Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Seokhyeon Lee, Bohyun Kim, Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):232-237. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.17
- 4,705 View
- 171 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aquaporin (AQP) expression has been investigated in various malignant neoplasms, and the overexpression of AQP is related to poor prognosis in some malignancies. However, the expression of AQP protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been extensively investigated by immunohistochemistry with large sample size.
Methods
We evaluated the AQP expression in 827 ccRCC with immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarray blocks and classified the cases into two categories, high and low expression.
Results
High expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) was found in 320 cases (38.7%), but aquaporin-3 was not expressed in ccRCC. High AQP1 expression was significantly related to younger age, low TNM stage, low World Health Organization/International Society of Urologic Pathology nuclear grade, and absence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, high AQP1 expression was also significantly associated with longer overall survival (OS; p<.001) and progression-specific survival (PFS; p<.001) and was an independent predictor of OS and PFS in ccRCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed the prognostic significance of AQP1 protein expression in ccRCC. These findings could be applied to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
César I. Gaspari, Carine Beaupere, Seth Richard, Estanislao Peixoto, Bouchra Lekbaby, Mirko Minini, Branko Dubravcic, Javier Vaquero, Marie Vallette, Ander Arbelaiz, Marion Janona, Corentin Louis, Pauline Le Gall, Cédric Coulouarn, Julieta Marrone, Juan E
The American Journal of Pathology.2026; 196(2): 428. CrossRef - Construction and validation of renal cell carcinoma tumor cell differentiation-related prognostic classification (RCC-TCDC): an integrated bioinformatic analysis and clinical study
Yifan Liu, Keqin Dong, Yuntao Yao, Bingnan Lu, Lei Wang, Guo Ji, Haoyu Zhang, Zihui Zhao, Xinyue Yang, Runzhi Huang, Wang Zhou, Xiuwu Pan, Xingang Cui
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Targeting PLOD2 induces epithelioid differentiation and improves therapeutic response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Xiangyu Chen, Dongkui Xu, Yu Ji, Xichen Dong, Xiaomei Dong, Zihan Li, Jingyu Tan, Qianqian Sun, Huixian Xin, Ziwei Liu, Qing Deng, Tao Wen, Yanjun Jia, Xuhui Zhu, Jian Liu
Journal of Advanced Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Exosomal MiR-874 as a Potential Biomarker for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Amal F. Gharib, Saad S. Al-Shehri, Abdulraheem Almalki, Ayman Alhazmi, Mamdouh Allahyani, Ahmed Alghamdi, Amani A. Alrehaili, Maha M. Bakhuraysah, Althobaiti Naif Saad M., Weal H. Elsawy
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
- Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Rare and Unique Intraosseous Lesion
- Boram Song, Hye Jin Ryu, Cheol Lee, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):499-504. Published online August 22, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.07.28
- 10,727 View
- 136 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Hibernoma is a rare benign tumor of adults that is composed of multivacuolated adipocytes resembling brown fat cells. Hibernoma typically occurs in soft tissue, and intraosseous examples are very rare. Intraosseous hibernomas can radiologically mimic metastatic carcinoma and other tumorous conditions. Methods: To collect the intraosseous hibernomas, we searched the pathologic database and reviewed the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained slides of bone biopsy samples performed to differentiate radiologically abnormal bone lesions from 2006 to 2016. A total of six intraosseous hibernoma cases were collected, and clinical and radiological information was verified from electronic medical records. H&E slide review and immunohistochemical staining for CD68, pan-cytokeratin, and S-100 protein were performed. Results: Magnetic resonance imaging of intraosseous hibernomas showed low signal intensity with slightly hyperintense foci on T1 and intermediate to high signal intensity on T2 weighted images. Intraosseous hibernomas appeared as heterogeneous sclerotic lesions with trabecular thickening on computed tomography scans and revealed mild hypermetabolism on positron emission tomography scans. Histopathologically, the bone marrow space was replaced by sheets of multivacuolated, foamy adipocytes resembling brown fat cells, without destruction of bone trabeculae. In immunohistochemical analysis, the tumor cells were negative for CD68 and pan-cytokeratin and positive for S-100 protein. Conclusions: Intraosseous hibernoma is very rare. This tumor can be overlooked due to its rarity and resemblance to bone marrow fat. Pathologists need to be aware of this entity to avoid misdiagnosis of this rare lesion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
Jawad Albashri, Ahmed Albashri, Muhannad Alhamrani, Abdulrahman Hassan, Hisham Shamah, Rayan Alhefzi, Najim Z. Alshahrani, Mohammed R. Algethami, Louis-Romée Le Nail, Ramy Samargandi
Current Oncology.2025; 32(10): 535. CrossRef - Imaging of Bone Surface Lesions
Utkarsh Parwal, Allison Khoo, Nicholas G. Rhodes, Patrick G. McEnulty, Eric V. Pang, Jonathan C. Baker, Benjamin E. Northrup, Theodore L. Vander Velde, Mariam A. Malik, Jack W. Jennings, Kelby B. Napier
RadioGraphics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma of the mandible: A case report
Jin-Woo Han
Journal of Korean Dental Association.2025; 63(10): 335. CrossRef - Intraosseous Lipoma of the Maxillary Sinus: First Documented Case in an Asian Patient and Review of the Literature
Eng Seng Yeoh, Tzy Harn Chua, Jacqueline S. G. Hwang, Sathiyamoorthy Selvarajan, Noah B. T. Teo, Kevin Seymour
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Case of Large Lateral Chest Wall Hibernoma
Lyubomir Gaydarski, Boycho Landzhov, Ivaylo Kamenov, Julian M Ananiev, Georgi P Georgiev
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma mimicking sclerotic bone metastasis—a case report
Ali Shaikh, Adil Basha, George Ray, Justin A. Bishop, Avneesh Chhabra
Skeletal Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Femoral hibernoma: unique intraosseous tumor
Gökhan Tonkaz, Ertugrul Cakir, Mehmet Tonkaz, Demet Sengul
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2024; 136(19-20): 581. CrossRef - Unusual Imaging Findings of Epithelioid Hemangioma: Case Report of Single Intramedullary Sclerotic Bone Lesion
Yun Chul Hwang, Tae Eun Kim, Jae Hyuck Yi
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(5): 986. CrossRef - Benign incidental do-not-touch bone lesions
Nuttaya Pattamapaspong, Wilfred CG Peh
The British Journal of Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma: clinicopathologic and imaging analysis of 18 cases
Chiraag N Gangahar, Carina A Dehner, David P Wang, Behrang Amini, Travis Hillen, Christopher O'Conor, Sydney N Jennings, Kathleen Byrnes, Elizabeth A Montgomery, Bogdan A Czerniak, Julia A Bridge, Molly C Schroeder, Jack W Jennings, Wei‐Lien Wang, John S
Histopathology.2023; 83(1): 40. CrossRef - Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Rare Entity in Orthopedics With Peculiar Radiological Features
Ramy Samargandi, Louis-Romée Le Nail, Gonzague de Pinieux, Matthias Tallegas, Elodie Miquelestorena-Standley
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma of the appendicular skeleton
Salvatore Gitto, Thom Doeleman, Michiel A. J. van de Sande, Kirsten van Langevelde
Skeletal Radiology.2022; 51(6): 1325. CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma: Two case reports and a review of the literature
Samantha N. Weiss, Ankit Mohla, Gord Guo Zhu, Christina Gutowski, Tae Won B Kim, Rohan Amin
Radiology Case Reports.2022; 17(7): 2477. CrossRef - Hibernoma of two contiguous vertebrae: uniqueness of a lesion already rare in itself
Donato MASTRANTUONO, Domenico MARTORANO, Guido REGIS, Federica ARABIA, Alessandra LINARI, Federica SANTORO
Journal of Radiological Review.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary extradural tumors of the spinal column
Varun Arvind, Edin Nevzati, Maged Ghaly, Mansoor Nasim, Mazda Farshad, Roman Guggenberger, Daniel Sciubba, Alexander Spiessberger
Journal of Craniovertebral Junction and Spine.2021; 12(4): 336. CrossRef - Spinal Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Mi-Kyung Um, Eugene Lee, Joon Woo Lee, Kyu Sang Lee, Yusuhn Kang, Joong Mo Ahn, Heung Sik Kang
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2020; 81(4): 965. CrossRef - Intraosseous hibernoma: A metastatic mimicker to consider on the differential
Allen Ko, Colin C. Rowell, James B. Vogler, Dmitri E. Samoilov
Radiology Case Reports.2020; 15(12): 2677. CrossRef - Co-expression of MDM2 and CDK4 in transformed human mesenchymal stem cells causes high-grade sarcoma with a dedifferentiated liposarcoma-like morphology
Yu Jin Kim, Mingi Kim, Hyung Kyu Park, Dan Bi Yu, Kyungsoo Jung, Kyoung Song, Yoon-La Choi
Laboratory Investigation.2019; 99(9): 1309. CrossRef - Intraosseous Hibernoma: Five Cases and a Review of the Literature
Francisco A. Myslicki, Andrew E. Rosenberg, Ivan Chaitowitz, Ty K. Subhawong
Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography.2019; 43(5): 793. CrossRef - Hibernoma Mimicking Atypical Lipomatous Tumor
Youssef Al Hmada, Inga-Marie Schaefer, Christopher D.M. Fletcher
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 42(7): 951. CrossRef
- Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
- Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):359-364. Published online June 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.16
- 9,088 View
- 168 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is presumed to be associated with adipogenic differentiation. Histone modification is known to be important for adipogenesis, and the function of histone demethylase plant homeodomain finger 2 (PHF2) has been noted. In addition, PHF2 may act as a tumor suppressor via epigenetic regulation of p53 and is reported to be reduced in colon cancer and stomach cancer tissues. In this study, we examined PHF2 expression in CCRCC specimens by immunohistochemistry.
Methods
We studied 254 CCRCCs and 56 non-neoplastic renal tissues from patients who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy between 2000 and 2003 at the Seoul National University Hospital. Tissue microarray blocks were prepared, and immunohistochemical staining for PHF2 was performed.
Results
Among 254 CCRCC cases, 150 cases (59.1%) showed high expression and 104 cases (40.1%) showed low expression. High expression of PHF2 was significantly correlated with a low Fuhrman nuclear grade (p < .001), smaller tumor size (p < .001), low overall stage (p = .003), longer cancer-specific survival (p = .002), and progression-free survival (p < .001) of the patients. However, it was not an independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis adjusted for Fuhrman nuclear grade and overall stage.
