Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diagnostic challenge in Burkitt lymphoma of the mandible initially misdiagnosed as osteomyelitis: a case report
- Jiwon Do, Jin-Young Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):460-466. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.18
- 1,833 View
- 92 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a highly aggressive B-cell neoplasm that rarely involves the mandible in elderly without apparent immunodeficiency. We report a case of a 72-year-old male who presented with persistent mandibular pain following extraction of tooth #46. Initial imaging findings were consistent with incipient osteomyelitis, and the patient was treated with antibiotics. Despite treatment, pain persisted, and follow-up imaging revealed swelling and diffusion restriction in the lateral pterygoid muscle without evidence of a distinct mass. Biopsy revealed BL confirmed by immunohistochemistry: CD10+, BCL6+, c-MYC+, Ki-67 >95%, and negative for BCL2, MUM-1, and Epstein-Barr virus. Although c-MYC immunopositivity was demonstrated, fluorescence in situ hybridization for MYC rearrangement could not be performed due to limited tissue, representing a diagnostic limitation. Notably, the patient had no trismus despite deep muscle involvement, but complained of facial paresthesia and showed remote swelling in the scapular area during hospitalization. Systemic staging with imaging, cerebrospinal fluid cytology, and imaging revealed disseminated nodal and extranodal involvement including the central nervous system, corresponding to stage IV disease by Lugano classification. This case highlights the diagnostic challenge of distinguishing lymphoma from osteomyelitis and underscores the importance of considering malignancy in cases of refractory mandibular inflammation with atypical features.
- Concurrent intestinal plasmablastic lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with a clonal relationship: a case report and literature review
- Nao Imuta, Kosuke Miyai, Motohiro Tsuchiya, Mariko Saito, Takehiro Sone, Shinichi Kobayashi, Sho Ogata, Fumihiko Kimura, Susumu Matsukuma
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):191-197. Published online June 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.14
- 4,729 View
- 223 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Herein, we report a case of plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that occurred concurrently in the large intestine. An 84-year-old female presented with a palpable rectal tumor and ileocecal tumor observed on imaging analyses. Endoscopic biopsy of both lesions revealed lymphomatous round cells. Hartmann’s operation and ileocecal resection were performed for regional control. The ileocecal lesion consisted of a proliferation of CD20/CD79a-positive lymphoid cells, indicative of DLBCL. In contrast, the rectal tumor showed proliferation of atypical cells with pleomorphic nuclei and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm, with immunohistochemical findings of CD38/CD79a/MUM1/MYC (+) and CD20/CD3/CD138/PAX5 (–). Tumor cells were positive for Epstein-Barr virus– encoded RNA based on in situ hybridization and MYC rearrangement in fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. These findings indicated the rectal tumor was most likely a PBL. Sequencing analysis for immunoglobulin heavy variable genes indicated a common B-cell origin of the two sets of lymphoma cells. This case report and literature review provide new insights into PBL tumorigenesis.
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,541 View
- 211 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma arising in an endovascular graft: first case report in Korea
- Min Gyoung Pak, Mee Sook Roh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):87-90. Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.28
- 4,077 View
- 267 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrin-associated large B-cell lymphoma (FA-LBCL) is an extremely rare subtype of LBCL that consists of microscopic aggregates of atypical large B cells in the background of fibrin. Here, we report the first case of FA-LBCL in Korea. A 57-year-old male presented with a large amount of thrombus in the thoracic aorta during follow-up for graft replacement of the thoracoabdominal aorta 8 years prior. The removed thrombus, measuring 4.3 × 3.1 cm, histologically exhibited eosinophilic fibrinous material with several small clusters of atypical lymphoid cells at the periphery. The atypical cells were positive for CD20 by immunohistochemistry and for Epstein-Barr virus by in situ hybridization. The Ki-67 proliferation rate was 85%. The patient was still alive with no recurrence at the 7-year follow-up after thrombectomy. Although the diagnosis can be very difficult and challenging due to its paucicellular features, pathologists should be aware of FALBCL, which has likely been underestimated in routine evaluations of thrombi.
- Clinicopathological implications of immunohistochemical expression of TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, CCR4, and TCF1 in nodal follicular helper T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
- Bogyeong Han, Sojung Lim, Jeemin Yim, Young Keun Song, Jiwon Koh, Sehui Kim, Cheol Lee, Young A Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):59-71. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.04
- 7,620 View
- 374 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The classification of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) has evolved according to histology, cell-of-origin, and genetic alterations. However, the comprehensive expression pattern of follicular helper T-cell (Tfh) markers, T-cell factor-1 (TCF1), and Th1- and Th2-like molecules in nodal PTCL is unclear.
Methods
Eighty-two cases of nodal PTCL were classified into 53 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas (AITLs)/nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma (nTFHL)-AI, 18 PTCLs-Tfh/nTFHL–not otherwise specified (NOS), and 11 PTCLs-NOS according to the revised 4th/5th World Health Organization classifications. Immunohistochemistry for TCF1, TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, and CCR4 was performed.
Results
TCF1 was highly expressed in up to 68% of patients with nTFHL but also in 44% of patients with PTCL-NOS (p > .05). CXCR3 expression was higher in AITLs than in non-AITLs (p = .035), whereas GATA3 expression was higher in non-AITL than in AITL (p = .007) and in PTCL-Tfh compared to AITL (p = .010). Of the cases, 70% of AITL, 44% of PTCLTfh/ nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the TBX21 subtype; and 15% of AITL, 38% of PTCL-Tfh/nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the GATA3 subtype. The others were an unclassified subtype. CCR4 expression was associated with poor progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PTCL-Tfh (p < .001) and nTFHL (p = .023). The GATA3 subtype showed poor overall survival in PTCL-NOS compared to TBX21 (p = .046) and tended to be associated with poor PFS in patients with non-AITL (p = .054).
Conclusions
The TBX21 subtype was more prevalent than the GATA3 subtype in AITL. The GATA3 subtype was associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-AITL and PTCL-NOS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
Xiaowen Yang, Min Sun, Xinyi Tang, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Wenzhi Shen
Frontiers in Immunology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - CXCR Family and Hematologic Malignancies in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Yanquan Liu, Huanwen Tang
Biomolecules.2025; 15(5): 716. CrossRef - Diagnostic and therapeutic pathways for lymphoma patients: expert consensus through Nominal Group Technique and Delphi methodology
Attilio Guarini, Valentina Bozzoli, Sabino Ciavarella, Michele Cimminiello, Francesca Donatelli, Angelo Fama, Vincenza Fernanda Fesce, Vincenzo Fraticelli, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppina Greco, Augusto Martellini, Francesca Merchionne, Rosanna Maria Miccoli
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of TBX21 and GATA3 Subtype Classification in Indolent Adult T‐Cell Leukemia‐Lymphoma With Cutaneous Lesions
Kazuhiro Kawai, Youhei Uchida, Takuro Kanekura
The Journal of Dermatology.2025; 52(11): 1674. CrossRef
- T-bet: biological functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic applications: a systematic review
- Immunohistochemical expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in neuroblastoma and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features
- Thu Dang Anh Phan, Thao Quyen Nguyen, Nhi Thuy To, Thien Ly Thanh, Dat Quoc Ngo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):29-34. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.12.07
- 5,272 View
- 290 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations have been identified as a prominent cause of some familial and sporadic neuroblastoma (NB). ALK expression in NB and its relationship with clinical and histopathological features remains controversial. This study investigated ALK expression and its potential relations with these features in NB.
Methods
Ninety cases of NB at the Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam from 01/01/2018 to 12/31/2021, were immunohistochemically stained with ALK (D5F3) antibody. The ALK expression and its relations with some clinical and histopathological features were investigated.
Results
The rate of ALK expression in NB was 91.1%. High ALK expression (over 50% of tumor cells were positive with moderate-strong intensity) accounted for 65.6%, and low ALK expression accounted for 34.4%. All the MYCN-amplified NB patients had ALK immunohistochemistry positivity, most cases had high ALK protein expression. The undifferentiated subtype of NB had a lower ALK-positive rate than the poorly differentiated and differentiated subtype. The percentages of ALK positivity were significantly higher in more differentiated histological types of NB (p = .024). There was no relation between ALK expression and: age group, sex, primary tumor location, tumor stage, MYCN status, clinical risk, Mitotic-Karyorrhectic Index, prognostic group, necrosis, and calcification.
Conclusions
ALK was highly expressed in NB. ALK expression was not related to several clinical and histopathological features. More studies are needed to elucidate the association between ALK expression and ALK gene status and to investigate disease progression, especially the oncogenesis of ALK-positive NB. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
Alberto D. Guerra, Smita Matkar, Christina Acholla, Colleen Casey, Grant Li, Martina Mazzeschi, Khushbu Patel, Kateryna Krytska, Chuan Chen, Skye Balyasny, Joshua Kalna, Paul Kamitsuka, Mark Gerelus, Grace Polkosnik, David Groff, Apratim Mukherje, Cynthia
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of ALK gene mutations and targeted therapies in pediatric high-risk neuroblastoma: advancements in precision oncology
Bhumika Bheemavarapu, Mohammad Khalil, Aseef Rehman, Saman Javid, FNU Cyrus, Sardar Noman Qayyum, Aasvi Gohil, Siraj Ul Muneer, Samim Noori
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2025; 87(10): 6470. CrossRef
- A humanized anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-directed antibody-drug conjugate with pyrrolobenzodiazepine payload demonstrates efficacy in ALK-expressing cancers
- Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes evaluated using digital image analysis predict the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Yunjoo Cho, Jiyeon Lee, Bogyeong Han, Sang Eun Yoon, Seok Jin Kim, Won Seog Kim, Junhun Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):12-21. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.02
- 5,076 View
- 269 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The implication of the presence of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TIL-T) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is yet to be elucidated. We aimed to investigate the effect of TIL-T levels on the prognosis of patients with DLBCL.
Methods
Ninety-six patients with DLBCL were enrolled in the study. The TIL-T ratio was measured using QuPath, a digital pathology software package. The TIL-T ratio was investigated in three foci (highest, intermediate, and lowest) for each case, resulting in TIL-T–Max, TIL-T–Intermediate, and TIL-T–Min. The relationship between the TIL-T ratios and prognosis was investigated.
Results
When 19% was used as the cutoff value for TIL-T–Max, 72 (75.0%) and 24 (25.0%) patients had high and low TIL-T–Max, respectively. A high TIL-T–Max was significantly associated with lower serum lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < .001), with patient group who achieved complete remission after RCHOP therapy (p < .001), and a low-risk revised International Prognostic Index score (p < .001). Univariate analysis showed that patients with a low TIL-T–Max had a significantly worse prognosis in overall survival compared to those with a high TIL-T–Max (p < .001); this difference remained significant in a multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazards (hazard ratio, 7.55; 95% confidence interval, 2.54 to 22.42; p < .001).
Conclusions
Patients with DLBCL with a high TIL-T–Max showed significantly better prognosis than those with a low TIL-T–Max, and the TIL-T–Max was an independent indicator of overall survival. These results suggest that evaluating TIL-T ratios using a digital pathology system is useful in predicting the prognosis of patients with DLBCL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
Valerie J. Poirier, Valeria Meier, Michelle Turek, Neil Christensen, Jacqueline Bowal, Matthew D. Ponzini, Stefan M. Keller
Veterinary and Comparative Oncology.2025; 23(1): 82. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment and PD-L1 Expression Associations with Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Yun-Li Xie, Long-Feng Ke, Wen-Wen Zhang, Fu Kang, Shu-Yi Lu, Chen-Yu Wu, Huan-Huan Zhu, Jian-Chao Wang, Gang Chen, Yan-Ping Chen
Blood and Lymphatic Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 15: 167. CrossRef - Metabolic-immune axis in the tumor microenvironment: a new strategy for prognostic assessment and precision therapy in DLBCL and FL
Chengqian Chen, Wei Guo, Haotian Wang, Luming Cao, Ou Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative analysis of a novel immunogenic PANoptosis‑related gene signature in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma for prognostication and therapeutic decision-making
Ming Xu, Ming Ruan, Wenhua Zhu, Jiayue Xu, Ling Lin, Weili Li, Weirong Zhu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
- Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma: a case report and literature review
- Ji Min Na, Wookjae Jung, Minhye Kim, Yun-Hong Cheon, Jong Sil Lee, Dae Hyun Song, Jung Wook Yang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(6):332-336. Published online November 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.30
- 5,737 View
- 235 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intravascular lymphoma is characterized by an exclusively intravascular distribution of tumor cells. Intravascular natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (IVNKTL) is extremely rare, highly aggressive, commonly Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive, and predominantly affects the skin and central nervous system. Here we report a case of IVNKTL diagnosed in a 67-year-old female, presenting with persistent intermittent fever and skin rashes throughout the body. Incisional biopsy of an erythematous lesion on the chest exhibited aggregation of medium to large-sized atypical lymphoid cells confined to the lumen of small vessels that were positive for CD3, granzyme B, and CD56 on immunohistochemistry and EBV-encoded RNA in situ hybridization. EBV DNA was also detected in serum after diagnosis. With a review of 26 cases of IVNKTL to date, we suggest that active biopsy based on EBV DNA detection may facilitate early diagnosis of IVNKTL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mimicry in the vasculature: a review of diagnostic clues in cutaneous intravascular lymphoid proliferations
MA Faraz, S Tu Zahra, F Ocampo-Gonzalez, SC Shalin, Aadil Ahmed
Diagnostic Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Intravascular Lymphoma: A Unique Pattern Underlying a Protean Disease
Mario Della Mura, Joana Sorino, Filippo Emanuele Angiuli, Gerardo Cazzato, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppe Ingravallo
Cancers.2025; 17(14): 2355. CrossRef - Cutaneous Intravascular Hematolymphoid Entities: A Review
Emily Hatheway Marshall, Bethany Brumbaugh, Allison Holt, Steven T. Chen, Mai P. Hoang
Diagnostics.2024; 14(7): 679. CrossRef - CD30- and CD56-positive atypical intravascular lymphocytes of the uterine cervix, mimicking intravascular lymphoma: A case report and review of the literature
Daisuke Yamashita, Munemichi Otani, Hayato Maruoka, Takuya Aoki, Shigeo Hara
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hematopathology.2024; 64(4): 328. CrossRef
- Mimicry in the vasculature: a review of diagnostic clues in cutaneous intravascular lymphoid proliferations
- Metallic implant-associated lymphoma: ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma associated with total knee replacement arthroplasty
- Jai-Hyang Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):75-78. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.10.30
- 5,104 View
- 116 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Metallic implant-associated lymphomas are extremely rare. Only seven cases have been reported in association with knee joint arthroplasty, and all tumors were large B-cell lymphomas. This report is the first case of anaplastic large cell lymphoma occurring after total knee replacement arthroplasty. An 80‑year‑old female patient was admitted because of right knee pain for 2 years. She had undergone total knee replacement arthroplasty 10 years prior. Computed tomography showed an irregular osteolytic lesion in the right lateral femoral condyle, adjacent to the metallic prosthesis. Histologic findings reveal sheets of anaplastic tumor cells that were positive for CD2, CD4, CD5, CD43, and CD30 but negative for CD3, CD20, CD15, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization was negative. Analysis of T-cell receptor γ gene rearrangement studies using BIOMED-2–based multiplex polymerase chain reaction confirmed monoclonal T cell proliferation. The woman was finally diagnosed with ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and microscopic evidence of biofilm formation on titanium miniplates applied in maxillofacial surgery: a case series analysis
Bramasto Purbo Sejati, Ahmad Kusumaatmaja, Maria Goreti Widiastuti, Tetiana Haniastuti
Case Reports in Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Granulomatous Mycosis Fungoides Associated with Knee Prostheses: A Case Report and Literature Review
Belloso Rosa Izu, Rodriguez Blandon Jurvist Stee, Peña Nekane Martinez, Colunga Barbara Lada, Izaguirre Ane Lobato, Apraiz Isabel Gainza, Ponsa Carla Valenti
International Journal of Dermatology and Clinical Research.2025; 11(1): 022. CrossRef - Primary bone diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma (PB‐DLBCL): a distinct extranodal lymphoma of germinal centre origin, with a common EZB‐like mutational profile and good prognosis
Vanesa‐Sindi Ivanova, John Davies, Thomas Menter, Damian Wild, Anne Müller, Fatime Krasniqi, Frank Stenner, Alexandros Papachristofilou, Stefan Dirnhofer, Alexandar Tzankov
Histopathology.2024; 84(3): 525. CrossRef - Osteosarcoma After Total Knee Arthroplasty
Pablo Martínez-Collado, Oriol Pujol, Andrés Bustos, Martí Plomer, María G. Carrasco, Tulio Silva, Roberto Vélez, Joan Minguell
JBJS Case Connector.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical and microscopic evidence of biofilm formation on titanium miniplates applied in maxillofacial surgery: a case series analysis
- Unsuspected systemic Epstein-Barr virus–positive T-cell lymphoma of childhood diagnosed at autopsy in a potential homicide case
- Daniel J. Robbins, Erik A. Ranheim, Jamie E. Kallan
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):123-127. Published online December 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.10.31
- 5,601 View
- 188 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Systemic Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–positive T-cell lymphoma of childhood (SETLC) is a rare, rapidly progressive, and often fatal disease of children and young adults characterized by monoclonal expansion of EBV-positive T cells in tissues or peripheral blood following infection with EBV. Its distinction from other EBV-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders with overlapping features can be difficult, and particular diagnostic features may not be manifest until autopsy examination. We present the case of a 10-year-old boy with significant disability due to remote traumatic brain injury following non-accidental head trauma who died unexpectedly at home. Given the history of physical abuse and the potential for homicide charges, significant medicolegal implications arose with this case. Pathologic investigation ultimately revealed conclusive diagnostic features of SETLC including extensive proliferation of EBV-positive T cells in multiple organs. A natural manner of death was confirmed, thereby excluding delayed homicide related to complications of non-accidental head trauma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The ‘Oma’s of the Gammas—Cancerogenesis by γ-Herpesviruses
Anwesha Banerjee, Debashree Dass, Soumik Mukherjee, Mollina Kaul, R. Harshithkumar, Parikshit Bagchi, Anupam Mukherjee
Viruses.2024; 16(12): 1928. CrossRef
- The ‘Oma’s of the Gammas—Cancerogenesis by γ-Herpesviruses
- Prognostic significance of BLK expression in R-CHOP treated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Soyeon Choi, Yoo Jin Lee, Yunsuk Choi, Misung Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Sukjoong Oh, Seoung Wan Chae, Hee Jeong Cha, Jae-Cheol Jo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):281-288. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.07.26
- 5,137 View
- 107 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic significance of B-cell lymphocyte kinase (BLK) expression for survival outcomes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients treated with R-CHOP.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 89 patients from two tertiary referral hospitals. The expression of BLK, SYK, and CDK1 were evaluated in a semiquantitative method using an H-score, and the proportions of BCL2 and C-MYC were evaluated.
Results
A total of 89 patients received R-CHOP chemotherapy as a first-line chemotherapy. The expression rates of BLK in tumor cells was 39.2% (n = 34). BLK expression status was not significantly associated with clinical variables; however, BLK expression in tumor cells was significantly associated with the expression of both C-MYC and BCL2 (p = .003). With a median follow-up of 60.4 months, patients with BLK expression had significantly lower 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival rates (49.8% and 60.9%, respectively) than patients without BLK expression (77.3% and 86.7%, respectively). In multivariate analysis for PFS, BLK positivity was an independent poor prognostic factor (hazard ratio, 2.208; p = .040).
