Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Spectrum of thyroiditis types: clinical, cytomorphological, and radiological findings
- Anam Singh, Indrajeet Kundu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):421-433. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.13
- 2,250 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
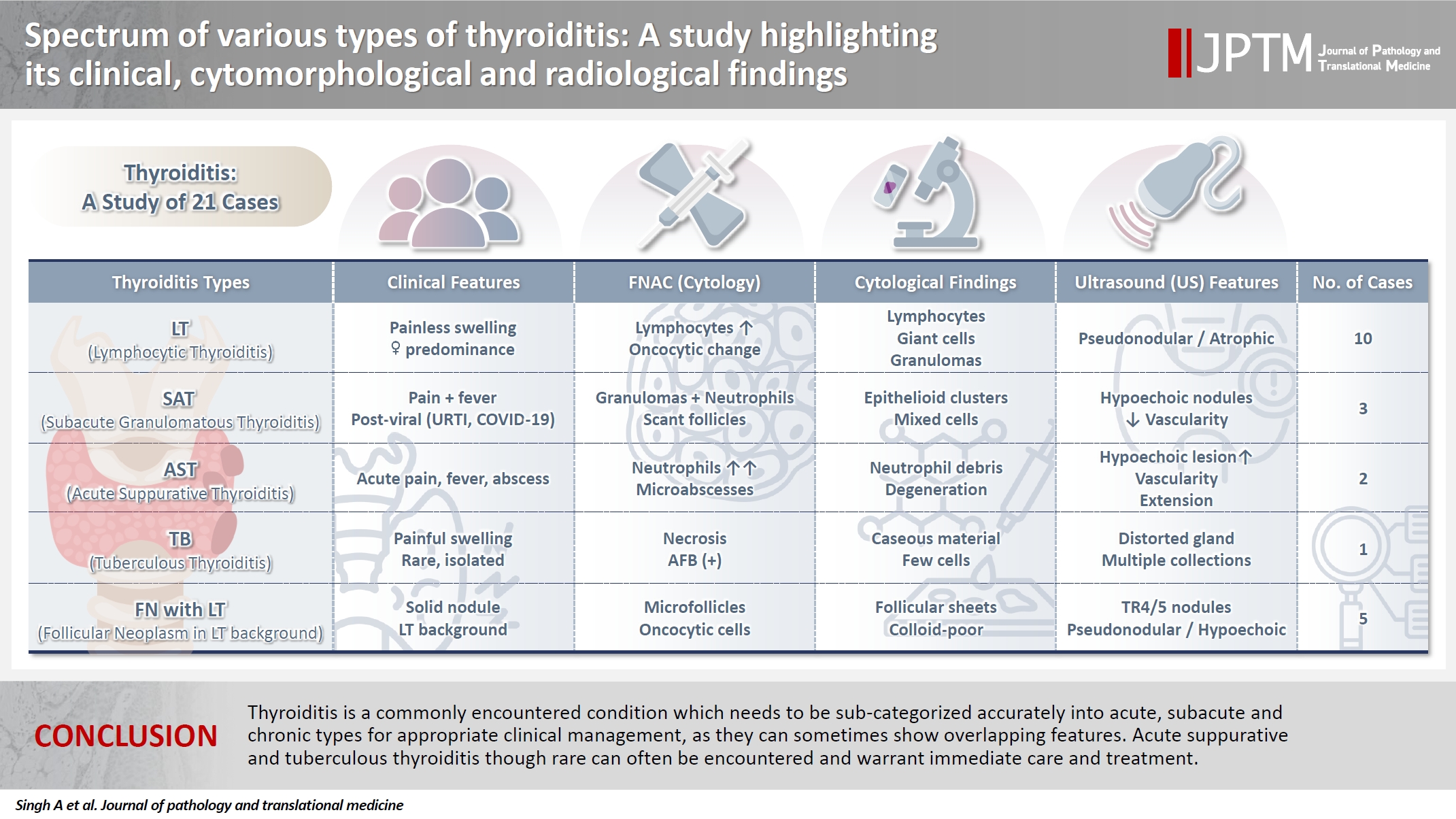
Thyroiditis encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions affecting the thyroid gland. Lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT) is a common form of thyroiditis, with acute suppuration of the thyroid, while tuberculous thyroiditis is relatively rare. Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) remains a safe and cost-effective tool for diagnosing thyroid-related diseases, especially when paired with ultrasound (US) and clinical examination. Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 21 cases. The cases were reported as thyroiditis on US and FNAC, and the findings were correlated with patient clinical history, symptoms during presentation, and serological profiles. Results: The cases of thyroiditis encompassed the more common forms, LT and subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), as well as relatively rare forms like tuberculous thyroiditis and thyroid abscess. Cases of follicular neoplasms (FN) arising in the context of LT also are included in this study. The case of tuberculous thyroiditis presented as a bulky thyroid gland that appeared heterogeneous on US with extensive necrosis on FNAC. The cases of thyroid abscess and SAT presented with painful neck swellings, with granulomas in the latter cases. US features of LT showed an array of appearances ranging from pseudonodular to an atrophic thyroid gland. All cases of FN showed a lymphocytic background. Conclusions: Thyroiditis is a commonly encountered condition that needs to be sub-categorized accurately into acute, subacute, and chronic types for appropriate clinical management, as they can sometimes show overlapping features. Though rare, acute suppurative and tuberculous thyroiditis are often encountered and warrant immediate care and treatment.
- Uncommon granulomatous manifestation in Epstein-Barr virus–positive follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report
- Henry Goh Di Shen, Yue Zhang, Wei Qiang Leow
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):133-138. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.27
- 3,666 View
- 346 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic Epstein-Barr virus–positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (EBV+ IFDCS) represents a rare form of liver malignancy. The absence of distinct clinical and radiological characteristics, compounded by its rare occurrence, contributes to a challenging diagnosis. Here, we report a case of a 54-year-old Chinese female with a background of chronic hepatitis B virus treated with entecavir and complicated by advanced fibrosis presenting with a liver mass found on her annual surveillance ultrasound. Hepatectomy was performed under clinical suspicion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunomorphologic characteristics of the tumor were consistent with EBV+ IFDCS with distinct non-caseating granulomatous inflammation. Our case illustrates the importance of considering EBV+ IFDCS in the differential diagnosis of hepatic inflammatory lesions. Awareness of this entity and its characteristic features is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing this rare neoplasm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef - EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma occurring in different organs: a case report and literature review
Wenhua Bai, Chunfang Hu, Zheng Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spleen EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a case report and literature review
Yi Xiao, Lanlan Li, Xiumei Zhan, Juner Xu, Yewu Chen, Qiuchan Zhao, Yinghao Fu, Xian Luo, Huadi Chen, Hao Xu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the liver: clinical features, imaging findings and potential diagnostic clues
Gui-Ling Huang, Man-Qian Huang, Yu-Ting Zhang, Hui-Ning Huang, Hong-Tao Liu, Xiao-Qing Pei
Abdominal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein‑Barr virus+ inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma with clonal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Qian Ye, Juan Zhao, Jiao He, Weishan Zhang
Oncology Letters.2025; 31(2): 1. CrossRef - Primary hepatic follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case study and literature review
Junjie Zhu, Ying Liang, Li Zhang, Bingqi Li, Danfeng Zheng, Hangyan Wang
Journal of International Medical Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
- Primary Necrobiotic Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis with Submandibular Gland Localization without Skin Involvement
- Myunghee Kang, Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Yeon Seok, Dong Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):261-265. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.01.08
- 8,926 View
- 169 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Necrobiotic xanthogranulomatous reaction is a multiorgan, non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis with an unknown etiology. Occurrence in the salivary gland is extremely rare. We recently identified a case of necrobiotic xanthogranulomatous sialadenitis in a 73-year-old Korean woman who presented with a painless palpable lesion in the chin. There was no accompanying cutaneous lesion. Partial resection and subsequent wide excision with neck dissection were performed. Pathological examination showed a severe inflammatory lesion that included foamy macrophages centrally admixed with neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and scattered giant cells, as well as necrobiosis. During the 12-month postoperative period, no grossly remarkable change in size was noted. Necrobiotic xanthogranulomatous inflammation may be preceded by or combined with hematologic malignancy. Although rare, clinicians and radiologists should be aware that an adhesive necrobiotic xanthogranuloma in the salivary gland may present with a mass-like lesion. Further evaluation for hematologic disease and close follow-up are needed when a pathologic diagnosis is made.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Salivary gland macrophages in health and disease: heterogeneity, niche crosstalk, and therapeutic avenues
Xinglei Li, Yan Feng, Huixin Xue, Xinxin Ni
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Five Cases of Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis
Satoshi Kiyama, Hiroyuki Iuchi, Kotoko Ito, Kengo Nishimoto, Tsutomu Matsuzaki, Masaru Yamashita
Practica Oto-Rhino-Laryngologica.2022; 115(4): 315. CrossRef - Xanthogranulomatous change in a pleomorphic adenoma: An extremely rare variant/degenerative change. Is it fine needle aspiration induced?