Conclusions
Our study showed that low expression of PHF2 is associated with aggressiveness and poor prognosis of CCRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
Dexter Kai Hao Thng, Lissa Hooi, Wai Khang Yong, Dennis Kappei, Tan Boon Toh, Edward Kai-Hua Chow
Oncogenesis.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Phosphoproteomics identifies determinants of PAK inhibitor sensitivity in leukaemia cells
Pedro Casado, Santiago Marfa, Marym M. Hadi, Henry Gerdes, Sandra M. Martin-Guerrero, Farideh Miraki-Moud, Vinothini Rajeeve, Pedro R. Cutillas
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of histone methylation in renal cell cancer: an update
Yanguang Hou, Yan Yuan, Yanze Li, Lei Wang, Juncheng Hu, Xiuheng Liu
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(3): 2735. CrossRef - Phosphorylation of PHF2 by AMPK releases the repressive H3K9me2 and inhibits cancer metastasis
Ying Dong, Hao Hu, Xuan Zhang, Yunkai Zhang, Xin Sun, Hanlin Wang, Weijuan Kan, Min-jia Tan, Hong Shi, Yi Zang, Jia Li
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HIF-1α-mediated augmentation of miRNA-18b-5p facilitates proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through attenuation PHF2
Peng Luo, Yan-dong Zhang, Feng He, Chang-jun Tong, Kai Liu, He Liu, Shi-zhuang Zhu, Jian-zhou Luo, Bing Yuan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of meta-analysis and supervised machine learning for pattern recognition in breast cancer using epigenetic data
Reza Panahi, Esmaeil Ebrahimie, Ali Niazi, Alireza Afsharifar
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2021; 24: 100629. CrossRef - PHF2 regulates homology-directed DNA repair by controlling the resection of DNA double strand breaks
Ignacio Alonso-de Vega, Maria Cristina Paz-Cabrera, Magdalena B Rother, Wouter W Wiegant, Cintia Checa-Rodríguez, Juan Ramón Hernández-Fernaud, Pablo Huertas, Raimundo Freire, Haico van Attikum, Veronique A J Smits
Nucleic Acids Research.2020; 48(9): 4915. CrossRef - Emerging of lysine demethylases (KDMs): From pathophysiological insights to novel therapeutic opportunities
Sarder Arifuzzaman, Mst Reshma Khatun, Rabeya Khatun
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 129: 110392. CrossRef - Biology and targeting of the Jumonji-domain histone demethylase family in childhood neoplasia: a preclinical overview
Tyler S. McCann, Lays M. Sobral, Chelsea Self, Joseph Hsieh, Marybeth Sechler, Paul Jedlicka
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2019; 23(4): 267. CrossRef - MiR-221 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Migration via Targeting PHF2
Yi Fu, Mingyan Liu, Fengxia Li, Li Qian, Ping Zhang, Fengwei Lv, Wenting Cheng, Ruixing Hou
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - PHF2 histone demethylase prevents DNA damage and genome instability by controlling cell cycle progression of neural progenitors
Stella Pappa, Natalia Padilla, Simona Iacobucci, Marta Vicioso, Elena Álvarez de la Campa, Claudia Navarro, Elia Marcos, Xavier de la Cruz, Marian A. Martínez-Balbás
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2019; 116(39): 19464. CrossRef - Plant homeodomain finger protein 2 as a novel IKAROS target in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Zheng Ge, Yan Gu, Qi Han, Justin Sloane, Qinyu Ge, Goufeng Gao, Jinlong Ma, Huihui Song, Jiaojiao Hu, Baoan Chen, Sinisa Dovat, Chunhua Song
Epigenomics.2018; 10(1): 59. CrossRef
- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
- Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor in the Stomach
- Sun Ah Shin, Jiwoon Choi, Kyung Chul Moon, Woo Ho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):428-432. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.16
- 9,803 View
- 141 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumors or PEComas can arise in any location in the body. However, a limited number of cases of gastric PEComa have been reported. We present two cases of gastric PEComas. The first case involved a 62-year-old woman who presented with a 4.2 cm gastric subepithelial mass in the prepyloric antrum, and the second case involved a 67-year-old man with a 5.0 cm mass slightly below the gastroesophageal junction. Microscopic examination revealed that both tumors were composed of perivascular epithelioid cells that were immunoreactive for melanocytic and smooth muscle markers. Prior to surgery, the clinical impression of both tumors was gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), and the second case was erroneously diagnosed as GIST even after microscopic examination. Although gastric PEComa is a very rare neoplasm, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of gastric submucosal lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor in the Ascending Colon: A Rare Case Involving a Patient With Tuberous Sclerosis
Kai Seharada, Masato Kitazawa, Satoshi Nakamura, Yuta Yamamoto, Yuji Soejima
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
Anuradha Sharma, Reetika Sharma, Jyoti Bala, Monika Sharma
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(1): 107. CrossRef - Unusual paediatric sigmoid perivascular epithelioid cell tumour with regional lymph node metastasis treated using gemcitabine and docetaxel: a case report and literature review
Hsiu-Chung Cheng, Chia-Yu Kuo, Ching-Wen Huang, Hsiang-Hung Shih, Chih-Hung Lin, Jaw-Yuan Wang
Journal of International Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gastric Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa)
Jinghong Xu, Yu Yan, Xueping Xiang, Peter Jiang, Xiangrong Hu, Wenjun Yang
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2019; 152(2): 221. CrossRef - Robotic wedge resection of a rare gastric perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: A case report
Alessandra Marano, Francesca Maione, Yanghee Woo, Luca Pellegrino, Paolo Geretto, Diego Sasia, Mirella Fortunato, Giulio Fraternali Orcioni, Roberto Priotto, Renato Fasoli, Felice Borghi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2019; 7(23): 4011. CrossRef
- A Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor in the Ascending Colon: A Rare Case Involving a Patient With Tuberous Sclerosis
- Mucinous Cystadenoma of the Testis: A Case Report with Immunohistochemical Findings
- Gilhyang Kim, Dohee Kwon, Hee Young Na, Sehui Kim, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):180-184. Published online February 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.30
- 10,622 View
- 126 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mucinous cystadenoma of the testis is a very rare tumor. Herein, we report a case of mucinous cystadenoma arising in the testis of a 61-year-old man, along with a literature review. Computed tomography showed a 2.5-cm-sized poorly enhancing cystic mass. Grossly, the tumor was a unilocular cystic mass filled with mucinous material and confined to the testicular parenchyma. Histologically, the cyst had a fibrotic wall lined by mucinous columnar epithelium without atypia. Immunohistochemical staining was positive for cytokeratin 20 and CDX2, as well as focally positive for cytokeratin 7. The pathologic diagnosis was mucinous cystadenoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of Paratesticular Appendageal Tumors, Morphology, Immunohistochemistry, and Recent Molecular Advances
Mathew Vega, Muhammad T. Idrees
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(1): 119. CrossRef - Cistoadenoma Mucinoso Paratesticular: Caso Interesante en el Instituto Guatemalteco de Seguridad Social
Edgar Estuardo González López, Carlos Gonzalo Estrada Pazos
Revista Guatemalteca de Urología.2023; 10(2): 16. CrossRef - Primary borderline mucinous tumor of the testis with postoperative metastasis: A rare case report
Yingyu Shi, Ling Song, Yan Luo
Radiology Case Reports.2023; 18(9): 3203. CrossRef - Case report: Misdiagnosis of primary mucinous cystadenoma of the testicle by ultrasound
Linlin Zhang, Jianyuan Xuan, Manxi Li, Mei Zhang, Yu Song, Ziang Pan, Bo Fan, Lin Lu, Hongyan Zhou, Yang Li
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Borderline Mucinous Testicular Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review
Changjuan Hao, Chunsong Kang, Xiaoyan Kang, Zhuanzhuan Yu, Tingting Li, Jiping Xue
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Ovarian-type Tumors (Mullerian Tumors) of the Testis: Clinicopathologic Findings with Recent Advances
Michelle S Lin, Alberto G Ayala, Jae Y Ro
annals of urologic oncology.2019; : 1. CrossRef - Borderline Mucinous Testicular Tumour: Diagnostic and Management difficulties
Krishan Pratap, Marlon Perera, Frances Malczewski, Rachel Esler
BMJ Case Reports.2018; 2018: bcr-2017-223787. CrossRef - Mucinous tumor arising in a giant sacrococcygeal teratoma
Fengtian Zhang, Xiaolong Yu, Jin Zeng, Min Dai
Medicine.2017; 96(47): e8759. CrossRef
- Review of Paratesticular Appendageal Tumors, Morphology, Immunohistochemistry, and Recent Molecular Advances
- Comparison of the FDA and ASCO/CAP Criteria for HER2 Immunohistochemistry in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
- Gilhyang Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):436-441. Published online October 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.12
- 10,600 View
- 121 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is one of the known oncogenes in urothelial carcinoma. However, the association between HER2 and the prognosis of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma (UUTUC) has not yet been fully clarified. The aim of this study was to evaluate HER2 expression using the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) criteria and American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) criteria and compare their prognostic significance in UUTUC.
Methods
HER2 expression was evaluated in 144 cases of UUTUC by immunohistochemistry (IHC) using tissue microarrays. We separately analyzed HER2 expression using the FDA and ASCO/CAP criteria. The IHC results were categorized into low (0, 1+) and high (2+, 3+) groups.
Results
Using the FDA criteria, 94 cases were negative, 38 cases were 1+, nine cases were 2+, and three cases were 3+. Using the ASCO/CAP criteria, 94 cases were negative, 34 cases were 1+, 13 cases were 2+, and three cases were 3+. Four cases showing 2+ according to the ASCO/CAP criteria were reclassified as 1+ by the FDA criteria. High HER2 expression by both the FDA criteria and ASCO/CAP criteria was significantly associated with International Society of Urological Pathology high grade (p = .001 and p < .001). The high HER2 expression group classified with the FDA criteria showed significantly shorter cancer-specific survival (p = .004), but the HER2 high and low expression groups classified with the ASCO/CAP criteria did not show significant differences (p = .161) in cancer-specific survival.
