Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cytological characteristics of Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterine corpus: a case report and literature review
- Junko Kuramoto, Chihiro Matsubara, Yasuko Sasamoto, Hitomi Tsukada, Shigemichi Hirose
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):340-347. Published online September 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.11
- 2,571 View
- 78 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterus is a rare morphological variant of uterine sarcoma. Müllerian adenosarcoma has been described histologically, though it is rare in the cytological literature. This report describes the cytological findings of a case of adenosarcoma arising from the endometrium. The patient was a Japanese woman in her 40s. Endometrial cytological and histological findings were observed for 5 years, from the appearance of a polypoid lesion until adenosarcoma was suspected, and then hysterectomy was performed. Based on these longitudinal cytological and histological observations, it was possible to identify the cytological characteristics of adenosarcoma: decrease in the glandular-to-stromal ratio; increase in stromal cell density; and progression of stromal cell atypia. This case stresses the importance and usefulness of endometrial cytology in the identification of the sarcomatous component in adenosarcoma.
- Primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a female patient: case report
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):84-90. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.30
- 4,760 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BCOR-rearranged sarcoma was classified by the World Health Organization in 2020 as a new subgroup of undifferentiated small round-cell sarcoma. It is known to occur very rarely in the kidney. This report presents the first case of a primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a 22-year-old woman. An 8-cm cystic mass was identified in the left kidney by abdominal pelvic computed tomography. Histopathologic examination revealed the mass to be composed of small round to oval or spindle cells with fibrous septa and a delicate vascular network. A BCOR::CCNB3 fusion was detected by next-generation sequencing–based molecular testing. BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma presents diagnostic difficulties, highlighting the importance of recognizing its histological features. Immunohistochemical markers are helpful for diagnosis, but genetic molecular testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis. These tumors have a very poor and aggressive prognosis, and an optimal therapeutic regimen has not yet been defined. Therefore, further studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
Jungo Imanishi, Kenji Sato, Yoshinao Kikuchi, Asako Yamamoto, Shiori Watabe, Taisuke Matsuyama, Chiaki Sato, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Hirotaka Kawano
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology.2025; 55(10): 1097. CrossRef
- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
- Uncommon granulomatous manifestation in Epstein-Barr virus–positive follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report
- Henry Goh Di Shen, Yue Zhang, Wei Qiang Leow
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):133-138. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.27
- 3,666 View
- 346 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic Epstein-Barr virus–positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (EBV+ IFDCS) represents a rare form of liver malignancy. The absence of distinct clinical and radiological characteristics, compounded by its rare occurrence, contributes to a challenging diagnosis. Here, we report a case of a 54-year-old Chinese female with a background of chronic hepatitis B virus treated with entecavir and complicated by advanced fibrosis presenting with a liver mass found on her annual surveillance ultrasound. Hepatectomy was performed under clinical suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunomorphologic characteristics of the tumor were consistent with EBV+ IFDCS with distinct non-caseating granulomatous inflammation. Our case illustrates the importance of considering EBV+ IFDCS in the differential diagnosis of hepatic inflammatory lesions. Awareness of this entity and its characteristic features is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing this rare neoplasm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef - EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma occurring in different organs: a case report and literature review
Wenhua Bai, Chunfang Hu, Zheng Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spleen EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report and literature review
Yi Xiao, Lanlan Li, Xiumei Zhan, Juner Xu, Yewu Chen, Qiuchan Zhao, Yinghao Fu, Xian Luo, Huadi Chen, Hao Xu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the liver: clinical features, imaging findings and potential diagnostic clues
Gui-Ling Huang, Man-Qian Huang, Yu-Ting Zhang, Hui-Ning Huang, Hong-Tao Liu, Xiao-Qing Pei
Abdominal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein‑Barr virus+ inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma with clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Qian Ye, Juan Zhao, Jiao He, Weishan Zhang
Oncology Letters.2025; 31(2): 1. CrossRef - Primary hepatic follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case study and literature review
Junjie Zhu, Ying Liang, Li Zhang, Bingqi Li, Danfeng Zheng, Hangyan Wang
Journal of International Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and ALK and cytokeratin expression: a case report
- Hyeong Rok An, Kyung-Ja Cho, Sang Woo Song, Ji Eun Park, Joon Seon Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):255-260. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.15
- 4,207 View
- 217 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) comprises of heterogeneous group of neoplasms that occasionally express epithelial markers on immunohistochemistry (IHC). We herein report the case of a patient who developed RMS of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and cytokeratin expression as cytomorphologic features. A 40-year-old man presented with a mass in his forehead. Surgical resection was performed, during which intraoperative frozen specimens were obtained. Squash cytology showed scattered or clustered spindle and epithelioid cells. IHC revealed that the resected tumor cells were positive for desmin, MyoD1, cytokeratin AE1/ AE3, and ALK. Although EWSR1 rearrangement was identified on fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK, and TFCP2 rearrangement were not noted. Despite providing adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, the patient died of tumor progression 10 months after diagnosis. We emphasize that a subset of RMS can express cytokeratin and show characteristic histomorphology, implying the need for specific molecular examination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Ahmed Shah, Andrew L. Folpe
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(3): 503. CrossRef - Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions
Erkan Gökçe, Murat Beyhan
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Morphology of Telangiectatic Osteosarcoma Associated With Сystic Content: A Case Report
David Makaridze, Armaz Mariamidze, Tamuna Gvianishvili, Giulia Ottaviani , Liana Gogiashvili
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,529 View
- 210 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- Primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone: a case report
- Ala Abu-Dayeh, Samir Alhyassat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):35-39. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.14
- 5,806 View
- 266 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary leiomyosarcoma of the bone is rare. Histologically, it resembles leiomyosarcoma of soft tissue. Given the rarity of this entity, its diagnosis should be made only after clinical studies and workup have excluded metastasis from other sites. Herein, we describe an additional case of primary bone leiomyosarcoma. We report a 32-year-old female patient, who presented with right knee pain and was found to have a right distal femur mass by imaging studies. Biopsy showed a neoplasm composed of fascicles of spindle cells, arranged in different patterns, with significant pleomorphism. The tumor cells were positive for smooth muscle actin, focally positive for desmin and H-caldesmon. No other masses in the body were detected by imaging studies. The diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma of the bone was rendered. Given the broad diagnostic differential of primary bone leiomyosarcoma, it is important to be aware of this rare bone tumor phenotype and of its histomorphologic and immunohistochemical features for an accurate diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Leiomyosarcoma of Bone: A Rare Case Series with Review of Literature
Jitin Goyal, Bineeta Parihar, Nitin Agarwal, Sulagna Manna, Anila Sharma, Sunil Kumar Puri
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Limb Leiomyosarcoma With Multifocal Musculoskeletal Soft Tissue Metastasis: A Case Report and Literature Review
Milad Haji Agha Bozorgi, Hoda Borooghani, Taghi Aghajanlou
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic Ethanol Exposure Induces Early Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Premalignant Changes in Gingival Keratinocytes: An In Vitro Model of Very Early Oral Carcinogenesis
Martin Philipp Dieterle, Thorsten Steinberg, Ayman Husari, Pascal Tomakidi
Cells.2025; 14(23): 1887. CrossRef
- Primary Leiomyosarcoma of Bone: A Rare Case Series with Review of Literature
- A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of primary and secondary breast angiosarcoma
- Evi Abada, Hyejeong Jang, Seongho Kim, Rouba Ali-Fehmi, Sudeshna Bandyopadhyay
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):342-353. Published online October 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.31
- 6,153 View
- 149 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
We aimed to study the clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical (IHC) (CD117, c-Myc, and p53) characteristics, and overall survival of primary and secondary breast angiosarcoma (BAS).
Methods
This was a retrospective study of BAS cases diagnosed between 1997 and 2020 at our institution. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides were reviewed for tumor morphology, margin status, and lymph node metastasis. CD117, p53, D2-40, CD31, and c-Myc IHC stains were performed on 11 viable tissue blocks. Additional clinical information was obtained from the electronic medical records.
Results
Seventeen patients with BAS were identified. Of these, five (29%) were primary and 12 (71%) were secondary BAS, respectively. The median age at diagnosis for primary BAS was 36 years. The median age at diagnosis for secondary BAS was 67 years. The median time to secondary BAS development following radiotherapy was 6.5 years (range, 2 to 12 years). There was no significant difference between primary and secondary BAS in several histopathologic parameters examined, including histologic grade, necrosis, mitotic count, lymph node metastasis, and positive tumor margins. There was also no difference in CD117, p53, D2-40, CD31, and c-Myc expression by IHC between primary and secondary BAS. During a median followup of 21 months, primary BAS had two (40%) reported deaths and secondary BAS had three (25%) reported deaths. However, this difference in survival between both groups was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.09 to 3.28; p = .450).
Conclusions
BAS is a rare and aggressive disease. No histologic, IHC (CD117, c-Myc, and p53), or survival differences were identified between primary and secondary BAS in this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Angiosarcoma: a systematic review of biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic strategies
Huyen Thuc Tran Luong, Sofie Vercammen, Ario de Marco, Hilde de Rooster, Antonio Cosma
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Etiology, pathogenesis, and management of angiosarcoma associated with implants and foreign body: Clinical cases and research updates
Ramy Samargandi
Medicine.2024; 103(18): e37932. CrossRef - Ovarian angiosarcoma: A systematic review of literature and survival analysis
Shafi Rehman, Arya Harikrishna, Amisha Silwal, B.R. Sumie, Safdar Mohamed, Nisha Kolhe, Meghana Maddi, Linh Huynh, Jesus Gutierrez, Yoshita Rao Annepu, Ameer Mustafa Farrukh
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 73: 152331. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for radiation associated angiosarcoma (RAAS) of the breast: A retrospective single center study
Stijn J.C. van der Burg, Sophie J.M. Reijers, Anke Kuijpers, Lotte Heimans, Astrid N. Scholten, Rick L.M. Haas, Hester van Boven, Willemijn M. Kolff, Marie-Jeanne T.F.D. Vrancken Peeters, Martijn Kerst, Beatrijs A. Seinstra, Neeltje Steeghs, Winette T.A.
The Breast.2024; 78: 103825. CrossRef - Lymph node involvement in secondary breast angiosarcoma – a case presentation
Adriana Irina Ciuvică, Tiberiu Augustin Georgescu , Andrei Dennis Voichiţoiu , Angela Arsene , Luchian Marinescu , George Ionuţ Bucur , Livia Iordache , Nahedd Saba
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology.2024; 65(3): 523. CrossRef - Primary ovarian angiosarcoma: Two case reports and review of literature
Ying Zhou, Yi-Wen Sun, Xiao-Yang Liu, Dan-Hua Shen
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(21): 5122. CrossRef
- Angiosarcoma: a systematic review of biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic strategies
- Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) in the differential diagnosis of osteogenic and non-osteogenic bone and soft tissue tumors
- Sharon Milton, Anne Jennifer Prabhu, V. T. K. Titus, Rikki John, Selvamani Backianathan, Vrisha Madhuri
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):270-280. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.07.11
- 7,230 View
- 134 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The diagnosis of osteosarcoma (OSA) depends on clinicopathological and radiological correlation. A biopsy is considered the gold standard for OSA diagnosis. However, since OSA is a great histological mimicker, diagnostic challenges exist. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) can serve as an adjunct for the histological diagnosis of OSA. Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) was recently described as a reliable adjunct immunohistochemical marker for the diagnosis of OSA.
Methods
We investigated the IHC expression of SATB2 in 95 OSA and 100 non-osteogenic bone and soft tissue tumors using a monoclonal antibody (clone EPNCIR30A). The diagnostic utility of SATB2 and correlation with clinicopathological parameters were analyzed.
Results
SATB2 IHC was positive in 88 out of 95 cases (92.6%) of OSA and 50 out of 100 cases (50.0%) of primary non-osteogenic bone and soft tissue tumors. Of the 59 bone tumors, 37 cases (62.7%) were positive for SATB2, and of the 41 soft tissue tumors, 13 cases (31.7%) were positive for SATB2. The sensitivity of SATB2 as a diagnostic test was 92.6%, specificity 50%, positive predictive value 63.8%, and negative predictive value 87.7%.
