Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Immunohistochemical expression in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at a single center in Vietnam
- Dat Quoc Ngo, Si Tri Le, Khanh Hoang Phuong Phan, Thao Thi Phuong Doan, Linh Ngoc Khanh Nguyen, Minh Hoang Dang, Thien Thanh Ly, Thu Dang Anh Phan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):174-181. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.02
- 4,382 View
- 270 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The identification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) requires a comprehensive analysis involving clinical manifestations and histological findings. This study aims to provide insights into the histopathological and immunohistochemical aspects of IIMs.
Methods
This retrospective case series involved 56 patients diagnosed with IIMs at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, from 2019 to 2023. The histology and immunohistochemical expression of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, C5b-9, Mx1/2/3, and p62 were detected.
Results
We examined six categories of inflammatory myopathy, including immunemediated necrotizing myopathy (58.9%), dermatomyositis (DM; 23.2%), overlap myositis (8.9%), antisynthetase syndrome (5.4%), inclusion body myositis (IBM; 1.8%), and polymyositis (1.8%). The average age of the patients was 49.7 ± 16.1 years, with a female-to-male ratio of 3:1. Inflammatory cell infiltration in the endomysium was present in 62.5% of cases, perifascicular atrophy was found in 17.8%, and fiber necrosis was observed in 42 cases (75.0%). Rimmed vacuoles were present in 100% of cases in the IBM group. Immunohistochemistry showed the following positivity rates: HLA-ABC (89.2%), HLA-DR (19.6%), C5b-9 (57.1%), and Mx1/2/3 (10.7%). Mx1/2/3 expression was high in DM cases. p62 vacuole deposits were noted in the IBM case. The combination of membrane attack complex and major histocompatibility complex I helped detect IIMs in 96% of cases.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of IIMs and their subtypes should be based on clinical features and histopathological characteristics. Immunohistochemistry plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and differentiation of these subgroups. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
Raghavee Neupane, Mustafa Haider, Perry Smith, Marc M Kesselman
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapidly Progressive Polymyositis With Vasculitis: The Pivotal Role of Histopathology in Diagnosis and Management
Amitha Venmanassery Karnalsingh, Arjun Karappilly Vijayan, Monica Roselin Edwin Peter, Dilan Davis
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Autoimmune Neuromuscular Disorders at a Molecular Crossroad: Linking Pathogenesis to Targeted Immunotherapy
Anca-Maria Florea, Dimela-Gabriela Luca, Eugenia Irene Davidescu, Bogdan-Ovidiu Popescu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(23): 11736. CrossRef
- Evaluating the Diagnostic Potential of Myxovirus Resistance Protein 1 (MX1) and Myxovirus Resistance Protein 2 (MX2) As Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,739 View
- 211 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- Inflammatory bowel disease–associated intestinal fibrosis
- Ji Min Park, Jeongseok Kim, Yoo Jin Lee, Sung Uk Bae, Hye Won Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):60-66. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.02
- 19,923 View
- 465 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrosis is characterized by a proliferation of fibroblasts and excessive extracellular matrix following chronic inflammation, and this replacement of organ tissue with fibrotic tissue causes a loss of function. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, and intestinal fibrosis is common in IBD patients, resulting in several complications that require surgery, such as a stricture or penetration. This review describes the pathogenesis and various factors involved in intestinal fibrosis in IBD, including cytokines, growth factors, epithelial-mesenchymal and endothelial-mesenchymal transitions, and gut microbiota. Furthermore, histopathologic findings and scoring systems used for stenosis in IBD are discussed, and differences in the fibrosis patterns of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are compared. Biomarkers and therapeutic agents targeting intestinal fibrosis are briefly mentioned at the end.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short-Chain Fatty Acids Elicit Differential Expression of Growth Factors and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Immortalized Rat Enteric Glial Cells
Michelle M. Beltran, Danielle M. Defries
Nutrients.2026; 18(3): 436. CrossRef - Leveraging Organ‐on‐Chip Models to Investigate Host–Microbiota Dynamics and Targeted Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tim Kaden, Raquel Alonso‐Román, Johannes Stallhofer, Mark S. Gresnigt, Bernhard Hube, Alexander S. Mosig
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prominence of Microbiota to Predict Fibrous Stenosis in Crohn’s Disease
Xue Yang, Yan Pan, Cai-Ping Gao, Hang Li, Ying-Hui Zhang, Chun-Li Huang, Lu Cao, Shi-Yu Xiao, Zhou Zhou
Journal of Inflammation Research.2025; Volume 18: 1413. CrossRef - Fibrosierende Erkrankungen im Gastrointestinaltrakt
Elke Roeb
Die Innere Medizin.2025; 66(7): 695. CrossRef - Roles of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and IBD-associated fibrosis
Takayoshi Ito, Hisako Kayama
International Immunology.2025; 37(7): 379. CrossRef - Disease Clearance in Ulcerative Colitis: A Narrative Review
Silvio Danese, Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet, Vipul Jairath, Ferdinando D'Amico, Shashi Adsul, Christian Agboton, Fernando Magro
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(6): 902. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota as a Mediator Between Intestinal Fibrosis and Creeping Fat in Crohn's Disease
Caiguang Liu, Rongchang Li, Jing Nie, Jinshen He, Zihao Lin, Xiaomin Wu, Jinyu Tan, Zishan Liu, Longyuan Zhou, Xiaozhi Li, Zhirong Zeng, Minhu Chen, Shixian Hu, Yijun Zhu, Ren Mao
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(7): 1092. CrossRef - Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): immunotoxicity at the primary sites of exposure
Emma Arnesdotter, Charlotte B. A. Stoffels, Wiebke Alker, Arno C. Gutleb, Tommaso Serchi
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2025; 55(4): 484. CrossRef - Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis
Harshal Sawant, Alip Borthakur
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5713. CrossRef - Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Thomas Grewal, Hauke Christian Tews, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(13): 6101. CrossRef - Revealing Fibrosis Genes as Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis: A Bioinformatics Study Based on ScRNA and Bulk RNA Datasets
Yandong Wang, Li Liu, Weihao Wang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2025; 25(9): 710. CrossRef - Fibrosis in Immune-Mediated and Autoimmune Disorders
Magdalena Żurawek, Iwona Ziółkowska-Suchanek, Katarzyna Iżykowska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6636. CrossRef - Plasma-activated media inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorates intestinal fibrosis through the PPARγ/TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway
Yi You, Yaping Shen, Yan Yang, Xiaoyang Wei, Yuheng Zhou, Foxing Tan, Longcheng Deng, Haolin Du, Sen Wang, Cheng Wang, Yan Huang, Vinay Kumar,
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0335225. CrossRef - (R)-Bambuterol attenuates DSS-induced chronic colitis by suppressing inflammation, repairing intestinal barrier, and modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolomic profile
Liangjun Deng, Le Tian, Dan Su, Jiukun Xie, Yuer Qian, Yipeng Li, Shidong Zhang, Shanping Wang, Zhihua Liu
European Journal of Pharmacology.2025; 1008: 178346. CrossRef - Beyond inflammation: what drives the self-perpetuating cycle of fibrosis in IBD?
Yutong Wei, Zhou Zhou, Shiyu Xiao
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Neurokinin-1 Receptor Regulation of Fibroblast Phenotype and Function
Scott P. Levick
Receptors.2025; 4(4): 23. CrossRef - Tumor Development in Ulcerative Colitis: Perspectives From Biomechanical Characteristics
Hirotaka Tao
Development, Growth & Differentiation.2025; 67(9): 487. CrossRef - Effects of maternal overnutrition and metabolic challenge in adult life on the histological integrity of the liver and intestinal epithelium in rabbits
Lucía Carolina Cano, Erika Navarrete, Pedro Medina, Juan Pablo Ochoa-Romo, Georgina Díaz, Rodrigo Montúfar-Chaveznava, Rosa María Vigueras-Villaseñor, Ivette Caldelas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Full-Thickness Resection of a Non-Lifting Adenoma in an Ulcerative Colitis Patient Using OVESCO: A Case Report
Fei Yang Pan, Rupert Leong, Saurabh Gupta, Talia Fuchs, Viraj Kariyawasam
Case Reports in Gastroenterology.2025; 19(1): 682. CrossRef - Resistance to apoptosis in complicated Crohn's disease: Relevance in ileal fibrosis
M. Seco-Cervera, D. Ortiz-Masiá, D.C. Macias-Ceja, S. Coll, L. Gisbert-Ferrándiz, J. Cosín-Roger, C. Bauset, M. Ortega, B. Heras-Morán, F. Navarro-Vicente, M. Millán, J.V. Esplugues, S. Calatayud, M.D. Barrachina
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(2): 166966. CrossRef - Characterization of patient-derived intestinal organoids for modelling fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ilaria Laudadio, Claudia Carissimi, Noemi Scafa, Alex Bastianelli, Valerio Fulci, Alessandra Renzini, Giusy Russo, Salvatore Oliva, Roberta Vitali, Francesca Palone, Salvatore Cucchiara, Laura Stronati
Inflammation Research.2024; 73(8): 1359. CrossRef - Food additives impair gut microbiota from healthy individuals and IBD patients in a colonic in vitro fermentation model
Irma Gonza, Elizabeth Goya-Jorge, Caroline Douny, Samiha Boutaleb, Bernard Taminiau, Georges Daube, Marie–Louise Scippo, Edouard Louis, Véronique Delcenserie
Food Research International.2024; 182: 114157. CrossRef - Epigenetic Regulation of EMP/EMT-Dependent Fibrosis
Margherita Sisto, Sabrina Lisi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2775. CrossRef - Mechanisms and therapeutic research progress in intestinal fibrosis
Yanjiang Liu, Tao Zhang, Kejian Pan, He Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Disease clearance in ulcerative colitis: A new therapeutic target for the future
Syed Adeel Hassan, Neeraj Kapur, Fahad Sheikh, Anam Fahad, Somia Jamal
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(13): 1801. CrossRef - Urinary Hydroxyproline as an Inflammation-Independent Biomarker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Muriel Huss, Tanja Elger, Johanna Loibl, Arne Kandulski, Benedicta Binder, Petra Stoeckert, Patricia Mester, Martina Müller, Christa Buechler, Hauke Christian Tews
Gastroenterology Insights.2024; 15(2): 486. CrossRef - Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Immune Function, Tissue Fibrosis and Current Therapies
Jesús Cosín-Roger
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(12): 6416. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease—Present and Future
Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Jolanta Gruszecka, Rafał Filip
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(13): 6935. CrossRef - Role of gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis: Insights from fecal microbiota transplantation in mouse model
Qiang Wu, Lian-Wen Yuan, Li-Chao Yang, Ya-Wei Zhang, Heng-Chang Yao, Liang-Xin Peng, Bao-Jia Yao, Zhi-Xian Jiang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(31): 3689. CrossRef - Ultrasound of the bowel with a focus on IBD: the new best practice
Christina Merrill, Stephanie R. Wilson
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 50(2): 555. CrossRef - Unveiling the anti-inflammatory potential of 11β,13-dihydrolactucin for application in inflammatory bowel disease management
Melanie S. Matos, María Ángeles Ávila-Gálvez, Antonio González-Sarrías, Nuno-Valério Silva, Carolina Lage Crespo, António Jacinto, Ana Teresa Serra, Ana A. Matias, Cláudia Nunes dos Santos
Food & Function.2024; 15(18): 9254. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and mesenteric adipose tissue interactions in shaping phenotypes and treatment strategies for Crohn’s disease
Anis Hasnaoui, Racem Trigui, Mario Giuffrida
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(46): 4969. CrossRef - Pathways Affected by Falcarinol-Type Polyacetylenes and Implications for Their Anti-Inflammatory Function and Potential in Cancer Chemoprevention
Ruyuf Alfurayhi, Lei Huang, Kirsten Brandt
Foods.2023; 12(6): 1192. CrossRef - Time to eRAASe chronic inflammation: current advances and future perspectives on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system and chronic intestinal inflammation in dogs and humans
Romy M. Heilmann, Georg Csukovich, Iwan A. Burgener, Franziska Dengler
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the epithelial barrier in intestinal fibrosis associated with inflammatory bowel disease: relevance of the epithelial-to mesenchymal transition
Dulce C. Macias-Ceja, M. Teresa Mendoza-Ballesteros, María Ortega-Albiach, M. Dolores Barrachina, Dolores Ortiz-Masià
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids Elicit Differential Expression of Growth Factors and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Immortalized Rat Enteric Glial Cells
- Primary pulmonary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare entity and a literature review
- Priyanka Singh, Aruna Nambirajan, Manish Kumar Gaur, Rahul Raj, Sunil Kumar, Prabhat Singh Malik, Deepali Jain
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):231-237. Published online July 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.05.08
- 6,813 View
- 129 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma (EIMS) is an aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions and is associated with high risk of local recurrence and poor prognosis. Herein, we present a young, non-smoking male who presented with complaints of cough and dyspnoea and was found to harbor a large right lower lobe lung mass. Biopsy showed a high-grade epithelioid to rhabdoid tumor with ALK and desmin protein expression. The patient initially received 5 cycles of crizotinib and remained stable for 1 year; however, he then developed multiple bony metastases, for which complete surgical resection was performed. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of EIMS, with ALK gene rearrangement demonstrated by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Postoperatively, the patient is asymptomatic with stable metastatic disease on crizotinib and has been started on palliative radiotherapy. EIMS is a very rare subtype of IMT that needs to be included in the differential diagnosis of ALKexpressing lung malignancies in young adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
Cancers.2025; 17(8): 1327. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: Case Series With a First Report of CLTC::ALK Fusion in an Aggressive Disease
Daisy Maharjan, Carina Dehner, Ali Alani, Robert Bell, Sheila Segura
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ALK rearranged malignant mesenchymal neoplasms of thorax: therapeutically targetable ‘ALKomas’ beyond the spectrum of non-small cell lung carcinomas and thoracic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors
Shreya Sadhu, Adarsh Barwad, Asit Ranjan Mridha, Prabhat Singh Malik, Aruna Nambirajan, Deepali Jain
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(5): 1003. CrossRef - Mediastinal epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with the EML4‐ALK fusion: A case report and literature review
Tingyu Pan, Xinyu Sun, Xiao Wu, Futing Tang, Xianmei Zhou, Qian Wang, Shi Chen
Respirology Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(3): 141. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: A Report of a Rare Case
Varun Ronanki, Vaddatti Tejeswini, Inuganti Venkata Renuka, Shaik Raheema, Bakkamanthala S K Kanth
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thoracic epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare and aggressive disease with case report and literature review
Linke Yang, Pei Li, Runze Liu, Baomin Feng, Huiqing Mao, Xiaoyong Tang, Guangjian Yang
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with exceptionally long response to lorlatinib—a case report
Rafał Becht, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Justyna Żychowska, Wojciech Poncyljusz, Aleksandra Łanocha, Katarzyna Kozak, Ewa Gabrysz-Trybek, Paweł Domagała
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rare giant epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the abdominal cavity in a child: a case report and review of the literature
Jinzhou Li, Haixing Su, Sheng Zhang, Xianyun Chen, Chongzhi Hou, Tao Cheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma treated with an ALK TKI ensartinib
Mengmeng Li, Ruyue Xing, Jiuyan Huang, Chao Shi, Chunhua Wei, Huijuan Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma With Poor Response to Crizotinib: A Case Report
Soheila Aminimoghaddam, Roghayeh Pourali
Clinical Medicine Insights: Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a case report and brief literature review
Weidong Dou, Yu Guan, Tao Liu, Hang Zheng, Shuo Feng, Yingchao Wu, Xin Wang, Zhanbing Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
- Non-conventional dysplastic subtypes in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of their diagnostic characteristics and potential clinical implications
- Won-Tak Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):83-93. Published online March 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.02.17
- 10,552 View
- 447 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The early detection and grading of dysplasia is the current standard of care to minimize mortality from colorectal cancer (CRC) in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. With the development of advanced endoscopic resection techniques, colectomy is now reserved for patients with invisible/flat dysplasia (either high-grade [HGD] or multifocal low-grade dysplasia) or endoscopically unresectable lesions. Although most pathologists are familiar with the morphologic criteria of conventional (intestinal type) dysplasia, the most well-recognized form of dysplasia, an increasing number of diagnostic material has led to the recognition of several different morphologic patterns of epithelial dysplasia. The term “non-conventional” dysplasia has been coined to describe these changes, but to date, the recognition and full appreciation of these novel forms of dysplasia by practicing pathologists is uneven. The recognition of these non-conventional subtypes is becoming increasingly important, as some of them appear to have a higher risk of developing HGD or CRC than conventional dysplasia or sporadic adenomas. This review describes the morphologic characteristics of all seven non-conventional subtypes that have been reported to date as well as our current understanding of their clinicopathologic and molecular features that distinguish them from conventional dysplasia or sporadic adenomas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological subtypes of colorectal low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia: diagnostic reproducibility, frequency and clinical impact
Corinna Lang-Schwarz, Maike Büttner-Herold, Stephan Burian, Ramona Erber, Arndt Hartmann, Moritz Jesinghaus, Kateřina Kamarádová, Carlos A Rubio, Gerhard Seitz, William Sterlacci, Michael Vieth, Simone Bertz
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 78(2): 103. CrossRef - “Artificial histology” in colonic Neoplasia: A critical approach
Gavino Faa, Matteo Fraschini, Luca Didaci, Luca Saba, Mario Scartozzi, Enrico Orvieto, Massimo Rugge
Digestive and Liver Disease.2025; 57(3): 663. CrossRef - Examination of non-conventional dysplasias adjacent to colorectal adenocarcinoma in patients with IBD
Szintia Almási, Zsófia Balajthy, Bence Baráth, Zsófia Krisztina Török, Panna Szaszák, Tamás Lantos, Bence Kővári, Anita Sejben
Pathology and Oncology Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics, Management, and Outcomes of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer and the Comparison With Sporadic Colorectal Cancer in Taiwan
Hsin-Yun Wu, Meng-Tzu Weng, Jen-Wei Chou, Hsu-Heng Yen, Chun-Chi Lin, Feng-Fan Chiang, Chen-Shuan Chung, Wei-Chen Lin, Chen-Wang Chang, Puo-Hsien Le, Chia-Jung Kuo, Ching-Pin Lin, Wen-Hung Hsu, Chiao-Hsiung Chuang, Tzung-Jiun Tsai, I-Che Feng, Shu-Chen We
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2025; 16(2): e00798. CrossRef - Dysplasia in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Shows Distinct Clinicopathologic Features Compared With that in Adult Patients
Dorukhan Bahceci, Shaomin Hu, Xiaoyan Liao, Lindsay Alpert, Hwajeong Lee, Huaibin Mabel Ko, Adam L. Booth, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won-Tak Choi
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(6): 100735. CrossRef - Nonconventional dysplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal adenocarcinoma: a case-cohort study
Siri A Urquhart, Namratha Pallipamu, Hima Varsha Voruganti, Bhavana Baraskar, Pratyusha Muddaloor, Arshia K Sethi, Renisha Redij, Keirthana Aedma, Keerthy Gopalakrishnan, Shivaram Poigai Arunachalam, Kelli N Burger, Douglas W Mahoney, Blake A Kassmeyer, R
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutting Edge: A Comprehensive Guide to Colorectal Cancer Surgery in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Ionut Eduard Iordache, Lucian-Flavius Herlo, Razvan Popescu, Daniel Ovidiu Costea, Luana Alexandrescu, Adrian Paul Suceveanu, Sorin Deacu, Gabriela Isabela Baltatescu, Alina Doina Nicoara, Nicoleta Leopa, Andreea Nelson Twakor, Andrei Octavian Iordache, L
Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences.2025; 12(1): 6. CrossRef - Inflammatory bowel disease‐associated serrated lesions with dysplasia are frequently associated with advanced neoplasia: supporting a unified classification approach
Dorukhan Bahceci, Anita Sejben, Lindsay Yassan, Gregory Miller, Xiaoyan Liao, Huaibin Mabel Ko, Marcela Salomao, Masato Yozu, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2025; 87(3): 408. CrossRef - Whole-Exome Sequencing Analysis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Serrated Dysplasia
