Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
- Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):353-360. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.12
- 2,288 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors composed of Schwann cells, which uncommonly involve the breast. Most breast schwannomas are clinically present as a superficial palpable breast mass but may also be detected on screening mammography. Excision is the preferred treatment if symptomatic, and these are not known to recur. Histomorphology is similar to other anatomic sites: bland spindle cells with wavy nuclei, nuclear palisading (Verocay bodies), variably hypercellular (Antoni A) and hypocellular (Antoni B) areas, myxoid stroma, hyalinized vessels and variable cystic degeneration. Classic immunohistochemistry is diffuse and strong labeling for S100 and Sox10. Notable diagnostic pitfalls specific to the breast include myofibroblastoma, particularly the palisaded variant, and fascicular pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia.
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Ahrong Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):26-38. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.01
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(2):147
- 12,134 View
- 426 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has long been recognized as a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for breast lesions. However, with the advent of core-needle biopsy (CNB), the role of FNAC has diminished in some clinical settings. This review aims to re-evaluate the diagnostic value of FNAC in the current era, focusing on its complementary use alongside CNB, the adoption of new approaches such as the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System, and the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation to reduce inadequate sample rates. Advances in liquid-based cytology, receptor expression testing, molecular diagnostics, and artificial intelligence are discussed, highlighting their potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of FNAC. Despite challenges, FNAC remains a valuable diagnostic method, particularly in low-resource settings and specific clinical scenarios, and its role continues to evolve with technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Daniella Serafin Couto Vieira, Laura Otto Walter, Maria Eduarda Cunha da Silva, Lisandra de Oliveira Silva, Heloísa Zorzi Costa, Chandra Chiappin Cardoso, Fernando Carlos de Lander Schmitt, Maria Cláudia Santos-Silva
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(23): 4771. CrossRef
- Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
- International Academy of Cytology standardized reporting of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology with cyto-histopathological correlation of breast carcinoma
- Shweta Pai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):241-248. Published online September 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.14
- 7,726 View
- 407 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Academy of Cytology (IAC) has developed a standardized approach for reporting the findings of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Accordingly, there are five chief categories of breast lesions, C1 (insufficient material), C2 (benign), C3 (atypical), C4 (suspicious), and C5 (malignant). The prognostication and management of breast carcinoma can be performed readily on the basis of this classification system. The aim of this study was to classify various breast lesions into one of the above-named categories and to further grade the C5 lesions specifically using the Robinson system. The latter grades were then correlated with modified Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grades.
Methods
This retrospective study was undertaken in the pathology department of a hospital located in the urban part of the city of Bangalore. All FNAC procedures performed on breast lumps spanning the year 2020 were included in the study.
Results
A total of 205 breast lesions was classified according to the IAC guidelines into C1 (6 cases, 2.9%), C2 (151 cases, 73.7%), C3 (13 cases, 6.3%), C4 (5 cases, 2.5%), and C5 (30 cases, 14.6%) groups. The C5 cases were further graded using Robinson’s system. The latter showed a significant correlation with the SBR system (concordance=83.3%, Spearman correlation=0.746, Kendall’s tau-b=0.736, kappa=0.661, standard error=0.095, p≤.001).
Conclusions
A standardized approach for FNAC reporting of breast lesions, as advocated for by the IAC, improves the quality and clarity of the reports and assures diagnostic reproducibility on a global scale. Further, the cytological grading of C5 lesions provides reliable cyto-prognostic scores that can help assess a tumor’s aggressiveness and predict its histological grade.
- Metastatic choroidal melanoma in the breast: a case report and review of the literature
- Loay Abudalu, Vinisha Malhotra, Nabila Nasir, Sami Titi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):238-241. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.07
- 4,982 View
- 128 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The breast is an unusual site for metastases, accounting for less than 2% of malignant breast lesions but include those from malignant melanomas, carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas from various organs. We diagnosed a very rare case of metastatic choroidal melanoma for a 67-year-old female who presented with a right breast lump and who had been previously diagnosed with choroidal melanoma-monosomy 3 in 2017. To the best of our knowledge, only five such cases have been published so far, with one in a male patient.
- A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of primary and secondary breast angiosarcoma
- Evi Abada, Hyejeong Jang, Seongho Kim, Rouba Ali-Fehmi, Sudeshna Bandyopadhyay
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):342-353. Published online October 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.31
- 6,153 View
- 149 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
We aimed to study the clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical (IHC) (CD117, c-Myc, and p53) characteristics, and overall survival of primary and secondary breast angiosarcoma (BAS).
Methods
This was a retrospective study of BAS cases diagnosed between 1997 and 2020 at our institution. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides were reviewed for tumor morphology, margin status, and lymph node metastasis. CD117, p53, D2-40, CD31, and c-Myc IHC stains were performed on 11 viable tissue blocks. Additional clinical information was obtained from the electronic medical records.
Results
Seventeen patients with BAS were identified. Of these, five (29%) were primary and 12 (71%) were secondary BAS, respectively. The median age at diagnosis for primary BAS was 36 years. The median age at diagnosis for secondary BAS was 67 years. The median time to secondary BAS development following radiotherapy was 6.5 years (range, 2 to 12 years). There was no significant difference between primary and secondary BAS in several histopathologic parameters examined, including histologic grade, necrosis, mitotic count, lymph node metastasis, and positive tumor margins. There was also no difference in CD117, p53, D2-40, CD31, and c-Myc expression by IHC between primary and secondary BAS. During a median followup of 21 months, primary BAS had two (40%) reported deaths and secondary BAS had three (25%) reported deaths. However, this difference in survival between both groups was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.09 to 3.28; p = .450).
Conclusions
BAS is a rare and aggressive disease. No histologic, IHC (CD117, c-Myc, and p53), or survival differences were identified between primary and secondary BAS in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Angiosarcoma: a systematic review of biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic strategies
Huyen Thuc Tran Luong, Sofie Vercammen, Ario de Marco, Hilde de Rooster, Antonio Cosma
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Etiology, pathogenesis, and management of angiosarcoma associated with implants and foreign body: Clinical cases and research updates
Ramy Samargandi
Medicine.2024; 103(18): e37932. CrossRef - Ovarian angiosarcoma: A systematic review of literature and survival analysis
Shafi Rehman, Arya Harikrishna, Amisha Silwal, B.R. Sumie, Safdar Mohamed, Nisha Kolhe, Meghana Maddi, Linh Huynh, Jesus Gutierrez, Yoshita Rao Annepu, Ameer Mustafa Farrukh
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 73: 152331. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for radiation associated angiosarcoma (RAAS) of the breast: A retrospective single center study
Stijn J.C. van der Burg, Sophie J.M. Reijers, Anke Kuijpers, Lotte Heimans, Astrid N. Scholten, Rick L.M. Haas, Hester van Boven, Willemijn M. Kolff, Marie-Jeanne T.F.D. Vrancken Peeters, Martijn Kerst, Beatrijs A. Seinstra, Neeltje Steeghs, Winette T.A.
The Breast.2024; 78: 103825. CrossRef - Lymph node involvement in secondary breast angiosarcoma – a case presentation
Adriana Irina Ciuvică, Tiberiu Augustin Georgescu , Andrei Dennis Voichiţoiu , Angela Arsene , Luchian Marinescu , George Ionuţ Bucur , Livia Iordache , Nahedd Saba
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology.2024; 65(3): 523. CrossRef - Primary ovarian angiosarcoma: Two case reports and review of literature
Ying Zhou, Yi-Wen Sun, Xiao-Yang Liu, Dan-Hua Shen
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(21): 5122. CrossRef
- Angiosarcoma: a systematic review of biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic strategies
- Fatty acid synthetase expression in triple-negative breast cancer
- Jin Hee Park, Hye Seung Han, So Dug Lim, Wook Youn Kim, Kyoung Sik Park, Young Bum Yoo, Seung Eun Lee, Wan-Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(2):73-80. Published online January 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.10.27
- 7,535 View
- 204 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has a relatively poor prognosis. Research has identified potential metabolic targets, including fatty acid metabolism, in TNBC. The absence of effective target therapies for TNBC led to exploration of the role of fatty acid synthetase (FASN) as a potential target for TNBC therapy. Here, we analyzed the expression of FASN, a representative lipid metabolism–related protein, and investigated the association between FASN expression and Ki-67 and the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) biomarkers in TNBC.
Methods
Immunohistochemical expression of FASN was analyzed in 166 patients with TNBC. For analytical purposes, patients with 0–1+ FASN staining were grouped as low-grade FASN and patients with 2–3+ FASN staining as high-grade FASN.
Results
FASN expression was observed in 47.1% of TNBC patients. Low and high expression of FASN was identified in 75.9% and 24.1%, respectively, and no statistically significant difference was found in T category, N category, American Joint Committee on Cancer stage, or recurrence rate between the low and high-FASN expression groups. Ki-67 proliferation level was significantly different between the low and high-FASN expression groups. FASN expression was significantly related to Ki-67 as the level increased. There was no significant difference in PD-L1 positivity between the low- and high-FASN expression groups.
Conclusions
We identified FASN expression in 166 TNBC patients. The Ki-67 proliferation index was positively correlated with FASN level, indicating higher proliferation activity as FASN increases. However, there was no statistical association with PD-L1 SP142, the currently FDA-approved assay, or FASN expression level. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid metabolism involved in progression and drug resistance of breast cancer
Wenxiang Fu, Aijun Sun, Huijuan Dai
Genes & Diseases.2025; 12(4): 101376. CrossRef - Unveiling the impact of lipid metabolism on triple-negative breast cancer growth and treatment options
Xin-xian Cai, Zhe-zhong Zhang, Xiao-xiao Yang, Wen-rui Shen, Liu-wei Yuan, Xi Ding, Ying Yu, Wen-yu Cai
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Protein biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer
Emeka Eze Joshua Iweala, Doris Nnenna Amuji, Faith Chinasaokwu Nnaji
Scientific African.2024; 25: e02308. CrossRef - Microarray analysis points to LMNB1 and JUN as potential target genes for predicting metastasis promotion by etoposide in colorectal cancer
Jiafei Liu, Hongjie Yang, Peng Li, Yuanda Zhou, Zhichun Zhang, Qingsheng Zeng, Xipeng Zhang, Yi Sun
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The signature of extracellular vesicles in hypoxic breast cancer and their therapeutic engineering
Baiheng Zhu, Kehao Xiang, Tanghua Li, Xin Li, Fujun Shi
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - NFYA promotes malignant behavior of triple-negative breast cancer in mice through the regulation of lipid metabolism
Nobuhiro Okada, Chihiro Ueki, Masahiro Shimazaki, Goki Tsujimoto, Susumu Kohno, Hayato Muranaka, Kiyotsugu Yoshikawa, Chiaki Takahashi
Communications Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of EGFR and FASN in breast cancer progression
Suchi Chaturvedi, Mainak Biswas, Sushabhan Sadhukhan, Avinash Sonawane
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling.2023; 17(4): 1249. CrossRef - Bioinformatics Method Was Used to Analyze the Highly Expressed Gene FAM83A of Breast Cancer in Young Women
Yongzhe Tang, Hao Wang, Qi He, Yuanyuan Chen, Jie Wang, Fahd Abd Algalil
Applied Bionics and Biomechanics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - NCAPH promotes proliferation as well as motility of breast cancer cells by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
Ting Zhang, Peng Li, Wanying Guo, Qipeng Liu, Weiqiang Qiao, Miao Deng
Physiology International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lipid metabolism involved in progression and drug resistance of breast cancer
- A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification
- Hye Ju Kang, Sun Young Kwon, Ahrong Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Soo Kee Min, So Young Park, Sun Hee Sung, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Hyang Im Lee, Ho Chang Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Sun Young Jun, Min Jung Jung, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Hye Jeong Choi, So Yeon Park, Jee Yeon Kim, In Ae Park, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):380-387. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
- 7,163 View
- 226 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
Methods
Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
Results
On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
Conclusions
Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
- Potential of AKT2 expression as a predictor of lymph-node metastasis in invasive breast carcinoma of no special type
- Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Kristina Anna Bethania, Kusmardi Kusmardi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(4):271-278. Published online June 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.04.26
- 5,997 View
- 154 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST) is the most common type of breast cancer and mainly causes regional lymph-node metastasis (LNM). We investigated the potential for AKT2 expression as a predictive biomarker for LNM in IBC-NST.
Methods
Forty-eight paraffin blocks containing IBC-NST primary tumors were divided into two groups based on presence or absence of LNM. Age, tumor grade, tumor size, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), and AKT expression were assessed. AKT2 expression was assessed based on immunohistochemical staining, while other data were collected from archives.
Results
Multiple logistic regression results showed that AKT2 expression and LVI were significantly associated with LNM (odds ratio [OR], 5.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.42 to 19.93 and OR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.17 to 16.97, respectively). AKT2 expression was able to discriminate against LNM (area under the receiver operating characteristic, 0.799 ± 0.063; 95% CI, 0.676 to 0.921) at an H-score cutoff of 104.62 (83.3% sensitivity, 62.5% specificity).
Conclusions
AKT2 expression has potential as a predictor of LNM in IBC-NST. The H-score cutoff for AKT2 expression can be used as a classification guide in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Src with Nottingham Prognostic Index in Breast Cancer: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognostication
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2024; 7(2): 90. CrossRef - CD4+ Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy-treated Invasive Breast Cancer of No Special Type
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Meike Pramono, Sinta Chaira Maulanisa
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2024; 7(3): 179. CrossRef - Potential of AKNA as a Predictive Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer and Its Relationship to Tumor Grading
P Rustamadji, E Wiyarta, M Miftahuzzakiyah, D Sukmawati, DA Suryandari, R Kodariah
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(9): 1089. CrossRef - Exploring the Expression of Survivin on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Ineke Anggreani
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(B): 1440. CrossRef - Effect of Omega-3-Rich Fish Oil on TNF- Expression in Mice's Colonic Tissue Induced with Azoxymethane (AOM) and Dextran Sodium Sulphate (DSS)
Elvan Wiyarta, Kusmardi Kusmardi, Yurnadi Hanafi Midoen
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 3179. CrossRef - The potential of lunasin extract for the prevention of breast cancer progression by upregulating E-Cadherin and inhibiting ICAM-1
Kusmardi Kusmardi, Elvan Wiyarta, Numlil Khaira Rusdi, Andi Muh. Maulana, Ari Estuningtyas, Hadi Sunaryo
F1000Research.2021; 10: 902. CrossRef - CD44 Variant Exon 6 Isoform Expression as a Potential Predictor of Lymph Node Metastasis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma of No Special Type
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Kristina A. Bethania, Rakesh Sathish Nair
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Correlation between CD 34 and CD 68 expression in placental malaria with maternal anemia
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Muhammad Takbir, Puspita Eka Wuyung, Kusmardi Kusmardi, Elvan Wiyarta
Tropical Parasitology.2021; 11(2): 92. CrossRef
- Association of Src with Nottingham Prognostic Index in Breast Cancer: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognostication
- Standardized pathology report for breast cancer
- Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):1-15. Published online January 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.11.20
- 15,839 View
- 724 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Given the recent advances in management and understanding of breast cancer, a standardized pathology report reflecting these changes is critical. To meet this need, the Breast Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists has developed a standardized pathology reporting format for breast cancer, consisting of ‘standard data elements,’ ‘conditional data elements,’ and a biomarker report form. The ‘standard data elements’ consist of the basic pathologic features used for prognostication, while other factors related to prognosis or diagnosis are described in the ‘conditional data elements.’ In addition to standard data elements, all recommended issues are also presented. We expect that this standardized pathology report for breast cancer will improve diagnostic concordance and communication between pathologists and clinicians, as well as between pathologists inter-institutionally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Breast Associated With an Incidental Radial Scar: A Cyto‐Histopathology Correlation
Rallapalli Rajyalakshmi, Valasapalli Rajani, Tanuku Sreedhar, Kollabathula Arpitha
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating discrepancies: The assessment of residual lymphovascular invasion in breast carcinoma after neoadjuvant treatment
Anikó Kovács, Åsa Rundgren-Sellei, Gunilla Rask, Annette Bauer, Anna Bodén, Johannes van Brakel, Eugenia Colón-Cervantes, Anna Ehinger, Johan Hartman, Balazs Acs
The Breast.2025; 82: 104519. CrossRef - Residual pure intralymphatic carcinoma component only (lymphovascular tumor emboli without invasive carcinoma) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with poor outcome: Not pathologic complete response
Hyunwoo Lee, Yunjeong Jang, Yoon Ah Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
Human Pathology.2024; 145: 1. CrossRef - Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with ductal carcinomain situ: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Colm O’Flaherty, Eoin F. Cleere, Aoife Nohilly, James Phelan, Evan Ronane, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Breast Associated With an Incidental Radial Scar: A Cyto‐Histopathology Correlation
- Automated immunohistochemical assessment ability to evaluate estrogen and progesterone receptor status compared with quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in breast carcinoma patients
- Taesung Jeon, Aeree Kim, Chungyeul Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):33-42. Published online December 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.09.29
- 12,514 View
- 233 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to investigate the capability of an automated immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation of hormonal receptor status in breast cancer patients compared to a well-validated quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) method.
Methods
This study included 93 invasive breast carcinoma cases that had both standard IHC assay and Oncotype Dx assay results. The same paraffin blocks on which Oncotype Dx assay had been performed were selected. Estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) receptor status were evaluated through IHC stains using SP1 monoclonal antibody for ER, and 1E2 monoclonal antibody for PR. All ER and PR immunostained slides were scanned, and invasive tumor areas were marked. Using the QuantCenter image analyzer provided by 3DHISTECH, IHC staining of hormone receptors was measured and converted to histochemical scores (H scores). Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated between Oncotype Dx hormone receptor scores and H scores, and between Oncotype Dx scores and Allred scores.
Results
H scores measured by an automated imaging system showed high concordance with RT-qPCR scores. ER concordance was 98.9% (92/93), and PR concordance was 91.4% (85/93). The correlation magnitude between automated H scores and RT-qPCR scores was high and comparable to those of Allred scores (for ER, 0.51 vs. 0.37 [p=.121], for PR, 0.70 vs. 0.72 [p=.39]).
Conclusions
Automated H scores showed a high concordance with quantitative mRNA expression levels measured by RT-qPCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer: role of immune-related gene expression
Hadeer Mahmoud, Abeer M. Abd El-Aziz, Osama Ezzat, Hany Ibrahim Kenawy, Ahmed A. Shokeir
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PUM1 in Breast Cancer: Tumor Expression and Prognostic and Predictive Significance
Abrar I. Aljohani
Medicina.2025; 61(10): 1810. CrossRef - Vision Transformers for Breast Cancer Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression Staging without Immunohistochemical Staining
Gelan Ayana, Eonjin Lee, Se-woon Choe
The American Journal of Pathology.2024; 194(3): 402. CrossRef - Extrahepatic Bile Duct Organoids as a Model to Study Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury During Liver Transplantation
P. Kreiner, E. Eggenhofer, L. Schneider, C. Rejas, M. Goetz, N. Bogovic, S. M. Brunner, K. Evert, H. J. Schlitt, E. K. Geissler, H. Junger
Transplant International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of DSCC1, a Biomarker Associated with Aggressive Features of Breast Cancer
Abrar I. Aljohani
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 1929. CrossRef - Marker assessments inER‐positive breast cancers: old markers, new applications?
Joshua J X Li, Gary M Tse
Histopathology.2023; 82(2): 218. CrossRef - The Story of the Magee Equations: The Ultimate in Applied Immunohistochemistry
Rohit Bhargava, David J. Dabbs
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(7): 490. CrossRef - Dose-Dependent Relationship between Protection of Thioacetamide-Induced Acute Liver Injury and Hyperammonemia and Concentration of Lactobacillus salivarius Li01 in Mice
Pengcheng Lou, Yangfan Shen, Aoxiang Zhuge, Longxian Lv, Xueling Zhu, Yin Yuan, Liya Yang, Kaicen Wang, Bo Li, Lanjuan Li, Joanna B. Goldberg
Microbiology Spectrum.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer: role of immune-related gene expression
- Imaging features of breast cancer molecular subtypes: state of the art
- Nariya Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):16-25. Published online November 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.09.03
- 54,795 View
- 402 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Characterization of breast cancer molecular subtypes has been the standard of care for breast cancer management. We aimed to provide a review of imaging features of breast cancer molecular subtypes for the field of precision medicine. We also provide an update on the recent progress in precision medicine for breast cancer, implications for imaging, and recent observations in longitudinal functional imaging with radiomics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction of HER2 changes post-neoadjuvant therapy based on fusion of ultrasound radiomics and clinicopathological features empowered by explainable AI: A multicenter study
Yuqi Yan, Xinzheng Xue, Jiayu Xie, Jian Liu, Lin Sui, Tian Jiang, Zhiyan Jin, Di Ou, Zhirui Chuan, Mingjie Jin, Yang Zhang, Vicky Yang Wang, Xiaomao Luo, Shihao Xu, Dong Xu
European Journal of Cancer.2026; 232: 116158. CrossRef - Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Deep Learning-Derived Malignancy Scoring in Breast Cancer Molecular Subtype Assessment
Antonia O. Ferenčaba, Dora Galić, Gordana Ivanac, Kristina Kralik, Martina Smolić, Justinija Steiner, Ivo Pedišić, Kristina Bojanic
Medicina.2026; 62(1): 115. CrossRef - Radiomics Integration of Mammography and DCE-MRI for Predicting Molecular Subtypes in Breast Cancer Patients
Xianwei Yang, Jing Li, Hang Sun, Jing Chen, Jin Xie, Yonghui Peng, Tao Shang, Tongyong Pan
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 17: 187. CrossRef - HER2 (2+)/SISH-positive vs. HER2 (3+) Breast Cancer: Pre-treatment MRI Differences and Accuracy of pCR Prediction on Post-treatment MRI
Ga Eun Park, Han Song Mun, Sung Hun Kim, Bong Joo Kang
Academic Radiology.2025; 32(8): 4395. CrossRef - Impact of Prior Mammograms on Radiologists and Radiographers' Detection of Different Breast Cancer Lesion Types
Judith D. Akwo, Phuong Dung (Yun) Trieu, Melissa L. Barron, Tess Reynolds, Sarah J. Lewis
Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences.2025; 72(4): 497. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging features and molecular subtypes of breast cancer
Junping Li, Guanghui Huo, Xiaoye Lei, Guang Li, Mengxing Yu, Ziyang Nie, Zhenhua Guo, Yue Zhang
Journal of Clinical Imaging Science.2025; 15: 37. CrossRef - Intertumoral Heterogeneity in Multifocal Breast Cancer Mimicking a Collision Tumor on Imaging: A Case Report
Yoshika Nagata, Izumi Kinoshita, Toshihiro Saeki, Daiji Uchiyama, Takahisa Fujikawa
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fractal measures as predictors of histopathological complexity in breast carcinoma mammograms
Abhijeet Das, Ramray Bhat, Mohit Kumar Jolly
Physical Biology.2025; 22(6): 066006. CrossRef - Association of clinicopathologic and molecular factors with the occurrence of positive margins in breast cancer
Anupama Praveen Kumar, Diego Vicente, Jianfang Liu, Praveen-Kumar Raj-Kumar, Brenda Deyarmin, Xiaoying Lin, Craig D. Shriver, Hai Hu
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 204(1): 15. CrossRef - The association of magnetic resonance imaging features with five molecular subtypes of breast cancer
Van Thi Nguyen, Duc Huu Duong, Quang Thai Nguyen, Duy Thai Nguyen, Thi Linh Tran, Tra Giang Duong
European Journal of Radiology Open.2024; 13: 100585. CrossRef - The effect of data resampling methods in radiomics
Aydin Demircioğlu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Treated Primary Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma With Later Metastasis Found in Clinical Presentation of Left Axilla Lymphadenopathy: A Case Report
Brigitte L Cochran, Sara Eliseo, Austin Vaughn, Tamryn L Van Der Horn, Enzo Ferrara, Jamie Edwards
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pushing the envelope in breast conserving surgery − is multiple-wire localization (3 or more wires) associated with increased risk of compromised margins and long-term recurrence?
Orit Golan, Marian Khatib, Tehillah S. Menes, Vivianne A.R. Freitas, Rivka Kessner, Rina Neeman, Michal Mauda-Havakuk, Diego Mercer, Yoav Amitai
European Journal of Radiology.2024; 176: 111511. CrossRef - A model combining BI-RADS® descriptors from pre-treatment B-mode breast ultrasound with clinicopathological tumor features shows promise in the prediction of residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Panagiotis Kapetas, Reena Aggarwal, Basmah Altuwayjiri, Katja Pinker, Paola Clauser, Thomas H. Helbich, Pascal A.T. Baltzer
European Journal of Radiology.2024; 178: 111649. CrossRef - Correlations of Imaging and Therapy in Breast Cancer Based on Molecular Patterns: An Important Issue in the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
Oana Maria Burciu, Ioan Sas, Tudor-Alexandru Popoiu, Adrian-Grigore Merce, Lavinia Moleriu, Ionut Marcel Cobec
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(15): 8506. CrossRef - Access to prior screening mammograms affects the specificity but not sensitivity of radiologists' performance
J.D. Akwo, P. D. (Yun) Trieu, M.L. Barron, T. Reynolds, S.J. Lewis
Clinical Radiology.2024; 79(12): e1549. CrossRef - Machine learning-based radiomics prognostic model for patients with proximal esophageal cancer after definitive chemoradiotherapy
Linrui Li, Zhihui Qin, Juan Bo, Jiaru Hu, Yu Zhang, Liting Qian, Jiangning Dong
Insights into Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - LYMPH NODES MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES AND BREAST CANCER SUBTYPES IN PREDICTION OF METASTASES
J. N. Akhundova, M. F. Amirova
World of Medicine and Biology.2024; 20(90): 15. CrossRef - Axillary lymph node changes in different molecular subtypes of breast cancer
J.N. Akhundova
Український радіологічний та онкологічний журнал.2024; 32(4): 529. CrossRef - Histogram analysis of multi-model high-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI in breast cancer: correlations with molecular prognostic factors and subtypes
Yanjin Qin, Feng Wu, Qilan Hu, Litong He, Min Huo, Caili Tang, Jingru Yi, Huiting Zhang, Ting Yin, Tao Ai
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - ASO Author Reflections: Sequence of Treatment in Clinically Node-Negative T1 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Kai Huang, James W. Jakub, Sarah A. McLaughlin
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(13): 8455. CrossRef - Circulating non-coding RNAs as a diagnostic and management biomarker for breast cancer: current insights
Hamed Hosseinalizadeh, Mehrdad Mahmoodpour, Ammar Ebrahimi
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(1): 705. CrossRef - MRI as a biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis
Francesca Galati, Veronica Rizzo, Rubina Manuela Trimboli, Endi Kripa, Roberto Maroncelli, Federica Pediconi
BJR|Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiparametric MRI Features of Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes
Madalina Szep, Roxana Pintican, Bianca Boca, Andra Perja, Magdalena Duma, Diana Feier, Bogdan Fetica, Dan Eniu, Sorin Marian Dudea, Angelica Chiorean
Medicina.2022; 58(12): 1716. CrossRef - Circulating tumor cells as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer: current status and future prospects
Evagelia Chantzara, Nikolaos Xenidis, Galatea Kallergi, Vassilis Georgoulias, Athanasios Kotsakis
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2021; 21(10): 1037. CrossRef
- Prediction of HER2 changes post-neoadjuvant therapy based on fusion of ultrasound radiomics and clinicopathological features empowered by explainable AI: A multicenter study
- Clinicopathological characteristics of BRCA-associated breast cancer in Asian patients
- Eun-Kyu Kim, So Yeon Park, Sung-Won Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):265-275. Published online May 14, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.04.07
- 11,899 View
- 267 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF BRCA 1/2 germline mutations account for the majority of hereditary breast cancers. Since the identification of theBRCA genes, several attempts have been made to define the clinicopathological characteristics ofBRCA -associated breast cancer in comparison with sporadic breast cancer. Asians constitute 60% of the world population, and although the incidence of breast cancer in Asia remains low compared to the West, breast cancer is the most prevalent female cancer in the region. The epidemiological aspects of breast cancer are different between Asians and Caucasians. Asian patients present with breast cancer at a younger age than Western patients. The contributions ofBRCA1/2 mutations to breast cancer incidence are expected to differ between Asians and Caucasians, and the different genetic backgrounds among races are likely to influence the breast cancer phenotypes. However, most large-scale studies on the clinicopathological characteristics ofBRCA -associated breast cancer have been on Western patients, while studies on Asian populations were small and sporadic. In this review, we provide an overview of the clinical and pathological characteristics ofBRCA -associated breast cancer, incorporating findings on Asian patients.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Harnessing Institutionally Developed Clinical Targeted Sequencing to Improve Patient Survival in Breast Cancer: A Seven-Year Experience
Jiwon Koh, Jinyong Kim, Go-Un Woo, Hanbaek Yi, So Yean Kwon, Jeongmin Seo, Jeong Mo Bae, Jung Ho Kim, Jae Kyung Won, Han Suk Ryu, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Dae-Won Lee, Miso Kim, Tae-Yong Kim, Kyung-Hun Lee, Tae-You Kim, Jee-Soo Lee, Moon-Woo Seong, Sheehyun Kim,
Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 57(2): 443. CrossRef - Part II: consensus statements and expert recommendations for BRCA-associated breast cancer in the Asia-Pacific region: clinical management
Yeon Hee Park, Soo Chin Lee, Christian F. Singer, Judith Balmaña, Rebecca Alexandra Dent, Veronique Kiak-Mien Tan, Nadia Ayu Mulansari, Mastura Md. Yusof, Frances Victoria F. Que, Yen-Shen Lu, Napa Parinyanitikul, Cam Phuong Pham, Nur Aishah Taib, Sun-You
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef -
Predicting
BRCA
mutation and stratifying targeted therapy response using multimodal learning: a multicenter study
Yi Li, Xiaomin Xiong, Xiaohua Liu, Mengke Xu, Boping Yang, Xiaoju Li, Yu Li, Bo Lin, Bo Xu
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - BRCA 1–2 Incidence in Synchronous and Metachronous Breast Cancer: a Tertiary Center Study
Ahmet Dağ, Bilal Arslan, Erkan Güler, Serdar Mermer
Indian Journal of Surgery.2023; 85(1): 25. CrossRef - Characteristics of breast cancer patients tested for germline BRCA1/2 mutations by next‐generation sequencing in Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
Songporn Oranratnachai, Watchalawalee Yamkaew, Atchara Tunteeratum, Thongchai Sukarayothin, Nareenart Iemwimangsa, Ravat Panvichien
Cancer Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic and predictive biomarkers with therapeutic targets in breast cancer: A 2022 update on current developments, evidence, and recommendations
Clement Chung, Vanessa T.Y. Yeung, Kenneth C.W. Wong
Journal of Oncology Pharmacy Practice.2023; 29(6): 1343. CrossRef - Mutations of TP53 and genes related to homologous recombination repair in breast cancer with germline BRCA1/2 mutations
Jinyong Kim, Kyeonghun Jeong, Hyeji Jun, Kwangsoo Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Myung Geun Song, Hanbaek Yi, Songyi Park, Go-un Woo, Dae-Won Lee, Tae-Yong Kim, Kyung-Hun Lee, Seock-Ah Im
Human Genomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Habitat Analysis of Breast Cancer‐Enhanced MRI Reflects BRCA1 Mutation Determined by Immunohistochemistry
Tianming Du, Haidong Zhao, Chen Li
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Factors Associated with BRCA1/2 Gene Mutation in Chinese Populations with Breast Cancer
Guoding Huang, Hongquan Lu, Qizhu Chen, Xinting Huang
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 6783. CrossRef - Association between fertility treatments and breast cancer risk in women with a family history or BRCA mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaojing Liu, Jing Yue, Ruqiya Pervaiz, Hanwang Zhang, Lan Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Baseline [18F]FDG PET/CT Semiquantitative Parameters and BRCA Mutational Status and Their Prognostic Role in Patients with Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma
Francesco Dondi, Domenico Albano, Pietro Bellini, Luca Camoni, Giorgio Treglia, Francesco Bertagna
Tomography.2022; 8(6): 2662. CrossRef - The clinical and diagnostic characteristics of BRCA-associated breast cancer
M.A. Golotyuk, A.A. Berezhnoy, N.V. Kazantseva, A.V. Dorofeev, S.A. Shevchenko, I.V. Borzunov, N.I. Rozhkova
Onkologiya. Zhurnal imeni P.A.Gertsena.2022; 11(6): 18. CrossRef - The Clinical and Pathological Profile of BRCA1 Gene Methylated Breast Cancer Women: A Meta-Analysis
Ilary Ruscito, Maria Luisa Gasparri, Maria Paola De Marco, Flavia Costanzi, Aris Raad Besharat, Andrea Papadia, Thorsten Kuehn, Oreste Davide Gentilini, Filippo Bellati, Donatella Caserta
Cancers.2021; 13(6): 1391. CrossRef - Changing Patterns in Clinicopathological Characteristics of Breast Cancer and Prevalence of BRCA Mutations: Analysis in a Rural Area of Southern China
Qiuming Wang, Heming Wu, Yongquan Lan, Jinhong Zhang, Jingna Wu, Yunuo Zhang, Liang Li, Donghua Liu, Jinfeng Zhang
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7371. CrossRef
- Harnessing Institutionally Developed Clinical Targeted Sequencing to Improve Patient Survival in Breast Cancer: A Seven-Year Experience
- Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
- Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):95-102. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.24
- 10,690 View
- 293 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pure mucinous carcinoma (PMC) is a rare type of breast cancer, estimated to represent 2% of invasive breast cancer. PMC is typically positive for estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive PMC have not been investigated.
Methods
Pathology archives were searched for PMC diagnosed from January 1999 to April 2018. Clinicopathologic data and microscopic findings were reviewed and compared between HER2-positive PMC and HER2-negative PMC. We also analyzed the differences in disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival according to clinicopathologic parameters including HER2 status in overall PMC cases.
Results
There were 21 HER2-positive cases (4.8%) in 438 PMCs. The average tumor size of HER2-positive PMC was 32.21 mm (± 26.55). Lymph node metastasis was present in seven cases. Compared to HER2-negative PMC, HER2-positive PMC presented with a more advanced T category (p < .001), more frequent lymph node metastasis (p = .009), and a higher nuclear and histologic grade (p < .001). Microscopically, signet ring cells were frequently observed in HER2-positive PMC (p < .001), whereas a micropapillary pattern was more frequent in HER2-negative PMC (p = .012). HER2-positive PMC was more frequently negative for ER (33.3% vs. 1.2%) and PR (28.6% vs. 7.2%) than HER2-negative PMC and showed a high Ki-67 labeling index. During follow-up, distant metastasis and recurrence developed in three HER2-positive PMC patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that only HER2-positivity and lymph node status were significantly associated with DFS.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that HER2-positive PMC is a more aggressive subgroup of PMC. HER2 positivity should be considered for adequate management of PMC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
Sunayana Misra, Mihir Gudi, Kimberly H Allison, Edi Brogi, Cecily Quinn, Hannah Y Wen, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of a 6-years study from national cancer center in Vietnam
Thi Huyen Phung, Thanh Tung Pham, Huu Thang Nguyen, Dinh Thach Nguyen, Thanh Long Nguyen, Thi Hoai Hoang
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(3): 667. CrossRef - Poor response of HER2-positive mucinous carcinomas of breast to neoadjuvant HER2-targeted therapy: A study of four cases
Min Han, Daniel Schmolze, Javier A. Arias-Stella, Christina H. Wei, Joanne Mortimer, Fang Fan
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 74: 152396. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Mesonephric Marker Expression in Low-grade Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma
Yurimi Lee, Sangjoon Choi, Hyun-Soo Kim
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(3): 221. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of circ-FOXO3 and miR-23a in radiosensitivity of breast cancer
Elahe Abdollahi, Hossein Mozdarani, Behrooz Z. Alizadeh
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(5): 714. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Spectrum of Mucin-containing Lesions of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Review with Pathologic Correlation
Janice N. Thai, Melinda F. Lerwill, Shinn-Huey S. Chou
RadioGraphics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Metastasis of the Mucionous adenocarcinoma of breast to the mandibular gingiva: Rare case report
Ivana Mijatov, Aleksandra Fejsa Levakov, Aleksandar Spasić, Jelena Nikolić, Saša Mijatov
Medicine.2022; 101(38): e30732. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Carcinoma mucosecretor de mama HER2-positivo, un caso clínico
A.M. González Aranda, E. Martínez Gómez, A. Santana Costa, F. Arnanz Velasco, M.H. González de Diego, A. Zapico Goñi
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2021; 48(4): 100685. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of unexpectedly HER2 positive breast carcinomas: An institutional experience
Carissa LaBoy, Kalliopi P. Siziopikou, Lauren Rosen, Luis Z. Blanco, Jennifer L. Pincus
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153441. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef
- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
- Analysis of the molecular subtypes of preoperative core needle biopsy and surgical specimens in invasive breast cancer
- Ye Sul Jeong, Jun Kang, Jieun Lee, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Sung Hun Kim, Ahwon Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):87-94. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.14
- 10,120 View
- 212 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Accurate molecular classification of breast core needle biopsy (CNB) tissue is important for determining neoadjuvant systemic therapies for invasive breast cancer. The researchers aimed to evaluate the concordance rate (CR) of molecular subtypes between CNBs and surgical specimens.
