Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Editorial
- History of the Official Journal Published by the Korean Society of Pathologists: From the Korean Journal of Pathology to the Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine
- Se Hoon Kim, Chong Jai Kim, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):1-6. Published online January 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.07
- 10,912 View
- 132 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Multistakeholder Approach to the Airport Gate Assignment Problem: Application of Fuzzy Theory for Optimal Performance Indicator Selection
Haonan Li, Xu Wu, Yinghui Liang, Chen Zhang, Yu-Ting Bai
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Multistakeholder Approach to the Airport Gate Assignment Problem: Application of Fuzzy Theory for Optimal Performance Indicator Selection
Letter to the Editor
- Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumors (PEComas) of the Orbit
- Panagiotis Paliogiannis, Giuseppe Palmieri, Francesco Tanda, Antonio Cossu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):7-8. Published online January 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.26
- 8,534 View
- 111 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pigmented perivascular epithelioid cell tumors of the orbit with NONO::TFE3 fusion: Molecular evaluation and literature review
Naoko Takeda-Miyata, Ken-ichi Yoshida, Miho Shirono, Akihide Watanabe, Yoji Kukita, Chie Sotozono, Eiichi Konishi
American Journal of Ophthalmology Case Reports.2025; 39: 102378. CrossRef - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the lacrimal gland
Wenqin Xu, Rui Ma, Yueyue Li, Zhicha Hu, Guolu Zhang, Jian Hu, Yan Hei, Xinji Yang
Orbit.2024; 43(3): 362. CrossRef - An orbital perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) in a 9-year-old boy: Case report and review of the literature
N. Bouzid, M. Bugada, D. Pissaloux, C. Burillon, F. Tirode, J. Barbier, A. de la Fouchardière, G. Kielwasser
Journal Français d'Ophtalmologie.2024; 47(7): 104215. CrossRef - Ocular PEComas are frequently melanotic and TFE3-translocated: report of two cases including the first description of PRCC-TFE3 fusion in PEComa
Y. Gao, G. Chen, C. Chow, I. Io, E. W. N. Wong, W. M. S. Tsui, W. Y. Lam, K. F. To, J. K. C. Chan, Wah Cheuk
Virchows Archiv.2021; 478(5): 1025. CrossRef - Orbital TFE3-Rearranged Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Silvia Feu-Basilio, Jessica Matas, Marina Dotti-Boada, Agustin Toll, Ana-Belen Larque, Ramon Pigem, Santiago Ortiz-Perez
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2021; 43(12): e263. CrossRef - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the pterygopalatine fossa
Michael I. Dougherty, Spencer C. Payne, Akriti Gupta, Jose L. Mattos
Clinical Case Reports.2020; 8(3): 553. CrossRef - Giant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Orbit: A Clinicopathological Analysis and Review of the Literature
Akshay G. Nair, Swaranjali S. Gore, Amol Y. Ganvir, Namrata G. Adulkar, Indumati Gopinathan, Anuradha K. Murthy, Nayana A. Potdar, Chhaya A. Shinde
Ocular Oncology and Pathology.2018; 4(5): 272. CrossRef
- Pigmented perivascular epithelioid cell tumors of the orbit with NONO::TFE3 fusion: Molecular evaluation and literature review
Original Articles
- Increased Expression of Thymosin β4 Is Independently Correlated with Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) and Worse Clinical Outcome in Human Colorectal Cancer
- Seung Yun Lee, Mee Ja Park, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Chang Nam Kim, Joo Heon Kim, Dong Wook Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):9-16. Published online October 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.23
- 11,509 View
- 163 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
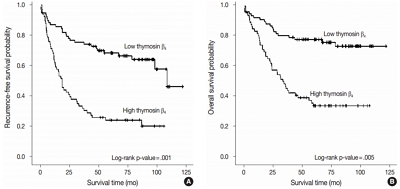
Thymosin β4 is a multi-functional hormone-like polypeptide, being involved in cell migration, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. This study was undertaken to clarify the clinicopathologic implications of thymosin β4 expression in human colorectal cancers (CRCs).
Methods
We investigated tissue sections from 143 patients with CRC by immunohistochemistry. In addition, we evaluated the expression patterns and the clinico-pathological significance of thymosin β4 expression in association with hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression in the CRC series.
Results
High expression of thymosin β4 was significantly correlated with lymphovascular invasion, invasion depth, regional lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, and TNM stage. Patients with high expression of thymosin β4 showed poor recurrence-free survival (p = .001) and poor overall survival (p = .005) on multivariate analysis. We also found that thymosin β4 and HIF-1α were overexpressed and that thymosin β4 expression increased in parallel with HIF-1α expression in CRC.
Conclusions
A high expression level of thymosin β4 indicates poor clinical outcomes and may be a useful prognostic factor in CRC. Thymosin β4 is functionally related with HIF-1α and may be a potentially valuable biomarker and possible therapeutic target for CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting the risk of lymph node metastasis in colon cancer: development and validation of an online dynamic nomogram based on multiple preoperative data
Longlian Deng, Lemuge Che, Haibin Sun, Riletu En, Bowen Ha, Tao Liu, Tengqi Wang, Qiang Xu
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymosin β4 Is an Endogenous Iron Chelator and Molecular Switcher of Ferroptosis
Joanna I. Lachowicz, Giusi Pichiri, Marco Piludu, Sara Fais, Germano Orrù, Terenzio Congiu, Monica Piras, Gavino Faa, Daniela Fanni, Gabriele Dalla Torre, Xabier Lopez, Kousik Chandra, Kacper Szczepski, Lukasz Jaremko, Mitra Ghosh, Abdul-Hamid Emwas, Mass
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(1): 551. CrossRef - Metal coordination of thymosin β4: Chemistry and possible implications
Joanna Izabela Lachowicz, Mariusz Jaremko, Lukasz Jaremko, Giuseppina Pichiri, Pierpaolo Coni, Marco Piludu
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2019; 396: 117. CrossRef - Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Ovarian Cancer Growth and Metastasis by Increasing Thymosin Beta 4X-Linked Expression
Yijing Chu, Min You, Jingjing Zhang, Guoqiang Gao, Rendong Han, Wenqiang Luo, Tingting Liu, Jianxin Zuo, Fuling Wang
Stem Cells International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - An Investigation on the Therapeutic Effect of Thymosinβ4 and Its Expression Levels in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice
Kyung Sook Cho, Dong-Jin Kim, Bomee Shim, Jung Yeon Kim, Jun Mo Kang, Seon Hwa Park, Sang-Ho Lee, Hyung-In Yang, Kyoung Soo Kim
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in colorectal carcinoma
Ahmed M. Abd ElAziz, Hanan S. Abd ElHamid, Rasha R. Mostafa, Yousra R.A. Shalaby
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2018; 38(1): 18. CrossRef
- Predicting the risk of lymph node metastasis in colon cancer: development and validation of an online dynamic nomogram based on multiple preoperative data
- Clinicopathologic Significance of Survivin Expression in Relation to CD133 Expression in Surgically Resected Stage II or III Colorectal Cancer
- Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, EunHee Choi, Mee-Yon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):17-23. Published online December 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.23
- 11,018 View
- 176 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
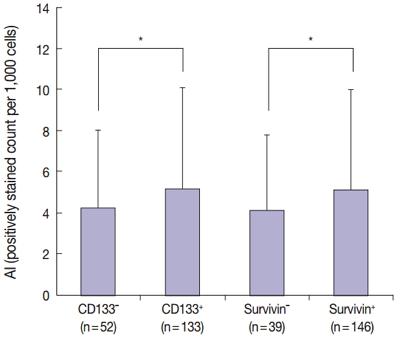
Cancer stem cells have been investigated as new targets for colorectal cancer (CRC) treatment. We recently reported that CD133+ colon cancer cells showed chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil through increased survivin expression and proposed the survivin inhibitor YM155 as an effective therapy for colon cancer in an in vitro study. Here, we investigate the relationship between survivin and CD133 expression in surgically resected CRC to identify whether the results obtained in our in vitro study are applicable to clinical samples.
Methods
We performed immunohistochemical staining for survivin and CD133 in surgically resected tissue from 187 stage II or III CRC patients. We also comparatively analyzed apoptosis according to survivin and CD133 expression using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling.
Results
The results of the Mantel-Haenszel test established a linear association between nuclear survivin and CD133 expression (p = .018), although neither had prognostic significance, according to immunohistochemical expression level. No correlation was found between survivin expression and the following pathological parameters: invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, or histologic differentiation (p > .05). The mean apoptotic index in survivin+ and CD133+ tumors was higher than that in negative tumors: 5.116 ± 4.894 in survivin+ versus 4.103 ± 3.691 in survivin– (p = .044); 5.165 ± 4.961 in CD133+ versus 4.231 ± 3.812 in CD133– (p = .034).