Conclusions
HER2 high expression groups were significantly associated with shorter cancer-specific survival, and our study revealed that the FDA criteria are more suitable for determining HER2 expression in UUTUC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review and meta-analysis for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 on upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients
Jianjun Ye, Xinyang Liao, Yu Qiu, Qiang Wei, Yige Bao
Tumori Journal.2024; 110(1): 25. CrossRef - ERBB2 Amplification as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
Annette Zimpfer, Said Kdimati, Melanie Mosig, Henrik Rudolf, Heike Zettl, Andreas Erbersdobler, Oliver W. Hakenberg, Matthias Maruschke, Björn Schneider
Cancers.2023; 15(9): 2414. CrossRef - Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) in Urologic Cancers
Hiroshi Fukushima, Baris Turkbey, Peter A. Pinto, Aki Furusawa, Peter L. Choyke, Hisataka Kobayashi
Cancers.2022; 14(12): 2996. CrossRef - Assessment of HER2 Protein Overexpression and Gene Amplification in Renal Collecting Duct Carcinoma: Therapeutic Implication
Manuela Costantini, Carla Azzurra Amoreo, Liborio Torregrossa, Greta Alì, Enrico Munari, Carmen Jeronimo, Rui Henrique, Sara Petronilho, Umberto Capitanio, Roberta Lucianò, Nazareno Suardi, Maria Teresa Landi, Umberto Anceschi, Aldo Brassetti, Vito Michel
Cancers.2020; 12(11): 3345. CrossRef
- A systematic review and meta-analysis for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 on upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Seminal Vesicle from Zinner Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Younghoon Kim, Hae Woon Baek, Eunoh Choi, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(1):85-88. Published online January 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.28
- 12,572 View
- 80 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Zinner Syndrome: Case report of atypical symptoms and literature
Alejandro Acuña-Pacheco, Eduardo González-Rojas, Pedro Iván Aguilar-Ordaz, Joel Porfirio Rodelo-López, Benjamin Bueno-Mendoza, Israel Hernández-Rivera, Jose Rene Jungfermann-Guzman, Jesús Rodolfo Favela-Camacho
Urology Case Reports.2025; 60: 102986. CrossRef - Zinner syndrome in pediatric patients: rare disease leading to challenging management
Ottavio Adorisio, Cinzia Orazi, Lorenzo Maria Gregori, Francesco De Peppo, Massimiliano Silveri
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinner syndrome: a rare diagnosis in infancy
Joanne Michelle Oida Rose, Ravi Banthia, Zain Tamboli, Hira Lal
BMJ Case Reports.2022; 15(5): e248558. CrossRef - Classifying seminal vesicle cysts in the diagnosis and treatment of Zinner syndrome: A report of six cases and review of available literature
Zhengwu Tan, Bing Li, Lan Zhang, Ping Han, Haitao Huang, Andrew Taylor, Xin Li
Andrologia.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental imaging findings suggesting Zinner syndrome in a young patient with pulmonary embolism: A case report
Benedikt Hergan, Franz A. Fellner, Kaveh Akbari
Radiology Case Reports.2020; 15(4): 437. CrossRef - Ectopic ureter associated with Zinner’s syndrome in a kidney recipient: case report and literature review
Korhan Tuncer, Gizem Kilinc, Ismail Sert, Goksever Akpinar, Cem Tugmen
Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira.2020; 66(5): 692. CrossRef - Zinner’s Syndrome: A Rare Diagnosis of Dysuria Based on Imaging
Ahmed Ibrahimi, Abdelmoughit Hosni, Idriss Ziani, Fatima Zahra Laamrani, Hachem El Sayegh, Laila Jroundi, Lounis Benslimane, Yassine Nouini, Apul Goel
Case Reports in Urology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the seminal vesicle
Lu Fang, Qian Hong, Lei Chen, Yi Wang, Liang-Kuan Bi, Dong-Dong Xie, De-Xin Yu
Medicine.2019; 98(12): e14788. CrossRef
- Zinner Syndrome: Case report of atypical symptoms and literature
- Transglutaminase 2 Expression and Its Prognostic Significance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Min Jee Park, Hae Woon Baek, Ye-Young Rhee, Cheol Lee, Jeong Whan Park, Hwal Woong Kim, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(1):37-43. Published online January 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.25
- 11,200 View
- 81 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
A few recent studies have demonstrated a possible role of transglutaminase 2 (TG2) in tumorigenesis or progression of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The aim of this study was to examine TG2 expression and its clinicopathologic significance in a large number of human clear cell RCCs (CCRCCs). Methods: We analyzed 638 CCRCC patients who underwent partial or radical nephrectomy between 1995 and 2005. The expression of TG2 was determined by immunohistochemistry and categorized into four groups, according to staining intensity: negative (0), mild (1+), moderate (2+), and strong (3+). Results: TG2 staining intensity was negative in 8.5% of CCRCC (n=54), 1+ in 32.6% (n=208), 2+ in 50.5% (n=322), and 3+ in 8.5% (n=54). Strong TG2 expression was correlated with high Fuhrman nuclear grade (p=.011), high T category (p=.049), metastasis (p=.043) and male sex (p<.001) but not with N category.The survival analysis showed a significant association between strong TG2 expression and worse overall and cancer-specific survival (p=.027 and p=.010, respectively). On multivariate analysis, strong TG2 expression was a marginally significant prognostic indicator for Fuhrman nuclear grade and TNM staging (p=.054). Conclusions: Our study is the first to demonstrate the clinicopathologic significance of TG2 expression in a large number of human CCRCC samples. Strong TG2 expression was associated with high nuclear grade and poor prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex-mediated effects of transglutaminase 2 inhibition on endothelial function in human resistance arteries from diabetic and non-diabetic patients
Khatera Saii, Judit Prat-Duran, Ulf Simonsen, Anders Riegels Knudsen, Jonas Amstrup Funder, Niels Henrik Buus, Estéfano Pinilla
Clinical Science.2025; 139(1): 1. CrossRef - Discovery of novel 1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4,7-dione based transglutaminase 2 inhibitors as p53 stabilizing anticancer agents in renal cell carcinoma
Ga-Ram Kim, Joon Hee Kang, Hyeon Joo Kim, Eunji Im, Jinsu Bae, Woo Sun Kwon, Sun Young Rha, Hyun Cheol Chung, Eun Yi Cho, Soo-Youl Kim, Yong-Chul Kim
Bioorganic Chemistry.2024; 143: 107061. CrossRef - Transglutaminase 2 is associated with adverse colorectal cancer survival and represents a therapeutic target
Patrizia Malkomes, Ilaria Lunger, Elsie Oppermann, Johannes Lorenz, Sara Fatima Faqar-Uz-Zaman, Jiaoyan Han, Sabrina Bothur, Paul Ziegler, Katrin Bankov, Peter Wild, Wolf Otto Bechstein, Michael A. Rieger
Cancer Gene Therapy.2023; 30(10): 1346. CrossRef - Transglutaminase Type 2-MITF axis regulates phenotype switching in skin cutaneous melanoma
Silvia Muccioli, Valentina Brillo, Tatiana Varanita, Federica Rossin, Elisabetta Zaltron, Angelo Velle, Giorgia Alessio, Beatrice Angi, Filippo Severin, Anna Tosi, Manuela D’Eletto, Luca Occhigrossi, Laura Falasca, Vanessa Checchetto, Roberto Ciaccio, Ame
Cell Death & Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of transglutaminase 2 in regulation of the balance between autophagy and apoptosis in tumor cells
Yu. A. Gnennaya, O. M. Semenov, N. A. Barlev
Advances in Molecular Oncology.2023; 10(4): 31. CrossRef - Application of a Fluorescence Anisotropy-Based Assay to Quantify Transglutaminase 2 Activity in Cell Lysates
Sandra Hauser, Paul Sommerfeld, Johanna Wodtke, Christoph Hauser, Paul Schlitterlau, Jens Pietzsch, Reik Löser, Markus Pietsch, Robert Wodtke
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 4475. CrossRef - The Biological and Biomechanical Role of Transglutaminase-2 in the Tumour Microenvironment
Robert Tempest, Sonia Guarnerio, Rawan Maani, Jamie Cooper, Nicholas Peake
Cancers.2021; 13(11): 2788. CrossRef - A Precision Strategy to Cure Renal Cell Carcinoma by Targeting Transglutaminase 2
Soo-Youl Kim, Jeffrey W. Keillor
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(7): 2493. CrossRef - Evaluation of nuclear NF-κB, transglutaminase2, and ERCC1 as predictors of platinum resistance in testicular tumors
Alan A. Azambuja, Paula Engroff, Bruna T. Silva, Roberta C. S. Zorzetti, Fernanda B. Morrone
International braz j urol.2020; 46(3): 353. CrossRef - Transglutaminase 2-Mediated p53 Depletion Promotes Angiogenesis by Increasing HIF-1α-p300 Binding in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Seon-Hyeong Lee, Joon Hee Kang, Ji Sun Ha, Jae-Seon Lee, Su-Jin Oh, Hyun-Jung Choi, Jaewhan Song, Soo-Youl Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(14): 5042. CrossRef - Role of Tissue Transglutaminase Catalytic and Guanosine Triphosphate-Binding Domains in Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression
Burge Ulukan, Ajna Bihorac, Tarik Sipahioglu, Robert Kiraly, Laszlo Fesus, Dilek Telci
ACS Omega.2020; 5(43): 28273. CrossRef - Transglutaminase 2: The Maestro of the Oncogenic Mediators in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Ayca Ece Nezir, Burge Ulukan, Dilek Telci
Medical Sciences.2019; 7(2): 24. CrossRef - Transglutaminase 2 takes center stage as a cancer cell survival factor and therapy target
Richard L. Eckert
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2019; 58(6): 837. CrossRef - Allosteric inhibition site of transglutaminase 2 is unveiled in the N terminus
Nayeon Kim, Joon Hee Kang, Won-Kyu Lee, Seul-Gi Kim, Jae-Seon Lee, Seon-Hyeong Lee, Jong Bae Park, Kyung-Hee Kim, Young-Dae Gong, Kwang Yeon Hwang, Soo-Youl Kim
Amino Acids.2018; 50(11): 1583. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma Is Abrogated by p53 Stabilization through Transglutaminase 2 Inhibition
Seon-Hyeong Lee, Won-Kyu Lee, Nayeon Kim, Joon Hee Kang, Kyung-Hee Kim, Seul-Gi Kim, Jae-Seon Lee, Soohyun Lee, Jongkook Lee, Jungnam Joo, Woo Sun Kwon, Sun Young Rha, Soo-Youl Kim
Cancers.2018; 10(11): 455. CrossRef - Tissue transglutaminase expression is necessary for adhesion, metastatic potential and cancer stemness of renal cell carcinoma
Yesim Bagatur, Ayca Zeynep Ilter Akulke, Ajna Bihorac, Merve Erdem, Dilek Telci
Cell Adhesion & Migration.2017; : 1. CrossRef - Characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by gene expression profiling
Bryan J. Thibodeau, Matthew Fulton, Laura E. Fortier, Timothy J. Geddes, Barbara L. Pruetz, Samreen Ahmed, Amy Banes-Berceli, Ping L. Zhang, George D. Wilson, Jason Hafron
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2016; 34(4): 168.e1. CrossRef - Prognostic role of tissue transglutaminase 2 in colon carcinoma
María Jesús Fernández-Aceñero, Sofía Torres, Irene Garcia-Palmero, Cristina Díaz del Arco, J. Ignacio Casal
Virchows Archiv.2016; 469(6): 611. CrossRef
- Sex-mediated effects of transglutaminase 2 inhibition on endothelial function in human resistance arteries from diabetic and non-diabetic patients
- ALK-Positive Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Large Series of Consecutively Resected Korean Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
- Cheol Lee, Jeong Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):452-457. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.452
- 9,651 View
- 67 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Recently, there have been a few reports of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cases with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (
ALK ) gene fusion. In this study, we screened consecutively resected RCCs from a single institution for ALK protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and then we performed fluorescencein situ hybridization to confirm theALK gene alteration in ALK immunohistochemistry-positive cases.Methods We screened 829 RCCs by ALK immunohistochemistry, and performed fluorescence
in situ hybridization analysis usingALK dual-color break-apart rearrangement probe. Histological review and additional immunohistochemistry analyses were done in positive cases.Results One ALK-positive case was found. Initial diagnosis of this case was papillary RCC type 2. This comprises 0.12% of all RCCs (1/829) and 1.9% of papillary RCCs (1/53). This patient was a 44-year-old male with RCC found during routine health check-up. He was alive without evidence of disease 12 years after surgery. The tumor showed a papillary and tubular pattern, and showed positivity for CD10 (focal), epithelial membrane antigen, cytokeratin 7, pan-cytokeratin, PAX-2, and vimentin.
