Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Liquid biopsy using extracellular vesicle–derived DNA in lung adenocarcinoma
- In Ae Kim, Jae Young Hur, Hee Joung Kim, Seung Eun Lee, Wan Seop Kim, Kye Young Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(6):453-461. Published online October 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.08.13
- 8,619 View
- 175 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Blood liquid biopsy has emerged as a way of overcoming the clinical limitations of repeat biopsy by testing for the presence of acquired resistance mutations to therapeutic agents. Despite its merits of repeatability and non-invasiveness, this method is currently only used as a supplemental test due to a relatively low sensitivity rate of 50%–60%, and cannot replace tissue biopsy. The circulating tumor DNAs used in blood liquid biopsies are passive products of fragmented DNA with a short half-life released following tumor cell death; the low sensitivity seen with liquid blood biopsy results from this instability, which makes increasing the sensitivity of this test fundamentally difficult. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are ideal carriers of cancer biomarkers, as cancer cells secret an abundance of EVs, and the contents of tumor cell-originated EVs reflect the molecular and genetic composition of parental cells. In addition, EV-derived DNAs (EV DNAs) consist of large-sized genomic DNAs and tumor-specific oncogenic mutant DNAs. For these reasons, liquid biopsy using EV DNA has the potential to overcome issues arising from tissue shortages associated with small biopsies, which are often seen in lung cancer patients, and the biopsy product can be used in other diagnostic methods, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation testing and next-generation sequencing (NGS). A higher sensitivity can be achieved when EV DNAs obtained from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) are used rather than those from blood. BALF, when obtained close to the tumor site, is a promising liquid biopsy tool, as it enables the gathering of both cellular and non-cellular fractions of the tumor microenvironment, and provides increased diagnostic sensitivity when compared to blood.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as Promising Biomarkers for Precession Diagnostics: A Perspective on Lung Cancer
Sunil Vasu, Vinith Johnson, Archana M, K. Anki Reddy, Uday Kumar Sukumar
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2025; 11(1): 95. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing among hematological malignancy patients with bloodstream infections after antimicrobial therapy
Yueyi Xu, Miaoxin Peng, Tong Zhou, Yonggong Yang, Peipei Xu, Ting Xie, Xuefang Cao, Bing Chen, Jian Ouyang
Journal of Infection.2025; 90(2): 106395. CrossRef - Application of extracellular vesicles in tumor liquid biopsy
Shuai Li, Yating Liu, Dayong Yang
Chinese Science Bulletin.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling extracellular vesicle DNA: Biogenesis, functions, and clinical implications
Mehraneh Nouri, Fateme Nasiri, Samaneh Sharif, Mohammad Reza Abbaszadegan
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 269: 155937. CrossRef - Nanobiotechnology: A smart platform of the future transform liquid biopsy era
Srijan Goswami, Palas Samanta, Manab Deb Adhikari
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2024; 3: 100137. CrossRef - Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: dedicator to maintain tumor homeostasis
Juncun Yao, Li Sun, Feng Gao, Wei Zhu
Human Cell.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Extracellular Vesicle-DNA: The Next Liquid Biopsy Biomarker for Early Cancer Diagnosis?
Irène Tatischeff
Cancers.2023; 15(5): 1456. CrossRef - Isolation of extracellular vesicles from human plasma samples: The importance of controls
Migmar Tsamchoe, Stephanie Petrillo, Anthoula Lazaris, Peter Metrakos
Biotechnology Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of extracellular vesicles in non-small-cell lung cancer, the unknowns, and how new approach methodologies can support new knowledge generation in the field
Sive Mullen, Dania Movia
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 188: 106516. CrossRef - Silicon microfabrication technologies for biology integrated advance devices and interfaces
Vuslat B. Juska, Graeme Maxwell, Pedro Estrela, Martyn E. Pemble, Alan O'Riordan
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 237: 115503. CrossRef - Bronchoalveolar Lavage as Potential Diagnostic Specimens to Genetic Testing in Advanced Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer
Xuwen Lin, Yazhou Cai, Chenyu Zong, Binbin Chen, Di Shao, Hao Cui, Zheng Li, Ping Xu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In-Cell Labeling Coupled to Direct Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles in the Conditioned Medium to Study Extracellular Vesicles Secretion with Minimum Sample Processing and Particle Loss
Anissa Viveiros, Vaibhavi Kadam, John Monyror, Luis Carlos Morales, Desmond Pink, Aja M. Rieger, Simonetta Sipione, Elena Posse de Chaves
Cells.2022; 11(3): 351. CrossRef - Recent advances in liquid biopsy in cancers: Diagnosis, disease state and treatment response monitoring
Zhixian Chen, Judy Wai Ping Yam
Clinical and Translational Discovery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cell-Secreted Vesicles: Novel Opportunities in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring and Treatment
Cristina Catoni, Veronica Di Paolo, Elisabetta Rossi, Luigi Quintieri, Rita Zamarchi
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 1118. CrossRef - DNA-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles in Liquid Biopsy: Tiny Players With Big Potential?
Susana García-Silva, Miguel Gallardo, Héctor Peinado
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA
Jae Young Hur, Kye Young Lee
Cancers.2021; 13(15): 3827. CrossRef - Bronchoalveolar Lavage as a Potential Diagnostic Specimens to Genetic Testing in Advanced Lung Cancer
Xuwen Lin, Xueying Wang, Yazhou Cai, Chenyu Zong, Dawei Liu, Jiming Yu, Chenxin Zhou, Jing Yao, Zheng Li, ping xu
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Omics Data Integration in Extracellular Vesicle Biology—Utopia or Future Reality?
Leona Chitoiu, Alexandra Dobranici, Mihaela Gherghiceanu, Sorina Dinescu, Marieta Costache
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(22): 8550. CrossRef
- Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as Promising Biomarkers for Precession Diagnostics: A Perspective on Lung Cancer
- Current status and future perspectives of liquid biopsy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Sunhee Chang, Jae Young Hur, Yoon-La Choi, Chang Hun Lee, Wan Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):204-212. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.02.27
- 11,248 View
- 296 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With advances in target therapy, molecular analysis of tumors is routinely required for treatment decisions in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Liquid biopsy refers to the sampling and analysis of circulating cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA) in various body fluids, primarily blood. Because the technique is minimally invasive, liquid biopsies are the future in cancer management. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ctDNA tests have been performed in routine clinical practice in advanced NSCLC patients to guide tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment. In the near future, liquid biopsy will be a crucial prognostic, predictive, and diagnostic method in NSCLC. Here we present the current status and future perspectives of liquid biopsy in NSCLC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
Yoon Kyung Kang, Dong Hoon Shin, Joon Young Park, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, JooYoung Na
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 60. CrossRef - Lab-in-a-Fiber detection and capture of cells
João C. Varela, Achar V. Harish, Pawel Maniewski, Timothy Gibbon, Oana Tudoran, Rainer Heuchel, Matthias Löhr, Walter Margulis, Aman Russom, Fredrik Laurell
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognostic Monitoring Through Cell-Free RNA via Liquid Biopsy
Yuanming Pan, Chongbo Jiang, Mengchan Ye, Dongmei Li, Jinghui Wang
Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management.2025; Volume 21: 1615. CrossRef - Unlocking the future of cancer diagnosis – promises and challenges of ctDNA-based liquid biopsies in non-small cell lung cancer
Chiara Reina, Berina Šabanović, Chiara Lazzari, Vanesa Gregorc, Christopher Heeschen
Translational Research.2024; 272: 41. CrossRef - Tailored point-of-care biosensors for liquid biopsy in the field of oncology
Sima Singh, Pritam Saha Podder, Matt Russo, Charles Henry, Stefano Cinti
Lab on a Chip.2023; 23(1): 44. CrossRef - Emerging role of non-invasive and liquid biopsy biomarkers in pancreatic cancer
Akash Bararia, Prosenjeet Chakraborty, Paromita Roy, Bitan Kumar Chattopadhay, Amlan Das, Aniruddha Chatterjee, Nilabja Sikdar
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(15): 2241. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy in the management of advanced lung cancer: Implementation and practical aspects
Gabriela Fernandes, Ana Rodrigues, Cláudia Matos, Fernando Barata, Luís Cirnes, Lurdes Ferreira, José Albino Lopes, Margarida Felizardo, Paula Fidalgo, Ulisses Brito, Bárbara Parente
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2023; 36: 100725. CrossRef - Tweezer PCR: A Highly Specific Method for Accurate Identification of Low-Abundance Mutations
Shanglin Li, Yin Gu, Zhi Geng, Kaiyi Li, Yawei Hu, Qiang Liu, Rongxin Fu, Peng Liu
Analytical Chemistry.2023; 95(48): 17679. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Exosomal MicroRNA Analyses in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines
Sora Kim, Gwang Ha Kim, Su Jin Park, Chae Hwa Kwon, Hoseok I, Moon Won Lee, Bong Eun Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(15): 4426. CrossRef - Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 181. CrossRef - Update on molecular pathology and role of liquid biopsy in nonsmall cell lung cancer
Pamela Abdayem, David Planchard
European Respiratory Review.2021; 30(161): 200294. CrossRef - Dynamics of Specific cfDNA Fragments in the Plasma of Full Marathon Participants
Takehito Sugasawa, Shin-ichiro Fujita, Tomoaki Kuji, Noriyo Ishibashi, Kenshirou Tamai, Yasushi Kawakami, Kazuhiro Takekoshi
Genes.2021; 12(5): 676. CrossRef - Future Perspectives in Detecting EGFR and ALK Gene Alterations in Liquid Biopsies of Patients with NSCLC
Daniela Ferreira, Juliana Miranda, Paula Martins-Lopes, Filomena Adega, Raquel Chaves
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(8): 3815. CrossRef - Real-World Analysis of the EGFR Mutation Test in Tissue and Plasma Samples from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Hyunwoo Lee, Joungho Han, Yoon-La Choi
Diagnostics.2021; 11(9): 1695. CrossRef - Objective Quantitation of EGFR Protein Levels using Quantitative Dot Blot Method for the Prognosis of Gastric Cancer Patients
Lei Xin, Fangrong Tang, Bo Song, Maozhou Yang, Jiandi Zhang
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2021; 21(4): 335. CrossRef - The Role of the Liquid Biopsy in Decision-Making for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
D. Akhoundova, J. Mosquera Martinez, L. E. Musmann, C. Britschgi, C. Rütsche, M. Rechsteiner, E. Nadal, M. R. Garcia Campelo, A. Curioni-Fontecedro
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(11): 3674. CrossRef - Expanding opportunities in precision oncology
T Raja
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2020; 3(4): 863. CrossRef
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Comparison of papanicolaou smear and human papillomavirus (HPV) test as cervical screening tools: can we rely on HPV test alone as a screening method? An 11-year retrospective experience at a single institution
- Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Jungsuk An, Sangho Lee, Jae Yeon Seok, Juhyeon Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):112-118. Published online January 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.29
- 13,944 View
- 266 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The decrease in incidence of cervical dysplasia and carcinoma has not been as dramatic as expected with the development of improved research tools and test methods. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test alone has been suggested for screening in some countries. The National Cancer Screening Project in Korea has applied Papanicolaou smears (Pap smears) as the screening method for cervical dysplasia and carcinoma. We evaluated the value of Pap smear and HPV testing as diagnostic screening tools in a single institution.
Methods
Patients co-tested with HPV test and Pap smear simultaneously or within one month of each other were included in this study. Patients with only punch biopsy results were excluded because of sampling errors. A total of 999 cases were included, and the collected reports encompassed results of smear cytology, HPV subtypes, and histologic examinations.
Results
Sensitivity and specificity of detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were higher for Pap smears than for HPV tests (sensitivity, 97.14%; specificity, 85.58% for Pap smears; sensitivity, 88.32%; specificity, 54.92% for HPV tests). HPV tests and Pap smears did not differ greatly in detection of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (85.35% for HPV test, 80.31% for Pap smears). When atypical glandular cells were noted on Pap smears, the likelihood for histologic diagnosis of adenocarcinoma following Pap smear was higher than that of high-risk HPV test results (18.8 and 1.53, respectively).
Conclusions
Pap smears were more useful than HPV tests in the diagnosis of HSIL, SCC, and glandular lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
Mohammad Panji, Mohammad Hossein Modarresi, Zahra Azizi, Moloud Absalan, Elahe Motevaseli
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of cervical precancerous lesions and cancer by small-scale RT-qPCR analysis of oppositely deregulated mRNAs pairs in cytological smears
Anastasia A. Artyukh, Mikhail K. Ivanov, Sergei E. Titov, Victoria V. Dzyubenko, Sergey E. Krasilnikov, Anastasia O. Shumeikina, Nikita A. Afanasev, Anastasia V. Malek, Sergei A. Glushkov, Eduard F. Agletdinov
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High burden of abnormal cervical smears in South African primary health care: health programmes implications
Olufemi B Omole, Joel M Francis, John M Musonda, Pumla P Sodo, Elizabeth Reji, Nyundu S J Phukuta, Honey L M Mabuza, Joyce S Musonda, Jimmy Akii, John V Ndimande, Olalekan A Ayo-Yusuf
Health Promotion International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis: a study of the microenvironment in cervical cancer (2000-2024)
Yun-Tao Zhang, Yan-Ni Wei, Chen-Chen Liu, Mai-Qing Yang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy biomarkers in cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Isaac Kinyua Njangiru, Bizhar Ahmed Tayeb, Hazhmat Ali, Rafl M. Kamil
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 10: 100328. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Human Papilloma Virus Testing in Comparison with Pap Cytology and Histopathology in Unvaccinated Women with Cervical High-Grade Dysplasia and Carcinoma in Botswana
Patricia Setsile Rantshabeng, Nametso Dire, Andrew Khulekani Ndlovu, Ishmael Kasvosve
Venereology.2025; 4(4): 15. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagmosis of cervical pathologies
D. Y. Chernov, O. A. Tikhonovskaya, S. V. Logvinov, I. A. Petrov, Y. S. Yuriev, A. A. Zhdankina, A. V. Gerasimov, I. V. Zingalyuk, G. A. Mikheenko
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 201. CrossRef - “Barriers and Advantages of Self-Sampling Tests, for HPV Diagnosis: A Qualitative Field Experience Before Implementation in a Rural Community in Ecuador”
Bernardo Vega-Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Ruth Maldonado - Rengel, Diana López, Dayanara Delgado-López, Gabriela Guerra Astudillo, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 947. CrossRef - Cervical Human Papillomavirus Testing
Carol N. Rizkalla, Eric C. Huang
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2024; 17(3): 431. CrossRef - Segmentation of Overlapping Cells in Cervical Cytology Images: A Survey
E Chen, Hua-Nong Ting, Joon Huang Chuah, Jun Zhao
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 114170. CrossRef - Knowledge and awareness regarding pap test and HPV typing for cervical cancer screening in Edo North, Nigeria
Amina Momodu, Johnsolomon Eghosa Ohenhen, Godfrey Innocent Iyare, Musa Abidemi Muhibi, Godwin Avwioro
Discover Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Colposcopy Value in Young Child-bearing Women: Is New Recommendations Necessary?
Fahimeh Sabet, Avishan Aminizad, Fariba Behnamfar, Tajossadat Allameh, Seyedeh Ghazal Shahrokh, Rostami Koushan, Amirmohammad Taravati, Leila Mousavi Seresht
Advanced Biomedical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Selection of endogenous control and identification of significant microRNA deregulations in cervical cancer
T. Stverakova, I. Baranova, P. Mikyskova, B. Gajdosova, H. Vosmikova, J. Laco, V. Palicka, H. Parova
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology Versus Molecular Diagnosis of HPV for Cervical Cancer Screening. Comparison of the Diagnostic Properties of Four Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Rocío Murillo, Cristina Ochoa Avilés
ESPOCH Congresses: The Ecuadorian Journal of S.T.E.A.M..2023; 3(1): 139. CrossRef - Attitudes towards prevention of cervical cancer and early diagnosis among female academicians
Nurhan Doğan, Gamze Fışkın
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(6): 1433. CrossRef - Role of Self-Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: Diagnostic Test Properties of Three Tests for the Diagnosis of HPV in Rural Communities of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz Segarra, Ruth Maldonado Rengel, Diana López, María Paz Orellana, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4619. CrossRef - Utility of Scoring System for Screening and Early Warning of Cervical Cancer Based on Big Data Analysis
Dan Hou, Binjie Yang, Yangdan Li, Ming Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine and Vaginal Self-Sampling versus Clinician-Based Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: A Field Comparison of the Acceptability of Three Sampling Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz S, Ruth Maldonado-Rengel, Diana López, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1614. CrossRef - Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 354. CrossRef - Primary screening of cervical cancer by Pap smear in women of reproductive age group
Ruchi Mishra, Dakshina Bisht, Manisha Gupta
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2022; 11(9): 5327. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Investigating host-virus interaction mechanism and phylogenetic analysis of viral proteins involved in the pathogenesis
Ahmad Abu Turab Naqvi, Farah Anjum, Alaa Shafie, Sufian Badar, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Timir Tripathi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(12): e0261497. CrossRef - Utility of Human Papillomavirus Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Mee-seon Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Moon-il Park, Jae Seok Lee, Kisu Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Hyoun Wook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(5): 1726. CrossRef
- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
- Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):210-216. Published online May 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.04.11
- 13,898 View
- 278 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the introduction of the Papanicolaou (Pap) smear system in 1943, cervicovaginal cytology has been used as a standard screening test for cervical cancer. The dissemination of this test contributed to reductions of the incidence and mortality of cervical cancer worldwide. In Korea, regular health check-ups for industrial workers and their family members were introduced in 1988 and were performed as part of the National Cancer Screening Program in 1999. As a result, the incidence of cervical cancer in Korea has been steadily decreasing. However, about 800 cases of cervical cancer-related deaths are reported each year due to false-negative test results. Hence, new screening methods have been proposed. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) was introduced in 1996 to overcome the limitations of conventional Pap smears. Since then, other LBC methods have been developed and utilized, including the human papilloma virus test—a method with higher sensitivity that requires fewer screenings. In this study, we review current issues and future perspectives related to cervical cancer screening in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 146. CrossRef - A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - Metastatic Cervical Cancer in the Asia-Pacific Region: Current Treatment Landscape and Barriers
Jeffrey Chee-Hong Goh, Chyong-Huey Lai, Efren Javier Domingo, Jae Hoon Kim, Carmel Spiteri, Danny Hsu, Soo Yeon Ihm, Peng Peng
Cancer Research Communications.2025; 5(8): 1429. CrossRef - Mathematical Assessment of the Roles of Vaccination and Pap Screening on the Burden of HPV and Related Cancers in Korea
Soyoung Park, Hyunah Lim, Abba B. Gumel
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A questionnaire study on disparity of cervical cancer prevention programs in Asia‐Oceania
Ka Yu Tse, Kimio Ushijima, Ai Ling Tan, Perapong Intasorn, Jitendra Pariyar, Chih‐Long Chang, Efren J. Domingo, Hiralal Konar, Suresh Kumarasamy, Brahmana Askandar Tjokroprawiro, Sarikapan Wilailak
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2023; 49(4): 1230. CrossRef - Current state of cytopathology residency training: a Korean national survey of pathologists
Uiju Cho, Tae Jung Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Kyo Young Lee, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Hyun Joo Choi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(2): 95. CrossRef - Meeting the challenges of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination in the UK
Roxanne Westwood, Joanna Lavery
Primary Health Care.2022; 32(01): 22. CrossRef - Local and Metastatic Relapses in a Young Woman with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 599. CrossRef - Serum Human Epididymis Protein 4 as a Prognostic Marker in Cervical Cancer
Woo Yeon Hwang, Dong Hoon Suh, Kidong Kim, Yong Beom Kim, Jae Hong No
Cancer Control.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV detection and/or cytological diagnostics
Sanja Milenković
Glasnik javnog zdravlja.2022; 96(3): 313. CrossRef - Clinical management of abnormal Pap tests: differences between US and Korean guidelines
Seyeon Won, Mi Kyoung Kim, Seok Ju Seong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 213. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practices in Korea: annual report on the Continuous Quality Improvement program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology for 2018
Yosep Chong, Haeyoen Jung, Jung-Soo Pyo, Soon Won Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 318. CrossRef - Cytomorphological Features of Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups in Liquid-Based Cervicovaginal Cytology: A Single Institutional Experience
Youngeun Lee, Cheol Lee, In Ae Park, Hyoung Jin An, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(6): 393. CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
- CpG Island Methylation in Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyp of the Colorectum: Implications for Differential Diagnosis of Molecularly High-Risk Lesions among Non-dysplastic Sessile Serrated Adenomas/Polyps
- Ji Ae Lee, Hye Eun Park, Seung-Yeon Yoo, Seorin Jeong, Nam-Yun Cho, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Jung Ho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):225-235. Published online March 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.03.12
- 9,525 View
- 245 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although colorectal sessile serrated adenomas/polyps (SSA/Ps) with morphologic dysplasia are regarded as definite high-risk premalignant lesions, no reliable grading or risk-stratifying system exists for non-dysplastic SSA/Ps. The accumulation of CpG island methylation is a molecular hallmark of progression of SSA/Ps. Thus, we decided to classify non-dysplastic SSA/Ps into risk subgroups based on the extent of CpG island methylation.
