang, Huiping Chen, Zeyang Yang, Shiqi Long, Yun Wang, Zhenling Shang, Zuquan Hu, Rui Zhang, Jian Zhang, Zhu Zeng
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2022; 1868(11): 166521. CrossRef - Cell Component and Function of Tumor Microenvironment in Thyroid Cancer
Eunah Shin, Ja Seung Koo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(20): 12578. CrossRef - TIM3 Expression in Anaplastic-Thyroid-Cancer-Infiltrating Macrophages: An Emerging Immunotherapeutic Target
Luz Maria Palacios, Victoria Peyret, María Estefania Viano, Romina Celeste Geysels, Yair Aron Chocobar, Ximena Volpini, Claudia Gabriela Pellizas, Juan Pablo Nicola, Claudia Cristina Motran, María Cecilia Rodriguez-Galan, Laura Fozzatti
Biology.2022; 11(11): 1609. CrossRef - Potential diagnostic of lymph node metastasis and prognostic values of TM4SFs in papillary thyroid carcinoma patients
Kun Wang, Haomin Li, Junyu Zhao, Jinming Yao, Yiran Lu, Jianjun Dong, Jie Bai, Lin Liao
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A distinct M2 macrophage infiltrate and transcriptomic profile decisively influence adipocyte differentiation in lipedema
Stefan Wolf, Jenna H. Rannikko, Reetta Virtakoivu, Paolo Cinelli, Gunther Felmerer, Anna Burger, Pietro Giovanoli, Michael Detmar, Nicole Lindenblatt, Maija Hollmén, Epameinondas Gousopoulos
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Macrophage targeting in cancer
Martha Lopez‐Yrigoyen, Luca Cassetta, Jeffrey W. Pollard
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2021; 1499(1): 18. CrossRef - Immune Landscape of Thyroid Cancers: New Insights
Elisa Menicali, Martina Guzzetti, Silvia Morelli, Sonia Moretti, Efisio Puxeddu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting tumor-associated macrophages to synergize tumor immunotherapy
Xiaonan Xiang, Jianguo Wang, Di Lu, Xiao Xu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - FOXE1-Dependent Regulation of Macrophage Chemotaxis by Thyroid Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
Sara Credendino, Marta De Menna, Irene Cantone, Carmen Moccia, Matteo Esposito, Luigi Di Guida, Mario De Felice, Gabriella De Vita
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(14): 7666. CrossRef - Hidden Treasures: Macrophage Long Non-Coding RNAs in Lung Cancer Progression
Annika Karger, Rajender Nandigama, Albrecht Stenzinger, Friedrich Grimminger, Soni Savai Pullamsetti, Werner Seeger, Rajkumar Savai
Cancers.2021; 13(16): 4127. CrossRef - A Prognostic Role for Circulating microRNAs Involved in Macrophage Polarization in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Alexia Monastirioti, Chara Papadaki, Konstantinos Rounis, Despoina Kalapanida, Dimitrios Mavroudis, Sofia Agelaki
Cells.2021; 10(8): 1988. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia-Induced miR-467 Drives Tumor Inflammation and Growth in Breast Cancer
Jasmine Gajeton, Irene Krukovets, Santoshi Muppala, Dmitriy Verbovetskiy, Jessica Zhang, Olga Stenina-Adognravi
Cancers.2021; 13(6): 1346. CrossRef - Targeting MARCO and IL37R on Immunosuppressive Macrophages in Lung Cancer Blocks Regulatory T Cells and Supports Cytotoxic Lymphocyte Function
Linnéa La Fleur, Johan Botling, Fei He, Catarina Pelicano, Chikai Zhou, Chenfei He, Giorgia Palano, Artur Mezheyeuski, Patrick Micke, Jeffrey V. Ravetch, Mikael C. I. Karlsson, Dhifaf Sarhan
Cancer Research.2021; 81(4): 956. CrossRef - Absent in melanoma 2-mediating M1 macrophages facilitate tumor rejection in renal carcinoma
Dafei Chai, Zichun Zhang, Shang yuchen Shi, Dong Qiu, Chen Zhang, Gang Wang, Lin Fang, Huizhong Li, Hui Tian, Hailong Li, Junnian Zheng
Translational Oncology.2021; 14(4): 101018. CrossRef - Hampering Stromal Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment as a Therapeutic Strategy to Destem Cancer Stem Cells
Katherine Po Sin Chung, Rainbow Wing Hei Leung, Terence Kin Wah Lee
Cancers.2021; 13(13): 3191. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Stem-Like Cells: From Microenvironmental Niches to Therapeutic Strategies
Elisa Stellaria Grassi, Viola Ghiandai, Luca Persani
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(7): 1455. CrossRef - Enhanced Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors via Drug-Loaded Nanocarriers: An Image-Based Computational Framework
Farshad Moradi Kashkooli, M. Soltani, Mohammad Masoud Momeni, Arman Rahmim
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and the emerging role of gut microbiome
R. Zou, Y. Wang, F. Ye, X. Zhang, M. Wang, S. Cui
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2021; 23(11): 2237. CrossRef - Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Sarcomas
Tomohiro Fujiwara, John Healey, Koichi Ogura, Aki Yoshida, Hiroya Kondo, Toshiaki Hata, Miho Kure, Hiroshi Tazawa, Eiji Nakata, Toshiyuki Kunisada, Toshiyoshi Fujiwara, Toshifumi Ozaki
Cancers.2021; 13(5): 1086. CrossRef - Secreted Factors by Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells Induce Tumor-Promoting M2-like Macrophage Polarization through a TIM3-Dependent Mechanism
Cinthia Carolina Stempin, Romina Celeste Geysels, Sunmi Park, Luz Maria Palacios, Ximena Volpini, Claudia Cristina Motran, Eva Virginia Acosta Rodríguez, Juan Pablo Nicola, Sheue-yann Cheng, Claudia Gabriela Pellizas, Laura Fozzatti
Cancers.2021; 13(19): 4821. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Landscape and Its Immunological Link With Hashimoto Thyroiditis at Single-Cell Resolution
Jun Pan, Fang Ye, Chengxuan Yu, Qinsheng Zhu, Jiaqi Li, Yaohui Zhang, Hedi Tian, Yunjin Yao, Minjie Zhu, Yibin Shen, Feng Zhu, Yingying Wang, Xinhui Zhou, Guoji Guo, Yijun Wu
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of solid tumor response to sequential treatment cycles via a new computational hybrid approach
Farshad Moradi Kashkooli, M. Soltani
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of outcomes and novel immune biomarkers in metaplastic breast cancer: a single institution retrospective study
Evan Morgan, Anupama Suresh, Akaansha Ganju, Daniel G. Stover, Robert Wesolowski, Sagar Sardesai, Anne Noonan, Raquel Reinbolt, Jeffrey VanDeusen, Nicole Williams, Mathew A. Cherian, Zaibo Li, Gregory Young, Marilly Palettas, Julie Stephens, Joseph Liu, A
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiated agonistic antibody targeting CD137 eradicates large tumors without hepatotoxicity
Ugur Eskiocak, Wilson Guzman, Benjamin Wolf, Christine Cummings, Lauren Milling, Hsin-Jung Wu, Michael Ophir, Conner Lambden, Pearl Bakhru, Dana C. Gilmore, Samantha Ottinger, Lucy Liu, William K. McConaughy, Sunny Q. He, Chao Wang, Cheuk Lun Leung, Jason
JCI Insight.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Tumor Microenvironment: A Milieu Hindering and Obstructing Antitumor Immune Responses
Alireza Labani-Motlagh, Mehrnoush Ashja-Mahdavi, Angelica Loskog
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Sevoflurane depletes macrophages from the melanoma microenvironment
Isabella Sztwiertnia, Judith Schenz, Katharina Bomans, Dominik Schaack, Johanna Ohnesorge, Sandra Tamulyte, Markus A. Weigand, Florian Uhle, Roger Chammas
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(5): e0233789. CrossRef - Lung cancer aggressiveness in an intermittent hypoxia murine model of postmenopausal sleep apnea
Marta Torres, Miguel Ángel Martinez-Garcia, Francisco Campos-Rodriguez, David Gozal, Josep M. Montserrat, Daniel Navajas, Ramon Farré, Isaac Almendros
Menopause.2020; 27(6): 706. CrossRef - Neck Disability and Swallowing Function in Posttreatment Head and Neck Cancer Patients
Alexandria Harris, Lingyun Lyu, Tamara Wasserman‐Winko, Susan George, Jonas T. Johnson, Marci Lee Nilsen
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2020; 163(4): 763. CrossRef - Metabolic modulation via mTOR pathway and anti-angiogenesis remodels tumor microenvironment using PD-L1-targeting codelivery
Binfan Chen, Ang Gao, Bin Tu, Yonghui Wang, Xiaolu Yu, Yingshu Wang, Yanfeng Xiu, Bing Wang, Yakun Wan, Yongzhuo Huang
Biomaterials.2020; 255: 120187. CrossRef - The Thyroid Tumor Microenvironment: Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention and Prognostication
Laura MacDonald, Jonathan Jenkins, Grace Purvis, Joshua Lee, Aime T. Franco
Hormones and Cancer.2020; 11(5-6): 205. CrossRef - The Contribution of Race to Breast Tumor Microenvironment Composition and Disease Progression
Gina Kim, Jessica M. Pastoriza, John S. Condeelis, Joseph A. Sparano, Panagiota S. Filippou, George S. Karagiannis, Maja H. Oktay
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognosis of Macrophage Density in the Absence of Neutrophils in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Amblessed E. Onuma, Lynn Schoenfield, Chengli Shen, Charity Edwards, John E. Phay, Lawrence A. Shirley, Allan Tsung
Journal of Surgical Research.2020; 256: 458. CrossRef - Targeting of CD163+ Macrophages in Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases
Maria K. Skytthe, Jonas Heilskov Graversen, Søren K. Moestrup
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(15): 5497. CrossRef - Synthetic chlorin derivative self-prevented from aggregation: Behavior in homogeneous medium for PDT applications
Bianca Martins Estevão, Camila Fabiano de Freitas, Douglas Santana Franciscato, Francisco Fávaro de Assis, Kleber Thiago de Oliveira, Noboru Hioka, Wilker Caetano, Edvani Curti Muniz
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2020; 320: 114363. CrossRef - Tumor‑associated macrophages in lung cancer: Friendly or evil? (Review)
Fei Xu, Ying Wei, Zhao Tang, Baojun Liu, Jingcheng Dong
Molecular Medicine Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Macrophage-secreted MMP9 induces mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells via PAR1 activation
Cansu Tekin, Hella L Aberson, Cynthia Waasdorp, Gerrit K J Hooijer, Onno J de Boer, Frederike Dijk, Maarten F Bijlsma, C Arnold Spek
Cellular Oncology.2020; 43(6): 1161. CrossRef - Cancer Stem Cells in Thyroid Tumors: From the Origin to Metastasis
Veronica Veschi, Francesco Verona, Melania Lo Iacono, Caterina D'Accardo, Gaetana Porcelli, Alice Turdo, Miriam Gaggianesi, Stefano Forte, Dario Giuffrida, Lorenzo Memeo, Matilde Todaro
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Crosstalk Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy
Zhe Ge, Shuzhe Ding
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Cell Confrontation in the Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Microenvironment
Zhenyu Xie, Xin Li, Yuzhen He, Song Wu, Shiyue Wang, Jianjian Sun, Yuchen He, Yu Lun, Jian Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Early macrophage infiltrates impair pancreatic cancer cell growth by TNF-α secretion
Cansu Tekin, Hella L. Aberson, Maarten F. Bijlsma, C. Arnold Spek
BMC Cancer.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuation of CD47-SIRPα Signal in Cholangiocarcinoma Potentiates Tumor-Associated Macrophage-Mediated Phagocytosis and Suppresses Intrahepatic Metastasis
Kulthida Vaeteewoottacharn, Ryusho Kariya, Phattarin Pothipan, Sawako Fujikawa, Chawalit Pairojkul, Sakda Waraasawapati, Kazuhiko Kuwahara, Chaisiri Wongkham, Sopit Wongkham, Seiji Okada
Translational Oncology.2019; 12(2): 217. CrossRef - Circulating CEA‐dNLR score predicts clinical outcome of metastatic gallbladder cancer patient
Jing‐Hui Du, Jun Lu
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Interplay between MicroRNAs and Cellular Components of Tumour Microenvironment (TME) on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Progression
Sook Shien Lee, Yoke Kqueen Cheah
Journal of Immunology Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma behavior: clues in the tumor microenvironment
Kensey Bergdorf, Donna C Ferguson, Mitra Mehrad, Kim Ely, Thomas Stricker, Vivian L Weiss
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2019; 26(6): 601. CrossRef - Interplay between thyroid cancer cells and macrophages: effects on IL-32 mediated cell death and thyroid cancer cell migration
Yvette J. E. Sloot, Katrin Rabold, Thomas Ulas, Dennis M. De Graaf, Bas Heinhuis, Kristian Händler, Joachim L. Schultze, Mihai G. Netea, Johannes W. A. Smit, Leo A. B. Joosten, Romana T. Netea-Maier
Cellular Oncology.2019; 42(5): 691. CrossRef - Iron accumulation in tumor-associated macrophages marks an improved overall survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma
Carl Maximilian Thielmann, Milene Costa da Silva, Thomas Muley, Michael Meister, Esther Herpel, Martina U. Muckenthaler
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Immune Landscape of Thyroid Cancer in the Context of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
Gilda Varricchi, Stefania Loffredo, Giancarlo Marone, Luca Modestino, Poupak Fallahi, Silvia Martina Ferrari, Amato de Paulis, Alessandro Antonelli, Maria Rosaria Galdiero
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(16): 3934. CrossRef - A review on the role of M2 macrophages in bladder cancer; pathophysiology and targeting
Laleh Sharifi, Mohammad Reza Nowroozi, Erfan Amini, Masoumeh Kourosh Arami, Mohsen Ayati, Monireh Mohsenzadegan
International Immunopharmacology.2019; 76: 105880. CrossRef - Tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in meningioma
Dustin T Proctor, Jordan Huang, Sanju Lama, Abdulrahman Albakr, Guido Van Marle, Garnette R Sutherland
Neuro-Oncology Advances.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Thyroid Cancer Microenvironment
Silvia Martina Ferrari, Poupak Fallahi, Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Ilaria Ruffilli, Giusy Elia, Francesca Ragusa, Sabrina Rosaria Paparo, Armando Patrizio, Valeria Mazzi, Gilda Varricchi, Gianni Marone, Alessandro Antonelli
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(18): 4413. CrossRef - Caveolin-2 deficiency induces a rapid anti-tumor immune response prior to regression of implanted murine lung carcinoma tumors
Yajun Liu, Xiaoqiang Qi, Guangfu Li, Grzegorz Sowa
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Paclitaxel Treatment and Proprotein Convertase 1/3 (PC1/3) Knockdown in Macrophages is a Promising Antiglioma Strategy as Revealed by Proteomics and Cytotoxicity Studies
Marie Duhamel, Mélanie Rose, Franck Rodet, Adriana Natalia Murgoci, Lea Zografidou, Anne Régnier-Vigouroux, Fabien Vanden Abeele, Firas Kobeissy, Serge Nataf, Laurent Pays, Maxence Wisztorski, Dasa Cizkova, Isabelle Fournier, Michel Salzet
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.2018; 17(6): 1126. CrossRef - Chloroquine and nanoparticle drug delivery: A promising combination
Joe Pelt, Sara Busatto, Mauro Ferrari, E. Aubrey Thompson, Kabir Mody, Joy Wolfram
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 191: 43. CrossRef - Conditioned medium from stimulated macrophages inhibits growth but induces an inflammatory phenotype in breast cancer cells
Wenzhe Song, Parth Thakor, David A. Vesey, Glenda C. Gobe, Christudas Morais
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2018; 106: 247. CrossRef - Potential involvement of neutrophils in human thyroid cancer
Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Gilda Varricchi, Stefania Loffredo, Claudio Bellevicine, Tiziana Lansione, Anne Lise Ferrara, Raffaella Iannone, Sarah di Somma, Francesco Borriello, Eduardo Clery, Maria Triassi, Giancarlo Troncone, Gianni Marone, Fabrizio Mattei