Zsófia Balajthy, Szintia Almási, Tamás Lantos, Levente Kuthi, Georgios Deftereos, Won-Tak Choi, Anita Sejben
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5704. CrossRef - Interobserver variability in the histologic evaluation of serrated epithelial change in inflammatory bowel disease among gastrointestinal pathologists: a comparison of two different definitions
Dorukhan Bahceci, Rish K Pai, Ian Brown, Joseph Misdraji, M Priyanthi Kumarasinghe, Sanjay Kakar, Gregory Y Lauwers, Dongliang Wang, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2025; 87(4): 606. CrossRef - A pilot evaluation of the artificial intelligence system CAD-EYE to optically characterise lesions in inflammatory bowel disease surveillance
Sherman Picardo, Shankar Menon, Kenji So, Kannan Venugopal, Wendy Cheng, Krish Ragunath
Therapeutic Advances in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent updates and debates on basal crypt dysplasia, serrated epithelial change, and p53 immunostaining in inflammatory bowel disease
Dorukhan Bahceci, Won-Tak Choi
Human Pathology.2025; : 105959. CrossRef - Hyperplasticus polypusszerű átalakulás gyulladásos bélbetegség diagnózisának felállításakor
Ádám Ferenczi, Anita Sejben
Orvosi Hetilap.2025; 166(31): 1230. CrossRef - Recently described types of dysplasia associated with IBD: tips and clues for the practising pathologist
Zahra Alipour, Kristen Stashek
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2024; 77(2): 77. CrossRef - Nonconventional Dysplasia is Frequently Associated With Goblet Cell Deficient and Serrated Variants of Colonic Adenocarcinoma in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Andrew Xiao, Masato Yozu, Bence P. Kővári, Lindsay Yassan, Xiaoyan Liao, Marcela Salomao, Maria Westerhoff, Anita Sejben, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won-Tak Choi
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(6): 691. CrossRef - Increased Active Inflammation in the Colon is Not a Reliable Predictor of an Elevated Risk of Dysplasia in Patients With Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Ulcerative Colitis
Ruth Zhang, Dongliang Wang, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won-Tak Choi
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(9): 1154. CrossRef - Dysplasia Detected in Patients With Serrated Epithelial Change Is Frequently Associated With an Invisible or Flat Endoscopic Appearance, Nonconventional Dysplastic Features, and Advanced Neoplasia
Dorukhan Bahceci, Lindsay Alpert, Tanner Storozuk, Xiaoyan Liao, Masato Yozu, Maria Westerhoff, Bence P. Kővári, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won-Tak Choi
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(10): 1326. CrossRef - Difficulties in diagnosis of non-conventional dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease
Kh. M. Akhrieva, A. S. Tertychnyy, N. V. Pachuashvili, L. S. Urusova
Bulletin of the Medical Institute "REAVIZ" (REHABILITATION, DOCTOR AND HEALTH).2024; 14(3): 21. CrossRef - Hypermucinosus és kehelysejtszegény, gyulladásos bélbetegséghez társult, non-conventionalis dysplasia colorectalis adenocarcinoma mellett
Szintia Almási, Bence Baráth, Panna Szaszák, Bence Kővári, Anita Sejben
Orvosi Hetilap.2023; 164(51): 2039. CrossRef - DNA content abnormality frequently develops in the right/proximal colon in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease and is highly predictive of subsequent detection of dysplasia
Ruth Zhang, Peter S. Rabinovitch, Aras N. Mattis, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2023; 83(1): 116. CrossRef - Non‐conventional dysplasia is frequently associated with low‐grade tubuloglandular and mucinous adenocarcinomas in inflammatory bowel disease
Fahire Goknur Akarca, Masato Yozu, Lindsay Alpert, Bence P Kővári, Lei Zhao, Marcela Salomao, Xiaoyan Liao, Maria Westerhoff, Gregory Y Lauwers, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2023; 83(2): 276. CrossRef - The yield of dysplasia and serrated lesions in a single-centre tertiary inflammatory bowel disease cohort
Fiona Yeaman, Lena Thin
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MYC overexpression in inflammatory bowel disease-associated conventional dysplasia and association of subsequent low-grade dysplasia in follow-up biopsies
Yuanxin Liang, Yansheng Hao, Yiqin Xiong, Minghao Zhong, Dhanpat Jain
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 248: 154642. CrossRef - Characteristics, Reporting, and Potential Clinical Significance of Nonconventional Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Won-Tak Choi
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2023; 16(4): 687. CrossRef - Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
Vladislava Stojic, Natasa Zdravkovic, Tamara Nikolic-Turnic, Nebojsa Zdravkovic, Jelena Dimitrijevic, Aleksandra Misic, Kristijan Jovanovic, Stefan Milojevic, Jelena Zivic
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - And the story goes on: non-conventional dysplasia of the colorectum
Lavisha S. Punjabi, Yi Neng Lai, Anjula Thomas
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of undetected dysplasia found in total colectomy or proctocolectomy specimens of patients with inflammatory bowel disease
Dorukhan Bahceci, Gregory Y Lauwers, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2022; 81(2): 183. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Non-conventional and Invisible Dysplasias in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ruth Zhang, Gregory Y Lauwers, Won-Tak Choi
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis.2022; 16(12): 1825. CrossRef - Increased histologic inflammation is an independent risk factor for nonconventional dysplasia in ulcerative colitis
Eric D. Nguyen, Dongliang Wang, Gregory Y. Lauwers, Won‐Tak Choi
Histopathology.2022; 81(5): 644. CrossRef
- Morphological subtypes of colorectal low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia: diagnostic reproducibility, frequency and clinical impact
- Quilty Lesions in the Endomyocardial Biopsies after Heart Transplantation
- Haeyon Cho, Jin-Oh Choi, Eun-Seok Jeon, Jung-Sun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):50-56. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.11.30
- 8,432 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical significance of Quilty lesions in endomyocardial biopsies (EMBs) of cardiac transplantation patients.
Methods
A total of 1190EMBs from 117 cardiac transplantation patients were evaluated histologically for Quilty lesions,acute cellular rejection, and antibody-mediated rejection. Cardiac allograft vasculopathy wasdiagnosed by computed tomography coronary angiography. Clinical information, including thepatients’ survival was retrieved by a review of medical records.
Results
Eighty-eight patients(75.2%) were diagnosed with Quilty lesions, which were significantly associated with acute cellularrejection, but not with acute cellular rejection ≥ 2R or antibody-mediated rejection. In patientsdiagnosed with both Quilty lesions and acute cellular rejection, the time-to-onset of Quilty lesionsfrom transplantation was longer than that of acute cellular rejections. We found a significant associationbetween Quilty lesions and cardiac allograft vasculopathy. No significant relationship wasfound between Quilty lesions and the patients’ survival.
Conclusions
Quilty lesion may be an indicator of previous acute cellular rejection rather than a predictor for future acute cellular rejection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
Andrea Fernandez Valledor, Cathrine M. Moeller, Adi Hertz, Daniel Oren, Ilan Richter, Boaz Elad, Julia Baranowska, Salwa Rahman, Carolyn Hennecken, Afsana Rahman, Dor Lotan, David Bae, Adil Yunis, Justin A. Fried, Ersilia M. DeFilippis, David T Majure, Ja
The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of tertiary lymphoid structures in orchestrating immune responses in peripheral organs
Keisuke Taniguchi, Takahisa Yoshikawa, Motoko Yanagita
Inflammation and Regeneration.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The human myocardium harbors a population of naive B-cells with a distinctive gene expression signature conserved across species
Kevin C. Bermea, Nicolas Kostelecky, Sylvie T. Rousseau, Chieh-Yu Lin, Luigi Adamo
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of tracheal allografts after long-term survival in dogs
Tao Lu, Yiwei Huang, Yulei Qiao, Yongxing Zhang, Yu Liu
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.2021; 59(1): 155. CrossRef - Essentials in the diagnosis of postoperative myocardial lesions similar to or unrelated to rejection in heart transplant
Costel Dumitru, Ancuta Zazgyva, Adriana Habor, Ovidiu Cotoi, Horațiu Suciu, Carmen Cotrutz, Bogdan Grecu, Ileana Anca Sin
Revista Romana de Medicina de Laborator.2021; 29(3): 307. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of donor heart with prolonged cold ischemic time: A single‐center study
Fazal Shafiq, Yixuan Wang, Geng Li, Zongtao Liu, Fei Li, Ying Zhou, Li Xu, Xingjian Hu, Nianguo Dong
Journal of Cardiac Surgery.2020; 35(2): 397. CrossRef - The XVth Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology the Banff Workshop Heart Report: Improving the diagnostic yield from endomyocardial biopsies and Quilty effect revisited
Jean-Paul Duong Van Huyen, Marny Fedrigo, Gregory A. Fishbein, Ornella Leone, Desley Neil, Charles Marboe, Eliot Peyster, Jan von der Thüsen, Alexandre Loupy, Michael Mengel, Monica P. Revelo, Benjamin Adam, Patrick Bruneval, Annalisa Angelini, Dylan V. M
American Journal of Transplantation.2020; 20(12): 3308. CrossRef
- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
- A Review of Inflammatory Processes of the Breast with a Focus on Diagnosis in Core Biopsy Samples
- Timothy M. D’Alfonso, Paula S. Ginter, Sandra J. Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(4):279-287. Published online June 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.06.11
- 29,332 View
- 491 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 49 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory and reactive lesions of the breast are relatively uncommon among benign breast lesions and can be the source of an abnormality on imaging. Such lesions can simulate a malignant process, based on both clinical and radiographic findings, and core biopsy is often performed to rule out malignancy. Furthermore, some inflammatory processes can mimic carcinoma or other malignancy microscopically, and vice versa. Diagnostic difficulty may arise due to the small and fragmented sample of a core biopsy. This review will focus on the pertinent clinical, radiographic, and histopathologic features of the more commonly encountered inflammatory lesions of the breast that can be characterized in a core biopsy sample. These include fat necrosis, mammary duct ectasia, granulomatous lobular mastitis, diabetic mastopathy, and abscess. The microscopic differential diagnoses for these lesions when seen in a core biopsy sample will be discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical-radiologic-pathologic characterization of diabetic mastopathy: an analysis of 21 cases
