Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Association study of TYMS gene expression with TYMS and ENOSF1 genetic variants in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response of gastric cancer
- Khadijeh Arjmandi, Iman Salahshourifar, Shiva Irani, Fereshteh Ameli, Mohsen Esfandbod
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):105-114. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.05
- 530 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The present research was designed to study the associations between genetic variants of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes with TYMS and ENOSF1 gene expression in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response among patients with gastric cancer. Methods: Formalin-embedded and paraffin-fixed matched tumor and normal gastric cancer tissue samples from patients who received neoadjuvant 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) treatment were obtained. DNA and RNA were extracted for all samples. A 28-bp variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) at the 5' untranslated region of TYMS gene and rs2612091 and rs2741171 variants in the ENOSF1 gene were genotyped for normal tissue samples. The real-time polymerase chain reaction method was used to study the expression of ENOSF1 and TYMS genes in both normal and tumor tissues. Data were analyzed using REST 2000 and SPSS ver. 26.0 software programs. Results: A significant association between TYMS 2R3R VNTR genotypes and 5-FU therapy was found (p = .032). The 3R3R and 2R2R genotypes were significantly associated with increased and decreased survival time, respectively (p = .003). The 3R3R genotype was significantly associated with TYMS overexpression (p < .001). Moreover, a significant association was found between the rs2612091 genotype and treatment outcome (p = .017). Conclusions: This study highlights the impact of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes as predictive indicators for survival and response to 5-FU–based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer patients.
Case Study
- Uncommon granulomatous manifestation in Epstein-Barr virus–positive follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report
- Henry Goh Di Shen, Yue Zhang, Wei Qiang Leow
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):133-138. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.27
- 1,028 View
- 237 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic Epstein-Barr virus–positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (EBV+ IFDCS) represents a rare form of liver malignancy. The absence of distinct clinical and radiological characteristics, compounded by its rare occurrence, contributes to a challenging diagnosis. Here, we report a case of a 54-year-old Chinese female with a background of chronic hepatitis B virus treated with entecavir and complicated by advanced fibrosis presenting with a liver mass found on her annual surveillance ultrasound. Hepatectomy was performed under clinical suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunomorphologic characteristics of the tumor were consistent with EBV+ IFDCS with distinct non-caseating granulomatous inflammation. Our case illustrates the importance of considering EBV+ IFDCS in the differential diagnosis of hepatic inflammatory lesions. Awareness of this entity and its characteristic features is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing this rare neoplasm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Original Article
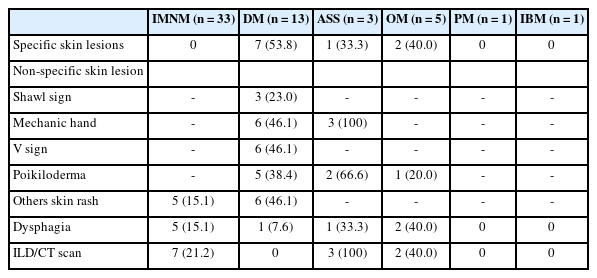
- Immunohistochemical expression in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at a single center in Vietnam
- Dat Quoc Ngo, Si Tri Le, Khanh Hoang Phuong Phan, Thao Thi Phuong Doan, Linh Ngoc Khanh Nguyen, Minh Hoang Dang, Thien Thanh Ly, Thu Dang Anh Phan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):174-181. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.02
- 1,651 View
- 237 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The identification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) requires a comprehensive analysis involving clinical manifestations and histological findings. This study aims to provide insights into the histopathological and immunohistochemical aspects of IIMs.
Methods
This retrospective case series involved 56 patients diagnosed with IIMs at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, from 2019 to 2023. The histology and immunohistochemical expression of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, C5b-9, Mx1/2/3, and p62 were detected.
Results
We examined six categories of inflammatory myopathy, including immunemediated necrotizing myopathy (58.9%), dermatomyositis (DM; 23.2%), overlap myositis (8.9%), antisynthetase syndrome (5.4%), inclusion body myositis (IBM; 1.8%), and polymyositis (1.8%). The average age of the patients was 49.7 ± 16.1 years, with a female-to-male ratio of 3:1. Inflammatory cell infiltration in the endomysium was present in 62.5% of cases, perifascicular atrophy was found in 17.8%, and fiber necrosis was observed in 42 cases (75.0%). Rimmed vacuoles were present in 100% of cases in the IBM group. Immunohistochemistry showed the following positivity rates: HLA-ABC (89.2%), HLA-DR (19.6%), C5b-9 (57.1%), and Mx1/2/3 (10.7%). Mx1/2/3 expression was high in DM cases. p62 vacuole deposits were noted in the IBM case. The combination of membrane attack complex and major histocompatibility complex I helped detect IIMs in 96% of cases.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of IIMs and their subtypes should be based on clinical features and histopathological characteristics. Immunohistochemistry plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and differentiation of these subgroups.
