Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Seokhyeon Lee, Bohyun Kim, Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):232-237. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.17
- 4,707 View
- 171 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
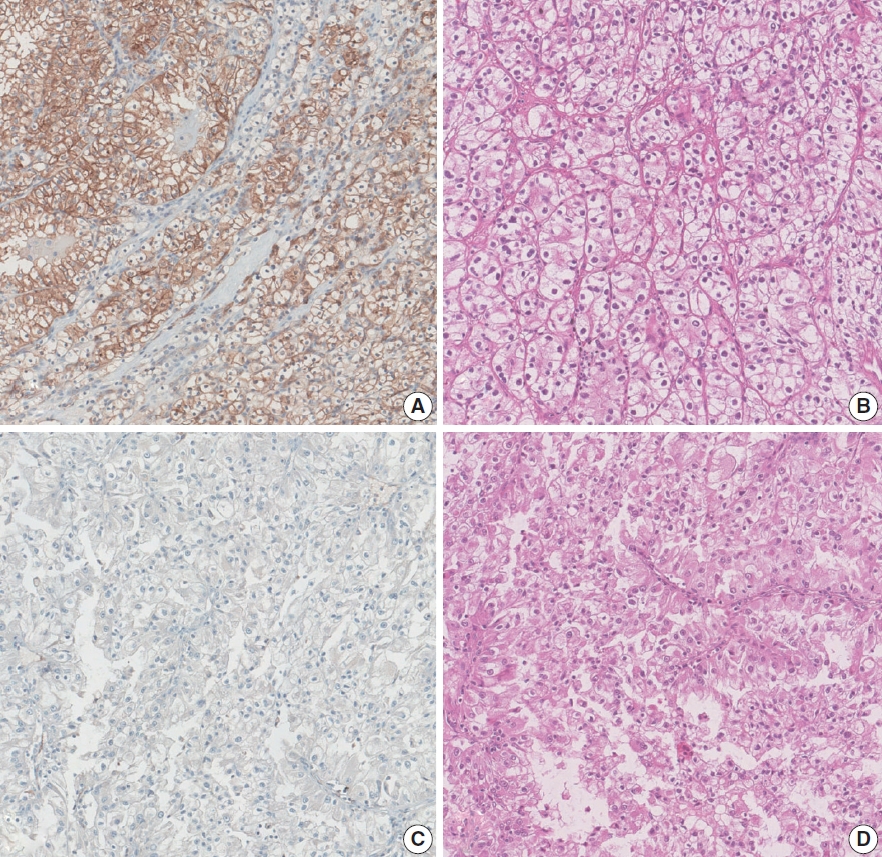
Aquaporin (AQP) expression has been investigated in various malignant neoplasms, and the overexpression of AQP is related to poor prognosis in some malignancies. However, the expression of AQP protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been extensively investigated by immunohistochemistry with large sample size.
Methods
We evaluated the AQP expression in 827 ccRCC with immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarray blocks and classified the cases into two categories, high and low expression.
Results
High expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) was found in 320 cases (38.7%), but aquaporin-3 was not expressed in ccRCC. High AQP1 expression was significantly related to younger age, low TNM stage, low World Health Organization/International Society of Urologic Pathology nuclear grade, and absence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, high AQP1 expression was also significantly associated with longer overall survival (OS; p<.001) and progression-specific survival (PFS; p<.001) and was an independent predictor of OS and PFS in ccRCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed the prognostic significance of AQP1 protein expression in ccRCC. These findings could be applied to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
César I. Gaspari, Carine Beaupere, Seth Richard, Estanislao Peixoto, Bouchra Lekbaby, Mirko Minini, Branko Dubravcic, Javier Vaquero, Marie Vallette, Ander Arbelaiz, Marion Janona, Corentin Louis, Pauline Le Gall, Cédric Coulouarn, Julieta Marrone, Juan E
The American Journal of Pathology.2026; 196(2): 428. CrossRef - Construction and validation of renal cell carcinoma tumor cell differentiation-related prognostic classification (RCC-TCDC): an integrated bioinformatic analysis and clinical study
Yifan Liu, Keqin Dong, Yuntao Yao, Bingnan Lu, Lei Wang, Guo Ji, Haoyu Zhang, Zihui Zhao, Xinyue Yang, Runzhi Huang, Wang Zhou, Xiuwu Pan, Xingang Cui
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Targeting PLOD2 induces epithelioid differentiation and improves therapeutic response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Xiangyu Chen, Dongkui Xu, Yu Ji, Xichen Dong, Xiaomei Dong, Zihan Li, Jingyu Tan, Qianqian Sun, Huixian Xin, Ziwei Liu, Qing Deng, Tao Wen, Yanjun Jia, Xuhui Zhu, Jian Liu
Journal of Advanced Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Exosomal MiR-874 as a Potential Biomarker for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Amal F. Gharib, Saad S. Al-Shehri, Abdulraheem Almalki, Ayman Alhazmi, Mamdouh Allahyani, Ahmed Alghamdi, Amani A. Alrehaili, Maha M. Bakhuraysah, Althobaiti Naif Saad M., Weal H. Elsawy
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
- Loss of Nuclear BAP1 Expression Is Associated with High WHO/ISUP Grade in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Young Chan Wi, Ahrim Moon, Min Jung Jung, Yeseul Kim, Seong Sik Bang, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik, Su-Jin Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):378-385. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.21
- 10,787 View
- 228 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) mutations are frequently reported in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); however, very few studies have evaluated the role of these mutations in other renal cell carcinoma (RCC) subtypes. Therefore, we analyzed BAP1 protein expression using immunohistochemistry in several RCC subtypes and assessed its relationship with clinicopathological characteristics of patients.
Methods
BAP1 expression was immunohistochemically evaluated in tissue microarray blocks constructed from 371 samples of RCC collected from two medical institutions. BAP1 expression was evaluated based on the extent of nuclear staining in tumor cells, and no expression or expression in < 10% of tumor cells was defined as negative.
Results
Loss of BAP1 expression was observed in ccRCC (56/300, 18.7%), chromophobe RCC (6/26, 23.1%), and clear cell papillary RCC (1/4, 25%), while we failed to detect BAP1 expression loss in papillary RCC, acquired cystic disease-associated RCC, or collecting duct carcinoma. In ccRCC, loss of BAP1 expression was significantly associated with high World Health Organization (WHO)/International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grade (p = .002); however, no significant correlation was observed between loss of BAP1 expression and survival in ccRCC. Loss of BAP1 expression showed no association with prognostic factors in chromophobe RCC.