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0199740. CrossRef - CSF1R-Expressing Tumor-Associated Macrophages, Smoking and Survival in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Analyses Using Quantitative Phosphor-Integrated Dot Staining
Kentaro Inamura, Yasuyuki Shigematsu, Hironori Ninomiya, Yasuhiro Nakashima, Maki Kobayashi, Haruyuki Saito, Katsuhiro Takahashi, Etsuko Futaya, Sakae Okumura, Yuichi Ishikawa, Hiroaki Kanda
Cancers.2018; 10(8): 252. CrossRef - Tumor heterogeneity and nanoparticle-mediated tumor targeting: the importance of delivery system personalization
K. Laxmi Swetha, Aniruddha Roy
Drug Delivery and Translational Research.2018; 8(5): 1508. CrossRef - Immune Gene Signature Delineates a Subclass of Papillary Thyroid Cancer with Unfavorable Clinical Outcomes
Kyuryung Kim, Sora Jeon, Tae-Min Kim, Chan Jung
Cancers.2018; 10(12): 494. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of TGF-Β1, SMAD4, SMAD7, TGFβRII and CD68-Positive TAM Densities in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Koni Ivanova, Irena Manolova, Maria-Magdalena Ignatova, Maya Gulubova
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2018; 6(3): 435. CrossRef - Bone marrow-derived cells are recruited by the melanoma tumor with endothelial cells contributing to tumor vasculature
R. Bonfim-Silva, L. E. B. Souza, F. U. F. Melo, V. C. Oliveira, D. A. R. Magalhães, H. F. Oliveira, D. T. Covas, A. M. Fontes
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2017; 19(1): 125. CrossRef - Stromal contributions to the carcinogenic process
Mark Spaw, Shrikant Anant, Sufi Mary Thomas
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2017; 56(4): 1199. CrossRef - The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis in Liver Cancer
Silvia Affo, Le-Xing Yu, Robert F. Schwabe
Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease.2017; 12(1): 153. CrossRef - PEDF increases the tumoricidal activity of macrophages towards prostate cancer cells in vitro
Dalia Martinez-Marin, Courtney Jarvis, Thomas Nelius, Werner de Riese, Olga V. Volpert, Stéphanie Filleur, Chih-Hsin Tang
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(4): e0174968. CrossRef - Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: from clinicopathology to genetics and advanced therapies
Eleonora Molinaro, Cristina Romei, Agnese Biagini, Elena Sabini, Laura Agate, Salvatore Mazzeo, Gabriele Materazzi, Stefano Sellari-Franceschini, Alessandro Ribechini, Liborio Torregrossa, Fulvio Basolo, Paolo Vitti, Rossella Elisei
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2017; 13(11): 644. CrossRef - Iron Induces Anti-tumor Activity in Tumor-Associated Macrophages
Milene Costa da Silva, Michael O. Breckwoldt, Francesca Vinchi, Margareta P. Correia, Ana Stojanovic, Carl Maximilian Thielmann, Michael Meister, Thomas Muley, Arne Warth, Michael Platten, Matthias W. Hentze, Adelheid Cerwenka, Martina U. Muckenthaler
Frontiers in Immunology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Reprogramming Tumor-Associated Macrophages To Reverse EGFRT790M Resistance by Dual-Targeting Codelivery of Gefitinib/Vorinostat
Huige Peng, Binfan Chen, Wei Huang, Yubo Tang, Yifan Jiang, Wenyuan Zhang, Yongzhuo Huang
Nano Letters.2017; 17(12): 7684. CrossRef - Numerical modeling of nanodrug distribution in tumors with heterogeneous vasculature
Cheng-Ying Chou, Wan-I Chang, Tzyy-Leng Horng, Win-Li Lin, Han-Chung Wu
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(12): e0189802. CrossRef - HPMA–Copolymer Nanocarrier Targets Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer
Melissa N. Zimel, Chloe B. Horowitz, Vinagolu K. Rajasekhar, Alexander B. Christ, Xin Wei, Jianbo Wu, Paulina M. Wojnarowicz, Dong Wang, Steven R. Goldring, P. Edward Purdue, John H. Healey
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2017; 16(12): 2701. CrossRef - Correlation of tumor-associated macrophages and NK cells with bladder cancer size and T stage in patients with solitary low-grade urothelial carcinoma
Kristian Krpina, Emina Babarović, Josip Španjol, Gordana Đorđević, Tobias Maurer, Nives Jonjić
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2016; 128(7-8): 248. CrossRef - The lymphatic system and pancreatic cancer
Darci M. Fink, Maria M. Steele, Michael A. Hollingsworth
Cancer Letters.2016; 381(1): 217. CrossRef - Jacalin-Activated Macrophages Exhibit an Antitumor Phenotype
Cláudia Danella Polli, Luciana Pereira Ruas, Luciana Chain Veronez, Thais Herrero Geraldino, Fabiana Rossetto de Morais, Maria Cristina Roque-Barreira, Gabriela Pereira-da-Silva
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - The immune network in thyroid cancer
Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Gilda Varricchi, Gianni Marone
OncoImmunology.2016; 5(6): e1168556. CrossRef - The Expression and Relationship of CD68-Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Microvascular Density With the Prognosis of Patients With Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Shujun Sun, Xinliang Pan, Limin Zhao, Jianming Zhou, Hongzeng Wang, Yonghong Sun
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2016; 9(3): 270. CrossRef - Role of pulmonary macrophages in initiation of lung metastasis in anaplastic thyroid cancer
Xiu Juan Li, Prakash Gangadaran, Senthilkumar Kalimuthu, Ji Min Oh, Liya Zhu, Shin Young Jeong, Sang‐Woo Lee, Jaetae Lee, Byeong‐Cheol Ahn
International Journal of Cancer.2016; 139(11): 2583. CrossRef - Perspectives for immunotherapy in endocrine cancer
S Latteyer, V Tiedje, B Schilling, D Führer
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2016; 23(10): R469. CrossRef - Macrophage Densities Correlated with CXC Chemokine Receptor 4 Expression and Related with Poor Survival in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Dae In Kim, Eunyoung Kim, Young A Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Jung Ah Lim, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 469. CrossRef - High expression of C-C chemokine receptor 2 associates with poor overall survival in gastric cancer patients after surgical resection
Ruochen Li, Heng Zhang, Hao Liu, Chao Lin, Yifan Cao, Weijuan Zhang, Zhenbin Shen, Jiejie Xu
Oncotarget.2016; 7(17): 23909. CrossRef - Polycationic carbosilane dendrimer decreases angiogenesis and tumor-associated macrophages in tumor-bearing mice
Ana Judith Perisé-Barrios, María Jesús Serramia, Javier de la Mata, Rafael Gomez, Angel Luis Corbí, Ángeles Domínguez-Soto, María Ángeles Muñoz-Fernandez
RSC Advances.2015; 5(126): 104110. CrossRef
- Immune cells in thyroid adenoma and carcinoma: uncovering a hidden value of assessing tumor-host interplay and its potential application in thyroid cytopathology
- Pathology-MRI Correlation of Hepatocarcinogenesis: Recent Update
- Jimi Huh, Kyung Won Kim, Jihun Kim, Eunsil Yu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):218-229. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.04.15
- 26,064 View
- 332 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Understanding the important alterations during hepatocarcinogenesis as well as the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and histopathological features will be helpful for managing patients with chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent advances in MRI techniques, such as fat/iron quantification, diffusion-weighted images, and gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI, have greatly enhanced our understanding of hepatocarcinogenesis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Imaging Features Associated With Histology, Subtype, and Prognosis Along With Changes to LI-RADS in 2024
Sergio P. Klimkowski, Ann Shi, Omar Altabbakh, Janio Szklaruk, AnuradhaS. Shenoy-Bhangle, Gauruv S. Likhari, Khaled M. Elsayes
Seminars in Roentgenology.2025; 60(1): 6. CrossRef - Advances in the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management of Liver Nodules: A Comprehensive Review
Chang Gao, Dongyang Chen, Youpeng Chen
Portal Hypertension & Cirrhosis.2025; 4(4): 232. CrossRef - Gadoxetic acid in hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases: pearls and pitfalls
H.M. Kwok, C.M. Chau, H.C.H. Lee, T. Wong, H.F. Chan, W.H. Luk, W.T.A. Yung, L.F. Cheng, K.F.J. Ma
Clinical Radiology.2023; 78(10): 715. CrossRef - Multi-phasic magnetic resonance imaging of hemodynamic interchanges in hepatocarcinogenesis
Ahmed Mahmoud Elzeneini, Mohsen Ahmed Abdelmohsen, Mohamed Ibrahim Yousef
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors for Hypervascularization in Hepatobiliary Phase Hypointense Nodules without Arterial Phase Hyperenhancement: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Tae-Hyung Kim, Sungmin Woo, Sangwon Han, Chong Hyun Suh, Richard Kinh Gian Do, Jeong Min Lee
Academic Radiology.2022; 29(2): 198. CrossRef - Comparison of IDEAL-IQ and IVIM-DWI for Differentiating between Alpha Fetoprotein-Negative Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
Shaopeng Li, Peng Wang, Jun Qiu, Yiju Xie, Dawei Yin, Kexue Deng
Oncologie.2022; 24(3): 527. CrossRef - Hepatocarcinogenesis
Alice Fung, Krishna P. Shanbhogue, Myles T. Taffel, Brian T. Brinkerhoff, Neil D. Theise
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinics of North America.2021; 29(3): 359. CrossRef - Pathologic, Molecular, and Prognostic Radiologic Features of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kathryn J. Fowler, Adam Burgoyne, Tyler J. Fraum, Mojgan Hosseini, Shintaro Ichikawa, Sooah Kim, Azusa Kitao, Jeong Min Lee, Valérie Paradis, Bachir Taouli, Neil D. Theise, Valérie Vilgrain, Jin Wang, Claude B. Sirlin, Victoria Chernyak
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(6): 1611. CrossRef - Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - Gadoxetate-enhanced dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for evaluation of liver function and liver fibrosis in preclinical trials
Jimi Huh, Su Jung Ham, Young Chul Cho, Bumwoo Park, Bohyun Kim, Chul-Woong Woo, Yoonseok Choi, Dong-Cheol Woo, Kyung Won Kim
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Hypervascular Hypointense Nodules at Gadoxetic Acid MRI: Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk Assessment with Emphasis on the Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
Chiara Briani, Marco Di Pietropaolo, Massimo Marignani, Francesco Carbonetti, Paola Begini, Vincenzo David, Elsa Iannicelli
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2018; 49(3): 302. CrossRef
- Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Imaging Features Associated With Histology, Subtype, and Prognosis Along With Changes to LI-RADS in 2024
- Role of Osteal Macrophages in Bone Metabolism
- Sun Wook Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(2):102-104. Published online March 12, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.02.02
- 12,380 View
- 137 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 27 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Macrophages have been shown to have pleiotropic functions in various pathophysiologies, especially in terms of anti-inflammatory and regenerative activity. Recently, the novel functions of bone marrow resident macrophages (called osteal macrophages) were intensively studied in bone development, remodeling and tissue repair processes. This review discusses the current evidence for a role of osteal macrophages in bone modeling, remodeling, and fracture healing processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 3D printed composite scaffold accelerates bone regeneration by modulating immunity and promoting angiogenesis
Yiye Fan, Jiaxin Yao, Wan Liu, Lebin Wang, Jing Yang, Xiaoyan Zheng, Junfeng Hui, Daidi Fan
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 240: 1. CrossRef - Transcriptomic profiling reveals a dramatic inflammatory shift in osteal macrophages during colitis-induced osteoporosis
Ryota Suzuki, Liyile Chen, Tsutomu Endo, Taiki Tokuhiro, Masaya Nakajo, Yuki Ogawa, Hend Alhasan, Taku Ebata, Daisuke Takahashi, Ken Kadoya, Masahiko Takahata, Norimasa Iwasaki, M. Alaa Terkawi
Inflammation Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Rescuing Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Macrophages Prevents Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Anti‐Resorptive Therapy
Hang Zhang, Xin Shen, Haiyang Liu, Xinxi Yuan, Mumin Cao, Xuepeng Lv, Ziji Ling, Songsong Guo, Rongyao Xu, Xiang Li, Hongbing Jiang
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical stress induced tumor immune suppressive environment
Fan Yang, Qing Hua, Xiaoyan Zhu, Pingbo Xu
Carcinogenesis.2024; 45(4): 185. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Outcomes of Reconstruction with Vascularised vs Non-Vascularised Bone Graft after Surgical Resection of Primary Malignant and Non-Malignant Bone Tumors
R. PATEL, G. MCCONAGHIE, M. M. KHAN, W. GIBSON, R. SINGH, R. BANERJEE
Acta chirurgiae orthopaedicae et traumatologiae Cechoslovaca.2024; 91(3): 143. CrossRef - Macrophage Polarization during MRONJ Development in Mice
A. Soundia, N. Elzakra, D. Hadaya, I. Gkouveris, O. Bezouglaia, S. Dry, T. Aghaloo, S. Tetradis
Journal of Dental Research.2024; 103(9): 899. CrossRef - 3D printing of gear-inspired biomaterials: Immunomodulation and bone regeneration
Xiaopeng Yu, Yufeng Wang, Meng Zhang, Hongshi Ma, Chun Feng, Bingjun Zhang, Xin Wang, Bing Ma, Qingqiang Yao, Chengtie Wu
Acta Biomaterialia.2023; 156: 222. CrossRef - Origin, production and molecular determinants of macrophages for their therapeutic targeting
Sangita Chowdhury, Arun K. Trivedi
Cell Biology International.2023; 47(1): 15. CrossRef - The Macrophage’s Role on Bone Remodeling and Osteogenesis: a Systematic Review
João Maria Orvalho, Juliana Campos Hasse Fernandes, Rogerio Moraes Castilho, Gustavo Vicentis Oliveira Fernandes
Clinical Reviews in Bone and Mineral Metabolism.2023; 21(1-4): 1. CrossRef - Neglected immunoregulation: M2 polarization of macrophages triggered by low‐dose irradiation plays an important role in bone regeneration
Shaoqing Chen, Su Ni, Chun Liu, Mu He, Yiwen Pan, Pengfei Cui, Cheng Wang, Xinye Ni
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2023; 27(8): 1095. CrossRef - Insight into the effect of biomaterials on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: A review from a mitochondrial perspective
Ziyi Feng, Meiqi Jin, Junzhi Liang, Junning Kang, Huazhe Yang, Shu Guo, Xiaoting Sun
Acta Biomaterialia.2023; 164: 1. CrossRef - Nano wear particles and the periprosthetic microenvironment in aseptic loosening induced osteolysis following joint arthroplasty
Yu Xie, Yujie Peng, Guangtao Fu, Jiewen Jin, Shuai Wang, Mengyuan Li, Qiujian Zheng, Feng-Juan Lyu, Zhantao Deng, Yuanchen Ma
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated computational and in vivo models reveal Key Insights into macrophage behavior during bone healing
Etienne Baratchart, Chen Hao Lo, Conor C. Lynch, David Basanta, Dominik Wodarz
PLOS Computational Biology.2022; 18(5): e1009839. CrossRef - Strategies of Macrophages to Maintain Bone Homeostasis and Promote Bone Repair: A Narrative Review
Yingkun Hu, Jinghuan Huang, Chunying Chen, Yi Wang, Zhuowen Hao, Tianhong Chen, Junwu Wang, Jingfeng Li
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2022; 14(1): 18. CrossRef - Macrophages and Stem Cells—Two to Tango for Tissue Repair?