Case Study
- Thyroid pathology, a clue to PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome
- Yurimi Lee, Young Lyun Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):178-183. Published online March 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.03.04
- 3,270 View
- 186 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) is a hereditary disorder caused by germline inactivating mutations in the PTEN tumor suppressor gene. As a type of PHTS, Cowden syndrome is associated with abnormalities of the thyroid, breast, uterus, and gastrointestinal tract. A 52-year-old-woman visited the outpatient clinic of our endocrinology clinic with multiple thyroid nodules and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Computed tomography imaging revealed a multinodular mass measuring up to 3.5 cm in the left thyroid lobe, causing laryngotracheal airway displacement. The total thyroidectomy specimen revealed multiple follicular adenomas and adenomatous nodules with lymphocytic thyroiditis and lipomatous metaplasia in the background. The patient was suspected of PTHS based on her thyroid pathology, family history, and numerous hamartomatous lesions of the breast, uterus, and skin. Her diagnosis was confirmed through molecular testing. This case demonstrates that pathologists must be well acquainted with thyroid pathology in PHTS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A clinical case of papillary thyroid cancer associated with a PTEN gene defect
R. A. Atanesyan, L. Ja. Klimov, T. M. Vdovina, G. A. Saneeva, E. I. Andreeva, I. A. Stremenkova, R. I. Arakelyan, I. K. Gasparyan
Rossiyskiy Vestnik Perinatologii i Pediatrii (Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics).2025; 69(6): 85. CrossRef - Pediatric cancer predisposition syndromes involving non-central nervous system solid pediatric tumors: a review on their manifestations with a focus on histopathology
B. Schurink, M. Reyes-Múgica, R. R. de Krijger
Virchows Archiv.2025; 486(1): 3. CrossRef - Dedifferentiated Leiomyosarcoma of the Uterine Corpus with Heterologous Component: Clinicopathological Analysis of Five Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution and Comprehensive Literature Review
Suyeon Kim, Hyunsik Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2024; 14(2): 160. CrossRef - Case report: Rare oral manifestations in Cowden syndrome with PTEN mutation
Wei Yuan, Yanbin Liu, Haibin Sun, Ming Su, Lizheng Qin, Xin Huang
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Can thyroid histomorphology identify patients with PTEN hamartoma tumour syndrome?
Melad N Dababneh, Laura Rabinowitz, Gilman Plitt, Charis Eng, Christopher C Griffith
Histopathology.2024; 85(6): 929. CrossRef - A novel mutation in PTEN in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: A case report
Yanli Zhao
Biomedical Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- A clinical case of papillary thyroid cancer associated with a PTEN gene defect
Case Report
- Solitary Peutz-Jeghers type harmartomatous polyp in duodenum with gastric foveolar epithelium: a case report
- Eugene Choi, Junghwan Lee, Youngsoo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):128-131. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.07
- 2,685 View
- 171 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Peutz-Jeghers type hamartomatous polyp is known to be associated with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, which shows characteristic multiple hamartomatous polyp involvement in the gastrointestinal tract, combined with mucocutaneous symptom, familial history of Peutz- Jeghers syndrome or STK11/LTB1 mutation. However, some cases showing histologic appearance of the polyps discovered in Peutz- Jeghers syndrome while lacking other diagnostic criteria of the syndrome have been reported, and these are called solitary Peutz- Jeghers type polyps. Herein, we report a case of solitary Peutz-Jeghers type polyp covered with heterotopic epithelium. The patient was 47-year-old female without any mucocutaneous symptoms nor familial history of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Microscopic examination revealed Peutz-Jeghers type hamartomatous polyp in duodenum covered with gastric type foveolar epithelium. Considering the definition of hamartomatous polyp, which is, the abnormal overgrowth of the indigenous epithelial component, the histological feature of current case is noteworthy in a point that it shows proliferation of heterotopic component, rather than the indigenous component.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Solitary Peutz-Jeghers Hamartomatous Polyp in the Gastric Body: A Case Report
Noelia Madera, Noemí Acevedo, Carmen González-Peralta, Rafael Castro, Vismelis Mezquita-Luna
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Solitary Peutz-Jeghers Hamartomatous Polyp in the Gastric Body: A Case Report
Original Article
- Blocking Toll-like receptor 9 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury
- Badr Alzahrani, Mohamed M. S. Gaballa, Ahmed A. Tantawy, Maha A. Moussa, Salma A. Shoulah, Said M. Elshafae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(2):81-91. Published online March 2, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.12.27
- 5,481 View
- 134 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is one of the most common complications in coronavirus disease 2019 patients suffering from acute lung injury (ALI). In ARDS, marked distortion of pulmonary architecture has been reported. The pulmonary lesions in ARDS include hemodynamic derangements (such as alveolar edema and hemorrhage), vascular and bronchiolar damage, interstitial inflammatory cellular aggregations, and eventually fibrosis. Bleomycin induces ARDS-representative pulmonary damage in mice and rats; therefore, we used bleomycin model mice in our study. Recently, Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) was implicated in the development of ARDS and ALI.