Conclusions
As observed in our in vitro study, survivin expression is significantly related to CD133 expression. Survivin may be considered as a new therapeutic target for chemoresistant CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
Nermin M. Mohamed, Rania Hassan Mohamed, John F. Kennedy, Mahmoud M. Elhefnawi, Nadia M. Hamdy
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2025; 311: 143616. CrossRef - Genetic Variants in BIRC5 (rs8073069, rs17878467, and rs9904341) Are Associated with Susceptibility in Mexican Patients with Breast Cancer: Clinical Associations and Their Analysis In Silico
María Renee Jiménez-López, César de Jesús Tovar-Jácome, Alejandra Palacios-Ramírez, Martha Patricia Gallegos-Arreola, Teresa Giovanna María Aguilar-Macedo, Rubria Alicia González-Sánchez, Efraín Salas-González, José Elías García-Ortiz, Clara Ibet Juárez-V
Genes.2025; 16(7): 786. CrossRef - Upregulation of EMR1 (ADGRE1) by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Colon Cancer Progression by Activating the JAK2/STAT1,3 Signaling Pathway in Tumor Cells
Rokeya Akter, Rackhyun Park, Soo Kyung Lee, Eun ju Han, Kyu-Sang Park, Junsoo Park, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4388. CrossRef - Antiapoptotic Gene Genotype and Allele Variations and the Risk of Lymphoma
Osama M. Al-Amer, Rashid Mir, Abdullah Hamadi, Mohammed I. Alasseiri, Malik A. Altayar, Waseem AlZamzami, Mamdoh Moawadh, Sael Alatawi, Hanan A. Niaz, Atif Abdulwahab A. Oyouni, Othman R. Alzahrani, Hanan E. Alatwi, Aishah E. Albalawi, Khalaf F. Alsharif,
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1012. CrossRef - The Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications of the Chemoresistance Gene BIRC5 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Getinet M. Adinew, Samia Messeha, Equar Taka, Karam F. A. Soliman
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5180. CrossRef - EMR1/ADGRE1 Expression in Cancer Cells Upregulated by Tumor-Associated Macrophages Is Related to Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
Rokeya Akter, Kwangmin Kim, Hye Youn Kwon, Youngwan Kim, Young Woo Eom, Hye-mi Cho, Mee-Yon Cho
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3121. CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of BIRC5/Survivin in Breast Cancer: Results from Three Independent Cohorts
Nina Oparina, Malin C. Erlandsson, Anna Fäldt Beding, Toshima Parris, Khalil Helou, Per Karlsson, Zakaria Einbeigi, Maria I. Bokarewa
Cancers.2021; 13(9): 2209. CrossRef - Obatoclax, a Pan-BCL-2 Inhibitor, Downregulates Survivin to Induce Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells Via Suppressing WNT/β-catenin Signaling
Chi-Hung R. Or, Chiao-Wen Huang, Ching-Chin Chang, You-Chen Lai, Yi-Ju Chen, Chia-Che Chang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(5): 1773. CrossRef - M1 Macrophages Promote TRAIL Expression in Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells, Which Suppresses Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer by Increasing Apoptosis of CD133+ Cancer Stem Cells and Decreasing M2 Macrophage Population
Young Woo Eom, Rokeya Akter, Wanlu Li, Suji Lee, Soonjae Hwang, Jiye Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(11): 3887. CrossRef - Emerging Importance of Survivin in Stem Cells and Cancer: the Development of New Cancer Therapeutics
Neerada Meenakshi Warrier, Prasoon Agarwal, Praveen Kumar
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(5): 828. CrossRef - MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient colorectal cancer cells: 5-Fluorouracil treatment response and correlation to CD133 and MGMT expression
Jaime A. Oliver, Raúl Ortiz, Cristina Jiménez-Luna, Laura Cabeza, Gloria Perazzoli, Octavio Caba, Cristina Mesas, Consolación Melguizo, Jose Prados
Journal of Biosciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Survivin rs9904341 polymorphism significantly increased the risk of cancer: evidence from an updated meta-analysis of case–control studies
Abdolkarim Moazeni-Roodi, Saeid Ghavami, Mohammad Hashemi
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2019; 24(4): 335. CrossRef - CRISPR-Cas9 mediated CD133 knockout inhibits colon cancer invasion through reduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Wanlu Li, Mee-Yon Cho, Suji Lee, Mirae Jang, Junsoo Park, Rackhyun Park, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220860. CrossRef - Diagnostic Approaches for Salivary Gland Tumors with Secretory and Microcystic Features
Ha Young Woo, Eun Chang Choi, Sun Och Yoon
Head and Neck Pathology.2018; 12(2): 237. CrossRef - MUC1‐ and Survivin‐based DNA Vaccine Combining Immunoadjuvants CpG and interleukin‐2 in a Bicistronic Expression Plasmid Generates Specific Immune Responses and Antitumour Effects in a Murine Colorectal Carcinoma Model
C. Liu, Y. Xie, B. Sun, F. Geng, F. Zhang, Q. Guo, H. Wu, B. Yu, J. Wu, X. Yu, W. Kong, H. Zhang
Scandinavian Journal of Immunology.2018; 87(2): 63. CrossRef - Activated STAT3 may participate in tumor progression through increasing CD133/survivin expression in early stage of colon cancer
Wanlu Li, Mi-Ra Lee, Taeyeong Kim, Young Wan Kim, Mee-Yon Cho
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 497(1): 354. CrossRef - MiRNA-142-3p increases radiosensitivity in human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells by inhibiting the expression of CD133
Fang Yuan, Lu Liu, Yonghong Lei, Yi Hu
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - MLH1 enhances the sensitivity of human endometrial carcinoma cells to cisplatin by activating the MLH1/c-Abl apoptosis signaling pathway
Yue Li, Shihong Zhang, Yuanjian Wang, Jin Peng, Fang Fang, Xingsheng Yang
BMC Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of CMab-43, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-CD133 Monoclonal Antibody, for Immunohistochemistry
Shunsuke Itai, Yuki Fujii, Takuro Nakamura, Yao-Wen Chang, Miyuki Yanaka, Noriko Saidoh, Saori Handa, Hiroyoshi Suzuki, Hiroyuki Harada, Shinji Yamada, Mika K. Kaneko, Yukinari Kato
Monoclonal Antibodies in Immunodiagnosis and Immunotherapy.2017; 36(5): 231. CrossRef
- A comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of survivin (BIRC5) in hepatocellular carcinoma hallmarks: A step toward precision
- KRAS Mutation Test in Korean Patients with Colorectal Carcinomas: A Methodological Comparison between Sanger Sequencing and a Real-Time PCR-Based Assay
- Sung Hak Lee, Arthur Minwoo Chung, Ahwon Lee, Woo Jin Oh, Yeong Jin Choi, Youn-Soo Lee, Eun Sun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):24-31. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.03
- 12,094 View
- 170 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Mutations in the KRAS gene have been identified in approximately 50% of colorectal cancers (CRCs). KRAS mutations are well established biomarkers in anti–epidermal growth factor receptor therapy. Therefore, assessment of KRAS mutations is needed in CRC patients to ensure appropriate treatment.
Methods
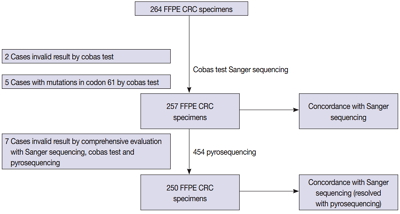
We compared the analytical performance of the cobas test to Sanger sequencing in 264 CRC cases. In addition, discordant specimens were evaluated by 454 pyrosequencing.
Results
KRAS mutations for codons 12/13 were detected in 43.2% of cases (114/264) by Sanger sequencing. Of 257 evaluable specimens for comparison, KRAS mutations were detected in 112 cases (43.6%) by Sanger sequencing and 118 cases (45.9%) by the cobas test. Concordance between the cobas test and Sanger sequencing for each lot was 93.8% positive percent agreement (PPA) and 91.0% negative percent agreement (NPA) for codons 12/13. Results from the cobas test and Sanger sequencing were discordant for 20 cases (7.8%). Twenty discrepant cases were subsequently subjected to 454 pyrosequencing. After comprehensive analysis of the results from combined Sanger sequencing–454 pyrosequencing and the cobas test, PPA was 97.5% and NPA was 100%.
Conclusions
The cobas test is an accurate and sensitive test for detecting KRAS-activating mutations and has analytical power equivalent to Sanger sequencing. Prescreening using the cobas test with subsequent application of Sanger sequencing is the best strategy for routine detection of KRAS mutations in CRC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single-center study on clinicopathological and typical molecular pathologic features of metastatic brain tumor
Su Hwa Kim, Young Suk Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Yeoun Eun Sung, Ahwon Lee, Jun Kang, Jae-Sung Park, Sin Soo Jeun, Youn Soo Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 217. CrossRef - Assessment of KRAS and NRAS status in metastatic colorectal cancer: Experience of the National Institute of Oncology in Rabat Morocco
Chaimaa Mounjid, Hajar El Agouri, Youssef Mahdi, Abdelilah Laraqui, En-nacer Chtati, Soumaya Ech-charif, Mouna Khmou, Youssef Bakri, Amine Souadka, Basma El Khannoussi
Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy.2022; 30(2): 80. CrossRef - The current understanding on the impact of KRAS on colorectal cancer
Mingjing Meng, Keying Zhong, Ting Jiang, Zhongqiu Liu, Hiu Yee Kwan, Tao Su
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 140: 111717. CrossRef - Droplet digital PCR revealed high concordance between primary tumors and lymph node metastases in multiplex screening of KRAS mutations in colorectal cancer
Barbora Vanova, Michal Kalman, Karin Jasek, Ivana Kasubova, Tatiana Burjanivova, Anna Farkasova, Peter Kruzliak, Dietrich Busselberg, Lukas Plank, Zora Lasabova
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2019; 19(2): 219. CrossRef - CRISPR Technology for Breast Cancer: Diagnostics, Modeling, and Therapy
Rachel L. Mintz, Madeleine A. Gao, Kahmun Lo, Yeh‐Hsing Lao, Mingqiang Li, Kam W. Leong
Advanced Biosystems.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Single-center study on clinicopathological and typical molecular pathologic features of metastatic brain tumor
- Aurora Kinase A Is a Prognostic Marker in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma
- Hyun Min Koh, Bo Geun Jang, Chang Lim Hyun, Young Sill Kim, Jin Won Hyun, Weon Young Chang, Young Hee Maeng
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):32-39. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.17
- 10,871 View
- 189 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aurora kinase A (AURKA), or STK15/BTAK, is a member of the serine/threonine kinase family and plays important roles in mitosis and chromosome stability. This study investigated the clinical significance of AURKA expression in colorectal cancer patients in Korea.