Juan Chen, Chao Zhang, Zhilong Liu, Zhuojun Qi, Lele Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of fatty acid composition in mammary adipose tissue using deep neural network with unsupervised training
Suneeta Chaudhary, Elizabeth G. Lane, Allison Levy, Anika McGrath, Eralda Mema, Melissa Reichmann, Katerina Dodelzon, Katherine Simon, Eileen Chang, Marcel Dominik Nickel, Linda Moy, Michele Drotman, Sungheon Gene Kim
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.2025; 93(5): 2163. CrossRef - Society of surgical oncology medical student & trainee primer for breast surgical oncology
Marissa K. Boyle, Julia M. Selfridge, Rachel E. Sargent, Y. Everett Warren, Julia M. Chandler, Christopher P. Childers
Surgical Oncology Insight.2025; 2(1): 100129. CrossRef - An update on multimodal imaging strategies for nipple discharge: from detection to decision
Mireia Pitarch, Rodrigo Alcantara, Laura Comerma, Ivonne Vázquez de Las Heras, Javier Azcona, Antonia Wiedemann, Maja Prutki, Eva Maria Fallenberg
Insights into Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Benign Breast Lesions: Diagnostic Utility and Drawbacks of Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology
Shirish S. Chandanwale, Kumar Roushan, Mallika Agarwal, Madhuri Singh, Abhishek Tambile, Ranjana Roy
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Health Care.2025; 17(1): 39. CrossRef - Squamous Metaplasia of Lactiferous Ducts (SMOLD) in a Male Patient: Clinical, Dermoscopic, and Histopathological Insights
Beata Zagórska, Przemysław Miłosz, Jakub Żółkiewicz, Urszula Maińska, Martyna Sławińska
Diagnostics.2025; 15(19): 2489. CrossRef - Ductal carcinoma in situ: Current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Jelena Petrović, Stefan Stevanović
Srpski medicinski casopis Lekarske komore.2025; 6(3): 318. CrossRef - The diagnostic dilemma of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with an emphasis on histopathologic findings
Kiana Anousha, Behnaz Jahanbin, Farid Azmoudeh Ardalan, Vahid Soleimani, Maryam Azizi, Amin Rezvani
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical profiles, imaging findings and antituberculosis treatment outcome in granulomatous mastitis: An Indian scenario
R. Mithen, R.R. Mahin Nallasivam, Dhanasekar Thangaswamy, T. Mohanapriya
Indian Journal of Tuberculosis.2024; 71(2): 163. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis: A diagnostic challenge—3 year single institutional experience
Adil Aziz Khan, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer, Charanjeet Ahluwalia, Mukul Singh, Sachin Kolte, Sunil Ranga
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(1): 50. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of rifampicin-based triple therapy for non-puerperal mastitis: A single-arm, open-label, prospective clinical trial
Fei Zhou, Huanjie Li, Fei Wang, Liyuan Liu, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhigang Yu
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2024; 140: 25. CrossRef - Periductal Mastitis, a Disease with Distinct Clinicopathological Features from Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis
Fei Zhou, Liyuan Liu, Fei Wang, Lixiang Yu, Yujuan Xiang, Chao Zheng, Shuya Huang, Zhen Yang, Zhigang Yu
Journal of Inflammation Research.2024; Volume 17: 3815. CrossRef - MASTITE GRANULOMATOSA E O DIFÍCIL MANEJO DA DOENÇA: UMA REVISÃO SISTEMÁTICA DE LITERATURA
Samara Alves Messias Viana, Laís Barbosa de Azevedo Bulsoni
REVISTA FOCO.2024; 17(6): e5136. CrossRef - Autoimmune Mastitis in a Patient with Behcet’s Syndrome: A Case Report with Rapid Changes in Radiologic Features and Characteristic Pathologic Findings
Yun Hwa Chang, Suk Jin Park, Joo Heon Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024; 85(6): 1221. CrossRef - Possibilities of MRI in the differential diagnosis of non-lactative mastitis and cancer
S. V. Serebryakova, T. A. Shumakova, E. A. Yukhno, O. B. Safronova, A. L. Serebryakov
Medical Visualization.2023; 27(2): 36. CrossRef - Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis in seventy seven-female patients: Management, follow up of an overlooked immune-mediated disease, and review of literature
Amira A. Shahin, Emad Khallaf, Lamiaa A. Salaheldin, Somia A.M. Soliman, Yosra S. Rezk, Marwa H. Niazy
The Egyptian Rheumatologist.2023; 45(3): 183. CrossRef - Increased breast cancer mortality due to treatment delay and needle biopsy type: a retrospective analysis of SEER-medicare
Rashmi Pathak, Macall Leslie, Priya Dondapati, Rachel Davis, Kenichi Tanaka, Elizabeth Jett, Inna Chervoneva, Takemi Tanaka
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(4): 627. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and therapeutic strategy of granulomatous mastitis accompanied by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: a retrospective cohort study
ShunBo Li, Qian Huang, PeiPei Song, XiaoRong Han, ZeYu Liu, Lin Zhou, Ping Ning
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano Uncaria gambir as Chemopreventive Agent Against Breast Cancer
Andika Pramudya Wardana, Nanik Siti Aminah, Alfinda Novi Kristanti, Mochamad Zakki Fahmi, Haninda Iffatuz Zahrah, W Widiyastuti, Hendrix Abdul Ajiz, Ummi Zubaidah, Priangga Adi Wiratama, Yoshiaki Takaya
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 4471. CrossRef - Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
Gulisa Turashvili, Xiaoxian Li
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(10): 1133. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Inflammatory granulomatous mastitis caused by Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii: A clinical challenge
I.M. Brouwer de Koning, A. Lemson, N.H.M. Renders, M. Bessems, P.T.G.A. Nooijen, W.A. Draaisma, K. Bosscha
Clinical Infection in Practice.2022; 15: 100147. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Case Report: Open biopsy and drainage for breast abscess caused by cholesterol granuloma is beneficial rather than breast core biopsy
Freda Halim, Ricarhdo Valentino Hanafi, Eka Julianta Wahjoepramono
F1000Research.2022; 11: 511. CrossRef - Exocrine gland structure-function relationships
Sameed Khan, Sarah Fitch, Sarah Knox, Ripla Arora
Development.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision pathology as applied to breast core needle biopsy evaluation: implications for management
Laura C. Collins
Modern Pathology.2021; 34: 48. CrossRef - Granulomatous mastitis, watch and wait is a good option
Gökay Çetinkaya, Ramazan Kozan, Ahmet Cihangir Emral, Ekmel Tezel
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2021; 190(3): 1117. CrossRef - Mammary duct ectasia in adult females; risk factors for the disease, a case control study
Ayad Ahmad Mohammed
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2021; 62: 140. CrossRef - Palpable Lumps after Mastectomy: Radiologic-Pathologic Review of Benign and Malignant Masses
Rend Al-Khalili, Ali Alzeer, Giang-Kimthi Nguyen, Erin P. Crane, Judy H. Song, Janice L. Jeon, Michael Nellamattathil, Erini V. Makariou, Victoria L. Mango
RadioGraphics.2021; 41(4): E967. CrossRef - A case report of TB versus idiopathic granulomatous mastitis with erythema nodosum, reactive arthritis, cough, and headache
Fatma Ben Abid, Hussam Abdel Rahman S. Al Soub
The Aging Male.2020; 23(5): 411. CrossRef - Imaging features of granulomatous mastitis in 36 patients with new sonographic signs
Afsaneh Alikhassi, Fahimeh Azizi, Fereshteh Ensani
Journal of Ultrasound.2020; 23(1): 61. CrossRef - Secreciones mamarias
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Ginecología-Obstetricia.2020; 56(1): 1. CrossRef - Mastitis in Autoimmune Diseases: Review of the Literature, Diagnostic Pathway, and Pathophysiological Key Players
Radjiv Goulabchand, Assia Hafidi, Philippe Van de Perre, Ingrid Millet, Alexandre Thibault Jacques Maria, Jacques Morel, Alain Le Quellec, Hélène Perrochia, Philippe Guilpain
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 958. CrossRef - Factors associated with treatment duration and recurrence rate of complicated mastitis
Ming-Jui Tsai, Wei-Chia Huang, Jann-Tay Wang, Ming-Yang Wang, Yi-Hsuan Lee, Shu-Wen Lin, Sung-Ching Pan, Shan-Chwen Chang
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.2020; 53(6): 875. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis: an update
Jessie M Wu, Gulisa Turashvili
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 73(8): 445. CrossRef - Coryneform Bacteria in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis: Morphological Diagnosis in Breast Biopsies
David Oddó, Angeles Stefanelli, Alejandra Villarroel, Gonzalo P. Méndez
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 27(4): 380. CrossRef - Sonographic features of inflammatory conditions of the breast
Alice Febery, Ian Bennett
Australasian Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2019; 22(3): 165. CrossRef - Écoulements mamelonnaires
C. Mathelin, N. Weingertner, M. Lodi, S. Molière
EMC - Gynécologie.2019; 34(4): 1. CrossRef - Etiología de la mastitis crónica: propuesta de secuencia diagnóstica
A. García-Vilanova Comas, J. Galbis Caravajal, V. Sabater Marco, C.A. Fuster Diana, F. Villalba Ferrer, M. Bruna Esteban, C. Zaragozá Fernández
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2018; 45(3): 98. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Manifestations at Multimodality Imaging and Pitfalls
Cedric W. Pluguez-Turull, Jennifer E. Nanyes, Cristina J. Quintero, Hamza Alizai, Daniel D. Mais, Kenneth A. Kist, Nella C. Dornbluth
RadioGraphics.2018; 38(2): 330. CrossRef - Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii in granulomatous mastitis: Analysis of formalin‐fixed, paraffin‐embedded biopsy specimens by immunostaining using low‐specificity bacterial antisera and real‐time polymerase chain reaction
Mari Fujii, Yasuyoshi Mizutani, Takahiko Sakuma, Kouichiro Tagami, Kiichiro Okamoto, Yasushi Kuno, Michihiko Harada, Koichi Kubouchi, Yutaka Tsutsumi
Pathology International.2018; 68(7): 409. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis Presenting as a Breast Pseudotumor: Case Reports with Review of the Literature
Nour Abdul Halim, Imad Uthman, Rayan Rammal, Hazem I. Assi
Case Reports in Rheumatology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - UTILITY OF FNAC IN UNCOMMON INFLAMMATORY AND REACTIVE LESIONS OF BREAST: AN UNSUSPECTED CLINICAL SCENARIO
Rallapalli Rajyalakshmi, Mohammad Akhtar, Rani Vijaya Bhaskar, Kada Venkataramana, Guttikonda Nageswararao, Rayachoti Sridhar
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2018; 5(44): 3070. CrossRef - Inflammatory breast disease: A pictorial essay with radiological‐pathological correlation
Rusiru P Gunawardena, Deepika Gunawardena, Cecily Metcalf, Donna Taylor, Liz Wylie
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2017; 61(1): 70. CrossRef - Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis associated with Corynebacterium including Corynebacterium kroppenstedtii
Kate J. Johnstone, Jennifer Robson, Sarah G. Cherian, Jenny Wan Sai Cheong, Kris Kerr, Judith F. Bligh
Pathology.2017; 49(4): 405. CrossRef - Is contrast‐enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) helpful in differentiating diabetic mastopathy from breast carcinoma?