Mukta Pujani, Dipti Sidam, Kanika Singh, Aparna Khandelwal, Khushbu Katarya
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case of Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis with Facial Palsy Mimicking Malignancy
Sang Hyun Kim, Sun Woo Kim, Sang Hyuk Lee
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2021; 64(6): 422. CrossRef - Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis, an Uncommon Reactive Change is Often Associated with Warthin’s Tumor
Lihong Bu, Hui Zhu, Emilian Racila, Sobia Khaja, David Hamlar, Faqian Li
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(2): 525. CrossRef - A Case of Xanthogranulomatous Sialadenitis of the Sublingual Gland:A Review of Literature
Naoya KITAMURA, Seiji OHNO, Tetsuya YAMAMOTO
Journal of Japanese Society of Oral Medicine.2019; 25(1): 20. CrossRef
- Salivary gland macrophages in health and disease: heterogeneity, niche crosstalk, and therapeutic avenues
- Bile Granuloma Mimicking Peritoneal Seeding: A Case Report
- Hasong Jeong, Hye Won Lee, Hye Ra Jung, Ilseon Hwang, Sun Young Kwon, Yu Na Kang, Sang Pyo Kim, Misun Choe
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):339-343. Published online July 16, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.06.02
- 8,171 View
- 118 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a widely used treatment method for most cholelithiasis and is a relatively safe procedure. Foreign body granulomatous reaction to bile or gallstone spillage during laparoscopic cholecystectomy has rarely been reported. We report a case of bile granuloma after laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which mimicked peritoneal seeding. A 59-year-old Korean man presented with right upper quadrant pain. He underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis. Pathologic examination revealed an incidental adenocarcinoma invading the lamina propria with acute cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. After 3 months, follow-up abdominal computed tomography revealed a subhepatic nodule, which showed hypermetabolism on positron emission tomography–computed tomography. Suspecting localized peritoneal seeding, wedge resection of the liver, wedge resection of the transverse colon, and omentectomy were performed. Pathologic examination of the resected specimens revealed multiple bile granulomas. Awareness of bile granuloma mimicking malignancy is noteworthy for patient management to reduce unnecessary procedure during postoperative surveillance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A mimic of peritoneal metastatic disease, multifocal intraabdominal foreign body granulomas secondary to feculent peritonitis
Damien Gibson, Christo Joseph, Diarmid P. Foulis, Christophe R. Berney
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2024; 94(4): 763. CrossRef - Practices and Attitudes of Surgeons With Regard to Spilled Gallstones During Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Cross-Sectional Study From Saudi Arabia
Mohammed Alfehaid, Moath Aljohani, Sajad A Salati , Shoug Alaodah, Wejdan Alresheedi, Raghad Almarshud
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Spilled gallstone mimicking intra-abdominal seeding of gallbladder adenocarcinoma: A case report
Cheng-Ken Huang, Ruey-Hwa Lu, Chien-Cheng Chen, Po-Chun Chen, Wen-Chang Hsu, Meng-Jui Tsai, Chin-Tsung Ting
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(2): 622. CrossRef - Peritoneal bile granuloma formation at the site of caesarean surgical scar
Lila Marshall, Sharlin Varghese, Mary Ciranni-Callon
Journal of Case Reports and Images in Obstetrics and Gynecology.2024; 10(2): 6. CrossRef - Biliary Granulomatous Peritoneal Reaction as Consequence of Cholecystectomy: Case Report and Literature Review
Giuseppe Tarantino, Denise Menghini, Maria Eva Argenziano, Miriam Palmieri, Alessandra Mandolesi, Enrico Dalla Bona, Antonio Benedetti, Mario Guerrieri, Maria Giovanna Danieli
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Foreign body reaction mimicking local recurrence from polyactide adhesion barrier film after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery
Tien-Chan Hsieh, Chao-Wen Hsu
Medicine.2022; 101(5): e28692. CrossRef - Spilled gallstones after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a systematic review
Sajad Ahmad Salati, Mohammed Alfehaid, Saleh Alsuwaydani, Lamees AlSulaim
Polish Journal of Surgery.2022; 94(4): 1. CrossRef - Foreign body granulomas mimic peritoneal dissemination caused by incarcerated femoral hernia perforation: A case report
Shinpei Ogino, Tatsuya Matsumoto, Yosuke Kamada, Noriaki Koizumi, Hiroshi Fujiki, Kenji Nakamura, Takeshi Yamano, Chouhei Sakakura
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 12(11): 1083. CrossRef
- A mimic of peritoneal metastatic disease, multifocal intraabdominal foreign body granulomas secondary to feculent peritonitis
- Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Intratumoral Granulomatous Reaction: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hayeon Kim, Jong Wook Kim, Aeree Kim, Hyeyoon Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):325-328. Published online March 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.09.08
- 9,694 View
- 122 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Granulomatous reaction associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is a rare finding, and only a few cases have been described in the literature. It is postulated to occur due to cancer- related antigenic factors such as cancer cells themselves or soluble tumor antigens shed into the blood. Herein, we describe a case of a 56-year-old male patient diagnosed with CCRCC with intratumoral granulomatous inflammation.
- IgG4-Related Disease Presented as a Mural Mass in the Stomach
- Chang Gok Woo, Jeong Hwan Yook, Ah Young Kim, Jihun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(1):67-70. Published online September 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.28
- 10,574 View
- 92 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Isolated gastric IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a very rare tumefactive inflammatory condition, with only a few cases reported to date. A 48-year-old woman was incidentally found to have a subepithelial tumor in the stomach. Given a presumptive diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor or neuroendocrine tumor, she underwent wedge resection. The lesion was vaguely nodular and mainly involved the submucosa and proper muscle layer. Microscopically, all classical features of type I autoimmune pancreatitis including lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and numerous IgG4-positive plasma cells were seen. She had no evidence of IgG4-RD in other organs. Although very rare, IgG4-RD should be considered one of the differential diagnoses in the setting of gastric wall thickening or subepithelial mass-like lesion. Deep biopsy with awareness of this entity might avoid unnecessary surgical intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Compromiso gástrico por enfermedad relacionada con IgG4
Gilberto Jaramillo Trujillo, Oscar Fernando Ruiz, Melissa González Pabón, Maria Andrea Jaramillo Trujillo
Revista Repertorio de Medicina y Cirugía.2024; 33(3): 319. CrossRef - Value of High‐Frequency Ultrasonography in the Qualitative and Semi‐Quantitative Assessment of Immunoglobulin G4‐Related Submandibular Sialadenitis
Lei Chen, Lin Nong, Jumei Liu, Luzeng Chen, Yuhong Shao, Xiuming Sun
Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2023; 42(10): 2235. CrossRef - IgG4-related pseudotumours: a series of 12 cases and a review of the literature
Andrea Maccagno, Bianca Grosser, László Füzesi, Björn Konukiewitz, Dmytro Vlasenko, Dorothea Weckermann, Stephan Raab, Johannes Zenk, Abbas Agaimy, Bruno Märkl
Pathology.2022; 54(5): 563. CrossRef - IgG4-Related Disease With Gastrointestinal Involvement: Case Reports and Literature Review
Xinhe Zhang, Xing Jin, Lin Guan, Xuyong Lin, Xuedan Li, Yiling Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of gastric IgG4‐related disease: Systematic scoping review