Conclusions
Here, we describe the clinicopathological features and survival outcome according to expression of BLK in DLBCL. Approximately 39% of DLBCL patients showed BLK positivity, which was associated as a predictive marker for poor prognosis in patients who received R-CHOP chemotherapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the cell-free total RNA transcriptome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma patients as biomarker source in blood plasma liquid biopsies
Philippe Decruyenaere, Edoardo Giuili, Kimberly Verniers, Jasper Anckaert, Katrien De Grove, Malaïka Van der Linden, Dries Deeren, Jo Van Dorpe, Fritz Offner, Jo Vandesompele
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring the cell-free total RNA transcriptome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma patients as biomarker source in blood plasma liquid biopsies
- Primary pulmonary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare entity and a literature review
- Priyanka Singh, Aruna Nambirajan, Manish Kumar Gaur, Rahul Raj, Sunil Kumar, Prabhat Singh Malik, Deepali Jain
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):231-237. Published online July 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.05.08
- 6,645 View
- 129 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma (EIMS) is an aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions and is associated with high risk of local recurrence and poor prognosis. Herein, we present a young, non-smoking male who presented with complaints of cough and dyspnoea and was found to harbor a large right lower lobe lung mass. Biopsy showed a high-grade epithelioid to rhabdoid tumor with ALK and desmin protein expression. The patient initially received 5 cycles of crizotinib and remained stable for 1 year; however, he then developed multiple bony metastases, for which complete surgical resection was performed. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of EIMS, with ALK gene rearrangement demonstrated by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Postoperatively, the patient is asymptomatic with stable metastatic disease on crizotinib and has been started on palliative radiotherapy. EIMS is a very rare subtype of IMT that needs to be included in the differential diagnosis of ALKexpressing lung malignancies in young adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
Cancers.2025; 17(8): 1327. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: Case Series With a First Report of CLTC::ALK Fusion in an Aggressive Disease
Daisy Maharjan, Carina Dehner, Ali Alani, Robert Bell, Sheila Segura
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ALK rearranged malignant mesenchymal neoplasms of thorax: therapeutically targetable ‘ALKomas’ beyond the spectrum of non-small cell lung carcinomas and thoracic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors
Shreya Sadhu, Adarsh Barwad, Asit Ranjan Mridha, Prabhat Singh Malik, Aruna Nambirajan, Deepali Jain
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(5): 1003. CrossRef - Mediastinal epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with the EML4‐ALK fusion: A case report and literature review
Tingyu Pan, Xinyu Sun, Xiao Wu, Futing Tang, Xianmei Zhou, Qian Wang, Shi Chen
Respirology Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(3): 141. CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma: A Report of a Rare Case
Varun Ronanki, Vaddatti Tejeswini, Inuganti Venkata Renuka, Shaik Raheema, Bakkamanthala S K Kanth
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thoracic epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a rare and aggressive disease with case report and literature review
Linke Yang, Pei Li, Runze Liu, Baomin Feng, Huiqing Mao, Xiaoyong Tang, Guangjian Yang
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma with exceptionally long response to lorlatinib—a case report
Rafał Becht, Kajetan Kiełbowski, Justyna Żychowska, Wojciech Poncyljusz, Aleksandra Łanocha, Katarzyna Kozak, Ewa Gabrysz-Trybek, Paweł Domagała
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rare giant epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the abdominal cavity in a child: a case report and review of the literature
Jinzhou Li, Haixing Su, Sheng Zhang, Xianyun Chen, Chongzhi Hou, Tao Cheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma treated with an ALK TKI ensartinib
Mengmeng Li, Ruyue Xing, Jiuyan Huang, Chao Shi, Chunhua Wei, Huijuan Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Sarcoma With Poor Response to Crizotinib: A Case Report
Soheila Aminimoghaddam, Roghayeh Pourali
Clinical Medicine Insights: Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma: a case report and brief literature review
Weidong Dou, Yu Guan, Tao Liu, Hang Zheng, Shuo Feng, Yingchao Wu, Xin Wang, Zhanbing Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: An Updated Review
- Lymphoproliferative disorder involving body fluid: diagnostic approaches and roles of ancillary studies
- Jiwon Koh, Sun Ah Shin, Ji Ae Lee, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):173-186. Published online July 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.05.16
- 10,790 View
- 319 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lymphocyte-rich effusions represent benign reactive process or neoplastic condition. Involvement of lymphoproliferative disease in body cavity is not uncommon, and it often causes diagnostic challenge. In this review, we suggest a practical diagnostic approach toward lymphocyte-rich effusions, share representative cases, and discuss the utility of ancillary tests. Cytomorphologic features favoring neoplastic condition include high cellularity, cellular atypia/pleomorphism, monomorphic cell population, and frequent apoptosis, whereas lack of atypia, polymorphic cell population, and predominance of small T cells usually represent benign reactive process. Involvement of non-hematolymphoid malignant cells in body fluid should be ruled out first, followed by categorization of the samples into either small/medium-sized cell dominant or large-sized cell dominant fluid. Small/medium-sized cell dominant effusions require ancillary tests when either cellular atypia or history/clinical suspicion of lymphoproliferative disease is present. Large-sized cell dominant effusions usually suggest neoplastic condition, however, in the settings of initial presentation or low overall cellularity, ancillary studies are helpful for more clarification. Ancillary tests including immunocytochemistry, in situ hybridization, clonality test, and next-generation sequencing can be performed using cytologic preparations. Throughout the diagnostic process, proper review of clinical history, cytomorphologic examination, and application of adequate ancillary tests are key elements for successful diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The case of the sneaky lymphoma: solved by flow cytometry
Renu Singh, Md Ali Osama, Rachana Meena, Shailaja Shukla, Jagdish Chandra
Indian Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2025; 41(9): 1258. CrossRef - The urgency of Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis in fluid cytology—A tertiary care experience
Soundarya Ravi, Anu K. Devi, Prabhu Manivannan, Debasis Gochhait, Rakhee Kar, Neelaiah Siddaraju
Cytopathology.2024; 35(2): 275. CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry on frozen-embedded cell block for the diagnosis of hematolymphoid cytology specimen: a straightforward alternative to the conventional cell block
Youjeong Seo, Sanzida Alam Prome, Lucia Kim, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Suk Jin Choi
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Lymphoma presenting as the first finding in pleural fluid cytology: A rare cytologic presentation
Kafil Akhtar, Gowthami Nagendhran, Anjum Ara, Masheera Akhtar
IP Archives of Cytology and Histopathology Research.2024; 8(4): 250. CrossRef
- The case of the sneaky lymphoma: solved by flow cytometry
- Follicular lymphoma: updates for pathologists
- Mahsa Khanlari, Jennifer R. Chapman
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(1):1-15. Published online December 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.09.29
- 30,865 View
- 1,032 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the most common indolent B-cell lymphoma and originates from germinal center B-cells (centrocytes and centroblasts) of the lymphoid follicle. Tumorigenesis is believed to initiate early in precursor B-cells in the bone marrow (BM) that acquire the t(14;18)(q32;q21). These cells later migrate to lymph nodes to continue their maturation through the germinal center reaction, at which time they acquire additional genetic and epigeneticabnormalities that promote lymphomagenesis. FLs are heterogeneous in terms of their clinicopathologic features. Most FLs are indolent and clinically characterized by peripheral lymphadenopathy with involvement of the spleen, BM, and peripheral blood in a substantial subset of patients, sometimes accompanied by constitutional symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Diagnosis is established by the histopathologic identification of a B-cell proliferation usually distributed in an at least partially follicular pattern, typically, but not always, in a lymph node biopsy. The B-cell proliferation is biologically of germinal center cell origin, thus shows an expression of germinal center-associated antigens as detected by immunophenotyping. Although many cases of FLs are typical and histopathologic features are straightforward, the biologic and histopathologic variability of FL is wide, and an accurate diagnosis of FL over this disease spectrum requires knowledge of morphologic variants that can mimic other lymphomas, and rarely non-hematologic malignancies, clinically unique variants, and pitfalls in the interpretation of ancillary studies. The overall survival for most patients is prolonged, but relapses are frequent. The treatment landscape in FL now includes the application of immunotherapy and targeted therapy in addition to chemotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Follicular Cholecystitis: A Case Report Highlighting the Diagnostic Challenges and Management Implications
Ativitch Asavachaisuvikom, Burana Khiankaew, Narongsak Rungsakulkij
Gastro Hep Advances.2026; 5(2): 100833. CrossRef - Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: Current Advances and Emerging Perspectives
Giulio Caridà, Enrica Antonia Martino, Antonella Bruzzese, Daniele Caracciolo, Caterina Labanca, Francesco Mendicino, Eugenio Lucia, Virginia Olivito, Teresa Rossi, Antonino Neri, Ernesto Vigna, Pierfrancesco Tassone, Pierosandro Tagliaferri, Fortunato Mo
European Journal of Haematology.2025; 114(5): 775. CrossRef - Frequency and Distribution of Lymphomas in Northwestern India: A Retrospective Analysis of 923 Cases Using the Latest World Health Organization Classification 5th Edition
Immanuel Paul Thayakaran, Biren Parikh
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - IGH/IGK gene rearrangement in the diagnosis of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: experience from three centers
Ke Yang, Zhizhong Wang, Beibei Xin, Yunhang Li, Jiuzhou Zhao, Rui Sun, Weizhen Wang, Dongxu Chen, Chengzhi Zhao, Yongjun Guo, Jie Ma, Bing Wei
Annals of Hematology.2025; 104(7): 3779. CrossRef - Imaging Evaluation of Periarticular Soft Tissue Masses in the Appendicular Skeleton: A Pictorial Review
Francesco Pucciarelli, Maria Carla Faugno, Daniela Valanzuolo, Edoardo Massaro, Lorenzo Maria De Sanctis, Elisa Zaccaria, Marta Zerunian, Domenico De Santis, Michela Polici, Tiziano Polidori, Andrea Laghi, Damiano Caruso
Journal of Imaging.2025; 11(7): 217. CrossRef - Understanding the clinical approach to “pathologically ambiguous follicular lymphoma” through a Real-World cohort
Sarah Matarasso Greenfeld, Svetlana Dmitrienko, Ian Shrier, Jean Luc Deschenes, Sarit Assouline
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2025; 66(12): 2332. CrossRef - Deciphering and targeting oncogenic pathways through integrated approaches and amino acid metabolism in hematologic malignancies
Farhan Ikhtiar, Adil Jamal, Syed M. Safeer Mehdi Bokhari
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transformation of low-grade follicular lymphoma to a high-grade follicular lymphoma with the histopathological diagnosis from oral biopsy: a case report
Gabriela Silveira de Araujo, Leandro Dorigan de Macedo, Alfredo Ribeiro-Silva, Hilton Marcos Alves Ricz, Lara Maria Alencar Ramos Innocentini
Hematology, Transfusion and Cell Therapy.2024; 46: S380. CrossRef - The follicular lymphoma tumor microenvironment at single-cell and spatial resolution
Andrea J. Radtke, Mark Roschewski
Blood.2024; 143(12): 1069. CrossRef - Chronic pancreatitis for the clinician: complications and special forms of the disease. Interdisciplinary position paper of the Catalan Society of Digestology (SCD) and the Catalan Pancreatic Society (SCPanc)
Xavier MOLERO, Juan R. AYUSO, Joaquim BALSELLS, Jaume BOADAS, Juli BUSQUETS, Anna CASTERÀS, Mar CONCEPCIÓN, Míriam CUATRECASAS, Gloria FERNÀNDEZ ESPARRACH, Esther FORT, Francisco GARCIA BOROBIA, Àngels GINÈS, Lucas ILZARBE, Carme LORAS, Miquel MASACHS, Xa
Minerva Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Concurrent identification of follicular lymphoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma
Lama A. Alzelfawi, Norah ALhumaidan, Abrar H. Alageel, Buthaina J. Yahya, Saud D. Alrasheedi, Adel S. Alqahtani
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2024; 122: 110009. CrossRef - Impact of Primary Disease Site of Involvement by Early-Stage Follicular Lymphoma on Patient Outcomes
Olivia Davis, Carmen Lessani, Rana Kasht, Andrew Cohoon, Sami Ibrahimi, Adam Asch, Silas Day, Taha Al-Juhaishi
Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia.2024; 24(12): 837. CrossRef - Recent developments in CD19-targeted therapies for follicular lymphoma
Aditi Saha, Julio C. Chavez
Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy.2024; 24(10): 1049. CrossRef - Unraveling the complexity of follicular lymphoma: insights and innovations
Xijing Li
American Journal of Cancer Research.2024; 14(12): 5573. CrossRef - Clinical features and prognostic factors in 49 patients with follicular lymphoma at a single center: A retrospective analysis
Hao Wu, Hui-Cong Sun, Gui-Fang Ouyang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(14): 3176. CrossRef - A rare case of follicular lymphoma of the bladder
Matthew DeSanto, Robert Strait, Jared Zopp, Kevin Brown, Samuel Deem
Urology Case Reports.2023; 51: 102542. CrossRef - Analysis of immunophenotypic features in hyaline vascular type Castleman disease
Yu Chang, Yu Ma, Chen Chang, Wensheng Li
Diagnostic Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Leg Edema Unveiled: The Uncommon Culprit of Follicular Lymphoma
Syed Muhammad IbnE Ali Jaffari, Samaha Nisar, Narjis Malik, Syed Muhammad Aun Ali Jaffari, Omar Nisar
Journal of Shalamar Medical & Dental College - JSHMDC.2023; 4(2): 125. CrossRef - A Review of the Totality of Evidence in the Development of ABP 798, A Rituximab Biosimilar
Patrick Cobb, Dietger Niederwieser, Stanley Cohen, Caroline Hamm, Gerd Burmester, Neungseon Seo, Sonya G Lehto, Vladimir Hanes
Immunotherapy.2022; 14(9): 727. CrossRef
- Follicular Cholecystitis: A Case Report Highlighting the Diagnostic Challenges and Management Implications
- An unusual case of microsatellite instability–high/deficient mismatch repair (MSI-H/dMMR) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma revealed by targeted gene sequencing
- Bogyeong Han, Sehui Kim, Jiwon Koh, Jeong Mo Bae, Hongseok Yun, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(2):92-96. Published online November 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.10.15
- 9,121 View
- 263 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Microsatellite instability-high/deficient mismatch repair (MSI-H/dMMR) status has been approved as a tissue-agnostic biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with solid tumors. We report the case of an MSI-H/dMMR diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) identified by targeted gene sequencing (TGS). A 90-year-old female who presented with vaginal bleeding and a large mass in the upper vagina was diagnosed with germinal center-B-cell-like DLBCL, which recurred at the uterine cervix at 9 months after chemotherapy. Based on TGS of 121 lymphoma-related genes and the LymphGen algorithm, the tumor was classified genetically as DLBCL of EZB subtype. Mutations in multiple genes, including frequent frameshift mutations, were detected by TGS and further suggested MSI. The MSI-H/dMMR and loss of MLH1 and PMS2 expression were determined in MSI-fragment analysis, MSI real-time polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemical tests. This case demonstrates the potential diagnostic and therapeutic utility of lymphoma panel sequencing for DLBCL with MSI-H/dMMR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shared genomic features of HIV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in two African cohorts
Sophia M. Roush, Mishalan Moodley, Jenny Coelho, Samantha Beck, Amon Chirwa, Edwards Kasonkanji, Marriam Mponda, Maurice Mulenga, Tamiwe Tomoka, Hanri van Zijl, Katherine Hodkinson, Arshad Ismail, Senzo Mtshali, Jonathan Featherston, Satish Gopal, Matthew
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Chimeric and mutant CARD9 constructs enable analyses of conserved and diverged autoinhibition mechanisms in the CARD‐CC protein family
Jens Staal, Yasmine Driege, Femke Van Gaever, Jill Steels, Rudi Beyaert
The FEBS Journal.2024; 291(6): 1220. CrossRef - PD-L1+diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with extremely high mutational burden and microsatellite instability due to acquiredPMS2mutation
Andrew W. Allbee, James Gerson, Guang Yang, Adam Bagg
Molecular Case Studies.2023; 9(4): a006318. CrossRef
- Shared genomic features of HIV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in two African cohorts
- Composite follicular lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- Han-Na Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Chul-Won Choi, Young Hyeh Ko
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(1):57-60. Published online November 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.10.09
- 7,717 View
- 244 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Composite lymphoma is very rare and a combination of Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and even histiocytic tumors can occur. Because of the unfamiliarity, not only can this cause diagnostic problems, but can also affect treatment plan. We report a case of composite lymphoma in a 40-year-old male. Initial biopsy showed a composite lymphoma of follicular lymphoma grade 1 and classic Hodgkin lymphoma. After chemotherapy, another lymph node was taken because of disease progression, which revealed follicular lymphoma, grade 3a without Hodgkin lymphoma component.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Composite Lymphoma: A Rare Case of Vomiting
Changqin Liu, Dongyan Han, Xiaomin Sun
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(5): 836. CrossRef - BCL2-Rearrangment-Negative CD23+ Follicle Center Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: A Rare Case of Biclonal Composite Lymphoma
Hira Qadir, Ejas Palathingal Bava, Juan Gomez-Gelvez, Wei Liu, Kedar Inamdar, Elizabeth Wey, John Carey, Yulei Shen, Philip Kuriakose, Sharmila Ghosh
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - T cell lymphoma and secondary primary malignancy risk after commercial CAR T cell therapy
Guido Ghilardi, Joseph A. Fraietta, James N. Gerson, Vivianna M. Van Deerlin, Jennifer J. D. Morrissette, Gabriel C. Caponetti, Luca Paruzzo, Jaryse C. Harris, Elise A. Chong, Sandra P. Susanibar Adaniya, Jakub Svoboda, Sunita D. Nasta, Ositadimma H. Ugwu
Nature Medicine.2024; 30(4): 984. CrossRef - Double trouble: insights from a rare case of extranodal composite lymphoma in an elderly man, with comprehensive literature review
Aadya Kerkar
American Journal of Translational Research.2024; 16(6): 2599. CrossRef - Composite Lymphoma with Follicular Lymphoma Transformation to Clonally Related Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and EBV-PositiveClassic Hodgkin Lymphoma
Christopher B. Ryder, Hayder Saeed, Mohammad Hussaini, Pier Paolo Piccaluga
Case Reports in Hematology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Plasticity in Classical Hodgkin Composite Lymphomas: A Systematic Review
Alexis Trecourt, Marie Donzel, Juliette Fontaine, Hervé Ghesquières, Laurent Jallade, Gabriel Antherieu, Camille Laurent, Claire Mauduit, Alexsandra Traverse-Glehen
Cancers.2022; 14(22): 5695. CrossRef
- Composite Lymphoma: A Rare Case of Vomiting
- Clinicopathologic implication of PD-L1 gene alteration in primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- Ki Rim Lee, Jiwon Koh, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Hyun Jung Kwon, Jeong-Ok Lee, Jin Ho Paik
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(1):32-39. Published online November 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.10.05
- 5,459 View
- 169 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary adrenal (PA) diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was previously reported as an aggressive subset of DLBCL, but its genetic features were not sufficiently characterized. From our previous study of DLBCL with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) gene alterations, we focused on PD-L1 gene alterations in PA-DLBCL with clinicopathologic implications.
Methods
We performed fluorescence in situ hybridization for PD-L1 gene translocation and amplification in PA-DLBCL (n = 18) and comparatively analyzed clinicopathologic characteristics with systemic non-adrenal (NA)-DLBCL (n = 90).
Results
PA-DLBCL harbored distinctive features (vs. NADLBCL), including high international prognostic index score (3–5) (72% [13/18] vs. 38% [34/90], p = .007), poor Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score (≥ 2) (47% [7/15] vs. 11% [10/90], p = .003), elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (78% [14/18] vs. 51% [44/87], p = .035) and MUM1 expression (87% [13/15] vs. 60% [54/90], p = .047). Moreover, PA-DLBCL showed frequent PD-L1 gene alterations (vs. NA-DLBCL) (39% [7/18] vs. 6% [5/86], p = .001), including translocation (22% [4/18] vs. 3% [3/87], p = .016) and amplification (17% [3/18] vs. 2% [2/87], p = .034). Within the PA-DLBCL group, PD-L1 gene–altered cases (vs. non-altered cases) tended to have B symptoms (p = .145) and elevated LDH (p = .119) but less frequent bulky disease (≥ 10 cm) (p = .119). In the survival analysis, PA-DLBCL had a poor prognosis for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) (vs. NA-DLBCL; p = .014 and p = .004). Within the PA-DLBCL group, PD-L1 translocation was associated with shorter OS and PFS (p < .001 and p = .012).
Conclusions
PA-DLBCL is a clinically aggressive and distinct subset of DLBCL with frequent PD-L1 gene alterations. PD-L1 gene translocation was associated with poor prognosis in PA-DLBCL.
- Upward trend in follicular lymphoma among the Korean population: 10-year experience at a large tertiary institution
- Meejeong Kim, Hee Sang Hwang, Hyungwoo Cho, Dok Hyun Yoon, Cheolwon Suh, Chan Sik Park, Heounjeong Go, Jooryung Huh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(5):330-337. Published online September 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.25
- 6,653 View
- 123 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the second most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in Western countries. However, it is relatively rare in Asia. This study examined epidemiologic characteristics of FL in South Korea, with an emphasis on recent trends of increase in cases.
Methods
We retrospectively examined 239 cases of newly diagnosed FL at a large tertiary institution in Korea (Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea) between 2008 and 2017. Age-adjusted incidence rates and clinicopathological variables were analyzed, and joinpoint regression analysis was used to identify the changes.
Results
The age-adjusted incidence of FL significantly increased during the study period (p = .034), and the ratio of (relative incidence) patients with FL to patients with NHL increased from 4.28% to 9.35% in the same period. Over the 10-year study assessment duration, the proportion of patients with stage III/IV FL (p = .035) and expression of BCL2 (p = .022) or BCL6 (p = .039) significantly increased. From 2013–2017, the proportion of patients with highrisk Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) score increased (21.5% to 28.7%), whereas that of low-risk FLIPI decreased (55.4% to 38.6%), although those results were not statistically significant (p = .066).