Methods
The CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) status of 132 non-dysplastic SSA/Ps was determined using eight CIMP-specific promoter markers. SSA/Ps with CIMP-high and/or MLH1 promoter methylation were regarded as a high-risk subgroup.
Results
Based on the CIMP analysis results, methylation frequency of each CIMP marker suggested a sequential pattern of CpG island methylation during progression of SSA/P, indicating MLH1 as a late-methylated marker. Among the 132 non-dysplastic SSA/Ps, 34 (26%) were determined to be high-risk lesions (33 CIMP-high and 8 MLH1-methylated cases; seven cases overlapped). All 34 high-risk SSA/Ps were located exclusively in the proximal colon (100%, p = .001) and were significantly associated with older age (≥ 50 years, 100%; p = .003) and a larger histologically measured lesion size (> 5 mm, 100%; p = .004). In addition, the high-risk SSA/Ps were characterized by a relatively higher number of typical base-dilated serrated crypts.
Conclusions
Both CIMP-high and MLH1 methylation are late-step molecular events during progression of SSA/Ps and rarely occur in SSA/Ps of young patients. Comprehensive consideration of age (≥ 50), location (proximal colon), and histologic size (> 5 mm) may be important for the prediction of high-risk lesions among non-dysplastic SSA/Ps. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MLH1 Methylation Status and Microsatellite Instability in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Manuel Alejandro Rico-Méndez, Miguel Angel Trujillo-Rojas, María de la Luz Ayala-Madrigal, Jesús Arturo Hernández-Sandoval, Anahí González-Mercado, Melva Gutiérrez-Angulo, José Geovanni Romero-Quintana, Jesús Alonso Valenzuela-Pérez, Ruth Ramírez-Ramírez,
Genes.2025; 16(2): 182. CrossRef - Histologic Reappraisal and Evaluation of MLH1 Protein Expression in Sessile Serrated Lesions of the Proximal Colon
Priscilla de Sene Portel Oliveira, Miriam Aparecida da Silva Trevisan, Rita Barbosa de Carvalho, Rita de Cássia Perina Martins, João José Fagundes, Claudio Saddy Rodrigues Coy, Ashwini Esnakula
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune microenvironmental heterogeneity according to tumor DNA methylation phenotypes in microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancers
Jung Ho Kim, Jiyun Hong, Ji Ae Lee, Minsun Jung, Eunwoo Choi, Nam-Yun Cho, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Sangwoo Kim
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How to "pick up" colorectal serrated lesions and polyps in daily histopathology practice: From terminologies to diagnostic pitfalls
Thai H Tran, Vinh H Nguyen, Diem TN Vo
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2024; 15(9): 1157. CrossRef - Serrated Colorectal Lesions: An Up-to-Date Review from Histological Pattern to Molecular Pathogenesis
Martino Mezzapesa, Giuseppe Losurdo, Francesca Celiberto, Salvatore Rizzi, Antonio d’Amati, Domenico Piscitelli, Enzo Ierardi, Alfredo Di Leo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4461. CrossRef - NTRK oncogenic fusions are exclusively associated with the serrated neoplasia pathway in the colorectum and begin to occur in sessile serrated lesions
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Hoon Hong, Yoon‐La Choi, Ji Ae Lee, Mi‐kyoung Seo, Mi‐Sook Lee, Sung Bin An, Min Jung Sung, Nam‐Yun Cho, Sung‐Su Kim, Young Kee Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
The Journal of Pathology.2021; 255(4): 399. CrossRef - Evolving pathologic concepts of serrated lesions of the colorectum
Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 276. CrossRef
- MLH1 Methylation Status and Microsatellite Instability in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
- Provisional Guideline Recommendation for EGFR Gene Mutation Testing in Liquid Samples of Lung Cancer Patients: A Proposal by the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
- Dong Hoon Shin, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Heae Surng Park, Yun La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Lucia Kim, Sun Hee Chang, Joon Seon Song, Hyo jin Kim, Jung Ho Han, Chang Hun Lee, Geon Kook Lee, Se Jin Jang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):153-158. Published online February 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.22
- 10,480 View
- 265 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Liquid biopsy for detection of mutation from circulating tumor DNA is a new technology which is attractive in that it is non-invasive. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) is an effective first line drug for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients who harbor activating EGFR mutation. During the course of treatment, resistance against TKI arises which can be contributed to EGFR T790M mutation in about 50–60% of patients. Third generation TKI may overcome the resistance. In patients who cannot undergo tissue biopsy due to variable reasons, liquid biopsy is an excellent alternative for the detection of EGFR T790M mutation. However, this relatively novel method requires standardization and vigorous quality insurance. Thus, a standard set of guideline recommendations for liquid biopsy for EGFR mutation testing suitable for the Korean medical community is necessary. In this article, we propose a set of provisional guideline recommendations that was discussed and approved by the Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
Yoon Kyung Kang, Dong Hoon Shin, Joon Young Park, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, JooYoung Na
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 60. CrossRef - Improving non-small-cell lung cancer survival through molecular characterization: Perspective of a multidisciplinary expert panel
M.G.O. Fernandes, A.S. Vilariça, B. Fernandes, C. Camacho, C. Saraiva, F. Estevinho, H. Novais e Bastos, J.M. Lopes, P. Fidalgo, P. Garrido, S. Alves, S. Silva, T. Sequeira, F. Barata
Pulmonology.2024; 30(1): 4. CrossRef - Unlocking the future of cancer diagnosis – promises and challenges of ctDNA-based liquid biopsies in non-small cell lung cancer
Chiara Reina, Berina Šabanović, Chiara Lazzari, Vanesa Gregorc, Christopher Heeschen
Translational Research.2024; 272: 41. CrossRef - Exosomes in Lung Cancer: Actors and Heralds of Tumor Development
Amaia Sandúa, Estibaliz Alegre, Álvaro González
Cancers.2021; 13(17): 4330. CrossRef - Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 181. CrossRef - Current status and future perspectives of liquid biopsy in non-small cell lung cancer
Sunhee Chang, Jae Young Hur, Yoon-La Choi, Chang Hun Lee, Wan Seop Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 204. CrossRef - Prevalence of T790M mutation among TKI-therapy resistant Lebanese lung cancer patients based on liquid biopsy analysis: a first report from a major tertiary care center
Hazem Assi, Arafat Tfayli, Nada Assaf, Sarah Abou Daya, Aram H. Bidikian, Dima Kawsarani, Puzant Fermanian, Ghazi Zaatari, Rami Mahfouz
Molecular Biology Reports.2019; 46(4): 3671. CrossRef
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Utility of BRAF VE1 Immunohistochemistry as a Screening Tool for Colorectal Cancer Harboring BRAF V600E Mutation
- Jeong-Hwa Kwon, Byung-Kwan Jeong, Yong Sik Yoon, Chang Sik Yu, Jihun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):157-163. Published online March 29, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.03.28
- 9,091 View
- 205 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
BRAF mutation has been recognized as an important biomarker of colorectal cancer (CRC) for targeted therapy and prognosis prediction. However, sequencing for every CRC case is not cost-effective. An antibody specific for BRAF V600E mutant protein has been introduced, and we thus examined the utility of BRAF VE1 immunohistochemistry for evaluating BRAF mutations in CRC.
Methods
Fifty-one BRAF-mutated CRCs and 100 age and sexmatched BRAF wild-type CRCs between 2005 and 2015 were selected from the archives of Asan Medical Center. Tissue microarrays were constructed and stained with BRAF VE1 antibody.
Results
Forty-nine of the 51 BRAF-mutant CRCs (96.1%) showed more than moderate cytoplasmic staining, except for two weakly stained cases. Six of 100 BRAF wild-type cases also stained positive with BRAF VE1 antibody; four stained weakly and two stained moderately. Normal colonic crypts showed nonspecific weak staining, and a few CRC cases exhibited moderate nuclear reactivity (3 BRAF-mutant and 10 BRAF wild-type cases). BRAF-mutated CRC patients had higher pathologic stages and worse survival than BRAF wild-type patients.
Conclusions
BRAF VE1 immunohistochemistry showed high sensitivity and specificity, but occasional nonspecific staining in tumor cell nuclei and normal colonic crypts may limit their routine clinical use. Thus, BRAF VE1 immunohistochemistry may be a useful screening tool for BRAF V600E mutation in CRCs, provided that additional sequencing studies can be done to confirm the mutation in BRAF VE1 antibody-positive cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Next-Generation Sequencing in Oncology—A Guiding Compass for Targeted Therapy and Emerging Applications
Laurenția Nicoleta Galeș, Mihai-Andrei Păun, Ioana Butnariu, Laurentiu Simion, Loredana Sabina Cornelia Manolescu, Oana Gabriela Trifănescu, Rodica Maricela Anghel
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(7): 3123. CrossRef - A multi-omic analysis reveals a predictive value of tertiary lymphoid structures in improving the prognosis of colorectal cancer patients with BRAF mutation
Chao Qin, Shumin Cheng, Jingyun Ma, Lujing Li, Yun Leng, Lei Zheng, Huiying Chen, Hui Mo, Shi Li, Yuhong Liang, Yi Zhang, Wenxia Li, Jing Liang, Yuxuan Liu, Junxuan Mai, Linlin Hou, Di Wang, Ke Zhu, Bihui Huang
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The evolving landscape of tissue‐agnostic therapies in precision oncology
Vivek Subbiah, Mohamed A. Gouda, Bettina Ryll, Howard A. Burris, Razelle Kurzrock
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2024; 74(5): 433. CrossRef - Deciphering the Role of BRAFV600E Immunohistochemistry in Breast Lesions: A Comprehensive Review
Simran Khan, Arvind Bhake, Shakti Sagar
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry as a Surrogate Marker of Underlying Molecular Derangements in Sporadic Colorectal Carcinoma in Children – A Series of Three Cases
Priyanka Maity, Aniket Halder, Ranajoy Ghosh, Uttara Chatterjee, Shibsankar Barman, Ruchirendra Sarkar
Fetal and Pediatric Pathology.2022; 41(1): 98. CrossRef - Risk assessment and genetic counseling for Lynch syndrome – Practice resource of the National Society of Genetic Counselors and the Collaborative Group of the Americas on Inherited Gastrointestinal Cancer
Spring Holter, Michael J. Hall, Heather Hampel, Kory Jasperson, Sonia S. Kupfer, Joy Larsen Haidle, Maureen E. Mork, Selvi Palaniapppan, Leigha Senter, Elena M. Stoffel, Scott M. Weissman, Matthew B. Yurgelun
Journal of Genetic Counseling.2022; 31(3): 568. CrossRef - Current concepts in ameloblastoma-targeted therapies in B-raf proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase V600E mutation: Systematic review
Rogelio González-González, Sandra López-Verdín, Jesús Lavalle-Carrasco, Nelly Molina-Frechero, Mario Isiordia-Espinoza, Ramón G Carreón-Burciaga, Ronell Bologna-Molina
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2020; 11(1): 31. CrossRef - Genetic and histopathological analysis of a case of primary intraosseous carcinoma, NOS with features of both ameloblastic carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
Akane Yukimori, Maiko Tsuchiya, Akane Wada, Yasuyuki Michi, Kou Kayamori, Kei Sakamoto, Tohru Ikeda
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Next-Generation Sequencing in Oncology—A Guiding Compass for Targeted Therapy and Emerging Applications
- Comparison of the Mismatch Repair System between Primary and Metastatic Colorectal Cancers Using Immunohistochemistry
- Jiyoon Jung, Youngjin Kang, Yoo Jin Lee, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Eunjung Lee, Joo Young Kim, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Chul Hwan Kim, Yang-Seok Chae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):129-136. Published online February 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.12.09
- 12,351 View
- 330 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. Approximately 10%–15% of the CRC cases have defective DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Although the high level of microsatellite instability status is a predictor of favorable outcome in primary CRC, little is known about its frequency and importance in secondary CRC. Immunohistochemical staining (IHC) for MMR proteins (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2) has emerged as a useful technique to complement polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analyses. Methods: In this study, comparison between the MMR system of primary CRCs and paired liver and lung metastatic lesions was done using IHC and the correlation with clinical outcomes was also examined. Results: Based on IHC, 7/61 primary tumors (11.4%) showed deficient MMR systems, while 13/61 secondary tumors (21.3%) showed deficiencies. In total, 44 cases showed proficient expression in both the primary and metastatic lesions. Three cases showed deficiencies in both the primary and paired metastatic lesions. In 10 cases, proficient expression was found only in the primary lesions, and not in the corresponding metastatic lesions. In four cases, proficient expression was detected in the secondary tumor, but not in the primary tumor. Conclusions: Although each IHC result and the likely defective genes were not exactly matched between the primary and the metastatic tumors, identical results for primary and metastatic lesions were obtained in 77% of the cases (47/61). These data are in agreement with the previous microsatellite detection studies that used PCR and IHC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immunotherapy-induced microsatellite instability status shift in recurrent perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A case report
Hailing Yu, Tan Deng, Hongbing Liu
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic and Predictive Value of Microsatellite Instability Analysis in Circulating Tumor DNA Using Digital Droplet PCR for Patients With Microsatellite Instability Colorectal Cancers
Camille Evrard, Tristan Rochelle, Marine Martel, Anis Al Achkar, Aurélie Ferru, Violaine Randrian, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, David Tougeron
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(8): 104176. CrossRef - HER2, HER3, and Mismatch Repair Protein Expression in Stage IV Small Bowel Adenocarcinoma: Results From a Multicenter Series
Alessandro Vanoli, Tommaso Colella, Paola Parente, Giuseppe De Lisi, Federica Grillo, Erica Quaquarini, Salvatore Corallo, Rondell Patrell Graham, Marc Ferrante, Annick Moens, Gert De Hertogh, Camilla Guerini, Roberta Riboni, Paola Alberizzi, Luca Mastrac
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(11): 100825. CrossRef - Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Current Status of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Dandan Cao, Aiping Zhou
Current Oncology.2025; 32(9): 493. CrossRef - MMR profile and microsatellite instability status in colorectal mucinous adenocarcinoma with synchronous metastasis: a new clue for the clinical practice
Paola Parente, Umberto Malapelle, Valentina Angerilli, Mariangela Balistreri, Sara Lonardi, Salvatore Pucciarelli, Caterina De Luca, Francesco Pepe, Gianluca Russo, Elena Vigliar, Angela Danza, Fabio Scaramuzzi, Giancarlo Troncone, Paolo Graziano, Matteo
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2023; 76(7): 492. CrossRef - Histomorphological and molecular genetic characterization of different intratumoral regions and matched metastatic lymph nodes of colorectal cancer with heterogenous mismatch repair protein expression
Jing Zhang, Xin Zhang, Qian Wang, Yu-yin Xu, Qian-lan Yao, Dan Huang, Wei-qi Sheng, Xiao-li Zhu, Xiao-yan Zhou, Qian-ming Bai
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(7): 3423. CrossRef - Intraindividual Tumor Heterogeneity of Mismatch Repair Status in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Qianpeng Huang, Tao Yu, Lei Li, Qi Zhang, Shiyao Zhang, Baosong Li, Xiaoping Li, Wanyi Xiao, Gang Liu
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(2): 84. CrossRef - Patterns of DNA mismatch repair protein expression for primary and recurrent colorectal cancer at an advanced surgical unit: A retrospective audit
Charles Risbey, Timothy Fielder, Daniel Steffens, Joo‐Shik Shin, Michael Solomon
Colorectal Disease.2023; 25(3): 369. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Genomic and Immunohistochemical Profiling with Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analysis of 17 Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution
Hyun-Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Biomedicines.2023; 11(8): 2269. CrossRef - Multilevel Heterogeneity of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Hao Chen, Chongya Zhai, Xian Xu, Haidong Wang, Weidong Han, Jiaying Shen
Cancers.2023; 16(1): 59. CrossRef - Heterogeneity of Mismatch Repair Status and Microsatellite Instability between Primary Tumour and Metastasis and Its Implications for Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancers
Camille Evrard, Stéphane Messina, David Sefrioui, Éric Frouin, Marie-Luce Auriault, Romain Chautard, Aziz Zaanan, Marion Jaffrelot, Christelle De La Fouchardière, Thomas Aparicio, Romain Coriat, Julie Godet, Christine Silvain, Violaine Randrian, Jean-Chri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4427. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic Factors Associated with Mismatch Repair Status Among Filipino Patients with Young-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Dennis Lee Sacdalan, Reynaldo L Garcia, Michele H Diwa, Danielle Benedict Sacdalan
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 2105. CrossRef - Recommendations for Specimen and Therapy Selection in Colorectal Cancer
Snehal B. Patel, Robert Bookstein, Navid Farahani, Myriam Chevarie-Davis, Andy Pao, Angela Aguiluz, Christian Riley, Jennelle C. Hodge, Serhan Alkan, Zhenqui Liu, Nan Deng, Jean R. Lopategui
Oncology and Therapy.2021; 9(2): 451. CrossRef - Evaluating Mismatch Repair/Microsatellite Instability Status Using Cytology Effusion Specimens to Determine Eligibility for Immunotherapy
Elizabeth M. Jacobi, Gene Landon, Russell R. Broaddus, Sinchita Roy-Chowdhuri
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(1): 46. CrossRef - Médecine de précision et immunoradiothérapie
C. Chargari, C. Robert, C. Genestie, E. Deutsch
Cancer/Radiothérapie.2021; 25(6-7): 570. CrossRef - Identificación del fenotipo de inestabilidad microsatelital en carcinoma colorrectal mediante el análisis de la expresión de proteínas reparadoras del ADN: Revisión narrativa
Orlando Rodas-Pernillo, Edith Oregón
Ciencia, Tecnología y Salud.2021; 8(2): 232. CrossRef - Japan Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion for the diagnosis and use of immunotherapy in patients with deficient DNA mismatch repair tumors, cooperated by Japanese Society of Medical Oncology, First Edition
Saori Mishima, Hiroya Taniguchi, Kiwamu Akagi, Eishi Baba, Yutaka Fujiwara, Akira Hirasawa, Masafumi Ikeda, Osamu Maeda, Kei Muro, Hiroshi Nishihara, Hiroyki Nishiyama, Tadao Takano, Katsuya Tsuchihara, Yasushi Yatabe, Yasuhiro Kodera, Takayuki Yoshino
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2020; 25(2): 217. CrossRef - Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer With an Immunogenic Phenotype: Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
James Saller, Dahui Qin, Seth Felder, Domenico Coppola
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2020; 19(2): 123. CrossRef - Should you repeat mismatch repair testing in cases of tumour recurrence? An evaluation of repeat mismatch repair testing by the use of immunohistochemistry in recurrent tumours of the gastrointestinal and gynaecological tracts
John J Aird, Michael J Steel, Christine Chow, Julie Ho, Robert Wolber, C Blake Gilks, Lynn N Hoang, David F Schaeffer
Histopathology.2020; 76(4): 521. CrossRef - Microsatellite instability as a unique characteristic of tumors and a predictor of response to immune therapy
A. A. Tryakin, M. Yu. Fedyanin, A. S. Tsukanov, Yu. A. Shelygin, I. A. Pokataev, E. O. Ignatova, G. G. Khakimova, M. A. Frolova, S. A. Tjulandin
Malignant tumours.2020; 9(4): 59. CrossRef - Spontaneous regression of transverse colon cancer with high-frequency microsatellite instability: a case report and literature review
Nozomi Karakuchi, Manabu Shimomura, Kazuhiro Toyota, Takao Hinoi, Hideki Yamamoto, Seiji Sadamoto, Koichi Mandai, Hiroyuki Egi, Hideki Ohdan, Tadateru Takahashi
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomarker concordance between primary colorectal cancer and its metastases
D.S. Bhullar, J. Barriuso, S. Mullamitha, M.P. Saunders, S.T. O'Dwyer, O. Aziz
EBioMedicine.2019; 40: 363. CrossRef - Identification of novel pathogenic MSH2 mutation and new DNA repair genes variants: investigation of a Tunisian Lynch syndrome family with discordant twins
Amira Jaballah-Gabteni, Haifa Tounsi, Maria Kabbage, Yosr Hamdi, Sahar Elouej, Ines Ben Ayed, Mouna Medhioub, Moufida Mahmoudi, Hamza Dallali, Hamza Yaiche, Nadia Ben Jemii, Afifa Maaloul, Najla Mezghani, Sonia Abdelhak, Lamine Hamzaoui, Mousaddak Azzouz,
Journal of Translational Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mismatch repair status between primary colorectal tumor and metastatic tumor, a retrospective consistent study
Zheng Wang, Xiaoli Tang, Xiaoqing Wu, Meiyuan Yang, Daorong Wang
Bioscience Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Heterogeneity of mismatch repair defect in colorectal cancer and its implications in clinical practice
Gaelle Tachon, Eric Frouin, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Luce Auriault, Julie Godet, Valerie Moulin, Qing Wang, David Tougeron
European Journal of Cancer.2018; 95: 112. CrossRef - DNA mismatch repair in cancer
Marina Baretti, Dung T. Le
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 189: 45. CrossRef - Discordant loss of mismatch repair proteins in advanced endometrial endometrioid carcinoma compared to paired primary uterine tumors
Robert M. Ta, Jonathan L. Hecht, Douglas I. Lin
Gynecologic Oncology.2018; 151(3): 401. CrossRef - The CpG island methylator phenotype is concordant between primary colorectal carcinoma and matched distant metastases
Stacey A. Cohen, Ming Yu, Kelsey Baker, Mary Redman, Chen Wu, Tai J. Heinzerling, Ralph M. Wirtz, Elpida Charalambous, George Pentheroudakis, Vassiliki Kotoula, Konstantine T. Kalogeras, George Fountzilas, William M. Grady
Clinical Epigenetics.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Immunotherapy-induced microsatellite instability status shift in recurrent perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A case report
- Clinical Significance of an HPV DNA Chip Test with Emphasis on HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 Detection in Korean Gynecological Patients
- Min-Kyung Yeo, Ahwon Lee, Soo Young Hur, Jong Sup Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):294-299. Published online June 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.05.09
- 10,542 View
- 80 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a major risk factor for cervical cancer.
