Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Frozen section histopathology and preanalytical factors affecting nucleic acid integrity in biobanked fresh-frozen human cancer tissues
- Soungeun Kim, Jaewon Kang, Boyeon Kim, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):398-407. Published online September 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.22
- 4,526 View
- 203 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
In this study, we evaluated the effects of storage duration and ischemic time on nucleic acid quality of fresh-frozen tissue (FFT) from colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and renal cell carcinoma (RCC) collected at the Cancer Tissue Bank of Seoul National University Hospital. Methods: A total of 102 FFT samples were analyzed to compare DNA integrity number (DIN) and RNA integrity number (RIN) according to storage duration and ischemic time. Additionally, the effects of histopathologic features—such as tumor cell proportion, inflammatory cell infiltration, and stromal fibrosis—on nucleic acid quality were evaluated. Results: DIN and RIN remained stable overall even though the storage duration increased, with no statistically significant differences observed. In particular, there was almost no decrease in RNA quality in HCC and RCC samples, but in COAD samples, RIN tended to decrease slightly as the storage duration increased. No significant difference was confirmed between ischemic time and nucleic acid quality, but in COAD tissue, RNA quality variability tended to increase as the ischemic time increased. Furthermore, RIN increased as the tumor cell proportion increased, whereas inflammatory cell infiltration and extracellular mucin pool were identified as independent negative predictors of RIN. Conclusions: This study confirmed that nucleic acid integrity can be maintained even during long-term storage of FFT and demonstrated that histologic features are closely related to RNA quality. This study would contribute to the establishment of quality assessment and management standards for biobank FFT samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
Zhiyong Liu, Jianhe Wu, Yuanwei Li, Qiang Lu, Yongjun Yang
BMC Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Day surgery mode of multi-modal image AI fusion targeted transperineal biopsy technique using electromagnetic navigation tracking system under local anesthesia
- Concurrent intestinal plasmablastic lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with a clonal relationship: a case report and literature review
- Nao Imuta, Kosuke Miyai, Motohiro Tsuchiya, Mariko Saito, Takehiro Sone, Shinichi Kobayashi, Sho Ogata, Fumihiko Kimura, Susumu Matsukuma
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):191-197. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.14
- 4,899 View
- 223 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Herein, we report a case of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that occurred concurrently in the large intestine. An 84-year-old female presented with a palpable rectal tumor and ileocecal tumor observed on imaging analyses. Endoscopic biopsy of both lesions revealed lymphomatous round cells. Hartmann’s operation and ileocecal resection were performed for regional control. The ileocecal lesion consisted of a proliferation of CD20/CD79a-positive lymphoid cells, indicative of DLBCL. In contrast, the rectal tumor showed proliferation of atypical cells with pleomorphic nuclei and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm, with immunohistochemical findings of CD38/CD79a/MUM1/MYC (+) and CD20/CD3/CD138/PAX5 (–). Tumor cells were positive for Epstein-Barr virus– encoded RNA based on in situ hybridization and MYC rearrangement in fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. These findings indicated the rectal tumor was most likely a PBL. Sequencing analysis for immunoglobulin heavy variable genes indicated a common B-cell origin of the two sets of lymphoma cells. This case report and literature review provide new insights into PBL tumorigenesis.
- Identification of invasive subpopulations using spatial transcriptome analysis in thyroid follicular tumors
- Ayana Suzuki, Satoshi Nojima, Shinichiro Tahara, Daisuke Motooka, Masaharu Kohara, Daisuke Okuzaki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Eiichi Morii
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):22-28. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.21
- 4,889 View
- 270 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follicular tumors include follicular thyroid adenomas and carcinomas; however, it is difficult to distinguish between the two when the cytology or biopsy material is obtained from a portion of the tumor. The presence or absence of invasion in the resected material is used to differentiate between adenomas and carcinomas, which often results in the unnecessary removal of the adenomas. If nodules that may be follicular thyroid carcinomas are identified preoperatively, active surveillance of other nodules as adenomas is possible, which reduces the risk of surgical complications and the expenses incurred during medical treatment. Therefore, we aimed to identify biomarkers in the invasive subpopulation of follicular tumor cells.
Methods
We performed a spatial transcriptome analysis of a case of follicular thyroid carcinoma and examined the dynamics of CD74 expression in 36 cases.
Results
We identified a subpopulation in a region close to the invasive area, and this subpopulation expressed high levels of CD74. Immunohistochemically, CD74 was highly expressed in the invasive and peripheral areas of the tumor.
Conclusions
Although high CD74 expression has been reported in papillary and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas, it has not been analyzed in follicular thyroid carcinomas. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of CD74 expression in thyroid tumors has not yet been reported. The CD74-positive subpopulation identified in this study may be useful in predicting invasion of follicular thyroid carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
Masashi Tanida, Tsuyoshi Takashima, Shinichiro Tahara, Masaharu Kohara, Haruka Kanai, Masami Suzuki, Motoyuki Suzuki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki, Shinya Sato, Daisuke Okuzaki, Satoshi Nojima, Takahiro Matsui, Hidenori Inohara, Eiichi Morii
Cancer Science.2026; 117(1): 257. CrossRef - An emerging role of CD74 in thyroid follicular cells in Hashimoto´s thyroiditis
Pablo Sacristán-Gómez, Ana Serrano-Somavilla, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Andrea Álvarez-Rodríguez, Eduardo Martínez-Parra, Miguel Sampedro-Nuñez, Fernando Sebastián-Valles, Mónica Marazuela, Rebeca Martínez-Hernández
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2026; 194: 118945. CrossRef - Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Spatial Transcriptomics in Thyroid Cancer: Applications, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Chaerim Song, Hye-Ji Park, Man S. Kim
Cells.2025; 14(12): 936. CrossRef - A New Tool to Decrease Interobserver Variability in Biomarker Annotation in Solid Tumor Tissue for Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis
Sravya Palavalasa, Emily Baker, Jack Freeman, Aditri Gokul, Weihua Zhou, Dafydd Thomas, Wajd N. Al-Holou, Meredith A. Morgan, Theodore S. Lawrence, Daniel R. Wahl
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2025; 47(7): 531. CrossRef
- Carbonic Anhydrase 12 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for High‐Risk Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma
- Perspectives on single-nucleus RNA sequencing in different cell types and tissues
- Nayoung Kim, Huiram Kang, Areum Jo, Seung-Ah Yoo, Hae-Ock Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):52-59. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.12.19
- 23,618 View
- 473 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Single-cell RNA sequencing has become a powerful and essential tool for delineating cellular diversity in normal tissues and alterations in disease states. For certain cell types and conditions, there are difficulties in isolating intact cells for transcriptome profiling due to their fragility, large size, tight interconnections, and other factors. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) is an alternative or complementary approach for cells that are difficult to isolate. In this review, we will provide an overview of the experimental and analysis steps of snRNA-seq to understand the methods and characteristics of general and tissue-specific snRNA-seq data. Knowing the advantages and limitations of snRNA-seq will increase its use and improve the biological interpretation of the data generated using this technique.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Genomics Approach Identifies Glial Transcriptomic Dysregulation and Risk in the Cortex of Individuals With Alcohol Use Disorder
Anna S. Warden, Nihal A. Salem, Eric Brenner, Greg T. Sutherland, Julia Stevens, Manav Kapoor, Alison M. Goate, R. Dayne Mayfield
Biological Psychiatry.2026; 99(1): 34. CrossRef - Müller cell glutamine metabolism links photoreceptor and endothelial injury in diabetic retinopathy
Katia Corano Scheri, Yi-Wen Hsieh, Thomas Tedeschi, James B Hurley, Amani A Fawzi
Life Science Alliance.2026; 9(2): e202503434. CrossRef - Leveraging Single-Cell Technologies to Advance Understanding of Myocardial Disease
Robert S. Gardner, Nathan R. Tucker, Kaushik Amancherla
Circulation Research.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-cell and spatial omics: exploring hypothalamic heterogeneity
Muhammad Junaid, Eun Jeong Lee, Su Bin Lim
Neural Regeneration Research.2025; 20(6): 1525. CrossRef - Exploring the utility of snRNA-seq in profiling human bladder tissue: A comprehensive comparison with scRNA-seq
Briana Santo, Emily E. Fink, Alexandra E. Krylova, Yi-Chia Lin, Mohamed Eltemamy, Alvin Wee, Oliver Wessely, Byron H. Lee, Angela H. Ting
iScience.2025; 28(1): 111628. CrossRef - Applications and emerging challenges of single-cell RNA sequencing technology in tumor drug discovery
Lu Zhang, Yueying Yang, Jianjun Tan
Drug Discovery Today.2025; 30(2): 104290. CrossRef - Techniques and analytic workflow for spatial transcriptomics and its application to allergy and inflammation
Haihan Zhang, Matthew T. Patrick, Jingyu Zhao, Xintong Zhai, Jialin Liu, Zheng Li, Yiqian Gu, Joshua Welch, Xiang Zhou, Robert L. Modlin, Lam C. Tsoi, Johann E. Gudjonsson
Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.2025; 155(3): 678. CrossRef - Single-cell RNA sequencing in autoimmune diseases: New insights and challenges
Jialing Huang, Yuelin Hu, Shuqing Wang, Yuefang Liu, Xin Sun, Xin Wang, Hongsong Yu
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2025; 267: 108807. CrossRef - SGK1 drives hippocampal demyelination and diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction in mice
Ziying Jiang, Bin Liu, Tangsheng Lu, Xiaoxing Liu, Renjun Lv, Kai Yuan, Mengna Zhu, Xinning Wang, Shangbin Li, Song Xu, Xinyu Wang, Yifei Wang, Zhenfang Gao, Peiqing Zhao, Zongyong Zhang, Junwei Hao, Lin Lu, Qingqing Yin
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling cell–cell communication with NicheNet by inferring active ligands from transcriptomics data
Chananchida Sang-aram, Robin Browaeys, Ruth Seurinck, Yvan Saeys
Nature Protocols.2025; 20(6): 1439. CrossRef - A versatile and efficient method to isolate nuclei from low-input cryopreserved tissues for single-nuclei transcriptomics
Cristopher Segovia, Vincent Desrosiers, Fatemeh Khadangi, Karine Robitaille, Victoria Saavedra Armero, Myreille D’Astous, Gabriel Khelifi, Alain Bergeron, Samer Hussein, Maxime Richer, Yohan Bossé, Yves Fradet, Vincent Fradet, Steve Bilodeau
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of single-cell sequencing technology and its clinical implications in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease: a narrative review
Zhonghao Chen, Jack Shi, Longfei Li
Advanced Technology in Neuroscience.2025; 2(1): 9. CrossRef - SGK1 upregulation in GFAP+ neurons in the frontal association cortex protects against neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury
Anbiao Wu, Guang Yang, Genyu Liu, Jiyan Zhang
Cell Death & Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expert recommendations to standardize transcriptomic analysis in inflammatory bowel disease clinical trials
Bryan Linggi, Salas Azucena, Boyd Steere, Bram Verstockt, Dahham Alsoud, David Casero, Dermot McGovern, Eileen Chan, Michelle I Smith, Federica Ungaro, Florian Rieder, Konrad Aden, Lisa M Shackelton, Luca Massimino, Markus Neurath, Matthieu Allez, Raja At
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptional characterization of sepsis in a LPS porcine model
Ryan Neill
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single nuclear‐spatial transcriptomic sequencing reveals distinct puncture‐induced cell subpopulations in the intervertebral disc of a rat model
Guoyan Liang, Jing Tan, Chong Chen, Yuying Liu, Yongyu Ye, Xiaolin Pan, Qiujian Zheng, Yunbing Chang, Feng‐Juan Lyu
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Harp: data harmonization for computational tissue deconvolution across diverse transcriptomics platforms
Zahra Nozari, Paul Hüttl, Jakob Simeth, Marian Schön, James A Hutchinson, Rainer Spang, Macha Nikolski
Bioinformatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transformation of an Olfactory Placode-Derived Cell into One with Stem Cell Characteristics by Disrupting Epigenetic Barriers
Ghazia Abbas, Rutesh Vyas, Joyce C. Noble, Brian Lin, Robert P. Lane
Cellular Reprogramming.2025; 27(4): 164. CrossRef - Altered Neuroinflammatory Transcriptomic Profile in the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Three Weeks After Lateral Fluid Percussion Injury in Rats
Anthony J. DeSana, Yara Alfawares, Roshni Khatri, Tracy M. Hopkins, Faith V. Best, Jennifer L. McGuire, Laura B. Ngwenya
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(18): 9140. CrossRef - Methodologies for Sample Multiplexing and Computational Deconvolution in Single‐Cell Sequencing
Yufei Gao, Weiwei Yin, Wei Hu, Wei Chen
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A single-nucleus transcriptomic atlas of the adult Aedes aegypti mosquito
Olivia V. Goldman, Alexandra E. DeFoe, Yanyan Qi, Yaoyu Jiao, Shih-Che Weng, Brittney Wick, Leah Houri-Zeevi, Priyanka Lakhiani, Takeshi Morita, Jacopo Razzauti, Adriana Rosas-Villegas, Yael N. Tsitohay, Madison M. Walker, Ben R. Hopkins, Joshua X.D. Ang,
Cell.2025; 188(25): 7267. CrossRef - Leveraging single-cell RNA-seq in helminthology
Yi Mu, Chika P. Zumuk, Malcolm K. Jones, Pengfei Cai
Trends in Parasitology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Administration of a barcoded AAV capsid library to the putamen of non-human primates identifies variants with efficient retrograde transport
Yulia Dzhashiashvili, Jodi L. McBride, Emily Fabyanic, Xin Huang, Brian M. Kelly, Greglynn D. Walton-Gibbs, Vimala Vemireddi, Joan Wicks, Mohamad Nayal, Ariel A. Hippen, Zhenming Yu, Pichai Raman, Elizabeth Ramsburg, Marcus Davidsson, Esteban A. Engel, To
Molecular Therapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-nucleus RNA sequencing resolves microenvironmental dynamics in brown/beige adipose tissue after bariatric surgery
Wei Wang, Yangxingyun Wang, Zhonghao Guo, Yao Lu, Wei Xie, Ruibin Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mapping the cellular landscape of Atlantic salmon head kidney by single cell and single nucleus transcriptomics
Adriana M.S. Andresen, Richard S. Taylor, Unni Grimholt, Rose Ruiz Daniels, Jianxuan Sun, Ross Dobie, Neil C. Henderson, Samuel A.M. Martin, Daniel J. Macqueen, Johanna H. Fosse
Fish & Shellfish Immunology.2024; 146: 109357. CrossRef - Single-cell and spatially resolved transcriptomics for liver biology
Ping Lin, Xi Yan, Siyu Jing, Yanhong Wu, Yiran Shan, Wenbo Guo, Jin Gu, Yu Li, Haibing Zhang, Hong Li
Hepatology.2024; 80(3): 698. CrossRef - Single-cell transcriptomics in thyroid eye disease
Sofia Ahsanuddin, Albert Y. Wu
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology.2024; 14(4): 554. CrossRef - Impaired cortical neuronal homeostasis and cognition after diffuse traumatic brain injury are dependent on microglia and type I interferon responses
Jonathan M. Packer, Chelsea E. Bray, Nicolas B. Beckman, Lynde M. Wangler, Amara C. Davis, Ethan J. Goodman, Nathaniel E. Klingele, Jonathan P. Godbout
Glia.2024; 72(2): 300. CrossRef - Adipose tissue macrophage heterogeneity in the single-cell genomics era
Haneul Kang, Jongsoon Lee
Molecules and Cells.2024; 47(2): 100031. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review on Circulating cfRNA in Plasma: Implications for Disease Diagnosis and Beyond
Pengqiang Zhong, Lu Bai, Mengzhi Hong, Juan Ouyang, Ruizhi Wang, Xiaoli Zhang, Peisong Chen
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 1045. CrossRef - Single-Cell Sequencing Technology in Ruminant Livestock: Challenges and Opportunities
Avery Lyons, Jocelynn Brown, Kimberly M. Davenport
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2024; 46(6): 5291. CrossRef - Single-Cell Transcriptomics Sheds Light on Tumor Evolution: Perspectives from City of Hope’s Clinical Trial Teams
Patrick A. Cosgrove, Andrea H. Bild, Thanh H. Dellinger, Behnam Badie, Jana Portnow, Aritro Nath
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(24): 7507. CrossRef - Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA-seq establishes a novel signature for prediction in gastric cancer
Fei Wen, Xin Guan, Hai-Xia Qu, Xiang-Jun Jiang
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2023; 15(7): 1215. CrossRef - Placental single cell transcriptomics: Opportunities for endocrine disrupting chemical toxicology
Elana R. Elkin, Kyle A. Campbell, Samantha Lapehn, Sean M. Harris, Vasantha Padmanabhan, Kelly M. Bakulski, Alison G. Paquette
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2023; 578: 112066. CrossRef - Analyzing alternative splicing in Alzheimer’s disease postmortem brain: a cell-level perspective
Mohammad-Erfan Farhadieh, Kamran Ghaedi
Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-nucleus transcriptome inventory of giant panda reveals cellular basis for fitness optimization under low metabolism
Shangchen Yang, Tianming Lan, Rongping Wei, Ling Zhang, Lin Lin, Hanyu Du, Yunting Huang, Guiquan Zhang, Shan Huang, Minhui Shi, Chengdong Wang, Qing Wang, Rengui Li, Lei Han, Dan Tang, Haimeng Li, Hemin Zhang, Jie Cui, Haorong Lu, Jinrong Huang, Yonglun
BMC Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Progress in research on tumor microenvironment-based spatial omics technologies
FANGMEI XIE, NAITE XI, ZEPING HAN, WENFENG LUO, JIAN SHEN, JINGGENG LUO, XINGKUI TANG, TING PANG, YUBING LV, JIABING LIANG, LIYIN LIAO, HAOYU ZHANG, YONG JIANG, YUGUANG LI, JINHUA HE
Oncology Research.2023; 31(6): 877. CrossRef
- Integrative Genomics Approach Identifies Glial Transcriptomic Dysregulation and Risk in the Cortex of Individuals With Alcohol Use Disorder
- Immunohistochemical expression of programmed death-ligand 1 and CD8 in glioblastomas
- Dina Mohamed El Samman, Manal Mohamed El Mahdy, Hala Sobhy Cousha, Zeinab Abd El Rahman Kamar, Khaled Abdel Karim Mohamed, Hoda Hassan Abou Gabal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):388-397. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.04
- 6,658 View
- 195 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive primary malignant brain tumor in adults and is characterized by poor prognosis. Immune evasion occurs via programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)/programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) interaction. Some malignant tumors have responded to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade treatment strategies, and PD-L1 has been described as a potential predictive biomarker. This study discussed the expression of PD-L1 and CD8 in glioblastomas.
Methods
Thirty cases of glioblastoma were stained immunohistochemically for PD-L1 and CD8, where PD-L1 expression in glioblastoma tumor tissue above 1% is considered positive and CD-8 is expressed in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. The expression of each marker was correlated with clinicopathologic parameters. Survival analysis was conducted to correlate progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) with PD-L1 and CD8 expression.
Results
Diffuse/fibrillary PD-L1 was expressed in all cases (mean expression, 57.6%), whereas membranous PD-L1 was expressed in six of 30 cases. CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD8+ TILs) had a median expression of 10%. PD-L1 and CD8 were positively correlated (p = .001). High PD-L1 expression was associated with worse PFS and OS (p = .026 and p = .001, respectively). Correlation of CD8+ TILs percentage with age, sex, tumor site, laterality, and outcomes were statistically insignificant. Multivariate analysis revealed that PD-L1 was the only independent factor that affected prognosis.
Conclusions
PD-L1 expression in patients with glioblastoma is robust; higher PD-L1 expression is associated with lower CD8+ TIL expression and worse prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dual biomarker role of PD-L1 and LC3B in glioblastoma: prognostic and therapeutic potential
Rana Fathy Torky, Rania Makboul, Dalia M. Badary, Wael M. A. El-Ghani, Ahmed El-Hakeem, Rabab M. H. El Ghorori
Neurosurgical Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathological diagnosis of central nervous system tumours in adults: what's new?
Evert-Jan Kooi, Lukas Marcelis, Pieter Wesseling
Pathology.2025; 57(2): 144. CrossRef - Expression of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Astrocytic Tumors and Its Correlation With Histopathological Grade and Proliferative Index (Ki-67): A Cross-Sectional Study
Namita Singh, Ranjana Giri, Prita Pradhan, Diptiranjan Satapathy, Ipsita Debata
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune intrinsic escape signature stratifies prognosis, characterizes the tumor immune microenvironment, and identifies tumorigenic PPP1R8 in glioblastoma multiforme patients
Ran Du, Lijun Jing, Denggang Fu
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 Clones and Their Relevance in Glioblastoma, IDH-Wildtype: A Comparative Analysis
Michal Hendrych, Frantisek Vana, Marketa Hermanova, Radek Lakomy, Tomas Kazda, Kvetoslava Matulova, Alena Kopkova, Martina Jelinkova, Radim Jancalek, Martin Smrcka, Vaclav Vybihal, Jiri Sana
Bratislava Medical Journal.2025; 126(9): 2233. CrossRef - Tumor-associated microenvironment, PD-L1 expression and their relationship with immunotherapy in glioblastoma, IDH-wild type: A comprehensive review with emphasis on the implications for neuropathologists
Giuseppe Broggi, Giuseppe Angelico, Jessica Farina, Giordana Tinnirello, Valeria Barresi, Magda Zanelli, Andrea Palicelli, Francesco Certo, Giuseppe Barbagallo, Gaetano Magro, Rosario Caltabiano
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 254: 155144. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Profile of Adult Glioblastoma IDH-Wildtype Microenvironment: A Cohort Study
Sofia Asioli, Lidia Gatto, Uri Vardy, Claudio Agostinelli, Vincenzo Di Nunno, Simona Righi, Alicia Tosoni, Francesca Ambrosi, Stefania Bartolini, Caterina Giannini, Enrico Franceschi
Cancers.2024; 16(22): 3859. CrossRef - Analysis of PD-L1 and CD3 Expression in Glioblastoma Patients and Correlation with Outcome: A Single Center Report
Navid Sobhani, Victoria Bouchè, Giovanni Aldegheri, Andrea Rocca, Alberto D’Angelo, Fabiola Giudici, Cristina Bottin, Carmine Antonio Donofrio, Maurizio Pinamonti, Benvenuto Ferrari, Stefano Panni, Marika Cominetti, Jahard Aliaga, Marco Ungari, Antonio Fi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 311. CrossRef - Immuno-PET Imaging of Tumour PD-L1 Expression in Glioblastoma
Gitanjali Sharma, Marta C. Braga, Chiara Da Pieve, Wojciech Szopa, Tatjana Starzetz, Karl H. Plate, Wojciech Kaspera, Gabriela Kramer-Marek
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3131. CrossRef
- Dual biomarker role of PD-L1 and LC3B in glioblastoma: prognostic and therapeutic potential
- Automated immunohistochemical assessment ability to evaluate estrogen and progesterone receptor status compared with quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in breast carcinoma patients
- Taesung Jeon, Aeree Kim, Chungyeul Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):33-42. Published online December 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.09.29
- 12,680 View
- 233 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to investigate the capability of an automated immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation of hormonal receptor status in breast cancer patients compared to a well-validated quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) method.
Methods
This study included 93 invasive breast carcinoma cases that had both standard IHC assay and Oncotype Dx assay results. The same paraffin blocks on which Oncotype Dx assay had been performed were selected. Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) receptor status were evaluated through IHC stains using SP1 monoclonal antibody for ER, and 1E2 monoclonal antibody for PR. All ER and PR immunostained slides were scanned, and invasive tumor areas were marked. Using the QuantCenter image analyzer provided by 3DHISTECH, IHC staining of hormone receptors was measured and converted to histochemical scores (H scores). Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated between Oncotype Dx hormone receptor scores and H scores, and between Oncotype Dx scores and Allred scores.
Results
H scores measured by an automated imaging system showed high concordance with RT-qPCR scores. ER concordance was 98.9% (92/93), and PR concordance was 91.4% (85/93). The correlation magnitude between automated H scores and RT-qPCR scores was high and comparable to those of Allred scores (for ER, 0.51 vs. 0.37 [p=.121], for PR, 0.70 vs. 0.72 [p=.39]).
Conclusions
Automated H scores showed a high concordance with quantitative mRNA expression levels measured by RT-qPCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer: role of immune-related gene expression
Hadeer Mahmoud, Abeer M. Abd El-Aziz, Osama Ezzat, Hany Ibrahim Kenawy, Ahmed A. Shokeir
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance
Abrar I. Aljohani
Medicina.2025; 61(10): 1810. CrossRef - Vision Transformers for Breast Cancer Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression Staging without Immunohistochemical Staining
Gelan Ayana, Eonjin Lee, Se-woon Choe
The American Journal of Pathology.2024; 194(3): 402. CrossRef - Extrahepatic Bile Duct Organoids as a Model to Study Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury During Liver Transplantation
P. Kreiner, E. Eggenhofer, L. Schneider, C. Rejas, M. Goetz, N. Bogovic, S. M. Brunner, K. Evert, H. J. Schlitt, E. K. Geissler, H. Junger
Transplant International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of DSCC1, a Biomarker Associated with Aggressive Features of Breast Cancer
Abrar I. Aljohani
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 1929. CrossRef - Marker assessments inER‐positive breast cancers: old markers, new applications?