Conclusions
Although SATB2 is a useful diagnostic marker for OSA, other clinical, histological and immunohistochemical features should be considered for the interpretation of SATB2. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The diagnostic utility of SATB2 immunohistochemistry as an adjunct for differentiating osteogenic from non-osteogenic bone tumors: A systematic review and Meta-analysis
Yuchen Lou, Xuan Liu, Chenxiao Ma, Xin Liu
Bone.2026; 203: 117721. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Characterization of Feline Giant Cell Tumor of Bone (GCTb): What We Know and What We Can Learn from the Human Counterpart
Ilaria Porcellato, Giuseppe Giglia, Leonardo Leonardi
Animals.2025; 15(5): 699. CrossRef - Epigallocatechin gallate impels osteogenic differentiation of human BMSCs by targeting the METTL3/SATB2/Wnt/β-catenin axis
Qiao Ren, Kang Chen, Lin Wang
Letters in Drug Design & Discovery.2025; 22(3): 100027. CrossRef - A case of cardiac undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma treated with post-operative radiotherapy followed by heart transplantation
Sungyeon Jung, Eun Na Kim, Hye In Lee, Hak Jae Kim, Jiwon Koh
Cardiovascular Pathology.2025; 79: 107760. CrossRef - Osteoblastic Osteosarcoma With Diverse Histomorphology: Diagnostic Insights From SATB2 and CD56 Immunoexpression
Padmaraj Hegde, Reshma Amin, Vijith Vittal Shetty, Pushparaja Shetty
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2025; 0: 1. CrossRef - High-throughput 3D engineered paediatric tumour models for precision medicine
MoonSun Jung, Valentina Poltavets, Joanna N Skhinas, Gabor Tax, Alvin Kamili, Jinhan Xie, Sarah Ghamrawi, Philipp Graber, Jie Mao, Marie Wong-Erasmus, Louise Cui, Kathleen Kimpton, Pooja Venkat, Chelsea Mayoh, Angela Lin, Emmy D G Fleuren, Ashleigh M Ford
Molecular Systems Biology.2025; 21(12): 1748. CrossRef - SATB2 immunohistochemistry in osteosarcoma: Utility in diagnosis and differentiation from histologic mimics
Supriya Gangula, Monalisa Hui, Shantveer G. Uppin, B Arvind Kumar, K Nageshwara Rao, B Rajeev Reddy, G Sadashivudu
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2025; 68(3): 518. CrossRef - Early-onset metastatic fibroblastic osteosarcoma of the metatarsus in a young cat: a case report
Mojtaba Kiakojoori, Hossein Kazemi Mehrjerdi, Ali Mirshahi, Mahdieh Zaeemi, Mohsen Maleki
BMC Veterinary Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Favorable treatment response to high‐grade sarcoma in neurofibromatosis 1
Michelle H. Talukder, Mauli M. Patel, Tala Al‐Saghir, Ghadir K. Katato, Janet Poulik, William J. Powell, Alysia K. Kemp, Steven Miller, Danielle Bell, Jeffrey W. Taub
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The diagnostic utility of SATB2 immunohistochemistry as an adjunct for differentiating osteogenic from non-osteogenic bone tumors: A systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Primary pulmonary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare entity and a literature review
- Priyanka Singh, Aruna Nambirajan, Manish Kumar Gaur, Rahul Raj, Sunil Kumar, Prabhat Singh Malik, Deepali Jain
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):231-237. Published online July 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.05.08
- 6,614 View
- 129 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma (EIMS) is an aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions and is associated with high risk of local recurrence and poor prognosis. Herein, we present a young, non-smoking male who presented with complaints of cough and dyspnoea and was found to harbor a large right lower lobe lung mass. Biopsy showed a high-grade epithelioid to rhabdoid tumor with ALK and desmin protein expression. The patient initially received 5 cycles of crizotinib and remained stable for 1 year; however, he then developed multiple bony metastases, for which complete surgical resection was performed. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of EIMS, with ALK gene rearrangement demonstrated by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Postoperatively, the patient is asymptomatic with stable metastatic disease on crizotinib and has been started on palliative radiotherapy. EIMS is a very rare subtype of IMT that needs to be included in the differential diagnosis of ALKexpressing lung malignancies in young adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
Cancers.2025; 17(8): 1327. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: Case Series With a First Report of CLTC::ALK Fusion in an Aggressive Disease
Daisy Maharjan, Carina Dehner, Ali Alani, Robert Bell, Sheila Segura
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ALK rearranged malignant mesenchymal neoplasms of thorax: therapeutically targetable ‘ALKomas’ beyond the spectrum of non-small cell lung carcinomas and thoracic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors
Shreya Sadhu, Adarsh Barwad, Asit Ranjan Mridha, Prabhat Singh Malik, Aruna Nambirajan, Deepali Jain
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(5): 1003. CrossRef - Mediastinal epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with the EML4‐ALK fusion: A case report and literature review
Tingyu Pan, Xinyu Sun, Xiao Wu, Futing Tang, Xianmei Zhou, Qian Wang, Shi Chen
Respirology Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(3): 141. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: A Report of a Rare Case
Varun Ronanki, Vaddatti Tejeswini, Inuganti Venkata Renuka, Shaik Raheema, Bakkamanthala S K Kanth
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thoracic epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare and aggressive disease with case report and literature review
Linke Yang, Pei Li, Runze Liu, Baomin Feng, Huiqing Mao, Xiaoyong Tang, Guangjian Yang
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with exceptionally long response to lorlatinib—a case report
Rafał Becht, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Justyna Żychowska, Wojciech Poncyljusz, Aleksandra Łanocha, Katarzyna Kozak, Ewa Gabrysz-Trybek, Paweł Domagała
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rare giant epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the abdominal cavity in a child: a case report and review of the literature
Jinzhou Li, Haixing Su, Sheng Zhang, Xianyun Chen, Chongzhi Hou, Tao Cheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma treated with an ALK TKI ensartinib
Mengmeng Li, Ruyue Xing, Jiuyan Huang, Chao Shi, Chunhua Wei, Huijuan Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma With Poor Response to Crizotinib: A Case Report
Soheila Aminimoghaddam, Roghayeh Pourali
Clinical Medicine Insights: Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a case report and brief literature review
Weidong Dou, Yu Guan, Tao Liu, Hang Zheng, Shuo Feng, Yingchao Wu, Xin Wang, Zhanbing Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
- Metastatic leiomyosarcoma of the thyroid gland: cytologic findings and differential diagnosis
- Jiyeon Lee, Yunjoo Cho, Kyue Hee Choi, Inwoo Hwang, Young Lyun Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(5):360-365. Published online August 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.06.23
- 5,448 View
- 102 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Metastatic leiomyosarcoma to the thyroid is an extremely rare occurrence, and only 18 cases have been reported. Here, we report a case of a 37-year-old woman who presented with multiple masses on the scalp. Excisional biopsy was done and the mass revealed fascicles of smooth muscle fibers which showed positive staining for smooth muscle actin, thus confirming the diagnosis of leiomyosarcoma. The patient was also found to have a 0.9 cm mass within the left thyroid. Fine-needle aspiration was done and the cytological smear showed hypercellular spindle cell clusters with hyperchromatic and large nuclei. Normal thyroid follicular cells were found within or around tumor cells. In this report, we present the cytologic findings of metastatic leiomyosarcoma to the thyroid and offer differential diagnoses of the aspirated spindle cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytological Features and Mimickers of Thyroid Gland Sarcomas: A Case-Based Study
Poorvi Mathur, Shipra Agarwal, Chanchal Rana
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 33(3): 711. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Metastatic Uterine Leiomyosarcoma to the Thyroid Gland
R. Sathish Kumar, H. Akshaykumar, C. Ramesan, J. Dipin
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 76(1): 1365. CrossRef - Neck Surgery for Non-Well Differentiated Thyroid Malignancies: Variations in Strategy According to Histopathology
Fernando López, Abir Al Ghuzlan, Mark Zafereo, Vincent Vander Poorten, K. Thomas Robbins, Marc Hamoir, Iain J. Nixon, Ralph P. Tufano, Gregory Randolph, Pia Pace-Asciak, Peter Angelos, Andrés Coca-Pelaz, Avi Khafif, Ohad Ronen, Juan Pablo Rodrigo, Álvaro
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1255. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef
- Cytological Features and Mimickers of Thyroid Gland Sarcomas: A Case-Based Study
- Rosette-forming epithelioid osteosarcoma in the rib: a rare case of location and morphology
- Sun-Ju Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):406-409. Published online August 3, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.06.22
- 5,541 View
- 138 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The rib is an unusual location for osteosarcoma and is reported in only 2% of all cases. The major histological variants of osteosarcoma are osteoblastic, chondroblastic, and fibroblastic, with a few rare variants including one epithelioid type. This report describes a 44-year-old male with an osteolytic mass in the right seventh rib. Histological examination revealed osteosarcoma with unique features of epithelioid appearance and rosette structures. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a rosette-forming osteosarcoma of the rib that showed epithelioid morphology. Despite successful surgery, the patient’s prognosis was poor because this malignancy had an unusual location within the axial skeleton and was a rare histological variant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinicopathological correlations and prognostic insights in osteosarcoma: a retrospective analysis
Ştefan Adrian Niculescu, Alexandru Florian Grecu , Alex Emilian Stepan , Mădălina Iuliana Muşat , Aritina-Elvira Moroşanu , Tudor Adrian Bălşeanu , Michael Hadjiargyrou , Dan Cristian Grecu
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology.2025; 65(4): 723. CrossRef - Cytohistologic Diagnosis of Rosette‐Forming Epithelioid Osteosarcoma
Brant G. Wang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinicopathological correlations and prognostic insights in osteosarcoma: a retrospective analysis
- Sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma arising in the female urethral diverticulum
- Heae Surng Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(4):298-302. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.04.23
- 6,276 View
- 119 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A sarcomatoid variant of urothelial carcinoma in the female urethral diverticulum has not been reported previously. A 66-year-old woman suffering from dysuria presented with a huge urethral mass invading the urinary bladder and vagina. Histopathological examination of the resected specimen revealed predominantly undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma with sclerosis. Only a small portion of conventional urothelial carcinoma was identified around the urethral diverticulum, which contained glandular epithelium and villous adenoma. The patient showed rapid systemic recurrence and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy despite high expression of programmed cell death ligand-1. We report the first case of urethral diverticular carcinoma with sarcomatoid features.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Urethral sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma with heterologous elements in a dog
Louise van der Weyden, Christof A. Bertram, Nora Dinhopl, Monika Triebl, Taryn A. Donovan, Eva M. Compérat
Journal of Comparative Pathology.2025; 219: 31. CrossRef - Rethinking Urethral Diverticulum: A Narrative Review of Clinical Outcomes and Cancer Associations
Carolyn Daniels, Thomas R. Wong, Ilaha Isali
International Urogynecology Journal.2025; 36(11): 2169. CrossRef - Reprint of: Female Urethral Carcinoma: A contemporary review of the clinicopathologic features, with emphasis on the histo-anatomic landmarks and potential staging issues
Maria Sarah Lagarde-Lenon, Manju Aron
Human Pathology.2023; 133: 126. CrossRef - Female Urethral Diverticula: a Contemporary Narrative Review of Aetiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
A. U. Nic an Ríogh, S. Monagas Arteaga, L. Tzelves, M. Karavitakis, A. K. Nambiar
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports.2022; 17(4): 250. CrossRef - Female urethral carcinoma: a contemporary review of the clinicopathologic features, with emphasis on the histoanatomic landmarks and potential staging issues
Maria Sarah Lagarde-Lenon, Manju Aron
Human Pathology.2022; 129: 71. CrossRef
- Urethral sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma with heterologous elements in a dog
- Sarcoma metastasis to the pancreas: experience at a single institution
- Miseon Lee, Joon Seon Song, Seung-Mo Hong, Se Jin Jang, Jihun Kim, Ki Byung Song, Jae Hoon Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):220-227. Published online April 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.03.04
- 8,654 View
- 167 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Reports of metastatic sarcoma to the pancreas are limited. We reviewed the clinicopathologic characteristics of such cases.
Methods
We reviewed 124 cases of metastatic tumors to the pancreas diagnosed at Asan Medical Center between 2000 and 2017.
Results
Metastatic tumors to the pancreas consisted of 111 carcinomas (89.5%), 12 sarcomas (9.6%), and one melanoma (0.8%). Primary sarcoma sites were bone (n = 4); brain, lung, and soft tissue (n = 2 for each); and the uterus and pulmonary vein (n = 1 for each). Pathologically, the 12 sarcomas comprised 2 World Health Organization grade III solitary fibrous tumors/hemangiopericytomas, and one case each of synovial sarcoma, malignant solitary fibrous tumor, undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, osteosarcoma, mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, intimal sarcoma, myxofibrosarcoma, myxoid liposarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, subtype uncertain, and high-grade spindle-cell sarcoma of uncertain type. The median interval between primary cancer diagnosis and pancreatic metastasis was 28.5 months. One case manifested as a solitary pancreatic osteosarcoma metastasis 15 months prior to detection of osteosarcoma in the femur and was initially misdiagnosed as sarcomatoid carcinoma of the pancreas.
Conclusions
The metastatic sarcoma should remain a differential diagnosis when spindle-cell malignancy is found in the pancreas, even for solitary lesions or in patients without prior history. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic synovial sarcoma masquerading as primary neuroendocrine tumor of pancreas: a diagnostic conundrum
Sherrin Jacob, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Rajni Yadav, Anany Gupta, Samagra Agarwal, Shamim A. Shamim, Sameer Rastogi, Adarsh Barwad, Deepali Jain
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2025; 18(3): 499. CrossRef - Metastatic tumors to the pancreas: An institutional experience
Matthew Romanish, Rana Naous
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 79: 152528. CrossRef - Visceral Metastases of Osteosarcoma in the Hepatopancreatobiliary System
Anna Hohensteiner, Lars Kowalscheck, Kevin Döring, Gerhard Martin Hobusch, Raphael Johannes Tanios, Oliver Strobel, Reinhard Windhager, Philipp Theodor Funovics
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8702. CrossRef - Metastatic clear cell sarcoma of the pancreas: A sporadic cancer
Vittorio Gebbia, Carlo Carnaghi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(18): 3291. CrossRef - Metastatic clear cell sarcoma of the pancreas: An overview
Rachid Ait Addi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(29): 6262. CrossRef - Myxofibrosarcoma with pancreatic metastasis, a case report and literature reviews
Kodai ABE, Yasutomo SEKIDO, Yasuo KABESHIMA
Suizo.2024; 39(5): 334. CrossRef - Metástasis pancreática de sarcoma, un hallazgo infrecuente
Daniel Aparicio-López, Jorge Chóliz-Ezquerro, Carlos Hörndler-Algárate, Mario Serradilla-Martín
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2023; 46(5): 376. CrossRef - Pancreatic metastasis from sarcoma, an infrequent finding
Daniel Aparicio-López, Jorge Chóliz-Ezquerro, Carlos Hörndler-Algárate, Mario Serradilla-Martín
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2023; 46(5): 376. CrossRef - Acute pancreatitis secondary to osteosarcoma metastasis
Pablo Salmón Olavarría, Ana Gordo Ortega, Maren Eizagirre Ubegun, Verónica Ubieto Capella, Elena Carracedo Vega, Juan Carrascosa Gil, David Ruiz-Clavijo García
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - First Recurrence of Synovial Sarcoma Presenting With Solitary Pancreatic Mass
Raja R Narayan, Greg W Charville, Daniel Delitto, Kristen N Ganjoo
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intravenous Leiomyosarcoma of the Lower Extremity: As Peripheral as It Gets
Levent F Umur, Selami Cakmak, Mehmet Isyar, Hamdi Tokoz
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Could the burden of pancreatic cancer originate in childhood?
Smaranda Diaconescu, Georgiana Emmanuela Gîlcă-Blanariu, Silvia Poamaneagra, Otilia Marginean, Gabriela Paduraru, Gabriela Stefanescu
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(32): 5322. CrossRef - Staged Surgical Resection of Primary Pulmonary Synovial Sarcoma with Synchronous Multiple Pancreatic Metastases: Report of a Rare Case and Review of the Literature
Panagiotis Dorovinis, Nikolaos Machairas, Stylianos Kykalos, Paraskevas Stamopoulos, George Agrogiannis, Nikolaos Nikiteas, Georgios C. Sotiropoulos
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2021; 52(3): 1151. CrossRef
- Metastatic synovial sarcoma masquerading as primary neuroendocrine tumor of pancreas: a diagnostic conundrum
- Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast: Study of Three Cases at One Institution with a Review of Primary Breast Sarcomas
- Junyoung Shin, Hee Jeong Kim, Dae-Yeon Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):308-316. Published online August 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.07.22
- 7,415 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary breast sarcoma (PBS) is rare, comprising approximately 1% of breast malignancies. Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) accounts for an extremely small proportion of PBSs, often leading to delayed histologic confirmation.
Methods
Upon reviewing Asan Medical Center’s pathology database between 2000 and 2018, 41 PBS cases were retrieved, including three cases of primary RMS of the breast. Their clinicopathological features were analyzed, and the literature related to PBS and primary RMS of the breast was reviewed.
Results
We identified three primary breast RMS cases from our institution database, comprising 7.3% of PBS: one case each of spindle cell/sclerosing RMS (ssRMS), alveolar RMS (aRMS), and embryonal RMS (eRMS). All cases involved adolescents or young adults (14, 16, and 25 years, respectively) who underwent mastectomy or radiotherapy and were confirmed using immunohistochemical testing for myogenin, desmin, and myogenic differentiation. The ssRMS patient experienced recurrence at the operation site 4 months post-surgery despite undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The aRMS patient had multiple metastases at diagnosis and showed FAX3-FOXO1 fusion transcripts; she died 22 months after the diagnosis. The eRMS patient had enlarged axillary lymph nodes; post-radiotherapy, the lesion recurred as multiple metastases to the bone and lung. She died 18 months post-diagnosis.
Conclusions
Our experience on RMS cases suggests that spindle cell or small round cell malignancy in breasts of young female should raise suspicion for the possibility of primary or secondary RMS. To our knowledge, this is the second report of primary breast ssRMS and it may help clinicians who encounter this rare disease in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of Pediatric Breast Masses for the Pediatric Surgeon: Expert Consensus Recommendations From the APSA Cancer Committee
Dana Schwartz, Elisabeth T. Tracy, Bindi Naik-Mathuria, Richard D. Glick, Stephanie F. Polites, Peter Mattei, David Rodeberg, Andres F. Espinoza, Sara A. Mansfield, Dave R. Lal, Meera Kotagal, Timothy Lautz, Jennifer Aldrink, Barrie S. Rich
Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2025; 60(2): 161916. CrossRef - Differential diagnosis of primary mesenchymal neoplasms of the breast
Mine Ozsen, Seyit Ali Volkan Polatkan, Ulviye Yalcınkaya, Sahsine Tolunay, Mustafa Sehsuvar Gokgoz
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2024; 27(1): 223. CrossRef - Primary breast rhabdomyosarcoma in a 17-year-old girl
Laxmi Singotia, V.S. Haritha
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(7): 2070. CrossRef - High-Grade Spindle Cell Lesions of the Breast
Esther Yoon, Qingqing Ding, Kelly Hunt, Aysegul Sahin
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2022; 15(1): 77. CrossRef - Primary Small Cell Malignancies of the Breast: Are They Rare Malignancies?
Kemal Behzatoğlu, Fernando Schmitt
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(4): 347. CrossRef - Recurrent malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast: An extremely rare case of recurrence with only rhabdomyosarcoma components
Jia Han, Shuice Liu, Akihoro Shioya, Motona Kumagai, Emi Morioka, Miki Noguchi, Masafumi Inokuchi, Sohsuke Yamada
SAGE Open Medical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary rhabdomyosarcoma: An extremely rare and aggressive variant of male breast cancer
Cătălin Bogdan Satală, Ioan Jung, Tivadar Jr Bara, Patricia Simu, Iunius Simu, Madalina Vlad, Rita Szodorai, Simona Gurzu
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(19): 4466. CrossRef
- Management of Pediatric Breast Masses for the Pediatric Surgeon: Expert Consensus Recommendations From the APSA Cancer Committee
- WITHDRAWN:Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
- Junyoung Shin, Hee Jeong Kim, Dae-Yeon Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Kyung-Ja Cho
- Received August 6, 2018 Accepted September 13, 2018 Published online October 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.14
- 4,097 View
- 62 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast in an Adult: An Extremely Rare Case
Helen J. Trihia, Natasa Novkovic, Ioannis Provatas, Anastasios Mavrogiorgis, Evangelos Lianos
Case Reports in Pathology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Primary Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Breast in an Adult: An Extremely Rare Case
- Endobronchial Smooth Muscle Tumors: A Series of Five Cases Highlighting Pitfalls in Diagnosis
- Tripti Nakra, Aanchal Kakkar, Shipra Agarwal, Karan Madan, Suresh C Sharma, Deepali Jain
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):219-225. Published online July 11, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.05.16
- 8,183 View
- 113 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary endobronchial smooth muscle tumors (SMTs), which are extremely rare, include endobronchial leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas. Clinically, SMTs present with signs and symptoms of bronchial obstruction, and lack specific radiological findings. Thus, histopathological examination is required for accurate diagnosis as well as for tumor grading. We examined the histomorphological and immunohistochemical features of endobronchial SMTs and highlighted pitfalls in diagnosis, particularly when using small biopsies.