Methods
AURKA protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in 151 patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma using tissue microarray blocks. We analyzed the relationship between clinicopathological characteristics and AURKA expression. In addition, the prognostic significance of various clinicopathological data for progression-free survival (PFS) was assessed. Also we evaluated copy number variations by array comparative genomic hybridization and AURKA gene amplification using fluorescence in situ hybridization in colorectal carcinoma tissues.
Results
AURKA gene amplification was found more frequently in the 20q13.2–13.33 gain-positive group than the group with no significant gain on the AURKA-containing locus. AURKA protein expression was detected in 45% of the cases (68/151). Positive staining for AURKA was observed more often in male patients (p = .035) and distally located tumors (p = .021). PFS was shorter in patients with AURKA expression compared to those with low-level AURKA expression (p < .001). Univariate analysis revealed that AURKA expression (p = .001), age (p = .034), lymphatic invasion (p = .001), perineural invasion (p = .002), and TNM stage (p = .013) significantly affected PFS. In a multivariate analysis of PFS, a Cox proportional hazard model confirmed that AURKA expression was an independent and significant prognostic factor in colorectal adenocarcinoma (hazard ratio, 3.944; p < .001).
Conclusions
AURKA could serve as an independent factor to predict a poor prognosis in Korean colorectal adenocarcinoma patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring pyrimidine scaffolds for cancer therapy: A triad of synthetic chemistry, computational studies, and in-vitro biological testing
Pooja Kumari, Anandkumar Tengli
Journal of Molecular Structure.2026; 1350: 144013. CrossRef - First-in-class dual inhibitors of MASTL and Aurora A kinase: Discovery of selective cyclohexa[b]thiophenes with potent anticancer activity
Somaya A. Abdel-Rahman, Hossam Nada, Moustafa T. Gabr
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 293: 117729. CrossRef - RNAi delivery mediated by milk extracellular vesicles in colon cancer
Jessie Santoro, Silvia Nuzzo, Andrea Soricelli, Marco Salvatore, Anna Maria Grimaldi
Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids.2025; 36(3): 102644. CrossRef - Potential Signature Therapeutic Biomarkers TOP2A, MAD2L1, and CDK1 in Colorectal Cancer: A Systems Biomedicine-Based Approach
P. Priyamvada, Sudha Ramaiah
Biochemical Genetics.2024; 62(3): 2166. CrossRef - Neutralizing IL-16 enhances the efficacy of targeting Aurora-A therapy in colorectal cancer with high lymphocyte infiltration through restoring anti-tumor immunity
Shiang-Jie Yang, Sheng-Tsung Chang, Kung-Chao Chang, Bo-Wen Lin, Kwang-Yu Chang, Yao-Wen Liu, Ming-Derg Lai, Liang-Yi Hung
Cell Death & Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of epigenetic modification-related signals for the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer
Xia Li, Jingjing Li, Jie Li, Nannan Liu, Liwei Zhuang
BMC Genomics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Updates on Oncogenic Signaling of Aurora Kinases in
Chemosensitive, Chemoresistant Cancers: Novel Medicinal Chemistry
Approaches for Targeting Aurora Kinases
Pooja Kumari, Narasimha Murthy Beeraka, Anandkumar Tengli, Gurupadayya Bannimath, Ramandeep Kaur Baath, Mayuri Patil
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 31(23): 3502. CrossRef - Identification of Aurora A kinase allosteric inhibitors: A comprehensive virtual screening through fingerprint-based similarity search, molecular docking, machine learning and molecular dynamics simulation
Mahima Sudhir Kolpe, Surbhi Pravin Pawar, Vikramsinh Sardarsinh Suryawanshi, Heba Taha M. Abdelghani, Pritee Chunarkar Patil, Shovonlal Bhowmick
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2024; 414: 126115. CrossRef - Exploring Core Genes by Comparative Transcriptomics Analysis for Early Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapies of Colorectal Cancer
Md. Ariful Islam, Md. Bayazid Hossen, Md. Abu Horaira, Md. Alim Hossen, Md. Kaderi Kibria, Md. Selim Reza, Khanis Farhana Tuly, Md. Omar Faruqe, Firoz Kabir, Rashidul Alam Mahumud, Md. Nurul Haque Mollah
Cancers.2023; 15(5): 1369. CrossRef - The Oncology Biomarker Discovery framework reveals cetuximab and bevacizumab response patterns in metastatic colorectal cancer
Alexander J. Ohnmacht, Arndt Stahler, Sebastian Stintzing, Dominik P. Modest, Julian W. Holch, C. Benedikt Westphalen, Linus Hölzel, Marisa K. Schübel, Ana Galhoz, Ali Farnoud, Minhaz Ud-Dean, Ursula Vehling-Kaiser, Thomas Decker, Markus Moehler, Matthias
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Disease Modeling on Tumor Organoids Implicates AURKA as a Therapeutic Target in Liver Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Sophie L. Boos, Leon P. Loevenich, Sebastian Vosberg, Thomas Engleitner, Rupert Öllinger, Jörg Kumbrink, Matjaz Rokavec, Marlies Michl, Philipp A. Greif, Andreas Jung, Heiko Hermeking, Jens Neumann, Thomas Kirchner, Roland Rad, Peter Jung
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 13(2): 517. CrossRef - Colorectal cancer on a dish: exploring the 3D-sphere culture of primary colorectal cancer cells from an Indonesian perspective
Murdani Abdullah, DR Noor, Amanda Pitarini Utari, Virly Nanda Muzellina, Nur Rahadiani, Radiana Dhewayani Antarianto
F1000Research.2022; 11: 182. CrossRef - Mitotic protein kinase-driven crosstalk of machineries for mitosis and metastasis
Chang-Hyeon Kim, Da-Eun Kim, Dae-Hoon Kim, Ga-Hong Min, Jung-Won Park, Yeo-Bin Kim, Chang K. Sung, Hyungshin Yim
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2022; 54(4): 414. CrossRef - AURKA is a prognostic biomarker for good overall survival in stage II colorectal cancer patients
Peter Jung, David Horst, Thomas Kirchner, Frederick Klauschen, Jens Neumann
Pathology - Research and Practice.2022; 235: 153936. CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Mitotic Kinases’ Inhibitors in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System
Aadil Javed, Gianluca Malagraba, Mahdieh Yarmohammadi, Catalina M. Perelló-Reus, Carles Barceló, Teresa Rubio-Tomás
Future Pharmacology.2022; 2(3): 214. CrossRef - Bioinformatics Analysis of RNA-seq Data Reveals Genes Related to Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancerogenesis
Kristian Urh, Nina Zidar, Emanuela Boštjančič
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13252. CrossRef - Unweaving the mitotic spindle: A focus on Aurora kinase inhibitors in lung cancer
Alessio Stefani, Geny Piro, Francesco Schietroma, Alessandro Strusi, Emanuele Vita, Simone Fiorani, Diletta Barone, Federico Monaca, Ileana Sparagna, Giustina Valente, Miriam Grazia Ferrara, Ettore D’Argento, Mariantonietta Di Salvatore, Carmine Carbone,
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased expression levels of AURKA and KIFC1 are promising predictors of progression and poor survival associated with gastric cancer
Jiyoon Jung, Hoiseon Jeong, Jung-Woo Choi, Hye-Sun Kim, Hwa Eun Oh, Eung Seok Lee, Young-Sik Kim, Ju-Han Lee
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 224: 153524. CrossRef - SALL Proteins; Common and Antagonistic Roles in Cancer
Claudia Álvarez, Aracelly Quiroz, Diego Benítez-Riquelme, Elizabeth Riffo, Ariel F. Castro, Roxana Pincheira
Cancers.2021; 13(24): 6292. CrossRef - AURKA gene polymorphisms and central nervous system tumor susceptibility in Chinese children
Yong-Ping Chen, Li Yuan, Hui-Ran Lin, Xiao-Kai Huang, Ji-Chen Ruan, Zhen-Jian Zhuo
Discover Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Palmatine induces G2/M phase arrest and mitochondrial-associated pathway apoptosis in colon cancer cells by targeting AURKA
Xiaojiang Liu, Yaru Zhang, Siqi Wu, Minmin Xu, Youfeng Shen, Min Yu, Jinhua Fan, Sijia Wei, Chaohang Xu, Lu Huang, Han Zhao, Xuegang Li, Xiaoli Ye
Biochemical Pharmacology.2020; 175: 113933. CrossRef - New landscapes and horizons in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy
Melchiorre Cervello, Maria R. Emma, Giuseppa Augello, Antonella Cusimano, Lydia Giannitrapani, Maurizio Soresi, Shaw M. Akula, Stephen L. Abrams, Linda S. Steelman, Alessandro Gulino, Beatrice Belmonte, Giuseppe Montalto, James A. McCubrey
Aging.2020; 12(3): 3053. CrossRef - The New Paradigm of Network Medicine to Analyze Breast Cancer Phenotypes
Anna Maria Grimaldi, Federica Conte, Katia Pane, Giulia Fiscon, Peppino Mirabelli, Simona Baselice, Rosa Giannatiempo, Francesco Messina, Monica Franzese, Marco Salvatore, Paola Paci, Mariarosaria Incoronato
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(18): 6690. CrossRef - The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues
François Aguet, Shankara Anand, Kristin G. Ardlie, Stacey Gabriel, Gad A. Getz, Aaron Graubert, Kane Hadley, Robert E. Handsaker, Katherine H. Huang, Seva Kashin, Xiao Li, Daniel G. MacArthur, Samuel R. Meier, Jared L. Nedzel, Duyen T. Nguyen, Ayellet V.