Haruki Sawada, Torrey Czech, Krixie Silangcruz, Landon Kozai, Adham Obeidat, Eric Andrew Wien, Midori Filiz Nishimura, Asami Nishikori, Yasuharu Sato, Yoshito Nishimura
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(10): 1865. CrossRef - Utility of gastric biopsy in diagnosing IgG4‐related gastrointestinal disease
Kaori Uchino, Kenji Notohara, Takeshi Uehara, Yasuhiro Kuraishi, Junya Itakura, Akihiro Matsukawa
Pathology International.2021; 71(2): 124. CrossRef - A reappraisal of sclerosing nodular and/or polypoid lesions of the gastrointestinal tract rich in IgG4‐positive plasma cells
Runjan Chetty
Histopathology.2020; 76(6): 832. CrossRef - Gastric IgG4-related disease presenting as a mass lesion and masquerading as a gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Banumathi Ramakrishna, Rohan Yewale, Kavita Vijayakumar, Patta Radhakrishna, Balakrishnan Siddartha Ramakrishna
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 258. CrossRef - IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease Forming a Gastric Submucosal Tumor Diagnosed after Laparoscopic Endoscopic Cooperative Surgery—Report of a Case—
Tatsuki ISHIKAWA, Katsunori NAKANO, Masafumi OSAKA, Yayoi KADOTANI, Kaori OKUGAWA, Kiyokazu AKIOKA, Kenta SHIGEMORI, Yohei HOSOKAWA
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2020; 81(2): 254. CrossRef - Calcifying fibrous tumor of the gastrointestinal tract: A clinicopathologic review and update
Donald Turbiville, Xu-Chen Zhang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 26(37): 5597. CrossRef - A Suspected Case of IgG4-Related Appendiceal Pseudotumor
Yudai Hojo, Yoshiharu Shirakata, Ai Izumi, Jun Matsui, Tokuyuki Yamashita, Hikaru Aoki, Makoto Kurimoto, Masaaki Hirata, Naoki Goda, Hiroaki Ito, Jun Tamura
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery.2020; 53(12): 976. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin G4-related gastric pseudotumor – An impostor: Case report
Manuel Santiago Mosquera, Andrea Suarez Gómez, Hugo Herrera, Karen Moreno-Medina, Alejandro González-Orozco, Carlos J-Perez Rivera
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 75: 333. CrossRef - Imaging and pathological features of gastric lesion of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: A case report and review of the recent literature
Dai Inoue, Norihide Yoneda, Kotaro Yoshida, Hiromi Nuka, Jun Kinoshita, Sachio Fushida, Fumihito Toshima, Tetsuya Minami, Masayuki Takahira, Shoko Hamaoka, Hiroko Ikeda, Toshifumi Gabata, Mitsuhiro Kawano
Modern Rheumatology.2019; 29(2): 377. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin G4-Related Gastric Ulcer Mimicking Advanced Stomach Cancer in a Patient with Type I Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Joung Ha Park, Jin Hee Noh, Jang ho Lee, Goeun Lee, Seung-Mo Hong, Kwang Bum Cho, Myung-Hwan Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(3): 287. CrossRef - Review of IgG4-related disease
Raquel Sánchez-Oro, Elsa María Alonso-Muñoz, Lidia Martí Romero
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2019; 42(10): 638. CrossRef - Revisión de la enfermedad relacionada con la IgG4
Raquel Sánchez-Oro, Elsa María Alonso-Muñoz, Lidia Martí Romero
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2019; 42(10): 638. CrossRef - Gastrointestinal manifestation of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: clarification through a multicenter survey
Kenji Notohara, Terumi Kamisawa, Kazushige Uchida, Yoh Zen, Mitsuhiro Kawano, Satomi Kasashima, Yasuharu Sato, Masahiro Shiokawa, Takeshi Uehara, Hajime Yoshifuji, Hiroko Hayashi, Koichi Inoue, Keisuke Iwasaki, Hiroo Kawano, Hiroyuki Matsubayashi, Yukitos
Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 53(7): 845. CrossRef - IgG4-Related Disease Mimicking Crohn’s Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Fabiana Ciccone, Antonio Ciccone, Mirko Di Ruscio, Filippo Vernia, Gianluca Cipolloni, Gino Coletti, Giuseppe Calvisi, Giuseppe Frieri, Giovanni Latella
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2018; 63(4): 1072. CrossRef - IgG4-related Disease in the Stomach which Was Confused with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature
Ho Seok Seo, Yoon Ju Jung, Cho Hyun Park, Kyo Young Song, Eun Sun Jung
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2018; 18(1): 99. CrossRef - Multivisceral IgG4-related disease presenting as recurrent massive gastrointestinal bleeding: a case report and literature review
Xuexue Deng, Ronghua Fang, Jianshu Zhang, Rongqiong Li
BMC Gastroenterology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease Presenting as a Gastric Submucosal Tumor
Takashi Masuda, Toshifumi Matsumoto, Yushi Kaishakuji, Hirotada Tajiri, Akinori Egashira, Hirofumi Kawanaka
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery.2018; 51(10): 599. CrossRef - A rare case of IgG4-related disease: a gastric mass, associated with regional lymphadenopathy
Dimitar Bulanov, Elena Arabadzhieva, Sasho Bonev, Atanas Yonkov, Diana Kyoseva, Tihomir Dikov, Violeta Dimitrova
BMC Surgery.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Compromiso gástrico por enfermedad relacionada con IgG4
- Paediatric Primary Pachymeningeal Xanthogranuloma with Scattered Foci Displaying Reticulohistiocytoma-like Features
- Miguel Fdo. Salazar, María del Rocío Estrada Hernández, Erick Gómez Apo, Laura G. Chávez Macías, Carlos Alfonso Rodríguez Álvarez
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):403-408. Published online June 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.05.28
- 10,471 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a unique case of a 4-year-old girl with an intriguing fibrohistiocytic tumour. Magnetic resonance imaging scans showed a dural mass of variegated intensity compressing the left occipital pole and apparently extending toward the superior sagittal sinus. Grossly, the cut surface of the surgical specimen was yellow, pale, and soft with reddish kernel-like crusts. Histologically, the yellow areas resembled cholesterol granulomas with widespread coagulative necrosis, cholesterol clefts, powdery calcification, foreign body-type giant cells, and foamy macrophages, while the scattered red spots contained numerous multinucleated giant cells of foreign-body and Touton types, the former with amphophilic to slightly eosinophilic cytoplasm. Immunoperoxidase reactions confirmed the expression of histiocytic markers and vimentin. As far as we know, no tumour displaying these peculiar morphological features has yet been described.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reticulohistiocytoses: a revision of the full spectrum
A. Bonometti, E. Berti
Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.2020; 34(8): 1684. CrossRef
- Reticulohistiocytoses: a revision of the full spectrum
- Clinicopathologic Features of Q Fever Patients with Acute Hepatitis
- Miji Lee, Jae Jeong Jang, Yang Soo Kim, Sang-Oh Lee, Sang-Ho Choi, Sung-Han Kim, Eunsil Yu
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):10-14. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.10
- 11,669 View
- 77 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Q fever caused by
Coxiella burnetii presents with diverse clinical and pathological features including subclinical or cholestatic hepatitis. However, the pathological features of liver biopsies from patients with Q fever have not been well described.Methods Clinical features and pathological findings of liver biopsies were reviewed in seven cases of Q fever that were confirmed by serological, microbiological, or molecular tests.
Results All cases presented with fever. Liver enzymes were mildly elevated except one case with marked hyperbilirubinemia. Characteristic fibrin ring granulomas were present in three cases, epithelioid granulomas with eosinophilic infiltration in two cases, extensive extravasated fibrins without ring configuration mimicking necrotizing granuloma in one case, and acute cholangitis without granuloma in one case. All cases were treated with antibiotics for 20 days. Six cases were completely cured, but one suffered from multiorgan failure.