Methods
Cases of primary endobronchial SMTs diagnosed at our Institute over the last 6 years (2012–2017) were retrieved from the departmental archives. Histopathological features and immunohistochemistry performed for establishing the diagnosis were reviewed.
Results
Five cases of SMTs occurring in endobronchial locations were identified. These included three cases of leiomyoma, and two cases of leiomyosarcoma. The age distribution of patients ranged from 13 to 65 years. Leiomyomas showed more consistent staining with smooth muscle markers (smooth muscle actin, desmin, and smooth muscle myosin heavy chain), while tumors of higher grade showed variable, focal staining, leading to erroneous diagnosis, especially on small biopsies.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of endobronchial SMTs relies on histopathological examination, for both confirmation of smooth muscle lineage and determination of the malignant potential of the lesion. Appropriate immunohistochemical panels including more than one marker of smooth muscle differentiation are extremely valuable for differential diagnosis from morphological mimics, which is necessary for instituting appropriate management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
Yinfeng Wang, Yixiang Zhang, Ruirui Tong
Open Life Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pediatric endobronchial tumors with a mimicker: A case series
Kulwiwat Promsawasdi, Teerasak Phewplung
Pediatric Pulmonology.2024; 59(10): 2669. CrossRef - Smooth Muscle Conditions of the Chest
Matthew R. McCann, Lucas R. Massoth, Carlos A. Rojas, Yin P. Hung, John P. Lichtenberger, Gerald F. Abbott, Justin T. Stowell
Journal of Thoracic Imaging.2021; 36(5): 263. CrossRef - A Well-Defined Endobronchial Tumor in a 26-Year-Old Man
Christina Triantafyllidou, Petros Effraimidis, Mirjam Schimanke, Simone Ignatova, Anders Ringman, Susann Skoog, Farkas Vánky, Miklós Boros, Karin Cederquist
Chest.2021; 159(5): e313. CrossRef - Primary Pulmonary Leiomyoma
Mohammad Abu-Hishmeh, Gowthami Kobbari, Fouzia Shakil, Oleg Epelbaum
Journal of Bronchology & Interventional Pulmonology.2020; 27(4): e54. CrossRef
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Metastatic Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Case Report
- Bobae Shim, Jiwon Koh, Ji Hye Moon, In Ae Park, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):262-266. Published online June 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.05.15
- 8,486 View
- 119 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignant soft tissue tumor which shows skeletal muscle differentiation. Leptomeningeal metastasis can occur as a late complication, but currently there are no reports that have documented the cytologic features in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). We report a case of metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma diagnosed in the CSF of a 28-year-old male who was originally diagnosed with rhabdomyosarcoma on the neck, and that went through systemic therapy. The tumor was positive for anaplastic lymphoma kinase, but progressed despite additional therapy with crizotinib. The CSF specimen revealed small round cells, large atypical cells with abundant cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei, and cells with horseshoe-shaped nuclei. These cytologic findings were in agreement with previous literature and well-correlated with histopathology. This is the first report to document the cytologic feature of rhabdomyosarcoma in CSF. In many cases it is difficult to perform ancillary tests in a CSF specimen and cytopathologists should be aware of the cytomorphologic characteristics to avoid misdiagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Effusion Cytomorphology of Small Round Cell Tumors
Lucy M. Han, Christopher J. VandenBussche, Mads Abildtrup, Ashish Chandra, Poonam Vohra
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(4): 336. CrossRef - Cytologic diagnosis of metastatic embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in cerebrospinal fluid: A case report
Muxia Yan, Ying Wu, Jianqing Xia, Xiaohong Zhang, Yiqian Wang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effusion cytology of epithelioid rhabdomyosarcoma
Andrew A. Renshaw, Edwin W. Gould
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(10): 1042. CrossRef
- A Review of Effusion Cytomorphology of Small Round Cell Tumors
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Carcinosarcoma in the Salivary Gland: An Extremely Rare Case Report
- Hyo Jung An, Hye Jin Baek, Jin Pyeong Kim, Min Hye Kim, Dae Hyun Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):136-139. Published online December 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.07.27
- 8,103 View
- 135 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Carcinosarcoma of the salivary gland is an extremely rare tumor that is composed of both malignant epithelial and mesenchymal components. Diagnosing carcinosarcoma with fine-needle aspiration cytology is challenging because of its overlapping cytomorphologic characteristics with other high-grade malignant salivary gland tumors. Among the many features, including pleomorphic oncocytoid epithelial components, necrotic background, and mitoses, recognizing the singly scattered atypical spindle cells is most essential in carcinosarcoma. We present a case of a 66-year-old male patient with characteristic features of carcinosarcoma, who was successfully treated by wide local excision and subsequent radiation therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Rare Osteoid Forming Carcinosarcoma Ex‐Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland
Nyein Nyein Htun, Daniel Nguyen, Beverly Y. Wang, Anoosh Montaser, Behdokht Nowroozizadeh, Suraiya Saleem
Case Reports in Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Carcinosarcoma of the parotid gland: a case report and review of the literature
Swachi Jain, Mohammed Abdelwahed, Daniel Hector Chavarria, Lucio Pereira, Gary Stone, Alan Johnson, Jian Yi Li
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is Primary Poorly Differentiated Sarcomatoid Malignancy of the Parotid Gland Sarcomatoid Undifferentiated/Dedifferentiated Melanoma? Report of Three Unusual Cases Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration Combined with Histological, Immunohistochemical, and Mol
Jerzy Klijanienko, Julien Masliah-Planchon, Olivier Choussy, Guillaume Rougier, Antoine Dubray Vautrin, Maria Lesnik, Nathalie Badois, Wahib Ghanem, Jan Klos, Christophe Le Tourneau, Gregoire Marret, Raymond Barnhill, Adel K. El-Naggar
Acta Cytologica.2024; 68(2): 107. CrossRef - Carcinosarcoma of the deep lobe of the parotid gland in the parapharyngeal region: A case report
Yue-Yang Tang, Gui-Quan Zhu, Zhi-Jian Zheng, Li-Hong Yao, Zi-Xin Wan, Xin-Hua Liang, Ya-Ling Tang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(31): 7663. CrossRef - Carcinosarcoma of Submandibular Salivary Gland with a Rare Sarcomatous Variant
Shalini Bhalla, Naseem Akhtar, Puneet Prakash, Malti Kumari, Madhu Mati Goel
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2019; 10(1): 61. CrossRef
- A Rare Osteoid Forming Carcinosarcoma Ex‐Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland
- A Rare Case of Intramural Müllerian Adenosarcoma Arising from Adenomyosis of the Uterus
- Sun-Jae Lee, Ji Y. Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):433-440. Published online June 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.06.11
- 10,858 View
- 158 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Müllerian adenosarcomas usually arise as polypoid masses in the endometrium of post-menopausal women. Occasionally, these tumors arise in the cervix, vagina, broad and round ligaments, ovaries and rarely in extragenital sites; these cases are generally associated with endometriosis. We experienced a rare case of extraendometrial, intramural adenosarcoma arising in a patient with adenomyosis. A 40-year-old woman presented with sudden-onset suprapubic pain. The imaging findings suggested leiomyoma with cystic degeneration in the uterine fundus. An ill-defined ovoid tumor with hemorrhagic degeneration, measuring 7.5 cm in diameter, was detected. The microscopic findings showed glandular cells without atypia and a sarcomatous component with pleomorphism and high mitotic rates. There was no evidence of endometrial origin. To recognize that adenosarcoma can, although rarely, arise from adenomyosis is important to avoid overstaging and inappropriate treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Intramural Adenosarcoma With Sarcomatous Overgrowth Associated With Adenomyosis and Endometriosis
Kyohei Kitamura, Sachiko Minamiguchi, Hiroaki Ito, Yosuke Yamada, Yuki Himoto, Koji Yamanoi, Ken Yamaguchi, Hironori Haga
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Whether surgical procedure can improve the prognosis of endometrial cancer arising in adenomyosis (EC-AIA)? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yi Sun, Shitong Lin, Weijia Wu, Fangfang Nie, Yuchen Liu, Jing Wen, Xiaoran Cheng, Qianwen Liu, Yuanpei Wang, Fang Ren
International Journal of Surgery.2024; 110(5): 3072. CrossRef - Mullerian adenosarcoma accidentally detected and coexisting with cervical carcinoma in situ: a rare case report
Xuemei Qing, Min Xie, Hongying Guo, Liying Zhang, Jiatian Ye, Yong Zhang, Ying Ma
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma originating from uterine adenomyosis: a case report
Satoshi Ohira, Ryota Tachibana, Sayaka Yasaki, Koji Tsunemi, Natsuki Uchiyama, Eri Ikeda, Kenji Sano
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endometrial Cancer Arising in Adenomyosis (EC-AIA): A Systematic Review
Antonio Raffone, Diego Raimondo, Manuela Maletta, Antonio Travaglino, Federica Renzulli, Daniele Neola, Umberto De Laurentiis, Francesco De Laurentiis, Mohamed Mabrouk, Manuel Maria Ianieri, Renato Seracchioli, Paolo Casadio, Antonio Mollo
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1142. CrossRef - Adenomyosis and Its Possible Malignancy: A Review of the Literature
Liviu Moraru, Melinda-Ildiko Mitranovici, Diana Maria Chiorean, Raluca Moraru, Laura Caravia, Andreea Taisia Tiron, Ovidiu Simion Cotoi
Diagnostics.2023; 13(11): 1883. CrossRef - Case Report: Uterine Adenosarcoma With Sarcomatous Overgrowth and Malignant Heterologous Elements
Yunuén I. García-Mendoza, Mario Murguia-Perez, Aldo I. Galván-Linares, Saulo Mendoza-Ramírez, Norma L. García-Salinas, Julio G. Moctezuma-Ramírez, Blanca O. Murillo-Ortiz, Luis Jonathan Bueno-Rosario, Marco A. Olvera-Olvera, Guillermo E. Corredor-Alonso
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adenomyosis as a Risk Factor for Myometrial or Endometrial Neoplasms—Review
Maria Szubert, Edward Kozirog, Jacek Wilczynski
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2294. CrossRef - Uterine adenosarcoma arising from a subserosal adenomyoma: A case report
Shazia Fakhar, Tehreem Zahid, Yamina Ishtiaq
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2022; 40: 100957. CrossRef - Uterine Adenosarcoma Originating in Adenomyosis: Report of an Extremely Rare Phenomenon and Review of Published Literature
Karen L. Talia, Yael Naaman, W. Glenn McCluggage
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2021; 40(4): 342. CrossRef - Uterine adenosarcoma. Report of 5 cases and review of literature
I.V. Barinova, I.N. Voloshchuk, A.A. Fedorov, N.V. Puchkova, S.N. Buyanova, M.A. Chechneva, A.A. Popov, O.V. Kapitanova, N.I. Kondrikov
Arkhiv patologii.2021; 83(3): 25. CrossRef - New Aspects of Sarcomas of Uterine Corpus—A Brief Narrative Review
Stoyan Kostov, Yavor Kornovski, Vesela Ivanova, Deyan Dzhenkov, Dimitar Metodiev, Rafał Watrowski, Yonka Ivanova, Stanislav Slavchev, Dimitar Mitev, Angel Yordanov
Clinics and Practice.2021; 11(4): 878. CrossRef - Uterine Adenosarcoma with Sarcomatous Overgrowth: A Case Report of Aggressive Disease in a 16-Year-Old Girl and a Literature Review
Hanyuan Liu, Zhen Shen, Dabao Wu, Ying Zhou
Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology.2018; 31(4): 426. CrossRef - Uterine Adenosarcoma
Uwe A. Ulrich, Dominik Denschlag
Oncology Research and Treatment.2018; 41(11): 693. CrossRef
- A Case of Intramural Adenosarcoma With Sarcomatous Overgrowth Associated With Adenomyosis and Endometriosis
- Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor with Heterologous Rhabdomyosarcomatous Differentiation: A Case Report
- Jeong-Hwa Kwon, Joon Seon Song, Hye Won Jung, Jong-Seok Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):171-175. Published online February 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.29
- 9,588 View
- 117 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Malignant solitary fibrous tumor (MSFT) is a well-described entity, from which heterologous differentiation is extremely rare. We encountered a case of MSFT with rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation in a 56-year-old man. This patient presented with a large mass in his posterior thigh. He had been treated with chemoradiation for sarcoma involving the cervical spine, right femoral head, and both lungs 6 months earlier. A wide excision was performed. The mass measured 10.6 cm and showed a fish-flesh cut surface with necrotic foci. Microscopically, the tumor showed heterogeneous cellularity with a hemangiopericytic vascular pattern. A hypercellular area showed spindle cells or epithelioid cells with high mitotic activity (63/10 high-power fields) and immunoreactivity for CD34 and CD99. A hypocellular area and a cystic area showed pleomorphic rhabdoid cells with immunoreactivity for desmin and myogenin. This is a report of a rare case of MSFT with rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation and presents new histologic features of MSFT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Rare Case of Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor on the Scalp
Kwang-Ryeol Kim, Ki Hong Kim
Keimyung Medical Journal.2023; 42(2): 107. CrossRef - Malignant solitary fibrous tumor of maxilla presenting as proptosis: A case report
Pravin Kumar, Arpita Jindal, Bhushan Bhalgat, Phanindra Kumar Swain, Raj Govind Sharma
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(Suppl 2): S991. CrossRef - Recurrent malignant solitary fibrous tumor of the scalp: a case report and literature review
Ahmed Rabie, Abdulkarim Hasan, Yasein Mohammed, Ayman Abdelmaksoud, Ali A. Rabaan
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(2): 103. CrossRef - Frozen Cytology of Meningeal Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor/Hemangiopericytoma
Myunghee Kang, Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Gie-Taek Yie
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(3): 192. CrossRef
- A Rare Case of Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor on the Scalp
- IDH Mutation Analysis in Ewing Sarcoma Family Tumors
- Ki Yong Na, Byeong-Joo Noh, Ji-Youn Sung, Youn Wha Kim, Eduardo Santini Araujo, Yong-Koo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):257-261. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.04.14
- 11,807 View
- 80 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to yield α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) with production of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Dysfunctional IDH leads to reduced production of α-KG and NADH and increased production of 2-hydroxyglutarate, an oncometabolite. This results in increased oxidative damage and stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor α, causing cells to be prone to tumorigenesis. Methods: This study investigated IDH mutations in 61 Ewing sarcoma family tumors (ESFTs), using a pentose nucleic acid clamping method and direct sequencing. Results: We identified four cases of ESFTs harboring IDH mutations. The number of IDH1 and IDH2 mutations was equal and the subtype of IDH mutations was variable. Clinicopathologic analysis according to IDH mutation status did not reveal significant results. Conclusions: This study is the first to report IDH mutations in ESFTs. The results indicate that ESFTs can harbor IDH mutations in previously known hot-spot regions, although their incidence is rare. Further validation with a larger case-based study would establish more reliable and significant data on prevalence rate and the biological significance of IDH mutations in ESFTs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting metastasis in paediatric bone sarcomas