Joshua J X Li, Gary M Tse
Histopathology.2023; 82(2): 218. CrossRef - The Story of the Magee Equations: The Ultimate in Applied Immunohistochemistry
Rohit Bhargava, David J. Dabbs
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(7): 490. CrossRef - Dose-Dependent Relationship between Protection of Thioacetamide-Induced Acute Liver Injury and Hyperammonemia and Concentration of Lactobacillus salivarius Li01 in Mice
Pengcheng Lou, Yangfan Shen, Aoxiang Zhuge, Longxian Lv, Xueling Zhu, Yin Yuan, Liya Yang, Kaicen Wang, Bo Li, Lanjuan Li, Joanna B. Goldberg
Microbiology Spectrum.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer: role of immune-related gene expression
- Analysis of PAX8 immunohistochemistry in lung cancers: a meta-analysis
- Jae Han Jeong, Nae Yu Kim, Jung-Soo Pyo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):300-309. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.08
- 9,494 View
- 155 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In this meta-analysis, we aimed to evaluate the PAX8 immunohistochemical expressions in primary lung cancers and metastatic cancers to the lung.
Methods
We identified and reviewed relevant articles from the PubMed databases. Ultimately, 18 articles were included in this meta-analysis. PAX8 expression rates were analyzed and compared between primary and metastatic lung cancers.
Results
The PAX8 expression rate in primary lung cancers was 0.042 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.025 to 0.071). PAX8 expression rates of small cell (0.129; 95% CI, 0.022 to 0.496) and non-small cell carcinomas of the lung (0.037; 95% CI, 0.022 to 0.061) were significantly different (p=.049 in a meta-regression test). However, the PAX8 expression rates of adenocarcinoma (0.013; 95% CI, 0.006 to 0.031) and squamous cell carcinoma (0.040; 95% CI, 0.016 to 0.097) were not significantly different. PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas to the lung varied, ranging from 1.8% to 94.9%. Metastatic carcinomas from the lung to other organs had a PAX8 expression rate of 6.3%. The PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas from the female genital organs, kidneys, and thyroid gland to the lung were higher than those of other metastatic carcinomas.
Conclusions
Primary lung cancers had a low PAX8 expression rate regardless of tumor subtype. However, the PAX8 expression rates of metastatic carcinomas from the female genital organs, kidneys, and thyroid were significantly higher than those of primary lung cancers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical significance of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 and miR-96-5p in non-small cell lung cancer
Qiaoling Ying, Hui Xu, Xiaojiao Wu, Hang Fang, Jingjing Shi, Hangcheng Pan
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung Metastatic Recurrence as Carcinosarcoma from Ovarian Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report
Kaito Nakama, Masayuki Ota, Takanori Aihara, Satoko Kageyama, Jun-ichiro Ikeda
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The TTF-1 and Napsin A Trap: Metastatic Endometrial Carcinoma Masquerading as Lung Primary
Carmen Alfonso-Rosa, Jesús Machuca-Aguado, Ana María Montaña-Ramírez, Francisco Javier Rubio-Garrido
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of PAX8 in small cell lung cancer
Fengyun Tao, Hangyan Zhu, Jiayun Xu, Yanan Guo, Xin Wang, Lei Shao, Deng Pan, Guosheng Li, Rong Fang
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28251. CrossRef - Cystic primary squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid
Sakurako Harada‐Kagitani, Yusuke Kouchi, Yoshiki Shinomiya, Takuto Hiramoto, Tomoyuki Arai, Toyoyuki Hanazawa, Kiyotaka Onodera, Kaito Nakama, Takanori Aihara, Masayuki Ota, Jun‐Ichiro Ikeda, Takashi Kishimoto
Pathology International.2024; 74(5): 292. CrossRef - The combination of p16 and Rb expression pattern is helpful to predict high-risk HPV infection and the primary site in lymph node metastases of squamous cell carcinoma
Ryosuke Kuga, Hidetaka Yamamoto, Fumiya Narutomi, Misa Suzuki, Rina Jiromaru, Takahiro Hongo, Kazuhisa Hachisuga, Nobuko Yasutake, Kiyoko Kato, Takashi Nakagawa, Yoshinao Oda
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155642. CrossRef - Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix with a prominent spindle cell component
Yingying Fan, Ying He, Liang Sun, Tianmin Liu, Yangmei Shen
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry of effusions: Processing and commonly used immunomarkers
Vinod B. Shidham, Beata Janikowski
Cytojournal.2022; 19: 6. CrossRef - Significance analysis of PAX8 expression in endometrial carcinoma
Shan Hu, Hua Gan, Fengmei Yang
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31159. CrossRef
- Clinical significance of lncRNA PAX8-AS1 and miR-96-5p in non-small cell lung cancer
- Prognostic Role of Claudin-1 Immunohistochemistry in Malignant Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Nae Yu Kim, Won Jin Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):173-179. Published online March 5, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.03
- 8,680 View
- 167 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although the correlation between low claudin-1 expression and worse prognosis has been reported, details on the prognostic implications of claudin-1 expression in various malignant tumors remain unclear. The present study aimed to elucidate the prognostic roles of claudin- 1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) in various malignant tumors through a meta-analysis.
Methods
The study included 2,792 patients from 22 eligible studies for assessment of the correlation between claudin-1 expression and survival rate in various malignant tumors. A subgroup analysis based on the specific tumor and evaluation criteria of claudin-1 IHC was conducted.
Results
Low claudin-1 expression was significantly correlated with worse overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio [HR], 1.851; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.506 to 2.274) and disease-free survival (DFS) (HR, 2.028; 95% CI, 1.313 to 3.134) compared to high claudin-1 expression. Breast, colorectal, esophageal, gallbladder, head and neck, and lung cancers, but not cervical, liver or stomach cancers, were significantly correlated with worse OS. Breast, colorectal, esophageal, and thyroid cancers with low claudin-1 expression were associated with poorer DFS. In the lower cut-off subgroup (< 25.0%) with respect to claudin-1 IHC, low claudin-1 expression was significantly correlated with worse OS and DFS.
Conclusions
Taken together, low claudin-1 IHC expression is significantly correlated with worse survival in various malignant tumors. More detailed criteria for claudin-1 IHC expression in various malignant tumors are needed for application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
Fangqian Du, Yuwei Xie, Shengze Wu, Mengling Ji, Bingzi Dong, Chengzhan Zhu
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 1801. CrossRef - The Significance of Relative Claudin Expression in Odontogenic Tumors
Ekarat Phattarataratip, Kraisorn Sappayatosok
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(2): 480. CrossRef - Claudin-1 upregulation is associated with favorable tumor features and a reduced risk for biochemical recurrence in ERG-positive prostate cancer
Simon Kind, Franziska Büscheck, Doris Höflmayer, Claudia Hube-Magg, Martina Kluth, Maria Christina Tsourlakis, Stefan Steurer, Till S. Clauditz, Andreas M. Luebke, Eike Burandt, Waldemar Wilczak, Andrea Hinsch, David Dum, Sören Weidemann, Christoph Fraune
World Journal of Urology.2020; 38(9): 2185. CrossRef - Characterisation of endogenous Claudin‐1 expression, motility and susceptibility to hepatitis C virus in CRISPR knock‐in cells
Camille M.H. Clément, Maika S. Deffieu, Cristina M. Dorobantu, Thomas F. Baumert, Nilda Vanesa Ayala‐Nunez, Yves Mély, Philippe Ronde, Raphael Gaudin
Biology of the Cell.2020; 112(5): 140. CrossRef - Comment on “Prognostic Role of Claudin-1 Immunohistochemistry in Malignant Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis”
Bolin Wang, Yan Huang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(6): 411. CrossRef
- Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- Hye Yoon Chang, Chan Kwon Jung, Junwoo Isaac Woo, Sanghun Lee, Joonyoung Cho, Sun Woo Kim, Tae-Yeong Kwak
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):1-12. Published online December 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.12.16
- 33,218 View
- 1,287 Download
- 128 Web of Science
- 142 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As in other domains, artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important in medicine. In particular,deep learning-based pattern recognition methods can advance the field of pathology byincorporating clinical, radiologic, and genomic data to accurately diagnose diseases and predictpatient prognoses. In this review, we present an overview of artificial intelligence, the brief historyof artificial intelligence in the medical domain, recent advances in artificial intelligence applied topathology, and future prospects of pathology driven by artificial intelligence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
Shuangshuang Li, Kaiwen Zhao, Wen Li, Qingsheng Lu, Jian Zhou, Jia He
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2026; 122: 895. CrossRef - An automatic, rapid and accurate method for the annotation of tumor components on whole slide images
Hong Tang, Xiaodong Wang, Xiaolin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Xinyue Tang, Yaqiong Ma, Ying Chen, Guanzhen Yu
Journal of Histotechnology.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Exploring the status of artificial intelligence for healthcare research in Africa: a bibliometric and thematic analysis
Tabu S. Kondo, Salim A. Diwani, Ally S. Nyamawe, Mohamed M. Mjahidi
AI and Ethics.2025; 5(1): 117. CrossRef - Prioritize Threat Alerts Based on False Positives Qualifiers Provided by Multiple AI Models Using Evolutionary Computation and Reinforcement Learning
Anup Sharma, V. G. Kiran Kumar, Asmita Poojari
Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B.2025; 106(4): 1305. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence versus human analysis: Interpreting data in elderly fat reduction study
Piotr Sporek, Mariusz Konieczny
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2025; 12(1): 13. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare applications targeting cancer diagnosis—part I: data structure, preprocessing and data organization
Anna Luíza Damaceno Araújo, Marcelo Sperandio, Giovanna Calabrese, Sarah S. Faria, Diego Armando Cardona Cardenas, Manoela Domingues Martins, Cristina Saldivia-Siracusa, Daniela Giraldo-Roldán, Caique Mariano Pedroso, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2025; 140(1): 79. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence–driven digital pathology in urological cancers: current trends and future directions
Inyoung Paik, Geongyu Lee, Joonho Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hong Koo Ha
Prostate International.2025; 13(4): 181. CrossRef - Optimizing deep learning for accurate blood cell classification: A study on stain normalization and fine-tuning techniques
Mohammed Tareq Mutar, Jaffar Nouri Alalsaidissa, Mustafa Majid Hameed, Ali Almothaffar
Iraqi Journal of Hematology.2025; 14(1): 60. CrossRef - Structural imbalance of medical resources amid population mobility and digital empowerment: a study of national and port-developed provinces in China
Haiwei Fu, Junjie Lu
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of artificial intelligence in pathology: a bibliometric and network analysis
Burcu Sanal Yılmaz
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2025; 6(3): 224. CrossRef - ШТУЧНИЙ ІНТЕЛЕКТ У СУЧАСНІЙ СТОМАТОЛОГІЇ
О. І. Бульбук, О. В. Бульбук, О. В. Шутак, Ю. І. Сухоребський
Art of Medicine.2025; : 101. CrossRef - Natural language processing in veterinary pathology: A review
Lev Stimmer, Raoul V. Kuiper, Laura Polledo, Lorenzo Ressel, Josep M. Monné Rodriguez, Inês B. Veiga, Jonathan Williams, Vanessa Herder
Veterinary Pathology.2025; 62(6): 829. CrossRef - Impact of Magnification, Image Type, and Number on Convolutional Neural Network Performance in Differentiating Canine Large Cell Lymphoma From Non‐Lymphoma via Lymph Node Cytology
Christina Pacholec, Hehuang Xie, Julianne Curnin, Amy Lin, Kurt Zimmerman
Veterinary Clinical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology image-based predictive model for individual survival time of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma patients
Vi Thi-Tuong Vo, Hyung-Jeong Yang, Taebum Lee, Soo-Hyung Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Artificial Intelligence's Potential to Enhance Conventional Anticancer Drug Development
Sorin‐Ștefan Bobolea, Miruna‐Ioana Hinoveanu, Andreea Dimitriu, Miruna‐Andrada Brașoveanu, Cristian‐Nicolae Iliescu, Cristina‐Elena Dinu‐Pîrvu, Mihaela Violeta Ghica, Valentina Anuța, Lăcrămioara Popa, Răzvan Mihai Prisada
Drug Development Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicability of PD-L1 expression in cancer cells based solely on H&E-stained sections
Gavino Faa, Matteo Fraschini, Pina Ziranu, Andrea Pretta, Giuseppe Porcu, Luca Saba, Mario Scartozzi, Nazar Shokun, Massimo Rugge
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 19: 100524. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
Umur Karan, Osman Elbek
Thoracic Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole Slide Imaging Technology and Its Applications: Current and Emerging Perspectives
Ekta Jain, Ankush Patel, Anil V. Parwani, Saba Shafi, Zoya Brar, Shivani Sharma, Sambit K. Mohanty
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(3): 433. CrossRef - ChatGPT as an aid for pathological diagnosis of cancer
Shaivy Malik, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 154989. CrossRef - Computational pathology: A survey review and the way forward
Mahdi S. Hosseini, Babak Ehteshami Bejnordi, Vincent Quoc-Huy Trinh, Lyndon Chan, Danial Hasan, Xingwen Li, Stephen Yang, Taehyo Kim, Haochen Zhang, Theodore Wu, Kajanan Chinniah, Sina Maghsoudlou, Ryan Zhang, Jiadai Zhu, Samir Khaki, Andrei Buin, Fatemeh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100357. CrossRef - Applications of artificial intelligence in the field of oral and maxillofacial pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Nishath Sayed Abdul, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Sunila Bukanakere Sangappa, Marco Di Blasio, Salvatore Crimi, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine-learning models are superior to severity scoring systems for the prediction of the mortality of critically ill patients in a tertiary medical center
Ruey-Hsing Chou, Benny Wei-Yun Hsu, Chun-Lin Yu, Tai-Yuan Chen, Shuo-Ming Ou, Kuo-Hua Lee, Vincent S. Tseng, Po-Hsun Huang, Der-Cherng Tarng
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2024; 87(4): 369. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Technology for the Differentiation of Fresh Human Blood Cells From Other Species Blood in the Investigation of Crime Scenes
Syed Sajid Hussain Shah, Ekramy Elmorsy, Rashad Qasem Ali Othman, Asmara Syed, Syed Umar Armaghan, Syed Usama Khalid Bokhari, Mahmoud E Elmorsy, Abdulhakim Bawadekji
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of Diagnostic and Immunohistochemical Workup and Literature Review Capabilities of Online Artificial Intelligence Assistance Models in Pathology
Johnika Dougan, Netra Patel, Svetoslav Bardarov
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - ChatENT: Augmented Large Language Model for Expert Knowledge Retrieval in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery
Cai Long, Deepak Subburam, Kayle Lowe, André dos Santos, Jessica Zhang, Sang Hwang, Neil Saduka, Yoav Horev, Tao Su, David W.J. Côté, Erin D. Wright
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2024; 171(4): 1042. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in forensic medicine and related sciences – selected issues = Sztuczna inteligencja w medycynie sądowej i naukach pokrewnych – wybrane zagadnienia
Michał Szeremeta, Julia Janica, Anna Niemcunowicz-Janica
Archives of Forensic Medicine and Criminology.2024; 74(1): 64. CrossRef - Unveiling the landscape of pathomics in personalized immunotherapy for lung cancer: a bibliometric analysis
Lei Yuan, Zhiming Shen, Yibo Shan, Jianwei Zhu, Qi Wang, Yi Lu, Hongcan Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PathEX: Make good choice for whole slide image extraction
Xinda Yang, Ranze Zhang, Yuan Yang, Yu Zhang, Kai Chen, Alberto Marchisio
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0304702. CrossRef - Automatic point detection on cephalograms using convolutional neural networks: A two-step method
Miki HORI, Makoto JINCHO, Tadasuke HORI, Hironao SEKINE, Akiko KATO, Ken MIYAZAWA, Tatsushi KAWAI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 701. CrossRef - The use of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in teaching and assessment of postgraduate students in pathology and microbiology
Dipmala Das, Asitava Deb Roy, Subhayan Dasgupta, Rohon Das Roy
Indian Journal of Microbiology Research.2024; 11(3): 140. CrossRef - Inteligencia artificial: desafíos éticos y futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence: ethical and future challenges
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inteligência artificial: desafios éticos e futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Constrained-Disorder Principle Assists in Overcoming Significant Challenges in Digital Health: Moving from “Nice to Have” to Mandatory Systems
Noa Hurvitz, Yaron Ilan
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(4): 994. CrossRef - Building a nonclinical pathology laboratory of the future for pharmaceutical research excellence
D.G. Rudmann, L. Bertrand, A. Zuraw, J. Deiters, M. Staup, Y. Rivenson, J. Kuklyte
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103747. CrossRef - Automated image analysis of keratin 7 staining can predict disease outcome in primary sclerosing cholangitis
Nelli Sjöblom, Sonja Boyd, Anniina Manninen, Sami Blom, Anna Knuuttila, Martti Färkkilä, Johanna Arola
Hepatology Research.2023; 53(4): 322. CrossRef - Application of convolutional neural network for analyzing hepatic fibrosis in mice
Hyun-Ji Kim, Eun Bok Baek, Ji-Hee Hwang, Minyoung Lim, Won Hoon Jung, Myung Ae Bae, Hwa-Young Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Toxicologic Pathology.2023; 36(1): 21. CrossRef - Machine Learning Techniques for Prognosis Estimation and Knowledge Discovery From Lab Test Results With Application to the COVID-19 Emergency
Alfonso Emilio Gerevini, Roberto Maroldi, Matteo Olivato, Luca Putelli, Ivan Serina
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 83905. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in dentistry—A review
Hao Ding, Jiamin Wu, Wuyuan Zhao, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Michael F. Burrow, James K. H. Tsoi
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Age Estimation Using the Demirjian Method: Statistical Analysis Using Neural Networks
Byung-Yoon Roh, Jong-Seok Lee, Sang-Beom Lim, Hye-Won Ryu, Su-Jeong Jeon, Ju-Heon Lee, Yo-Seob Seo, Ji-Won Ryu, Jong-Mo Ahn
Korean Journal of Legal Medicine.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence in health care. Problems of identification of patients' conditions in the processes of detailing the diagnosis
Mintser O
Artificial Intelligence.2023; 28(AI.2023.28): 8. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation for Mature White Blood Cell Image Classification in Deep Learning — Selection of an Optimal Technique for Hematological Morphology Recognition —
Hiroyuki NOZAKA, Kosuke KAMATA, Kazufumi YAMAGATA
IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems.2023; E106.D(5): 707. CrossRef - Rectal Cancer Stages T2 and T3 Identification Based on Asymptotic Hybrid Feature Maps
Shujing Sun, Jiale Wu, Jian Yao, Yang Cheng, Xin Zhang, Zhihua Lu, Pengjiang Qian
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences.2023; 137(1): 923. CrossRef - How to use AI in pathology
Peter Schüffler, Katja Steiger, Wilko Weichert
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2023; 62(9): 564. CrossRef - Cutting-Edge Technologies for Digital Therapeutics: A Review and Architecture Proposals for Future Directions
Joo Hun Yoo, Harim Jeong, Tai-Myoung Chung
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6929. CrossRef - A convolutional neural network STIFMap reveals associations between stromal stiffness and EMT in breast cancer
Connor Stashko, Mary-Kate Hayward, Jason J. Northey, Neil Pearson, Alastair J. Ironside, Johnathon N. Lakins, Roger Oria, Marie-Anne Goyette, Lakyn Mayo, Hege G. Russnes, E. Shelley Hwang, Matthew L. Kutys, Kornelia Polyak, Valerie M. Weaver
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based PTEN Loss Assessment as an Early Predictor of Prostate Cancer Metastasis After Surgery: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Palak Patel, Stephanie Harmon, Rachael Iseman, Olga Ludkowski, Heidi Auman, Sarah Hawley, Lisa F. Newcomb, Daniel W. Lin, Peter S. Nelson, Ziding Feng, Hilary D. Boyer, Maria S. Tretiakova, Larry D. True, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Peter R. Carroll, Matthew R. Co
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(10): 100241. CrossRef - Minimum resolution requirements of digital pathology images for accurate classification
Lydia Neary-Zajiczek, Linas Beresna, Benjamin Razavi, Vijay Pawar, Michael Shaw, Danail Stoyanov
Medical Image Analysis.2023; 89: 102891. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in the Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Sangjoon Choi, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 410. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Based Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms
Jin-Seok Park, Seok Jeong
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2023; 28(3): 53. CrossRef - Framework for Classifying Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Algorithms in Clinical Medicine
Thomas Gniadek, Jason Kang, Talent Theparee, Jacob Krive
Online Journal of Public Health Informatics.2023; 15: e50934. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Future of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Oral Pathology, and Oral Surgery in the Hands of Technology
Ishita Singhal, Geetpriya Kaur, Dirk Neefs, Aparna Pathak
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - AI-Powered Biomolecular-Specific and Label-Free Multispectral Imaging Rapidly Detects Malignant Neoplasm in Surgically Excised Breast Tissue Specimens
Rishikesh Pandey, David Fournier, Gary Root, Machele Riccio, Aditya Shirvalkar, Gianfranco Zamora, Noel Daigneault, Michael Sapack, Minghao Zhong, Malini Harigopal
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(11): 1298. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence for patient scheduling in the real-world health care setting: A metanarrative review
Dacre R.T. Knight, Christopher A. Aakre, Christopher V. Anstine, Bala Munipalli, Parisa Biazar, Ghada Mitri, Jose Raul Valery, Tara Brigham, Shehzad K. Niazi, Adam I. Perlman, John D. Halamka, Abd Moain Abu Dabrh
Health Policy and Technology.2023; 12(4): 100824. CrossRef - Towards Autonomous Healthcare: Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Personalized Medicine and Disease Prediction
Nitin Rane, Saurabh Choudhary, Jayesh Rane
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical imaging and multimodal artificial intelligence models for streamlining and enhancing cancer care: opportunities and challenges
Kevin Pierre, Manas Gupta, Abheek Raviprasad, Seyedeh Mehrsa Sadat Razavi, Anjali Patel, Keith Peters, Bruno Hochhegger, Anthony Mancuso, Reza Forghani
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2023; 23(12): 1265. CrossRef - Automated differential diagnostics of respiratory diseases using an electronic stethoscope
Diana Arhypenko, Denis Panaskin, Dmytro Babko
Polish Journal of Medical Physics and Engineering.2023; 29(4): 208. CrossRef - Application of machine learning in identification of pathogenic microbes
Lakshmi Venkata S Kutikuppala, Kanishk K Adhit, Reewen George D Silva
Digital Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Beginning of a New Era
C Nandini, Shaik Basha, Aarchi Agarawal, R Parikh Neelampari, Krishna P Miyapuram, R Jadeja Nileshwariba
Advances in Human Biology.2023; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Respiratory Medicine
K Kalaiyarasan, R Sridhar
Journal of Association of Pulmonologist of Tamil Nadu.2023; 6(2): 53. CrossRef - Automated abstraction of myocardial perfusion imaging reports using natural language processing
Parija Sharedalal, Ajay Singh, Neal Shah, Diwakar Jain
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.2022; 29(3): 1188. CrossRef - Polyploid giant cancer cell characterization: New frontiers in predicting response to chemotherapy in breast cancer
Geetanjali Saini, Shriya Joshi, Chakravarthy Garlapati, Hongxiao Li, Jun Kong, Jayashree Krishnamurthy, Michelle D. Reid, Ritu Aneja
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 81: 220. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Markov Random Field and Conditional Random Field Approaches in Pathology Image Analysis
Yixin Li, Chen Li, Xiaoyan Li, Kai Wang, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Changhao Sun, Hao Chen, Xinran Wu, Hong Zhang, Qian Wang
Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering.2022; 29(1): 609. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology: From bench to clinic
Jamal Elkhader, Olivier Elemento
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 84: 113. CrossRef - Yeast‐like organisms phagocytosed by circulating neutrophils: Evidence of disseminated histoplasmosis
Yue Zhao, Jenna McCracken, Endi Wang
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2022; 44(1): 51. CrossRef - Whole-slide imaging, tissue image analysis, and artificial intelligence in veterinary pathology: An updated introduction and review
Aleksandra Zuraw, Famke Aeffner
Veterinary Pathology.2022; 59(1): 6. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of computer-aided whole-slide image analysis: from datasets to feature extraction, segmentation, classification and detection approaches
Xintong Li, Chen Li, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Hongzan Sun, Xiaoqi Li, Jian Wu, Yudong Yao, Marcin Grzegorzek
Artificial Intelligence Review.2022; 55(6): 4809. CrossRef - Liquid Biopsy and Artificial Intelligence as Tools to Detect Signatures of Colorectal Malignancies: A Modern Approach in Patient’s Stratification
Octav Ginghina, Ariana Hudita, Marius Zamfir, Andrada Spanu, Mara Mardare, Irina Bondoc, Laura Buburuzan, Sergiu Emil Georgescu, Marieta Costache, Carolina Negrei, Cornelia Nitipir, Bianca Galateanu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated bone marrow cytology using deep learning to generate a histogram of cell types
Rohollah Moosavi Tayebi, Youqing Mu, Taher Dehkharghanian, Catherine Ross, Monalisa Sur, Ronan Foley, Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Clinton J. V. Campbell
Communications Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risultati di esami di laboratorio per intelligenza artificiale e "machine learning"
Marco PRADELLA
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Deception of Certainty: how Non-Interpretable Machine Learning Outcomes Challenge the Epistemic Authority of Physicians. A deliberative-relational Approach
Florian Funer
Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy.2022; 25(2): 167. CrossRef - Deep discriminative learning model with calibrated attention map for the automated diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Sautami Basu, Ravinder Agarwal, Vishal Srivastava
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2022; 76: 103728. CrossRef - Question and Answer Techniques for Financial Audits in Universities Based on Deep Learning
Qiang Li, Hangjun Che
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Noninvasive Screening Tool for Hyperkalemia Using a Single-Lead Electrocardiogram and Deep Learning: Development and Usability Study
Erdenebayar Urtnasan, Jung Hun Lee, Byungjin Moon, Hee Young Lee, Kyuhee Lee, Hyun Youk
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(6): e34724. CrossRef - Impact of artificial intelligence on pathologists’ decisions: an experiment
Julien Meyer, April Khademi, Bernard Têtu, Wencui Han, Pria Nippak, David Remisch
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2022; 29(10): 1688. CrossRef - Rapid Screening Using Pathomorphologic Interpretation to Detect BRAFV600E Mutation and Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer
Satoshi Fujii, Daisuke Kotani, Masahiro Hattori, Masato Nishihara, Toshihide Shikanai, Junji Hashimoto, Yuki Hama, Takuya Nishino, Mizuto Suzuki, Ayatoshi Yoshidumi, Makoto Ueno, Yoshito Komatsu, Toshiki Masuishi, Hiroki Hara, Taito Esaki, Yoshiaki Nakamu
Clinical Cancer Research.2022; 28(12): 2623. CrossRef - Using Deep Learning to Predict Final HER2 Status in Invasive Breast Cancers That are Equivocal (2+) by Immunohistochemistry
Sean A. Rasmussen, Valerie J. Taylor, Alexi P. Surette, Penny J. Barnes, Gillian C. Bethune
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(10): 668. CrossRef - Deep Neural Network for the Prediction of KRAS Genotype in Rectal Cancer
Waleed M Ghareeb, Eman Draz, Khaled Madbouly, Ahmed H Hussein, Mohammed Faisal, Wagdi Elkashef, Mona Hany Emile, Marcus Edelhamre, Seon Hahn Kim, Sameh Hany Emile
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 235(3): 482. CrossRef - Next Generation Digital Pathology: Emerging Trends and Measurement Challenges for Molecular Pathology
Alex Dexter, Dimitrios Tsikritsis, Natalie A. Belsey, Spencer A. Thomas, Jenny Venton, Josephine Bunch, Marina Romanchikova
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2022; 3(3): 168. CrossRef - Animation Design of Multisensor Data Fusion Based on Optimized AVOD Algorithm
Li Ding, Guobing Wei, Kai Zhang, Gengxin Sun
Journal of Sensors.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Study on Machine Translation Teaching Model Based on Translation Parallel Corpus and Exploitation for Multimedia Asian Information Processing
Yan Gong
ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and Estimation of Pathological Data and Findings with Deep Learning Methods
Ahmet Anıl ŞAKIR, Ali Hakan IŞIK, Özlem ÖZMEN, Volkan İPEK
Veterinary Journal of Mehmet Akif Ersoy University.2022; 7(3): 175. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Pathology: Friend or Enemy?