Conclusions C. burnetii infection is uncommon, but should always be considered in patients with acute hepatitis and fever. Because variable-sized circumferential or radiating fibrin deposition was a consistent feature of the present cases, Q fever can be strongly suggested by pathological features and confirmed by serological and/or molecular tests.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Actualités sur la fièvre Q
Maxime Colson, Matthieu Million, Pierre-Edouard Fournier, Sophie Edouard
Revue Francophone des Laboratoires.2025; 2025(573): 39. CrossRef - Coxiella burnetii: Emerging threats, molecular insights, and advances in diagnosis and control measures
Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Safoura Moradkasani, Mina Latifian, Saber Esmaeili
Journal of Microbiological Methods.2025; 237: 107213. CrossRef - Q fever as a cause of fever of unknown origin in a patient on hemodialysis
Emilio Guirao-Arrabal, Ana Delgado-Ureña, Elena Borrego-García, Rosa Ríos-Pelegrina
Nefrología.2024; 44(6): 906. CrossRef - Q fever as a cause of fever of unknown origin in a patient on hemodialysis
Emilio Guirao-Arrabal, Ana Delgado-Ureña, Elena Borrego-García, Rosa Ríos-Pelegrina
Nefrología (English Edition).2024; 44(6): 906. CrossRef - (Seltene) infektiöse Hepatitiden als wichtige Differenzialdiagnose der unklaren Hepatopathie
Michael Wührl, Marc Ringelhan, Ursula Ehmer, Jochen Schneider, Juliane Kager, Tobias Lahmer, Anna Schneider, Wilko Weichert, Carolin Mogler
Die Pathologie.2023; 44(1): 53. CrossRef - Sero-epidemiological study of zoonotic bacterial abortifacient agents in small ruminants
Muhammad Abid Zeeshan, Sarmad Ali, Ishtiaq Ahmed, Aziz ur Rehman, Muhammad Kamran Rafique, Amar Nasir, Aman Ullah Khan, Muhammad Kashif, Katja Mertens-Scholz, Muhammad Imran Arshad, Syed Ehtisham-ul-Haque, Heinrich Neubauer
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The First Case of Coxiella Burnetti Infection Detected Through Bone Marrow Biopsy in Vietnam
Do Thi Vinh An, Bui Thi Viet Ha, Dao Xuan Co, Vu Minh Tam, Le Thi Diem Tuyet, Vu Van Truong
Clinical Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathological study and molecular detection of zoonotic diseases in small ruminants at slaughter houses in Mymensingh, Bangladesh
Nazneen Sultana, Munmun Pervin, Sajeda Sultana, Mahmuda Islam, Moutuza Mostaree, Mohammad Abu Hadi Noor Ali Khan
Veterinary World.2022; : 2119. CrossRef - The First Report of Coxiella burnetii as a Potential Neglected Pathogen of Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Causes in Egypt
Mohamed A. El-Mokhtar, Ibrahim M. Sayed, Ayat M. Kamel, Ahmed Atef Mesalam, Elsayed A. Elgohary, Khaled Abo bakr Khalaf, Sara Adel, Azza Abo Elfadl, Walaa A. Khalifa, Haidi Karam-Allah Ramadan
Microorganisms.2022; 10(11): 2168. CrossRef - A case of coexistent acute severe alcoholic and Q fever hepatitis: The useful contribution of repeated liver biopsies
Lucia Zampaglione, Aurélie Bornand, Nicolas Goossens, Lucas Ramer, Giulia Magini, Marie Ongaro, Andreas Cerny, Laura Rubbia-Brandt, Jean-Louis Frossard, Laurent Spahr
Annals of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 6(1): 034. CrossRef - Q-fever associated granulomatous hepatitis
Nicolas Dauby, Maria Gomez Galdon, Isabel Montesinos, Marjan Van Esbroeck, Thomas Sersté
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 95: 113. CrossRef - Pathologic changes and immune responses against Coxiella burnetii in mice following infection via non-invasive intratracheal inoculation
Xueyuan Hu, Yonghui Yu, Junxia Feng, Mengjiao Fu, Lupeng Dai, Zhiyu Lu, Wenbo Luo, Jinglin Wang, Dongsheng Zhou, Xiaolu Xiong, Bohai Wen, Baohua Zhao, Jun Jiao, Daniel E. Voth
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0225671. CrossRef - Fibrin Ring Granulomas in Checkpoint Inhibitor-induced Hepatitis
Jamie Everett, Amitabh Srivastava, Joseph Misdraji
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2017; 41(1): 134. CrossRef - Clinical and Genetic Features ofCoxiella burnetiiin a Patient with an Acute Febrile Illness in Korea
Seung Hun Lee, Jung Yeon Heo, Hae Kyung Lee, Yeong Seon Lee, Hye Won Jeong, Seon Do Hwang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(6): 1038. CrossRef - Q Fever Presented as a Large Retroperitoneal Pseudotumoral Mass
Behdokht Nowroozizadeh, Negar Haghighi Mehmandari, Nicolas Gallegos, Mari Perez-Rosendahl, Di Lu
Case Reports in Pathology.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - From Q Fever to Coxiella burnetii Infection: a Paradigm Change
Carole Eldin, Cléa Mélenotte, Oleg Mediannikov, Eric Ghigo, Matthieu Million, Sophie Edouard, Jean-Louis Mege, Max Maurin, Didier Raoult
Clinical Microbiology Reviews.2017; 30(1): 115. CrossRef - Prolonged Pyrexia and Hepatitis: Q fever
Caitlin Dugdale, Brian Chow, Evgeny Yakirevich, Erna Kojic, Bettina Knoll
The American Journal of Medicine.2014; 127(10): 928. CrossRef
- Actualités sur la fièvre Q
- Brucella Prostatitis: A First Case Report Diagnosed in Korea.
- Seong Yeol Ryu, Hyun Ah Kim, Jiyoung Park, Misun Choe, Kunyoung Kwon
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S66-S69.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S66
- 4,823 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Brucellosis is a zoonosis caused by several species of Brucella. Brucellosis is usually an acute or sub-acute febrile illness that histologically develops granulomatous inflammation. Brucella prostatitis is a very rare complication and is usually accompanied by epididymo-orchitis. We now report a case of histologically proven granulomatous prostatitis due to Brucella without clinical evidence of epididymo-orchitis. A 61-year-old farmer presented with myalgia, low back pain, and fever. A needle biopsy of the prostate was performed due to symptoms of urinary frequency and high prostate specific antigen levels (17.3 ng/mL). Histologically, the prostate showed granulomatous inflammation without caseous necrosis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies of blood and prostatic tissue for Brucella were positive, while a PCR study for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative. The patient was treated with doxycycline and rifampin. A possibility of Brucella prostatitis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of granulomatous prostatitis or prostatitis of unknown origin associated with or without epididymo-orchitis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Imported Case of Brucella melitensis Infection in South Korea
Jee Young Lee, Yongduk Jeon, Mi Young Ahn, Hea Won Ann, In Young Jung, Wooyong Jung, Moo Hyun Kim, Jin Young Ahn, Je Eun Song, Yong Chan Kim, Dong Hyun Oh, Eun Jin Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Nam Su Ku, Hyunsoo Kim, Kyungwon Lee, June Myung Kim, Jun Yong Choi
Infection & Chemotherapy.2018; 50(2): 149. CrossRef - Brucellosis Prostatitis: A Neglected Diagnosis for a Tropical Disease
Jing Liu, Bhavika Kaul, Andrea Shioleno, Niraj Mehta, Rojelio Mejia
Current Tropical Medicine Reports.2016; 3(4): 181. CrossRef
- An Imported Case of Brucella melitensis Infection in South Korea
- Comparison of Various Detection Methods of Mycobacterium Species in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue with Chronic Granulomatous Inflammation.
- Hyun Seung Lee, Hyoungnam Lee, Soyoung Im, Yun Su Lee, Kyo Young Lee, Yeong Jin Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):259-266.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.259
- 4,704 View
- 52 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To determine the most effective method for detecting mycobacteria in formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue, we compared the results of Ziehl-Neelsen stain (ZNS) and mycobacterial culture with those of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time quantitative PCR (RQ-PCR).
METHODS
We analyzed 54 cases diagnosed as chronic granulomatous inflammation. In all cases, ZNS and nested PCR using three different primers, IS6110, Mpb64 and IS6110/Rpobeta were done. RQ-PCR with the IS6110/Rpobeta primer was done in 51 cases.
RESULTS
Mycobacteria were identified by ZNS in 15/54 (27.8%) cases. RQ-PCR had the highest sensitivity (80.0%) compared to PCR with IS6110 (73.3%), Mpb64 (60.0%) and IS6110/Rpobeta (73.3%). Specificity was higher in all PCR experiments (79.5-82.1%) than in RQ-PCR (69.4%) experiments. The false negative rate was lowest for RQ-PCR (20.0%) than for PCR with IS6110 (26.7%), Mpb64 (40.0%) and IS6110/Rpobeta (26.7%). The false positive rate was highest for RQ-PCR (30.6%) compared to PCR with IS6110 (20.5%), Mpb64 (17.9%) and IS6110/Rpobeta (20.5%).
CONCLUSIONS
RQ-PCR had the highest sensitivity, and the lowest false negative rate, but it also had a higher false positive rate than PCR for detection of mycobacteria in FFPE tissues. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Usefulness of PCR for Differential Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection in Paraffin-Embedded Lung Tissues
Yo Na Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Ha Na Choi, Ju Hyung Lee, Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Myoung Ja Chung
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2015; 17(5): 597. CrossRef - Usefulness of PCR to Mycobacterium Tuberculous and Nontuberculous Mycobacteria from Paraffin-embedded Tissues
Yeon-Il Choi, Hye-Young Kim
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2014; 46(2): 47. CrossRef
- Clinical Usefulness of PCR for Differential Diagnosis of Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection in Paraffin-Embedded Lung Tissues
- Pseudofungi Associated with a Granulomatous Response in a Lymph Node: A Case Report.