Conclusions
We found an increasing incidence of FL, with a disproportionate increase in the incidence of high-stage disease and recent changes in the clinicopathologic features of the Korean patient population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence Trend of Follicular Lymphoma in Taiwan Compared to Japan and Korea, 2001–2019
Liang-Chun Chiu, Chih-Wen Lin, Hung-Ju Li, Jian-Han Chen, Fu-Cheng Chuang, Sheng-Fung Lin, Yu Chang, Yu-Chieh Su
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1417. CrossRef - A Case Report on the Complete Response of a Patient with Recurrent Follicular Lymphoma Treated with Integrative Medicine
Kyung-dug Park, Jisoo Kim, Yoona Oh, Beom-Jin Jeong, Yu-jin Jung, Sunhwi Bang
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2023; 44(3): 585. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma
Ga-Young Song, Deok-Hwan Yang
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(5): 231. CrossRef - Classical Hodgkin lymphoma following follicular lymphoma: a case report
Bomi Kim
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(Suppl): S113. CrossRef - Incidence, clinicopathological features and genetics of in‐situ follicular neoplasia: a comprehensive screening study in a Japanese cohort
Naoki Oishi, Takahiro Segawa, Kunio Miyake, Kunio Mochizuki, Tetsuo Kondo
Histopathology.2022; 80(5): 820. CrossRef
- Incidence Trend of Follicular Lymphoma in Taiwan Compared to Japan and Korea, 2001–2019
- A case of concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration against a mutated EGFR background in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
- Ki-Chang Lee, Jiwon Koh, Doo Hyun Chung, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):139-144. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.12.16
- 5,222 View
- 111 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rare cases of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) with concomitant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) translocation have been reported. However, their clonal and evolutional relationship remains unclear. We report a case of early-stage EGFR-mutated LUAD with a focal concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration. A 63-year-old male underwent lobectomy to remove a 1.9-cm-sized lung nodule, which was diagnosed with EGFR-mutated LUAD. ALK immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed focal positivity within the part of the tumor characterized by lepidic pattern, also confirmed by fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH). Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed separately on the ALK IHC/FISH-positive and -negative areas. EGFR L833V/L858R mutations were detected in both areas, whereas EML4 (echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4)-ALK translocations was confirmed only in the ALK IHC/FISH-positive area, suggesting the divergence of an EGFR/ALK co-altered subclone from the original EGFR-mutant clone. Our study suggests that concurrent alterations of EGFR and ALK can arise via divergent tumor evolution, even in the relatively early phases of tumorigenesis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Machine learning-based characterization of a PANoptosis-associated model for enhancing prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Ziqiao Fu, Jia Zeng, Xiaomin Xiong, Weimin Zhong
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of molecular subtype and prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma based on neutrophil extracellular traps
Yanhua Zuo, Guangyi Leng, Ping Leng
Pathology and Oncology Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Integration Develops a Macrophage-Related Index for Predicting Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Zuwei Li, Minzhang Guo, Wanli Lin, Peiyuan Huang
Archives of Medical Research.2023; 54(7): 102897. CrossRef - Big data analysis identified a telomere-related signature predicting the prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
Weiyi Zhang
Medicine.2023; 102(46): e35526. CrossRef
- Machine learning-based characterization of a PANoptosis-associated model for enhancing prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma patients
- Renal intravascular large B cell lymphoma: the first case report in Korea and a review of the literature
- Moonsik Kim, Haerim Chung, Woo Ick Yang, Hyeon Joo Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):426-431. Published online August 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.18
- 6,208 View
- 121 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Herein, we describe the first case of renal intravascular large B cell lymphoma in Korea occurring in a 66-year-old female. She presented with mild fever and dyspnea. On physical and laboratory evaluations, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis was suspected, but the bone marrow biopsy results were unremarkable. During the work-up, massive proteinuria developed, which led to a renal biopsy. The renal architecture was relatively well-preserved, but the glomeruli were hypercellular with the infiltration of atypical, large lymphoid cells with increased nucleus-cytoplasm ratio and clumped chromatin. Similar cells were also present in the peritubular capillaries. The tumor cells exhibited membranous staining for CD20 and CD79a. After the diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma, the patient received rituximab-based chemotherapy under close follow-up.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system with renal involvement: a case report and literature review
Jun Li, Zhaojiao Li, Yifeng Shi, Jiajie Chen, Heng Zhao, Xueye Mao, Shan Li, Huiying Wang, Qiang Meng, Lingchun Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - EBV-Positive Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the Small Intestine: A Case Report and Literature Review
Chenglong Pan, Xiaoling Ma, Yanfei Yao, Chunyan Wang
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(3): 586. CrossRef - Intravascular large B‐cell lymphoma in renal cell carcinoma incidentally detected by robot‐assisted partial nephrectomy
Michio Noda, Yutaka Enomoto, Yukari Shirasugi, Sumiyo Ando, Yukimasa Matsuzawa, Haruki Kume
IJU Case Reports.2022; 5(3): 191. CrossRef - Case Report: Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of Four Cases With Review of Additional 331 Cases in the Literature
Yingying Han, Qingjiao Li, Dan Wang, Lushan Peng, Tao Huang, Chunlin Ou, Keda Yang, Junpu Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renal Involvement of CD20-Negative Intravascular Large B Cell Lymphoma with Neurological Manifestations
Faten Aqeel, Serena M. Bagnasco, Duvuru Geetha, Yoshihide Fujigaki
Case Reports in Nephrology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system with renal involvement: a case report and literature review
- Gastric crystal-storing histiocytosis with concomitant mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma
- Mee Joo, Nam-Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):332-335. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.04.20
- 6,145 View
- 114 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Crystal-storing histiocytosis (CSH) is a rare entity that is characterized by intrahistiocytic accumulation of crystallized immunoglobulins. CSH is not a malignant process per se, but the majority of CSH cases are associated with underlying lymphoproliferative disorder. Although CSH can occur in a variety of organs, gastric CSH is very rare. We present a localized gastric CSH with concomitant mucosaassociated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, manifesting as an ulcer bleeding in a 56-year-old man. Histologically, the biopsied gastric mucosa demonstrated expansion of the lamina propria by prominent collections of large eosinophilic mononuclear cells containing fibrillary crystalloid inclusions. Immunohistochemical studies revealed that the crystal-storing cells were histiocytes harboring kappa light chain-restricted immunoglobulin crystals. Within the lesion, atypical centrocyte-like cells forming lymphoepithelial lesions were seen, consistent with MALT lymphoma. Since this entity is rare and unfamiliar, difficulties in diagnosis may arise. Particularly, in this case, the lymphomatous area was obscured by florid CSH, making the diagnosis more challenging.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sunny side up
João Pedro Pereira, Joanne Lopes, Fatima Carneiro, Francisco Baldaque-Silva
Frontline Gastroenterology.2025; 16(4): 344. CrossRef - Crystal-Storing Histiocytosis of the Stomach: An Unusual Clinical Context of a Rare Entity
Jenna Magri, Katsiaryna Khatskevich, Lauren Shealy, David Lewin, Chadi Hajar
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Crystal-storing histiocytosis in the stomach: A case report and review of the literature
Linghong Kong, Liyan Xue, Yanfeng Zhong, Shenglan Wang, Danfeng Zheng, Lining Wang, Yang Jiao, Xinpeng Zhang, Huizhong Xue, Xiaogang Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lambda-Restricted Crystal-Storing Histiocytosis of Stomach: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Nalini Bansal, Pankaj Puri, Nishant Nagpal, Rahul Naithani, Rahul Gupta
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunoglobulin-Storing Histiocytosis: A Case Based Systemic Review
Hanne Wiese-Hansen, Friedemann Leh, Anette Lodvir Hemsing, Håkon Reikvam
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(9): 1834. CrossRef
- Sunny side up
- Primary hepatic extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
- Soyeon Choi, Ji Hye Kim, Kyungbin Kim, Misung Kim, Hye Jeong Choi, Young Min Kim, Jae Hee Suh, Min Jung Seo, Hee Jeong Cha
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):340-345. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.03.18
- 7,854 View
- 135 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma), is one of the specific type of low-grade B-cell lymphoma not infrequently found worldwide. It typically involves mucosal sites such as stomach and conjunctiva; however, primary hepatic MALT lymphoma has been extremely rarely reported. We describe a case of hepatic MALT lymphoma in a 70-year-old male patient who underwent left hepatectomy due to the incidentally detected liver masses at a medical checkup. The resected specimen revealed multinodular masses consisting of small-to-intermediate-sized lymphoid cells with serpentine pattern and focal lymphoepithelial lesions. The tumor cells were diffusely positive for CD20 and Bcl-2 but negative for CD3, CD10, CD5, CD23, CD43, and cyclinD1. The Ki-67 labeling index was 10% and immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement study confirmed monoclonal proliferation. In this paper, we discuss several unique clinicopathologic characteristics which will be helpful to the differential diagnosis of hepatic MALT lymphoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oral administration of Limosilactobacillus reuteri VHProbi® M07 alleviates ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice
Guoqing Meng, Hongchang Cui, Congrui Feng, Chaoqun Guo, Lei Song, Zhi Duan, Misbahuddin Rafeeq
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0317587. CrossRef - Response‑adapted involved site radiation therapy for hepatic marginal zone B‑cell lymphoma: A case report
Shin-Ting Chen, Yu-Guang Chen, Wen-Yen Huang, Cheng-Hsiang Lo
Oncology Letters.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management approaches for primary hepatic lymphoma: 10 year institutional experience with comprehensive literature review
Jennifer Ma, Remy Daou, Josiane Bou Eid, Beatrice Fregonese, Joe El-Khoury, N. Ari Wijetunga, Brandon S. Imber, Joachim Yahalom, Carla Hajj
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Hepatic Mucosa-Associated B-Cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis—A Case Ultimately Requiring Liver Transplantation
Jerica Novak, Mihajlo Đokić, Miha Petrič, Diana Vozlič, Milanka Živanović, Branislava Ranković, Blaž Trotovšek
Diagnostics.2025; 15(16): 2082. CrossRef - Primary hepatic mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: a case report and literature review
Tao He, Jieyu Zou
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - “Speckled Enhancement” on Gd-EOB-DTPA Enhanced MR Imaging of Primary Hepatic Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma
Ryota Hyodo, Yasuo Takehara, Ayumi Nishida, Masaya Matsushima, Shinji Naganawa
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences.2023; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Primary hepatic extranodal marginal zone B-cell mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma treated by laparoscopic partial hepatectomy: a case report
Keisuke Okura, Satoru Seo, Hironori Shimizu, Hiroto Nishino, Tomoaki Yoh, Ken Fukumitsu, Takamichi Ishii, Koichiro Hata, Hironori Haga, Etsuro Hatano
Surgical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Findings in Pediatric Patients: How to Manage Liver Incidentaloma in Pediatric Patients
Andrius Cekuolis, Dagmar Schreiber-Dietrich, Rasa Augustinienė, Heike Taut, Judy Squires, Edda L. Chaves, Yi Dong, Christoph F. Dietrich
Cancers.2023; 15(8): 2360. CrossRef - Primary hepatic mucosa‐associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: Case report and literature review
Wing Yu Lau, Kit‐Man Ho, Fiona Ka‐Man Chan, Shi Lam, Kai‐Chi Cheng
Surgical Practice.2022; 26(1): 56. CrossRef - 18F-FDG Versus 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in Visualizing Primary Hepatic Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
Yizhen Pang, Long Zhao, Qihang Shang, Tinghua Meng, Haojun Chen
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2022; 47(4): 375. CrossRef - Primary hepatopancreatobiliary lymphoma: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management
Qianwen Wang, Kangze Wu, Xuzhao Zhang, Yang Liu, Zhouyi Sun, Shumei Wei, Bo Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Positive effect of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis VHProbi YB11 in improving gastrointestinal movement of mice having constipation
Hongchang Cui, Qian Wang, Congrui Feng, Chaoqun Guo, Jingyan Zhang, Xinping Bu, Zhi Duan
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A case of primary hepatic extranodal marginal zone B-cell mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma treated by radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and a literature review
Zhe Xu, Chong Pang, Jidong Sui, Zhenming Gao
Journal of International Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oral administration of Limosilactobacillus reuteri VHProbi® M07 alleviates ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice
- Morphologic variant of follicular lymphoma reminiscent of hyaline-vascular Castleman disease
- Jiwon Koh, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):253-257. Published online February 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.12.17
- 8,134 View
- 239 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Follicular lymphoma (FL) with hyaline-vascular Castleman disease (FL-HVCD)-like features is a rare morphologic variant, with fewer than 20 cases in the literature. Herein, we report a case of FL-HVCD in a 37-year-old female who presented with isolated neck lymph node enlargement. The excised lymph node showed features reminiscent of HVCD, including regressed germinal centers (GCs) surrounded by onion skin-like mantle zones, lollipop lesions composed of hyalinized blood vessels penetrating into regressed GCs, and hyalinized interfollicular stroma. In addition, focal areas of abnormally conglomerated GCs composed of homogeneous, small centrocytes with strong BCL2, CD10, and BCL6 expression were observed, indicating partial involvement of the FL. Several other lymphoid follicles showed features of in situ follicular neoplasia. Based on the observations, a diagnosis of FL-HVCD was made. Although FLHVCD is very rare, the possibility of this variant should be considered in cases resembling CD. Identification of abnormal, neoplastic follicles and ancillary immunostaining are helpful for proper diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unicentric Castleman Disease: Illustration of Its Morphologic Spectrum and Review of the Differential Diagnosis
Siba El Hussein, Andrew G. Evans, Hong Fang, Wei Wang, L. Jeffrey Medeiros
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(1): 99. CrossRef - Finding a Needle in the Haystack
Hung-Yu Lin, Yi-Jen Peng, Yi-Ying Wu, Ping-Ying Chang
Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 43(6): 292. CrossRef - Analysis of immunophenotypic features in hyaline vascular type Castleman disease
Yu Chang, Yu Ma, Chen Chang, Wensheng Li
Diagnostic Pathology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In‐situ follicular neoplasia: a clinicopathological spectrum
Gurdip S Tamber, Myriam Chévarie‐Davis, Margaret Warner, Chantal Séguin, Carole Caron, René P Michel
Histopathology.2021; 79(6): 1072. CrossRef
- Unicentric Castleman Disease: Illustration of Its Morphologic Spectrum and Review of the Differential Diagnosis
- Diffuse Involvement of Primary Colorectal Lymphoma Simulating Ulcerative Colitis
- Ji-Ye Kim, Sun Hee Chang, Han Seong Kim, Mee Joo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):332-336. Published online August 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.07.12
- 6,614 View
- 93 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diffuse involvement of colorectal lymphoma masquerading as colitis is a very rare presentation of primary colorectal lymphoma. Detecting occult lymphoma is difficult in the setting of diffuse colonic involvement with no definite mass and inflammatory mucosal changes. We encountered a case of diffuse-type primary colorectal lymphoma simulating ulcerative colitis in a previously healthy 31-year-old woman. Despite multiple mucosal biopsies, the biopsy diagnosis was not made due to unawareness of atypical lymphocytes admixed with dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. The present case emphasizes the importance of being aware of this rare presentation of primary colorectal lymphoma in order to avoid misdiagnosis.
- Primary Peripheral Gamma Delta T-Cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System: Report of a Case Involving the Intramedullary Spinal Cord and Presenting with Myelopathy
- Jeemin Yim, Seung Geun Song, Sehui Kim, Jae Won Choi, Kyu-Chong Lee, Jeong Mo Bae, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):57-61. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.21
- 7,331 View
- 159 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary central nervous system lymphoma of T-cell origin (T-PCNSL) is rare, and its clinicopathological features remain unclear. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma of γδ T-cell origin is an aggressive lymphoma mainly involving extranodal sites. Here, we report a case of γδ T-PCNSL involving the intramedullary spinal cord and presenting with paraplegia. A 75-year-old Korean woman visited the hospital complaining of back pain and lower extremity weakness. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed multifocal enhancing intramedullary nodular lesions in the thoracic and lumbar spinal cord. An enhancing nodular lesion was observed in the periventricular white matter of the lateral ventricle in the brain. There were no other abnormalities in systemic organs or skin. Laminectomy and tumor removal were performed. The tumor consisted of monomorphic, medium-to-large atypical lymphocytes with pale-to-eosinophilic cytoplasm. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were CD3(+), TCRβF1(-), TCRγ(+), CD30(-), CD4(-), CD8(-), CD56(+), TIA1(+), granzyme B(+), and CD103(+). Epstein-Barr virus in situ was negative. This case represents a unique T-PCNSL of γδ T-cell origin involving the spinal cord.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- B-Cell Lymphoma Intramedullary Tumor: Case Report and Systematic Review
Daniel Gregório Gonsalves, Paulo Eduardo Albuquerque Zito Raffa, Gabriela Gerenutti de Sousa, Melissa Esposito Gomes Rigueiral, Iracema Araújo Estevão, Cesar Cozar Pacheco, Roger Thomaz Rotta Medeiros, Paulo Roberto Franceschini, Paulo Henrique Pires de A
Asian Journal of Neurosurgery.2023; 18(02): 231. CrossRef - Primary intramedullary spinal cord lymphoma misdiagnosed as longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis: a case report and literature review
Huizhen Ge, Li Xu, Huajie Gao, Suqiong Ji
BMC Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and Genetic Features of Primary T-cell Lymphomas of the Central Nervous System
Jeemin Yim, Jiwon Koh, Sehui Kim, Seung Geun Song, Jeong Mo Bae, Hongseok Yun, Ji-Youn Sung, Tae Min Kim, Sung-Hye Park, Yoon Kyung Jeon
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 46(4): 486. CrossRef - Peripheral T-Cell Lymphomas Involving the Central Nervous System: A Report From the Czech Lymphoma Study Group Registry
Heidi Mocikova, Robert Pytlík, Katerina Benesova, Andrea Janikova, Juraj Duras, Alice Sykorova, Katerina Steinerova, Vit Prochazka, Vit Campr, David Belada, Marek Trneny
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- B-Cell Lymphoma Intramedullary Tumor: Case Report and Systematic Review
- Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia with Mass-Formation: Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Nine Cases and Review of the Literature
- Jongmin Sim, Hyun Hee Koh, Sangjoon Choi, Jinah Chu, Tae Sung Kim, Hojoong Kim, Joungho Han
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):211-218. Published online June 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.27
- 13,413 View
- 389 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia (PNLH) is a non-neoplastic pulmonary lymphoid disorder that can be mistaken for malignancy on radiography. Herein, we present nine cases of PNLH, emphasizing clinicoradiological findings and histological features.
Methods
We analyzed radiological and clinicopathological features from the electronic medical records of nine patients (eight females and one male) diagnosed with PNLH. IgG and IgG4 immunohistochemical staining was performed in three patients.
Results
Two of the nine patients had experienced tuberculosis 40 and 30 years prior, respectively. Interestingly, none were current smokers, although two were ex-smokers. Three patients complaining of persistent cough underwent computed tomography of the chest. PNLH was incidentally discovered in five patients during examination for other reasons. The remaining patient was diagnosed with the disease following treatment for pneumonia. Imaging studies revealed consolidation or a mass-like lesion in eight patients. First impressions included invasive adenocarcinoma and mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue‒type lymphoma. Aspergillosis was suspected in the remaining patient based on radiological images. Resection was performed in all patients. Microscopically, the lesions consisted of nodular proliferation of reactive germinal centers accompanied by infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages in various degrees and surrounding fibrosis. Ultimately, all nine patients were diagnosed with PNLH and showed no evidence of recurrence on follow-up.