Methods
This study was conducted with invasive breast cancer patients who underwent surgery after CNB at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital between December 2014 and December 2017. Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and Ki67 were analyzed using immunohistochemistry. ER and PR were evaluated by Allred score (0–8). HER2 was graded from 0 to +3, and all 2+ cases were reflex tested with silver in situ hybridization. The labeling index of Ki67 was counted by either manual scoring or digital image analysis. Molecular subtypes were classified using the above surrogate markers.
Results
In total, 629 patients were evaluated. The CRs of ER, PR, HER2, and Ki67 were 96.5% (kappa, 0.883; p<.001), 93.0% (kappa, 0.824; p<.001), 99.7% (kappa, 0.988; p<.001), and 78.7% (kappa, 0.577; p<.001), respectively. Digital image analysis of Ki67 in CNB showed better concordance with Ki67 in surgical specimens (CR, 82.3%; kappa, 0.639 for digital image analysis vs. CR, 76.2%; kappa, 0.534 for manual counting). The CRs of luminal A, luminal B, HER2, and triple negative types were 89.0%, 70.0%, 82.9%, and 77.2%, respectively.
Conclusions
CNB was reasonably accurate for determining ER, PR, HER2, Ki67, and molecular subtypes. Using digital image analysis for Ki67 in CNB produced more accurate molecular classifications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting the Efficacy of Breast Cancer Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Ultrasonography and Machine Learning
Meihong Jia, Huizhan Li, Wenli Xiao, Jiping Xue, Zhifen Wang, Xia He, Xin Wang, Dianxia Men
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between ultrasonography and elastography parameters and molecular subtypes of breast cancer in young women
Dian-xia Men, Hui-zhan Li, Juan Dong, Meng-hua Xue, Zhi-fen Wang, Wen-li Xiao, Ji-ping Xue, Mei-hong Jia
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Concordance of Oncotype DX Breast Recurrence Score Assay Results Between Paired Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Excision Specimens in Hormone Receptor Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Negative, Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Aziza Nassar, Jodi Carter, Paige Innis, Andrea Pingitore Blacklock, Jennifer Racz, Matthew Petitt, Purva Singla, Helena Hanna, Abigail Lochala, Christy A. Russell, Minetta C. Liu
JCO Precision Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of immunohistochemistry staining conditions on the incidence of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-low breast cancer
Min Chong Kim, Sun Young Kwon, Hye Ra Jung, Young Kyung Bae
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(6): 1117. CrossRef - Study on Intratumoral Heterogeneity of Expression of Estrogen Receptor, Progesterone Receptor, and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 in Carcinoma Breast
Ragavi Uthayasuriyan, Sheba K Jacob, Saloni Naresh Shah
Apollo Medicine.2024; 21(1): 51. CrossRef - Concordance of HER2 status between core needle biopsy and surgical resection specimens of breast cancer: an analysis focusing on the HER2-low status
Sei Na, Milim Kim, Yujun Park, Hyun Jung Kwon, Hee-Chul Shin, Eun-Kyu Kim, Mijung Jang, Sun Mi Kim, So Yeon Park
Breast Cancer.2024; 31(4): 705. CrossRef - Concordance of immunohistochemistry for predictive and prognostic factors in breast cancer between biopsy and surgical excision: a single-centre experience and review of the literature
Chiara Rossi, Sara Fraticelli, Marianna Fanizza, Alberta Ferrari, Elisa Ferraris, Alessia Messina, Angelica Della Valle, Chiara Annunziata Pasqualina Anghelone, Angioletta Lasagna, Gianpiero Rizzo, Lorenzo Perrone, Maria Grazia Sommaruga, Giulia Meloni, S
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2023; 198(3): 573. CrossRef - Single-center study on clinicopathological and typical molecular pathologic features of metastatic brain tumor
Su Hwa Kim, Young Suk Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Yeoun Eun Sung, Ahwon Lee, Jun Kang, Jae-Sung Park, Sin Soo Jeun, Youn Soo Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 217. CrossRef - The Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Based on Maximum-Intensity Projection in Young Patients with Marked Background Parenchymal Enhancement on Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI
Ga-Eun Park, Bong-Joo Kang, Sung-hun Kim, Na-Young Jung
Life.2023; 13(8): 1744. CrossRef - Concordance between core needle biopsy and surgical excision specimens for Ki‐67 in breast cancer – a systematic review of the literature
Jahnavi Kalvala, Ruth M Parks, Andrew R Green, Kwok‐Leung Cheung
Histopathology.2022; 80(3): 468. CrossRef - İnvaziv Meme Kanserinde Preoperatif Kor İğne Biyopsi ile Postoperatif Cerrahi Spesmenler Arasında ER, PR, HER2 ve Ki67 Açısından Karşılaştırma
Pınar CELEPLİ, Pelin Seher ÖZTEKİN, Salih CELEPLİ, İrem BİGAT, Sema HÜCÜMENOĞLU
Akdeniz Medical Journal.2022; : 179. CrossRef - Concordance of breast cancer biomarker testing in core needle biopsy and surgical specimens: A single institution experience
Jessica A. Slostad, Nicole K. Yun, Aimee E. Schad, Surbhi Warrior, Louis F. Fogg, Ruta Rao
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(24): 4954. CrossRef - N-Cadherin Distinguishes Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma from Liver Metastases of Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas
Tiemo S. Gerber, Benjamin Goeppert, Anne Hausen, Hagen R. Witzel, Fabian Bartsch, Mario Schindeldecker, Lisa-Katharina Gröger, Dirk A. Ridder, Oscar Cahyadi, Irene Esposito, Matthias M. Gaida, Peter Schirmacher, Peter R. Galle, Hauke Lang, Wilfried Roth,
Cancers.2022; 14(13): 3091. CrossRef - Association of Ki-67 Change Pattern After Core Needle Biopsy and Prognosis in HR+/HER2− Early Breast Cancer Patients
Shuai Li, Xiaosong Chen, Kunwei Shen
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - MRI Features for Prediction Malignant Intra-Mammary Lymph Nodes: Correlations with Mammography and Ultrasound
Meejung Kim, Bong Joo Kang, Ga Eun Park
Investigative Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2022; 26(2): 135. CrossRef - A single centre experience in Turkey for comparison between core needle biopsy and surgical specimen evaluation results for HER2, SISH, estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors in breast cancer patients
Hatice Karaman, Fatma Senel, Arzu Tasdemir, Ipek Özer, Merve Dogan
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2022; 18(6): 1789. CrossRef - Meme kanseri trucut ve rezeksiyon materyallerinde yeni moleküler sınıflama, tanı ve hormon reseptörlerinin durumu tutarlı mı?
Yeliz ARMAN KARAKAYA, Sevda YILMAZ, Hande KARABAŞ
Pamukkale Medical Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - What shear wave elastography parameter best differentiates breast cancer and predicts its histologic aggressiveness?
Hyunjin Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Bong Joo Kang, Sung Hun Kim
Ultrasonography.2021; 40(2): 265. CrossRef - Risk-based decision-making in the treatment of HER2-positive early breast cancer: Recommendations based on the current state of knowledge
Christian Jackisch, Patricia Cortazar, Charles E. Geyer, Luca Gianni, Joseph Gligorov, Zuzana Machackova, Edith A. Perez, Andreas Schneeweiss, Sara M. Tolaney, Michael Untch, Andrew Wardley, Martine Piccart
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2021; 99: 102229. CrossRef - Factors influencing agreement of breast cancer luminal molecular subtype by Ki67 labeling index between core needle biopsy and surgical resection specimens
Kristina A. Tendl-Schulz, Fabian Rössler, Philipp Wimmer, Ulrike M. Heber, Martina Mittlböck, Nicolas Kozakowski, Katja Pinker, Rupert Bartsch, Peter Dubsky, Florian Fitzal, Martin Filipits, Fanny Carolina Eckel, Eva-Maria Langthaler, Günther Steger, Mich
Virchows Archiv.2020; 477(4): 545. CrossRef
- Predicting the Efficacy of Breast Cancer Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Ultrasonography and Machine Learning
- HER2 status in breast cancer: changes in guidelines and complicating factors for interpretation
- Soomin Ahn, Ji Won Woo, Kyoungyul Lee, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):34-44. Published online November 6, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.03
- 38,004 View
- 1,323 Download
- 189 Web of Science
- 187 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein overexpression and/or HER2 gene amplification is found in about 20% of invasive breast cancers. It is a sole predictive marker for treatment benefits from HER2 targeted therapy and thus, HER2 testing is a routine practice for newly diagnosed breast cancer in pathology. Currently, HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) is used for a screening test, and in situ hybridization is used as a confirmation test for HER2 IHC equivocal cases. Since the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)/College of American Pathologists (CAP) guidelines on HER2 testing was first released in 2007, it has been updated to provide clear instructions for HER2 testing and accurate determination of HER2 status in breast cancer. During HER2 interpretation, some pitfalls such as intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity and increase in chromosome enumeration probe 17 signals may lead to inaccurate assessment of HER2 status. Moreover, HER2 status can be altered after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or during metastatic progression, due to biologic or methodologic issues. This review addresses recent updates of ASCO/CAP guidelines and factors complicating in the interpretation of HER2 status in breast cancers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Model Outperformed the Single Radiomics Model in Noninvasively Predicting the HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Cancer
Weimin Liu, Yiqing Yang, Xiaohong Wang, Chao Li, Chen Liu, Xiaolei Li, Junzhe Wen, Xue Lin, Jie Qin
Academic Radiology.2025; 32(1): 24. CrossRef - Multiparametric MRI Radiomics With Machine Learning for Differentiating HER2-Zero, -Low, and -Positive Breast Cancer: Model Development, Testing, and Interpretability Analysis
Yongxin Chen, Siyi Chen, Wenjie Tang, Qingcong Kong, Zhidan Zhong, Xiaomeng Yu, Yi Sui, Wenke Hu, Xinqing Jiang, Yuan Guo
American Journal of Roentgenology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Unknown Origin and Remote Primary at a Tertiary Cancer Centre in North India: Case Series with Review of Literature
Kriti Grover, Siddharth Arora, Mansi Dey, Deepti Awasthi, Harshad Sharma, Bibhu Prasad Mishra, Nitesh Mohan, Cheena Garg, Arjun Agarwal
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2025; 77(1): 424. CrossRef - Pooled clinical trial analyses evaluating outcomes of HER2-low vs HER2-0 expression in patients with metastatic breast cancer following chemotherapy
Elizabeth B. Lamont, Emily Stein, Paolo Tarantino, Sara M. Tolaney, Corinne Ahlberg, Krishna Chinnathambu, Jiezhi Qi, Jackie Bilan, Ruthie Davi, Lisa Ensign
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 210(1): 11. CrossRef - Insights into AI advances in immunohistochemistry for effective breast cancer treatment: a literature review of ER, PR, and HER2 scoring
Genevieve Chyrmang, Kangkana Bora, Anup Kr. Das, Gazi N. Ahmed, Lopamudra Kakoti
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2025; 41(1): 115. CrossRef - Prediction of Lung Adenocarcinoma Driver Genes Through Protein–Protein Interaction Networks Utilizing GenePlexus
Fei Yuan, Yu‐Hang Zhang, FeiMing Huang, Xiaoyu Cao, Lei Chen, JiaBo Li, WenFeng Shen, KaiYan Feng, YuSheng Bao, Tao Huang, Yu‐Dong Cai
PROTEOMICS.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative expression of estrogen, progesterone and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 and their correlation with immunohistochemistry in breast cancer at Uganda Cancer Institute
Henry Wannume, Nixon Niyonzima, Sam Kalungi, Julius Boniface Okuni, Tonny Okecha, Edward Kakungulu, Steven Mpungu Kiwuwa, Geoffrey Waiswa, Sylvester Kadhumbula, Monica Namayanja, Martin Nabwana, Jackson Orem, Kenji Fujiwara
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0311185. CrossRef - Automated Quantification of HER2 Amplification Levels Using Deep Learning
Ching-Wei Wang, Kai-Lin Chu, Ting-Sheng Su, Keng-Wei Liu, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2025; 29(1): 333. CrossRef - CAR-macrophage therapy for HER2-overexpressing advanced solid tumors: a phase 1 trial
Kim A. Reiss, Mathew G. Angelos, E. Claire Dees, Yuan Yuan, Naoto T. Ueno, Paula R. Pohlmann, Melissa L. Johnson, Joseph Chao, Olga Shestova, Jonathan S. Serody, Maggie Schmierer, Madison Kremp, Michael Ball, Rehman Qureshi, Benjamin H. Schott, Poonam Son
Nature Medicine.2025; 31(4): 1171. CrossRef - Human Cytomegalovirus Infection and Breast Cancer: A Literature Review of Clinical and Experimental Data
Rancés Blanco, Juan P. Muñoz
Biology.2025; 14(2): 174. CrossRef - An antibody-photosensitiser bioconjugate overcomes trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer
Mireia Jordà-Redondo, Ana Piqueras, Ana Castillo, Pedro Luis Fernández, Roger Bresolí-Obach, Lidia Blay, Joan Francesc Julián Ibáñez, Santi Nonell
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 290: 117511. CrossRef - Dynamic HER2-low status among patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and the impact of repeat biopsies
Yael Bar, Geoffrey Fell, Aylin Dedeoglu, Natalie Moffett, Neelima Vidula, Laura Spring, Seth A. Wander, Aditya Bardia, Naomi Ko, Beverly Moy, Leif W. Ellisen, Steven J. Isakoff
npj Breast Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical significances of RPL15 gene expression in circulating tumor cells of patients with breast cancer
Ying Zhuang, Keli Su, Shushu Liu, Wei Fan, Huijuan Lv, Wei Zhong
Biomedical Reports.2025; 22(5): 1. CrossRef - Advancing Breast Cancer Treatment: The Role of Immunotherapy and Cancer Vaccines in Overcoming Therapeutic Challenges
Marco Palma
Vaccines.2025; 13(4): 344. CrossRef - Complete preclinical evaluation of the novel antibody mimetic Nanofitin-IRDye800CW for diverse non-invasive diagnostic applications in the management of HER-2 positive tumors
Margherita Iaboni, Federico Crivellin, Francesca Arena, Francesca La Cava, Alessia Cordaro, Francesco Stummo, Daniele Faletto, Simon Huet, Leo Candela, Jessy Pedrault, Eugenia R. Zanella, Andrea Bertotti, Francesco Blasi, Alessandro Maiocchi, Luisa Poggi,
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights on Galectin-9 expression in cancer prognosis: An updated systemic review and meta-analysis
Chun Yan So, Yusong Li, Kwan Ting Chow, Xiaosheng Tan
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(3): e0320441. CrossRef - Role of artificial intelligence –based machine learning model in predicting HER2/neu gene status in breast cancer
Ghada Mohamed, Omar Hamdy, Anwar Alkallas, Youssef Tahoun, Mohammed Mohammed Gomaa, Inas Moaz, Ahmed Orabi, Yasmine Hany elzohery, AL-Shimaa Zakaria, Mahitab Ibrahim Eltohamy
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 270: 155927. CrossRef - HER2 mRNA Score From Quantitative ERBB2 mRNA Expression of Oncotype Dx
Hyunwoo Lee, Jai Min Ryu, Se Kyung Lee, Byung Joo Chae, Jonghan Yu, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Won Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Yoon Ah Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 49(8): 807. CrossRef - Neratinib and metformin: A novel therapeutic approach against HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Hadeel Kheraldine, Arij Fouzat Hassan, Sumayyah Saeed, Maysaloun Merhi, Jericha Miles Mateo, Monika Ulamec, Melita Peric-Balja, Semir Vranic, Hamda Al-Thawadi, Ala-Eddin Al Moustafa
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2025; 187: 118034. CrossRef - Machine learning prediction of HER2-low expression in breast cancers based on hematoxylin–eosin-stained slides
Jun Du, Jun Shi, Dongdong Sun, Yifei Wang, Guanfeng Liu, Jingru Chen, Wei Wang, Wenchao Zhou, Yushan Zheng, Haibo Wu
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting sentinel lymph node metastatic burden with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in clinical early-stage breast cancer patients
Mingli Jin, Fang Xiao, Qi Zhao, Ying Jiang, Zhihua Pan, Zhicai Duan, Juxi Jiang, Miaoqi Zhang, Jian Shu
Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2025; 121: 110397. CrossRef - HbA1c levels and breast cancer prognosis in women without diabetes
Jonas Busk Holm, Jens Meldgaard Bruun, Peer Christiansen, Reimar Wernich Thomsen, Jan Frystyk, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Signe Borgquist
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes in Early-Stage HER2-Low and HER2-Zero Breast Cancer: Single-Center Experience
Jamshid Hamdard, Mehmet Haluk Yücel, Harun Muğlu, Özgür Açıkgöz, Aslı Çakır, Ahmet Bilici, Ömer Fatih Ölmez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(9): 2937. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanism of Breast Cancer and Predisposition of Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus Propagation Cycle
Arya Ghosh, Subash C.B. Gopinath
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 32(12): 2330. CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF RECEPTOR CONVERSION ROLE FOR ADVANCED BREAST CANCER ON THE CHEMORESISTANCE OCCURRENCE
Oleksii V. Movchan, Ivan I. Smolanka, Andriy O. Lyashenko, Anton D. Loboda, Iryna V. Dosenko, Oksana M. Ivankova
Clinical and Preventive Medicine.2025; (3): 56. CrossRef - Combining conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) parameters with clinicopathologic data for differentiation of the three-tiered human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer
W. Liu, C. Liu, Y. Yang, Y. Chen, A. Muhetaier, Z. Lin, Z. Weng, X. Wang, P. Zhang, J. Qin
Clinical Radiology.2025; 86: 106955. CrossRef - IN SILICO STUDY: THE POTENTIAL OF KILEMO (Litsea cubeba) ENDEMIC PLANT FROM KALIMANTAN AS ANTI-BREAST CANCER THROUGH HER2 INHIBITION
Dwi Utami, Tarisha Elmaningtyas Zahro, Khairun Nisa, Muhammad Farid
JIIS (Jurnal Ilmiah Ibnu Sina): Ilmu Farmasi dan Kesehatan.2025; 10(1): 166. CrossRef - Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Metastatic Breast Cancer: Real-World Multicentric Study in the Portuguese Population
Luísa Soares Miranda, Maria João Sousa, Miguel Martins Braga, Marisa Couto, Isabel Vieira Fernandes, Francisca Abreu, Inês Eiriz, Catarina Lopes Fernandes, Alice Fonseca Marques, Maria Teresa Marques, Raquel Romão, Fernando Gonçalves, Joana Simões, Antóni
Cancers.2025; 17(12): 1911. CrossRef - Factors influencing pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable breast cancer: A retrospective study
Jian Kang, Huifen Xiong, Xiaoliu Jiang, Zhaohui Huang, Yonghong Guo, Yali Cao, Jingxian Ding
Oncology Letters.2025; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Association of HER2-low with clinicopathological features in patients with early invasive lobular breast cancer: an international multicentric study
Karen Van Baelen, Ha-Linh Nguyen, François Richard, Gitte Zels, Maria Margarete Karsten, Guilherme Nader-Marta, Peter Vermeulen, Luc Dirix, Adam David Dordevic, Evandro de Azambuja, Denis Larsimont, Marion Maetens, Elia Biganzoli, Hans Wildiers, Ann Smeet
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Collagenase type IV improves the quality of HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization for breast cancers
Shang-En Lee, Sheng-Chi Hsu, Tsai-Hsien Hung, Kwai-Fong Ng, Tse-Ching Chen
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(3): 342. CrossRef - Resonant multi-focal scanning super-resolution microscopy with extended depth and field-of-view
Kidan Tadesse, Keyi Han, Wenhao Liu, Oliver S. Lee, Shu Jia
Cell Reports Physical Science.2025; 6(7): 102680. CrossRef - Scalable Nuclei Detection in HER2-SISH Whole Slide Images via Fine-Tuned Stardist with Expert-Annotated Regions of Interest
Zaka Ur Rehman, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Fazly Salleh Abas, Phaik-Leng Cheah, Seow-Fan Chiew, Lai-Meng Looi
Diagnostics.2025; 15(13): 1584. CrossRef - Molecular landscape of HER2-mutated non-small cell lung cancer in Northeastern Brazil: Clinical, histopathological, and genomic insights
Cleto Dantas Nogueira, Samuel Frota, Huylmer Lucena Chaves, Juliana Cordeiro de Sousa, Guilherme de Sousa Veloso, Francisco Jonathan dos Santos Araujo, Gabriel Barbosa Silva, Samuel Silva Ferreira, Marclesson Santos Alves, Fabio Nasser, Ezequiel Rangel, F
Oncotarget.2025; 16(1): 467. CrossRef - Correlation between CTMP expression levels and resistance to trastuzumab in HER2 + metastatic breast cancer
Mania Makhoul, Maher Saifo, Fariz Ahmad, Jumana Saleh
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between body mass index and neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with breast cancer
Jonas Busk Holm, Stine Blaabjerg Skovbjerg, Hanne Melgaard Nielsen, Peer Christiansen, Jens Meldgaard Bruun, Jan Alsner, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Signe Borgquist
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An immunohistochemical characterization of basal cell carcinoma in patients below 40 years of age
Vincent Waller, Myriam Boeschen, Thomas Lingscheidt, Mathias Stiller, Lena Eickenscheidt, Thomas Wilhelm, Sonja Grunewald, Mirjana Ziemer, Jan‐Christoph Simon, Hendrik Bläker, Maximilian von Laffert
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2025; 23(11): 1414. CrossRef - Clinical Relationship Between Serum ApoB, HER2, and Myocardial Ischemia Risk in Breast Cancer Patients
Yeyan Lei, Dongmei Li, Shuang Bai, Xing Zeng, Rongyuan Yang, Qing Liu
Cancer Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual-targeting and steric hindrance resolution in HER2 IHC: a novel approach to improve diagnostic sensitivity
Li Luo, Xi Zhang, Linqiong Chen, Zhuohan Chen, Yuchen Wang, Kaihao Huang, Xiaoyun Lin, Hongxiang Zhu, Wangqi Du
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Time‐Dependent Diffusion MRI‐Based Microstructural Mapping for Characterizing HER2‐Zero, ‐Low, ‐Ultra‐Low, and ‐Positive Breast Cancer
Xiaoxia Wang, Yao Huang, Ying Cao, Huifang Chen, Xueqin Gong, Xiaosong Lan, Jiuquan Zhang, Zhaoxiang Ye
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2025; 62(6): 1754. CrossRef - Digital pathology enabling lean management of HER2/neu testing in breast Cancer
Aishwarya Sharma, Prarthna Shah, Manali Ranade, Trupti Pai, Ayushi Sahay, Asawari Patil, Tanuja Shet, Heena Gupta, Devika Chauhan, Puneet Somal, Sankalp Sancheti, Sangeeta Desai
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 19: 100515. CrossRef - Enhancing HER2-low breast cancer detection with quantitative transcriptomics
Maria-Anna Misiakou, Maj-Britt Jensen, Maj-Lis Talman, Bent Ejlertsen, Maria Rossing
npj Breast Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Caracterización inmunohistoquímica del cáncer de mama correlacionado con histopatología,estudio realizado en un hospital de Ecuador
María Fernanda Calderón León, Diego Mauricio Cabrera Moyano, Jorge Daniel Cárdenas Rodríguez, Paula Andrea Vásquez Jaramillo, Andrea Alexandra Saltos Román, Maryoli González Sánchez
Journal of the Selva Andina Research Society.2025; 16(2): 116. CrossRef - Relationship of vitamin D receptor expression with hormone receptors and other clinicopathological features in primary breast carcinomas: A retrospective cross-sectional study
Yaşar Ünlü, Ethem Ömeroğlu, Abdülhalim Serden Ay, Meryem İlkay Eren Karanis, Kilinç Ayşe Nur Uğur, Esra Yilmaz
Medicine.2025; 104(35): e44222. CrossRef - Improving HER2 Diagnostics with Digital Real‐Time PCR for Ultrafast, Precise Prediction of Anti‐HER2 Therapy Response in Patients with Breast Cancer
Hee‐Joo Choi, Soo Young Park, Minsik Song, Jinhyuk Chang, YoonSik Kim, Hosub Park, Chihwan David Cha, Sohyeon Yang, Nam Hun Heo, Min Ji Song, Da Sol Kim, Hayeon Kim, Minuk Kim, Jae Eun Park, Yesung Lee, EunChae Ji, Heekyoung Chung, Ilecheon Jeong, Mineui
Small Methods.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unveiling Metabolic Signatures as Potential Biomarkers in Common Cancers: Insights from Lung, Breast, Colorectal, Liver, and Gastric Tumours
Kha Wai Hon, Rakesh Naidu
Biomolecules.2025; 15(10): 1376. CrossRef - Validation of ancillary procedures on formalin liquid fixed aspiration cytologic samples: from minimum to maximum
Orsolya Rideg, Tímea Dergez, Arnold Tóth, Tamás Tornóczky, Gábor Pavlovics, Endre Kálmán
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(6): 924. CrossRef - Challenges & recommendations for identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor -2 (HER2)-low metastatic breast cancer in India: Expert opinion statement
Neeraj Arora, Jyoti Bajpai, Amanjit Bal, Atul Batra, Anurag Gupta, Deepak Kumar Mishra, Geetashree Mukherjee, Trupti Pai, Mayur Parihar, Geeta V. Patil Okaly, Shilpa Prabhudesai, Milap Shah, Somashekhar S.P.
The Indian Journal of Medical Research.2025; 162: 279. CrossRef - Eine immunhistologische Charakterisierung des Basalzellkarzinoms bei Patienten unter 40 Jahren
Vincent Waller, Myriam Boeschen, Thomas Lingscheidt, Mathias Stiller, Lena Eickenscheidt, Thomas Wilhelm, Sonja Grunewald, Mirjana Ziemer, Jan‐Christoph Simon, Hendrik Bläker, Maximilian von Laffert
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2025; 23(11): 1414. CrossRef - Comparison of Immunohistochemical 2 (+) HER2 Gene Status with SISH in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Alper Sayiner, Hatice Karaman, Fatma Şenel, Arzu Tasdemir, Merve Doğan, İpek Özer
Sakarya Medical Journal.2025; 15(4): 338. CrossRef - Concurrent genomic assessment of circulating tumour cells and ctDNA to guide therapy in metastatic breast cancer
Rebecca C. Allsopp, Karen Page, Evie Wren, Georgios Nteliopoulos, Kelly L. T. Gleason, Gurdeep Matharu Lall, Shradha Bhagani, Emmanuel Acheampong, Marc K. Wadsley, Raoul Charles Coombes, Jacqueline A. Shaw
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management Strategies and Outcomes in HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors and Subsequent Therapies
Katarzyna Pogoda, Hubert Pawlik, Anna Balata, Magdalena Czopowicz, Agata Bak, Iwona Twardowska, Malgorzata Meluch, Maria Wojda, Agnieszka Mlodzinska, Ewa Szombara, Renata Sienkiewicz, Aleksandra Konieczna, Elzbieta Brewczynska, Izabela Lemanska, Anna Majs
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 17: 1307. CrossRef - Identification of novel chemical scaffolds against kinase domain of cancer causing human epidermal growth factor receptor 2: a systemic chemoinformatic approach
Faris Alrumaihi
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; 42(12): 6269. CrossRef - Standardized pathology report for HER2 testing in compliance with 2023 ASCO/CAP updates and 2023 ESMO consensus statements on HER2-low breast cancer
Mariia Ivanova, Francesca Maria Porta, Marianna D’Ercole, Carlo Pescia, Elham Sajjadi, Giulia Cursano, Elisa De Camilli, Oriana Pala, Giovanni Mazzarol, Konstantinos Venetis, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Giuseppe Curigliano, Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 3. CrossRef - Analytical Performance Evaluation of a 523-Gene Circulating Tumor DNA Assay for Next-Generation Sequencing–Based Comprehensive Tumor Profiling in Liquid Biopsy Samples
Johannes Harter, Eleonora Buth, Janina Johaenning, Florian Battke, Maria Kopp, Henning Zelba, Martin Schulze, Jiri Koedding, Saskia Biskup
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2024; 26(1): 61. CrossRef - Are There More HER2 FISH in the Sea? An Institution’s Experience in Identifying HER2 Positivity Using Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization in Patients with HER2 Negative Immunohistochemistry
Camille Suydam, Fairouz Chibane, Nicole Brown, Madeleine Schlafly, Alicia H. Arnold, Intisar Ghleilib, Melissa Easley, Joseph White
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 376. CrossRef - HER2 copy number determination in breast cancer using the highly sensitive droplet digital PCR method
Beate Alinger-Scharinger, Cornelia Kronberger, Georg Hutarew, Wolfgang Hitzl, Roland Reitsamer, Klaassen-Federspiel Frederike, Martina Hager, Thorsten Fischer, Karl Sotlar, Heidi Jaksch-Bogensperger
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(1): 53. CrossRef - Impact of HER2-low status for patients with early-stage breast cancer and non-pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a National Cancer Database Analysis
Huiyue Li, Jennifer K. Plichta, Kan Li, Yizi Jin, Samantha M. Thomas, Fei Ma, Li Tang, Qingyi Wei, You-Wen He, Qichen Chen, Yuanyuan Guo, Yueping Liu, Jian Zhang, Sheng Luo
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 204(1): 89. CrossRef - Qualification of a multiplexed tissue imaging assay and detection of novel patterns of HER2 heterogeneity in breast cancer
Jennifer L. Guerriero, Jia-Ren Lin, Ricardo G. Pastorello, Ziming Du, Yu-An Chen, Madeline G. Townsend, Kenichi Shimada, Melissa E. Hughes, Siyang Ren, Nabihah Tayob, Kelly Zheng, Shaolin Mei, Alyssa Patterson, Krishan L. Taneja, Otto Metzger, Sara M. Tol
npj Breast Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Utility and Benefits of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Cancer
Melissa Yuwono Tjota, Jeremy P Segal, Peng Wang
The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine.2024; 9(1): 76. CrossRef - High contrast breast cancer biomarker semi-quantification and immunohistochemistry imaging using upconverting nanoparticles
Sanathana Konugolu Venkata Sekar, Hui Ma, Katarzyna Komolibus, Gokhan Dumlupinar, Matthias J. Mickert, Krzysztof Krawczyk, Stefan Andersson-Engels
Biomedical Optics Express.2024; 15(2): 900. CrossRef - HER2-low breast cancer and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a population-based cohort study
Ximena Baez-Navarro, Mieke R. van Bockstal, Agnes Jager, Carolien H.M. van Deurzen
Pathology.2024; 56(3): 334. CrossRef - Fast-tracking drug development with biomarkers and companion diagnostics
Noreen McBrearty, Devika Bahal, Suso Platero
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging Landscape of Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancers With Low Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Protein Expression
Gary Tozbikian, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Marilyn M. Bui, Michael Feldman, David G. Hicks, Shabnam Jaffer, Thaer Khoury, Shi Wei, Hannah Wen, Paula Pohlmann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(2): 242. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns and Health Outcomes among Patients with HER2 IHC0/-Low Metastatic or Recurrent Breast Cancer
Eliya Farah, Chantelle Carbonell, Devon J. Boyne, Darren R. Brenner, Jan-Willem Henning, Daniel Moldaver, Simran Shokar, Winson Y. Cheung
Cancers.2024; 16(3): 518. CrossRef - Clinical Internal Dosimetry and Biodistribution of 177Lu-DOTA-Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Metastatic and Locally Advanced Breast Carcinoma
Yoga S. Narwadkar, Rahul V. Parghane, Sudeep Sahu, Sangita Lad, Kamal Deep, Gaurav Wanage, Tejal Suralkar, Sharmila Banerjee, Sudeep Gupta, Sandip Basu, Rajendra A. Badwe
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2024; 49(4): e149. CrossRef - Molecular Classifications in Gastric Cancer: A Call for Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Cristina Díaz del Arco, María Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Luis Ortega Medina
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2649. CrossRef - The combined immunohistochemical expression of AMBRA1 and SQSTM1 identifies patients with poorly differentiated cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at risk of metastasis: A proof of concept study
Michael H. Alexander, William J. Cousins, Tom Ewen, Andrew P. South, Penny Lovat, Niki Stefanos
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2024; 51(6): 450. CrossRef - Concordance between pathologists and between specimen types in detection of HER2-low breast carcinoma by immunohistochemistry
Jing Wang, Esther Yoon, Savitri Krishnamurthy
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 70: 152288. CrossRef - Detection of HER2 expression using 99mTc-NM-02 nanobody in patients with breast cancer: a non-randomized, non-blinded clinical trial
Lingzhou Zhao, Yan Xing, Changcun Liu, Shaofei Ma, Wenhua Huang, Zhen Cheng, Jinhua Zhao
Breast Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pyrotinib and Trastuzumab Plus Chemotherapy Serve as an Acceptable Neoadjuvant Regimen Exhibiting Good Efficacy and Tolerance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients
Yibo Chen, Tianyi Zhang, Rui Zhang, Xuchen Cao
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2024; 39(6): 435. CrossRef - Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of VEGF, PDGF-B, and HER2/neu expression in gallbladder cancer
Pooja Shukla, Kumudesh Mishra, Ratnakar Shukla, Ruchira Vishwakarma, Niraj Kumari, Narendra Krishnani, Anu Behari, Vinay K. Kapoor
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2024; 20(1): 349. CrossRef - Open questions, current challenges, and future perspectives in targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-low breast cancer
G. Curigliano, R. Dent, H. Earle, S. Modi, P. Tarantino, G. Viale, S.M. Tolaney
ESMO Open.2024; 9(4): 102989. CrossRef - Concordance of HER2 status between core needle biopsy and surgical resection specimens of breast cancer: an analysis focusing on the HER2-low status
Sei Na, Milim Kim, Yujun Park, Hyun Jung Kwon, Hee-Chul Shin, Eun-Kyu Kim, Mijung Jang, Sun Mi Kim, So Yeon Park
Breast Cancer.2024; 31(4): 705. CrossRef - Impact of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) on Biomarker Expression in Breast Cancer
Suji Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, So Jeong Lee, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Kyung Bin Kim, Jung Hee Lee, Dong Hoon Shin, Kyung Un Choi, Chang Hun Lee, Gi Yeong Huh, Ahrong Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(5): 737. CrossRef - Clinical Use of Molecular Biomarkers in Canine and Feline Oncology: Current and Future
Heike Aupperle-Lellbach, Alexandra Kehl, Simone de Brot, Louise van der Weyden
Veterinary Sciences.2024; 11(5): 199. CrossRef - Clinical Validation of Artificial Intelligence–Powered PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score Interpretation for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response Prediction in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
Hyojin Kim, Seokhwi Kim, Sangjoon Choi, Changhee Park, Seonwook Park, Sergio Pereira, Minuk Ma, Donggeun Yoo, Kyunghyun Paeng, Wonkyung Jung, Sehhoon Park, Chan-Young Ock, Se-Hoon Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Jin-Haeng Chung
JCO Precision Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor amplification correlates with adverse pathological features and poor clinical outcome in colorectal cancer
Qiu-Xiao Yu, Ping-Ying Fu, Chi Zhang, Li Li, Wen-Ting Huang
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(5): 1395. CrossRef - Lipid nanoparticles-based RNA therapies for breast cancer treatment
Luigia Serpico, Yuewen Zhu, Renata Faria Maia, Sumedha Sumedha, Mohammad-Ali Shahbazi, Hélder A. Santos
Drug Delivery and Translational Research.2024; 14(10): 2823. CrossRef - Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer: practice points and challenges
Natthawadee Laokulrath, Mihir Gudi, Syed Ahmed Salahuddin, Angela Phek Yoon Chong, Cristine Ding, Jabed Iqbal, Wei Qiang Leow, Benjamin Yongcheng Tan, Gary Tse, Emad Rakha, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2024; 85(3): 371. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Biomarkers in the Invasive Micropapillary Cancer of the Breast
Ozden Oz, Funda Alkan Tasli, Resmiye Irmak Yuzuguldu, Baha Zengel, Demet Kocatepe Cavdar, Merih Guray Durak, Raika Durusoy, Pranshu Sahgal
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing HER2-low breast cancer management: enhancing diagnosis and treatment strategies
Simona Borstnar, Ivana Bozovic-Spasojevic, Ana Cvetanovic, Natalija Dedic Plavetic, Assia Konsoulova, Erika Matos, Lazar Popovic, Savelina Popovska, Snjezana Tomic, Eduard Vrdoljak
Radiology and Oncology.2024; 58(2): 258. CrossRef - Peer‐to‐peer validation of Ki‐67 scoring in a pathology quality circle as a tool to assess interobserver variability: are we better than we thought?