Conclusions We found the first RCC case with
ALK gene rearrangement in Korean patients by ALK immunohistochemistry among 829 RCCs. This case showed similar histological and immunohistochemical features to those of previous adult cases withALK rearrangement, and showed relatively good prognosis.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Renal cell carcinoma with ALK-TPM3 gene fusion and ALK amplification: A case report and literature review
Xinzhuo Tu, Min Zhu, Qingyue Liu, Xu Liu, Yayun Qi, Yuanlin Zhang, Haili Li, Tianzhu Tao, Jinjin Chang, Jianping Zhu, Dawei Mu, Li Ren, Dengfeng Cao, Teng Li
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 266: 155814. CrossRef -
ALK-Rearranged Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report with Review of Literature
Gauri Deshpande, Amandeep Arora, Aparna Katdare, Gagan Prakash, Amit Joshi, Vedang Murthy, Sangeeta Desai, Santosh Menon
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of ALK-Rearranged Renal Cell Carcinoma
瑞珂 王
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(12): 746. CrossRef - ALK-Rearranged Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Study of 9 Cases With Expanding the Morphologic and Molecular Genetic Spectrum
Ming Zhao, Xiaona Yin, Xiaoqun Yang, Hualei Gan, Ni Chen, Guangjie Duan, Yanfeng Bai, Xiaodong Teng, Jiayun Xu, Rong Fang, Suying Wang, Shan Zhong, Xiaotong Wang, Lisong Teng
Modern Pathology.2024; 37(8): 100536. CrossRef - Activity of ALK Inhibitors in Renal Cancer with ALK Alterations: A Systematic Review
Giovanni Maria Iannantuono, Silvia Riondino, Stefano Sganga, Mario Roselli, Francesco Torino
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 3995. CrossRef - Novel, emerging and provisional renal entities: The Genitourinary Pathology Society (GUPS) update on renal neoplasia
Kiril Trpkov, Sean R. Williamson, Anthony J. Gill, Adebowale J. Adeniran, Abbas Agaimy, Reza Alaghehbandan, Mahul B. Amin, Pedram Argani, Ying-Bei Chen, Liang Cheng, Jonathan I. Epstein, John C. Cheville, Eva Comperat, Isabela Werneck da Cunha, Jennifer B
Modern Pathology.2021; 34(6): 1167. CrossRef - ESC, ALK, HOT and LOT: Three Letter Acronyms of Emerging Renal Entities Knocking on the Door of the WHO Classification
Farshid Siadat, Kiril Trpkov
Cancers.2020; 12(1): 168. CrossRef - ALK-rearranged renal cell carcinoma with a novel PLEKHA7-ALK translocation and metanephric adenoma-like morphology
Jen-Fan Hang, Hsiao-Jen Chung, Chin-Chen Pan
Virchows Archiv.2020; 476(6): 921. CrossRef - Characteristics of Renal Cell Carcinoma Harboring TPM3-ALK Fusion
Chang Gok Woo, Seok Jung Yun, Seung-Myoung Son, Young Hyun Lim, Ok-Jun Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(3): 262. CrossRef - Report From the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consultation Conference on Molecular Pathology of Urogenital Cancers
Sean R. Williamson, Anthony J. Gill, Pedram Argani, Ying-Bei Chen, Lars Egevad, Glen Kristiansen, David J. Grignon, Ondrej Hes
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2020; 44(7): e47. CrossRef - ALK rearranged renal cell carcinoma (ALK-RCC): a multi-institutional study of twelve cases with identification of novel partner genes CLIP1, KIF5B and KIAA1217
Naoto Kuroda, Kiril Trpkov, Yuan Gao, Maria Tretiakova, Yajuan J. Liu, Monika Ulamec, Kengo Takeuchi, Abbas Agaimy, Christopher Przybycin, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Soichiro Fushimi, Fumiyoshi Kojima, Malthide Sibony, Jen-Fan Hang, Chin-Chen Pan, Asli Yilma
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(12): 2564. CrossRef - ALK rearrangement in TFE3-positive renal cell carcinoma: Alternative diagnostic option to exclude Xp11.2 translocation carcinoma
Yiqi Zhu, Ning Liu, Wei Guo, Xiaohong Pu, Hongqian Guo, Weidong Gan, Dongmei Li
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(12): 153286. CrossRef - New and emerging renal entities: a perspective post‐WHO 2016 classification
Kiril Trpkov, Ondřej Hes
Histopathology.2019; 74(1): 31. CrossRef - Lack of expression of ALK and CD30 in breast carcinoma by immunohistochemistry irrespective of tumor characteristics
Samer Nassif, Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Michel Attieh, Maya Hijazi, Najla Fakhreddin, Tarek Aridi, Fouad Boulos
Medicine.2019; 98(32): e16702. CrossRef - Targeted next-generation sequencing revealed distinct clinicopathologic and molecular features of VCL-ALK RCC: A unique case from an older patient without clinical evidence of sickle cell trait
Xiao-tong Wang, Ru Fang, Sheng-bing Ye, Ru-song Zhang, Rui Li, Xuan Wang, Rong-hao Ji, Zhen-feng Lu, Heng-hui Ma, Xiao-jun Zhou, Qiu-yuan Xia, Qiu Rao
Pathology - Research and Practice.2019; 215(11): 152651. CrossRef - ALK-rearranged renal cell carcinomas in Polish population
Adam Gorczynski, Piotr Czapiewski, Aleksandra Korwat, Lukasz Budynko, Monika Prelowska, Krzysztof Okon, Wojciech Biernat
Pathology - Research and Practice.2019; 215(12): 152669. CrossRef - ALK-TPM3 rearrangement in adult renal cell carcinoma: a case report and literature review
Jing Yang, Lei Dong, Hong Du, Xiu-bo Li, Yan-xiao Liang, Guo-rong Liu
Diagnostic Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Genetics of Renal Cell Tumors: A Practical Diagnostic Approach
Reza Alaghehbandan, Delia Perez Montiel, Ana Silvia Luis, Ondrej Hes
Cancers.2019; 12(1): 85. CrossRef - ALK-TPM3 rearrangement in adult renal cell carcinoma: Report of a new case showing loss of chromosome 3 and literature review
Yohan Bodokh, Damien Ambrosetti, Valérie Kubiniek, Branwel Tibi, Matthieu Durand, Jean Amiel, Morgane Pertuit, Anne Barlier, Florence Pedeutour
Cancer Genetics.2018; 221: 31. CrossRef - Prognostic implications of polycomb proteins ezh2, suz12, and eed1 and histone modification by H3K27me3 in sarcoma
Yong Jin Cho, Soo Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Jung Woo Han, Kyoo-Ho Shin, Hyuk Hu, Kyung Sik Kim, Young Deuk Choi, Sunghoon Kim, Young Han Lee, Jin-Suck Suh, Joong Bae Ahn, Hyun Cheol Chung, Sung Hoon Noh, Sun Young Rha, Sung-Taek Jung, Hyo Song Kim
BMC Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Responses to Alectinib in ALK-rearranged Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sumanta K. Pal, Paulo Bergerot, Nazli Dizman, Cristiane Bergerot, Jacob Adashek, Russell Madison, Jon H. Chung, Siraj M. Ali, Jeremy O. Jones, Ravi Salgia
European Urology.2018; 74(1): 124. CrossRef - Genetic analysis and clinicopathological features of ALK‐rearranged renal cell carcinoma in a large series of resected Chinese renal cell carcinoma patients and literature review
Wenjuan Yu, Yuewei Wang, Yanxia Jiang, Wei Zhang, Yujun Li
Histopathology.2017; 71(1): 53. CrossRef - A case of anaplastic lymphoma kinase‐positive renal cell carcinoma coincident with Hodgkin lymphoma
Yuzo Oyama, Haruto Nishida, Takahiro Kusaba, Hiroko Kadowaki, Motoki Arakane, Tsutomu Daa, Dai Watanabe, Yasuyuki Akita, Fuminori Sato, Hiromitsu Mimata, Shigeo Yokoyama
Pathology International.2017; 67(12): 626. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and Molecular Pathology of Collecting Duct Carcinoma and Related Renal Cell Carcinomas
An Na Seo, Ghilsuk Yoon, Jae Y. Ro
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2017; 24(2): 65. CrossRef - The role of the polycomb repressive complex pathway in T and NK cell lymphoma: biological and prognostic implications
Soo Hee Kim, Woo Ick Yang, Yoo Hong Min, Young Hyeh Ko, Sun Och Yoon
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(2): 2037. CrossRef - New and emerging renal tumour entities
Naoto Kuroda, Ondřej Hess, Ming Zhou
Diagnostic Histopathology.2016; 22(2): 47. CrossRef - ALK‐rearranged renal cell carcinomas in children
Mariana M. Cajaiba, Lawrence J. Jennings, Stephen M. Rohan, Antonio R. Perez‐Atayde, Adrian Marino‐Enriquez, Jonathan A. Fletcher, James I. Geller, Katrin M. C. Leuer, Julia A. Bridge, Elizabeth J. Perlman
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2016; 55(5): 442. CrossRef - Two Cases of Renal Cell Carcinoma Harboring a Novel STRN-ALK Fusion Gene
Hironori Kusano, Yuki Togashi, Jun Akiba, Fukuko Moriya, Katsuyoshi Baba, Naomi Matsuzaki, Yoshiaki Yuba, Yusuke Shiraishi, Hiroshi Kanamaru, Naoto Kuroda, Seiji Sakata, Kengo Takeuchi, Hirohisa Yano
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(6): 761. CrossRef - Expanding the spectrum of ALK‐rearranged renal cell carcinomas in children: Identification of a novel HOOK1‐ALK fusion transcript
Mariana M. Cajaiba, Lawrence J. Jennings, David George, Elizabeth J. Perlman
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2016; 55(10): 814. CrossRef - TFE3-positive renal cell carcinomas are not always Xp11 translocation carcinomas: Report of a case with a TPM3-ALK translocation
Paul Scott Thorner, Mary Shago, Paula Marrano, Furqan Shaikh, Gino R. Somers
Pathology - Research and Practice.2016; 212(10): 937. CrossRef - ALK rearrangements-associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with unique pathological features in an adult
Marie Jeanneau, Valerie Gregoire, Claude Desplechain, Fabienne Escande, Dan Petre Tica, Sebastien Aubert, Xavier Leroy
Pathology - Research and Practice.2016; 212(11): 1064. CrossRef
- Renal cell carcinoma with ALK-TPM3 gene fusion and ALK amplification: A case report and literature review
- Histologic Variations and Immunohistochemical Features of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):426-432. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.426
- 12,932 View
- 89 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Due to advancements in treatment of metastatic and advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), it has become increasingly important to diagnose metastatic RCC and the specific subtype. In this study, we investigated the diverse histologic features of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cases in comparison with corresponding primary lesions.