Science.2020; 369(6509): 1318. CrossRef - Upregulation of aurora kinase A promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by activating the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in aortic-dissecting aneurysms
Jia Meng, He-Liang Liu, Dong Ma, Hong-Yan Wang, Yue Peng, Hong-Li Wang
Life Sciences.2020; 262: 118491. CrossRef - Inhibition of AURKA Reduces Proliferation and Survival of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells With Activated KRAS by Preventing Activation of RPS6KB1
Lihong Wang-Bishop, Zheng Chen, Ahmed Gomaa, Albert Craig Lockhart, Safia Salaria, Jialiang Wang, Keeli B. Lewis, Jeffrey Ecsedy, Kay Washington, Robert Daniel Beauchamp, Wael El-Rifai
Gastroenterology.2019; 156(3): 662. CrossRef - Discovery and Validation of Novel Biomarkers for Detection of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Hagen Kulbe, Raik Otto, Silvia Darb-Esfahani, Hedwig Lammert, Salem Abobaker, Gabriele Welsch, Radoslav Chekerov, Reinhold Schäfer, Duska Dragun, Michael Hummel, Ulf Leser, Jalid Sehouli, Elena Ioana Braicu
Cells.2019; 8(7): 713. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation of AURKA by miR-4715-3p in upper gastrointestinal cancers
Ahmed Gomaa, Dunfa Peng, Zheng Chen, Mohammed Soutto, Khaled Abouelezz, Alejandro Corvalan, Wael El-Rifai
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The functional diversity of Aurora kinases: a comprehensive review
Estelle Willems, Matthias Dedobbeleer, Marina Digregorio, Arnaud Lombard, Paul Noel Lumapat, Bernard Rogister
Cell Division.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring pyrimidine scaffolds for cancer therapy: A triad of synthetic chemistry, computational studies, and in-vitro biological testing
- PD-L1 Expression and Combined Status of PD-L1/PD-1–Positive Tumor Infiltrating Mononuclear Cell Density Predict Prognosis in Glioblastoma Patients
- Jiheun Han, Yongkil Hong, Youn Soo Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):40-48. Published online December 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.08.31
- 16,100 View
- 278 Download
- 34 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in tumor cells is known to promote immune escape of cancer by interacting with programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) in tumor infiltrating immune cells. Immunotherapy targeting these molecules is emerging as a new strategy for the treatment of glioblastoma (GBM). Understanding the relationship between the PD-L1/PD-1 axis and prognosis in GBM patients may be helpful to predict the effects of immunotherapy.
Methods
PD-L1 expression and PD-1–positive tumor infiltrating mononuclear cell (PD-1+tumor infiltrating mononuclear cell [TIMC]) density were evaluated using tissue microarray containing 54 GBM cases by immunohistochemical analysis; the associations with patient clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Results
PD-L1 expression and high PD-1+TIMC density were observed in 31.5% and 50% of GBM cases, respectively. High expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells was an independent and significant predictive factor for worse overall survival (OS; hazard ratio, 4.958; p = .007) but was not a significant factor in disease-free survival (DFS). PD-1+TIMC density was not correlated with OS or DFS. When patients were classified based on PD-1 expression and PD-1+TIMC density, patients with PD-L1+/PD-1+TIMC low status had the shortest OS (13 months, p = .009) and DFS (7 months, p = .053).
Conclusions
PD-L1 expression in GBM was an independent prognostic factor for poor OS. In addition, combined status of PD-L1 expression and PD-1+TIMC density also predicted patient outcomes, suggesting that the therapeutic role of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis should be considered in the context of GBM immunity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression features of targets for anti-glioma CAR-T cell immunotherapy
Peng Zhang, Chunzhao Li, Yi Wang, Xiaohan Chi, Tai Sun, Qianhe Zhang, Yang Zhang, Nan Ji
Journal of Neuro-Oncology.2025; 171(1): 179. CrossRef - Expression of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Astrocytic Tumors and Its Correlation With Histopathological Grade and Proliferative Index (Ki-67): A Cross-Sectional Study
Namita Singh, Ranjana Giri, Prita Pradhan, Diptiranjan Satapathy, Ipsita Debata
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic significance of PD-L1 and CD45RO+ cells in glioblastoma: The modulating role of MMR status
Yousef Mohammadi, Elina Kaviani, Simin Ahmadvand, Amirreza Dehghanian, Abbas Ghaderi
Journal of Neuroimmunology.2025; 406: 578669. CrossRef - PD-L1 Clones and Their Relevance in Glioblastoma, IDH-Wildtype: A Comparative Analysis
Michal Hendrych, Frantisek Vana, Marketa Hermanova, Radek Lakomy, Tomas Kazda, Kvetoslava Matulova, Alena Kopkova, Martina Jelinkova, Radim Jancalek, Martin Smrcka, Vaclav Vybihal, Jiri Sana
Bratislava Medical Journal.2025; 126(9): 2233. CrossRef - Tumor-associated microenvironment, PD-L1 expression and their relationship with immunotherapy in glioblastoma, IDH-wild type: A comprehensive review with emphasis on the implications for neuropathologists
Giuseppe Broggi, Giuseppe Angelico, Jessica Farina, Giordana Tinnirello, Valeria Barresi, Magda Zanelli, Andrea Palicelli, Francesco Certo, Giuseppe Barbagallo, Gaetano Magro, Rosario Caltabiano
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 254: 155144. CrossRef - Treatment advances in high-grade gliomas
Xi Chen, Yi Cui, Liqun Zou
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - TRP-2 / gp100 DNA vaccine and PD-1 checkpoint blockade combination for the treatment of intracranial tumors
Joshua R. D. Pearson, Carles Puig-Saenz, Jubini E. Thomas, Lydia D. Hardowar, Murrium Ahmad, Louise C. Wainwright, Adam M. McVicar, Victoria A. Brentville, Chris J. Tinsley, A. Graham Pockley, Lindy G. Durrant, Stephanie E. B. McArdle
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advanced immunotherapies for glioblastoma: tumor neoantigen vaccines in combination with immunomodulators
Berta Segura-Collar, Sara Hiller-Vallina, Olaya de Dios, Marta Caamaño-Moreno, Lucia Mondejar-Ruescas, Juan M. Sepulveda-Sanchez, Ricardo Gargini
Acta Neuropathologica Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Analysis of PD-1 and FOXP3 in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Human Gliomas
Priyanka Kanagaraj, Archana Balasubramanian, Raveena Suresh, Bhargavi Somasundaram, Sandhya Sundaram, Priyathersini Nagarajan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression, prognostic significance and therapeutic implications of PD‐L1 in gliomas
Gayaththri Vimalathas, Bjarne Winther Kristensen
Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 tumor expression is associated with poor prognosis and systemic immunosuppression in glioblastoma
Carolina Noronha, Ana Sofia Ribeiro, Ricardo Taipa, Dina Leitão, Fernando Schmitt, Joaquim Reis, Cláudia Faria, Joana Paredes
Journal of Neuro-Oncology.2022; 156(3): 453. CrossRef - Assessment of radiographic and prognostic characteristics of programmed death-ligand 1 expression in high-grade gliomas
Makoto Ohno, Shigehisa Kitano, Kaishi Satomi, Akihiko Yoshida, Yasuji Miyakita, Masamichi Takahashi, Shunsuke Yanagisawa, Yukie Tamura, Koichi Ichimura, Yoshitaka Narita
Journal of Neuro-Oncology.2022; 160(2): 463. CrossRef - The prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression in patients with glioblastoma: A meta-analysis
Xin Guo, Yuelin Zhang, Hengxing Jiao, Xingyu Miao
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - LncRNA UCA1 attenuated the killing effect of cytotoxic CD8 + T cells on anaplastic thyroid carcinoma via miR-148a/PD-L1 pathway
Xiaoming Wang, Yan Zhang, Jian Zheng, Cuixian Yao, Xiubo Lu
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2021; 70(8): 2235. CrossRef - Low tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte density in primary and recurrent glioblastoma
Kelsey Maddison, Moira C. Graves, Nikola A. Bowden, Michael Fay, Ricardo E. Vilain, Sam Faulkner, Paul A. Tooney
Oncotarget.2021; 12(21): 2177. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of the Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T-Cells/PD-L1 Axis in High-Grade Glial Tumors: Toward Personalized Immuno-Oncology