Selim Sevim, Ezgi Dicle Serbes, Murat Bahadır, Mustafa Said Kartal, Serpil Dizbay Sak
Journal of Ankara University Faculty of Medicine.2022; 75(1): 13. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding artificial intelligence in histopathology: A cross-sectional study among oral pathologists in India
M. Indu, Vidya Gurram Shankar, Latha Mary Cherian, Revathi Krishna, Sabu Paul, Pradeesh Sathyan
Saudi Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 9(3): 157. CrossRef - Evaluation Challenges in the Validation of B7-H3 as Oral Tongue Cancer Prognosticator
Meri Sieviläinen, Anna Maria Wirsing, Aini Hyytiäinen, Rabeia Almahmoudi, Priscila Rodrigues, Inger-Heidi Bjerkli, Pirjo Åström, Sanna Toppila-Salmi, Timo Paavonen, Ricardo D. Coletta, Elin Hadler-Olsen, Tuula Salo, Ahmed Al-Samadi
Head and Neck Pathology.2021; 15(2): 469. CrossRef - Amsterdam International Consensus Meeting: tumor response scoring in the pathology assessment of resected pancreatic cancer after neoadjuvant therapy
Boris V. Janssen, Faik Tutucu, Stijn van Roessel, Volkan Adsay, Olca Basturk, Fiona Campbell, Claudio Doglioni, Irene Esposito, Roger Feakins, Noriyoshi Fukushima, Anthony J. Gill, Ralph H. Hruban, Jeffrey Kaplan, Bas Groot Koerkamp, Seung-Mo Hong, Alyssa
Modern Pathology.2021; 34(1): 4. CrossRef - Fabrication of ultra-thin 2D covalent organic framework nanosheets and their application in functional electronic devices
Weikang Wang, Weiwei Zhao, Haotian Xu, Shujuan Liu, Wei Huang, Qiang Zhao
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2021; 429: 213616. CrossRef - Generalizability of Deep Learning System for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Various Cancers
Hyun-Jong Jang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 808. CrossRef - Integrated digital pathology at scale: A solution for clinical diagnostics and cancer research at a large academic medical center
Peter J Schüffler, Luke Geneslaw, D Vijay K Yarlagadda, Matthew G Hanna, Jennifer Samboy, Evangelos Stamelos, Chad Vanderbilt, John Philip, Marc-Henri Jean, Lorraine Corsale, Allyne Manzo, Neeraj H G Paramasivam, John S Ziegler, Jianjiong Gao, Juan C Peri
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2021; 28(9): 1874. CrossRef - Translational Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Diagnostic Pathology in Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Comprehensive and Evolutive Analysis
Julia Moran-Sanchez, Antonio Santisteban-Espejo, Miguel Angel Martin-Piedra, Jose Perez-Requena, Marcial Garcia-Rojo
Biomolecules.2021; 11(6): 793. CrossRef - Development and operation of a digital platform for sharing pathology image data
Yunsook Kang, Yoo Jung Kim, Seongkeun Park, Gun Ro, Choyeon Hong, Hyungjoon Jang, Sungduk Cho, Won Jae Hong, Dong Un Kang, Jonghoon Chun, Kyoungbun Lee, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Kyoung Chul Moon, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyu Sang Lee, Jeong Hwan Park, Won-Ki Jeong, Se Yo
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sliding window based deep ensemble system for breast cancer classification
Amin Alqudah, Ali Mohammad Alqudah
Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology.2021; 45(4): 313. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and computational pathology
Miao Cui, David Y. Zhang
Laboratory Investigation.2021; 101(4): 412. CrossRef - Effects of Image Quantity and Image Source Variation on Machine Learning Histology Differential Diagnosis Models
Elham Vali-Betts, Kevin J. Krause, Alanna Dubrovsky, Kristin Olson, John Paul Graff, Anupam Mitra, Ananya Datta-Mitra, Kenneth Beck, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Cynthia Loomis, Antonio Galvao Neto, Esther Adler, Hooman H. Rashidi
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 5. CrossRef - Feasibility of deep learning‐based fully automated classification of microsatellite instability in tissue slides of colorectal cancer
Sung Hak Lee, In Hye Song, Hyun‐Jong Jang
International Journal of Cancer.2021; 149(3): 728. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare
Yamini D Shah, Shailvi M Soni, Manish P Patel
Indian Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2021; 8(2): 102. CrossRef - Proof of Concept for a Deep Learning Algorithm for Identification and Quantification of Key Microscopic Features in the Murine Model of DSS-Induced Colitis
Agathe Bédard, Thomas Westerling-Bui, Aleksandra Zuraw
Toxicologic Pathology.2021; 49(4): 897. CrossRef - An empirical analysis of machine learning frameworks for digital pathology in medical science
S.K.B. Sangeetha, R Dhaya, Dhruv T Shah, R Dharanidharan, K. Praneeth Sai Reddy
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2021; 1767(1): 012031. CrossRef - Application of Single-Cell Approaches to Study Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Biology
Daniel Royston, Adam J. Mead, Bethan Psaila
Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America.2021; 35(2): 279. CrossRef - Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) and Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI): Diagnostic Algorithm Based on the Quantitative Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM)
Rolf Teschke, Gaby Danan
Diagnostics.2021; 11(3): 458. CrossRef - Searching Images for Consensus
Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Phedias Diamandis, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Amir Safarpoor, Shivam Kalra, Danial Maleki, Abtin Riasatian, Morteza Babaie
The American Journal of Pathology.2021; 191(10): 1702. CrossRef - Automated Classification and Segmentation in Colorectal Images Based on Self‐Paced Transfer Network
Yao Yao, Shuiping Gou, Ru Tian, Xiangrong Zhang, Shuixiang He, Zhiguo Zhou
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and sleep: Advancing sleep medicine
Nathaniel F. Watson, Christopher R. Fernandez
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2021; 59: 101512. CrossRef - Prospective Of Artificial Intelligence: Emerging Trends In Modern Biosciences Research
Pradeep Kumar, Ajit Kumar Singh Yadav, Abhishek Singh
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1020(1): 012008. CrossRef - Use and Control of Artificial Intelligence in Patients Across the Medical Workflow: Single-Center Questionnaire Study of Patient Perspectives
Simon Lennartz, Thomas Dratsch, David Zopfs, Thorsten Persigehl, David Maintz, Nils Große Hokamp, Daniel Pinto dos Santos
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(2): e24221. CrossRef - HEAL: an automated deep learning framework for cancer histopathology image analysis
Yanan Wang, Nicolas Coudray, Yun Zhao, Fuyi Li, Changyuan Hu, Yao-Zhong Zhang, Seiya Imoto, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Geoffrey I Webb, Roger J Daly, Jiangning Song, Zhiyong Lu
Bioinformatics.2021; 37(22): 4291. CrossRef - A Review of Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Gastroenterology
Khalid Nawab, Ravi Athwani, Awais Naeem, Muhammad Hamayun, Momna Wazir
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Cancer-Related Biomarkers Based on Pathological Images: A Systematic Review
Xiaoliang Xie, Xulin Wang, Yuebin Liang, Jingya Yang, Yan Wu, Li Li, Xin Sun, Pingping Bing, Binsheng He, Geng Tian, Xiaoli Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based histopathological segmentation for whole slide images of colorectal cancer in a compressed domain
Hyeongsub Kim, Hongjoon Yoon, Nishant Thakur, Gyoyeon Hwang, Eun Jung Lee, Chulhong Kim, Yosep Chong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Ex Vivo Fluorescent Confocal Microscopy Data: A Feasibility Study
Veronika Shavlokhova, Sameena Sandhu, Christa Flechtenmacher, Istvan Koveshazi, Florian Neumeier, Víctor Padrón-Laso, Žan Jonke, Babak Saravi, Michael Vollmer, Andreas Vollmer, Jürgen Hoffmann, Michael Engel, Oliver Ristow, Christian Freudlsperger
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(22): 5326. CrossRef - A Pathologist-Annotated Dataset for Validating Artificial Intelligence: A Project Description and Pilot Study
Sarah N. Dudgeon, Si Wen, Matthew G. Hanna, Rajarsi Gupta, Mohamed Amgad, Manasi Sheth, Hetal Marble, Richard Huang, Markus D. Herrmann, Clifford H. Szu, Darick Tong, Bruce Werness, Evan Szu, Denis Larsimont, Anant Madabhushi, Evangelos Hytopoulos, Weijie
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 45. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: A Multinational Multi-Center Survey on the Medical and Dental Students' Perception
Sotirios Bisdas, Constantin-Cristian Topriceanu, Zosia Zakrzewska, Alexandra-Valentina Irimia, Loizos Shakallis, Jithu Subhash, Maria-Madalina Casapu, Jose Leon-Rojas, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Dilys Miriam Andrews, Claudia Zeicu, Ahmad Mohammad Bouhuwaish
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital/Computational Technology for Molecular Cytology Testing: A Short Technical Note with Literature Review
Robert Y. Osamura, Naruaki Matsui, Masato Kawashima, Hiroyasu Saiga, Maki Ogura, Tomoharu Kiyuna
Acta Cytologica.2021; 65(4): 342. CrossRef - Advances in Digital Pathology: From Artificial Intelligence to Label-Free Imaging
Frederik Großerueschkamp, Hendrik Jütte, Klaus Gerwert, Andrea Tannapfel
Visceral Medicine.2021; 37(6): 482. CrossRef - Feasibility of fully automated classification of whole slide images based on deep learning
Kyung-Ok Cho, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2020; 24(1): 89. CrossRef - Same same but different: A Web‐based deep learning application revealed classifying features for the histopathologic distinction of cortical malformations
Joshua Kubach, Angelika Muhlebner‐Fahrngruber, Figen Soylemezoglu, Hajime Miyata, Pitt Niehusmann, Mrinalini Honavar, Fabio Rogerio, Se‐Hoon Kim, Eleonora Aronica, Rita Garbelli, Samuel Vilz, Alexander Popp, Stefan Walcher, Christoph Neuner, Michael Schol
Epilepsia.2020; 61(3): 421. CrossRef - Segmentation and Classification in Digital Pathology for Glioma Research: Challenges and Deep Learning Approaches
Tahsin Kurc, Spyridon Bakas, Xuhua Ren, Aditya Bagari, Alexandre Momeni, Yue Huang, Lichi Zhang, Ashish Kumar, Marc Thibault, Qi Qi, Qian Wang, Avinash Kori, Olivier Gevaert, Yunlong Zhang, Dinggang Shen, Mahendra Khened, Xinghao Ding, Ganapathy Krishnamu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology
B. Acs, M. Rantalainen, J. Hartman
Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 288(1): 62. CrossRef - Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology
Soojeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(2): 125. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine
Zeeshan Ahmed, Khalid Mohamed, Saman Zeeshan, XinQi Dong
Database.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Scoring pleurisy in slaughtered pigs using convolutional neural networks
Abigail R. Trachtman, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Angelo Porrello, Andrea Capobianco Dondona, Ercole Del Negro, Andrea Paolini, Giorgio Vignola, Simone Calderara, Giuseppe Marruchella
Veterinary Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status of Computational Intelligence Applications in Dermatological Clinical Practice
Carmen Rodríguez-Cerdeira, José Luís González-Cespón, Roberto Arenas
The Open Dermatology Journal.2020; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - New unified insights on deep learning in radiological and pathological images: Beyond quantitative performances to qualitative interpretation
Yoichi Hayashi
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2020; 19: 100329. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology: Present and Future
Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, Zachi Attia, Adelaide M. Arruda-Olson, Rickey Carter, Panithaya Chareonthaitawee, Hayan Jouni, Suraj Kapa, Amir Lerman, Christina Luong, Jose R. Medina-Inojosa, Peter A. Noseworthy, Patricia A. Pellikka, Margaret M. Redfield, Vero
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(5): 1015. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology
Hideyuki Shimizu, Keiichi I. Nakayama
Cancer Science.2020; 111(5): 1452. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and the future of global health
Nina Schwalbe, Brian Wahl
The Lancet.2020; 395(10236): 1579. CrossRef - The future of pathology is digital
J.D. Pallua, A. Brunner, B. Zelger, M. Schirmer, J. Haybaeck
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153040. CrossRef - Weakly-supervised learning for lung carcinoma classification using deep learning
Fahdi Kanavati, Gouji Toyokawa, Seiya Momosaki, Michael Rambeau, Yuka Kozuma, Fumihiro Shoji, Koji Yamazaki, Sadanori Takeo, Osamu Iizuka, Masayuki Tsuneki
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in oncologic histopathology
Ahmed S. Sultan, Mohamed A. Elgharib, Tiffany Tavares, Maryam Jessri, John R. Basile
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2020; 49(9): 849. CrossRef - Convergence of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Tools in Anatomic Pathology Practice: Current Landscape and Future Directions
Anil V. Parwani, Mahul B. Amin
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2020; 27(4): 221. CrossRef - Advances in tissue-based imaging: impact on oncology research and clinical practice
Arman Rahman, Chowdhury Jahangir, Seodhna M. Lynch, Nebras Alattar, Claudia Aura, Niamh Russell, Fiona Lanigan, William M. Gallagher
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2020; 20(10): 1027. CrossRef - Current Trends of Artificial Intelligence for Colorectal Cancer Pathology Image Analysis: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Hongjun Yoon, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1884. CrossRef - Explainable Machine Learning Model for Predicting GI Bleed Mortality in the Intensive Care Unit
Farah Deshmukh, Shamel S. Merchant
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 115(10): 1657. CrossRef - Prediction of clinically actionable genetic alterations from colorectal cancer histopathology images using deep learning
Hyun-Jong Jang, Ahwon Lee, J Kang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 26(40): 6207. CrossRef - Application of system analysis methods for modeling the development of hand-arm vibration syndrome: problems and approaches to solution
M P Diakovich, M V Krivov
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1661(1): 012029. CrossRef - Histo-ELISA technique for quantification and localization of tissue components
Zhongmin Li, Silvia Goebel, Andreas Reimann, Martin Ungerer
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of artificial intelligence in diagnostic oral pathology-A modern approach
Ayinampudi Bhargavi Krishna, Azra Tanveer, Pancha Venkat Bhagirath, Ashalata Gannepalli
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2020; 24(1): 152. CrossRef - Applications of deep learning for the analysis of medical data
Hyun-Jong Jang, Kyung-Ok Cho
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2019; 42(6): 492. CrossRef - PROMISE CLIP Project: A Retrospective, Multicenter Study for Prostate Cancer that Integrates Clinical, Imaging and Pathology Data
Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Yong Hyun Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong, Choung-Soo Kim, Heounjeong Go, Seong Soo Jeon, Minyong Kang, Hak Jong Lee, Sung Il Hwang, Ji Youl Lee
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(15): 2982. CrossRef - Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence
Christopher J. Kelly, Alan Karthikesalingam, Mustafa Suleyman, Greg Corrado, Dominic King
BMC Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning for Whole Slide Image Analysis: An Overview
Neofytos Dimitriou, Ognjen Arandjelović, Peter D. Caie
Frontiers in Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers to Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Healthcare Management: A Systematic Review
Mir Mohammed Assadullah
SSRN Electronic Journal .2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
- Prognostic Role of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungseek Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):331-338. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.07
- 9,330 View
- 131 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study is to elucidate the clinicopathological significances, including the prognostic role, of metastatic lymph node ratio (mLNR) and tumor deposit diameter in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) through a retrospective review and meta-analysis.
Methods
We categorized the cases into high (≥ 0.44) and low mLNR (< 0.44) and investigated the correlations with clinicopathological parameters in 64 PTCs with neck level VI lymph node (LN) metastasis. In addition, meta-analysis of seven eligible studies was used to investigate the correlation between mLNR and survival.
Results
Among 64 PTCs with neck level VI LN metastasis, high mLNR was found in 34 PTCs (53.1%). High mLNR was significantly correlated with macrometastasis (tumor deposit diameter ≥ 0.2 cm), extracapsular spread, and number of metastatic LNs. Based on linear regression test, mLNR was significantly increased by the largest LN size but not the largest metastatic LN (mLN) size. High mLNR was not correlated with nuclear factor κB or cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression, Ki-67 labeling index, or other pathological parameters of primary tumor. Based on meta-analysis, high mLNR significantly correlated with worse disease-free survival at the 5-year and 10-year follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 4.866; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.527 to 6.714 and HR, 5.769; 95% CI, 2.951 to 11.275, respectively).
Conclusions
Our data showed that high mLNR significantly correlated with worse survival, macrometastasis, and extracapsular spread of mLNs. Further cumulative studies for more detailed criteria of mLNR are needed before application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Chang Liu, Shangjie Yang, Tian Xue, Qian Zhang, Yanjing Zhang, Yufang Zhao, Guolin Yin, Xiaohui Yan, Ping Liang, Liping Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of a Nomogram Based on Ultrasound Radiomics, Clinical Factors, and Enhanced Ultrasound Features for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Lei Gao, Xiuli Wen, Guanghui Yue, Hui Wang, Ziqing Lu, Beibei Wu, Zhihong Liu, Yuming Wu, Dongmei Lin, Shijian Yi, Wei Jiang, Yi Hao
Ultrasonic Imaging.2025; 47(2): 93. CrossRef - Lymph Node Metastasis Ratio: Prognostic Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ana Rita Ferreira, Diogo Ramalho, Daniela Martins, Andreia Amado, Susana Graça, Carlos Soares, Bela Pereira, Maria João Oliveira, Manuel Oliveira, Antónia Póvoa
Indian Journal of Surgery.2025; 87(6): 1047. CrossRef - CD105 (Endoglin) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
İlker Çordan, Tuğba Günler
Clinical Endocrinology.2025; 103(4): 596. CrossRef - Application and subgroup analysis of competing risks model based on different lymph node staging systems in differentiated thyroid cancer
Zhe Xu Cao, Jiang Sheng Huang, Ming Ming Wang
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(5): 1927. CrossRef - Цитологічне прогнозування агресії раку щитоподібної залози як новий перспективний напрямок у клінічній тиреоїдології
H.V. Zelinska
Endokrynologia.2024; 29(4): 363. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin expression, Ki-67 index, and lymph node ratio in the prognostic assessment of papillary thyroid cancer
Helene Lindfors, Marie Karlsen, Ellinor Karlton, Jan Zedenius, Catharina Larsson, Catharina Ihre Lundgren, C. Christofer Juhlin, Ivan Shabo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Node Metastasis as an Independent Factor of Worse Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Renan Aguera Pinheiro, Ana Kober Leite, Beatriz Godoi Cavalheiro, Evandro Sobroza de Mello, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Leandro Luongo Matos
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 943. CrossRef - A High-Quality Nomogram for Predicting Lung Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study
WenYi Wang, JiaJing Liu, XiaoFan Xu, LiQun Huo, XuLin Wang, Jun Gu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Low Lymph Node Yield
Il Ku Kang, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 2947. CrossRef - Superiority of metastatic lymph node ratio over number of node metastases and TNM/AJCC N classification in predicting cancer‐specific survival in medullary thyroid cancer
Andreas Machens, Kerstin Lorenz, Frank Weber, Henning Dralle
Head & Neck.2022; 44(12): 2717. CrossRef - Value of Combining Clinical Factors, Conventional Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features in Preoperative Prediction of Central Lymph Node Metastases of Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Yanfang Wang, Fang Nie, Guojuan Wang, Ting Liu, Tiantian Dong, Yamin Sun
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3403. CrossRef - Atypical Histiocytoid Cells and Multinucleated Giant Cells in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid Predict Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Ji Eun Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 816. CrossRef - Patients Aged ≥55 Years With Stage T1-2N1M1 Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Should Be Downstaged in the Eighth Edition AJCC/TNM Cancer Staging System
Zeming Liu, Sichao Chen, Yihui Huang, Di Hu, Min Wang, Wei Wei, Chao Zhang, Wen Zeng, Liang Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Colorectal Cancers: Comparison Depending on Tumor Location
Jung-Soo Pyo, Young-Min Shin, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1812. CrossRef
- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Thyroid Cytology in India: Contemporary Review and Meta-analysis
- Shipra Agarwal, Deepali Jain
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(6):533-547. Published online October 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.04
- 13,426 View
- 247 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a screening test for triaging thyroid nodules, aiding in subsequent clinical management. However, the advantages have been overshadowed by the multiplicity of reporting systems and a wide range of nomenclature used. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) was formulated in 2007, to give the world a uniform thyroid cytology reporting system, facilitating easy interpretation by the clinicians. Here, we review the status of thyroid FNAC in India in terms of various reporting systems used including a meta-analysis of the previously published data. An extensive literature search was performed using internet search engines. The reports with detailed classification system used in thyroid cytology were included. The meta-analysis of published data was compared with the implied risk of malignancy by TBSRTC. More than 50 studies were retrieved and evaluated. TBSRTC is currently the most widely used reporting system with different studies showing good efficacy and interobserver concordance. Ancillary techniques have, as of now, limited applicability and acceptability in thyroid cytology in India. Twenty-eight published articles met the criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis. When compared with TBSRTC recommendations, the meta-analysis showed a higher risk of malignancy for categories I and III. Thyroid FNAC is practiced all over India. TBSRTC has found widespread acceptance, with most institutions using this system for routine thyroid cytology reporting. However, reasons for a high malignancy risk for categories I and III need to be looked into. Various possible contributing factors are discussed in the review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spinal metastases in primary thyroid malignancies: Single center experience of 44 cases
Basir Ahmed, Edmond Jonathan, M. J. Paul, Krishna Prabhu
World Journal of Surgery.2025; 49(2): 409. CrossRef - Cytopathology in India: Past, Present, and Future
Jitendra Singh Nigam, Jyotsna Naresh Bharti, Ashutosh Rath, Immanuel Pradeep, Biswajit Dey, Ravi Mehrotra
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(9): 466. CrossRef - Evaluation of concordance between the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology 2023 (TBSRTC) and ACR-TIRADS at a tertiary care center in Gujarat
Sushrita Biswas, Ina Shah, Hansa Goswami, Avik Chaudhuri
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2025; 68(2): 338. CrossRef - Thermal imaging based pre-diagnostics tool for Graves’ disease
Vaishali Sharma, Vandana K Dhingra, Snehlata Shakya, Ashok Kumar, Mayank Goswami
Measurement Science and Technology.2024; 35(3): 035702. CrossRef - High Malignancy Risk and Its Predictors in South Indian Patients With Bethesda II Thyroid Nodules
Sunanda Tirupati, Pradeep Puthenveetil, Shilpa Lakkundi, Anudeep Gaddam, Vijaya Sarathi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nuclear features in thyroid cytology: features helpful for a morphological diagnosis in routine practice
Priya Bhagwat, Sabine Pomplun
Diagnostic Histopathology.2024; 30(6): 312. CrossRef - DIAGNOSTIC EFFICACY OF FNAC IN THYROID LESIONS, CLASSIFIED ACCORDING TO BETHESDA SYSTEM WITH CYTOHISTOLOGICAL CORRELATION
KIRAN KUMARI MEENA, SANDHYA BORDIA, POOJA KANWAT, SEEMA MEENA, PRAGYA JAKHAR
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2024; : 125. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thyroid Lesions by the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology
Syed Asif Hashmi, Monika Aggrawal, Rahul Pandey, Deepika Gulati, Inam Danish Khan
Journal of Marine Medical Society.2023; 25(1): 73. CrossRef - Incidence and Malignancy Rates in Thyroid Nodules in North-East Indian Population by Bethesda System: A Single Institutional Experience of 3 Years
Suvamoy Chakraborty, Manu C. Balakrishnan, Vandana Raphael, Prachurya Tamuli, Anuradha Deka
South Asian Journal of Cancer.2023; 12(02): 166. CrossRef - Evaluation of Concordance of Ultrasound, Cytology, and Histopathology in Solitary Thyroid Nodules
Sunil Chumber, Surabhi Vyas, Kamal Kataria, Shipra Agarwal, Yashwant S Rathore, Gopal Puri, Sushma Yadav, Kanika Sharma, Amit Patidar
Indian Journal of Endocrine Surgery and Research.2023; 18(1): 17. CrossRef - Cytomorphological Spectrum of Head and Neck Lesions by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in a Tertiary Care Center
Amandeep Kaur, Sonali Poonia, Karandeep Singh, Dalbir Kaur, Mohit Madhukar, Ravish Godara
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2023; 15(Suppl 1): S315. CrossRef - The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(6): 289. CrossRef - Cytomorphological Categorization of Thyroid Lesions according to The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytology and Correlation with their Histological Outcome
Meenakshi Kamboj, Anurag Mehta, Sunil Pasricha, Gurudutt Gupta, Anila Sharma, Garima Durga
Journal of Cytology.2022; 39(1): 44. CrossRef - Is Surgery Necessary in Benign Thyroid Lesions?