Methods
We evaluated the clinical significance of the HPV DNA chip genotyping assay (MyHPV chip, Mygene Co.) compared with the Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2) chemiluminescent nucleic acid hybridization kit (Digene Corp.) in 867 patients.
Results
The concordance rate between the MyHPV chip and HC2 was 79.4% (kappa coefficient, κ = 0.55). The sensitivity and specificity of both HPV tests were very similar (approximately 85% and 50%, respectively). The addition of HPV result (either MyHPV chip or HC2) to cytology improved the sensitivity (95%, each) but reduced the specificity (approximately 30%, each) compared with the HPV test or cytology alone. Based on the MyHPV chip results, the odds ratio (OR) for ≥ high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs) was 9.9 in the HPV-16/18 (+) group and 3.7 in the non-16/18 high-risk (HR)-HPV (+) group. Based on the HC2 results, the OR for ≥ HSILs was 5.9 in the HR-HPV (+) group. When considering only patients with cytological diagnoses of “negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy” and “atypical squamous cell or atypical glandular cell,” based on the MyHPV chip results, the ORs for ≥ HSILs were 6.8 and 11.7, respectively, in the HPV-16/18 (+) group.
Conclusions
The sensitivity and specificity of the MyHPV chip test are similar to the HC2. Detecting HPV-16/18 with an HPV DNA chip test, which is commonly used in many Asian countries, is useful in assessing the risk of high-grade cervical lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Human papilloma virus identification in ocular surface squamous neoplasia by p16 immunohistochemistry and DNA chip test
Tina Shrestha, Won Choi, Ga Eon Kim, Jee Myung Yang, Kyung Chul Yoon
Medicine.2019; 98(2): e13944. CrossRef - Comparison of the PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip Test with the Cobas 4800 HPV and Hybrid Capture 2 Tests for Detection of HPV in ASCUS Women
Eun Young Ki, Yoon Kyung Lee, Ahwon Lee, Jong Sup Park
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(5): 662. CrossRef
- Human papilloma virus identification in ocular surface squamous neoplasia by p16 immunohistochemistry and DNA chip test
- Differential Features of Microsatellite-Unstable Colorectal Carcinomas Depending on EPCAM Expression Status
- Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Kyung-Ju Kim, Ye-Young Rhee, Younghoon Kim, Nam-Yun Cho, Hye Seung Lee, Mee Soo Chang, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(4):276-282. Published online August 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.4.276
- 13,053 View
- 63 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Recent studies have revealed that a small subset of Lynch syndrome-associated colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) is caused by a germline
EPCAM deletion-inducedMSH2 epimutation. Based on the finding of this genetic alteration, we investigated the implications of EPCAM expression changes in microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) CRCs.Methods Expression of EPCAM and DNA mismatch repair proteins was assessed by immunohistochemistry in 168 MSI-H CRCs. Using DNA samples of these tumors,
MLH1 promoter methylation status was also determined by methylation-specific real-time polymerase chain reaction method (MethyLight).Results Among 168 MSI-H CRCs, complete loss (CL) and focal loss (FL) of EPCAM expression was observed in two (1.2%) and 22 (13.1%) cases, respectively. Both of the EPCAM-CL cases were found in MSH2-negative tumors without
MLH1 promoter methylation. However, only nine of the 22 EPCAM-FL tumors had MSH2 deficiency. Of the 22 EPCAM-FL tumors, 13 showed MLH1 loss, and among them, nine cases were determined to haveMLH1 methylation. EPCAM-FL was significantly associated with advanced stage (p=.043), distant metastasis (p=.003), poor differentiation (p=.001), and signet ring cell component (p=.004).Conclusions Loss of EPCAM expression is differentially associated with clinicopathological and molecular features, depending on the completeness of the loss, in MSI-H CRCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Significance of EPCAM Pathogenic Germline Variant
Jun-Ha Jang, Kyoung-Bo Kim, Jong Eun Park, Mi-Ae Jang, Dongju Won, Boyoung Park, Jung-Sook Ha, Sun-Young Kong
Laboratory Medicine Online.2025; 15(4): 263. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in colon cancer: Insights from a Propensity Score-Matched Study
Hilmi Yazici, Ayse Eren Kayaci, Melike Zeynep Can Sahin, Cisil Bayir, Aysenur Yildiz, Esin Zeynep Cinal, Muhammer Ergenc, Tevfik Kivilcim Uprak
Current Problems in Surgery.2024; 61(12): 101633. CrossRef - Unraveling the multifaceted role of EpCAM in colorectal cancer: an integrated review of its function and interplay with non-coding RNAs
Xingyu Jiang, Sumeng Wang, Qi Liang, Yiqian Liu, Lingxiang Liu
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of Definitive Treatment of Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma of the Rectum: Is Minimal Invasive Surgery Detrimental in Signet Ring Rectal Cancers?
S. Raghavan, Deepak Kumar Singh, J. Rohila, A. DeSouza, R. Engineer, A. Ramaswamy, V. Ostwal, A. Saklani
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2020; 11(4): 597. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Role of Circulating Tumor Cells and Microsatellite Instability Status in Predicting Outcome of Advanced CRC Patients
Ippokratis Messaritakis, Maria Sfakianaki, Konstantinos Vogiatzoglou, Asimina Koulouridi, Chara Koutoulaki, Dimitrios Mavroudis, Maria Tzardi, Nikolaos Gouvas, John Tsiaoussis, John Souglakos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2020; 10(4): 235. CrossRef - Is Ep-CAM Expression a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer? A Systematic Meta-Analysis
Susu Han, Shaoqi Zong, Qi Shi, Hongjia Li, Shanshan Liu, Wei Yang, Wen Li, Fenggang Hou
EBioMedicine.2017; 20: 61. CrossRef - Prognostic factors in sporadic colon cancer with high-level microsatellite instability
Bo Young Oh, Jung Wook Huh, Yoon Ah Park, Yong Beom Cho, Seong Hyeon Yun, Hee Cheol Kim, Woo Yong Lee, Ho-Kyung Chun
Surgery.2016; 159(5): 1372. CrossRef - Clinical significance of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 expression in patients with residual rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy: relationship with KRAS or BRAF mutations and MSI status
Ghilsuk Yoon, Hwayoung Lee, Jae-Hoon Kim, Keun Hur, An Na Seo
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(8): 10209. CrossRef - Subcellular differential expression of Ep-ICD in oral dysplasia and cancer is associated with disease progression and prognosis
Raj Thani Somasundaram, Jatinder Kaur, Iona Leong, Christina MacMillan, Ian J. Witterick, Paul G. Walfish, Ranju Ralhan
BMC Cancer.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - BRAF, PIK3CA, and HER2 Oncogenic Alterations According to KRAS Mutation Status in Advanced Colorectal Cancers with Distant Metastasis
Soo Kyung Nam, Sumi Yun, Jiwon Koh, Yoonjin Kwak, An Na Seo, Kyoung Un Park, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Wayne A Phillips
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(3): e0151865. CrossRef - Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition according to microsatellite instability status in colon cancer cells
Bo Young Oh, So-Young Kim, Yeo Song Lee, Hye Kyung Hong, Tae Won Kim, Seok Hyung Kim, Woo Yong Lee, Yong Beom Cho
Oncotarget.2016; 7(35): 57066. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic, molecular, and prognostic implications of the loss of EPCAM expression in colorectal carcinoma
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Young Seok Song, Nam-Yun Cho, Hye Seung Lee, Gyeong Hoon Kang
Oncotarget.2016; 7(12): 13372. CrossRef - Pathologic Factors Associated with Prognosis after Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage II/III Microsatellite-Unstable Colorectal Cancers
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Mo Bae, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Hye Seung Lee, Gyeong Hoon Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(2): 118. CrossRef - HER3 protein expression in relation to HER2 positivity in patients with primary colorectal cancer: clinical relevance and prognostic value
An Na Seo, Yoonjin Kwak, Woo Ho Kim, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Gheeyoung Choe, Hye Seung Lee
Virchows Archiv.2015; 466(6): 645. CrossRef - Clinical and prognostic value of MET gene copy number gain and chromosome 7 polysomy in primary colorectal cancer patients
An Na Seo, Kyoung Un Park, Gheeyoung Choe, Woo Ho Kim, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Hye Seung Lee
Tumor Biology.2015; 36(12): 9813. CrossRef - c-MYC Copy-Number Gain Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Kyu Sang Lee, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyung Han Nam, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Gheeyoung Choe, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Andreas Krieg
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(10): e0139727. CrossRef - Nuclear Ep-ICD accumulation predicts aggressive clinical course in early stage breast cancer patients
Gunjan Srivastava, Jasmeet Assi, Lawrence Kashat, Ajay Matta, Martin Chang, Paul G Walfish, Ranju Ralhan
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Significance of EPCAM Pathogenic Germline Variant
- Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Upper Genital Tract: Utility of p16INK4a Expression and HPV DNA Status in its Differential Diagnosis from Extended Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Su Hyun Yoo, Eun-Mi Son, Chang Okh Sung, Kyu-Rae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):549-556. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.549
- 8,783 View
- 65 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the upper genital tract, including the endometrium, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, is extremely rare. It must be distinguished from the mucosal extension of primary cervical SCC because determination of the primary tumor site is important for tumor staging. However, patients with SCC of the fallopian tubes or ovarian surface have often undergone prior hysterectomy with inadequate examination of the cervix, making it difficult to determine the primary site.
Methods We compared histologic findings, p16INK4a expression, and human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA status in four patients with primary SCC of the upper genital tract and five patients with primary cervical SCC extending to the mucosa of the upper genital tract.
Results All five SCCs of cervical origin showed strong expression of p16INK4a, whereas all four SCCs of the upper genital tract were negative, although one showed weak focal staining. Three of the five cervical SCCs were positive for HPV16 DNA, whereas all four primary SCCs of the upper genital tract were negative for HPV DNA.
Conclusions Although a thorough histological examination is important, immunonegativity for p16INK4a and negative for HPV DNA may be useful adjuncts in determining primary SCCs of the upper genital tract.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Clinically Thought to be Arising From Bursa of Knee Joint
Shoichi Sakamoto, Yuki Yamamoto, Michihiro Takiwaki, Yumi Nakantani, Seiji Kanno, Yoshimasa Mera, Masazumi Tanigami, Yusuke Inada, Yutaka Inaba, Kayo Kunimoto, Hiroshi Yamada, Yoshifumi Iwahashi, Shin‐ichi Murata, Masatoshi Jinnin
Australasian Journal of Dermatology.2025; 66(3): 175. CrossRef - PAX8 Positivity, Abnormal p53 Expression, and p16 Negativity in a Primary Endometrial Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Daniela Fanni, Michele Peiretti, Valerio Mais, Elena Massa, Clara Gerosa, Francesca Ledda, Maria Luisa Fais, Gavino Faa, Stefano Angioni
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2022; 41(4): 431. CrossRef - Molecular Analysis of HPV-independent Primary Endometrial Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals TP53 and CDKN2A Comutations
Mark R. Hopkins, Doreen N. Palsgrove, Brigitte M. Ronnett, Russell Vang, Jeffrey Lin, Tricia A. Murdock
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 46(12): 1611. CrossRef - Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the endometrium—Case report with cytological characteristics in direct and indirect endometrial samples
Sanda Rajhvajn, Ana Barišić, Lada Škopljanac‐Mačina, Danijela Jurič, Vesna Mahovlić
Cytopathology.2021; 32(6): 823. CrossRef - Überraschung in der Abradatdiagnostik
U. Kellner, A. Kellner, U. Cirkel
Der Pathologe.2015; 36(3): 317. CrossRef - Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Metastasis in 54 Patients with Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Who Underwent Surgery-Based Treatment
Eun-Jae Chung, Go-Woon Kim, Bum-Ki Cho, Sung-Jin Cho, Dae-Young Yoon, Young-Soo Rho
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2015; 22(9): 3049. CrossRef
- A Case of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Clinically Thought to be Arising From Bursa of Knee Joint
- Comparison of Direct Sequencing, PNA Clamping-Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Pyrosequencing Methods for the Detection of
EGFR Mutations in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma and the Correlation with Clinical Responses to EGFR Tyrosin - Hyun Ju Lee, Xianhua Xu, Hyojin Kim, Yan Jin, Pingli Sun, Ji Eun Kim, Jin-Haeng Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):52-60. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.52
- 12,606 View
- 93 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The aims of this study were to evaluate the abilities of direct sequencing (DS), peptide nucleic acid (PNA) clamping, and pyrosequencing methods to detect epidermal growth factor receptor (
EGFR ) mutations in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) samples and to correlateEGFR mutational status as determined by each method with the clinical response toEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).Methods Sixty-one NSCLC patients treated with EGFR TKIs were identified to investigate somatic mutations in the
EGFR gene (exons 18-21).Results Mutations in the
EGFR gene were detected in 38 of the 61 patients (62%) by DS, 35 (57%) by PNA clamping and 37 (61%) by pyrosequencing. A total of 44 mutations (72%) were found by at least one of the three methods, and the concordances among the results were relatively high (82-85%; kappa coefficient, 0.713 to 0.736). There were 15 discordant cases (25%) among the three different methods.Conclusions All three
EGFR mutation tests had good concordance rates (over 82%) for FFPE samples. These results suggest that if the DNA quality and enrichment of tumor cells are assured, then DS, PNA clamping, and pyrosequencing are appropriate methods for the detection ofEGFR mutations.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Trends of Lung Cancer in Korea
Jae Guk Lee, Ho Cheol Kim, Chang-Min Choi
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2021; 84(2): 89. CrossRef - Predictive value of KRAS mutation and excision repair cross-complementing 1 (ERCC1) protein overexpression in patients with colorectal cancer administered FOLFOX regimen
Sun Min Park, Sung Bong Choi, Yoon Suk Lee, In Kyu Lee
Asian Journal of Surgery.2021; 44(5): 715. CrossRef - Recent advances in diagnostic technologies in lung cancer
Hye Jung Park, Sang Hoon Lee, Yoon Soo Chang
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(2): 257. CrossRef - Afatinib is effective in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma with uncommon EGFR p.L747P and p.L747S mutations
Sheng-Kai Liang, Jen-Chung Ko, James Chih-Hsin Yang, Jin-Yuan Shih
Lung Cancer.2019; 133: 103. CrossRef - Biomarker Testing for Patients With Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Issues and Tough Choices
Nathan A. Pennell, Maria E. Arcila, David R. Gandara, Howard West
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2019; (39): 531. CrossRef - Evaluation of EGFR mutations in NSCLC with highly sensitive droplet digital PCR assays
Xi‑Wen Jiang, Wei Liu, Xiao‑Ya Zhu, Xiao‑Xie Xu
Molecular Medicine Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping and Direct Sequencing in the Detection of Oncogenic Alterations in Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jae-Uk Song, Jonghoo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(2): 211. CrossRef - Distribution of KRAS, DDR2, and TP53 gene mutations in lung cancer: An analysis of Iranian patients
Zahra Fathi, Seyed Ali Javad Mousavi, Raheleh Roudi, Farideh Ghazi, Sumitra Deb
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(7): e0200633. CrossRef - EGFR T790M mutation testing within the osimertinib AURA Phase I study
Simon Dearden, Helen Brown, Suzanne Jenkins, Kenneth S. Thress, Mireille Cantarini, Rebecca Cole, Malcolm Ranson, Pasi A. Jänne
Lung Cancer.2017; 109: 9. CrossRef - Molecular Testing of Lung Cancers
Hyo Sup Shim, Yoon-La Choi, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Tae-Jung Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jin-Haeng Chung, Se Jin Jang, Geon Kook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 242. CrossRef - Mutations of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Aeri Kim, Min Hye Jang, Soo Jung Lee, Young Kyung Bae
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(2): 150. CrossRef - Double primary lung adenocarcinoma diagnosed by epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
Oh Jung Kwon, Min Hyeok Lee, Sung Ju Kang, Seul Gi Kim, In Beom Jeong, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun Jung Cha, Do Yeun Cho, Young Jin Kim, Ji Woong Son
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2017; 34(2): 270. CrossRef - Generation of lung cancer cell lines harboring EGFR T790M mutation by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing
Mi-Young Park, Min Hee Jung, Eun Young Eo, Seokjoong Kim, Sang Hoon Lee, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young Jae Cho, Jin Haeng Chung, Cheol Hyeon Kim, Ho Il Yoon, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(22): 36331. CrossRef - Comparison of EGFR mutation detection between the tissue and cytology using direct sequencing, pyrosequencing and peptide nucleic acid clamping in lung adenocarcinoma: Korean multicentre study
Kyueng-Whan Min, Wan-Seop Kim, Se Jin Jang, Yoo Duk Choi, Sunhee Chang, Soon Hee Jung, Lucia Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Choong Sik Lee, Jung Weon Shim, Mi Jin Kim, Geon Kook Lee