- Haeryoung Kim, Ja Seung Koo, Hyosup Shim, Gijong Yi, Sang Ho Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(1):64-67.
- 2,063 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - . We present herein a case of pseudofungi incidentally found in the mediastinal lymph nodes of a 31-year-old woman who had a left pneumonectomy for a pulmonary blastoma. The pseudofungi were located in the subcapsular sinuses of the lymph nodes with an associated granulomatous reaction. They revealed yellowish-brown hyphae-like structures with pseudosepta and irregular branching at various angles intermingled with round yeast-like forms. These structures stained positively with periodic acid-Schiff and Gomori methenamine silver, but also stained strongly positive for Prussian blue suggesting that they contain iron. The characteristic morphological features of pseudofungi are discussed with emphasis on the features that distinguish them from true fungal organisms.
- Cardiac Sarcoidosis Treated by Cardiac Transplantation: A Case Report.
- Jaejung Jang, Kwangseon Min, Gyeong cheon Jung, Jaejung Kim, Inchul Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2001;35(1):71-75.
- 1,831 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sarcoidosis, in general, has a low mortality rate. But cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is a serious condition which may lead to death. Here, we report a rare case of CS that was treated by heart transplantation. A 47-year-old male had occasional syncopes and atypical chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia with right bundle branch block was noted by electrocardiogram. Multiple fixed myocardial perfusion defects in the interventricular septum and both the inferior-posterior ventricular walls were observed by thallium scan. Coronary angiography was unremarkable. Neither perihilar nor mediastinal lymphadenopathy was noted. The patient also suffered three times from tonic-clonic generalized seizures in 3 years, but no neurologic abnormalities were detected. The explanted heart displayed multiple white patches on the endomyocardial surface, measuring up to 8x7 cm. On microscopic examination, the lesion consisted of multiple well-formed and confluent granulomas with numerous scattered multinucleated giant cells, CD68-positive epithelioid histiocytes, and T-lymphocytes. Neither microorganisms nor foreign material was identified on special stain and culture study. It has been six months since the heart transplant, and the patient has been doing well.
- Eosinophilic Liver Abscess in Patients with Gastric Carcinoma.
- Soon Won Hong, Ho Guen Kim, Chan Il Park, Sang In Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(1):27-33.
- 2,326 View
- 41 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sixteen cases of heavy eosinophil infiltration or eosinophilic abscess of the liver in patients with gastric carcinoma were analyzed to draw attention to this interesting combination and to persue the pathogenetic mechanism. Peripheral blood eosinophilia and hepatic granuloma were found in only 5 and 4 cases, respectively. Neither the patients' stool nor the hepatic tissues disclosed any parasitic worms or eggs, although the skin tests for Clonorchis sinensis and Paragonimus westermani were positive in 2 cases. Among stomach carcinomas, early gastric cancer tended to have more eosinophils than advanced carcinoma, but was less frequently associated with the infiltration of mast cells. In the regional lymph nodes, there was no infiltration of eosinophils even in the presence of tumor metastasis. In the liver, none of the 16 cases had metastatic gastric carcinoma and mast cells were found in only 2 cases. The results suggest that heavy hepatic infiltration of eosinophils in gastric carcinoma patients is not of the parasitic or allergic cause, but of certain eosinophil chemotactic factor which may gain access to accumulate in the liver following released from the gastric carcinoma and transfered through the portal vein.
- Crohn's Disease Involving Small Intestine and Colon: 2 cases report.
- Shi Nae Lee, Sun Hee Chang, Hee Soo Yoon, Hea Soo Koo, Ok Kyung Kim, Ryung Ah Lee, Eung Beum Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(4):379-382.
- 2,105 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Crohn's disease was originally described as a small bowel disorder and has been known to involve the large bowel in approximately 40% of all cases with or without concomitant ileal component. We describe two cases of Crohn's diseas of small intestine and colon with a summary of differential diagnosis with ulcerative colitis. Both cases were originally diagnosed and treated as ileal tuberculosis. Grossly, there were skip lesions in both cases with prominent pseudopolyps and ulcerations in colon. Also noted were typical serpentine lesions in ileum as well as in colon. Microscopically, transmural inflammation was confirmed and one case showed scattered noncaseating granulomas in the wall. Submucosal edema and fibrosis with thickening of the wall was not prominent in colon. Polymerase chain reaction performed on paraffin block for the demonstration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in one case showed negative reaction.
- Combined Xanthogranulomatous Urachitis and Bullous Cystitis: A Case Report.
- Ji Eun Kwak, Han Seong Kim, Mee Joo, Sun Hee Chang, Sang Hwa Shim, Je G Chi, In Rae Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(1):41-44.
- 2,290 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Xanthogranulomatous inflammation of the urachus is a very rare benign chronic inflammatory disease of an unknown etiology. Herein we report a case of a 31-year-old woman who complained of lower abdominal pain and dysuria. Cystoscopy revealed a bullous change at the dome of the urinary bladder. MRI revealed a cystic mass above the bladder dome that extended to the umbilicus. A partial cystectomy with urachal resection was performed. Pathological examination revealed xanthogranulomatous urachitis combined with bullous cystitis.
- Exceptionally Good Lymphocytic Infiltration with Histiocytes and Multinucleated Giant Cells of Stomach Cancer: A case report.
- Dongsoo Suk, Sook Hee Hong, Hye Kyung Yoon, Hyung Gin Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 1986;20(1):112-115.
- 2,204 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stomach of 34 year old man showed an early stage of the cancer with slight involvement of the superficial part of the inner muscle layer and accompanied with one metastatic lymph node. The cancer is that of medium differentiated adenocarcinoma. There is an heavy infiltration of lymphocytes mixed with histiocytic mononuclear cells and multinucleated giant cells. Some giant cells appear as Langhans' type suggesting phagocytic cells of their origin containing PAS positive materials in the cytoplasma. In other places, they appear as atrophic cancer nests suggesting that these tumor nests were arrested and undergone to regressive cellular process because of the over-whelming immunological pressure by the host.
- Granulomatous Mycosis Fungoides: A case report.
- Kyung Sin Lee, Young Oak Kim, Kee Suck Suh, Sang Tae Kim, Man Ha Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(5):694-697.
- 1,866 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Granulomatous mycosis fungoides is an extremely rare and unusual histologic variant of mycosis fungoides. This form is clinically characterized by spontaneous resolution of ulcerated nodular lesions into poikiloderma. Histologically, a strong granulomatous component can obscure the underlying cutaneous lymphoma, which is frequently mistaken for non-neoplastic dermatitides or cutaneous sarcoidosis. We report a case of granulomatous mycosis fungoides occurring on the left cheek of 34-year-old man confirmed histologically with an aid of immunohistochemistry and clinical course (immediate response to PROMACE-CYTOBAM chemotherapy), with emphasis on differential diagnosis, along with a review of literature. This is the first documented report in the Korean literature.
- Right Atrial Myxoma Showing Granulomatous Lesion with Pulmonary Infart: A case report.
- Kun Chang Song, Soon Hee Jung, Dong Hwan Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(5):501-503.
- 2,017 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cardiac myxoma is the most common primary tumor of the heart. The tumor contains a variety of cell types that are thought to arise from a focus of primitive pluripotential mesenchymal cells in the area of the fossa ovalis. Throughout the myxoid stroma, there are variable amounts of reticular fivers, collagen, elastic fibers and smooth muscle cells. A 38-year-old female had right atrial myxoma with multiple pulmonary infarcts. In this case, we experienced an unusual degenerative change in the tumor of granulomatous lesion consisting of hemosiderin pigments, foreign body giant cells and peculiar, spheroid, semilunar or bamboo-shaped degenerated elastic fibers. Microscopically it resembles Gamna-Gandy nodule seen in the spleen of chronic passive congestion.
- Clinicopathologic Features of Granulomatous Mastitis.
- Yee Jeong Kim, Yoon Jung Choi, Ji Young Kim, Hee Jung Kim, Yang Soon Park, Soon Won Hong, Chanil Park, Doyil Kim, Hyde Lee, Woo Hee Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(3):181-186.
- 2,359 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Granulomatous mastitis (GM) is a rare chronic inflammatory condition that clinically mimics a carcinoma. The diagnosis of idiopathic GM depends on the exclusion of other granulomatous inflammations. The purpose of this study is to correlate the clinicopathological features of GM with etiologies.
METHODS
We reviewed the clinical records of 58 cases that were histologically diagnosed as GM. We performed special stains for microorganisms such as Ziehl-Neelsen, periodic acid Schiff and gram stains, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB PCR).