Conclusions
Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in both ccRCC and chromophobe RCC. In addition, BAP1 expression loss was associated with poor prognostic factors such as high WHO/ISUP grade in ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) in Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): Biology, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Opportunities
Alberto Bongiovanni, Pierfranco Conte, Vincenza Conteduca, Matteo Landriscina, Giuseppe Di Lorenzo, Francesco Cognetti
Current Oncology.2025; 32(12): 690. CrossRef - Clinical and Genomic Features of Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis of a Multi-Institutional Database
Corbin J. Eule, Junxiao Hu, Dale Hedges, Alkesh Jani, Thomas Pshak, Brandon J. Manley, Alejandro Sanchez, Robert Dreicer, Zin W. Myint, Yousef Zakharia, Elaine T. Lam
Cancers.2024; 16(10): 1920. CrossRef - Immune regulation and prognosis indicating ability of a newly constructed multi-genes containing signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Ziwei Gui, Juan Du, Nan Wu, Ningning Shen, Zhiqing Yang, Huijun Yang, Xuzhi Wang, Na Zhao, Zixin Zeng, Rong Wei, Wenxia Ma, Chen Wang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiogenomic Associations Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: An Exploratory Study
Derek H Liu, Komal A Dani, Sharath S Reddy, Xiaomeng Lei, Natalie L Demirjian, Darryl H Hwang, Bino A Varghese, Suhn Kyong Rhie, Felix Y. Yap, David I. Quinn, Imran Siddiqi, Manju Aron, Ulka Vaishampayan, Haris Zahoor, Steven Y Cen, Inderbir S Gill, Vinay
Oncology.2023; 101(6): 375. CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of renal epithelial neoplasms
Mahmut Akgul, Sean R Williamson
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - BRCA1-Associated Protein 1 (BAP-1) as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
Shuchi Gulati, Melissa Previtera, Primo N. Lara
Kidney Cancer.2022; 6(1): 23. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Review and Update
Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Luan D. Truong
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 657. CrossRef - CD117, BAP1, MTAP, and TdT Is a Useful Immunohistochemical Panel to Distinguish Thymoma from Thymic Carcinoma
Mounika Angirekula, Sindy Y Chang, Sarah M. Jenkins, Patricia T. Greipp, William R. Sukov, Randolph S. Marks, Kenneth R. Olivier, Stephen D. Cassivi, Anja C Roden
Cancers.2022; 14(9): 2299. CrossRef - BAP1 in cancer: epigenetic stability and genome integrity
Sabrina Caporali, Alessio Butera, Ivano Amelio
Discover Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioinformatic analysis identifying FGF1 gene as a new prognostic indicator in clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Xiaoqin Zhang, Ziyue Wang, Zixin Zeng, Ningning Shen, Bin Wang, Yaping Zhang, Honghong Shen, Wei Lu, Rong Wei, Wenxia Ma, Chen Wang
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of Four Pathological Stage‐Relevant Genes in Association with Progression and Prognosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
Dengyong Xu, Yuzi Xu, Yiming Lv, Fei Wu, Yunlong Liu, Ming Zhu, Dake Chen, Bingjun Bai, Rui Liu
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Functional characterisation guides classification of novel BAP1 germline variants
Jing Han Hong, Siao Ting Chong, Po-Hsien Lee, Jing Tan, Hong Lee Heng, Nur Diana Binte Ishak, Sock Hoai Chan, Bin Tean Teh, Joanne Ngeow
npj Genomic Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Tissue-Based Immunohistochemical Markers for Diagnosis and Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Liang G Qu, Vaisnavi Thirugnanasundralingam, Damien Bolton, Antonio Finelli, Nathan Lawrentschuk
Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal.2020; 1(1): 68. CrossRef - Radiogenomics: bridging imaging and genomics
Zuhir Bodalal, Stefano Trebeschi, Thi Dan Linh Nguyen-Kim, Winnie Schats, Regina Beets-Tan
Abdominal Radiology.2019; 44(6): 1960. CrossRef
- The Role of Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) in Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): Biology, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Opportunities
- Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):359-364. Published online June 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.16
- 9,088 View
- 168 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is presumed to be associated with adipogenic differentiation. Histone modification is known to be important for adipogenesis, and the function of histone demethylase plant homeodomain finger 2 (PHF2) has been noted. In addition, PHF2 may act as a tumor suppressor via epigenetic regulation of p53 and is reported to be reduced in colon cancer and stomach cancer tissues. In this study, we examined PHF2 expression in CCRCC specimens by immunohistochemistry.
Methods
We studied 254 CCRCCs and 56 non-neoplastic renal tissues from patients who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy between 2000 and 2003 at the Seoul National University Hospital. Tissue microarray blocks were prepared, and immunohistochemical staining for PHF2 was performed.
Results
Among 254 CCRCC cases, 150 cases (59.1%) showed high expression and 104 cases (40.1%) showed low expression. High expression of PHF2 was significantly correlated with a low Fuhrman nuclear grade (p < .001), smaller tumor size (p < .001), low overall stage (p = .003), longer cancer-specific survival (p = .002), and progression-free survival (p < .001) of the patients. However, it was not an independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis adjusted for Fuhrman nuclear grade and overall stage.
Conclusions
Our study showed that low expression of PHF2 is associated with aggressiveness and poor prognosis of CCRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
Dexter Kai Hao Thng, Lissa Hooi, Wai Khang Yong, Dennis Kappei, Tan Boon Toh, Edward Kai-Hua Chow
Oncogenesis.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Phosphoproteomics identifies determinants of PAK inhibitor sensitivity in leukaemia cells
Pedro Casado, Santiago Marfa, Marym M. Hadi, Henry Gerdes, Sandra M. Martin-Guerrero, Farideh Miraki-Moud, Vinothini Rajeeve, Pedro R. Cutillas
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of histone methylation in renal cell cancer: an update
Yanguang Hou, Yan Yuan, Yanze Li, Lei Wang, Juncheng Hu, Xiuheng Liu
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(3): 2735. CrossRef - Phosphorylation of PHF2 by AMPK releases the repressive H3K9me2 and inhibits cancer metastasis
Ying Dong, Hao Hu, Xuan Zhang, Yunkai Zhang, Xin Sun, Hanlin Wang, Weijuan Kan, Min-jia Tan, Hong Shi, Yi Zang, Jia Li
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HIF-1α-mediated augmentation of miRNA-18b-5p facilitates proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through attenuation PHF2
Peng Luo, Yan-dong Zhang, Feng He, Chang-jun Tong, Kai Liu, He Liu, Shi-zhuang Zhu, Jian-zhou Luo, Bing Yuan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of meta-analysis and supervised machine learning for pattern recognition in breast cancer using epigenetic data
Reza Panahi, Esmaeil Ebrahimie, Ali Niazi, Alireza Afsharifar
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2021; 24: 100629. CrossRef - PHF2 regulates homology-directed DNA repair by controlling the resection of DNA double strand breaks
Ignacio Alonso-de Vega, Maria Cristina Paz-Cabrera, Magdalena B Rother, Wouter W Wiegant, Cintia Checa-Rodríguez, Juan Ramón Hernández-Fernaud, Pablo Huertas, Raimundo Freire, Haico van Attikum, Veronique A J Smits
Nucleic Acids Research.2020; 48(9): 4915. CrossRef - Emerging of lysine demethylases (KDMs): From pathophysiological insights to novel therapeutic opportunities