Pushkar Chaudhary, Naseem Noorunnisa
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University.2022; 17(3): 799. CrossRef - Effect of the Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm With Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP) Nomenclature Revision on Indian Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Practice
Chanchal Rana, Pooja Ramakant, Divya Goel, Akanksha Singh, KulRanjan Singh, Suresh Babu, Anand Mishra
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2021; 156(2): 320. CrossRef - The combination of ACR‐Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data system and The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology in the evaluation of thyroid nodules—An institutional experience
Shanmugasundaram Sakthisankari, Sreenivasan Vidhyalakshmi, Sivanandam Shanthakumari, Balalakshmoji Devanand, Udayasankar Nagul
Cytopathology.2021; 32(4): 472. CrossRef - Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Anita M. Borges
Journal of Head & Neck Physicians and Surgeons.2021; 9(2): 69. CrossRef - Risk of malignancy in Thyroid “Atypia of undetermined significance/Follicular lesion of undetermined significance” and its subcategories – A 5-year experience
Abha Thakur, Haimanti Sarin, Dilpreet Kaur, Deepak Sarin
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2019; 62(4): 544. CrossRef - Thyroid FNA cytology in Asian practice—Active surveillance for indeterminate thyroid nodules reduces overtreatment of thyroid carcinomas
K. Kakudo, M. Higuchi, M. Hirokawa, S. Satoh, C. K. Jung, A. Bychkov
Cytopathology.2017; 28(6): 455. CrossRef - The Use of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Cytology in Patients with Thyroid Nodules in Asia: A Brief Overview of Studies from the Working Group of Asian Thyroid FNA Cytology
Chan Kwon Jung, SoonWon Hong, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 571. CrossRef
- Spinal metastases in primary thyroid malignancies: Single center experience of 44 cases
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Korean Breast Cancer Patients by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Meta-Analysis of Human Papillomavirus and Breast Cancer
- Jinhyuk Choi, Chungyeul Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim, Jinhwan Lee, Hyeyoon Chang, Aeree Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):442-450. Published online October 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.08
- 14,236 View
- 225 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a well-established oncogenic virus of cervical, anogenital, and oropharyngeal cancer. Various subtypes of HPV have been detected in 0% to 60% of breast cancers. The roles of HPV in the carcinogenesis of breast cancer remain controversial. This study was performed to determine the prevalence of HPV-positive breast cancer in Korean patients and to evaluate the possibility of carcinogenic effect of HPV on breast.
Methods
Meta-analysis was performed in 22 case-control studies for HPV infection in breast cancer. A total of 123 breast cancers, nine intraductal papillomas and 13 nipple tissues of patients with proven cervical HPV infection were tested by real-time polymerase chain reaction to detect 28 subtypes of HPV. Breast cancers were composed of 106 formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) breast cancer samples and 17 touch imprint cytology samples of breast cancers.
Results
The overall odds ratio between breast cancer and HPV infection was 5.43 (95% confidence interval, 3.24 to 9.12) with I2 = 34.5% in meta-analysis of published studies with case-control setting and it was statistically significant. HPV was detected in 22 cases of breast cancers (17.9%) and two cases of intaductal papillomas (22.2%). However, these cases had weak positivity.
Conclusions
These results failed to serve as significant evidence to support the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. Further study with larger epidemiologic population is merited to determine the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
Zhi-yong Liu, Ran Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in human papillomavirus detection for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis: challenges of conventional methods and opportunities for emergent tools
O. Fashedemi, Okoroike C. Ozoemena, Siwaphiwe Peteni, Aderemi B. Haruna, Leshweni J. Shai, Aicheng Chen, Frankie Rawson, Maggie E. Cruickshank, David Grant, Oluwafunmilola Ola, Kenneth I. Ozoemena
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(7): 1428. CrossRef - Bacterial-Viral Interactions in Human Orodigestive and Female Genital Tract Cancers: A Summary of Epidemiologic and Laboratory Evidence
Ikuko Kato, Jilei Zhang, Jun Sun
Cancers.2022; 14(2): 425. CrossRef - Breast cancer association with oncogenic papillomaviruses: papillomaviral DNA detection in breast cancer cells
G. M. Volgareva
Advances in Molecular Oncology.2022; 9(2): 10. CrossRef - Presence of Human Papillomavirus DNA in Malignant Neoplasia and Non-Malignant Breast Disease
Erika Maldonado-Rodríguez, Marisa Hernández-Barrales, Adrián Reyes-López, Susana Godina-González, Perla I. Gallegos-Flores, Edgar L. Esparza-Ibarra, Irma E. González-Curiel, Jesús Aguayo-Rojas, Adrián López-Saucedo, Gretel Mendoza-Almanza, Jorge L. Ayala-
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3648. CrossRef - Risk Role of Breast Cancer in Association with Human Papilloma Virus among Female Population in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Chia-Hsin Liu, Chi-You Liao, Ming-Hsin Yeh, James Cheng-Chung Wei
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2235. CrossRef - HPV-Associated Breast Cancer: Myth or Fact?
Erik Kudela, Eva Kudelova, Erik Kozubík, Tomas Rokos, Terezia Pribulova, Veronika Holubekova, Kamil Biringer
Pathogens.2022; 11(12): 1510. CrossRef - Assessment of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Risk Factors in Egyptian Women With Breast Cancer
Nabila El-Sheikh, Nahla O Mousa, Amany M Tawfeik, Alaa M Saleh, Iman Elshikh, Mohamed Deyab, Faten Ragheb, Manar M Moneer, Ahmed Kawashti, Ahmed Osman, Mohamed Elrefaei
Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Detection by Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (CISH) and p16 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) in Breast Intraductal Papilloma and Breast Carcinoma
Hua Guo, Juan P. Idrovo, Jin Cao, Sudarshana Roychoudhury, Pooja Navale, Louis J. Auguste, Tawfiqul Bhuiya, Silvat Sheikh-Fayyaz
Clinical Breast Cancer.2021; 21(6): e638. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus in Breast Carcinogenesis: A Passenger, a Cofactor, or a Causal Agent?
Rancés Blanco, Diego Carrillo-Beltrán, Juan P. Muñoz, Alejandro H. Corvalán, Gloria M. Calaf, Francisco Aguayo
Biology.2021; 10(8): 804. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of the papillomavirus prevalence in breast cancer fresh tissues
Geilson Gomes de Oliveira, Ana Katherine Gonçalves, José Eleutério, Luiz Gonzaga Porto Pinheiro
Breast Disease.2021; 41(1): 123. CrossRef - Is human papillomavirus associated with breast cancer or papilloma presenting with pathologic nipple discharge?
Fatih Levent Balci, Cihan Uras, Sheldon Marc Feldman
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2019; 19: 100122. CrossRef - Is the HPV virus responsible for the development of breast cancer?
Erik Kudela, Marcela Nachajova, Jan Danko
The Breast Journal.2019; 25(5): 1053. CrossRef - Absence of Human Papillomavirus in Benign and Malignant Breast Tissue
Maryam Kazemi Aghdam, Seyed Alireza Nadji, Azadeh Alvandimanesh, Maliheh Khoddami, Yassaman Khademi
Iranian Journal of Pathology.2019; 14(4): 279. CrossRef - Oncogenic Viruses and Breast Cancer: Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus (MMTV), Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), and Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)
James S. Lawson, Brian Salmons, Wendy K. Glenn
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Viral infections and breast cancer – A current perspective
O.M. Gannon, A. Antonsson, I.C. Bennett, N.A. Saunders
Cancer Letters.2018; 420: 182. CrossRef - Prevalence of EBV, HPV and MMTV in Pakistani breast cancer patients: A possible etiological role of viruses in breast cancer
Wasifa Naushad, Orooj Surriya, Hajra Sadia
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2017; 54: 230. CrossRef
- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
- Morphometric Analysis of Thyroid Follicular Cells with Atypia of Undetermined Significance
- Youngjin Kang, Yoo Jin Lee, Jiyoon Jung, Youngseok Lee, Nam Hee Won, Yang Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):287-293. Published online June 13, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.04.04
- 11,373 View
- 96 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) is a category that encompasses a heterogeneous group of thyroid aspiration cytology. It has been reclassified into two subgroups based on the cytomorphologic features: AUS with cytologic atypia and AUS with architectural atypia. The nuclear characteristics of AUS with cytologic atypia need to be clarified by comparing to those observed in Hashimoto thyroiditis and benign follicular lesions.
Methods
We selected 84 cases of AUS with histologic follow-up, 24 cases of Hashimoto thyroiditis, and 26 cases of benign follicular lesions. We also subcategorized the AUS group according to the follow-up biopsy results into a papillary carcinoma group and a nodular hyperplasia group. The differences in morphometric parameters, including the nuclear areas and perimeters, were compared between these groups.
Results
The AUS group had significantly smaller nuclear areas than the Hashimoto thyroiditis group, but the nuclear perimeters were not statistically different. The AUS group also had significantly smaller nuclear areas than the benign follicular lesion group; however, the AUS group had significantly longer nuclear perimeters. The nuclear areas in the papillary carcinoma group were significantly smaller than those in the nodular hyperplasia group; however, the nuclear perimeters were not statistically different.
Conclusions
We found the AUS group to be a heterogeneous entity, including histologic follow-up diagnoses of papillary carcinoma and nodular hyperplasia. The AUS group showed significantly greater nuclear irregularities than the other two groups. Utilizing these features, nuclear morphometry could lead to improvements in the accuracy of the subjective diagnoses made with thyroid aspiration cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining structural equation modeling analysis with machine learning for early malignancy detection in Bethesda Category III thyroid nodules
Zeliha Aydın Kasap, Burçin Kurt, Ali Güner, Elif Özsağır, Mustafa Emre Ercin
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.2025; 167: 103186. CrossRef - Meta-analysis on the utility of morphometry in the cytological differential diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms
Prema Saldanha
MGM Journal of Medical Sciences.2024; 11(1): 49. CrossRef - Gray zone Bethesda category III – Atypia of undetermined significance lesions of the thyroid: Potential diagnostic issues and image morphometry as a useful adjunct to cytomorphology
Tarunpreet Saini, Reetu Kundu, Manish Rohilla, Parikshaa Gupta, Nalini Gupta, Radhika Srinivasan, Uma Nahar Saikia, Pranab Dey
Cytojournal.2024; 21: 38. CrossRef - Morphometric study in thyroid tumors
Iuliana Mohorea, Bogdan Socea, Alexandru Carâp, Dragoș Șerban, Zenaida Ceaușu, Mihail Ceaușu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Usefulness of Immunocytochemistry of CD56 in Determining Malignancy from Indeterminate Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
Hyunseo Cha, Ju Yeon Pyo, Soon Won Hong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(6): 404. CrossRef
- Combining structural equation modeling analysis with machine learning for early malignancy detection in Bethesda Category III thyroid nodules
- Aquaporin 1 Is an Independent Marker of Poor Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Sumi Yun, Ping-Li Sun, Yan Jin, Hyojin Kim, Eunhyang Park, Soo Young Park, Kyuho Lee, Kyoungyul Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):251-257. Published online June 7, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.30
- 11,812 View
- 123 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) overexpression has been shown to be associated with uncontrolled cell replication, invasion, migration, and tumor metastasis. We aimed to evaluate AQP1 expression in lung adenocarcinomas and to examine its association with clinicopathological features and prognostic significance. We also investigated the association between AQP1 overexpression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers.
Methods
We examined AQP1 expression in 505 cases of surgically resected lung adenocarcinomas acquired at the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital from 2003 to 2012. Expression of AQP1 and EMT-related markers, including Ecadherin and vimentin, were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and tissue microarray.
Results
AQP1 overexpression was associated with several aggressive pathological parameters, including venous invasion, lymphatic invasion, and tumor recurrence. AQP1 overexpression tended to be associated with higher histological grade, advanced pathological stage, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) translocation; however, these differences were not statistically significant. In addition, AQP1 overexpression positively correlated with loss of E-cadherin expression and acquired expression of vimentin. Lung adenocarcinoma patients with AQP1 overexpression showed shorter progression- free survival (PFS, 46.1 months vs. 56.2 months) compared to patients without AQP1 overexpression. Multivariate analysis confirmed that AQP1 overexpression was significantly associated with shorter PFS (hazard ratio, 1.429; 95% confidence interval, 1.033 to 1.977; p=.031).
Conclusions
AQP1 overexpression was thereby concluded to be an independent factor of poor prognosis associated with shorter PFS in lung adenocarcinoma. These results suggested that AQP1 overexpression might be considered as a prognostic biomarker of lung adenocarcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Expanding Role of Aquaporin-1, Aquaporin-3 and Aquaporin-5 as Transceptors: Involvement in Cancer Development and Potential Druggability
Catarina Pimpão, Inês V. da Silva, Graça Soveral
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(3): 1330. CrossRef - The comprehensive potential of AQP1 as a tumor biomarker: evidence from kidney neoplasm cohorts, cell experiments and pan-cancer analysis
Yifan Liu, Donghao Lyu, Yuntao Yao, Jinming Cui, Jiangui Liu, Zikuan Bai, Zihui Zhao, Yuanan Li, Bingnan Lu, Keqin Dong, Xiuwu Pan
Human Genomics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Aquaporins with MAPK Signaling Pathway Unveils Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer: A Transcriptomics Approach
Inês V. da Silva, Paula A. Lopes, Elisabete Fonseca, Emanuel Vigia, Jorge Paulino, Graça Soveral
Biomolecules.2025; 15(4): 488. CrossRef - Obesity Impacts Post‐Myocardial Infarction Neovascularization by Downregulating AQP1 Expression via the TRPC5‐NFATc3 Signaling Pathway
Mengru Gao, Jing Han, Yifei Zhu, Xin Wen, Lei Feng, Tingting Zhou
Comprehensive Physiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin‐1, aquaporin‐3 and aquaporin‐5 differentially modulate cell biophysical and biomechanical properties, impacting cell stiffness and cell–cell adhesion
Catarina Pimpão, Filomena A. Carvalho, Inês Vieira da Silva, Andreia Barateiro, Nuno C. Santos, Graça Soveral
The FEBS Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Clinical application of cold atmospheric-pressure plasma: mechanisms and irradiation conditions
Eun Ji Jeong, Hyun Min Park, Dong Jae Lee, Jun Lee, Jun Yeong Cho, Kyung Deok Seo, Seokjun Je, Min Hyung Jung, Woo Yeon Hwang, Kyung Sook Kim
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics.2024; 57(37): 373001. CrossRef - Aquaporins in Cancer Biology
Chul So Moon, David Moon, Sung Koo Kang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comprehensive Prognostic Analysis of Tumor-Related Blood Group Antigens in Pan-Cancers Suggests That SEMA7A as a Novel Biomarker in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
Yange Wang, Chenyang Li, Xinlei Qi, Yafei Yao, Lu Zhang, Guosen Zhang, Longxiang Xie, Qiang Wang, Wan Zhu, Xiangqian Guo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8799. CrossRef - Differential modulation of lung aquaporins among other pathophysiological markers in acute (Cl2 gas) and chronic (carbon nanoparticles, cigarette smoke) respiratory toxicity mouse models
Sukanta S. Bhattacharya, Brijesh Yadav, Ekta Yadav, Ariel Hus, Niket Yadav, Perminder Kaur, Lauren Rosen, Roman Jandarov, Jagjit S. Yadav
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin water channels as regulators of cell-cell adhesion proteins
Sarannya Edamana, Frédéric H. Login, Soichiro Yamada, Tae-Hwan Kwon, Lene N. Nejsum
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2021; 320(5): C771. CrossRef - Targeting Aquaporins in Novel Therapies for Male and Female Breast and Reproductive Cancers
Sidra Khan, Carmela Ricciardelli, Andrea J. Yool
Cells.2021; 10(2): 215. CrossRef - Targeting ion channels for the treatment of lung cancer
Liqin Zhang, Shuya Bing, Mo Dong, Xiaoqiu Lu, Yuancheng Xiong
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2021; 1876(2): 188629. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Aquaporin Superfamily in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Guofu Lin, Luyang Chen, Lanlan Lin, Hai Lin, Zhifeng Guo, Yingxuan Xu, Chanchan Hu, Jinglan Fu, Qinhui Lin, Wenhan Chen, Yiming Zeng, Yuan Xu
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of urinary aquaporin-1 as a biomarker for renal cell carcinoma
Abhilash Cheriyan, Arun Jose Nellickal, Nirmal Thampi John, Lakshmanan Jeyaseelan, Santosh Kumar, Antony Devasia, Nitin Kekre
Indian Journal of Urology.2021; 37(1): 59. CrossRef - Aquaporin 1, 3, and 5 Patterns in Salivary Gland Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma: Expression in Surgical Specimens and an In Vitro Pilot Study
Mérin Barbara Stamboni, Ágatha Nagli de Mello Gomes, Milena Monteiro de Souza, Katia Klug Oliveira, Claudia Fabiana Joca Arruda, Fernanda de Paula, Barbara Beltrame Bettim, Márcia Martins Marques, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Clóvis Antônio Lopes Pinto, Victor El
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(4): 1287. CrossRef - Combined Systematic Review and Transcriptomic Analyses of Mammalian Aquaporin Classes 1 to 10 as Biomarkers and Prognostic Indicators in Diverse Cancers
Pak Hin Chow, Joanne Bowen, Andrea J Yool
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1911. CrossRef - Aquaporins in lung health and disease: Emerging roles, regulation, and clinical implications
Ekta Yadav, Niket Yadav, Ariel Hus, Jagjit S. Yadav
Respiratory Medicine.2020; 174: 106193. CrossRef - Dissecting gene‐environment interactions: A penalized robust approach accounting for hierarchical structures
Cen Wu, Yu Jiang, Jie Ren, Yuehua Cui, Shuangge Ma
Statistics in Medicine.2018; 37(3): 437. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of Aquaporin-1 in Fluoro-Edenite-Induced Malignant Mesothelioma: A Preliminary Report
Giuseppe Angelico, Rosario Caltabiano, Carla Loreto, Antonio Ieni, Giovanni Tuccari, Caterina Ledda, Venerando Rapisarda
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(3): 685. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Aquaporin-Facilitated Cancer Invasion and Metastasis
Michael L. De Ieso, Andrea J. Yool
Frontiers in Chemistry.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin 1 suppresses apoptosis and affects prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Yuzo Yamazato, Atsushi Shiozaki, Daisuke Ichikawa, Toshiyuki Kosuga, Katsutoshi Shoda, Tomohiro Arita, Hirotaka Konishi, Shuhei Komatsu, Takeshi Kubota, Hitoshi Fujiwara, Kazuma Okamoto, Mitsuo Kishimoto, Eiichi Konishi, Yoshinori Marunaka, Eigo Otsuji
Oncotarget.2018; 9(52): 29957. CrossRef - Aquaporin 1 expression is associated with response to adjuvant chemotherapy in stage�II and III colorectal cancer
Hideko Imaizumi, Keiichiro Ishibashi, Seiichi Takenoshita, Hideyuki Ishida
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Aquaporin 3 facilitates tumor growth in pancreatic cancer by modulating mTOR signaling
Xunwei Huang, Li Huang, Minhua Shao
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2017; 486(4): 1097. CrossRef - Prognostic implication of aquaporin 1 overexpression in resected lung adenocarcinoma†
Guido Bellezza, Jacopo Vannucci, Fortunato Bianconi, Giulio Metro, Rachele Del Sordo, Marco Andolfi, Ivana Ferri, Paola Siccu, Vienna Ludovini, Francesco Puma, Angelo Sidoni, Lucio Cagini
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2017; 25(6): 856. CrossRef
- The Expanding Role of Aquaporin-1, Aquaporin-3 and Aquaporin-5 as Transceptors: Involvement in Cancer Development and Potential Druggability
- Detection of Tumor Multifocality Is Important for Prediction of Tumor Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):278-286. Published online June 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.29
- 12,140 View
- 111 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The clinicopathological characteristics and conclusive treatment modality for multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (mPTMC) have not been fully established.
Methods
A retrospective study, systematic review, and meta-analysis were conducted to elucidate the clinicopathological significance of mPTMC. We investigated the multiplicity of 383 classical papillary thyroid microcarcinomas (PTMCs) and the clinicopathological significance of incidental mPTMCs. Correlation between tumor recurrence and multifocality in PTMCs was evaluated through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Results
Tumor multifocality was identified in 103 of 383 PTMCs (26.9%). On linear regression analysis, primary tumor diameter was significantly correlated with tumor number (R2=0.014, p=.021) and supplemental tumor diameter (R2=0.117, p=.023). Of 103 mPTMCs, 61 (59.2%) were non-incidental, with tumor detected on preoperative ultrasonography, and 42 (40.8%) were diagnosed (incidental mPTMCs) on pathological examination. Lymph node metastasis and higher tumor stage were significantly correlated with tumor multifocality. However, there was no difference in nodal metastasis or tumor stage between incidental and non-incidental mPTMCs. On meta-analysis, tumor multifocality was significantly correlated with tumor recurrence in PTMCs (odds ratio, 2.002; 95% confidence interval, 1.475 to 2.719, p<.001).