Methods
In this study, we evaluated the efficiency of a TLR9 blocker (ODN2088) on bleomycin-induced pulmonary damage. We measured the apoptosis rate, inflammatory reaction, and fibroplasia in bleomycin- and bleomycin + ODN2088-treated mice.
Results
Our results showed a significant amelioration in bleomycin-induced damage to pulmonary architecture following ODN2088 treatment. A marked decrease in pulmonary epithelial and endothelial apoptosis rate as measured by cleaved caspase-3 expression, inflammatory reaction as indicated by tumor necrosis factor α expression, and pulmonary fibrosis as demonstrated by Van Gieson staining and α-smooth muscle actin immunohistochemistry were observed following ODN2088 treatment.
Conclusions
All these findings indicate that blocking downstream TLR9 signaling could be beneficial in prevention or mitigation of ARDS through hemodynamic derangements, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel mouse model of myositis-associated interstitial lung disease was established by using TLR9 agonist combined with muscle homogenate
Ling Bai, Jiarui Zhu, Wenlan Ma, Peipei Zhao, Feifei Li, Cen Zhang, Sigong Zhang
Clinical and Experimental Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Toll-like Receptor 9 Inhibition Mitigates Fibroproliferative Responses in Translational Models of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Glenda Trujillo, Alicia Regueiro-Ren, Chunjian Liu, Buqu Hu, Ying Sun, Farida Ahangari, Vitoria Fiorini, Genta Ishikawa, Karam Al Jumaily, Johad Khoury, John McGovern, Chris J. Lee, Xue Yan Peng, Taylor Pivarnik, Huanxing Sun, Anjali Walia, Samuel Woo, Sh
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.2025; 211(1): 91. CrossRef - CD103+ dendritic cell–fibroblast crosstalk via TLR9, TDO2, and AHR signaling drives lung fibrogenesis
Hannah Carter, Rita Medina Costa, Taylor S. Adams, Talon M. Gilchrist, Claire E. Emch, Monica Bame, Justin M. Oldham, Steven K. Huang, Angela L. Linderholm, Imre Noth, Naftali Kaminski, Bethany B. Moore, Stephen J. Gurczynski
JCI Insight.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms underlying dose-limiting toxicities of conventional chemotherapeutic agents
Mohammad Amin Manavi, Mohammad Hosein Fathian Nasab, Razieh Mohammad Jafari, Ahmad Reza Dehpour
Journal of Chemotherapy.2024; 36(8): 623. CrossRef - Innate Immune Response-Mediated Inflammation in Viral Pneumonia
Weiwei Ni, Xin Wei, Rui Wu
Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2024; 19(03): 140. CrossRef - Combination of losartan with pirfenidone: a protective anti-fibrotic against pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats
Arian Amirkhosravi, Maryamossadat Mirtajaddini Goki, Mahmoud Reza Heidari, Somayyeh Karami-Mohajeri, Maryam Iranpour, Maryam Torshabi, Mitra Mehrabani, Ali Mandegary, Mehrnaz Mehrabani
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Suppression of miR-17 Alleviates Acute Respiratory Distress-associated Lung Fibrosis by Regulating Mfn2
Mei-xia Xu, Tao Xu, Ning An
Current Medical Science.2024; 44(5): 964. CrossRef - TLR9: A friend or a foe
Mona M. Saber, Nada Monir, Azza S. Awad, Marwa E. Elsherbiny, Hala F. Zaki
Life Sciences.2022; 307: 120874. CrossRef
- A novel mouse model of myositis-associated interstitial lung disease was established by using TLR9 agonist combined with muscle homogenate
Case Studies
- Adrenal hemangioblastoma
- Joo-Yeon Koo, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Joon Hyuk Choi, Ho Seok Chung, Chan Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(3):161-166. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.12.28
- 3,966 View
- 150 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hemangioblastoma (HB) is a rare benign tumor that most commonly occurs in the cerebellum. HB is composed of neoplastic stromal cells and abundant small vessels. However, the exact origin of stromal cells is controversial. Extraneural HBs have been reported in a small series, and peripheral HBs arising in the adrenal gland are extremely rare. Herein, we report a case of sporadic adrenal HB in a 54-year-old woman. The tumor was a well-circumscribed, yellow mass measuring 4.2 cm in diameter. Histologically, the tumor was composed of small blood vessels and vacuolated stromal cells with clear cytoplasm. On immunohistochemical stain, the stromal cells were positive for S-100 protein, neuron-specific enolase, and synaptophysin. The tumor did not reveal mutation of VHL alleles. We herein present a case of HB of the adrenal gland and review of the literature.