QJM.2016; 109(3): 167. CrossRef - Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Gene Fusion: Detection in Malignant Pleural Effusion by RNA or PNA Analysis
Yi-Lin Chen, Chung-Ta Lee, Cheng-Chan Lu, Shu-Ching Yang, Wan-Li Chen, Yang-Cheng Lee, Chung-Hsien Yang, Shu-Ling Peng, Wu-Chou Su, Nan-Haw Chow, Chung-Liang Ho, Javier S Castresana
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(6): e0158125. CrossRef - IDH Mutation Analysis in Ewing Sarcoma Family Tumors
Ki Yong Na, Byeong-Joo Noh, Ji-Youn Sung, Youn Wha Kim, Eduardo Santini Araujo, Yong-Koo Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(3): 257. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical demonstration of alteration of β-catenin during tumor metastasis by different mechanisms according to histology in lung cancer
XIANHUA XU, JI EUN KIM, PING-LI SUN, SEOL BONG YOO, HYOJIN KIM, YAN JIN, JIN-HAENG CHUNG
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2015; 9(2): 311. CrossRef - Detection of EGFR-TK Domain–activating Mutations in NSCLC With Generic PCR-based Methods
Rajendra B. Shahi, Sylvia De Brakeleer, Jacques De Grève, Caroline Geers, Peter In’t Veld, Erik Teugels
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2015; 23(3): 163. CrossRef - Frequent aerogenous spread with decreased E-cadherin expression of ROS1- rearranged lung cancer predicts poor disease-free survival
Yan Jin, Ping-Li Sun, Soo Young Park, Hyojin Kim, Eunhyang Park, Gilhyang Kim, Sukki Cho, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon-Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Lung Cancer.2015; 89(3): 343. CrossRef - Membranous Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF1R) Expression Is Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
Eunhyang Park, Soo Young Park, Hyojin Kim, Ping-Li Sun, Yan Jin, Suk Ki Cho, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon-Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(5): 382. CrossRef - Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping Versus Direct Sequencing for the Detection of EGFR Gene Mutation in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Seong-Hoon Yoon, Yoo-Duk Choi, In-Jae Oh, Kyu-Sik Kim, Hayoung Choi, Jinsun Chang, Hong-Joon Shin, Cheol-Kyu Park, Young-Chul Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2015; 47(4): 661. CrossRef - Analysis of Mutations in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Korean Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Summary of a Nationwide Survey
Sang Hwa Lee, Wan Seop Kim, Yoo Duk Choi, Jeong Wook Seo, Joung Ho Han, Mi Jin Kim, Lucia Kim, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee, Mee Hye Oh, Gou Young Kim, Sun Hee Sung, Kyo Young Lee, Sun Hee Chang, Mee Sook Rho, Han Kyeom Kim, Soon Hee Jung, Se Jin Jang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(6): 481. CrossRef - Novel EGFR mutation-specific antibodies for lung adenocarcinoma: Highly specific but not sensitive detection of an E746_A750 deletion in exon 19 and an L858R mutation in exon 21 by immunohistochemistry
An Na Seo, Tae-In Park, Yan Jin, Ping-Li Sun, Hyojin Kim, Hyun Chang, Jin-Haeng Chung
Lung Cancer.2014; 83(3): 316. CrossRef - Simultaneous diagnostic platform of genotyping EGFR, KRAS, and ALK in 510 Korean patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer highlights significantly higher ALK rearrangement rate in advanced stage
Tae‐Jung Kim, Chan Kwon Park, Chang Dong Yeo, Kihoon Park, Chin Kook Rhee, Jusang Kim, Seung Joon Kim, Sang Haak Lee, Kyo‐Young Lee, Hyoung‐Kyu Yoon
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2014; 110(3): 245. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangements in lung cancer with nodular ground-glass opacity
Sung-Jun Ko, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young-Jae Cho, Ho Il Yoon, Jin-Haeng Chung, Tae Jung Kim, Kyung Won Lee, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon, Hyojin Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytoplasmic YAP Expression is Associated with Prolonged Survival in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinomas and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment
Ping-Li Sun, Ji Eun Kim, Seol Bong Yoo, Hyojin Kim, Yan Jin, Sanghoon Jheon, Kwhanmien Kim, Choon Taek Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2014; 21(S4): 610. CrossRef - Sensitive methods for detection of the S768R substitution in exon 18 of the DDR2 gene in patients with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer
Marcin Nicoś, Tomasz Powrózek, Paweł Krawczyk, Bożena Jarosz, Beata Pająk, Marek Sawicki, Krzysztof Kucharczyk, Tomasz Trojanowski, Janusz Milanowski
Medical Oncology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of c-MYC copy number gain in lung adenocarcinomas
A N Seo, J M Yang, H Kim, S Jheon, K Kim, C T Lee, Y Jin, S Yun, J-H Chung, J H Paik
British Journal of Cancer.2014; 110(11): 2688. CrossRef - KRASMutation Detection in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Using a Peptide Nucleic Acid-Mediated Polymerase Chain Reaction Clamping Method and Comparative Validation with Next-Generation Sequencing
Boram Lee, Boin Lee, Gangmin Han, Mi Jung Kwon, Joungho Han, Yoon-La Choi
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(2): 100. CrossRef - Guideline Recommendations forEGFRMutation Testing in Lung Cancer: Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Hyo Sup Shim, Jin-Haeng Chung, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Geon Kook Lee, Soon-Hee Jung, Se Jin Jang
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(2): 100. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Classification of Primary and Secondary Glioblastomas
Kyu Sang Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyung Han Nam, An Na Seo, Sumi Yun, Kyung Ju Kim, Hwa Jin Cho, Sung Hye Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(6): 541. CrossRef
- Recent Trends of Lung Cancer in Korea
- Radiotherapy Response in Microsatellite Instability Related Rectal Cancer
- Joo-Shik Shin, Thein Ga Tut, Tao Yang, C. Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):1-8. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.1
- 12,037 View
- 99 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Preoperative radiotherapy may improve the resectability and subsequent local control of rectal cancers. However, the extent of radiation induced regression in these tumours varies widely between individuals. To date no reliable predictive marker of radiation sensitivity in rectal cancer has been identified. At the cellular level, radiation injury initiates a complex molecular network of DNA damage response (DDR) pathways that leads to cell cycle arrest, attempts at re-constituting the damaged DNA and should this fail, then apoptosis. This review presents the details which suggest the roles of DNA mismatch repair proteins, the lack of which define a distinct subset of colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability (MSI), in the DDR pathways. Hence routine assessment of the MSI status in rectal cancers may potentially serve as a predictor of radiotherapy response, thereby improving patient stratification in the administration of this otherwise toxic treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy up-regulates PD-L1 in radioresistant colorectal cancer
Sung Uk Bae, Hye Won Lee, Jee Young Park, Incheol Seo, Jae-Min Cho, Jin Young Kim, Ju Yup Lee, Yoo Jin Lee, Seong Kyu Baek, Nam Kyu Kim, Sang Jun Byun, Shin Kim
Clinical and Translational Radiation Oncology.2025; 51: 100906. CrossRef - Incidence and Outcomes of Patients With Mismatch Repair Deficient Rectal Cancer Operated in 2016: A Nationwide Cohort From The Netherlands
Eline G.M. van Geffen, Cornelis R.C. Hogewoning, Sanne-Marije J.A. Hazen, Tania C. Sluckin, Marilyne M. Lange, Petur Snaebjornsson, Regina G.H. Beets-Tan, Corrie A.M. Marijnen, Cornelis Verhoef, Myriam Chalabi, Pieter J. Tanis, Miranda Kusters, Tjeerd S.
Clinical Colorectal Cancer.2025; 24(2): 188. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and mucin expression of early papillary gastric adenocarcinoma
Jiaqi Chen, Xiujie Cui, Chengjun Zhou, Mulan Jin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Colorectal cancers associated with mismatch repair deficiency
Mingzhu Sun, Kevin Monahan, Jayne Moquet, Stephen Barnard
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential risks associated with the use of ionizing radiation for imaging and treatment of colorectal cancer in Lynch syndrome patients
Mingzhu Sun, Jayne Moquet, Michele Ellender, Simon Bouffler, Christophe Badie, Rachel Baldwin-Cleland, Kevin Monahan, Andrew Latchford, David Lloyd, Susan Clark, Nicola A. Anyamene, Elizabeth Ainsbury, David Burling
Familial Cancer.2023; 22(1): 61. CrossRef - Not All Patients With Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Benefit From Neoadjuvant Therapy
Carolyn Chang, Jonathan T. Bliggenstorfer, Jessie Liu, Jennifer Shearer, Paul Dreher, Katherine Bingmer, Sharon L. Stein, Emily Steinhagen
The American Surgeon™.2023; 89(11): 4327. CrossRef - Survival outcomes in locally advanced dMMR rectal cancer: surgery plus adjunctive treatment vs. surgery alone
Kemin Ni, Yixiang Zhan, Zhaoce Liu, Zhen Yuan, Shuyuan Wang, Xuan-zhu Zhao, Hangyu Ping, Yaohong Liu, Wanting Wang, Suying Yan, Ran Xin, Qiurong Han, Qinghuai Zhang, Guoxun Li, Xipeng Zhang, Guihua Wang, Zili Zhang, Hong Ma, Chunze Zhang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Rectal Cancer in Patients with Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer Compared with Sporadic Cases: Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation and Local Recurrence
Khaled M Madbouly, Sameh Hany Emile, Yasmine Amr Issa
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 234(5): 793. CrossRef - Molecular Recognition and Quantification of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and KRAS in Biological Samples
Raluca-Ioana Stefan-van Staden, Ruxandra-Maria Ilie-Mihai, Maria Coros, Stela Pruneanu
ECS Sensors Plus.2022; 1(3): 031606. CrossRef - Magnetic Resonance Imaging Downstaging, Pathological Response, and Microsatellite Instability Status in Patients with Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma Rectum Undergoing Preoperative Long-course Chemoradiation
B. Rajkrishna, Saikat Das, Dipti Masih, Tharani Putta, Rajat Raghunath, Thomas Samuel Ram
Current Medical Issues.2022; 20(3): 154. CrossRef - Biomarkers and cell-based models to predict the outcome of neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer patients
Aylin Alkan, Tobias Hofving, Eva Angenete, Ulf Yrlid
Biomarker Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microsatellite Instability (MSI) as an Independent Predictor of Pathologic Complete Response (PCR) in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Shaakir Hasan, Paul Renz, Rodney E. Wegner, Gene Finley, Moses Raj, Dulabh Monga, James McCormick, Alexander Kirichenko
Annals of Surgery.2020; 271(4): 716. CrossRef - Delivery of Personalized Care for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Incorporating Pathological, Molecular Genetic, and Immunological Biomarkers Into the Multimodal Paradigm
Éanna J. Ryan, Ben Creavin, Kieran Sheahan
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of mismatch repair status with survival and response to neoadjuvant chemo(radio)therapy in rectal cancer
Shu-Biao Ye, Yi-Kan Cheng, Lin Zhang, Yi-Feng Zou, Ping Chen, Yan-Hong Deng, Yan Huang, Jian-Hong Peng, Xiao-Jian Wu, Ping Lan
npj Precision Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of expression of MMR proteins and clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancer
Renu Verma, Puja Sakhuja, Ritu Srivastava, Prakash Chand Sharma
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Mismatch Repair–Deficient Rectal Cancer and Resistance to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Andrea Cercek, Gustavo Dos Santos Fernandes, Campbell S. Roxburgh, Karuna Ganesh, Shu Ng, Francisco Sanchez-Vega, Rona Yaeger, Neil H. Segal, Diane L. Reidy-Lagunes, Anna M. Varghese, Arnold Markowitz, Chao Wu, Bryan Szeglin, Charles-Etienne Gabriel Sauvé
Clinical Cancer Research.2020; 26(13): 3271. CrossRef - The Mismatch Repair System (MMR) in Head and Neck Carcinogenesis and Its Role in Modulating the Response to Immunotherapy: A Critical Review
Maria Cilona, Luca Giovanni Locatello, Luca Novelli, Oreste Gallo
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 3006. CrossRef - Genetics of rectal cancer and novel therapies: primer for radiologists
Sebastian Mondaca, Rona Yaeger
Abdominal Radiology.2019; 44(11): 3743. CrossRef - Mismatch repair deficiency as a predictive marker for response to adjuvant radiotherapy in endometrial cancer
Casper Reijnen, Heidi V.N. Küsters-Vandevelde, Clemens F. Prinsen, Leon F.A.G. Massuger, Marc P.M.L. Snijders, Stefan Kommoss, Sara Y. Brucker, Janice S. Kwon, Jessica N. McAlpine, Johanna M.A. Pijnenborg
Gynecologic Oncology.2019; 154(1): 124. CrossRef - Mismatch Repair System Deficiency Is Associated With Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer
Nicolas Meillan, Dewi Vernerey, Jérémie H. Lefèvre, Gilles Manceau, Magali Svrcek, Jeremy Augustin, Jean-François Fléjou, Olivier Lascols, Jean-Marc Simon, Romain Cohen, Philippe Maingon, Jean-Baptiste Bachet, Florence Huguet
International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics.2019; 105(4): 824. CrossRef - Promoter methylation and expression of DNA repair genes MGMT and ERCC1 in tissue and blood of rectal cancer patients
Sally M. Shalaby, Amal S. El-Shal, Lobna A. Abdelaziz, Eman Abd-Elbary, Mostafa M. Khairy
Gene.2018; 644: 66. CrossRef - RBBP6 increases radioresistance and serves as a therapeutic target for preoperative radiotherapy in colorectal cancer
Chao Xiao, Yupeng Wang, Miao Zheng, Jian Chen, Guohe Song, Zhijie Zhou, Chongzhi Zhou, Xing Sun, Lin Zhong, Erxun Ding, Yi Zhang, Liu Yang, Gang Wu, Shifeng Xu, Hong Zhang, Xiaoliang Wang
Cancer Science.2018; 109(4): 1075. CrossRef - Baseline MAPK signaling activity confers intrinsic radioresistance to KRAS-mutant colorectal carcinoma cells by rapid upregulation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K)
Stefan Eder, Annette Arndt, Andreas Lamkowski, Wassiliki Daskalaki, Alexis Rump, Markus Priller, Felicitas Genze, Eva Wardelmann, Matthias Port, Konrad Steinestel
Cancer Letters.2017; 385: 160. CrossRef - The current value of determining the mismatch repair status of colorectal cancer: A rationale for routine testing
E. Ryan, K. Sheahan, B. Creavin, H.M. Mohan, D.C. Winter
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2017; 116: 38. CrossRef - Exploration of Mutation and DNA Methylation of Polo-Like Kinase 1 (PLK1) in Colorectal Cancer
Wayne Ng, Joo-Shik Shin, Bin Wang, Cheok Soon Lee
Open Journal of Pathology.2017; 07(03): 45. CrossRef - Expression of Mismatch Repair Proteins in Early and Advanced Gastric Cancer in Poland
Katarzyna Karpińska-Kaczmarczyk, Magdalena Lewandowska, Małgorzata Ławniczak, Andrzej Białek, Elżbieta Urasińska
Medical Science Monitor.2016; 22: 2886. CrossRef - DNA Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Rectal Cancer: Benchmarking Its Impact on Prognosis, Neoadjuvant Response Prediction, and Clinical Cancer Genetics
Nicole de Rosa, Miguel A. Rodriguez-Bigas, George J. Chang, Jula Veerapong, Ester Borras, Sunil Krishnan, Brian Bednarski, Craig A. Messick, John M. Skibber, Barry W. Feig, Patrick M. Lynch, Eduardo Vilar, Y. Nancy You
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2016; 34(25): 3039. CrossRef -
miRNA-148b regulates radioresistance in non-small lung cancer cells via regulation of MutL homologue 1
Guangsheng Zhai, Gaozhong Li, Bo Xu, Tongfu Jia, Yinping Sun, Jianbo Zheng, Jianbin Li
Bioscience Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive and prognostic biomarkers for neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer
S.H. Lim, W. Chua, C. Henderson, W. Ng, J.-S. Shin, L. Chantrill, R. Asghari, C.S. Lee, K.J. Spring, P. de Souza
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2015; 96(1): 67. CrossRef - Potential of DNA methylation in rectal cancer as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers
Ruth Exner, Walter Pulverer, Martina Diem, Lisa Spaller, Laura Woltering, Martin Schreiber, Brigitte Wolf, Markus Sonntagbauer, Fabian Schröder, Judith Stift, Fritz Wrba, Michael Bergmann, Andreas Weinhäusel, Gerda Egger
British Journal of Cancer.2015; 113(7): 1035. CrossRef - Study of Liver Transplant Rejection in Alcoholism-Induced Cirrhosis
J. Tinoco González, C. Bernal Bellido, G. Jimenez Riera, V. Camacho Marente, L.M. Marín Gómez, G. Suárez Artacho, J.M. Álamo Martínez, J. Serrano Díez-Canedo, R.J. Padillo Ruíz, M.A. Gómez Bravo
Transplantation Proceedings.2013; 45(10): 3650. CrossRef
- Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy up-regulates PD-L1 in radioresistant colorectal cancer
- Expression of CHOP in Squamous Tumor of the Uterine Cervix
- Hyun Hee Chu, Jun Sang Bae, Kyoung Min Kim, Ho Sung Park, Dong Hyu Cho, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Myoung Ja Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):463-469. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.463
- 9,341 View
- 40 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background High-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection and abnormal p53 expression are closely involved in carcinogenesis of squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) of uterine cervix. Recent studies have suggested that virus-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress modulates various cell survival and cell death signaling pathways. The C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) is associated with ER stress-mediated apoptosis and is also involved in carcinogenesis of several human cancers. We hypothesized that CHOP is involved in the carcinogenesis of uterine cervical cancer in association with HR-HPV and/or p53.
Methods Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze CHOP and p53 protein expression of tissue sections from 191 patients with invasive cancer or preinvasive lesions of the uterine cervix (61 cases of SqCC, 66 cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [CIN] III, and 64 cases of CIN I).
Results CHOP was expressed in 59.4% of CIN I, 48.5% of CIN III, and 70.5% of SqCC cases. It was also significantly more frequent in invasive SqCC than in preinvasive lesions (p=0.042). Moreover, CHOP expression significantly correlated with HR-HPV infection and p53 expression (p=0.009 and p=0.038, respectively).