RESULTS
The mean age of patients was 35.3 years. Most patients were parous except three. Seven patients (12.1%) were related with pregnancy or lactation. TB PCR was positive in nine patients (15.5%). Five patients (8.6%) had gram positive bacilli that were recognizable as coryneform bacteria. Culture study demonstrated Staphylococcus aureus in only one case. Infectious GM had a greater tendency to form abscesses. Fat necrosis was more likely to be present in idiopathic GM, but other histological features were similar to each other. Twenty-two cases (37.9%) showed recurrence.
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that TB PCR and gram stain are essential tests for the differential diagnosis of GM, because the histologic features considerably overlap irrespective of the various etiologies.
- Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis: 3 cases report.
- Jae Hoon Park, Youn Wha Kim, Yong Koo Park, Ju Hie Lee, Moon Ho Yang
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(1):41-44.
- 2,224 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis is a rare form of inflammatory disease of the gall bladder and was first described in 1970 by Christensen and Ishak as fibroxanthogranulomatous inflammation of the gall bladder. Recently authors experienced three cases of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis, two of which were erroneously diagnosed as malignant tumor in preoperative clinical and radiological examinations. Grossly, the gallbladders were enlarged and the walls were thickened with yellowish granular necrotic areas ranging from a few millimeters to 1.0 cm in diameter. Microscopically, all of three cases showed diffuse infiltration of the foamy histiocytes containing bile pigments and mononuclear leukocytes associated with fibroblastic proliferation and foreign body reactions. The pathogenesis of the xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis is uncertain, but opinion favours an inflammatory response to extravasated bile probably, from ruptured Rokitanky-Aschoff sinuses. Three cases of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis with brief review of literature are presented.
- Granulomatous(Lobular) Mastitis in a Pregnant Woman: A case report.
- Kyu Rae Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Yeon Lim Suh, Jung Hyun Yang, Howe Jung Ree
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(3):261-265.
- 2,507 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Granulomatous(lobular) mastitis is a distinct disease entity of unknown etiology which is characterized by noncaseating granulomatous lobulocentric inflammation. We describe a rare case of granulomatous(lobular) mastitis of a 36 year-old pregnant woman a review of the literature. The mass which was discovered in the third month of her pregnancy, began as a localized, nontender mass on the left breast and persisted during her entire pregnancy. It decreased slightly in size when she began taking post-partum bromocriptine. Clinically and mammographically, the mass was highly suspected as a carcinoma with axillary lymph node metastasis. Fine needle aspiration smears revealed numerous aggregates of granulomas composed of epithelioid histiocytes admixed with multinucleated giant cells of Langhans' and foreign body type, and collections of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Ziehl-Neelsen, silver methenamine and PAS stain were negative for acid-fast bacilli, fungus, and bacilli on the smear respectively. Histologically, granulomatous inflammation was centered on the breast lobules. Caseation necrosis was absent, instead, numerous microabscesses were formed in the center of the granulomas. Cultures of the fresh tissue for the AFB, aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and fungus were all negative. Excision of the mass was performed without further treatment and there was no recurrence of the mass 6 months postoperatively. An autoimmune mechanism, infection, and some association with oral contraceptives have been suggested as etiologic factors in the literature.
- Localized Pseudopolyposis of the Ascending Colon Associated with Granulomatous Colitis: A case report.
- Jeong Ja Kwak, Kye Hyun Kwon, So Young Jin, Dong Wha Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(1):82-85.
- 2,058 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pseudopolyps represent discrete areas of mucosal inflammation and regeneration that are seen in a variety of inflammatory bowel disease including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. These polyps are typically short, measuring less than 1.5 cm in height. Rarely, localized giant pseudopolyposis can occur, i.e., a collection of larger inflammatory pseudopolyps giving rise to a mass lesion within the colon. The most serious problem concerned with pseudopolyposis is a confusion with carcinoma. We experienced a case of localized giant pseudopolyposis causing partial large bowel obstruction. Right hemicolectomy was done for a preoperative diagnosis of ascending colon carcinoma. The resected specimen contained a circumferential lesion, which was composed of numerous interconnecting cylindrical villi, measuring 12 cm in length and 3 cm in height. Microscopically, these polypoid lesions were inflammatory pseudopolyps. Several deep fissure-like ulcerations were noted with multifocal microabscess, lymphoid hyperplasia and an area of noncaseating granuloma.
- Subcutaneous Granuloma Annulare of the Scalp: A case report.
- Geon Kook Lee, Joong Seok Seo, Kye Yong Song, Seong Hye Park, Je G Chi, Kyoung Chan Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(2):178-182.
- 2,124 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Subcutaneous granuloma annulare (SGA) is a rare, benign noninfectious histiocytic disease of unknown cause, characterized by necrobiosis of the connective tissue surrounded by infiltrates of histiocytes and lymphocytes. We report a case of SGA in a 49/12-year-old boy. The lesions were five nontender subcutaneous nodules in the parieto-occipital scalp, measuring 1.0 cm to 2.0 cm in diameter. Microscopical examination revealed variable stages of multiple necrobiotic areas, which showed central necrobiosis with palisading histiocytes, involving both the lower dermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue. Electron microscopic findings revealed many histiocytes in the necrobiotic areas with degenerating and necrotic collagen fibers as well as regenerating fibroblasts.
- Granulomatous Inflammation of Hand following Sea Urchin Sting: 2 cases report.
- Jung Ran Kim, Dong Hoon Kim, Tae Jung Jang, Jong Im Lee, Hyun Sul Lim, Hyeon Kyeong Lee, Sung Han Bae
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(1):68-71.
- 2,395 View
- 36 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Injuries from sea urchins are induced by from penetration of the calcareous spines into the skin. Apart from the transient episode of excruciating pain, there is usually no residual disability. Complications arise, however, when spines are embedded over bony prominences, or within joints. Two cases are reported with injury and protracted disability of fingers resulting from contact with the purple sea urchin, Anthocidaris crassispina, a common echinoderm inhabitant of the Korean east coast. After a latent period of several months in both cases, Case 1 presented as caseating granulomas in the synovium and case 2 exhibited as the usual soft tissue nonsynovial foreign body and noncaseating granulomas. There appears to be a paucity of published data regarding the effects of puncture wounds caused by the spines of this animal. The granulomas have appeared after a latent interval of several months in a proportion of the sufferers, suggests a delayed hyperserisitivity reaction similar to that produced by Mycobacterium species.
- Histopathological Differences between Silicone Granuloma and Paraffinoma.
- Yeon Mee Kim, Hye Kyung Lee, Hye Je Cho, Je Geun Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):427-436.
- 5,470 View
- 310 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - During the past two decades, silicone (polydimethylsiloxane) has become one of the most extensively applied biomaterials. Although pure silicone is relatively inert and usually causes only minimal tissue reactions, it has been reported to evoke a definite foreign body reaction. We studied five cases of silicone-induced granulomas in various sites; two in the breast, one in the breast and axillary lymph nodes, one in the subcutis of the abdomen, back and extremities and one in the eyeball, to illustrate the salient histopathologic features of reactions to silicone with particular emphasis to its differences from paraffin granuloma. For this, 17 paraffinomas were also studied. Tissue reaction to silicone liquid and gel was characterized by numerous round to oval empty cystic vacuoles, mild to moderate fat necrosis, foreign body reaction, a variable degree of mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration and mild focal fibrosis. The cystic spaces were relatively uniform and showed a snow-man like appearance. In contrast to the silicone granulomas, the paraffinomas, also refered to as sclerosing lipogranulomas showed diffuse sclerosis and frequent calcification around the cystic vacuoles. The cystic spaces in paraffinomas were swiss cheese-like configuration, and the content of the cystic spaces was dirty and frequently calcified. However, there were certain similarities between these two types of granulomas particularly in the early phases of the reaction, therefore, the history of silicone injection or implant, is sometimes critical to the diagnosis of silicone granuloma. Despite great technologic advances in the manufacturing of prostheses and medical equipment, droplets and/or particles of silicone still escape into the body tissues in a variety of ways; therefores, the pathologist should always wonder whether the histologic reaction observed is due to silicone or to some other foreign material including paraffin.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Bilateral Granulomatous Mastitis: A Cese Report.
- Seung Sam Paik, Seok Hoon Jeon, Eun Kyung Hong, Moon Hyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1995;6(2):174-178.