Mahdi Abdoli Shadbad, Zahra Asadzadeh, Negar Hosseinkhani, Afshin Derakhshani, Nazila Alizadeh, Oronzo Brunetti, Nicola Silvestris, Behzad Baradaran
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in glioblastoma: a systematic review, meta-analysis and validation based on dataset
Huan Wang, Youchao Xiao, Xingguang Ren, Dahai Wan
Bioengineered.2021; 12(2): 10366. CrossRef - Expression of Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 and Associated Lymphocyte Infiltration in Olfactory Neuroblastoma
Nyall R. London, Lisa M. Rooper, Justin A. Bishop, Haiying Xu, Lydia J. Bernhardt, Masaru Ishii, Christine L. Hann, Janis M. Taube, Evgeny Izumchenko, Daria A. Gaykalova, Gary L. Gallia
World Neurosurgery.2020; 135: e187. CrossRef - CCR2 inhibition reduces tumor myeloid cells and unmasks a checkpoint inhibitor effect to slow progression of resistant murine gliomas
Joseph A. Flores-Toro, Defang Luo, Adithya Gopinath, Matthew R. Sarkisian, James J. Campbell, Israel F. Charo, Rajinder Singh, Thomas J. Schall, Meenal Datta, Rakesh K. Jain, Duane A. Mitchell, Jeffrey K. Harrison
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2020; 117(2): 1129. CrossRef - Treatment Results for Recurrent Glioblastoma and Alteration of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression After Recurrence
Kyoung Su Sung, Tae Hoon Roh, Ju Hyung Moon, Eui Hyun Kim, Seok-Gu Kang, Se Hoon Kim, Jong Hee Chang
World Neurosurgery.2020; 135: e459. CrossRef - Current advances in PD-1/PD-L1 axis-related tumour-infiltrating immune cells and therapeutic regimens in glioblastoma
Chang Shu, Qingguo Li
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2020; 151: 102965. CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression in Glioblastoma, the Clinical and Prognostic Significance: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Chengcheng Hao, Gang Chen, Huishan Zhao, Yan Li, Jianxin Chen, Hongmei Zhang, Shan Li, Yuze Zhao, Feng Chen, Wenbin Li, Wen G. Jiang
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy for glioblastoma: current progress, challenges and future outlook
Patrick C. Gedeon, Cosette D. Champion, Kristen E. Rhodin, Karolina Woroniecka, Hanna R. Kemeny, Alexa N. Bramall, Joshua D. Bernstock, Bryan D. Choi, John H. Sampson
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2020; 13(10): 1147. CrossRef - Current clinical management of elderly patients with glioma
Alessia Pellerino, Francesco Bruno, Valeria Internò, Roberta Rudà, Riccardo Soffietti
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2020; 20(12): 1037. CrossRef - The Prognostic and Therapeutic Value of PD-L1 in Glioma
Ruo Qiao Chen, Feng Liu, Xin Yao Qiu, Xiao Qian Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Challenges and potential of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade immunotherapy for glioblastoma
Xin Wang, Gaochao Guo, Hui Guan, Yang Yu, Jie Lu, Jinming Yu
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression and Clinicopathological Characteristics, Structural Recurrence, and Biochemical Recurrence/Persistent Disease in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Xiao Shi, Peng-Cheng Yu, Bo-Wen Lei, Cui-Wei Li, Yan Zhang, Li-Cheng Tan, Rong-Liang Shi, Jie Wang, Ben Ma, Wei-Bo Xu, Xiao Wang, Jia-Qian Hu, Nai-Si Huang, Wen-Jun Wei, Yu Wang, Tong-Zhen Chen, Yu-Long Wang, Qing-Hai Ji
Thyroid.2019; 29(9): 1269. CrossRef - The Binding of PD-L1 and Akt Facilitates Glioma Cell Invasion Upon Starvation via Akt/Autophagy/F-Actin Signaling
Ruo Qiao Chen, Xiao Hong Xu, Feng Liu, Chun Yang Li, Yuan Jun Li, Xiang Rui Li, Guo Yong Jiang, Feng Hu, Di Liu, Feng Pan, Xin Yao Qiu, Xiao Qian Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of PD-L1 expression in salivary duct carcinoma with its efficacy as a tumor marker
Yong Ju Lee, Yoon Woo Koh, Sun Och Yoon, Hyang Joo Ryu, Hye Ryun Kim, Hyang Ae Shin
Korean Society for Head and Neck Oncology.2019; 35(1): 13. CrossRef - Prognostic relevance of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in glioblastoma
Kyu Sang Lee, Kyoungyul Lee, Sumi Yun, Seyoung Moon, Yujun Park, Jung Ho Han, Chae-Yong Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Gheeyoung Choe
Journal of Neuro-Oncology.2018; 136(3): 453. CrossRef - Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression and Its Correlation with Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hyo Jung An, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jeong-Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Dong Chul Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim, Jin Pyeong Kim, Eun Jung Jung, Dae Hyun Song
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(1): 9. CrossRef - Radiological evaluation of response to immunotherapy in brain tumors: Where are we now and where are we going?
Michele Porcu, Cinzia Solinas, Paolo Garofalo, Evandro de Azambuja, Mario Scartozzi, Karen Willard-Gallo, Matthias Preusser, Luca Saba
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2018; 126: 135. CrossRef - The expression of programed death ligand‐1 could be related with unfavorable prognosis in salivary duct carcinoma
Fumihiko Sato, Jun Akiba, Akihiko Kawahara, Yoshiki Naito, Takeharu Ono, Yorihiko Takase, Kazuya Murata, Hideyuki Abe, Tomohiko Yamaguchi, Hiroaki Miyoshi, Yushi Abe, Yutaro Mihara, Masahiko Tanikawa, Momoko Akashi, Hirofumi Kurose, Hirohito Umeno, Hirohi
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2018; 47(7): 683. CrossRef - Expression Patterns, Prognostic Value, and Intratumoral Heterogeneity of PD-L1 and PD-1 in Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma
Dwight Owen, Benjamin Chu, Amy M. Lehman, Lakshmanan Annamalai, Jennifer H. Yearley, Konstantin Shilo, Gregory A. Otterson
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2018; 13(8): 1204. CrossRef - PD-L1 and immune escape: insights from melanoma and other lineage-unrelated malignancies
Noah Frydenlund, Meera Mahalingam
Human Pathology.2017; 66: 13. CrossRef - Clinical Trials Investigating Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Glioblastoma
Russell Maxwell, Christopher M. Jackson, Michael Lim
Current Treatment Options in Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Topotecan Decreases the Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Glioblastoma Cell Lines; Implications for Immunotherapy
Joshua Bernstock, Daniel Ye, Florian Gessler, Luca Peruzzotti-Jametti, Mark Gilbert, Yves Pommier, Stefano Pluchino, Ichiro Nakano, John Hallenbeck
Matters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between expression of PD-L1 and tumor angiogenesis, proliferation, and invasion in glioma
Song Xue, Man Hu, Peifeng Li, Ji Ma, Li Xie, Feifei Teng, Yufang Zhu, Bingjie Fan, Dianbin Mu, Jinming Yu
Oncotarget.2017; 8(30): 49702. CrossRef
- Expression features of targets for anti-glioma CAR-T cell immunotherapy
- Diagnostic Significance of Cellular Neuroglial Tissue in Ovarian Immature Teratoma
- Yun Chai, Chang Gok Woo, Joo-Young Kim, Chong Jai Kim, Shin Kwang Khang, Jiyoon Kim, In Ah Park, Eun Na Kim, Kyu-Rae Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):49-55. Published online October 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.19
- 18,298 View
- 487 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
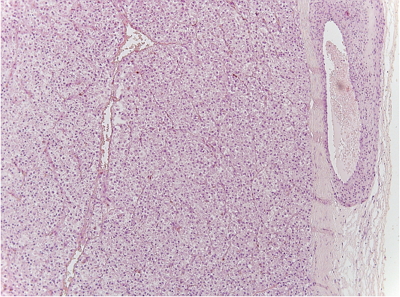
Immature teratoma (IT) is a tumor containing immature neuroectodermal tissue, primarily in the form of neuroepithelial tubules. However, the diagnosis of tumors containing only cellular neuroglial tissue (CNT) without distinct neuroepithelial tubules is often difficult, since the histological characteristics of immature neuroectodermal tissues remain unclear. Here, we examined the significance of CNT and tried to define immature neuroectodermal tissues by comparing the histological features of neuroglial tissues between mature teratoma (MT) and IT.
Methods
The histological features of neuroglial tissue, including the cellularity, border between the neuroglial and adjacent tissues, cellular composition, mitotic index, Ki-67 proliferation rate, presence or absence of tissue necrosis, vascularity, and endothelial hyperplasia, were compared between 91 MT and 35 IT cases.