Emma C. Bull, Archana Singh, Amy M. Harden, Kirsty Soanes, Hala Habash, Lisa Toracchio, Marianna Carrabotta, Christina Schreck, Karan M. Shah, Paulina Velasco Riestra, Margaux Chantoiseau, Maria Eugénia Marques Da Costa, Gaël Moquin-Beaudry, Pan Pantziark
Molecular Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting developmental vulnerabilities in childhood sarcomas
Elise Young, Barnaby Kelly, Jason E. Cain
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Ewing’s Sarcoma Presenting in the Paranasal Sinus – A Case Report
Yashika Kewalramani, Ajay Parihar, Prashanthi Reddy, Rashi Mandlik
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 14(2): 228. CrossRef - Glutamine-dependent effects of nitric oxide on cancer cells subjected to hypoxia-reoxygenation
Dianna Xing, Gloria A. Benavides, Michelle S. Johnson, Ran Tian, Stephen Barnes, Victor M. Darley-Usmar
Nitric Oxide.2023; 130: 22. CrossRef - Hypoxia and HIFs in Ewing sarcoma: new perspectives on a multi-facetted relationship
A. Katharina Ceranski, Martha J. Carreño-Gonzalez, Anna C. Ehlers, Maria Vittoria Colombo, Florencia Cidre-Aranaz, Thomas G. P. Grünewald
Molecular Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic adaptations in cancers expressing isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations
Ingvild Comfort Hvinden, Tom Cadoux-Hudson, Christopher J. Schofield, James S.O. McCullagh
Cell Reports Medicine.2021; 2(12): 100469. CrossRef - Isocitrate dehydrogenase gene variants in cancer and their clinical significance
Thomas Cadoux-Hudson, Christopher J. Schofield, James S.O. McCullagh
Biochemical Society Transactions.2021; 49(6): 2561. CrossRef - Advances in sarcoma gene mutations and therapeutic targets
Peng Gao, Nicole A. Seebacher, Francis Hornicek, Zheng Guo, Zhenfeng Duan
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2018; 62: 98. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Features of the Non-CNS Primary Ewing Sarcoma Family of Tumors in the Head and Neck Region
Chang Gok Woo, Bora Lee, Joon Seon Song, Kyung-Ja Cho
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2018; 26(9): 632. CrossRef - EWS/FLI is a Master Regulator of Metabolic Reprogramming in Ewing Sarcoma
Jason M. Tanner, Claire Bensard, Peng Wei, Nathan M. Krah, John C. Schell, Jamie Gardiner, Joshua Schiffman, Stephen L. Lessnick, Jared Rutter
Molecular Cancer Research.2017; 15(11): 1517. CrossRef
- Targeting metastasis in paediatric bone sarcomas
- A Case of Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Common Bile Duct: Initially Diagnosed as Cholangiocarcinoma
- Soon Wook Lee, In Seok Lee, Yu Kyung Cho, Jae Myung Park, Sang Woo Kim, Myung-Gyu Choi, Kyu Yong Choi, Myung Ah Lee, Tae Ho Hong, Young Kyoung You, Eun-Sun Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):445-448. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.445
- 9,894 View
- 44 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term survival after chemotherapy combined immunotherapy for recurrent mixed neuroendocrine–non-neuroendocrine neoplasms of the common bile duct
Jia Li, Chunyan Yuan, Yulin Pan, Yuanyuan Yang, Nannan Lai, Xia Sheng
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2025; 18(4): 653. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the common hepatic duct coexisting with distal cholangiocarcinoma: A case report and review of literature
Fei Chen, Wei-Wei Li, Juan-Fen Mo, Min-Jie Chen, Su-Hang Wang, Shu-Ying Yang, Zheng-Wei Song
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(5): 1449. CrossRef - Comparison of Metastatic Patterns Among Neuroendocrine Tumors, Neuroendocrine Carcinomas, and Nonneuroendocrine Carcinomas of Various Primary Organs
Hyung Kyu Park, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma of the distal bile duct: a case report
Takashi Maeda, Kyohei Yugawa, Nao Kinjo, Hiroto Kayashima, Daisuke Imai, Koto Kawata, Shinichiro Ikeda, Keitaro Edahiro, Kazuki Takeishi, Tomohiro Iguchi, Noboru Harada, Mizuki Ninomiya, Shohei Yamaguchi, Kozo Konishi, Shinichi Tsutsui, Hiroyuki Matsuda
Surgical Case Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The clinical profiles, management, and prognostic factors of biliary mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasms
Li-Jia Wen, Jun-Hong Chen, Hong-Ji Xu, Qiong Yu, Yu Deng, Kai Liu
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23271. CrossRef - Rapidly progressed neuroendocrine carcinoma in the extrahepatic bile duct: a case report and review of the literature
Mariko Kamiya, Naoto Yamamoto, Yuto Kamioka, Hirohide Inoue, Hirokazu Yotsumoto, Masaaki Murakawa, Toru Aoyama, Kota Washimi, Kae Kawachi, Takashi Oshima, Makoto Ueno, Norio Yukawa, Yasushi Rino, Munetaka Masuda, Soichiro Morinaga
Surgical Case Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma of the hepatic bile duct: a case report and review of the literature
Sulai Liu, Zhendong Zhong, Meng Xiao, Yinghui Song, Youye Zhu, Bo Hu, Zengpeng Sun, Weimin Yi, Chuang Peng
BMC Gastroenterology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mixed adenoendocrine carcinoma in the extrahepatic biliary tract: A case report and literature review
Liang Zhang, Zhengtao Yang, Qing Chen, Mengxia Li, Xiaolu Zhu, Dalong Wan, Haiyang Xie, Shusen Zheng
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Coexisting with Adenocarcinoma in the Extrahepatic Bile Duct
Masami Yuda, Teruyuki Usuba, Shin Hagiwara, Masahisa Okuma, Hisatoshi Asano, Hitoshi Sakuda, Hiroaki Katagi, Yoshiyuki Furukawa
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery.2018; 51(3): 187. CrossRef - Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Distal Bile Duct
Chiaki Uchida, Yoshikazu Toyoki, Keinosuke Ishido, Daisuke Kudo, Norihisa Kimura, Shinji Tsutsumi, Takuji Kagiya, Toshiro Kimura, Kenichi Hakamada
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery.2017; 50(1): 43. CrossRef - Mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma of the distal bile duct: A case report
Toshiaki Komo, Toshihiko Kohashi, Akira Nakashima, Ichiro Ohmori, Jun Hihara, Hidenori Mukaida, Mayumi Kaneko, Naoki Hirabayashi
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2017; 39: 203. CrossRef - Common Hepatic Duct Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma Masquerading as Cholangiocarcinoma
Sali Priyanka Akhilesh, Yadav Kamal Sunder, Tampi Chandralekha, Parikh Samir, Wagle Prasad Kashinath
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Long-term survival after chemotherapy combined immunotherapy for recurrent mixed neuroendocrine–non-neuroendocrine neoplasms of the common bile duct
- Indolent CD56-Positive Clonal T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of the Stomach Mimicking Lymphomatoid Gastropathy
- Mineui Hong, Won Seog Kim, Young Hyeh Ko
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):430-433. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.430
- 10,616 View
- 70 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indolent T- and Natural Killer-Cell Lymphomas and Lymphoproliferative Diseases—Entities in Evolution
Chi Sing Ng
Lymphatics.2025; 3(4): 41. CrossRef - Case Report: Primary Indolent Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease Involving the Central Nervous System
Kun Wang, Jinjian Li, Xuehui Zhou, Junhui Lv, Yirong Wang, Xinwei Li
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Indolent NK cell proliferative lesion mimicking NK/T cell lymphoma in the gallbladder
Su Hyun Hwang, Joon Seong Park, Seong Hyun Jeong, Hyunee Yim, Jae Ho Han
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2016; 5: 39. CrossRef
- Indolent T- and Natural Killer-Cell Lymphomas and Lymphoproliferative Diseases—Entities in Evolution
- Primary Leiomyosarcoma of Adrenal Gland with Tissue Eosinophilic Infiltration
- Seungkoo Lee, Gail Domecq C. Tanawit, Rolando A. Lopez, Jaime T. Zamuco, Betsy Grace G. Cheng, Menandro V. Siozon
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):423-425. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.423
- 9,818 View
- 48 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary adrenal leiomyosarcoma
Syed Muhammad Nazim, Muhammad Hummam Siddique, Imran Khan Jalbani, Ayesha Nusrat
BMJ Case Reports.2025; 18(10): e266476. CrossRef - Outcomes and Follow-Up Trends in Adrenal Leiomyosarcoma: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Case Report
Federico Maria Mongardini, Maddalena Paolicelli, Antonio Catauro, Alessandra Conzo, Luigi Flagiello, Giusiana Nesta, Rosetta Esposito, Andrea Ronchi, Alessandro Romano, Renato Patrone, Ludovico Docimo, Giovanni Conzo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(12): 3499. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagnosis of the enigmatic primary adrenal leiomyosarcoma: two case reports and review of the literature
Sawako Suzuki, Naoya Takahashi, Masafumi Sugo, Kazuki Ishiwata, Akiko Ishida, Suzuka Watanabe, Katsushi Igarashi, Yutaro Ruike, Kumiko Naito, Masanori Fujimoto, Hisashi Koide, Yusuke Imamura, Shinichi Sakamoto, Tomohiko Ichikawa, Yoshihiro Kubota, Takeshi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary adrenal leiomyosarcoma: clinical case and literature review
S. V. Lukyanov, K. M. Blikyan, S. S. Todorov, V. Y. Deribas, N. S. Lukyanov
Endocrine Surgery.2021; 15(1): 36. CrossRef Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma of the Adrenal Gland in a Young Woman: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Yuanyuan Wang, Yongliang Teng, Shibo Na, Ye Yuan
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4705. CrossRef- Primary Adrenal Leiomyosarcoma: Clinical, Radiological, and Histopathological Characteristics
Fatema Jabarkhel, Henri Puttonen, Lina Hansson, Andreas Muth, Oskar Ragnarsson
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary adrenal leiomyosarcoma with inferior vena cava extension in a 70-year-old man
Sai K Doppalapudi, Tejash Shah, Valerie A Fitzhugh, Vladislav Bargman
BMJ Case Reports.2019; 12(3): e227670. CrossRef - Primary Adrenal Leiomyosarcoma: An Extremely Rare Mesenchymal Tumor
D Lokanatha, Linu Abraham Jacob, MC Suresh Babu, KN Lokesh, Ram Krishna Sai, AH Rudresha, LK Rajeev, Smitha Saldanha, MN Suma, A Usha
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2019; 40(04): 559. CrossRef
- Primary adrenal leiomyosarcoma
- Combined Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Follicular Carcinoma of the Thyroid
- Da Hye Son, Jong-Lyel Roh, Kyung-Ja Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):418-422. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.418
- 9,873 View
- 58 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of combined immunotherapy and targeted therapy in overcoming barriers to postoperative recurrence in squamous subtype anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with abscess: a case report and literature review
Shuyun Jiang, Xiaowu Wang, Zhijun Ma
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - State of Knowledge About Thyroid Cancers in the Era of COVID-19—A Narrative Review
Agnieszka Bronowicka-Szydełko, Maciej Rabczyński, Ilias Dumas, Żanna Fiodorenko-Dumas, Beata Wojtczak, Łukasz Kotyra, Irena Kustrzeba-Wójcicka, Łukasz Lewandowski, Beata Ponikowska, Aleksandra Kuzan, Joanna Kluz, Andrzej Gamian, Katarzyna Madziarska
Biomedicines.2024; 12(12): 2829. CrossRef - Primary and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland: Two case reports
Xing Zhao, Pengyu Hao, Jiangbei Tian, Jirun Sun, Dawei Chen, Zhehui Cui, Libo Xin, Yanmin Song, Gang Zhang
Open Life Sciences.2022; 17(1): 1148. CrossRef - Aggressive Thyroid Gland Carcinoma: A Case Series
JP Dworkin-Valenti
Archives of Otolaryngology and Rhinology.2017; : 129. CrossRef
- Efficacy of combined immunotherapy and targeted therapy in overcoming barriers to postoperative recurrence in squamous subtype anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with abscess: a case report and literature review
- Myoepithelial Carcinoma of Soft Tissue: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Chang Hwan Choi, Young Chae Chu, Lucia Kim, Suk Jin Choi, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(6):413-417. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.6.413
- 13,646 View
- 128 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myoepithelial Carcinoma Mimicking Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report
Farlin Asharaff, Neena Nayak, Roger Webb, Karwan Moutasim, Soogan Lalla
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration cytology of retroperitoneal myoepithelial carcinoma: A rare encounter with diagnostic dilemmas
Aadya Kerkar, Ajay Savlania, Reetu Kundu, Suvradeep Mitra, Manish Rohilla, Harmandeep Singh, Harish Bhujade
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - EWSR1::NR4A3 gene fusion in a cutaneous atypical myoepithelial neoplasm
Ashley Rose Scholl, Evelyna Kliassov, Diana M. Cardona, Rex Bentley, Rami N. Al‐Rohil
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2023; 50(7): 601. CrossRef - Abdominal myoepithelial carcinoma: A rare abdominal wall entity of an uncommon tumor
Daania Shoaib, Saqib Raza Khan, Yasmin Abdul Rashid, Muhammad Nauman Zahir
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2022; 99: 107618. CrossRef - Adult soft tissue myoepithelial carcinoma: treatment outcomes and efficacy of chemotherapy
Florence Chamberlain, Elena Cojocaru, Mariana Scaranti, Jonathan Noujaim, Anastasia Constantinou, Khin Thway, Cyril Fisher, Christina Messiou, Dirk C. Strauss, Aisha Miah, Shane Zaidi, Charlotte Benson, Spyridon Gennatas, Robin L. Jones
Medical Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Foot plantar soft tissue malignant myoepithelioma tumor: Case report and review of the literature
Manuel Trevino, Chetan Moorthy, Lisa Kafchinski, Daniel Bustamante
Clinical Imaging.2020; 61: 90. CrossRef - Presumed choroidal metastasis from soft tissue myoepithelial carcinoma
Michelle M. Hui, Rohan Merani, Fiona Bonar, Angela M. Hong, Adrian T. Fung
American Journal of Ophthalmology Case Reports.2019; 14: 55. CrossRef - Myoepithelial carcinoma of the elbow diagnosed by immunohistochemistry: Case report of an uncommon neoplasm with metastatic recurrence
Madhura Mahapatra, Travis Lambert, Abdal Rahman El-Mallah, Andressa Balbi, Mohamad Aziz
Case Reports International.2019; 8(2): 1. CrossRef
- Myoepithelial Carcinoma Mimicking Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report
- Expression of HuR and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Nodular Fasciitis and Low-Grade Sarcoma: An Immunohistochemical Study
- Hyun-Jin Son, Tae-Hwa Baek, Seung Yun Lee, Joo-Heon Kim, Dong-Wook Kang, Hye-Kyung Lee, Mee-Ja Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(4):270-275. Published online August 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.4.270
- 8,647 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Nodular fasciitis is the most common reactive mesenchymal lesion to be misidentified as a type of sarcoma. HuR is an mRNA-binding protein that can stabilize cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA leading to COX-2 overexpression. The aim of this study is a comparison of the expressions of COX-2 and HuR and the relationships between their expressions and the clinicopathological parameters in nodular fasciitis and low-grade sarcoma.
Methods We measured the expression of HuR and COX-2 in 21 cases of nodular fasciitis and 37 cases of low-grade sarcoma using immunohistochemistry.
Results The frequency of cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for HuR was 5 of 21 cases of nodular fasciitis (23.8%) and 23 of 37 cases of low-grade sarcoma (62.1%) (p=.013). COX-2 expression was moderate or strong in nodular fasciitis (12/21, 57.1%) and in low-grade sarcoma (29/37, 78.4%) (p=.034). In addition, a significant difference existed between these two entities in terms of the relationship between moderate or strong COX-2 expression and HuR cytoplasmic immunoreactivity (p=.009). Moderate or strong COX-2 immunoreactivity correlated with nuclear (p=.016) or cytoplasmic HuR (p=.024) expression in low-grade sarcoma but not in nodular fasciitis.