- Juxtacortical chondromyxoid fibroma in the small bones: two cases with unusual location and a literature review
- Sun-Ju Oh, So Hak Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(3):157-160. Published online January 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.12.15
- 4,198 View
- 187 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare bone tumor of cartilaginous origin, representing less than 1% of all bone tumors. It preferentially arises in the eccentric location of the metaphysis of a long tubular bone. Juxtacortical locations are reported infrequently in the long bones and even more rarely in short tubular bones, with only three cases documented. Here we present two new cases of juxtacortical chondromyxoid fibroma in the small bones. One was an intracortical osteolytic lesion of the metatarsal bone of the foot with degenerative atypia that histologically should be differentiated from chondrosarcoma. The other was a phalangeal mass protruding into the interphalangeal joint of the hand, which had been labeled mistakenly as a soft tissue mass preoperatively. These cases illustrated that chondromyxoid fibromas have various the manifestations and should be included in the differential diagnosis of an osteolytic lesion or an exophytic mass in the small bones.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cartilage Forming Tumors of the Skeleton
Julio A. Diaz-Perez, Andrew E. Rosenberg
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2025; 32(2): 132. CrossRef
- Cartilage Forming Tumors of the Skeleton
Original Article
- Clinicopathologic implication of PD-L1 gene alteration in primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Ki Rim Lee, Jiwon Koh, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Hyun Jung Kwon, Jeong-Ok Lee, Jin Ho Paik
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(1):32-39. Published online November 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.10.05
- 4,122 View
- 164 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary adrenal (PA) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was previously reported as an aggressive subset of DLBCL, but its genetic features were not sufficiently characterized. From our previous study of DLBCL with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) gene alterations, we focused on PD-L1 gene alterations in PA-DLBCL with clinicopathologic implications.
Methods
We performed fluorescence in situ hybridization for PD-L1 gene translocation and amplification in PA-DLBCL (n = 18) and comparatively analyzed clinicopathologic characteristics with systemic non-adrenal (NA)-DLBCL (n = 90).
Results
PA-DLBCL harbored distinctive features (vs. NADLBCL), including high international prognostic index score (3–5) (72% [13/18] vs. 38% [34/90], p = .007), poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score (≥ 2) (47% [7/15] vs. 11% [10/90], p = .003), elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (78% [14/18] vs. 51% [44/87], p = .035) and MUM1 expression (87% [13/15] vs. 60% [54/90], p = .047). Moreover, PA-DLBCL showed frequent PD-L1 gene alterations (vs. NA-DLBCL) (39% [7/18] vs. 6% [5/86], p = .001), including translocation (22% [4/18] vs. 3% [3/87], p = .016) and amplification (17% [3/18] vs. 2% [2/87], p = .034). Within the PA-DLBCL group, PD-L1 gene–altered cases (vs. non-altered cases) tended to have B symptoms (p = .145) and elevated LDH (p = .119) but less frequent bulky disease (≥ 10 cm) (p = .119). In the survival analysis, PA-DLBCL had a poor prognosis for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) (vs. NA-DLBCL; p = .014 and p = .004). Within the PA-DLBCL group, PD-L1 translocation was associated with shorter OS and PFS (p < .001 and p = .012).
Conclusions
PA-DLBCL is a clinically aggressive and distinct subset of DLBCL with frequent PD-L1 gene alterations. PD-L1 gene translocation was associated with poor prognosis in PA-DLBCL.