Marit Bernhardt, Leonie Weinhold, Christine Sanders, Oliver Hommerding, Jan‐Frederic Lau, Marieta Toma, Verena Tischler, Matthias Schmid, Tomasz Zienkiewicz, Ralf Hildenbrand, Peter Gerlach, Hui Zhou, Martin Braun, Gunnar Müller, Erich Sieber, Christian M
APMIS.2024; 132(10): 718. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of Cyclin D1 and p16 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Association with Clinicopathological Parameters
Shaivy Malik, Shakthivel V., Sana Ahuja, Charanjeet Ahluwalia
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(4): 864. CrossRef - Novel engineered HER2 specific recombinant protein nanocages for targeted drug delivery
Javad Kheshti, Mohammad Ahmadyousefi, Meysam Soleimani
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating C-reactive protein levels as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer across body mass index groups
J. B. Holm, E. Baggesen, D. Cronin-Fenton, J. Frystyk, J. M. Bruun, P. Christiansen, S. Borgquist
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Standardized molecular pathology workflow for ctDNA-based ESR1 testing in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer
Elena Guerini-Rocco, Konstantinos Venetis, Giulia Cursano, Eltjona Mane, Chiara Frascarelli, Francesco Pepe, Mariachiara Negrelli, Edoardo Olmeda, Davide Vacirca, Alberto Ranghiero, Dario Trapani, Carmen Criscitiello, Giuseppe Curigliano, Christian Rolfo,
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2024; 201: 104427. CrossRef - The differences between pure and mixed invasive micropapillary breast cancer: the epithelial–mesenchymal transition molecules and prognosis
Ozden Oz, Resmiye Irmak Yuzuguldu, Ayse Yazici, Demet Kocatepe Cavdar, Cengiz Yilmaz, Mucteba Ozturk, Hilal Duzel, Duygu Gurel
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 208(1): 41. CrossRef - Best practices for achieving consensus in HER2‐low expression in breast cancer: current perspectives from practising pathologists
Gary Tozbikian, Marilyn M. Bui, David G Hicks, Shabnam Jaffer, Thaer Khoury, Hannah Y Wen, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Shi Wei
Histopathology.2024; 85(3): 489. CrossRef - Consensus Guidelines on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-Low Testing in Breast Cancer in Malaysia
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Sarala Ravindran, Bang Rom Lee, Suria Hayati Md Pauzi, Seow Fan Chiew, Kean Hooi Teoh, Navarasi S. Raja Gopal, Mastura Md Yusof, Cheng Har Yip
Cancers.2024; 16(13): 2325. CrossRef - Revolutionizing Pathology with Artificial Intelligence: Innovations in Immunohistochemistry
Diana Gina Poalelungi, Anca Iulia Neagu, Ana Fulga, Marius Neagu, Dana Tutunaru, Aurel Nechita, Iuliu Fulga
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(7): 693. CrossRef - Interobserver Variability in HER‐2 Immunostaining Interpretation of Metastatic HER2 Low Breast Cancers in Cytology Specimens
Niyati Desai, Courtney F. Connelly, Simon Sung, Adela Cimic, Swikrity U. Baskota
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(12): 722. CrossRef - Weakly-supervised deep learning models enable HER2-low prediction from H &E stained slides
Renan Valieris, Luan Martins, Alexandre Defelicibus, Adriana Passos Bueno, Cynthia Aparecida Bueno de Toledo Osorio, Dirce Carraro, Emmanuel Dias-Neto, Rafael A. Rosales, Jose Marcio Barros de Figueiredo, Israel Tojal da Silva
Breast Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the spectrum of HER2 status in breast cancer: From HER2-positive to ultra-low HER2
Sana Ahuja, Adil Aziz Khan, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 262: 155550. CrossRef - Systematic review of added immunotherapy in traditional treatment for HER2 positive breast cancer patients
Rohan Choudhari
Innovative Practice in Breast Health.2024; 3-4: 100013. CrossRef - Detecting early-stage breast cancer with GATA3-positive circulating tumor cells
Chun-Hsin Hsieh, Ya-Herng Chang, Pei-Ying Ling, Ying-Tai Jin, Pei-Hsuan Lo, Hei-Jen Jou
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2024; 63(5): 745. CrossRef - First-in-human study of DP303c, a HER2-targeted antibody-drug conjugate in patients with HER2 positive solid tumors
Jian Zhang, Yiqun Du, Yanchun Meng, Xiaojun Liu, Yuxin Mu, Yunpeng Liu, Yehui Shi, Jufeng Wang, Aimin Zang, Shanzhi Gu, Tianshu Liu, Huan Zhou, Hongqian Guo, Silong Xiang, Xialu Zhang, Suqiong Wu, Huanhuan Qi, Mengke Li, Xichun Hu
npj Precision Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting CD276 for T cell-based immunotherapy of breast cancer
Ilona Hagelstein, Laura Wessling, Alexander Rochwarger, Latifa Zekri, Boris Klimovich, Christian M. Tegeler, Gundram Jung, Christian M. Schürch, Helmut R. Salih, Martina S. Lutz
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Androgen Receptor Expression With Ki67 Proliferative Index and Other Clinicopathological Characteristics in Invasive Mammary Carcinomas
D Keerthana Devi, V Pavithra, Leena D Joseph, Chithra Bhanu Challa
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CD81-guided heterologous EVs present heterogeneous interactions with breast cancer cells
Elena Gurrieri, Giulia Carradori, Michela Roccuzzo, Michael Pancher, Daniele Peroni, Romina Belli, Caterina Trevisan, Michela Notarangelo, Wen-Qiu Huang, Agata S. A. Carreira, Alessandro Quattrone, Guido Jenster, Timo L. M. Ten Hagen, Vito Giuseppe D’Agos
Journal of Biomedical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering HER2-low breast cancer (BC): insights from real-world data in early stage breast cancer
Anna Pous, Adrià Bernat-Peguera, Assumpció López-Paradís, Beatriz Cirauqui, Vanesa Quiroga, Iris Teruel, Eudald Felip, Angelica Ferrando-Díez, Milana Bergamino, Laia Boronat, Margarita Romeo, Gemma Soler, Christian Mariño, Paula Rodríguez-Martínez, Laura
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy-based technologies: a promising tool for biomarker identification in her2-low breast cancer patients for improved therapeutic outcomes
Aldo D’Alessandro, Anca Florentina Deaconu, Sandro Mandolesi, Federico Pio Fabrizio, Massimo Lombardi, Giovanna Liguori, Giovanni Pepe, Nicola Marino, Aureliano Stingi, Alessandro D’Alessandro, Antonio Giordano
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - SPP1 mRNA Expression Is Associated with M2 Macrophage Infiltration and Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Yu-Chia Chen, Chia-Ching Chen, Rong-Fu Chen, Hsin-Hung Chen, Po-Ming Chen
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2024; 46(12): 13499. CrossRef - MicroRNAs and their role in breast cancer metabolism (Review)
Wen Lee, Bann Yeo, Rozi Mahmud, Geok Tan, Mohamed Wahid, Yoke Cheah
International Journal of Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CDH1 methylation and expression of E-cadherin and other markers in breast cancer
Luiz Fernando de Queiroz, Marcelo Soares da Mota e Silva, Fernando Colonna Rosman, Siane Lopes Bittencourt Rosas, Heitor Siffert Pereira de Souza, Maria da Glória da Costa Carvalho
Mastology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical Management of the Axilla in HR+/HER2– Breast Cancer in the Z1071 Era: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of the National Cancer Database
Vayda R. Barker, Samer A. Naffouje, Melissa A. Mallory, Susan A. Hoover, Christine Laronga
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(13): 8371. CrossRef - Noninvasive identification of HER2-low-positive status by MRI-based deep learning radiomics predicts the disease-free survival of patients with breast cancer
Yuan Guo, Xiaotong Xie, Wenjie Tang, Siyi Chen, Mingyu Wang, Yaheng Fan, Chuxuan Lin, Wenke Hu, Jing Yang, Jialin Xiang, Kuiming Jiang, Xinhua Wei, Bingsheng Huang, Xinqing Jiang
European Radiology.2023; 34(2): 899. CrossRef - Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
Lan Deng, Le Zhao, Lifen Liu, Haomin Huang
Open Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HER2-low expression in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors
B. Uzunparmak, C. Haymaker, G. Raso, S. Masciari, L. Wang, H. Lin, A. Gorur, B. Kirby, A.-M. Cimo, A. Kennon, Q. Ding, G. Urschel, Y. Yuan, G. Feng, Y. Rizvi, A. Hussain, C. Zhu, P. Kim, G. Abbadessa, V. Subbiah, T.A. Yap, J. Rodon, S.A. Piha-Paul, F. Mer
Annals of Oncology.2023; 34(11): 1035. CrossRef - Data on 2D culture characterisation of potential markers in human HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines
Son H. Pham, Lyn R. Griffiths, Rachel K. Okolicsanyi, Larisa M. Haupt
Data in Brief.2023; 46: 108880. CrossRef - Determining HER2 Status by Artificial Intelligence: An Investigation of Primary, Metastatic, and HER2 Low Breast Tumors
Christiane Palm, Catherine E. Connolly, Regina Masser, Barbara Padberg Sgier, Eva Karamitopoulou, Quentin Simon, Beata Bode, Marianne Tinguely
Diagnostics.2023; 13(1): 168. CrossRef - Gene amplification mutations originate prior to selective stress in Acinetobacter baylyi
Jennifer A Herrmann, Agata Koprowska, Tesa J Winters, Nancy Villanueva, Victoria D Nikityuk, Feini Pek, Elizabeth M Reis, Constancia Z Dominguez, Daniel Davis, Eric McPherson, Staci R Rocco, Cynthia Recendez, Shyla M Difuntorum, Kelly Faeth, Mario D Lopez
G3.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow Rate-Independent Multiscale Liquid Biopsy for Precision Oncology
Jie Wang, Robert Dallmann, Renquan Lu, Jing Yan, Jérôme Charmet
ACS Sensors.2023; 8(3): 1200. CrossRef - Single-cell HER2 quantification via instant signal amplification in microdroplets
Xiaoxian Liu, Yifan Zhu, Caoxin Li, Yanyun Fang, Jinna Chen, Fei Xu, Yanqing Lu, Perry Ping Shum, Ying Liu, Guanghui Wang
Analytica Chimica Acta.2023; 1251: 340976. CrossRef - Molecular imaging of HER2 receptor: Targeting HER2 for imaging and therapy in nuclear medicine
Daniela Miladinova
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CORRELATION BETWEEN DIFFERENT CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF FEMALE BREAST CARCINOMA IN SOUTH REGION OF IRAQ
Yassir Alaa Muhammed Hassan Shubbar
Wiadomości Lekarskie.2023; 76(1): 97. CrossRef - Pathological identification of HER2-low breast cancer: Tips, tricks, and troubleshooting for the optimal test
Elham Sajjadi, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Elisa De Camilli, Oriana Pala, Giovanni Mazzarol, Konstantinos Venetis, Mariia Ivanova, Nicola Fusco
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective Effect of HER2 Gene Polymorphism rs24537331 in the Outcome of Canine Mammary Tumors
Ana Canadas-Sousa, Marta Santos, Patrícia Dias-Pereira
Animals.2023; 13(8): 1384. CrossRef - Can Patients with HER2-Low Breast Cancer Benefit from Anti-HER2 Therapies? A Review
Jin Wang, Dongying Liao, Xuemin Zhang, Changhong Miao, Kuang Chen
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 281. CrossRef - HER2 Low Breast Cancer: A New Subtype or a Trojan for Cytotoxic Drug Delivery?
Marina Popović, Tajana Silovski, Marija Križić, Natalija Dedić Plavetić
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8206. CrossRef - HER2-Low Breast Cancer—Diagnostic Challenges and Opportunities for Insights from Ongoing Studies: A Podcast
Aditya Bardia, Giuseppe Viale
Targeted Oncology.2023; 18(3): 313. CrossRef - Histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of predictive and prognostic markers in spontaneous canine mammary cancer
Vladimír Tancoš, Marcel Kovalik, Martin Levkut, Martina Bobrovská, Petra Kolenčíková, Ľubomír Straka, Zuzana Ševčíková, Ondřej Škor, Martina Antošová, Lukáš Plank, Keith L. Thoday
Acta Veterinaria Brno.2023; 92(2): 143. CrossRef - Dissecting sources of variability in patient response to targeted therapy: anti-HER2 therapies as a case study
Timothy Qi, Yanguang Cao
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 186: 106467. CrossRef - The Effect of HER2-Low Status on Pathological Complete Response and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yakup Ergun, Baran Akagunduz, Cengiz Karacin, Sema Turker, Gokhan Ucar
Clinical Breast Cancer.2023; 23(6): 567. CrossRef - Efficacy, toxicity and prognostic factors of pyrotinib‑involved neoadjuvant therapy in HER2‑positive breast cancer: A retrospective study
Hao Wang, Hailing Cao, Zhiyun Guo
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer
Feng Ye, Saikat Dewanjee, Yuehua Li, Niraj Kumar Jha, Zhe-Sheng Chen, Ankush Kumar, Vishakha, Tapan Behl, Saurabh Kumar Jha, Hailin Tang
Molecular Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weakly supervised bilayer convolutional network in segmentation of HER2 related cells to guide HER2 targeted therapies
Ching-Wei Wang, Kun-Lin Lin, Hikam Muzakky, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics.2023; 108: 102270. CrossRef - Immune Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving the Predictivity of Current Testing Methods
Francesca Maria Porta, Elham Sajjadi, Konstantinos Venetis, Chiara Frascarelli, Giulia Cursano, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Nicola Fusco, Mariia Ivanova
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(7): 1176. CrossRef - HER2 Equivocal (Score = 2+) Breast Carcinoma Cases Identified by Immunohistochemistry at a South African Hospital. What is the Impact of Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Testing?
Reena Dhansukh Mohanlal, Nikki Bouwer, Pascale Willem
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(8): 555. CrossRef - Discordance of HER2 Expression and/or Amplification on Repeat Testing
Timothy P. DiPeri, Kathleen Kong, Kaushik Varadarajan, Daniel D. Karp, Jaffer A. Ajani, Shubham Pant, Michael F. Press, Sarina A. Piha-Paul, Ecaterina E. Dumbrava, Funda Meric-Bernstam
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2023; 22(8): 976. CrossRef - Low and Ultra-Low HER2 in Human Breast Cancer: An Effort to Define New Neoplastic Subtypes
Mariausilia Franchina, Cristina Pizzimenti, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Maurizio Martini, Giuseppina Rosaria Rita Ricciardi, Nicola Silvestris, Antonio Ieni, Giovanni Tuccari
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12795. CrossRef - Genetic analysis of oligo-recurrence breast cancer: correlation with clinical outcomes
Kuikui Jiang, Danyang Zhou, Fei Xu, Wen Xia, Qiufan Zheng, Qianyi Lu, Rongzhen Luo, Ruoxi Hong, Shusen Wang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single domain antibodies specific for HER2 dimerization domain effectively disrupts HER2 dimerization
Ahmad Najafi, Reza Valadan, Hossein Asgarian-Omran, Alireza Rafiei, Mohsen Tehrani
International Immunopharmacology.2023; 124: 110999. CrossRef - Récepteur du facteur de croissance épidermique HER2, tests utilisés pour rechercher son amplification dans le cancer du sein : principes et limites
Imane Eliahiai, Mohammed Eljiar, Sanae Chaib, Jinane KHarmoum, Mariame Chraïbi
Bulletin du Cancer.2023; 110(12): 1301. CrossRef - Integrated Molecular Characterization of HER2-Low Breast Cancer Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Jean-Louis Merlin, Marie Husson, Nassim Sahki, Pauline Gilson, Vincent Massard, Alexandre Harlé, Agnès Leroux
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3164. CrossRef - GLUCOSE LEVELS OF PLEURAL EFFUSION FLUID AND HER2 STATUS IN PLEURAL-METASTATIC BREAST CANCER
Muhammad Dhanny Irawan, Desak Gede Agung Suprabawati, Heru Purwanto
Majalah Biomorfologi.2023; 33(2): 75. CrossRef - Design of a Ratiometric Plasmonic Biosensor for Herceptin Detection in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Neda Shahbazi, Rouholah Zare-Dorabei, Seyed Morteza Naghib
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2022; 8(2): 871. CrossRef - A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
Mahdi Sadeghi, Soheila Kashanian, Seyed Morteza Naghib, Esfandyar Askari, Fateme Haghiralsadat, Davood Tofighi
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 793. CrossRef - Anti-HER2 therapy in metastatic breast cancer: many choices and future directions
Carrie S. Wynn, Shou-Ching Tang
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2022; 41(1): 193. CrossRef - Electroanalytical overview: screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms for the detection of vital cardiac, cancer and inflammatory biomarkers
Robert D. Crapnell, Alejandro Garcia-Miranda Ferrari, Nina C. Dempsey, Craig E. Banks
Sensors & Diagnostics.2022; 1(3): 405. CrossRef - FTO genotype was associated with breast cancer in HER2 negative patients
Fateme Montazeri, Hossein Hatami, Soroor Fathi, Naeemeh Hasanpour Ardekanizadeh, Fatemeh Bourbour, Samira Rastgoo, Fatemeh Shafiee, Mohammad Esmail Akbari, Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Seyed Alireza Mosavi Jarrahi, Saeid Doaei
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 49: 495. CrossRef - Breast Cancer Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 mRNA Molecular Testing Compared to Immunohistochemistry with Correlation to Neoadjuvant Therapy Response
Mahmoud Behairy, Samia Mohamed Gabal, Mohamed Sherif Negm
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 352. CrossRef - Validity and utility of HER2/ERBB2 copy number variation assessed in liquid biopsies from breast cancer patients: A systematic review
Noortje Verschoor, Teoman Deger, Agnes Jager, Stefan Sleijfer, Saskia M. Wilting, John W.M. Martens
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2022; 106: 102384. CrossRef - RETRACTED: Longitude Variation of the microRNA-497/FGF-23 Axis during Treatment and Its Linkage with Neoadjuvant/Adjuvant Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients
Hui Liu, Xiaoyan Hu, Lingyun Wang, Tao Du, Jing Feng, Ming Li, Lei Liu, Xiaofang Liu
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Radionuclide-Based Imaging Methods in Breast Cancer
Betül Altunay, Agnieszka Morgenroth, Felix M. Mottaghy
Seminars in Nuclear Medicine.2022; 52(5): 561. CrossRef - Functional regulations between genetic alteration-driven genes and drug target genes acting as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
Li Wang, Lei Yu, Jian Shi, Feng Li, Caiyu Zhang, Haotian Xu, Xiangzhe Yin, Lixia Wang, Shihua Lin, Anastasiia Litvinova, Yanyan Ping, Shangwei Ning, Hongying Zhao
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 and endocrine resistance in hormone-dependent breast cancer
Anastasia Alataki, Mitch Dowsett
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2022; 29(8): R105. CrossRef - The Evolution of Targeted Radionuclide Diagnosis of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Olga D. Bragina, Sergei M. Deyev, Vladimir I. Chernov, Vladimir M. Tolmachev
Acta Naturae.2022; 14(2): 4. CrossRef - Deriving tumor purity from cancer next generation sequencing data: applications for quantitative ERBB2 (HER2) copy number analysis and germline inference of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
Stephanie E. Siegmund, Danielle K. Manning, Phani K. Davineni, Fei Dong
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(10): 1458. CrossRef - Current challenges and unmet needs in treating patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive advanced breast cancer
Matti Aapro, Fatima Cardoso, Giuseppe Curigliano, Alexandru Eniu, Joseph Gligorov, Nadia Harbeck, Andreas Mueller, Olivia Pagani, Shani Paluch-Shimon, Elzbieta Senkus, Beat Thürlimann, Khalil Zaman
The Breast.2022; 66: 145. CrossRef - [Retracted] Application of Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Assisted by Fluorescence Microscope in Detection of Her2 Gene in Breast Cancer Patients
Fang Lu, Tingting Zhou, Yan Liu, Liying Song, Bin Zhang, Yuyan Li, Sorayouth Chumnanvej
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High sensitivity label-free detection of HER2 using an Al–GaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor-based biosensor
Shivanshu Mishra, Pharyanshu Kachhawa, Amber Kumar Jain, Rajiv Ranjan Thakur, Nidhi Chaturvedi
Lab on a Chip.2022; 22(21): 4129. CrossRef - Indian Data on HER2 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Invasive Breast Cancer with Immunohistochemically Equivocal Results As Per 2018 ASCO/CAP Guidelines
B. R. Nagarjun, Biren Parikh, Manaswi Nareshkumar Patel, Pina J. Trivedi, Dharmesh M. Patel
South Asian Journal of Cancer.2022; 11(04): 281. CrossRef - S‑phase fraction, lymph node status and disease staging as the main prognostic factors to differentiate between young and older patients with invasive breast carcinoma
António Pinto, João Matos, Teresa Pereira, Giovani Silva, Saudade André
Oncology Letters.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inferring tumor-specific cancer dependencies through integrating ex vivo drug response assays and drug-protein profiling
Alina Batzilla, Junyan Lu, Jarno Kivioja, Kerstin Putzker, Joe Lewis, Thorsten Zenz, Wolfgang Huber, James Gallo
PLOS Computational Biology.2022; 18(8): e1010438. CrossRef - Clinical possibilities of HER2-positive breast cancer diagnosis using alternative scaffold proteins
O. D. Bragina, V. I. Chernov, S. M. Deyev, V. M. Tolmachev
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2022; 21(3): 132. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, An Na Seo
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2022; 22(4): 264. CrossRef - Loss of NECTIN1 triggers melanoma dissemination upon local IGF1 depletion
Julien Ablain, Amira Al Mahi, Harriet Rothschild, Meera Prasad, Sophie Aires, Song Yang, Maxim E. Dokukin, Shuyun Xu, Michelle Dang, Igor Sokolov, Christine G. Lian, Leonard I. Zon
Nature Genetics.2022; 54(12): 1839. CrossRef - Advanced diagnosis technologies for HER2 breast cancer markers
Mengxue Zhang
Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology.2022; 14: 44. CrossRef - An Overview of Clinical Development of Agents for Metastatic or Advanced Breast Cancer Without ERBB2 Amplification (HER2-Low)
Aleix Prat, Aditya Bardia, Giuseppe Curigliano, M. Elizabeth H. Hammond, Sibylle Loibl, Sara M. Tolaney, Giuseppe Viale
JAMA Oncology.2022; 8(11): 1676. CrossRef - Development of T-cell engagers selective for cells co-expressing two antigens
Danielle M. Dicara, Sunil Bhakta, Mary Ann Go, James Ziai, Ron Firestein, Bill Forrest, Chen Gu, Steven R. Leong, Genee Lee, Shang-Fan Yu, Andrew G. Polson, Nicholas J. Agard
mAbs.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The clinical significance of HER2 expression in DCIS
Ioanna Akrida, Francesk Mulita
Medical Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Breast Cancer: Spotlight on HER2
Rachel Occhiogrosso Abelman, Arielle Medford, Laura Spring, Aditya Bardia
The Cancer Journal.2022; 28(6): 423. CrossRef - The Clinical Utility of Droplet Digital PCR for Profiling Circulating Tumor DNA in Breast Cancer Patients
Ugur Gezer, Abel J. Bronkhorst, Stefan Holdenrieder
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3042. CrossRef - Lapatinib and lapatinib plus trastuzumab therapy versus trastuzumab therapy for HER2 positive breast cancer patients: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Ye Yuan, Xumei Liu, Yi Cai, Wenyuan Li
Systematic Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactions dietary components with expression level of breast cancer-related genes
Fatemeh Bourbour, Azam Pourtaheri, Khadijeh Abbasi, Naeemeh Hasanpour Ardekanizadeh, Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Azadeh Hajipour, Sepideh Abdollahi, Seyedeh Elaheh Bagheri, Mina Ahmadzadeh, Saeid Doaei, Arezoo Haghighian
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HER2-directed antibodies, affibodies and nanobodies as drug-delivery vehicles in breast cancer with a specific focus on radioimmunotherapy and radioimmunoimaging
Betül Altunay, Agnieszka Morgenroth, Mohsen Beheshti, Andreas Vogg, Nicholas C. L. Wong, Hong Hoi Ting, Hans-Jürgen Biersack, Elmar Stickeler, Felix M. Mottaghy
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2021; 48(5): 1371. CrossRef - Risk-based decision-making in the treatment of HER2-positive early breast cancer: Recommendations based on the current state of knowledge
Christian Jackisch, Patricia Cortazar, Charles E. Geyer, Luca Gianni, Joseph Gligorov, Zuzana Machackova, Edith A. Perez, Andreas Schneeweiss, Sara M. Tolaney, Michael Untch, Andrew Wardley, Martine Piccart
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2021; 99: 102229. CrossRef - Histologic Patterns of Cutaneous Metastases of Breast Carcinoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 232 Cases
Shira Ronen, David Suster, Wei-Shen Chen, Natali Ronen, Sri Krishna C. Arudra, Celestine Trinidad, Doina Ivan, Victor G. Prieto, Saul Suster
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2021; 43(6): 401. CrossRef - Standardized pathology report for breast cancer
Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(1): 1. CrossRef - The impact of oral contraceptive use on breast cancer risk: State of the art and future perspectives in the era of 4P medicine
R. Bonfiglio, M.L. Di Pietro
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2021; 72: 11. CrossRef - The Co-Expression of Melanoma-Antigen Family a Proteins and New York Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma-1 in Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study
Yu-Xin Wang, Feng-Lian Li, Li-Xin Du, Jun-Fang Liu, Li-Gang Huo, Shu-Qing Li, Bin Tian
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 6123. CrossRef - Targeting HER2 protein in individual cells using ICP-MS detection and its potential as prognostic and predictive breast cancer biomarker
A. Fernández Asensio, M. Corte-Rodríguez, J. Bettmer, L.M. Sierra, M. Montes-Bayón, E. Blanco- González
Talanta.2021; 235: 122773. CrossRef - Development of a 99mTc-Labeled Single-Domain Antibody for SPECT/CT Assessment of HER2 Expression in Breast Cancer
Lingzhou Zhao, Changcun Liu, Yan Xing, Jin He, Jim O’Doherty, Wenhua Huang, Jinhua Zhao
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2021; 18(9): 3616. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Nouvelles stratégies thérapeutiques dans les cancers du sein HER2-surexprimé
Benoîte Mery, Philippe Toussaint, Pierre-Etienne Heudel, Armelle Dufresne, Mélodie Carbonnaux, Hélène Vanacker, Thomas Bachelot, Olivier Trédan
Bulletin du Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective observational study of HER2 immunohistochemistry in borderline breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy, with an emphasis on Group 2 (HER2/CEP17 ratio ≥2.0, HER2 copy number <4.0 signals/cell) cases
Emad A. Rakha, Islam M. Miligy, Cecily M. Quinn, Elena Provenzano, Abeer M. Shaaban, Caterina Marchiò, Michael S. Toss, Grace Gallagy, Ciara Murray, Janice Walshe, Ayaka Katayama, Karim Eldib, Nahla Badr, Bruce Tanchel, Rebecca Millican-Slater, Colin Purd
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 124(11): 1836. CrossRef - Loss of HER2‐positivity following neoadjuvant targeted therapy for breast cancer is not associated with inferior oncologic outcomes
Catherine L. Wetzel, Thomas L. Sutton, Stuart Gardiner, Maryam Farinola, Nathalie Johnson, Jennifer R. Garreau
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2021; 124(8): 1224. CrossRef - Clinical and Genetic Predictive Models for the Prediction of Pathological Complete Response to Optimize the Effectiveness for Trastuzumab Based Chemotherapy
Lun Li, Min Chen, Shuyue Zheng, Hanlu Li, Weiru Chi, Bingqiu Xiu, Qi Zhang, Jianjing Hou, Jia Wang, Jiong Wu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - tRNA‐derived fragments: tRF‐Gly‐CCC‐046, tRF‐Tyr‐GTA‐010 and tRF‐Pro‐TGG‐001 as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer
Yue Zhang, Zhao Bi, Xiaohan Dong, Miao Yu, Kangyu Wang, Xingguo Song, Li Xie, Xianrang Song
Thoracic Cancer.2021; 12(17): 2314. CrossRef - Detection of secondary metastatic breast cancer by measurement of plasma CA 15.3
L. De Cock, J. Heylen, A. Wildiers, K. Punie, A. Smeets, C. Weltens, P. Neven, J. Billen, A. Laenen, H. Wildiers
ESMO Open.2021; 6(4): 100203. CrossRef - Standardized Pathology Report for Breast Cancer
Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
Journal of Breast Cancer.2021; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Circular RNA circ-ERBB2 promotes HER2-positive breast cancer progression and metastasis via sponging miR-136-5p and miR-198
Jin-xiu Zhong, Yun-yuan Kong, Rong-guang Luo, Guo-jin Xia, Wen-xing He, Xue-zhong Chen, Wei-wei Tan, Qing-jie Chen, Yu-yin Huang, Yan-xing Guan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nouvelles stratégies thérapeutiques dans les cancers du sein HER2-surexprimé
Benoîte Mery, Philippe Toussaint, Pierre-Etienne Heudel, Armelle Dufresne, Mélodie Carbonnaux, Hélène Vanacker, Thomas Bachelot, Olivier Trédan
Bulletin du Cancer.2021; 108(11): 11S8. CrossRef - Association of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors with Clinicopathological Prognostic Factors in Breast Cancer
Ali Abdul Hadi Abdul-Kareem, Qahtan A. Mahdi
Medical Journal of Babylon.2021; 18(2): 111. CrossRef - HER2 alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer – Druggable or undruggable?
Suresh Kumar Bondili, Ravindra Nandhana, Vanita Noronha, Swayamprabha Pawar, Nandini Menon, Omshree Shetty, Anuradha Chougule, Abhishek Mahajan, Rajiv Kumar, Vijay M. Patil, Amit Joshi, Kumar Prabhash
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2021; 4(2): 374. CrossRef - UCNP-based Photoluminescent Nanomedicines for Targeted Imaging and Theranostics of Cancer
Evgenii L. Guryev, Anita S. Smyshlyaeva, Natalia Y. Shilyagina, Evgeniya A. Sokolova, Samah Shanwar, Alexey B. Kostyuk, Alexander V. Lyubeshkin, Alexey A. Schulga, Elena V. Konovalova, Quan Lin, Indrajit Roy, Irina V. Balalaeva, Sergey M. Deyev, Andrei V.
Molecules.2020; 25(18): 4302. CrossRef - Impact of the Updated Guidelines on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) Testing in Breast Cancer
Min Chong Kim, Su Hwan Kang, Jung Eun Choi, Young Kyung Bae
Journal of Breast Cancer.2020; 23(5): 484. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Model Outperformed the Single Radiomics Model in Noninvasively Predicting the HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast: Study of Three Cases at One Institution with a Review of Primary Breast Sarcomas
- Junyoung Shin, Hee Jeong Kim, Dae-Yeon Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):308-316. Published online August 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.07.22
- 7,415 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary breast sarcoma (PBS) is rare, comprising approximately 1% of breast malignancies. Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) accounts for an extremely small proportion of PBSs, often leading to delayed histologic confirmation.
Methods
Upon reviewing Asan Medical Center’s pathology database between 2000 and 2018, 41 PBS cases were retrieved, including three cases of primary RMS of the breast. Their clinicopathological features were analyzed, and the literature related to PBS and primary RMS of the breast was reviewed.
Results
We identified three primary breast RMS cases from our institution database, comprising 7.3% of PBS: one case each of spindle cell/sclerosing RMS (ssRMS), alveolar RMS (aRMS), and embryonal RMS (eRMS). All cases involved adolescents or young adults (14, 16, and 25 years, respectively) who underwent mastectomy or radiotherapy and were confirmed using immunohistochemical testing for myogenin, desmin, and myogenic differentiation. The ssRMS patient experienced recurrence at the operation site 4 months post-surgery despite undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The aRMS patient had multiple metastases at diagnosis and showed FAX3-FOXO1 fusion transcripts; she died 22 months after the diagnosis. The eRMS patient had enlarged axillary lymph nodes; post-radiotherapy, the lesion recurred as multiple metastases to the bone and lung. She died 18 months post-diagnosis.
Conclusions
Our experience on RMS cases suggests that spindle cell or small round cell malignancy in breasts of young female should raise suspicion for the possibility of primary or secondary RMS. To our knowledge, this is the second report of primary breast ssRMS and it may help clinicians who encounter this rare disease in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Pediatric Breast Masses for the Pediatric Surgeon: Expert Consensus Recommendations From the APSA Cancer Committee
Dana Schwartz, Elisabeth T. Tracy, Bindi Naik-Mathuria, Richard D. Glick, Stephanie F. Polites, Peter Mattei, David Rodeberg, Andres F. Espinoza, Sara A. Mansfield, Dave R. Lal, Meera Kotagal, Timothy Lautz, Jennifer Aldrink, Barrie S. Rich
Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2025; 60(2): 161916. CrossRef - Differential diagnosis of primary mesenchymal neoplasms of the breast
Mine Ozsen, Seyit Ali Volkan Polatkan, Ulviye Yalcınkaya, Sahsine Tolunay, Mustafa Sehsuvar Gokgoz
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2024; 27(1): 223. CrossRef - Primary breast rhabdomyosarcoma in a 17-year-old girl
Laxmi Singotia, V.S. Haritha
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(7): 2070. CrossRef - High-Grade Spindle Cell Lesions of the Breast
Esther Yoon, Qingqing Ding, Kelly Hunt, Aysegul Sahin
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2022; 15(1): 77. CrossRef - Primary Small Cell Malignancies of the Breast: Are They Rare Malignancies?
Kemal Behzatoğlu, Fernando Schmitt
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(4): 347. CrossRef - Recurrent malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast: An extremely rare case of recurrence with only rhabdomyosarcoma components
Jia Han, Shuice Liu, Akihoro Shioya, Motona Kumagai, Emi Morioka, Miki Noguchi, Masafumi Inokuchi, Sohsuke Yamada
SAGE Open Medical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary rhabdomyosarcoma: An extremely rare and aggressive variant of male breast cancer
Cătălin Bogdan Satală, Ioan Jung, Tivadar Jr Bara, Patricia Simu, Iunius Simu, Madalina Vlad, Rita Szodorai, Simona Gurzu
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(19): 4466. CrossRef
- Management of Pediatric Breast Masses for the Pediatric Surgeon: Expert Consensus Recommendations From the APSA Cancer Committee
- Association between p53 Expression and Amount of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Miseon Lee, In Ah Park, Sun-Hee Heo, Young-Ae Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Hee Jin Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):180-187. Published online March 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.08
- 9,628 View
- 205 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Most triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) have a high histologic grade, are associated with high endoplasmic stress, and possess a high frequency of TP53 mutations. TP53 missense mutations lead to the production of mutant p53 protein and usually show high levels of p53 protein expression. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) accumulate as part of the anti-tumor immune response and have a strong prognostic and predictive significance in TNBC. We aimed to elucidate the association between p53 expression and the amount of TILs in TNBC.
Methods
In 678 TNBC patients, we evaluated TIL levels and expression of endoplasmic stress molecules. Immunohistochemical examination of p53 protein expression was categorized into three groups: no, low, and high expression.
Results
No, low, and high p53 expression was identified in 44.1% (n = 299), 20.1% (n = 136), and 35.8% (n = 243) of patients, respectively. Patients with high p53 expression showed high histologic grade (p < .001), high TIL levels (p = .009), and high expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated molecules (p-eIF2a, p = .013; XBP1, p = .007), compared to patients with low p53 expression. There was no significant difference in disease-free (p = .406) or overall survival rates (p = .444) among the three p53 expression groups.