Conclusions This study suggests that HuR and COX-2 expression may be useful to differentiate nodular fasciitis from low-grade sarcoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nodular Fasciitis of the Cubital Fossa in a Young Female Mimicking a Neurogenic Tumor
Hyung-Joon Lee, Ji-Kang Park, Seok-Won Kim, Min-Boo Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2023; 58(2): 179. CrossRef - Nodular fasciitis of the anterior chest wall mimicking myxofibrosarcoma: A case report and literature review
Antonino Cattafi, Mariarosaria Galeano, Pietro Pitrone, Carmelo Sofia, Maria Adele Marino, Giorgio Ascenti, Maria Lentini, Antonio Ieni, Roberta Cardia, Alfio Luca Costa, Dario Familiari, Mario Barone, Francesco Monaco, Michele Rosario Colonna
Radiology Case Reports.2021; 16(6): 1557. CrossRef
- Nodular Fasciitis of the Cubital Fossa in a Young Female Mimicking a Neurogenic Tumor
- A Case of Metastatic Angiosarcoma Diagnosed by Liquid-Based Preparation: Peculiar Cytoplasmic Changes
- Min Jung Jung, Young Ok Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(3):241-247. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.241
- 8,726 View
- 51 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Angiosarcoma with predominantly epithelioid features is a rare soft tissue neoplasm and the interpretation of its cytopathologic findings may be difficult. We report a case of metastatic angiosarcoma with predominantly epithelioid features diagnosed by liquid-based cytology. The cytopathologic findings in this case differed from those of the conventional preparation and we found a clean background, no hyperchromatic nuclei and several cytoplasmic changes, including intracytoplasmic vacuoles with peculiar shapes, juxtanuclear condensation and perinuclear clearing. Identification of these changes using liquid-based cytology supplemented with immunochemistry may be helpful in reaching a correct cytopathologic diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytological Features of a Metastatic Angiosarcoma in the Lymph Node Diagnosed via Liquid-Based Cytology
Jie-Yang Jhuang, Chih-Yi Liu, Min-Hui Tseng, Shih-Sung Chuang
Diagnostics.2023; 13(12): 2124. CrossRef - Radiation-associated Angiosarcoma Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
Hirokazu Ogino, Makoto Tobiume, Kozo Kagawa, Hiroshi Kawano, Satoshi Sakaguchi, Atsuro Saijo, Daisuke Matsumoto, Hiromitsu Takizawa, Yuriko Morikawa, Yoshimi Bando, Hisatsugu Goto, Hiroshi Nokihara, Yasuhiko Nishioka
Internal Medicine.2022; 61(9): 1393. CrossRef - Delayed diagnosis of angiosarcoma of the spleen: clinically presenting as recurrent haemoperitoneum following embolisation
Verena Kornmann, Philip van Rijn, Dries Mulder, Koen Reijnders
BMJ Case Reports.2015; 2015: bcr2014208956. CrossRef - A Case of Angiosarcoma of the Scalp with Invasion to the Pleural Effusion
Yusuke Amano, Yukari Obana, Yoko Nakanishi, Ryusuke Tsujimura, Kayomi Wakamatsu, Fumiko Uemura, Yoshihisa Katsura, Masahiko Sugitani, Norimichi Nemoto
Journal of Nihon University Medical Association.2015; 74(3): 113. CrossRef
- Cytological Features of a Metastatic Angiosarcoma in the Lymph Node Diagnosed via Liquid-Based Cytology
- Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Promote Tumor Progression in Fibrosarcoma and Gastric Cancer Cells
- Byunghoo Song, Bokyung Kim, Se-Ha Choi, Kyo Young Song, Yang-Guk Chung, Youn-Soo Lee, Gyeongsin Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(3):217-224. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.217
- 9,532 View
- 57 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Extensive evidence has accumulated regarding the role of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) in tumor progression, but the exact effects and mechanisms underlying this role remain unclear. We investigated the effects of MSC-associated tumor progression in MSC-sarcoma models and a gastric cancer metastatic model.
Methods We conducted an
in vitro growth kinetics assay and anin vivo tumor progression assay for sarcoma cells and gastric cancer cells in the presence or absence of MSCs.Results MSC-cocultured human fibrosarcoma cells (HT1080) showed accelerated growth compared with HT1080 alone (79- vs 37-fold change, p<.050). For HT1080, human MSC-coinjected tumors showed significantly greater and highly infiltrative growth compared to those of HT1080 alone (p=.035). For mouse fibrosarcoma cells (WEHI164), mouse MSC-coinjected tumors had greater volume than those of WEHI164 alone (p=.141). For rat sarcoma cells (RR1022), rat MSC-coinjected tumors exhibited greater volume and infiltrative growth than those of RR1022 alone (p=.050). For human gastric cancer cells (5FU), tumors of 5FU alone were compact, nodular in shape, and expansile with good demarcation and no definite lung metastatic nodules, whereas tumors grown in the presence of human MSCs showed highly desmoplastic and infiltrative growth and multiple lung metastasis.
Conclusions We observed morphological evidence for MSC-associated tumor progression of fibrosarcomas and gastric cancer cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transition between canonical to non-canonical Wnt signaling during interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and osteosarcomas
Asulin Masha, Ghedalia-Peled Noa Ben, Erez Ifat Cohen, Ventura Yvonne, Vago Razi
Open Journal of Orthopedics and Rheumatology.2020; : 037. CrossRef - Mesenchymal stem-cell therapy for perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
F. Cheng, Z. Huang, Z. Li
Techniques in Coloproctology.2019; 23(7): 613. CrossRef - Human mesenchymal stromal cells do not promote recurrence of soft tissue sarcomas in mouse xenografts after radiation and surgery
PAOLA A. FILOMENO, KYUNG-PHIL KIM, NARA YOON, IRAN RASHEDI, VICTOR DAYAN, RITA A. KANDEL, XING-HUA WANG, TANIA C. FELIZARDO, ELLIOT BERINSTEIN, SALOMEH JELVEH, ANDREA FILOMENO, JEFFREY A. MEDIN, PETER C. FERGUSON, ARMAND KEATING
Cytotherapy.2018; 20(8): 1001. CrossRef - Review article: mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases
C. Grégoire, C. Lechanteur, A. Briquet, É. Baudoux, F. Baron, E. Louis, Y. Beguin
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2017; 45(2): 205. CrossRef - Effect of hGC-MSCs from human gastric cancer tissue on cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor tissue of gastric cancer tumor-bearing mice
Lin Song, Xin Zhou, Hong-Jun Jia, Mei Du, Jin-Ling Zhang, Liang Li
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine.2016; 9(8): 796. CrossRef - BMP9 inhibits the growth and migration of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in a bone marrow stromal cell-derived microenvironment through the MAPK/ERK and NF-κB pathways
JING WANG, YAGUANG WENG, MINGHAO ZHANG, YA LI, MENGTIAN FAN, YANGLIU GUO, YANTING SUN, WANG LI, QIONG SHI
Oncology Reports.2016; 36(1): 410. CrossRef - Comparative proteomic analysis of fibrosarcoma and skin fibroblast cell lines
Ogunc Meral, Hamdi Uysal
Tumor Biology.2015; 36(2): 561. CrossRef - Involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the mesenchymal stem cells promote metastatic growth and chemoresistance of cholangiocarcinoma
Weiwei Wang, Wei Zhong, Jiahui Yuan, Congcong Yan, Shaoping Hu, Yinping Tong, Yubin Mao, Tianhui Hu, Bing Zhang, Gang Song
Oncotarget.2015; 6(39): 42276. CrossRef
- Transition between canonical to non-canonical Wnt signaling during interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and osteosarcomas
- Multifocal Osteosarcoma of the Skull: Multiple Primary or Metastatic? A Case Report
- Hyuck Cho, Bong-jin Park, Yong-Koo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):146-150. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.146
- 11,816 View
- 57 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Osteosarcoma of the skull is a very rare condition. Moreover, it is extremely rare for osteosarcoma to present as multiple lesions confined to the skull. A 58-year-old woman was admitted with two masses in the parietal area of the skull, accompanied by mild headache and tenderness. Imaging revealed two masses with a heterogeneous consistency in the cranial bones. Excision craniectomy was performed and the pathology was consistent with osteoblastic osteosarcoma. Two nodules in the heart were found on routine follow-up imaging while the patient was undergoing chemotherapy. The nodules were biopsied and found to be metastatic osteosarcoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A telomere-related signature for predicting prognosis and assessing immune microenvironment in osteosarcoma
Shihao Li, Lina Zhang, Haiyang Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteosarcoma multicéntrico sincrónico. Un caso en niño de 10 años y revisión de la literatura
Jesús Pérez-García, Osvaldo Velasco-Donado, Karoll Robles-Pérez
Revista Española de Patología.2022; 55: S11. CrossRef - Reconstruction using a frozen autograft for a skull and humeral lesion of synchronous multicentric osteosarcoma after undergoing successful neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a case report and review of the literature
Yoshihiro Araki, Katsuhiro Hayashi, Norio Yamamoto, Akihiko Takeuchi, Shinji Miwa, Kentaro Igarashi, Takashi Higuchi, Kensaku Abe, Yuta Taniguchi, Hirotaka Yonezawa, Sei Morinaga, Yohei Asano, Takayuki Nojima, Hiroyuki Tsuchiya
BMC Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - What’s that big thing on your head? Diagnosis of a large frontoparietal lesion on an Eastern Zhou skull from Henan, China
Kate Pechenkina, Wenquan Fan, Xiaodong Luo
International Journal of Paleopathology.2019; 26: 84. CrossRef - Kalvaryumda multifokal osteosarkom: Nadir bir vaka sunumu ve literatür derlemesi
Neslihan KURTUL, Nursel YURTTUTAN, A. Yasir BAHAR, Gökmen AKTAŞ
Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2019; 14(3): 151. CrossRef - Radiological review of skull lesions
Carrie K. Gomez, Scott R. Schiffman, Alok A. Bhatt
Insights into Imaging.2018; 9(5): 857. CrossRef - Multifocal Osteosarcoma
Somali Gavane, Anita P. Price, Heather Magnan, Sonia Mahajan, Neeta Pandit-Taskar
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2017; 42(4): e202. CrossRef
- A telomere-related signature for predicting prognosis and assessing immune microenvironment in osteosarcoma
- Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Variant Presenting as a Colonic Polyp
- Shien-Tung Pan, Chih-Yuan Cheng, Nie-Sue Lee, Peir-In Liang, Shih-Sung Chuang
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):140-145. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.140
- 11,500 View
- 105 Download
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Follicular dendritic cell (FDC) sarcoma is rare and is classified either as conventional type or inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT)-like variant. Extranodal presentation is uncommon and nearly all gastrointestinal FDC tumors are of the conventional type. IPT-like variant tumors occur almost exclusively in the liver and spleen and are consistently associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Here we report the case of a 78-year-old woman with an IPT-like FDC sarcoma presenting as a pedunculated colonic polyp. Histologically, scanty atypical ovoid to spindle cells were mixed with a background of florid lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, which led to an initial misdiagnosis of pseudolymphoma. These atypical cells expressed CD21, CD23, CD35, and D2-40, and were positive for EBV by
in situ hybridization, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was free of disease five months after polypectomy without adjuvant therapy. Although extremely rare, the differential diagnosis for colonic polyp should include FDC sarcoma to avoid an erroneous diagnosis. A review of the 24 cases of IPT-like FDC sarcoma reported in the literature reveal that this tumor occurs predominantly in females with a predilection for liver and spleen, and has a strong association with EBV.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The fifth edition of the WHO classification of mature T cell, NK cell and stroma-derived neoplasms
Ayoma D Attygalle, Kennosuke Karube, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Wah Cheuk, Govind Bhagat, John K C Chan, Kikkeri N Naresh
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 78(4): 217. CrossRef - Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma: A Multicenter Study
Yan Li, Ze-Lin Weng, Han-Xiao Fei, Hai-Feng Li, Yi-Na Liu, Le-Le Zhang, Qiong Zhang, Xin Weng, Yuan-Yuan Wang, Wen-Yong Huang, Zhi-Xing Cao, Kai-Yan Yang, Xi-Liang Chen, Jie Gao, Wen-Sheng Yang, Fang Liu, Juan-Juan Yong, Jing-Ping Yun, Hua Zhang, Yu-Hua H
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(10): 100864. CrossRef - What is new in the 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of mature B and T/NK cell tumors and stromal neoplasms?
Ayoma D. Attygalle, John K. C. Chan, Sarah E. Coupland, Ming-Qing Du, Judith A. Ferry, Daphne de Jong, Dita Gratzinger, Megan S. Lim, Alina Nicolae, German Ott, Andreas Rosenwald, Anna Schuh, Reiner Siebert
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(2): 71. CrossRef - Pathologic characteristics of histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms
Sun Och Yoon
Blood Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-barr virus (EBV)-positive inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (IPT-like FDCS) presenting as thrombocytopenia: A case report and literature review
Jiawei Jin, Xiaolong Zhu, Yi Wan, Yang Shi
Heliyon.2024; 10(12): e32997. CrossRef - EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the colon with clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Xia Xu, Xiuzhen Li, Qun Deng, Kaihang Yu, Jinfan Li
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31947. CrossRef - Challenges in the Diagnosis of Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma
Yan Li, Xia Yang, Lili Tao, Weimei Zeng, Min Zuo, Shuo Li, Liyan Wu, Yanshong Lin, Ziying Zhang, Jingping Yun, Yuhua Huang
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 47(4): 476. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma Presenting as a Colonic Polyp: Report of a Case with a Literature Review
Jiahui Hu, Dongdong Huang, Chengfu Xu, Yi Chen, Han Ma, Zhe Shen
Medicina.2023; 59(7): 1341. CrossRef - A Clinicopathology Review and Update of Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Mesenchymal Tumors
Oswald Zhao Jian Lee, Noorjehan Omar, Joshua K. Tay, Victor Kwan Min Lee
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5563. CrossRef - Granulomatous splenic mass with necrosis revealing an EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Irena Antonia Ungureanu, Renato Micelli Lupinacci, Marie Parrens, Jean-François Emile
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A rare case and minireview of the literature
Fan Ding, Chao Wang, Chi Xu, Hui Tang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of gastrointestinal tract with two emerging distinct subtypes: a case report and systemic review
Hongxing Gui, Jigisha Chaudhari, Rifat Mannan
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical treatment of liver inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case report
Li-Yue Fu, Jiu-Liang Jiang, Meng Liu, Jun-Jun Li, Kai-Ping Liu, Hai-Tao Zhu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2022; 14(11): 2288. CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular/fibroblastic dendritic cell sarcoma: focus on immunohistochemical profile and association with Epstein-Barr virus
Francesca Pagliuca, Andrea Ronchi, Annamaria Auricchio, Eva Lieto, Renato Franco
Infectious Agents and Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Digestive Tract Tumors: Updates From the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization “Blue Book”
Raul S. Gonzalez, Anwar Raza, Robert Propst, Oyedele Adeyi, Justin Bateman, Sabrina C. Sopha, Janet Shaw, Aaron Auerbach
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(5): 607. CrossRef - Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor: a case report
Ana Daniela Pascariu, Andreea Ioana Neagu, Andrei Valentin Neagu, Alexandru Băjenaru, Cezar Iulian Bețianu
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: Literature review of 67 cases
Hao Wu, Peng Liu, Xiao-Ran Xie, Jing-Shu Chi, Huan Li, Can-Xia Xu
World Journal of Meta-Analysis.2021; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - New Clinicopathologic Scenarios of EBV+ Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma
Xiang-Nan Jiang, Yan Zhang, Tian Xue, Jie-Yu Chen, Alex C.L. Chan, Wah Cheuk, John K.C. Chan, Xiao-Qiu Li
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2021; 45(6): 765. CrossRef - Select Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Digestive Tract Lesions for the Practicing Pathologist
Zainab I. Alruwaii, Elizabeth A. Montgomery
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(5): 562. CrossRef - Overview of Gastrointestinal Lymphoproliferative disorders✰
Aaron Auerbach, Nadine S. Aguilera
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2021; 38(4): 1. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Fabio Facchetti, Matteo Simbeni, Luisa Lorenzi
Pathologica.2021; 113(5): 316. CrossRef - Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor with hepatic lymphoma history
Jiang Li, Hai-su Tao, Dong Chen, Zhi-yong Huang, Er-lei Zhang
Medicine.2021; 100(39): e27392. CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Dayong Sun, Gang Zhang
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumour-like follicular dendritic cell tumour of the colon with plasmacytosis mimicking EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disorder
Ying-Ren Chen, Chi-Lin Lee, Yen-Chien Lee, Kung-Chao Chang
Pathology.2020; 52(4): 484. CrossRef - Beware the inflammatory cell-rich colonic polyp: a rare case of EBV-positive inflammatory pseudotumour-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma with increased IgG4-positive plasma cells
Lynne Goh, Nan Zun Teo, Lai Mun Wang
Pathology.2020; 52(6): 713. CrossRef - Epstein–Barr virus‐positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma presenting as a solitary colonic mass: two rare cases and a literature review