Emilia Manole, Cristina Niculite, Ioana Maria Lambrescu, Gisela Gaina, Octavian Ioghen, Laura Cristina Ceafalan, Mihail Eugen Hinescu
Biomolecules.2021; 11(5): 697. CrossRef - Bone remodeling stages under physiological conditions and glucocorticoid in excess: Focus on cellular and molecular mechanisms
V. V. Povoroznyuk, N. V. Dedukh, M. A. Bystrytska, V. S. Shapovalov
Regulatory Mechanisms in Biosystems.2021; 12(2): 212. CrossRef - Menaquinone-7 Supplementation Improves Osteogenesis in Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Asim Cengiz Akbulut, Grzegorz B. Wasilewski, Nikolas Rapp, Francesco Forin, Heike Singer, Katrin J. Czogalla-Nitsche, Leon J. Schurgers
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Biomaterial Implant Wear Debris on Osteoblasts
Li Zhang, El-Mustapha Haddouti, Kristian Welle, Christof Burger, Dieter C. Wirtz, Frank A. Schildberg, Koroush Kabir
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Local Cellular Responses to Metallic and Ceramic Nanoparticles from Orthopedic Joint Arthroplasty Implants
Li Zhang, El-Mustapha Haddouti, Kristian Welle, Christof Burger, Koroush Kabir, Frank A Schildberg
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 6705. CrossRef- Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing
Jukka Pajarinen, Tzuhua Lin, Emmanuel Gibon, Yusuke Kohno, Masahiro Maruyama, Karthik Nathan, Laura Lu, Zhenyu Yao, Stuart B. Goodman
Biomaterials.2019; 196: 80. CrossRef - Inflammation, mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration
Hongrui Liu, Dongfang Li, Yi Zhang, Minqi Li
Histochemistry and Cell Biology.2018; 149(4): 393. CrossRef - Inflammatory and degenerative phases resulting from anterior cruciate rupture in a non‐invasive murine model of post‐traumatic osteoarthritis
Sophie J. Gilbert, Cleo S. Bonnet, Paulina Stadnik, Victor C. Duance, Deborah J. Mason, Emma J. Blain
Journal of Orthopaedic Research.2018; 36(8): 2118. CrossRef - M2 macrophages are closely associated with accelerated clavicle fracture healing in patients with traumatic brain injury: a retrospective cohort study
Ran Zhang, Yi Liang, Shuxiang Wei
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Digesting the role of bone marrow macrophages on hematopoiesis
Esther Heideveld, Emile van den Akker
Immunobiology.2017; 222(6): 814. CrossRef - Concise Review: Stem Cells in Osteoimmunology
Fernando A. Fierro, Jan A. Nolta, Iannis E. Adamopoulos
Stem Cells.2017; 35(6): 1461. CrossRef - Aging, inflammation, stem cells, and bone healing
Emmanuel Gibon, Laura Lu, Stuart B. Goodman
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of immune cells in bone healing; what we know, do not know and future perspectives
Jehan J. El-Jawhari, Elena Jones, Peter V. Giannoudis
Injury.2016; 47(11): 2399. CrossRef
- 3D printed composite scaffold accelerates bone regeneration by modulating immunity and promoting angiogenesis
- Unilateral Pigmented Extramammary Paget's Disease of the Axilla Associated with a Benign Mole: A Case Study and a Review of Literature
- Aleem Ladak, Maria Bramley, Sami Titi
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(4):292-296. Published online August 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.4.292
- 11,723 View
- 88 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Pigmented extramammary Paget's disease (PEMPD) is an uncommon intraepithelial adenocarcinoma and a rare variant of Paget's disease affecting skin that is rich in apocrine sweat glands such as the axilla, perianal region and vulva. It most commonly occurs in postmenopausal women and presents as a superficial pigmented scaly macule, mimicking a melanocytic lesion. The histological presentation is adenocarcinoma
in situ with an increased number of melanocytes scattered between the Paget's cells. Therefore, PEMPD may be misdiagnosed as a melanocytic tumour both clinically and histologically. The tumour cells are usually positive for cytokeratin 7, epithelial membrane antigen, Cam 5.2, HER2, and mucicarmine stain while S100 and human melanoma black-45 highlight the processes of reactive dendritic cells. The association between Paget's cells and intratumoural reactive melanocytes is still unclear. We report our first case of PEMPD associated with an intradermal naevus involving the axilla in a 63-year-old woman.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pigmented Extramammary Paget’s Disease of the Axilla: Two Case Reports and a Literature Review
Yi-Xiao Wang, Xiao-Mei Cui, Qing Zhang, Xiao-Qing Xu, Yao Sun, Min Gao, Li-Xiong Gu
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.2025; Volume 18: 1909. CrossRef - Atypical cells on reflectance confocal microscopy may not represent melanoma: A case of axillary pigmented extramammary Paget disease
Nadiya Chuchvara, Catherine Reilly, Attiya Haroon, Cindy Wassef, Amin Maghari, Babar Rao
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2020; 47(12): 1170. CrossRef - “Pigmented Extramammary Paget Disease”—A Potential Mimicker of Malignant Melanoma and a Pitfall in Diagnosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Katrin Kiavash, Steve Kim, Andrew D. Thompson
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2019; 41(1): 45. CrossRef - Vulvar cancer: a review for dermatologists
Anastasiya Atanasova Chokoeva, Georgi Tchernev, Elena Castelli, Elisabetta Orlando, Shyam B. Verma, Markus Grebe, Uwe Wollina
Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift.2015; 165(7-8): 164. CrossRef
- Pigmented Extramammary Paget’s Disease of the Axilla: Two Case Reports and a Literature Review
- Effects of Fixation and Storage of Human Tissue Samples on Nucleic Acid Preservation
- Soo Kyung Nam, Joon Im, Yoonjin Kwak, Nayoung Han, Kyung Han Nam, An Na Seo, Hye Seung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):36-42. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.36
- 13,848 View
- 179 Download
- 41 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Because of recent advances in the molecular diagnosis of cancer patients, tissue quality has become more important in daily practice.
Methods To evaluate the effects of fixative, duration of fixation, decalcification, and storage periods on nucleic acid integrity, DNA and RNA were extracted from gastrointestinal cancer tissue. The yield and purity were analyzed, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; 60 bp), β-actin (148 bp), and human growth hormone (hGH; 434 bp) and real-time reverse transcription-PCR for β-actin (97 bp) were performed.
Results All formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) and methacarn-fixed paraffin-embedded (MFPE) samples tested positive for GAPDH and β-actin by PCR. hGH was successfully detected in all MFPE samples, but in only 46.7% of the FFPE samples. Prolonged formalin fixation resulted in fewer GAPDH and β-actin PCR products, and amplification of hGH was not successful. The PCR and reverse transcription-PCR results were significantly affected by the duration of decalcification. The yield, purity, and integrity of mRNA progressively decreased with increased storage periods of paraffin blocks.
Conclusions Fixation and storage should therefore be standardized in order to improve the quality of molecular pathologic diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A nanoscale quality control framework for assessing FFPE DNA integrity in cancer research
Zixuan Huang, Yunpei Si, Yi Zhang, Zicheng Huang, Xuehao Xiu, Yunshan Wang, YuDong Wang, Chunhai Fan, Ping Song
Nanoscale Horizons.2025; 10(8): 1692. CrossRef - Cutting-edge methods for the preservation and storage of forensic pathology tissue samples
Suneel Prajapati, Niyati Sevak, Lakshmi Panicker, Aditi Mishra, Megha Sapkota, Mahipal Singh Sankhla
Problems of Forensic Sciences.2025; (141): 75. CrossRef - Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 398. CrossRef - InDEL instability in two different tumoral tissues and its forensic significance
İpek Gürel, Faruk Aşıcıoğlu, Gökhan Ersoy, Özlem Bülbül, Tülin Öztürk, Gönül Filoğlu
Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology.2024; 20(4): 1241. CrossRef - Utility of bronchoscopically obtained frozen cytology pellets for next-generation sequencing
Chihiro Mimura, Rei Takamiya, Shodai Fujimoto, Takafumi Fukui, Atsuhiko Yatani, Jun Yamada, Mizuki Takayasu, Naoya Takata, Hiroki Sato, Kiyoko Fukuda, Koichi Furukawa, Daisuke Hazama, Naoko Katsurada, Masatsugu Yamamoto, Shingo Matsumoto, Koichi Goto, Mot
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive molecular pathology after prolonged fixation: A study on tissue from anatomical body donors
Anja Böckers, Leon Schurr, Michael Schön, Tatjana Scholl, Tobias M. Böckers, Konrad Steinestel, Annette Arndt
Experimental and Molecular Pathology.2024; 137: 104899. CrossRef - Tiempos y condiciones de almacenamiento de las muestras en anatomía patológica. Recomendaciones de la Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica parte 1: muestras destinadas al diagnóstico
Francesc Tresserra Casas, Esther Rosello Sastre, María Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Lara Zaragoza Macián, Javier Azúa Romeo, Clara Alfaro-Cervelló, Samuel Navarro Fos, Eugenia García Fernández, Jordi Temprana-Salvador, Mar Iglesias Coma, Francesc Olivares Veg
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(4): 235. CrossRef - RNA-Seq Analysis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: What Is the Best Sample from Clinical Practice?