María del Mar Travieso Aja, Gloria Santana López, Mario Rodríguez Rodríguez, Octavio P Luzardo
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology.2016; 60(5): 639. CrossRef - Lesiones inflamatorias mamarias benignas
Andrés García-Vilanova Comas, Vicente Sabater Marco, Carlos Fuster Diana, Francisco Villalba Ferrer, José Medrano González, Ramón Gómez Contreras
Revista Española de Patología.2016; 49(3): 169. CrossRef - Granulomatous lobular mastitis
Fei Zhou, Li‐Xiang Yu, Zhong‐Bing Ma, Zhi‐Gang Yu
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2016; 2(1): 17. CrossRef - Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Cytologic and Histologic Study of 65 Egyptian Patients
Thanaa El A. Helal, Lobna S. Shash, Somaia A. Saad El-Din, Sally M. Saber
Acta Cytologica.2016; 60(5): 438. CrossRef
- Clinical-radiologic-pathologic characterization of diabetic mastopathy: an analysis of 21 cases
- Advances in the Endoscopic Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Cooperation between Endoscopic and Pathologic Evaluations
- Jae Hee Cheon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):209-217. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.04.09
- 14,554 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Endoscopic assessment has a crucial role in the management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is particularly useful for the assessment of IBD disease extension, severity, and neoplasia surveillance. Recent advances in endoscopic imaging techniques have been revolutionized over the past decades, progressing from conventional white light endoscopy to novel endoscopic techniques using molecular probes or electronic filter technologies. These new technologies allow for visualization of the mucosa in detail and monitor for inflammation/dysplasia at the cellular or sub-cellular level. These techniques may enable us to alter the IBD surveillance paradigm from four quadrant random biopsy to targeted biopsy and diagnosis. High definition endoscopy and dye-based chromoendoscopy can improve the detection rate of dysplasia and evaluate inflammatory changes with better visualization. Dye-less chromoendoscopy, including narrow band imaging, iScan, and autofluorescence imaging can also enhance surveillance in comparison to white light endoscopy with optical or electronic filter technologies. Moreover, confocal laser endomicroscopy or endocytoscopy have can achieve real-time histology evaluation in vivo and have greater accuracy in comparison with histology. These new technologies could be combined with standard endoscopy or further histologic confirmation in patients with IBD. This review offers an evidence-based overview of new endoscopic techniques in patients with IBD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Moxifloxacin promotes two-photon microscopic imaging for discriminating different stages of DSS-induced colitis on mice
Yingtong Chen, Xiaoyi Xu, Min Wang, Xiang Wang, Yan Wang, Yong Zhang, Jin Huang, Yuwen Tao, Wentao Fan, Lili Zhao, Li Liu, Zhining Fan
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2024; 48: 104220. CrossRef - Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: review of the evidence
D. S. Keller, A. Windsor, R. Cohen, M. Chand
Techniques in Coloproctology.2019; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel diseases: a case series
Jung Won Park, Tae Il Kim, Jae Hee Cheon
Intestinal Research.2018; 16(4): 641. CrossRef - How to Assess and Document Endoscopies in IBD Patients by Including Standard Scoring Systems
Anna M. Buchner, Gary R. Lichtenstein
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2016; 22(4): 1010. CrossRef - Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia: A marker of low-grade inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome?
Anna Chiara Piscaglia, Lucrezia Laterza, Valentina Cesario, Viviana Gerardi, Rosario Landi, Loris Riccardo Lopetuso, Giovanni Calò, Giovanna Fabbretti, Massimo Brisigotti, Maria Loredana Stefanelli, Antonio Gasbarrini
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(46): 10198. CrossRef
- Moxifloxacin promotes two-photon microscopic imaging for discriminating different stages of DSS-induced colitis on mice
- Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Variant Presenting as a Colonic Polyp
- Shien-Tung Pan, Chih-Yuan Cheng, Nie-Sue Lee, Peir-In Liang, Shih-Sung Chuang
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):140-145. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.140
- 11,624 View
- 105 Download
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Follicular dendritic cell (FDC) sarcoma is rare and is classified either as conventional type or inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT)-like variant. Extranodal presentation is uncommon and nearly all gastrointestinal FDC tumors are of the conventional type. IPT-like variant tumors occur almost exclusively in the liver and spleen and are consistently associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Here we report the case of a 78-year-old woman with an IPT-like FDC sarcoma presenting as a pedunculated colonic polyp. Histologically, scanty atypical ovoid to spindle cells were mixed with a background of florid lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, which led to an initial misdiagnosis of pseudolymphoma. These atypical cells expressed CD21, CD23, CD35, and D2-40, and were positive for EBV by
in situ hybridization, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was free of disease five months after polypectomy without adjuvant therapy. Although extremely rare, the differential diagnosis for colonic polyp should include FDC sarcoma to avoid an erroneous diagnosis. A review of the 24 cases of IPT-like FDC sarcoma reported in the literature reveal that this tumor occurs predominantly in females with a predilection for liver and spleen, and has a strong association with EBV.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The fifth edition of the WHO classification of mature T cell, NK cell and stroma-derived neoplasms
Ayoma D Attygalle, Kennosuke Karube, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Wah Cheuk, Govind Bhagat, John K C Chan, Kikkeri N Naresh
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 78(4): 217. CrossRef - Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma: A Multicenter Study
Yan Li, Ze-Lin Weng, Han-Xiao Fei, Hai-Feng Li, Yi-Na Liu, Le-Le Zhang, Qiong Zhang, Xin Weng, Yuan-Yuan Wang, Wen-Yong Huang, Zhi-Xing Cao, Kai-Yan Yang, Xi-Liang Chen, Jie Gao, Wen-Sheng Yang, Fang Liu, Juan-Juan Yong, Jing-Ping Yun, Hua Zhang, Yu-Hua H
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(10): 100864. CrossRef - What is new in the 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of mature B and T/NK cell tumors and stromal neoplasms?
Ayoma D. Attygalle, John K. C. Chan, Sarah E. Coupland, Ming-Qing Du, Judith A. Ferry, Daphne de Jong, Dita Gratzinger, Megan S. Lim, Alina Nicolae, German Ott, Andreas Rosenwald, Anna Schuh, Reiner Siebert
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(2): 71. CrossRef - Pathologic characteristics of histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms
Sun Och Yoon
Blood Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-barr virus (EBV)-positive inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (IPT-like FDCS) presenting as thrombocytopenia: A case report and literature review
Jiawei Jin, Xiaolong Zhu, Yi Wan, Yang Shi
Heliyon.2024; 10(12): e32997. CrossRef - EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the colon with clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement: A case report and literature review
Xia Xu, Xiuzhen Li, Qun Deng, Kaihang Yu, Jinfan Li
Heliyon.2024; 10(11): e31947. CrossRef - Challenges in the Diagnosis of Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma
Yan Li, Xia Yang, Lili Tao, Weimei Zeng, Min Zuo, Shuo Li, Liyan Wu, Yanshong Lin, Ziying Zhang, Jingping Yun, Yuhua Huang
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 47(4): 476. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma Presenting as a Colonic Polyp: Report of a Case with a Literature Review
Jiahui Hu, Dongdong Huang, Chengfu Xu, Yi Chen, Han Ma, Zhe Shen
Medicina.2023; 59(7): 1341. CrossRef - A Clinicopathology Review and Update of Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Mesenchymal Tumors
Oswald Zhao Jian Lee, Noorjehan Omar, Joshua K. Tay, Victor Kwan Min Lee
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5563. CrossRef - Granulomatous splenic mass with necrosis revealing an EBV-positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Irena Antonia Ungureanu, Renato Micelli Lupinacci, Marie Parrens, Jean-François Emile
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A rare case and minireview of the literature
Fan Ding, Chao Wang, Chi Xu, Hui Tang
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of gastrointestinal tract with two emerging distinct subtypes: a case report and systemic review
Hongxing Gui, Jigisha Chaudhari, Rifat Mannan
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical treatment of liver inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A case report
Li-Yue Fu, Jiu-Liang Jiang, Meng Liu, Jun-Jun Li, Kai-Ping Liu, Hai-Tao Zhu
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2022; 14(11): 2288. CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular/fibroblastic dendritic cell sarcoma: focus on immunohistochemical profile and association with Epstein-Barr virus
Francesca Pagliuca, Andrea Ronchi, Annamaria Auricchio, Eva Lieto, Renato Franco
Infectious Agents and Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Advances in Digestive Tract Tumors: Updates From the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization “Blue Book”
Raul S. Gonzalez, Anwar Raza, Robert Propst, Oyedele Adeyi, Justin Bateman, Sabrina C. Sopha, Janet Shaw, Aaron Auerbach
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(5): 607. CrossRef - Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor: a case report
Ana Daniela Pascariu, Andreea Ioana Neagu, Andrei Valentin Neagu, Alexandru Băjenaru, Cezar Iulian Bețianu
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: Literature review of 67 cases
Hao Wu, Peng Liu, Xiao-Ran Xie, Jing-Shu Chi, Huan Li, Can-Xia Xu
World Journal of Meta-Analysis.2021; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - New Clinicopathologic Scenarios of EBV+ Inflammatory Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma
Xiang-Nan Jiang, Yan Zhang, Tian Xue, Jie-Yu Chen, Alex C.L. Chan, Wah Cheuk, John K.C. Chan, Xiao-Qiu Li
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2021; 45(6): 765. CrossRef - Select Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Digestive Tract Lesions for the Practicing Pathologist
Zainab I. Alruwaii, Elizabeth A. Montgomery
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(5): 562. CrossRef - Overview of Gastrointestinal Lymphoproliferative disorders✰
Aaron Auerbach, Nadine S. Aguilera
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2021; 38(4): 1. CrossRef - Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Fabio Facchetti, Matteo Simbeni, Luisa Lorenzi
Pathologica.2021; 113(5): 316. CrossRef - Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor with hepatic lymphoma history
Jiang Li, Hai-su Tao, Dong Chen, Zhi-yong Huang, Er-lei Zhang
Medicine.2021; 100(39): e27392. CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of extranodal follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Dayong Sun, Gang Zhang
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumour-like follicular dendritic cell tumour of the colon with plasmacytosis mimicking EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disorder
Ying-Ren Chen, Chi-Lin Lee, Yen-Chien Lee, Kung-Chao Chang
Pathology.2020; 52(4): 484. CrossRef - Beware the inflammatory cell-rich colonic polyp: a rare case of EBV-positive inflammatory pseudotumour-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma with increased IgG4-positive plasma cells
Lynne Goh, Nan Zun Teo, Lai Mun Wang
Pathology.2020; 52(6): 713. CrossRef - Epstein–Barr virus‐positive inflammatory follicular dendritic cell sarcoma presenting as a solitary colonic mass: two rare cases and a literature review
Xiaokang Ke, Huihua He, Qingping Zhang, Jingping Yuan, Qilin Ao
Histopathology.2020; 77(5): 832. CrossRef - Inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: A brief report of two cases
Bi-Xi Zhang, Zhi-Hong Chen, Yu Liu, Yuan-Jun Zeng, Yan-Chun Li
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2019; 11(12): 1231. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated lymphoid proliferations, a 2018 update
Sherif A. Rezk, Xiaohui Zhao, Lawrence M. Weiss
Human Pathology.2018; 79: 18. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Epstein-Barr Virus Negative Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma Presenting as a Solitary Colonic Mass in a 53-Year-Old Woman; Case Report and Review of Literature
Rossana Kazemimood, Farid Saei Hamedani, Asma Sharif, Sujata Gaitonde, Elizabeth Wiley, Pier Cristoforo Giulianotti, John Vincent Groth
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2017; 25(5): e30. CrossRef - A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma of the Lymph Node in the Small Bowel Mesentery Accompanied by Myasthenia Gravis
Daichi KITAGUCHI, Katsuji HISAKURA, Taiki SATO, Masanao KURATA, Tatsuya ODA, Nobuhiro OHKOHCHI
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association).2017; 78(3): 527. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features of inflammatory pseudotumour‐like follicular dendritic cell tumour of the abdomen
Yanyang Chen, Huijuan Shi, Hui Li, Tiantian Zhen, Anjia Han
Histopathology.2016; 68(6): 858. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Follicular Dendritic Cell Sarcoma with Pseudochylous Effusion and Review of Literature From India
Kamal Kant Sahu, Gaurav Prakash, Sandeep Rao, Amanjit Bal, Pankaj Malhotra, Jasmina Ahluwalia, Rakesh K. Vashistha
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion.2015; 31(2): 307. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus–associated inflammatory pseudotumor presenting as a colonic mass
Shunyou Gong, Iwona Auer, Rajan Duggal, Stefania Pittaluga, Mark Raffeld, Elaine S. Jaffe
Human Pathology.2015; 46(12): 1956. CrossRef - Response of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma to gemcitabine and docetaxel: report of two cases and literature review
Robert M Conry
Clinical Sarcoma Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- The fifth edition of the WHO classification of mature T cell, NK cell and stroma-derived neoplasms
- Epstein-Barr virus-associated Inflammatory Pseudotumor-like Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor in the Spleen of a Patient with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
- Sun Och Yoon, Hyoungsuk Ko, Baek hui Kim, Ghee Young Kwon, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Chul Woo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2007;41(3):198-202.