Case Studies
- Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma with an unusual location in the rib
- Sun-Ju Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):75-78. Published online December 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.10.08
- 4,226 View
- 109 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma is a rare bone tumor, with fewer than 35 cases reported in the literature since 1984. This tumor usually occurs in the long bones of children and adolescents. In the current case, the tumor affected a rib. A 17-year-old boy presented with a mass in the right fifth rib. Radiologic findings revealed an osteolytic mass with cortical destruction and calcification; en bloc resection was performed. The tumor showed three distinct histologic features: bland spindle cell proliferation, benign cartilage nodules, and epiphyseal plate-like enchondral ossification. The pathologic diagnosis was fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma. The patient remains free of disease 1 year after the surgery. Pathological diagnosis of fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma can be challenging, especially when the tumor occurs in an unusual site. When any fibro-osseous lesion with a cartilaginous component is encountered, the possibility of fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma should be considered because of its locally aggressive behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma: a case report and a literature review
A. A. Karyagina, V. Yu. Roshchin, I. V. Sidorov, D. M. Konovalov
Pediatric Hematology/Oncology and Immunopathology.2024; 23(3): 158. CrossRef - Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma of pelvis—a potential diagnostic pitfall
Monalisa Hui, Shantveer G. Uppin, Ramakrishna Narayanan, K. Nageshwara Rao, B. Aravind Kumar
Skeletal Radiology.2023; 52(4): 791. CrossRef
- Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma: a case report and a literature review
- Pediatric granular cell tumor in the posterior wall of the larynx extending to the trachea
- Jungsuk Ahn, Na Rae Kim, Yong Han Sun
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):336-339. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.02.28
- 4,274 View
- 120 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Granular cell tumor (GCT) is a slow-growing benign neoplasm that can be found in any organ. Pediatric laryngotracheal GCT is rare. We experienced a 6-year-old boy suffering from a barking cough and symptoms of stridor and croup for one month. Head and neck computed tomography revealed a protruding mass that occluded 60% of the airway lumen. Under the impression of hemangioma or papilloma, excision revealed a submucosal non-encapsulated mass. Histologically, the mass was composed of sheets of large polyhedralshaped tumor cells containing plump eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and centrally placed, small, bland-appearing nuclei. The tumor cells were positive for S-100 protein, and voluminous eosinophilic cytoplasm was stained by diastase-resistant periodic acid-Schiff. The present report describes a unique case of a huge pediatric laryngeal GCT extending to the subglottic trachea. We also review the clinical course of pediatric laryngotracheal GCT and emphasize the importance of diagnosing GCT in children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric granular cell tumor of the larynx: A case report and literature review
Jing Ke, Junwei Xiong, Juhong Zhang, Haiyu Ma, Wei Yuan
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(4): 1070. CrossRef
- Pediatric granular cell tumor of the larynx: A case report and literature review
Original Articles
- Comparison of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue between Young and Old Patients
- Gyuheon Choi, Joon Seon Song, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim, Jong-Lyel Roh, Bu-Kyu Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):369-377. Published online October 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.16
- 6,887 View
- 184 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The worldwide incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue (SCCOT) in young patients has been increasing. We investigated clinicopathologic features of this unique population and compared them with those of SCCOT in the elderly to delineate its pathogenesis.
Methods
We compared clinicopathological parameters between patients under and over 45 years old. Immunohistochemical assays of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, androgen receptor, p53, p16, mdm2, cyclin D1, and glutathione S-transferase P1 were also compared between them.
Results
Among 189 cases, 51 patients (27.0%) were under 45 years of age. A higher proportion of women was seen in the young group, but was not statistically significant. Smoking and drinking behaviors between age groups were similar. Histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis showed no significant difference by age and sex other than higher histologic grades observed in young patients.
Conclusions
SCCOT in young adults has similar clinicopathological features to that in the elderly, suggesting that both progress via similar pathogenetic pathways. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Failure Rates in Young Nonsmoker Nondrinkers With Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue
Brianna M. Jones, Dillan F. Villavisanis, Eric J. Lehrer, Daniel R. Dickstein, Kunal K. Sindhu, Krzysztof J. Misiukiewicz, Marshall Posner, Jerry T. Liu, Vishal Gupta, Sonam Sharma, Scott A. Roof, Marita Teng, Eric M. Genden, Richard L. Bakst
The Laryngoscope.2023; 133(5): 1110. CrossRef - Characteristics of oral squamous cell carcinoma focusing on cases unaffected by smoking and drinking: A multicenter retrospective study
Hiroyuki Harada, Masahiro Kikuchi, Ryo Asato, Kiyomi Hamaguchi, Hisanobu Tamaki, Masanobu Mizuta, Ryusuke Hori, Tsuyoshi Kojima, Keigo Honda, Takashi Tsujimura, Yohei Kumabe, Kazuyuki Ichimaru, Yoshiharu Kitani, Koji Ushiro, Morimasa Kitamura, Shogo Shino
Head & Neck.2023; 45(7): 1812. CrossRef - Genetic characteristics of advanced oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma in young patients
Sehui Kim, Chung Lee, Hyangmi Kim, Sun Och Yoon
Oral Oncology.2023; 144: 106466. CrossRef - Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Frequency in Young Patients from Referral Centers Around the World