Conclusions
PNLH is an uncommon but distinct entity with a benign nature, and understanding the radiological and clinicopathological characteristics of PNLH is important. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Imaging Features of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Dong-Lei Nie, Yan-Hong Shi, Xin-Min Li, Xiao-Jiang Wang, Bao-Li Han, Guo-Fu Zhang
Journal of Thoracic Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathologic Findings of Pulmonary Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Yoshiaki Zaizen, Junya Fukuoka
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2025; 46(4): 272. CrossRef - Utilizing Immunoglobulin G4 Immunohistochemistry for Risk Stratification in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated with Hashimoto Thyroiditis
Faridul Haq, Gyeongsin Park, Sora Jeon, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(3): 468. CrossRef - Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia Evaluated with Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Findings: A Case Report and Review of the Literature on Japanese Patients
Sakiko Moriyama, Takashi Kido, Noriho Sakamoto, Mai Fuchigami, Takatomo Tokito, Daisuke Okuno, Takuto Miyamura, Shota Nakashima, Atsuko Hara, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Yoshitaka Imaizumi, Kazuto Tsuruda, Katsunori Yanagihara, Junya Fukuoka, Hiroshi Mukae
Internal Medicine.2023; 62(1): 95. CrossRef - A Case of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia Responding to Corticosteroid Treatment
Jonathan Teow Koon Goh, Issam Al Jajeh, Jessica Han Ying Tan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as cavitating lung mass
Aqeel Alameer, Chary Duraikannu, Avinash Kumar Kanodia, David Dorward
BMJ Case Reports.2023; 16(8): e254121. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Characteristics and Curative Effect of Lymphoma Based on Sampling Theory
Shuxiang Ding, Leipo Liu
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia presenting as multifocal subsolid nodules: A case report and literature review
Yoon Jin Cha, Duk Hwan Moon, Ji Hyun Park, Sungsoo Lee, Ji Ae Choi, Tae Hoon Kim, Chul Hwan Park
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2022; 36: 101581. CrossRef - Pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia in a 53-year-old man with malignant sign: a case report
Zhen Yang, Lianshuang Wei, Xu Li, Xin Liu
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The diagnostic challenge of adenocarcinoma in pulmonary nodular lymphoid hyperplasia
Anita Savić Vuković, Melita Kukuljan, Morana Dinter, Ksenija Jurinović, Nives Jonjić
SAGE Open Medical Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical and Imaging Features of Pulmonary Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia
- An Autopsy Case of Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System in an Immunocompromised Host
- Sun-Young Park, Seong Ik Kim, Hannah Kim, Yoojin Lee, Sung-Hye Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):51-55. Published online August 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.23
- 9,606 View
- 173 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lymphomas arising in the central nervous system (CNS) of immunocompromised hosts are most commonly non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas and are highly associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Here we report an autopsy case of EBV-associated CNS diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in a host suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus who underwent immunosuppressive therapy. After autopsy, EBV-associated CNS DLBCL as well as pulmonary mixed aspergillosis and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia were added to the cause of clinical manifestations of complicated pneumonia and cerebral hemorrhage in this immunocompromised patient. In conclusion, complex disease processes were revealed by autopsy in this case, indicating that the clinicopathological correlations observed through autopsy can improve our understanding of disease progression and contribute to the management of similar patients in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary central nervous system lymphoma in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: case-based review
Takanori Ichikawa, Yasuhiro Shimojima, Dai Kishida, Tomoki Kaneko, Yoshiki Sekijima
Rheumatology International.2021; 41(5): 1009. CrossRef
- Primary central nervous system lymphoma in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: case-based review
- Molecular Testing of Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Current Status and Perspectives
- Yoon Kyung Jeon, Sun Och Yoon, Jin Ho Paik, Young A Kim, Bong Kyung Shin, Hyun-Jung Kim, Hee Jeong Cha, Ji Eun Kim, Jooryung Huh, Young-Hyeh Ko
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):224-241. Published online May 10, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.04.09
- 21,815 View
- 710 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Molecular pathologic testing plays an important role for the diagnosis, prognostication and decision of treatment strategy in lymphoproliferative disease. Here, we briefly review the molecular tests currently used for lymphoproliferative disease and those which will be implicated in clinical practice in the near future. Specifically, this guideline addresses the clonality test for B- and T-cell proliferative lesions, molecular cytogenetic tests for malignant lymphoma, determination of cell-of-origin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and molecular genetic alterations incorporated in the 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Finally, a new perspective on the next-generation sequencing for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic purpose in malignant lymphoma will be summarized.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric lymphoproliferative disorders – Emerging insights and management: A narrative review
Emmanuel Ifeanyi Obeagu
Medicine.2026; 105(4): e47367. CrossRef - Presence of minimal residual disease determined by next-generation sequencing is not a reliable prognostic biomarker in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Elizabeta Krstevska Bozhinovikj, Nadica Matevska-Geshkovska, Marija Staninova Stojovska, Emilija Gjorgievska, Aleksandra Jovanovska, Nevenka Ridova, Irina Panovska Stavridis, Svetlana Kocheva, Aleksandar Dimovski
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2025; 66(6): 1121. CrossRef - Haematogenous seeding in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: current evidence and clinical implications
Robert Gniadecki, Emmanuella Guenova, Christiane Querfeld, Jan P Nicolay, Julia Scarisbrick, Lubomir Sokol
British Journal of Dermatology.2025; 192(3): 381. CrossRef - Exploring External Quality Control Methods for PCR–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis–Based Lymphocyte Receptor Gene Rearrangement Assays in Korea
Jieun Kim, Ho Hyun Song, Soobin Chae, GeonWoo Choi, Jeong Won Shin
Journal of Laboratory Medicine and Quality Assurance.2025; 47(2): 43. CrossRef - Laboratory analysis of 182 cases of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders other than typical chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Single-center study
Shams Salah Mahdi, Nuha Abd Ali Al-Sarai
Iraqi Journal of Hematology.2025; 14(2): 218. CrossRef - Assessment of Bone Marrow Involvement in B‐Cell non‐Hodgkin Lymphoma Using Immunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement Analysis with Next‐Generation Sequencing
Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Chul Won Choi, Ha Nui Kim, Jung Ah Kwon, Soo‐Young Yoon, Jung Yoon
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymus and lung mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma with adenocarcinoma of the lung: a case report and literature review
Yu Pang, Daosheng Li, Yiqian Chen, Qinqin Liu, Yuheng Wu, Qingliang Teng, Yuyu Liu
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and implementation of an automated and highly accurate reporting process for NGS-based clonality testing
Sean T. Glenn, Phillip M. Galbo, Jesse D. Luce, Kiersten Marie Miles, Prashant K. Singh, Manuel J. Glynias, Carl Morrison
Oncotarget.2023; 14(1): 450. CrossRef - A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and next-generation sequencing in the detection of immunoglobulin heavy chain H and light chain κ gene rearrangements in the diagnosis of classic hodgkin’s lymphoma
Juan-Juan Zhang, Yu-Xin Xie, Li-Lin Luo, Xuan-Tao Yang, Yi-Xing Wang, Yue Cao, Zheng-Bo Long, Wan-Pu Wang
Bioengineered.2022; 13(3): 5868. CrossRef - Lymphoproliferative disorder involving body fluid: diagnostic approaches and roles of ancillary studies
Jiwon Koh, Sun Ah Shin, Ji Ae Lee, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(4): 173. CrossRef - Diagnostic Workup of Primary Cutaneous B Cell Lymphomas: A Clinician's Approach
Giulia Tadiotto Cicogna, Martina Ferranti, Mauro Alaibac
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Kappa and lambda immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization in the evaluation of atypical cutaneous lymphoid infiltrates
Alexandra C. Hristov, Nneka I. Comfere, Claudia I. Vidal, Uma Sundram
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2020; 47(11): 1103. CrossRef - Primary lung mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma accompanied by multiple sclerosis
Ke-Ke Yu, Lei Zhu, Ji-Kai Zhao, Rui-Ying Zhao, Yu-Chen Han
Chinese Medical Journal.2019; 132(13): 1625. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry in mantle cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
Woojoo Lee, Eun Shin, Bo-Hyung Kim, Hyunchul Kim, Riccardo Dolcetti
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(11): e0225096. CrossRef - Views of dermatopathologists about clonality assays in the diagnosis of cutaneous T‐cell and B‐cell lymphoproliferative disorders
Nneka Comfere, Uma Sundram, Maria Yadira Hurley, Brian Swick
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2018; 45(1): 39. CrossRef - A Next-Generation Sequencing Primer—How Does It Work and What Can It Do?
Yuriy O. Alekseyev, Roghayeh Fazeli, Shi Yang, Raveen Basran, Thomas Maher, Nancy S. Miller, Daniel Remick
Academic Pathology.2018; 5: 2374289518766521. CrossRef
- Pediatric lymphoproliferative disorders – Emerging insights and management: A narrative review
- A Small Case Series of Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma with Unexpected Findings: Subset of Cases with Concomitant Extravascular Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement Mimicking Primary CNS Lymphoma
- Kate Poropatich, Dave Dittmann, Yi-Hua Chen, Kirtee Raparia, Kristy Wolniak, Juehua Gao
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):284-291. Published online April 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.02.16
- 12,873 View
- 226 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL) is a rare type of extranodal lymphoma with growth mainly in the lumina of vessels. We studied a small series of IVLBCL and focused on its central nervous system (CNS) involvement.
Methods
Searching the medical records of Northwestern Memorial Hospital, we identified five cases of IVLBCL from January 2007 to January 2015. Clinical information, hematoxylin and eosin stained histologic slides and immunohistochemistry studies were reviewed for all cases. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis for the immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy and light chain gene rearrangement was performed on all five cases.
Results
Three of the five cases of IVLBCL were autopsies. Patients’ age ranged from 56 to 84. CNS involvement was present in two cases—in both patients, the CNS involvement showed an extravascular pattern with confluent sheet-like formation. PCR analysis confirmed that in one case the systemic intravascular and CNS extravascular components were clonally identical.
Conclusions
In a small case series of IVLBCL, we observed that CNS involvement by IVLBCL often has an extravascular morphology, but is clonally identical to the intravascular counterpart by PCR analysis. As IVLBCL can have a rapidly progressing poor outcome, it should be kept in the differential diagnoses for patients presenting with lymphoma of the CNS. The presence of extravascular growth patterns in the CNS should not exclude IVLBCL as a diagnosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical manifestations and outcomes of patients with intravascular large B-cell lymphoma with neurological involvement: highlighting longitudinally extensive myelopathy as a distinct feature
Ekdanai Uawithya, Palakorn Lertsakworakul, Weerapat Owatthanapanich, Jiraporn Jitprapaikulsan
BMJ Neurology Open.2025; 7(1): e000915. CrossRef - Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system with renal involvement: a case report and literature review
Jun Li, Zhaojiao Li, Yifeng Shi, Jiajie Chen, Heng Zhao, Xueye Mao, Shan Li, Huiying Wang, Qiang Meng, Lingchun Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A single institution series of intravascular lymphoma: Neurological manifestations and neuroimaging findings
J. Corroza, C. Alburquerque, L. Martínez-Martínez, I. Gastón, L. Torné, M.C. Gil-Alzueta, J. Oteiza, T. Cabada, M.C. Viguria, A. Panizo, M.E. Erro
Neurología.2025; 40(8): 768. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Adrenal Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosed via Percutaneous Needle Biopsy
Jiafei Zeng, Jin Li, Shuai Luo, Jinjing Wang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Intravascular Lymphoma: A Unique Pattern Underlying a Protean Disease
Mario Della Mura, Joana Sorino, Filippo Emanuele Angiuli, Gerardo Cazzato, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppe Ingravallo
Cancers.2025; 17(14): 2355. CrossRef - A single institution series of intravascular lymphoma: Neurological manifestations and neuroimaging findings
J. Corroza, C. Alburquerque, L. Martínez-Martínez, I. Gastón, L. Torné, M.C. Gil-Alzueta, J. Oteiza, T. Cabada, M.C. Viguria, A. Panizo, M.E. Erro
Neurología (English Edition).2025; 40(8): 768. CrossRef - Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Migraine with Aura: A Case Report
Sydney Moseley, Robert Fekete
Case Reports in Neurology.2025; 17(1): 176. CrossRef - A case report and literature review of cutaneous intravascular large B-cell lymphoma presenting clinically as panniculitis: a difficult diagnosis, but a good prognosis
Deniz Bayçelebi, Levent Yıldız, Nilgün Şentürk
Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia.2021; 96(1): 72. CrossRef - Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with significant intravascular invasion. Close resemblance of its clinicopathological features to intravascular large B-cell lymphoma, but not to DLBCL-not otherwise specified
Hiroe Itami, Hirokazu Nakamine, Masayuki Kubo, Kohei Ogawa, Rina Tani, Shinji Nakamura, Maiko Takeda, Yuji Nitta, Tomoko Uchiyama, Tomomi Fujii, Kinta Hatakeyama, Chiho Ohbayashi
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hematopathology.2021; 61(3): 152. CrossRef - Unusual and Fatal Case of an Undiagnosed Intravascular Large B‐cell Lymphoma: The Oncologist’s Great Imitator†
Rosario Barranco, Fiorella Caputo, Davide Bedocchi, Francesca Maria Elena Frigiolini, Lara Castelletti, Giulio Fraternali Orcioni, Francesco Ventura
Journal of Forensic Sciences.2020; 65(1): 314. CrossRef - Pituitary Gland and Neurological Involvement in a Case of Hemophagocytic Syndrome Revealing an Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Sylvain Raoul Simeni Njonnou, Bruno Couturier, Yannick Gombeir, Sylvain Verbanck, France Devuyst, Georges El Hachem, Ivan Theate, Anne-Laure Trepant, Virginie De Wilde, Frédéric-Alain Vandergheynst
Case Reports in Hematology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Accurate Detection of Tumor Infiltration by 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography in a Patient with Central Nervous System Intravascular Lymphoma: A Case Report
Shoji Yomo, Keiji Tsutsumi, Takehiro Yako, Hiromasa Sato, Takao Hashimoto, Kazuhiro Oguchi
Case Reports in Oncology.2018; 11(2): 577. CrossRef
- Clinical manifestations and outcomes of patients with intravascular large B-cell lymphoma with neurological involvement: highlighting longitudinally extensive myelopathy as a distinct feature
- GLUT1 as a Prognostic Factor for Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Correlation with PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression
- Young Wha Koh, Jae-Ho Han, Seong Yong Park, Dok Hyun Yoon, Cheolwon Suh, Jooryung Huh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(2):152-158. Published online February 21, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.11.03
- 11,626 View
- 236 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) expression is linked to glucose metabolism and tissue hypoxia. A recent study reported that GLUT1 was significantly associated with programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) as a therapeutic target in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cHL). The purpose of this study was to measure the expression of GLUT1 and assess its prognostic significance and potential relationships with PD-L1, programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2), and programmed death-1 (PD-1) expressions in cHL. Methods: Diagnostic tissues from 125 patients with cHL treated with doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine were evaluated retrospectively via immunohistochemical analysis of GLUT1, PD-L1, PD-L2, and PD-1 expression. Results: The median follow-up time was 4.83 years (range, 0.08 to 17.33 years). GLUT1, PD-L1, PD-L2, and PD-1 were expressed in 44.8%, 63.2%, 9.6%, and 13.6% of the specimens, respectively. Positive correlations were found between GLUT1 and PD-L1 expression (p = .004) and between GLUT1 and PD-L2 expression (p = .031). GLUT1 expression in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells was not associated with overall survival or event-free survival (EFS) in the entire cohort (p = .299 and p = .143, respectively). A subgroup analysis according to the Ann Arbor stage illustrated that GLUT1 expression in HRS cells was associated with better EFS in advanced-stage disease (p = .029). A multivariate analysis identified GLUT1 as a marginally significant prognostic factor for EFS (p = .068). Conclusions: This study suggests that GLUT1 expression is associated with better clinical outcomes in advanced-stage cHL and is significantly associated with PD-L1 and PD-L2 expressions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transcriptomic and miRNA Signatures of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Response Using Machine Learning
Jinting Lin, Qinglan Ma, Lei Chen, Wei Guo, Kaiyan Feng, Tao Huang, Yu-Dong Cai
Life.2025; 15(6): 981. CrossRef - Metabolic Reprogramming and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Lymphoma
Yuyang Pang, Tingxun Lu, Zijun Y. Xu-Monette, Ken H. Young
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 5493. CrossRef - Peptide-based PROTAC degrader of FOXM1 suppresses cancer and decreases GLUT1 and PD-L1 expression
Kun Wang, Xiaoyong Dai, Albert Yu, Chunyan Feng, Kewei Liu, Laiqiang Huang
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - TIMP-1 Dependent Modulation of Metabolic Profiles Impacts Chemoresistance in NSCLC
Wei Xiao, Pankaj Ahluwalia, Lan Wang, John Howard, Ravindra Kolhe, Amyn M. Rojiani, Mumtaz V. Rojiani
Cells.2022; 11(19): 3036. CrossRef - Hypoxia-related tumor environment correlated with immune infiltration and therapeutic sensitivity in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Chen Liu, Lin Liu
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-invasive measurement of PD-L1 status and prediction of immunotherapy response using deep learning of PET/CT images
Wei Mu, Lei Jiang, Yu Shi, Ilke Tunali, Jhanelle E Gray, Evangelia Katsoulakis, Jie Tian, Robert J Gillies, Matthew B Schabath
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2021; 9(6): e002118. CrossRef - Tumor immunity is related to 18F‐FDG uptake in thymic epithelial tumor
Hisao Imai, Kyoichi Kaira, Kosuke Hashimoto, Hiroyuki Nitanda, Ryo Taguchi, Akitoshi Yanagihara, Tetsuya Umesaki, Ou Yamaguchi, Atsuto Mouri, Tomonori Kawasaki, Masanori Yasuda, Kunihiko Kobayashi, Hirozo Sakaguchi, Ichiei Kuji, Hiroshi Kagamu
Cancer Medicine.2021; 10(18): 6317. CrossRef - Transcutaneous Carbon Dioxide Decreases Immunosuppressive Factors in Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vivo
Nanae Yatagai, Takumi Hasegawa, Rika Amano, Izumi Saito, Satomi Arimoto, Daisuke Takeda, Yasumasa Kakei, Masaya Akashi, Peter J. Oefner
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Role of Functional Imaging in the Management of Lymphoma
Bruce D. Cheson, Michel Meignan
Current Oncology Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG-PET to predict the tumour immune status defined by tumoural PD-L1 and CD8+tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Maria Togo, Takehiko Yokobori, Kimihiro Shimizu, Tadashi Handa, Kyoichi Kaira, Takaaki Sano, Mariko Tsukagoshi, Tetsuya Higuchi, Satoshi Yokoo, Ken Shirabe, Tetsunari Oyama
British Journal of Cancer.2020; 122(11): 1686. CrossRef - Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape
Xianjie Jiang, Jie Wang, Xiangying Deng, Fang Xiong, Junshang Ge, Bo Xiang, Xu Wu, Jian Ma, Ming Zhou, Xiaoling Li, Yong Li, Guiyuan Li, Wei Xiong, Can Guo, Zhaoyang Zeng
Molecular Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Fluorodeoxyglucose uptake is associated with low tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte levels in patients with small cell lung cancer
Norimitsu Kasahara, Kyoichi Kaira, Koichi Yamaguchi, Hiroaki Masubuchi, Hiroaki Tsurumaki, Kenichiro Hara, Yasuhiko Koga, Reiko Sakurai, Tetsuya Higuchi, Tadashi Handa, Tetsunari Oyama, Takehiko Yokobori, Kimihiro Shimizu, Takayuki Asao, Takeshi Hisada
Lung Cancer.2019; 134: 180. CrossRef - MYC Expression and Metabolic Redox Changes in Cancer Cells: A Synergy Able to Induce Chemoresistance
Barbara Marengo, Ombretta Garbarino, Andrea Speciale, Lorenzo Monteleone, Nicola Traverso, Cinzia Domenicotti
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Sustain, Adapt, and Overcome—Hypoxia Associated Changes in the Progression of Lymphatic Neoplasia
Orsolya Matolay, Gábor Méhes
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of tumor-related immunity with 18F-FDG-PET in pulmonary squamous-cell carcinoma
Norimitsu Kasahara, Kyoichi Kaira, Pinjie Bao, Tetsuya Higuchi, Yukiko Arisaka, Bilguun Erkhem-Ochir, Noriaki Sunaga, Yoichi Ohtaki, Toshiki Yajima, Takayuki Kosaka, Tetsunari Oyama, Takehiko Yokobori, Takayuki Asao, Masahiko Nishiyama, Yoshito Tsushima,
Lung Cancer.2018; 119: 71. CrossRef - High Serum Level of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 is Associated With a Poor Prognosis in Hodgkin Lymphoma
Xiaofang Guo, Juan Wang, Jietian Jin, Hao Chen, Zijun Zhen, Wenqi Jiang, Tongyu Lin, Huiqiang Huang, Zhongjun Xia, Xiaofei Sun
Translational Oncology.2018; 11(3): 779. CrossRef - Hodgkin lymphoma and imaging in the era of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy
Margarita Kirienko, Martina Sollini, Arturo Chiti
Clinical and Translational Imaging.2018; 6(6): 417. CrossRef - New developments in the pathology of malignant lymphoma: a review of the literature published from January to April 2017
J. Han van Krieken
Journal of Hematopathology.2017; 10(1): 25. CrossRef - Programmed cell death ligands expression in phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas: Relationship with the hypoxic response, immune evasion and malignant behavior
David J. Pinato, James R. Black, Sebastian Trousil, Roberto E. Dina, Pritesh Trivedi, Francesco A. Mauri, Rohini Sharma
OncoImmunology.2017; 6(11): e1358332. CrossRef
- Transcriptomic and miRNA Signatures of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine Response Using Machine Learning
- Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: In Relation to Polycomb Repressive Complex Pathway Proteins and H3K27 Trimethylation
- Eun Ji Oh, Soo Hee Kim, Woo Ick Yang, Young Hyeh Ko, Sun Och Yoon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):369-376. Published online August 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.06
- 10,959 View
- 174 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
A long non-coding RNA hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) is involved in epigenetic regulation through chromatin remodeling by recruiting polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) proteins (EZH2, SUZ12, and EED) that induce histone H3 trimethylation at lysine 27 (H3K27me3). Deregulation of c-MYC and interaction between c-MYC and EZH2 are well known in lymphomagenesis; however, little is known about the expression status of HOTAIR in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs).
Methods
The expression status of PRC2 (EZH2, SUZ12, and EED), H3K27me3, c-MYC, and BCL2 was analyzed using immunohistochemistry (n = 231), and HOTAIR was investigated by a quantification real-time polymerase chain reaction method (n = 164) in DLBCLs.