- 2,469 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell tumor (IPT-like FDC tumor). The tumor occurred in the spleen of a 64-year-old woman with a history of a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of neck nodes that presented four years ago. The splenectomy specimen revealed a 5 cm-sized, tan-colored and well-circumscribed mass. Histologically, spindle or ovoid cells with large vesicular nuclei were admixed with abundant inflammatory cells. Immunohistochemically, spindle cells were positive for FDC marker CD35, but negative for CD20, CD30 and ALK. EBV was detected almost exclusively in spindle cells by EBER in situ hybridization. IPT-like FDC tumors are rare, and are recognized as a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of FDC tumors. Among only 18 similar cases reported in the English language literature, the present case is the first case of a patient with a history of DLBCL.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Lung: Report of A Case Misdiagnosed as Adenocarcinoma .
- Wan Seop Kim, Eun Kyung Hong, Moon Hyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1999;10(2):145-149.
- 2,169 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cytologic features of inflammatory pseudotumor of the lung have not been described frequently. We report fine needle aspiration cytologic(FNAC) finding of a case of inflammatory pseudotumor misdiagnosed as adenocarcinoma in a 63-year-old man. The FNAC displayed a mixture of histiocytes, myofibroblasts, pneumocytes, and plasma cells. Some histiocytes and myofibroblasts had large nuclei with irregular nuclear membrane and prominent nucleoli, which mislead the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma on FNAC. The heterogeneous cell population is the unique cytologic features of inflammatory pseudotumor, which are helpful to distinguish it from other circumscribed benign and malignant lesions. Familiarity with these features is essential to avoid misdiagnosis and possible overtreatment.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Paratesticular Area: A Case Report.
- Na Rae Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jae Gul Chung, Joungho Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(3):208-211.
- 2,253 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumors of the paratesticular area are rare, and are often reported in the literature by various terms, e.g., proliferative funiculitis, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation and fibrous pseudotumor. This is one of the most common lesions of that region, and typically presents as a longstanding, painless scrotal mass. Here, we describe a 34 year-old man who has had a palpable scrotal mass for the past 10 years. The excised mass was composed of multiple conglomerated nodules, which had homogeneous rubbery cut surfaces. Histologically, each was a well circumscribed, but unencapsulated mass of hyalinized collagenous tissue interspersed with lymphoplasmacytic cells and lymphoid follicle formation. A small fraction of paucicellular spindle cells was positive for vimentin, smooth muscle actin and CD68. Ultrastructurally, abundant collagen fibrils were mixed with paucicellular spindle cells and inflammatory cells. These spindle cells had abundant rough endoplasmic reticula and myofilaments with focal densities, indicating myofibroblastic differentiation.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Lymph Node: A case report.
- Yee Jeong Kim, Kun Chang Song, Woo Hee Jung, Woon Sup Han
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(2):164-168.
- 2,314 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 21-year-old man presented with a 7 days history of fever. Careful clinical examination led to the discovery of left supraclavicular lymphadenopathy without hepatosplenomegaly. Serologic tests for Ebstein-Barr virus, HIV, hepatitis type B & C, syphilis and typhoid fever were negative. Blood, urine, and stool cultures yielded no growth. Histologically, the process mainly involved the connective tissue framework of the lymph node, sharing the features of inflammatory pseudotmor(IPT) of other organs: a storiform growth pattern, increased vascularity with associated vascular lesions, and a polymorphous inflammatory infiltrate in a collagen-rich stroma. Immunohistochemical study for spindle cells showed positive reaction for actin and vimentin but not for desmin, and lymphoid cells revealed polyclonality. Characteristics of mass formation, and the inflammatory nautre of the process enabled us adopt the term IPT which should be differentiated from hematolymphoid proliferative disorder or mesenchymal neoplasia.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor in Mesentery: A Case Report.
- Hyun Jin Son, Joo Heon Kim, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Ho Yeul Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2000;11(1):35-40.
- 2,151 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor was initially recognized in the lung, this tumor has been described in other extrapulmonary sites. In spite of relatively uniform histologic findings in various organs, a rarity in extrapulmonary sites and highly vascular characteristics frequently lead to a misdiagnosis in preoperative radiology and fine needle aspiration cytology. We present a case of inflammatory myofibro blastic tumor occurring in the mesentery of a 4-month-old girl. Fine needle aspira tion cytology smear disclosed characteristic spindle cells intermixed with prominent mature plasma cells and lymphocytes. According to the immunohistochemical staining, we recognized that the intervening spindle cells are myofibroblasts which have reactivity for the both actin and vimentin.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Kidney.
- Hwa Eun Oh, Jeong Seok Moon, Sung Jin Cho, Nam Hee Won
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(6):592-594.
- 2,140 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor, originally described in the lung, is a relatively rare tumor-like lesion that occurs in various organs and tissues. It is usually well demarcated from the surrounding tissue, however it can be unfortunately resected as a malignant tumor. A few inflammtory pseudotumor in the kidney have been reported in English literature, but there have been no reports in Korea. We report a case with inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. A 48 year old woman had an intermittent flank pain on the right side. An ultrasonographic study suggested a renal cell carcinoma and a nephrectomy was done. Grossly, there were two separate masses with a well demarcated yellowish appearance, measuring 2.3 cm and 1.3 cm in diameter, respectively. Histologically, they were composed of smooth muscle actin positive spindle cells and a large number of foamy histiocytes, lymphocytes, and plasma cells in the fibrotic backgound.
- Effect of Atorvastatin, a HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor, in Experimental Colitis in Mice.
- Hyo Jin Park, Tae Woon Kim, Jae Nam Seo, Kwon Ik Oh, Eun Young Choi, Hyung Sik Shin, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(6):401-407.
- 2,242 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The statins, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors, are approved for cholesterol reduction, and may also be beneficial in the treatment of inflammatory disease. In this study, atorvastatin was tested in experimental colitis, a disease model of inflammatory bowel disease.
METHODS
To induce colitis, dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) or trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) were administrated to C57BL/6 or BALB/c mice. Mice were monitored daily for loss of body weight and survival for indicated days. Colon length and histology were examined after sacrifice.
RESULTS
The administration of DSS induced marked colonic inflammation and shortening, and resulted in a loss of body weight. DSSinduced colitis was not affected by atorvastatin treatment, but in contrast, the administration of atorvastatin relieved TNBS-induced colitis with a resultant rapid recovery of weight loss and a reduction in colonic length shortening. Histologically, inflammatory cell infiltration in the colonic wall, mucosal ulceration and crypt disruption were also suppressed in atorvastatin treated mice.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that atorvastatin preserves intestinal integrity in colitis, probably via the modulation of Th cell-mediated immune response, in a manner independent of innate immunity.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings of Gastric Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: A case report.
- Ji Hye Lee, Bong Kyung Shin, Chung Yeul Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Han Kyeom Kim, In Sun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2001;12(2):117-120.
- 1,963 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, histologically characterized by the presence of bland-looking spindle cells and infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells, is extremely rare in the gastric wall. We report a case of gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in a 27-month-old boy. The fine needle aspiration biopsy from the mass showed loose clusters or scattered spindle cells and inflammatory cells, predominantly of lymphocytes and plasma cells. The spindle cells resembled fibroblasts or myofibroblasts. Differential diagnosis from benign and malignant diseases involving abdominal cavity was discussed.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Breast: A Case Report.
- Myoung Ja Chung, So Yeong Oh, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(1):54-58.
- 2,311 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is characterized by a clonal proliferation of myofibroblasic spindle cells, and this is accompanied by a lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. In the majority of cases, this disease has occurred in the lungs and only 9 cases of IMT in the breast have been previously reported. We report here on an IMT in a 25-year-old-female who presented with a palpable mass in the right breast. Histologically, it was characterized by plump spindle cells admixed with prominent inflammation, that was composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells. Immunohistochemically, the spindle cells were positive for vimentin and -smooth muscle actin.
- Immunohistochemical Findings in 10 Cases of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor.
- Soo Jin Jung, Mi Seon Kang, Chang Hoon Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):717-722.
- 2,410 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A wide range of denomination has been used for inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT). IMT is not entirely homogeneous, even though it shows some overlapping histologic features such as haphazard proliferation of spindle cell and polymorphic chronic inflammatory cell infiltraion. The spindle cell is considered to be of myofibroblastic origin but follicular dendritic cell origin was reported recently. IMT is known as nonneoplastic, aberrant inflammatory response. However, IMT could show local invasion, recurrence, vascular invasion, and malignant transformation, and clonal characteristics and aneuploidy of IMT support the hypothesis that IMT may be a neoplastic process. In order to define the nature of spindle cell of IMT, immunohistochemical stains for smooth muscle actin (SMA), vimentin (VMT), lysozyme, S-100 protein, cytokeratin, CD21 were done. Additional immunohistochemical stains for MIB-1 for proliferating activity and LMP (latent membrane protein) for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) were done. IMTs were composed of each 2 cases from lung, liver and lymph node and one case from common bile duct, maxillary sinus, bladder and thigh, and were histologically subclassified according to Coffin et al. Nine cases (90%) were positive for SMA and VMT, but no correlation between SMA and VMT immunoreactivity and histologic types was identified. Five cases (50%) were positive for lysozyme and S-100 protein, and histologic type III was negative for lysozyme and S-100 protein, and immunoreactivity for S-100 protein was different according to the histologic subtypes. All 11 cases were negative for CD21 and EBV LMP. MIB-1 labelling index was less than 1% in all cases. In summary, the spindle cell is regarded as myofibroblastic origin rather than follicular dendritic cell origin. Relationship with EBV is not clear, and negligible MIB-1 reaction suggests that IMT might have a good prognosis.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Mesentery: A case report.
- Sung Jig Lim, Gou Young Kim, Jae Hoon Park, Youn Wha Kim, Yong Koo Park, Ju Hie Lee, Moon Ho Yang
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(9):729-732.