Lorenzo Nibid, Giovanna Sabarese, Luca Andreotti, Benedetta Canalis, Daniela Righi, Filippo Longo, Margherita Grazi, Pierfilippo Crucitti, Giuseppe Perrone
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(8): 851. CrossRef - A Study on the Stainability and DNA Conservation of Tissue Slides according to Fixation Time and Temperature
Da-som JEONG
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2024; 56(3): 217. CrossRef - Selection and Evaluation of mRNA and miRNA Reference Genes for Expression Studies (qPCR) in Archived Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Colon Samples of DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model
Ana Unkovič, Emanuela Boštjančič, Aleš Belič, Martina Perše
Biology.2023; 12(2): 190. CrossRef - The quality of DNA isolated from autopsy formalin-fixed and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues: study of 1662 samples
Katarina Vitošević, Danijela Todorović, Živana Slović, Tatjana Varljen, Ivana Radaković, Dušan Radojević, Vanja Čanović, Miloš Todorović
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(8): 6323. CrossRef - Morphometric and Molecular Analysis of Five-Spine Epidinium Morphotypes Taken from the Rumen of European Bison, Bison bonasus
Silvia Ivorová, Anna Kopčaková, Peter Pristaš, Svetlana Kišidayová
Life.2023; 13(12): 2350. CrossRef - Retrieving high-quality genomic DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues for multiple molecular analyses
Ha Thi Nguyen, Vinay Bharadwaj Tatipamula, Duy Ngoc Do, Thien Chi Huynh, Mai Kim Dang
Preparative Biochemistry & Biotechnology.2022; 52(1): 48. CrossRef - Evaluation of DNA Isolation and Amplification from Various Organs Preserved through Frozen, Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sample method
Mifta Rizqina Amalia, Anna Roosdiana, Yudit Oktanella, Andreas Bandang Hardian, Dini Agusti Paramanandi, Kharisma Kurnia Utami, Andi Tri Rakhmat Akbar, Made Venika Nareswari, Fajar Shodiq Permata
Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences.2022; 10(3): 643. CrossRef - DNA isolated from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded healthy tissue after 30 years of storage can be used for forensic studies
Katarina Vitošević, Miloš Todorović, Živana Slović, Tatjana Varljen, Stevan Matić, Danijela Todorović
Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology.2021; 17(1): 47. CrossRef - Extraction of DNA and RNA from Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded Tissue Specimens
NIdhi Shukla, Narmadhaa Siva, Madhu Sivakumar, Rabia Parveen, Ashwani Mishra, Avadh Shah, Krishna Medicherla, Prashanth Suravajhala
BIO-PROTOCOL.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A and miR-671-5p expression profile in Iranian glioblastoma multiforme
Tayyebali Salmani, Sayyed Mohammad Hossein Ghaderian, Mohammadreza Hajiesmaeili, Omidvar Rezaei Mirghaed, Azadeh Rakhshan, Mohammad Javad Nasiri, Mahan Mohammadi
Gene Reports.2020; 19: 100620. CrossRef - Comparison between Fluorescence in-situ Hybridization (FISH), Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) and fragment analysis, for detection of t (X; 18) (p11; q11) translocation in synovial sarcomas
Omshree Shetty, Trupti Pai, Mamta Gurav, Bharat Rekhi
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2020; 63(1): 64. CrossRef - Comparison of HPV detection rate in formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded tissues of head and neck carcinoma using two DNA extraction kits and three amplification methods
Ljiljana Božić, Tanja Jovanović, Aleksandra Šmitran, Marko Janković, Aleksandra Knežević
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 128(6): 501. CrossRef - Formalin Fixation of Human Healthy Autopsied Tissues: The Influence of Type of Tissue, Temperature and Incubation Time on the Quality of Isolated DNA
Danijela Todorovic, Katarina Vitosevic, Milos Todorovic, Zivana Slovic
Serbian Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research .2020; 21(4): 307. CrossRef - Detection of Disease-specific Fusion Genes of Soft Tissue Tumors Using Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded Tissues; Its Diagnostic Usefulness and Factors Affecting the Detection Rates
Takahiro Matsushige, Satoshi Kuwamoto, Michiko Matsushita, Lusi Oka Wardhani, Yasushi Horie, Kazuhiko Hayashi, Yukisato Kitamura
Yonago Acta Medica.2019; 62(1): 115. CrossRef - The Biospecimen Preanalytical Variables Program: A Multiassay Comparison of Effects of Delay to Fixation and Fixation Duration on Nucleic Acid Quality
Latarsha J. Carithers, Rachana Agarwal, Ping Guan, Hana Odeh, Michael C. Sachs, Kelly B. Engel, Sarah R. Greytak, Mary Barcus, Conrado Soria, Chih-Jian (Jason) Lih, P. Mickey Williams, Philip A. Branton, Leslie Sobin, Benjamin Fombonne, Therese Bocklage,
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(9): 1106. CrossRef - Pathobiology and innate immune responses of gallinaceous poultry to clade 2.3.4.4A H5Nx highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection
Kateri Bertran, Mary J. Pantin-Jackwood, Miria F. Criado, Dong-Hun Lee, Charles L. Balzli, Erica Spackman, David L. Suarez, David E. Swayne
Veterinary Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimized Storage Methods of RNA Extraction from Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissue
Mehdi Barati, Mahdieh Shokrollahi Barough, Fatemeh Pak, Vahid Semnani, Mehrnoosh Pashaei, Parviz Kokhaei
Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of formalin fixation on pcr amplification of DNA isolated from healthy autopsy tissues
Katarina Vitošević, Miloš Todorović, Tatjana Varljen, Živana Slović, Stevan Matić, Danijela Todorović
Acta Histochemica.2018; 120(8): 780. CrossRef - EFFECT OF HEAT-INDUCED ANTIGEN RETRIEVAL PROCEDURE ON DNA FLUORESCENT STAINING QUALITY IN HISTOLOGIC SECTIONS
E A Kolos, D E Korzhevskii
Medical academic journal.2018; 18(1): 71. CrossRef - Evaluation of the optimal provision of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded material for reverse transcription-PCR in soft-tissue tumour diagnosis
Khin Thway, Dorte Wren, Jasmin Lee, Lisa Thompson, Cyril Fisher, David Gonzalez
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2017; 70(1): 20. CrossRef - Molecular Testing for Gastrointestinal Cancer
Hye Seung Lee, Woo Ho Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Jiwon Koh, Jeong Mo Bae, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Mee Soo Chang, Hye Seung Han, Joon Mee Kim, Hwal Woong Kim, Hee Kyung Chang, Young Hee Choi, Ji Y. Park, Mi Jin Gu, Min Jin Lhee, Jung Yeon Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(2): 103. CrossRef - Reference genes for studies in infectious parasitic diseases in five types of human tissues
Cristina Silva Meira-Strejevitch, Vera Lucia Pereira-Chioccola, Marta Marques Maia, Daise Damaris Carnietto de Hippolito, Hui-Tzu Lin Wang, Gabriela Motoie, Aparecida Helena de Souza Gomes, Cristina Takami Kanamura, Roosecelis Brasil Martines, Cinara Cáss
Gene Reports.2017; 7: 98. CrossRef - Establishment of a primary culture of polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma cells
Lucas Novaes Teixeira, Victor Angelo Martins Montalli, Silvia Borges Pimentel de Oliveira, Thais Fernanda Santos Toledo, Elizabeth Ferreira Martinez, Vera Cavalcanti de Araújo
Archives of Oral Biology.2017; 82: 188. CrossRef - DNA degrades during storage in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue blocks
Alice Guyard, Alice Boyez, Anaïs Pujals, Cyrielle Robe, Jeanne Tran Van Nhieu, Yves Allory, Julien Moroch, Odette Georges, Jean-Christophe Fournet, Elie-Serge Zafrani, Karen Leroy
Virchows Archiv.2017; 471(4): 491. CrossRef - Prevalence of exon 11 internal tandem duplications in the C‐KIT proto‐oncogene in Australian canine mast cell tumours
VS Tamlin, AE Kessell, RJ Mccoy, EC Dobson, TS Smith, M Hebart, L Brown, D Mitrovic, AE Peaston
Australian Veterinary Journal.2017; 95(10): 386. CrossRef - Robust transcriptional tumor signatures applicable to both formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and fresh-frozen samples
Rou Chen, Qingzhou Guan, Jun Cheng, Jun He, Huaping Liu, Hao Cai, Guini Hong, Jiahui Zhang, Na Li, Lu Ao, Zheng Guo
Oncotarget.2017; 8(4): 6652. CrossRef - Clinical impact of targeted amplicon sequencing for meningioma as a practical clinical-sequencing system
Sayaka Yuzawa, Hiroshi Nishihara, Shigeru Yamaguchi, Hiromi Mohri, Lei Wang, Taichi Kimura, Masumi Tsuda, Mishie Tanino, Hiroyuki Kobayashi, Shunsuke Terasaka, Kiyohiro Houkin, Norihiro Sato, Shinya Tanaka
Modern Pathology.2016; 29(7): 708. CrossRef - Comparison of the Diagnostic Value Between Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay and Histopathologic Examination in Sentinel Lymph Nodes for Patients With Gastric Carcinoma
Yoonjin Kwak, Soo Kyung Nam, Eun Shin, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Hee Eun Lee, Do Joong Park, Woo Ho Kim, Hyung-Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2016; 145(5): 651. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Selection of reference genes in five types of human tissues for normalization of gene expression studies in infectious diseases
Cristina Silva Meira-Strejevitch, Vera Lucia Pereira-Chioccola, Marta Marques Maia, Daise Damaris Carnietto de Hipólito, Hui-Tzu Lin Wang, Gabriela Motoie, Aparecida Helena de Souza Gomes, Cristina Takami Kanamura, Roosecelis Brasil Martines, Cinara Cássi
Gene.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of Fresh Frozen vs. Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Specimens of Canine Mammary Tumors via Branched-DNA Assay
Florenza Lüder Ripoli, Annika Mohr, Susanne Conradine Hammer, Saskia Willenbrock, Marion Hewicker-Trautwein, Silvia Hennecke, Hugo Murua Escobar, Ingo Nolte
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(5): 724. CrossRef - Expression of caspase-3 predicts prognosis in advanced noncardia gastric cancer
Sousana Amptoulach, Andreas C. Lazaris, Ioanna Giannopoulou, Nikolaos Kavantzas, Efstratios Patsouris, Nikolaos Tsavaris
Medical Oncology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The Importance of Reference Gene Analysis of Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Samples from Sarcoma Patients — An Often Underestimated Problem
Ninna Aggerholm-Pedersen, Akmal Safwat, Steen Bærentzen, Marianne Nordsmark, Ole Steen Nielsen, Jan Alsner, Brita S. Sørensen
Translational Oncology.2014; 7(6): 687. CrossRef - Comparison of histomorphology and DNA preservation produced by fixatives in the veterinary diagnostic laboratory setting
William F. Craft, Julia A. Conway, Michael J. Dark
PeerJ.2014; 2: e377. CrossRef - Histotechnical solutions for quality improvement of nucleic acid specimens extracted from paraffin blocks
A. N Vaganova
Genes & Cells.2014; 9(2): 96. CrossRef
- A nanoscale quality control framework for assessing FFPE DNA integrity in cancer research
- Myxoid Liposarcoma with Cartilaginous Differentiation: A Case Study with Cytogenetical Analysis
- Hyunchul Kim, Won Hwangbo, Sangjeong Ahn, Suhjin Kim, Insun Kim, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):284-288. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.284
- 9,415 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Myxoid liposarcoma is a subtype of liposarcoma. This specific subtype can be identified based on its characteristic histological and cytogenetical features. The tumor has a fusion transcript of the
CHOP andTLS genes, which is caused by t(12;16)(q13;p11). Most of the fusion transcripts that have been identified fall into three categories, specifically type I (exons 7-2), type II (exons 5-2), and type III (exons 8-2). A total of seven myxoid liposarcomas associated with the rare phenomenon of cartilaginous differentiation have been documented in the literature. Currently, only one of these cases has been cytogenetically analyzed, and the analysis indicated that it was a type IITLS-CHOP fusion transcript in both the typical myxoid liposarcoma and cartilaginous areas. This study presents a second report of myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation, and includes a cytogenetical analysis of both the myxoid and cartilaginous areas.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
Naoki Kojima, Takashi Kubo, Taisuke Mori, Kaishi Satomi, Yuko Matsushita, Shintaro Iwata, Yasushi Yatabe, Koichi Ichimura, Akira Kawai, Hitoshi Ichikawa, Akihiko Yoshida
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 71. CrossRef - The Conundrum of Dedifferentiation in a Liposarcoma at a Peculiar Location: A Case Report and Literature Review
Ana-Maria Ciongariu, Adrian-Vasile Dumitru, Cătălin Cîrstoiu, Bogdan Crețu, Maria Sajin, Dana-Antonia Țăpoi, Aminia-Diana Ciobănoiu, Adrian Bejenariu, Andrei Marin, Mariana Costache
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 967. CrossRef - Myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation showing DDIT3 rearrangement
Kayo Suzuki, Taketoshi Yasuda, Kenta Watanabe, Takeshi Hori, Masahiko Kanamori, Tomoatsu Kimura
Oncology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
- Radiotherapy Response in Microsatellite Instability Related Rectal Cancer
- Joo-Shik Shin, Thein Ga Tut, Tao Yang, C. Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):1-8. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.1
- 12,097 View
- 99 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Preoperative radiotherapy may improve the resectability and subsequent local control of rectal cancers. However, the extent of radiation induced regression in these tumours varies widely between individuals. To date no reliable predictive marker of radiation sensitivity in rectal cancer has been identified. At the cellular level, radiation injury initiates a complex molecular network of DNA damage response (DDR) pathways that leads to cell cycle arrest, attempts at re-constituting the damaged DNA and should this fail, then apoptosis. This review presents the details which suggest the roles of DNA mismatch repair proteins, the lack of which define a distinct subset of colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability (MSI), in the DDR pathways. Hence routine assessment of the MSI status in rectal cancers may potentially serve as a predictor of radiotherapy response, thereby improving patient stratification in the administration of this otherwise toxic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy up-regulates PD-L1 in radioresistant colorectal cancer
Sung Uk Bae, Hye Won Lee, Jee Young Park, Incheol Seo, Jae-Min Cho, Jin Young Kim, Ju Yup Lee, Yoo Jin Lee, Seong Kyu Baek, Nam Kyu Kim, Sang Jun Byun, Shin Kim
Clinical and Translational Radiation Oncology.2025; 51: 100906. CrossRef - Incidence and Outcomes of Patients With Mismatch Repair Deficient Rectal Cancer Operated in 2016: A Nationwide Cohort From The Netherlands
Eline G.M. van Geffen, Cornelis R.C. Hogewoning, Sanne-Marije J.A. Hazen, Tania C. Sluckin, Marilyne M. Lange, Petur Snaebjornsson, Regina G.H. Beets-Tan, Corrie A.M. Marijnen, Cornelis Verhoef, Myriam Chalabi, Pieter J. Tanis, Miranda Kusters, Tjeerd S.