Results
The present study confirmed the positive correlation among PRC2 proteins, H3K27me3, and c-MYC in DLBCLs. Expression level of HOTAIR was also positively correlated to EZH2 (p < .05, respectively). Between c-MYC and HOTAIR, and between c- MYC/BCL2 co-expression and HOTAIR, however, negative correlation was observed in DLBCLs (p < .05, respectively). High level of H3K27me3 was determined as an independent prognostic marker in poor overall survival (hazard ratio, 2.0; p = .023) of DLBCL patients. High expression of HOTAIR, however, was associated with favorable overall survival (p = .004) in the univariate analysis, but the impact was not significant in the multivariate analysis. The favorable outcome of DLBCL with HOTAIR high expression levels may be related to the negative correlation with c- MYC expression or c-MYC/BCL2 co-expression.
Conclusions
HOTAIR expression could be one of possible mechanisms for inducing H3K27me3 via EZH2-related PRC2 activation, and induced H3K27me3 may be strongly related to aggressive DLBCLs which show poor patient outcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- EZH2 Dysregulation and Its Oncogenic Role in Human Cancers
Shiv Verma, Nikita Goyal, Suhani Goyal, Parminder Kaur, Sanjay Gupta
Cancers.2025; 17(19): 3111. CrossRef - HOTAIR in cancer: diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic perspectives
Majid Nazari, Emad Babakhanzadeh, Arghavan Mollazadeh, Mohadese Ahmadzade, Elham Mohammadi Soleimani, Elnaz Hajimaqsoudi
Cancer Cell International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in human lymphomas
Ali Gholami, Khosro Farhadi, Fatemeh Sayyadipour, Masoud Soleimani, Fakhredin Saba
Genes & Diseases.2022; 9(4): 900. CrossRef - Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in HIV-mediated carcinogenesis: Role in cell homeostasis, cell survival processes and drug resistance
Lilian Makgoo, Salerwe Mosebi, Zukile Mbita
Non-coding RNA Research.2022; 7(3): 184. CrossRef - Biomedical impact of the expression of HOX locus-associated LncRNAs HOTAIR and HOTTIP in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Mona Salah Eldin Habieb, Suzy Fawzy Goher, Abd-Elmonem Abd-Elkader El-Torgman, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Najlaa Zanati Ali Abd-Elfattah
Human Gene.2022; 34: 201112. CrossRef - Mechanism of LncHOTAIR Regulating Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Autophagy of Lymphoma Cells through hsa-miR-6511b-5p/ATG7 Axis
Fu Gui, Xinyi Yu, Yemeng Wu, Chao Wu, Yulan Zhang, Peng-Yue Zhang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef -
Circulating RNA biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review
Philippe Decruyenaere, Fritz Offner, Jo Vandesompele
Experimental Hematology & Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating long non-coding RNAs HOTAIR, Linc-p21, GAS5 and XIST expression profiles in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: association with R-CHOP responsiveness
Mahmoud A. Senousy, Aya M. El-Abd, Raafat R. Abdel-Malek, Sherine M. Rizk
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An immunotherapeutic approach to decipher the role of long non-coding RNAs in cancer progression, resistance and epigenetic regulation of immune cells
Krishnapriya M. Varier, Hemavathi Dhandapani, Wuling Liu, Jialei Song, Chunlin Wang, Anling Hu, Yaacov Ben-David, Xiangchun Shen, Yanmei Li, Babu Gajendran
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer‑associated fibroblast‑derived CCL5 contributes to cisplatin resistance in A549 NSCLC cells partially through upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR expression
Xiangjun Sun, Zhijie Chen
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Involving miRNA and lncRNA in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Current Advances and Clinical Perspectives
Mara Fernandes, Herlander Marques, Ana Luísa Teixeira, Rui Medeiros
Biomedicines.2021; 9(12): 1934. CrossRef - EZH2 expression is dependent on MYC and TP53 regulation in diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma
Eduardo Henrique Neves Filho, Carlos Gustavo Hirth, Igor Allen Frederico, Rommel Mario Burbano, Thiago Carneiro, Silvia Helena Rabenhorst
APMIS.2020; 128(4): 308. CrossRef Long Noncoding RNAs in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Current Advances and Perspectives
Xianbo Huang, Wenbin Qian, Xiujin Ye
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4295. CrossRef- Lnc SMAD5-AS1 as ceRNA inhibit proliferation of diffuse large B cell lymphoma via Wnt/β-catenin pathway by sponging miR-135b-5p to elevate expression of APC
Chen-Chen Zhao, Yang Jiao, Yi-Yin Zhang, Jie Ning, Yi-Ruo Zhang, Jing Xu, Wei Wei, Gu Kang-Sheng
Cell Death & Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - H3K18Ac as a Marker of Cancer Progression and Potential Target of Anti-Cancer Therapy
Marta Hałasa, Anna Wawruszak, Alicja Przybyszewska, Anna Jaruga, Małgorzata Guz, Joanna Kałafut, Andrzej Stepulak, Marek Cybulski
Cells.2019; 8(5): 485. CrossRef - HOTAIR as a Prognostic Predictor for Diverse Human Cancers: A Meta- and Bioinformatics Analysis
Halil Ibrahim Toy, Didem Okmen, Panagiota I. Kontou, Alexandros G. Georgakilas, Athanasia Pavlopoulou
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 778. CrossRef - Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Promotes Endometrial Carcinoma Cell Proliferation by Binding to PTEN via the Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathway
Xiao-Hui Zhang, Pin Hu, Yang-Qin Xie, Yong-Jun Kang, Min Li
Molecular and Cellular Biology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - EZH2 abnormalities in lymphoid malignancies: underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Boheng Li, Wee-Joo Chng
Journal of Hematology & Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The prognostic impact of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in leukemia and lymphoma: a meta-analysis
Yun Lin, Zhihong Fang, Zhijuan Lin, Zhifeng Li, Jintao Zhao, Yiming Luo, Bing Xu
Hematology.2018; 23(9): 600. CrossRef - Retracted: Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR and EZH2 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Human Breast Cancer Cells
Lu Han, Hai-Chao Zhang, Li Li, Cai-Xia Li, Xu Di, Xin Qu
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2018; 33(6): 241. CrossRef - Long Non-Coding RNAs Guide the Fine-Tuning of Gene Regulation in B-Cell Development and Malignancy
Mette Dahl, Lasse Sommer Kristensen, Kirsten Grønbæk
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(9): 2475. CrossRef - HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA, is a marker of abnormal cell cycle regulation in lung cancer
Minghui Liu, Hongyi Zhang, Ying Li, Rui Wang, Yongwen Li, Hongbing Zhang, Dian Ren, Hongyu Liu, Chunsheng Kang, Jun Chen
Cancer Science.2018; 109(9): 2717. CrossRef - The evolving concept of cancer stem-like cells in thyroid cancer and other solid tumors
Heather Hardin, Ranran Zhang, Holly Helein, Darya Buehler, Zhenying Guo, Ricardo V Lloyd
Laboratory Investigation.2017; 97(10): 1142. CrossRef - Emerging roles for long noncoding RNAs in B-cell development and malignancy
M. Winkle, J.L. Kluiver, A. Diepstra, A. van den Berg
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2017; 120: 77. CrossRef
- EZH2 Dysregulation and Its Oncogenic Role in Human Cancers
- Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Concomitant EGFR, KRAS, and ALK Mutation: Clinicopathologic Features of 12 Cases
- Taebum Lee, Boram Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Joungho Han, Myung-Ju Ahn, Sang-Won Um
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):197-203. Published online April 18, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.09
- 21,997 View
- 319 Download
- 72 Web of Science
- 65 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS), and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were thought to be mutually exclusive, some tumors harbor concomitant mutations. Discovering a driver mutation on the basis of morphologic features and therapeutic responses with mutation analysis can be used to understand pathogenesis and predict resistance in targeted therapy.
Methods
In 6,637 patients with NSCLC, 12 patients who had concomitant mutations were selected and clinicopathologic features were reviewed. Clinical characteristics included sex, age, smoking history, previous treatment, and targeted therapy with response and disease-free survival. Histologic features included dominant patterns, nuclear and cytoplasmic features.
Results
All patients were diagnosed with adenocarcinoma and had an EGFR mutation. Six patients had concomitant KRAS mutations and the other six had ALK mutations. Five of six EGFR-KRAS mutation patients showed papillary and acinar histologic patterns with hobnail cells. Three of six received EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and showed partial response for 7–29 months. All six EGFR-ALK mutation patients showed solid or cribriform patterns and three had signet ring cells. Five of six EGFR-ALK mutation patients received EGFR TKI and/or ALK inhibitor and four showed partial response or stable disease, except for one patient who had acquired an EGFR mutation.
Conclusions
EGFR and ALK mutations play an important role as driver mutations in double mutated NSCLC, and morphologic analysis can be used to predict treatment response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative multi-omics machine learning reveals novel driver genes associations in lung adenocarcinoma
Fei Yuan, FeiMing Huang, Xiaoyu Cao, Yu-Hang Zhang, KaiYan Feng, YuSheng Bao, Tao Huang, Yu-Dong Cai
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics.2026; 1874(1): 141113. CrossRef - Ensartinib for EML4-ALK-positive lung adenocarcinoma with comorbid mutations in TP53, EGFR, and ERBB2: a case report
Xiaoqing Huang, Lingxian Zhou, Jianyong Xia, Haifeng Jian, Jinji Liu, Yunying Huang, Qingsheng Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual EGFR L858R and KRAS G12A Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review
Gang Wei, Jun Tang, Huaiwen Wang, Dongdong Zhang
Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine.2025; Volume 18: 189. CrossRef -
Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Imaging: From Data to Therapy
Michaela Cellina, Giuseppe De Padova, Nazarena Caldarelli, Dario Libri, Maurizio Cè, Carlo Martinenghi, Marco Alì, Sergio Papa, Gianpaolo Carrafiello
Critical Reviews™ in Oncogenesis.2024; 29(2): 1. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence for Cardiothoracic Imaging: Overview of Current and Emerging Applications
Bruno Hochhegger, Romulo Pasini, Alysson Roncally Carvalho, Rosana Rodrigues, Stephan Altmayer, Leonardo Kayat Bittencourt, Edson Marchiori, Reza Forghani
Seminars in Roentgenology.2023; 58(2): 184. CrossRef - Genomic Landscape of Primary Resistance to Osimertinib Among Hispanic Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Results of an Observational Longitudinal Cohort Study
Diego F. Chamorro, Andrés F. Cardona, July Rodríguez, Alejandro Ruiz-Patiño, Oscar Arrieta, Darwin A. Moreno-Pérez, Leonardo Rojas, Zyanya Lucia Zatarain-Barrón, Dora V. Ardila, Lucia Viola, Gonzalo Recondo, Juan B. Blaquier, Claudio Martín, Luis Raez, Su
Targeted Oncology.2023; 18(3): 425. CrossRef - Histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat regulates metabolic reprogramming in killing KRAS‐mutant human lung cancer cells
Rebecca M. Peter, Md. Shahid Sarwar, Sarah Z. Mostafa, Yujue Wang, Xiaoyang Su, Ah‐Ng Kong
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2023; 62(8): 1136. CrossRef - Differential Distribution of Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Based on Mutation Status
Bihong T. Chen, Taihao Jin, Ningrong Ye, Sean W. Chen, Russell C. Rockne, Stephanie Yoon, Isa Mambetsariev, Ebenezer Daniel, Ravi Salgia
Brain Sciences.2023; 13(7): 1057. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognostic significance of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell components: meta-analysis and SEER analysis
Yang Tan, Ying-he Huang, Jia-wen Xue, Rui Zhang, Run Liu, Yan Wang, Zhen-Bo Feng
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2023; 23(8): 4341. CrossRef - Ganoderma microsporum immunomodulatory protein as an extracellular epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) degrader for suppressing EGFR-positive lung cancer cells
Wei-Jyun Hua, Hsin Yeh, Zhi-Hu Lin, Ai-Jung Tseng, Li-Chen Huang, Wei-Lun Qiu, Tsung-Hsi Tu, Ding-Han Wang, Wei-Hung Hsu, Wei-Lun Hwang, Tung-Yi Lin
Cancer Letters.2023; 578: 216458. CrossRef - Next generation sequencing for detection of EGFR alterations in NSCLC: is more better?
Ullas Batra, Shrinidhi Nathany, Mansi Sharma, Parveen Jain, Anurag Mehta
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2022; 75(3): 164. CrossRef - Enkurin domain containing 1 (ENKD1) regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of non‐small cell lung cancer cells
Ting Song, Peng Zhou, Chunjiao Sun, Na He, Haixia Li, Jie Ran, Jun Zhou, Yue Wu, Min Liu
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting Mutant Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Difficulties, Integrative Treatments and Future Perspectives
Jia-Xin Li, Run-Ze Li, Lin-Rui Ma, Peng Wang, Dong-Han Xu, Jie Huang, Li-Qi Li, Ling Tang, Ying Xie, Elaine Lai-Han Leung, Pei-Yu Yan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone H3K9 methyltransferase SETDB1 augments invadopodia formation to promote tumor metastasis
Shuhei Ueshima, Jia Fang
Oncogene.2022; 41(24): 3370. CrossRef - ESMO expert consensus statements on the management of EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer
A. Passaro, N. Leighl, F. Blackhall, S. Popat, K. Kerr, M.J. Ahn, M.E. Arcila, O. Arrieta, D. Planchard, F. de Marinis, A.M. Dingemans, R. Dziadziuszko, C. Faivre-Finn, J. Feldman, E. Felip, G. Curigliano, R. Herbst, P.A. Jänne, T. John, T. Mitsudomi, T.
Annals of Oncology.2022; 33(5): 466. CrossRef - Molecular Targets in Lung Cancer: Study of the Evolution of Biomarkers Associated with Treatment with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors—Has NF1 Tumor Suppressor a Key Role in Acquired Resistance?
Begoña O. Alen, Lara S. Estévez-Pérez, María Teresa Hermida-Romero, Ana Reguera-Arias, Rosario García-Campelo, Mercedes de la Torre-Bravos, Ángel Concha
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3323. CrossRef - Analytical and clinical validation of a custom 15-gene next-generation sequencing panel for the evaluation of circulating tumor DNA mutations in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Yock Ping Chow, Norziha Zainul Abidin, Ken Siong Kow, Lye Mun Tho, Chieh Lee Wong, Rama Krishna Kancha
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0276161. CrossRef - Potential Therapeutic Strategy for EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer With Concomitant EML4-ALK Rearrangement—Combination of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and ALK Inhibitors
Ming-Hung Huang, Jih-Hsiang Lee, Pei-Shan Hung, James Chih-Hsin Yang
JTO Clinical and Research Reports.2022; 3(11): 100405. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer Imaging: Unfolding the Future
Michaela Cellina, Maurizio Cè, Giovanni Irmici, Velio Ascenti, Natallia Khenkina, Marco Toto-Brocchi, Carlo Martinenghi, Sergio Papa, Gianpaolo Carrafiello
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2644. CrossRef - A single center analysis of first-line treatment in advanced KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer: real-world practice
Yanxia Liu, Yuan Gao, Ying Wang, Cong Zhao, Zhiyun Zhang, Baolan Li, Tongmei Zhang
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High frequency of KRAS and EGFR mutation profiles in BRAF-negative thyroid carcinomas in Indonesia
Didik Setyo Heriyanto, Vincent Laiman, Nikko Vanda Limantara, Widyan Putra Anantawikrama, Fara Silvia Yuliani, Rita Cempaka, Sumadi Lukman Anwar
BMC Research Notes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Mutation in South Indians with Non-Small Lung Cancer
Gautam Balaram, Renjan Thomas, Suhas N. Ghorpade, Prarthana V. Kowsik, Baby Dharman, Yogesh Shivakumar, Shekar Patil, Satheesh Chiradoni Thungappa, HP Shashidhara, Somorat Bhattacharjee, Sridhar Papaiah Susheela, Radheshyam Naik, Srinivas Belagutty Jayapp
Journal of Precision Oncology.2022; 2(1): 3. CrossRef - Targeted next-generation sequencing for cancer-associated gene mutation and copy number detection in 206 patients with non–small-cell lung cancer
Songbai Zheng, Xiaodan Wang, Ying Fu, Beibei Li, Jianhua Xu, Haifang Wang, Zhen Huang, Hui Xu, Yurong Qiu, Yaozhou Shi, Kui Li
Bioengineered.2021; 12(1): 791. CrossRef - How mathematical modeling could contribute to the quantification of metastatic tumor burden under therapy: insights in immunotherapeutic treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
Pirmin Schlicke, Christina Kuttler, Christian Schumann
Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A case of concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration against a mutated EGFR background in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
Ki-Chang Lee, Jiwon Koh, Doo Hyun Chung, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(2): 139. CrossRef - Malfeasance of KRAS mutations in carcinogenesis
Rupal Tripathi, Shrinidhi Nathany, Anurag Mehta, Ullas Batra, Sakshi Mattoo, Mansi Sharma
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2021; 21(3): 439. CrossRef - Detection of Low-Frequency KRAS Mutations in cfDNA From EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Patients After First-Line EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Giorgia Nardo, Jessica Carlet, Ludovica Marra, Laura Bonanno, Alice Boscolo, Alessandro Dal Maso, Andrea Boscolo Bragadin, Stefano Indraccolo, Elisabetta Zulato
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma
Valerio Gristina, Maria La Mantia, Antonio Galvano, Sofia Cutaia, Nadia Barraco, Marta Castiglia, Alessandro Perez, Marco Bono, Federica Iacono, Martina Greco, Katia Calcara, Valentina Calò, Sergio Rizzo, Lorena Incorvaia, Maria Chiara Lisanti, Giulia San
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2021; 2(2): 173. CrossRef - Testing for EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Considerations for Countries in Emerging Markets
Mercedes L Dalurzo, Alejandro Avilés-Salas, Fernando Augusto Soares, Yingyong Hou, Yuan Li, Anna Stroganova, Büge Öz, Arif Abdillah, Hui Wan, Yoon-La Choi
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4671. CrossRef - Untangling the KRAS mutated lung cancer subsets and its therapeutic implications
Kulshrestha Ritu, Pawan Kumar, Amit Singh, K. Nupur, Sonam Spalgias, Parul Mrigpuri, Rajkumar
Molecular Biomedicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lorlatinib Induces Durable Disease Stabilization in a Pancreatic Cancer Patient with a ROS1 p.L1950F Mutation: Case Report
Janna-Lisa Velthaus, Peter Iglauer, Ronald Simon, Carsten Bokemeyer, Peter Bannas, Niklas Beumer, Charles D. Imbusch, Eray Goekkurt, Sonja Loges
Oncology Research and Treatment.2021; 44(9): 495. CrossRef - Proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad7 is critical for lung cancer metastasis
Lu Tong, Shihui Shen, Quan Huang, Junjiang Fu, Tianzhen Wang, Linian Pan, Pei Zhang, Geng Chen, Tingmei Huang, Ke Li, Qingwu Liu, Shaofang Xie, Xiao Yang, Robb E. Moses, Xiaotao Li, Lei Li
Cell Death & Differentiation.2020; 27(6): 1795. CrossRef - Circulating Cell-Free Dna As A Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Zhoumiao Chen, Huiwen Miao, Qingxin Zeng, Shaohua Xu, Zhao Chen, Kai Liu
Biomarkers in Medicine.2020; 14(7): 587. CrossRef - Influence of EGFR-activating mutations on sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer cell line
Yoshinori Tsukumo, Mikihiko Naito, Takayoshi Suzuki, Srikumar Chellappan
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(3): e0229712. CrossRef - KRAS oncogene may be another target conquered in non‐small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Hanxiao Chen, Jun Zhao
Thoracic Cancer.2020; 11(12): 3425. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Features of NSCLC Gene Alterations in Hispanic Patients from Puerto Rico