Conclusions Our results suggest that CHOP is involved in the carcinogenesis of the uterine cervix SqCC via association with HR-HPV and p53.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interplay between the cellular stress pathway, stemness markers, and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer
Mehran Gholamin, Atena Mansouri, Mohammad Reza Abbaszadegan, Mohammad Ali Karimi, Hossein Barzegar, Fatemeh Fardi Golyan, Hanie Mahaki, Hamid Tanzadehpanah, Reihaneh Alsadat Mahmoudian
Gene Reports.2025; 40: 102263. CrossRef - Role of C-reactive protein in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia/cancer
Adriana Pedreañez, Yenddy Carrero, Renata Vargas, Juan P.Hernández Fonseca, Jesús Mosquera
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 276: 156274. CrossRef - Expression of GRP78 and its copartners in HEK293 and pancreatic cancer cell lines (BxPC-3/PANC-1) exposed to MRI and CT contrast agents
Ali Ahmed Azzawri, Ibrahim Halil Yildirim, Zeynep Yegin, Abdurrahim Dusak
Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids.2024; 43(5): 391. CrossRef - Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Homeostasis in Reproductive Physiology and Pathology
Elif Guzel, Sefa Arlier, Ozlem Guzeloglu-Kayisli, Mehmet Tabak, Tugba Ekiz, Nihan Semerci, Kellie Larsen, Frederick Schatz, Charles Lockwood, Umit Kayisli
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(4): 792. CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway PERK‐eIF2α confers radioresistance in oropharyngeal carcinoma by activating NF‐κB
Qiao Qiao, Chaonan Sun, Chuyang Han, Ning Han, Miao Zhang, Guang Li
Cancer Science.2017; 108(7): 1421. CrossRef - Curcumin induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis through selective generation of reactive oxygen species in cervical cancer cells
Boyun Kim, Hee Seung Kim, Eun-Ji Jung, Jung Yun Lee, Benjamin K. Tsang, Jeong Mook Lim, Yong Sang Song
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2016; 55(5): 918. CrossRef - Down-regulation of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) expression in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma: Their relationship with clinicopathological parameters and prognostic significance
Xiao-Juan Zhu, She-Gan Gao, San-Qiang Li, Zhen-Guo Shi, Zhi-Kun Ma, Shan-Shan Zhu, Xiao-Shan Feng
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2015; 39(3): 391. CrossRef - MG289 in <i>Mycoplasma genitalium</i> Enhances Microbial Invasion and Bacterial Persistence in Benign Human Prostate Cells
Wasia Rizwani, Leticia Reyes, Jeongsoon Kim, Steve Goodison, Charles J. Rosser
Open Journal of Urology.2013; 03(06): 232. CrossRef
- Interplay between the cellular stress pathway, stemness markers, and Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer
- Difference of Genome-Wide Copy Number Alterations between High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions and Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Uterine Cervix
- Bum Hee Lee, Sangyoung Roh, Yu Im Kim, Ahwon Lee, Su Young Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):123-130. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.123
- 8,393 View
- 46 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background About 10% of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs) progress to invasive carcinomas within 2-10 years. By delineating the events that occur in the early stage of the invasion, the pathogenesis of cervical cancer could be better understood. This will also propose the possible methods for inhibiting the tumor invasion and improving the survival of patients.
Methods We compared the genomic profiles between the HSIL and the invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) using an array comparative genomic hybridization. Using recurrently altered genes, we performed a principal component analysis to see variation of samples in both groups. To find possibly affected pathways by altered genes, we analyzed genomic profiles with the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway database and GOEAST software.
Results We found 11q12.3 and 2p24.1 regions have recurrent copy number gains in both groups. 16p12-13 and 20q11-13 regions showed an increased copy number only in cases of HSIL. 1q25.3 and 3q23-29 regions showed copy number gains only in cases of SCC. Altered genes in the SCC group were related to the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and the RNA transport. Altered genes in the HSIL group were related to the ubiquitin mediated proteolysis and cell adhesion molecules.
Conclusions Our results showed not only that gains in 11q12.3 and 2p24.1 were early events occurring in the premalignant lesions and then maintained in cases of SCC but also that gains in 1q25.3 and 3q23-29 were late events occurring after invasion in those of SCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytokeratin and protein expression patterns in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity provide evidence for two distinct pathogenetic pathways
GESCHE FROHWITTER, HORST BUERGER, PAUL J. VAN DIEST, EBERHARD KORSCHING, JOHANNES KLEINHEINZ, THOMAS FILLIES
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(1): 107. CrossRef - 'Drawing' a Molecular Portrait of CIN and Cervical Cancer: a Review of Genome-Wide Molecular Profiling Data
Olga V Kurmyshkina, Pavel I Kovchur, Tatyana O Volkova
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(11): 4477. CrossRef
- Cytokeratin and protein expression patterns in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity provide evidence for two distinct pathogenetic pathways
- CpG Island Hypermethylation in Gastric Carcinoma and Its Premalignant Lesions
- Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):1-9. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.1
- 10,589 View
- 50 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Gastric cancers arise through a multistep process characterized by the progressive accumulation of molecular alterations in which genetic and epigenetic mechanisms have been implicated. Gastric cancer is one of the human malignancies in which aberrant promoter CpG island hypermethylation is frequently found.
Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus, which are known carcinogens for gastric cancer, are closely associated with enhanced hypermethylation of CpG island loci in gastric non-neoplastic epithelial cells and cancer cells, respectively. Aberrant CpG island hypermethylation occurs early in the multistep cascade of gastric carcinogenesis and tends to increase with the step-wise progression of the lesion. Approximately 400 genes that are actively expressed in normal gastric epithelial cells are estimated to be inactivated in gastric cancers as a result of promoter CpG island hypermethylation. In this review, a variety of information is summarized regarding CpG island hypermethylation in gastric cancer.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathogenicity of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer
Shamshul Ansari, Nada Ahmed
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Genome-wide characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in gastric cancer and its potential role in carcinogenesis and cancer progression
Xianming Jiang, Xiaoguang Pan, Wenchao Li, Peng Han, Jiaying Yu, Jing Li, Haoran Zhang, Wei Lv, Ying Zhang, Yulong He, Xi Xiang
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of DNA methylation in endometrial biopsies to predict risk of endometrial cancer
Francesco Multinu, Jun Chen, Joseph D. Madison, Michelle Torres, Jvan Casarin, Daniel Visscher, Viji Shridhar, Jamie Bakkum-Gamez, Mark Sherman, Nicolas Wentzensen, Andrea Mariani, Marina Walther-Antonio
Gynecologic Oncology.2020; 156(3): 682. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori severely reduces expression of DNA repair proteins PMS2 and ERCC1 in gastritis and gastric cancer
Yasir Raza, Ayaz Ahmed, Adnan Khan, Arif Ali Chishti, Syed Shakeel Akhter, Muhammad Mubarak, Carol Bernstein, Beryl Zaitlin, Shahana Urooj Kazmi
DNA Repair.2020; 89: 102836. CrossRef - Genomic and Epigenomic Profiling of High-Risk Intestinal Metaplasia Reveals Molecular Determinants of Progression to Gastric Cancer
Kie Kyon Huang, Kalpana Ramnarayanan, Feng Zhu, Supriya Srivastava, Chang Xu, Angie Lay Keng Tan, Minghui Lee, Suting Tay, Kakoli Das, Manjie Xing, Aliya Fatehullah, Syed Muhammad Fahmy Alkaff, Tony Kiat Hon Lim, Jonathan Lee, Khek Yu Ho, Steven George Ro
Cancer Cell.2018; 33(1): 137. CrossRef - Decreased Methylation of IFNAR Gene Promoter from Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Is Associated with Oxidative Stress in Chronic Hepatitis B
Jing-wen Wang, Jing-wei Wang, Jun Zhang, Chen-si Wu, Yu Fang, Wei-wei Su, Yu-chen Fan, Kai Wang
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2018; 38(11): 480. CrossRef - Genomic landscape of gastric cancer: molecular classification and potential targets
Jiawei Guo, Weiwei Yu, Hui Su, Xiufeng Pang
Science China Life Sciences.2017; 60(2): 126. CrossRef - Hypermethylation of the galectin-3 promoter is associated with poor prognosis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure
Jing Zhao, Yu-Chen Fan, Xin-Yuan Liu, Ze-Hua Zhao, Feng Li, Kai Wang
Digestive and Liver Disease.2017; 49(6): 664. CrossRef - Proteomics-Based Identification and Analysis of Proteins Associated with Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Cancer
Jianjiang Zhou, Wenling Wang, Yuan Xie, Yan Zhao, Xian Chen, Wenjie Xu, Yan Wang, Zhizhong Guan, Hiromu Suzuki
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(1): e0146521. CrossRef - Lack of Correlation between Aberrant p16, RAR-β2, TIMP3, ERCC1, and BRCA1 Protein Expression and Promoter Methylation in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Accompanying Candida albicans-Induced Inflammation
Yui Terayama, Tetsuro Matsuura, Kiyokazu Ozaki, Javier S Castresana
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(7): e0159090. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori CagA induces tumor suppressor gene hypermethylation by upregulating DNMT1 via AKT-NFκB pathway in gastric cancer development
Bao-gui Zhang, Lei Hu, Ming-de Zang, He-xiao Wang, Wei Zhao, Jian-fang Li, Li-ping Su, Zhifeng Shao, Xiaodong Zhao, Zheng-gang Zhu, Min Yan, Bingya Liu
Oncotarget.2016; 7(9): 9788. CrossRef - Promoter methylation status and expression of PPAR-γ gene are associated with prognosis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure
Ze-Hua Zhao, Yu-Chen Fan, Qi Zhao, Cheng-Yun Dou, Xiang-Fen Ji, Jing Zhao, Shuai Gao, Xin-You Li, Kai Wang
Clinical Epigenetics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Epigenetics in EBV Regulation and Pathogenesis
Hans Helmut Niller, Zsófia Tarnai, Gábor Decsi, Ádám Zsedényi, Ferenc Bánáti, Janos Minarovits
Future Microbiology.2014; 9(6): 747. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori Induces Hypermethylation of CpG Islands Through Upregulation of DNA Methyltransferase: Possible Involvement of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species
Hye-Kyung Na, Jeong-Hwa Woo
Journal of Cancer Prevention.2014; 19(4): 259. CrossRef - Mallory–Denk Body (MDB) formation modulates ufmylation expression epigenetically in alcoholic hepatitis (AH) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Hui Liu, Ming Gong, Barbara A. French, Jun Li, Brittany Tillman, Samuel W. French
Experimental and Molecular Pathology.2014; 97(3): 477. CrossRef - RETRACTED ARTICLE: Role of p16 gene promoter methylation in gastric carcinogenesis: a meta-analysis
He-Ling Wang, Ping-Yi Zhou, Peng Liu, Yu Zhang
Molecular Biology Reports.2014; 41(7): 4481. CrossRef - Exportin 4 gene expression and DNA promoter methylation status in chronic hepatitis B virus infection
F. Zhang, Y.‐C. Fan, N.‐N Mu, J. Zhao, F.‐K. Sun, Z.‐H. Zhao, S. Gao, K. Wang
Journal of Viral Hepatitis.2014; 21(4): 241. CrossRef - Microarray-based DNA methylation study of Ewing’s sarcoma of the bone
HYE-RIM PARK, WOON-WON JUNG, HYUN-SOOK KIM, YONG-KOO PARK
Oncology Letters.2014; 8(4): 1613. CrossRef - Pathologic Diagnosis of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia
Nari Shin, Do Youn Park
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2013; 13(2): 84. CrossRef
- Pathogenicity of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer
- Expression of DNA Topoisomerase II-alpha as a Proliferating Marker in Urothelial Carcinoma of Urinary Bladder based on World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology Consensus Classification: A Correlation with Expression of Ki-67 and Apoptosis
- Tae Jin Lee, Dong Ki Lee, Eon Sub Park, Jae Hyung Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(5):305-313.
- 1,992 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
DNA topoisomerase II-alpha is linked with active cell proliferation in mammalian cells. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between the expression of DNA topoisomerase II-alpha as a proliferating marker, and the expression of Ki-67 and apoptosis in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder based on World Health Organization/International Society of Urological Pathology (WHO/ISUP) consensus classification.
METHODS
73 urothelial carcinomas of the urinary bladder after transurethral resection and 25 carcinomas after radical cystectomy were investigated for histologic grading based on WHO and WHO/ISUP consensus classification. Formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue of 98 specimens from 73 patients were immunohistochemically stained for DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and Ki-67, and in situ TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling method for evaluation of apoptotic cells was performed. For each case, a DNA topoisomerase II-alpha, Ki-67, and apoptotic indices were determined.
RESULTS
The histologic grades of 73 cases based on the WHO grading system were 21.9% (16 cases) in grade 1, 65.8% (48 cases) in grade 2, and 12.3% (9 cases). 5.5% (4 cases) of papillary neoplasm of low malignant potential, 47.9% (35 cases) of urothelial carcinoma of low grade, and 46.6% (34 cases) in urothelial carcinoma of high grade were reclassified using the WHO/ISUP consensus classification. Histologic grades based on two grading systems were correlated to invasion and stage (p<0.05). DNA topoisomerase II-alpha, Ki-67, and apoptotic indices were correlated to histologic grades based on two grading system and invasion. Also, the correlation of DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and Ki-67 indices, and DNA topoisomerase II-alpha and apoptotic indices were significant, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
DNA topoisomerase II-alpha appears to be an useful marker for assessing the proliferation potential of urothelial carcinoma of in the urinary bladder.
- Cytomorphologic Features According to HPV DNA Type in Histologically Proven Cases of the Uterine Cervix.
- In Ho Choi, So Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee, Dong Won Kim, Yoon Mi Jeen
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):612-620.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.612
- 4,860 View
- 37 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This study investigated whether human papillomavirus (HPV) genotype is related to koilocytic changes in cervical cytology and histology, and what factors cause discrepancies among cytology, HPV DNA chip tests, and biopsies.
METHODS
We examined 174 of 949 cases histologically confirmed by both cytology and HPV DNA chip testing. We analyzed koilocytic changes in cytology and biopsies according to HPV genotype.
RESULTS
HPV-16 significantly coincided with nuclear size variation and hyperchromasia, although the cytomorphologic features correlated with other HPV genotypes were not statistically significant. By analyzing 68 cases in which there were discrepancies between the HPV DNA chip test and histological results, we confirmed that artifacts or glycogen acanthosis resulted in the over-diagnoses of four HPV-negative cases with normal cytology. Four diagnostic errors and four sampling errors were present in eight HPV-positive cases. The degree of nuclear size variation significantly influenced the cytologically under-diagnosed cases (p=0.006).
CONCLUSIONS
Other than HPV-16, HPV genotype exhibited no cytological or histological differences. The discrepancy between the results of HPV DNA chip test and histology was created by glycogen acanthosis, immature squamous metaplasia, artifacts, and sampling errors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Koilocytic changes are not elicited by human papillomavirus genotypes with higher oncogenic potential
Mitsuaki Okodo, Kaori Okayama, Koji Teruya, Hirokazu Kimura, Natsumi Noji, Yasuyoshi Ishii, Masahiko Fujii, Mizue Oda, Toshiyuki Sasagawa
Journal of Medical Virology.2020; 92(12): 3766. CrossRef - Analysis of Sequence Variation and Risk Association of Human Papillomavirus 52 Variants Circulating in Korea
Youn Jin Choi, Eun Young Ki, Chuqing Zhang, Wendy C. S. Ho, Sung-Jong Lee, Min Jin Jeong, Paul K. S. Chan, Jong Sup Park, Xuefeng Liu
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0168178. CrossRef - Uncommon and Rare Human Papillomavirus Genotypes Relating to Cervical Carcinomas
Na Rae Kim, Myunghee Kang, Soon Pyo Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Jungsuk An, Dong Hae Chung, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 43. CrossRef - Distribution of Human Papillomavirus 52 and 58 Genotypes, and Their Expression of p16 and p53 in Cervical Neoplasia
Tae Eun Kim, Hwal Woong Kim, Kyung Eun Lee
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 24. CrossRef
- Koilocytic changes are not elicited by human papillomavirus genotypes with higher oncogenic potential
- Comparison of the DNA Preservation in Neutral-Buffered Formalin Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue and in Non-Buffered Formalin Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue.
- An Na Seo, Jae Hoon Kim, Dakeun Lee, Ji Yun Jeong, Ji Young Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):549-556.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.549
- 5,178 View
- 62 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The preservation of optimized DNA and its extraction from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues are important issues. There has been some doubt over whether 10% neutral-buffered formalin is an ideal fixation solution for DNA preservation over non-buffered formalin, as conventionally recommended. In this study, the correlation between the efficiency of DNA extraction from FFPE tissues and buffered formalin was evaluated.
METHODS
Several tissues with same conditions except fixatives were fixed in four different formalin solution groups and were routinely processed as paraffin-embedding protocols. DNAs were extracted from four different FFPE tissues that were stored for over 3 months and over 9 months. The quantity and quality of the DNAs were assessed with a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer, and the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and degradation were analyzed via microchip electrophoresis. KRAS mutation analysis and microsatellite instability (BAT25) PCR were performed with each sample.
RESULTS
The results showed no remarkable difference in the four groups.
CONCLUSIONS
The study findings demonstrate that DNA preservation is fairly unaffected by a neutral buffer where there is short formalin manufacture period and an adequate formalin fixation time before embedding in paraffin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Forensic analysis of formalin-fixed non-paraffin-embedded tissues: a comparative study of STR and mtDNA profiling
Kangana Aggarwal, Nidhi Sharma, Braja Kishore Mohapatra, Kamal Chauhan, Harpreet Singh, Chittaranjan Behera
Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Direct Sequencing, PNA Clamping-Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction, and Pyrosequencing Methods for the Detection ofEGFRMutations in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma and the Correlation with Clinical Responses to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
Hyun Ju Lee, Xianhua Xu, Hyojin Kim, Yan Jin, Pingli Sun, Ji Eun Kim, Jin-Haeng Chung
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(1): 52. CrossRef
- Forensic analysis of formalin-fixed non-paraffin-embedded tissues: a comparative study of STR and mtDNA profiling
- CpG Island Methylation According to the Histologic Patterns of Early Gastric Adenocarcinoma.
- Junjeong Choi, Mee Yon Cho, So Young Jung, Khalilullah Mia Jan, Hyun Soo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):469-476.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.469
- 4,678 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although the importance of aberrant DNA methylation in the development of gastric adenocarcinoma has been described, the mechanism of pathogenesis has not been revealed yet. We quantitatively analyzed methylation of four CpG islands and one repetitive DNA element, according to the histologic features of adenocarcinoma with precursor lesions.
METHODS
We divided the cases as adenocarcinoma with intestinal type precursors (type A, n=19 cases) and adenocarcinoma with diffuse type precursors (type B, n=19 cases). We micro-dissected tumor cells and matched non-neoplastic gastric mucosa from the hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides.
RESULTS
A total of 20 CpG sites of long interspersed nucleotide element-1 (LINE1), RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORA), Kruppel-like factor 7 (KLF7), mutL homolog 1 (MLH1), MINT25, and CD133 were analyzed. Methylation was determined by bisulfate-pyro-sequencing, and hypomethylation of LINE1 and CD133 was noted in the tumors, compared to the levels in the non-neoplastic gastric mucosa (p=0.014 and p=0.015, respectively). A statistically different methylation pattern of CpG sites at CD133 and KLF7 was noted only in type B lesions, compared to that in matched non-neoplastic gastric mucosa (p=0.027 and p=0.043, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
Given that aberrant methylation occurs in a relatively early phase of carcinogenesis, different patterns of methylation may determine the carcinoma phenotype. However, further large-scale study is required to clarify the significance of this difference. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular function of Krüppel-like factor 7 in biology
Yi Mao, Yuechan Chen, Zhiwei Zhang
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2023; 55(5): 713. CrossRef - DNA methylation status of a distinctively different subset of genes is associated with each histologic Lauren classification subtype in early gastric carcinogenesis
YOSEP CHONG, KHALILULLAH MIA-JAN, HOON RYU, JAMSHID ABDUL-GHAFAR, JIJGEE MUNKHDELGER, SAYAMAA LKHAGVADORJ, SO YOUNG JUNG, MIRA LEE, SUN-YOUNG JI, EUNHEE CHOI, MEE-YON CHO
Oncology Reports.2014; 31(6): 2535. CrossRef
- Molecular function of Krüppel-like factor 7 in biology
- The Usefulness of p16INK4a Immunocytochemical Staining in ASC-H Patients.
- Kwang Il Yim, Yeo Ju Kang, Tae Eun Kim, Gyeongsin Park, Eun Sun Jung, Yeong Jin Choi, Kyo Young Lee, Chang Seok Kang, Ahwon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):290-295.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.290
- 4,610 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The grey zone of cervical cytology, and in particular atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) causes diagnostic difficulties and increases medical expenses. We analyzed p16INK4a expression in ASC-H liquid-based cytology specimens (LBCS) to develop more effective methods for the management of ASC-H patients.