Rafael Ferreira e Costa, Marina Luiza Baião Leão, Maria Sissa Pereira Sant’Ana, Ricardo Alves Mesquita, Ricardo Santiago Gomez, Alan Roger Santos-Silva, Syed Ali Khurram, Artysha Tailor, Ciska-Mari Schouwstra, Liam Robinson, Willie F. P. van Heerden, Rami
Head and Neck Pathology.2022; 16(3): 755. CrossRef - Early-onset oral cancer as a clinical entity: aetiology and pathogenesis
E.S. Kolegova, M.R. Patysheva, I.V. Larionova, I.K. Fedorova, D.E. Kulbakin, E.L. Choinzonov, E.V. Denisov
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 51(12): 1497. CrossRef - The effect of age on the clinicopathological features of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Alaa S Saeed, Bashar H Abdullah
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2022; 34(1): 25. CrossRef - Survival Outcomes in Oral Tongue Cancer: A Mono-Institutional Experience Focusing on Age
Mohssen Ansarin, Rita De Berardinis, Federica Corso, Gioacchino Giugliano, Roberto Bruschini, Luigi De Benedetto, Stefano Zorzi, Fausto Maffini, Fabio Sovardi, Carolina Pigni, Donatella Scaglione, Daniela Alterio, Maria Cossu Rocca, Susanna Chiocca, Sara
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Meta-analysis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Young Adults with a Comparison to the Older Group Patients (2014–2019)
Khadijah Mohideen, C. Krithika, Nadeem Jeddy, Thayumanavan Balakrishnan, R. Bharathi, S. Leena Sankari
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 213. CrossRef - Modern perspectives of oral squamous cell carcinoma
A.A. Ivina
Arkhiv patologii.2020; 82(3): 55. CrossRef
- High Failure Rates in Young Nonsmoker Nondrinkers With Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Tongue
- Reclassification of Mongolian Diffuse Gliomas According to the Revised 2016 World Health Organization Central Nervous System Tumor Classification
- Enkhee Ochirjav, Bayarmaa Enkhbat, Tuul Baldandorj, Gheeyoung Choe
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):298-307. Published online August 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.07.15
- 5,946 View
- 110 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of central nervous system (CNS) tumors has been modified to incorporate the IDH mutation and 1p/19q co-deletion in the diagnosis of diffuse gliomas. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the feasibility and prognostic significance of the revised 2016 WHO classification of CNS tumors in Mongolian patients with diffuse gliomas.
Methods
A total of 124 cases of diffuse gliomas were collected, and tissue microarray blocks were made. IDH1 mutation was tested using immunohistochemistry, and 1p/19q co-deletion status was examined using fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis.
Results
According to the 2016 WHO classification, 124 cases of diffuse brain glioma were reclassified as follows: 10 oligodendroglioma, IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted; three anaplastic oligodendroglioma, IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted; 35 diffuse astrocytoma, IDHmut, 11 diffuse astrocytoma, IDHwt, not otherwise specified (NOS); 22 anaplastic astrocytoma, IDHmut, eight anaplastic astrocytoma, IDHwt, NOS; and 35 glioblastoma, IDHwt, NOS, respectively. The 2016 WHO classification presented better prognostic value for overall survival in patients with grade II tumors than traditional histological classification. Among patients with grade II tumors, those with oligodendroglioma IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted and diffuse astrocytoma IDHmut showed significantly higher survival than those with diffuse astrocytoma IDHwt, NOS (p<.01).
Conclusions
Mongolian diffuse gliomas could be reclassified according to the new 2016 WHO classification. Reclassification revealed substantial changes in diagnosis of both oligodendroglial and astrocytic entities. We have confirmed that the revised 2016 WHO CNS tumor classification has prognostic significance in Mongolian patients with diffuse gliomas, especially those with grade II tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeted next‐generation sequencing of adult gliomas for retrospective prognostic evaluation and up‐front diagnostics
J. K. Petersen, H. B. Boldt, M. D. Sørensen, S. Blach, R. H. Dahlrot, S. Hansen, M. Burton, M. Thomassen, T. Kruse, F. R. Poulsen, L. Andreasen, H. Hager, B. P. Ulhøi, S. Lukacova, G. Reifenberger, B. W. Kristensen
Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.2021; 47(1): 108. CrossRef
- Targeted next‐generation sequencing of adult gliomas for retrospective prognostic evaluation and up‐front diagnostics
- Association between Expression of 8-OHdG and Cigarette Smoking in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Ae Ri An, Kyoung Min Kim, Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Yong Chul Lee, Jong Hun Kim, Han Jung Chae, Myoung Ja Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):217-224. Published online March 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.20
- 7,513 View
- 239 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Exposure to cigarette smoking (CS) is a major risk factor for the development of lung cancer. CS is known to cause oxidative DNA damage and mutation of tumor-related genes, and these factors are involved in carcinogenesis. 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) is considered to be a reliable biomarker for oxidative DNA damage. Increased levels of 8-OHdG are associated with a number of pathological conditions, including cancer. There are no reports on the expression of 8-OHdG by immunohistochemistry in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods
We investigated the expression of 8-OHdG and p53 in 203 NSCLC tissues using immunohistochemistry and correlated it with clinicopathological features including smoking.
Results
The expression of 8-OHdG was observed in 83.3% of NSCLC. It was significantly correlated with a low T category, negative lymph node status, never-smoker, and longer overall survival (p < .05) by univariate analysis. But multivariate analysis revealed that 8-OHdG was not an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in NSCLC patients. The aberrant expression of p53 significantly correlated with smoking, male, squamous cell carcinoma, and Ki-67 positivity (p < .05).