Sarder Arifuzzaman, Mst Reshma Khatun, Rabeya Khatun
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 129: 110392. CrossRef - Biology and targeting of the Jumonji-domain histone demethylase family in childhood neoplasia: a preclinical overview
Tyler S. McCann, Lays M. Sobral, Chelsea Self, Joseph Hsieh, Marybeth Sechler, Paul Jedlicka
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2019; 23(4): 267. CrossRef - MiR-221 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Migration via Targeting PHF2
Yi Fu, Mingyan Liu, Fengxia Li, Li Qian, Ping Zhang, Fengwei Lv, Wenting Cheng, Ruixing Hou
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - PHF2 histone demethylase prevents DNA damage and genome instability by controlling cell cycle progression of neural progenitors
Stella Pappa, Natalia Padilla, Simona Iacobucci, Marta Vicioso, Elena Álvarez de la Campa, Claudia Navarro, Elia Marcos, Xavier de la Cruz, Marian A. Martínez-Balbás
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2019; 116(39): 19464. CrossRef - Plant homeodomain finger protein 2 as a novel IKAROS target in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Zheng Ge, Yan Gu, Qi Han, Justin Sloane, Qinyu Ge, Goufeng Gao, Jinlong Ma, Huihui Song, Jiaojiao Hu, Baoan Chen, Sinisa Dovat, Chunhua Song
Epigenomics.2018; 10(1): 59. CrossRef
- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
- Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma Arising from Adenofibroma in a Patient with Endometriosis of the Ovary
- Inju Cho, Sung-Chul Lim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):155-159. Published online October 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.08.07
- 11,321 View
- 134 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ovarian clear cell adenocarcinomas (CCACs) are frequently associated with endometriosis and, less often with clear cell adenofibromas (CCAFs). We encountered a case of ovarian CCAC arising from benign and borderline adenofibromas of the clear cell and endometrioid types with endometriosis in a 53-year-old woman. Regions of the adenofibromas showed transformation to CCAC and regions of the endometriosis showed atypical endometriotic cysts. This case demonstrates that CCAC can arise from CCAF or endometriosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pure non-gestational ovarian choriocarcinoma in a postmenopausal woman coexisting with a clear cell adenofibroma and endometriosis foci: A case report and review of the literature
Ainhoa Ordoñez Arrillaga, Miguel Ángel Resano Abarzuza, Marta Rezola Bajineta, Begoña Aguiar Losada, Yessica P. Rodríguez-Velandia, Manuel Moreno Valladares, Iraide Bernal Simón, Ibon Jaunarena Marín, Irune Ruiz Díaz
Revista Española de Patología.2026; 59(1): 100856. CrossRef - Ovarian Clear Cell Adenofibroma of Low Malignant Potential Developing Into Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
Zhiwei Yin, Stephen Peters, Ravi Chokshi, Debra Heller
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 26(6): 578. CrossRef - Origins based clinical and molecular complexities of epithelial ovarian cancer
Thingreila Muinao, Mintu Pal, Hari Prasanna Deka Boruah
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2018; 118: 1326. CrossRef
- Pure non-gestational ovarian choriocarcinoma in a postmenopausal woman coexisting with a clear cell adenofibroma and endometriosis foci: A case report and review of the literature
- Histologic Variations and Immunohistochemical Features of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):426-432. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.426
- 12,932 View
- 89 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Due to advancements in treatment of metastatic and advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), it has become increasingly important to diagnose metastatic RCC and the specific subtype. In this study, we investigated the diverse histologic features of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cases in comparison with corresponding primary lesions.
Methods We identified 119 metastatic CCRCC cases from 81 corresponding primary lesions diagnosed between 1995 and 2010 and evaluated the diverse histologic and immunohistochemical features of these lesions.
Results A total of 44 primary lesions (54.3%) had a non-clear cell component in addition to a typical clear cell component. Of the 119 metastatic lesions, 63 lesions (52.9%) contained a non-clear cell component, and 29 metastatic lesions were composed of a non-clear cell component only. Rhabdoid features were the most frequent non-clear cell histology among the metastatic lesions. Metastatic CCRCCs mainly showed positive CD10 and epithelial membrane antigen staining and negative cytokeratin 7 staining.
Conclusions Metastatic CCRCC commonly showed a variety of histologic features. If there is a difficulty to diagnose metastatic CCRCC due to a variety of histologic features or small biopsy specimen, histologic review of the primary lesion and immunohistochemical analysis can help determine the correct diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
Adebowale J. Adeniran, Brian Shuch, Peter A. Humphrey
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(7): e65. CrossRef - Emerging Antibody-Drug Conjugate Therapies and Targets for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Harrison C. Gottlich, Reza Nabavizadeh, Mihai Dumbrava, Rodrigo Rodrigues Pessoa, Ahmed M. Mahmoud, Ishita Garg, Jacob Orme, Brian A. Costello, John Cheville, Fabrice Lucien
Kidney Cancer.2023; 7(1): 161. CrossRef - Painful, bleeding fingertip papule
Jane Gay, Sarah Simpson, Patrick Rush, Alex Holliday
JAAD Case Reports.2022; 21: 130. CrossRef - Development and initial clinical testing of a multiplexed circulating tumor cell assay in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Rory M. Bade, Jennifer L. Schehr, Hamid Emamekhoo, Benjamin K. Gibbs, Tamara S. Rodems, Matthew C. Mannino, Joshua A. Desotelle, Erika Heninger, Charlotte N. Stahlfeld, Jamie M. Sperger, Anupama Singh, Serena K. Wolfe, David J. Niles, Waddah Arafat, John
Molecular Oncology.2021; 15(9): 2330. CrossRef - Laparoscopic cytoreductive nephrectomy and adrenalectomy for metachronous RCC metastases—Case report
Bogdan Petrut, Cristina Eliza Bujoreanu, Vasile Vlad Hardo, Adrian Barbos, Bogdan Fetica
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 74: 268. CrossRef - Does CARMENA mark the end of cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Steven L. Chang, Toni K. Choueiri, Lauren C. Harshman
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2019; 37(8): 525. CrossRef - Metastatic TFE3-overexpressing renal clear cell carcinoma with dense granules: a histological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study
Shoujun Chen, Elba A. Turbat-Herrera, Guillermo A. Herrera, Meghna Chadha, Rodney E. Shackelford, Eric X. Wei
Ultrastructural Pathology.2018; 42(4): 369. CrossRef - The Clinical Activity of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Metastatic Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Rana R. McKay, Dominick Bossé, Wanling Xie, Stephanie A.M. Wankowicz, Abdallah Flaifel, Raphael Brandao, Aly-Khan A. Lalani, Dylan J. Martini, Xiao X. Wei, David A. Braun, Eliezer Van Allen, Daniel Castellano, Guillermo De Velasco, J. Connor Wells, Daniel
Cancer Immunology Research.2018; 6(7): 758. CrossRef - Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 359. CrossRef - Pulmonary metastasectomy from renal cell carcinoma including 3 cases with sarcomatoid component
Tsuyoshi Ueno, Motohiro Yamashita, Shigeki Sawada, Ryujiro Sugimoto, Noriko Nishijima, Yoshifumi Sugawara, Iku Ninomiya
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2016; 64(3): 149. CrossRef - Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer?