Conclusions
High p53 expression is associated with increased expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress molecules and TIL influx. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The search for a TNBC vaccine: the guardian vaccine
Cory Fines, Helen McCarthy, Niamh Buckley
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlating p53 immunostaining patterns with somatic TP53 mutation and functional properties of mutant p53 in triple‐negative breast cancer
Meejeong Kim, Miseon Lee, Ahwon Lee, Byung‐Ock Choi, Woo‐Chan Park, Sung Hun Kim, Jieun Lee, Jun Kang
Histopathology.2025; 87(2): 299. CrossRef - GD3 synthase drives resistance to p53-induced apoptosis in breast cancer by modulating mitochondrial function
Vivek Anand, Fouad El-Dana, Natalia Baran, Jenny Borgman, Zheng Yin, Hong Zhao, Stephen T. Wong, Michael Andreeff, V. Lokesh Battula
Oncogene.2025; 44(30): 2646. CrossRef - Topoisomerase Inhibitor Resistance in Breast Cancer: Exploring Alterations in Cellular Metabolism and Properties Driving Drug Insensitivity
Juhong Lee, Youngjoo Kwon
Drug Targets and Therapeutics.2025; 4(2): 185. CrossRef - Updated Austrian treatment algorithm for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
Rupert Bartsch, Gabriel Rinnerthaler, Edgar Petru, Daniel Egle, Michael Gnant, Marija Balic, Thamer Sliwa, Christian Singer
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2024; 136(11-12): 347. CrossRef - Triple negative breast cancer: Immunogenicity, tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy
Sotiris Loizides, Anastasia Constantinidou
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic benefit of TILs independent of clinicopathological and molecular factors
Koen Brummel, Anneke L. Eerkens, Marco de Bruyn, Hans W. Nijman
British Journal of Cancer.2023; 129(5): 737. CrossRef - Dihydroartemisinin-Transferrin Adducts Enhance TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in a P53-Independent and ROS-Dependent Manner
Xinyu Zhou, Abel Soto-Gamez, Fleur Nijdam, Rita Setroikromo, Wim J. Quax
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Challenges in the Differential Diagnosis of High-Grade Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Serous Carcinoma
Andrii Puzyrenko, Chandler S Cortina, Julie M Jorns
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(7): 728. CrossRef - Prognostic analysis of cuproptosis-related gene in triple-negative breast cancer
Shengnan Sha, Luyi Si, Xinrui Wu, Yuanbiao Chen, Hui Xiong, Ying Xu, Wangrui Liu, Haijun Mei, Tao Wang, Mei Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - p53 Missense Mutation is Associated with Immune Cell PD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Ai-Yan Xing, Long Liu, Ke Liang, Bin Wang
Cancer Investigation.2022; 40(10): 879. CrossRef - Crosstalk between Immune Checkpoint Modulators, Metabolic Reprogramming and Cellular Plasticity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Arpita Poddar, Sushma R. Rao, Prashanth Prithviraj, George Kannourakis, Aparna Jayachandran
Current Oncology.2022; 29(10): 6847. CrossRef - The tumor microenvironment and triple-negative breast cancer aggressiveness: shedding light on mechanisms and targeting
Natsuki Furukawa, Vered Stearns, Cesar A. Santa-Maria, Aleksander S. Popel
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2022; 26(12): 1041. CrossRef - Intracellular partners of fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 - implications for functions
Katarzyna Dominika Sluzalska, Jakub Slawski, Martyna Sochacka, Agata Lampart, Jacek Otlewski, Malgorzata Zakrzewska
Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews.2021; 57: 93. CrossRef - Targeted Chinese Medicine Delivery by A New Family of Biodegradable Pseudo-Protein Nanoparticles for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Hiu Yee Kwan, Qinghua Xu, Ruihong Gong, Zhaoxiang Bian, Chih-Chang Chu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptomic Properties of HER2+ Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Associate with Absence of Immune Cells
Marie Colombe Agahozo, Marcel Smid, Ronald van Marion, Dora Hammerl, Thierry P. P. van den Bosch, Mieke A. M. Timmermans, Chayenne J. Heijerman, Pieter J. Westenend, Reno Debets, John W. M. Martens, Carolien H. M. van Deurzen
Biology.2021; 10(8): 768. CrossRef - With Our Powers Combined
Lawrence Kasherman, Katherine Karakasis, Amit M. Oza
The Cancer Journal.2021; 27(6): 511. CrossRef The Research Progress on the Prognostic Value of the Common Hematological Parameters in Peripheral Venous Blood in Breast Cancer
Li Chen, Xiangyi Kong, Chengrui Yan, Yi Fang, Jing Wang
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1397. CrossRefBiomolecular Factors Represented by Bcl-2, p53, and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Predict Response for Adjuvant Anthracycline Chemotherapy in Patients with Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Xenia Elena Bacinschi, Anca Zgura, Inga Safta, Rodica Anghel
Cancer Management and Research.2020; Volume 12: 11965. CrossRef
- The search for a TNBC vaccine: the guardian vaccine
- Uterine Malignant Mixed Müllerian Tumors Following Treatment with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Report of 13 Cases and Their Clinicopathologic Characteristics
- Byung-Kwan Jeong, Chang O. Sung, Kyu-Rae Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):31-39. Published online December 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.11.16
- 8,431 View
- 102 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Breast cancer treatment with selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) increasesthe incidence of uterine malignant mixed Müllerian tumors (uMMMTs). We examine clinicopathologiccharacteristics and prognosis of SERM-associated uMMMTs (S-uMMMTs) and discusspossible pathogenetic mechanisms.
Methods
Among 28,104 patients with breast cancer, clinicopathologicfeatures and incidence of uMMMT were compared between patients who underwentSERM treatment and those who did not. Of 92 uMMMT cases that occurred during the same period,incidence, dose, and duration of SERM treatment, as well as overall survival rate, were comparedfor patients with breast cancer who underwent SERM treatment and those who did not (S-uMMMTvs NS-uMMMT) and for patients without breast cancer (de novo-uMMMT). Histopathologicalfindings and immunophenotypes for myogenin, desmin, p53, WT-1, estrogen receptor (ER) α, ERβ,progesterone receptor, and GATA-3 were compared between S-uMMMT and de novo-uMMMT.
Results
The incidence of S-uMMMT was significantly higher than that of NS-uMMMT (6.35-fold).All patients with SERM were postmenopausal and received daily 20–40 mg SERM. CumulativeSERM dose ranged from 21.9 to 73.0 g (mean, 46.0) over 39–192 months (mean, 107). Clinicopathologicfeatures, such as International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage andoverall survival, were not significantly different between patients with S-uMMMT and NS-uMMMTor between patients with S-uMMMT and de novo-uMMMT. All 11 S-uMMMT cases available forimmunostaining exhibited strong overexpression/null expression of p53 protein and significantlyincreased ERβ expression in carcinomatous and sarcomatous components.
Conclusions
SERMtherapy seemingly increases risk of S-uMMMT development; however, clinicopathologic featureswere similar in all uMMMTs from different backgrounds. p53 mutation and increased ERβ expressionmight be involved in the etiology of S-uMMMT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Uterine carcinosarcomas: A case series of 9 cases from a low-income country
Boubacar Efared, Halidou Hamadou Koura, Aïchatou Balaraba Abani Bako, Idrissa Boubacar, Habiba Salifou Boureima, Garba Mahamadou, Hassan Nouhou
Medicine.2024; 103(40): e39773. CrossRef - Uterine carcinosarcoma: Unraveling the role of epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition in progression and therapeutic potential
Mohan Shankar Gopinatha Pillai, Pallab Shaw, Arpan Dey Bhowmik, Resham Bhattacharya, Geeta Rao, Shailendra Kumar Dhar Dwivedi
The FASEB Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Tamoxifen/toremifene
Reactions Weekly.2019; 1758(1): 330. CrossRef - Molecular Basis of Tumor Heterogeneity in Endometrial Carcinosarcoma
Susanna Leskela, Belen Pérez-Mies, Juan Manuel Rosa-Rosa, Eva Cristobal, Michele Biscuola, María L. Palacios-Berraquero, SuFey Ong, Xavier Matias-Guiu Guia, José Palacios
Cancers.2019; 11(7): 964. CrossRef
- Uterine carcinosarcomas: A case series of 9 cases from a low-income country
- Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases
- Jiwon Koh, Jihyeon Lee, So Youn Jung, Han Sung Kang, Tak Yun, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(2):119-124. Published online November 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.18
- 8,865 View
- 179 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Primary malignant melanoma of the breast (PMMB) is a rare tumor with only a few case reports available in the literature. We report two cases of PMMB, one derived from the breast parenchyma and the other from the breast skin. The first case consisted of atypical epithelioid cells without overt melanocytic differentiation like melanin pigments. The tumor cells showed diffuse positivity for S100 protein, tyrosinase, and BRAF V600E. However, the tumor cells were negative for cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen, and HMB-45. The second case showed atypical melanocytic proliferation with heavy melanin pigmentation. The tumor cells were positive for S100 protein, HMB-45, tyrosinase, and BRAF V600E. These two cases represent two distinct presentations of PMMB in terms of skin involvement, melanin pigmentation, and HMB-45 positivity. Although PMMB is very rare, the possibility of this entity should be considered in malignant epithelioid neoplasms in the breast parenchyma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First Case of Primary Breast Melanoma in Central America: Case Report and Literature Review
Ana García‐Urbina, Denis Espinoza‐Vásquez, Johanna Obregón‐Silva, Arlin Montoya Rodríguez
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary nipple melanoma in a patient with breast cancer: A diagnosis to consider
Lucia Giudice, Sofia Vidali, Pietro Antonini, Elena Nucci, Federica Di Naro, Ludovica Anna Incardona, Vania Vezzosi, Vincenzo De Giorgi, Jacopo Nori
Radiology Case Reports.2024; 19(12): 6359. CrossRef - Is primary breast melanoma a true pathological entity? The argument against it
Alexis R. Narvaez-Rojas, Samantha Linhares, Shaina Sedighim, Kyle Daniel Klingbeil, Clara Milikowski, George Elgart, Natalia Jaimes, Lynn Feun, Jose Lutzky, Gabriel De la Cruz Ku, Eli Avisar, Mecker G. Möller
Heliyon.2024; 10(18): e37224. CrossRef - Comprehensive Literature Review on Melanoma of Unknown Primary Site Triggered by an Intriguing Case Report
Eliza-Maria Bordeanu-Diaconescu, Andrei Cretu, Andreea Grosu-Bularda, Mihaela-Cristina Andrei, Florin-Vlad Hodea, Catalina-Stefania Dumitru, Valentin Enache, Cosmin-Antoniu Creanga, Ioan Lascar, Cristian-Sorin Hariga
Diagnostics.2024; 14(19): 2210. CrossRef - Primary malignant melanoma of the breast: A case report without relapse
Alejandro Caballero, Mario Perez, Issis Rodriguez
Malignancy Spectrum.2024; 1(4): 339. CrossRef - Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Breast Presenting as a Breast Abscess: A Case Report
Hyung In Choi, You Me Kim, Junwon Min, Yong Moon Lee, Hee Jeong Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2023; 84(3): 763. CrossRef - Case Report: Care Report: Primary malignant melanoma of the breast
Juee Meghe, Yeshwant Lamture, Varsha Gajhbhiye, Pankaj Gharde, Akash Inamdar
F1000Research.2023; 12: 1323. CrossRef - Series of rare cases of breast tumour: 8-year review at mankweng Breast Oncology clinic, Limpopo, South Africa
Mirza M. Z. U. Bhuiyan
EUREKA: Health Sciences.2023; (4): 3. CrossRef - Primary breast parenchyma melanoma: case report
Eduardo Doria, Gion Aléssio Rocha Brunn, Diego Noya Brandão, Rafael Silva Ribeiro, Adriano Mata Pires Freire Carvalho, Miguel Ângelo Brandrão
Brazilian Journal of Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignant melanoma of the breast: controversies in the diagnosis and therapeutic management of a rare nosologic entity
Aikaterini Mastoraki, Dimitrios Schizas, Ilias Giannakodimos, Athanasios Rebakos, Ioannis Margaris, Ioannis Katsaros, Ilias Vagios, Pantelis Vassiliu, Emmanouil Pikoulis
International Journal of Dermatology.2020; 59(9): 1057. CrossRef - Uncommon Subtypes of Malignant Melanomas: A Review Based on Clinical and Molecular Perspectives
Matías Chacón, Yanina Pfluger, Martín Angel, Federico Waisberg, Diego Enrico
Cancers.2020; 12(9): 2362. CrossRef - Primary Melanoma of the Breast Parenchyma: An Oncoplastic Approach
Emma Snashall, Tamara Kiernan, Aenone Harper-Machin, Rieka Taghizadeh
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open.2020; 8(12): e3276. CrossRef - Significance of 5-S-Cysteinyldopa as a Marker for Melanoma
Kazumasa Wakamatsu, Satoshi Fukushima, Akane Minagawa, Toshikazu Omodaka, Tokimasa Hida, Naohito Hatta, Minoru Takata, Hisashi Uhara, Ryuhei Okuyama, Hironobu Ihn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(2): 432. CrossRef
- First Case of Primary Breast Melanoma in Central America: Case Report and Literature Review
- Loss of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer
- Hong Sik Park, Uiju Cho, So Young Im, Chang Young Yoo, Ji Han Jung, Young Jin Suh, Hyun Joo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(2):75-85. Published online November 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.11
- 9,180 View
- 191 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) molecules play important roles in regulating immune responses. Loss or reduction of HLA-I expression has been shown to be associated with prognosis in several cancers. Regulatory T-cells (Tregs) also play critical functions in immune response regulation. Evaluation of HLA-I expression status by the EMR8-5 antibody and its clinical impact in breast cancer have not been well studied, and its relationship with Tregs remains unclear.
Methods
We evaluated HLA-I expression and Treg infiltration by immunohistochemistry in 465 surgically resected breast cancer samples. We examined the correlation between HLA-I expression and Treg infiltration and clinicopathologic characteristics and survival analyses were performed.
Results
Total loss of HLA-I expression was found in 84 breast cancer samples (18.1%). Univariate survival analysis revealed that loss of HLA-I expression was significantly associated with worse disease-specific survival (DSS) (p = .029). HLA-I was not an independent prognostic factor in the entire patient group, but it was an adverse independent prognostic factor for DSS in patients with advanced disease (stage II–IV) (p = .031). Treg numbers were significantly higher in the intratumoral stroma of HLA-I–positive tumors than in HLA-I–negative tumors (median 6.3 cells/high power field vs 2.1 cells/high power field, p < .001). However, Tregs were not an independent prognostic factor in our cohort.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that the loss of HLA-I expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients, highlighting the role of HLA-I alterations in immune evasion mechanisms of breast cancer. HLA-I could be a promising marker that enables the application of more effective and precise immunotherapies for patients with advanced breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estrogen Signaling in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Impact on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
Chiara Corti, Busem Binboğa Kurt, Beyza Koca, Tasnim Rahman, Fabio Conforti, Laura Pala, Giampaolo Bianchini, Carmen Criscitiello, Giuseppe Curigliano, Ana C. Garrido-Castro, Sheheryar K. Kabraji, Adrienne G. Waks, Elizabeth A. Mittendorf, Sara M. Tolaney
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2025; 132: 102852. CrossRef - MHC-I upregulation by macbecin II in the solid tumors potentiates the effect of active immunotherapy
Ravindra Pramod Deshpande, Kerui Wu, Shih-Ying Wu, Abhishek Tyagi, Eleanor C Smith, Jee-Won Kim, Kounosuke Watabe
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2025; 17(4): 797. CrossRef - Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) and major Histocompatibility Complex Class I (MHC Class I) Expression Patterns and Their Pathologic Associations in triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Ponkrit Kaewkedsri, Piyapharom Intarawichian, Sirawich Jessadapattarakul, Waritta Kunprom, Supinda Koonmee, Malinee Thanee, Ongart Somintara, Anongporn Wongbuddha, Payia Chadbunchachai, Supajit Nawapun, Chaiwat Aphivatanasiri
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 17: 123. CrossRef - Comment on “Prognostic and Clinical Significance of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression in Breast Cancer: A Meta‑Analysis”
Wei Han, Li-zhou Shi, Yu-wei Zhang, Hao-nan Wang
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2024; 28(2): 237. CrossRef - Immunotherapy resistance in solid tumors: mechanisms and potential solutions
Daniel S. Lefler, Steven A. Manobianco, Babar Bashir
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of cancer cell‐expressed HLA class I molecules and their immunopathological implications
Terufumi Kubo, Shiori Asano, Kenta Sasaki, Kenji Murata, Takayuki Kanaseki, Tomohide Tsukahara, Yoshihiko Hirohashi, Toshihiko Torigoe
HLA.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression and Natural Killer Cell Infiltration and Its Correlation with Prognostic Features in Luminal Breast Cancers
Maria Vernet-Tomas, Ivonne Vazquez, Francesc Olivares, David Lopez, Jose Yelamos, Laura Comerma
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2024; Volume 16: 657. CrossRef - Upregulation of MHC I antigen processing machinery gene expression in breast cancer cells by Trichostatin A
A. H. Murtadha, N. A. Sharudin, I. I.M. Azahar, A. T. Che Has, N. F. Mokhtar
Молекулярная биология.2024; 58(1): 121. CrossRef - HLA-I and breast cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Francisco Cezar Aquino de Moraes, Jorge Henrique Cavalcanti Orestes Cardoso, Francinny Alves Kelly, Michele Kreuz, Lilianne Rodrigues Fernandes, Maria Cristina Figueroa Magalhães, Rommel Mario Rodríguez Burbano
Human Immunology.2024; 85(6): 111148. CrossRef - Cancer Immunology: Immune Escape of Tumors—Expression and Regulation of HLA Class I Molecules and Its Role in Immunotherapies
Yuan Wang, Simon Jasinski-Bergner, Claudia Wickenhauser, Barbara Seliger
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2023; 30(3): 148. CrossRef - In Silico Pipeline to Identify Tumor-Specific Antigens for Cancer Immunotherapy Using Exome Sequencing Data
Diego Morazán-Fernández, Javier Mora, Jose Arturo Molina-Mora
Phenomics.2023; 3(2): 130. CrossRef - HLA and tumour immunology: immune escape, immunotherapy and immune-related adverse events
Ning Jiang, Yue Yu, Dawei Wu, Shuhang Wang, Yuan Fang, Huilei Miao, Peiwen Ma, Huiyao Huang, Min Zhang, Yu Zhang, Yu Tang, Ning Li
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(2): 737. CrossRef - Relationship between Systemic Inflammatory Markers, GLUT1 Expression, and Maximum 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Their Prognostic Significance
Sonya Youngju Park, Deog-Gon Cho, Byoung-Yong Shim, Uiju Cho
Diagnostics.2023; 13(6): 1013. CrossRef - Prognostic and Clinical Significance of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Weiqiang Qiao, Zhiqiang Jia, Wanying Guo, Qipeng Liu, Xiao Guo, Miao Deng
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2023; 27(5): 573. CrossRef - Challenges and solutions for therapeuticTCR‐based agents
Manish Malviya, Zita E. H. Aretz, Zaki Molvi, Jayop Lee, Stephanie Pierre, Patrick Wallisch, Tao Dao, David A. Scheinberg
Immunological Reviews.2023; 320(1): 58. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of impaired antigenic presentation as a cause of tumor escape from immune surveillance
A.A. Korotaeva, A.A. Borunova, A.Yu. Kuzevanova, T.N. Zabotina, A.A. Alimov
Russian Journal of Archive of Pathology.2023; 85(6): 76. CrossRef - Immune Escape Mechanism of Cancer
Ayse Caner
Current Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 10(1): 9. CrossRef - Upregulation of MHC I Antigen Processing Machinery Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Cells by Trichostatin A
A. H. Murtadha, N. A. Sharudin, I. I. M. Azahar, A. T. Che Has, N. F. Mokhtar
Molecular Biology.2023; 57(6): 1212. CrossRef - Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Antigen-Processing Machinery Upregulation by Anticancer Therapies in the Era of Checkpoint Inhibitors
Ananthan Sadagopan, Theodoros Michelakos, Gabriella Boyiadzis, Cristina Ferrone, Soldano Ferrone
JAMA Oncology.2022; 8(3): 462. CrossRef - Mechanisms of MHC-I Downregulation and Role in Immunotherapy Response
Brandie C. Taylor, Justin M. Balko
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: Resistance Mechanisms and Future Perspectives
Ioannis A. Vathiotis, Ioannis Trontzas, Niki Gavrielatou, Georgia Gomatou, Nikolaos K. Syrigos, Elias A. Kotteas
Clinical Breast Cancer.2022; 22(7): 642. CrossRef - Aberrant synaptophysin expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Soyoung Im, Jeong-A. Kim, Gyeongsin Park, Uiju Cho
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of HLA class I is associated with immune cell infiltration and patient outcome in breast cancer
Song-Hee Han, Milim Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Ji Won Woo, Hye Yeon Choi, So Yeon Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune landscape and therapeutic strategies: new insights into PD-L1 in tumors
Yuan Wei, Xiao Xiao, Xiang-Ming Lao, Limin Zheng, Dong-Ming Kuang
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2021; 78(3): 867. CrossRef - Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of breast cancer
Leisha A Emens, Sylvia Adams, Ashley Cimino-Mathews, Mary L Disis, Margaret E Gatti-Mays, Alice Y Ho, Kevin Kalinsky, Heather L McArthur, Elizabeth A Mittendorf, Rita Nanda, David B Page, Hope S Rugo, Krista M Rubin, Hatem Soliman, Patricia A Spears, Sara
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2021; 9(8): e002597. CrossRef - Resistance mechanisms to checkpoint inhibitors
Sarah A Weiss, Mario Sznol
Current Opinion in Immunology.2021; 69: 47. CrossRef - The Immunology of Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Jonathan Goldberg, Ricardo G. Pastorello, Tuulia Vallius, Janae Davis, Yvonne Xiaoyong Cui, Judith Agudo, Adrienne G. Waks, Tanya Keenan, Sandra S. McAllister, Sara M. Tolaney, Elizabeth A. Mittendorf, Jennifer L. Guerriero
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - B4GALNT2 Gene Promotes Proliferation, and Invasiveness and Migration Abilities of Model Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells by Interacting With HLA-B Protein
Pu Yu, Lili Zhu, Kang Cui, Yabing Du, Chaojie Zhang, Wang Ma, Jia Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Recurrence biomarkers of triple negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and anti-EGFR antibodies
Nina Radosevic-Robin, Pier Selenica, Yingjie Zhu, Helen H. Won, Michael F. Berger, Lorenzo Ferrando, Emiliano Cocco, Maud Privat, Flora Ponelle-Chachuat, Catherine Abrial, Jean-Marc Nabholtz, Frederique Penault-Llorca, Jorge S. Reis-Filho, Maurizio Scaltr
npj Breast Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Beyond an era of chemoradiation?
Liam Masterson, James Howard, Jazmina Gonzalez‐Cruz, Christopher Jackson, Catherine Barnett, Lewis Overton, Howard Liu, Rahul Ladwa, Fiona Simpson, Margie McGrath, Ben Wallwork, Terry Jones, Christian Ottensmeier, Melvin L.K. Chua, Chris Perry, Rajiv Khan
International Journal of Cancer.2020; 146(8): 2305. CrossRef - Co-expression of HLA-I loci improved prognostication in HER2+ breast cancers
Julia Y. Tsang, Chun-Sing Ho, Yun-Bi Ni, Yan Shao, Ivan K. Poon, Siu-Ki Chan, Sai-Yin Cheung, Ka-Ho Shea, Monalyn Marabi, Gary M. Tse
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2020; 69(5): 799. CrossRef - Breast cancer patients overall survival depends on a combination of the polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor gene and HLA-haplotypes
T.F. Malivanova, E.V. Alferova, A.S. Ostashkin, T.A. Astrelina, N.N. Mazurenko
Molecular Genetics Microbiology and Virology (Russian version).2020; 38(1): 40. CrossRef - The Overall Survival of Breast Cancer Patients Depends on a Combination of Polymorphisms of Tumor Necrosis Factor Gene and HLA Haplotypes
T. F. Malivanova, E. V. Alferova, A. S. Ostashkin, T. A. Astrelina, N. N. Mazurenko
Molecular Genetics, Microbiology and Virology.2020; 35(1): 38. CrossRef - The Emergence of Natural Killer Cells as a Major Target in Cancer Immunotherapy
Fernando Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, Joseph Cursons, Nicholas D. Huntington
Trends in Immunology.2019; 40(2): 142. CrossRef
- Estrogen Signaling in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Impact on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
- The Prognostic Impact of Synchronous Ipsilateral Multiple Breast Cancer: Survival Outcomes according to the Eighth American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging and Molecular Subtype
- Jinah Chu, Hyunsik Bae, Youjeong Seo, Soo Youn Cho, Seok-Hyung Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):396-403. Published online October 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.03
- 8,140 View
- 102 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the current American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system of breast cancer, only tumor size determines T-category regardless of whether the tumor is single or multiple. This study evaluated if tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and can be used to subclassify breast cancer.
Methods
We included 5,758 patients with invasive breast cancer who underwent surgery at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, from 1995 to 2012.
Results
Patients were divided into two groups according to multiplicity (single, n = 4,744; multiple, n = 1,014). Statistically significant differences in lymph node involvement and lymphatic invasion were found between the two groups (p < .001). Patients with multiple masses tended to have luminal A molecular subtype (p < .001). On Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, patients with multiple masses had significantly poorer disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .016). The prognostic significance of multiplicity was seen in patients with anatomic staging group I and prognostic staging group IA (p = .019 and p = .032, respectively). When targeting patients with T1-2 N0 M0, hormone receptor–positive, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative cancer, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis also revealed significantly reduced DFS with multiple cancer (p = .031). The multivariate analysis indicated that multiplicity was independently correlated with worse DFS (hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.03 to 1.47; p = .025). The results of this study indicate that tumor multiplicity is frequently found in luminal A subtype, is associated with frequent lymph node metastasis, and is correlated with worse DFS.
Conclusions
Tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and could be used to subclassify invasive breast cancer at early stages. Adjuvant chemotherapy would be necessary for multiple masses of T1–2 N0 M0, hormone-receptor-positive, and HER2-negative cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
Neyaz Ahmad, Khushboo Rani, Zenith Kerketta, Krishna Murari, Anish Baxla, Ujala Murmu, Amit Nishant, Shreya .
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Large Format Histology in Diagnosis of Breast Carcinoma
Hari Shankar Pandey, Sanya Bhasin, Suman Kumari Pandey
NMO Journal.2025; 19(2): 189. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Multiple Synchronous T1 Breast Cancer
Hongki Gwak, Sung Hoo Jung, Young Jin Suh, Seok Jin Nam, Jai Hong Han, Se Jeong Oh, Eun Hwa Park, Seong Hwan Kim
Cancers.2024; 16(23): 4019. CrossRef - Deep learning-based system for automatic prediction of triple-negative breast cancer from ultrasound images
Alexandre Boulenger, Yanwen Luo, Chenhui Zhang, Chenyang Zhao, Yuanjing Gao, Mengsu Xiao, Qingli Zhu, Jie Tang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2023; 61(2): 567. CrossRef - Multicentre prospective cohort study of unmet supportive care needs among patients with breast cancer throughout their cancer treatment trajectory in Penang: a PenBCNeeds Study protocol
Noorsuzana Mohd Shariff, Nizuwan Azman, Rohayu Hami, Noor Mastura Mohd Mujar, Mohammad Farris Iman Leong Bin Abdullah
BMJ Open.2021; 11(3): e044746. CrossRef - The subgross morphology of breast carcinomas: a single-institution series of 2033 consecutive cases documented in large-format histology slides
Tibor Tot, Maria Gere, Syster Hofmeyer, Annette Bauer, Ulrika Pellas
Virchows Archiv.2020; 476(3): 373. CrossRef - Editorial for “Synchronous Breast Cancer: Phenotypic Similarities on MRI”
Uma Sharma
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2020; 52(1): 309. CrossRef - Synchronous Multiple Breast Cancers—Do We Need to Reshape Staging?
Minodora Onisâi, Adrian Dumitru, Iuliana Iordan, Cătălin Aliuș, Oana Teodor, Adrian Alexandru, Daniela Gheorghiță, Iulian Antoniac, Adriana Nica, Alexandra-Ana Mihăilescu, Sebastian Grădinaru
Medicina.2020; 56(5): 230. CrossRef - Molecular mechanism of triple‑negative breast cancer‑associated BRCA1 and the identification of signaling pathways
Feng Qi, Wen‑Xing Qin, Yuan‑Sheng Zang
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
- WITHDRAWN:Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
- Junyoung Shin, Hee Jeong Kim, Dae-Yeon Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Kyung-Ja Cho
- Received August 6, 2018 Accepted September 13, 2018 Published online October 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.14
- 4,097 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast in an Adult: An Extremely Rare Case
Helen J. Trihia, Natasa Novkovic, Ioannis Provatas, Anastasios Mavrogiorgis, Evangelos Lianos
Case Reports in Pathology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Primary Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast in an Adult: An Extremely Rare Case
- High Cytoplasmic CXCR4 Expression Predicts Prolonged Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Adjuvant Chemotherapy
- Bobae Shim, Min‐Sun Jin, Ji Hye Moon, In Ae Park, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):369-377. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.19
- 14,455 View
- 185 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Chemokine receptor CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and its ligand CXC motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12; stromal cell-derived factor-1) are implicated in tumor growth, metastasis, and tumor cell-microenvironment interaction. A number of studies have reported that increased CXCR4 expression is associated with worse prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), but its prognostic significance has not been studied in TNBC patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods
Two hundred eighty-three TNBC patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy were retrospectively analyzed. Tissue microarray was constructed from formalinfixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue and immunohistochemistry for CXCR4 and CXCL12 was performed. Expression of each marker was compared with clinicopathologic characteristics and outcome.
Results
High cytoplasmic CXCR4 expression was associated with younger age (p = .008), higher histologic grade (p = .007) and lower pathologic stage (p = .045), while high CXCL12 expression was related to larger tumor size (p = .045), positive lymph node metastasis (p = .005), and higher pathologic stage (p = .017). The patients with high cytoplasmic CXCR4 experienced lower distant recurrence (p = .006) and better recurrence-free survival (RFS) (log-rank p = .020) after adjuvant chemotherapy. Cytoplasmic CXCR4 expression remained an independent factor of distant recurrence (p = .019) and RFS (p = .038) after multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
High cytoplasmic CXCR4 expression was associated with lower distant recurrence and better RFS in TNBC patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. This is the first study to correlate high CXCR4 expression to better TNBC prognosis, and the underlying mechanism needs to be elucidated in further studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bisphenol A-induced cancer-associated adipocytes promotes breast carcinogenesis via CXCL12/AKT signaling
Zhiyuan Dong, Liping He, Jinyi Wu, Chunfeng Xie, Shanshan Geng, Jieshu Wu, Caiyun Zhong, Xiaoting Li
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2025; 599: 112473. CrossRef - Dissecting the tumor microenvironment in primary breast angiosarcoma: insights from single-cell RNA sequencing
Peikai Ding, Shengbin Pei, Yi Zhai, Zheng Qu, Yazhe Yang, Xiaolong Feng, Qiang Liu, Xiangyu Wang, Wenxiang Zhang, Zhongzhao Wang, Xiangyi Kong, Jing Wang, Yi Fang
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer and tumor stage correlation
Fang Cao, Yang Zhang, Jianhao Xu, Jiarui Min, Jihao Su, Zhe Chen, Jingfeng Gu, Zijie Xu, Song Xu
Gene Reports.2025; 40: 102281. CrossRef - Distinct profiles of proliferating CD8+/TCF1+ T cells and CD163+/PD-L1+ macrophages predict risk of relapse differently among treatment-naïve breast cancer subtypes
Konstantinos Ntostoglou, Sofia D. P. Theodorou, Tanja Proctor, Ilias P. Nikas, Sinclair Awounvo, Athanasia Sepsa, Vassilis Georgoulias, Han Suk Ryu, Ioannis S. Pateras, Christos Kittas
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Unravelling the CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in breast cancer: Insights into metastasis, microenvironment interactions, and therapeutic opportunities
Priyanka Garg, Venkateswara Rao Jallepalli, Sonali Verma
Human Gene.2024; 40: 201272. CrossRef - New Emerging Chemokine Receptors: CCR5 or CXCR5 on Tumor Is Associated with Poor Response to Chemotherapy and Poor Prognosis in Locally Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Neslihan Cabioglu, Semen Onder, Hüseyin Karatay, Aysel Bayram, Gizem Oner, Mustafa Tukenmez, Mahmut Muslumanoglu, Abdullah Igci, Ahmet Dinccag, Vahit Ozmen, Adnan Aydiner, Pınar Saip, Ekrem Yavuz
Cancers.2024; 16(13): 2388. CrossRef - Cancer-Associated-Fibroblast-Mediated Paracrine and Autocrine SDF-1/CXCR4 Signaling Promotes Stemness and Aggressiveness of Colorectal Cancers
Chao-Yang Chen, Shih-Hsien Yang, Ping-Ying Chang, Su-Feng Chen, Shin Nieh, Wen-Yen Huang, Yu-Chun Lin, Oscar Kuang-Sheng Lee
Cells.2024; 13(16): 1334. CrossRef - Associations of CXCL12 polymorphisms with clinicopathological features in breast cancer: a case-control study
Shuai Lin, Yi Zheng, Meng Wang, Linghui Zhou, Yuyao Zhu, Yujiao Deng, Ying Wu, Dai Zhang, Na Li, Huafeng Kang, Zhijun Dai
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(3): 2255. CrossRef - The clinicopathological and prognostic value of CXCR4 expression in patients with lung cancer: a meta-analysis
Liping Qiu, Yuanyuan Xu, Hui Xu, Biyun Yu
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Demystifying the CXCR4 conundrum in cancer biology: Beyond the surface signaling paradigm
Mushtaq Ahmad Nengroo, Muqtada Ali Khan, Ayushi Verma, Dipak Datta
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2022; 1877(5): 188790. CrossRef - Targeted dendrimers for antagonizing the migration and viability of NALM-6 lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Chuda Chittasupho, Chaiyawat Aonsri, Witcha Imaram
Bioorganic Chemistry.2021; 107: 104601. CrossRef - CXCR4 and RANK Combination as a Predictor of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis in Indonesia
Yulian Erwin D
Journal of Surgery and Surgical Research.2021; : 020. CrossRef - CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in the microenvironment of solid tumors: A critical mediator of metastasis
Keywan Mortezaee
Life Sciences.2020; 249: 117534. CrossRef - Impact of the Chemokine Receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 on Clinical Outcome in Adrenocortical Carcinoma
Irina Chifu, Britta Heinze, Carmina T. Fuss, Katharina Lang, Matthias Kroiss, Stefan Kircher, Cristina L. Ronchi, Barbara Altieri, Andreas Schirbel, Martin Fassnacht, Stefanie Hahner
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bisphenol A-induced cancer-associated adipocytes promotes breast carcinogenesis via CXCL12/AKT signaling
- TFE3-Expressing Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Breast
- Hyunjin Kim, Jimin Kim, Se Kyung Lee, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):62-65. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.30
- 9,311 View
- 157 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) is a very rare mesenchymal tumor with a distinctive morphology and immunophenotype. PEComas usually harbor TSC2 alterations, although TFE3 translocations, which occur in MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma, are also possible. We recently experienced a case of PEComa with TFE3 expression arising in the breast. An 18-year-old female patient presented with a right breast mass. Histologically, the tumor consisted of epithelioid cells with alveolar structure and showed a diffuse strong expression of HMB45 and TFE3. TSC2 was preserved. Melan A and smooth muscle actin were negative. To our knowledge, this is the first Korean case of PEComa of the breast that intriguingly presented with TFE3 expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
Anuradha Sharma, Reetika Sharma, Jyoti Bala, Monika Sharma
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(1): 107. CrossRef - Malignant lung PEComa (clear cell tumor): rare case report and literature review
Marcos Adriano Garcia Campos, Lucas Fernandes Vasques, Rafael Goulart de Medeiros, Érico Murilo Monteiro Cutrim, Ana Júlia Favarin, Sarah Rebecca Machado Silva, Gyl Eanes Barros Silva, Marcelo Padovani de Toledo Moraes, Mariana Lopes Zanatta, Diego Aparec
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cathepsin K: A Versatile Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Various Cancers
Die Qian, Lisha He, Qing Zhang, Wenqing Li, Dandan Tang, Chunjie Wu, Fei Yang, Ke Li, Hong Zhang
Current Oncology.2022; 29(8): 5963. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef - Invasive Lobular Carcinoma With Extensive Clear Cells: A Pitfall in Diagnosis
Mark H. Kavesh, Daniel Sanchez, Jaya Ruth Asirvatham
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2020; 28(2): 169. CrossRef - Glycogen-rich Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review
Semir Vranic, Faruk Skenderi, Vanesa Beslagic, Zoran Gatalica
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2020; 28(9): 655. CrossRef - TFE3-expressing primary perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the Lymph node mimicking nodal relapse of rectal cancer
Jongmin Park, An Na Seo
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2019; 59(C): 46. CrossRef
- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
- Prognostic Significance of a Micropapillary Pattern in Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Comparative Analysis with Micropapillary Carcinoma
- Hyun-Jung Kim, Kyeongmee Park, Jung Yeon Kim, Guhyun Kang, Geumhee Gwak, Inseok Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):403-409. Published online June 9, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.18
- 9,247 View
- 201 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is an indolent tumors with a favorable prognosis; however, micropapillary features tend to lead to aggressive behavior. Thus, mucinous carcinoma and micropapillary carcinoma exhibit contrasting biologic behaviors. Here, we review invasive mucinous carcinoma with a focus on micropapillary features and correlations with clinicopathological factors.