Results
CNTs with a cellularity grade of ≥ 2 were observed in 96% of IT cases and 4% of MT cases (p < .001); however, CNT with a cellularity grade of 3 in MT cases was confined to the histologically distinct granular layer of mature cerebellar tissue. Moreover, CNT in IT exhibited significantly higher rates of Ki-67 proliferation, mitoses, and necrosis than those in MT (p < .001). Furthermore, an infiltrative border of neuroglial tissue and glomeruloid endothelial hyperplasia were significantly more frequent in IT cases than in MT cases (p < .001).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that if CNT with a cellularity grade of ≥ 2 is not a component of cerebellar tissue, such cases should be diagnosed as IT containing immature neuroectodermal tissue, particularly if they exhibit an infiltrative border, mitoses, necrosis, and increased Ki-67 proliferation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Atypical Presentation of a Pediatric Mature Teratoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Ahmed M Othman, Abdulaziz A Abu Alnasr, Reem E Kordi, Shahad A Abu Alnasr
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immature Teratoma: Diagnosis and Management—A Review of the Literature
Liviu Moraru, Melinda-Ildiko Mitranovici, Diana Maria Chiorean, Marius Coroș, Raluca Moraru, Ioan Emilian Oală, Sabin Gligore Turdean
Diagnostics.2023; 13(9): 1516. CrossRef - Congenital Immature Grade ΙΙΙ Teratoma of the Neck: A Case Report
Nazneen Liaqat, Israr Ud Din, Zeeshan Ali, Majid Rashid, Afsheen Liaqat
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign ovarian teratoma in the dog with predominantly nervous tissue: A case report
P Makovicky, AV Makarevich, P Makovicky, A Seidavi, L Vannucci, K Rimarova
Veterinární medicína.2022; 67(2): 99. CrossRef - Fascin as a Useful Marker for Identifying Neural Components in Immature Teratomas of Human Ovary and Those Derived From Murine Embryonic Stem Cells
Ryunosuke Umehara, Atsushi Kurata, Masakatsu Takanashi, Hirotsugu Hashimoto, Koji Fujita, Toshitaka Nagao, Masahiko Kuroda
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2019; 38(4): 377. CrossRef - Cerebellar Differentiation in Ovarian Teratoma: A Report of 6 Cases
Colin J.R. Stewart, Maxine L. Crook
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2018; 37(4): 316. CrossRef - Mitotic activity of epithelia of ectoand entodermal types in spontaneous and experimental teratomas of mice
Pavel A. Dyban
Medical academic journal.2018; 18(4): 42. CrossRef - Ovarian cystectomy in the treatment of apparent early-stage immature teratoma
Ting Zhao, Yan Liu, Xiao Wang, Hao Zhang, Yuan Lu
Journal of International Medical Research.2017; 45(2): 771. CrossRef
- An Atypical Presentation of a Pediatric Mature Teratoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Size of Non-lepidic Invasive Pattern Predicts Recurrence in Pulmonary Mucinous Adenocarcinoma: Morphologic Analysis of 188 Resected Cases with Reappraisal of Invasion Criteria
- Soohyun Hwang, Joungho Han, Misun Choi, Myung-Ju Ahn, Yong Soo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):56-68. Published online October 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.17
- 11,995 View
- 237 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We reviewed a series of 188 resected pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinomas (MAs) to clarify the prognostic significance of lepidic and non-lepidic patterns.
Methods
Non-lepidic patterns were divided into bland, non-distorted acini with uncertain invasiveness (pattern 1), unequivocal invasion into stroma (pattern 2), or invasion into alveolar spaces (pattern 3).
Results
The mean proportion of invasive patterns (patterns 2 and 3) was lowest in small (≤ 3 cm) tumors, and gradually increased in intermediate (> 3 cm and ≤ 7 cm) and large (> 7 cm) tumors (8.4%, 34.3%, and 50.1%, respectively). Adjusted T (aT) stage, as determined by the size of invasive patterns, was positively correlated with adverse histologic and clinical features including older age, male sex, and ever smokers. aTis tumors, which were exclusively composed of lepidic pattern (n = 9), or a mixture of lepidic and pattern 1 (n = 40) without any invasive patterns, showed 100% disease- free survival (DFS). The aT1mi tumors, with minimal (≤ 5 mm) invasive patterns (n = 63), showed a 95.2% 5-year DFS, with recurrences (n = 2) limited to tumors greater than 3 cm in total size (n = 23). Both T and aT stage were significantly associated with DFS; however, survival within the separate T-stage subgroups was stratified according to the aT stage, most notably in the intermediatestage subgroups. In multivariate analysis, the size of invasive patterns (p = .020), pleural invasion (p < .001), and vascular invasion (p = .048) were independent predictors of recurrence, whereas total size failed to achieve statistical significance (p = .121).
Conclusions
This study provides a rationale for histologic risk stratification in pulmonary MA based on the extent of invasive growth patterns with refined criteria for invasion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distinct Recurrence Pattern and Survival Outcomes of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: The Potential Role of Local Therapy in Intrapulmonary Spread
Dong Woog Yoon, Soohyun Hwang, Tae Hee Hong, Yoon-La Choi, Hong Kwan Kim, Yong Soo Choi, Jhingook Kim, Young Mog Shim, Jong Ho Cho
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 201. CrossRef - Pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
Wei‐Chin Chang, Yu Zhi Zhang, Andrew G Nicholson
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 18. CrossRef - Micropapillary Pattern in Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Comparison With Invasive Non-Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
Hui He, Lue Li, Yuan-yuan Wen, Li-yong Qian, Zhi-qiang Yang
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(5): 926. CrossRef - Radiological and clinical features of screening-detected pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
Dae Hyeon Kim, So Young Bae, Kwon Joong Na, Samina Park, In Kyu Park, Chang Hyun Kang, Young Tae Kim
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2022; 34(2): 229. CrossRef - Micropapillary Pattern in Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Comparison with Invasive Non-Mucinous Adenocarcinoma
Hui He, Yuanyuan Wen, Liyong Qian, Zhiqiang Yang
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal method for measuring invasive size that predicts survival in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung
Tomonari Oki, Keiju Aokage, Shogo Nomura, Kenta Tane, Tomohiro Miyoshi, Norihiko Shiiya, Kazuhito Funai, Masahiro Tsuboi, Genichiro Ishii
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2020; 146(5): 1291. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Histopathologic Features in Pulmonary Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinomas
Wei-Chin Chang, Yu Zhi Zhang, Eric Lim, Andrew G Nicholson
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 154(1): 88. CrossRef
- Distinct Recurrence Pattern and Survival Outcomes of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: The Potential Role of Local Therapy in Intrapulmonary Spread
- Evaluation of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Experience in a Single Institution over a 10-Year Period
- Misun Choi, Yeon Hee Park, Jin Seok Ahn, Young-Hyuck Im, Seok Jin Nam, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):69-78. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.05
- 12,647 View
- 268 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has been associated with favorable clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. However, the possibility that the prognostic significance of pCR differs among various definitions has not been established. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated the pathologic response after NAC in 353 breast cancer patients and compared the prognoses after applying the following different definitions of pCR: ypT0/is, ypT0, ypT0/is ypN0, and ypT0 ypN0. Results: pCR was significantly associated with improved distant disease-free survival (DDFS) regardless of the definition (ypT0/is, p = .002; ypT0, p = .008; ypT0/is ypN0, p < .001; ypT0 ypN0, p = .003). Presence of tumor deposits of any size in the lymph nodes (LNs; ypN ≥ 0(i+)) was associated with worse DDFS (ypT0 ypN0 vs ypT0 ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .036 and ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .015), and presence of isolated tumor cells was associated with decreased overall survival (OS; ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN0(i+), p = .013). Residual ductal carcinoma in situ regardless of LN status showed no significant difference in DDFS or OS (DDFS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .373 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .462; OS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .441 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .758). In subsequent analysis using ypT0/is ypN0, pCR was associated with improved DDFS and OS in triple-negative tumors (p < .001 and p = .003, respectively). Conclusions: Based on our study results, the prognosis and rate of pCR differ according to the definition of pCR and ypT0/is ypN0 might be considered a more preferable definition of pCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
Christine Hong Ngoc Che Thai, Selena J. An, Conner R. Haase, Julia M. Selfridge, Chris B. Agala, Philip M. Spanheimer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(2): 315. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Study on Response Rate and Toxicity
Matt Galloway, Paula Barlow, Jody Jordan, Edward Lo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(20): 7362. CrossRef - Association of residual ductal carcinoma in situ with breast cancer treatment outcomes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to hormone receptor status
Eunju Shin, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Jisun Kim, Il Yong Chung, Beom Seok Ko, Hee Jeong Kim, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son, Sae Byul Lee
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mammographic Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection in Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Ga Eun Park, Bong Joo Kang, Sung Hun Kim, Han Song Mun