Xiaokang Ke, Huihua He, Qingping Zhang, Jingping Yuan, Qilin Ao
Histopathology.2020; 77(5): 832. CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A brief report of two cases
Bi-Xi Zhang, Zhi-Hong Chen, Yu Liu, Yuan-Jun Zeng, Yan-Chun Li
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2019; 11(12): 1231. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated lymphoid proliferations, a 2018 update
Sherif A. Rezk, Xiaohui Zhao, Lawrence M. Weiss
Human Pathology.2018; 79: 18. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Epstein-Barr Virus Negative Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma Presenting as a Solitary Colonic Mass in a 53-Year-Old Woman; Case Report and Review of Literature
Rossana Kazemimood, Farid Saei Hamedani, Asma Sharif, Sujata Gaitonde, Elizabeth Wiley, Pier Cristoforo Giulianotti, John Vincent Groth
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2017; 25(5): e30. CrossRef - A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Lymph Node in the Small Bowel Mesentery Accompanied by Myasthenia Gravis
Daichi KITAGUCHI, Katsuji HISAKURA, Taiki SATO, Masanao KURATA, Tatsuya ODA, Nobuhiro OHKOHCHI
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2017; 78(3): 527. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features of inflammatory pseudotumour‐like follicular dendritic cell tumour of the abdomen
Yanyang Chen, Huijuan Shi, Hui Li, Tiantian Zhen, Anjia Han
Histopathology.2016; 68(6): 858. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma with Pseudochylous Effusion and Review of Literature From India
Kamal Kant Sahu, Gaurav Prakash, Sandeep Rao, Amanjit Bal, Pankaj Malhotra, Jasmina Ahluwalia, Rakesh K. Vashistha
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion.2015; 31(2): 307. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus–associated inflammatory pseudotumor presenting as a colonic mass
Shunyou Gong, Iwona Auer, Rajan Duggal, Stefania Pittaluga, Mark Raffeld, Elaine S. Jaffe
Human Pathology.2015; 46(12): 1956. CrossRef - Response of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma to gemcitabine and docetaxel: report of two cases and literature review
Robert M Conry
Clinical Sarcoma Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- The fifth edition of the WHO classification of mature T cell, NK cell and stroma-derived neoplasms
- Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosacoma of Uterus: A Case Study
- Dae Woon Kim, Jung Hwan Shin, Ho Jung Lee, Young Ok Hong, Jong Eun Joo, Eun Kyung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(4):388-391. Published online August 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.388
- 10,404 View
- 59 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Uterine rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) typically presents as a mixed epithelial and mesenchymal tumors. Pure RMSs of the female genital tract are uncommon. Spindle cell variant of RMS is a rare morphologic subtype of embryonal RMS and mostly occurs in the paratesticular region of children. Here, we present a case of uterine spindle cell RMS in a 76-year-old woman. The tumor, 20×15×7 cm in size, was highly necrotic and adherent to the colon and rectum. Tumor cells were mostly spindle-shaped, and isolated rhabdomyoblasts were scattered. Immunohistochemical stains for myoglobin and myo-D1 showed diffuse positivity for tumor cells. The patient died only of disease three months after diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare adult case of primary uterine rhabdomyosarcoma with mixed pattern: a clinicopathological & immunohistochemical study with literature review
Nehal K.H. Kamel, Eiman Adel Hasby
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the uterine corpus: a clinicopathological and molecular analysis of 21 cases highlighting a frequent association with DICER1 mutations
Jennifer A. Bennett, Zehra Ordulu, Robert H. Young, Andre Pinto, Koen Van de Vijver, Eike Burandt, Pankhuri Wanjari, Rajeev Shah, Leanne de Kock, William D. Foulkes, W. Glenn McCluggage, Lauren L. Ritterhouse, Esther Oliva
Modern Pathology.2021; 34(9): 1750. CrossRef - Vaginal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma in young woman: A case report and literature review
Lalya Issam, Laatitioui Sana, Essadi Ismail, El Omrani Abdelhamid, Khouchani Mouna
Archives of Cancer Science and Therapy.2020; 4(1): 034. CrossRef - Is fertility-preservation safe for adult non-metastatic gynecologic rhabdomyosarcoma patients? Systematic review and pooled survival analysis of 137 patients
Maha AT Elsebaie, Zeinab Elsayed
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.2018; 297(3): 559. CrossRef - Spindle cell sarcoma – a rare diagnosis
SK Kathpalia, Manju Mehrotra, Pinky Jena, Archana H Deshpande
Women's Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignant mesenchymal tumors of the uterus – time to advocate a genetic classification
Birgit Rommel, Carsten Holzmann, Jörn Bullerdiek
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2016; 16(11): 1155. CrossRef - Human rhabdomyosarcoma cells express functional pituitary and gonadal sex hormone receptors: Therapeutic implications
AGATA PONIEWIERSKA-BARAN, GABRIELA SCHNEIDER, WENYUE SUN, AHMED ABDELBASET-ISMAIL, FREDERIC G. BARR, MARIUSZ Z. RATAJCZAK
International Journal of Oncology.2016; 48(5): 1815. CrossRef - Primary third ventricular tumor in an 18‐year‐old man
Tianping Yu, Mengni Zhang, Qiao Zhou, Jing Gong, Ling Nie, Xueqin Chen, Ni Chen
Neuropathology.2015; 35(6): 599. CrossRef - Rhabdomyosarcoma of vulva in a young lady
Tapesh Bhattacharyya, Firuza D. Patel, Radhika Srinivasan, Bhavana Rai, Pradeep Saha, R. Nijhawan
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2015; 11(3): 650. CrossRef - Uterine sarcoma in a 14 year-old girl presenting with uterine rupture
Jane Özcan, Özlem Dülger, Latif Küpelioğlu, Ali İhsan Gönenç, Aynur Erşahin
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2014; 10: 44. CrossRef
- A rare adult case of primary uterine rhabdomyosarcoma with mixed pattern: a clinicopathological & immunohistochemical study with literature review
- Myxoid Liposarcoma with Cartilaginous Differentiation: A Case Study with Cytogenetical Analysis
- Hyunchul Kim, Won Hwangbo, Sangjeong Ahn, Suhjin Kim, Insun Kim, Chul Hwan Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):284-288. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.284
- 9,412 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Myxoid liposarcoma is a subtype of liposarcoma. This specific subtype can be identified based on its characteristic histological and cytogenetical features. The tumor has a fusion transcript of the
CHOP andTLS genes, which is caused by t(12;16)(q13;p11). Most of the fusion transcripts that have been identified fall into three categories, specifically type I (exons 7-2), type II (exons 5-2), and type III (exons 8-2). A total of seven myxoid liposarcomas associated with the rare phenomenon of cartilaginous differentiation have been documented in the literature. Currently, only one of these cases has been cytogenetically analyzed, and the analysis indicated that it was a type IITLS-CHOP fusion transcript in both the typical myxoid liposarcoma and cartilaginous areas. This study presents a second report of myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation, and includes a cytogenetical analysis of both the myxoid and cartilaginous areas.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
Naoki Kojima, Takashi Kubo, Taisuke Mori, Kaishi Satomi, Yuko Matsushita, Shintaro Iwata, Yasushi Yatabe, Koichi Ichimura, Akira Kawai, Hitoshi Ichikawa, Akihiko Yoshida
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 71. CrossRef - The Conundrum of Dedifferentiation in a Liposarcoma at a Peculiar Location: A Case Report and Literature Review
Ana-Maria Ciongariu, Adrian-Vasile Dumitru, Cătălin Cîrstoiu, Bogdan Crețu, Maria Sajin, Dana-Antonia Țăpoi, Aminia-Diana Ciobănoiu, Adrian Bejenariu, Andrei Marin, Mariana Costache
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 967. CrossRef - Myxoid liposarcoma with cartilaginous differentiation showing DDIT3 rearrangement
Kayo Suzuki, Taketoshi Yasuda, Kenta Watanabe, Takeshi Hori, Masahiko Kanamori, Tomoatsu Kimura
Oncology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
- Multiple Jejunal Myeloid Sarcomas Presenting with Intestinal Obstruction in a Non-leukemic Patient: A Case Report with Ultrastructural Observations
- Na Rae Kim, Woon Kee Lee, Jong In Lee, Hyun Yee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):590-594. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.590
- 8,802 View
- 72 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Myeloid sarcoma is a rare extramedullary myeloid tumor, which is frequently misdiagnosed when no evidence of leukemia is initially observed. Here, we report on a peculiar case of a 49-year-old man afflicted with multiple masses in the jejunum, the superior mesentery, and the serosa of the transverse colon, without leukemic manifestation. The tumor was composed of undifferentiated small round cells containing eosinophilic cytoplasm, which were negative for myeloperoxidase, nonspecific esterase, lysozyme, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, leukocyte common antigen, CD3, CD4, CD15, CD20, CD30, CD43, CD56, CD68/PG-M1, CD79a, human melanoma black-45, c-kit, and CD34 with positivity only for CD68/KP1, CD99, and vimentin. Under electron microscopy, those cells had abundant membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules that measured 200 to 300 nm in diameter, which were consistent with granulocytic azurophilic granules. The tumor was finally diagnosed as a myeloid sarcoma. The presence of non-leukemic myeloid sarcomas showing immunonegativity for conventional myeloid-leukemic markers necessitated a diagnosis by ultrastructural observation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myeloid sarcoma presenting as intestinal obstruction: A case report of the first presentation of acute myeloid leukemia
Deepsikha Dharamsaktu, Anuradha Pandit, Charanjeet Ahluwalia, Sana Ahuja
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2025; 133: 111522. CrossRef - Myeloid sarcoma of the gastrointestinal tract: Wolf in sheep’s clothing!
Nisha Meena, Surbhi Goyal, Prerna Arora, Sanjeev Sachdeva, Puja Sakhuja
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2025; 68(2): 452. CrossRef - Primary ileal myeloid sarcoma presenting with bowel obstruction: a case report
Hitoshi Minagi, Nobuhiko Kanaya, Yoshitaka Kondo, Yoshihiko Kakiuchi, Shinji Kuroda, Ryohei Shoji, Hajime Kashima, Yuki Matsumi, Satoru Kikuchi, Kunitoshi Shigeyasu, Fuminori Teraishi, Shunsuke Kagawa, Toshiyoshi Fujiwara
Surgical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Isolated myeloid sarcoma presenting with small bowel obstruction: a case report
Rie Mizumoto, Masanori Tsujie, Tomoko Wakasa, Kotaro Kitani, Hironobu Manabe, Shuichi Fukuda, Kaoru Okada, Shumpei Satoi, Hajime Ishikawa, Toshihiko Kawasaki, Hitoshi Hanamoto, Masao Yukawa, Masatoshi Inoue
Surgical Case Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Myeloid Sarcoma of the Ileum and Mesentery Causing Small Bowel Obstruction: Case Report and Literature Review
Andrej Nikolovski, Dragoslav Mladenovikj, Aleksandra Veljanovska, Gordana Petrusevka
Lietuvos chirurgija.2020; 19(1-2): 55. CrossRef - Utility of Transmission Electron Microscopy in Small Round Cell Tumors
Na Rae Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(2): 93. CrossRef
- Myeloid sarcoma presenting as intestinal obstruction: A case report of the first presentation of acute myeloid leukemia
- Extraskeletal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma in the Axillary Region: Reports of Two Cases
- Chang-Young Seo, Sung-Taek Jung, Jae-Wook Byun
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):483-488. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.483
- 9,545 View
- 44 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcomas (EMCs) are relatively uncommon, and a location in the upper extremity, especially in the shoulder or axillary region, is rare. Furthermore, the radiographic findings of EMCs do not show any features that distinguish them from other neoplasms, and therefore, definitive diagnoses are made based on histological features. EMC is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis, and requires wide surgical excision. However, its treatment may involve peculiarities such as a difficulty in obtaining a proper surgical margin in the axillary region or shoulder. In this report, the authors present two rare cases of EMCs in the axillary region.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extraskeletal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma of the Arm: A Rare Case Report with a Review of Literature
Anubhuti Chaturvedi, Nimisha Dhankar, Swapnil Suman, Nita Khurana, Chandra Bhushan Singh, Sapna Singh
Journal of Bone and Joint Diseases.2025; 40(3): 170. CrossRef - Complete surgical excision of a high‐grade extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, resulting in a longer survival than previously reported
Hannah Reeves, Tesh Smalle
Veterinary Record Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Locally recurrent extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the shoulder: a case of complete neoadjuvant radiotherapy response
Luca Improta, Sergio Valeri, Rossana Alloni, Chiara Pagnoni, Francesco Mallozzi Santa Maria, Beniamino Brunetti, Carlo Greco, Irene Aprile, Mirella Maselli, Bruno Vincenzi, Alessandro Gronchi
Clinical Sarcoma Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary extraskeletal chondrosarcoma in the axillary region of a dog with review of the literature
Catrina Pennington, Josep Monne Rodriguez, Marlene Finck, Ben Walton
Veterinary Record Case Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma of Bone and Soft Tissue: A Systematic Review of 107 Patients in the Past 20 Years
Jie Xu, Dasen Li, Lu Xie, Shun Tang, Wei Guo, David M Loeb
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(4): e0122216. CrossRef - Management of renal extraskeletal mesenchymal chondrosarcoma
Vitalie Gherman, Ciprian Tomuleasa, Catalina Bungardean, Nicolae Crisan, Victor-Dan Ona, Bogdan Feciche, Alexandru Irimie, Ioan Coman
BMC Surgery.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Extraskeletal Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma of the Arm: A Rare Case Report with a Review of Literature
- Primary Pulmonary Myxoid Liposarcoma with Translocation t(12;16)(q13;p11) in a Young Female Patient: A Brief Case Report
- Choonhee Son, Phil Jo Choi, Mee Sook Roh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):392-394. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.392
- 7,741 View
- 50 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Primary liposarcoma of the lung is an extremely rare disease. To date, only 14 cases have been reported in the literature. We experienced a case of myxoid liposarcoma of the lung treated by surgery. The tumor was well-defined, solid, lobulated mass measuring 3.5×2 cm, involving the bronchus of the left lower lobe. Microscopically, myxoid liposarcoma was identified. The fluorescence
in situ hybridization confirmed the presence of a reciprocal translocation involving DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3 ) and fused in sarcoma (FUS ) genes. The patient is still alive with no recurrence or metastasis at the time of writing this report (on 20 months postoperatively). To our knowledge, this is the first cytogenetic case report of pulmonary myxoid liposarcoma.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Liposarcoma of the Spleen: Case Report With Review of the Literature
Elisa M. Wächtershäuser, Gabriele Köhler, Verena Böhmer, Alexander Marx, Achim Hellinger
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 33(4): 928. CrossRef - Primary intrathoracic liposarcomas: A clinicopathologic and molecular study of 43 cases in one of the largest medical centers of China
You Xie, Wenyi Jing, Wei Zhao, Ran Peng, Min Chen, Ting Lan, Heng Peng, Xin He, Huijiao Chen, Zhang Zhang, Hongying Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Pulmonary Liposarcoma with Pancreatic Metastasis: A Rarest of Rare Intrathoracic Malignancy
Anirban Halder, Rituparna Biswas, Sujit Shukla, Nisha Rana, Vikas Yadav, Jaspreet Kaur
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2020; 41(04): 605. CrossRef - Primary dedifferentiated liposarcoma of the lung with rhabdomyoblastic and chrondroblastic differentiation
Anthony Longano, Alexandra DuGuesclin, Catherine Mitchell
Histopathology.2015; 67(6): 923. CrossRef
- Primary Liposarcoma of the Spleen: Case Report With Review of the Literature
- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma with Rapid Growth in Parapharynx: A Case Report
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Guhyun Kang, Sung-Im Do, Seoung Wan Chae, Kyungeun Kim, Sang Hyuk Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Joon Hyuk Choi, Jin Hee Sohn, Dong-Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):306-310. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.306
- 8,472 View
- 54 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (FDCS) is a rare malignancy arising from the antigen-presenting cells in the lymph node and extranodal tissue. We describe a 31-year-old male patient who presented with a swelling of the left parapharynx. The radiologic findings showed a 4.7×4.5×1.9 cm-sized, ill-defined mass in the left parapharyngeal space. A fine-needle aspiration cytology was performed and it showed scattered, irregular, cohesive clusters of tumor cells with a spindle-to-ovoid shape with irregular contours in a background of lymphocytes. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of spindle cell neoplasm was made. The surgically resected tumor was composed of elongated, ovoid or polygonal cells showing positive immunohistochemistry for CD21, CD23, and CD35. Postoperatively, the residual tumor was observed to undergo a rapidly growth. There is an overlap in the cytologic and histologic findings between FDCS of the parapharynx and other tumors. Pathologists should therefore be aware of its characteristics not only to provide an accurate diagnosis but also to recommend the appropriate clinical management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Head and Neck Region: A Clinicopathological Study of 7 Cases