Ruifang Zheng, Zhiwei Yin, Albert Alhatem, Derek Lyle, Bei You, Andrew S. Jiang, Dongfang Liu, Zsolt Jobbagy, Qing Wang, Seena Aisner, Jie-Gen Jiang
Cancers.2020; 12(12): 3492. CrossRef - Comprehensive pancancer genomic analysis reveals (RTK)-RAS-RAF-MEK as a key dysregulated pathway in cancer: Its clinical implications
Robin Imperial, Omer M Toor, Arif Hussain, Janakiraman Subramanian, Ashiq Masood
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2019; 54: 14. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), KRAS, and BRAF mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: A study from India
Varsha Singh, Prerna Guleria, Prabhat Singh Malik, Anant Mohan, Sanjay Thulkar, R M Pandey, Kalpana Luthra, Sudheer Arava, Ruma Ray, Deepali Jain
Current Problems in Cancer.2019; 43(5): 391. CrossRef - Clinical Validation of Coexisting Activating Mutations Within EGFR, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathways in Lung Cancers
Federico De Marchi, Lisa Haley, Henderson Fryer, Junaid Ibrahim, Katie Beierl, Gang Zheng, Christopher D. Gocke, James R. Eshleman, Deborah Belchis, Peter Illei, Ming-Tseh Lin
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(2): 174. CrossRef - A sequential Monte Carlo algorithm for inference of subclonal structure in cancer
Oyetunji E. Ogundijo, Kaiyi Zhu, Xiaodong Wang, Dimitris Anastassiou, Xiang Li
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0211213. CrossRef - The Presence of Concomitant Mutations Affects the Activity of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients
Anna Rachiglio, Francesca Fenizia, Maria Piccirillo, Domenico Galetta, Lucio Crinò, Bruno Vincenzi, Emiddio Barletta, Carmine Pinto, Francesco Ferraù, Matilde Lambiase, Agnese Montanino, Cristin Roma, Vienna Ludovini, Elisabetta Montagna, Antonella De Luc
Cancers.2019; 11(3): 341. CrossRef - Concurrent Driver Gene Mutations as Negative Predictive Factors in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Minjiang Chen, Yan Xu, Jing Zhao, Wei Zhong, Li Zhang, Yalan Bi, Mengzhao Wang
EBioMedicine.2019; 42: 304. CrossRef - Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-positive Tumors
Rohan Gupta, Idoroenyi Amanam, Syed Rahmanuddin, Isa Mambetsariev, Yingyu Wang, Charity Huang, Karen Reckamp, Lalit Vora, Ravi Salgia
American Journal of Clinical Oncology.2019; 42(4): 337. CrossRef - Clinical features and therapeutic options in non‐small cell lung cancer patients with concomitant mutations of EGFR, ALK, ROS1, KRAS or BRAF
Xibin Zhuang, Chao Zhao, Jiayu Li, Chunxia Su, Xiaoxia Chen, Shengxiang Ren, Xuefei Li, Caicun Zhou
Cancer Medicine.2019; 8(6): 2858. CrossRef - Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance
Eric Santoni-Rugiu, Linea C. Melchior, Edyta M. Urbanska, Jan N. Jakobsen, Karin de Stricker, Morten Grauslund, Jens B. Sørensen
Cancers.2019; 11(7): 923. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer in patients harboring uncommon EGFR mutation
J. Chantharasamee, N. Poungvarin, P. Danchaivijitr, S. Techawatanawanna
BMC Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Deregulated lncRNA expression profile in the mouse lung adenocarcinomas with KRAS‐G12D mutation and P53 knockout
Meiqin Zhang, Nan Jiang, Renjie Cui, Sichen Du, Huayuan Ou, Tinglan Chen, Runsheng Ge, Duan Ma, Jin Zhang
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2019; 23(10): 6978. CrossRef - Open-Sourced CIViC Annotation Pipeline to Identify and Annotate Clinically Relevant Variants Using Single-Molecule Molecular Inversion Probes
Erica K. Barnell, Adam Waalkes, Matt C. Mosior, Kelsi Penewit, Kelsy C. Cotto, Arpad M. Danos, Lana M. Sheta, Katie M. Campbell, Kilannin Krysiak, Damian Rieke, Nicholas C. Spies, Zachary L. Skidmore, Colin C. Pritchard, Todd A. Fehniger, Ravindra Uppalur
JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics.2019; (3): 1. CrossRef - EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, ALK, and cMET genetic alterations in 1440 Sardinian patients with lung adenocarcinoma
Maria Colombino, Panagiotis Paliogiannis, Antonio Cossu, Davide Adriano Santeufemia, Maria Cristina Sini, Milena Casula, Grazia Palomba, Antonella Manca, Marina Pisano, Valentina Doneddu, Giuseppe Palmieri
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Concomitant Presence of EGFR and ALK Fusion Gene Mutation in Adenocarcinoma of Lung: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Nishitha Thumallapally, Hana Yu, Mohammad Farhan, Uroosa Ibrahim, Maricel Odiami
Journal of Pharmacy Practice.2018; 31(2): 244. CrossRef - Double Trouble: A Case Series on Concomitant Genetic Aberrations in NSCLC
Nele Van Der Steen, Yves Mentens, Marc Ramael, Leticia G. Leon, Paul Germonpré, Jose Ferri, David R. Gandara, Elisa Giovannetti, Godefridus J. Peters, Patrick Pauwels, Christian Rolfo
Clinical Lung Cancer.2018; 19(1): 35. CrossRef - KRAS oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer: clinical perspectives on the treatment of an old target
Marta Román, Iosune Baraibar, Inés López, Ernest Nadal, Christian Rolfo, Silvestre Vicent, Ignacio Gil-Bazo
Molecular Cancer.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma, Harboring Both an EGFR Mutation and ALK Rearrangement, Presenting a Stable Disease to Erlotinib and a Partial Response to Alectinib
Akira Yokoyama, Atsuhisa Tamura, Kazuko Miyakawa, Kei Kusaka, Masahiro Shimada, Takashi Hirose, Hirotoshi Matsui, Masashi Kitani, Akira Hebisawa, Ken Ohta
Internal Medicine.2018; 57(16): 2377. CrossRef - Long-term survival with erlotinib in advanced lung adenocarcinoma harboring synchronous EGFR G719S and KRAS G12C mutations
Biagio Ricciuti, Sara Baglivo, Vienna Ludovini, Angelo Sidoni, Giulio Metro, Marta Brambilla, Annamaria Siggillino, Maria Sole Reda, Alberto Rebonato, Daniele Maiettini, Rita Chiari
Lung Cancer.2018; 120: 70. CrossRef - Concomitant driver mutations in advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer and their impact on erlotinib treatment
Jan Nyrop Jakobsen, Eric Santoni-Rugiu, Morten Grauslund, Linea Melchior, Jens Benn Sørensen
Oncotarget.2018; 9(40): 26195. CrossRef - Implications of KRAS mutations in acquired resistance to treatment in NSCLC
Marzia Del Re, Eleonora Rofi, Giuliana Restante, Stefania Crucitta, Elena Arrigoni, Stefano Fogli, Massimo Di Maio, Iacopo Petrini, Romano Danesi
Oncotarget.2018; 9(5): 6630. CrossRef - Alk Immunohistochemistry is Highly Sensitive and Specific for the Detection of Alk Translocated Lung Adenocarcinomas: Lessons from An Audit of Lung Cancer Molecular Testing
YC Kheng, K Walsh, L Williams, WA Wallace, DJ Harrison, A Oniscu
Journal of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh.2018; 48(1): 20. CrossRef - Targeting KRAS mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A history of failures and a future of hope for a diverse entity
Alexios Matikas, Dimitrios Mistriotis, Vasilios Georgoulias, Athanasios Kotsakis
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2017; 110: 1. CrossRef - Clinical Outcome of ALK -Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients with De Novo EGFR or KRAS Co-Mutations Receiving Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs)
Sabine Schmid, Oliver Gautschi, Sacha Rothschild, Michael Mark, Patrizia Froesch, Dirk Klingbiel, Hermann Reichegger, Wolfram Jochum, Joachim Diebold, Martin Früh
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(4): 681. CrossRef - EGFR and KRAS molecular genotyping for pulmonary carcinomas: Feasibility of a simple and rapid technique implementable in any department of pathology
Vincent Thomas De Montpréville, Maria-Rosa Ghigna, Ludovic Lacroix, Antoinette Lemoine, Benjamin Besse, Olaf Mercier, Élie Fadel, Peter Dorfmuller, Thierry Le Chevalier
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(7): 793. CrossRef - MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Implications and Prognostic Values
Geun Dong Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Doo-Yi Oh, Dan-bi Yu, Hae Min Jeong, Jooseok Kim, Sungyoul Hong, Hun Soon Jung, Ensel Oh, Ji-Young Song, Mi-Sook Lee, Mingi Kim, Kyungsoo Jung, Jhingook Kim, Young Kee Shin, Yoon-La Choi, Hyeong Ryul Kim
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(8): 1233. CrossRef - Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring ALK Translocations: Clinical Characteristics and Management in a Real-Life Setting: a French Retrospective Analysis (GFPC 02–14 Study)
Jean-Bernard Auliac, Isabelle Monnet, Catherine Dubos-Arvis, Anne Marie Chiappa, Nathalie Baize, Suzana Bota, Alain Vergnenegre, Helene Doubre, Chrystele Locher, Acya Bizieux, Gilles Robinet, Christos Chouaid
Targeted Oncology.2017; 12(6): 833. CrossRef - Concomitant EML4-ALK rearrangement and EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a literature review of 100 cases
Giuseppe Lo Russo, Martina Imbimbo, Giulia Corrao, Claudia Proto, Diego Signorelli, Milena Vitali, Monica Ganzinelli, Laura Botta, Nicoletta Zilembo, Filippo de Braud, Marina Chiara Garassino
Oncotarget.2017; 8(35): 59889. CrossRef - Management of non-small cell lung cancer in the era of personalized medicine
Gaetano Rocco, Alessandro Morabito, Alessandra Leone, Paolo Muto, Francesco Fiore, Alfredo Budillon
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2016; 78: 173. CrossRef - A long-term survivor of non-small-cell lung cancer harboring concomitant EGFR mutation and ALK translocation
Fumio Imamura, Takako Inoue, Madoka Kimura, Kazumi Nishino, Toru Kumagai
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2016; 19: 137. CrossRef
- Integrative multi-omics machine learning reveals novel driver genes associations in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulated Neuro-oncological Ventral Antigen 1 (NOVA1) Expression Is Specific to Mature and Immature T- and NK-Cell Lymphomas
- Eun Kyung Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Soo Hee Kim, Woo Ick Yang, Yoon Ah Cho, Soo Jeong Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):104-112. Published online February 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.02.08
- 11,154 View
- 72 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Recent studies have revealed that the splicing factor neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 (NOVA1) is enriched in fibroblasts and accumulated T cells of tertiary lymphoid structures. In the present study, we investigated NOVA1 expression in various subtypes of mature and immature T- and natural killer (NK)-cell lymphomas as well as in various B-cell lymphoma subtypes. Methods: NOVA1 immunoexpression was evaluated in hyperplastic palatine tonsils (n = 20), T- and NK-cell lymphomas (n = 177), diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (n = 151), and other types of B cell lymphomas (n = 31). Nuclear staining intensity and percentage of positive tumor cells were graded. NOVA1 mRNA expression was analyzed in various lymphoma cell lines. Results: Tumor cells of T- and NK-cell lymphomas showed higher expression levels of NOVA1 than did normal paracortical T cells, and 56.5% of T- and NK-cell lymphoma cases showed diffuse and strong expression. The NOVA1 expression level varied according to the subtype; it was higher in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (T-LBL), but it was lower in ALK-positive ALCL. In almost all B-cell lymphomas, NOVA1 expression was very low or negative. NOVA1 mRNA was also expressed in Jurkat, a T-LBL cell line. Conclusions: The present findings suggest that NOVA1 upregulation may be involved in certain subtypes of T- and NK-cell lymphomas, but not in B-cell lymphomas. Upregulated NOVA1 expression seems to be a specific biological feature of activated T cells such as T- and NK-cell lymphomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intraoperative pathologic diagnosis of central nervous system lymphomas: A comparison of frozen and permanent section diagnoses, and the significance of preoperative imaging
Aslı Kahraman, Fikret Dirilenoğlu, İsmail Güzeliş, Kenan Çetinoğlu
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 69: 152246. CrossRef - NOVA1 acts on Impact to regulate hypothalamic function and translation in inhibitory neurons
Yoko Tajima, Keiichi Ito, Yuan Yuan, Mayu O. Frank, Yuhki Saito, Robert B. Darnell
Cell Reports.2023; 42(2): 112050. CrossRef - MicroRNA miR-27a-3p accelerates cardiac hypertrophy by targeting neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1
Dongyun Li, Mingzhi Shen, Xinxin Deng, Yongyi Bai
Bioengineered.2022; 13(4): 8982. CrossRef - NOVA1 promotes NSCLC proliferation and invasion by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Lianyue Qu, Yulong Tian, Fan Wang, Zixuan Li
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the Functions and Prognostic Values of RNA Binding Proteins in Bladder Cancer
Yue Wu, Zheng Liu, Xian Wei, Huan Feng, Bintao Hu, Bo Liu, Yang Luan, Yajun Ruan, Xiaming Liu, Zhuo Liu, Shaogang Wang, Jihong Liu, Tao Wang
Frontiers in Genetics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nervous system and gastric cancer
Ke Wang, Xin-hui Zhao, Jun Liu, Rui Zhang, Ji-peng Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2020; 1873(1): 188313. CrossRef - The RNA-binding protein RBM47 inhibits non-small cell lung carcinoma metastasis through modulation of AXIN1 mRNA stability and Wnt/β-catentin signaling
Di-jian Shen, You-hua Jiang, Jian-qiang Li, Li-wei Xu, Kai-yi Tao
Surgical Oncology.2020; 34: 31. CrossRef - Genome-Wide Profiling of Cervical RNA-Binding Proteins Identifies Human Papillomavirus Regulation of RNASEH2A Expression by Viral E7 and E2F1
Junfen Xu, Habin Liu, Yanqin Yang, Xiaohong Wang, Poching Liu, Yang Li, Craig Meyers, Nilam Sanjib Banerjee, Hsu-Kun Wang, Maggie Cam, Weiguo Lu, Louise T. Chow, Xing Xie, Jun Zhu, Zhi-Ming Zheng, Xiang-Jin Meng, James Pipas, Xuefeng Liu, Lucia Pirisi-cre
mBio.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - NOVA1 induction by inflammation and NOVA1 suppression by epigenetic regulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Eun Kyung Kim, Yoon Ah Cho, Mi-kyoung Seo, Hyunmi Ryu, Byoung Chul Cho, Yoon Woo Koh, Sun Och Yoon
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The RNA binding protein neuro‐oncological ventral antigen 1 (NOVA1) regulates IL-6 mRNA stability to enhance JAK2-STAT3 signaling in CRC
Yong-gang Hong, Guo-shu Xu, Guan-yu Yu, Ji-dian Zhou, Qi-zhi Liu, Jun-sheng Ni, Hong-li Yan, Wei Zhang, Li-qiang Hao
Surgical Oncology.2019; 31: 67. CrossRef - NOVA1 acts as an oncogene in melanoma via regulating FOXO3a expression
Xin Yu, Heyi Zheng, Matthew T.V. Chan, William K.K. Wu
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2018; 22(5): 2622. CrossRef - Neuro‐oncological ventral antigen 1 (NOVA1): Implications in neurological diseases and cancers
Yu Xin, Zheng Li, Heyi Zheng, Jeffery Ho, Matthew T. V. Chan, William K. K. Wu
Cell Proliferation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - New developments in the pathology of malignant lymphoma. A review of the literature published from January–April 2016
J. Han van Krieken
Journal of Hematopathology.2016; 9(2): 73. CrossRef
- Intraoperative pathologic diagnosis of central nervous system lymphomas: A comparison of frozen and permanent section diagnoses, and the significance of preoperative imaging
- Prognostic Implication of Semi-quantitative Immunohistochemical Assessment of CD20 Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Chang Hwan Choi, Young Hoon Park, Joo Han Lim, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):96-103. Published online February 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.01.12
- 11,548 View
- 135 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Immunohistochemical demonstration of CD20 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is prerequisite not only for the diagnosis but also for assigning patients to rituximab-containing chemotherapy. However, little is known about the impact of abundance of CD20 expression assessed by immunohistochemistry on the clinical outcome of DLBCL. We performed a semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of CD20 expression in DLBCL to examine the prognostic implication of the level of CD20 expression. Methods: Pre-treatment diagnostic tissue samples from 48 DLBCL patients who were treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) regimen were represented in a tissue microarray and immunostained for CD20. The relative abundance of CD20 expression was semi-quantitatively scored using a web-based ImmunoMembrane plug-in. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to determine a prognostically relevant cut-off score in order to dichotomize the patients into CD20-high versus CD20-low groups. Results: The levels of CD20 expression were heterogeneous among the patients, with a wide and linear distribution of scores. Patients in CD20-low group showed significantly poor clinical outcome. Conclusions: The levels of CD20 expression in DLBCL are heterogeneous among the patients with DLBCL. A subgroup of the patients with CD20 expression levels below the cut-off score showed poor clinical outcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Expression Levels of CD20 as a Prognostic Value in Feline B-Cell Nasal Lymphoma: A Pilot Study
Kravee Chaipoca, Theerapol Sirinarumitr, Supreeya Srisampan, Charuwan Wongsali, Attawit Kovitvadhi, Tassanee Jaroensong
Animals.2024; 14(7): 1043. CrossRef - Prognostic molecular biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era and their therapeutic implications
Sotirios G. Papageorgiou, Thomas P. Thomopoulos, Ioannis Katagas, Anthi Bouchla, Vassiliki Pappa
Therapeutic Advances in Hematology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel tumour–infiltrating lymphocyte-related risk stratification based by flow cytometry for patients with de novo angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma
Qiqi Zhu, Xueqin Deng, Wenqing Yao, Zihang Chen, Yunxia Ye, Limin Gao, Wenyan Zhang, Weiping Liu, Sha Zhao
Annals of Hematology.2021; 100(3): 715. CrossRef - Induced CD20 Expression on B-Cell Malignant Cells Heightened the Cytotoxic Activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Engineered T Cells
Yingxi Xu, Saisai Li, Ying Wang, Jia Liu, Xinhe Mao, Haiyan Xing, Zheng Tian, Kejing Tang, Xiaolong Liao, Qing Rao, Dongsheng Xiong, Min Wang, Jianxiang Wang
Human Gene Therapy.2019; 30(4): 497. CrossRef - Characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma arising in young patients: Particular focus on molecular alteration and tumor immunity
Hyang Joo Ryu, Eun Kyung Kim, Byoung Chul Cho, Sun Och Yoon
Head & Neck.2019; 41(1): 198. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin D (IgD) and IgD receptor expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Xing Dai, Yu-Jing Wu, Xiao-Yi Jia, Yan Chang, Hua-Xun Wu, Chun Wang, Wei Wei
Hematology.2019; 24(1): 544. CrossRef - The implications of TrkA and MET aberrations in de novo salivary duct carcinoma
Hyang Joo Ryu, Yoon Woo Koh, Sun Och Yoon
Human Pathology.2018; 81: 18. CrossRef - Prognostic stratification improvement by integrating ID1/ID3/IGJ gene expression signature and immunophenotypic profile in adult patients with B-ALL
Nataly Cruz-Rodriguez, Alba L. Combita, Leonardo J. Enciso, Lauren F. Raney, Paula L. Pinzon, Olga C. Lozano, Alba M. Campos, Niyireth Peñaloza, Julio Solano, Maria V. Herrera, Jovanny Zabaleta, Sandra Quijano
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Implications of infiltrating immune cells within bone marrow of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Juhyeon Jeong, Eun Ji Oh, Woo Ick Yang, Soo Jeong Kim, Sun Och Yoon
Human Pathology.2017; 64: 222. CrossRef - Architectural patterns of p16 immunohistochemical expression associated with cancer immunity and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Hyang Joo Ryu, Eun Kyung Kim, Su Jin Heo, Byoung Chul Cho, Hye Ryun Kim, Sun Och Yoon
APMIS.2017; 125(11): 974. CrossRef - New developments in the pathology of malignant lymphoma. A review of the literature published from January–April 2016
J. Han van Krieken
Journal of Hematopathology.2016; 9(2): 73. CrossRef - Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure—what to do?