Aleksandra Semeniuk-Wojtaś, Rafał Stec, Cezary Szczylik
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2016; 34(5): 215. CrossRef - Concordance of Pathologic Features Between Metastatic Sites and the Primary Tumor in Surgically Resected Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sarah P. Psutka, John C. Cheville, Brian A. Costello, Suzanne B. Stewart-Merrill, Christine M. Lohse, Bradley C. Leibovich, Stephen A. Boorjian, R. Houston Thompson
Urology.2016; 96: 106. CrossRef - The Correlation of Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Lesions: A Tissue Microarray Study
Sung Han Kim, Weon Seo Park, Eun Young Park, Boram Park, Jungnam Joo, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
The Korean Journal of Urological Oncology.2016; 14(3): 152. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up and clinical course of a rare case of von Hippel-Lindau disease: A case report and review of the literature
YU ZOU, JINGJING XU, MINMING ZHANG
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(5): 3273. CrossRef - Genetic alterations in renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation
Carmen M. Perrino, Vishwanathan Hucthagowder, Michael Evenson, Shashikant Kulkarni, Peter A. Humphrey
Human Pathology.2015; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - High expression of APRIL correlates with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
Pathology - Research and Practice.2015; 211(11): 824. CrossRef - A Case of Cutaneous Metastasis from a Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with an Eosinophilic Cell Component to the Submandibular Region
Yusuke Amano, Sumie Ohni, Toshiyuki Ishige, Taku Homma, Tsutomu Yamada, Nobuyuki Nishimori, Norimichi Nemoto
Journal of Nihon University Medical Association.2015; 74(2): 73. CrossRef
- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report of 15 Cases Including Three Cases of Concurrent Other-Type Renal Cell Carcinomas
- Jeong Hwan Park, Cheol Lee, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):541-547. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.541
- 9,853 View
- 65 Download
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma (CCPRCC) is a recently established subtype of renal epithelial tumor. The aim of this study was to identify the diagnostic criteria of CCPRCC with an emphasis on immunohistochemical studies, and to report three cases with concurrent other-type renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods A total of 515 RCC patients that consecutively underwent surgical resection at Seoul National University Hospital from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2011 were screened. Each case was reviewed based on the histologic features and was evaluated immunohistochemically.
Results A total of 15 CCPRCCs were identified, which composed 2.9% of the total RCCs. The mean age was 52 years, and the average tumor size was 1.65 cm. All 15 cases showed low nuclear grade, no lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. The CCPRCCs showed variable architectural patterns including cystic, trabecular, papillary, and acinar. All of the cases showed moderate to intense immunoreactivity for cytokeratin 7 (CK7). CD10 was negative or showed focal weak positivity. Three cases had concurrent other-type RCC, including a clear cell RCC and an acquired cystic disease-associated RCC.
Conclusions The strong CK7 and negative or focal weak CD10 expression will be useful for the diagnosis of CCPRCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
Ankur R Sangoi, Harrison Tsai, Lara Harik, Jonathan Mahlow, Maria Tretiakova, Sean R Williamson, Michelle S Hirsch
Histopathology.2024; 84(7): 1167. CrossRef - Clinical features and Surgical Outcome of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Tumor: result from a prospective cohort
Si Hyun Kim, Jang Hee Han, Seung-hwan Jeong, Hyeong Dong Yuk, Ja Hyeon Ku, Cheol Kwak, Hyeon Hoe Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Chang Wook Jeong
BMC Urology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of multiple clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma with renal oncocytoma: a case report
Amine Hermi, Ahmed Saadi, Seif Mokadem, Ahlem Blel, Marouene Chakroun, Mohamed Riadh Ben Slama
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 2017. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Review and Update
Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Luan D. Truong
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 657. CrossRef - The Clinicopathologic and Molecular Landscape of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications in Diagnosis and Management
Stanley Weng, Renzo G. DiNatale, Andrew Silagy, Roy Mano, Kyrollis Attalla, Mahyar Kashani, Kate Weiss, Nicole E. Benfante, Andrew G. Winer, Jonathan A. Coleman, Victor E. Reuter, Paul Russo, Ed Reznik, Satish K. Tickoo, A. Ari Hakimi
European Urology.2021; 79(4): 468. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Characteristics and survival outcomes from a large single institutional series
James E. Steward, Sean Q. Kern, Liang Cheng, Ronald S. Boris, Yan Tong, Clint D. Bahler, Timothy A. Masterson, K. Clint Cary, Hristos Kaimakliotis, Thomas Gardner, Chandru P. Sundaram
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2021; 39(6): 370.e21. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: an update after 15 years
Sean R. Williamson
Pathology.2021; 53(1): 109. CrossRef - Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Jianping Zhao, Eduardo Eyzaguirre
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(9): 1154. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma – An indolent subtype of renal tumor
Wei-Jen Chen, Chin-Chen Pan, Shu-Huei Shen, Hsiao-Jen Chung, Chih-Chieh Lin, Alex T.L. Lin, Yen-Hwa Chang
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2018; 81(10): 878. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature
Sung Han Kim, Whi-An Kwon, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
World Journal of Nephrology.2018; 7(8): 155. CrossRef - Clinical features and survival analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A 10‑year retrospective study from two institutions
Yiqiu Wang, Ying Ding, Jian Wang, Min Gu, Zengjun Wang, Chao Qin, Conghui Han, Hongxia Li, Xia Liu, Pengfei Wu, Guangchao Li
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A contemporary series of renal masses with emphasis on recently recognized entities and tumors of low malignant potential: A report based on 624 consecutive tumors from a single tertiary center
Maria Rosaria Raspollini, Ilaria Montagnani, Rodolfo Montironi, Liang Cheng, Guido Martignoni, Andrea Minervini, Sergio Serni, Giulio Nicita, Marco Carini, Antonio Lopez-Beltran
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(7): 804. CrossRef - Renal Neoplasms With Overlapping Features of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Hari P. Dhakal, Jesse K. McKenney, Li Yan Khor, Jordan P. Reynolds, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Christopher G. Przybycin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(2): 141. CrossRef - New and emerging renal tumour entities
Naoto Kuroda, Ondřej Hess, Ming Zhou
Diagnostic Histopathology.2016; 22(2): 47. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Panel for Differentiating Renal Cell Carcinoma with Clear and Papillary Features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Pathology & Oncology Research.2015; 21(4): 893. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical panel for differentiating renal cell carcinoma with clear and papillary features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2015; 3(2): 68. CrossRef - Clear Cell-Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Kidney Not Associated With End-stage Renal Disease
Manju Aron, Elena Chang, Loren Herrera, Ondrej Hes, Michelle S. Hirsch, Eva Comperat, Philippe Camparo, Priya Rao, Maria Picken, Michal Michal, Rodolfo Montironi, Pheroze Tamboli, Federico Monzon, Mahul B. Amin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(7): 873. CrossRef - Papillary or pseudopapillary tumors of the kidney
Fang-Ming Deng, Max X. Kong, Ming Zhou
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(2): 124. CrossRef - Do Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinomas Have Malignant Potential?