Methods
A total of 64 patients with invasive breast cancer with mucinous or micropapillary features were enrolled in the study. Of 36 pure mucinous carcinomas, 17 (47.2%) had micropapillary features and were termed mucinous carcinoma with micropapillary features (MUMPC), and 19 (52.8%) had no micropapillary features and were termed mucinous carcinoma without micropapillary features. MUMPC were compared with 15 invasive micropapillary carcinomas (IMPC) and 13 invasive ductal and micropapillary carcinomas (IDMPC).
Results
The clinicopathological factors of pure mucinous carcinoma and MUMPC were not significantly different. In contrast to IMPC and IDMPC, MUMPC had a low nuclear grade, lower mitotic rate, higher expression of hormone receptors, negative human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status, lower Ki-67 proliferating index, and less frequent lymph node metastasis (p < .05). According to univariate analyses, progesterone receptor, HER2, T-stage, and lymph node metastasis were significant risk factors for overall survival; however, only T-stage remained significant in a multivariate analysis (p < .05).
Conclusions
In contrast to IMPC and IDMPC, the micropapillary pattern in mucinous carcinoma does not contribute to aggressive behavior. However, further analysis of a larger series of patients is required to clarify the prognostic significance of micropapillary patterns in mucinous carcinoma of the breast. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pure mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast with the rare lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: A case report with review of literature
Yash Hasmukhbhai Prajapati, Vishal Bhabhor, Kahan Samirkumar Mehta, Mithoon Barot, Husen Boriwala, Mohamed Omar
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Expression of autocrine motility factor receptor (AMFR) in human breast and lung invasive micropapillary carcinomas
Jing Xu, Hongfei Ma, Qi Wang, Hui Zhang
International Journal of Experimental Pathology.2023; 104(1): 43. CrossRef - The Spectrum of Mucinous Lesions of the Breast
Upasana Joneja, Juan Palazzo
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(1): 19. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023; 5(2): 180. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Micropapillary Breast Carcinoma: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Prognosis
Georgios-Ioannis Verras, Levan Tchabashvili, Francesk Mulita, Ioanna Maria Grypari, Sofia Sourouni, Evangelia Panagodimou, Maria-Ioanna Argentou
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 14: 41. CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: distinctive histopathologic and genetic characteristics
Minjung Jung
Kosin Medical Journal.2022; 37(3): 176. CrossRef - Triple-Positive Breast Carcinoma: Histopathologic Features and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Jennifer Zeng, Marcia Edelweiss, Dara S. Ross, Bin Xu, Tracy-Ann Moo, Edi Brogi, Timothy M. D'Alfonso
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(6): 728. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Sonographic Features of Pure Mucinous Breast Carcinoma With Micropapillary Pattern
Wu Zhou, Yong-Zhong Li, Li-Min Gao, Di-Ming Cai
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 95. CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma with micropapillary features is morphologically, clinically and genetically distinct from pure mucinous carcinoma of breast
Peng Sun, Zaixuan Zhong, Qianyi Lu, Mei Li, Xue Chao, Dan Chen, Wenyan Hu, Rongzhen Luo, Jiehua He
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(10): 1945. CrossRef - Micropapillary pattern in pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast – does it matter or not?
Xiaoli Xu, Rui Bi, Ruohong Shui, Baohua Yu, Yufan Cheng, Xiaoyu Tu, Wentao Yang
Histopathology.2019; 74(2): 248. CrossRef - An Update of Mucinous Lesions of the Breast
Beth T. Harrison, Deborah A. Dillon
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2018; 11(1): 61. CrossRef - The clinicopathological significance of micropapillary pattern in colorectal cancers
Jung-Soo Pyo, Mee Ja Park, Dong-Wook Kang
Human Pathology.2018; 77: 159. CrossRef - The sonographic findings of micropapillary pattern in pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Heqing Zhang, Li Qiu, Yulan Peng
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic dilemma of micropapillary variant of mucinous breast cancer
Geok Hoon Lim, Zhiyan Yan, Mihir Gudi
BMJ Case Reports.2018; 2018: bcr-2018-225775. CrossRef
- Pure mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast with the rare lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: A case report with review of literature
- Mammary Carcinoma Arising in Microglandular Adenosis: A Report of Five Cases
- Mimi Kim, Milim Kim, Yul Ri Chung, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):422-427. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.11.11
- 15,515 View
- 202 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mammary carcinoma arising in microglandular adenosis (MGA) is extremely rare, and MGA is regarded as a non-obligate precursor of triple-negative breast cancer. We report five cases of carcinoma arising in MGA of the breast. All cases showed a spectrum of proliferative lesions ranging from MGA to atypical MGA, ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive carcinoma. Immunohistochemically, all cases were triple-negative and expression of S-100 protein gradually decreased as the lesions progressed from MGA to atypical MGA and carcinoma. Three cases showed acinic cell differentiation with reactivity to α1-antitrypsin, and one case was metaplastic carcinoma. During clinical follow-up, one patient developed local recurrence. Carcinoma arising in MGA is a rare but distinct subset of triple-negative breast cancer with characteristic histologic and immunohistochemical findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microglandular adenosis associated with invasive breast carcinoma: Tertiary care oncology centre experience of an under-recognized entity
Ayushi Sahay, Asawari Patil, Trupti Pai, Poonam Panjwani, Shalaka Joshi, Palak Popat Thakkar, Sangeeta B. Desai, Tanuja M. Shet
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152576. CrossRef - Two similar but distinct types of breast acinar cell carcinoma: evidence from histological, immunohistochemical and molecular features
Mingfang Sun, Lin Fu, Hongjiu Ren, Jian Wang, Xuyong Lin, Qingfu Zhang
Histopathology.2025; 87(6): 904. CrossRef - Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Population‐Based Clinicopathologic Study
Faruk Skenderi, Giridhara Rathnaiah Babu, Una Glamoclija, Emir Veledar, Zoran Gatalica, Janez Lamovec, Semir Vranic
Cancer Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Ihab S Atta
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Histological and electron microscopic features of the extracellular matrix of invasive breast ductal carcinoma of no special type. Report of 5 cases and literature review
M.V. Mnikhovich, A.V. Romanov, T.M. Nguyen, T.V. Bezuglova, D.A. Pastukhova
Ultrastructural Pathology.2023; 47(4): 261. CrossRef - Ductal carcinoma in situ arises from microglandular adenosis and atypical microglandular adenosis in a young woman
Nguyen Thu Huong, Tran-Thi Hue, Nguyen Duy Hung, Nguyen Minh Duc
Journal of Clinical Imaging Science.2023; 13: 15. CrossRef - Primary acinic cell carcinoma of the breast: A case report and literature review
Zhi-Min Deng, Yi-Ping Gong, Feng Yao, Ma-Li Wu, Zi-Tao Wang, Jing-Ping Yuan, Yan-Xiang Cheng
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e20160. CrossRef - Two cases of mammary acinic cell carcinomas with microglandular structures mimicking microglandular adenosis
Fang Yu, Li Niu, Bicheng Wang, Wei Fan, Jian Xu, Qiongrong Chen
Pathology International.2022; 72(6): 343. CrossRef - Metaplastic Matrix-Producing Carcinoma and Apocrine Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Associated with Microglandular Adenosis: A Unique Case Report
Nektarios Koufopoulos, Dionysios Dimas, Foteini Antoniadou, Kyparissia Sitara, Dimitrios Balalis, Ioannis Boutas, Alina Roxana Gouloumis, Adamantia Kontogeorgi, Lubna Khaldi
Diagnostics.2022; 12(6): 1458. CrossRef - Salivary gland-like breast tumors: A review of diagnostic features and prognosis
Vicente Marco
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2022; 35: S43. CrossRef - Acinic cell carcinoma of the breast: A comprehensive review
Azra Ajkunic, Faruk Skenderi, Nada Shaker, Saghir Akhtar, Janez Lamovec, Zoran Gatalica, Semir Vranic
The Breast.2022; 66: 208. CrossRef - Unusual cerebrospinal fluid finding of intracytoplasmic granules in metaplastic carcinoma of the breast with acinar differentiation
Ruhani Sardana, Anil V Parwani, Xiaoyan Cui, Jayalakshmi Balakrishna
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Salivary gland-type mammary carcinoma arising in microglandular adenosis: A case report and clinicopathological review of the literature
Victoria Rico, Yukiko Shibahara, Marjorie Monteiro, Elzbieta Slodkowska, Samantha Tam, Pearl Zaki, Carlo De Angelis, Edward Chow, Katarzyna Joanna Jerzak
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2020; 24: 100178. CrossRef - Triple negative metaplastic breast carcinoma presenting in the background of atypical microglandular adenosis with candidacy for atezolizumab immunotherapy
Hector Chavarria, Sean Hacking, Cao Jin, Nidhi Kataria, Florin Glodan, Tawfiqul Bhuiya, Mansoor Nasim
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2020; 21: 200398. CrossRef
- Microglandular adenosis associated with invasive breast carcinoma: Tertiary care oncology centre experience of an under-recognized entity
- Metaplastic Carcinoma with Chondroid Differentiation Arising in Microglandular Adenosis
- Ga-Eon Kim, Nah Ihm Kim, Ji Shin Lee, Min Ho Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):418-421. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.06
- 8,819 View
- 113 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Microglandular adenosis (MGA) of the breast is a rare, benign proliferative lesion but with a significant rate of associated carcinoma. Herein, we report an unusual case of metaplastic carcinoma with chondroid differentiation associated with typical MGA. Histologically, MGA showed a direct transition to metaplastic carcinoma without an intervening atypical MGA or ductal carcinoma in situ component. The immunohistochemical profile of the metaplastic carcinoma was mostly similar to that of MGA. In both areas, all the epithelial cells were positive for S-100 protein, but negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, HER2/neu, and epidermal growth factor receptor. An increase in the Ki-67 and p53 labelling index was observed from MGA to invasive carcinoma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of metaplastic carcinoma with chondroid differentiation arising in MGA in Korea. This case supports the hypothesis that a subset of MGA may be a non-obligate morphologic precursor of breast carcinoma, especially the triple-negative subtype.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two similar but distinct types of breast acinar cell carcinoma: evidence from histological, immunohistochemical and molecular features
Mingfang Sun, Lin Fu, Hongjiu Ren, Jian Wang, Xuyong Lin, Qingfu Zhang
Histopathology.2025; 87(6): 904. CrossRef - Elucidating the nature of acinic cell carcinoma of the breast with high-grade morphology: evidence from case report
Yunjie Ge, Xianping Wei, Jing-Nan Liu, Ping-Li Sun, Hongwen Gao
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights into acinic cell carcinoma of the breast: clinicopathology, origin of histology, molecular features, prognosis, and treatment
Yunjie Ge, Xianping Wei, Jing-Nan Liu, Ping-Li Sun, Hongwen Gao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metaplastic Matrix-Producing Carcinoma and Apocrine Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Associated with Microglandular Adenosis: A Unique Case Report
Nektarios Koufopoulos, Dionysios Dimas, Foteini Antoniadou, Kyparissia Sitara, Dimitrios Balalis, Ioannis Boutas, Alina Roxana Gouloumis, Adamantia Kontogeorgi, Lubna Khaldi
Diagnostics.2022; 12(6): 1458. CrossRef - Salivary gland-type mammary carcinoma arising in microglandular adenosis: A case report and clinicopathological review of the literature
Victoria Rico, Yukiko Shibahara, Marjorie Monteiro, Elzbieta Slodkowska, Samantha Tam, Pearl Zaki, Carlo De Angelis, Edward Chow, Katarzyna Joanna Jerzak
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2020; 24: 100178. CrossRef - Microglandular adenosis is an advanced precursor breast lesion with evidence of molecular progression to matrix-producing metaplastic carcinoma
Christopher J. Schwartz, Igor Dolgalev, Esther Yoon, Iman Osman, Adriana Heguy, Eleazar C. Vega-Saenz de Miera, Diana Nimeh, George Jour, Farbod Darvishian
Human Pathology.2019; 85: 65. CrossRef
- Two similar but distinct types of breast acinar cell carcinoma: evidence from histological, immunohistochemical and molecular features
- Evaluation of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Experience in a Single Institution over a 10-Year Period
- Misun Choi, Yeon Hee Park, Jin Seok Ahn, Young-Hyuck Im, Seok Jin Nam, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):69-78. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.05
- 12,874 View
- 268 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has been associated with favorable clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. However, the possibility that the prognostic significance of pCR differs among various definitions has not been established. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated the pathologic response after NAC in 353 breast cancer patients and compared the prognoses after applying the following different definitions of pCR: ypT0/is, ypT0, ypT0/is ypN0, and ypT0 ypN0. Results: pCR was significantly associated with improved distant disease-free survival (DDFS) regardless of the definition (ypT0/is, p = .002; ypT0, p = .008; ypT0/is ypN0, p < .001; ypT0 ypN0, p = .003). Presence of tumor deposits of any size in the lymph nodes (LNs; ypN ≥ 0(i+)) was associated with worse DDFS (ypT0 ypN0 vs ypT0 ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .036 and ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .015), and presence of isolated tumor cells was associated with decreased overall survival (OS; ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN0(i+), p = .013). Residual ductal carcinoma in situ regardless of LN status showed no significant difference in DDFS or OS (DDFS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .373 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .462; OS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .441 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .758). In subsequent analysis using ypT0/is ypN0, pCR was associated with improved DDFS and OS in triple-negative tumors (p < .001 and p = .003, respectively). Conclusions: Based on our study results, the prognosis and rate of pCR differ according to the definition of pCR and ypT0/is ypN0 might be considered a more preferable definition of pCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
Christine Hong Ngoc Che Thai, Selena J. An, Conner R. Haase, Julia M. Selfridge, Chris B. Agala, Philip M. Spanheimer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(2): 315. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Study on Response Rate and Toxicity
Matt Galloway, Paula Barlow, Jody Jordan, Edward Lo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(20): 7362. CrossRef - Association of residual ductal carcinoma in situ with breast cancer treatment outcomes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to hormone receptor status
Eunju Shin, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Jisun Kim, Il Yong Chung, Beom Seok Ko, Hee Jeong Kim, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son, Sae Byul Lee
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mammographic Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection in Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Ga Eun Park, Bong Joo Kang, Sung Hun Kim, Han Song Mun
Life.2024; 14(11): 1449. CrossRef - Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment – How to assess residual disease
Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
The Breast.2022; 62: S25. CrossRef - Pathological examination of breast cancer samples before and after neoadjuvant therapy: recommendations from the Italian Group for the Study of Breast Pathology - Italian Society of Pathology (GIPaM-SIAPeC)
Nicola Fusco, Antonio Rizzo, Leopoldo Costarelli, Alfredo Santinelli, Bruna Cerbelli, Cristian Scatena, Ettore Macrì, Francesca Pietribiasi, Giulia d’Amati, Anna Sapino, Isabella Castellano
Pathologica.2022; 114(2): 104. CrossRef - Pathological complete response as a surrogate to improved survival in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Ferdia Browne, Nicola Miller, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neoadjuvant therapy with doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by weekly paclitaxel in early breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of 200 consecutive patients treated in a single center with a median follow-up of 9.5 years
Lisi M. Dredze, Michael Friger, Samuel Ariad, Michael Koretz, Bertha Delgado, Ruthy Shaco-Levy, Margarita Tokar, Michael Bayme, Ravit Agassi, Maia Rosenthal, Victor Dyomin, Olga Belochitski, Shai Libson, Tamar Mizrahi, David B. Geffen
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 193(3): 597. CrossRef - “No Ink on Tumor” in Breast-Conserving Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Giulia Atzori, Marco Gipponi, Chiara Cornacchia, Raquel Diaz, Marco Sparavigna, Maurizio Gallo, Tommaso Ruelle, Federica Murelli, Simonetta Franchelli, Francesca Depaoli, Daniele Friedman, Piero Fregatti
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1031. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models and Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Carmen Herrero Vicent, Xavier Tudela, Paula Moreno Ruiz, Víctor Pedralva, Ana Jiménez Pastor, Daniel Ahicart, Silvia Rubio Novella, Isabel Meneu, Ángela Montes Albuixech, Miguel Ángel Santamaria, María Fonfria, Almudena Fuster-Matanzo, Santiago Olmos Antó
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3508. CrossRef - Applying artificial intelligence technology to assist with breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction
Meredith A. Jones, Warid Islam, Rozwat Faiz, Xuxin Chen, Bin Zheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemotherapy response score as a prognostic tool in patients with advanced stage endometrial carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ina Jani, Ricardo R Lastra, Katherine S Brito, Chuanhong Liao, Isabel Lazo, Nita Karnik Lee, S Diane Yamada, Katherine C Kurnit
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2021; 31(6): 852. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with anlotinib in occult breast cancer: A case report and review of literature
Yu Zhang, Di Wu, Bo Zhao, Xue-Liang Tian, Tian-Cheng Yao, Feng Li, Wei-Fang Liu, Ai-Ping Shi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(4): 919. CrossRef - Pathologic Complete Response and Its Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Patient’s Survival after Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Hui Liu, Liqiong Lv, Hui Gao, Ming Cheng, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Impact of Surgical Margins in Breast Cancer After Preoperative Systemic Chemotherapy on Local Recurrence and Survival
K. Wimmer, M. Bolliger, Z. Bago-Horvath, G. Steger, D. Kauer-Dorner, R. Helfgott, C. Gruber, F. Moinfar, M. Mittlböck, F. Fitzal
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2020; 27(5): 1700. CrossRef - Predictive factors for omitting lymphadenectomy in patients with node‐positive breast cancer treated with neo‐adjuvant systemic therapy
Sergi Fernandez‐Gonzalez, Catalina Falo, Maria J. Pla, Paula Verdaguer, Diana Nuñez, Anna Guma, Teresa Soler, Andrea Vethencourt, Silvia Vázquez, Maria Eulalia Fernandez‐Montoli, Miriam Campos, Sonia Pernas, Miguel Gil, Jordi Ponce, Amparo Garcia‐Tejedor
The Breast Journal.2020; 26(5): 888. CrossRef - Is There a Role for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy for T1-2N1 Breast Cancers With Node-Positive Pathology After Patients Become Node-Negative Pathology Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?
Qian Wang, Jingjing Zhao, Xiaowei Han, Puchun Er, Xiangying Meng, Jinyan Shi, Huiru Sun, Jingyang Zhu, Li Zhu, Shikai Wu, Wencheng Zhang, Bing Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic role of microRNA 182 and microRNA 18a in locally advanced triple negative breast cancer
Rajat Bajaj, Rupal Tripathi, T. S. Sridhar, Aruna Korlimarla, Kumardeep Dutta Choudhury, Moushumi Suryavanshi, Anurag Mehta, Dinesh Chandra Doval, Elda Tagliabue
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242190. CrossRef - Association of Pathologic Complete Response with Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Min Huang, Joyce O'Shaughnessy, Jing Zhao, Amin Haiderali, Javier Cortés, Scott D. Ramsey, Andrew Briggs, Peter Hu, Vassiliki Karantza, Gursel Aktan, Cynthia Z. Qi, Chenyang Gu, Jipan Xie, Muhan Yuan, John Cook, Michael Untch, Peter Schmid, Peter A. Fasch
Cancer Research.2020; 80(24): 5427. CrossRef - Multiparametric MR imaging to assess response following neoadjuvant systemic treatment in various breast cancer subtypes: Comparison between different definitions of pathologic complete response
G Santamaría, X Bargalló, S Ganau, I Alonso, M Muñoz, M Mollà, PL Fernández, A Prat
European Journal of Radiology.2019; 117: 132. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of residual nodal burden using lymph node ratio in locally advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Reshu Agarwal, Arun Philip, Keechilat Pavithran, Anupama Rajanbabu, Gaurav Goel, DK Vijaykumar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2019; 56(3): 228. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in occult breast cancer
Haisong Yang, Ling Li, Mengmeng Zhang, Shiyong Zhang, Shu Xu, Xiaoxia Ma
Medicine.2017; 96(40): e8200. CrossRef - Wnt7a Deficiency Could Predict Worse Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Kijong Yi, Kyueng-Whan Min, Young Chan Wi, Yeseul Kim, Su-Jin Shin, Min Sung Chung, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(4): 361. CrossRef
- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
- Mucinous Carcinoma with Extensive Signet Ring Cell Differentiation: A Case Report
- Hye Min Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ja Seung Koo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):176-179. Published online December 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.17
- 11,587 View
- 167 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Breast cancers that present with mucin include mucinous carcinoma and carcinoma with signet ring cell differentiation. The former shows extracellular mucin and the latter shows abundant intracellular mucin. Here, we report a case of breast cancer showing both extracellular mucin and extensive signet ring cell differentiation due to abundant intracellular mucin. Unlike mucinous carcinoma, this case had the features of high-grade nuclear pleomorphism, high mitotic index, estrogen receptor negativity, progesterone receptor negativity, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positivity, and ductal type with positivity for E-cadherin. In a case with signet ring cell differentiation, differential diagnosis with metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach and colon is essential. In this case, the presence of accompanied ductal carcinoma in situ component and mammaglobin and gross cystic disease fluid protein-15 positivity were findings that suggested the breast as the origin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Signet ring cell carcinoma of the urachus: survival and pathologic outcomes from the national cancer database
Deerush Kannan Sakthivel, Pushan Prabhakar, Mohamed Javid Raja Iyub, Rohan Garje, Murugesan Manoharan
International Urology and Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research on the Histological Features and Pathological Types of Gastric Adenocarcinoma With Mucinous Differentiation
Nian-Long Meng, Yang-kun Wang, Hai-Li Wang, Jun-Ling Zhou, Su-nan Wang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 95. CrossRef - Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-positive Mucinous Carcinoma with Signet Ring Cell Differentiation, Which Showed Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Yunjeong Jang, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
Journal of Breast Cancer.2019; 22(2): 336. CrossRef
- Signet ring cell carcinoma of the urachus: survival and pathologic outcomes from the national cancer database
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Korean Breast Cancer Patients by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Meta-Analysis of Human Papillomavirus and Breast Cancer
- Jinhyuk Choi, Chungyeul Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim, Jinhwan Lee, Hyeyoon Chang, Aeree Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):442-450. Published online October 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.08
- 14,092 View
- 225 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a well-established oncogenic virus of cervical, anogenital, and oropharyngeal cancer. Various subtypes of HPV have been detected in 0% to 60% of breast cancers. The roles of HPV in the carcinogenesis of breast cancer remain controversial. This study was performed to determine the prevalence of HPV-positive breast cancer in Korean patients and to evaluate the possibility of carcinogenic effect of HPV on breast.
Methods
Meta-analysis was performed in 22 case-control studies for HPV infection in breast cancer. A total of 123 breast cancers, nine intraductal papillomas and 13 nipple tissues of patients with proven cervical HPV infection were tested by real-time polymerase chain reaction to detect 28 subtypes of HPV. Breast cancers were composed of 106 formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) breast cancer samples and 17 touch imprint cytology samples of breast cancers.
Results
The overall odds ratio between breast cancer and HPV infection was 5.43 (95% confidence interval, 3.24 to 9.12) with I2 = 34.5% in meta-analysis of published studies with case-control setting and it was statistically significant. HPV was detected in 22 cases of breast cancers (17.9%) and two cases of intaductal papillomas (22.2%). However, these cases had weak positivity.
Conclusions
These results failed to serve as significant evidence to support the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. Further study with larger epidemiologic population is merited to determine the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
Zhi-yong Liu, Ran Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in human papillomavirus detection for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis: challenges of conventional methods and opportunities for emergent tools
O. Fashedemi, Okoroike C. Ozoemena, Siwaphiwe Peteni, Aderemi B. Haruna, Leshweni J. Shai, Aicheng Chen, Frankie Rawson, Maggie E. Cruickshank, David Grant, Oluwafunmilola Ola, Kenneth I. Ozoemena
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(7): 1428. CrossRef - Bacterial-Viral Interactions in Human Orodigestive and Female Genital Tract Cancers: A Summary of Epidemiologic and Laboratory Evidence
Ikuko Kato, Jilei Zhang, Jun Sun
Cancers.2022; 14(2): 425. CrossRef - Breast cancer association with oncogenic papillomaviruses: papillomaviral DNA detection in breast cancer cells
G. M. Volgareva
Advances in Molecular Oncology.2022; 9(2): 10. CrossRef - Presence of Human Papillomavirus DNA in Malignant Neoplasia and Non-Malignant Breast Disease
Erika Maldonado-Rodríguez, Marisa Hernández-Barrales, Adrián Reyes-López, Susana Godina-González, Perla I. Gallegos-Flores, Edgar L. Esparza-Ibarra, Irma E. González-Curiel, Jesús Aguayo-Rojas, Adrián López-Saucedo, Gretel Mendoza-Almanza, Jorge L. Ayala-
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3648. CrossRef - Risk Role of Breast Cancer in Association with Human Papilloma Virus among Female Population in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Chia-Hsin Liu, Chi-You Liao, Ming-Hsin Yeh, James Cheng-Chung Wei
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2235. CrossRef - HPV-Associated Breast Cancer: Myth or Fact?
Erik Kudela, Eva Kudelova, Erik Kozubík, Tomas Rokos, Terezia Pribulova, Veronika Holubekova, Kamil Biringer
Pathogens.2022; 11(12): 1510. CrossRef - Assessment of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Risk Factors in Egyptian Women With Breast Cancer
Nabila El-Sheikh, Nahla O Mousa, Amany M Tawfeik, Alaa M Saleh, Iman Elshikh, Mohamed Deyab, Faten Ragheb, Manar M Moneer, Ahmed Kawashti, Ahmed Osman, Mohamed Elrefaei
Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Detection by Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (CISH) and p16 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) in Breast Intraductal Papilloma and Breast Carcinoma
Hua Guo, Juan P. Idrovo, Jin Cao, Sudarshana Roychoudhury, Pooja Navale, Louis J. Auguste, Tawfiqul Bhuiya, Silvat Sheikh-Fayyaz
Clinical Breast Cancer.2021; 21(6): e638. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus in Breast Carcinogenesis: A Passenger, a Cofactor, or a Causal Agent?
Rancés Blanco, Diego Carrillo-Beltrán, Juan P. Muñoz, Alejandro H. Corvalán, Gloria M. Calaf, Francisco Aguayo
Biology.2021; 10(8): 804. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of the papillomavirus prevalence in breast cancer fresh tissues
Geilson Gomes de Oliveira, Ana Katherine Gonçalves, José Eleutério, Luiz Gonzaga Porto Pinheiro
Breast Disease.2021; 41(1): 123. CrossRef - Is human papillomavirus associated with breast cancer or papilloma presenting with pathologic nipple discharge?
Fatih Levent Balci, Cihan Uras, Sheldon Marc Feldman
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2019; 19: 100122. CrossRef - Is the HPV virus responsible for the development of breast cancer?
Erik Kudela, Marcela Nachajova, Jan Danko
The Breast Journal.2019; 25(5): 1053. CrossRef - Absence of Human Papillomavirus in Benign and Malignant Breast Tissue
Maryam Kazemi Aghdam, Seyed Alireza Nadji, Azadeh Alvandimanesh, Maliheh Khoddami, Yassaman Khademi
Iranian Journal of Pathology.2019; 14(4): 279. CrossRef - Oncogenic Viruses and Breast Cancer: Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus (MMTV), Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), and Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)
James S. Lawson, Brian Salmons, Wendy K. Glenn
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Viral infections and breast cancer – A current perspective
O.M. Gannon, A. Antonsson, I.C. Bennett, N.A. Saunders
Cancer Letters.2018; 420: 182. CrossRef - Prevalence of EBV, HPV and MMTV in Pakistani breast cancer patients: A possible etiological role of viruses in breast cancer
Wasifa Naushad, Orooj Surriya, Hajra Sadia
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2017; 54: 230. CrossRef
- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
- Pathologic Evaluation of Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Therapy
- Cheol Keun Park, Woo-Hee Jung, Ja Seung Koo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):173-180. Published online April 11, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.02
- 17,638 View
- 562 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Breast cancer, one of the most common cancers in women, has various treatment modalities. Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) has been used in many clinical trials because it is easy to evaluate the treatment response to therapeutic agents in a short time period; consequently, NAT is currently a standard treatment modality for large-sized and locally advanced breast cancers, and its use in early-stage breast cancer is becoming more common. Thus, chances to encounter breast tissue from patients treated with NAT is increasing. However, systems for handling and evaluating such specimens have not been established. Several evaluation systems emphasize a multidisciplinary approach to increase the accuracy of breast cancer assessment. Thus, detailed and systematic evaluation of clinical, radiologic, and pathologic findings is important. In this review, we compare the major problems of each evaluation system and discuss important points for handling and evaluating NAT-treated breast specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of Multimodal Radiomics in Assessing Neoadjuvant Therapeutic Efficacy for Breast Cancer
聪 刘
Journal of Clinical Personalized Medicine.2026; 05(01): 324. CrossRef - Evaluating the Tumor Burden, Histological Changes, and Immune Landscape of Breast Cancer Post-neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Insights From 50 Cases
Arasi Rajesh, Dharma Saranya Gurusamy, Rajalakshmi Manikkam
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a comprehensive subtype-specific analysis
Soo-Young Lee, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Sae Byul Lee, Jisun Kim, Il Yong Chung, Beom Seok Ko, Hee Jeong Kim, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Tru-Cut and Surgical Biopsy Specimens in Breast Carcinoma Cases Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Tuba Devrim, Gamze Erkılınç, Saniye Sevim Tuncer, Helin Tinas Abacı, Fazilet Uğur Duman, Eyup Kebapçı
Dicle Tıp Dergisi.2025; 52(4): 827. CrossRef - Good practice: The experiences with the utilization of residual cancer burden—A single institution study
Anita Sejben, Fanni Hegedűs, Szintia Almási, Márton Berta, Orsolya Oláh‐Németh, Tamás Zombori
Thoracic Cancer.2023; 14(11): 963. CrossRef - Assessing the Correlation of Rate of Pathological Complete Response and Outcome in Post Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Setting and Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
Ahmad Omair, Abdulmohsen Alkushi, Ghaida Alamri, Talal Almojel, Sara Alsadun, Emad Masuadi, Haitham Arabi, Amin E Mohamed, Omalkhair A Abulkhair
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Compression OCT-elastography combined with speckle-contrast analysis as an approach to the morphological assessment of breast cancer tissue
Anton A. Plekhanov, Ekaterina V. Gubarkova, Marina A. Sirotkina, Alexander A. Sovetsky, Dmitry A. Vorontsov, Lev A. Matveev, Sergey S. Kuznetsov, Alexandra Y. Bogomolova, Alexey Y. Vorontsov, Alexander L. Matveyev, Sergey V. Gamayunov, Elena V. Zagaynova,
Biomedical Optics Express.2023; 14(6): 3037. CrossRef - Ambiguity-aware breast tumor cellularity estimation via self-ensemble label distribution learning
Xiangyu Li, Xinjie Liang, Gongning Luo, Wei Wang, Kuanquan Wang, Shuo Li
Medical Image Analysis.2023; 90: 102944. CrossRef - Concurrent Chemo-radiation As a Means of Achieving Pathologic Complete Response in Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Maryam Nemati Shafaee, Shalini Makawita, Bora Lim, Matthew J Ellis, Michelle S Ludwig
Clinical Breast Cancer.2022; 22(4): e536. CrossRef - Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment – How to assess residual disease
Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
The Breast.2022; 62: S25. CrossRef - Efficacy Evaluation of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer by MRI
Yongguang Liu, Mingxiang Wu, Wenyong Tan, Jingshan Gong, Jie Ma, Mohammad Farukh Hashmi
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Role of Soluble IL-6R, TNF-R1/2, and Cell Adhesion Molecules Serum Levels in the Preoperative and Adjuvant Therapy in Women with Nonmetastatic Breast Cancer: A Preliminary Study
Weronika Bulska-Będkowska, Paulina Czajka-Francuz, Sylwia Cisoń-Jurek, Aleksander J. Owczarek, Tomasz Francuz, Jerzy Chudek
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2022; 42(11): 557. CrossRef - The prognostic role of lymph node ratio in breast cancer patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A dose-response meta-analysis
Jinzhao Liu, Yifei Li, Weifang Zhang, Chenhui Yang, Chao Yang, Liang Chen, Mingjian Ding, Liang Zhang, Xiaojun Liu, Guozhong Cui, Yunjiang Liu
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of miR-375-3p, miR-210-3p and Let-7e-5p in the Pathological Response of Breast Cancer Patients to Neoadjuvant Therapy
Lorena Alexandra Lisencu, Andrei Roman, Simona Visan, Eduard-Alexandru Bonci, Andrei Pașca, Emilia Grigorescu, Elena Mustea, Andrei Cismaru, Alexandru Irimie, Cosmin Lisencu, Loredana Balacescu, Ovidiu Balacescu, Oana Tudoran
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1494. CrossRef - Post-Neoadjuvant Treatment Strategies for Patients with Early Breast Cancer
Elisa Agostinetto, Flavia Jacobs, Véronique Debien, Alex De Caluwé, Catalin-Florin Pop, Xavier Catteau, Philippe Aftimos, Evandro de Azambuja, Laurence Buisseret
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5467. CrossRef - Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer—Updates on Therapeutic Implications and Pathologic Assessment
Joshua J. Li, Julia Y. Tsang, Gary M. Tse
Cancers.2021; 13(16): 4233. CrossRef - SPIE-AAPM-NCI BreastPathQ challenge: an image analysis challenge for quantitative tumor cellularity assessment in breast cancer histology images following neoadjuvant treatment
Nicholas Petrick, Shazia Akbar, Kenny H. Cha, Sharon Nofech-Mozes, Berkman Sahiner, Marios A. Gavrielides, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Karen Drukker, Anne L. Martel, for the BreastPathQ Challenge Group
Journal of Medical Imaging.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of digital breast tomosynthesis for predicting response to neoadjuvant systemic therapy in breast cancer patients: A comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and full-field digital mammography
Ryusuke Murakami, Hitomi Tani, Shinichiro Kumita, Nachiko Uchiyama
Acta Radiologica Open.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Los márgenes
Laia Bernet, María Angeles Montero Fernández
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2021; 34: S25. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in non‐metastatic breast cancer: a study on practice trends in a regional cancer treatment service
Edmond Ang, Navin Wewala, Rebecca Carroll, Garry Forgeson, Malcolm Anderson, Jennifer Fernando, Jody Jordan, Richard Isaacs
Internal Medicine Journal.2020; 50(3): 315. CrossRef - Examination of Tumor Regression Grading Systems in Breast Cancer Patients Who Received Neoadjuvant Therapy
Anita Sejben, Renáta Kószó, Zsuzsanna Kahán, Gábor Cserni, Tamás Zombori
Pathology & Oncology Research.2020; 26(4): 2747. CrossRef - Integrating evolutionary dynamics into cancer therapy
Robert A. Gatenby, Joel S. Brown
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2020; 17(11): 675. CrossRef - Assessing the accuracy of conventional gadolinium‐enhanced breast MRI in measuring the nodal response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in breast cancer
Lisa Christine Murphy, Edel Marie Quinn, Zeeshan Razzaq, Claire Brady, Vicki Livingstone, Lorna Duddy, Josephine Barry, Henry Paul Redmond, Mark Anthony Corrigan
The Breast Journal.2020; 26(11): 2151. CrossRef - Early prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response for advanced breast cancer using PET/MRI image deep learning
Joon Ho Choi, Hyun-Ah Kim, Wook Kim, Ilhan Lim, Inki Lee, Byung Hyun Byun, Woo Chul Noh, Min-Ki Seong, Seung-Sook Lee, Byung Il Kim, Chang Woon Choi, Sang Moo Lim, Sang-Keun Woo
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Patterns of Regression in Breast Cancer after Primary Systemic Treatment
Tamás Zombori, Gábor Cserni
Pathology & Oncology Research.2019; 25(3): 1153. CrossRef - The Role of Neutrophil-lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response in Breast Cancer
Hee Yeon Kim, Tae Hyun Kim, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Anbok Lee
Journal of Breast Cancer.2019; 22(3): 425. CrossRef - Higher underestimation of tumour size post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy with breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—A concordance comparison cohort analysis
Wen-Pei Wu, Hwa-Koon Wu, Chih-Jung Chen, Chih-Wie Lee, Shou-Tung Chen, Dar-Ren Chen, Chen-Te Chou, Chi Wei Mok, Hung-Wen Lai, Pascal A. T. Baltzer
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0222917. CrossRef - Multimodal image-guided surgery of HER2-positive breast cancer using [111In]In-DTPA-trastuzumab-IRDye800CW in an orthotopic breast tumor model
Marion M. Deken, Desirée L. Bos, Willemieke S. F. J. Tummers, Taryn L. March, Cornelis J. H. van de Velde, Mark Rijpkema, Alexander L. Vahrmeijer
EJNMMI Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mammographic density is a potential predictive marker of pathological response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
Ida Skarping, Daniel Förnvik, Hanna Sartor, Uffe Heide-Jørgensen, Sophia Zackrisson, Signe Borgquist
BMC Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - ALDH1 and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes as predictors for neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in breast cancer
Anbok Lee, Kyu Yeoun Won, Sung-Jig Lim, Sun Young Cho, Sang-Ah Han, SaeGwang Park, Jeong-Yoon Song
Pathology - Research and Practice.2018; 214(5): 619. CrossRef - Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI and Ultrasound in Breast Cancer
Yunju Kim, Sung Hun Kim, Byung Joo Song, Bong Joo Kang, Kwang-il Yim, Ahwon Lee, Yoonho Nam
Korean Journal of Radiology.2018; 19(4): 682. CrossRef - Outcomes of neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy in stage 2 and 3 non-small cell lung cancer: an analysis of the National Cancer Database
Matthew MacLean, Xin Luo, Shidan Wang, Kemp Kernstine, David E. Gerber, Yang Xie
Oncotarget.2018; 9(36): 24470. CrossRef - Automatic cellularity assessment from post‐treated breast surgical specimens
Mohammad Peikari, Sherine Salama, Sharon Nofech‐Mozes, Anne L. Martel
Cytometry Part A.2017; 91(11): 1078. CrossRef - The importance of tissue confirmation of metastatic disease in patients with breast cancer: lesson from a brain metastasis case
Jingxian Ding, Pinghua Hu, Jun Chen, Xiaobo Wu, Yali Cao
Oncoscience.2016; 3(9-10): 268. CrossRef
- Application of Multimodal Radiomics in Assessing Neoadjuvant Therapeutic Efficacy for Breast Cancer
- Interobserver Variability of Ki-67 Measurement in Breast Cancer
- Yul Ri Chung, Min Hye Jang, So Yeon Park, Gyungyub Gong, Woo-Hee Jung, The Korean Breast Pathology Ki- Study Group
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):129-137. Published online February 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.12.24
- 12,941 View
- 130 Download
- 29 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
As measurement of Ki-67 proliferation index is an important part of breast cancer diagnostics, we conducted a multicenter study to examine the degree of concordance in Ki-67 counting and to find factors that lead to its variability. Methods: Thirty observers from thirty different institutions reviewed Ki-67–stained slides of 20 different breast cancers on whole sections and tissue microarray (TMA) by online system. Ten of the 20 breast cancers had hot spots of Ki-67 expression. Each observer scored Ki-67 in two different ways: direct counting (average vs. hot spot method) and categorical estimation. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of Ki-67 index was calculated for comparative analysis. Results: For direct counting, ICC of TMA was slightly higher than that of whole sections using average method (0.895 vs 0.858). The ICC of tumors with hot spots was lower than that of tumors without (0.736 vs 0.874). In tumors with hot spots, observers took an additional counting from the hot spot; the ICC of whole sections using hot spot method was still lower than that of TMA (0.737 vs 0.895). In categorical estimation, Ki-67 index showed a wide distribution in some cases. Nevertheless, in tumors with hot spots, the range of distribution in Ki-67 categories was decreased with hot spot method and in TMA platform. Conclusions: Interobserver variability of Ki-67 index for direct counting and categorical estimation was relatively high. Tumors with hot spots showed greater interobserver variability as opposed to those without, and restricting the measurement area yielded lower interobserver variability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of Ki-67 labeling index morphometry using deep learning, conventional image analysis, and manual counting
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Kwangil Yim, Phoebe Liang, Joe Yeh, Chifu Chang, Yosep Chong
Translational Oncology.2025; 51: 102159. CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Approaches for Breast Density Estimation from Mammograms: A Comprehensive Review
Khaldoon Alhusari, Salam Dhou
Journal of Imaging.2025; 11(2): 38. CrossRef - Letter re: A critical appraisal of the DATA trial analysis on the prognostic and predictive value of the luminal-like subtype
M. Rizk, K. Mokbel
ESMO Open.2025; 10(5): 105067. CrossRef - Clinico-Histomorphological and Mib-1 Analysis of Recurrent Meningiomas: A Retrospective Study
Sujata Sarangi, Asha Shenoy, Ashvini Kolhe, Kanchan Kothari
Asian Journal of Neurosurgery.2025; 20(04): 785. CrossRef - Emerging Diagnostics and Therapies in Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Critical Review
Jorge H. Hernandez-Felix, Monica Isabel Meneses-Medina, Rachel Riechelmann, Jonathan Strosberg, Rocio Garcia-Carbonero, Jaydira del Rivero
Cancers.2025; 17(22): 3632. CrossRef - Ki-67 Testing in Breast Cancer: Assessing Variability With Scoring Methods and Specimen Types and the Potential Subsequent Impact on Therapy Eligibility
Therese Bocklage, Virgilius Cornea, Caylin Hickey, Justin Miller, Jessica Moss, Mara Chambers, S. Emily Bachert
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2024; 32(3): 119. CrossRef - Interobserver agreement and diagnostic challenges of Congo red staining for amyloid detection on fat pad aspiration biopsies
Levent Trabzonlu, T. Leif Helland, Melanie C. Kwan, Nathalie Kumiega, M. Lisa Zhang, Ivan Chebib, Vanda F. Torous
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2024; 13(5): 359. CrossRef - Assessment of the Predictive Role of Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Patients’ Responses to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Ghizlane Rais, Rania Mokfi, Farah Boutaggount, Meryem Maskrout, Soundouss Bennour, Chaymae Senoussi, Fadoua Rais
European Journal of Breast Health.2024; : 199. CrossRef - Improving the accuracy of reporting Ki-67 IHC by using an AI tool
Sahil Ajit Saraf, Aahan Singh, Wai Po Kevin Teng, Sencer Karakaya, M. Logaswari, Kaveh Taghipour, Rajasa Jialdasani, Li Yan Khor, Kiat Hon Lim, Sathiyamoorthy Selvarajan, Vani Ravikumar, Md Ali Osama, Priti Chatterjee, Santosh KV
Heliyon.2024; 10(22): e40193. CrossRef - Predictive Value of Ki-67 Index in Evaluating Sporadic Vestibular Schwannoma Recurrence: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Kunal Vakharia, Hirotaka Hasegawa, Christopher Graffeo, Mohammad H. A. Noureldine, Salomon Cohen-Cohen, Avital Perry, Matthew L. Carlson, Colin L. W. Driscoll, Maria Peris-Celda, Jamie J. Van Gompel, Michael J. Link
Journal of Neurological Surgery Part B: Skull Base.2023; 84(02): 119. CrossRef - Venous invasion and lymphatic invasion are correlated with the postoperative prognosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm
Sho Kiritani, Junichi Arita, Yuichiro Mihara, Rihito Nagata, Akihiko Ichida, Yoshikuni Kawaguchi, Takeaki Ishizawa, Nobuhisa Akamatsu, Junichi Kaneko, Kiyoshi Hasegawa
Surgery.2023; 173(2): 365. CrossRef - Automated Molecular Subtyping of Breast Carcinoma Using Deep Learning Techniques
S. Niyas, Ramya Bygari, Rachita Naik, Bhavishya Viswanath, Dhananjay Ugwekar, Tojo Mathew, J Kavya, Jyoti R Kini, Jeny Rajan
IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine.2023; 11: 161. CrossRef - Grade Progression and Intrapatient Tumor Heterogeneity as Potential Contributors to Resistance in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Diana Grace Varghese, Jaydira Del Rivero, Emily Bergsland
Cancers.2023; 15(14): 3712. CrossRef - Diagnostic Role and Prognostic Impact of PSAP Immunohistochemistry: A Tissue Microarray Study on 31,358 Cancer Tissues
Laura Sophie Tribian, Maximilian Lennartz, Doris Höflmayer, Noémi de Wispelaere, Sebastian Dwertmann Rico, Clara von Bargen, Simon Kind, Viktor Reiswich, Florian Viehweger, Florian Lutz, Veit Bertram, Christoph Fraune, Natalia Gorbokon, Sören Weidemann, C
Diagnostics.2023; 13(20): 3242. CrossRef - AI-Powered Segmentation of Invasive Carcinoma Regions in Breast Cancer Immunohistochemical Whole-Slide Images
Yiqing Liu, Tiantian Zhen, Yuqiu Fu, Yizhi Wang, Yonghong He, Anjia Han, Huijuan Shi
Cancers.2023; 16(1): 167. CrossRef - Expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors, HER2 protein and Ki-67 proliferation index in breast carcinoma in both tumor tissue and tissue microarray
UP Hacısalihoğlu, MA Dogan
Biotechnic & Histochemistry.2022; 97(4): 298. CrossRef - Diffusive Ki67 and vimentin are associated with worse recurrence-free survival of upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study from bench to bedside
Che Hsueh Yang, Wei Chun Weng, Yen Chuan Ou, Yi Sheng Lin, Li Hua Huang, Chin Heng Lu, Tang Yi Tsao, Chao Yu Hsu, Min Che Tung
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2022; 40(3): 109.e21. CrossRef - Should Ki-67 be adopted to select breast cancer patients for treatment with adjuvant abemaciclib?