METHODS
We carried out p16INK4a immunostaining with 57 LBCS of ASC-H diagnostic categories, all of which were histologically cofirmed and 43 cases of which were compared with the results of a human papillomavirus (HPV) chip test.
RESULTS
p16INK4a immunostaining with ASC-H LBCS was positive in 20% (3/15) of cervicitis, 25.0% (3/12) of tissue-low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, 75.0% (18/24) of tissue-high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL), and 100% (6/6) of invasive cancer cases. The positivity of p16INK4a in LBCS was correlated with higher grade of histologic diagnosis (r=0.578, p=0.000). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of p16INK4a immunostaining for the prediction of tissue-HSIL+ were 80.0%, 77.8%, 80.0%, and 77.8%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of p16INK4a immunostaining plus HPV chip test for predicting tissue-HSIL+ were 71.2%, 86.4%, 84.2%, and 79.2%.
CONCLUSIONS
p16INK4a immunostaining as well as HPV chip testing with remaining LBCS with ASC-H are useful objective markers for the prediction of tissue-HSIL+. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Usefulness of p16INK4a Immunocytochemical staining for the Differentiation between Atrophy and ASCUS in Diagnosis of Uterine Cervical Cancer
Hye Ryoung Shin, Taekil Eom, Wan-Su Choi
Biomedical Science Letters.2023; 29(3): 144. CrossRef
- Usefulness of p16INK4a Immunocytochemical staining for the Differentiation between Atrophy and ASCUS in Diagnosis of Uterine Cervical Cancer
- Copy Number Alterations of BCAS1 in Squamous Cell Carcinomas.
- Yu Im Kim, Ahwon Lee, Jennifer Kim, Bum Hee Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Suk Woo Nam, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo, Jung Young Lee, Sang Ho Kim, Su Young Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(3):271-275.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.3.271
- 4,417 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Breast carcinoma amplified sequence 1 (BCAS1), located in 20q13, is amplified and overexpressed in breast cancers. Even though BCAS1 is expected to be an oncogene candidate, its contribution to tumorigenesis and copy number status in other malignancies is not reported. To elucidate the role of BCAS1 in squamous cell carcinomas, we investigated the copy number status and expression level of BCAS1 in several squamous cell carcinoma cell lines, normal keratinocytes and primary tumors.
METHODS
We quantitated BCAS1 gene by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Expression level of BCAS1 was measured by real-time reverse transcription-PCR and immunoblot.
RESULTS
Seven (88%) of 8 squamous cell carcinoma cell lines showed copy number gain of BCAS1 with various degrees. BCAS1 gene in primary tumors (73%) also showed copy number gain. However, expression level did not show a linear correlation with copy number changes.
CONCLUSIONS
We identified copy number gain of BCAS1 in squamous cell carcinomas. Due to lack of linear correlation between copy numbers of BCAS1 and its expression level, we could not confirm that the overexpression of BCAS1 is a common finding in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. However, this study shows that the copy number gain of BCAS1 is a common finding in squamous cell carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electrochemical Approaches for Preparation of Tailor-Made Amino Acids
Nana Wang, Jingcheng Xu, Haibo Mei, Hiroki Moriwaki, Kunisuke Izawa, Vadim A. Soloshonok, Jianlin Han
Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry.2021; 41(8): 3034. CrossRef
- Electrochemical Approaches for Preparation of Tailor-Made Amino Acids
- Rapid and Sensitive Detection of KRAS Mutation by Peptide Nucleic Acid-based Real-time PCR Clamping: A Comparison with Direct Sequencing between Fresh Tissue and Formalin-fixed and Paraffin Embedded Tissue of Colorectal Cancer.
- Dongjun Jeong, Yujun Jeong, Jonghyun Lee, Moo Jun Baek, Yongbae Kim, Ji Hye Lee, Hyun Deuk Cho, Mee Hye Oh, Chang Jin Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):151-159.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.151
- 5,966 View
- 84 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Rapid and sensitive detection of KRAS mutation is needed to maximize the benefits for patients who are being treated with monoclonal antibodies to target the epidermal growth factor receptor in colorectal cancer. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of the peptide nucleic acid clamp real-time PCR (PCqPCR) as compared to that of direct sequencing (DS) between using fresh colorectal cancer tissue and the matched formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) colorectal cancer tissue.
METHODS
The efficacy of PCqPCR was evaluated and compared with that of DS using fresh tissue and matched FFPE tissue from 30 cases of colorectal cancer.
RESULTS
PCqPCR is more sensitive than DS for detecting KRAS mutation. PCqPCR detected 1% of mutants in 1 ng DNA. PCqPCR detected mutation in 1% of mutant cells, while DS barely detected, by manual reading, that in 20-50% of mutant cells. In the clinical samples, PCqPCR detected KRAS mutation in 60.0% while DS detected KRAS mutation in 53.3% of the colorectal cancers. The two methods showed a 100% concordance rate for detecting KRAS mutation between the fresh tissue and FFPE tissue.
CONCLUSIONS
The PCqPCR method is efficiently applicable for the detection of KRAS mutation in a clinical setting. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- NTRK oncogenic fusions are exclusively associated with the serrated neoplasia pathway in the colorectum and begin to occur in sessile serrated lesions
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Hoon Hong, Yoon‐La Choi, Ji Ae Lee, Mi‐kyoung Seo, Mi‐Sook Lee, Sung Bin An, Min Jung Sung, Nam‐Yun Cho, Sung‐Su Kim, Young Kee Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
The Journal of Pathology.2021; 255(4): 399. CrossRef - Discrimination of the V600E Mutation in BRAF by Rolling Circle Amplification and Förster Resonance Energy Transfer
Mariia Dekaliuk, Xue Qiu, Frédéric Troalen, Pierre Busson, Niko Hildebrandt
ACS Sensors.2019; 4(10): 2786. CrossRef - Sensitive Genotyping of Somatic Mutations in the EGFR, KRAS, PIK3CA, BRAF Genes from NSCLC Patients Using Hydrogel Biochips
Marina Emelyanova, Ksenia Arkhipova, Natalia Mazurenko, Alexander Chudinov, Irina Demidova, Irina Zborovskaya, Lyudmila Lyubchenko, Alexander Zasedatelev, Tatiana Nasedkina
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2015; 23(4): 255. CrossRef - Low Frequency of KRAS Mutation in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas in Korean Patients and Its Prognostic Value
Mi Jung Kwon, Jang Yong Jeon, Hye-Rim Park, Eun Sook Nam, Seong Jin Cho, Hyung Sik Shin, Ji Hyun Kwon, Joo Seop Kim, Boram Han, Dong Hoon Kim, Yoon-La Choi
Pancreas.2015; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Comparison of PNA clamping and direct sequencing for detecting KRAS mutations in matched tumour tissue, cell block, pleural effusion and serum from patients with malignant pleural effusion
Ji Young Kang, Chan Kwon Park, Chang Dong Yeo, Hea Yeon Lee, Chin Kook Rhee, Seung Joon Kim, Seok Chan Kim, Young Kyoon Kim, Mi Sun Park, Hyeon Woo Yim
Respirology.2015; 20(1): 138. CrossRef - BRAF V600E Mutation Analysis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas by Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamp Real-time PCR
Dongjun Jeong, Yujun Jeong, Ji Hye Park, Sun Wook Han, Sung Yong Kim, Yeo Joo Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Young Hwangbo, Soyoung Park, Hyun Deuk Cho, Mee Hye Oh, Seung Ha Yang, Chang Jin Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2013; 20(3): 759. CrossRef - Detection and comparison of EGFR mutations in matched tumor tissues, cell blocks, pleural effusions, and sera from patients with NSCLC with malignant pleural effusion, by PNA clamping and direct sequencing
Chang Dong Yeo, Jin Woo Kim, Kwan Hyoung Kim, Jick Hwan Ha, Chin Kook Rhee, Seung Joon Kim, Young Kyoon Kim, Chan Kwon Park, Sang Haak Lee, Mi Sun Park, Hyeon Woo Yim
Lung Cancer.2013; 81(2): 207. CrossRef - Detection ofBRAFV600EMutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas by Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamp Real-Time PCR: A Comparison with Direct Sequencing
Dongjun Jeong, Yujun Jeong, Sungche Lee, Hyeran Lee, Wanju Lee, Hyungjoo Kim, Doosan Park, Soyoung Park, Wenxia Mu, Hyun-Deuk Cho, Mee-Hye Oh, Sung Soo Lee, Seung-Ha Yang, Chang-Jin Kim
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 61. CrossRef
- NTRK oncogenic fusions are exclusively associated with the serrated neoplasia pathway in the colorectum and begin to occur in sessile serrated lesions
- Mutation and Expression of DNA2 Gene in Gastric and Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Sung Hak Lee, Yoo Ri Kim, Nam Jin Yoo, Sug Hyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):354-359.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.354
- 4,750 View
- 35 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Deregulation of DNA repair and replication are involved in cancer development. DNA2 is a nuclease/helicase that plays roles in DNA repair and replication. The aim of this study was to explore DNA2 mutation and DNA2 protein expression in gastric cancers (GCs) and colorectal cancers (CRCs).
METHODS
We analyzed two mononucleotide repeats in DNA2 in 27 GCs with high microsatellite instability (MSI-H), 34 GCs with stable MSI (MSS), 29 CRCs with MSI-H and 35 CRCs with MSS by single-strand conformation polymorphism. We also analyzed DNA2 expression in GCs and CRCs either with MSI-H or MSS.
RESULTS
We found DNA2 mutations in two GCs (7.1%) and two CRCs with MSI-H (6.9%), but not in cancers with MSS. The mutations consisted of three cases of a c.2593delT and one of a c.2592_2593delTT, which would result in premature stopping of amino acid synthesis (p.Ser865Hisfsx6 and p.Ser865Thrfsx20, respectively). DNA2 expression was observed in 16 (80%) of the GCs and 15 (75%) of the CRCs with MSI-H, but all of the cancers with DNA2 frameshift mutations were weak or negative for DNA2.
CONCLUSIONS
Our data indicate that DNA2 mutation and loss of DNA2 expression occur in GCs and CRCs, and suggest that these alterations may contribute to cancer pathogenesis by deregulating DNA repair and replication. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multiple roles of DNA2 nuclease/helicase in DNA metabolism, genome stability and human diseases
Li Zheng, Yuan Meng, Judith L Campbell, Binghui Shen
Nucleic Acids Research.2020; 48(1): 16. CrossRef - Integration of multiple networks and pathways identifies cancer driver genes in pan-cancer analysis
Claudia Cava, Gloria Bertoli, Antonio Colaprico, Catharina Olsen, Gianluca Bontempi, Isabella Castiglioni
BMC Genomics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Replication intermediates that escape Dna2 activity are processed by Holliday junction resolvase Yen1
Gizem Ölmezer, Maryna Levikova, Dominique Klein, Benoît Falquet, Gabriele Alessandro Fontana, Petr Cejka, Ulrich Rass
Nature Communications.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multiple roles of DNA2 nuclease/helicase in DNA metabolism, genome stability and human diseases
- The Loss of E-cadherin is Associated with the Epigenetic Alteration of CDH1 in Breast Cancer and it is also Associated with an Abnormal beta-catenin Expression in Lobular Carcinoma.
- Gwangil Kim, Ji Young Kim, Hee Jung An, Haeyoun Kang, Tae Heon Kim, Jung Yon Shim, Jin Hyung Heo, Hai Lin Park, Young Kil Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(5):400-407.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.5.400
- 4,319 View
- 41 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
APC and E-cadherin are the key molecules in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. We attempted to define the epigenetic alteration of APC and CDH1 (the E-cadherin gene) and the expression of Wnt-related molecules in human mammary carcinomas.
METHODS
Sixty-four mammary carcinomas, including 52 invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs) and 12 invasive lobular carcinomas (ILCs), were evaluated using methylation-specific PCR and immunohistochemistry. We performed immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC, Wnt1, cyclin D1, ER, PR and C-erb B2.
RESULTS
Hypermethylation of APC and CDH1 was observed in 38 (59%) and 28 (44%) cases, respectively. CDH1 hypermethylation in ILCs was increased compared to that in IDCs (p=0.002) and it was associated with the loss of E-cadherin (p=0.02) and beta-catenin (p=0.042). APC methylation was positively correlated with the ER expression (p=0.021). Abnormal cytoplasmic localization of beta-catenin was found in 10 cases and any expression was not detected in six cases. In ILCs, the E-cadherin or beta-catenin expression was markedly decreased compared to that in IDCs (p<0.001 in both).
CONCLUSIONS
Methylation of APC or CDH1 was relatively frequent in mammary carcinomas. The loss of E-cadherin in mammary carcinoma was associated with CDH1 methylation, and abnormal beta-catenin expression was related to the loss of E-cadherin in ILC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activation reverses gemcitabine resistance by attenuating Beclin1-mediated autophagy in the MG63 human osteosarcoma cell line
Hao Tao, Feng Chen, Haifei Liu, Yanling Hu, Yingzhen Wang, Haiyan Li
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017; 16(2): 1701. CrossRef
- Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activation reverses gemcitabine resistance by attenuating Beclin1-mediated autophagy in the MG63 human osteosarcoma cell line
- Prevalence and Genotype Distribution of Cervical Human Papillomavirus DNA in Korean Women: A Multicenter Study.
- Sung Ran Hong, In Sun Kim, Dong Won Kim, Mi Jin Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Young Ok Kim, Hye Sun Kim, Seo Hee Rha, Gyeong Sin Park, Yong Koo Park, Yong Wook Park, Ho Sung Park, Kwang Sun Suh, Jin Hee Sohn, Mi Kyung Shin, Hoon Kyu Oh, Ki Jung Yun, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Shi Nae Lee, Ah Won Lee, Hyo Jin Lee, Hyun Yee Cho, Chan Choi, Woon Won Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):342-350.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.342
- 6,286 View
- 63 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
DNA prevalence and type distribution of human papillomavirus (HPV) varies geographically. We investigated HPV prevalence and type distribution in Korean women using the MyHPV DNA chip testing. Methods: A total of 2,368 women from five regions of the country underwent Pap smear examination and MyHPV chip testing. Results: Overall HPV positivity was 15.8% and 78.4% in women with normal and abnormal cytology, respectively. High-risk HPV infection was strongly correlated with cytological atypia. In women with abnormal cytology, the five most common HPV types were 16, 58, 18, 52, and 56/53, and HPV16 was significantly the most common type in most geographical regions. After HPV16, HPV58, and 52 were the next most frequently detected types. Women with normal cytology, in contrast, showed heterogeneity in HPV type distribution. High-grade intraepithelial lesions infected with HPV16, 18, 31 or 45 are more likely to progress to carcinoma. Conclusions: The HPV chip test can provide useful data regarding HPV positivity and type. The most common HPV type in Korean women with abnormal cytology is HPV16, with HPV58 and 52 being frequently present. Our data may have important implications for vaccination programs and the development of cervical screening. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HPV genotyping by L1 amplicon sequencing of archived invasive cervical cancer samples: a pilot study
Charles D. Warden, Preetam Cholli, Hanjun Qin, Chao Guo, Yafan Wang, Chetan Kancharla, Angelique M. Russell, Sylvana Salvatierra, Lorraine Z. Mutsvunguma, Kerin K. Higa, Xiwei Wu, Sharon Wilczynski, Raju Pillai, Javier Gordon Ogembo
Infectious Agents and Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhanced disease progression due to persistent HPV-16/58 infections in Korean women: a systematic review and the Korea HPV cohort study
Jaehyun Seong, Sangmi Ryou, JeongGyu Lee, Myeongsu Yoo, Sooyoung Hur, Byeong-Sun Choi
Virology Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of FFPE histological versus LBP cytological samples for HPV detection and typing in cervical cancer
Geehyuk Kim, Hyemi Cho, Dongsup Lee, Sunyoung Park, Jiyoung Lee, Hye-young Wang, Sunghyun Kim, Kwang Hwa Park, Hyeyoung Lee
Experimental and Molecular Pathology.2017; 102(2): 321. CrossRef - Distribution of Oncogenic Human Papillomavirus Genotypes at High Grade Cervical Lesions above CIN 2 Grade with Histological Diagnosis
Geehyuk Kim, Sungyoung Park, Hye-young Wang, Sunghyun Kim, Sangjung Park, Kwangmin Yu, Boohyung Lee, Seung-Ju Ahn, Eun-Joong Kim, Dongsup Lee
Biomedical Science Letters.2016; 22(2): 37. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus Prevalence and Genotype Distribution in Normal and ASCUS Specimens: Comparison of a Reverse Blot Hybridization Assay with a DNA Chip Test
Sunghyun Kim, In-soo Lee, Dongsup Lee
Biomedical Science Letters.2015; 21(1): 32. CrossRef - Genotype Analysis of Human Papilloma Virus Infection in Accordance with Cytological Diagnoses
Mi-Suk Park, Hyun-Wook Cho, Jin-Gak Kim, Nan-Young Bae, Dong-Sun Oh, Ho-Hyun Park
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2015; 47(1): 39. CrossRef - Comparison of the Cobas 4800 HPV and HPV 9G DNA Chip Tests for Detection of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus in Cervical Specimens of Women with Consecutive Positive HPV Tests But Negative Pap Smears
Sun-Young Jun, Eun Su Park, Jiyoung Kim, Jun Kang, Jae Jun Lee, Yoonjin Bae, Sang-Il Kim, Lee-So Maeng, Magdalena Grce
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(10): e0140336. CrossRef - Uncommon and Rare Human Papillomavirus Genotypes Relating to Cervical Carcinomas
Na Rae Kim, Myunghee Kang, Soon Pyo Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Jungsuk An, Dong Hae Chung, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 43. CrossRef - Evaluation of Human Papillomavirus Genotyping from Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded Specimens in Cervical Cancers
Hyunwoo Jin
Journal of Life Science.2014; 24(9): 1025. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the HPV28 Detection and HPV DNA Chip Test for Detecting and Genotyping Human Papillomaviruses
Eunsim Shin, Heojin Bae, Wan-Keun Song, Sun-Kyung Jung, Yoo-Sung Hwang
Laboratory Medicine Online.2013; 3(4): 234. CrossRef - Significance of HPV-58 Infection in Women Who Are HPV-Positive, Cytology-Negative and Living in a Country with a High Prevalence of HPV-58 Infection
Joon Seon Song, Eun Ju Kim, Jene Choi, Gyungyub Gong, Chang Ohk Sung, Robert D. Burk
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(3): e58678. CrossRef - REBA HPV‐ID® for efficient genotyping of human papillomavirus in clinical samples from Korean patients
Sunghyun Kim, Dongsup Lee, Sangjung Park, Tae Ue Kim, Bo‐Young Jeon, Kwang Hwa Park, Hyeyoung Lee
Journal of Medical Virology.2012; 84(8): 1248. CrossRef - Dynamin 2 expression as a biomarker in grading of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Yoo-Young Lee, Sang Yong Song, In-Gu Do, Tae-Joong Kim, Byoung-Gie Kim, Jeong-Won Lee, Duk-Soo Bae
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2012; 164(2): 180. CrossRef - Cytomorphologic Features According to HPV DNA Type in Histologically Proven Cases of the Uterine Cervix
In Ho Choi, So-Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee, Dong Won Kim, Yoon Mi Jeen
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(6): 612. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus Prevalence in Gangwon Province Using Reverse Blot Hybridization Assay
Dongsup Lee, Sunghyun Kim, Sangjung Park, Hyunwoo Jin, Tae Ue Kim, Kwang Hwa Park, Hyeyoung Lee
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(4): 348. CrossRef - Pediatric vulvar squamous cell carcinoma in a liver transplantation recipient: a case report
Na-Rae Kim, Soyi Lim, Hyun Yee Cho
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2011; 22(3): 207. CrossRef
- HPV genotyping by L1 amplicon sequencing of archived invasive cervical cancer samples: a pilot study
- The Usefulness of the HPV DNA Microchip Test for Women with ASC-US.