Life.2024; 14(11): 1449. CrossRef - Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment – How to assess residual disease
Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
The Breast.2022; 62: S25. CrossRef - Pathological examination of breast cancer samples before and after neoadjuvant therapy: recommendations from the Italian Group for the Study of Breast Pathology - Italian Society of Pathology (GIPaM-SIAPeC)
Nicola Fusco, Antonio Rizzo, Leopoldo Costarelli, Alfredo Santinelli, Bruna Cerbelli, Cristian Scatena, Ettore Macrì, Francesca Pietribiasi, Giulia d’Amati, Anna Sapino, Isabella Castellano
Pathologica.2022; 114(2): 104. CrossRef - Pathological complete response as a surrogate to improved survival in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Ferdia Browne, Nicola Miller, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neoadjuvant therapy with doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by weekly paclitaxel in early breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of 200 consecutive patients treated in a single center with a median follow-up of 9.5 years
Lisi M. Dredze, Michael Friger, Samuel Ariad, Michael Koretz, Bertha Delgado, Ruthy Shaco-Levy, Margarita Tokar, Michael Bayme, Ravit Agassi, Maia Rosenthal, Victor Dyomin, Olga Belochitski, Shai Libson, Tamar Mizrahi, David B. Geffen
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 193(3): 597. CrossRef - “No Ink on Tumor” in Breast-Conserving Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Giulia Atzori, Marco Gipponi, Chiara Cornacchia, Raquel Diaz, Marco Sparavigna, Maurizio Gallo, Tommaso Ruelle, Federica Murelli, Simonetta Franchelli, Francesca Depaoli, Daniele Friedman, Piero Fregatti
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1031. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models and Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Carmen Herrero Vicent, Xavier Tudela, Paula Moreno Ruiz, Víctor Pedralva, Ana Jiménez Pastor, Daniel Ahicart, Silvia Rubio Novella, Isabel Meneu, Ángela Montes Albuixech, Miguel Ángel Santamaria, María Fonfria, Almudena Fuster-Matanzo, Santiago Olmos Antó
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3508. CrossRef - Applying artificial intelligence technology to assist with breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction
Meredith A. Jones, Warid Islam, Rozwat Faiz, Xuxin Chen, Bin Zheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemotherapy response score as a prognostic tool in patients with advanced stage endometrial carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ina Jani, Ricardo R Lastra, Katherine S Brito, Chuanhong Liao, Isabel Lazo, Nita Karnik Lee, S Diane Yamada, Katherine C Kurnit
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2021; 31(6): 852. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with anlotinib in occult breast cancer: A case report and review of literature
Yu Zhang, Di Wu, Bo Zhao, Xue-Liang Tian, Tian-Cheng Yao, Feng Li, Wei-Fang Liu, Ai-Ping Shi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(4): 919. CrossRef - Pathologic Complete Response and Its Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Patient’s Survival after Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Hui Liu, Liqiong Lv, Hui Gao, Ming Cheng, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Impact of Surgical Margins in Breast Cancer After Preoperative Systemic Chemotherapy on Local Recurrence and Survival
K. Wimmer, M. Bolliger, Z. Bago-Horvath, G. Steger, D. Kauer-Dorner, R. Helfgott, C. Gruber, F. Moinfar, M. Mittlböck, F. Fitzal
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2020; 27(5): 1700. CrossRef - Predictive factors for omitting lymphadenectomy in patients with node‐positive breast cancer treated with neo‐adjuvant systemic therapy
Sergi Fernandez‐Gonzalez, Catalina Falo, Maria J. Pla, Paula Verdaguer, Diana Nuñez, Anna Guma, Teresa Soler, Andrea Vethencourt, Silvia Vázquez, Maria Eulalia Fernandez‐Montoli, Miriam Campos, Sonia Pernas, Miguel Gil, Jordi Ponce, Amparo Garcia‐Tejedor
The Breast Journal.2020; 26(5): 888. CrossRef - Is There a Role for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy for T1-2N1 Breast Cancers With Node-Positive Pathology After Patients Become Node-Negative Pathology Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?
Qian Wang, Jingjing Zhao, Xiaowei Han, Puchun Er, Xiangying Meng, Jinyan Shi, Huiru Sun, Jingyang Zhu, Li Zhu, Shikai Wu, Wencheng Zhang, Bing Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic role of microRNA 182 and microRNA 18a in locally advanced triple negative breast cancer
Rajat Bajaj, Rupal Tripathi, T. S. Sridhar, Aruna Korlimarla, Kumardeep Dutta Choudhury, Moushumi Suryavanshi, Anurag Mehta, Dinesh Chandra Doval, Elda Tagliabue
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242190. CrossRef - Association of Pathologic Complete Response with Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Min Huang, Joyce O'Shaughnessy, Jing Zhao, Amin Haiderali, Javier Cortés, Scott D. Ramsey, Andrew Briggs, Peter Hu, Vassiliki Karantza, Gursel Aktan, Cynthia Z. Qi, Chenyang Gu, Jipan Xie, Muhan Yuan, John Cook, Michael Untch, Peter Schmid, Peter A. Fasch
Cancer Research.2020; 80(24): 5427. CrossRef - Multiparametric MR imaging to assess response following neoadjuvant systemic treatment in various breast cancer subtypes: Comparison between different definitions of pathologic complete response
G Santamaría, X Bargalló, S Ganau, I Alonso, M Muñoz, M Mollà, PL Fernández, A Prat
European Journal of Radiology.2019; 117: 132. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of residual nodal burden using lymph node ratio in locally advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Reshu Agarwal, Arun Philip, Keechilat Pavithran, Anupama Rajanbabu, Gaurav Goel, DK Vijaykumar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2019; 56(3): 228. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in occult breast cancer
Haisong Yang, Ling Li, Mengmeng Zhang, Shiyong Zhang, Shu Xu, Xiaoxia Ma
Medicine.2017; 96(40): e8200. CrossRef - Wnt7a Deficiency Could Predict Worse Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Kijong Yi, Kyueng-Whan Min, Young Chan Wi, Yeseul Kim, Su-Jin Shin, Min Sung Chung, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(4): 361. CrossRef
- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
- Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation: Comparative Analysis with Partial Hepatectomy
- Kyuho Lee, Kyoung-Bun Lee, Nam-Joon Yi, Kyung-Suk Suh, Ja-June Jang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):79-86. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.13
- 9,049 View
- 150 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Liver transplantation (LT) is the treatment of choice for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of this study was to investigate the recurrence rate of HCC after LT and prognostic factors for recurrence by comparing LT with non-transplanted resection. Methods: The participants were 338 patients who underwent LT between 1996 and 2012 at Seoul National University Hospital (LT group) and 520 HCC patients who underwent partial hepatectomy between 1995 and 2006 (control group, non-LT group). Results: In the LT group, 68 of 338 patients (19.8%) showed relapse, and the recurrence rate was lower than that in the non-LT group (64.9%, 357/520, p < .001). Stratification analysis by American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage showed that the stage I-II LT group had a lower recurrence rate than the non-LT group. Univariate comparative analysis demonstrated that multiplicity of tumor, tumor size, gross type, Edmondson- Steiner (ES) nuclear grade, extent of tumor, angioinvasion, AJCC stage, Milan criteria, University of California at San Francisco criteria on explant pathology (all p < .001), positive expression of cytokeratin 19 (p = .002), and preoperative α-fetoprotein (AFP) (p < .001) were predictors of tumor recurrence. In multivariate analysis, LT, preoperative AFP, multiplicity of tumor, extent of tumor, size of tumor, and ES nuclear grade were independent prognostic factors. Conclusions: LT might have a protective effect against the late recurrence of stage I-II HCC compared to non-LT, and the prognostic factors for recurrence were similar to previously well-known prognostic factors for HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Locoregional and Surgical Treatment of Single-Nodule Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis
Marco Maria Pascale, Camilla Marandola, Francesco Frongillo, Erida Nure, Salvatore Agnes
Cancers.2025; 17(9): 1501. CrossRef - Risk Factor Analysis of Death in Patients With Hepatic Cellular Carcinoma After Radical Operation: A Consecutive Cohort of 433 Patients
Zhengyang He, Wenfeng Lu, Dongze Qiu, Weimin She
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Related Factors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Associated With Hyperglycemia After Liver Transplantation
Yujian Zheng, Qing Cai, Lishan Peng, Shibo Sun, Shaoping Wang, Jie Zhou
Transplantation Proceedings.2021; 53(1): 177. CrossRef - Oncological Outcomes of Hepatic Resection vs Transplantation for Localized Hepatocellular Carcinoma
A.T. Akcam, A.G. Saritas, A. Ulku, A. Rencuzogullari
Transplantation Proceedings.2019; 51(4): 1147. CrossRef - Clustering Asian Countries According to the Trend of liver cancer Mortality Rates: an Application of Growth Mixture Models
Maryam Salari, Anoshirvan Kazemnejad, Farid Zayeri
Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Locoregional and Surgical Treatment of Single-Nodule Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis
Case Studies
- A Rare Case of Recurrent Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
- Hye Seung Lee, Han Kyeom Kim, Bong Kyung Shin, Jin Hyuk Choi, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):87-91. Published online August 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.16
- 12,293 View