- 2,017 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Granulomatous mastitis is a rare inflammatory breast lesion, usually presented with rapidly enlarging palpable mass in young parous women and can simulate carcinoma. Unnecessary surgical procedure can be avoided if the nature of the lesion were defined by fine needle aspiratio(FNA) cytology. We experienced a case of bilateral granulomatous mastitis diagnosed by FNA cytology. The patients was a 31-year-old woman with one month history of a rapidly enlarging mass in the left breast. considered clinically to be malignant. After 4 years. she presented with a palpable mass in the right breast. The FNA cytology smears contained numerous aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes admixed with Langhans' and foreign body giant cells, lymphoytes, neutrophils and apoptotic debris leading to a diagnosis of granulomatous mastitis. The subsequent lumpectomy of the left breast confirmed the diagnosis of granulomatous mastitis. The FNA cytology smears from right breast showed identical cytologic findings.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Sparganosis.
- Sung Suk Paeng, Yoon Ju Kim, Seong Eun Yang, Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh, Young Chun Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1996;7(1):59-63.
- 2,057 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human sparganosis is a rare parasitic disease in which the larval cestode proliferates in the various organs in the body. It usually presents as a subcutaneous or soft- tissue mass. By fine needle aspiration this lesion can be diagnosed with its characteristic cytologic findings. We experienced 3 cases of sparganosis diagnosed by the fine needle aspiration. Aspirates were taken from subcutaneous mass in the abdomen and both thighs respectively. The aspirates showed a portion of body of sparganum with numerous calcospherules, smooth muscles and tegmentat cells. They also revealed granulomas with various inflammatory infiltration of eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells.
- Necrobiotic Xanthogranuloma with Paraproteinemia: A case report.
- Yee Jeong Kim, Kwang Gil Lee, Soo Il Chun, Hyung Soon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(6):589-593.
- 2,474 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma(NXG) is a characteristic cutaneous manifestation associated with paraproteinemia. A case of NXG associated with an IgG (lambda) monoclonal gammopathy occurred in a 48-year-old man. Skin lesions were dome-shaped, hard palpable nodules, 2x3 cm to 4x4 cm sized, on both arms and forearms. They were arranged in a linear pattern. Also, hard palpable tumors, 1x2 cm to 2x3 cm in size, were present on the left leg and the dorsum of the left foot. They were violaceous, slightly protruded, and hard on palpation. Histologically, the lesion was characterized by inflammatory xanthogranuloma with broad hands of hyaline necrobiosis. Many foreign body type of bizarre giant cells, Touton type of giant cells and foamy histiocytes were infiltrated into the dermis and subcutaneous fat tissue. Three days after medication with ledercort and immuran, the cutaneous masses decreased in size and became soft.
- Syphilitic Granulomatous Pancreatitis: A case report.
- Seong Eun Yang, Yoon Ju Kim, Sung Suk Paeng, Duck Hwan Kim, Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(8):721-725.
- 2,728 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Syphilitic granulomatous pancreatitis is an extremely rare condition,and can occur in the generalized acquired syphilitic patient in tertiary or secondary phase. The most serious problem with granulomatous pancreatic lesion is clinical or radiological misdiagnosis as cancer. We experienced a case of syphilitic granulomatous pancreatitis arising in 54 year old female patient. She was treated for syphilis 20years ago. But she and her husband are still strong positive to VDRL and TPHA. On abdominal computed tomography and endoscopic pancreatico- duodenography, there was an obstructive mass of low density in the distal common bile duct or pancreatic head. Under the preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic head carcinoma, Whipple's operation was done. On gross examination, the pancreas was fibrotic, and the common bile duct was well preserved without tumor mass. Microscopically, numerous intralobular noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas with multinucleated giant cells are identified. They surround thick-walled, small to medium sized arteries and involve vascular wall with luminal narrowing or obliteration, which are characteristic findings of the syphilitic granuloma. The remaining parenchyme shows fibrosis, acinar atrophy or destruction with dense infiltration of lymphohistiocytes, plasma cells with granuloma formation. Although the Warthin-Starry stain reveals no spirochetes, the serologic result and pathologic findings are compatible with syphilitic granulomatous pancreatitis.
- Juvenile Xanthogranuloma of the Nasal Cavity: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
- Jung Suk An, Sun Hee Han, Ju Han Lee, Eung Seok Lee, Heum Rye Park, Young Sik Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(3):241-244.
- 2,311 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a benign and self-limiting non-Langerhans-cell histiocytosis that generally occurs during infancy and childhood. It develops frequently in the head and neck but is very rare in the nasal cavity. To date, only five cases of JXG in the nasal cavity have been reported. Here, we report the second case of JXG in the nasal cavity in Korea. A 19-year-old male patient presented with a protruding 1.1 cm mass in the left nasal vestibule. Histologically, a dense dermal infiltrate of histiocytes with Touton giant cells was observed. Immunohistochemically, the histiocytes tested positive for CD68 and the S-100 protein but negative for CD1a. This shows that a S-100-positive histiocytic lesion dose not exclude a diagnosis of JXG.
- Wegener's Granulomatosis Involving Lung and Middle Ear: A case report.
- Kye Weon Kwon, Yoon Jung Choi, Hee Jeong Ahn, Min Soo Han, Dong Hwan Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(6):470-473.
- 2,068 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- A case of Wegener's granulomatosis is described, with special attention focused on the typical histologic findings and involvement of both middle ear and lung. The patient is a 37-year-old man presented with four-month history of cough and sputum. He had a past history of surgery of both ears because of otitis media followed by left facial palsy. Chest radiographs showed variable sized ill defined nodules in both lower lobes with internal airspace consolidation. Histologic preparations of the open lung biopsy specimens demonstrated a diffusely scattered palisading micro and macrogranulomas with central focus of neutrophils and necrotic collagen surrounded by histiocytes, histiocytic giant cells. Fibrinoid necrosis involved blood vessels and lung parenchyma. Chronic inflammation, diffuse granulation tissue formation and irregular fibrosis are also found in the lung parenchyma. The histologic findings of middle ear which was previously biopsied showed scattered palisading ill defined microgranulomas mixed with fibrotic tissue.
- Pathological Findings of Crohn's Disease in the Stomach .
- Changyoung Yoo, Bo In Lee, Kyu Yong Choi, Lee So Maeng, Anhi Lee, Chang Suk Kang, Ghee Young Kwon, Kyoung Mee Kim, Cheol Keun Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(4):269-273.
- 2,466 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The incidence of Crohn's disease in the upper digestive tract, and especially in the stomach, is recently increasing. Focal inflammatory reaction without Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is thought to be the characteristic pathologic findings suggesting Crohn's disease in the stomach. Yet gastric involvement of Crohn's disease has not been studied in Korea. We studied the endoscopic and pathologic findings of patients with Crohn's disease in the stomach by taking biopsies.
METHODS
Thirty patients with Crohn's disease who underwent gastroduodenoscopy followed by biopsies were included in the study. The pathology of the gastric biopsy specimens and the presence of H. pylori were evaluated.
RESULTS
Among 30 cases, 22 cases (73.3%) were H. pylori negative and 8 cases (26.7%) were H. pylori positive. For the H. pylori negative cases, all but one cases showed pit abscess and focal lymphocytic collections in the antrum. Granulomas were found in 6 cases (20%) and they were exclusively located in the antrum.
CONCLUSIONS
In the stomach, pit abscess and focal lymphocytic collections that are not associated with H. pylori infection are the characteristic pathologic findings found in Crohn's disease.
- Eosinophilic Granuloma of the Lung.
- Sang Ae Yoon, Won Bo Jo, Yang Seok Chae, Kap No Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(3):270-276.
- 1,897 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Eosinophilic granuloma of the lung, first described by Farrinaci et al. in 1951, is rare. A 35-year-old male smoker presented with recurrent pneumothorax. Open thoracotomy with bleb resection and biopsy was performed. Microscopically there was histological changes consistent with typical eosinophilic granuloma and intertitial fibrosis. The Langerhans cells showed positive reaction for S-100 protein and typical Birbeck granules in their cytoplasm. A brief summary of histopathological aspect of this disease and a review of literature are presented.
- Infantile Solitary Eosinophilic Granuloma of the Lymph Node: A case report.
- Sun Hee Sung, Woo Ick Yang, Jae Ok Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(3):277-282.