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2025; 24(2): 188. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and mucin expression of early papillary gastric adenocarcinoma
Jiaqi Chen, Xiujie Cui, Chengjun Zhou, Mulan Jin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Colorectal cancers associated with mismatch repair deficiency
Mingzhu Sun, Kevin Monahan, Jayne Moquet, Stephen Barnard
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential risks associated with the use of ionizing radiation for imaging and treatment of colorectal cancer in Lynch syndrome patients
Mingzhu Sun, Jayne Moquet, Michele Ellender, Simon Bouffler, Christophe Badie, Rachel Baldwin-Cleland, Kevin Monahan, Andrew Latchford, David Lloyd, Susan Clark, Nicola A. Anyamene, Elizabeth Ainsbury, David Burling
Familial Cancer.2023; 22(1): 61. CrossRef - Not All Patients With Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Benefit From Neoadjuvant Therapy
Carolyn Chang, Jonathan T. Bliggenstorfer, Jessie Liu, Jennifer Shearer, Paul Dreher, Katherine Bingmer, Sharon L. Stein, Emily Steinhagen
The American Surgeon™.2023; 89(11): 4327. CrossRef - Survival outcomes in locally advanced dMMR rectal cancer: surgery plus adjunctive treatment vs. surgery alone
Kemin Ni, Yixiang Zhan, Zhaoce Liu, Zhen Yuan, Shuyuan Wang, Xuan-zhu Zhao, Hangyu Ping, Yaohong Liu, Wanting Wang, Suying Yan, Ran Xin, Qiurong Han, Qinghuai Zhang, Guoxun Li, Xipeng Zhang, Guihua Wang, Zili Zhang, Hong Ma, Chunze Zhang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Rectal Cancer in Patients with Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer Compared with Sporadic Cases: Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation and Local Recurrence
Khaled M Madbouly, Sameh Hany Emile, Yasmine Amr Issa
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 234(5): 793. CrossRef - Molecular Recognition and Quantification of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and KRAS in Biological Samples
Raluca-Ioana Stefan-van Staden, Ruxandra-Maria Ilie-Mihai, Maria Coros, Stela Pruneanu
ECS Sensors Plus.2022; 1(3): 031606. CrossRef - Magnetic Resonance Imaging Downstaging, Pathological Response, and Microsatellite Instability Status in Patients with Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma Rectum Undergoing Preoperative Long-course Chemoradiation
B. Rajkrishna, Saikat Das, Dipti Masih, Tharani Putta, Rajat Raghunath, Thomas Samuel Ram
Current Medical Issues.2022; 20(3): 154. CrossRef - Biomarkers and cell-based models to predict the outcome of neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer patients
Aylin Alkan, Tobias Hofving, Eva Angenete, Ulf Yrlid
Biomarker Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microsatellite Instability (MSI) as an Independent Predictor of Pathologic Complete Response (PCR) in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Shaakir Hasan, Paul Renz, Rodney E. Wegner, Gene Finley, Moses Raj, Dulabh Monga, James McCormick, Alexander Kirichenko
Annals of Surgery.2020; 271(4): 716. CrossRef - Delivery of Personalized Care for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Incorporating Pathological, Molecular Genetic, and Immunological Biomarkers Into the Multimodal Paradigm
Éanna J. Ryan, Ben Creavin, Kieran Sheahan
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of mismatch repair status with survival and response to neoadjuvant chemo(radio)therapy in rectal cancer
Shu-Biao Ye, Yi-Kan Cheng, Lin Zhang, Yi-Feng Zou, Ping Chen, Yan-Hong Deng, Yan Huang, Jian-Hong Peng, Xiao-Jian Wu, Ping Lan
npj Precision Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of expression of MMR proteins and clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancer
Renu Verma, Puja Sakhuja, Ritu Srivastava, Prakash Chand Sharma
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Mismatch Repair–Deficient Rectal Cancer and Resistance to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Andrea Cercek, Gustavo Dos Santos Fernandes, Campbell S. Roxburgh, Karuna Ganesh, Shu Ng, Francisco Sanchez-Vega, Rona Yaeger, Neil H. Segal, Diane L. Reidy-Lagunes, Anna M. Varghese, Arnold Markowitz, Chao Wu, Bryan Szeglin, Charles-Etienne Gabriel Sauvé
Clinical Cancer Research.2020; 26(13): 3271. CrossRef - The Mismatch Repair System (MMR) in Head and Neck Carcinogenesis and Its Role in Modulating the Response to Immunotherapy: A Critical Review
Maria Cilona, Luca Giovanni Locatello, Luca Novelli, Oreste Gallo
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 3006. CrossRef - Genetics of rectal cancer and novel therapies: primer for radiologists
Sebastian Mondaca, Rona Yaeger
Abdominal Radiology.2019; 44(11): 3743. CrossRef - Mismatch repair deficiency as a predictive marker for response to adjuvant radiotherapy in endometrial cancer
Casper Reijnen, Heidi V.N. Küsters-Vandevelde, Clemens F. Prinsen, Leon F.A.G. Massuger, Marc P.M.L. Snijders, Stefan Kommoss, Sara Y. Brucker, Janice S. Kwon, Jessica N. McAlpine, Johanna M.A. Pijnenborg
Gynecologic Oncology.2019; 154(1): 124. CrossRef - Mismatch Repair System Deficiency Is Associated With Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Nicolas Meillan, Dewi Vernerey, Jérémie H. Lefèvre, Gilles Manceau, Magali Svrcek, Jeremy Augustin, Jean-François Fléjou, Olivier Lascols, Jean-Marc Simon, Romain Cohen, Philippe Maingon, Jean-Baptiste Bachet, Florence Huguet
International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics.2019; 105(4): 824. CrossRef - Promoter methylation and expression of DNA repair genes MGMT and ERCC1 in tissue and blood of rectal cancer patients
Sally M. Shalaby, Amal S. El-Shal, Lobna A. Abdelaziz, Eman Abd-Elbary, Mostafa M. Khairy
Gene.2018; 644: 66. CrossRef - RBBP6 increases radioresistance and serves as a therapeutic target for preoperative radiotherapy in colorectal cancer
Chao Xiao, Yupeng Wang, Miao Zheng, Jian Chen, Guohe Song, Zhijie Zhou, Chongzhi Zhou, Xing Sun, Lin Zhong, Erxun Ding, Yi Zhang, Liu Yang, Gang Wu, Shifeng Xu, Hong Zhang, Xiaoliang Wang
Cancer Science.2018; 109(4): 1075. CrossRef - Baseline MAPK signaling activity confers intrinsic radioresistance to KRAS-mutant colorectal carcinoma cells by rapid upregulation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K)
Stefan Eder, Annette Arndt, Andreas Lamkowski, Wassiliki Daskalaki, Alexis Rump, Markus Priller, Felicitas Genze, Eva Wardelmann, Matthias Port, Konrad Steinestel
Cancer Letters.2017; 385: 160. CrossRef - The current value of determining the mismatch repair status of colorectal cancer: A rationale for routine testing
E. Ryan, K. Sheahan, B. Creavin, H.M. Mohan, D.C. Winter
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2017; 116: 38. CrossRef - Exploration of Mutation and DNA Methylation of Polo-Like Kinase 1 (PLK1) in Colorectal Cancer
Wayne Ng, Joo-Shik Shin, Bin Wang, Cheok Soon Lee
Open Journal of Pathology.2017; 07(03): 45. CrossRef - Expression of Mismatch Repair Proteins in Early and Advanced Gastric Cancer in Poland
Katarzyna Karpińska-Kaczmarczyk, Magdalena Lewandowska, Małgorzata Ławniczak, Andrzej Białek, Elżbieta Urasińska
Medical Science Monitor.2016; 22: 2886. CrossRef - DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Rectal Cancer: Benchmarking Its Impact on Prognosis, Neoadjuvant Response Prediction, and Clinical Cancer Genetics
Nicole de Rosa, Miguel A. Rodriguez-Bigas, George J. Chang, Jula Veerapong, Ester Borras, Sunil Krishnan, Brian Bednarski, Craig A. Messick, John M. Skibber, Barry W. Feig, Patrick M. Lynch, Eduardo Vilar, Y. Nancy You
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2016; 34(25): 3039. CrossRef -
miRNA-148b regulates radioresistance in non-small lung cancer cells via regulation of MutL homologue 1
Guangsheng Zhai, Gaozhong Li, Bo Xu, Tongfu Jia, Yinping Sun, Jianbo Zheng, Jianbin Li
Bioscience Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive and prognostic biomarkers for neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
S.H. Lim, W. Chua, C. Henderson, W. Ng, J.-S. Shin, L. Chantrill, R. Asghari, C.S. Lee, K.J. Spring, P. de Souza
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2015; 96(1): 67. CrossRef - Potential of DNA methylation in rectal cancer as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers
Ruth Exner, Walter Pulverer, Martina Diem, Lisa Spaller, Laura Woltering, Martin Schreiber, Brigitte Wolf, Markus Sonntagbauer, Fabian Schröder, Judith Stift, Fritz Wrba, Michael Bergmann, Andreas Weinhäusel, Gerda Egger
British Journal of Cancer.2015; 113(7): 1035. CrossRef - Study of Liver Transplant Rejection in Alcoholism-Induced Cirrhosis
J. Tinoco González, C. Bernal Bellido, G. Jimenez Riera, V. Camacho Marente, L.M. Marín Gómez, G. Suárez Artacho, J.M. Álamo Martínez, J. Serrano Díez-Canedo, R.J. Padillo Ruíz, M.A. Gómez Bravo
Transplantation Proceedings.2013; 45(10): 3650. CrossRef
- Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy up-regulates PD-L1 in radioresistant colorectal cancer
- Difference of Genome-Wide Copy Number Alterations between High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions and Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Uterine Cervix
- Bum Hee Lee, Sangyoung Roh, Yu Im Kim, Ahwon Lee, Su Young Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):123-130. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.123
- 8,452 View
- 46 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background About 10% of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs) progress to invasive carcinomas within 2-10 years. By delineating the events that occur in the early stage of the invasion, the pathogenesis of cervical cancer could be better understood. This will also propose the possible methods for inhibiting the tumor invasion and improving the survival of patients.
Methods We compared the genomic profiles between the HSIL and the invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) using an array comparative genomic hybridization. Using recurrently altered genes, we performed a principal component analysis to see variation of samples in both groups. To find possibly affected pathways by altered genes, we analyzed genomic profiles with the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway database and GOEAST software.
Results We found 11q12.3 and 2p24.1 regions have recurrent copy number gains in both groups. 16p12-13 and 20q11-13 regions showed an increased copy number only in cases of HSIL. 1q25.3 and 3q23-29 regions showed copy number gains only in cases of SCC. Altered genes in the SCC group were related to the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and the RNA transport. Altered genes in the HSIL group were related to the ubiquitin mediated proteolysis and cell adhesion molecules.
Conclusions Our results showed not only that gains in 11q12.3 and 2p24.1 were early events occurring in the premalignant lesions and then maintained in cases of SCC but also that gains in 1q25.3 and 3q23-29 were late events occurring after invasion in those of SCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytokeratin and protein expression patterns in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity provide evidence for two distinct pathogenetic pathways
GESCHE FROHWITTER, HORST BUERGER, PAUL J. VAN DIEST, EBERHARD KORSCHING, JOHANNES KLEINHEINZ, THOMAS FILLIES
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(1): 107. CrossRef - 'Drawing' a Molecular Portrait of CIN and Cervical Cancer: a Review of Genome-Wide Molecular Profiling Data
Olga V Kurmyshkina, Pavel I Kovchur, Tatyana O Volkova
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(11): 4477. CrossRef
- Cytokeratin and protein expression patterns in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity provide evidence for two distinct pathogenetic pathways
- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
- Seung Yeon Ha, Joungho Han, Wan-Seop Kim, Byung Seong Suh, Mee Sook Roh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):42-47. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.42
- 9,571 View
- 48 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Distinguishing small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) of the lung is difficult with little information about interobserver variability.
Methods One hundred twenty-nine cases of resected SCLC and LCNEC were independently evaluated by four pathologists and classified according to the 2004 World Health Organization criteria. Agreement was regarded as "unanimous" if all four pathologists agreed on the classification. The kappa statistic was calculated to measure the degree of agreement between pathologists. We also measured cell size using image analysis, and receiver-operating-characteristic curve analysis was performed to evaluate cell size in predicting the diagnosis of high-grade neuroendocrine (NE) carcinomas in 66 cases.
Results Unanimous agreement was achieved in 55.0% of 129 cases. The kappa values ranged from 0.35 to 0.81. Morphometric analysis reaffirmed that there was a continuous spectrum of cell size from SCLC to LCNEC and showed that tumors with cells falling in the middle size range were difficult to categorize and lacked unanimous agreement.
Conclusions Our results provide an objective explanation for considerable interobserver variability in the diagnosis of high-grade pulmonary NE carcinomas. Further studies would need to define more stringent and objective definitions of cytologic and architectural characteristics to reliably distinguish between SCLC and LCNEC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case report: A patient with EGFR L861Q positive adenosquamous lung carcinoma transforming into large cell neuroendocrine cancer after treatment with Almonertinib
Kele Cheng, Yong Zhu, Ran Sang, Zhongsheng Kuang, Yang Cao
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning–Based Retinoblastoma Protein Subtyping of Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma on Small Hematoxylin and Eosin–Stained Specimens
Teodora E. Trandafir, Frank W.J. Heijboer, Farhan Akram, Jules L. Derks, Yunlei Li, Lisa M. Hillen, Ernst-Jan M. Speel, Zsolt Megyesfalvi, Balazs Dome, Andrew P. Stubbs, Anne-Marie C. Dingemans, Jan H. von der Thüsen
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(9): 104192. CrossRef - Treatment outcomes in patients with stage IV large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a nationwide registry study
Frank W.J. Heijboer, Jules L. Derks, Francien H. van Nederveen, Lisa M. Hillen, Michael A. den Bakker, Teodora Radonic, Ronald A.M. Damhuis, Ernst-Jan M. Speel, Jan H. von der Thüsen, Anne-Marie C. Dingemans
Lung Cancer.2025; 210: 108830. CrossRef - Updates on lung neuroendocrine neoplasm classification
Giulia Vocino Trucco, Luisella Righi, Marco Volante, Mauro Papotti
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 67. CrossRef - Recent advancement of HDAC inhibitors against breast cancer
Syed Abdulla Mehmood, Kantrol Kumar Sahu, Sounok Sengupta, Sangh Partap, Rajshekhar Karpoormath, Brajesh Kumar, Deepak Kumar
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genomic Feature of a Rare Case of Mix Small-Cell and Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Lung Carcinoma: A Case Report
Youcai Zhu, Feng Zhang, Dong Yu, Fang Wang, Manxiang Yin, Liangye Chen, Chun Xiao, Yueyan Huang, Feng Ding
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Lung: What We Learned about It?