Conclusions
Our results show that tumor multifocality in PTMC, regardless of manner of detection, is significantly correlated with aggressive tumor behavior. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
Chih-Chieh Hsu, Chun-Yi Tsai, Li-Ching Lin, Shang-Yu Wang, Chun-Nan Yeh, Miaw-Jene Liou, Szu-Tah Chen
Cancer Management and Research.2026; Volume 18: 1. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Multifocality and Bilaterality on Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Merima Goran, Marko Buta, Srdjan Nikolic, Nada Santrac, Nikola Jeftic, Nevena Savkovic, Jovan Raketic, Zoran Kozomara, Natasa Medic-Milijic, Ana Cvetkovic, Saska Pavlovic, Ivan Markovic
Diagnostics.2026; 16(2): 208. CrossRef - A machine learning model utilizing Delphian lymph node characteristics to predict contralateral central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a prospective multicenter study
Jia-ling He, Yu-zhao Yan, Yan Zhang, Jin-sui Li, Fei Wang, Yi You, Wei Liu, Ying Hu, Ming-Hao Wang, Qing-wen Pan, Yan Liang, Ming-shijing Ren, Zi-wei Wu, Kai You, Yi Zhang, Jun Jiang, Peng Tang
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(1): 360. CrossRef - Individual risk factors for recurrence after hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in the presence of autoimmune thyroiditis
E.V. Ryabchenko
P.A. Herzen Journal of Oncology.2023; 12(3): 20. CrossRef - The value of total tumor diameter in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis
Zhu-juan Wu, Bao-ying Xia, Zi-wei Chen, Hao Gong, Munire Abuduwaili, Zhi-chao Xing, An-ping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Negative Histopathological Prognostic Factors Affecting Morbidity in T1 Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Mine Araz, Elgin Özkan, Pınar Gunduz, Cigdem Soydal, N. Özlem Küçük, K. Metin Kır
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2022; 37(1): 56. CrossRef - Total tumor diameter is a better indicator of multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
Ke-cheng Jiang, Bei Lin, Yu Zhang, Ling-qian Zhao, Ding-cun Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective comparison of individual risk factors hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland in combination with autoimmune thyroiditis
E. V. Ryabchenko
Head and neck tumors (HNT).2022; 12(4): 71. CrossRef - The relationship between lipotoxicity and risk of extrathyroidal extension in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Changlin Li, Haixia Guan, Qiao He, Yishen Zhao, Nan liang, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Hui Sun
Endocrine.2021; 74(3): 646. CrossRef - Multifocality and Progression of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma During Active Surveillance
Ryuta Nagaoka, Aya Ebina, Kazuhisa Toda, Tomoo Jikuzono, Marie Saitou, Masaomi Sen, Hiroko Kazusaka, Mami Matsui, Keiko Yamada, Hiroki Mitani, Iwao Sugitani
World Journal of Surgery.2021; 45(9): 2769. CrossRef - Correlation of ThyroSeq Results with Surgical Histopathology in Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
Patrick D. Chin, Catherine Y. Zhu, Dipti P. Sajed, Gregory A. Fishbein, Michael W. Yeh, Angela M. Leung, Masha J. Livhits
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(4): 377. CrossRef - Application of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Management of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Huang, MD Kun, Liu, MD Ji-Bin
ADVANCED ULTRASOUND IN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY.2020; 4(4): 284. CrossRef - Analysis of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms with a Striking Rise of Papillary Microcarcinoma in an Endemic Goiter Region
Alka Mary Mathai, K. Preetha, S. Valsala Devi, Sam Vicliph, Raja Pradeep, Aqib Shaick
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2019; 71(S1): 121. CrossRef - The first postoperative-stimulated serum thyroglobulin is a prognostic factor for thyroid microcarcinomas
Isabela de Oliveira Amui, José Vicente Tagliarini, Emanuel C. Castilho, Mariângela de Alencar Marques, Yoshio Kiy, José Eduardo Corrente, Gláucia M.F.S. Mazeto
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2019; 85(1): 37. CrossRef - Surgical management of follicular thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents: A study of 30 cases
Claudio Spinelli, Leonardo Rallo, Riccardo Morganti, Valentina Mazzotti, Alessandro Inserra, Giovanni Cecchetto, Maura Massimino, Paola Collini, Silvia Strambi
Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2019; 54(3): 521. CrossRef - The role of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in elderly patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a multicentric study
Claudio Gambardella, Renato Patrone, Francesco Di Capua, Chiara Offi, Claudio Mauriello, Guglielmo Clarizia, Claudia Andretta, Andrea Polistena, Alessandro Sanguinetti, Pietrogiorgio Calò, Giovanni Docimo, Nicola Avenia, Giovanni Conzo
BMC Surgery.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Lymph Node Metastases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, in the Central and Lateral Compartments, in Children and Adolescents: Predictive Factors
C. Spinelli, F. Tognetti, S. Strambi, R. Morganti, M. Massimino, P. Collini
World Journal of Surgery.2018; 42(8): 2444. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Challenges and Prospects
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Zachary A. Hurst, Yi Seok Chang, Guang Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of lobectomy and total thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective individual risk factor-matched cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 176(4): 371. CrossRef - Total thyroidectomy may be more reasonable as initial surgery in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a single-center experience
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Lack of Efficacy of Radioiodine Remnant Ablation for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Verification Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Minkyu Han, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2017; 24(9): 2596. CrossRef - Radioactive Iodine Ablation Decrease Recurrences in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma with Lateral Lymph Node Metastasis in Chinese Patients
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgery.2017; 41(12): 3139. CrossRef - The Prognostic Value of Tumor Multifocality in Clinical Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Fei Wang, Xiaolong Yu, Xiaopei Shen, Guangwu Zhu, Yueye Huang, Rengyun Liu, David Viola, Rossella Elisei, Efisio Puxeddu, Laura Fugazzola, Carla Colombo, Barbara Jarzab, Agnieszka Czarniecka, Alfred K Lam, Caterina Mian, Federica Vianello, Linwah Yip, Gar
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(9): 3241. CrossRef - Evaluation of surgical results of micropapillary thyroid cancers according to tumor size and focality
Bekir Uçan, Muhammed Erkam Sencar, Muhammed Kızılgül, Mustafa Özbek, İlknur Öztürk Ünsal, Erman Çakal
Ortadoğu Tıp Dergisi.2017; 9(3): 123. CrossRef - Contrastive study of two screening criteria for active surveillance in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 1001 patients
Kai Qian, Kai Guo, Xiaoke Zheng, Tuanqi Sun, Duanshu Li, Yi Wu, Qinghai Ji, Zhuoying Wang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(39): 65836. CrossRef - 10.1016/j.bjorlp.2018.01.005
CrossRef Listing of Deleted DOIs.2000;[Epub] CrossRef
- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Core Needle Biopsy Is a More Conclusive Follow-up Method Than Repeat Fine Needle Aspiration for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Inconclusive Results: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):217-224. Published online April 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.15
- 13,073 View
- 119 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study investigated the appropriate management of thyroid nodules with prior non-diagnostic or atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance (AUS/FLUS) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
This study included 4,235 thyroid nodules from 26 eligible studies. We investigated the conclusive rate of follow-up core needle biopsy (CNB) or repeat fine needle aspiration (rFNA) after initial fine needle aspiration (FNA) with non-diagnostic or AUS/FLUS results. A diagnostic test accuracy (DTA) review was performed to determine the diagnostic role of the follow-up CNB and to calculate the area under the curve (AUC) on the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve.
Results
The conclusive rates of follow-up CNB and rFNA after initial FNA were 0.879 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.801 to 0.929) and 0.684 (95% CI, 0.627 to 0.736), respectively. In comparison of the odds ratios of CNB and rFNA, CNB had more frequent conclusive results than rFNA (odds ratio, 5.707; 95% CI, 2.530 to 12.875). Upon subgroup analysis, follow-up CNB showed a higher conclusive rate than rFNA in both initial non-diagnostic and AUS/FLUS subgroups. In DTA review of followup CNB, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.94 (95% CI, 0.88 to 0.97) and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.91), respectively. The AUC for the SROC curve was 0.981, nearing 1.
Conclusions
Our results show that CNB has a higher conclusive rate than rFNA when the initial FNA produced inconclusive results. Further prospective studies with more detailed criteria are necessary before follow-up CNB can be applied in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
Mohammad Ali Hasannia, Ramin Pourghorban, Hoda Asefi, Amir Aria, Elham Nazar, Hojat Ebrahiminik, Alireza Mohamadian
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(3): 180. CrossRef - Comparison of Diagnostic Yield Between Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodule
Yeongrok Lee, Myung Jin Ban, Do Hyeon Kim, Jin-Young Kim, Hyung Kwon Byeon, Jae Hong Park
Diagnostics.2025; 15(20): 2566. CrossRef - Repeatedly non-diagnostic thyroid nodules: the experience of two thyroid clinics
Filippo EGALINI, Mattia ROSSI, Chiara MELE, Yanina LIZET CASTILLO, Francesca MALETTA, Barbara PULIGHEDDU, Ezio GHIGO, Ruth ROSSETTO GIACCHERINO, Loredana PAGANO, Mauro PAPOTTI
Minerva Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology vs. Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective, Experimental Study Using Surgical Specimen
Hyuk Kwon, Jandee Lee, Soon Won Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Jin Young Kwak, Jung Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2022; 83(3): 645. CrossRef - Comparison of Core Needle Biopsy and Repeat Fine-Needle Aspiration in Avoiding Diagnostic Surgery for Thyroid Nodules Initially Diagnosed as Atypia/Follicular Lesion of Undetermined Significance
Leehi Joo, Dong Gyu Na, Ji-hoon Kim, Hyobin Seo
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(2): 280. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of core needle biopsy as a first‐line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules according to ultrasound patterns: Comparison with fine needle aspiration using propensity score matching analysis
Hye Shin Ahn, Inyoung Youn, Dong Gyu Na, Soo Jin Kim, Mi Yeon Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2021; 94(3): 494. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - 2021 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System and Imaging-Based Management of Thyroid Nodules: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology Consensus Statement and Recommendations
Eun Ju Ha, Sae Rom Chung, Dong Gyu Na, Hye Shin Ahn, Jin Chung, Ji Ye Lee, Jeong Seon Park, Roh-Eul Yoo, Jung Hwan Baek, Sun Mi Baek, Seong Whi Cho, Yoon Jung Choi, Soo Yeon Hahn, So Lyung Jung, Ji-hoon Kim, Seul Kee Kim, Soo Jin Kim, Chang Yoon Lee, Ho K
Korean Journal of Radiology.2021; 22(12): 2094. CrossRef - Malignancy rate of Bethesda category III thyroid nodules according to ultrasound risk stratification system and cytological subtype
Won Sang Yoo, Hwa Young Ahn, Hye Shin Ahn, Yun Jae Chung, Hee Sung Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Mirinae Seo, Jae Hoon Moon, Young Joo Park
Medicine.2020; 99(2): e18780. CrossRef - 2019 Practice guidelines for thyroid core needle biopsy: a report of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association
Chan Kwon Jung, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Gyu Na, Young Lyun Oh, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 64. CrossRef - Laser Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Non-Functioning Thyroid Nodules: Six-Month Results of a Randomized, Parallel, Open-Label, Trial (LARA Trial)
Roberto Cesareo, Claudio Maurizio Pacella, Valerio Pasqualini, Giuseppe Campagna, Mario Iozzino, Andrea Gallo, Angelo Lauria Pantano, Roberto Cianni, Claudio Pedone, Paolo Pozzilli, Chiara Taffon, Anna Crescenzi, Silvia Manfrini, Andrea Palermo
Thyroid.2020; 30(6): 847. CrossRef - Diagnostic Efficacy and Safety of Core Needle Biopsy as a First-Line Diagnostic Method for Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Cohort Study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Hunkyung Lee
Thyroid.2020; 30(8): 1141. CrossRef - Is thyroid core needle biopsy a valid compliment to fine-needle aspiration?
Liron Pantanowitz, Lester D.R. Thompson, Xin Jing, Esther Diana Rossi
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2020; 9(5): 383. CrossRef - A Monocentric Retrospective Study about the Correlation between Histology and Cytology of Thyroid Indeterminate Nodules Classified as TIR 3A and TIR 3B, according to 2014 Italian Consensus for Classification and Reporting of Thyroid Cytology
Francesco Quaglino, Giulia Arnulfo, Sergio Sandrucci, Claudio Rossi, Valentina Marchese, Roberto Saracco, Stefano Guzzetti, Stefano Taraglio, Enrico Mazza
Advances in Medicine.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Comparison of Core needle biopsy and thyroidectomy specimens
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Younghye Kim, Seung Yeon Ha
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2018; 32: 35. CrossRef - Statement and Recommendations on Interventional Ultrasound as a Thyroid Diagnostic and Treatment Procedure
Christoph F. Dietrich, Thomas Müller, Jörg Bojunga, Yi Dong, Giovanni Mauri, Maija Radzina, Manjiri Dighe, Xin-Wu Cui, Frank Grünwald, Andreas Schuler, Andre Ignee, Huedayi Korkusuz
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2018; 44(1): 14. CrossRef - Role of core needle biopsy as a first-line diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules: a retrospective cohort study
Min Ji Hong, Dong Gyu Na, Soo Jin Kim, Dae Sik Kim
Ultrasonography.2018; 37(3): 244. CrossRef - Core Needle Biopsy of the Thyroid: 2016 Consensus Statement and Recommendations from Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology
Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, So Lyung Jung, Ji-hoon Kim, Jin Yong Sung, Kyu Sun Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hee Shin, Yoon Jung Choi, Eun Ju Ha, Hyun Kyung Lim, Soo Jin Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Kwang Hwi Lee, Young Jun Choi, Inyoung Youn, Young Joong Kim, Hye Sh
Korean Journal of Radiology.2017; 18(1): 217. CrossRef - Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy: comparison of post-biopsy hematoma rates and risk factors
In Hye Chae, Eun-Kyung Kim, Hee Jung Moon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Vivian Y. Park, Jin Young Kwak
Endocrine.2017; 57(1): 108. CrossRef - The Role of Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Indeterminate Results on Previous Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
C.H. Suh, J.H. Baek, C. Park, Y.J. Choi, J.H. Lee
American Journal of Neuroradiology.2017; 38(7): 1421. CrossRef
- Diagnostic yield of fine needle aspiration with simultaneous core needle biopsy for thyroid nodules
- Prognostic Implication of Semi-quantitative Immunohistochemical Assessment of CD20 Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Chang Hwan Choi, Young Hoon Park, Joo Han Lim, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):96-103. Published online February 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.01.12
- 11,681 View
- 135 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Immunohistochemical demonstration of CD20 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is prerequisite not only for the diagnosis but also for assigning patients to rituximab-containing chemotherapy. However, little is known about the impact of abundance of CD20 expression assessed by immunohistochemistry on the clinical outcome of DLBCL. We performed a semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of CD20 expression in DLBCL to examine the prognostic implication of the level of CD20 expression. Methods: Pre-treatment diagnostic tissue samples from 48 DLBCL patients who were treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) regimen were represented in a tissue microarray and immunostained for CD20. The relative abundance of CD20 expression was semi-quantitatively scored using a web-based ImmunoMembrane plug-in. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to determine a prognostically relevant cut-off score in order to dichotomize the patients into CD20-high versus CD20-low groups. Results: The levels of CD20 expression were heterogeneous among the patients, with a wide and linear distribution of scores. Patients in CD20-low group showed significantly poor clinical outcome. Conclusions: The levels of CD20 expression in DLBCL are heterogeneous among the patients with DLBCL. A subgroup of the patients with CD20 expression levels below the cut-off score showed poor clinical outcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Expression Levels of CD20 as a Prognostic Value in Feline B-Cell Nasal Lymphoma: A Pilot Study
Kravee Chaipoca, Theerapol Sirinarumitr, Supreeya Srisampan, Charuwan Wongsali, Attawit Kovitvadhi, Tassanee Jaroensong
Animals.2024; 14(7): 1043. CrossRef - Prognostic molecular biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era and their therapeutic implications
Sotirios G. Papageorgiou, Thomas P. Thomopoulos, Ioannis Katagas, Anthi Bouchla, Vassiliki Pappa
Therapeutic Advances in Hematology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel tumour–infiltrating lymphocyte-related risk stratification based by flow cytometry for patients with de novo angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma
Qiqi Zhu, Xueqin Deng, Wenqing Yao, Zihang Chen, Yunxia Ye, Limin Gao, Wenyan Zhang, Weiping Liu, Sha Zhao
Annals of Hematology.2021; 100(3): 715. CrossRef - Induced CD20 Expression on B-Cell Malignant Cells Heightened the Cytotoxic Activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Engineered T Cells
Yingxi Xu, Saisai Li, Ying Wang, Jia Liu, Xinhe Mao, Haiyan Xing, Zheng Tian, Kejing Tang, Xiaolong Liao, Qing Rao, Dongsheng Xiong, Min Wang, Jianxiang Wang
Human Gene Therapy.2019; 30(4): 497. CrossRef - Characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma arising in young patients: Particular focus on molecular alteration and tumor immunity
Hyang Joo Ryu, Eun Kyung Kim, Byoung Chul Cho, Sun Och Yoon
Head & Neck.2019; 41(1): 198. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin D (IgD) and IgD receptor expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Xing Dai, Yu-Jing Wu, Xiao-Yi Jia, Yan Chang, Hua-Xun Wu, Chun Wang, Wei Wei
Hematology.2019; 24(1): 544. CrossRef - The implications of TrkA and MET aberrations in de novo salivary duct carcinoma
Hyang Joo Ryu, Yoon Woo Koh, Sun Och Yoon
Human Pathology.2018; 81: 18. CrossRef - Prognostic stratification improvement by integrating ID1/ID3/IGJ gene expression signature and immunophenotypic profile in adult patients with B-ALL
Nataly Cruz-Rodriguez, Alba L. Combita, Leonardo J. Enciso, Lauren F. Raney, Paula L. Pinzon, Olga C. Lozano, Alba M. Campos, Niyireth Peñaloza, Julio Solano, Maria V. Herrera, Jovanny Zabaleta, Sandra Quijano
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Implications of infiltrating immune cells within bone marrow of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Juhyeon Jeong, Eun Ji Oh, Woo Ick Yang, Soo Jeong Kim, Sun Och Yoon
Human Pathology.2017; 64: 222. CrossRef - Architectural patterns of p16 immunohistochemical expression associated with cancer immunity and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Hyang Joo Ryu, Eun Kyung Kim, Su Jin Heo, Byoung Chul Cho, Hye Ryun Kim, Sun Och Yoon
APMIS.2017; 125(11): 974. CrossRef - New developments in the pathology of malignant lymphoma. A review of the literature published from January–April 2016
J. Han van Krieken
Journal of Hematopathology.2016; 9(2): 73. CrossRef - Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure—what to do?
Bertrand Coiffier, Clémentine Sarkozy
Hematology.2016; 2016(1): 366. CrossRef
- The Expression Levels of CD20 as a Prognostic Value in Feline B-Cell Nasal Lymphoma: A Pilot Study
- Comparison of Analytical and Clinical Performance of HPV 9G DNA Chip, PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip, and Hybrid-Capture II Assay in Cervicovaginal Swabs
- Ho Young Jung, Hye Seung Han, Hyo Bin Kim, Seo Young Oh, Sun-Joo Lee, Wook Youn Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):138-146. Published online January 13, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.21
- 10,312 View
- 68 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can be detected by using several molecular methods, including Hybrid-Capture II (HC2) assay and variable HPV DNA chip tests, although each method has different sensitivities and specificities. Methods: We performed HPV 9G DNA Chip (9G) and PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip (PANArray) tests on 118 cervicovaginal swabs and compared the results with HC2, cytology, histology, and direct sequencing results. Results: The overall and high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) positivity rates were 62.7% and 44.9% using 9G, and 61.0% and 30.5% using PANArray, respectively. The positivity rates for HR-HPV with these two chips were significantly lower than 55.1% when HC2 was used. The sensitivity of overall HPV positivity in detecting histologically confirmed low-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions or higher was 88.7% for all three tests. The specificity was 58.5% for 9G and 61.5% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 72.3% for HC2. With the HR-HPV+ genotype threshold, the sensitivity decreased to 75.5% for 9G and 52.8% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 88.7% for HC2. Comparison of the two chips showed concordant results in 55.1% of the samples, compatible results in 16.9%, and discordant results in 28.0%, exhibiting poor agreement in detecting certain HPV genotypes. Compared with direct sequencing, 9G yielded no discordant results, whereas PANArray yielded 31 discordant results (26.7%). Conclusions: Compared with HC2, the HPV genotyping tests showed lower sensitivity in histologic correlation. When the two chips were compared, the 9G was more sensitive and accurate for detecting HR-HPV than the PANArray. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
Habtamu Biazin
Journal of Virological Methods.2022; 301: 114435. CrossRef - The clinical performance of human papillomavirus genotyping using PANArray HPV chip: Comparison to ThinPrep cytology alone and co-testing
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Lee-So Maeng
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153121. CrossRef - Analytic performance of PANArray HPV and HPV 9G DNA chip tests for genotyping of high-risk human papillomavirus in cervical ThinPrep PreservCyt samples
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Magdalena Grce
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0224483. CrossRef
- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
- MUC2 Expression Is Correlated with Tumor Differentiation and Inhibits Tumor Invasion in Gastric Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang, Dong-Hoon Kim, Kyungeun Kim, In-Gu Do, Dong Hyun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):249-256. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.03.27
- 10,194 View
- 72 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
While MUC2 is expressed in intestinal metaplasia and malignant lesions, the clinico-pathological significance of MUC2 expression is not fully elucidated in gastric carcinoma (GC). Methods: The present study investigated the correlation between MUC2 expression and clinico-pathological parameters in 167 human GCs. In addition, to confirm the clinicopathological significance of MUC2 expression, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis in 1,832 GCs. Results: MUC2 expression was found in 58 of 167 GCs (34.7%). MUC2-expressing GC showed lower primary tumor (T), regional lymph node (N), and tumor node metastasis (TNM) stages compared with GCs without MUC2 expression (p=.001, p=.001, and p=.011, respectively). However, MUC2 expression was not correlated with Lauren’s classification and tumor differentiation. In meta-analysis, MUC2 expression was significantly correlated with differentiation and lower tumor stage (odds ratio [OR], 1.303; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.020 to 1.664; p = .034 and OR, 1.352; 95% CI, 1.055 to 1.734; p = .017, respectively) but not with Lauren’s classification, pN stage, or pTNM stage. Conclusions: MUC2 expression was correlated with a lower tumor depth and lower lymph node metastasis in our study; the meta-analysis showed a correlation of MUC2 expression with tumor differentiation and lower tumor depth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of mucin family members expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
Shunda Wang, Yongrun Mu, Jianwei Zhang, Chengfeng Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic gastrointestinal markers in primary lung cancer and pulmonary metastases
Karina Malmros, Andreas Lindholm, Halla Vidarsdottir, Karin Jirström, Björn Nodin, Johan Botling, Johanna S. M. Mattsson, Patrick Micke, Maria Planck, Mats Jönsson, Johan Staaf, Hans Brunnström
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(2): 347. CrossRef - Gastric epithelial histology and precancerous conditions
Hang Yang, Wen-Juan Yang, Bing Hu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2022; 14(2): 396. CrossRef - COX-2 strengthens the effects of acid and bile salts on human esophageal cells and Barrett esophageal cells
Shen Jiangang, Kang Nayoung, Wang Hongfang, Li Junda, Chen Li, Bai Xuefeng, Li Mingsong
BMC Molecular and Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative genomic analysis of primary tumors and paired brain metastases in lung cancer patients by whole exome sequencing: a pilot study
Pascale Tomasini, Fabrice Barlesi, Sophie Gilles, Isabelle Nanni-Metellus, Riccardo Soffietti, Emilie Denicolai, Eric Pellegrino, Emilie Bialecki, L’Houcine Ouafik, Philippe Metellus
Oncotarget.2020; 11(50): 4648. CrossRef - A High Ki67/BCL2 Index Could Predict Lower Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Intestinal-Type Gastric Cancer
Kyueng-Whan Min, Dong-Hoon Kim, Byoung Kwan Son, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun-Kyung Kim, Jinwon Seo, Sang Bong Ahn, Yun Ju Jo, Young Sook Park, Junghoon Ha
European Surgical Research.2017; 58(3-4): 158. CrossRef
- Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of mucin family members expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
- In-house Manual Construction of High-Density and High-Quality Tissue Microarrays by Using Homemade Recipient Agarose-Paraffin Blocks
- Kyu Ho Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Yeon Il Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):238-244. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.238
- 11,762 View
- 94 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Self-made tissue punches can be effectively used to punch holes in blank recipient paraffin blocks and extract tissue cores from the donor paraffin blocks for the low-cost construction of tissue microarrays (TMAs). However, variable degrees of section distortion and loss of the tissue cores can occurs during cutting of the TMAs, posing technical problems for in-house manual construction of high-density TMAs. We aimed to update the method for in-house manual TMA construction to improve the quality of high-density TMAs.