Mairo L. Diolombi, Liang Cheng, Pedram Argani, Jonathan I. Epstein
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(12): 1621. CrossRef - Targeted next‐generation sequencing and non‐coding RNA expression analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma suggests distinct pathological mechanisms from other renal tumour subtypes
Charles H Lawrie, Erika Larrea, Gorka Larrinaga, Ibai Goicoechea, María Arestin, Marta Fernandez‐Mercado, Ondrej Hes, Francisco Cáceres, Lorea Manterola, José I López
The Journal of Pathology.2014; 232(1): 32. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma is the fourth most common histologic type of renal cell carcinoma in 290 consecutive nephrectomies for renal cell carcinoma
Haijun Zhou, Shaojiang Zheng, Luan D. Truong, Jae Y. Ro, Alberto G. Ayala, Steven S. Shen
Human Pathology.2014; 45(1): 59. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Incidence, morphological features, immunohistochemical profile, and biologic behavior: A single institution study
Borislav A. Alexiev, Cinthia B. Drachenberg
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(4): 234. CrossRef - MRI Phenotype in Renal Cancer
Naomi Campbell, Andrew B. Rosenkrantz, Ivan Pedrosa
Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2014; 23(2): 95. CrossRef
- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
- Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Ki Yong Na, Hyun-Soo Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Sung-Goo Chang, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):382-386. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.382
- 10,518 View
- 77 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney (ADPKD) is rare. To date, 54 cases of RCC in ADPKD have been reported. Among these, only 2 cases have different histologic types of RCC. Here we describe a 45-year-old man who received radical nephrectomy for multifocal RCC with synchronous papillary and clear cell histology in ADPKD and chronic renal failure under regular hemodialysis. The case reported herein is another example of the rare pathological finding of RCC arising in a patient with ADPKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
Consolato M. Sergi, Luis Guerra, Josef Hager
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(9): 3965. CrossRef - Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Patients Requiring Nephrectomy: Characteristics and Surgical Considerations
Joel Ern Zher Chan, Kate S. Olakkengil, Shantanu Bhattacharjya, Santosh Antony Olakkengil
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2025; 95(7-8): 1605. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Background of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
Poorva Vias, Shikha Goyal, Renu Madan, Nandita Kakkar, Ridhi Sood, Kannan Periasamy, Rajender Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024; 45(02): 188. CrossRef - Detection of two synchronous histologically different renal cell carcinoma subtypes in the same kidney: a case report and review of the literature
Mohamed Sakr, Merhan Badran, Sarah Ahmed Hassan, Mohamed Elsaqa, Mohamed Anwar Elwany, Nevine M. F. El Deeb, Mohamed Sharafeldeen
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Importance of Genetic Testing in the Differential Diagnosis of Atypical TSC2-PKD1 Contiguous Gene Syndrome—Case Series
Petronella Orosz, Zita Kollák, Ákos Pethő, András Fogarasi, György Reusz, Kinga Hadzsiev, Tamás Szabó
Children.2023; 10(3): 420. CrossRef - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease coming up with an unusual presentation of renal cell carcinoma on its first encounter
Asma Shoukat Masumdar, Anitha Padmanabhan, Nitin Gadgil, Gargi Padalkar
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2023; 10(4): 417. CrossRef - Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review
Yuji Hakozaki, Kiyotaka Uchiyama, Akane Yanai, Daisuke Yamada, Yuka Kamijo, Yoshitaka Ishibashi
CEN Case Reports.2021; 10(2): 199. CrossRef - CT and MRI findings of cystic renal cell carcinoma: comparison with cystic collecting duct carcinoma
Qingqiang Zhu, Jun Ling, Jing Ye, Wenrong Zhu, Jingtao Wu, Wenxin Chen
Cancer Imaging.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental occurrence of papillary renal cell carcinoma in the native kidney with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease after renal transplantation: A case report
Mahmoud Abbas, Melanie Pätzel, Angelika Thurn, Olaf Brinkmann, Olaf Bettendorf
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patient with preserved renal function
Hyuk Huh, Hyung Ah Jo, YongJin Yi, Seung Hyup Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Curie Ahn, Hayne Cho Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 1108. CrossRef - The Association between Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and Renal Cell Carcinoma
Chase C. Hansen, Michael Derrick, Irfan Warriach, James Thomas Cammack, James Thomas Cammack, Werner de Riese
Open Journal of Urology.2015; 05(06): 84. CrossRef - The MSCT and MRI findings of collecting duct carcinoma
Q. Zhu, J. Wu, Z. Wang, W. Zhu, W. Chen, S. Wang
Clinical Radiology.2013; 68(10): 1002. CrossRef - Thyroid-like follicular carcinoma of the kidney in a patient with nephrolithiasis and polycystic kidney disease: a case report
Metka Volavšek, Margareta Strojan-Fležar, Gregor Mikuz
Diagnostic Pathology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
- Cytologic Findings of Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Urethra: A Case Report
- Jee-Young Han, Kyu-Ho Kim, Lucia Kim, Suk-Jin Choi, In-Suh Park, Joon-Mee Kim, Young-Chae Chu, Sang-Min Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):210-214. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.210
- 9,829 View
- 59 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the urethra is a rare disease entity with an uncertain histogenesis. Here, we present a case of primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the female urethra with its cytological findings. A 54-year-old woman presented with a painless gross hematuria lasting 3 months. On vaginal sonography, there was a sausage-like, elongated mass in the urethra, measuring 3.8×4.3 cm. The voided urine cytology revealed small clusters of rounded or papillary cells. The necrotic debris and inflammatory cells were present within some clusters of tumor cells. These tumor cells were enlarged and had abundant clear or granular cytoplasm with cytoplasmic vacuoles. The nucleus was granular and contained vesicular chromatin with prominent nucleoli. The hobnail cells and hyaline globules were also present as in a histologic section. The histologic findings were compatible with clear cell adenocarcinoma. The tumor showed distinctive cytological features. Cytologically, however, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis from other adenocarcinoma or high-grade urothelial carcinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytological and histological findings of upper tract mucinous urothelial carcinoma with clear cell component: A case report and review of literature
Go Kobayashi, Naohiro Uraoka, Kazuhiro Sentani, Jun Shibata, Ryosuke Nobuhiro, Yoichi Saito, Daiki Taniyama, Masanori Hanamoto, Hiroyuki Nose, Naohide Oue
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Presentación de reporte de caso: adenocarcinoma de célula clara de uretra
Nataly González, Yuly Ramirez, Jose Szelezsán, Daniel Rojas
Revista Urología Colombiana / Colombian Urology Journal.2018; 27(02): 191. CrossRef - Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Urethra: Review of the Literature
Anthony Kodzo-Grey Venyo
International Journal of Surgical Oncology.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef
- Cytological and histological findings of upper tract mucinous urothelial carcinoma with clear cell component: A case report and review of literature
- Clear Cell Islet Cell Tumor of the Pancreas: An Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural study.