Luisella Righi, Marco Volante, Mauro Papotti
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(4): 257. CrossRef - Hierarchical identification of a transcriptional panel for the histological diagnosis of lung neuroendocrine tumors
Juxuan Zhang, Jiaxing Deng, Xiao Feng, Yilong Tan, Xin Li, Yixin Liu, Mengyue Li, Haitao Qi, Lefan Tang, Qingwei Meng, Haidan Yan, Lishuang Qi
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Staining With Neuroendocrine Markers is Essential in the Diagnosis of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Esophagogastric Junction
Dea N.M. Jepsen, Anne-Marie K. Fiehn, Rajendra S. Garbyal, Ulla Engel, Jakob Holm, Birgitte Federspiel
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2021; 29(6): 454. CrossRef - Improving differential diagnosis of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and small cell lung cancer via a transcriptomic, biological pathway-based machine learning model
Junhong Guo, Likun Hou, Wei Zhang, Zhengwei Dong, Lei Zhang, Chunyan Wu
Translational Oncology.2021; 14(12): 101222. CrossRef - Are Neuroendocrine Negative Small Cell Lung Cancer and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma with WT RB1 two Faces of the Same Entity?
Dmitriy Sonkin, Anish Thomas, Beverly A Teicher
Lung Cancer Management.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Ki-67 labeling index of neuroendocrine tumors of the lung has a high level of correspondence between biopsy samples and surgical specimens when strict counting guidelines are applied
Alessandra Fabbri, Mara Cossa, Angelica Sonzogni, Mauro Papotti, Luisella Righi, Gaia Gatti, Patrick Maisonneuve, Barbara Valeri, Ugo Pastorino, Giuseppe Pelosi
Virchows Archiv.2017; 470(2): 153. CrossRef - The Use of Immunohistochemistry Improves the Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Differential Diagnosis. An International Reproducibility Study in a Demanding Set of Cases
Erik Thunnissen, Alain C. Borczuk, Douglas B. Flieder, Birgit Witte, Mary Beth Beasley, Jin-Haeng Chung, Sanja Dacic, Sylvie Lantuejoul, Prudence A. Russell, Michael den Bakker, Johan Botling, Elisabeth Brambilla, Erienne de Cuba, Kim R. Geisinger, Kenzo
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(2): 334. CrossRef - Reply to Letter “The Use of Immunohistochemistry Improves the Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Differential Diagnosis. An International Reproducibility Study in a Demanding Set of Cases.”
Erik Thunnissen, Birgit I. Witte, Masayuki Noguchi, Yasushi Yatabe
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(6): e70. CrossRef - What clinicians are asking pathologists when dealing with lung neuroendocrine neoplasms?
Giuseppe Pelosi, Alessandra Fabbri, Mara Cossa, Angelica Sonzogni, Barbara Valeri, Luisella Righi, Mauro Papotti
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(6): 469. CrossRef - Unraveling Tumor Grading and Genomic Landscape in Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors
Giuseppe Pelosi, Mauro Papotti, Guido Rindi, Aldo Scarpa
Endocrine Pathology.2014; 25(2): 151. CrossRef - Grading the neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: an evidence-based proposal
G Rindi, C Klersy, F Inzani, G Fellegara, L Ampollini, A Ardizzoni, N Campanini, P Carbognani, T M De Pas, D Galetta, P L Granone, L Righi, M Rusca, L Spaggiari, M Tiseo, G Viale, M Volante, M Papotti, G Pelosi
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2014; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Controversial issues and new discoveries in lung neuroendocrine tumors
Giuseppe Pelosi, Kenzo Hiroshima, Mari Mino-Kenudson
Diagnostic Histopathology.2014; 20(10): 392. CrossRef - BAI3, CDX2 and VIL1: a panel of three antibodies to distinguish small cell from large cell neuroendocrine lung carcinomas
Muhammad F Bari, Helen Brown, Andrew G Nicholson, Keith M Kerr, John R Gosney, William A Wallace, Irshad Soomro, Salli Muller, Danielle Peat, Jonathan D Moore, Lesley A Ward, Maxim B Freidin, Eric Lim, Manu Vatish, David R J Snead
Histopathology.2014; 64(4): 547. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine tumours—challenges in the diagnosis and classification of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
M A den Bakker, F B J M Thunnissen
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2013; 66(10): 862. CrossRef - Morphologic Analysis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Seung Seok Lee, Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk An, Mee Sook Roh, Chang Won Ha, Jungho Han
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(1): 16. CrossRef - Altered expression of microRNA miR‐21, miR‐155, and let‐7a and their roles in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors
Hyoun Wook Lee, Eun Hee Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Chang Hun Lee, Hee Kyung Chang, Sunhee Chang, Kun Young Kwon, Il Seon Hwang, Mee Sook Roh, Jeong Wook Seo
Pathology International.2012; 62(9): 583. CrossRef
- Case report: A patient with EGFR L861Q positive adenosquamous lung carcinoma transforming into large cell neuroendocrine cancer after treatment with Almonertinib
- Nuclear Image Analysis Study of Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Meeja Park, Taehwa Baek, Jongho Baek, Hyunjin Son, Dongwook Kang, Jooheon Kim, Hyekyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):38-41. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.38
- 8,076 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background There is a subjective disagreement about nuclear chromatin in the field of pathology. Objective values of red, green, and blue (RGB) light intensities for nuclear chromatin can be obtained through a quantitative analysis using digital images.
Methods We examined 10 cases of well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the rectum, small cell lung carcinomas, and moderately differentiated squamous cell lung carcinomas respectively. For each case, we selected 30 representative cells and captured typical microscopic findings. Using an image analyzer, we determined the longest nuclear line profiles and obtained graph files and Excel data on RGB light intensities. We assessed the meaningful differences in graph files and Excel data among the three different tumors.
Results The nucleus of hematoxylin and eosin-stained tumor cells was expressed as a combination of RGB light sources. The highest intensity was from blue, whereas the lowest intensity was from green. According to the graph files, green showed the most noticeable change in the light intensity, which is consistent with the difference in standard deviations.
Conclusions The change in the light intensity for green has an important implication for differentiating between tumors. Specific features of the nucleus can be expressed in specific values of RGB light intensities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hyekyung Lee, Tae Hwa Baek, Meeja Park, Seung Yun Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Dong Wook Kang, Joo Heon Kim, Soo Young Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(5): 355. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef
- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Copy Number Alterations of BCAS1 in Squamous Cell Carcinomas.
- Yu Im Kim, Ahwon Lee, Jennifer Kim, Bum Hee Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Suk Woo Nam, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo, Jung Young Lee, Sang Ho Kim, Su Young Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):271-275.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.271
- 4,467 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Breast carcinoma amplified sequence 1 (BCAS1), located in 20q13, is amplified and overexpressed in breast cancers. Even though BCAS1 is expected to be an oncogene candidate, its contribution to tumorigenesis and copy number status in other malignancies is not reported. To elucidate the role of BCAS1 in squamous cell carcinomas, we investigated the copy number status and expression level of BCAS1 in several squamous cell carcinoma cell lines, normal keratinocytes and primary tumors.
METHODS
We quantitated BCAS1 gene by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Expression level of BCAS1 was measured by real-time reverse transcription-PCR and immunoblot.
RESULTS
Seven (88%) of 8 squamous cell carcinoma cell lines showed copy number gain of BCAS1 with various degrees. BCAS1 gene in primary tumors (73%) also showed copy number gain. However, expression level did not show a linear correlation with copy number changes.
CONCLUSIONS
We identified copy number gain of BCAS1 in squamous cell carcinomas. Due to lack of linear correlation between copy numbers of BCAS1 and its expression level, we could not confirm that the overexpression of BCAS1 is a common finding in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. However, this study shows that the copy number gain of BCAS1 is a common finding in squamous cell carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electrochemical Approaches for Preparation of Tailor-Made Amino Acids
Nana Wang, Jingcheng Xu, Haibo Mei, Hiroki Moriwaki, Kunisuke Izawa, Vadim A. Soloshonok, Jianlin Han
Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry.2021; 41(8): 3034. CrossRef
- Electrochemical Approaches for Preparation of Tailor-Made Amino Acids
- Morphometric Analysis for Pulmonary Small Cell Carcinoma Using Image Analysis.
- Sun Min Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Sanghui Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):87-91.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.87
- 4,309 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
There are few studies of how to diagnose small cell lung cancer in cytological tests through morphometric analysis. We tried to measure and analyze characteristics of small cell carcinoma in lung by image analysis.
METHODS
We studied three types of cytologic specimens from 89 patients who were diagnosed with small cell lung cancer by immunohistochemistry. We measured area, perimeter, maximal length and maximal width of cells from small cell carcinoma using image analysis.
RESULTS
In lung aspirates, the nuclear mean area, perimeter, maximal length and maximal width of small cell lung cancer were 218.69 microm2, 55 microm, 18.48 microm and 14.65 microm. In bronchial washings, nuclear measurements were 194.66 microm2, 50.07 microm, 16.27 microm and 14.1 microm. In pleural fluid, values were 177.85 microm2, 48.09 microm, 15.7 microm and 13.37 microm.
CONCLUSIONS
Nuclear size of small cell lung carcinoma is variable and depends on the cytology method. Nuclei are spindle-shaped and larger in small cell carcinoma from lung aspirates than in bronchial washings or pleural fluid. The cytoplasms of the cells in bronchial washings and pleural fluid were swollen. Therefore, one should consider morphologic changes when trying to diagnose small cell lung cancer through cytological tests. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
Seung Yeon Ha, Joungho Han, Wan-Seop Kim, Byung Seong Suh, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 42. CrossRef
- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
- Immunohistochemical Identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Liquid-based Cytology of Bronchoalveolar Lavage: Nine Cases Report.
- Jeong Hyeon Lee, Ji Young Lee, Mi Ran Shin, Hyeong Kee Ahn, Chul Whan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):115-118.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.115
- 4,794 View
- 48 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is specific to humans. PCP could be a source of opportunistic infection in adults that are immunosuppressed and children with prematurity or malnutrition. The diagnosis should be confirmed by identification of the causative organism, by analysis of the sputum, a bronchoalveolar lavage or a tissue biopsy. In both histologic and cytologic specimens, the cysts are contained within frothy exudates, which form aggregated clumps. The cysts often collapse forming crescent-shaped bodies that resemble ping-pong balls. We recently diagnosed nine cases of PCP using an immunohistochemical stain for Pneumocystis. The patients consisted of five human immunodeficiency virus positive individuals, two renal transplant recipients, and two patients with a malignant disease. All nine patients were infected with P. jirovecii, which was positive for monoclonal antibody 3F6. In conclusion, the immunohistochemical stain used in this report is a new technique for the detection of P. jirovecii infection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic Changes in Serum Metabolome of Beagle Dogs Fed Black Ginseng
Dahye Yoon, Ye Jin Kim, Wan Kyu Lee, Bo Ram Choi, Seon Min Oh, Young Seob Lee, Jae Kwang Kim, Dae Young Lee
Metabolites.2020; 10(12): 517. CrossRef - Effects of Red or Black Ginseng Extract in a Rat Model of Inflammatory Temporomandibular Joint Pain
Hyeon-Jeong Lee, Yun-Kyung Kim, Ja-Hyeong Choi, Jung-Hwa Lee, Hye-Jin Kim, Mi-Gyung Seong, Min-Kyung Lee
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2017; 17(1): 65. CrossRef - Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cytology in the Diagnosis ofPneumocystis jiroveciiPneumonia: A Review of 30 Cases
Ji-Youn Sung, Joungho Han, Young Lyun Oh, Gee Young Suh, Kyeongman Jeon, Taeeun Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2011; 71(5): 322. CrossRef
- Metabolic Changes in Serum Metabolome of Beagle Dogs Fed Black Ginseng
- Expression of Minichromosome Maintenance Protein 7 and Smad 4 in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus.
- Ji Hyun Ahn, Hee Kyung Chang
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):346-353.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.346
- 4,605 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Minichromosome maintenance protein 7 (MCM 7) performs a direct role in the initiation of DNA replication, which suggests that it may prove useful as a marker of cell proliferation. Smad 4 is a tumor suppressor gene that mediates the transforming growth factor beta pathway. The principal objective of this study was to characterize the expression of MCM 7 and Smad 4 and to analyze their relationship to clinicopathological parameters in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
METHODS
Expression levels of MCM 7 and Smad 4 were evaluated via immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues from 67 cases of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
RESULTS
High levels of MCM 7 expression were detected in 53 cases (74.6%), and were associated with higher T stages (p = 0.030). Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated that patients with higher levels of MCM 7 expression had poorer prognoses, although this association was not significant (p = 0.086). Loss of Smad 4 expression was noted in 18 cases (23.4%), and was not associated with clinicopathological characteristics, including MCM 7 expression, or prognosis.
CONCLUSIONS
MCM 7 expression is associated with the invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Altered expression of Smad 4 does not appear to have pathobiological significance in esophageal carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- scDiffCoAM: A complete framework to identify potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using scRNA-Seq data analysis
Manaswita Saikia, Dhruba K Bhattacharyya, Jugal K Kalita
Journal of Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 in benign and malignant salivary gland tumors
Nafiseh Shamloo, Nasim Taghavi, Samane Ahmadi, Soudeh Shalpoush
Dental Research Journal.2022; 19(1): 17. CrossRef - Expression of Minichromosome Maintenance Proteins in Actinic Keratosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Jelena Stojkovic-Filipovic, Dimitrije Brasanac, Martina Bosic, Novica Boricic, Branislav Lekic
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2018; 26(3): 165. CrossRef - Ki-67 protein predicts survival in oral squamous carcinoma cells: an immunohistochemical study
Verena Karla Monteiro LOPES, Adriana Souza de JESUS, Lucas Lacerda de SOUZA, Ligia Akiko Ninokata MIYAHARA, Douglas Magno GUIMARÃES, Helder Antônio Rebelo PONTES, Flavia Sirotheau Correa PONTES, Pedro Luiz de CARVALHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of MCM2 in Nonmelanoma Epithelial Skin Cancers
Asmaa Gaber Abdou, Mohammed Gaber Abd Elwahed, Marwa Mohammed Serag El-dien, Dina Sharaf Eldien
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2014; 36(12): 959. CrossRef
- scDiffCoAM: A complete framework to identify potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using scRNA-Seq data analysis
- Complex Bronchopulmonary Foregut Malformation: Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration Communicating with an Esophageal Duplication Cyst: A Case Report.