Methods Blocks of agarose gel were subjected to the standard tissue processing and embedding procedure to prepare recipient agarose-paraffin blocks. The self-made tissue punches and recipient agarose-paraffin blocks were used to construct TMAs, which were completely melted and re-embedded in paraffin to make finished TMA blocks.
Results The donor tissue cores were completely integrated into the surrounding paraffin of the recipient blocks. This method enabled us to construct high-density TMAs with significantly less section distortion or loss of tissue cores during microtomy.
Conclusions Simple and inexpensive construction of high-density and high-quality TMAs can be warranted by using paraffinized agarose gels as recipient blocks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using Quality Function Deployment to Design an Image-Guided, Multibiopsy Tool for Neurosurgical Applications
Kaytlin Andrews, Hunter Dejean, Cameron MacLeod, Kate Prieditis, Heidi-Lynn Ploeg, James Purzner, Teresa Purzner
Operative Neurosurgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An introduction of an easy-operating and economical technique for tissue microarray preparation
Yi-Jing Chen, Chun-Mei Yang, Jiang-Sheng Huang, Ping Wang, Yan-Hua Lv, Cheng Tang, Wei Deng
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 73(7): 403. CrossRef - Optimization of Tissue Microarrays from Banked Human Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues in the Cancer Research Setting
Tammy Sexton, Gregory L. Kucera, Edward A. Levine, Kounosuke Watabe, Stacey S. O'Neill
Biopreservation and Biobanking.2019; 17(5): 452. CrossRef - Monocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 are independent prognostic biomarkers for the survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and those receiving therapy targeting angiogenesis
Yan-Wei Cao, Yong Liu, Zhen Dong, Lei Guo, En-Hao Kang, Yong-Hua Wang, Wei Zhang, Hai-Tao Niu
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2018; 36(6): 311.e15. CrossRef - Platelet-derived growth factor receptor α in hepatocellular carcinoma is a prognostic marker independent of underlying liver cirrhosis
Jung-Hwan Yu, Joon Mee Kim, Ja Kyung Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Kwan Sik Lee, Jin-Woo Lee, Hye Young Chang, Jung Il Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(24): 39534. CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Semi-quantitative Immunohistochemical Assessment of CD20 Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Chang Hwan Choi, Young Hoon Park, Joo Han Lim, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(2): 96. CrossRef - High Quality Tissue Miniarray Technique Using a Conventional TV/Radio Telescopic Antenna
Mohamed A. Elkablawy, Abdulkader M. Albasri
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(3): 1129. CrossRef
- Using Quality Function Deployment to Design an Image-Guided, Multibiopsy Tool for Neurosurgical Applications
- Comparison of Direct Sequencing, PNA Clamping-Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Pyrosequencing Methods for the Detection of
EGFR Mutations in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma and the Correlation with Clinical Responses to EGFR Tyrosin - Hyun Ju Lee, Xianhua Xu, Hyojin Kim, Yan Jin, Pingli Sun, Ji Eun Kim, Jin-Haeng Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):52-60. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.52
- 12,819 View
- 93 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The aims of this study were to evaluate the abilities of direct sequencing (DS), peptide nucleic acid (PNA) clamping, and pyrosequencing methods to detect epidermal growth factor receptor (
EGFR ) mutations in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) samples and to correlateEGFR mutational status as determined by each method with the clinical response toEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).Methods Sixty-one NSCLC patients treated with EGFR TKIs were identified to investigate somatic mutations in the
EGFR gene (exons 18-21).Results Mutations in the
EGFR gene were detected in 38 of the 61 patients (62%) by DS, 35 (57%) by PNA clamping and 37 (61%) by pyrosequencing. A total of 44 mutations (72%) were found by at least one of the three methods, and the concordances among the results were relatively high (82-85%; kappa coefficient, 0.713 to 0.736). There were 15 discordant cases (25%) among the three different methods.Conclusions All three
EGFR mutation tests had good concordance rates (over 82%) for FFPE samples. These results suggest that if the DNA quality and enrichment of tumor cells are assured, then DS, PNA clamping, and pyrosequencing are appropriate methods for the detection ofEGFR mutations.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Trends of Lung Cancer in Korea
Jae Guk Lee, Ho Cheol Kim, Chang-Min Choi
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2021; 84(2): 89. CrossRef - Predictive value of KRAS mutation and excision repair cross-complementing 1 (ERCC1) protein overexpression in patients with colorectal cancer administered FOLFOX regimen
Sun Min Park, Sung Bong Choi, Yoon Suk Lee, In Kyu Lee
Asian Journal of Surgery.2021; 44(5): 715. CrossRef - Recent advances in diagnostic technologies in lung cancer
Hye Jung Park, Sang Hoon Lee, Yoon Soo Chang
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(2): 257. CrossRef - Afatinib is effective in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma with uncommon EGFR p.L747P and p.L747S mutations
Sheng-Kai Liang, Jen-Chung Ko, James Chih-Hsin Yang, Jin-Yuan Shih
Lung Cancer.2019; 133: 103. CrossRef - Biomarker Testing for Patients With Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Issues and Tough Choices
Nathan A. Pennell, Maria E. Arcila, David R. Gandara, Howard West
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2019; (39): 531. CrossRef - Evaluation of EGFR mutations in NSCLC with highly sensitive droplet digital PCR assays
Xi‑Wen Jiang, Wei Liu, Xiao‑Ya Zhu, Xiao‑Xie Xu
Molecular Medicine Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping and Direct Sequencing in the Detection of Oncogenic Alterations in Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jae-Uk Song, Jonghoo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(2): 211. CrossRef - Distribution of KRAS, DDR2, and TP53 gene mutations in lung cancer: An analysis of Iranian patients
Zahra Fathi, Seyed Ali Javad Mousavi, Raheleh Roudi, Farideh Ghazi, Sumitra Deb
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(7): e0200633. CrossRef - EGFR T790M mutation testing within the osimertinib AURA Phase I study
Simon Dearden, Helen Brown, Suzanne Jenkins, Kenneth S. Thress, Mireille Cantarini, Rebecca Cole, Malcolm Ranson, Pasi A. Jänne
Lung Cancer.2017; 109: 9. CrossRef - Molecular Testing of Lung Cancers
Hyo Sup Shim, Yoon-La Choi, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Tae-Jung Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jin-Haeng Chung, Se Jin Jang, Geon Kook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 242. CrossRef - Mutations of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Aeri Kim, Min Hye Jang, Soo Jung Lee, Young Kyung Bae
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(2): 150. CrossRef - Double primary lung adenocarcinoma diagnosed by epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
Oh Jung Kwon, Min Hyeok Lee, Sung Ju Kang, Seul Gi Kim, In Beom Jeong, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun Jung Cha, Do Yeun Cho, Young Jin Kim, Ji Woong Son
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2017; 34(2): 270. CrossRef - Generation of lung cancer cell lines harboring EGFR T790M mutation by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing
Mi-Young Park, Min Hee Jung, Eun Young Eo, Seokjoong Kim, Sang Hoon Lee, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young Jae Cho, Jin Haeng Chung, Cheol Hyeon Kim, Ho Il Yoon, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(22): 36331. CrossRef - Comparison of EGFR mutation detection between the tissue and cytology using direct sequencing, pyrosequencing and peptide nucleic acid clamping in lung adenocarcinoma: Korean multicentre study
Kyueng-Whan Min, Wan-Seop Kim, Se Jin Jang, Yoo Duk Choi, Sunhee Chang, Soon Hee Jung, Lucia Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Choong Sik Lee, Jung Weon Shim, Mi Jin Kim, Geon Kook Lee
QJM.2016; 109(3): 167. CrossRef - Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Gene Fusion: Detection in Malignant Pleural Effusion by RNA or PNA Analysis
Yi-Lin Chen, Chung-Ta Lee, Cheng-Chan Lu, Shu-Ching Yang, Wan-Li Chen, Yang-Cheng Lee, Chung-Hsien Yang, Shu-Ling Peng, Wu-Chou Su, Nan-Haw Chow, Chung-Liang Ho, Javier S Castresana
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(6): e0158125. CrossRef - IDH Mutation Analysis in Ewing Sarcoma Family Tumors
Ki Yong Na, Byeong-Joo Noh, Ji-Youn Sung, Youn Wha Kim, Eduardo Santini Araujo, Yong-Koo Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(3): 257. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical demonstration of alteration of β-catenin during tumor metastasis by different mechanisms according to histology in lung cancer
XIANHUA XU, JI EUN KIM, PING-LI SUN, SEOL BONG YOO, HYOJIN KIM, YAN JIN, JIN-HAENG CHUNG
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2015; 9(2): 311. CrossRef - Detection of EGFR-TK Domain–activating Mutations in NSCLC With Generic PCR-based Methods
Rajendra B. Shahi, Sylvia De Brakeleer, Jacques De Grève, Caroline Geers, Peter In’t Veld, Erik Teugels
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2015; 23(3): 163. CrossRef - Frequent aerogenous spread with decreased E-cadherin expression of ROS1- rearranged lung cancer predicts poor disease-free survival
Yan Jin, Ping-Li Sun, Soo Young Park, Hyojin Kim, Eunhyang Park, Gilhyang Kim, Sukki Cho, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon-Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Lung Cancer.2015; 89(3): 343. CrossRef - Membranous Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF1R) Expression Is Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
Eunhyang Park, Soo Young Park, Hyojin Kim, Ping-Li Sun, Yan Jin, Suk Ki Cho, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon-Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(5): 382. CrossRef - Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping Versus Direct Sequencing for the Detection of EGFR Gene Mutation in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Seong-Hoon Yoon, Yoo-Duk Choi, In-Jae Oh, Kyu-Sik Kim, Hayoung Choi, Jinsun Chang, Hong-Joon Shin, Cheol-Kyu Park, Young-Chul Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2015; 47(4): 661. CrossRef - Analysis of Mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Korean Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Summary of a Nationwide Survey
Sang Hwa Lee, Wan Seop Kim, Yoo Duk Choi, Jeong Wook Seo, Joung Ho Han, Mi Jin Kim, Lucia Kim, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee, Mee Hye Oh, Gou Young Kim, Sun Hee Sung, Kyo Young Lee, Sun Hee Chang, Mee Sook Rho, Han Kyeom Kim, Soon Hee Jung, Se Jin Jang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(6): 481. CrossRef - Novel EGFR mutation-specific antibodies for lung adenocarcinoma: Highly specific but not sensitive detection of an E746_A750 deletion in exon 19 and an L858R mutation in exon 21 by immunohistochemistry
An Na Seo, Tae-In Park, Yan Jin, Ping-Li Sun, Hyojin Kim, Hyun Chang, Jin-Haeng Chung
Lung Cancer.2014; 83(3): 316. CrossRef - Simultaneous diagnostic platform of genotyping EGFR, KRAS, and ALK in 510 Korean patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer highlights significantly higher ALK rearrangement rate in advanced stage
Tae‐Jung Kim, Chan Kwon Park, Chang Dong Yeo, Kihoon Park, Chin Kook Rhee, Jusang Kim, Seung Joon Kim, Sang Haak Lee, Kyo‐Young Lee, Hyoung‐Kyu Yoon
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2014; 110(3): 245. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangements in lung cancer with nodular ground-glass opacity
Sung-Jun Ko, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young-Jae Cho, Ho Il Yoon, Jin-Haeng Chung, Tae Jung Kim, Kyung Won Lee, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon, Hyojin Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytoplasmic YAP Expression is Associated with Prolonged Survival in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinomas and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment
Ping-Li Sun, Ji Eun Kim, Seol Bong Yoo, Hyojin Kim, Yan Jin, Sanghoon Jheon, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2014; 21(S4): 610. CrossRef - Sensitive methods for detection of the S768R substitution in exon 18 of the DDR2 gene in patients with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer
Marcin Nicoś, Tomasz Powrózek, Paweł Krawczyk, Bożena Jarosz, Beata Pająk, Marek Sawicki, Krzysztof Kucharczyk, Tomasz Trojanowski, Janusz Milanowski
Medical Oncology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of c-MYC copy number gain in lung adenocarcinomas
A N Seo, J M Yang, H Kim, S Jheon, K Kim, C T Lee, Y Jin, S Yun, J-H Chung, J H Paik
British Journal of Cancer.2014; 110(11): 2688. CrossRef - KRASMutation Detection in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Using a Peptide Nucleic Acid-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reaction Clamping Method and Comparative Validation with Next-Generation Sequencing
Boram Lee, Boin Lee, Gangmin Han, Mi Jung Kwon, Joungho Han, Yoon-La Choi
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(2): 100. CrossRef - Guideline Recommendations forEGFRMutation Testing in Lung Cancer: Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Hyo Sup Shim, Jin-Haeng Chung, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Geon Kook Lee, Soon-Hee Jung, Se Jin Jang
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(2): 100. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Classification of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas
Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyung Han Nam, An Na Seo, Sumi Yun, Kyung Ju Kim, Hwa Jin Cho, Sung Hye Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(6): 541. CrossRef
- Recent Trends of Lung Cancer in Korea
- Construction of High-Density Tissue Microarrays at Low Cost by Using Self-Made Manual Microarray Kits and Recipient Paraffin Blocks
- Chang Hwan Choi, Kyu Ho Kim, Ju Young Song, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):562-568. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.562
- 12,184 View
- 109 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Advances of tissue microarray (TMA) technology have enabled simultaneous
in situ analysis of biomarker expression in a large number of archived pathology specimens. However, the relatively high cost of TMA construction may hamper many researchers from using this essential tool of modern pathology research. We discuss methods for making TMA kits and recipient blocks for manual construction of high-density TMAs at low cost.Methods Ordinary cannula piercing needles, hypodermic needles, bone marrow biopsy needles, metallic ink cartridges of ballpoint pens, and disposable skin biopsy punches were used to construct self-made manual TMA kits. The recipient blocks were manufactured by boring holes in the conventional bare paraffin blocks. A mini electric hand drill and a microcompound table assembled on a drill stand were used to maximize the capacity of the recipient blocks.
Results By using TMA kits made from cannula piercing needles (16- and 18-gauge), it was possible to construct TMAs with 1 mm×140 cores, 0.6 mm×320 cores, 2 mm×70 cores, 3 mm×35 cores, and 5 mm×12 cores. The capacity of the recipient blocks could be dramatically increased by drilling holes.
Conclusions Construction of TMAs using self-made TMA kits is an inexpensive alternative to construction of TMAs using commercial devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic Potential of CD44, CD133, and VDR in Epithelial Ovarian Tumors: Association with Histopathology Parameters
Ljubiša Jovanović, Branka Šošić-Jurjević, Anđa Ćirković, Sandra Dragičević, Branko Filipović, Svetlana Milenković, Stefan Dugalić, Miroslava Gojnić-Dugalić, Aleksandra Nikolić
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(8): 3729. CrossRef - Comparison of programmed death-1 (PD-1)-positive T-cells with known prognostic indicators in breast cancer
Ankit Kaushik, Anamika Jaiswal, B Priya, Ashish Jain, Sonal Sharma
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2025; 14(11): 4631. CrossRef - Constructing high-density tissue microarrays with a novel method and a self-made tissue-arraying instrument
Ping Qin, Liu Li, Li Zhao, Piaopiao Bian, Zhongtang Xiong
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 245: 154430. CrossRef - The correlation of PD-L1 expression in cytological and histological material of serous high-grade ovarian cancer
Ljubiša Jovanović, Anđa Ćirković, Ljubinka Nikolić, Milena Jović, Darko Mikić, Svetlana Milenković, Radmila Janković
Srpski medicinski casopis Lekarske komore.2023; 4(3): 246. CrossRef - Expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors, HER2 protein and Ki-67 proliferation index in breast carcinoma in both tumor tissue and tissue microarray
UP Hacısalihoğlu, MA Dogan
Biotechnic & Histochemistry.2022; 97(4): 298. CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression in High-Grade Serous and Clear Cell Ovarian Cancer
Ljubiša Jovanović, Andja Ćirković, Milena Jović, Radmila Janković
Indian Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression in Different Segments and Histological Types of Ovarian Cancer According to Lymphocytic Infiltrate
Ljubiša Jovanović, Radmila Janković, Andja Ćirković, Milena Jović, Tijana Janjić, Slaviša Djuričić, Svetlana Milenković
Medicina.2021; 57(12): 1309. CrossRef - Optimization of Tissue Microarrays from Banked Human Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues in the Cancer Research Setting
Tammy Sexton, Gregory L. Kucera, Edward A. Levine, Kounosuke Watabe, Stacey S. O'Neill
Biopreservation and Biobanking.2019; 17(5): 452. CrossRef - Peripheral nerve sheath tumor invading the nasal cavities of a 6-year-old female Pointer dog
Alessandra Sfacteria, Laura Perillo, Francesco Macrì, Giovanni Lanteri, Claudia Rifici, Giuseppe Mazzullo
Veterinary Quarterly.2015; 35(3): 170. CrossRef - High Quality Tissue Miniarray Technique Using a Conventional TV/Radio Telescopic Antenna
Mohamed A. Elkablawy, Abdulkader M. Albasri
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(3): 1129. CrossRef - Overview on Techniques to Construct Tissue Arrays with Special Emphasis on Tissue Microarrays
Ulrich Vogel
Microarrays.2014; 3(2): 103. CrossRef - Tissue Microarray
Kathleen Barrette, Joost J. van den Oord, Marjan Garmyn
Journal of Investigative Dermatology.2014; 134(9): 1. CrossRef - Altered Expression of PTEN and Its Major Regulator MicroRNA-21 in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Hyoun Wook Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 17. CrossRef - Optimizing tissue microarray construction procedure to improve quality of sections
Hua Chang, Diane Peluso, Sadiq Hussain, Michail Shipitsin, Peter Blume-Jensen
Journal of Histotechnology.2014; 37(3): 95. CrossRef - In-house Manual Construction of High-Density and High-Quality Tissue Microarrays by Using Homemade Recipient Agarose-Paraffin Blocks
Kyu Ho Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Yeon Il Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(3): 238. CrossRef
- Diagnostic Potential of CD44, CD133, and VDR in Epithelial Ovarian Tumors: Association with Histopathology Parameters
- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
- Seung Yeon Ha, Joungho Han, Wan-Seop Kim, Byung Seong Suh, Mee Sook Roh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):42-47. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.42
- 9,653 View
- 48 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Distinguishing small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) of the lung is difficult with little information about interobserver variability.
Methods One hundred twenty-nine cases of resected SCLC and LCNEC were independently evaluated by four pathologists and classified according to the 2004 World Health Organization criteria. Agreement was regarded as "unanimous" if all four pathologists agreed on the classification. The kappa statistic was calculated to measure the degree of agreement between pathologists. We also measured cell size using image analysis, and receiver-operating-characteristic curve analysis was performed to evaluate cell size in predicting the diagnosis of high-grade neuroendocrine (NE) carcinomas in 66 cases.
Results Unanimous agreement was achieved in 55.0% of 129 cases. The kappa values ranged from 0.35 to 0.81. Morphometric analysis reaffirmed that there was a continuous spectrum of cell size from SCLC to LCNEC and showed that tumors with cells falling in the middle size range were difficult to categorize and lacked unanimous agreement.
Conclusions Our results provide an objective explanation for considerable interobserver variability in the diagnosis of high-grade pulmonary NE carcinomas. Further studies would need to define more stringent and objective definitions of cytologic and architectural characteristics to reliably distinguish between SCLC and LCNEC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case report: A patient with EGFR L861Q positive adenosquamous lung carcinoma transforming into large cell neuroendocrine cancer after treatment with Almonertinib
Kele Cheng, Yong Zhu, Ran Sang, Zhongsheng Kuang, Yang Cao
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning–Based Retinoblastoma Protein Subtyping of Pulmonary Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma on Small Hematoxylin and Eosin–Stained Specimens
Teodora E. Trandafir, Frank W.J. Heijboer, Farhan Akram, Jules L. Derks, Yunlei Li, Lisa M. Hillen, Ernst-Jan M. Speel, Zsolt Megyesfalvi, Balazs Dome, Andrew P. Stubbs, Anne-Marie C. Dingemans, Jan H. von der Thüsen
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(9): 104192. CrossRef - Treatment outcomes in patients with stage IV large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a nationwide registry study
Frank W.J. Heijboer, Jules L. Derks, Francien H. van Nederveen, Lisa M. Hillen, Michael A. den Bakker, Teodora Radonic, Ronald A.M. Damhuis, Ernst-Jan M. Speel, Jan H. von der Thüsen, Anne-Marie C. Dingemans
Lung Cancer.2025; 210: 108830. CrossRef - Updates on lung neuroendocrine neoplasm classification
Giulia Vocino Trucco, Luisella Righi, Marco Volante, Mauro Papotti
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 67. CrossRef - Recent advancement of HDAC inhibitors against breast cancer
Syed Abdulla Mehmood, Kantrol Kumar Sahu, Sounok Sengupta, Sangh Partap, Rajshekhar Karpoormath, Brajesh Kumar, Deepak Kumar
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genomic Feature of a Rare Case of Mix Small-Cell and Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Lung Carcinoma: A Case Report
Youcai Zhu, Feng Zhang, Dong Yu, Fang Wang, Manxiang Yin, Liangye Chen, Chun Xiao, Yueyan Huang, Feng Ding
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Lung: What We Learned about It?
Luisella Righi, Marco Volante, Mauro Papotti
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(4): 257. CrossRef - Hierarchical identification of a transcriptional panel for the histological diagnosis of lung neuroendocrine tumors
Juxuan Zhang, Jiaxing Deng, Xiao Feng, Yilong Tan, Xin Li, Yixin Liu, Mengyue Li, Haitao Qi, Lefan Tang, Qingwei Meng, Haidan Yan, Lishuang Qi
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Staining With Neuroendocrine Markers is Essential in the Diagnosis of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Esophagogastric Junction
Dea N.M. Jepsen, Anne-Marie K. Fiehn, Rajendra S. Garbyal, Ulla Engel, Jakob Holm, Birgitte Federspiel
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2021; 29(6): 454. CrossRef - Improving differential diagnosis of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and small cell lung cancer via a transcriptomic, biological pathway-based machine learning model
Junhong Guo, Likun Hou, Wei Zhang, Zhengwei Dong, Lei Zhang, Chunyan Wu
Translational Oncology.2021; 14(12): 101222. CrossRef - Are Neuroendocrine Negative Small Cell Lung Cancer and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma with WT RB1 two Faces of the Same Entity?
Dmitriy Sonkin, Anish Thomas, Beverly A Teicher
Lung Cancer Management.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Ki-67 labeling index of neuroendocrine tumors of the lung has a high level of correspondence between biopsy samples and surgical specimens when strict counting guidelines are applied
Alessandra Fabbri, Mara Cossa, Angelica Sonzogni, Mauro Papotti, Luisella Righi, Gaia Gatti, Patrick Maisonneuve, Barbara Valeri, Ugo Pastorino, Giuseppe Pelosi
Virchows Archiv.2017; 470(2): 153. CrossRef - The Use of Immunohistochemistry Improves the Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Differential Diagnosis. An International Reproducibility Study in a Demanding Set of Cases
Erik Thunnissen, Alain C. Borczuk, Douglas B. Flieder, Birgit Witte, Mary Beth Beasley, Jin-Haeng Chung, Sanja Dacic, Sylvie Lantuejoul, Prudence A. Russell, Michael den Bakker, Johan Botling, Elisabeth Brambilla, Erienne de Cuba, Kim R. Geisinger, Kenzo
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(2): 334. CrossRef - Reply to Letter “The Use of Immunohistochemistry Improves the Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Differential Diagnosis. An International Reproducibility Study in a Demanding Set of Cases.”
Erik Thunnissen, Birgit I. Witte, Masayuki Noguchi, Yasushi Yatabe
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(6): e70. CrossRef - What clinicians are asking pathologists when dealing with lung neuroendocrine neoplasms?