- Seung Sam Paik, Young Ha Oh, Eun Kyung Hong, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(2):162-166.
- 2,014 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A clear cell islet cell tumor of the pancreas is extremely rare and characterized by extensive clear cell components. Electron microscopic and immunohistochemical findings are essential to prove that the mass with clear cells is an unusual manifestation of an islet cell tumor. Herein, we report a case of clear cell islet cell tumor of a 54-year-old woman with abdominal pain. The tumor was composed of polygonal clear cells arranged in nests, trabeculae, and ribbon pattern with the extensively fibrous stroma. These tumor cells showed strong reactivity for chromogranin and weak reactivity for somatostatin and glucagon. An electron microscope revealed that the important contributing factor of the clear cytoplasmic change was mainly due to an accumulation of lipid droplets, coupled with cytoplasmic swelling in some areas. Some tumor cells showed many endosecretory granules ranging from 111 to 297nm in diameter. In the clinical and immunohistochemical findings these granules were consistent with somatostatin granules in morphology and size.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Glycogen-Rich Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases .
- Wan Seop Kim, Won Mi Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1998;9(2):213-219.
- 2,107 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma of the breast is an unusual variant of carcinoma with a recorded incidence of 1.4-3% of breast carcinomas. The cytologic characteristics have not been well described. We report two cases of glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma with corresponding fine needle aspiration(FNA) cytologic findings and compare them to infiltrating ductal carcinoma and other clear cell malignancies with a review of literature. One was a 62-year-old woman exhibiting a palpable mass of the right breast. The smears showed atypical tight cell clusters and individually scattered single cells containing foamy or clear abundant cytoplasm with well defined cytoplasmic margins. Mild to moderate nuclear pleomorphism and a prominent nucleolus were present. The other was a 42-year-old woman who was admitted with a right breast mass. The smears showed moderately cellular, tightly cohesive tumor cells. The cytoplasmic outline was generally well demarcated. The tumor cells contained foamy to clear abundant cytoplasm with large and small vacuoles. The nuclear pleomorphism was marked. Both tumors resected by modified radical mastectomy, were diagnosed as glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma. Histologically, the clear cell nature of tumor cells were not characteristic enough to predict this type of the tumor. Some cytologic features can be distinguished other clear cell breast cancer from glycogen-rich carcinoma. Recognition of these unusual patterns in a breast FNAC should raise the suspicion of a clear cell carcinoma including glycogen-rich subtype. Cytological localization of glycogen using PAS and D-PAS staining may permit the correct identification and differential diagnosis of this tumor.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Clear Cell Sarcoma: A Case Report.
- Sung Chul Lim, You Kyung Chung, Dong Chool Kim, Yoon Kyung Lee, Eun Taik Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1998;9(2):233-233.
- 2,023 View
- 34 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell sarcoma(CCS) is an uncommon soft tissue sarcoma that occurs in tendons and aponeuroses, usually of the lower extremities and is believed to be of neural crest origin that have a capability to produce melanin. These tumors commonly metastasize and have a very poor prognosis. The fine needle aspiration cytologic finding of CCS is not well documented. We recently experienced a case of CCS. The patient was a 54-year-old male with painful swelling of the right inguinal area. Fine needle aspiration cytology revealed polygonal or fusiform tumor cells with clear or granular cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei containing one or two nucleoli. Im munohistochemical staining for S-100 protein and HMB-45 revealed strong positivity, and variable developing stages of premelanosomes were observed by electron microscopy in the excised specimen.
- Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney: A case report.
- Soon Ae Oak, Bang Hur, Man Ha Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):81-84.
- 2,168 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney(CCSK) is a rare malignant childhood tumor which is distinguished from Wilms tumor by its pathologic features, clinical presentation and frequent occurrence of metastasis to bone. We report a case of CCSK from a 2 year-old girl in the right kidney, followed by metastasis to thoracic vertebrae and left temporal lobe. Histogenesis of this tumor is controversial, although some studies suggest primitive mesenchymal origin. This case was studied with the aids of immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy in an effort to verify the histogenesis of the tumor. Vimentin was reactive in tumor cell, but cytokeratin, GFAP, S-100 protein and desmin were not stained, which confirmed the previous reports by others. Ultrastructural observation of the tumor cells showed neither features of epithelial cell nor differentiated mesenchymal cells.
- Clear Cell Ependymoma.
- Jae Hee Suh, Seung Mo Hong, In Chul Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):383-387.
- 3,137 View
- 66 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The clear cell variant of ependymoma is a rare, recently described, intracranial tumor which is composed of clear neoplastic ependymal cells. Clear cell ependymomas may share characteristic histologic features of oligodendrogliomas or central neurocytomas; striking nuclear uniformity, perinuclear halos, and numerous angulated capillaries. In contrast to oligodendrogliomas, however, clear cell ependymomas are noninfiltrating tumors with sharp boundaries. Perivascular pseudorosette formation is frequent. Oligodendrogliomas are usually nonreactive for GFAP compared to diffuse immunoreactivity of clear cell ependymoma. Central neurocytomas may also be differentiated by their immunoreactivity for synaptophysin. This is a case of clear cell ependymoma in a 40-year-old man. By computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans, a well circumscribed cystic tumor with mural nodule was demonstrated in the right frontal lobe. It was 6cm in diameter and well enhanced. Histologically, it was sharply demarcated from the brain parenchyma. The cystic wall was lined by atypical ependymal cells, which "transformed" to clear cells in the solid area. The cells had uniform nuclei and perinuclear halos. Mitotic figures and necrotic foci were focally present. The cells were immunoreactive for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), while synaptophysin was negative. Electron microscopy revealed densely packed polyheadral cells with scant organelles and well developed intercellular junctions.
- Clear Cell Chondrosarcoma Arising in Hyoid Bone.
- Hae Jin Jeong, Sug Kyoung Ko, Myeng Sun Park, Hee Kyung Chang, Man Ha Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(5):470-475.
- 2,052 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell chondrosarcoma, first described by Unni in 1976, is distinguished from classical chondrosarcoma by a typical histological picture, mostly an epiphyseal site of origin, and relatively a benign clinical course. We present a case of clear cell chondrosarcoma arising from hyoid bone in a 70-year-old male. Histologically, large areas of closely packed cells with characteristic clear cytoplasm were seen in addition to the usual elements of a conventional chondrosarcoma. Our search and review of the literature did not reveal any reported case of clear cell chondrosarcoma arising from hyoid bone.
- Borderline Clear Cell Adenofibromatous Tumors of the Ovary: Two Case Reports.
- Heejeong Lee, Tae Jung Kim, Jeana Kim, Eun Joo Seo, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(6):420-423.