Conclusions
The expression of 8-OHdG was associated with good prognostic factors. It was positively correlated with never-smokers in NSCLC, suggesting that oxidative damage of DNA cannot be explained by smoking alone and may depend on complex control mechanisms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable framework for automated segmentation and prediction of lung cancer in CT image using CapsNet with U-net segmentation
S.R. Vijayakumar, S. Aarthy, D. Deepa, P. Suresh
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2025; 99: 106873. CrossRef - Increased pretreatment triglyceride glucose-body mass index associated with poor prognosis in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Shaoming Guo, Yi Zhao, Yue Jiang, Huaping Ye, Ying Wang
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2024; 59: 412. CrossRef - Oxidative Damage and Telomere Length as Markers of Lung Cancer Development among Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Smokers
Elizabeth Córdoba-Lanús, Luis M. Montuenga, Angélica Domínguez-de-Barros, Alexis Oliva, Delia Mayato, Ana Remírez-Sanz, Francisca Gonzalvo, Bartolomé Celli, Javier J. Zulueta, Ciro Casanova
Antioxidants.2024; 13(2): 156. CrossRef - Automated determination of 8-OHdG in cells and tissue via immunofluorescence using a specially created antibody
Tobias Jung, Nicole Findik, Bianca Hartmann, Katja Hanack, Kai Grossmann, Dirk Roggenbuck, Marc Wegmann, René Mantke, Markus Deckert, Tilman Grune
Biotechnology Reports.2024; 42: e00833. CrossRef - Combination treatment of zinc and selenium intervention ameliorated BPA-exposed germ cell damage in SD rats: elucidation of molecular mechanisms
Chittaranjan Sahu, Gopabandhu Jena
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024; 397(9): 6685. CrossRef - Interplay of arsenic exposure and cigarette smoking on oxidative DNA damage in healthy males
Sepideh Nemati-Mansour, Mohammad Mosaferi, Javad Babaie, Asghar Mohammadpoorasl, Reza Dehghanzadeh, Leila Nikniaz, Mohammad Miri
Environmental Sciences Europe.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of tissue persistent organic pollutants and genetic polymorphisms in patients with benign and malignant kidney tumors
Rasih Kocagöz, İlgen Onat, Merve Demirbügen Öz, Burak Turna, Banu Sarsık Kumbaracı, Mehmet Nurullah Orman, Halit Sinan Süzen, Hilmi Orhan
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2024; 110: 104495. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Plasticity and Glucose Metabolic Alterations in Human Cancer under Oxidative Stress—From Viewpoints of Chronic Inflammation and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
Hui-Ting Lee, Chen-Sung Lin, Chao-Yu Liu, Po Chen, Chang-Youh Tsai, Yau-Huei Wei
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(17): 9458. CrossRef - Oxidative DNA Damage and Arterial Hypertension in Light of Current ESC Guidelines
Radka Hazuková, Zdeněk Zadák, Miloslav Pleskot, Petr Zdráhal, Martin Pumprla, Miloš Táborský
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(23): 12557. CrossRef - Significance of 8-OHdG Expression as a Predictor of Survival in Colorectal Cancer
Myunghee Kang, Soyeon Jeong, Sungjin Park, Seungyoon Nam, Jun-Won Chung, Kyoung Oh Kim, Jungsuk An, Jung Ho Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(18): 4613. CrossRef - Serum 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine Predicts Severity and Prognosis of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Peng Cao, Chen Zhang, Dong-Xu Hua, Meng-Die Li, Bian-Bian Lv, Lin Fu, Hui Zhao
Lung.2022; 200(1): 31. CrossRef - Redox signaling at the crossroads of human health and disease
Jing Zuo, Zhe Zhang, Maochao Luo, Li Zhou, Edouard C. Nice, Wei Zhang, Chuang Wang, Canhua Huang
MedComm.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of MDA and 8-OHdG expressions in ovine pulmonary adenocarcinomas by immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence methods
Emin Karakurt, Enver Beytut, Serpil Dağ, Hilmi Nuhoğlu, Ayfer Yıldız, Emre Kurtbaş
Acta Veterinaria Brno.2022; 91(3): 235. CrossRef - Dietary Antioxidants and Lung Cancer Risk in Smokers and Non-Smokers
Naser A. Alsharairi
Healthcare.2022; 10(12): 2501. CrossRef - Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy
Henry Jay Forman, Hongqiao Zhang
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery.2021; 20(9): 689. CrossRef - Association between tobacco substance usage and a missense mutation in the tumor suppressor gene P53 in the Saudi Arabian population
Mikhlid H. Almutairi, Bader O. Almutairi, Turki M. Alrubie, Sultan N. Alharbi, Narasimha R. Parine, Abdulwahed F. Alrefaei, Ibrahim Aldeailej, Abdullah Alamri, Abdelhabib Semlali, Alvaro Galli
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(1): e0245133. CrossRef - Measurement of uranium concentrations in urine samples of adult healthy groups in Najaf governorate with estimation of urine concentrations of 8-OHdG compound as biomarker for DNA damage
Samia K. Abbas, Dhuha S. Saleh, Hayder S. Hussain
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2021; 1879(3): 032097. CrossRef - Common Data Model and Database System Development for the Korea Biobank Network
Soo-Jeong Ko, Wona Choi, Ki-Hoon Kim, Seo-Joon Lee, Haesook Min, Seol-Whan Oh, In Young Choi
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11825. CrossRef - EVALUATION OF OXIDATIVE STATUS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS AND ADDITIONAL TOBACCO ABUSE: A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY
Didem ÖZKAL EMİNOĞLU, Varol ÇANAKÇI
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; : 1. CrossRef
- Sustainable framework for automated segmentation and prediction of lung cancer in CT image using CapsNet with U-net segmentation
- Guanabenz Acetate Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress–Related Cell Death in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- Hyo Jeong Kang, Hyang Sook Seol, Sang Eun Lee, Young-Ah Suh, Jihun Kim, Se Jin Jang, Eunsil Yu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(2):94-103. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.01.14
- 8,195 View
- 197 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Development of chemotherapeutics for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been lagging. Screening of candidate therapeutic agents by using patient-derived preclinical models may facilitate drug discovery for HCC patients.