- Soyoung Im, Sun Mi Lee, Ji Han Jung, Jinyoung Yoo, Kyu Do Cho, Seok Jin Kang, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):207-210.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.207
- 4,489 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a case of a rare, complex bronchopulmonary foregut malformation (BPFM) that was composed of an extralobar pulmonary sequestration communicating with an esophageal duplication cyst. A 33-year-old female presented with an incidentally detected chest mass. The computed tomography revealed a 7.5 x 4.0 cm sized heterogeneous, solid and cystic lesion in the right superior mediastinum. Surgical resection demonstrated the solid portion to be isolated lung tissue invested in its own pleura. A unilocular cyst was communicating with the bronchus of the sequestrated lung, and microscopically the cyst was lined by squamous epithelium overlying the thick layers of smooth muscle. This case is important for understanding the spectrum of BPFMs and for differentiating a mediastinal mass, especially one at the unusual location.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prenatal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and therapeutic options for fetal thoracic anomalies: a pictorial essay
Pablo Caro-Domínguez, Teresa Victoria, Pierluigi Ciet, Estrella de la Torre, Ángel Chimenea Toscano, Lutgardo García Diaz, José Antonio Sainz-Bueno
Pediatric Radiology.2023; 53(10): 2106. CrossRef - Concurrent bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: a rare case of right-sided extralobar pulmonary sequestration and bronchogenic cyst
Carolyn Hanna, Priya G. Sharma, Moiz M. Mustafa, Jennifer Reppucci, Archana Shenoy, Dhanashree Rajderkar
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prenatal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and therapeutic options for fetal thoracic anomalies: a pictorial essay
- Adnexal Clear Cell Carcinoma with Comedonecrosis: A Case Report.
- Seo Hee Kim, Sun Hee Han, Jung Suk An, Ju Han Lee, Eung Seok Lee, Heum Rye Park, Young Sik Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):92-96.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.92
- 4,762 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adnexal clear cell carcinoma with comedonecrosis (ACCCC) is a very rare malignancy of the skin with an aggressive clinical course and a predilection for the scalp. This is the first reported case of ACCCC in Korea. A 79-year-old male presented with left abdominal masses that proved to be two subcutaneous nodules. The tumors histologically consisted of epithelial nests that showed a distinctive zonal arrangement. The centrally located clear cell areas with comedonecroses were merged with the peripheral squamoid cells, often exhibiting retraction artifacts and an infiltrating border. Nuclear pleomorphism and frequent mitoses were prominent. The clear cells were immunopositive for carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen. We report here on a case of ACCCC involving the abdominal skin, and this tumor should be distinguished from the more indolent squamous cell and tricholemmal carcinomas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adnexal Clear Cell Carcinoma Exhibiting Comedonecrosis of the Ear: A Rare Case Treated With Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Helen Z Chen, Mohamad Jabin, Michelle Tarbox, Russell Akin, Ashley Sturgeon
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adnexal Clear Cell Carcinoma Exhibiting Comedonecrosis of the Ear: A Rare Case Treated With Mohs Micrographic Surgery
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Endometrial Adenocarcinomas in Young Women.
- Gawon Choi, Jeong Won Kim, Shin Kwang Khang, Kyu Rae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(5):441-447.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.5.441
- 4,130 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Despite an increased incidence of endometrial carcinomas in young Korean women, clinicopathologic characteristics and treatment outcomes have not been analyzed.
METHODS
We investigated clinicopathologic characteristics of endometrial carcinoma in 48 women who were under the age of 40 in order to determine treatment guideline.
RESULTS
According To The Criteria Of The Korean Society For Obesity, 70.8% Of Study Patients Were Overweight Or Obese, With An Average Body Mass Index (Bmi) Of 26.0 kg/m2. Twelve Patients Received Progesterone Treatment Only, And 6 Of Them Later Had Successful Pregnancies. The Histologic Subtype Was Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma In All Patients. Figo Stages Were 1A(41.7%), 1B(47.1%), II (2.8%), IIB2.8%), IIIA(2.8%), And IIIC (2.8%). Figo Grades Were Grade 1 (79%) Or 2 (21%). The Average Depth Of Invasion, Excluding Stage 1a, Was 4.6 Mm In The Hysterectomy Specimens. Two Patients Were Given Post-operative Radiation Treatment And 4 Were Treated With Chemotherapy. All But One Case Had An Uneventful Postoperative Course During Follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
A majority of endometrial carcinomas in young Korean women were associated with an early FIGO stage, favorable histologic subtype and grades, and a good prognosis. Progesterone treatment with close observation was a successful treatment option in a selected group of young patients.
- Microscopic Colitis: The Pathologic Features of 24 Korean Patients.
- Sun Ah Lee, Min Jung Kang, Sung Ae Jung, Heasoo Koo
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(2):133-138.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.2.133
- 4,160 View
- 25 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The clinical presentation of microscopic colitis (MC) consists of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea for weeks or months at a time, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits with a normal mucosal appearance upon performing colonoscopy. MC includes two relatively well established histopathologic entities: collagenous colitis (CC) and lymphocytic colitis (LC) as well as atypical forms. The recognition of the microscopic findings of this heterogeneous entity is very important for making the correct diagnosis and providing proper treatment.
METHODS
We studied the colonoscopic biopsy specimens that were obtained from 26 patients who had clinical findings that were suggestive of MC.
RESULTS
Fifteen patients (M:F=9:6) and 9 patients (M:F=5:4) showed the microscopic features of LC and MC, not otherwise specified, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The clinicopathologic findings (the incidence of the subtypes, the patients' ages and the male/female ratio) of the 24 cases of MC in this study showed differences from the previously reported findings from other countries. Further studies with a sufficient number of patients from multi-centers would be necessary to confirm the regional or ethnic influence. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcal Enterocolitis with Subsequent Development of Lymphocytic Colitis
Joong Ho Bae, Dong Soo Han, Hye Sun Park, Yil Sik Hyun, Tae Yeob Kim, Chang Soo Eun, Yong Cheol Jeon, Joo Hyun Sohn
Intestinal Research.2011; 9(2): 139. CrossRef
- A Case of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcal Enterocolitis with Subsequent Development of Lymphocytic Colitis
- Detecting Malignant Urothelial Cells by Morphometric Analysis of ThinPrep(R) Liquid-based Urine Cytology Specimens.
- Bong Kyung Shin, Young Suk Lee, Hoiseon Jeong, Sang Ho Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Aree Kim, Insun Kim, Han Kyeom Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2008;19(2):136-143.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3338/kjc.2008.19.2.136
- 3,457 View
- 23 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Urothelial carcinoma accounts for 90% of all the cases of bladder cancer. Although many cases can be easily managed by local excision, urothelial carcinoma rather frequently recurs, tends to progress to muscle invasion, and requires regular follow-ups. Urine cytology is a main approach for the follow-up of bladder tumors. It is noninvasive, but it has low sensitivity of around 50% with using the conventional cytospin preparation. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) has been developed as a replacement for the conventional technique. We compared the cytomorphometric parameters of ThinPrep(R) and cytospin preparation urine cytology to see whether there are definite differences between the two methods and which technique allows malignant cells to be more effectively discriminated from benign cells. The nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio value, as measured by digital image analysis, was efficient for differentiating malignant and benign urothelial cells, and this was irrespective of the preparation method and the tumor grade. Neither the ThinPrep(R) nor the conventional preparation cytology was definitely superior for distinguishing malignant cells from benign cells by cytomorphometric analysis of the adequately preserved cells. However, the ThinPrep(R) preparation showed significant advantages when considering the better preservation and cellularity with a clear background.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utility of Image Morphometry in the Atypical Urothelial Cells and High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Categories of the Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology
K.C. Sharan, Manish Rohilla, Pranab Dey, Radhika Srinivasan, Nandita Kakkar, Ravimohan S. Mavuduru
Journal of Cytology.2024; 41(3): 137. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef - A Comparison Between ThinPrep Monolayer and Cytospin Cytology for the Detection of Bladder Cancer
Ji Yong Kim, Hyung Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Urology.2014; 55(6): 390. CrossRef - Cytological and Morphometric Study of Urinary Epithelial Cells with Histopathological Correlation
Asim Kumar Manna, Manisha Sarkar, Ujjal Bandyopadhyay, Srabani Chakrabarti, Swapan Pathak, Diptendra Kumar Sarkar
Indian Journal of Surgery.2014; 76(1): 26. CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine Cytology in Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Comparison of CellprepPlus® Liquid-Based Cytology and Conventional Smear
Seung-Myoung Son, Ji Hae Koo, Song-Yi Choi, Ho-Chang Lee, Yong-Moon Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Hae-Kyung Hwang, Hye-Suk Han, Seok-Joong Yun, Wun-Jae Kim, Eun-Joong Kim, Ok-Jun Lee
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 68. CrossRef
- Utility of Image Morphometry in the Atypical Urothelial Cells and High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Categories of the Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology
- Congenital Subglottic Stenosis of the Larynx Associated with Tracheoesophageal Fistula: 1 autopsy case.
- In Sook Kim, Tae Jung Kwon, Dong Wha Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(3):350-354.
- 2,371 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Congenital subglottic stenosis of the larynx is one of the most common cause of chronic airway obstruction im infancy and childhood. It is defined as narrowing of the space bounded inferiorly by the inferior margin of the cricoid cartilage amd superiorly by the insertion of the fibers of the conus elasticus into the true vocal cords. In case we experienced was a female full-term baby delivered by Cesarean section. The stenosis was believed by hypertrophy of stromal soft tissue and cricoid cartilage in the subglottic area. The lesion was associated with tracheoesophageal fistula of H1 type. A brief review of the literature was done.
- Kaposi's Sarcoma: A report of three cases.
- Yeon Soo Lee, Yeong Jin Choi, Mi Kyung Jee, Seok Jin Kang, Byoung Kee Kim, Sun Moo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(3):385-390.
- 2,334 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The classic type of Kaposi's sarcoma, or multifocal hemorrhagic sarcoma histologically characterized by proliferating fibroblastic and microvascular elements was described by Kaposi as a relatively rare neoplasm. During the past nine years, we experienced three cases of sporadic, classic Kaposi's sarcomas. They were presented as multiple papules, macules and nodules on the skin of the hands, lower logs and feet without systemic involvement. Histologically, Kaposi's sarcoma is divided into three stages, early patch, plaque and nodular stages. The nodular lesions(case 1, 2 and 3) showed extensive proliferatiion of spindle shaped, somewhat pleomorphic cells having dark prominent nuclei, proliferation of small vessels with solid aggregates of endothelial cells, and extravasation of erythrocytes. In early patch stage(case 3), widely dilated, anastomosing, thin-walled vascular spaces are noted in the upper half of the dermis. In plaque stage(case I and 3), there are proliferation of spindle shaped cells with extravasated erythrocytes and aggregates of blood vessels lined by prominent endothelial cells.
- An Image Analytical Study on the Structural Spectrum of Intestinal Metaplasia-Dysplasia-Carcinoma of the Stomach.
- Sang Woo Juhng, Dong Ha Park, Ji Shin Lee, Kyu Hyuk Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):50-57.
- 2,022 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia of the stomach have been stressed as precursors of gastric carcinoma of the intestinal type, although their preneoplastic nature is still debated. In this study, the cytomorphometric and cytokinetic spectra of the suggested preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions of the stomach were investigated. From the resected stomachs of early gastric carcinoma of intestinal type, areas of normal, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma were selected. They were immunostained for proliferating cell nuclear antigen, counterstained with propidium iodide, and various nuclear parameters were measured by image analysis. Normal and intestinal metaplastic mucosae differed by the localization of proliferation zone, but not by nuclear profile area, circular shape factor, and proliferation index. In dysplasia, proliferation zone covered large parts of the dysplastic area. Nuclear profile area and proliferation index were larger whereas circular shape factor was smaller than in normal or intestinal metaplasia. Carcinomatous lesion had diffuse proliferation activity, the largest nuclear profile area and proliferating index, and circular shape factor in-between those of normal or intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia. The above results showed a structural spectrum among normal of intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma of intestinal type in cytomorphometric and cytokinetic terms. The structural spectrum raises the possibility that dysplasia of the stomach is a preneoplastic lesion.
- Computerization of Surgical Pathology Reporting and Data Storage by Automatic Coding System using Personal Computer.
- Woo Ho Kim, Jeong Wook Seo, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(4):410-415.
- 1,866 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors developed a computer program for use in report printing as well as data storage and retrieval system at the surgical pathology and its efficacy was evaluated at the Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital. This program used IBM PC XT and was written in DBASE III plus language. The main features of the program included an automatic coding and decoding of the diagnosis, automatic searching of the previous biopsy during gross dictation, powerful word processing function and flexibility of the program. The data storage was carried out during the typewriting of the report, so that the typist's workload became markedly reduced. Two kinds of data files wer stored in the hard disk ; the temporary file contained full informations and the permanent file contained the core data only. Searching of a specific case was performed by pathology accession number, chart number, patient's name or by SNOMED code within a second. All the cases were arranged by copied to the diskette during the daily service automatically, with which data were easily restored in case of hard disk failure. The advantages of this program using a persosnal computer were discussed with comparison to those of larger computer system. Based on the experience of 8 months usage in Seoul National University, we assume that this program gives a sufficient solution to the surgical pathology service of many institutes where a large computer system with well designed software is not available yet.
- Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia(Immotile Cilia Syndrome): Clinical and electron microscopic analysis of 17 cases.
- Je G Chi, Chul Jong Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(2):99-107.
- 2,506 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Immotile cilia syndrome is a genetically determined disorder characterized by immotility or poor motility of the cilia in the airways and elsewhere. Since its first description in 1976 determination of a ciliary abnormality has now clarified its variable expression and pleiotropism. Certain specific defects in the ciliary axoneme can be found and are pathognmoic of the syndrome. These defects include missing dynein arms, abnormally short dynein, arms, spokes with no central sheath, missing central microtubules, and displacement of one of the nine peripheral doublets. We have studied 80 cases of bronchial or nasal mucosal biopsies that were performed with the suspicion of immotile cilia syndrome. Of 80 cases only 17 cases were sampled optimally to be able to observe under transmission and scanning electron microscopes. All 17 cases had certain abnormality of the cilia. They consisted of Ia(3 cases), Ib(3 cases), Id only(3 cases) and Id+other types(6 cases) a according to Sturgess classification. Seven cases consisted of 1 solitary and 6 combined form; II+Id(1 case) and II+Id+III(5 case). All 5 cases of type III were combined with Id and II. Clinically most pronounced manifestations were cough(82%), sputum(59%), rhinorrhea(41%) and nasal stuffiness(35%), All the patients were below the age of 15 years, and there were 6 boys and 11 girls.