Methods We identified 119 metastatic CCRCC cases from 81 corresponding primary lesions diagnosed between 1995 and 2010 and evaluated the diverse histologic and immunohistochemical features of these lesions.
Results A total of 44 primary lesions (54.3%) had a non-clear cell component in addition to a typical clear cell component. Of the 119 metastatic lesions, 63 lesions (52.9%) contained a non-clear cell component, and 29 metastatic lesions were composed of a non-clear cell component only. Rhabdoid features were the most frequent non-clear cell histology among the metastatic lesions. Metastatic CCRCCs mainly showed positive CD10 and epithelial membrane antigen staining and negative cytokeratin 7 staining.
Conclusions Metastatic CCRCC commonly showed a variety of histologic features. If there is a difficulty to diagnose metastatic CCRCC due to a variety of histologic features or small biopsy specimen, histologic review of the primary lesion and immunohistochemical analysis can help determine the correct diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
Adebowale J. Adeniran, Brian Shuch, Peter A. Humphrey
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(7): e65. CrossRef - Emerging Antibody-Drug Conjugate Therapies and Targets for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Harrison C. Gottlich, Reza Nabavizadeh, Mihai Dumbrava, Rodrigo Rodrigues Pessoa, Ahmed M. Mahmoud, Ishita Garg, Jacob Orme, Brian A. Costello, John Cheville, Fabrice Lucien
Kidney Cancer.2023; 7(1): 161. CrossRef - Painful, bleeding fingertip papule
Jane Gay, Sarah Simpson, Patrick Rush, Alex Holliday
JAAD Case Reports.2022; 21: 130. CrossRef - Development and initial clinical testing of a multiplexed circulating tumor cell assay in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Rory M. Bade, Jennifer L. Schehr, Hamid Emamekhoo, Benjamin K. Gibbs, Tamara S. Rodems, Matthew C. Mannino, Joshua A. Desotelle, Erika Heninger, Charlotte N. Stahlfeld, Jamie M. Sperger, Anupama Singh, Serena K. Wolfe, David J. Niles, Waddah Arafat, John
Molecular Oncology.2021; 15(9): 2330. CrossRef - Laparoscopic cytoreductive nephrectomy and adrenalectomy for metachronous RCC metastases—Case report
Bogdan Petrut, Cristina Eliza Bujoreanu, Vasile Vlad Hardo, Adrian Barbos, Bogdan Fetica
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 74: 268. CrossRef - Does CARMENA mark the end of cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Steven L. Chang, Toni K. Choueiri, Lauren C. Harshman
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2019; 37(8): 525. CrossRef - Metastatic TFE3-overexpressing renal clear cell carcinoma with dense granules: a histological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study
Shoujun Chen, Elba A. Turbat-Herrera, Guillermo A. Herrera, Meghna Chadha, Rodney E. Shackelford, Eric X. Wei
Ultrastructural Pathology.2018; 42(4): 369. CrossRef - The Clinical Activity of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Metastatic Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Rana R. McKay, Dominick Bossé, Wanling Xie, Stephanie A.M. Wankowicz, Abdallah Flaifel, Raphael Brandao, Aly-Khan A. Lalani, Dylan J. Martini, Xiao X. Wei, David A. Braun, Eliezer Van Allen, Daniel Castellano, Guillermo De Velasco, J. Connor Wells, Daniel
Cancer Immunology Research.2018; 6(7): 758. CrossRef - Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 359. CrossRef - Pulmonary metastasectomy from renal cell carcinoma including 3 cases with sarcomatoid component
Tsuyoshi Ueno, Motohiro Yamashita, Shigeki Sawada, Ryujiro Sugimoto, Noriko Nishijima, Yoshifumi Sugawara, Iku Ninomiya
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2016; 64(3): 149. CrossRef - Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer?
Aleksandra Semeniuk-Wojtaś, Rafał Stec, Cezary Szczylik
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2016; 34(5): 215. CrossRef - Concordance of Pathologic Features Between Metastatic Sites and the Primary Tumor in Surgically Resected Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sarah P. Psutka, John C. Cheville, Brian A. Costello, Suzanne B. Stewart-Merrill, Christine M. Lohse, Bradley C. Leibovich, Stephen A. Boorjian, R. Houston Thompson
Urology.2016; 96: 106. CrossRef - The Correlation of Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Lesions: A Tissue Microarray Study
Sung Han Kim, Weon Seo Park, Eun Young Park, Boram Park, Jungnam Joo, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
The Korean Journal of Urological Oncology.2016; 14(3): 152. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up and clinical course of a rare case of von Hippel-Lindau disease: A case report and review of the literature
YU ZOU, JINGJING XU, MINMING ZHANG
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(5): 3273. CrossRef - Genetic alterations in renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation
Carmen M. Perrino, Vishwanathan Hucthagowder, Michael Evenson, Shashikant Kulkarni, Peter A. Humphrey
Human Pathology.2015; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - High expression of APRIL correlates with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
Pathology - Research and Practice.2015; 211(11): 824. CrossRef - A Case of Cutaneous Metastasis from a Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with an Eosinophilic Cell Component to the Submandibular Region
Yusuke Amano, Sumie Ohni, Toshiyuki Ishige, Taku Homma, Tsutomu Yamada, Nobuyuki Nishimori, Norimichi Nemoto
Journal of Nihon University Medical Association.2015; 74(2): 73. CrossRef
- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report of 15 Cases Including Three Cases of Concurrent Other-Type Renal Cell Carcinomas
- Jeong Hwan Park, Cheol Lee, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):541-547. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.541
- 9,852 View
- 65 Download
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma (CCPRCC) is a recently established subtype of renal epithelial tumor. The aim of this study was to identify the diagnostic criteria of CCPRCC with an emphasis on immunohistochemical studies, and to report three cases with concurrent other-type renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods A total of 515 RCC patients that consecutively underwent surgical resection at Seoul National University Hospital from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2011 were screened. Each case was reviewed based on the histologic features and was evaluated immunohistochemically.
Results A total of 15 CCPRCCs were identified, which composed 2.9% of the total RCCs. The mean age was 52 years, and the average tumor size was 1.65 cm. All 15 cases showed low nuclear grade, no lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. The CCPRCCs showed variable architectural patterns including cystic, trabecular, papillary, and acinar. All of the cases showed moderate to intense immunoreactivity for cytokeratin 7 (CK7). CD10 was negative or showed focal weak positivity. Three cases had concurrent other-type RCC, including a clear cell RCC and an acquired cystic disease-associated RCC.
Conclusions The strong CK7 and negative or focal weak CD10 expression will be useful for the diagnosis of CCPRCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
Ankur R Sangoi, Harrison Tsai, Lara Harik, Jonathan Mahlow, Maria Tretiakova, Sean R Williamson, Michelle S Hirsch
Histopathology.2024; 84(7): 1167. CrossRef - Clinical features and Surgical Outcome of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Tumor: result from a prospective cohort
Si Hyun Kim, Jang Hee Han, Seung-hwan Jeong, Hyeong Dong Yuk, Ja Hyeon Ku, Cheol Kwak, Hyeon Hoe Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Chang Wook Jeong
BMC Urology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of multiple clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma with renal oncocytoma: a case report
Amine Hermi, Ahmed Saadi, Seif Mokadem, Ahlem Blel, Marouene Chakroun, Mohamed Riadh Ben Slama
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 2017. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Review and Update
Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Luan D. Truong
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 657. CrossRef - The Clinicopathologic and Molecular Landscape of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications in Diagnosis and Management
Stanley Weng, Renzo G. DiNatale, Andrew Silagy, Roy Mano, Kyrollis Attalla, Mahyar Kashani, Kate Weiss, Nicole E. Benfante, Andrew G. Winer, Jonathan A. Coleman, Victor E. Reuter, Paul Russo, Ed Reznik, Satish K. Tickoo, A. Ari Hakimi
European Urology.2021; 79(4): 468. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Characteristics and survival outcomes from a large single institutional series
James E. Steward, Sean Q. Kern, Liang Cheng, Ronald S. Boris, Yan Tong, Clint D. Bahler, Timothy A. Masterson, K. Clint Cary, Hristos Kaimakliotis, Thomas Gardner, Chandru P. Sundaram
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2021; 39(6): 370.e21. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: an update after 15 years
Sean R. Williamson
Pathology.2021; 53(1): 109. CrossRef - Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Jianping Zhao, Eduardo Eyzaguirre
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(9): 1154. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma – An indolent subtype of renal tumor
Wei-Jen Chen, Chin-Chen Pan, Shu-Huei Shen, Hsiao-Jen Chung, Chih-Chieh Lin, Alex T.L. Lin, Yen-Hwa Chang
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2018; 81(10): 878. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature
Sung Han Kim, Whi-An Kwon, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
World Journal of Nephrology.2018; 7(8): 155. CrossRef - Clinical features and survival analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A 10‑year retrospective study from two institutions
Yiqiu Wang, Ying Ding, Jian Wang, Min Gu, Zengjun Wang, Chao Qin, Conghui Han, Hongxia Li, Xia Liu, Pengfei Wu, Guangchao Li
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A contemporary series of renal masses with emphasis on recently recognized entities and tumors of low malignant potential: A report based on 624 consecutive tumors from a single tertiary center
Maria Rosaria Raspollini, Ilaria Montagnani, Rodolfo Montironi, Liang Cheng, Guido Martignoni, Andrea Minervini, Sergio Serni, Giulio Nicita, Marco Carini, Antonio Lopez-Beltran
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(7): 804. CrossRef - Renal Neoplasms With Overlapping Features of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Hari P. Dhakal, Jesse K. McKenney, Li Yan Khor, Jordan P. Reynolds, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Christopher G. Przybycin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(2): 141. CrossRef - New and emerging renal tumour entities
Naoto Kuroda, Ondřej Hess, Ming Zhou
Diagnostic Histopathology.2016; 22(2): 47. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Panel for Differentiating Renal Cell Carcinoma with Clear and Papillary Features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Pathology & Oncology Research.2015; 21(4): 893. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical panel for differentiating renal cell carcinoma with clear and papillary features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2015; 3(2): 68. CrossRef - Clear Cell-Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Kidney Not Associated With End-stage Renal Disease
Manju Aron, Elena Chang, Loren Herrera, Ondrej Hes, Michelle S. Hirsch, Eva Comperat, Philippe Camparo, Priya Rao, Maria Picken, Michal Michal, Rodolfo Montironi, Pheroze Tamboli, Federico Monzon, Mahul B. Amin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(7): 873. CrossRef - Papillary or pseudopapillary tumors of the kidney
Fang-Ming Deng, Max X. Kong, Ming Zhou
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(2): 124. CrossRef - Do Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinomas Have Malignant Potential?