Methods
Four primary cultured HCC cells from surgically resected tumor tissues and six HCC cell lines were used for high-throughput screening of 252 drugs from the Prestwick Chemical Library. The efficacy and mechanisms of action of the candidate anti-cancer drug were analyzed via cell viability, cell cycle assays, and western blotting.
Results
Guanabenz acetate, which has been used as an antihypertensive drug, was screened as a candidate anti-cancer agent for HCC through a drug sensitivity assay by using the primary cultured HCC cells and HCC cell lines. Guanabenz acetate reduced HCC cell viability through apoptosis and autophagy. This occurred via inhibition of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34, increased phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, increased activating transcription factor 4, and cell cycle arrest.
Conclusions
Guanabenz acetate induces endoplasmic reticulum stress–related cell death in HCC and may be repositioned as an anti-cancer therapeutic agent for HCC patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current trends and future prospects of drug repositioning in gastrointestinal oncology
Nayeralsadat Fatemi, Mina Karimpour, Hoda Bahrami, Mohammad Reza Zali, Vahid Chaleshi, Andrea Riccio, Ehsan Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, Mehdi Totonchi
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - ER stress signaling at the interphase between MASH and HCC
Younis Hazari, Eric Chevet, Béatrice Bailly-Maitre, Claudio Hetz
Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Small molecules for impairing endoplasmic reticulum in cancer
Tripti Mishra, Navneet Dubey, Sudipta Basu
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry.2024; 22(44): 8689. CrossRef -
Guanabenz acetate, an antihypertensive drug repurposed as an inhibitor of
Escherichia coli
biofilm
Arakkaveettil Kabeer Farha, Olivier Habimana, Harold Corke, Olaya Rendueles
Microbiology Spectrum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The integrated stress response in cancer progression: a force for plasticity and resistance
Caleb L. Lines, Morgan J. McGrath, Tanis Dorwart, Crystal S. Conn
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Multiple regulatory roles in hepatocellular carcinoma
Jiacheng Wu, Shan Qiao, Yien Xiang, Menying Cui, Xiaoxiao Yao, Ruixin Lin, Xuewen Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 142: 112005. CrossRef - The two faces of the Integrated Stress Response in cancer progression and therapeutic strategies
Eugenia Licari, Luis Sánchez-del-Campo, Paola Falletta
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2021; 139: 106059. CrossRef - Repurposing of Guanabenz acetate by encapsulation into long-circulating nanopolymersomes for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
Yusuf A. Haggag, Mohamed Yasser, Murtaza M. Tambuwala, Suleiman S. El Tokhy, Mohammad Isreb, Ahmed A. Donia
International Journal of Pharmaceutics.2021; 600: 120532. CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum stress: New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of retinal degenerative diseases
Marina S. Gorbatyuk, Christopher R. Starr, Oleg S. Gorbatyuk
Progress in Retinal and Eye Research.2020; 79: 100860. CrossRef - Delineating the role of eIF2α in retinal degeneration
Christopher R. Starr, Marina S. Gorbatyuk
Cell Death & Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Repositioning of Guanabenz in Conjugation with Gold and Silver Nanoparticles against Pathogenic Amoebae Acanthamoeba castellanii and Naegleria fowleri
Areeba Anwar, Mohammad Ridwane Mungroo, Ayaz Anwar, William J. Sullivan, Naveed Ahmed Khan, Ruqaiyyah Siddiqui
ACS Infectious Diseases.2019; 5(12): 2039. CrossRef
- Current trends and future prospects of drug repositioning in gastrointestinal oncology

 E-submission
E-submission












 First
First Prev
Prev