- 2,139 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor or inflammatory pseudotumor is characterized by spindle cell proliferation with inflammatory cell infiltration, predominantly plasma cells and lymphocytes. We have experienced a case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the mesentery in a 57-year-old male patient with intermittent abdominal pain. On computer tomography, a well demarcated mass was seen in the mesenteric side of the ascending colon. Right hemicolectomy was performed under the impression of the metastatic tumor of lymph nodes. Grossly, a rather well-circumscribed gray white mass was noted in the mesentery of the ascending colon. Microscopically, the lesion consisted of plump spindle cells and accompanying inflammatory cellular infiltrates. The spindle cells were positive for vimentin.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Liver: A case report.
- Young Hee Maeng, Jae Hoon Park, Youn Wha Kim, Yong Koo Park, Ju Hie Lee, Moon Ho Yang
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(1):90-92.
- 1,940 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the Aver is a rare benign lesion that usually has been discovered at laparotomy. This lesion is inflamrhatory and reactive, but the etiology remains unknown. In-flammatory pseudotumor of the liver is of the interest not only because of its rarity also because it needs to be clinically differentiated from hepatocellular carcinoma and other malignant tu-mors. In this report, we describe a case of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver with fever and weight loss in a 46-year-old male. Grossly, the lesion showed a rather well demarcated, gray white to pale yellowish nodular mass mesuring 7 x 5.5 x 5 cm in dimensions. M icroscqpically, the tumor was composed of diffuse infiltration of predominantly plasma cells, lymphocytes and histocytes associated with fibroblastic proliferation.
- Inflammatory Pseud0tumor of the Liver: A case report.
- Young Ju Woo, Rye Kyoung Yoon, Jong Eun Joo
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(1):93-95.
- 2,039 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver is a relatively rare entity, and frequently misdiagnosed as a malignant tumor. We report a case of inflammatory pseudotumor involving the liver in a 53year-old man. The liver function test and serum alpha-fetoprotein level were within normal range. His preoperative diagnosis was as hepatocellular carcinoma by radiologic studies, and ultrasonography guided fine needle aspiration cytology and biopsy were done but confirmative diagnosis of malignancy or pseudotumor was not given. Grossly a relatively well marginated reddish brown soft mass with focal hemorrhage, measuring 5.0 cm in the largest diameter, was noted in the left lobe of liver. Surrounding hepatic parenchyma was yellowish brown in color without cirrhosis. Microscopically the mass showed typical findings of inflammatory pseudotumor and the ing liver tissue revealed diffuse fatty change and moderate chronic inflammatory cell on in the portal areas.
- Xanthomatous Pseudotumor of the Breast: A Brief Case Report.
- Lee So Maeng, Se Jeong Oh, Kyoung Mee Kim, Anhi Lee, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(5):345-347.
- 2,875 View
- 103 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory (xanthomatous) pseudotumors of the breast are very rare and this case is the first reported case in Korea. A healthy, pregnant 29-year-old woman presented with a right breast mass. Ultrasonography of the breast revealed a 1.8 x 1.9 x 1.1 cm, sized lobulated, partially spiculated mass in the upper and outer quadrant of the breast. Macroscopically, the mass was well circumscribed, bright yellow, and lobulated. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of foamy histiocytes with multifocal neutrophilic infiltration, accompanying chronic inflammatory cellul infiltration, fibrosis and ductal-lobular atrophy.
- A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Urinary Biadder.
- Hye Rim Park, Min Chul Lee, Nack Kyu Choi, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(3):256-262.
- 2,738 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder is a proliferative spindle cell lesion that microscopically may suggest a sarcoma but that are benign without a recent history of an operation. The first such case was reported by Roth, in 1980, and thereafter about seven more cases were reported in medical literatures. We reported a case of inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder mimicking leiomyosarcoma. Patient was a 36-year-old woman with complaint of painless total and gross hematuria for 3 weeks. Partial cystectomy specimen showed a well-demarcated nodular mass of yellow white color, involving the submucosal and muscular layers. Microscopic examination revealed proliferating bundles of spindle cells interspersed with infiltration of many inflammatory cells including eosinophils. Spindle cells were positive for vimentin on immunohistochemistry and corresponding to myofibroblasts on the electron microscopic examination.
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Nose and Salivary Gland: A case report.
- Mee Sook Roh, Jin Sook Jeong, Sook Hee Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(12):1203-1206.
- 2,227 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is a rare type of benign histiocytosis characterized histologically by intracellular engulfment of lymphocytes. Extranodal RDD may occur as a part of generalized process involving lymph nodes or may involve extranodal sites independent of the lymph node status. We have experienced a case of extranodal Rosai-Dorfman disease of the nose as an initial lesion prior to nodal involvement. The patient was a 20-year-old woman who complained of nasal obstruction for 4 years, remotely, and left submandibular mass for 3 months, recently. Histologically, the lesion taken from nasal cavity, submandibular gland and left upper jugular lymph node all showed an heavy infiltrate consisted of plasma cells, lymphocytes and sheets of macrophages with abundant pale cytoplasm, which replaced organ architecture. The associated focal fibrosis made it difficult to differentiate from inflammatory pseudotumor. Some macrophages demonstrated phagocytosis of lymphocytes, plasma cells and occasionally neutrophils. The macrophages were strongly positive for S-100 protein.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Urinary Bladder: An Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study.
- Seung Sam Paik, Joo Seob Keum, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):447-452.
- 2,086 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder is an unusual, benign mesenchymal proliferative lesion of the submucosal stroma easily mistaken for a malignant neoplasm clinically and histologically. We present a case and describe the clinical presentation and radiologic, histologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural findings. A 23-year old patient presented with sudden onset of gross painless hematuria for 3 months. There was no previous instrumentation or surgery involving the genitourinary tract. Cystoscopy revealed a large polypoid and ulcerated bladder mass. The lesion consisted of plump spindle shaped, fibroblast-like cells embedded in a myxoid stroma. Mitotic figures were negligible and the lesion showed encroachment on the superficial muscle bundles. The spindle cells were immunoreactive for vimentin and muscle specific actin. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural findings revealed the fibroblastic-myofibroblastic nature of this lesion. Complete surgical excision by partial cystectomy was successful in eradicating the lesion. The findings are described with a discussion of the pathogenesis and review of the literature.
- Cytomegalovirus Infection in Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 6 Cases.
- Won Ae Lee, Hye Sung Hahn, Woo Ho Kim, Yong Il Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1998;32(2):125-130.
- 2,245 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is an uncommon association with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) often leading to a variety of serious complications. A total of 41 resected cases of IBD were examined to elucidate the pathologic features of intestinal CMV infection which was assessed by histologic examination and confirmed by immunohistochemistry with CMV antibody. Six cases were positve for CMV antibody; five cases in 19 ulcerative colitis (UC, 26.3%) and one case in 22 Crohn's disease (CD, 4.5%). Of 7 cases of the steroid-treated UC group, five cases were superinfected with CMV (71.4%) but none in 12 cases of the steroid-untreated UC group. All of the five CMV-positive cases in UC showed deep ulceration and transmural inflammation, while none of 10 UC cases without above features were CMV positive. Fibrinoid necrosis and thrombi were found in 83.3% of the CMV infected group, while none in the CMV-negative group of UC cases (p=0.01). We conclude that IBD, particularly UC, is susceptible to the CMV infection when steroid hormone is administered, and that deep colonic ulceration, transmural inflammation and fibrinoid necrosis of vasculature may suggest superinfection of CMV in UC patients. It seems that deep colonic ulceration may be the consequence of an ischemic change following vascular luminal occlusion or vasculitis by CMV infection.
- Endobronchial Inflammatory Pseudotumor: A case report.
- Seoung Wan Chae, Young Hee Choi, Hye KYung Ahn, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(2):213-215.
- 1,865 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Inflammatory pseudotumors of the bronchus have been reported infrequently. Histologic diagnosis remains difficult because of their Polymorphic histologic characteristics and confusing terminology, which are also the problems in the diagnosis of intrapulmonary pseudotumors. We report a case of inflammatory pseudotumor in the left main bronchus which occurred in a 37-year-old man. Histologically, the main portion of the tumor was composed of pale eosinophilic spindle shaped cells covered by respiratory epithelium with squamous metaplasia. Mononuclear inflammatory cells, including plasma cells but acute inflammatory cells were also present in the superficial portion.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings of Inflammatory Breast Diseases.
- Hye Kyoung Yoon, Seol Mi Park, Mi Sun Kang, Young Il Yang, Chan Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1995;6(2):156-162.
- 2,090 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine needle aspiration of the breast is an important diagnostic tool in malignant lesions, but is also useful in differentiation of inflammatory breast diseases mimicking carcinoma clinically and radiologically. Recently. the authors have experienced eight biopsy-proven cases of chronic inflammatory diseases of the breast, which consisted of 4 cases of duct ectasia, 2 cases of fat necrosis, and a case of tuberculous mastitis and granulomatous mastitis respectively, Their cytologic features mainly based on the components and the relative frequency of inflammatory cells were evaluated for differential diagnosis of chronic inflammatory breast diseases. The results are as follows: 1. In cases of duct ectasia, varying amount of neutrophils, mononuclear leukocytes, histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells were intermixed with benign epithelial cell clusters. 2. Abundant fat tissue fragments were diagnostic for fat necrosis. Histiocytes and mononuclear cells were main components but not rich, and neutrophils and giant cells were infrequently observed. 3. Characteristic granulomas composed of epithelioid cells, mononuclear leukocytes and Langhans} type giant cells and lymphocytic infiltrates were conspicuous in tuberculous mastitis, and occasionally neutrophils, necrotic materials and epithelial cell clusters were found. 4. In granulomatous mastitis, epithelioid cell granulomas were also noted but numerous neutrophils and histiocytes were intermingled within or outside the granulomas.
- roded Polypoid Hyperplasia of the Rectosigmoid Colon: Report of 2 cases with special reference to its relation to mucosal prolapse syndrome.
- Nam Hoon Cho, Hee Jeong Ahn, Chan Il Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(3):297-301.
- 2,270 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Polypoid prolapse of mucosal folds can occur at various sites and in various conditions predominantly associated with strain during defecation. There are two well known types of mucosal prolapse syndrome(MPS), the inflammatory cloacogenic polyp(ICP) and the mucosal redundant polyp associated with diverticular disease(N4RPD). ICP is a mucosal prolapse of the anorectal junction and MRPD is a proximal analogue involving the sigmoid colon. We experienced two cases of eroded polypoid hyperplasia(EPH) of the rectosigmoid colon which manifested as a huge gyriform mass simulating the gross features of gastrointestinal lymphomas or other malignant tumors. The EPH consisted of confluent polypoid mucosal folds with rolled-up submucosa to form stalk, The polypoid lesion represented hyperplastic epithelium, erosion of the mucosal surface and congestive vascular ectasia of lamina propria and submucosa. To explain the whole morphologic features, the initial phenomenon should be the mucosal prolapse. Vascular stretching with ischemic erosion of the mucosal surface and compensatory epithelial hyperplasia ensue as the result. The ominous endoscopic and gross features of EPH should be kept in mind to avoid erroneous radical surgery.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Lung: A Case Report.