Bertrand Coiffier, Clémentine Sarkozy
Hematology.2016; 2016(1): 366. CrossRef
- The Expression Levels of CD20 as a Prognostic Value in Feline B-Cell Nasal Lymphoma: A Pilot Study
- Analysis of Histologic Features Suspecting Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Expressing Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
- In Ho Choi, Dong Won Kim, Sang Yun Ha, Yoon-La Choi, Hee Jeong Lee, Joungho Han
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(4):310-317. Published online June 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.05.13
- 12,150 View
- 93 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Since 2007 when anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements were discovered in non-small cell lung cancer, the ALK gene has received attention due to ALK-targeted therapy, and a notable treatment advantage has been observed in patients harboring the EML4/ALK translocation. However, using ALK-fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) as the standard method has demerits such as high cost, a time-consuming process, dependency on interpretation skill, and tissue preparation. We analyzed the histologic findings which could complement the limitation of ALK-FISH test for pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Methods: Two hundred five cases of ALK-positive and 101 of ALK-negative pulmonary adenocarcinoma from January 2007 to May 2013 were enrolled in this study. The histologic findings and ALK immunohistochemistry results were reviewed and compared with the results of ALK-FISH and EGFR/KRAS mutation status. Results: Acinar, cribriform, and solid growth patterns, extracellular and intracellular mucin production, and presence of signet-ring-cell element, and psammoma body were significantly more often present in ALK-positive cancer. In addition, the presence of goblet cell-like cells and presence of nuclear inclusion and groove resembling papillary thyroid carcinoma were common in the ALK-positive group. Conclusions: The above histologic parameters can be helpful in predicting ALK rearranged pulmonary adenocarcinoma, leading to rapid FISH analysis and timely treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evidential deep learning-based ALK-expression screening using H&E-stained histopathological images
Sai Chandra Kosaraju, Sai Phani Parsa, Dae Hyun Song, Hyo Jung An, Yoon-La Choi, Joungho Han, Jung Wook Yang, Mingon Kang
npj Digital Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological significances of cribriform pattern in lung adenocarcinoma
Jung-Soo Pyo, Byoung-Hoon Lee, Kyueng-Whan Min, Nae Yu Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 155035. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognostic significance of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell components: meta-analysis and SEER analysis
Yang Tan, Ying-he Huang, Jia-wen Xue, Rui Zhang, Run Liu, Yan Wang, Zhen-Bo Feng
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2023; 23(8): 4341. CrossRef - Lung-Cancer Risk in Mice after Exposure to Gamma Rays, Carbon Ions or Neutrons: Egfr Pathway Activation and Frequent Nuclear Abnormality
Kenshi Suzuki, Shunsuke Yamazaki, Ken-ichi Iwata, Yutaka Yamada, Takamitsu Morioka, Kazuhiro Daino, Mutsumi Kaminishi, Mari Ogawa, Yoshiya Shimada, Shizuko Kakinuma
Radiation Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathological cytomorphologic features and the percentage of ALK FISH-positive cells predict pulmonary adenocarcinoma prognosis: a prospective cohort study
Fenge Jiang, Congcong Wang, Ping Yang, Ping Sun, Jiannan Liu
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cribriform pattern in lung invasive adenocarcinoma correlates with poor prognosis in a Chinese cohort
Yang Qu, Haifeng Lin, Chen Zhang, Kun Li, Haiqing Zhang
Pathology - Research and Practice.2019; 215(2): 347. CrossRef - Incidence of brain metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma at initial diagnosis on the basis of stage and genetic alterations
Bumhee Yang, Hyun Lee, Sang-Won Um, Kyunga Kim, Jae Il Zo, Young Mog Shim, O Jung Kwon, Kyung Soo Lee, Myung-Ju Ahn, Hojoong Kim
Lung Cancer.2019; 129: 28. CrossRef - Qualitative and quantitative cytomorphological features of primary anaplastic lymphoma kinase‐positive lung cancer
Ryuko Tsukamoto, Hiroyuki Ohsaki, Sho Hosokawa, Yasunori Tokuhara, Shingo Kamoshida, Toshiko Sakuma, Tomoo Itoh, Chiho Ohbayashi
Cytopathology.2019; 30(3): 295. CrossRef - Double Trouble: A Case Series on Concomitant Genetic Aberrations in NSCLC
Nele Van Der Steen, Yves Mentens, Marc Ramael, Leticia G. Leon, Paul Germonpré, Jose Ferri, David R. Gandara, Elisa Giovannetti, Godefridus J. Peters, Patrick Pauwels, Christian Rolfo
Clinical Lung Cancer.2018; 19(1): 35. CrossRef - Update on the potential significance of psammoma bodies in lung adenocarcinoma from a modern perspective
Akio Miyake, Koji Okudela, Mai Matsumura, Mitsui Hideaki, Hiromasa Arai, Shigeaki Umeda, Shoji Yamanaka, Yoshihiro Ishikawa, Michihiko Tajiri, Kenichi Ohashi
Histopathology.2018; 72(4): 609. CrossRef - Integrin β3 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Activity of ALK Inhibitor in ALK-Rearranged NSCLC
Ka-Won Noh, Insuk Sohn, Ji-Young Song, Hyun-Tae Shin, Yu-Jin Kim, Kyungsoo Jung, Minjung Sung, Mingi Kim, Sungbin An, Joungho Han, Se-Hoon Lee, Mi-Sook Lee, Yoon-La Choi
Clinical Cancer Research.2018; 24(17): 4162. CrossRef - An anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive lung cancer microlesion: A case report
Tetsuo Kon, Youichiro Baba, Ichiro Fukai, Gen Watanabe, Tomoko Uchiyama, Tetsuya Murata
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2017; 7: 11. CrossRef - The prevalence of ALK rearrangement in pulmonary adenocarcinomas in an unselected Caucasian population from a defined catchment area: impact of smoking
Birgit G Skov, Paul Clementsen, Klaus R Larsen, Jens B Sørensen, Anders Mellemgaard
Histopathology.2017; 70(6): 889. CrossRef - Ciliated muconodular papillary tumor of the lung harboring ALK gene rearrangement: Case report and review of the literature
Yan Jin, Xuxia Shen, Lei Shen, Yihua Sun, Haiquan Chen, Yuan Li
Pathology International.2017; 67(3): 171. CrossRef - Molecular breakdown: a comprehensive view of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)‐rearranged non‐small cell lung cancer
Ka‐Won Noh, Mi‐Sook Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Ji‐Young Song, Hyun‐Tae Shin, Yu Jin Kim, Doo Yi Oh, Kyungsoo Jung, Minjung Sung, Mingi Kim, Sungbin An, Joungho Han, Young Mog Shim, Jae Ill Zo, Jhingook Kim, Woong‐Yang Park, Se‐Hoon Lee, Yoon‐La Choi
The Journal of Pathology.2017; 243(3): 307. CrossRef - Anaplastic lymphoma kinase immunohistochemistry in lung adenocarcinomas: Evaluation of performance of standard manual method using D5F3 antibody
D Jain, K Jangra, PS Malik, S Arulselvi, K Madan, S Mathur, MC Sharma
Indian Journal of Cancer.2017; 54(1): 209. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Features and Therapeutic Responses of Chinese Patients with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement
Danxia Lin, De Zeng, Chen Chen, Xiao Wu, Miaojun Wang, Jiongyu Chen, Hui Lin, Xihui Qiu
Oncology Research and Treatment.2017; 40(1-2): 27. CrossRef - A Validation Study for the Use of ROS1 Immunohistochemical Staining in Screening for ROS1 Translocations in Lung Cancer
Patrizia Viola, Manisha Maurya, James Croud, Jana Gazdova, Nadia Suleman, Eric Lim, Tom Newsom-Davis, Nick Plowman, Alexandra Rice, M. Angeles Montero, David Gonzalez de Castro, Sanjay Popat, Andrew G. Nicholson
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2016; 11(7): 1029. CrossRef - Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Concomitant EGFR, KRAS, and ALK Mutation: Clinicopathologic Features of 12 Cases
Taebum Lee, Boram Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Joungho Han, Myung-Ju Ahn, Sang-Won Um
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(3): 197. CrossRef - ALK gene rearranged lung adenocarcinomas: molecular genetics and morphology in cohort of patients from North India
Amanjit Bal, Navneet Singh, Parimal Agarwal, Ashim Das, Digambar Behera
APMIS.2016; 124(10): 832. CrossRef
- Evidential deep learning-based ALK-expression screening using H&E-stained histopathological images
- Human Herpesvirus 8-Negative and Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Effusion-Based Lymphoma in a Patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Jung-Woo Choi, Younghye Kim, Ju-Han Lee, Young-Sik Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):409-412. Published online June 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.06.03
- 9,734 View
- 65 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 39-year-old man infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was admitted to our hospital because of sudden onset of chest pain. Chest radiography revealed pneumothorax of the right lung. Computed tomographic scans disclosed a 5.8-cm-sized emphysematous bulla in the right middle lobe of the lung. Histologically, the wedge-resected lung showed medium to large atypical cells within the bullous cavity of the Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, without solid mass formation. These atypical cells were confirmed to be large B-cell lymphoma, Epstein-Barr virus–positive and human herpesvirus 8–negative. Therefore, this case was not diagnosed as primary effusion lymphoma, but effusion-based lymphoma arising in an emphysematous cavity of an HIV-infected patient. This type of effusion-based lymphoma has never been reported, and, although rare, it should be noted in order to clinically diagnose this lymphoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Effusion Lymphoma: A Timely Review on the Association with HIV, HHV8, and EBV
Chih-Yi Liu, Bo-Jung Chen, Shih-Sung Chuang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 713. CrossRef - Human herpesvirus 8-negative effusion-based large B-cell lymphoma: a distinct entity with unique clinicopathologic characteristics
Savanah D. Gisriel, Ji Yuan, Ryan C. Braunberger, Danielle L.V. Maracaja, Xueyan Chen, Xiaojun Wu, Jenna McCracken, Mingyi Chen, Yi Xie, Laura E. Brown, Peng Li, Yi Zhou, Tarsheen Sethi, Austin McHenry, Ronald G. Hauser, Nathan Paulson, Haiming Tang, Eric
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(10): 1411. CrossRef - Age and CD20 Expression Are Significant Prognostic Factors in Human Herpes Virus-8-negative Effusion-based Lymphoma
Tomomi Kubota, Yosuke Sasaki, Eisuke Shiozawa, Masafumi Takimoto, Tsunekazu Hishima, Ja-Mun Chong
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 42(12): 1607. CrossRef
- Primary Effusion Lymphoma: A Timely Review on the Association with HIV, HHV8, and EBV
- Smad1 Expression in Follicular Lymphoma
- Jai Hyang Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(3):243-248. Published online May 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.03.30
- 8,663 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follicular lymphomas present with various immunohistologic patterns. The immunohistochemical markers used in the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma show variable degrees of sensitivity and specificity, and thus, additional germinal center markers are required. Smad1 has been reported to be overexpressed in follicular lymphoma, but little is known regarding the expression patterns of Smad proteins in human lymphoid tissue. Methods: In the present study, we performed immunohistochemistry for traditional germinal center markers and for Smad1 in human reactive lymphoid and follicular lymphoma tissues to investigate Smad1’s usefulness in the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma. Results: In the reactive germinal centers, most cells were positive for Smad1. Among the 27 follicular lymphoma cases, 17 of 21 (80%) were Smad1 positive, 17 of 27 (63%) were positive for CD10, and 23 of 27 (85%) were positive for Bcl6. Notably, three cases expressed CD10 only, and one only expressed Bcl6. All these cases were grade 3 tumors and showed follicular and diffuse growth patterns. Conclusions: These results indicate that Smad1 is a candidate as a germinal center marker. Furthermore, they suggest that the Smad signaling pathway might be involved in follicular lymphoma.
- Current Concepts in Primary Effusion Lymphoma and Other Effusion-Based Lymphomas
- Yoonjung Kim, Chan Jeong Park, Jin Roh, Jooryung Huh
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):81-90. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.81
- 15,817 View
- 173 Download
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a human herpes virus 8 (HHV8)-positive large B-cell neoplasm that presents as an effusion with no detectable tumor in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus infection or other immune deficiencies. PEL is an aggressive neoplasm with a poor prognosis. PEL cells show diverse morphologies, ranging from immunoblastic or plasmablastic to anaplastic. The immunophenotype of PEL is distinct, but its lineage can be misdiagnosed if not assessed thoroughly. PEL cells usually express CD45, lack B- and T-cell-associated antigens, and characteristically express lymphocyte activation antigens and plasma cell-associated antigens. Diagnosis of PEL often requires the demonstration of a B-cell genotype. HHV8 must be detected in cells to diagnose PEL. In most cases, PEL cells also harbor the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome. Similar conditions associated with HHV8 but not effusion-based are called "extracavitary PELs." PELs should be differentiated from HHV8-negative, EBV-positive, body cavity-based lymphomas in patients with long-standing chronic inflammation; the latter can occur in tuberculous pleuritis, artificial pneumothorax, chronic liver disease and various other conditions. Despite their morphological similarity, these various lymphomas require different therapeutic strategies and have different prognostic implications. Correct diagnosis is essential to manage and predict the outcome of patients with PEL and related disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Imaging Findings of Thoracic Extranodal Lymphoma: A Pictorial Essay
Songa Seo, Soo-yeon Jeong, Mi Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2025; 86(6): 1011. CrossRef - Update: The molecular spectrum of virus-associated high-grade B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas
H. Witte, A. Künstner, N. Gebauer
Blood Reviews.2024; 65: 101172. CrossRef - Oncolytic strategy using new bifunctional HDACs/BRD4 inhibitors against virus-associated lymphomas
Jungang Chen, Zhengyu Wang, Tran Phuc, Zhigang Xu, Donglin Yang, Zhengzhu Chen, Zhen Lin, Samantha Kendrick, Lu Dai, Hong-yu Li, Zhiqiang Qin, Michael Lagunoff
PLOS Pathogens.2023; 19(1): e1011089. CrossRef - Primary Effusion Lymphoma: A Timely Review on the Association with HIV, HHV8, and EBV
Chih-Yi Liu, Bo-Jung Chen, Shih-Sung Chuang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 713. CrossRef - Lymphoproliferative disorder involving body fluid: diagnostic approaches and roles of ancillary studies
Jiwon Koh, Sun Ah Shin, Ji Ae Lee, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(4): 173. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Management of Patients With Concomitant Liver Cirrhosis and Lymphoma: A Systematic Review
Jelena Jelicic, Thomas Stauffer Larsen, Annette Dam Fialla, Zoran Bukumiric, Bosko Andjelic
Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia.2022; 22(11): e981. CrossRef - HHV8-unrelated primary effusion lymphoma: Two case reports and a review of literature
Ryan W. Kendall, Ricky A. Thompson, Christopher P. Garwacki, Alan Z. Skarbnik
Current Problems in Cancer: Case Reports.2021; 4: 100087. CrossRef - Targeting Host Cellular Factors as a Strategy of Therapeutic Intervention for Herpesvirus Infections
Kumari Asha, Neelam Sharma-Walia
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Case of Extracavitary Primary Effusion Lymphoma in the Bladder and Ureter
Jiankun Tong, Sana Jadallah, William H. Rodgers, Gabriel Jung, Malvina Fulman, Abhisek Swaika
Case Reports in Hematology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - KSHV: Immune Modulation and Immunotherapy
Grant Broussard, Blossom Damania
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Ki 67 Labelling Index as an Adjunct to Histopathological Diagnosis for Grading of CNS Tumours
Priyanka Rai, Chandni Krishnani, Goswami S. S.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(16): 1331. CrossRef - Brentuximab vedotin as frontline treatment for HIV-related extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma
Jose D. Sandoval-Sus, Amanda Brahim, Alina Khan, Barbara Raphael, Ali Ansari-Lari, Marco Ruiz
International Journal of Hematology.2019; 109(5): 622. CrossRef - High-dose Therapy and Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation as Consolidation Treatment for Primary Effusion Lymphoma
Abu-Sayeef Mirza, Bhagirathbhai R. Dholaria, Mohammad Hussaini, Sarah Mushtaq, Pedro Horna, Adharsh Ravindran, Ambuj Kumar, Ernesto Ayala, Mohamed A. Kharfan-Dabaja, Celeste Bello, Julio C. Chavez, Lubomir Sokol
Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia.2019; 19(9): e513. CrossRef - Remission of an HHV8-related extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in an HIV-positive patient during antiretroviral treatment containing dolutegravir
Laura Campogiani, Carlotta Cerva, Gaetano Maffongelli, Elisabetta Teti, Livio Pupo, Sara Vaccarini, Maria Cantonetti, Alfredo Pennica, Massimo Andreoni, Loredana Sarmati
AIDS Research and Therapy.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Effusion Lymphoma in a Non-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Patient: A Case Report
Beum Jin Kim, Mi Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2019; 80(4): 810. CrossRef - Pleural effusion in a human immunodeficiency virus‐infected patient
Rafael Martínez‐Girón, Santiago Martínez‐Torre
Cytopathology.2019; 30(6): 673. CrossRef - Case report of a primary effusion lymphoma successfully treated with oral valganciclovir after failing chemotherapy
Juan Marquet, Kyra Velazquez‐Kennedy, Sandra López, Amparo Benito, María‐Jesús Blanchard, Jose Antonio Garcia‐Vela
Hematological Oncology.2018; 36(1): 316. CrossRef - Primary effusion lymphoma in Taiwan shows two distinctive clinicopathological subtypes with rare human immunodeficiency virus association
Bo‐Jung Chen, Ran‐Ching Wang, Chung‐Han Ho, Chang‐Tsu Yuan, Wan‐Ting Huang, Sheau‐Fang Yang, Pin‐Pen Hsieh, Yun‐Chih Yung, Shih‐Yao Lin, Chen‐Fang Hsu, Ying‐Zhen Su, Chun‐Chi Kuo, Shih‐Sung Chuang
Histopathology.2018; 72(6): 930. CrossRef - Effusion‐based lymphoma with morphological regression but with clonal genetic features after aspiration
Meng‐Chen Tsai, Chun‐Chi Kuo, Ying‐Zhen Su, Yen‐Chuan Hsieh, Shih‐Sung Chuang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(8): 685. CrossRef - Biology and management of primary effusion lymphoma
Kazuyuki Shimada, Fumihiko Hayakawa, Hitoshi Kiyoi
Blood.2018; 132(18): 1879. CrossRef - EBV‐associated but HHV8‐unrelated double‐hit effusion‐based lymphoma
Bo‐Jung Chen, David Yen‐Ting Chen, Chun‐Chi Kuo, Shih‐Sung Chuang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2017; 45(3): 257. CrossRef - HHV8/KSHV-Positive Lymphoproliferative Disorders and the Spectrum of Plasmablastic and Plasma Cell Neoplasms
Amy Chadburn, Jonathan Said, Dita Gratzinger, John K. C. Chan, Daphne de Jong, Elaine S. Jaffe, Yasodha Natkunam, John R. Goodlad
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2017; 147(2): 171. CrossRef - Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) related lymphomas, pathology view point
Ebru Linke-Serinsöz, Falko Fend, Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2017; 34(4): 352. CrossRef - Anticancer drug-loaded quantum dots engineered polymeric nanoparticles: Diagnosis/therapy combined approach
D. Belletti, G. Riva, M. Luppi, G. Tosi, F. Forni, M.A. Vandelli, B. Ruozi, F. Pederzoli
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2017; 107: 230. CrossRef - CD20-negative diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a comprehensive analysis of 695 cases
Jing Li, Shu Zhao, Jingxuan Wang, Jingyu Chen, Wen Wen, Qingyuan Zhang
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(3): 3619. CrossRef - Co-infections and Pathogenesis of KSHV-Associated Malignancies
Suhani Thakker, Subhash C. Verma
Frontiers in Microbiology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology of Extranodal Lymphoma
Emily Heckendorn, Aaron Auerbach
Radiologic Clinics of North America.2016; 54(4): 639. CrossRef - 2015 update on the diagnosis and management of neoplastic pericardial disease
Chiara Lestuzzi, Massimiliano Berretta, Witold Tomkowski
Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy.2015; 13(4): 377. CrossRef - CD20-negative diffuse large B-cell lymphomas: biology and emerging therapeutic options
Jorge J Castillo, Julio C Chavez, Francisco J Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, Santiago Montes-Moreno
Expert Review of Hematology.2015; 8(3): 343. CrossRef - Primary Effusion Lymphoma: Cytological Diagnosis of a Rare Entity - Report of Two Cases in HIV-Uninfected Patients from a Single Institution
Marta Nicola, Monica Onorati, Chiara Luisa Bianchi, Giuseppe Pepe, Stefano Bellone, Franca Di Nuovo
Acta Cytologica.2015; 59(5): 425. CrossRef
- Imaging Findings of Thoracic Extranodal Lymphoma: A Pictorial Essay
- Characteristics of Cutaneous Lymphomas in Korea According to the New WHO-EORTC Classification: Report of a Nationwide Study
- Jae Ho Han, Young-Hyeh Ko, Yun Kyung Kang, Wan-Seop Kim, Yoon Jung Kim, Insun Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soo Kee Min, Chan-Kum Park, Chan-Sik Park, Bong-Kyung Shin, Woo Ick Yang, Young-Ha Oh, Jong Sil Lee, Juhie Lee, Tae Hui Lee, Hyekyung Lee, Ho Jung Lee, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Hee Jeong Cha, Yoo-Duk Choi, Chul Woo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):126-132. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.126
- 10,244 View
- 118 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Previously, cutaneous lymphomas were classified according to either the European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) or the World Health Organization (WHO) classification paradigms. The aim of this study was to determine the relative frequency of Korean cutaneous lymphoma according to the new WHO-EORTC classification system.
Methods A total of 517 patients were recruited during a recent 5 year-period (2006-2010) from 21 institutes and classified according to the WHO-EORTC criteria.
Results The patients included 298 males and 219 females, and the mean age at diagnosis was 49 years. The lesions preferentially affected the trunk area (40.2%). The most frequent subtypes in order of decreasing prevalence were mycosis fungoides (22.2%), peripheral T-cell lymphoma (17.2%), CD30+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder (13.7%), and extranodal natural killer/T (NK/T) cell lymphoma, nasal type (12.0%). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounted for 11.2% of cases, half of which were secondary cutaneous involvement; other types of B-cell lymphoma accounted for less than 1% of cases.