- Hee Eun Kyeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Sanghui Park, Hyun Yee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):254-259.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.254
- 4,029 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
This study was performed to ascertain the usefulness of the human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA microchip test for the screening and management of women with atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US).
METHODS
The subject group consisted of 534 patients, and all of whom were diagnosed as ASC-US according to a Papanicolaou smear, and they all underwent concomitant HPV DNA microchip test.
RESULTS
The occurrence rates of overall squamous lesions and high risk lesion (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 and grade 3, and invasive carcinoma) of the HPV-positive ASC-US patients were significantly higher than those of the HPV-negative ASC-US patients. High risk lesion was detected more frequently among the older patients and the patients with HPV 56, 33 or 70. On the follow-up HPV DNA microchip test, only 1 of 11 (9.1%) HPV type-switched women developed squamous lesion compared with 8 of 13 (61.6%) HPV type-persistent women who developed squamous lesion.
CONCLUSIONS
The HPV DNA microchip test is useful for the management of ASC-US patients. HPV-positive ASC-US patients should undergo a HPV DNA microchip test periodically. If the same genotype of HPV is persistent on the follow-up test, more increased surveillance is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced disease progression due to persistent HPV-16/58 infections in Korean women: a systematic review and the Korea HPV cohort study
Jaehyun Seong, Sangmi Ryou, JeongGyu Lee, Myeongsu Yoo, Sooyoung Hur, Byeong-Sun Choi
Virology Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Enhanced disease progression due to persistent HPV-16/58 infections in Korean women: a systematic review and the Korea HPV cohort study
- Analysis of HPV-other Samples by Performing HPV DNA Sequencing.
- Yoo Duk Choi, Chang Woo Han, Woon Jae Chung, Woon Won Jung, Ji Shin Lee, Jong Hee Nam, Min Cheol Lee, Sang Woo Juhng, Ho Sun Choi, Chang Soo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):250-253.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.250
- 4,918 View
- 47 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
HPV-other samples are designated as being positive on HPV-PCR, but negative when using specific HPV hybridization probes. We wanted to determine the types on the HPV-other samples by performing sequencing, and to know the pathologic status of the uterine cervix according to the HPV type detected on sequencing.
METHODS
For HPV genotying, we used the commercially available HPV DNA Chip test, which contains 15 types of high-risk HPV and 9 types of low-risk HPV. The HPV DNA sequencing was performed for the HPV-other samples of 209 patients who subsequently underwent cervical biopsy.
RESULTS
For 204 of the 209 samples, the HPV types detected by sequencing were absent types at used HPV DNA chip. For the remaining 5 samples, sequencing was impossible due to mixed peaks. HPV-81 (19.6%), HPV-61 (18.6%), HPV-62 (16.7%) and HPV-84 (13.9%) were frequently detected. For the HPV-81, -62, -71, and -72 samples, most of the samples displayed normal or LSIL. However, HPV-84 and -61 were more associated with HSIL or worse, as compared to the other types.
Conclusion
HPV-81, -61, -62 and -84 were frequently found on sequencing analysis of the HPV-other samples. The pathologic status was diverse, according to the HPV type detected on sequencing. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in microbial composition and interaction patterns of female urogenital tract and rectum in response to HPV infection
Yong-Hong Dong, Yu-Hua Luo, Chen-Jian Liu, Wen-Yu Huang, Lin Feng, Xing-Yuan Zou, Jin-Yan Zhou, Xiao-Ran Li
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Dysplasia, Infection, and Phylogeny of Human Papillomavirus in HIV‐Infected and HIV‐Uninfected Women at a Reproductive Health Clinic in Nairobi, Kenya
Agnes Omire, Nancy L. M. Budambula, Leah Kirumbi, Hillary Langat, Danvas Kerosi, Washingtone Ochieng, Raphael Lwembe, Jorge F. Quarleri
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular characterisation of genital human papillomavirus among women in Southwestern, Nigeria
Yewande T. Nejo, David O. Olaleye, Georgina N. Odaibo, Jason Blackard
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(11): e0224748. CrossRef - Sequencing analysis of HPV-other type on an HPV DNA chip
Min-Jeong Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Sunmie Kim
Obstetrics & Gynecology Science.2018; 61(2): 235. CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology and genotype distribution of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) among Arab women in the state of Qatar
Devendra Bansal, Asha A Elmi, Sini Skariah, Pascale Haddad, Laith J Abu-Raddad, Aysha H Al Hamadi, Nady Mohamed-Nady, Nahla M Affifi, Randa Ghedira, Elham Hassen, Asma AJ Al-Thani, Afaf AHM Al-Ansari, Ali A Sultan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV Prevalence and Detection of Rare HPV Genotypes in Hong Kong Women from Southern China with Cytological Abnormalities
Ngai Na Chloe Co, Lai-On Chu, Joseph K. F. Chow, Joseph W. O. Tam, Enders K. O. Ng
ISRN Virology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Type-specific prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus by cervical cytology and age: Data from the health check-ups of 7,014 Korean women
Min-Jeong Kim, Jin Ju Kim, Sunmie Kim
Obstetrics & Gynecology Science.2013; 56(2): 110. CrossRef
- Changes in microbial composition and interaction patterns of female urogenital tract and rectum in response to HPV infection
- The Relationship between the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Genotypes and the Methylation Status of the CpG Island Loci, LINE-1 and Alu in Prostate Adenocarcinoma.
- Jung Ho Kim, Nam Yun Cho, Baek Hee Kim, Wook Youn Kim, Bo Sung Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(1):26-35.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.1.26
- 4,747 View
- 34 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Genetic polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), in association with the influence of MTHFR upon DNA methylation, may cause differences of the methylation profile of cancer. Thus, we investigated the relationship between the methylation status of prostate adenocarcinoma and the genetic polymorphism of MTHFR.
METHODS
We examined 179 cases of prostate adenocarcinoma for determining the genotypes of MTHFR 677 and 1298, the methylation status of 16 CpG island loci and the methylation levels of the LINE-1 and Alu repeats with using polymerase chain reaction/restriction fragment length polymorphism, methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and combined bisulphite restriction analysis, respectively.
RESULTS
There was a higher proportion of the CT genotype of MTHFR 677 in the prostate adenocarcinoma than that in the normal control. The TT genotype of MTHFR 677 showed the highest frequency of methylation in six out of nine major CpG island loci, and these were which were frequently hypermethylated in prostate adenocarcinoma. The CT type showed the lowest methylation levels of LINE-1 and Alu among the MTHFR 677 genotypes. Interestingly, the CC type of MTHFR 1298 demonstrated favorable prognostic factors.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study is the first to examine the methylation profile of prostate adenocarcinoma according to the MTHFR genotypes. The differences of the cancer risk, the genomic hypomethylation and the prognosis between the MTHFR genotypes in prostate adenocarcinoma should be further explored. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between MTHFR 1298A>C Polymorphism and Spontaneous Abortion with Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy
Shin Young Kim, So Yeon Park, Ji Won Choi, Do Jin Kim, Shin Yeong Lee, Ji Hyae Lim, Jung Yeol Han, Hyun Mee Ryu, Min Hyoung Kim
American Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2011; 66(4): 252. CrossRef - Distinctive patterns of age-dependent hypomethylation in interspersed repetitive sequences
Pornrutsami Jintaridth, Apiwat Mutirangura
Physiological Genomics.2010; 41(2): 194. CrossRef
- Association Between MTHFR 1298A>C Polymorphism and Spontaneous Abortion with Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy
- Comparison of Clinical Efficacy between an HPV DNA Chip and a Hybrid-Capture II Assay in a Patient with Abnormal Colposcopic Findings.
- Tae Jung Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Ahwon Lee, Eun Sun Jung, Young Jin Choi, Kyo Young Lee, Jong Sup Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2008;19(2):119-125.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3338/kjc.2008.19.2.119
- 3,213 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study was performed to compare the efficacy between a DNA chip method and a Hybrid-Capture II assay (HC-II) for detecting human papillomavirus in patients with intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix. From May, 2005, to June, 2006, 192 patients with abnormal colposcopic findings received cervical cytology, HC-II and HPV DNA chip tests, and colposcopic biopsy or conization. We compared the results of HC-II and HPV DNA chip in conjunction with liquid based cervical cytology (LBCC) and confirmed the results of biopsy or conization. The sensitivity of the HPV DNA chip test was higher than HC-II or LBCC. The HPV DNA chip in conjunction with LBCC showed higher sensitivity than any single method and higher sensitivity than HC-II with LBCC. We confirmed that the HPV DNA chip test was more sensitive for detecting HPV in cervical lesions than HC-II, and that it would provide more useful clinical information about HPV type and its multiple infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Analytical and Clinical Performance of HPV 9G DNA Chip, PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip, and Hybrid-Capture II Assay in Cervicovaginal Swabs
Ho Young Jung, Hye Seung Han, Hyo Bin Kim, Seo Young Oh, Sun-Joo Lee, Wook Youn Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(2): 138. CrossRef
- Comparison of Analytical and Clinical Performance of HPV 9G DNA Chip, PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip, and Hybrid-Capture II Assay in Cervicovaginal Swabs
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus DNA 16/18 in Cervical Adenocarcinomas by Polymerase Chain Reaction.
- Sang Sook Lee, Nam Jo Park, Chong Guk Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(4):502-510.
- 2,395 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty-five paraffin-embedded tumor tissues were analyzed for detection of HPV 16 and 18 in cervical adenocarcinoma by polymerase chain reaction with type specific primers and by non-radioactive Southern blot hybridization for confirmation . The suitability of paraffin-embedded tissue as PCR material was confirmed by successful amplification of 100% of cervical specimens with human -globin specific primer. Eighty four percent of the cervical adenocarcinoma tissues were positive for HPV 16 and/or 18. HPV 16 positive rate was 68%, HPV 18 was 60%. The double infection with HPV 16 and 18 was found in 44%. Three cases of the negative specimen in PCR for each type of HPV DNA 16 and 18 were positive in Southern blot hybridization. The total positive rate was 92% for HPV 16 and/or HPV 18, HPV 16 positive rate was 80%. HPV 18 was 72%. The double infection with HPV 16 and 18 was 60%. These results suggest that the pattern of HPV types 16 and 18 is closely associated with carcinogenesis of cervical cancers. HPV type 18 appears to be preferentially related to cervical adenocarcinoma and the poor prognosis of these patients. Therefore, determination of HPV DNA type in cervical carcinoma patients is important in treatment and prognosis.
- Pathologic Characteristics of Colorectal Cancers with DNA Replication Errors.
- Hoguen Kim, Yoon Mi Jeen, Jeong Yeon Shim, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):590-595.
- 1,873 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Unstable microsatellite repeat sequences or DNA replication errors(RER) due to defective mismatch repair genes have been reported in a subset of sporadic colorectal tumors and in most tumors of patients of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma(HNPCC). To elucidate the clinicopathological correlation of these RER-positive cancers, we examined 16 cases of colorectal carcinoma of different histologic subtypes(6 cases of carcinoma with no gland formation, 5 cases of mucinous carcinoma and 5 cases of gland forming carcinoma). We detected RER in five cases. The patients with RER-positive cancers had a marked preponderance of carcinoma with no gland formations out of 6 carcinomas with no gland formation were RER-positive cancers) and of cancers proximal to splenic flexure(all of the RER-positive cases were proximal colon carcinomas). We conclude that RER-positive cancers have wiique pathologic features that may be useful for the screening and counselling of patients with hereditary colon cancers.
- Detection of HBV DNA in Needle Biopsied Paraffin Embedded Liver Tissues of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients by PCR: Comparison with Serological and Immunohistochemical Studies.
- Hye Soo Lee, Kahng Yeul Oh, Joo Heon Kim, Yoon Jeong Kim, Sam Im Choi, Dong Geun Lee, Sang Ho Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(6):495-504.
- 2,062 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the prevalence of Hepatitis B virus(HBV) DNA in the needle biopsied paraffin embedded liver tissues of chronic hepatitis B patients by rapid nested PCR was examined. DNA was extracted by NaOH with boiling, and amplified by rapid air thermocycler with glass capillary tubes and nested PCR with two primer sets specific for the surface and the core genes of HBV. The PCR results were compared to that of serum HBeAg, serum HBV DNA by dot blot hybridization with a radioactive DNA probe, and tissue immunohistochemical (HBsAg/ HBcAg) studies. Among 44 patients with chronic hepatitis with serum HBsAg positivity, HBV DNA could be detected by PCR in 43 liver tissues (98%). This results were comparable to the positive rates of 94%(31/33) for serum HBV DNA, 80%(35/44) for serum HBeAg, and 59%(26/44) and 75%(33/44) for tissue HBsAg and HBcAg, respectively. The accordance rate between tissue PCR and serum DNA probe testing was 91%. The results indicate that HBV DNA detection by rapid nested PCR of paraffin embedded liver tissues by needle biopsy is a more sensitive method to detect the HBV DNA carrier than the serum HBeAg or tissue HBsAg/HBcAg status, and is well correlated with the result of serum HBV DNA probe testing. Therefore this method is a practical indicator for the diagnosis and replication status in retrospective analysis.
- The Study of p53 Expression and DNA Ploidy in Colorectal Carcinoma.
- Ji Shin Lee, Kwang Soo Cheon, Chang Soo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(9):775-783.
- 1,971 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mutation of the p53 gene frequently results in overexpression of the p53 protein and loss of its tumor-suppressing properties. The overexpression of the p53 gene could be an indicator of rapid proliferation, poor differentiation, advanced stages, or poor prognosis. The prognostic value of the overexpression of the p53 gene in colorectal carcinoma is equivocal. The presence of DNA aneuploidy has been described as a powerful adverse prognostic indicator in relation to survival. To investigate the prognostic significance of p53 expression, and the relationship with DNA ploidy, 92 cases of colorectal carcinomas were analyzed. The overexpression of p53 gene product was present in 50(54.4%) of 92 cases. p53 expression only correlated with recurrence or metastasis during the follow-up periods (p=0.045). DNA aneuploidy was observed in 32(39.1%) of 82 cases. DNA ploidy was strongly associated with lymph node invasion(p=0.005), Dukes' stage(p=0.003), TNM classification (p=0.003), and recurrence or metastasis during the follow-up periods (p=0.045). The frequency of DNA aneuploidy was higher in the p53-positive colorectal carcinomas(58.3%) than in the p53-negative colorectal carcinomas (21.6%) (p=0.003). p53-positive colorectal carcinomas had a higher rate of cell proliferation than p53-negative cases(p<0.001). These results suggest that checking the p53 expression and DNA ploidy could be useful prognostic indicators of colorectal carcinoma.
- Flow Cytometric DNA Analysis in Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid Gland: comparison with Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining.
- Mee Joo, Hye Je Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(11):959-965.
- 1,944 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nuclear DNA content was measured using a flow cytometric method to analyze 36 paraffin- embedded and 7 fresh tissues of 43 papillary carcinomas of thyroid gland. DNA aneuploidy was found in 3 cases(6.9%) and diploidy in 40 cases(93.1%). But there were no suggestive findings in clinical history, and cytological and morphological features for aneuploidy. In 40 diploid cases, S-phase fraction(SPF) were analyzed with regard to sex, age, tumor size, presence or absence of capsular invasion, lymph node involvement and ground glass nuclei. Among the multiple factors, only the tumor size, especially the larger sized-group(above 2cm in tumor diameter) was found to have a statistically significant higher SPF than the smaller sized-group (p<0.05). And high SPF groups relatively well corresponded to the high risk group. Thirty nine cases of papillary carcinoma have also been evaluated for proliferative activity with Ki-67 monoclonal antibody. The average Ki-67 labeling index was 0.36% in total cases, and that of the aneuploid cases was 0.73%, which was higher than that of the diploid cases(0.33%). So. We think that the low aneuploid rate and low Ki-67 labeling index relatively well represent the usual good clinical course of this tumor and the high SPF is a suggestive finding for a high risk group.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with its Correlation to p53 mutation.
- Wan Seop Kim, Eun Kyung Hong, In Kyu Kim, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(11):1018-1026.
- 1,827 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - HPV infection has been implicated strongly in the pathogenesis of human squamous cell carcinoma(SCC). We analysed a series of 28 surgically removed, invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus by polymerase chain reaction to detect HPV DNA using consensus primers and 8 type-specific primers of HPV (6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 51). HPV 6, 31, 35 or 51 DNA were detected in 20 out of 28 cases (71.4%) of the esophageal SCCs. HPV 51 was the most frequently detected type, occuring in 13 out of 28 cases (46.4%). p53 immunohistochemical staining was also performed to demonstrate any relationship to HPV DNA positivity. It showed positivity in 16 out of 28(57.1%) esophageal SCCs, and HPV DNA and p53 positivity were concurrently detected in 11 out of 28 cases of SCCs. There was no significant inverse relation between HPV DNA positivity and p53 expression(p>0.05). Our results supported HPV involvement in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and suggested there may be another pathway not related to the p53-binding pathway in the carcinogenesis of esophageal SCCs by HPV.
- The p53 Mutation and DNA Ploidy in Human Metastatic Breast Cancer.
- Seong Jin Cho, Ae Ree Kim, Nam Hee Won
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(2):135-144.
- 2,024 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The p53 gene, one of the tumor suppressor genes, is believed to play an important role through mutation and overexpression in the progression of various human malignant tumors. To compare the p53 mutation status between the primary and metastatic lesions of breast cancers and to investigate the mutational pattern of p53, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and polymerase chain reaction and single strand conformational polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) were performed in 25 cases of breast cancers with paraffin embedded tissue. Mutant protein products or point mutation were detected through IHC or PCR-SSCP method. And flow cytometrical (FCM) analysis were performed in the same paraffin blocks to correlate the DNA ploidy and p53 mutation. The following results are summarized. 1. The detection of the p53 gene mutation and overexpression of the p53 protein were measured in 40% and 48%, respectively, in 25 primary tumors, either or both methods was detected in 64%. 2. A concordance rate of the p53 protein expression between the primary and metastatic lesions of 25 breast cancers was 100%, but the concordance rate of the p53 gene mutation was 72%. 3. The correlation between the p53 mutation and the DNA aneuploidy was not statistically significant (p=0.38) 4. A p53 mutation by IHC or PCR-SSCP was more frequently detected in grade III breast cancers than in grade I or II. 5. Among 5 to 9 exons of the p53 gene, exon 7 was the most frequent mutation spot in this study. 6. Additional mutation of the p53 gene was developed in the three metastatic lesions. With the above results it is suggested that the p53 protein overexpression by immunohistochemistry is not correlated with the p53 mutation by PCR-SSCP. The p53 mutation pattern between the primary and metastatic lesions are not idenitical and an additional point mutation can occur in the metastatic lesion. The DNA aneuploidy is more frequently detected in the cases with the p53 protein overexpression than in the p53 protein negative, but it is not statistically significant.
- E-Cadherin Expression and DNA Ploidy Analysis in Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix Comparison with those of CIN.
- Yoo Jin Kim, Mee Young Sol, Man Ha Huh, Sun Kyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(6):557-565.