Mairo L. Diolombi, Liang Cheng, Pedram Argani, Jonathan I. Epstein
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(12): 1621. CrossRef - Targeted next‐generation sequencing and non‐coding RNA expression analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma suggests distinct pathological mechanisms from other renal tumour subtypes
Charles H Lawrie, Erika Larrea, Gorka Larrinaga, Ibai Goicoechea, María Arestin, Marta Fernandez‐Mercado, Ondrej Hes, Francisco Cáceres, Lorea Manterola, José I López
The Journal of Pathology.2014; 232(1): 32. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma is the fourth most common histologic type of renal cell carcinoma in 290 consecutive nephrectomies for renal cell carcinoma
Haijun Zhou, Shaojiang Zheng, Luan D. Truong, Jae Y. Ro, Alberto G. Ayala, Steven S. Shen
Human Pathology.2014; 45(1): 59. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Incidence, morphological features, immunohistochemical profile, and biologic behavior: A single institution study
Borislav A. Alexiev, Cinthia B. Drachenberg
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(4): 234. CrossRef - MRI Phenotype in Renal Cancer
Naomi Campbell, Andrew B. Rosenkrantz, Ivan Pedrosa
Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2014; 23(2): 95. CrossRef
- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
- ERG Immunohistochemistry and Clinicopathologic Characteristics in Korean Prostate Adenocarcinoma Patients
- Ja Hee Suh, Jeong-Whan Park, Cheol Lee, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):423-428. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.423
- 10,281 View
- 47 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Transmembrane protease serine 2-ETS related gene (
TMPRSS2-ERG ) gene fusion, the most common genetic alternation in prostate cancer, is associated with protein expression of the oncogeneERG . Recently, an immunohistochemical staining method using an anti-ERG antibody was shown to have a strong correlation with altered ERG protein expression.Methods We analyzed a total of 303 radical prostatectomy specimens (obtained from Korean prostate cancer cases) using a constructed tissue microarray and ERG immunohistochemical staining. Thereafter, we evaluated the association between ERG expression and clinicopathological factors.
Results The ERG-positive rate was 24.4% (74/303) and significantly higher ERG expression was observed in the subgroup with a lower Gleason score (p=0.004). Analysis of the histologic pattern of prostate adenocarcinomas revealed that tumors with discrete glandular units (Gleason pattern 3) displayed higher frequency of ERG expression (p=0.016). The ERG-positive rate was lower than that found (approximately 50%) in studies involving western populations. Other factors including age, tumor volume, initial protein-specific antigen level, a pathological stage and margin status were not significantly related with the ERG expression.
Conclusions ERG immunohistochemical staining is significantly higher in tumors with well-formed glands and is associated with a lower Gleason score.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cross-sectional study of ERG expression and the relationship with clinicopathological features of Prostate cancer in Southwestern Uganda
Yekosani Mitala, Brian Ssenkumba, Abraham Birungi, Ritah Kiconco, Marvin Mwesigwa Mutakooha, Raymond Atwine
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relevance of ERG immunoexpression intensity for prostatic adenocarcinoma in radical prostatectomy of 635 samples
Priscilla Mariana Freitas Aguiar Feitosa, Carlos Gustavo Hirth, Isabelle Joyce De Lima Silva‐Fernandes, Conceição Aparecida Dornelas
APMIS.2023; 131(9): 465. CrossRef - Application and Pitfalls of Immunohistochemistry in Diagnosis of Challenging Genitourinary Cases
Jenny Ross, Guangyuan Li, Ximing J. Yang
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2020; 144(3): 290. CrossRef - ERG expression in prostate cancer: diagnostic significance and histopathological correlations
ManarA Abdel-Rahman, HanyO Habashy
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2020; 40(2): 212. CrossRef - The expression profile and heterogeneity analysis of ERG in 633 consecutive prostate cancers from a single center
Ling Nie, Xiuyi Pan, Mengni Zhang, Xiaoxue Yin, Jing Gong, Xueqin Chen, Miao Xu, Qiao Zhou, Ni Chen
The Prostate.2019; 79(8): 819. CrossRef - MiR-1271 Inhibits Cell Growth in Prostate Cancer by Targeting ERG
Miao Wang, Wei Gao, Dehong Lu, Lianghong Teng
Pathology & Oncology Research.2018; 24(2): 385. CrossRef - Ethnicity and ERG frequency in prostate cancer
Jason Sedarsky, Michael Degon, Shiv Srivastava, Albert Dobi
Nature Reviews Urology.2018; 15(2): 125. CrossRef - The Role of Immunohistochemical Analysis as a Tool for the Diagnosis, Prognostic Evaluation and Treatment of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Arie Carneiro, Álan Roger Gomes Barbosa, Lucas Seiti Takemura, Paulo Priante Kayano, Natasha Kouvaleski Saviano Moran, Carolina Ko Chen, Marcelo Langer Wroclawski, Gustavo Caserta Lemos, Isabela Werneck da Cunha, Marcos Takeo Obara, Marcos Tobias-Machado,
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic implications of ERG, PTEN, and fatty acid synthase expression in localized prostate cancer
Anan Fathi, Naglaa A. Mostafa, Nabila Hefzi, Khaled A. Mansour
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2018; 38(1): 162. CrossRef - Intrafocal heterogeneity of ERG protein expression and gene fusion pattern in prostate cancer
Ja Hee Suh, Jeong Hwan Park, Cheol Lee, Kyung Chul Moon
The Prostate.2017; 77(14): 1438. CrossRef - Diverse Immunoprofile of Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate with an Emphasis on the Prognostic Factors
Se Un Jeong, Anuja Kashikar Kekatpure, Ja-Min Park, Minkyu Han, Hee Sang Hwang, Hui Jeong Jeong, Heounjeong Go, Yong Mee Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(5): 471. CrossRef - Correlation of ERG immunohistochemistry with molecular detection of TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion
Ji-Youn Sung, Hwang Gyun Jeon, Byong Chang Jeong, Seong Il Seo, Seong Soo Jeon, Hyun Moo Lee, Han Yong Choi, So Young Kang, Yoon-La Choi, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2016; 69(7): 586. CrossRef - Prostate Cancer Prognosis Defined by the Combined Analysis of 8q, PTEN and ERG
Maria P. Silva, João D. Barros-Silva, Elin Ersvær, Wanja Kildal, Tarjei Sveinsgjerd Hveem, Manohar Pradhan, Joana Vieira, Manuel R. Teixeira, Håvard E. Danielsen
Translational Oncology.2016; 9(6): 575. CrossRef - Overexpression of ERG and Wild-Type PTEN Are Associated with Favorable Clinical Prognosis and Low Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer
Sung Han Kim, Soo Hee Kim, Jae Young Joung, Geon Kook Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Kyung Min Kang, Ami Yu, Byung Ho Nam, Jinsoo Chung, Ho Kyung Seo, Weon Seo Park, Kang Hyun Lee, Rui Medeiros
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(4): e0122498. CrossRef - ERG oncoprotein expression in prostate carcinoma patients of different ethnicities
GREGORY M. KELLY, YINK HEAY KONG, ALBERT DOBI, SHIV SRIVASTAVA, ISABELL A. SESTERHENN, RAJADURAI PATHMANATHAN, HUI MENG TAN, SHYH-HAN TAN, SOK CHING CHEONG
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2015; 3(1): 23. CrossRef - ERG positive prostatic cancer may show a more angiogenetic phenotype
Aleksandra Strzępek, Karolina Kaczmarczyk, Magdalena Białas, Joanna Szpor, Grzegorz Dyduch, Tomasz Szopiński, Piotr Chłosta, Krzysztof Okoń
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(12): 897. CrossRef - Recurrent Gene Fusions in Prostate Cancer: Their Clinical Implications and Uses
Daphne Hessels, Jack A. Schalken
Current Urology Reports.2013; 14(3): 214. CrossRef - ETV1 directs androgen metabolism and confers aggressive prostate cancer in targeted mice and patients
Esther Baena, Zhen Shao, Douglas E. Linn, Kimberly Glass, Melanie J. Hamblen, Yuko Fujiwara, Jonghwan Kim, Minh Nguyen, Xin Zhang, Frank J. Godinho, Roderick T. Bronson, Lorelei A. Mucci, Massimo Loda, Guo-Cheng Yuan, Stuart H. Orkin, Zhe Li
Genes & Development.2013; 27(6): 683. CrossRef
- A cross-sectional study of ERG expression and the relationship with clinicopathological features of Prostate cancer in Southwestern Uganda
- Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Its Prognostic Significance in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Ji Won Lee, Jeong Hwan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Ji-Young Choe, Hae Yoen Jung, Ji Yoen Chae, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):237-245. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.237
- 9,927 View
- 52 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The prognostic value of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remains unclear. The purposes of this study are to elucidate the clinical significance of COX-2 in clear cell RCC (CCRCC) and to assess the treatment effect of COX-2 inhibition on CCRCC cell lines.
Methods Using tumor samples obtained from 137 patients who had undergone nephrectomy at Seoul National University Hospital, we evaluated COX-2 expression on immunohistochemistry. Moreover, we performed the cell proliferation assay using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and cell invasion assay. Thus, we evaluated the effect of meloxicam, an inhibitor of COX-2, in two human CCRCC cell lines.
Results Cancer-specific survival (p=0.038) and progression-free survival (p=0.031) were shorter in the COX-2 high expression group. A multivariate logistic regression model showed that COX-2 expression was an independent risk factor for pTNM stage and Fuhrman nuclear grade. The MTT assay revealed that COX-2 inhibition led to the suppression of the proliferation of CCRCC cell lines. Moreover, it also reduced their invasion capacity.