P. Tarantino, H.J. Burstein, N.U. Lin, I.E. Krop, E.P. Winer, S.J. Schnitt, E.P. Hamilton, S.A. Hurvitz, H.S. Rugo, G. Curigliano, S.M. Tolaney
Annals of Oncology.2022; 33(3): 234. CrossRef - A novel deep classifier framework for automated molecular subtyping of breast carcinoma using immunohistochemistry image analysis
Tojo Mathew, S. Niyas, C.I. Johnpaul, Jyoti R. Kini, Jeny Rajan
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2022; 76: 103657. CrossRef - Deep learning for the standardized classification of Ki-67 in vulva carcinoma: A feasibility study
Matthias Choschzick, Mariam Alyahiaoui, Alexander Ciritsis, Cristina Rossi, André Gut, Patryk Hejduk, Andreas Boss
Heliyon.2021; 7(7): e07577. CrossRef - Oncotype DX Predictive Nomogram for Recurrence Score Output: The Novel System ADAPTED01 Based on Quantitative Immunochemistry Analysis
Fabio Marazzi, Roberto Barone, Valeria Masiello, Valentina Magri, Antonino Mulè, Angela Santoro, Federica Cacciatori, Luca Boldrini, Gianluca Franceschini, Francesca Moschella, Giuseppe Naso, Silverio Tomao, Maria Antonietta Gambacorta, Giovanna Mantini,
Clinical Breast Cancer.2020; 20(5): e600. CrossRef - Study of Ki-67 index in the molecular subtypes of breast cancer: Inter-observer variability and automated scoring
Divya Meermira, Meenakshi Swain, Swarnalata Gowrishankar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2020; 57(3): 289. CrossRef - Improving the accuracy of gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumor grading with deep learning
Darshana Govind, Kuang-Yu Jen, Karen Matsukuma, Guofeng Gao, Kristin A. Olson, Dorina Gui, Gregory. E. Wilding, Samuel P. Border, Pinaki Sarder
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Practical approaches to automated digital image analysis of Ki-67 labeling index in 997 breast carcinomas and causes of discordance with visual assessment
Ah-Young Kwon, Ha Young Park, Jiyeon Hyeon, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Jong-Han Yu, Se Kyung Lee, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Irina V. Lebedeva
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(2): e0212309. CrossRef - Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens
Soomin Ahn, Junghye Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Sanghui Park, Sun Hee Sung
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(3): 364. CrossRef - Assessment of Ki-67 for Predicting Effective Prognosis in Breast Cancer Subtypes
Sangjung Park, Sunyoung Park, Jungho Kim, Sungwoo Ahn, Kwang Hwa Park, Hyeyoung Lee
Biomedical Science Letters.2018; 24(1): 9. CrossRef - Quantitative tumor heterogeneity assessment on a nuclear population basis
Anne‐Sofie Wessel Lindberg, Knut Conradsen, Rasmus Larsen, Michael Friis Lippert, Rasmus Røge, Mogens Vyberg
Cytometry Part A.2017; 91(6): 574. CrossRef - A comparison of Ki-67 counting methods in luminal Breast Cancer: The Average Method vs. the Hot Spot Method
Min Hye Jang, Hyun Jung Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Yangkyu Lee, So Yeon Park, William B. Coleman
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(2): e0172031. CrossRef - A Novel Breast Cancer Index for Prediction of Distant Recurrence in HR+ Early-Stage Breast Cancer with One to Three Positive Nodes
Yi Zhang, Brock E. Schroeder, Piiha-Lotta Jerevall, Amy Ly, Hannah Nolan, Catherine A. Schnabel, Dennis C. Sgroi
Clinical Cancer Research.2017; 23(23): 7217. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of Ki-67 labeling index morphometry using deep learning, conventional image analysis, and manual counting
- Current Issues and Clinical Evidence in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Breast Cancer
- Sung Gwe Ahn, Joon Jeong, SoonWon Hong, Woo Hee Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):355-363. Published online August 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.29
- 16,170 View
- 244 Download
- 45 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With the advance in personalized therapeutic strategies in patients with breast cancer, there is an increasing need for biomarker-guided therapy. Although the immunogenicity of breast cancer has not been strongly considered in research or practice, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are emerging as biomarkers mediating tumor response to treatments. Earlier studies have provided evidence that the level of TILs has prognostic value and the potential for predictive value, particularly in triple-negative and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer. Moreover, the level of TILs has been associated with treatment outcome in patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. To date, no standardized methodology for measuring TILs has been established. In this article, we review current issues and clinical evidence for the use of TILs in breast cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytokine Networks in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Targets, and Emerging Strategies
María Rosado-Sanz, Nuria Martínez-Alarcón, Adrián Abellán-Soriano, Raúl Golfe, Eva M. Trinidad, Jaime Font de Mora
Biomedicines.2025; 13(8): 1945. CrossRef - Unveiling Metabolic Signatures as Potential Biomarkers in Common Cancers: Insights from Lung, Breast, Colorectal, Liver, and Gastric Tumours
Kha Wai Hon, Rakesh Naidu
Biomolecules.2025; 15(10): 1376. CrossRef - Systemic chemotherapy in metastatic TNBC polarizes effector T cell differentiation
Hye-Yeon Ju, Hyundong Yoon, Seungpil Jung, Serk In Park, Tae Kon Kim, Mi-Ryung Han
Cancer Cell International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune characteristics and clinical significance of peripheral blood lymphocytes in breast cancer
Hongyu Gao, Dengjie Ouyang, Xinyu Guan, Jiachi Xu, Qitong Chen, Liyun Zeng, Jian Pang, Qiongyan Zou, Ke Qian, Wenjun Yi
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision unveiled: Synergistic genomic landscapes in breast cancer—Integrating single‐cell analysis and decoding drug toxicity for elite prognostication and tailored therapeutics
Chenglu Jiang, Shengke Zhang, Lai Jiang, Zipei Chen, Haiqing Chen, Jinbang Huang, Jingyi Tang, Xiufang Luo, Guanhu Yang, Jie Liu, Hao Chi
Environmental Toxicology.2024; 39(6): 3448. CrossRef - Exploring histological predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy response in non–small cell lung cancer
Uiju Cho, Soyoung Im, Hyung Soon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(2): 49. CrossRef - Review: Merging from traditional to potential novel breast cancer biomarkers
Hanan Alismail
Journal of King Saud University - Science.2024; 36(11): 103551. CrossRef - A non-inferiority, phase III trial of gemcitabine plus capecitabine versus gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line therapy and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer
Xiaodong Liu, Weipeng Zhao, Yongsheng Jia, Yehui Shi, Xu Wang, Shufen Li, Pin Zhang, Chen Wang, Chunfang Hao, Zhongsheng Tong
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive and Prognostic Role of Tumor‐Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy
Gaurav Agarwal, K. M. M. Vishvak Chanthar, Shweta Katiyar, Niraj Kumari, Narendra Krishnani, M. Sabaretnam, Gyan Chand, Anjali Mishra, Punita Lal
World Journal of Surgery.2023; 47(5): 1238. CrossRef - The role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer and the research progress of adoptive cell therapy
Ruonan Li, Lili Cao
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Using Self-Assembling ADDomer Platform to Display B and T Epitopes of Type O Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus
Chaowei Luo, Quanhui Yan, Juncong Huang, Jiameng Liu, Yuwan Li, Keke Wu, Bingke Li, Mingqiu Zhao, Shuangqi Fan, Hongxing Ding, Jinding Chen
Viruses.2022; 14(8): 1810. CrossRef - Modification of the Tumor Microenvironment Enhances Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma
Guilan Shi, Megan Scott, Cathryn G. Mangiamele, Richard Heller
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(11): 2429. CrossRef - Assessment of Immune Status in Dynamics for Patients with Cancer Undergoing Immunotherapy
Bacinschi Xenia Elena, Laurentia Nicoleta Gales, Anca Florina Zgura, Laura Iliescu, Rodica Maricela Anghel, Bogdan Haineala, Xiaosheng Wang
Journal of Oncology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Differences in immune-related gene expressions and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes according to chemotherapeutic response in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma
Kyung Un Choi, Ahrong Kim, Jee Yeon Kim, Ki Hyung Kim, Chungsu Hwang, So Jung Lee, Won Young Park, Sejin Jung, Hye Jeong Choi, Kyungbin Kim
Journal of Ovarian Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Predictors of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response in Breast Cancer: A Review
Weilin Xu, Xiu Chen, Fei Deng, Jian Zhang, Wei Zhang, Jinhai Tang
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 5887. CrossRef- Immune phenotype of patients with stage IV metastatic inflammatory breast cancer
Sandra V. Fernandez, Alexander W. MacFarlane, Mowafaq Jillab, Maria F. Arisi, Jennifer Yearley, Lakshmanan Annamalai, Yulan Gong, Kathy Q. Cai, R. Katherine Alpaugh, Massimo Cristofanilli, Kerry S. Campbell
Breast Cancer Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Infiltrating stromal immune cells in inflammatory breast cancer are associated with an improved outcome and increased PD-L1 expression
C. Van Berckelaer, C. Rypens, P. van Dam, L. Pouillon, M. Parizel, K. A. Schats, M. Kockx, W. A. A. Tjalma, P. Vermeulen, S. van Laere, F. Bertucci, C. Colpaert, L. Dirix
Breast Cancer Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The composition of T cell infiltrates varies in primary invasive breast cancer of different molecular subtypes as well as according to tumor size and nodal status
Anna Glajcar, Joanna Szpor, Diana Hodorowicz-Zaniewska, Katarzyna Ewa Tyrak, Krzysztof Okoń
Virchows Archiv.2019; 475(1): 13. CrossRef - Retinoid X receptor agonist LG100268 modulates the immune microenvironment in preclinical breast cancer models
Ana S. Leal, Kayla Zydeck, Sarah Carapellucci, Lyndsey A. Reich, Di Zhang, Jessica A. Moerland, Michael B. Sporn, Karen T. Liby
npj Breast Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Stromal tumor‑infiltrating lymphocytes evaluated on H&E‑stained slides are an independent prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer and ovarian serous carcinoma
Chungsu Hwang, So Lee, Jung Lee, Ki Kim, Dong Suh, Byung‑Su Kwon, Kyung Choi
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The therapeutic candidate for immune checkpoint inhibitors elucidated by the status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC)
Nobumoto Tomioka, Manabu Azuma, Mayuko Ikarashi, Mitsugu Yamamoto, Masako Sato, Ken-ichi Watanabe, Katsushige Yamashiro, Masato Takahashi
Breast Cancer.2018; 25(1): 34. CrossRef - Triple negative breast cancer – prognostic role of immune-related factors: a systematic review
Elisabeth Specht Stovgaard, Dorte Nielsen, Estrid Hogdall, Eva Balslev
Acta Oncologica.2018; 57(1): 74. CrossRef - Lack of effective translational regulation of PLD expression and exosome biogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer cells
Julian Gomez-Cambronero
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2018; 37(2-3): 491. CrossRef - Expression of Myxovirus Resistance A (MxA) Is Associated with Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)–Positive Breast Cancers
So Jeong Lee, Cheong-Soo Hwang, Young-Keum Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Sang-Jeong Ahn, Nari Shin, Jung Hee Lee, Dong Hoon Shin, Kyung Un Choi, Do Youn Park, Chang Hun Lee, Gi Young Huh, Mi Young Sol, Hee Jin Lee, Gyungyub Gong, Jee Yeon Kim, Ahrong Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2017; 49(2): 313. CrossRef - Glutaminase expression is a poor prognostic factor in node-positive triple-negative breast cancer patients with a high level of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
Joo Young Kim, Sun-Hee Heo, Seul Ki Choi, In Hye Song, In Ah Park, Young-Ae Kim, Hye Seon Park, Suk Young Park, Won Seon Bang, Gyungyub Gong, Hee Jin Lee
Virchows Archiv.2017; 470(4): 381. CrossRef - Whole Slide Imaging for Analytical Anatomic Pathology and Telepathology: Practical Applications Today, Promises, and Perils
Alton Brad Farris, Cynthia Cohen, Thomas E. Rogers, Geoffrey H. Smith
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2017; 141(4): 542. CrossRef - Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and breast cancer: Beyond the prognostic and predictive utility
Andrea Ravelli, Giandomenico Roviello, Daniele Cretella, Andrea Cavazzoni, Alessandra Biondi, Maria Rosa Cappelletti, Laura Zanotti, Giuseppina Ferrero, Marco Ungari, Fabrizio Zanconati, Alberto Bottini, Roberta Alfieri, Pier Giorgio Petronini, Daniele Ge
Tumor Biology.2017; 39(4): 101042831769502. CrossRef - Predictive Value of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Assessed by High Endothelial Venule Counts in the Neoadjuvant Setting of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
In Hye Song, Sun-Hee Heo, Won Seon Bang, Hye Seon Park, In Ah Park, Young-Ae Kim, Suk Young Park, Jin Roh, Gyungyub Gong, Hee Jin Lee
Cancer Research and Treatment.2017; 49(2): 399. CrossRef - Lymphocyte count or percentage: which can better predict the prognosis of advanced cancer patients following palliative care?
Weiwei Zhao, Peng Wang, Huixun Jia, Menglei Chen, Xiaoli Gu, Minghui Liu, Zhe Zhang, Wenwu Cheng, Zhenyu Wu
BMC Cancer.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in tumour cell and tumour infiltrating lymphocytes of HER2-positive breast cancer and its prognostic value
Ahrong Kim, So Jeong Lee, Young Keum Kim, Won Young Park, Do Youn Park, Jee Yeon Kim, Chang Hun Lee, Gyungyub Gong, Gi Yeong Huh, Kyung Un Choi
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Negative association between GATA3 and fascin could predict relapse-free and overall survival in patients with breast cancer
Kyueng-Whan Min, Dong-Hoon Kim, Sung-Im Do, Seoung Wan Chae, Kyungeun Kim, Jin Hee Sohn, Jung-Soo Pyo, Hyun Joo Lee, Dong Hyun Kim, Sukjoong Oh, Seon Hyeong Choi, Yong Lai Park, Chan Heun Park, Eun-Kyung Kim, Mi Jung Kwon, Jinwon Seo, Kyoung Min Moon
Virchows Archiv.2016; 468(4): 409. CrossRef - Cytoplasmic expression of high mobility group B1 (HMGB1) is associated with tumor‐infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer
Hee Jin Lee, Ahrong Kim, In Hye Song, In Ah Park, Jong Han Yu, Jin Hee Ahn, Gyungyub Gong
Pathology International.2016; 66(4): 202. CrossRef - Clinical pharmacologic aspects of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy
Kyu-pyo Kim, Hun Jung
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2016; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - The next level of 3D tumour models: immunocompetence
Agata Nyga, Joana Neves, Katerina Stamati, Marilena Loizidou, Mark Emberton, Umber Cheema
Drug Discovery Today.2016; 21(9): 1421. CrossRef - An Examination of the Local Cellular Immune Response to Examples of Both Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) of the Breast and DCIS With Microinvasion, With Emphasis on Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Tumor Infiltrating Lymphoctytes
Ahrong Kim, Sun-Hee Heo, Young-Ae Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Hee Jin Lee
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2016; 146(1): 137. CrossRef - High Ki67/BCL2 index is associated with worse outcome in early stage breast cancer
Kyueng-Whan Min, Dong-Hoon Kim, Sung-Im Do, Jung-Soo Pyo, Seoung Wan Chae, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungeun Kim, Hyun Joo Lee, Dong Hyun Kim, Sukjoong Oh, Seon Hyeong Choi, Yong Lai Park, Chan Heun Park, Mi Jung Kwon, Kyoung Min Moon
Postgraduate Medical Journal.2016; 92(1094): 707. CrossRef - Expression of T-Lymphocyte Markers in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer
Changro Lee, Seho Park, Joo Heung Kim, Sung Mook Lim, Hyung Seok Park, Seung Il Kim, Byeong-Woo Park
Journal of Breast Cancer.2016; 19(4): 385. CrossRef
- Cytokine Networks in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Targets, and Emerging Strategies
- A Review of Inflammatory Processes of the Breast with a Focus on Diagnosis in Core Biopsy Samples
- Timothy M. D’Alfonso, Paula S. Ginter, Sandra J. Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(4):279-287. Published online June 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.06.11
- 28,963 View
- 491 Download
- 34 Web of Science
- 48 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory and reactive lesions of the breast are relatively uncommon among benign breast lesions and can be the source of an abnormality on imaging. Such lesions can simulate a malignant process, based on both clinical and radiographic findings, and core biopsy is often performed to rule out malignancy. Furthermore, some inflammatory processes can mimic carcinoma or other malignancy microscopically, and vice versa. Diagnostic difficulty may arise due to the small and fragmented sample of a core biopsy. This review will focus on the pertinent clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic features of the more commonly encountered inflammatory lesions of the breast that can be characterized in a core biopsy sample. These include fat necrosis, mammary duct ectasia, granulomatous lobular mastitis, diabetic mastopathy, and abscess. The microscopic differential diagnoses for these lesions when seen in a core biopsy sample will be discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimation of fatty acid composition in mammary adipose tissue using deep neural network with unsupervised training
Suneeta Chaudhary, Elizabeth G. Lane, Allison Levy, Anika McGrath, Eralda Mema, Melissa Reichmann, Katerina Dodelzon, Katherine Simon, Eileen Chang, Marcel Dominik Nickel, Linda Moy, Michele Drotman, Sungheon Gene Kim
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.2025; 93(5): 2163. CrossRef - Society of surgical oncology medical student & trainee primer for breast surgical oncology
Marissa K. Boyle, Julia M. Selfridge, Rachel E. Sargent, Y. Everett Warren, Julia M. Chandler, Christopher P. Childers
Surgical Oncology Insight.2025; 2(1): 100129. CrossRef - An update on multimodal imaging strategies for nipple discharge: from detection to decision
Mireia Pitarch, Rodrigo Alcantara, Laura Comerma, Ivonne Vázquez de Las Heras, Javier Azcona, Antonia Wiedemann, Maja Prutki, Eva Maria Fallenberg
Insights into Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign Breast Lesions: Diagnostic Utility and Drawbacks of Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology
Shirish S. Chandanwale, Kumar Roushan, Mallika Agarwal, Madhuri Singh, Abhishek Tambile, Ranjana Roy
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Health Care.2025; 17(1): 39. CrossRef - Squamous Metaplasia of Lactiferous Ducts (SMOLD) in a Male Patient: Clinical, Dermoscopic, and Histopathological Insights
Beata Zagórska, Przemysław Miłosz, Jakub Żółkiewicz, Urszula Maińska, Martyna Sławińska
Diagnostics.2025; 15(19): 2489. CrossRef - Ductal carcinoma in situ: Current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Jelena Petrović, Stefan Stevanović
Srpski medicinski casopis Lekarske komore.2025; 6(3): 318. CrossRef - The diagnostic dilemma of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with an emphasis on histopathologic findings
Kiana Anousha, Behnaz Jahanbin, Farid Azmoudeh Ardalan, Vahid Soleimani, Maryam Azizi, Amin Rezvani
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical profiles, imaging findings and antituberculosis treatment outcome in granulomatous mastitis: An Indian scenario
R. Mithen, R.R. Mahin Nallasivam, Dhanasekar Thangaswamy, T. Mohanapriya
Indian Journal of Tuberculosis.2024; 71(2): 163. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis: A diagnostic challenge—3 year single institutional experience
Adil Aziz Khan, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer, Charanjeet Ahluwalia, Mukul Singh, Sachin Kolte, Sunil Ranga
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(1): 50. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of rifampicin-based triple therapy for non-puerperal mastitis: A single-arm, open-label, prospective clinical trial
Fei Zhou, Huanjie Li, Fei Wang, Liyuan Liu, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhigang Yu
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2024; 140: 25. CrossRef - Periductal Mastitis, a Disease with Distinct Clinicopathological Features from Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis
Fei Zhou, Liyuan Liu, Fei Wang, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhen Yang, Zhigang Yu
Journal of Inflammation Research.2024; Volume 17: 3815. CrossRef - MASTITE GRANULOMATOSA E O DIFÍCIL MANEJO DA DOENÇA: UMA REVISÃO SISTEMÁTICA DE LITERATURA
Samara Alves Messias Viana, Laís Barbosa de Azevedo Bulsoni
REVISTA FOCO.2024; 17(6): e5136. CrossRef - Autoimmune Mastitis in a Patient with Behcet’s Syndrome: A Case Report with Rapid Changes in Radiologic Features and Characteristic Pathologic Findings
Yun Hwa Chang, Suk Jin Park, Joo Heon Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(6): 1221. CrossRef - Possibilities of MRI in the differential diagnosis of non-lactative mastitis and cancer
S. V. Serebryakova, T. A. Shumakova, E. A. Yukhno, O. B. Safronova, A. L. Serebryakov
Medical Visualization.2023; 27(2): 36. CrossRef - Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis in seventy seven-female patients: Management, follow up of an overlooked immune-mediated disease, and review of literature
Amira A. Shahin, Emad Khallaf, Lamiaa A. Salaheldin, Somia A.M. Soliman, Yosra S. Rezk, Marwa H. Niazy
The Egyptian Rheumatologist.2023; 45(3): 183. CrossRef - Increased breast cancer mortality due to treatment delay and needle biopsy type: a retrospective analysis of SEER-medicare
Rashmi Pathak, Macall Leslie, Priya Dondapati, Rachel Davis, Kenichi Tanaka, Elizabeth Jett, Inna Chervoneva, Takemi Tanaka
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(4): 627. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and therapeutic strategy of granulomatous mastitis accompanied by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: a retrospective cohort study
ShunBo Li, Qian Huang, PeiPei Song, XiaoRong Han, ZeYu Liu, Lin Zhou, Ping Ning
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano Uncaria gambir as Chemopreventive Agent Against Breast Cancer
Andika Pramudya Wardana, Nanik Siti Aminah, Alfinda Novi Kristanti, Mochamad Zakki Fahmi, Haninda Iffatuz Zahrah, W Widiyastuti, Hendrix Abdul Ajiz, Ummi Zubaidah, Priangga Adi Wiratama, Yoshiaki Takaya
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 4471. CrossRef - Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
Gulisa Turashvili, Xiaoxian Li
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(10): 1133. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Inflammatory granulomatous mastitis caused by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: A clinical challenge
I.M. Brouwer de Koning, A. Lemson, N.H.M. Renders, M. Bessems, P.T.G.A. Nooijen, W.A. Draaisma, K. Bosscha
Clinical Infection in Practice.2022; 15: 100147. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Exocrine gland structure-function relationships
Sameed Khan, Sarah Fitch, Sarah Knox, Ripla Arora
Development.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision pathology as applied to breast core needle biopsy evaluation: implications for management
Laura C. Collins
Modern Pathology.2021; 34: 48. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis, watch and wait is a good option
Gökay Çetinkaya, Ramazan Kozan, Ahmet Cihangir Emral, Ekmel Tezel
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2021; 190(3): 1117. CrossRef - Mammary duct ectasia in adult females; risk factors for the disease, a case control study
Ayad Ahmad Mohammed
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2021; 62: 140. CrossRef - Palpable Lumps after Mastectomy: Radiologic-Pathologic Review of Benign and Malignant Masses
Rend Al-Khalili, Ali Alzeer, Giang-Kimthi Nguyen, Erin P. Crane, Judy H. Song, Janice L. Jeon, Michael Nellamattathil, Erini V. Makariou, Victoria L. Mango
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(4): E967. CrossRef - A case report of TB versus idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with erythema nodosum, reactive arthritis, cough, and headache
Fatma Ben Abid, Hussam Abdel Rahman S. Al Soub
The Aging Male.2020; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Imaging features of granulomatous mastitis in 36 patients with new sonographic signs
Afsaneh Alikhassi, Fahimeh Azizi, Fereshteh Ensani
Journal of Ultrasound.2020; 23(1): 61. CrossRef - Secreciones mamarias
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Ginecología-Obstetricia.2020; 56(1): 1. CrossRef - Mastitis in Autoimmune Diseases: Review of the Literature, Diagnostic Pathway, and Pathophysiological Key Players
Radjiv Goulabchand, Assia Hafidi, Philippe Van de Perre, Ingrid Millet, Alexandre Thibault Jacques Maria, Jacques Morel, Alain Le Quellec, Hélène Perrochia, Philippe Guilpain
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 958. CrossRef - Factors associated with treatment duration and recurrence rate of complicated mastitis
Ming-Jui Tsai, Wei-Chia Huang, Jann-Tay Wang, Ming-Yang Wang, Yi-Hsuan Lee, Shu-Wen Lin, Sung-Ching Pan, Shan-Chwen Chang
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.2020; 53(6): 875. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis: an update
Jessie M Wu, Gulisa Turashvili
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 73(8): 445. CrossRef - Coryneform Bacteria in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis: Morphological Diagnosis in Breast Biopsies
David Oddó, Angeles Stefanelli, Alejandra Villarroel, Gonzalo P. Méndez
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 27(4): 380. CrossRef - Sonographic features of inflammatory conditions of the breast
Alice Febery, Ian Bennett
Australasian Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2019; 22(3): 165. CrossRef - Écoulements mamelonnaires
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Gynécologie.2019; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Etiología de la mastitis crónica: propuesta de secuencia diagnóstica
A. García-Vilanova Comas, J. Galbis Caravajal, V. Sabater Marco, C.A. Fuster Diana, F. Villalba Ferrer, M. Bruna Esteban, C. Zaragozá Fernández
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2018; 45(3): 98. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Manifestations at Multimodality Imaging and Pitfalls
Cedric W. Pluguez-Turull, Jennifer E. Nanyes, Cristina J. Quintero, Hamza Alizai, Daniel D. Mais, Kenneth A. Kist, Nella C. Dornbluth
RadioGraphics.2018; 38(2): 330. CrossRef - Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii in granulomatous mastitis: Analysis of formalin‐fixed, paraffin‐embedded biopsy specimens by immunostaining using low‐specificity bacterial antisera and real‐time polymerase chain reaction
Mari Fujii, Yasuyoshi Mizutani, Takahiko Sakuma, Kouichiro Tagami, Kiichiro Okamoto, Yasushi Kuno, Michihiko Harada, Koichi Kubouchi, Yutaka Tsutsumi
Pathology International.2018; 68(7): 409. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis Presenting as a Breast Pseudotumor: Case Reports with Review of the Literature
Nour Abdul Halim, Imad Uthman, Rayan Rammal, Hazem I. Assi
Case Reports in Rheumatology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - UTILITY OF FNAC IN UNCOMMON INFLAMMATORY AND REACTIVE LESIONS OF BREAST: AN UNSUSPECTED CLINICAL SCENARIO
Rallapalli Rajyalakshmi, Mohammad Akhtar, Rani Vijaya Bhaskar, Kada Venkataramana, Guttikonda Nageswararao, Rayachoti Sridhar
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2018; 5(44): 3070. CrossRef - Inflammatory breast disease: A pictorial essay with radiological‐pathological correlation
Rusiru P Gunawardena, Deepika Gunawardena, Cecily Metcalf, Donna Taylor, Liz Wylie
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2017; 61(1): 70. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis associated with Corynebacterium including Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii
Kate J. Johnstone, Jennifer Robson, Sarah G. Cherian, Jenny Wan Sai Cheong, Kris Kerr, Judith F. Bligh
Pathology.2017; 49(4): 405. CrossRef - Is contrast‐enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) helpful in differentiating diabetic mastopathy from breast carcinoma?