- 1,974 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) is a Ca2+ -dependent cell-cell adhesion molecule that connects cells via homotypic interactions. Its function is critical in the induction and maintenance of cell polarity and differentiation, and its loss is associated with an invasive and poorly differentiated phenotype in a wide range of tumors. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections from 36 cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and 14 cervical squamous cell carcinomas were investigated for the expression of E-cadherin immunohistochemically. While E-cadherin expression was usually restricted on the cell membrane of basal and parabasal cells in normal cervix, the presence of cytoplasmic E-cadherin was found to be associated with its grade in CIN lesions. Also, marked cytoplasmic staining was commonly revealed in poorly differentiated ones than well-differentiated squamous cell carcinomas. More intense reactivity of cytoplasmic E-cadherin was frequently seen in the foci of invasion than adjacent carcinoma in situ, and in its periphery than the center of tumor islands. In addition, DNA ploidy and S-phase fraction of squamous cell carcinomas were analyzed and compared with those of CIN lesion. We found that invasive squamous cell carcinomas more frequently disclosed DNA aneuploidy than CIN lesions, and there was correlation between cytoplasmic E-cadherin expression and DNA aneuploidy. Also, cytoplasmic E-cadherin-reactive cervical neoplasms had a higher rate of cell proliferation than that of membranous E-cadherin-reactive cases. These data suggest that the increased cytoplasmic E-cadherin expression may represent one of the abnormalities underlying the loss of polarity and invasiveness of cancer cells, and the abnormal E-cadherin expression combined with/without DNA ploidy or S-phase fraction may serve as a prognostic indicator.
- Flow Cytometric DNA Analysis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors .
- Mee Yon Cho, Soon Won Hong, Soon Hee Jung, Hogeun Kim, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):608-616.
- 2,060 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To evaluate the correlation between the histologic grade and DNA ploidy or proliferation index/S phase fraction (SPF) of gastrointestinal stromal tumors, we performed the DNA analysis using the flow cytometry. Paraffin embedded tissue samples of 57 gastrointestinal stromal tumors were used. The sites of the tumors were: stomach (28), small intestine (23), and large intestine(6). DNA index, proliferative index, and SPF by the flow cytomery were compared with histologic grade. The histologic grade of the gastric tumors were benign (12), borderline (10), and malignant (6). Those of the small intestinal timors were benign (2), borderline (13), and malignant(8). The large intestine were borderline (2), and malignant (4). In stomach, aneuploidy was found in 25.0% of benign, 40.0% of borderline, and 100% of malignant. And there was statistically significant correlation between the histologic grade and ploidy (p < 0.05). By contrast, small and large intestinal tumors showed more frequent aneuploidy in benign than in malignant. The proliferative index was correlated with the histologic grade in gastric tumors (p<0.05), but the SPF was not. In conclusion, the ploidy and proliferative index of gastric tumors are closely correlated to the histologic grade. However, aneuploidy in tumors of the small and large intestine were difficult to predict the malignancy.
- A Study on the Expression of p53 Oncogene Products, PCNA Index and DNA Ploidy in Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Jong Jae Jung, Ji Shin Lee, Chan Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):672-682.
- 1,911 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mutant p53 is associated with the advanced stages of some human tumor but there is a wide variation in the reported incidence of p53 mutation in renal cell carcinoma and its prognostic significances. We designed this study to assess the expression of p53 in renal cell carcinomas and to compare with the established prognostic factors. Immunoreactivity for p53 protein and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were assessed in 44 cases of primary renal cell carcinoma, and flow cytometric analysis of DNA ploidy was perfon-ned in 37 of those cases. p53 protein was over-expressed in 16/44 (36.4%) renal cell carcinomas and 5 rumors had more than 10 immunoreactive tumor cells. The expression of p53 protein was positively related to nuclear grade (p=0.007) and PCNA index (p=0.002), but was independent of stage and DNA ploidy. In univariate survival analysis, stage (p<0.001), nuclear grade (p=0.017), DNA ploidy (p=0.045) and PCNA index (p<0.001) were significantly associated with patient survival. However, considering the stage, all of the last three factors had no prognostic influence. Cases showing strong positivity of p53 expression had worse prognosis than those with no or weak p53 expression, especially in early lesions (stage I,II) (p<0.001).
- Correlation between p53 Immunohistochemical Expression, DNA Ploidy and Ki-67 Expression in Gastric Carcinoma.
- Young Lyun Oh, Joung Ho Han, Young Hyeh Ko, Cheol Keun Park, Hwoe J Ree
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(12):1264-1271.
- 2,302 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We examined the p53 protein overexpression and evaluated its correlation with pathobiological variables, including: (1) patient age, sex, tumor size, histological type and grade, invasion depth, vascular invasion, perineural invasion and lymph node status; (2) the Ki-67 labeling index in 100 gastric carcinomas; and (3) the DNA ploidy pattern, S phase fraction (SPF), and the proliferation index (PI) in 84 cases using flow cytometry. The positive rate of p53 staining was 48% and the p53 immunoreactivity was independent of variable clinicopathologic factors. No correlation was made between the Ki-67 labeling index with p53 immunostaining and DNA ploidy parameters. Aneuploidy rate was slightly higher in the p53 positive group (55.6%) than the p53 negative group (44.4%)(p=0.097). The mean values of SPF and PI were significantly higher in the p53 protein positive group. Aneuploidy was more often observed in the intestinal type (p=0.038), advanced gastric carcinoma (p=0.015) and lymph node positive group(p=0.039). The above results suggest that although the p53 protein overexpression has no significant correlation with pathological factors and the Ki-67 labeling index, it may play an important role in tumor cell proliferation. Since p53 protein overexpression was slightly higher in the aneuploidy group showing significant correlation with poor prognostic parameters, it is thought that re-evaluation of the p53 mutation by molecular biological study is needed.
- The Role of gadd and p53 Genes in Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Delay by Genotoxic Agents.
- Jung Young Lee, Jung Duk Lee, Seung Myung Dong, Eun Young Na, Min Sun Shin, Su Young Kim, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(4):239-247.
- 2,281 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aim of this study was to investigate the relationships between the gadd genes expression and an apoptosis induction in two different growing cell types after treatments with cisplatin and methylmethan sulfonate (MMS). We have examined the kinetics and specificity of gadd45 and gadd153 expression following cisplatin and MMS treatments to HL-60 cells and primary cultured human kidney (HKN) cells. We have also determined an induction time of apoptosis by DNA fragmentation analysis and the presence of the cell cycle arrest by a flow cytometric measurement. The results were as follows. In non-adherent HL-60 cells, a typical ladder pattern was observed within 4 hours after treatments of 20 micrometer of cisplatin and 100 microgram/ml of MMS. At the same time while adherent HKN cells failed to exhibit a ladder pattern at even higher doses of genotoxic agents. Since HL-60 cells do not have p53 gene, these findings suggest the presence of a p53-independent apoptotic pathway. The increasing patterns of the mRNA levels of gadd45 and gadd153 varied with the type of genotoxic agents. In the case of MMS treatment, the induction was rapid and transient, regardless of the cell types. The mRNA level peaked at 4 hours after MMS treatment and markedly decreased after 12 hours. On the other hand, cisplatin-induced transcriptions of gadd45 and gadd153 continued to increase for at least 24 hours and reached a peak level at 48 hours after cisplatin treatment, regardless of the cell types. HL-60 cells revealed G2 arrest following 24 hours after cisplatin and MMS treatments. These findings suggest that the regulation mechanism of apoptosis between adherent and non-adherent cells, might be different and that gadd45 and gadd153 might have an important role in DNA repair rather than apoptosis. Also, the findings suggest that an expression pattern of gadd45 and gadd153 might be different according to the type of genotoxic agents.
- Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes Using RNA Fingerprinting in Cell after DNA Damage.
- Jung Young Lee, Min Sun Shin, Seung Myung Dong, Eun Young Na, Su Young Kim, Sug Hyung Lee, Won Sang Park, Nam Jin Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(5):321-327.
- 1,917 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- RNA fingerprinting using on arbitrary primed polymerase chain reaction (RAP-PCR) was carried out to identify differentially expressed genes in HL-60 cell after treatment of methylmethane sulfonate (MMS). Twenty differentially expressed PCR products were cloned and analyzed. We have successfully obtained eight partial cDNA sequences by TA cloning method. Among these, six cDNAs were up-regulated and two cDNAs were down-regulated after the MMS treatment. Of these six up-regulated cDNAs, 3 cDNAs were equivalent to known genes in the GenBank/EMBL databases with 98~100% homology searched by BLAST program: genomic DNA fragment containing CpGg island (clone 26h8), Human Rev interacting protein-1 (RIP-1), and human zinc finger protein-4 (HZF4). The sequences of the three remaining cDNA were entirely new genes, but we didn't try to identify a full cDNA sequence. Two clones called KIAA0060 and KIAA0065, were down-regulated in HL-60 cells after the MMS treatment. These findings suggest that the RNA fingerprinting method using RAP-PCR is an effective method which can identify and separate the differentially expressed cDNAs and that the isolated cDNAs might involve in regulation mechanism of apoptosis and/or cell cycle delay, especially a p53-independent pathway, in the cells after DNA damage. But the nature of cDNAs that we have isolated remains to be elucidated.
- DNA Sequencing of p53 Gene Mutation in Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Young Ran Shim, Joon Hyuk Choi, Won Hee Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(6):422-433.
- 2,267 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mutations in the p53 gene occur during the development of colorectal carcinomas, and play an important role in the conversion of adenoma into carcinoma. To detect the p53 gene mutation and its pattern of expression in colorectal carcinomas, polymerase chain reaction for exons 5, 6, 7, and 8, recombinant gene cloning, and automated DNA sequencing were performed with 30 fresh colorectal carcinomas. Each tissue was also analyzed by immunohistochemical staining for p53 protein. p53 protein was detected in 25 of 30 (83.3%) colorectal carcinomas by immunohistochemical study. p53 mutation was detected in 4 of 30 (13.3%) colorectal carcinomas. The distribution of these mutations among these exons investigated was as follows: Three mutations in exon 5 (66.7%) and 1 mutation in exon 7 (33.3%). One case with mutation in exon 5 had mutations at three different codons. Mutations in exon 5 were found at codon 153 (GGG to AGG: Gly to Arg), 170 (TGC to GGC: Cys to Gly), 186 (CTA to TTA: silent mutation), 158 (GCG to ACG: Ala to Thr), and 176 (ACG to ATG: Thr to Met). Mutation in exon 7 was found at codon 248 (AGG to AGA: silent mutation). Four of them were missense mutations. Two of 6 mutations were silent mutations. Five transition mutations and 1 transversion mutation were also detected. All cases with mutations by automated DNA sequencing showed positive p53 protein immunohistochemical stainining. In conclusion, p53 gene mutation was detected in 4 of 30 (13.3%) colorectal carcinomas, located in codon 153, 158, 170, 176, and 186 of exon 5 and codon 248 of exon 7. Further studies are needed to evaluate the significance of the codon 153 mutation which was not recognized in other studies on colorectal carcinomas.
- DNA Ploidy Analysis as a Prognostic Indicator in Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast.
- Hee Jung Kim, Jae Ho Han, Woo Hee Jung, Hy De Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(7):507-516.
- 2,204 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - DNA ploidy analysis using flow cytometry was performed on sixty six cases of phyllodes tumor of the breast including benign, low grade and high grade malignant phyllodes tumor. The rate of aneuploidy was 41.2% in high grade malignant phyllodes tumor and 4.8% in benign phyllodes tumor. No aneuploidy was noted in low grade malignant phyllodes tumor. The recurrence rate according to DNA ploidy pattern revealed 16.7% of aneuploidy and 7.7% of diploidy. In the aneuploid cases, the DNA index of high grade malignant phyllodes tumor was higher than benign phyllodes tumor. Morever, in diploid cases, %SG2M were significantly higher in high grade malignant phyllodes tumor. Therefore, we conclude that DNA ploidy analysis as well as histologic characteristics such as cellularity, pleomorphism of stromal cells and mitoses is useful parameters in the diagnosis, recurrence and prognostic predictors of phyllodes tumor.
- Expression of Biologic Markers and DNA Ploidy Analysis in Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast.
- Hee Jung Kim, Woo Hee Jung, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Hy De Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(11):1076-1089.
- 2,026 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Status of margins and the size of the lesion are independent prognostic factors of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Histologic grading of DCIS and expression of biologic marker also appear to act as prognostic factors. However, DNA ploidy analysis using flow cytometry in the DCIS and atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) has been rarely reported, and the biologic behavior of ADH is unknown. We performed immunohistochemical staining and DNA ploidy analysis using flow cytometry on 45 cases of pure DCIS without microinvasion and 34 cases of ADH to compare the expression of biologic markers and DNA ploidy patterns according to the histologic grade of DCIS, to evaluate the usefulness of the Van Nuys classification, and to investigate the biologic behavior of ADH and low grade DCIS. A total of 41.9% of DCIS and 32.1% of ADH were detected mammographically in asymptomatic patients. The most common subtype of the high grade DCIS was comedo type (56.3%), while the low and intermediate grade DCIS were cribriform type. Expression of ER, c-erbB-2 and Ki-67 proliferative index (PI) was significantly associated with nuclear grade and histologic grade of DCIS. Expression of c-erbB-2 was also significantly correlated with presence of necrosis. In low grade DCIS, Ki-67 PI was significantly higher than ADH. A total of 63.6% of DCIS and 70% of ADH were diploidy and 15.9% of DCIS was aneuploidy. There was no aneuploidy in ADH. No significant association was noted between DNA ploidy and histologic grade or nuclear grade. However, in high grade DCIS, the frequency of aneuploidy was high. In conclusion, histologic grading of DCIS employing nuclear grade and necrosis is a useful tool accounting for biologic behavior. High grade DCIS and comedo DCIS impart aggressive biologic behavior and suggest a higher possibility of local recurrence or progression to invasive carcinoma. In the differential diagnosis of ADH and low grade DCIS, the use of Ki-67 PI and DNA ploidy analysis by flow cytometry will be helpful for accurate diagnosis and prediction of biologic behavior.
- Expression Pattern of DNA Mismatch Repair Genes in Tumors of Microsatellite Mutator Phenotype.
- Jung Jin Kim, Myung Jin Baek, Nam Gyun Kim, Yun Hee Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Hoguen Kim, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(9):609-614.
- 2,036 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Microsatellite mutator phenotype (MMP) tumors were reported in a subset of gastrointestinal carcinomas. The molecular pathogenesis of MMP tumors shows defects in the DNA mismatch repair genes, and also many germline and somatic mutations were reported in the MMP tumors. However, the detection of genetic defects in the MMP tumors is very difficult, mainly because many genes are included in the DNA mismatch repair genes. This study was undertaken to determine the best strategy for detecting defects in the DNA mismatch repair genes in gastrointestinal carcinomas. One of the effective ways for detecting defects in DNA mismatch repair genes is to screen the MMP tumors and evaluate the products of DNA mismatch repair genes by performing the multiplex RT-PCR method. We have screened the MMP tumors by using 5 microsatellite markers in the 12 cancer cell lines, 120 colon carcinomas and 99 gastric carcinomas and found 6 MMP cell lines, 10 MMP colon cancers, and 9 MMP gastric carcinomas. In addition, we evaluated 6 DNA mismatch repair gene products (hMSH2, hMSH3, hMSH6, hMLH1, hPMS1 and hPMS2) by multiplex RT-PCR analysis and found decreased expression of the DNA mismatch repair genes in 5 (hMSH6 in DLD-1 and HCT-15; hMSH2 in LoVo; hMLH1 and hMSH3 in HCT-116; hMLH1 in SNU-638) out of 6 MMP cell lines. We also found a decreased expression of hMLH1 in 3 out of 10 MMP colon carcinomas, and in 6 out of 9 MMP gastric carcinomas. Our results indicate that the expression analysis of the DNA mismatch repair genes by multiplex RT-PCR method can reduce the number of genes subjected to mutational analysis and is convenient for screening the responsible DNA mismatch repair genes.
- Methylotion Analysis of p16/INK4A in Gastric Low-Grade Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphomas after Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy.
- Young A Kim, Sung Shin Park, Bo Young Lee, You Sun Kim, In Sung Song, Chul Woo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(1):13-20.
- 1,931 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Inactivation of p16 has been associated with promoter region hypermethylation in different types of malignancies, including non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHLs). This loss of p16 was found frequently in cases of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas. Recent studies indicate that promoter hypermethylation is often an early event in tumor progression in the follow-up of NHLs.
METHODS
To investigate the usefulness of p16 methylation in the diagnosis and follow-up of gastric low-grade MALT lymphomas, we analyzed methylation status of p16 using methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction methods in the sequential biopsy specimens of 13 patients with gastric low-grade MALT lymphomas undergoing Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy.
RESULTS
Five of thriteen cases showed p16 hypermethylation upon diagnosis. In four of five methylation positive cases, abnormal methylation was detected in the specimen even after the treatment, although there were no histologic evidence of disease. This methylation disappeared in the later samples of two of the cases, and they have remained in complete remission. Immunohistochemically, the loss of p16 protein expression was detected in one of three methylation-positive cases, and in none of the methylation-negative cases.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that p16 methylation is relatively fequent in low-grade gastric MALT lymphomas, and it may have clinical applications in the management and follow-up of low-grade gastric MALT lymphomas.
- Inactivation Pattern of p16 Gene in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas.
- Hyun Deuk Cho, In Sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(6):365-373.
- 2,036 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and mutation of the p16 tumor suppressor gene have been detected in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHLs). Recently, hypermethylation of the p16 gene has been reported. The role of p16 gene alterations in the genesis of NHLs and their high-grade transformations require explanation.
METHODS
LOH of D9S171 and IFNA microsatellite markers, DNA hypermethylation, and mutation of exon 1 and 2A were assessed in 43 cases of NHLs. The genetic abnormalities were compared with the protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and they were evaluated according to the histologic subtypes, grades and immunophenotypes.
RESULTS
DNA hypermethylation was the most common p16 gene abnormality and was found in 30 of 39 cases (76.9%). Eight cases (18.6%) showed LOH in one or both microsatellite markers, and five cases (11.6%) showed mutations in exon 1 or 2A. Loss of protein expression was seen in 17 cases (39.5%) and was associated with mutation and LOH. Loss of protein was more frequent in high-grade lymphomas than in low-grade lymphomas.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that the functional loss of the p16 gene contributes to the development of NHLs, especially to the development of high-grade lymphomas.
- HER-2/neu Oncogene Amplification by Chromogenic in situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemical Expression of Topoisomerase II-alpha in the Breast Cancer.
- Tae Jin Lee, Hyung Goon Oh, Gui Young Kwon, Mi Kyung Kim, Eon Sub Park, Jae Hyung Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(1):26-34.
- 1,979 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Amplifications of the HER-2/neu oncogene and the Topoisomerase II-alpha gene are important determiners of the response to chemotherapy in the breast cancer. For detecting HER-2/neu amplification, fluorescent in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry are currently regarded as standard methods. Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) is investigated as a new modification of in situ hybridization. The purpose of this study is to compare the efficacy of CISH and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in detecting HER-2/neu oncogene amplification and to investigate the prognostic significance of the HER-2/neu oncogene and the Topoisomerase II-alpha gene in breast cancer.
METHODS
Using CISH and IHC the amplifications and protein expressions of the HER-2/neu oncogene were studied on paraffin sections of 43 infiltrating duct carcinomas. The expression of the Topoisomerase II-alpha gene was studied immunohistochemically.
RESULTS
Of the 43 infiltrating duct carcinomas, amplifications of the HER-2/neu oncogene by CISH were observed in 8 cases (18.6%), and the HER-2/neu protein was deemed overexpressed by IHC in 9 cases (20.9%). The amplifications of the HER-2/neu oncogene showed a statistically significant correlation with tumor size, histological grade, and the Topoisomerase II-alpha index. The Topoisomerase II-alpha index showed a statistically significant correlation with tumor size, lymph node status, stage, histologic grade, and estrogen receptor status.
CONCLUSIONS
CISH is a useful alternative for determining HER-2/neu amplification, especially for confirming the immunohistochemical staining results. HER-2/neu amplification and the Topoisomerase II-alpha gene index may be prognostic factors of breast cancer.

 E-submission
E-submission



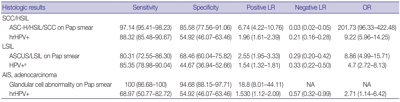
 First
First Prev
Prev