Nasir Ud Din, Zubair Ahmad, Shabina Rahim, Karen Fritchie, Muhammad Usman Tariq, Arsalan Ahmed
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(6): 1067. CrossRef - Cytomorphology of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a report of 7 cases with an emphasis on the diagnostic challenges
Cody Weimholt, Jalal B. Jalaly, Cedric Bailey
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(3): 229. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cells
Seham A. Abd El‐Aleem, Entesar Ali Saber, Neven M. Aziz, Hani El‐Sherif, Asmaa M. Abdelraof, Laiche Djouhri
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2022; 237(4): 2019. CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Dayong Sun, Gang Zhang
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological diagnosis of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case report and review of literature
A. Dutta, P. Arun, P. Roy, I. Arun
Cytopathology.2018; 29(5): 461. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cells and related sarcoma
Fabio Facchetti, Luisa Lorenzi
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2016; 33(5): 262. CrossRef - Extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A clinicopathological report of four cases and a literature review
RUI-FEN WANG, WEI HAN, LEI QI, LI-HUI SHAN, ZHENG-CAI WANG, LI-FENG WANG
Oncology Letters.2015; 9(1): 391. CrossRef - Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of Parapharyngeal Space: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Turki Al-Hussain, Muhammad Saleem, Suresh Babu Velagapudi, Mohammad Anas Dababo
Head and Neck Pathology.2015; 9(1): 135. CrossRef - Clinical and pathological features of head and neck follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Ji Li, Min-Li Zhou, Shui-Hong Zhou
Hematology.2015; 20(10): 571. CrossRef
- Extranodal Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Head and Neck Region: A Clinicopathological Study of 7 Cases
- Primary Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma Arising in the Mesentery: Case Report of an Extremely Rare Mesenteric Sarcoma Confirmed by Molecular Detection of a
SYT-SSX2 Fusion Transcript - Han Suk Ryu, Ilyeong Heo, Jae Soo Koh, Sung-Ho Jin, Hye Jin Kang, Soo Youn Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):187-191. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.187
- 7,805 View
- 42 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Synovial sarcoma arises in the para-articular tissues, and it can also occur in various unexpected sites. We report a rare case of primary monophasic synovial sarcoma (MSS) arising in the mesentery. A 59-year-old man presented with a palpable abdominal mass. On microscopic examination, the entire tumor comprised a dense proliferation of the spindle cells without epithelial components. The tumor cells were positive for transducin-like enhancer of split 1, bcl-2, epithelial membrane antigen and CD99 but negative for CD34, CD117, alpha-smooth muscle actin, cytokeratin, and calretinin on immunohistochemistry. The reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction revealed a single 151-bp fragment representing the
SYT-SSX2 fusion transcript. Because mesenteric MSS is extremely rare and many cases display histologic findings that overlap with those of more frequently involved tumors such as hemangiopericytoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor, there is a chance of making an incorrect diagnosis that can result in an inappropriate treatment.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of primary mesenteric synovial sarcoma: a challenging presentation
Nihed Abdessayed, Malek Barka, Samiha Mabrouk, Zeineb Nfikha, Zeineb Maatoug, Yosra Fejji, Mohamed Salah Jarrar, Sabri Youssef, Moncef Mokni
Surgical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pelvis: A case report and review of literature
Gerardo Palmieri, Carmine Grassi, Luigi Conti, Filippo Banchini, Maria Diletta Daccò, Gaetano M. Cattaneo, Patrizio Capelli
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 77: S52. CrossRef - Tumeur neuroectodermique gastro-intestinale (GNET) : à propos d’un cas de tumeur du grêle avec métastases hépatiques
Thibault Kervarrec, Claire Lecointre, Rémy Kerdraon, Guido Bens, Arnaud Piquard, Patrick Michenet
Annales de Pathologie.2015; 35(6): 506. CrossRef
- A case of primary mesenteric synovial sarcoma: a challenging presentation
- Diagnostic Value of
MDM2 andDDIT3 FluorescenceIn Situ Hybridization in Liposarcoma Classification: A Single-Institution Experience - Junhun Cho, Seung Eun Lee, Yoon-La Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):115-122. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.115
- 10,709 View
- 97 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The amplification of murine double minutes (
MDM2 ) is the primary feature of well-differentiated liposarcomas (WDLPS) and dedifferentiated liposarcomas (DDLPS), whileDDIT3 rearrangement is the main one of myxoid liposarcomas (MLPS). Our aim was to evaluate the added value ofMDM2 amplification andDDIT3 rearrangement in making a diagnosis and classifying lipogenic tumors.Methods Eighty-two cases of liposarcoma and 60 lipomas diagnosed between 1995 and 2010 were analysed for
MDM2 amplification andDDIT3 rearrangement using a fluorescencein situ hybridization (FISH). The subtypes of liposarcoma were reclassified according to the molecular results, whose results were reviewed with an analysis of the relevant histologic and immunohistochemical findings.Results One case of lipoma (1.67%) was reclassified as a WDLPS. Of the liposarcomas, 13.4% (16/82) were reclassified after the molecular testing. Five cases of MLPS were reclassified as four cases of DDLPS and one case of myxoid lipoma. Two cases of WDLPS were reclassified as one case of spindle cell lipoma and another case of myxofibrosarcoma. Four cases of DDLPS were reclassified as two cases of leiomyosarcoma, one case of angiomyolipoma and another case of fibroinflammatory lesion. Of the six cases of pleomorphic liposarcoma, five were reclassified as DDLPS.
Conclusions In our series, a critical revision of diagnosis was found at a rate of 3.5% (5/142) after a review of the lipomatous lesions. The uses of molecular testing by
MDM2 andDDIT3 FISH were valuable to make an accurate subtyping of liposarcomas as well as to differentiate WDLPS from benign lipomatous tumor.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
Naoki Kojima, Takashi Kubo, Taisuke Mori, Kaishi Satomi, Yuko Matsushita, Shintaro Iwata, Yasushi Yatabe, Koichi Ichimura, Akira Kawai, Hitoshi Ichikawa, Akihiko Yoshida
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 71. CrossRef - FISH Diagnostic Assessment of MDM2 Amplification in Liposarcoma: Potential Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Recommendations
Alessandro Gambella, Luca Bertero, Milena Rondón-Lagos, Ludovica Verdun Di Cantogno, Nelson Rangel, Chiara Pitino, Alessia Andrea Ricci, Luca Mangherini, Isabella Castellano, Paola Cassoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1342. CrossRef - Expression of CTAG1B clone EPR13780 versus DDIT3 gene rearrangement distinguishes myxoid liposarcoma from its mimics with detection of novel DDIT3 gene copy number variations
Marwa M. Abdelaziz, Hanan Y. Tayel, Amany Abdel-Bary, Omnia M. Badawy
Journal of Histotechnology.2022; 45(2): 56. CrossRef - Musculoskeletal Tumors
Amit Singla, David S. Geller
Pediatric Clinics of North America.2020; 67(1): 227. CrossRef - Vulvar Myxoid Liposarcoma, an Extremely Rare Diagnosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Ligia Redroban, Nelson Montalvo
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2019; 38(1): 17. CrossRef - Molecular updates in adipocytic neoplasms✰
Elizabeth G. Demicco
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2019; 36(2): 85. CrossRef - Application of MDM2 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry in Distinguishing Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma From Other High-grade Sarcomas
Min Jeong Song, Kyung-Ja Cho, Jong-Seok Lee, Joon Seon Song
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2017; 25(10): 712. CrossRef - FluorescenceIn SituHybridization forMDM2Amplification as a Routine Ancillary Diagnostic Tool for Suspected Well-Differentiated and Dedifferentiated Liposarcomas: Experience at a Tertiary Center
Khin Thway, Jayson Wang, John Swansbury, Toon Min, Cyril Fisher
Sarcoma.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Complete response of a recurrent-metastatic liposarcoma with dedifferentiated histological features following the administration of trabectedin and review of literature
Tulay Kus, Gokmen Aktas, Mehmet Emin Kalender, Ediz Tutar, Esra Ulker, Celaletdin Camci
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2015; 11(4): 974. CrossRef
- Myxoid liposarcoma with nuclear pleomorphism: a clinicopathological and molecular study
- Metaplastic Thymoma: Report of 4 Cases
- Guhyun Kang, Nara Yoon, Joungho Han, Young Eun Kim, Tae Sung Kim, Kwhanmien Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):92-95. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.92
- 10,589 View
- 76 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metaplastic thymoma (MT), accepted in the World Health Organization 2004 scheme, is a circumscribed tumor of the thymus exhibiting biphasic morphology. We herein describe the clinicopathologic features of four MTs and the differential diagnoses of this unusual tumor. There were three women and one man with mean age of 49.5 years. The patients were found to have mediastinal masses, and underwent surgical excision. One exhibited symptoms of myasthenia gravis, and the serum titer for anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody was positive. Grossly, the tumors were encapsulated, and showed vaguely multinodular, solid, tan-white to yellow cut surfaces. Histologically, they comprised epithelial islands intertwining with bundles of delicate spindle cells. The patients remained well after surgical excision at 5-55 months. Because of the distinctive histological appearance and benign clinical course, MT should be distinguished from other more aggressive mediastinal neoplasms displaying biphasic feature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Giant Metaplastic Thymoma With Extensive Calcification
Keisuke Todoroki, Satoshi Kawakami, Keiya Nagata, Kentaro Miura, Momoko Takizawa, Yasunari Fujinaga
Journal of Thoracic Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Case of Metaplastic Thymoma Presenting With Myasthenia Gravis
Ilianne Vega Prado, John Shymansky, Anisha Apte, Keith Mortman, Henry J. Kaminski, Stephanie Barak
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(1): 155. CrossRef - Thymic epithelial tumours: histopathological classification and differential diagnosis
Jan von der Thüsen
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 196. CrossRef - Epigenetics of Thymic Epithelial Tumors
Vanessa Nicolì, Fabio Coppedè
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 360. CrossRef - Expanding the Clinicopathologic Spectrum of YAP1::MAML2–Rearranged Thymic Neoplasm
Eric Eunshik Kim, Ye Yoon Suh, Sang Won Lee, Jeong Mo Bae, Kyoungbun Lee, Sungyoung Lee, Hongseok Yun, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jiwon Koh
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(2): 100048. CrossRef -
Significance of
YAP1–MAML2
rearrangement and
GTF2I
mutation in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of metaplastic thymoma
Minghao Wang, Hongtao Xu, Qiang Han, Liang Wang
Annals of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Loss of YAP1 C‐terminus expression as an ancillary marker for metaplastic thymoma: a potential pitfall in detecting YAP1::MAML2 gene rearrangement
Xuan Wang, Lei‐lei Liu, Qing Li, Qiu‐yuan Xia, Rui Li, Sheng‐bing Ye, Ru‐song Zhang, Ru Fang, Hui Chen, Nan Wu, Qiu Rao
Histopathology.2023; 83(5): 798. CrossRef - A Case of Metaplastic Thymoma
Ryoichi TAKENAKA, Kenji NEZU, Daijiro TAKEMOTO, Tatsuya HAYASHI, Hisato YAMAMOTO, Shoichi MATSUKAGE
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2023; 84(4): 538. CrossRef - Malignant Transformation of Metaplastic Thymoma into High-Grade Sarcomatoid Carcinoma: A Case Report
Zheng Hua Piao, Jin Ping Chen, Hai Ren Chen, Xin Cheng Zhou
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(5): 564. CrossRef - YAP1-MAML2 Fusion as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Metaplastic Thymoma
Jikai Zhao, Ruiying Zhao, Chan Xiang, Jinchen Shao, Lianying Guo, Yuchen Han
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Metaplastic thymoma: a distinctive thymic neoplasm characterized by YAP1-MAML2 gene fusions
Marina Vivero, Phani Davineni, Valentina Nardi, John K.C. Chan, Lynette M. Sholl
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(4): 560. CrossRef - Metaplastic thymoma: Report of two cases
Yoshikazu Shinohara, Mariko Tanaka, Kentaro Kitano, Kazuhiro Nagayama, Masaaki Sato, Jun Nakajima
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2020; 34(7): 733. CrossRef - Type AB thymoma is not a mixed tumor of type A and type B thymomas, but a distinct type of thymoma
Yukari Miki, Kana Hamada, Tadashi Yoshino, Katsuya Miyatani, Kiyoshi Takahashi
Virchows Archiv.2014; 464(6): 725. CrossRef - Potential Role of Adjuvant Radiation Therapy in Cervical Thymic Neoplasm Involving Thyroid Gland or Neck
Jae Myoung Noh, Sang Yun Ha, Yong Chan Ahn, Dongryul Oh, Seung Won Seol, Young Lyun Oh, Joungho Han
Cancer Research and Treatment.2014; 47(3): 436. CrossRef - A Case of Metaplastic Thymoma
Eiji MIYAHARA, Tomoko ITAGAKI, Masaki KUWAHARA, Akira KAMEDA, Yoshihiro MIYATA, Kazuhiro SENTANI, Wataru YASUI
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2014; 75(2): 360. CrossRef
- Giant Metaplastic Thymoma With Extensive Calcification
- Dedifferentiated Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma of the Masticator Space: A Case Report.
- Geunyoung Jung, Kyung Ja Cho, Seung Ho Choi, Mi Jung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S101-S105.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S101
- 4,680 View
- 36 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We describe a 69-year-old woman who presented with a dedifferentiated extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma arising in the left masticator space. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 5 cm sized mass in the left masticator space. Histologically, the tumor consisted of two distinct areas. The less cellular area was a low-grade extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, composed of strands or cords of uniform spindle cells and abundant myxoid stroma. The more cellular, dedifferentiated area corresponded to a high grade myxofibrosarcoma, consisting of anaplastic tumor cells in myxoid stroma and geographic necrosis. The tumor cells of the former area were positive for S-100 protein, microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2) and class III beta-tubulin, but negative for cytokeratin, smooth muscle actin, and desmin. The tumor cells in the latter, pleomorphic area showed MAP-2 and beta-tubulin immunoreactivity with a high Ki-67 labeling index. Based on its histologic and immunohistochemical features, the tumor was considered a dedifferentiated extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the parotid gland
NyimiBushabu Fidele, Wu Tianfu, Bing Liu, Yanfang Sun, Zhao Yifang
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2019; 9(2): 439. CrossRef - Myxoid chondrosarcoma of maxilla: A rare case report
Hiralal Ash, Ajoy Kumar Shahi, Kabita Chatterjee, Dipankar Samaddar
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2016; 28(3): 273. CrossRef - Maxillo-facial Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: A Case Report and Discussion
Ratnadeep Ganguly, Abhishek Mukherjee
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(6): 639. CrossRef
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the parotid gland
- High-Grade Myxofibrosarcoma Showing Pleomorphic Hyalinizing Angiectatic Tumor-like Appearance: A Case Report.
- Mi Seon Kang, Hye Jung Jo, Sung Hee Son
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S1-S4.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S1
- 3,947 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Myxofibrosarcomas (MFSs), which consist of multiple nodules with a variable cellular population in a myxoid matrix, are primarily located in subcutaneous tissue. Pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumors (PHATs) are rare soft-tissue tumors characterized by a proliferation of highly pleomorphic spindle or polygonal cells and abundant ectatic blood vessels in cellular or myxoid stroma. We present here an unusual case of a high-grade MFS with a PHAT-like appearance. A 67-year-old man presented with an asymptomatic subcutaneous mass in the right forearm. The tumor had myxoid, hypo-, and hypercellular areas with highly pleomorphic spindle or polygonal tumor cells that showed frequent mitoses and nuclear pseudoinclusions. Foci of punctuate necrosis and inflammatory infiltration were present throughout the tumor, and abundant ectatic, thick-walled vessels containing blood clots were noted. The tumor cells were immunohistochemically positive for vimentin but negative for CD34, S-100 protein, smooth muscle actin, desmin, and bcl-2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Children's kinetic family drawings and their internalizing problem behaviors
Jin Kyung Kim, Joo Hyun Suh
The Arts in Psychotherapy.2013; 40(2): 206. CrossRef
- Children's kinetic family drawings and their internalizing problem behaviors
- Maxillo-facial Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma: A Case Report and Discussion.