María del Mar Travieso Aja, Gloria Santana López, Mario Rodríguez Rodríguez, Octavio P Luzardo
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2016; 60(5): 639. CrossRef - Lesiones inflamatorias mamarias benignas
Andrés García-Vilanova Comas, Vicente Sabater Marco, Carlos Fuster Diana, Francisco Villalba Ferrer, José Medrano González, Ramón Gómez Contreras
Revista Española de Patología.2016; 49(3): 169. CrossRef - Granulomatous lobular mastitis
Fei Zhou, Li‐Xiang Yu, Zhong‐Bing Ma, Zhi‐Gang Yu
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2016; 2(1): 17. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Cytologic and Histologic Study of 65 Egyptian Patients
Thanaa El A. Helal, Lobna S. Shash, Somaia A. Saad El-Din, Sally M. Saber
Acta Cytologica.2016; 60(5): 438. CrossRef
- Estimation of fatty acid composition in mammary adipose tissue using deep neural network with unsupervised training
- Cystic Brunner’s Gland Hamartoma in the Gastric Body: A Case Report
- Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Hyun Yee Cho, Yoon Jae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):371-374. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.371
- 10,903 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref
- Low-Grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast with Diverse Expression Patterns of Myoepithelial Cell Markers on Immunohistochemistry: A Case Study
- Yoon Jin Cha, Gi Jeong Kim, Byeong-Woo Park, Ja Seung Koo
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(3):229-233. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.229
- 8,362 View
- 66 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This paper reports a case of low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma (LGASC) arising in a 69-year-old woman, who presented with a 1-cm palpable mass on her right breast. Core needle biopsy diagnosed the mass as a fibroadenoma. After six months, the mass increased in size, and the patient received subsequent mammotome excision. On microscopic examination, bland-looking small glands were infiltrating into the fibrotic stroma with lymphocytic infiltrates at the periphery. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed relatively easily detectable myoepithelial cells along the outside in each of the glandular structures with variable degrees of squamous metaplasia. Based on histologic features, the patient was diagnosed with LGASC. LGASC is a rare variant of metaplastic carcinoma, which is characterized by a favorable prognosis. Due to the bland cytology and presence of myoepithelial cells, LGASC can be misdiagnosed as benign lesion. Additionally, inconsistent expression of myoepithelial markers could aid the diagnosis of LGASC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low-Grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast Masquerading as a Fibroepithelial Lesion on Core Biopsy: A Challenging Case
Natthawadee Laokulrath, Esther Chuwa, Mihir Gudi, Puay Hoon Tan
Pathobiology.2024; 91(6): 455. CrossRef - Low-Grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast: A Single-Center Retrospective Study and a Systematic Literature Review
Anselm Tamminen, Pia Boström
Cancers.2024; 16(24): 4246. CrossRef - High rate of PIK3CA mutations but no TP53 mutations in low‐grade adenosquamous carcinoma of the breast
Guillaume Bataillon, Laetitia Fuhrmann, Elodie Girard, Emanuelle Menet, Marick Laé, Mathieu Capovilla, Isabelle Treilleux, Laurent Arnould, Frederique Penault‐Llorca, Roman Rouzier, Caterina Marchiò, Ivan Bieche, Anne Vincent‐Salomon
Histopathology.2018; 73(2): 273. CrossRef - Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma Coexisting with Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast: A Case Report
Ryoko Oi, Ichiro Maeda, Yoshio Aida, Yukari Yabuki, Toru Nishikawa, Yoshihide Kanemaki, Koichiro Tsugawa, Masayuki Takagi
Journal of St. Marianna University.2017; 8(1): 31. CrossRef - Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast
Haruko SAKAMOTO, Akihiko SHIMANA, Hideaki HORI, Kouki TOKUDA, Hitoshi TSUBOUCHI, Miki TAKENAKA, Rin YAMAGUCHI
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2017; 78(9): 1983. CrossRef - Small Glandular Proliferations of the Breast With Absent or Attenuated Myoepithelial Reactivity by Immunohistochemistry: A Review Focusing on the Differential Diagnosis and Interpretative Pitfalls
Paula S. Ginter, Sandra J. Shin, Timothy M. D'Alfonso
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2016; 140(7): 651. CrossRef - Bilateral synchronous low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma of the breast: A Case report with review of the current literature
J.L. Senger, P. Meiers, R. Kanthan
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2015; 14: 53. CrossRef - A Nation-Wide Cancer Registry-Based Study of Adenosquamous Carcinoma in Taiwan
Yuan-Tzu Lan, Kuo-Hung Huang, Chien-An Liu, Ling-Chen Tai, Ming-Huang Chen, Yee Chao, Anna Fen-Yau Li, Shih-Hwa Chiou, Yi-Ming Shyr, Chew-Wun Wu, Wen-Liang Fang, Sheng-Nan Lu
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(10): e0139748. CrossRef
- Low-Grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Breast Masquerading as a Fibroepithelial Lesion on Core Biopsy: A Challenging Case
- Primary Sigmoid Adenocarcinoma Metastasis to the Breast in a 28-Year-Old Female: A Case Study and a Review of Literature
- Amna Ahmad, Kweku Baiden-Amissah, Adegoke Oyegade, Mohammed Absar, Kate Swainson, Sami Titi
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):58-61. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.58
- 9,336 View
- 52 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metastasis to the breast from colorectal carcinoma is rare, only a few cases have been reported in the literature, and no cases have been reported in a young, 28-year-old patient. This report confirms the occurrence of the disease in a younger age group. The patient was referred to the Breast Clinic with a history of a gradually increasing lump in her right breast for two weeks' duration. On clinical examination, a 2-cm firm lump was noted in the upper inner quadrant of the right breast, which was clinically benign; however, histological examination of the breast core biopsy together with immunohistochemistry confirmed metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma. The primary colorectal carcinoma was later confirmed to be a stage pT4N2M1 tumor, and the Duke stage was C1. Histology with immunohistochemistry is very important in the diagnosis of cases of this nature, but the clinical correlation should be taken into consideration at multidisciplinary team meetings to decide the final management of the patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Breast mass as the first sign of metastasis from rectal carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
Jiawei Xu, Chao Liu, Chengdong Yu, Tenghua Yu, Fan Fan, Xiaofang Zhang, Chuansheng Huang, Wen Chen, Zhengkui Sun, Meng Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A case report of multiple bilateral breast metastases after colorectal cancer
Khaled Arnaout, Nouran Hawa, Sarab Agha, Lama Kadoura, Marwa Aloulou, Kusay Ayoub
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2021; 81: 105759. CrossRef - Metastatic Breast Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma from a Colonic Primary: Review of a Rare Case Report
Ghazaleh Shaker, Hayedeh Haeri, Behnaz Jahanbin
International Journal of Cancer Management.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast metastasis from rectal cancer with BRAF V600E mutation: a case report with a review of the literature
Hiroko Hasegawa, Yoko Nagata, Yuko Sakakibara, Masakazu Miyake, Kiyoshi Mori, Norikazu Masuda, Masayuki Mano, Shoichi Nakazuru, Hisashi Ishida, Eiji Mita
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 13(2): 153. CrossRef - Colonic mucinous adenocarcinoma with secondary in the breast: A case report and literature review
Ameera Balhareth, Abdullah A. AlQatari, Fozan Aldulaijan, Amani Joudeh
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 76: 364. CrossRef - Breast metastasis from colorectal cancer treated by multimodal therapy
Tien-Chan Hsieh, Chao-Wen Hsu
Medicine.2019; 98(51): e18016. CrossRef - A case series of metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies
Tanvi Vaidya, Subhash Ramani, Ashita Rastogi
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging.2018; 28(04): 470. CrossRef - Metástasis mamaria de un adenocarcinoma mucinoso de colon: descripción de un caso y revisión de la literatura
Marta Seoane Vigo, María Berdeal Díaz, Lourdes Galán Raposo, Fabio Ares Farpón, Alejandro García Varona, Luis González Crespo
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2017; 30(1): 28. CrossRef - Metastases of transverse colon cancer to bilateral ovaries (Krukenberg tumor) and the left breast: A case report
Xin-Yu Luo, Jue Wang, Jia Zhao, Rui Chen, Xiao-Ming Zha
Oncology Letters.2017; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Metastasis of rectal signet ring adenocarcinoma to the breast in a young woman after 10 years, a rare case report and review of the literature
Bita Geramizadeh, Ali Mohammad Bananzadeh, Mohammad Reza Sasani, Asieh Khorshidi, Mahsa Marzban
Cancer Treatment Communications.2016; 7: 58. CrossRef - Metastatic Colonic Adenocarcinoma in Breast: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature
Jiten P. Kothadia, Rezina Arju, Monica Kaminski, Arvind Ankireddypalli, Sushil Duddempudi, Jonathan Chow, Shah Giashuddin
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef
- Breast mass as the first sign of metastasis from rectal carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
- Cystic Benign Phyllodes Tumor in the Inguinal Region
- Jai Hyang Go
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):583-586. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.583
- 9,291 View
- 38 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The present lesion was the first reported case of a benign intracystic phyllodes tumor in the inguinal region. We report the case of a 51-year-old female patient who presented with an inguinal mass. A clinical diagnosis of malignant lymphoma was considered in this case. The resected tumor was well-circumscribed and showed numerous papillary nodular protrusions into a central cystic cavity (3.5×2.5 cm). The microscopic findings showed hyperplastic epithelium-lined cysts with leaf-like intraluminal epithelium-lined bland stromal projections. The epithelial cell linings were strongly positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- BENIGN PHYLLODES TUMOR ARISING IN AXILLARY BREAST TISSUE; A RARE CASE WITH AVAILABLE REVIEW OF LITERATURE
MONICA DASH, PRAGNYA PARAMITA MISHRA, PREMANAND PANDA
International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research.2025; : 124. CrossRef - Benign phyllodes tumor arising from accessory breast tissue of the axilla: An inquisitive rarity
Sonam Sharma
Saudi Surgical Journal.2024; 12(1): 54. CrossRef - Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of metastatic pleural lesion with pleural effusion in patients with breast carcinoma
P. M. Kotlyarov, I. D. Lagkueva, N. I. Sergeev
Russian Pulmonology.2019; 29(1): 112. CrossRef - Mama ectópica en la región inguinal
V.Y. Presas, L.M. Mastronardi, S. Saucedo, E. Rojas Bilbao
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2017; 44(2): 89. CrossRef
- BENIGN PHYLLODES TUMOR ARISING IN AXILLARY BREAST TISSUE; A RARE CASE WITH AVAILABLE REVIEW OF LITERATURE
- Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau, α-Tubulin and βIII-Tubulin Expression in Breast Cancer
- Soyoung Im, Changyoung Yoo, Ji-Han Jung, Ye-Won Jeon, Young Jin Suh, Youn Soo Lee, Hyun Joo Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):534-540. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.534
- 9,062 View
- 62 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The microtubule-associated protein Tau binds to both inner and outer surfaces of microtubules, leading to tubulin assembly and microtubule stabilization. The aim of this study was to evaluate the significance of Tau, α-tubulin, and βIII-tubulin expression in breast carcinoma and to assess their relationships with disease progression in the context of taxane treatment.
Methods Immunohistochemical expressions of Tau, α-tubulin, and βIII-tubulin were assessed in 183 breast cancer cases. Expression was correlated with clinicopathologic parameters, disease progression and overall survival.
Results Tau expression was correlated with lymph node metastasis and estrogen receptor (ER) positivity (p=.003 and p<.001, respectively). Loss of α-tubulin was significantly correlated with distant metastasis (p=.034). Loss of βIII-tubulin was correlated with lymph node metastasis and ER positivity (p=.004 and p<.001, respectively). In taxane-treated cases, Tau expression and loss of α-tubulin and βIII-tubulin expression were related to disease progression (p=.001, p=.028, and p=.030, respectively). Tau expression was associated with a worse survival rate in taxane-treated patients (p=.049).
Conclusions Tau expression and loss of α-tubulin and βIII-tubulin expression were correlated with aggressive behavior in taxane-treated breast cancer. Further evaluation of Tau, α-tubulin and βIII-tubulin may be useful in predicting clinical behavior and seeking therapeutic measures in taxane-based chemotherapy for breast cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytoskeletal dynamics in breast cancer: mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities
RamaRao Malla, Anshu Tumbali, Pavani Chode, Krithika Manda, Anuveda Sree Samudrala, Yerusha Nuthalapati, Charanteja Mangam, Priyamvada Bhamidipati, Mundla Srilatha, Ganji Purnachandra Nagaraju
Journal of the National Cancer Center.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Genes Related to Motility in an Ionizing Radiation and Estrogen Breast Cancer Model
Tania Koning, Gloria M. Calaf
Biology.2024; 13(11): 849. CrossRef - Tubulin Isotypes: Emerging Roles in Defining Cancer Stem Cell Niche
Tessy Thomas Maliekal, Dhrishya Dharmapal, Suparna Sengupta
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - RAD6 inhibition enhances paclitaxel sensitivity of triple negative breast cancer cells by aggravating mitotic spindle damage
Brittany M. Haynes, Kristen Cunningham, Malathy P. V. Shekhar
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Paclitaxel and Doxorubicin Therapy of ßIII-Tubulin, Carbonic Anhydrase IX, and Survivin in Chemically Induced Breast Cancer in Female Rat
Alena Pastornická, Silvia Rybárová, Slávka Drahošová, Jozef Mihalik, Andrea Kreheľová, Andriana Pavliuk-Karachevtseva, Ingrid Hodorová
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(12): 6363. CrossRef - Intelligently thermoresponsive flower-like hollow nano-ruthenium system for sustained release of nerve growth factor to inhibit hyperphosphorylation of tau and neuronal damage for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Hui Zhou, Youcong Gong, Yanan Liu, Anlian Huang, Xufeng Zhu, Jiawei Liu, Guanglong Yuan, Li Zhang, Ji-an Wei, Jie Liu
Biomaterials.2020; 237: 119822. CrossRef - HE4 promotes collateral resistance to cisplatin and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer cells
J. R. Ribeiro, C. Schorl, N. Yano, N. Romano, K. K. Kim, R. K. Singh, R. G. Moore
Journal of Ovarian Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A strategy to identify housekeeping genes suitable for analysis in breast cancer diseases
Tatiana M. Tilli, Cláudio da Silva Castro, Jack A. Tuszynski, Nicolas Carels
BMC Genomics.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased expression of αTubulin is associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer after surgical resection
Chao Lin, Guo-chao Zhao, Ya-dong Xu, Dan-song Wang, Da-yong Jin, Yuan Ji, Wen-hui Lou, Wen-chuan Wu
Oncotarget.2016; 7(37): 60657. CrossRef - Oblongifolin C inhibits metastasis by up-regulating keratin 18 and tubulins
Xiaoyu Wang, Yuanzhi Lao, Naihan Xu, Zhichao Xi, Man Wu, Hua Wang, Xiyi Li, Hongsheng Tan, Menghong Sun, Hongxi Xu
Scientific Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of human MAPT gene expression
Marie-Laure Caillet-Boudin, Luc Buée, Nicolas Sergeant, Bruno Lefebvre
Molecular Neurodegeneration.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cytoskeletal dynamics in breast cancer: mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities
- Hedgehog Related Protein Expression in Breast Cancer: Gli-2 Is Associated with Poor Overall Survival
- Soyoung Im, Hyun Joo Choi, Changyoung Yoo, Ji-Han Jung, Ye-Won Jeon, Young Jin Suh, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):116-123. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.116
- 9,668 View
- 98 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is known to play a critical role in various malignancies, but its clinicopathologic role in breast cancer is yet to be established.
Methods Tissue microarray blocks from 334 cases of breast cancer were prepared. The expression of six Hh signaling proteins including sonic hedgehog (Shh), patched (Ptch), smoothened (Smo), and the glioma-associated oncogene (Gli)-1, Gli-2, and Gli-3 were analyzed immunohistochemically.
Results The expression of Hh signaling proteins was significantly correlated with some prognostic factors including the correlation of lymph node metastasis with the expression of Shh (p=0.001) and Ptch (p=0.064), the correlation of the stages with Shh and Gli-3 expression (p=0.007 and p=0.024, respectively), the correlation of the nuclear grade with the Smo (p=0.004) and Gli-3 (p=0.000), and the correlation of the histologic grade with the Ptch (p=0.016), Smo (p=0.007), and Gli-3 (p=0.000). The Shh, Ptch, Smo, Gli-1, and Gli-2 expression was significantly different between the phenotypes (p=0.000, p=0.001, p=0.004, p=0.039, and p=0.031, respectively). Gli-2 expression was correlated with a worse overall survival outcome (p=0.012).
Conclusions Hh pathway activation is correlated with a more aggressive clinical behavior in breast carcinomas. The comparison of phenotypes suggested that the Hh pathway may be a useful therapeutic target for breast carcinoma. Patients with Gli-2 expression had a significantly lower overall survival rate and, therefore, it showed promise as a prognostic marker.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysregulation of deubiquitination in breast cancer
Lili Kong, Xiaofeng Jin
Gene.2024; 902: 148175. CrossRef - siRNA treatment targeting integrin α11 overexpressed via EZH2-driven axis inhibits drug-resistant breast cancer progression
Prakash Chaudhary, Kiran Yadav, Ho Jin Lee, Keon Wook Kang, Jongseo Mo, Jung-Ae Kim
Breast Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implicating clinical utility of altered expression of PTCH1 & SMO in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Hitarth V. Patel, Jigna S. Joshi, Franky D. Shah
Journal of Molecular Histology.2024; 55(4): 379. CrossRef - A clinicopathological exploration of Hedgehog signaling: implications in oral carcinogenesis
Hitarth V. Patel, Jigna S. Joshi, Franky D. Shah
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(18): 16525. CrossRef - GLI3 and androgen receptor are mutually dependent for their malignancy-promoting activity in ovarian and breast cancer cells
Min Lin, Haiyan Zhu, Qi Shen, Lu-Zhe Sun, Xueqiong Zhu
Cellular Signalling.2022; 92: 110278. CrossRef - Persistent Properties of a Subpopulation of Cancer Cells Overexpressing the Hedgehog Receptor Patched
Álvaro Javier Feliz Morel, Anida Hasanovic, Aurélie Morin, Chloé Prunier, Virginie Magnone, Kevin Lebrigand, Amaury Aouad, Sarah Cogoluegnes, Judith Favier, Claude Pasquier, Isabelle Mus-Veteau
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(5): 988. CrossRef - Case Report: Submucosal gastroblastoma with a novel PTCH1::GLI2 gene fusion in a 58-year-old man
Cuimin Chen, Junliang Lu, Huanwen Wu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Higher Expressions of SHH and AR Are Associated with a Positive Receptor Status and Have Impact on Survival in a Cohort of Croatian Breast Cancer Patients
Ivan Budimir, Čedna Tomasović-Lončarić, Kristina Kralik, Josipa Čonkaš, Domagoj Eljuga, Rado Žic, Božo Gorjanc, Hrvoje Tucaković, Doroteja Caktaš, Josip Jaman, Valentino Lisek, Zlatko Vlajčić, Krešimir Martić, Petar Ozretić
Life.2022; 12(10): 1559. CrossRef - New insight into the role of PTCH1 protein in serous ovarian carcinomas
Valentina Karin‑Kujundzic, Adriana Covarrubias‑Pinto, Anita Skrtic, Semir Vranic, Ljiljana Serman
International Journal of Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hedgehog gene expression patterns among intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic relevance
Araceli García-Martínez, Ariadna Pérez-Balaguer, Fernando Ortiz-Martínez, Eloy Pomares-Navarro, Elena Sanmartín, Marta García-Escolano, Yoel G. Montoyo-Pujol, Elena Castellón-Molla, Gloria Peiró
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 223: 153478. CrossRef - Coexpression of Epha10 and Gli3 Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Migration
Jing Peng, Danhua Zhang
Journal of Investigative Medicine.2021; 69(6): 1215. CrossRef - The Role of Smoothened-Dependent and -Independent Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Tumorigenesis
Jian Yi Chai, Vaisnevee Sugumar, Mohammed Abdullah Alshawsh, Won Fen Wong, Aditya Arya, Pei Pei Chong, Chung Yeng Looi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(9): 1188. CrossRef - HER2-mediated GLI2 stabilization promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis of breast cancer cells
Parul Gupta, Nehal Gupta, Neel M. Fofaria, Alok Ranjan, Sanjay K. Srivastava
Cancer Letters.2019; 442: 68. CrossRef - Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Breast Cancer: Pathogenesis and Therapeutics
Natalia Riobo-Del Galdo, Ángela Lara Montero, Eva Wertheimer
Cells.2019; 8(4): 375. CrossRef - Carbonic anhydrase XII expression is linked to suppression of Sonic hedgehog ligand expression in triple negative breast cancer cells
G. Guerrini, J. Durivault, I. Filippi, M. Criscuoli, S. Monaci, J. Pouyssegur, A. Naldini, F. Carraro, S.K. Parks
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 516(2): 408. CrossRef - Sonic hedgehog and Wnt/β-catenin pathways mediate curcumin inhibition of breast cancer stem cells
Xiaoting Li, Xiaoqian Wang, Chunfeng Xie, Jianyun Zhu, Yu Meng, Yue Chen, Yuan Li, Ye Jiang, Xue Yang, Shijia Wang, Jiaqi Chen, Qi Zhang, Shanshan Geng, Jieshu Wu, Caiyun Zhong, Yu Zhao
Anti-Cancer Drugs.2018; 29(3): 208. CrossRef - Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog Inhibitors Have the Potential of Suppressing Cancer Stem Cells of Breast Cancer
Kuo-Shyang Jeng, Chi-Juei Jeng, I-Shyan Sheen, Szu-Hua Wu, Ssu-Jung Lu, Chih-Hsuan Wang, Chiung-Fang Chang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(5): 1375. CrossRef - Cancer Stem Cell Metabolism and Potential Therapeutic Targets
Vusala Snyder, Tamika C. Reed-Newman, Levi Arnold, Sufi Mary Thomas, Shrikant Anant
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting the Multidrug Transporter Ptch1 Potentiates Chemotherapy Efficiency
Anida Hasanovic, Isabelle Mus-Veteau
Cells.2018; 7(8): 107. CrossRef - Combined inhibition of GLI and FLT3 signaling leads to effective anti-leukemic effects in human acute myeloid leukemia
Emily-Marie Latuske, Hauke Stamm, Marianne Klokow, Gabi Vohwinkel, Jana Muschhammer, Carsten Bokemeyer, Manfred Jücker, Maxim Kebenko, Walter Fiedler, Jasmin Wellbrock
Oncotarget.2017; 8(17): 29187. CrossRef - Prognostic role of Gli1 expression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis
Bilan Wang, Ting Yu, Yuzhu Hu, Mengmeng Xiang, Haoning Peng, Yunzhu Lin, Lu Han, Lingli Zhang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(46): 81088. CrossRef - Inhibition of Ciliogenesis Promotes Hedgehog Signaling, Tumorigenesis, and Metastasis in Breast Cancer
Nadia B. Hassounah, Martha Nunez, Colleen Fordyce, Denise Roe, Ray Nagle, Thomas Bunch, Kimberly M. McDermott
Molecular Cancer Research.2017; 15(10): 1421. CrossRef - The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway contributes to the development of salivary gland neoplasms regardless of perineural infiltration
Manuela Torres Andion Vidal, Sílvia Vanessa Lourenço, Fernando Augusto Soares, Clarissa Araújo Gurgel, Eduardo J. B. Studart, Ludmila de Faro Valverde, Iguaracyra Barreto de Oliveira Araújo, Eduardo Antônio Gonçalves Ramos, Flávia Caló de Aquino Xavier, J
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(7): 9587. CrossRef - Cancer stem cells and HER2 positive breast cancer: The story so far
Deep Shah, Clodia Osipo
Genes & Diseases.2016; 3(2): 114. CrossRef - Tamoxifen Resistance: Emerging Molecular Targets
Milena Rondón-Lagos, Victoria Villegas, Nelson Rangel, Magda Sánchez, Peter Zaphiropoulos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(8): 1357. CrossRef - The Hedgehog signaling pathway is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients with the CD44+/CD24− phenotype
Haishan Zhao, Hongtao Tang, Qinghuan Xiao, Miao He, Lin Zhao, Yingzi Fu, Huizhe Wu, Zhaojin Yu, Qian Jiang, Yuanyuan Yan, Feng Jin, Minjie Wei
Molecular Medicine Reports.2016; 14(6): 5261. CrossRef - Significance of the hedgehog pathway-associated proteins Gli-1 and Gli-2 and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated proteins Twist and E-cadherin in hepatocellular carcinoma
Hyung Wook Chun, Ran Hong
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(3): 1753. CrossRef - Taxane‐induced hedgehog signaling is linked to expansion of breast cancer stem‐like populations after chemotherapy
Jennifer Sims‐Mourtada, Lynn M. Opdenaker, Joshua Davis, Kimberly M. Arnold, Daniel Flynn
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2015; 54(11): 1480. CrossRef - Loss of Tumor Suppressor ARID1A Protein Expression Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Primary Breast Cancer
Hyun Deuk Cho, Jong Eun Lee, Hae Yoen Jung, Mee-Hye Oh, Ji-Hye Lee, Si-Hyong Jang, Kyung-Ju Kim, Sun Wook Han, Sung Yong Kim, Han Jo Kim, Sang Byung Bae, Hyun Ju Lee
Journal of Breast Cancer.2015; 18(4): 339. CrossRef - Prognostic impact of the expression of Hedgehog proteins in cervical carcinoma FIGO stages I–IV treated with radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy
Louise Bohr Mordhorst, Cecilia Ahlin, Bengt Sorbe
Gynecologic Oncology.2014; 135(2): 305. CrossRef - Sonic hedgehog signaling may promote invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by activating MMP-9 and E-cadherin expression
Hai-Xia Fan, Shan Wang, Hong Zhao, Nian Liu, Dong Chen, Miao Sun, Jin-Hua Zheng
Medical Oncology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dysregulation of deubiquitination in breast cancer
EGFR Gene Amplification and Protein Expression in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast- Won Hwangbo, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Sangjeong Ahn, Seojin Kim, Kyong Hwa Park, Chul Hwan Kim, Insun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):107-115. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.107
- 14,041 View
- 82 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a surrogate marker for basal-like breast cancer. A recent study suggested that EGFR may be used as a target for breast cancer treatment.
Methods A total of 706 invasive ductal carcinomas (IDC) of the breast were immunophenotyped, and 82 cases with EGFR protein expression were studied for
EGFR gene amplification.Results EGFR protein was expressed in 121 of 706 IDCs (17.1%); 5.9% were of luminal type, 25.3% of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) type, and 79.3% of basal-like tumors.