Giuseppe Pelosi, Alessandra Fabbri, Mara Cossa, Angelica Sonzogni, Barbara Valeri, Luisella Righi, Mauro Papotti
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(6): 469. CrossRef - Unraveling Tumor Grading and Genomic Landscape in Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors
Giuseppe Pelosi, Mauro Papotti, Guido Rindi, Aldo Scarpa
Endocrine Pathology.2014; 25(2): 151. CrossRef - Grading the neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: an evidence-based proposal
G Rindi, C Klersy, F Inzani, G Fellegara, L Ampollini, A Ardizzoni, N Campanini, P Carbognani, T M De Pas, D Galetta, P L Granone, L Righi, M Rusca, L Spaggiari, M Tiseo, G Viale, M Volante, M Papotti, G Pelosi
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2014; 21(1): 1. CrossRef - Controversial issues and new discoveries in lung neuroendocrine tumors
Giuseppe Pelosi, Kenzo Hiroshima, Mari Mino-Kenudson
Diagnostic Histopathology.2014; 20(10): 392. CrossRef - BAI3, CDX2 and VIL1: a panel of three antibodies to distinguish small cell from large cell neuroendocrine lung carcinomas
Muhammad F Bari, Helen Brown, Andrew G Nicholson, Keith M Kerr, John R Gosney, William A Wallace, Irshad Soomro, Salli Muller, Danielle Peat, Jonathan D Moore, Lesley A Ward, Maxim B Freidin, Eric Lim, Manu Vatish, David R J Snead
Histopathology.2014; 64(4): 547. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine tumours—challenges in the diagnosis and classification of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
M A den Bakker, F B J M Thunnissen
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2013; 66(10): 862. CrossRef - Morphologic Analysis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Seung Seok Lee, Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk An, Mee Sook Roh, Chang Won Ha, Jungho Han
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(1): 16. CrossRef - Altered expression of microRNA miR‐21, miR‐155, and let‐7a and their roles in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors
Hyoun Wook Lee, Eun Hee Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Chang Hun Lee, Hee Kyung Chang, Sunhee Chang, Kun Young Kwon, Il Seon Hwang, Mee Sook Roh, Jeong Wook Seo
Pathology International.2012; 62(9): 583. CrossRef
- Case report: A patient with EGFR L861Q positive adenosquamous lung carcinoma transforming into large cell neuroendocrine cancer after treatment with Almonertinib
- Expression of Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
- Yun Kyung Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):281-289.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.281
- 4,437 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) encoded by ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B (Mdr/Tap), member 1 (ABCB1) mediates cross-resistance to antineoplastic drugs, and its expression is related to tumor aggressiveness.
METHODS
MDR1 expression was investigated in 100 hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) by immunohistochemical staining. The epigenetic mechanisms underlying ABCB1 transcriptional regulation were investigated in cell lines.
RESULTS
MDR1 was normally localized in the bile canalicular surface of the hepatocytes. Among 100 HCCs, 45 showed canalicular/luminal (CL) staining similar to the normal pattern, another 45 displayed membranous/cytoplasmic (MC) overexpression, and the remaining 10 revealed loss of expression. MC pattern or null staining of HCCs correlated with a higher histological grade and had a poorer prognosis than HCCs with a CL pattern (p<0.05). They also tended to have a poor prognosis by multivariate survival analysis. The ABCB1 promoter was hypomethylated regardless of MDR1 expression or ABCB1 mRNA levels in 10 HCC cell lines. Histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment induced ABCB1 upregulation in 4 cell lines with low or moderate ABCB1 levels.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggest that either an increase or a loss of MDR1 expression may contribute to the poor outcome of HCCs; histone deacetylation may be one of the epigenetic mechanisms directing the ABCB1 expression in HCCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preferential expression of prostate specific membrane in CD34 labeled Neo-vasculature of Hepatocellular carcinoma: Prognostic and therapeutic potentials
Safaa MM Abd El Khalek, Mona QR Mohammed, Amira M Al Balakosy
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2023; 43(1): 66. CrossRef
- Preferential expression of prostate specific membrane in CD34 labeled Neo-vasculature of Hepatocellular carcinoma: Prognostic and therapeutic potentials
- Morphometric Analysis for Pulmonary Small Cell Carcinoma Using Image Analysis.
- Sun Min Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk An, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Sanghui Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):87-91.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.87
- 4,356 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
There are few studies of how to diagnose small cell lung cancer in cytological tests through morphometric analysis. We tried to measure and analyze characteristics of small cell carcinoma in lung by image analysis.
METHODS
We studied three types of cytologic specimens from 89 patients who were diagnosed with small cell lung cancer by immunohistochemistry. We measured area, perimeter, maximal length and maximal width of cells from small cell carcinoma using image analysis.
RESULTS
In lung aspirates, the nuclear mean area, perimeter, maximal length and maximal width of small cell lung cancer were 218.69 microm2, 55 microm, 18.48 microm and 14.65 microm. In bronchial washings, nuclear measurements were 194.66 microm2, 50.07 microm, 16.27 microm and 14.1 microm. In pleural fluid, values were 177.85 microm2, 48.09 microm, 15.7 microm and 13.37 microm.
CONCLUSIONS
Nuclear size of small cell lung carcinoma is variable and depends on the cytology method. Nuclei are spindle-shaped and larger in small cell carcinoma from lung aspirates than in bronchial washings or pleural fluid. The cytoplasms of the cells in bronchial washings and pleural fluid were swollen. Therefore, one should consider morphologic changes when trying to diagnose small cell lung cancer through cytological tests. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
Seung Yeon Ha, Joungho Han, Wan-Seop Kim, Byung Seong Suh, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 42. CrossRef
- Interobserver Variability in Diagnosing High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung and Comparing It with the Morphometric Analysis
- Significance of Osteopontin Expression in the Progression of Human Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.
- Ghil Suk Yoon, Tae Sook Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(5):462-468.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.5.462
- 4,222 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Osteopontin (OPN) is a cytokine related to cell-matrix adhesion and cell survival and is expressed in the distal convoluted tubules in normal adult kidneys. Only one in vitro study has investigated the role of OPN in mechanically stretched podocytes and their actin cytoskeleton rearrangement.
METHODS
Glomerular OPN expression was investigated in biopsies from patients with human idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) (n = 25) and in normal renal biopsies (n = 16) by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
OPN was expressed in the podocytes from patients with FSGS. OPN expression increased in podocytes from both non-sclerotic hypertrophic and sclerotic glomerular tufts in patients with FSGS compared to the podocytes in normal controls.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that OPN plays a role in the early adaptive response of podocytes to the increased mechanical load caused by glomerular hypertrophy preceding FSGS. OPN was involved in cell-matrix adhesion and influenced the detachment delay of podocytes from the glomerular basement membrane and apoptosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Podocyte Expression of Osteopontin and FSP-1/S100A4 in Human Crescentic Glomerulonephritis
Ghil Suk Yoon, Tae Sook Kim
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(3): 237. CrossRef
- Podocyte Expression of Osteopontin and FSP-1/S100A4 in Human Crescentic Glomerulonephritis
- Gene Expression Profiles of Uterine Normal Myometrium and Leiomyoma and Their Estrogen Responsiveness In Vitro.
- Eun Ju Lee, Prati Bajracharya, Dong Mok Lee, Kyung Hyun Cho, Keuk Jun Kim, Young Kyung Bae, Mi Jin Kim, Ki Ho Lee, Hang Jin Kim, Gun Ho Song, Sang Sik Chun, Inho Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):272-283.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.272
- 5,084 View
- 41 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Uterine leiomyomas are common benign smooth muscle tumors among the reproductive aged-women. The research has been aimed to identify the differentially expressed genes between normal myometrium and leiomyoma and to investigate the effects of E2 on their expression.
METHODS
Gene microarray analysis was performed to identify the differentially expressed genes between normal myomerium and leiomyoma. The data was confirmed at protein level by tissue microarray.
RESULTS
Gene microarray analysis revealed 792 upregulated genes in leiomyoma. Four genes (tropomyosin 4 [TPM4], collagen, type IV, alpha 2 [COL4alpha2], insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 [IGFBP5], tripartite motif-containing 28 [TRIM28]) showed the most dramatic upregulation in all leiomyoma samples. Tissue microarray analyses of 262 sample pairs showed significantly elevated expression of TPM4, IGFBP5, estrogen receptor-alpha, and progesterone receptor (PR) protein in leiomyoma from the patients in their forties, COL4alpha2 in the forties and fifties age-groups, and TRIM28 in the thirties age-group. PR, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and IGFBP5 were induced by E2 in in vitro culture of tissue explants from which cells migrated throughout the plate. Among these, PR, IGF-1, IGFBP5 genes showed higher expression in tissue compared to cells-derived from tissue in leiomyoma and IGF-1R in leiomyoma cell.
CONCLUSIONS
This observation implies the importance of the whole tissue context including the cells-derived from tissue in the research for the understanding of molecular mechanism of leiomyoma. Here, we report higher expression of TRIM28 in leiomyoma for the first time and identify E2-responsive genes that may have important roles in leiomyoma development. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vivo mechanisms of uterine myoma volume reduction with ulipristal acetate treatment
Guillaume E. Courtoy, Jacques Donnez, Etienne Marbaix, Marie-Madeleine Dolmans
Fertility and Sterility.2015; 104(2): 426. CrossRef - Common fibroid-associated genes are differentially expressed in phenotypically dissimilar cell populations isolated from within human fibroids and myometrium
Sarah J Holdsworth-Carson, Marina Zaitseva, Jane E Girling, Beverley J Vollenhoven, Peter A W Rogers
REPRODUCTION.2014; 147(5): 683. CrossRef - Complex networks of multiple factors in the pathogenesis of uterine leiomyoma
Md Soriful Islam, Olga Protic, Piergiorgio Stortoni, Gianluca Grechi, Pasquale Lamanna, Felice Petraglia, Mario Castellucci, Pasquapina Ciarmela
Fertility and Sterility.2013; 100(1): 178. CrossRef
- In vivo mechanisms of uterine myoma volume reduction with ulipristal acetate treatment
- An Approach to Diagnosing Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Using Immunohistochemistry of c-kit and PDGFRA with Molecular Analysis.
- Jeong Shik Kim, Jae Hoon Kim, Hyun Jin Oh, In Soo Suh, Jong Gwang Kim, Byung Wook Kang, Wan Sik Yu, Ho Young Chung, Han Ik Bae
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):173-178.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.173
- 4,063 View
- 45 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) are the most common mesenchymal tumors in the gastrointestinal tract. Recently, many methods for the diagnosis of GIST have been developed including molecular diagnosis.
METHODS
We selected 90 cases of GIST that had presented at Kyungpook National University Hospital between 1998 and 2007. Tissue microarrays were made using core areas of tumor tissues. Immunohistochemical staining for c-kit, protein kinase C-theta, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) was done. Direct sequencing of hot spot exonal areas for c-kit and PDGFRA were done using extracted DNAs of all 90 paraffin block tissues.
RESULTS
Among the 90 cases, 83.3% (75/90) were c-kit positive, 16.6% (15/90) were c-kit negative, 93.3% (84/90) were PDGFRA positive, and 6.6% (6/90) cases were PDGFRA negative. Fifteen cases of c-kit negative GIST included 1 case of PDGFRA negative and 5 cases of PDGFRA negative GIST were ckit positive. The one case in which both c-kit and PDGFRA were negative, showed a c-kit mutation in exon 11.
CONCLUSIONS
Combined immunohistochemical staining of c-kit, discovered on GIST 1 (DOG1) and PDGFRA is helpful for the diagnosis of GIST. When all staining tests are negative for immunoreactivity, c-kit mutation analysis for exon 11, 9 should be done. Genotyping of kit and PDGFRA do not need to be examined initially, if it is only for the diagnosis of GIST.
- Histopathological Evaluation of Pediatric Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction: Quantitative Morphometric Analysis of Pathological Changes in the Enteric Nervous System.
- Hyung Kyung Kim, Harin Cheong, Hanna Kang, Ji Yoon Bae, Dong Eun Song, Min Sun Cho, Sun Hee Sung, Woon Sup Han, Heasoo Koo
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):162-172.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.162
- 4,409 View
- 43 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This study was done to obtain comprehensive data on changes in the structural components of the enteric nervous system in pediatric patients with intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO). We evaluated routinely processed, in formalin-fixed tissues by quantitative morphometric analysis. In addition, we used formalin-fixed tissue to explore the possibility of using previously proposed diagnostic criteria to evaluate frozen serial sections for intestinal neuronal dysplasia (IND) type B and hypoganglionosis.
METHODS
We analyzed data for 19 IPO cases. Morphometric analysis for quantification of ganglia and ganglion cells (GCs) was done for the myentric and the submucous plexus. In addition, we determined the presence of immature GCs and the distribution of nerve fibers and interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC).
RESULTS
Nine patients showed combined hypoganglionosis, IND, and decreased ICC; others showed various combinations of these. Several morphometric factors were significantly different between patient groups as well as being different than the control group.
CONCLUSIONS
Our pediatric IPO cases showed extensive overlapping of pathological findings. And the findings suggest the utility of using previously proposed morphometrically measured factors in multiple frozen sections as diagnostic criteria for IND type B and hypoganglionosis in formalin-fixed tissue. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histomorphology of enteric neurons and enteric ganglia in different layers of human fetal colon
Chacchu Bhattarai, Phanindra P. Poudel, Arnab Ghosh, Sneha G. Kalthur
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2022; 17(4): 556. CrossRef - Diagnostic utility of Bcl-2 immunohistochemical expression in pediatric functional bowel obstruction cases with ganglionated specimens
Lobna Abd El Fattah Mohamed, Nedal Ahmed Hegazy, Faten Abd El Aziz Ghazal, Ahmed Mohy El Din Zaki, Ahmed Bassiouny Radwan, Sarah Adel Hakim
Annals of Pediatric Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PTEN Immunohistochemistry
Simone Antunes Terra, Pedro Luiz Toledo de Arruda Lourenção,, Maria Aparecida Marchesan Rodrigues
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2022; 147(5): 577. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagnosis of intestinal neuronal dysplasia type B: A look beyond the number of ganglion cells
Simone Antunes Terra, Anderson Cesar Gonçalves, Pedro Luiz Toledo de Arruda Lourenção, Maria Aparecida Marchesan Rodrigues
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(44): 7649. CrossRef - Morphometric profile of large intestinal neuronal plexuses in normal perinatal autopsies and Hirschsprung disease
H. Subramanian, B. A. Badhe, P. C. Toi, K. Sambandan
Neurogastroenterology & Motility.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Histomorphology of enteric neurons and enteric ganglia in different layers of human fetal colon
- The Analysis and Clinical Usefulness of HPV DNA Chip Test in the Uterine Cervix.
- Joo hyeon Jeong, Hyun Yee Cho, Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Sanghui Park, Seung Yeon Ha
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):77-82.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.77
- 4,477 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The genotypes of human papillomavirus (HPV) are important in carcinogenesis in uterine cervical cancer and may be different in geographic distribution.
METHODS
In 2,086 women, we analyzed the prevalence of HPV and HPV genotypes in uterine cervix by HPV-DNA chip test (n = 2,086), cytology (PAP smear, n = 1997) and biopsy (n = 546).
RESULTS
Of the 2,086 cases, 1,019 cases (48.8%) were HPV-positive and 1,067 cases (51.2%) were negative for HPV. Single infection occurred most commonly (72.1% of women). HPV genotypes in the high-risk and low-risk groups, respectively were HPV-16/-58/-18/-52/-53 and HPV-70/-6/-11. The detection rates of HPV-70 in subjects older than 50 years increased significantly (p < 0.05). Infection in high risk subjects was detected in high grade lesions compared with infection in low risk subjects (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
HPV-16/-58/-18/-52/-53/-70/-6/-11 genotypes were common in the patient group similar to findings in East Asia. HPV-70 infection is predominant in those older than 40 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(4): 210. CrossRef - Cervical cytology of atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intra-epithelial lesion: significance of age, human papillomavirus DNA detection and previous abnormal cytology on follow-up outcomes
Chang Ohk Sung, Young Lyun Oh, Sang Yong Song
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2011; 159(1): 155. CrossRef - Cytomorphologic Features According to HPV DNA Type in Histologically Proven Cases of the Uterine Cervix
In Ho Choi, So-Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee, Dong Won Kim, Yoon Mi Jeen
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(6): 612. CrossRef
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
- Analysis of HPV-other Samples by Performing HPV DNA Sequencing.
- Yoo Duk Choi, Chang Woo Han, Woon Jae Chung, Woon Won Jung, Ji Shin Lee, Jong Hee Nam, Min Cheol Lee, Sang Woo Juhng, Ho Sun Choi, Chang Soo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):250-253.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.250
- 5,008 View
- 48 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
HPV-other samples are designated as being positive on HPV-PCR, but negative when using specific HPV hybridization probes. We wanted to determine the types on the HPV-other samples by performing sequencing, and to know the pathologic status of the uterine cervix according to the HPV type detected on sequencing.
METHODS
For HPV genotying, we used the commercially available HPV DNA Chip test, which contains 15 types of high-risk HPV and 9 types of low-risk HPV. The HPV DNA sequencing was performed for the HPV-other samples of 209 patients who subsequently underwent cervical biopsy.
RESULTS
For 204 of the 209 samples, the HPV types detected by sequencing were absent types at used HPV DNA chip. For the remaining 5 samples, sequencing was impossible due to mixed peaks. HPV-81 (19.6%), HPV-61 (18.6%), HPV-62 (16.7%) and HPV-84 (13.9%) were frequently detected. For the HPV-81, -62, -71, and -72 samples, most of the samples displayed normal or LSIL. However, HPV-84 and -61 were more associated with HSIL or worse, as compared to the other types.
Conclusion
HPV-81, -61, -62 and -84 were frequently found on sequencing analysis of the HPV-other samples. The pathologic status was diverse, according to the HPV type detected on sequencing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in microbial composition and interaction patterns of female urogenital tract and rectum in response to HPV infection
Yong-Hong Dong, Yu-Hua Luo, Chen-Jian Liu, Wen-Yu Huang, Lin Feng, Xing-Yuan Zou, Jin-Yan Zhou, Xiao-Ran Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Dysplasia, Infection, and Phylogeny of Human Papillomavirus in HIV‐Infected and HIV‐Uninfected Women at a Reproductive Health Clinic in Nairobi, Kenya
Agnes Omire, Nancy L. M. Budambula, Leah Kirumbi, Hillary Langat, Danvas Kerosi, Washingtone Ochieng, Raphael Lwembe, Jorge F. Quarleri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular characterisation of genital human papillomavirus among women in Southwestern, Nigeria
Yewande T. Nejo, David O. Olaleye, Georgina N. Odaibo, Jason Blackard
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(11): e0224748. CrossRef - Sequencing analysis of HPV-other type on an HPV DNA chip
Min-Jeong Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Sunmie Kim
Obstetrics & Gynecology Science.2018; 61(2): 235. CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology and genotype distribution of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) among Arab women in the state of Qatar
Devendra Bansal, Asha A Elmi, Sini Skariah, Pascale Haddad, Laith J Abu-Raddad, Aysha H Al Hamadi, Nady Mohamed-Nady, Nahla M Affifi, Randa Ghedira, Elham Hassen, Asma AJ Al-Thani, Afaf AHM Al-Ansari, Ali A Sultan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV Prevalence and Detection of Rare HPV Genotypes in Hong Kong Women from Southern China with Cytological Abnormalities
Ngai Na Chloe Co, Lai-On Chu, Joseph K. F. Chow, Joseph W. O. Tam, Enders K. O. Ng
ISRN Virology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Type-specific prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus by cervical cytology and age: Data from the health check-ups of 7,014 Korean women
Min-Jeong Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Sunmie Kim
Obstetrics & Gynecology Science.2013; 56(2): 110. CrossRef
- Changes in microbial composition and interaction patterns of female urogenital tract and rectum in response to HPV infection
- Detecting Malignant Urothelial Cells by Morphometric Analysis of ThinPrep(R) Liquid-based Urine Cytology Specimens.
- Bong Kyung Shin, Young Suk Lee, Hoiseon Jeong, Sang Ho Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Aree Kim, Insun Kim, Han Kyeom Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2008;19(2):136-143.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3338/kjc.2008.19.2.136
- 3,487 View
- 23 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Urothelial carcinoma accounts for 90% of all the cases of bladder cancer. Although many cases can be easily managed by local excision, urothelial carcinoma rather frequently recurs, tends to progress to muscle invasion, and requires regular follow-ups. Urine cytology is a main approach for the follow-up of bladder tumors. It is noninvasive, but it has low sensitivity of around 50% with using the conventional cytospin preparation. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) has been developed as a replacement for the conventional technique. We compared the cytomorphometric parameters of ThinPrep(R) and cytospin preparation urine cytology to see whether there are definite differences between the two methods and which technique allows malignant cells to be more effectively discriminated from benign cells. The nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio value, as measured by digital image analysis, was efficient for differentiating malignant and benign urothelial cells, and this was irrespective of the preparation method and the tumor grade. Neither the ThinPrep(R) nor the conventional preparation cytology was definitely superior for distinguishing malignant cells from benign cells by cytomorphometric analysis of the adequately preserved cells. However, the ThinPrep(R) preparation showed significant advantages when considering the better preservation and cellularity with a clear background.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Utility of Image Morphometry in the Atypical Urothelial Cells and High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Categories of the Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology
K.C. Sharan, Manish Rohilla, Pranab Dey, Radhika Srinivasan, Nandita Kakkar, Ravimohan S. Mavuduru
Journal of Cytology.2024; 41(3): 137. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef - A Comparison Between ThinPrep Monolayer and Cytospin Cytology for the Detection of Bladder Cancer
Ji Yong Kim, Hyung Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Urology.2014; 55(6): 390. CrossRef - Cytological and Morphometric Study of Urinary Epithelial Cells with Histopathological Correlation
Asim Kumar Manna, Manisha Sarkar, Ujjal Bandyopadhyay, Srabani Chakrabarti, Swapan Pathak, Diptendra Kumar Sarkar
Indian Journal of Surgery.2014; 76(1): 26. CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine Cytology in Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Comparison of CellprepPlus® Liquid-Based Cytology and Conventional Smear
Seung-Myoung Son, Ji Hae Koo, Song-Yi Choi, Ho-Chang Lee, Yong-Moon Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Hae-Kyung Hwang, Hye-Suk Han, Seok-Joong Yun, Wun-Jae Kim, Eun-Joong Kim, Ok-Jun Lee
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 68. CrossRef
- Utility of Image Morphometry in the Atypical Urothelial Cells and High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Categories of the Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology
- Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Hee Jeong Cha, Dong Kyun Woo, Sun Hee Kim, Yong ll Kim, Jae Gahb Park, Woo Ho Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(2):111-114.
- 2,199 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Microsatellite instability (MSI), which is caused by a deficient mismatch repair system, is seen in most of the hereditary non-polyposis colon cancers and a portion of sporadic colorectal cancers.
METHODS
Two hundreds forty-six consecutive sporadic colorectal cancer patients were analyzed for MSI using an ABI 377 automatic sequencer and fluorescent dye-labelled primers (BAT-25 and BAT-26).
RESULTS
The overall incidence of MSI in studied cases was 9.8% (24/246). This incidence is lower than most of the reported incidences in western countries. The incidence of MSI tumors in the proximal colon was 29.6%, while that of the distal colon was only 4.2% (p<0.001). MSI in sporadic colorectal cancers was more prevalent in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. In contrast to western countries, mucinous carcinoma did not show higher incidence of MSI.
CONCLUSION
The results suggest that MSI frequently occurs in cancers of the proximal colon and in tumors with poorly differentiated histology.
- An Image Analytical Study on the Structural Spectrum of Intestinal Metaplasia-Dysplasia-Carcinoma of the Stomach.
- Sang Woo Juhng, Dong Ha Park, Ji Shin Lee, Kyu Hyuk Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):50-57.
- 2,038 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia of the stomach have been stressed as precursors of gastric carcinoma of the intestinal type, although their preneoplastic nature is still debated. In this study, the cytomorphometric and cytokinetic spectra of the suggested preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions of the stomach were investigated. From the resected stomachs of early gastric carcinoma of intestinal type, areas of normal, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma were selected. They were immunostained for proliferating cell nuclear antigen, counterstained with propidium iodide, and various nuclear parameters were measured by image analysis. Normal and intestinal metaplastic mucosae differed by the localization of proliferation zone, but not by nuclear profile area, circular shape factor, and proliferation index. In dysplasia, proliferation zone covered large parts of the dysplastic area. Nuclear profile area and proliferation index were larger whereas circular shape factor was smaller than in normal or intestinal metaplasia. Carcinomatous lesion had diffuse proliferation activity, the largest nuclear profile area and proliferating index, and circular shape factor in-between those of normal or intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia. The above results showed a structural spectrum among normal of intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma of intestinal type in cytomorphometric and cytokinetic terms. The structural spectrum raises the possibility that dysplasia of the stomach is a preneoplastic lesion.
- Application of Gene Rearrangement Analysis for Diagnosis of Malignant Lymphoma.
- Kyung Soo Kim, Chan Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(4):415-422.
- 2,112 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To evaluate the utility of gene rearrangement analysis, eight cases of malignant lymphoma, one case of Hodgkin's disease, two cases of angioiminunoblastic lymphadenopathy (AILD) and two cases of non-specific lymphadenitis were studied by immunohistochemical and genetic analysis. Southern blot analysis was perfon-ned by a using vacuum transfer system and a biotin labelled probe. This method was faster, safer, and more convenient than conventional methods. Gene rearrangement study showed rearranged novel bands in five of six cases of B cell lymphoma, in all cases of T cell lymphoma, and in all cases of AILD. No rearrangement of the B cell receptor(BCR) or of the T cell receptor(TCR) was seen in Hodgkin's disease or in nonspecific lymphadenitis. These results suggest that gene rearrangement analysis of BCR and TCR is a recommended method for the diagnosis of clonality in lymphoproliferative disorders. It would allow pathologists to differentiate lymphoma from polyclonal lymphoid proliferation and to provide information for cell lineage.