- Ratnadeep Ganguly, Abhishek Mukherjee
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):639-643.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.639
- 4,236 View
- 25 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this report, we share our experience of a case of maxillo-facial extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, a very rare location for this neoplasm. In addition, a literature review is provided. The patient, a 61-year-old male, had a maxillary mass encroaching on the nasal cavity. After debulking, the tumor recurred, attaining its pre-surgical proportion in two months. The patient improved clinically with radiation and remained stable for about one year. However, he ultimately developed metastases in his lung which were treated with palliative chemotherapy with a good outcome lasting three months. We could find only eight reported cases of this tumor in the head region of which two are in the maxilla; hence, ruling out other primary sites is mandatory for a patient presenting with a primary head and neck mass. Surgical removal may be complicated because of the location. A combination of surgery and radiation is the management of choice, with palliative chemotherapy in metastasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma of Floor of Mouth—A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature
Surendra K Dabas, Nandini N Menon, Reetesh Ranjan, Bikas Gurung, Sukirti Tiwari, Bharat Bhushan Bassan, Himanshu Shukla, Sunil Pasricha, Ajit Sinha, Rahul Kapoor, Vinay Kumar Verma, Devesh Verma, Saurabh Arora, Ashwani Sharma, Sourabh Mukharjee, Rishu Sin
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 76(1): 1290. CrossRef - Intracranial Metastasis of Extracranial Chondrosarcoma: Systematic Review With Illustrative Case
Charles E. Mackel, Harry Rosenberg, Hemant Varma, Erik J. Uhlmann, Rafael A. Vega, Ron L. Alterman
Brain Tumor Research and Treatment.2023; 11(2): 103. CrossRef
- Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma of Floor of Mouth—A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature
- Type and Incidence of Soft Tissue Sarcomas in Korea: 2001-2007.
- Kyung Un Choi, Hae Youn Kang, Heasoo Koo, Mi Seon Kwon, Dong Hoon Kim, Mi Jung Kim, Su Jin Kim, Young Sill Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Yong Koo Park, Hye Rim Park, Seung Sam Paik, Jin Young Yoo, Anhi Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hyekyung Lee, Kyu Yun Jang, Young Chae Chu, Joon Hyuk Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):557-563.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.557
- 4,708 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The Korean Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists conducted a nationwide retrospective analysis of soft tissue sarcoma (STS) to provide the clinicopathologic characteristics of STS within the population of the Republic of Korea.
METHODS
The cases of STS were collected during a 7-year period (2001-2007) from 19 institutes in Korea. All cases were classified according to the histologic criteria proposed by the World Health Organization. Clinicopathologic data were reviewed.
RESULTS
Data from 722 patients (median age, 50 years) were collected. Data showed a slight male predominance. The most frequent types of STS in decreasing order were liposarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, leiomyosarcoma, and synovial sarcoma. STS occurred throughout the body, although approximately half (47.8%) were located in the extremities. The majority of STS was histologically classified as high grade with a large tumor size (>5 cm). The overall survival rate for the patients was 76.3% (median follow-up time, 26 months; range, 1 to 89 months). Histologic grade, tumor size, American Joint Committee on Cancer stage, tumor site, and resection status were prognostic. Significant independent adverse prognostic factors were large tumor size (>5 cm) and tumor site other than extremities.
CONCLUSIONS
We reported the distribution and characteristics of STS in the Republic of Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distribution and survival of primary sarcoma in Korea: A single center analysis of 2017 cases
Sung Jun Jo, Kyeong Sik Kim, Kyo Won Lee, Jae Berm Park, Yoon-La Choi, Jeong Il Yu, Su Jin Lee, Dong Il Choi, Sung Joo Kim
Korean Journal of Clinical Oncology.2018; 14(1): 30. CrossRef
- Distribution and survival of primary sarcoma in Korea: A single center analysis of 2017 cases
- Diagnostic Utility of the JAZF1/JJAZ1 Gene Fusion in Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas and Their Histologic Variants.
- Sang Ryung Lee, Joon Seon Song, Ga Hye Kim, Jene Choi, Hyung Kyoung Kim, Yonghee Lee, Kyu Rae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):498-505.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.498
- 3,743 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The diagnosis of endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is often difficult in cases showing diverse histological differentiation or in undifferentiated endometrial sarcoma (UES). Recently, JAZF1/JJAZ1 gene fusion has been described as a defining feature of low-grade ESS (LGESS). However, its prevalence is variably reported, and the diagnostic utility has rarely been examined for cases showing various histological differentiation.
METHODS
To test the diagnostic utility of JAZF1/JJAZ1 gene fusion in difficult cases, we compared the prevalence of the JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion gene in LGESS with and without histological differentiation.
RESULTS
The JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion transcript was detected in 18 of 21 LGESS (85.7%), including 14 classical LGESS (93%), four LGESS with diverse histological differentiation (67%), and two with UES (28.6%). Positive cases included two LGESS with sex cord-like differentiation, one with osseous differentiation, and two UES. LGESS showing smooth muscle differentiation revealed the fusion transcript only in the classic area. Direct sequencing analysis of two LGESS revealed a previously reported breakpoint at t(7;17)(p15;q21).
CONCLUSIONS
The JAZF1/JJAZ1 fusion gene was identified in a significant proportion of LGESS showing secondary histological differentiation except in cases with smooth muscle differentiation. Thus, this fusion gene may be useful to confirm the diagnosis in difficult cases of LGESS.
- 14-bp Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the HLA-G Gene in Osteosarcoma Patients.
- Ahrim Moon, Su Kang Kim, Joo Ho Chung, Ki Yong Na, Liliana G Olvi, Eduardo Santini-Araujo, Youn Wha Kim, Yong Koo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):485-490.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.485
- 4,750 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The major histocompatibility complex class I, G (human leukocyte antigen-G [HLA-G]) gene plays a vital role in the suppression of immune responses. Recently, a number of studies have reported an association between HLA-G and diseases (pregnancy complications, organ transplantation, and tumors). Some of the studies have revealed that the 14-bp insertion/deletion polymorphism might be associated with various diseases. The aim of the present study was to explore a possible influence of the 14-bp insertion/deletion polymorphism on osteosarcoma.
METHODS
Genomic DNA was extracted from 75 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissues derived from patients with conventional osteosarcoma (OSA) and 183 peripheral blood samples of healthy controls. Fifty-eight cases were South Korean patients with OSA and 17 cases were Argentine patients with OSA. The HLA-G 14-bp insertion/deletion polymorphism at exon 8 of the HLA-G locus was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
There was a significantly different distribution profile for the 14-bp genotypes between the Korean OSA and Korean control groups. Specifically, there were more heterozygote 210 bp/224 bp genotypes in the Korean OSA group when compared to the Korean control group (62.1% vs 40.4%, p=0.002).
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that HLA-G heterozygote patients may be more susceptible to OSA in the Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 14-bp Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the HLA-G gene in Breast Cancer among Women from North Western Iran
Mehdi Haghi, Mohammad Ali Hosseinpour Feizi, Majid Sadeghizadeh, Abbas Sahebghadam Lotfi
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(14): 6155. CrossRef
- 14-bp Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the HLA-G gene in Breast Cancer among Women from North Western Iran
- Parotid Gland Carcinosarcoma with Osteosarcoma as a Sarcomatous Component: A Case Report with Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings.
- Se Min Jang, Young Jin Jun, Hulin Han, Ki Seok Jang, Seung Sam Paik
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):412-416.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.412
- 4,495 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Carcinosarcoma of the salivary glands is a rare malignant tumor showing both malignant epithelial and mesenchymal components. Herein, we present a carcinosarcoma of the parotid gland in a 67-year-old man consisting of osteosarcoma and adenocarcinoma components with fine needle aspiration cytological findings. The tumor was composed predominantly of osteosarcoma and small areas of adenocarcinomatous components and a hyalinized nodule reminiscent of pleomorphic adenoma. The tumor showed infiltrative growth features with perineural, lymphatic, and vascular invasion. Despite postoperative adjuvant radiation therapy, multiple metastatic lesions occurred in the both lungs 5 months after surgery. As salivary gland carcinosarcoma has been known to demonstrate highly aggressive behavior, an accurate pathological diagnosis is prerequisite for appropriate treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Morphological Aspects of Aggressive Salivary Gland Mixed Tumors: A Narrative Review
Alexandra Corina Faur, Alina Maria Șișu, Laura Andreea Ghenciu, Roxana Iacob, Emil Robert Stoicescu, Ovidiu Alin Hațegan, Mărioara Cornianu
Diagnostics.2024; 14(17): 1942. CrossRef - Carcinosarcoma of the parotid gland with abdominal metastasis: a case report and review of literature
Chang Gok Woo, Seung-Myoung Son
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical and Morphological Aspects of Aggressive Salivary Gland Mixed Tumors: A Narrative Review
- A Case of Intimal Sarcoma Arising in the Left Common Iliac Artery.
- Ji Young Park, Kun Young Kwon, Hyoung Tae Kim, Sang Sook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):311-314.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.311
- 3,793 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary tumors of the great vessels are rare. Most encountered cases are sarcomas which most commonly develop in the aorta, pulmonary artery, and inferior vena cava. We experienced an intimal sarcoma arising in the left common iliac artery in a 68-year-old male, who suffered from claudication in his left lower extremity for a year and was diagnosed as arteriosclerosis obliterans, clinically. Bypass surgery was performed on the obstructive lesion. Grossly, the vascular lumen was filled with dark hemorrhagic materials. Microscopically, the lesion showed proliferation of anaplastic spindle cells with a marked nuclear atypia, arranged haphazardly. There were numerous mitotic figures. Foci of cholesterol clefts were also found in the intima. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and cytokeratin in certain areas. Stains for CD34, desmin, myosin heavy chain, caldesmon, and S-100 protein were negative. A pathologic diagnosis was made as intimal sarcoma with myofibroblastic differentiation.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings of Angiosarcoma: Report of Two Cases.
- Jin Xian Ji, Young Chae Chu, Lucia Kim, Suk Jin Choi, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Kyu Ho Kim, Ju Young Song
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):217-222.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.217
- 4,984 View
- 36 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angiosarcoma is a rare malignant vascular neoplasm which can arise in any part of the body. Specific recognition of this neoplasm in cytological specimens is difficult in the absence of an ancillary method. Herein, we present the cytologic findings of two cases of angiosarcomas diagnosed on fine needle aspiration cytology. One case is a recurred angiosarcoma in the left chest wall and the other case is a lymphedema-associated angiosarcoma in the left lower leg. The cytologic findings of both cases are similar. Cytologic features that identified this neoplasm as an angiosarcoma included arborizing microtissue fragments, irregular anastomosing vascular spaces lined by atypical cells, microacini, intracytoplasmic lumen, and intracellular red blood cells, marked cell discohesiveness, spindle to ovoid, irregular, hyperchromatic nuclei, and elongated cytoplasmic processes with indistinct borders. This report emphasizes that when aspiration smears show vasoformative features in a bloody background, angiosarcoma should be included in the differential diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case Series and Literature Review of Angiosarcoma With Malignant Effusion—A Challenging Cytologic Diagnosis With Dire Prognostic Implications
Jamie C. Y. Lam, Iris Y. H. Liu, Joanna K. M. Ng, Joshua J. X. Li
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Four newly reported ophichthid leptocephali species revealed by mitochondrial 12S rDNA, with implications of their occurrence in Korea
Hwan Sung Ji, Hae Won Lee, Byung Kyu Hong, Jin Koo Kim
Animal Cells and Systems.2012; 16(5): 415. CrossRef
- A Case Series and Literature Review of Angiosarcoma With Malignant Effusion—A Challenging Cytologic Diagnosis With Dire Prognostic Implications
- Sarcomatoid Carcinoma of the Gallbladder with Pure Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Brief Case Report.
- Seungkoo Lee, Song Yi Kim, Seong Kweon Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):209-211.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.209
- 4,251 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a rare case of sarcomatoid carcinoma that contained an epithelial component of squamous cell carcinoma. A 77-year-old woman was found to have a gallbladder mass. The gallbladder showed a diffuse infiltrative wall mass with a polypoid lesion, and the mass measured 8x7x3 cm. There were no gallstones. Histologically, the tumor was composed of two components of squamous cell carcinoma and spindle cell malignancy. The tumor extended to the perimuscular connective tissue and one regional lymph node. The postoperative course was uneventful and the patient was well without tumor recurrence at one and a half months after surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carcinosarcoma of gallbladder: A world review
Thomas Zheng Jie Teng, Branden Qi Yu Chua, Vishal G Shelat
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 12(12): 1244. CrossRef
- Carcinosarcoma of gallbladder: A world review

 E-submission
E-submission
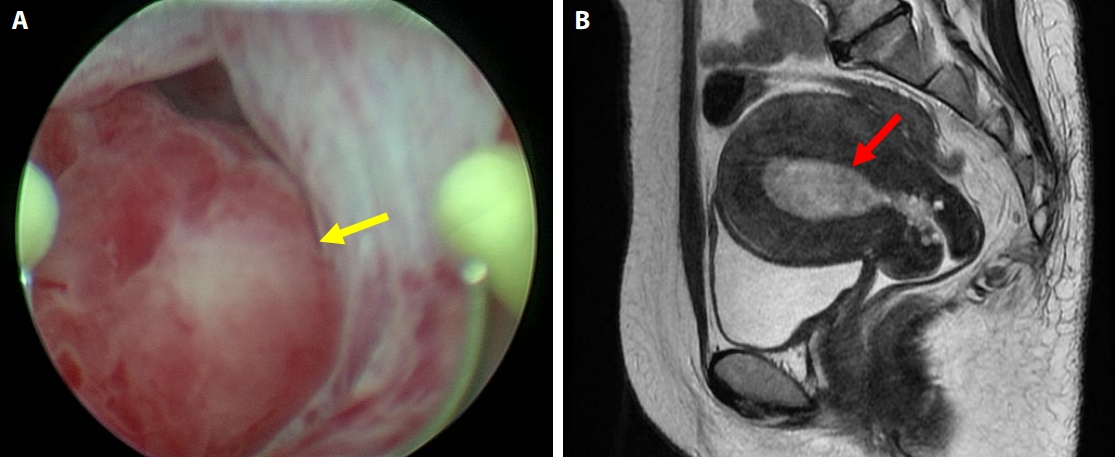
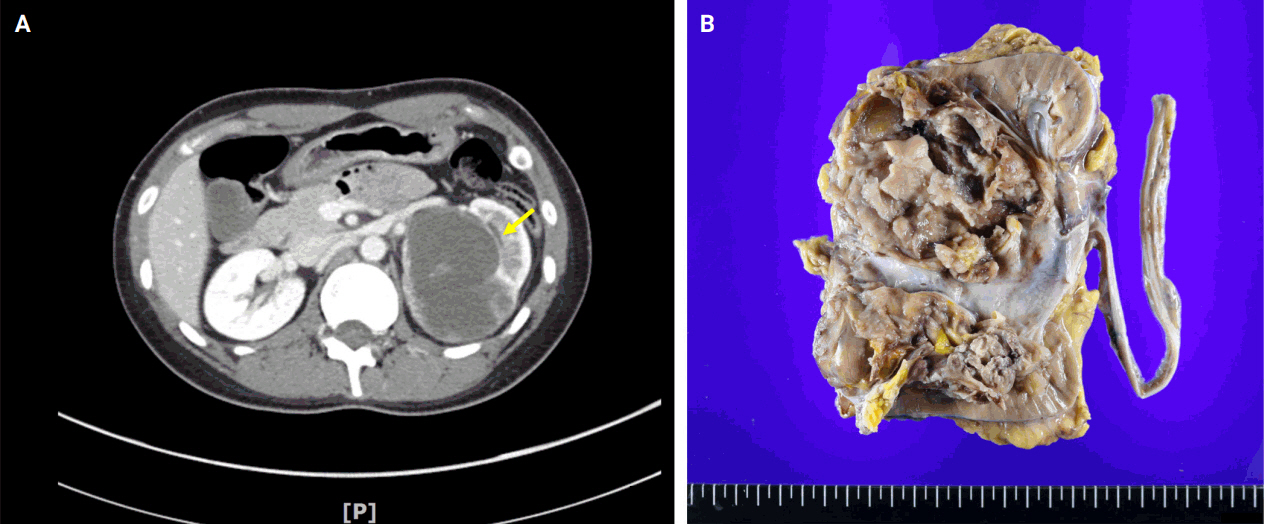











 First
First Prev
Prev