EGFR gene amplification and high polysomy (fluorescentin situ hybridization [FISH]-positive) were found in 18 of 82 cases (22.0%); 41.2% of the HER-2+, EGFR+, cytokeratin 5/6- (CK5/6-) group, 11.2% of the HER-2-, EGFR+, CK5/6- group, and 19.1% of the HER-2-, EGFR+, CK5/6+ group. FISH-positive cases were detected in 8.3% of the EGFR protein 1+ expression cases, 15.9% of 2+ expression cases, and 38.5% of 3+ expression cases. In group 2, the tumors had a high Ki-67 labeling (>60%), but the patients showed better disease-free survival than those with tumors that co-expressed HER-2 or CK5/6.Conclusions EGFR-directed therapy can be considered in breast cancer patients with EGFR protein overexpression and gene amplification, and its therapeutic implication should be determined in HER-2 type breast cancer patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An overview of phenylsulfonylfuroxan-based nitric oxide donors for cancer treatment
Chao Gao, Xingyu Li, Tong Liu, Wanning Wang, Jianhui Wu
Bioorganic Chemistry.2025; 154: 108020. CrossRef - Identification of a cross-talk between EGFR and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in HepG2 liver cancer cells
Gurjinder Singh, Md Mehedi Hossain, Aadil Qadir Bhat, Mir Owais Ayaz, Nasima Bano, Rafiqa Eachkoti, Mohd Jamal Dar
Cellular Signalling.2021; 79: 109885. CrossRef - Blocking c-MET/ERBB1 Axis Prevents Brain Metastasis in ERBB2+ Breast Cancer
Shailendra K. Gautam, Ranjana K. Kanchan, Jawed A. Siddiqui, Shailendra K. Maurya, Sanchita Rauth, Naveenkumar Perumal, Pranita Atri, Ramakanth C. Venkata, Kavita Mallya, Sameer Mirza, Moorthy P. Ponnusamy, Vimla Band, Sidharth Mahapatra, Maneesh Jain, Su
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 2838. CrossRef - Evaluation of lapatinib cytotoxicity and genotoxicity on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line
Mona A.M. Abo-Zeid, Mahmoud T. Abo-Elfadl, Amira M. Gamal-Eldeen
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2019; 71: 103207. CrossRef - Improved characterization of the relationship between long intergenic non‐coding RNA Linc00152 and the occurrence and development of malignancies
Jiasheng Xu, Jingjing Guo, Yangkai Jiang, Yujun Liu, Kaili Liao, Zhonghua Fu, Zhenfang Xiong
Cancer Medicine.2019; 8(10): 4722. CrossRef - Relationship between EGFR expression and subcellular localization with cancer development and clinical outcome
Ge Yan, Mohamed E.M. Saeed, Sebastian Foersch, Jose Schneider, Wilfried Roth, Thomas Efferth
Oncotarget.2019; 10(20): 1918. CrossRef - A novel matrine derivative WM622 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
Xiao Sun, Xiao-bin Zhuo, Yi-ping Hu, Xuan Zheng, Qing-jie Zhao
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2018; 449(1-2): 47. CrossRef - lncRNA LINC00152 knockdown had effects to suppress biological activity of lung cancer via EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway
Yan Zhang, Cheng Xiang, Yuling Wang, Yuanyuan Duan, Ci Liu, Yongli Jin, Yajing Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2017; 94: 644. CrossRef - Copy Number Profiling of MammaPrint™ Genes Reveals Association with the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Patients
Areej Fatima, Fomaz Tariq, Muhammad Faraz Arshad Malik, Muhammad Qasim, Farhan Haq
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(3): 246. CrossRef - Evaluation of serum epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in correlation to circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer
Malgorzata Banys-Paluchowski, Isabell Witzel, Sabine Riethdorf, Brigitte Rack, Wolfgang Janni, Peter A. Fasching, Erich-Franz Solomayer, Bahriye Aktas, Sabine Kasimir-Bauer, Klaus Pantel, Tanja Fehm, Volkmar Müller
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - EGFR Is Regulated by TFAP2C in Luminal Breast Cancer and Is a Target for Vandetanib
James P. De Andrade, Jung M. Park, Vivian W. Gu, George W. Woodfield, Mikhail V. Kulak, Allison W. Lorenzen, Vincent T. Wu, Sarah E. Van Dorin, Philip M. Spanheimer, Ronald J. Weigel
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2016; 15(3): 503. CrossRef - Prognostic and predictive values of EGFR overexpression and EGFR copy number alteration in HER2-positive breast cancer
H J Lee, A N Seo, E J Kim, M H Jang, Y J Kim, J H Kim, S-W Kim, H S Ryu, I A Park, S-A Im, G Gong, K H Jung, H J Kim, S Y Park
British Journal of Cancer.2015; 112(1): 103. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor protein overexpression and gene amplification are associated with aggressive biological behaviors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
GANG LIN, XIAO-JIANG SUN, QIAN-BO HAN, ZHUN WANG, YA-PING XU, JIA-LEI GU, WEI WU, GU ZHANG, JIN-LIN HU, WEN-YONG SUN, WEI-MIN MAO
Oncology Letters.2015; 10(2): 901. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Classification of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas
Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyung Han Nam, An Na Seo, Sumi Yun, Kyung Ju Kim, Hwa Jin Cho, Sung Hye Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(6): 541. CrossRef - A Comparison of Tumor Biology in Primary Ductal CarcinomaIn SituRecurring as Invasive Carcinoma versus a NewIn Situ
Wenjing Zhou, Christine Johansson, Karin Jirström, Anita Ringberg, Carl Blomqvist, Rose-Marie Amini, Marie-Louise Fjallskog, Fredrik Wärnberg
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
- An overview of phenylsulfonylfuroxan-based nitric oxide donors for cancer treatment
- Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: Cytologic Finding and Expression of MUC5 Are Different from Mucinous Carcinoma
- Sung Eun Kim, Ji Hye Park, SoonWon Hong, Ja Seung Koo, Joon Jeong, Woo-Hee Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):611-616. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.611
- 9,629 View
- 66 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (MCA) in the breast is a rare neoplasm. There have been 13 cases of primary breast MCA reported. The MCA presents as a large, partially cystic mass in postmenopausal woman with a good prognosis. The microscopic findings resemble those of ovarian, pancreatic, or appendiceal MCA. The aspiration findings showed mucin-containing cell clusters in the background of mucin and necrotic material. The cell clusters had intracytoplasmic mucin displacing atypical nuclei to the periphery. Histologically, the tumor revealed an abundant mucin pool with small floating clusters of mucin-containing tumor cells. There were also small cysts lined by a single layer of tall columnar mucinous cells, resembling those of the uterine endocervix. The cancer cells were positive for mucin (MUC) 5 and negative for MUC2 and MUC6. This mucin profile is different from ordinary mucinous carcinoma and may be a unique characteristic of breast MCA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- BMP2 alterations in mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: insights from whole-exome sequencing
Zhenyu Li, Yi Gong, Guangxin Li, Qingming Jiang, Juanhui Dong, Rui Chen
PeerJ.2025; 13: e19948. CrossRef - Primary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast commonly harbours TP53 mutations and PI3K/AKT pathway alterations
Cheng Xu, Jing Wu, Ying Ding, Zhihong Zhang, Cong Wang
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(6): 1235. CrossRef - Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast harbours TRPS1 expressions and PIK3CA alterations
Wei‐Yu Chen, Yu‐Hsuan Hu, Yu‐Hsin Tsai, Jen‐Fan Hang, Puay Hoon Tan, Chih‐Jung Chen
Histopathology.2024; 84(3): 550. CrossRef - Pure mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast with the rare lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: A case report with review of literature
Yash Hasmukhbhai Prajapati, Vishal Bhabhor, Kahan Samirkumar Mehta, Mithoon Barot, Husen Boriwala, Mohamed Omar
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - HER2‐positive mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast coexisting with invasive lobular carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature
Ismail Guzelis, Betul Bolat Kucukzeybek, Mehmet Ali Uyaroglu, Melek Bekler Gokova, Gulten Sezgin, Yuksel Kucukzeybek
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: A case report and literature review
Xi Cao, Yongchao Luo, Songjie Shen, Xinyu Ren
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mammary mucinous cystadenocarcinoma with long-term follow-up: molecular information and literature review
Ting Lei, Yong Qiang Shi, Tong Bing Chen
Diagnostic Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast Intermixed with Pleomorphic Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: The First Report of This Rare Association
Federica Vegni, Nicoletta D’Alessandris, Angela Santoro, Giuseppe Angelico, Giulia Scaglione, Angela Carlino, Damiano Arciuolo, Michele Valente, Stefania Sfregola, Maria Natale, Alejandro Martin Sanchez, Valeria Masciullo, Gian Franco Zannoni, Antonino Mu
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(6): 948. CrossRef - Special Histologic Type and Rare Breast Tumors – Diagnostic Review and Clinico-Pathological Implications
Benjamin Yongcheng Tan, Elaine Hsuen Lim, Puay Hoon Tan
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2022; 15(1): 29. CrossRef - Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: a new entity with broad differentials—a case report
Kanwalpreet Kaur, Ashini Shah, Jahnvi Gandhi, Priti Trivedi
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: distinctive histopathologic and genetic characteristics
Minjung Jung
Kosin Medical Journal.2022; 37(3): 176. CrossRef - Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: A Rare Case Report With Review of Literature
Ekta Jain, Abhishek Kumar, Raajul Jain, Shivani Sharma
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2021; 29(7): 740. CrossRef - Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: Report of 2 Cases Including One With Long-Term Local Recurrence
Anupma Nayak, Ira J. Bleiweiss, Kimberly Dumoff, Tawfiqul A. Bhuiya
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 26(8): 749. CrossRef - Mucinous breast carcinoma with tall columnar cells
N Tsoukalas, M Kiakou, M Tolia, ID Kostakis, M Galanopoulos, G Nakos, D Tryfonopoulos, G Kyrgias, G Koumakis
The Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England.2018; 100(5): e132. CrossRef - Radiologic Findings of Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
Minjung Seong, Eun Young Ko, Boo-Kyung Han, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Se Kyung Lee, Jeong Eon Lee
Journal of Breast Cancer.2016; 19(3): 330. CrossRef - Primary Mucinous Cystadenocarcinoma of the Breast with Endocervical-Like Mucinous Epithelium
Dong-Liang Lin, Ji-Lin Hu, Shi-Hong Shao, Dong-Mei Sun, Ji-Gang Wang
Breast Care.2013; 8(6): 445. CrossRef
- BMP2 alterations in mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the breast: insights from whole-exome sequencing
- Methylation and Immunoexpression of
p16INK4a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Primary Breast Cancer Tissue and Their Quantitativep16INK4a Hypermethylation in Plasma by Real-Time PCR - Jae Jun Lee, Eunkyung Ko, Junhun Cho, Ha Young Park, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Jin Nam, Duk-Hwan Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):554-561. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.554
- 9,581 View
- 56 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The
p16INK4a gene methylation has been reported to be a major tumorigenic mechanism.Methods We evaluated the methylation status of the
p16INK4a genes in 231 invasive breast cancer and 90 intraductal carcinoma specimens using a methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and p16 protein expression using immunohistochemistry. The quantity of cell-free methylatedp16INK4a DNA in the plasma samples of 200 patients with invasive breast cancer was also examined using a fluorescence-based real-time polymerase chain reaction assay.Results The frequencies of
p16INK4a methylation in invasive and intraductal tumors were 52.8% (122/231) and 57.8% (52/90), respectively. The p16 protein was overexpressed in 145 of the 231 invasive carcinomas (62.8%) and 63 of the 90 intraductal carcinomas (70%). High p16 expression in invasive carcinomas correlated significantly with a high histologic grade, a negative estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status, p53 immunoreactivity and high Ki-67 expression with immunohistochemistry. In addition, the methylation index ofp16INK4a was significantly higher in the cancer patients than the normal controls (p<0.001).Conclusions High p16 immunoreactivity correlated with a loss of differentiation in breast carcinomas and high frequency of
p16INK4a promoter methylation in both invasive and intraductal carcinomas, suggesting it may be involved in the pathogenesis of breast cancer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s
Hua Yang, Yu Fang, Haijuan Wang, Ting Lu, Qihua Chen, Hui Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epigenetic Silencing of p16INK4a gene in Sporadic Breast Cancer
Satya P. Singh, Mallika Tewari, Alok K. Singh, Raghvendra R. Mishra, Hari S. Shukla
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2023; 14(4): 822. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Chia-Jung Li, Yen-Dun Tony Tzeng, Yi-Han Chiu, Hung-Yu Lin, Ming-Feng Hou, Pei-Yi Chu
Cancers.2021; 13(12): 2978. CrossRef - Mechanisms of resistance to estrogen receptor modulators in ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancer
Jin Zhang, Qianying Wang, Qing Wang, Jiangran Cao, Jiafu Sun, Zhengmao Zhu
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2020; 77(4): 559. CrossRef - Aberrantly Methylated cfDNA in Body Fluids as a Promising Diagnostic Tool for Early Detection of Breast Cancer
Igor Stastny, Pavol Zubor, Karol Kajo, Peter Kubatka, Olga Golubnitschaja, Zuzana Dankova
Clinical Breast Cancer.2020; 20(6): e711. CrossRef - Epigenetic modulation of BRCA‐1 and MGMT genes, and histones H4 and H3 are associated with breast tumors
Parisa Paydar, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Hamid Zeynali Nejad, Hamed Akbari, Moslem Abolhassani, Vahid Moazed, Mohammad Hadi Nematollahi, Ghasem Ebrahimi, Hossein Fallah
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(8): 13726. CrossRef - The 9p21 locus: A potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker in breast cancer
Mahdi Rivandi, Mohammad‐Sadegh Khorrami, Hamid Fiuji, Soodabeh Shahidsales, Malihe Hasanzadeh, Mir Hadi Jazayeri, Seyed Mahdi Hassanian, Gordon A. Ferns, Nafiseh Saghafi, Amir Avan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(7): 5170. CrossRef - p16INK4a overexpression as a predictor of survival in ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Sheetal Chauhan, Seema Sen, Anjana Sharma, Seema Kashyap, Radhika Tandon, Mandeep S Bajaj, Neelam Pushker, Murugesan Vanathi, Shyam S Chauhan
British Journal of Ophthalmology.2018; 102(6): 840. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer
Ju-Han Lee, Hoiseon Jeong, Jung-Woo Choi, Hwa Eun Oh, Young-Sik Kim
Medicine.2018; 97(42): e12862. CrossRef - EZH2 inhibition sensitizes tamoxifen‑resistant breast cancer cells through cell cycle regulation
Si Chen, Fan Yao, Qinghuan Xiao, Qiannan Liu, Yikun Yang, Xuejuan Li, Guanglie Jiang, Takayoshi Kuno, Yue Fang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Aberrant promoter methylation of cancer-related genes in human breast cancer
Liang Wu, Ye Shen, Xianzhen Peng, Simin Zhang, Ming Wang, Guisheng Xu, Xianzhi Zheng, Jianming Wang, Cheng Lu
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(6): 5145. CrossRef - Centrosome aberrations in human mammary epithelial cells driven by cooperative interactions between p16INK4a deficiency and telomere-dependent genotoxic stress
Daniel Domínguez, Purificación Feijoo, Aina Bernal, Amaia Ercilla, Neus Agell, Anna Genescà, Laura Tusell
Oncotarget.2015; 6(29): 28238. CrossRef - Relationships Betweenp16Gene Promoter Methylation and Clinicopathologic Features of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 27 Cohort Studies
Yan-Zhi Chen, Dan Liu, Yu-Xia Zhao, He-Tong Wang, Ya Gao, Ying Chen
DNA and Cell Biology.2014; 33(10): 729. CrossRef - Endocrine disruption of the epigenome: a breast cancer link
Kevin C Knower, Sarah Q To, Yuet-Kin Leung, Shuk-Mei Ho, Colin D Clyne
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2014; 21(2): T33. CrossRef - Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p16 and p27, demonstrate different expression patterns in thymoma and thymic carcinoma
Mutsuko Omatsu, Toshiaki Kunimura, Tetsuya Mikogami, Akira Shiokawa, Atsuko Masunaga, Tomoko Nagai, Akihiko Kitami, Takashi Suzuki, Mitsutaka Kadokura
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2014; 62(11): 678. CrossRef - Limoniastrum guyonianum aqueous gall extract induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells involving p16INK4A re-expression related to UHRF1 and DNMT1 down-regulation
Mounira Krifa, Mahmoud Alhosin, Christian D Muller, Jean-Pierre Gies, Leila Chekir-Ghedira, Kamel Ghedira, Yves Mély, Christian Bronner, Marc Mousli
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating tumor-related DNA in cancer patients
Diego M Marzese, Hajime Hirose, Dave S B Hoon
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2013; 13(8): 827. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and trichostatin A synergistically inhibit human lymphoma cell proliferation through epigenetic modification of p16INK4a
DAN-SEN WU, JIAN-ZHEN SHEN, AI-FANG YU, HAI-YING FU, HUA-RONG ZHOU, SONG-FEI SHEN
Oncology Reports.2013; 30(6): 2969. CrossRef
- Progress in epigenetic research of breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis since the 2000s
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease in the Breast with Increased IgG4 Expressing Plasma Cells: A Case Report
- Yoon Jin Cha, Woo Ick Yang, Se Ho Park, Ja Seung Koo
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):489-493. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.489
- 9,582 View
- 54 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) can present in any anatomic site, but breast involvement is rarely reported. Recently, a relationship between RDD and IgG4-related sclerosing disease has been suggested. Here we report another case of RDD with overlapping features of IgG4-related sclerosing disease occurring in a right breast of a 62-year-old female. On microscopic examination, the mass demonstrated a characteristic zonal pattern of proliferation of large polygonal histiocytes and lymphoplasma cells with stromal fibrosis. Emperipolesis was observed in histiocytes with abundant cytoplasm, which showed immunoreactivity for S-100 protein and CD68; the diagnosis of RDD was made. Sheets of plasma cells in the fibrotic stroma demonstrated positive reactions for IgG and IgG4. The mean count of IgG4-positive plasma cells was 100.2/high power field, and the ratio of IgG4/IgG was 56.7%. Additional findings of stromal fibrosis and obliteration of preexisting breast lobules suggested overlapping features with IgG4-related sclerosing disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From Tumor Suspicion to Immune Revelation: A Breast Lump Signals IgG4-related Disease
Renu Singh, Gurwinder Kaur, Md Ali Osama, Chitresh Kumar, Devender Bairwa
Indian Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Kathryn W Zamora, Stefanie Zalasin, Ami Desai, Hua Guo
Journal of Breast Imaging.2025; 7(5): 576. CrossRef - Extranodal Rosai–Dorfman Disease With Increased IgG4-Positive Plasma Cells Involving the Breast: A Case Report With Review of the Literature
Raymond Chimatira, Raisa Wessels
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis and management of Rosai–Dorfman disease of the breast: Case report and literature review
Jessman King Lun Lo, Sara Wai Wun Fung, Zara Chui San Tsang
Surgical Practice.2024; 28(4): 229. CrossRef - IgG4-related Breast Disease: Review of the Literature
Helana Jeries, Yolanda Braun-Moscovici, Alexandra Balbir-Gurman
Rambam Maimonides Medical Journal.2024; 15(4): e0018. CrossRef - Pathology of IgG4-related sclerosing mastitis
Polycarp Erivwo, Gulisa Turashvili
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2021; 74(8): 475. CrossRef - Rosai–Dorfman Disease: Breast Involvement—Case Report and Literature Review
George Iancu, Nicolae Gica, Laura Mihaela Mustata, Anca Maria Panaitescu, Danut Vasile, Gheorghe Peltecu
Medicina.2021; 57(11): 1167. CrossRef - Sonographic features of Rosai‐Dorfman disease in the breast: A case report
Gi W. Shin, Young M. Park, Young J. Heo, Jin W. Baek, Yoo J. Lee, Ji Y. Han, Hayoung Park
Journal of Clinical Ultrasound.2020; 48(2): 108. CrossRef - Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Breast With Variable IgG4+ Plasma Cells
Jenny C. Hoffmann, Chieh-Yu Lin, Siddhartha Bhattacharyya, Olga K. Weinberg, Karen M. Chisholm, Michael Bayerl, Michael Cascio, Girish Venkataraman, Kimberly Allison, Megan Troxell, Chung-Che Chang, Adam Bagg, Tracy I. George, Dennis O’Malley, Robert S. O
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 43(12): 1653. CrossRef - Rosai-Dorfman disease presenting as a breast mass
Ding Dai, Qi Cai, Nasreen A. Vohra, Jan Wong, Zsuzsanna P. Therien, Karlene Hewan-Lowe, Ann Sutton
Archives of Pathology and Clinical Research.2019; 3(1): 008. CrossRef - Erdheim-Chester Disease Involving Lymph Nodes and Liver Clinically Mimicking Lymphoma: A Case Report
Yeoun Eun Sung, Yoon Seo Lee, Jieun Lee, Kyo Young Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(3): 183. CrossRef - Enfermedad de Rosai-Dorfman en mama de paciente masculino: una entidad rara
Paola Iturralde Rosas-Priego, José Daniel Flores-Alatriste, Daniela Stuht López, Javier Gómez Pedroso-Rea, Cecilia Ortiz-de-Iturbide, Jorge Valenzuela-Tamariz, Manuel Ubiergo-García
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2018; 31(2): 72. CrossRef - Increased Immunoglobulin G4-positive Plasma Cells in Lymphadenoma of the Salivary Gland: An Immunohistochemical Comparison Among Lymphoepithelial Lesions
Jiyoon Kim, Joon Seon Song, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim, Kyung-Ja Cho
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2018; 26(6): 420. CrossRef - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease of the Breast in a Male Patient
Taisia Vitkovski, Galina S. Marder, Dominic A. Filardi, Ekta Gupta, Frank Breuer
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2017; 25(8): 711. CrossRef - Extranodal manifestation of Rosai-Dorfman disease in the breast tissue
Qiao Zhou, Umer Ansari, Nandan Keshav, Fiona Davis, Maria Cundiff
Radiology Case Reports.2016; 11(3): 125. CrossRef - Rosai-Dorfman Disease with Massive Cutaneous Nodule on the Shoulder and Back
Han Ma, Yue Zheng, Guoxing Zhu, Jie Wu, Chun Lu, Wei Lai
Annals of Dermatology.2015; 27(1): 71. CrossRef - IgG4-related disease of the breast: a systemic disease whose mammary manifestations mimic breast cancer
Takuya Moriya, Hisashi Hirakawa, Maki Nagashima, Mitsuhiko Yasuda, Izo Kimijima
International Cancer Conference Journal.2015; 4(2): 67. CrossRef - Primary Cutaneous Marginal IgG4 Lymphoma and Rosai–Dorfman's Disease Coexisting in Several Lesions of the Same Patient
Salma Machan, Camino Medina, Socorro María Rodríguez-Pinilla, José M. Suárez-Peñaranda, Yolanda Castro, Paula Molés, Celia Requena, Carles Saus, Luis Requena, Carlos Santonja
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2015; 37(5): 413. CrossRef - A subset of Rosai–Dorfman disease cases show increased IgG4‐positive plasma cells: another red herring or a true association with IgG4‐related disease?
Madhu P Menon, Moses O Evbuomwan, Juan Rosai, Elaine S Jaffe, Stefania Pittaluga
Histopathology.2014; 64(3): 455. CrossRef - Freiburg Neuropathology Case Conference: A Partially Calcified, Dura-based Tumour of the Frontal Lobe
C. A. Taschner, O. Staszewski, R. Jabbarli, A. Keuler, M. Prinz
Clinical Neuroradiology.2013; 23(1): 63. CrossRef - Pulmonary IgG4+ Rosai-Dorfman disease
Karim El-Kersh, Rafael L Perez, Juan Guardiola
BMJ Case Reports.2013; 2013: bcr2012008324. CrossRef
- From Tumor Suspicion to Immune Revelation: A Breast Lump Signals IgG4-related Disease
- Expressional Difference of RHEB, HDAC1, and WEE1 Proteins in the Stromal Tumors of the Breast and Their Significance in Tumorigenesis
- Minseob Eom, Airi Han, Mi Jeong Lee, Kwang Hwa Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):324-330. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.324
- 9,476 View
- 56 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Fibroadenoma (FA) and phyllodes tumor (PT) are stromal tumors of breast and are histologically similar. There are no established differences in tumorigenesis and oncogene expression among them. Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB) plays an important role in cell growth and cell-cycle control, histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an important factor in breast tumor progression and prognosis, and WEE1 homolog (WEE1) functions as a tumor suppressor. No studies on the expressional differences of these proteins in FA and PT have been reported to date.
Methods The expression of these proteins in FA, PT, and normal breast was compared. We used 102 cases of FA and 25 cases of benign PT.
Results In epithelial cells, the expression of RHEB, HDAC1, and WEE1 was lowest in PT, higher in FA, and most enhanced in normal breast. In addition, the expression of RHEB and HDAC1 was higher in the stromal cells of PT than in FA and normal breast.
Conclusions Both epithelial and stromal cells of FA and PT express these proteins, which indicates that epithelial cells play an important role in the development of stromal tumors. In addition, the expressional differences of these proteins may be associated with the tumorigenesis of breast stromal tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gut microbiota-derived 3-phenylpropionic acid promotes intestinal epithelial barrier function via AhR signaling
Jun Hu, Jianwei Chen, Xiaojian Xu, Qiliang Hou, Jing Ren, Xianghua Yan
Microbiome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genome-scale meta-analysis of breast cancer datasets identifies promising targets for drug development
Reem Altaf, Humaira Nadeem, Mustafeez Mujtaba Babar, Umair Ilyas, Syed Aun Muhammad
Journal of Biological Research-Thessaloniki.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Wee1 Kinase: A Potential Target to Overcome Tumor Resistance to Therapy
Francesca Esposito, Raffaella Giuffrida, Gabriele Raciti, Caterina Puglisi, Stefano Forte
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10689. CrossRef - MiR-503 enhances the radiosensitivity of laryngeal carcinoma cells via the inhibition of WEE1
Huimin Ma, Rong Lian, Zhiyan Wu, Xiao Li, Wenfa Yu, Yun Shang, Xixia Guo
Tumor Biology.2017; 39(10): 101042831770622. CrossRef - Rheb phosphorylation is involved in p38-regulated/activated protein kinase-mediated tumor suppression in liver cancer
MIN ZHENG, SHENGBING ZANG, LINNA XIE, XUETING FANG, YU ZHANG, XIAOJIE MA, JINGFENG LIU, DEXIN LIN, AIMIN HUANG
Oncology Letters.2015; 10(3): 1655. CrossRef - Expression of CDK1Tyr15, pCDK1Thr161, Cyclin B1 (Total) and pCyclin B1Ser126 in Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Relations with Clinicopatological Features and Prognosis
Zhihui Wang, Ana Slipicevic, Mette Førsund, Claes G. Trope, Jahn M. Nesland, Ruth Holm, Xin-Yuan Guan
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(4): e0121398. CrossRef - High expression of wee1 is associated with malignancy in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma patients
Gry Irene Magnussen, Ellen Hellesylt, Jahn M Nesland, Claes G Trope, Vivi Ann Flørenes, Ruth Holm
BMC Cancer.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Gut microbiota-derived 3-phenylpropionic acid promotes intestinal epithelial barrier function via AhR signaling
- HDAC1 Expression in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast and Its Value as a Good Prognostic Factor
- Minseob Eom, Sung Soo Oh, Sayamaa Lkhagvadorj, Airi Han, Kwang Hwa Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):311-317. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.311
- 8,733 View
- 60 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is associated with the expression and function of estrogen receptors and the proliferation of tumor cells, and has been considered a very important factor in breast tumor progression and prognosis. Several studies have reported an association between HDAC1 expression and poorer prognosis in cancers including breast cancer, with a few exceptions. However, because of the dearth of studies on HDAC1 expression in breast cancer, its significance for breast cancer prognosis has not been well defined. Therefore, we examined HDAC1 expression in invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), the most common breast cancer, and investigated its potential prognostic significance.
Methods We used 203 IDC tissue samples. Immunohistochemical stains for HDAC1 and real-time polymerase chain reaction for HDAC1 mRNA were performed and the results were compared to generally well-established prognostic factors in breast cancer and patient survival rates.
Results HDAC1 expression was significantly reduced in proportion to higher histologic grade, higher nuclear pleomorphism score, and higher mitotic counts, and with lower estrogen receptor expression. Furthermore, it was significantly associated with the survival rate.
Conclusions HDAC1 expression is a good prognostic indicator in IDC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are HDAC and Glutamine Synthetase Expression Levels Associated with Ga68-DOTATATE PET/CT Data and Prognosis in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours?
Ozge Ulas, Ramazan Oguz Yuceer, Zekiye Hasbek, Hatice Ozer, Kerim Seker, Mukaddes Yılmaz, Mahmut Uçar
Medicina.2025; 61(11): 1952. CrossRef - SNP rs4971059 predisposes to breast carcinogenesis and chemoresistance via TRIM46‐mediated HDAC1 degradation
Zihan Zhang, Xiaoping Liu, Lei Li, Yang Yang, Jianguo Yang, Yue Wang, Jiajing Wu, Xiaodi Wu, Lin Shan, Fei Pei, Jianying Liu, Shu Wang, Wei Li, Luyang Sun, Jing Liang, Yongfeng Shang
The EMBO Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Androgen Receptor and Histone Deacetylase 1 Expression on the Prognosis of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Choong Man Lee, Il Yong Chung, Yangsoon Park, Keong Won Yun, Hwi Gyeong Jo, Hye Jin Park, Hee Jin Lee, Sae Byul Lee, Hee Jeong Kim, Beom Seok Ko, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son, Sei Hyun Ahn, Jisun Kim
Journal of Breast Cancer.2020; 23(6): 610. CrossRef - Prognostic and clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in breast cancer: A meta-analysis
Weiqiang Qiao, Heyang Liu, Ruidong Liu, Qipeng Liu, Ting Zhang, Wanying Guo, Peng Li, Miao Deng
Clinica Chimica Acta.2018; 483: 209. CrossRef - HDAC1 triggers the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells via upregulation of interleukin-8
Zhaohui Tang, Sijuan Ding, Honglin Huang, Pengfei Luo, Bohua Qing, Siyuan Zhang, Ruoting Tang
Biological Chemistry.2017; 398(12): 1347. CrossRef - Identification of novel histone deacetylase 1 inhibitors by combined pharmacophore modeling, 3D-QSAR analysis, in silico screening and Density Functional Theory (DFT) approaches
Sanjay K. Choubey, Richard Mariadasse, Santhosh Rajendran, Jeyakanthan Jeyaraman
Journal of Molecular Structure.2016; 1125: 391. CrossRef - The Potential of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Therapy
Namita Chatterjee, Martin Tenniswood
Breast Cancer Management.2015; 4(2): 85. CrossRef
- Are HDAC and Glutamine Synthetase Expression Levels Associated with Ga68-DOTATATE PET/CT Data and Prognosis in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours?
- Proposal for Creating a Guideline for Cancer Registration of Microinvasive Tumors of the Breast and Ovary (II)
- Jin Hee Sohn, Gyungyub Gong, Kyu Rae Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Youn Soo Lee, Jin Man Kim, Woo Hee Jung, Kwang Sun Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):226-232. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.226
- 11,346 View
- 63 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Cancer registration in Korea has a longer than 30-years of history, during which time cancer registration has improved and become well-organized. Cancer registries are fundamental for cancer control and multi-center collaborative research. However, there have been discrepancies in assigning behavior codes. Thus, we intend to propose appropriate behavior codes for the International Classification of Disease Oncology, 3rd edition (ICD-O-3) for microinvasive tumors of the ovary and breast not only to improve the quality of the cancer registry but also to prevent conflicts.
Methods As in series I, two pathology study groups and the Cancer Registration Committee of the Korean Society of Pathologists (KSP) participated. To prepare a questionnaire on provisional behavior code, the relevant subjects were discussed in the workshop, and consensus was obtained by convergence of opinion from members of KSP.
Results Microinvasive tumor of the breast should be designated as a microinvasive carcinoma which was proposed as malignant tumor (/3). Serous borderline tumor with microinvasion of the ovary was proposed as borderline tumor (/1), and mucinous borderline tumor with microinvasion of the ovary as either borderline (/1) or carcinoma (/3) according to the tumor cell nature.
Conclusions Some issues should be elucidated with the accumulation of more experience and knowledge. Here, however, we present our second proposal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the Proposal for Creating a Guideline for Cancer Registration of the Gastrointestinal Tumors (I-2)
Eun Sun Jung, Yun Kyung Kang, Mee-Yon Cho, Joon Mee Kim, Won Ae Lee, Hee Eun Lee, Sunhoo Park, Jin Hee Sohn, So-Young Jin
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(5): 443. CrossRef - A Proposal for Creating a Guideline for Cancer Registration of the Fibromatosis, PEComa Group, Malignant LymphomaIn Situand Dendritic Cell Tumors (III)
Changyoung Yoo, Chang Suk Kang, Yoon La Choi, Hye Yoon Kang, Jin Man Kim, Young Hye Koh, Joo Hee Lee, Seung Sook Lee, In Sun Kim, Dong Hoon Kim, Yong Ku Park, Jin Hee Sohn
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(5): 436. CrossRef
- Update on the Proposal for Creating a Guideline for Cancer Registration of the Gastrointestinal Tumors (I-2)
- Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma Arising in Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: A Case Report
- Yoomi Choi, Kyoung Yul Lee, Min Hye Jang, Hyesil Seol, Sung-Won Kim, So Yeon Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):205-209. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.205
- 9,141 View
- 57 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Phyllodes tumor is an uncommon fibroepithelial neoplasm of the breast. And it is characterized by expanded stroma with increased cellularity and elongated epithelium-lined clefts. Mammary carcinomas within phyllodes tumors have been rarely reported. To date, however, no reports have described the invasive cribriform carcinoma arising in malignant phyllodes tumor. Here, we report a 62-year-old woman who presented with a large breast mass. Microscopically, the mass was a typical malignant phyllodes tumor showing well developed leaf-like architecture and stromal overgrowth with high cellularity and nuclear pleomorphism. In a portion of the tumor, however, the epithelial component showed a cribriform pattern of proliferation in the absence of myoepithelial cells, suggestive of the invasive cribriform carcinoma. To our knowledge, this is rare and it is difficult to make a differential diagnosis of it. Here, we report our case with a review of literatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Concurrent Malignant Phyllodes Tumor and Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Jie Jane Chen, Iowis Zhu, Akshat Patel, Gregor Krings, Yunn-Yi Chen, Florence Yuen, Rita A. Mukhtar, Michelle Melisko, Lisa Singer, Catherine C. Park, Nicolas D. Prionas
Advances in Radiation Oncology.2024; 9(5): 101448. CrossRef - High-grade ductal carcinoma in-situ detected by microcalcification within borderline phyllodes tumor: Report of a case and literature review
Wing Nam Yuen, Joshua J.X. Li, Man Yi Chan, Gary M. Tse
Human Pathology Reports.2023; 31: 300697. CrossRef - Cribriform carcinoma arising in a benign phyllodes tumor
Elia Shazniza Shaaya, Nurwahyuna Rosli, Nurismah M D Isa
Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Unexpectedly High Coexistence Rate of In Situ/Invasive Carcinoma In Phyllodes Tumors. 10-Year Retrospective and Review Study
Öykü Dila Gemci, Serdar Altınay, Rümeysa İlbar Tartar, Sina Ferahman
European Journal of Breast Health.2022; 18(4): 343. CrossRef - A Case of Phyllodes Tumor Combined with Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast with Microinvasion
Daiki IMANISHI, Satoru NODA, Tsutomu TAKASHIMA, Yukie TAUCHI, Shinya NOMURA, Hiroshi OHTANI, Noriko SAKAIDA
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2022; 83(12): 2049. CrossRef - Invasive ductal carcinoma within borderline phyllodes tumor with lymph node metastases: A case report and review of the literature
DI WU, HAIPENG ZHANG, LIANG GUO, XU YAN, ZHIMIN FAN
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(4): 2502. CrossRef
- Management of Concurrent Malignant Phyllodes Tumor and Invasive Breast Carcinoma
- The Clinicopathologic Features of Molecular Apocrine Breast Cancer
- Yoon Jin Cha, Woo-Hee Jung, Ja Seung Koo
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):169-176. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.169
- 8,369 View
- 52 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background To elucidate the clinicopathologic features and their implications on the immunohistochemistry in cases of molecular apocrine breast cancer (MABC).
Methods Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for estrogen receptor (ER), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2), cytokeratin (CK) 5/6, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), androgen receptor (AR), gamma-glutamyltrasferase 1 (GGT1) and Ki-67 was performed on tissue microarray breast cancer samples from 204 patients. Phenotypes of breast cancer were divided based on the IHC status of ER, AR and GGT1 into the following: luminal type, ER positive and AR and/or GGT1 positive; basal type, ER, AR, and GGT1 negative; non-basal type, ER positive and AR and GGT1 negative; and MABC type, ER negative and AR and/or GGT1 positive.
Results In our series of patients (n=204), there were 26 cases of MABC. Besides, there were 18, 60, and 100 cases of luminal type, basal type and non-basal type, respectively. The MABC demonstrated apocrine histology and a higher prevalence of HER-2 positivity than other phenotypes. With the basal type, the MABC manifested a more frequent expression of CK5/6 and EGFR and a higher Ki-67 index than other phenotypes (p<0.001). There were no significant differences in patient prognosis between the phenotypes of breast cancer.
Conclusions MABC are distinguishable from other phenotypes based on the apocrine histology and a higher expression rate of HER-2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of histopathologic testing on apocrine carcinoma of the breast
Burak Ilhan, Selman Emiroğlu, Rustu Türkay, Rıdvan Ilhan
Current Problems in Cancer.2020; 44(2): 100501. CrossRef - Cancer du sein triple négatif exprimant le récepteur aux androgènes : de la biologie à la thérapeutique
Thomas Grellety
Bulletin du Cancer.2020; 107(4): 506. CrossRef - Triple‐negative apocrine carcinoma: A rare pathologic subtype with a better prognosis than other triple‐negative breast cancers
Cletus A. Arciero, Albert H. Diehl, Yuan Liu, Qin Sun, Theresa Gillespie, Xiaoxian Li, Preeti Subhedar
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2020; 122(6): 1232. CrossRef - Apocrine lesions of the breast: part 2 of a two-part review. Invasive apocrine carcinoma, the molecular apocrine signature and utility of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of apocrine lesions of the breast
Clare D'Arcy, Cecily M Quinn
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2019; 72(1): 7. CrossRef - Enhancing Abiraterone Acetate Efficacy in Androgen Receptor–positive Triple-negative Breast Cancer: Chk1 as a Potential Target
Thomas Grellety, Celine Callens, Elodie Richard, Adrien Briaux, Valérie Vélasco, Marina Pulido, Anthony Gonçalves, Pierre Gestraud, Gaetan MacGrogan, Hervé Bonnefoi, Bruno Cardinaud
Clinical Cancer Research.2019; 25(2): 856. CrossRef - A clinicopathologic study of invasive apocrine carcinoma of the breast: A single-center experience
Denira Imamovic, Nurija Bilalovic, Faruk Skenderi, Vanesa Beslagic, Timur Ceric, Berisa Hasanbegovic, Semir Beslija, Semir Vranic
The Breast Journal.2018; 24(6): 1105. CrossRef - Dose invasive apocrine adenocarcinoma has worse prognosis than invasive ductal carcinoma of breast: evidence from SEER database
Ning Zhang, Hanwen Zhang, Tong Chen, Qifeng Yang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(15): 24579. CrossRef - Pure Apocrine Carcinomas Represent a Clinicopathologically Distinct Androgen Receptor–Positive Subset of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers
Anne M. Mills, Chelsea E. Gottlieb, Scott M. Wendroth, Christiana M. Brenin, Kristen A. Atkins
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(8): 1109. CrossRef - Androgen Receptor: A Complex Therapeutic Target for Breast Cancer
Ramesh Narayanan, James Dalton
Cancers.2016; 8(12): 108. CrossRef - Early versus late distant metastasis and adjuvant chemotherapy alone versus both radiotherapy and chemotherapy in molecular apocrine breast cancer
Xiaozhen Liu, Yang Yang, Xiaolong Feng, Honghong Shen, Jian Liu, Xia Liu, Yun Niu
Oncotarget.2016; 7(31): 48905. CrossRef - Molecular and diagnostic features of apocrine breast lesions
Pavel Gromov, Jaime A Espinoza, Irina Gromova
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2015; 15(8): 1011. CrossRef - Prevalencia de receptores androgénicos en el cáncer de mama
Claudia Janeth Rodríguez-Silva, José Luis González-Vela, Ascary Alcides Velázquez-Pacheco
Gaceta Mexicana de Oncología.2015; 14(3): 135. CrossRef
- The role of histopathologic testing on apocrine carcinoma of the breast
- Mimicry of Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-like Nodules to Metastatic Deposits in a Patient with Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hala Kfoury, Maria A. Arafah, Maha M. Arafah, Sami Alnassar, Waseem Hajjar
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):87-91. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.87
- 10,172 View
- 66 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules (MPMNs) are incidentally found lesions in lung resection specimens and autopsies. MPMNs have been associated with neoplastic and non-neoplastic pulmonary conditions and occasionally with extrapulmonary diseases. We report a case of a female patient presenting with invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast and MPMNs, masquerading as metastatic deposits. We describe the morphological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural features of MPMNs and emphasize the importance of their recognition for proper staging and treatment of patients. To our knowledge, this is the first case in the English literature describing this coexistence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis with pan-TRK expression by immunohistochemistry: a novel finding and potential pitfall
Cansu Karakas, Michael A. Nead, Moises J. Velez
Diagnostic Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diffuse Pulmonary Meningotheliomatosis: Clinic-Pathologic Entity or Indolent Metastasis from Meningioma (or Both)?
Laura Melocchi, Giulio Rossi, Mirca Valli, Maria Cecilia Mengoli, Michele Mondoni, Luigi Lazzari-Agli, Giacomo Santandrea, Fabio Davoli, Chiara Baldovini, Alberto Cavazza, Thomas V. Colby
Diagnostics.2023; 13(4): 802. CrossRef - Pathological diagnosis and immunohistochemical analysis of minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules: A case report
Xin Ruan, Liu-Sheng Wu, Zheng-Yang Fan, Qi Liu, Jun Yan, Xiao-Qiang Li
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(33): 8022. CrossRef - Benign disease prone to be misdiagnosed as malignant pulmonary nodules: Minute meningothelioid nodules
Xiao‐Xiao Peng, Li‐Xu Yan, Chao Liu, Si‐Yun Wang, Wen‐Feng Li, Xing Gao, Xue‐Wu Wei, Qing Zhou
Thoracic Cancer.2019; 10(5): 1182. CrossRef - Atypical finding of meningothelial-like inclusions in cervical lymph nodes
Rebecca Donkin, Andrew Dettrick, Penelope Wyche, Sarah Grigg
Pathology.2018; 50(7): 785. CrossRef - Minute Pulmonary Meningothelial-Like Nodules Simulating Hematogenous Lung Metastasis: A Case Report
Sang Kook Lee, Gi Jeong Kim, Young Jae Kim, Ah Young Leem, Eu Dong Hwang, Se Kyu Kim, Joon Chang, Young Ae Kang, Song Yee Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2013; 75(2): 67. CrossRef - Diffuse Pulmonary Meningotheliomatosis Diagnosed by Transbronchial Lung Biopsy
Roberto Bernabeu Mora, Juan Miguel Sánchez Nieto, Chunshao Hu, Eduardo Alcaraz Mateos, Alberto Giménez Bascuñana, Manuel Rodríguez Rodríguez
Respiration.2013; 86(2): 145. CrossRef
- Diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis with pan-TRK expression by immunohistochemistry: a novel finding and potential pitfall

 E-submission
E-submission
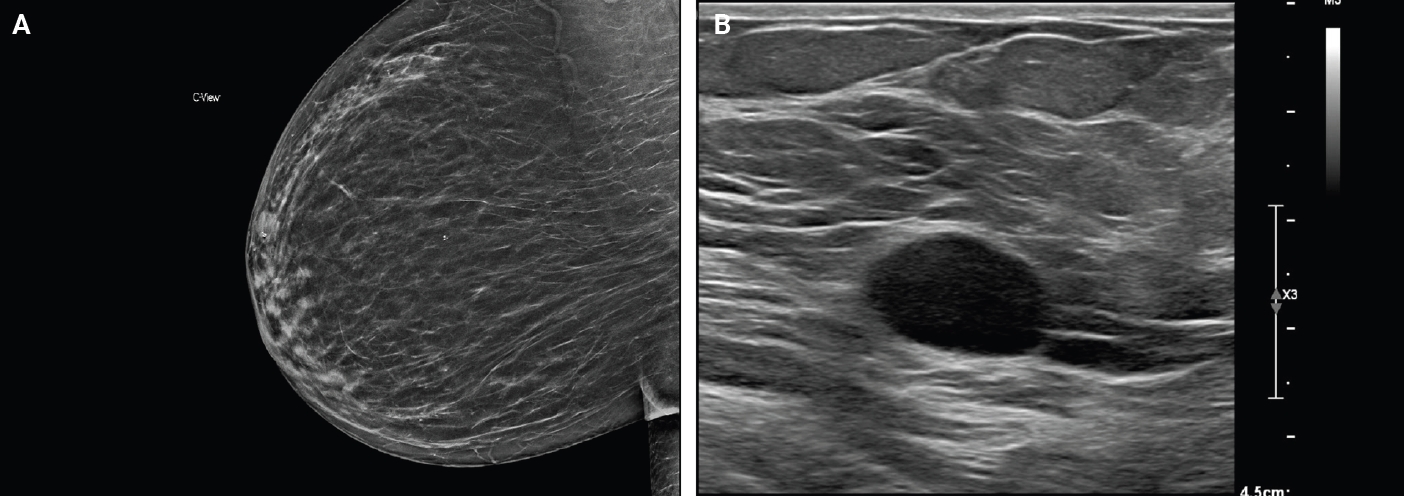











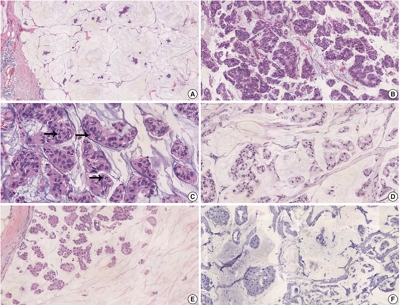

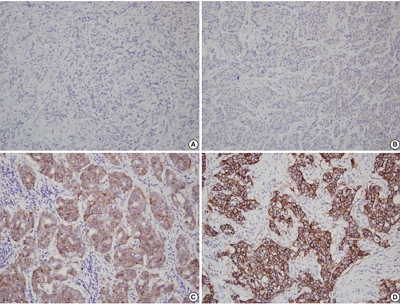
 First
First Prev
Prev