- 2,145 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Borderline clear cell adenofibromatous tumors are rare with only 26 cases reported in the English literature. Five of these cases exhibited microinvasion and 4 demonstrated intraepithelial carcinoma. We report 2 cases, one typical case and the other with microinvasion. The histological findings revealed widely spaced and focally crowded, variably-sized atypical glands or tubules lined by clear, eosinophilic or hobnail cells set in a dense fibrous stroma. One of the two cases had small solid nests or single cells in the stroma around the proliferative glands less than 1 mm in length that was considered to be a microinvasion.
- Immunohistochemical Markers for Metastasis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Kyungeun Kim, Cheryn Song, Jae Y Ro, Hanjong Ahn, Yong Mee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(2):81-86.
- 2,488 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is notorious for its high metastatic potential, and 30% of RCC patients present with metastatic disease at the initial presentation and 50% of them will develop metastasis or recurrence after radical surgery.
METHODS
In an attempt to identify the best predictive marker(s) for metastasis in patients with clear cell RCCs (CRCCs), we examined the expression patterns of 7 metastasis/prognosis-related markers by constructing a tissue microarray including primary CRCC specimens from 30 metastatic and 60 nonmetastatic CRCCs. The markers we studied were Ki-67, MUC1, CD44s, PTEN, gelsolin, CA9 and p53.
RESULTS
The expressions of Ki-67, PTEN, CD44s, gelsolin and p53 were increased, whereas those of MUC1 and CA9 were decreased in the metastatic CRCCs compared with the non-metastatic CRCCs. The receiver operating characteristic curve-area under the curve (AUC) value of Ki-67 was 0.671, which was the highest among the 7 markers. The optimal cut-off value, sensitivity and specificity of the Ki-67 expression were 1.67%, 86.7% and 41.7%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
These results demonstrate that the Ki-67 expression was increased in metastatic CRCCs, and it had the highest predictive value among the 7 markers. This suggests that Ki-67 could be an excellent predictive marker for metastasis in CRCC patients.
- Clear Cell Meningioma.
- Hee Jeung Cha, Soo Kee Min, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(8):782-787.
- 3,200 View
- 87 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell meningioma is a recently recognized morphologically unique entity. It shows no sex predilection, affects primarily the lumbar region, and the cerebellopontine angle. Despite its benign appearance, it may be aggressive, particularly in intracranial cases. All lesions are moderately cellular, with the exception of stromal hyalinization. The tumor consists largely of a sheet- like or somewhat lobular pattern of polygonal cells, the cytoplasm of which is clear. No close association is noted between the recurrence or the clinical outcome and factors such as mitotic activity, the PCNA index, and the DNA ploidy status. But the MIB-1 proliferation index is appreciably higher in recurrent tumors. We experienced a case of clear-cell meningioma showing a characteristic histologic finding. A 39-year-old man was admitted due to the recent onset of right-sided, facial-nerve palsy, left hemiparesis and general weakness. A CT scan of the head showed a well defined mass in the petroclival area. After surgical resection, the patient was in good condition, but 1 year later symptoms recurred. A CT scan of the head showed a huge, recurrent petroclival tumor with adhesion to the surrounding brain parenchyme.
- Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Accompanied by Vesical Endometriosis.
- Eun Kyung Han, So Yeon Park, Nam Hoon Cho, Woo Ik Yang, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(4):489-496.
- 1,935 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A case of clear cell adenocarcinoma arising in the female urinary bladder, which is accompanied by endometriosis of the urinary bladder and the uterus, is reported. The carcinoma protruded into the vesical lumen as a fungating mass, and had a tubulocyotic pattern. The tumor cell had intracytoplasmic glycogen and electron microscopically short microvilli on their surface, resembling clear cell acenocarcinoma of the female genital tract including ovary. This is the fourth case report of clear cell adenocarcinoma complicating vesical endometriosis, and may support the view that clear cell carcinome arises from endometriosis which, in turn, from the Mullerian remnant.
- Cytology of the Uterine Cervico-vaginal Smear of Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma in Uterine Cervix: Report of a Case.
- Leeso Maeng, Kyoung Mee Kim, Anhi Lee, Chang Suk Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2004;15(2):116-119.
- 2,110 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of uterine cervix is rare and cytomorphology in the vaginal smear have not been previously described in Korean literatures. The cytologic characteristics of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix include : malignant cells with abundant, finely vacuolated cytoplasm ; hobnail appearance ; and distinctive basement membrane-like hyaline materials within cellular aggregates. A 36-year-old woman presented with vaginal bleeding. Cytologic examination of vaginal smear and histopathologic examination of a radical hysterectomy specimen allowed the diagnosis of hemorrhagic tumor in the uterine cervix as a clear cell adenocarcinoma. Cytologic findings were very characteristic. The tumor cells had abundant, pale, finely vacuolated cytoplasm with indistinct cytoplasmic membrane. The nuclei were round to oval with finely dispersed chromatin. Extracellular basement membrane-like hyaline substance, which stained a light green color in Papanicolaou's preparation, was frequently observed within the cancer cell clusters.
- Clear Cell Meningioma arising from Lumbar Nerve Root in a Child: A case report.
- Eun Kyung Hong, Geun Shin Lyu, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(2):179-184.
- 2,033 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Meningioma of unusual age of onset, location, histogenesis and histologic type is reported. The patient, 4 year-old girl, had an intradural spinal meningioma arising from lumbar nerve root with no dural attachement. The meningioma revealed glycogen-rich, clear cell type with extensive and blocky hyalinization of the stroma. The tumor shared common fibrous sheath with attached lumbar nerve, and nerve fibers were scattered within the tumor. Ultrastructurally, the tumor cells had abundant glycogen particles, intermediate filaments and intercellular desmosomes. Hyalinized material revealed large amianthoid collagen fibers.
- Cytologic Findings of Clear Cell Carcinoma of Ovary.
- Ji Young Park, Hye Sun Kim, Jong Sun Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(1):32-37.
- 2,681 View
- 87 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The objective of this study was to evaluate the cytomorphologic features of histologically confirmed clear cell carcinoma of the ovary and to evaluate the applicability of scrape or fine-needle aspiration cytology in making an intraoperative diagnosis. We reviewed scrape or fine-needle aspiration cytology findings in tissues taken from 6 patients with clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. The cytologic diagnosis was based primarily on findings in alcohol-fixed, hematoxylin-eosin (H-E) stained smears. The formation of material resembling a basement membrane was a characteristic finding in these smears. This extracellular hyaline material was stained light pink with H-E and was frequently found within tumor cell clusters as well as in the background material. Multinucleated giant cells were found occasionally. Each tumor cell had an abundant, clear, or granular cytoplasm with a distinct cellular membrane. Scrape cytology is a simple and rapid supportive method and could be helpful in diagnosing clear cell carcinoma of the ovary, especially when marked artifacts appear in the frozen section.
- Glycogen-Rich Clear Cell Carcinoma of Breast: A case report.
- Nam Hoon Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Young Hyeh Ko, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(3):316-318.