- Image Analysis of Glomerular Changes in Patients with Post-transplant IgA Nephropathy.
- Kye Won Kwon, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):206-211.
- 2,038 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
IgA nephropathy after renal transplantation (post-transplant IgAN) may recapitulate the IgAN of native kidneys, however, little has been reported about the histologic characteristics. The aim of this study is to apply glomerular morphometry using an image analyser to examine the histologic characteristics of post-transplant IgAN.
METHODS
The outer margin of the glomerulus (Bowman's area, BA) and glomerular tuft area (GA) were traced manually. The measured area were automatically calculated by KS300 image analysis system (Kontron, Munchen, Germany). The mesangial area (MA) was calculated with a summing each manually traced mesangial area. The total number of glomerular (GC) and mesangial cells (MC) were counted. Eight cases of renal section obtained by nephrectomy due to renal cell carcinoma (normal control: N-CTRL) and nineteen cases of renal section obtained from post-transplantation patients without IgAN (transplantation control: Tx-CTRL) served as controls.
RESULTS
A total of 35 biopsies were finally selected for measurement. BA and GA of post-transplant IgAN were 1.6 and 1.4 times larger than the N-CTRL, respectively, and were not significantly different from Tx-CTRL. MA was 1.4 times significantly larger than that of the Tx-CTRL. As compared to that of the N-CTRL, it was 1.2 times larger, but this difference was not statistically significant. The GC and MC of post-transplant IgAN and the Tx-CTRL were significantly lower than the N-CTRL. There were no significant correlations between glomerular hypertrophy and duration after renal transplantation, mesangial changes, segmental sclerosis, or degree of renal cortical interstitial fibrosis in post-transplant IgAN.
CONCLUSIONS
Prominent glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion suggest a hyperfiltration injury in post-transplant IgAN and a possible way to glomerulosclerosis.
- Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1,2,3 and Type IV Collagen in Gastric Adenocarcinoma: Influence on Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis.
- Eun Sun Jung, Byung Gee Kim, Jo Hyun Park, Sang In Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(4):251-258.
- 2,030 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Matrix metalloproteinases are believed to play an important role in tumor invasion and metastasis. But little is known about the role of them in the gastric adenocarcinoma. We investigated the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1,2,3 in eighty paraffin blocks of the primary gastric adenocarcinoma tissues with immunohistochemistry and analysed their correlation with lymph node metastasis and survival. MMP-1,2,3 were expressed most intensely in the fibroblasts around the tumor stroma. In our study the increased immunoreactivity of MMP-2 only showed statistically significant correlation with lymph node metastasis (P=0.0517, Odd's ratio=2.274). But MMP-1,2,3 all were correlated with survival. Type IV collagen was observed in the vascular basement membranes and tumor basement membranes and showed statistically significant correlation with lymph node metastasis (P=0.0002, Odd's ratio=0.194) and prognosis (P=0.0001). The immunoreactivity of MMP-2 and type IV collagen was inversely correlated (Kendall's Tau-b correlation = 0.37482, P=0.0001). Our results suggest that in human gastric adenocarcinoma the increased immunoreactivity of MMP-2 and the decreased immunoreactivity of type IV collagen has an important role in lymph node metastasis and prognosis. MMP-1,3 are not correlated with lymph node metastasis but correlated with survival. The mechanism responsible for the production of MMP by the host fibroblasts remains obscure and requires further investigation.
- Malignant Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor of the Esophagus: A Case Report.
- Hae Joung Sul, Kyeong Hee Kim, Dae Young Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):252-255.
- 2,087 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) predominate in the stomach and small intestine but have rarely been documented in the esophagus. We report a rare case of GIST of the esophagus in a 47-year-old woman. Histologically, the tumors showed a combination of solid, myxoid, and perivascular collar-like patterns, with spindle and epithelioid cells. The tumor cells were positive for CD117, CD34, and S-100 protein and negative for desmin and -smooth muscle actin.
- Immunohistochemical Localization of Extracellular Matrix Components in Diabetic Nephropathy.
- Seung Sam Paik, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(5):427-435.
- 1,940 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Normal human glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and mesangial matrix (MM) contain several different basement membrane components in varying degrees. The characteristic morphological and ultrastructural changes in patients with diabetic nephropathy are the thickening of the GBM and the expansion of the MM. In order to investigate the changes of extracellular matrix components in diabetes, the immunohistochemical localization was performed in 17 cases with different degrees using antisera to human collagen types I, III, IV, VI, fibronectin, and laminin. The following results were obtained: 1. The reactivity for collagen IV was increased in expanded MM in the diffuse glomerulosclerosis (GS). With the progression to the nodule formation, collagen IV was prominently decreased in the peripheral area of the nodules. 2. Collagen VI was increased in GBM and MM in the diffuse GS, it was especially prominent in the expanded MM. With the progression to nodule formation, collagen VI was prominently increased in the periphery of the nodules. 3. Interstitial collagen I and III were not stained in many of the cases with the diffuse GS. With the progression to nodule formation, these were slightly expressed. A lamellar pattern of positive reaction was noted at the periphery of the late nodular lesions. 4. Fibronectin was increased in GBM & MM in the diffuse GS, it was especially intense in the MM. With the progression to the nodule formation, the reactivity of antibody to the fibronectin was decreased. 5. Laminin was weakly stained along the GBM & trace in the MM, but was not changed in the nodular GS. In summary, the expanded mesangial matrix in the diffuse GS showed a markedly increased staining for collagen IV, fibronectin and collagen VI. Less intense linear staining for collagen VI, fibronectin, laminin, collagen IV and collagen III was noted along the GBM. In the nodular GS, the composition of the early nodules resembled that of the diffuse GS. However, the late nodular lesion of the nodular GS revealed decreased reactivity for collagen IV and fibronectin at the periphery of the nodule, where collagen VI and interstitial collagen I and III were increased in laminated pattern.
- Morphological Observations on the Hair Development of Human Fetal Skin.
- Kil Seo Kim, Joong Seok Seo, Key Yong Song, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(1):39-49.
- 2,356 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The developing process of the hair of the fetal skin was studied. The ages of 103 human embryos and fetuses ranged from 4 to 40 gestation weeks. Ten different sites were selected, i.e., scalp, forehead, cheek, chest, abdomen, back, palm, sole, finger and toe. For the embryos 3 sites were studied, i.e., cephalic, trunk, and caudal portions. Following results were made: 1) The primitive hair germ was first noted the 10th week in the face skin as nubbins of mesenchymal cells beneath discrete foci of crowdes, elongated germinative epithelial cells. The developing hair germs and hair pegs were observes at the cephalic portion by 11 weeks. At 15 weeks the hair pegs including hair germs were noted in the trunk skin. The bulbous hair peg stage started at the 16th week in the cephalic portion and at the 18th week in the trunk. 2) Relative number of fetal hairs progressively increase up to 20 weeks of gestation but, thereafter decreased although it was different by the site of the body. 3) The diameter of fetal hair follicles increased with fetal age to the term with slight difference by the portion of body. 4) The developmental process of hair was more rapid in the cephalic portion than the trunk in views of morphologic changes of the hair structures, number and diameter of hair follicles.
- Analysis of DNA Ploidy Patterns and Nuclear Morphometry in Diethylnitrosamine Induced Hepatocyte Nodules and Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Rats.
- Chan Choi, Myung Kwan Kim, Kwan Mook Chae, Eun Cheol Kim, Hyung Bae Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):226-234.
- 2,286 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to answer the question; (1) How does the DNA ploidy pattern change in hepatocarcinogenesis? (2) How does the nuclear morphology change in hepatocarcinogenesis? Diethylnitrosamine(DEN) (16.5 mg per kg) was subcutaneously injected to female Sprague-Dawley rats(150~200g) by weekly interval for 30 weeks. DNA ploidy and parameters of nuclear morphology were measured by image analyser(IBAS 200, Kontron, FRG). The DNA ploidy pattern was divided into three basic patterns(diploid, polyploid, and aneuploid modes). In 8 cases of saline-injected control rats, the DNA histograms showed all polyploid pattern. Inhepatocyte nodules(hyperplastic nodules), DNA diploidy was the most frequent pattern, being followed by polyploid and aneuploid DNA patterns, contrast to hepatocelular carcinomas in which polyploid DNA pattern was most frequently noted being followed by diploid and aneuploid DNA pattern. Although the nuclei of hepatocytes in hepatocyte nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas were larger and more pleomorphic than those of normal hepatocytes, they were as same as those of normal hepatocytes in regard to nuclear hyperchromasia. DNA content, which was increased in hepatocarcinogenesis, was significantly related to the nuclear area.
- Body Stalk Anomaly: Analysis of 10 Autopsy Cases.
- Seung Sook Lee, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):235-242.
- 2,329 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Body stalk anomaly represents an extreme maldevelopment of embryonic body folding and is characterized by absence of the umbilicus and umbilical cord. The failure of complete obliteration of the extraembryonic coelom is responsible for the absence of the umbilical cord formation and the wide-based insertio of the amnioperitoneal membrane onto the placental chorionic plate. We have analyzed 10 autopsy cases of various midline anomalies of the body that could best be classified into body stalk anomaly. All cases were either stillborns or dead immediately after birth. The pregnancy was interrupted due to this anomaly in 6 cases, and their gestational ages varied from 17 weeks to 37 weeks. The affected fetuses were characterized bt absent or vestigial umbilical cord, and ruptured amnion with direct amnioperitoneal connection without the mediation of the umbilical cord. Exomphalos with abdominal wall defect and serve scoliosis were characteristic components of this anomaly, that provided important clues in differentiating other similar anomalies. Other associated anomalies included neural tube defect, intestinal atresia, genitourinary and skeletal defects, pulmonary hypoplasia, single umbilical artery and narrow-spaced chest and abdomen, etc. These findings strongly suggest that anomaly of body stalk represents mechanical teratogenesis due to early amnion repture and subsequent effect, and should be categorized into amniotic band disruption syndrome.

 E-submission
E-submission

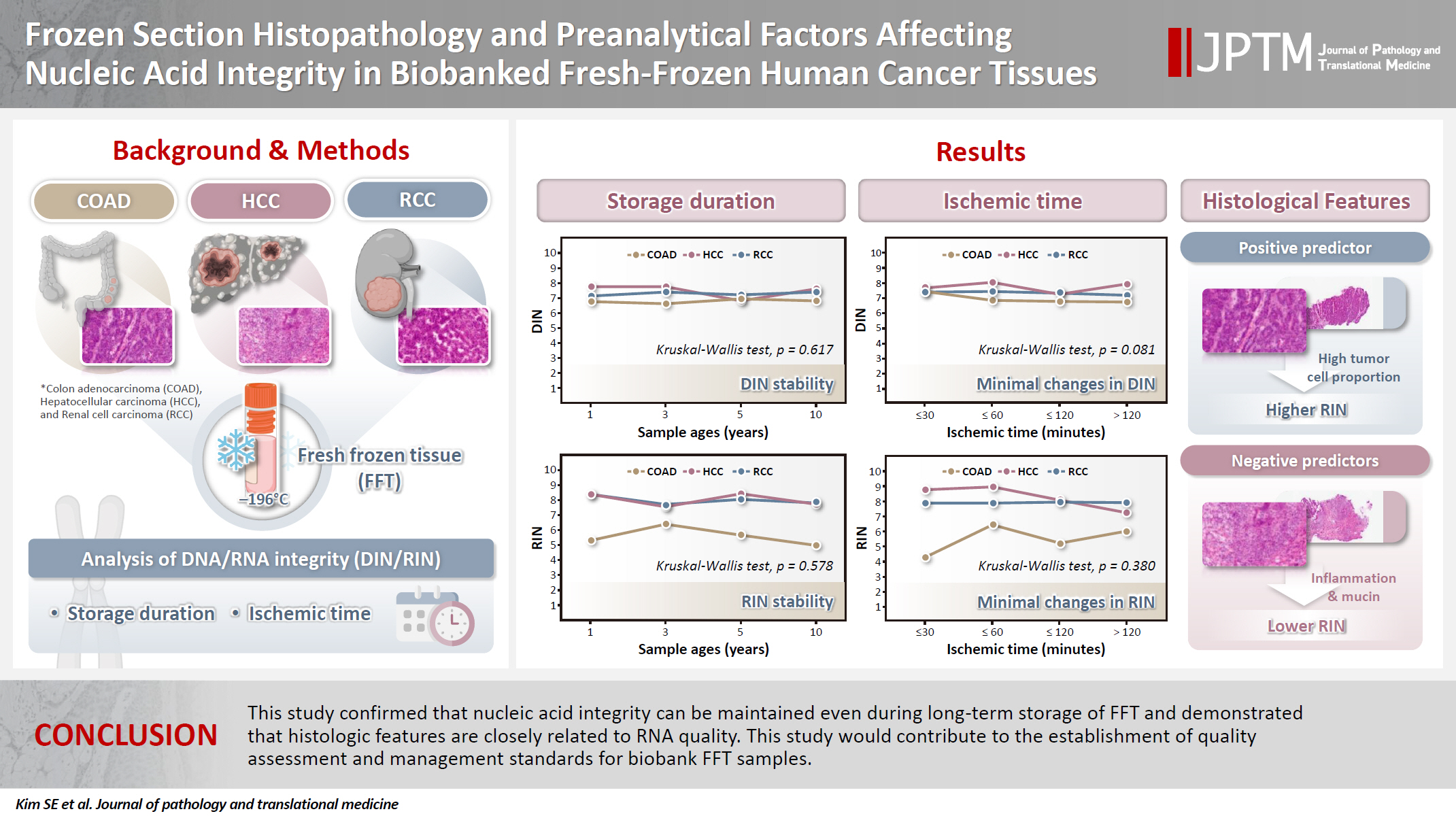






 First
First Prev
Prev