- Discriminant Analysis of Tumor Cell Subpopulation Based on Morphometric and Photometric Features: Observations on tumor cells of the uterine cervix carcinoma.
- Chang Soo Park, Dae Yong Choi, Min Cheol Lee, Sang Woo Juhng
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(2):108-114.
- 2,027 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - DNA aneuploid cells are poorly characterized in both biochemical and morphological terms. This study was performed to see the relationship between DNA ploidy and morphometric and photometric nuclear features. DNA contents of tumor cells were measured by image cytometry in 46 cases of micro- or early invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Also measured were nuclear area, perimeter, maximum diameter, chromatin pattern index, and staining intensity. Among the 46 cases, 20 cases which had both DNA diploid and aneuploid cell subpopulations were selected, and the two subpopulations were discriminated statistically. Multivariate discriminant analysis seperated clearly the two subpopulations, whereas univariate analysis failed. For canonical discriminant function, nuclear area was selected first, followed by staining intensity in each case. Other variables selected afterwards were nuclear perimeter, maximum diameter, and/or chromatin pattern index in random fashion. Correlation coefficient between the canoncial discriminant function and the variables were 0.20~0.40 for nuclear area and 0.25 or less for the others. The above results suggest that DNA ploidy is a parameter more or less independent on individual morphometric and photometric parameters.
- Image Analysis of Glomerular Changes in Patients with Post-transplant IgA Nephropathy.
- Kye Won Kwon, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(3):206-211.
- 2,049 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
IgA nephropathy after renal transplantation (post-transplant IgAN) may recapitulate the IgAN of native kidneys, however, little has been reported about the histologic characteristics. The aim of this study is to apply glomerular morphometry using an image analyser to examine the histologic characteristics of post-transplant IgAN.
METHODS
The outer margin of the glomerulus (Bowman's area, BA) and glomerular tuft area (GA) were traced manually. The measured area were automatically calculated by KS300 image analysis system (Kontron, Munchen, Germany). The mesangial area (MA) was calculated with a summing each manually traced mesangial area. The total number of glomerular (GC) and mesangial cells (MC) were counted. Eight cases of renal section obtained by nephrectomy due to renal cell carcinoma (normal control: N-CTRL) and nineteen cases of renal section obtained from post-transplantation patients without IgAN (transplantation control: Tx-CTRL) served as controls.
RESULTS
A total of 35 biopsies were finally selected for measurement. BA and GA of post-transplant IgAN were 1.6 and 1.4 times larger than the N-CTRL, respectively, and were not significantly different from Tx-CTRL. MA was 1.4 times significantly larger than that of the Tx-CTRL. As compared to that of the N-CTRL, it was 1.2 times larger, but this difference was not statistically significant. The GC and MC of post-transplant IgAN and the Tx-CTRL were significantly lower than the N-CTRL. There were no significant correlations between glomerular hypertrophy and duration after renal transplantation, mesangial changes, segmental sclerosis, or degree of renal cortical interstitial fibrosis in post-transplant IgAN.
CONCLUSIONS
Prominent glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion suggest a hyperfiltration injury in post-transplant IgAN and a possible way to glomerulosclerosis.
- Analysis of DNA Ploidy Patterns and Nuclear Morphometry in Diethylnitrosamine Induced Hepatocyte Nodules and Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Rats.
- Chan Choi, Myung Kwan Kim, Kwan Mook Chae, Eun Cheol Kim, Hyung Bae Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):226-234.
- 2,306 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was designed to answer the question; (1) How does the DNA ploidy pattern change in hepatocarcinogenesis? (2) How does the nuclear morphology change in hepatocarcinogenesis? Diethylnitrosamine(DEN) (16.5 mg per kg) was subcutaneously injected to female Sprague-Dawley rats(150~200g) by weekly interval for 30 weeks. DNA ploidy and parameters of nuclear morphology were measured by image analyser(IBAS 200, Kontron, FRG). The DNA ploidy pattern was divided into three basic patterns(diploid, polyploid, and aneuploid modes). In 8 cases of saline-injected control rats, the DNA histograms showed all polyploid pattern. Inhepatocyte nodules(hyperplastic nodules), DNA diploidy was the most frequent pattern, being followed by polyploid and aneuploid DNA patterns, contrast to hepatocelular carcinomas in which polyploid DNA pattern was most frequently noted being followed by diploid and aneuploid DNA pattern. Although the nuclei of hepatocytes in hepatocyte nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas were larger and more pleomorphic than those of normal hepatocytes, they were as same as those of normal hepatocytes in regard to nuclear hyperchromasia. DNA content, which was increased in hepatocarcinogenesis, was significantly related to the nuclear area.
- Clinicopathological Analysis on the 104 Cases of Malignant Melanoma.
- Kye Yong Song, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Kwang Hyun Cho, Je Geun Chi, Eui Geun Ham
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(6):566-573.
- 2,312 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The cliniopathological analysis was done on the 104 cases of malignant melanoma diagnosed at the Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) from 1984 to 1993. The basic clinical data and the pathological items were based on the New Mexico Melanoma Registry Worksheet. The results were as follows. The male to female ratio was 1 : 0.79. Primary cutaneous melanoma was more common in the male (M : F=1 : 0.56) but primary extracutaneous melanoma with slight female dominancy (M : F=1 : 1.25). The peak age was the 6th decade in both cutaneous and extracutaneous malignant melanoma. In 66% (35 cases) of primary cutaneous malignant melanoma, the primary site was located in the acral area (including cases of acral lentiginous and nodular type), of which 63% (41% of total cutaneous melanoma) was acral lentiginous type. Major components of tumor cells were epithelioid. Clark's level of tumor was III or more at the time of the first visit in the majority of the cases (85%). The incidence rate of extracutaneous melanoma was 34.6% (36 cases) among the primary melanoma, and the eyeball (17.3%) was the most prevalent organ. All these features suggest that the racial difference between the Korean and the Caucasian is evident and also that etiologic role of sun damage is not quite marked in the Korean. We also suggest that an early detection program is very important to cure this malignant tumor.
- The Effect of Ginseng Saponin on the Dopaminergic Neurons in the Parkinson's Disease Model in Mice.
- Chang Ok Kim, Ki Sok Kim, Young Buhm Huh, Byeong Woo Ahn, Beom Seok Han, Kwang Sik Choi, Ki Yul Nam, Sang Woo Juhng
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(9):805-814.
- 2,815 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Saponin has been known to be a major antioxidant component in panax ginseng. Recent experimental study suggests that some antioxidant materials prevent Parkinson's disease caused by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in an animal model. The present study was performed to demonstrate the effect of ginseng saponins in the Parkinson's disease model induced by MPTP. To verify the effect of ginseng saponin on dopaminergic neurons in the mice brain, the tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive (TH-ir) neurons were observed by immunohistochemical stain and immunoelectron microscopy (preembedding method). Also, in order to estimate the immunoreactivity of dopaminergic neuropils, they were quantified by image analysis. The number of TH-ir neurons of substantia nigra was significantly increased in the high-dose (0.46 mg/kg) ginseng saponin group compared with the MPTP injected group. The immunoreactivity of TH-ir neuropils in striatum was significantly increased in both high and low-dose (0.1 mg/kg) ginseng saponin groups compared with the MPTP injected group. In immunoelectron microscopic observation, TH-ir neurons of the control and both ginseng saponin injected group showed normal nuclei and well preserved cytoplasmic organelles. In the MPTP injected group, dying dopaminergic neurons showed destroyed nuclei and cytoplasmic organelles. These results suggest that ginseng saponin has a protective effect on the Parkinson's disease model induced by MPTP.
- Study on Creating A Classifier for Grading of Bladder Carcinoma Based on Computerized Method.
- Hyun Ju Choi, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Heung Kook Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(3):154-162.
- 1,909 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We have described an objective and reproducible classification method for grading malignancy in the Feulgen stained bladder carcinoma. To create an optimized classifier for malignancy grading of histological bladder carcinoma cell images, it is necessary to extract the features that accurately describle the order/disorder of the nuclear variation and to evaluate the significance of the features. Above all, features selection considered about the correlation of features is very important, because the performance of the classification method depends on the selected features.
METHODS
First, we acquired 40 representative histological bladder carcinoma cell images from each of four groups (Grade 1, Grade 2A, Grade 2B, Grade 3) and extracted morphology features, texture features and the texture features of wavelet transformed images. Second, we evaluated the significance of the extracted features using variance analysis. Third, we created classifiers for each selected feature and its combination set using discriminant analysis. Finally, we compared and analyzed the correct classification rate of each classifer.
RESULTS
The optimized classifier was created from the combination of morphology features, texture features and the texture features of wavelet transformed images.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that the correlation of features is more important than one feature's great significance in grading the malignancy of bladder carcinoma, and we have confirmed that the correct classification rate is determined by feature extractin, feature evaluation and feature selection.
- Evaluation of DNA Ploidy of Bronchogenic Carcinomas by Image Analysis.
- Soo Sung Kim, Jae Hyuck Lee, Sang Woo Jung, Joo Yong Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(3):238-244.
- 1,881 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to extract useful tumor cell-specific information. DNA contents and other morphological parameters were measured by image analysis. Single cell preparation was made from archived paraffin blocks of 14 cases of bronchogenic squamous cell carcinoma, poorly differentiated, by protease treatment. The cells were Feulgen stained, and DNA content, area, perimeter, and major axis of the tumor cell nuclei were measured. Inflammatory lymphocytes concurrent with the tumor cells were used as an internal standard. DNA ploidies of the lymphocytes and 2C tumor cells showed simple peaks with Gaussian distribution and mean coefficients of variation of 10% and 14% respectively. By the location and proportion of the tumor cells other than 2C cells, DNA ploidies could be classified into diploidy(1 case), polyploidy(2 cases), and aneuploidy(11 cases). The mean proportion of DNA aneuploidal tumor cells relative to the total tumor cells was 82.8%. In 8 cases, nuclear areas showed more or less overlapped distribution, whereas DNA contents showed discrete peaks. THes results suggest that many bronchogenic squamous cell carcinomas, poorly differentiated, have DNA aneuploidy and high proportion of aneuploidal cells, and that nuclear size and DNA content are more or less independent parameters.
- DNA Ploidy in Anaplastic Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland by Image Analysis.
- Ji Shin Lee, Min Cheol Lee, Chang Soo Park, Sang Woo Juhng
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1995;6(1):10-17.
- 2,069 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid gland is one of the most malignant tumors. Recently, DNA ploidy measured by flow cytometry and image analysis has been suggested as an additional useful indicator of tumor behavior. Studies on the occurrence and clinical significance of DNA aneuploidy in anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid are rare. In this study, the pattern of DNA ploidy was measured by image analysis on Papanicolaou stained slides in four cases of anaplastic carcinoma and also measured by flow cytometry using paraffin blocks in two cases. In all cases of anaplastic carcinoma. DNA aneuploidy was found by image analaysis. By flow cytometry, one case had a diploid peak and the other case had an arieuploid peak. According to the above results, we conclude that anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid glands have a high incidence of DNA aneuploidy and image analysis using Papanicolaou stained slides is a useful method in detecting DNA aneuploidy.
- Histopathological Differences between Silicone Granuloma and Paraffinoma.
- Yeon Mee Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Hye Je Cho, Je Geun Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):427-436.
- 5,508 View
- 312 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - During the past two decades, silicone (polydimethylsiloxane) has become one of the most extensively applied biomaterials. Although pure silicone is relatively inert and usually causes only minimal tissue reactions, it has been reported to evoke a definite foreign body reaction. We studied five cases of silicone-induced granulomas in various sites; two in the breast, one in the breast and axillary lymph nodes, one in the subcutis of the abdomen, back and extremities and one in the eyeball, to illustrate the salient histopathologic features of reactions to silicone with particular emphasis to its differences from paraffin granuloma. For this, 17 paraffinomas were also studied. Tissue reaction to silicone liquid and gel was characterized by numerous round to oval empty cystic vacuoles, mild to moderate fat necrosis, foreign body reaction, a variable degree of mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration and mild focal fibrosis. The cystic spaces were relatively uniform and showed a snow-man like appearance. In contrast to the silicone granulomas, the paraffinomas, also refered to as sclerosing lipogranulomas showed diffuse sclerosis and frequent calcification around the cystic vacuoles. The cystic spaces in paraffinomas were swiss cheese-like configuration, and the content of the cystic spaces was dirty and frequently calcified. However, there were certain similarities between these two types of granulomas particularly in the early phases of the reaction, therefore, the history of silicone injection or implant, is sometimes critical to the diagnosis of silicone granuloma. Despite great technologic advances in the manufacturing of prostheses and medical equipment, droplets and/or particles of silicone still escape into the body tissues in a variety of ways; therefores, the pathologist should always wonder whether the histologic reaction observed is due to silicone or to some other foreign material including paraffin.
- Morphometric Analysis of Cirrhotic Nodules in Hepatocellular Carcinoma-bearing Livers.
- Gyeong Hoon Kang, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(4):338-345.
- 2,232 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It has been well known that liver cirrhosis, regardless of its etiology, is an important predisposing factor in hepatocarcinogenesis. However, the type of cirrhosis in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)-bearing liver varies not only by geographic areas but also with the cirteria applied for morphological classification of cirrhosis. To elucidate the relationship between the nodule size of HCC-bearing cirrhotic liver and clinicopathologic features, we measured cirrhotic nodule areas of 49 surgically resected HCC cases using image analyzer. The morphological type of cirrhosis was predominantly macronodular(49%), and followed by mixed(37%) and micronodular(14%). Seventy percent of the cases showed seropositivity for HBsAg. The average area of cirrhotic nodules was significantly larger in HBsAg-positive cases(mean: 6.14 mm2) than that of HBsAg-negative cases(mean: 2.5 mm2)(p<0.05), and their size was bigger in cases with grossly expansile pattern of HCC than those cases with infiltrative ones(p<0.05). Based on the above findings, we assume that seropositivity of HBsAg may influence on the regenerative activity of cirrhotic nodules and also subsequent increase of risk for further development of HCC. The presence of cirrhohsis and nodule size seem to be the important contributing factors to determine the growing patterns of HCC.
- Molecular Subtypes of Primary Glioblastoma Identified by Gene Expression Profiling.
- Ghee Young Choe, S Mischel Paul
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(5):328-337.
- 1,966 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The over-expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) occurs in nearly 50% of primary glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Disruption of multiple signaling pathways is a critical factor in regulating the biological and clinical behavior of GBMs. In the future, therapy that specifically targets these disrupted pathways may represent the best potential treatment for patients with GBM. Large scale gene expression profiling provides a powerful approach to identify these disrupted genetic pathways and to uncover previously unknown molecular subtypes.
METHODS
We used 13 cases of primary GBM biopsy samples obtained from untreated patients and Affymetrix high-density oligonucleotide arrays to identify novel subsets of primary GBMs.
RESULTS
We showed that the expression of 90 genes differentiate EGFR+ from EGFR non-expressing (EGFR-) de novo GBMs, including expression of a number of potentially targetable molecules that act as growth/survival factors for GBMs. We also demonstrated the presence of two additional molecular subtypes of primary GBMs, including one characterized by the coordinate upregulation of contiguous genes on chromosome 12q13-15, which has a distinct global gene expression profile and expresses both astrocytic and oligodendroglial genes.
CONCLUSION
We have shown that there are EGFR+ primary GBMs, GBMs with coordinate upregulation of genes on chromosome 12q13-15, and primary GBMs lacking either alteration. Moreover, they have distinct transcriptional profiles. Our findings strongly suggest that the three GBMs are biologically different tumor types, despite their identical microscopic appearance, and provide an important first step in developing a molecular taxonomy of GBMs.
- A Cytopathologic Analysis of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Lung: A Six-year Correlation Study in 322 Cases.
- Sook Kim, Dong Won Kim, So Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1995;6(2):140-147.
- 1,821 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In a six-year period (from May 1988 to April 1994), fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of 322 pulmonary lesions from 296 patients were performed at Soonchunhyang University Hospital. Of these 322, malignancy was diagnosed cytologically in 139 (43.2%), suspicious malignancy in 7 (2.2%), negative in 164 (50.8%), and insufficient material in 12 (3.8%). Malignant lesion consisted of 54 cases of adenocarcinoma, 50 cases of squamous cell carcinoma, 18 cases of small cell carcinoma. They were verified by histologic confirmation in 70 cases. There were 2 (0.6%) false positive cases due to florid bronchoalveolar hyperplasia and atypical bronchial epithelial cells associated with granulomatous lesion. Overall accuracy rate was 90%, the sensitivity 84.3% and the specificity 94.7%.
- Evaluation of DNA Ploidy and Other Morphometric Parameters of Ovarian Mucinous Tumors.
- Yun Mee Kim, Sang Woo Juhng, Joo Yong Yoo, Kyu Hyuk Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(5):397-406.
- 1,966 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Biological behavior of malignant tumors has been assessed by morphological grading, clinical staging, and estimating other tumor markers. Recently DNA ploidy measured by flow cytometry and image analyser has been suggested as an additional useful indicator of the tumor behavior. In order to extract useful tumor cell-specific information in ovarian mucinous tumors, DNA contents and other morphologic parameters were measured by image analysis and DNA ploidy was also measured by flow cytometry. In all cases of cystadenoma, DNA diploidies were observed. In borderline malignancy, DNA diploidies were chiefly observed except one case of polyploidy. In true malignancy, DNA aneuploidies were observed except one case of polyploidy and two cases of diploidies by image analysis, and except four cases of diploides and one cas of polyploidy by flow cytometry. The statistical significance were observed in DNA ploidy pattern by image analysis. In nuclear areas, perimeters and major axis, statistical significance were not observed. These results suggest that DNA ploidy pattern are more or less independent parameter as an additional useful indicator of the histological grade of malignancy and that image analysis are better than flow cytometry in detecting DNA aneuploidy.
- A study of Digital Image Analysis of Chromatin Texture for Discrimination of Thyroid Neoplastic Cells.
- Sang Woo Juhng, Jae Hyuk Lee, Eun Kyung Bum, Chang Won Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1996;7(1):23-30.
- 2,009 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chromatin texture, which partly reflects nuclear organization, is evolving as an important parameter indicating cell activation or transformation. In this study, chromatin pattern was evaluated by image analysis of the electron micrographs of follicular and papillary carcinoma cells of the thyroid gland and tested for discrimination of the two neoplasms. Digital grey images were converted from the electron micrographs; nuclear images, excluding nucleolus and intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions, were obtained by segmentation; grey levels were standardized; and grey level histograms were generated. The histograms in follicular carcinoma showed Gaussian or near-Gaussian distribution and had a single peak, whereas those in papillary carcinoma had two peaks(bimodal), one at the black zone and the other at the white zone. In papillary carcinoma. the peak in the black zone represented an increased amount of heterochromatin particles and that at the white zone represented decreased electron density of euchromatin or nuclear matrix. These results indicate that the nuclei of follicular and papillary carcinoma cells differ intheir chromatin pattern and the difference may be due to decondensed chromatin and/or matrix substances.
- A Histopathological Analysis on 73 Cases of Enucleated Eyeballs.
- Kyoung Chan Choi, Joon Hyuk Choi, Won Hee Choi, Tae Sook Lee, Myung Mi Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(5):460-468.
- 1,865 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A total of 73 enucleated eyeballs is reviewed and analyzed clinicopthologically. These eyeballs were selected among the enucleated spceimens that had been removed at the Yeungnam University Hospital during a period of 10 years beginning from 1983 to 1992. Following results were obtained. 1) When the eyeballs were classified according to me direct cause of removal, the neoplasm was the most common single cause accounting for 26 cases(35.6%) out of 73 cases, followed by phthisis bulbi l6 cases(21.9%), trauma 10 cases(13.7%), glaucoma 8 cases(10.9%), inflammation 5 cases(6.8%), staphyloma 4 cases(5.5%), retinal detachment 1 cases(1.4%), Coat's disease 1 cases(1.4%), corneal disease 1 cases(1.4%) and choroidal hemorrhage 1 cases(1.4%). 2) 39 cases(53.4%) were male and 34(46.6%) were female. 23 cases(31.5%) were below 10 years of age, which was the highest rate. 3) The neoplastic lesion included retinoblastoma 20 cases(76.9%) in 26 neoplasms, malignant melanoma 4 cases(15.3%), hemagioblastoma of optic disc 1 cases(3.9%), adenocarcinoma of Meibomian gland 1 cases(3.9%). 4) Retinoblastoma was the commonest intraocular tumor accounting for 20 out of 26 cases, In growth pattern, 80.0% of the tumor grew endophtytically. True rosette were seen 60% of the retinoblastoma.

 E-submission
E-submission
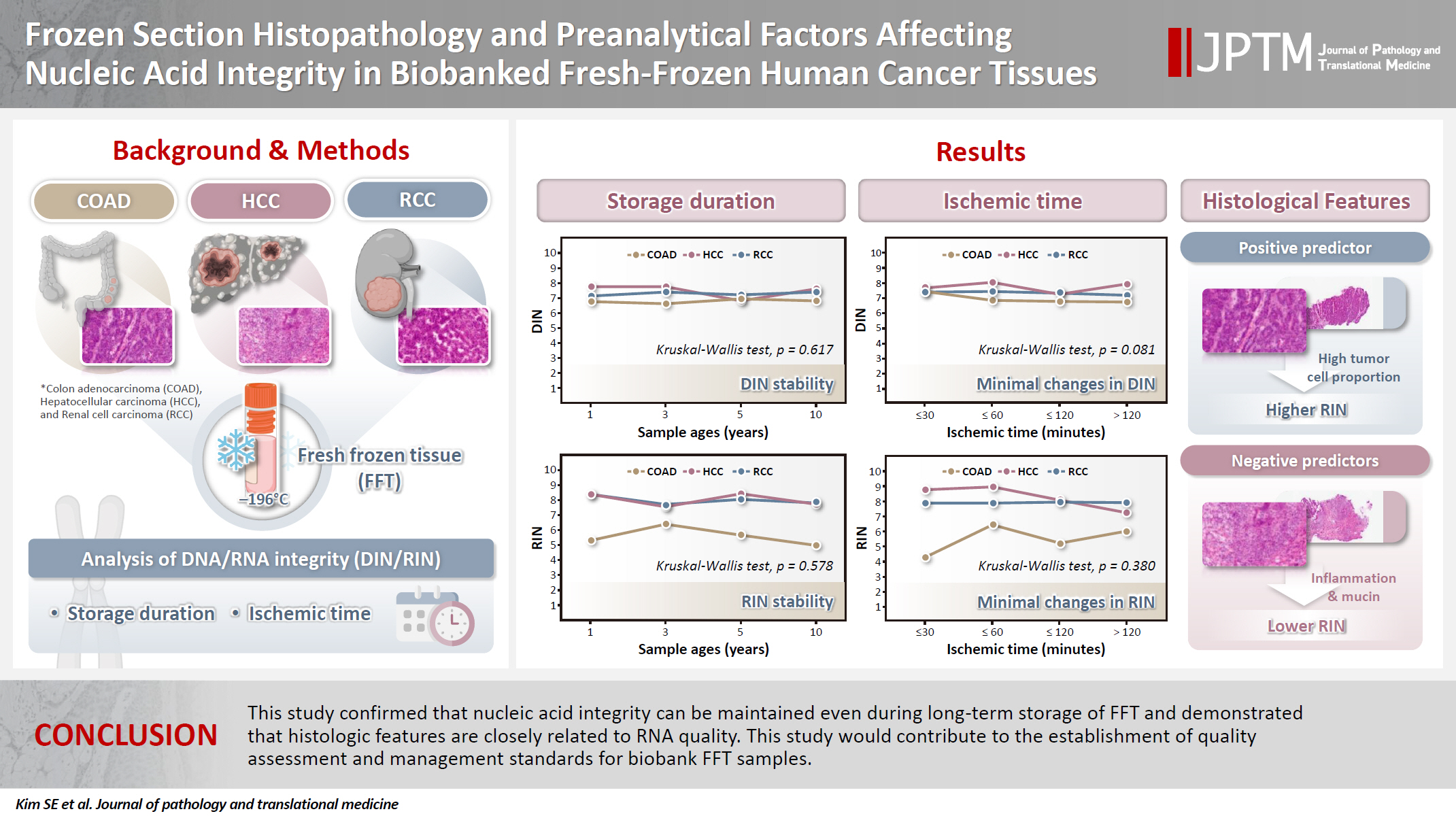







 First
First Prev
Prev