- Gyeongsin Park, Kyungji Lee, Sun Mi Lee, Kyo Young Lee, Sang In Shim, Chang Suk Kang, Youn Soo Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(1):63-68.
- 2,502 View
- 64 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT), normally referred to as inflammatory pseudotumor, is a fairly rare condition. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) of IMT has only rarely been reported. Here, we describe one such case of pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. A 30-year-old man presented with a 2.8cm-sized mass in his lung. Chest CT revealed a well defined, poorly enhancing mass. FNAC showed some fascicular or swirled clusters of spindle cells, admixed with occasional inflammatory cells and foamy histiocytes. The majority of the tumor cells evidenced bland, elongated nuclei, but infrequent pleomorphic nuclei. Some of the tumor cells evidenced nuclear grooves and intranuclear inclusions. Although the cytological differentiation of IMT from malignant lesions is not immensely problematic, due to the general paucity of cytological and nuclear atypia, a definite cytological diagnosis of IMT cannot be rendered simply by FNAC. Therefore, a diagnosis of IMT may be suggested via exclusive diagnosis.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Stomach: A Case Report.
- Joon Mee Kim, In Suh Park, Lucia Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Jee young Han, Young Chae Chu, Kyoung Rae Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(2):148-150.
- 2,230 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the stomach is a rare tumor-like, benign disease with an uncertain pathogenesis. A 15-year-old male presented with epigastric pain. Endoscopic ultrasonography revealed a 2.3 cm sized ovoid intramuscular mass in the lower body of the stomach at the lesser curvature. Histologically, the tumor was composed of smooth muscle actin positive- and vimentin positive spindle cells and there were a large number of lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes in the fibrotic background. The spindle cells were also positive for ALK1, but negative for EBV in situ hybridization.
- Follicular Lymphoma with Monoclonal Plasma Cell Differentiation: A Case Report.
- Hyun chul Kim, Young Seok Lee, Jung woo Choi, Ae ree Kim, Bom Woo Yeom, Han kyeom Kim, In sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2006;40(2):151-155.
- 2,338 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We present a case of recurrent follicular lymphoma with an extensive plasma cell component involving infra-auricular lymph nodes in a 64 year-old woman. Immunohistochemical staining showed a strongly positive reaction of the follicles with CD20, bcl-2, bcl-6, CD10 and CD21 on the first biopsy specimen. The intrafollicular and interfollicular plasma cells showed monoclonality for IgG heavy chain and lambda light chain. The histological and immunohistochemical findings in the recurrent tumor were identical with those of the original. Discussion is focused on the importance of the differential diagnosis between reactive lymphoid hyperplasia and other lymphomas having plasmacytic differentiation.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Lung: Three cases report.
- Hye Soog Kim, Bang Hur, Hee Kyung Chang, Man Ha Hur
- Korean J Pathol. 1988;22(3):317-323.
- 2,064 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The inflammatory pseudotumor of the lung is a non-neoplastic pulmonary mass lesion, composed of a variey of inflammatory cells including plasma cells, histiocytes(often xanthomatous), mast cells, lymphocytes, and spindle shaped mesenchymal cells. Although the pathogenetic etiology of this lesion is not estabilished, it has been claimed that it is associated with local inflammatory reaction. From 1984 to 1986, we experienced three cases of pathologically confirmed inflammatory pseudotumor of the lung. All three cases revealed similar gross and microscopic features, with only minor differences in components on microscopic level. All specimens were products of lobectomy. They showed a relatively well defined, yellowish white and solid mass, measuring about 5.0 cm in diameter. Histologically, the lesions, which were well demarcated from the uninvolved region, were characterized by dense infiltration of plasma cells and xanthomatous histiocytes admixed with lymphocytes, spindle shaped mesenchymal cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. At periphery, bronchi and bronchioles were entrapped by these cells. In focal areas, spindle shaped mesenchymal cells were aggregated, resulting in formation of thick bundles in which plasma cells were infiltrated. In case 1 and 2, myxoid change of stromal tissue was noted. Also noted were foci of osteoid metaplasia of the stromal layer in case 1. The authors report three cases of inflammatory pseudotumor of the lung, with comparative observation of each case, associated with literature review, with emphasis on the pathogenesis of this rather infrequent lesion. And some reviews were made on differential diagnosis between inflammatory pseudotumor and non-neoplastic or neoplastic lung mass including so called sclerosing hemangioma.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytologic Findings of Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Lymph Node .
- So Young Park, Gyung Yub Gong, Joo Ryung Huh, Eun Sil Yu, In Chul Lee, On Ja Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1997;8(1):87-92.
- 1,929 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Reports on the cytologic or histopathologic findings of inflammatory pseudotumors are relatively infrequent and most of them have dealt with those involving the lung, liver, genitourinary tract, alimentary tract, spleen, mediastinum, retroperitoneum, etc. Moreover there have not been any cytologic studies of those involving lymph nodes. We present fine needle aspiration cytologic features of inflammatory pseudotumor occurring in a lymph node in a 64 year-old man. The aspirate consisted of proliferating spindle cells and admixed histiocytes, fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Histiocytes were present either singly or in loosely cohesive small clusters. A few multinucleated giant cells were present as well. However, tuberculosis could be excluded by the absence of typical granuloma, caseation necrosis, or characteristic mixed spindle and inflammatory cell components. Other benign and malignant lymphadenopathies could also be differentiated based on cytologic findings.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor (InflammatoryFibrosarcoma) of the Lung: A Case Report.
- Minseob Eom, Tae Heon Kim, Jin Kyu Park, Kwang Hwa Park, Soon Hee Jung, Kwang Gil Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(4):291-295.
- 2,148 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, also known as inflammatory fibrosarcoma, has been frequently diagnosed as inflammatory pseudotumor. Although there are six cases reported as inflammatory pseudotumors or inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors in the lung, no cases of pulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor with features of inflammatory fibrosarcoma have been reported in Korea. We experienced a case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory fibrosarcoma)characterized by high cellularity, severe nuclear pleomorphism, necrosis, or increased mitoticcounts. A 31-year-old male patient with a solitary pulmonary nodule on the routine chest x-rayreceived a right lower lobectomy. The tumor was an ovoid solid mass with multifocal necrosis, showing diffuse irregular proliferation of spindle cells with high cellularity and focal nuclear pleomorphism, admixed with dense lymphoplasmacytic cells. Although spindle cells are focally immunoreactivefor smooth muscle actin, the ultrastructural examination failed to demonstrate smooth muscledifferentiation. In cases of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory fibrosarcoma), a completeexcision and close follow-up without radical surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy are needed.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Maxillary Sinus: A case report.
- Hyun Jin Son, Seung O Ko, Myoung Ja Chung, Ho Yeul Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2000;34(8):601-604.
- 1,928 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a space occupying lesion which is composed of myofibroblasts, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. IMT of the maxillary sinus is rare and its etiology is unknown. We present a case of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor occurring in the right maxillary sinus of a 57-year-old woman. Radiologically, this tumor was interpreted as malignant neoplasm. On histologic examination, bundles of spindle cells were admixed with inflammatory cells including mature plasma cells and lymphocytes. On the basis of the immunohistochemical findings and ultrastructural features, we recognized that the intervening spindle cells were myofibroblasts. We discussed etiology and prognostic factors of this tumor.
- A Pathological and Immunohistochemical Study of 9 Cases of Inflammatory Fibroid Polyp.
- Nam Hoon Cho, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Ho Guen Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1989;23(1):20-28.
- 2,112 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We aimed to study the clinicopathologic features of inflammatory fibroid polyp by histological and immunohistochemical methods. The materials used in this study consisted of 9 cases of inflammatory fibroid polyp: 4 in the stomach, 4 in the small intestine and 1 in the cecum. The results were as follows: Females were affected more frequently than males and the average age was 45 years(range:27-61). In cases of gastric lesion, the size tended to be smaller, the mass was mainly located along the greater curvature side of antrum, and confined to the submucosa. However inflammatory fibroid polyp of the small intestine was over 2.5 cm in size, located along the antemesenteric border, and involved the proper muscle layer. In addition, intussusception was accompanied by polyp in 2 cases of small intestinal lesions. Histologically inflammatory fibroid polyps of the stomach were characterized by prominent lymphocytic infiltration and occasional onion-skinning of stromal cells, whereas plasmocytic infiltration was prominent in those of the small intestine. Main component cells comprising this lesion were confirmed to be fibroblasts by immunohistochemistry which revealed strong reactivity to vimentin in the cytoplasm of slindle cells.
- Intestinal Spargnanosis Presenting as an Inflammatory Mass: A case report.
- Weon Seo Park, Seung Sook Lee, Yong Il Kim, Seon Hee Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 1992;26(4):414-416.
- 1,967 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 39-year-old male patient presented with chronic abdominal pain and intermittent diarrhea for 8 months. Colon study showed an annular stricture at the ileocecal value. He underwent ileocecectomy with clinica impression of intestinal tuberculosis. The resected intestinal wall along the lieocecal junction demonstrated a localized, annular constriction and intramural nodular inflammatory growth in which were clusters of multiple microabscesses as well as acute and chronic inflammatory cell infiltration including eosinophils and fibrosis. Encountered were a few resolving phase of parasitic granulomatous tunnels in which fragments of degenerated sparganum with foreign body reaction were found in one focus. He had history of ingesting uncooked frogs 2 years ago. The above case suggests that differential diagnosis of inflammatory tumorous lesions in the intestine should include sparganosis in Korea.
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor in Posterior Mediastinum.
- Seung Sam Paik, Seok Hoon Jeon, Se Jin Jang, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(1):63-67.
- 2,171 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor(IMT) or inflammatory pseudotumor is a rare, solid tumor that most often affects children. This tumor is characterized by a spindle cell proliferation admixed with a variety of inflammatory cells. Although it has disputed nosology, a distinctive fibroinflammatory and even pseudosarcomatous appearance have been well appreciated. Herein, we report a case of IMT in the posterior mediastinum in a 19-year-old girl with clinical findings. The immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies on the tumor cells are reported, and their distinctive characteristics are discussed in details.

 E-submission
E-submission
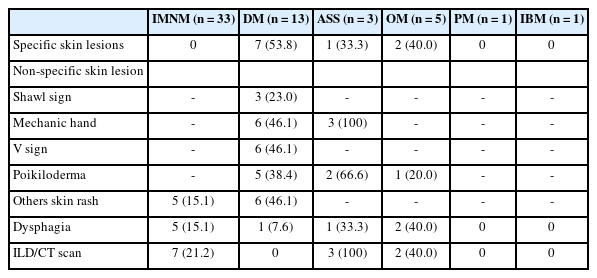





 First
First Prev
Prev