Conclusions This study postulates that COX-2 is a poor prognostic indicator in human CCRCC, suggesting that COX-2 inhibition can be a potential therapy in CCRCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Arachidonic acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in AKI-to-CKD transition
Xiao-Jun Li, Ping Suo, Yan-Ni Wang, Liang Zou, Xiao-Li Nie, Ying-Yong Zhao, Hua Miao
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The tumor microenvironment and immune targeting therapy in pediatric renal tumors
Amy B. Hont, Benoit Dumont, Kathryn S. Sutton, John Anderson, Alex Kentsis, Jarno Drost, Andrew L. Hong, Arnauld Verschuur
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Free-fatty acid receptor-1 (FFA1/GPR40) promotes papillary RCC proliferation and tumor growth via Src/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB but suppresses migration by inhibition of EGFR, ERK1/2, STAT3 and EMT
Priyanka F. Karmokar, Nader H. Moniri
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Flavonoids derived from Anemarrhenae Rhizoma ameliorate inflammation of benign prostatic hyperplasia via modulating COX/LOX pathways
Xiaotong Cao, Ying Shang, Weigui Kong, Shuqing Jiang, Jun Liao, Ronghua Dai
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 284: 114740. CrossRef - Kirenol, darutoside and hesperidin contribute to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Siegesbeckia pubescens makino by inhibiting COX-2 expression and inflammatory cell infiltration
Yu-Sang Li, Jian Zhang, Gui-Hua Tian, Hong-Cai Shang, He-Bin Tang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2021; 268: 113547. CrossRef - Differential expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and cyclin D1 in salivary gland tumors
Jefferson da Rocha Tenório, Leorik Pereira da Silva, Marília Gabriela de Aguiar Xavier, Thalita Santana, George João Ferreira do Nascimento, Ana Paula Veras Sobral
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2018; 275(9): 2341. CrossRef - Retrospective evaluation ofCOX‐2 expression, histological and clinical factors as prognostic indicators in dogs with renal cell carcinomas undergoing nephrectomy
S. Carvalho, A. L. Stoll, S. L. Priestnall, A. Suarez‐Bonnet, K. Rassnick, S. Lynch, I. Schoepper, G. Romanelli, P. Buracco, M. Atherton, E. M. de Merlo, A. Lara‐Garcia
Veterinary and Comparative Oncology.2017; 15(4): 1280. CrossRef - Functional PTGS2 polymorphism-based models as novel predictive markers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients receiving first-line sunitinib
Arancha Cebrián, Teresa Gómez del Pulgar, María José Méndez-Vidal, María Luisa Gonzálvez, Nuria Lainez, Daniel Castellano, Iciar García-Carbonero, Emilio Esteban, Maria Isabel Sáez, Rosa Villatoro, Cristina Suárez, Alfredo Carrato, Javier Munárriz-Ferránd
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - COX-2 expression in ovarian cancer: an updated meta-analysis
Haiming Sun, Xuelong Zhang, Donglin Sun, Xueyuan Jia, Lidan Xu, Yuandong Qiao, Yan Jin
Oncotarget.2017; 8(50): 88152. CrossRef - COX-2 Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma and Correlations with Tumor Grade, Stage and Patient Prognosis
Hedieh Moradi Tabriz, Marzieh Mirzaalizadeh, Shahram Gooran, Farzaneh Niki, Maryam Jabri
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2016; 17(2): 535. CrossRef - Lipidomic Signatures and Associated Transcriptomic Profiles of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Kosuke Saito, Eri Arai, Keiko Maekawa, Masaki Ishikawa, Hiroyuki Fujimoto, Ryo Taguchi, Kenji Matsumoto, Yae Kanai, Yoshiro Saito
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Intratumoral expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a negative prognostic marker for patients with cutaneous melanoma
Łukasz Kuźbicki, Dariusz Lange, Agata Stanek-Widera, Barbara W. Chwirot
Melanoma Research.2016; 26(5): 448. CrossRef - New Insights on COX-2 in Chronic Inflammation Driving Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Honor J. Hugo, C. Saunders, R. G. Ramsay, E. W. Thompson
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia.2015; 20(3-4): 109. CrossRef - The Role of Prostaglandin E2 in Renal Cell Cancer Development: Future Implications for Prognosis and Therapy
Katarzyna Kaminska, Cezary Szczylik, Fei Lian, Anna M Czarnecka
Future Oncology.2014; 10(14): 2177. CrossRef - Genomics and epigenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Recent developments and potential applications
Małgorzata Rydzanicz, Tomasz Wrzesiński, Hans A.R. Bluyssen, Joanna Wesoły
Cancer Letters.2013; 341(2): 111. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of the Association of COX-2 (Cyclooxygenase-2) Immunoexpression with Prognosis in Human Osteosarcoma: A Meta-Analysis
Zhe Wang, Maolin He, Zengming Xiao, Hao Wu, Yang Wu, Dominique Heymann
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(12): e82907. CrossRef
- Arachidonic acid metabolism as a therapeutic target in AKI-to-CKD transition
- Practical Standardization in Renal Biopsy Reporting.
- So Young Jin, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Sun Hee Sung, Beom Jin Lim, Jee Young Han, Soon Won Hong, Hyun Ee Yim, Yeong Jin Choi, Yong Mee Cho, Myoung Jae Kang, Kyung Chul Moon, Hee Jeong Cha, Seung Yeon Ha, Mi Seon Kang, Mee Young So, Kwang Sun Suh, Jong Eun Joo, Yong Jin Kim, Nam Hee Won, Moon Hyang Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(6):613-622.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.6.613
- 5,698 View
- 185 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To standardize renal biopsy reporting and diagnosis, The Renal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists (RPSKSP) has developed a renal pathology reporting format for the native and allograft kidney.
METHODS
A consensus checklist of a provisional renal biopsy format was sent to all members of the RPSKSP. Feed back opinions regarding the practical application of the checklist to the diagnostic work were received.
RESULTS
Kidney biopsies require three essential examinations: by light microscopy, immunofluorescence (IF), and electron microscopy (EM). A final report of a renal biopsy should include information on specimen adequacy and a description of the morphologic change using a systematic semiquantitative method for each of the compartments, with optional separate IF and EM reports.
CONCLUSIONS
A standard renal biopsy report format is important in establishing clinicopathologic correlations, making reliable prognostic considerations, comparing the findings in sequential biopsies and evaluating the effects of therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional antihypertensive effect of magnesium supplementation with an angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypomagnesemic rats
Kyubok Jin, Tae Hee Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Yang Wook Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2013; 28(2): 197. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Features of IgA-Dominant Postinfectious Glomerulonephritis
Tai Yeon Koo, Gheun-Ho Kim, Hyang Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(2): 105. CrossRef
- Additional antihypertensive effect of magnesium supplementation with an angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypomagnesemic rats
- The Prognostic Implications of Cystic Change in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Heae Surng Park, Eun Jung Jung, Jae Kyung Myung, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):149-154.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.149
- 6,371 View
- 94 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cystic renal cell carcinoma has been reported to have a good prognosis. However, previous studies included cases of multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma, which has an excellent prognosis, and renal cell carcinoma with cystic necrosis, which has an adverse prognosis. Therefore, we analyzed the prognostic influence of cystic change in clear cell renal cell carcinoma after excluding those morphological features.
METHODS
We identified 225 patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma who underwent nephrectomy between 2001 and 2003. The clinicopathologic features were compared with clinical outcomes.
RESULTS
Cystic change in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (n = 66) was significantly associated with younger patient age (< 55), smaller tumor size (< or = 4 cm), lower pT stage (pT1, T2), M0 stage at initial diagnosis, lower tumor, node, and metastasis stage (I, II), and lower nuclear grade (1, 2). Patients with cystic change in clear cell renal cell carcinoma had significantly longer cancer-specific (p = 0.015) and progression-free survival (p = 0.004) than those without cystic change, by univariate analysis. Multivariate analysis revealed that cystic change significantly decreased the risk of cancer progression (risk ratio, 0.27; 95% confidence interval, 0.11 to 0.69).
CONCLUSIONS
In patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma, cystic change is a good independent predictor for survival. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on MRI of Cystic Renal Masses Including Bosniak Version 2019
Satheesh Krishna, Nicola Schieda, Ivan Pedrosa, Nicole Hindman, Ronaldo H. Baroni, Stuart G. Silverman, Matthew S. Davenport
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2021; 54(2): 341. CrossRef - Klotho plays a critical role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and clinical outcome
Ji-Hee Kim, Kyu-Hee Hwang, Sayamaa Lkhagvadorj, Jae Hung Jung, Hyun Chul Chung, Kyu-Sang Park, In Deok Kong, Minseob Eom, Seung-Kuy Cha
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2016; 20(3): 297. CrossRef - Insulin Receptor Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Relation to Prognosis
Sayamaa Lkhagvadorj, Sung Soo Oh, Mi-Ra Lee, Jae Hung Jung, Hyun Chul Chung, Seung-Kuy Cha, Minseob Eom
Yonsei Medical Journal.2014; 55(4): 861. CrossRef - Determination of the Cutoff Value of the Proportion of Cystic Change for Prognostic Stratification of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Heae Surng Park, Kyoungbun Lee, Kyung Chul Moon
Journal of Urology.2011; 186(2): 423. CrossRef
- Update on MRI of Cystic Renal Masses Including Bosniak Version 2019
- Expression of E-cadherin in Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma and Its Prognostic Implication.
- Eun Jung Jung, Heae Sung Park, Sun Young Min, Jeong Mo Bae, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):238-243.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.238
- 4,778 View
- 42 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma is a category of renal cell carcinoma composed of histologically characteristic tumor cells. E-cadherin is an intercellular adhesion protein that has been correlated with tumor aggressiveness in many carcinomas, including clear cell renal cell carcinoma. However, the significance of an E-cadherin expression in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma is not known.
METHODS
We evaluated the E-cadherin expression status of 65 chromophobe renal cell carcinomas by performing immunohistochemical staining with the tissue microarray method. The percentage of positively stained tumor cells was evaluated and this was then classified into two categories: a low expression where 0 to 25% of the cells are positive, and a high expression where more than 25% of the cells are positive.
RESULTS
Among 65 cases, 11 cases (17%) showed a low expression, and 54 cases (83.0%) showed a high expression. The tumors with low expression were more likely to have a higher stage but this was not significant (p=0.056). On the survival analysis, a low E-cadherin expression was significantly associated with poor cancer-specific survival (p=0.005) and progression-free survival (p=0.003).