- 234 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 61-year-old woman visited our hospital for bilateral multiple lung nodules and a mass in her thorax. She had a long history of multiple metastatic recurrences of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN); 24 years previously, the patient had undergone pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for a 9.9 × 8.6 cm mass in the pancreatic head. The tumor was diagnosed as an SPN. Nine years later, metastatic nodules were found on computed tomography in the patient’s liver and peritoneum and were excised. She subsequently underwent an additional eight metastatectomy procedures in diverse organs. For the presented event, the lung nodules were removed. The prevalence of malignant SPN in the general population is 5%–15%. However, multiple metastatic recurrence of malignant SPN is rare; the lung is a particularly rare site of metastasis, found in only three cases in the literature. Here, we describe this exceptional case and provide a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
Jun Hyung Kim, Hyung Sun Kim, Jung Min Lee, Ji Hae Nahm, Joon Seong Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2025; 29(1): 83. CrossRef - Curative Resection for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of Pancreas—a Case Series
Aparna M. Jagannathan, Manbha L. Rymbai, Abhilasha Anand, Anoop Paul, Borna Das, Thomas Alex Kodiatte, Frederick L. Vyas, Ravish Sanghi Raju, Philip Joseph
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S2): 232. CrossRef - Malignant Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: An Orthogonal Analysis
Andrew M. Fleming, Leah E. Hendrick, Danny Yakoub, Hafeez Abdelhafeez, Jeremiah L. Deneve, Max R. Langham, Evan S. Glazer, Andrew M. Davidoff, Nipun B. Merchant, Paxton V. Dickson, Andrew J. Murphy
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 475. CrossRef - A Unique Presentation of Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas Requiring Pancreaticoduodenectomy Without Pancreatojejunostomy: A Case Report and Literature Review
Alexis L Carmona, Sameh A Fayek
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Clinical analysis and literature review of five cases of metastatic solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas
Run Hu, Renjie Gui, Xi Nie, Huaxin Duan
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case of Treatment of Solid Pseudopapillary Pancreatic Tumor
F. S. Rakhimova, N. D. Mamashev, O. A. Shimkina, B. Kh. Bebezov
Creative surgery and oncology.2023; 13(2): 178. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: A report of 18 cases
Ayiguzaili Maimaijiang, Haiyun Wang, Wanfu Li, Yaqi Wang
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Large tumor size, lymphovascular invasion, and synchronous metastasis are associated with the recurrence of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas
Goeun Lee, You-Na Sung, Sung Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Lee, Ki-Byung Song, Dae Wook Hwang, Jihun Kim, Sang Soo Lee, Song Cheol Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
HPB.2021; 23(2): 220. CrossRef - Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A 63-Case Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Features and Risk Factors of Malignancy
Hongchun Chen, Yuchen Huang, Ningning Yang, Wentian Yan, Ruxue Yang, Shan Zhang, Panpan Yang, Nan Li, Zhenzhong Feng
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3335. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Approach for Pancreatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm and Initially Undiagnosed Slowly Progressing Liver Tumor
Shohei Takaichi, Yoshifumi Iwagami, Shogo Kobayashi, Yoshito Tomimaru, Hirofumi Akita, Tadafumi Asaoka, Takehiro Noda, Kunihito Gotoh, Masaki Mori, Yuichiro Doki, Hidetoshi Eguchi
Pancreas.2020; 49(8): e70. CrossRef - Rare Solid Tumor of the Exocrine Pancreas: A Pictorial Review
Marco Dioguardi Burgio, Maxime Ronot, Valérie Vilgrain
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2019; 40(6): 483. CrossRef - The Stomach: a Rare Site for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
Prajwala S. Prakash, Dexter Yak Seng Chan, Krishnakumar Madhavan
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2018; 22(4): 759. CrossRef - European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms
Gut.2018; 67(5): 789. CrossRef
- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
- A Rare Case of Angioleiomyoma Arising in the Subglottic Area to Upper Trachea of a Patient with Underlying Asthma
- Yeoun Eun Sung, Chin Kook Rhee, Kyo Young Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):92-95. Published online August 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.21
- 9,466 View
- 113 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angioleiomyoma is a rare disease that is histologically characterized by smooth muscle cells arranged around vascular spaces. Although angioleiomyomas occur rarely in the head and neck region, they can cause various symptoms according the site involved. Here, we present a 44-yearold male patient with a 15-year history of asthma, who presented with recent onset of chest discomfort, globus sensation and throat pain. Medication was not effective in relieving his symptoms, and further evaluation revealed a polypoid ovoid mass, almost obstructing the airway at the border of the larynx and upper trachea on chest computed tomography. The mass was completely resected via a rigid bronchoscopy procedure. Histopathologic examination revealed that the excised mass was angioleiomyoma, which was immunohistochemically positive for smooth muscle actin and negative for desmin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Angioleiomyoma of the Epiglottis Mimicking Epiglottic Hemangioma: Clinical Experience and Literature Review
Yang-Yang Bao, Xiao-Jie Shi, Li-Bo Dai, Yu Guo, Hong-Tian Yao, Shui-Hong Zhou
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025; 104(3): NP125. CrossRef - Angioleiomyoma of the Larynx: A Case Report and Literature Review
Federica Perardi, Giuseppe Abbate, Leonardo R. Iannuzzelli, Rossella Contini, Manuela De Munari, Francesco G. Sciuto, Monica Leutner, Antonio Scotti
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2020; 99(10): 658. CrossRef - Flexible bronchoscopy and cryoextraction for critical airway obstruction caused by an endobronchial angioleiomyoma
Sumit Chatterji, Efrat Ofek, Tiberiu Shulimzon
Respirology Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Angioleiomyoma of the Epiglottis Mimicking Epiglottic Hemangioma: Clinical Experience and Literature Review
Brief Case Reports
- Adult Intussusception Caused by Inverted Meckel’s Diverticulum Containing Mesenteric Heterotopic Pancreas and Smooth Muscle Bundles
- Seungkoo Lee, Seong Whi Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):96-98. Published online August 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.15
- 11,492 View
- 138 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intestinal Intussusception Secondary to Meckel's Diverticulum: A Case Report
Christian Ballardo Medina, Jose Manuel Rocha Chavez, Maria V Figueroa Beltran, Paul Humberto Valdez Castillejo, Rodolfo Lopez Hernandez, Ana Karen Carrasco Gaxiola
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Concomitant Heterotopic Pancreas and Endometriosis as a Rare Cause of Ileo-Ileal Intussusception in a Young Woman with Spina Bifida: Case Report and Literature Review
A. Sciannamea, S. Vaccari, G. Marasco, B. Dalla Via, A. Lauro, I. R. Marino, F. Vasuri, M. Cervellera, V. D’Andrea, V. Tonini
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2020; 65(10): 2800. CrossRef - Ectopic pancreas in the ileum
Saiheng Xiang, Fenming Zhang, Guoqiang Xu
Medicine.2019; 98(44): e17691. CrossRef
- Intestinal Intussusception Secondary to Meckel's Diverticulum: A Case Report
- Human Herpes Virus 8/Epstein-Barr Virus–Copositive, Plasmablastic Microlymphoma Arising in Multicentric Castleman’s Disease of an Immunocompetent Patient
- Yong-Moon Lee, Jin-Man Kim, Sam-Yong Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):99-102. Published online December 24, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.30
- 9,389 View
- 159 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epstein–Barr virus reactivation influences clonal evolution in human herpesvirus‐8‐related lymphoproliferative disorders
Massimo Granai, Mattia Facchetti, Virginia Mancini, Jacqueline Goedhals, Alicia Sherriff, Lucia Mundo, Cristiana Bellan, Teresa Amato, Ester Sorrentino, Marco Ungari, Martine Raphael, Lorenzo Leoncini, Fabio Facchetti, Stefano Lazzi
Histopathology.2021; 79(6): 1099. CrossRef - Germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder: a systematic review
Magda Zanelli, Maurizio Zizzo, Alessandra Bisagni, Elisabetta Froio, Loredana De Marco, Riccardo Valli, Alessandra Filosa, Stefano Luminari, Giovanni Martino, Fulvio Massaro, Stefano Fratoni, Stefano Ascani
Annals of Hematology.2020; 99(10): 2243. CrossRef - Human herpesvirus 8‐positive multicentric Castleman disease with germinotropic plasmablastic aggregates: Overlapping spectrum of human herpesvirus 8‐associated lymphoproliferative disorder
Yosuke Nakaya, Naomi Ishii, Yu Kasamatsu, Katsujun Shimizu, Naoko Tatsumi, Minako Tsutsumi, Masahiro Yoshida, Takuro Yoshimura, Yoshiki Hayashi, Takafumi Nakao, Takeshi Inoue, Takahisa Yamane
Pathology International.2020; 70(8): 574. CrossRef - EBV–Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Sherif A. Rezk, Lawrence M. Weiss
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2019; 12(3): 745. CrossRef - Lymphoproliferative disorders with concurrent HHV8 and EBV infection: beyond primary effusion lymphoma and germinotropic lymphoproliferative disorder
Wei Wang, Rashmi Kanagal‐Shamanna, L Jeffrey Medeiros
Histopathology.2018; 72(5): 855. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated lymphoid proliferations, a 2018 update
Sherif A. Rezk, Xiaohui Zhao, Lawrence M. Weiss
Human Pathology.2018; 79: 18. CrossRef - Persistent KSHV Infection Increases EBV-Associated Tumor Formation In Vivo via Enhanced EBV Lytic Gene Expression
Donal McHugh, Nicole Caduff, Mario Henrique M. Barros, Patrick C. Rämer, Ana Raykova, Anita Murer, Vanessa Landtwing, Isaak Quast, Christine T. Styles, Michael Spohn, Adeola Fowotade, Henri-Jacques Delecluse, Alexandra Papoudou-Bai, Yong-Moon Lee, Jin-Man
Cell Host & Microbe.2017; 22(1): 61. CrossRef
- Epstein–Barr virus reactivation influences clonal evolution in human herpesvirus‐8‐related lymphoproliferative disorders

 E-submission
E-submission



 First
First Prev
Prev