- 2,941 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma of the breast is very rare(l -3% of breast cancer). It is defined as a tumor composed of more than 50% of optically clear, neoplastic cells, characterized by centrally located nuclei and abundant cytoplasm, being positive for periodic acid Schiff(PAS) and negative for periodic acid Schiff after diastase(D-PAS) treatment. In the absence of intraductal or in situ lobular carcinoma component, metastatic clear cell carcinomas of other organs should be considered as diagnostic possibilities. We report a case of glycogen-rich clear cell carcinoma arisen in a 62-year-old woman. The tumor revealed both solid and papillary pattern with intraductal component. The neoplastic cells had clear cytoplasm, which were PAS positive, D-PAS negative, mucicarmine negative and oil red 0 negative. More than 90% of tumor cells exhibited moderate staining for anti-estrogen receptor monoclonal antibody. Flow cytometric DNA analysis revealed diploid DNA content.
- Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney: Report of two cases.
- Woo Hee Jung, Jee Young Han, So Yeon Park, Jae Eok Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(6):581-588.
- 2,041 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell sarcoma is a rare malignant rumor of the kidney which occurs in children and is differentiated from Wilms' tumor by its different clinicopathologic features and natural history. Previous studies indicate that this tumor may be of mesenchymal cell origin; however, this has not been proven conclusively. Further accumulation and study need to be conducted in order to clarify the histogenesis of this tumor. We report two cases of clear cell sarcoma of the kidney which occurred in a 2 and a half-year old and a 2-year old boy. This report places special emphasis on the clinicopathologic characteristics of these two cases including electron microscopic and immunohistochemical findings. Attempts were also made to differentiate the clinicopathologic aspects of clear cell sarcoma from Wilms' tumor and speculate on the histogenesis of this rumor.
- Clear Cell Hidradenoma: A report of five cases.
- Mi Kyung Jee, Seok Jin Gang, Byung Kee Kim, Sun Moo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(2):180-189.
- 3,658 View
- 150 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The clear hidradenoma, generally regarded as an eccrine sweat gland origin, is an uncommon tumor and occurs as a slowly growing, usually solitary nodule. The histologic patterns varies from one tumor to another and in different parts of the same tumor. The histologically variable patterns, therefore, are expressed in various names, including nodular hidradenoma, eccrine acrospiroma, squamous poroadenoma, and solid cystic hidradenoma. During the past 16 years the authors experienced 5 cases of clear cell hidradenoma which were diagnosed by the histopathological examination of the tumor mass removed by surgical excision. Clinical and pathological features were reviewed and the following results were obtained. 1) The mean age was 34 years with a range from 27 to 45 years. Three were male and two female. 2) The chiefr complaint was intradermal or subcutaneous nodules for a period of several years to 15 years. All cases occured as a solitary nodule without a distinct predilection for certain sites. A nodule which situated in the dermis and was accompanied by superficial ulceration was elevated above the skin surface in one case. 3) Grossly, the tumors were relatively well circumscribed and composed of multiloblated masses in 4 cases. They ranged in size between 1.5 and 3.5 cm. 4) Microscopically, all cases disclosed lobulated solid masses separated by varying amounts of collagenous connective tissue. There were often cystic spaces, which were lined by a single row of cuboidal cells in four cases and were bordered by tumor cells in remaining one case. These cysts contained a faintly eosinophilic homogeneous material. On solid portions of the tumor there were two types of cells (clear cell and polygonal cell), the proportions of which varied from tumor to tumor in three cases. The remaining two cases were predominantly composed of clear cells. Tubular lumina which were lined by cuboidal or columnar ductal cells were found in two cases. Areas of squamous differentiation and squamous eddies were seen in one case. Intracytolasmic PAS-positive materials were shown in all cases, but diastase-resistant PAS materials in two cases.
- Interstitial Mononuclear Cell Infiltration and its Phenotypes in IgA Nephropathy.
- Hyeon Joo Jeong, Hyunee Yim, Sun Hee Sung, In Joon Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(5):506-510.
- 2,178 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To know the correlation between glomerular and tubulointerstitial lesion and to define the characteristics of interstitial inflammatory cell in IgA nephropathy and classified according to WHO classification and graded tubulointerstitial lesion as mild, moderate and severe. Paraffin-embedded 5u sections were stained with UCHL-l, L26 and CD68 antibodies. More than 20 fields were examined in each case under the high power microscopy and the number of positive cells were counted. There was positive correlation between the severity of glomerular and that of tubulointerstitial lesion. The mostcommoninflammatory cells in the interstitiuin were UCHL-l positive cells followed by CD68 and L26 positive cells. As the WHO grade or tubulointerstitial lesion increased, the numbers of positive cells were increased in all three groups. The proportion of UCHL-1 Positive cells were increased in cases with high WHO grade whereas that of L26 positive cells incases with severe tubulointerstitial lesion Proteinuria was correlated with the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration, especially with that of L26 positive cells.
- Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney: A case in 39 year old man.
- Hyun Ju Yoo, Yun Kyung Kang, Mee Joo, Hye Kyung Lee, Dae Woo Kim, Suk San Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(12):1138-1143.
- 2,451 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clear cell sarcoma of kidney(CCSK) is a rare pediatric neoplasm characterized by a predominating component of clear cells, a predilection for metastases to bone, and a poor prognosis. The incidence of CCSK peaks during the 2nd year of life and adult cases are very rare. We report a case of CCSK encountered in the right kidney of a 39-year-old man. Grossly, it was a lobulated mass showing infiltrative margin, measured 7x5.5x5cm and had a homogeneous gray-tan color with a soft, fish-flesh consistency. Microscopically, about half of the tumor revealed the classic pattern of CCSK, having tumor cell cords or nests separated by the characteristic alveolar capillary networks. The tumor cells had clear pale cytoplasm, bland looking round nuclei and inconspicuous nucleoli. The other half showed the epithelioid-trabecular pattern forming pseudorosette or cord-like structures. Immunohistochemically, there was only a focal positive reaction to vimentin. Ultrastructurally, the tumor cells showed the primitive nephrogenic mesenchymal differentiation such as electron lucent cytoplasm, a small amount of organelles, scanty heterochromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and a lack of flocculant basal lamina material around the cytoplasmic membrane. We consider that this is a case of CCSK occuring in the oldest patient ever reported, confirmed by both immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy.
- Oxyphilic Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary: A case report.
- Chang Won Ha, Jae Soo Koh, Na Hye Myoung, Kyung Ja Cho, Sang Yoon Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Ja June Jang
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(5):500-503.
- 2,306 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Oxyphilic clear cell carcinoma of the ovary is a variant of clear cell carcinoma with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm described by Young & Scully in 1987. Thorough samplin is needed to identify typical foci of clear cell carcinoma for the differential diagnoses from a variety of ovarian tumors with oxyphilic cells. We report a case of oxyphilic clear cell carcinoma in a 65-year-old female patient who presented with vaginal spotting and lower abdominal discomfort. The excised mass was a 10x8x7cm sized, well circumscribe yellowish white solid ovarian tumor. Microscopically, the tumor showed glandular, papillary and alveolar growth patterns composed of cuboidal or hobnail-shaped oxyphilic cells.

 E-submission
E-submission

 First
First Prev
Prev