CONCLUSIONS
The E-cadherin expression is a good prognostic marker for survival in patients with chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review and meta-analysis combined with bioinformatic analysis on the predictive value of E-cadherin in patients with renal cell carcinoma
Zikuan Zhang, Bo Xue, Yongquan Chen, Yuan Shao, Dongwen Wang
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2024; 24(9): 859. CrossRef
- A systematic review and meta-analysis combined with bioinformatic analysis on the predictive value of E-cadherin in patients with renal cell carcinoma
- The Relationship between the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Genotypes and the Methylation Status of the CpG Island Loci, LINE-1 and Alu in Prostate Adenocarcinoma.
- Jung Ho Kim, Nam Yun Cho, Baek Hee Kim, Wook Youn Kim, Bo Sung Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(1):26-35.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.1.26
- 4,835 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Genetic polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), in association with the influence of MTHFR upon DNA methylation, may cause differences of the methylation profile of cancer. Thus, we investigated the relationship between the methylation status of prostate adenocarcinoma and the genetic polymorphism of MTHFR.
METHODS
We examined 179 cases of prostate adenocarcinoma for determining the genotypes of MTHFR 677 and 1298, the methylation status of 16 CpG island loci and the methylation levels of the LINE-1 and Alu repeats with using polymerase chain reaction/restriction fragment length polymorphism, methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and combined bisulphite restriction analysis, respectively.
RESULTS
There was a higher proportion of the CT genotype of MTHFR 677 in the prostate adenocarcinoma than that in the normal control. The TT genotype of MTHFR 677 showed the highest frequency of methylation in six out of nine major CpG island loci, and these were which were frequently hypermethylated in prostate adenocarcinoma. The CT type showed the lowest methylation levels of LINE-1 and Alu among the MTHFR 677 genotypes. Interestingly, the CC type of MTHFR 1298 demonstrated favorable prognostic factors.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study is the first to examine the methylation profile of prostate adenocarcinoma according to the MTHFR genotypes. The differences of the cancer risk, the genomic hypomethylation and the prognosis between the MTHFR genotypes in prostate adenocarcinoma should be further explored. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between MTHFR 1298A>C Polymorphism and Spontaneous Abortion with Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy
Shin Young Kim, So Yeon Park, Ji Won Choi, Do Jin Kim, Shin Yeong Lee, Ji Hyae Lim, Jung Yeol Han, Hyun Mee Ryu, Min Hyoung Kim
American Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2011; 66(4): 252. CrossRef - Distinctive patterns of age-dependent hypomethylation in interspersed repetitive sequences
Pornrutsami Jintaridth, Apiwat Mutirangura
Physiological Genomics.2010; 41(2): 194. CrossRef
- Association Between MTHFR 1298A>C Polymorphism and Spontaneous Abortion with Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy
- Transthoracic Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Lung .
- Min Suk Kim, In Ae Park, Sun Hoo Park, Sung Shin Park, Hwal Wong Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Young Ah Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Ki Wha Park, Jeong wook Seo, Hyun Soon Lee, Eui Keun Ham
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1999;10(1):13-19.
- 2,039 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors analysed 2,653 cases of transthoracic fine needle aspiration cytology of the lung to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and its limitation. A comparison was made between the original cytologic and the final histologic diagnoses on 1,149 cases from 1,074 patients. A diagnosis of malignancy was established in 38.3% benign in 48.1%, atypical lesion in 2.3%, and inadequate one in 11.9% of the cases. Statistical data on cytologic diagnoses were as follows; specificity 98.9%: sensitivity of procedure, 76.8%: sensitivity of diagnosis, 95.5%: false positive 5 cases: false negative 18 cases: predictive value for malignancy, 98.8%: predictive value for benign lesion, 79.5%: overall diagnostic efficiency, 87.5%: typing accuracy in malignant tumor, 80%.
- Twist Expression in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Affects Patients Disease Free Survival and is Associated with Tumor Grade.
- Dong Il Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Seog Yun Park, Bomi Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(5):324-328.
- 2,093 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is critical for morphogenesis during embryonic development and is also implicated in the conversion of early-stage tumors into invasive malignancies. Recently, Twist has been identified to play an important role in EMTmediated metastatic progression of several types of human cancer. The present study examined the expression of Twist and evaluated its clinicopathologic significance in urothelial carcinoma of upper urinary tract.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical staining for Twist expression was performed on 70 upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas (UUT-UCs) using tissue microarray.
RESULTS
Immunohistochemical staining for Twist was positive in 31/70 cases (44.3%) of UUT-UCs. Twist expression was associated with high-grade and advanced-stage (ISUP grade, p<0.01; stage, p=0.045). The patients with Twist positive-tumors revealed lower disease free survival rate than those with Twist negative-tumors (p<0.01). The overall survival for patients with Twist positive-tumors was slightly worse than the patients with Twist negative- tumors, but the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.12).
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that Twist is a novel marker for advanced UUT-UC.
- The Prognostic Implications of the Histologic Subtype and the Expression of Phosphorylated ERK 1/2 in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Bo Sung Kim, Dong Il Kim, Tae Hoon Kang, Eun Shin, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(4):215-222.
- 2,035 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The authors of this study wanted to confirm the prognostic implication of the histologic subtype; further, we wanted to explore the expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (pERK) in papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC) and determine its clinicopathologic and prognostic significance.
METHODS
A total of 45 patients who underwent nephrectomy for PRCC were enrolled in this study. The hematoxylin and eosin slides were reviewed and pERK immunohistochemistry was performed.
RESULTS
Type 2 PRCC was significantly correlated with a larger tumor size (p=0.030), a higher nuclear grade (p<0.001), a more advanced tumor stage (p=0.041) and more frequent distant metastasis (p=0.019). The tumors were pERK-low (0 and 1+) in 30 cases (66.7%) and pERK-high (2+) in 15 cases (33.3%). The pERK-high PRCC was significantly associated with a smaller tumor size (p=0.001) and an earlier tumor stage (p=0.004). On the univariate analysis, the histologic subtype, the TNM stage and the pERK status were significantly associated with progression-free survival (PFS). Multivariate analysis showed that the histologic subtype (hazard ratio 22.81, p=0.042) and the TNM stage (hazard ratio 23.48, p=0.009) were independent prognostic factors for PFS.
CONCLUSIONS
Type 2 PRCC, together with the TNM stage, was identified as one of independent poor prognostic factors for PFS. The pERK status was a prognostic factor for PFS on the univariate analysis, but not on the multivariate analysis.
- Undifferentiated Sarcoma of the Liver: Clinical and Pathologic Study of 9 Cases.
- Kyung Chul Moon, Chong Jai Kim, Je G Chi, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(1):50-57.
- 2,297 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Undifferentiated sarcoma of the liver (USL) is a rare malignant tumor that is found in children and young adults.
METHODS
We performed a clinicopathologic analysis of 9 cases (M:F=4:5) of USL using immunohistochemical staining for vimentin, desmin, -smooth muscle actin (SMA), CD68, CD117, S-100, cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), and p53.
RESULTS
Grossly, the tumors were large, single, and well demarcated with areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. Microscopically, the tumors were composed of spindle to stellate cells and variable numbers of multinucleated giant cells with a myxoid background. The tumors had eosinophilic globules, small cystic spaces and fibrous pseudocapsule. Under immunohistochemical study, the tumor cells were positive for vimentin, CD68 and desmin, but negative for S-100 protein. p53 overexpression was noted in most cases, and four cases showed immunoreactivity for CD117. All patients received chemotherapy before or after the excision of the tumors. Two patients died during chemotherapy, but six patients survived without recurrence for 18, 35, 53, 57, 65 and 126 months after the initial diagnosis. The remaining one patient survived with recurrence for 20 months after the initial diagnosis.
CONCLUSION
Our cases showed unique pathological and immunohistochemical features similar to the cases of previous reports. In contrast to the previous reports, the outcome of our cases were not poor. Modern multimodal treatment including surgical resection combined with multiagent chemotherapy may contribute to the better prognoses.

 E-submission
E-submission
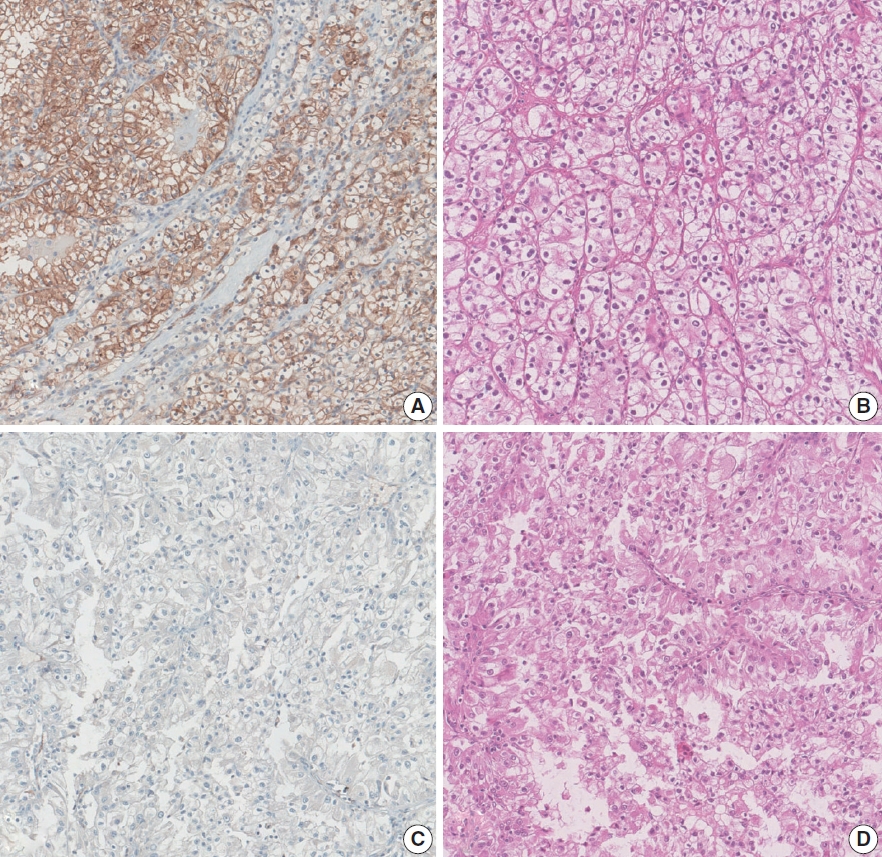

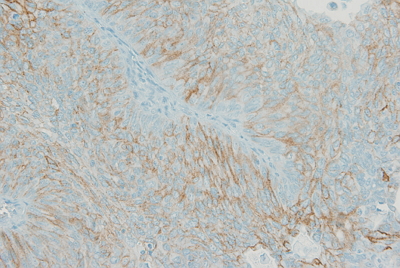
 First
First Prev
Prev