- 2,202 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Infantile form of histiocytosis X is commonly presented as multiorgan desseminated form such as Letterer-Siwe disease. Lymph node involvement of histiocytosis X is usually accompanied by adjacent bone or skin lesion. Solitary nodal eosinophilic granuloma without evidence of other organ involvement is very rare. A case herein report is a 11 month-old female infant presented with fever and palpable both inguinal lymph nodes. There was neither skin lesion nor hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory evaluation was within normal range except increased alkaline phosphatase and many neutrophils in urine. Radiologic examination revealed no remarkable bone lesions. And she showed good clinical outcome without evidence of other organ involvements. On microscopic examination of inguinal lymph node it was replaced by infiltration of histiocytes mainly along the sinusoid. Some of histiocytes showed morphologic features of "histiocytosis X cell" having nuclear grooves or multilobulation. Multinulceated giant cells were frequently see. Numerous eosinphils were also infiltrated and showed multifocal microabscess formation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed that majority of histiocytes were postitive for S-100 protein but multinucleated histriocytes, phagocytic histiocytes and those around the abscess were positive for macrophage marker, suck as CD68 and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin. Interestingly some histiocytes showed positivity for both S-100 protein and macrophage marker. These results suggest that histiocytosis X is proliferative disorder of phenotypically heterogenous population of histiocytes in contrast to the theory that it is a proliferative disorder of Langerhans cells.
- Perianal Granuloma Caused by a Female Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis): A case report.
- Seok hyung Kim, Je Geun Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(8):605-607.
- 2,362 View
- 48 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The intestinal nematode Enterobius vermicularis is the most common metazoan endoparasite in humans, with humans being the only host. But complicated perianal granulomas due to Enterobius are unusual. The literature reports only 13 previous cases of enterobiasis presenting as perianal mass or abscess. We describe an additional case of a perianal mass caused by granulomatous inflammation containing Enterobius vermicularis eggs and dead bodies in a 7-year-old boy. The lesion was located in the anus and measured 2 1 cm. Clinical impression was lipoma and excisional biopsy was done. Microscopic examination revealed necrotizing granuloma which contained several 50~60 20~30 micrometer sized eggs which were identified as those of Enterobius vermicularis. The adult worm could not be identified with clarity due to necrosis.
- Silica Granuloma after Intermittent Intramuscular Injections: A Case Report.
- Suk Jin Choi, Jong Im Lee, Jung Ran Kim, Tae Jung Jang, Ki Kwon Kim, Phil Hyun Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(5):369-372.
- 2,554 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most silica-contaminated wounds of the skin heal without complications. Cutaneous silica granuloma is a poorly understood, uncommon condition resembling a sarcoidosis. We report a case of silica granuloma after intermittent intramuscular injections. A 70-year-old man presented a painless mass in his right buttock for 2 weeks. He had received intermittent intramuscular injections of antihistamine drugs due to chronic dermatitis for 30 years. The histolopathological findings showed numerous hyalinized collagenous nodules with concentric layers, and an ill-defined chronic granulomatous inflammation containing foreign material. A polarized light microscopic examination revealed birefrigent particles. The presence of silica components was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis.
- Fibrocalcific Nodule in the Liver Capsule Caused by Ascaris Eggs: A case report.
- Yeon Lim Suh, So Young Park, Je G Chi
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(4):411-413.
- 2,363 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ascariasis is probably the most common helminthic infestation of man, but it seldom causes severe illness. Pathologic conditions of Ascaris may be caused by adult worms, eggs or larvae. We describe a case of Ascaris egg granulomas that were found incidentally on the surface of the liver in a 75-year-old woman who had undergone a segmentectomy for an intrahepatic stone. Grossly, there were several yellowish calcific nodules of 0.4 cm in diameter on the lateral surface of the left lobe of the liver. Microscopically, the lesions were located in the hepatic capsule and consisted of fibrocalific nodules with many eggs. The eggs were round to oval, thick-shelled and measured 50~75x30~50 um. Most of the morphologically preserved eggs were fertilized eggs, but they had smooth shells without external protein coats. This case is of interest for the unusual location of the lesion, the presence of eggs without mammillation, and the association with the intrahepatic stone.
- Comparison of Ziehl-Neelsen Stain and TB-PCR on Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosisin Formalin-fixed, Paraffin-embedded Tissues of Chronic Granulomatous Inflammation.
- Min Sun Cho, Shi Nae Lee, Sun Hee Sung, Woon Sup Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(6):379-383.
- 4,442 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
TB-PCR is a faster and more sensitive method to detect mycobacterium than acid-fast bacilli (AFB) stain, which is laborious and time consuming. We compared the sensitivity and specificity of AFB stain and TB-PCR and examined the possibility of TB-PCR as a confirmative test without AFB stain in the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
METHODS
We performed Ziehl-Neelsen stain and nested PCR using a commercially available TB-PCR kit amplifying IS6110 sequence in 81 cases of paraffin-embedded tissues diagnosed as chronic granulomatous inflammation. In addition, we evaluated the morphology of granuloma and the presence of caseation necrosis.
RESULTS
Of the 81 cases studied, 22 (27.2%) and 40 (49.4%) were positive for AFB stain and TB-PCR, respectively. Of 49 cases accompanying caseation necrosis, 19 (38.8%) were AFB stain positive and 37 (75.5%) were TB-PCR positive; a result that is comparable with that of other reports. Of the 22 AFB-positive cases, 2 were TB-PCR negative.
CONCLUSION
TB-PCR is very helpful for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in routinely processed, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples. Nevertheless, AFB stain should continue to be performed at the same time.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pulmonary Lesions in Wegener's Granulomatosis: A Case Report.
- Eun Joo Seo, Hi Jeong Kwon, Ki Ouk Min
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1998;9(1):85-88.
- 2,001 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We described the findings of fine needle aspiration cytology of the lung from a patient with Wegener's granulomatosis. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of the patients with Wegener's granulomatosis is essential for a better prognosis. However, the variety of clinical presentations and nonspecific radiologic infiltrates of Wegener's granulomatosis frequently make the diagnosis difficult. Although an open lung biopsy is required for a firm diagnosis, fine needle aspiration cytology & biopsy preparation can also provide an adequate tissue sample, when the findings of fine needle aspiration are considered with clinical manifestations and ANCA value in the serum. The cytologic smears showed scattered necrotic tissue fragments entrapping many neutrophils and occasional epithelioid cells. Multinucleated giant cells were infrequently observed. Ziehl-Neelsen stain for acid fast bacilli was negative. All the cytologic features recapitulated the histopathologic findings of purulent and necrotizing granulomatous inflammation seen in Wegener's granulomatosis.
- Primary Necrotizing Granulomatous Vasculitis of the Stomach.
- Myeong Cherl Kook, Sang Yong Song, Yong Il Kim, In Sung Song, Keun Wook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(1):68-74.
- 2,343 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 55-year-old woman suffered from upper abdominal pain for two months and remained refractile against the anti-ulcer regimen. The palliative gastrectomy specimen revealed multiple shallow ulcerations on the thickened mucosal folds mainly in the antrum and body along the greater curvature where multiple, whitish nodules were found in the submucosa. Microscopically, individual submucosal nodules clearly corresponded to the necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis which were featured with diffuse fibrinoid necrosis of arterial walls accompanying granuloma formation and heavy infiltration of neutrophils, eosinophils, histiocytes and giant cells. Similar vasculitic lesions involved venules and arterioles. There were scattered vasculitic changes in the liver biopsy specimens and omentum. There were no clinical presentations or serological support of systemic involvement including systemic lupus erythematosus, Henoch-Schoenlein purpura, cryoglobulinemia or Churg-Strauss granulomatous vasculitis. We conclude that this is a hitherto undescribed primary necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis predominantly involving the stomach.
- Mesenteric Lymphadenitis Due to Yersinia enterocolitica: A case report.
- Hyang Mi Shin, Hwa Sook Jeong, Hyun Dug Wang, Young Don Lee, Ro Hyun Sung
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(12):1022-1024.
- 3,926 View
- 72 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mesenteric lymphadenitis due to Yersinia enterocolitica infection is not common in Korea. Although most cases of Yersinia enterocolitica-induced mesenteric adenitis are self limited, cardinal features of Yersinia enterocolitica-induced mesenteric adenitis are so similar to those of acute appendicitis that some of the patients undergo laparotomy with suspected appendicitis. The findings on laparotomy in such patients are usually enlarged mesenteric nodes with a normal or slightly inflamed appendix. Because histologic examination of the removed mesenteric lymph nodes reveals reactive hyperplasia in most cases, it is usually difficult to suspect Yersinia enterocolitica infection on morphology of the resected nodes. But suppurative granulomata of mesenteric lymph nodes, uncommonly encountered in Yersinia enterocolitica infection, strongly suggest yersinial infection. We report a case of mesenteric lymphadenitis in a 10-year-old boy, who underwent laparotomy with suspected acute appendicitis. The removed lymph node showed several suppurative granulomata in the cortex, suggesting yersinial infection. Serologic study confirmed Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 infection.

 E-submission
E-submission



 First
First Prev
Prev