Conclusions In comparison with data from Western countries, this study revealed relatively lower rates of mycosis fungoides and B-cell lymphoma in Korean patients, as well as higher rates of subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma and NK/T cell lymphoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Varied presentations of primary cutaneous lymphoma: A case series from a tertiary care center in South India
Baby Shana, Betsy Ambooken, Sunitha Balakrishnan, Asokan Neelakandan, Kidangazhiyathmana Ajithkumar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2024; 61(1): 172. CrossRef - A retrospective study of prognostic factors and treatment outcome in advanced-stage Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome
Zhuo-fan Xu, Hongyun Chen, Yuehua Liu, Wei Zhang, Hongzhong Jin, Jie Liu
Hematology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, clinical features, and survival outcome trends of 627 patients with primary cutaneous lymphoma over 29 years: a retrospective review from single tertiary center in Korea
Ik Jun Moon, Chong Hyun Won, Sung Eun Chang, Chan-Sik Park, Dok-Hyun Yoon, Si Yeol Song, Mi Woo Lee, Woo Jin Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The First Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia With t(10;11)(p13;q21);PICALM-MLLT10 Rearrangement Presenting With Extensive Skin Involvement
Min-Seung Park, Hyun-Young Kim, Jae Joon Lee, Duck Cho, Chul Won Jung, Hee-Jin Kim, Sun-Hee Kim
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2023; 43(3): 310. CrossRef - Recent advances on cutaneous lymphoma epidemiology
G. Dobos, M. Miladi, L. Michel, C. Ram-Wolff, M. Battistella, M. Bagot, A. de Masson
La Presse Médicale.2022; 51(1): 104108. CrossRef - Specific cutaneous infiltrates in patients with haematological neoplasms: a retrospective study with 49 patients
Rebeca Calado, Maria Relvas, Francisca Morgado, José Carlos Cardoso, Oscar Tellechea
Australasian Journal of Dermatology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 16,953 Patients
Gabor Dobos, Anne Pohrt, Caroline Ram-Wolff, Céleste Lebbé, Jean-David Bouaziz, Maxime Battistella, Martine Bagot, Adèle de Masson
Cancers.2020; 12(10): 2921. CrossRef - Primary cutaneous lymphoma in Argentina: a report of a nationwide study of 416 patients
Alejandra Abeldaño, Paula Enz, Matias Maskin, Andrea B. Cervini, Natallia Torres, Ana C. Acosta, Marina Narbaitz, Silvia Vanzulli, Mirta Orentrajch, Marta A. Villareal, Maria L. Garcia Pazos, Mariana Arias, Evelyn A. Zambrano Franco, Maria I. Fontana, Rob
International Journal of Dermatology.2019; 58(4): 449. CrossRef - Post-thymic CD4 positive cytotoxic T cell infiltrates of the skin: A clinical and histomorphologic spectrum of the unique CD4 positive T cell of immunosenescence
Cynthia M. Magro, Luke C. Olson, Shabnam Momtahen
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2019; 38: 99. CrossRef - Cutaneous lymphomas in Taiwan: A review of 118 cases from a medical center in southern Taiwan
Chaw-Ning Lee, Chao-Kai Hsu, Kung-Chao Chang, Cheng-Lin Wu, Tsai-Yun Chen, Julia Yu-Yun Lee
Dermatologica Sinica.2018; 36(1): 16. CrossRef - Imaging analysis of superficial soft tissue lymphomas
In Sook Lee, You Seon Song, Seung Hyun Lee, Young Jin Choi, Sung Moon Lee
Clinical Imaging.2018; 49: 111. CrossRef - Epidemiologic, clinical and demographic features of primary cutaneous lymphomas in Castilla‐La Mancha, Spain: are we different?
C. Ramos‐Rodríguez, M. García‐Rojo, G. Romero‐Aguilera, M. García‐Arpa, L. González‐López, M.P. Sánchez‐Caminero, J. González‐García, M. Delgado‐Portela, M.P. Cortina‐De La Calle, M.F. Relea‐Calatayud, F. Martín‐Dávila, R. López‐Pérez, M. Ramos‐Rodríguez
Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphomas are more frequently T rather than NK lineage based on T-cell receptor gene, RNA, and protein studies: lineage does not predict clinical behavior
Mineui Hong, Taehee Lee, So Young Kang, Suk-Jin Kim, Wonseog Kim, Young-Hyeh Ko
Modern Pathology.2016; 29(5): 430. CrossRef - Cutaneous lymphoma: Kids are not just little people
Katalin Ferenczi, Hanspaul S. Makkar
Clinics in Dermatology.2016; 34(6): 749. CrossRef
- Varied presentations of primary cutaneous lymphoma: A case series from a tertiary care center in South India
- Guideline Recommendations for Testing of
ALK Gene Rearrangement in Lung Cancer: A Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group - Hyojin Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Lucia Kim, Tae-Jung Kim, Kun Young Kwon, Geon Kook Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):1-9. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.1
- 16,099 View
- 130 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rearrangement of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (
ALK ) gene is the best predictor of response to crizotinib, an ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor. However, the prevalence of theALK fusion is low, so accurate patient identification is crucial for successful treatment using ALK inhibitors. Furthermore, most patients with lung cancer present with advanced-stage disease at the time of diagnosis, so it is important for pathologists to detectALK -rearranged patients while effectively maximizing small biopsy or cytology specimens. In this review, we propose a guideline recommendation for ALK testing approved by the Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Characteristics of Radon Associated Lung Cancer Highlights MET Alterations
Gabriele Gamerith, Marcel Kloppenburg, Finn Mildner, Arno Amann, Sabine Merkelbach-Bruse, Carina Heydt, Janna Siemanowski, Reinhard Buettner, Michael Fiegl, Claudia Manzl, Georg Pall
Cancers.2022; 14(20): 5113. CrossRef -
ALK Translocation in ALK-Positive Mesenchymal Tumors: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Insights
Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon, Jeongmo Bae, Tae Min Kim, Miso Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Cheol Lee
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2022; 146(12): 1460. CrossRef - Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 181. CrossRef - Testing for EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Considerations for Countries in Emerging Markets
Mercedes L Dalurzo, Alejandro Avilés-Salas, Fernando Augusto Soares, Yingyong Hou, Yuan Li, Anna Stroganova, Büge Öz, Arif Abdillah, Hui Wan, Yoon-La Choi
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4671. CrossRef - Molecular testing for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Malaysia: Consensus statement from the College of Pathologists, Academy of Medicine Malaysia, the Malaysian Thoracic Society, and the Malaysian Oncological Society
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Phaik Leng Cheah, Soon Hin How, Chong Kin Liam, Muhammad Azrif Ahmad Annuar, Norhayati Omar, Noriah Othman, Nurhayati Mohd Marzuki, Yong Kek Pang, Ros Suzanna Ahmad Bustamam, Lye Mun Tho
Lung Cancer.2019; 136: 65. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2018; 13(3): 323. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2018; 20(2): 129. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benja
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(3): 321. CrossRef - 5′/ 3′ imbalance strategy to detect ALK fusion genes in circulating tumor RNA from patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Yongqing Tong, Zhijun Zhao, Bei Liu, Anyu Bao, Hongyun Zheng, Jian Gu, Mary McGrath, Ying Xia, Bihua Tan, Chunhua Song, Yan Li
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular testing and treatment patterns for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: PIvOTAL observational study
Dae Ho Lee, Ming-Sound Tsao, Karl-Otto Kambartel, Hiroshi Isobe, Ming-Shyan Huang, Carlos H. Barrios, Adnan Khattak, Filippo de Marinis, Smita Kothari, Ashwini Arunachalam, Xiting Cao, Thomas Burke, Amparo Valladares, Javier de Castro, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0202865. CrossRef - Microfluidics-based immunofluorescence for fast staining of ALK in lung adenocarcinoma
Saška Brajkovic, Benjamin Pelz, Maria-Giuseppina Procopio, Anne-Laure Leblond, Grégoire Repond, Ariane Schaub-Clerigué, Diego G Dupouy, Alex Soltermann
Diagnostic Pathology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanded Circulating Tumor Cells from a Patient with ALK- Positive Lung Cancer Present with EML4-ALK Rearrangement Along with Resistance Mutation and Enable Drug Sensitivity Testing: A Case Study
Zhuo Zhang, Hiroe Shiratsuchi, Nallasivam Palanisamy, Sunitha Nagrath, Nithya Ramnath
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(2): 397. CrossRef - Molecular Testing of Lung Cancers
Hyo Sup Shim, Yoon-La Choi, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Tae-Jung Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jin-Haeng Chung, Se Jin Jang, Geon Kook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 242. CrossRef - Novel ALK fusion partners in lung cancer
Aglaya G. Iyevleva, Grigory A. Raskin, Vladislav I. Tiurin, Anna P. Sokolenko, Natalia V. Mitiushkina, Svetlana N. Aleksakhina, Aigul R. Garifullina, Tatiana N. Strelkova, Valery O. Merkulov, Alexandr O. Ivantsov, Ekatherina Sh. Kuligina, Kazimir M. Pozha
Cancer Letters.2015; 362(1): 116. CrossRef - Strategic management of transthoracic needle aspirates for histological subtyping and EGFR testing in patients with peripheral lung cancer: An institutional experience
Choonhee Son, Eun‐Ju Kang, Mee Sook Roh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2015; 43(7): 532. CrossRef - Current and future molecular diagnostics in non-small-cell lung cancer
Chun Man Li, Wing Ying Chu, Di Lun Wong, Hin Fung Tsang, Nancy Bo Yin Tsui, Charles Ming Lok Chan, Vivian Wei Wen Xue, Parco Ming Fai Siu, Benjamin Yat Ming Yung, Lawrence Wing Chi Chan, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2015; 15(8): 1061. CrossRef - Role of biopsy sampling for diagnosis of early and progressed hepatocellular carcinoma
Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology.2014; 28(5): 813. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions
Mee Sook Roh
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2014; 77(2): 49. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangements in lung cancer with nodular ground-glass opacity
Sung-Jun Ko, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young-Jae Cho, Ho Il Yoon, Jin-Haeng Chung, Tae Jung Kim, Kyung Won Lee, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon, Hyojin Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular Characteristics of Radon Associated Lung Cancer Highlights MET Alterations
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Arising in Warthin's Tumor: Case Study and Review of the Literature
- Güliz Özkök, Funda Taşlı, Nazan Özsan, Rafet Öztürk, Hakan Postacı
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):579-582. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.579
- 8,760 View
- 55 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Warthin's tumor is the second most common type of salivary gland tumor. Microscopically, Warthin's tumor displays a proliferative epithelial component and lymphoid stroma. Carcinomas arising from the epithelial component are well known, but malignant transformations of the lymphoid stroma are rare. When they do occur, they are most commonly B-cell type non-Hodgkin lymphomas. A 60-year-old male patient underwent surgical resection of a parotid mass. After superficial parotidectomy, microscopic examination indicated that the tumor was of epithelial components with basaloid and oncocytic columns of cells neighboring lymphoid components. In addition to the lymphoid follicles with distinct germinal centers, there were large, bizarre and extremely atypical neoplastic cells seen in the lymphoid component. Large neoplastic cells were diffusely CD20 and CD30 positive. The patient was diagnosed with "Warthin's tumor and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with expression of CD30." The histopathologic and clinical features are discussed along with a review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From the archives of MD Anderson Cancer Center: Small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia diagnosed in Warthin tumor
Jing Zhou, L. Jeffrey Medeiros
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 79: 152533. CrossRef - Warthin’s Tumor Involved by Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis: A Case Report
Alexie Kindy, Ziang Wang, Robin Gautam, Robert Bennett, Zijian Wang
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Warthin tumor concomitant with mantle cell lymphoma: a case report and review of literature
Hai-Chao Tong, Shuang Ma, Lan Chen, Xiangyun Meng, Ying-Chun Li, Le-Yao Li, Lingyun Dong, Wan-Lin Zhang, Tyler Wildes, Lian-He Yang, Endi Wang
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Diagnosis of Parotid Gland Follicular Lymphoma Arising in Warthin Tumor: Case Report and Literature Review
Ido Vaknin, Irit Allon, Shirley Zafrir-Haver, Alex Abramson
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 2086. CrossRef - Warthin’s Tumor of the Parotid Gland With Degeneration to Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Mauricio Gutierrez-Alvarez, Cynthia Martinez, Ana Priscila Campollo Lopez, Kevin Fuentes, Jorge Alberto Robles Aviña
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis Analysis of Salivary Gland Tumors Through the Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1)
Aisyah Izzatul Muna, Maria Evata Krismawati Surya, Meiske Margaretha, Jane Kosasih, Mei Syafriadi
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2023; 75(4): 3098. CrossRef - Role of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expression in the pathogenesis of Warthin’s tumor growth
Alvionika Nadyah Qotrunnada, Tecky Indriana, Jane Kosasih, Meiske Margaretha, Mei Syafriadi
Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi).2022; 55(4): 194. CrossRef - Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma of Salivary Glands
Lester D.R. Thompson, Rumeal D. Whaley
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2021; 14(1): 75. CrossRef - Follicular Lymphoma Diagnosed in Warthin Tumor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Fnu Alnoor, Jatin S. Gandhi, Matthew K. Stein, Joel F. Gradowski
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(2): 386. CrossRef - Prevalence of Lymphoid Neoplasia in a Retrospective Analysis of Warthin Tumor: A Single Institution Experience
F. N. U. Alnoor, Jatin S. Gandhi, Matthew K. Stein, Jorge Solares, Joel F. Gradowski
Head and Neck Pathology.2020; 14(4): 944. CrossRef - A Case of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma in Submandibular Gland
Sang Hoo Park, Min Gyoung Pak, Dong Kun Lee
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2020; 31(1): 111. CrossRef - Analysis of the Clinical Relevance of Histological Classification of Benign Epithelial Salivary Gland Tumours
Henrik Hellquist, António Paiva-Correia, Vincent Vander Poorten, Miquel Quer, Juan C. Hernandez-Prera, Simon Andreasen, Peter Zbären, Alena Skalova, Alessandra Rinaldo, Alfio Ferlito
Advances in Therapy.2019; 36(8): 1950. CrossRef - Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma arising from follicular lymphoma with warthin’s tumor of the parotid gland - immunophenotypic and genetic features: A case report
Chang-Song Wang, Xia Chu, Di Yang, Lei Ren, Nian-Long Meng, Xue-Xia Lv, Tian Yun, Yan-Sha Cao
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2019; 7(22): 3895. CrossRef - Presentation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma in a Warthin Tumor: Case Report and Literature Review
Hadeel Jawad, Peter McCarthy, Gerard O’Leary, Cynthia C. Heffron
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 26(3): 256. CrossRef - Bilateral Warthin tumor in psoriatic patients in therapy with multiple immunosuppressive therapy
M Burlando, E Cozzani, C Chinazzo, M larosa, M Boggio, A Parodi
International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology.2015; 28(1): 138. CrossRef - Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma in a Warthin Tumor of the Parotid Gland
Arianna Di Napoli, Giuseppe Mallel, Armando Bartolazzi, Elena Cavalieri, Roberto Becelli, Claudia Cippitelli, Luigi Ruco
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 23(5): 419. CrossRef
- From the archives of MD Anderson Cancer Center: Small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia diagnosed in Warthin tumor
- Diagnostic Utility of a Clonality Test for Lymphoproliferative Diseases in Koreans Using the BIOMED-2 PCR Assay
- Young Kim, Yoo Duk Choi, Chan Choi, Jong-Hee Nam
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):458-465. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.458
- 12,395 View
- 102 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background A clonality test for immunoglobulin (IG) and T cell receptor (TCR) is a useful adjunctive method for the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative diseases (LPDs). Recently, the BIOMED-2 multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay has been established as a standard method for assessing the clonality of LPDs. We tested clonality in LPDs in Koreans using the BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR and compared the results with those obtained in European, Taiwanese, and Thai participants. We also evaluated the usefulness of the test as an ancillary method for diagnosing LPDs.
Methods Two hundred and nineteen specimens embedded in paraffin, including 78 B cell lymphomas, 80 T cell lymphomas and 61 cases of reactive lymphadenitis, were used for the clonality test.
Results Mature B cell malignancies showed 95.7% clonality for IG, 2.9% co-existing clonality, and 4.3% polyclonality. Mature T cell malignancies exhibited 83.8% clonality for TCR, 8.1% co-existing clonality, and 16.2% polyclonality. Reactive lymphadenitis showed 93.4% polyclonality for IG and TCR. The majority of our results were similar to those obtained in Europeans. However, the clonality for IGK of B cell malignancies and TCRG of T cell malignancies was lower in Koreans than Europeans.
Conclusions The BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR assay was a useful adjunctive method for diagnosing LPDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infectious mononucleosis complicated by transitory Epstein-Barr virus infection of T and natural killer cells
Yanlin Zhang, JianLan Xie, Yuanyuan Zheng, XiaoGe Zhou
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(3): 129. CrossRef - Experiencia en el uso de protocolos Biomed-2 para el estudio de reordenamientos de TCR e inmunoglobulinas en proliferaciones linfoides en el Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, Colombia
Nicolás Villamizar-Rivera, Natalia Olaya
Biomédica.2022; 42(Sp. 1): 64. CrossRef - Enhancing diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma using non-recombined T-cell receptor sequences
Yi-Lin Chen, Chung-Liang Ho, Chen-Yan Hung, Wan-Li Chen, Chen Chang, Yi-Hsin Hou, Jian-Rong Chen, Pin-Jun Chen, Nan-Haw Chow, Wenya Huang, Ya-Ting Hsu, Tsai-Yun Chen, Tsunglin Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The utility and limitations of B- and T-cell gene rearrangement studies in evaluating lymphoproliferative disorders
Hadrian Mendoza, Christopher A. Tormey, Henry M. Rinder, John G. Howe, Alexa J. Siddon
Pathology.2021; 53(2): 157. CrossRef - Combined detection of lymphocyte clonality and MALT1 translocations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosing pulmonary lymphomas
Takashi Kido, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Hiroshi Ishii, Kanako Hara, Mutsumi Ozasa, Hiroki Kawabata, Toshinori Kawanami, Yu Suzuki, Hiroki Yoshikawa, Atsuko Hara, Noriho Sakamoto, Nobuhiro Matsumoto, Chiharu Yoshii, Junya Fukuoka, Masaki Fujita, Masamitsu Nakazato
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiation of lymphocytic‐plasmacytic enteropathy and small cell lymphoma in cats using histology‐guided mass spectrometry
Sina Marsilio, Shelley J. Newman, James Scot Estep, Paula R. Giaretta, Jonathan A. Lidbury, Emma Warry, Andi Flory, Paul S. Morley, Katy Smoot, Erin H. Seeley, Matthew J. Powell, Jan S. Suchodolski, Jörg M. Steiner
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2020; 34(2): 669. CrossRef - T-Cell Receptor Rearrangements Determined Using Fragment Analysis in Patients With T-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Hyerim Kim, In-Suk Kim, Chulhun L. Chang, Sun-Young Kong, Young Tak Lim, Seom Gim Kong, Eun Hae Cho, Eun-Yup Lee, Ho-Jin Shin, Hyeon Jin Park, Hyeon-Seok Eom, Hyewon Lee
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2019; 39(2): 125. CrossRef - Monitoring immunoglobulin heavy chain and T‑cell receptor gene rearrangement in cfDNA as minimal residual disease detection for patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Ling Zhong, Jiao Chen, Xiaobing Huang, Yanxing Li, Tao Jiang
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular pathology diagnosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma using BIOMED-2 clonal gene rearrangements
Saeid Ghorbian
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2017; 29: 28. CrossRef - Improved clonality detection in B‐cell lymphoma using a semi‐nested modification of the BIOMED‐2 PCR assay for IGH rearrangement: A paraffin‐embedded tissue study
Yuma Sakamoto, Ayako Masaki, Satsuki Aoyama, Shusen Han, Kosuke Saida, Kana Fujii, Hisashi Takino, Takayuki Murase, Shinsuke Iida, Hiroshi Inagaki
Pathology International.2017; 67(9): 453. CrossRef - The prognostic significance of monoclonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in conjunction with histologic B‐cell aggregates in the bone marrow of patients with diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma
Yoon Ah Cho, Woo Ick Yang, Jae‐Woo Song, Yoo Hong Min, Sun Och Yoon
Cancer Medicine.2016; 5(6): 1066. CrossRef - Nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphomas are more frequently T rather than NK lineage based on T-cell receptor gene, RNA, and protein studies: lineage does not predict clinical behavior
Mineui Hong, Taehee Lee, So Young Kang, Suk-Jin Kim, Wonseog Kim, Young-Hyeh Ko
Modern Pathology.2016; 29(5): 430. CrossRef - Long-term Tumor-free Survival With Untreated Primary Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma of the Tonsil
Xiaojing Zhang, Yuanyuan Zheng, Jianlan Xie, Jun Zhu, Yuqin Song, Xiaojing Teng, Wei Liu, Yi Ding, Yuhua Huang, Xiaoge Zhou
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(11): 1493. CrossRef - Evaluation diagnostic usefulness of immunoglobulin light chains (Igκ, Igλ) and incomplete IGH D-J clonal gene rearrangements in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas using BIOMED-2 protocol
S. Ghorbian, I. Jahanzad, G. R. Javadi, E. Sakhinia
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2014; 16(11): 1006. CrossRef
- Infectious mononucleosis complicated by transitory Epstein-Barr virus infection of T and natural killer cells
- Cytologic Features of
ALK -Positive Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma - Seung Yeon Ha, Jungsuk Ahn, Mee Sook Roh, Joungho Han, Jae Jun Lee, Boin Lee, Jun Yim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):252-257. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.252
- 9,886 View
- 33 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The aim of this study was to determine the cytologic features of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (
ALK ) expressing pulmonary adenocarcinoma.Methods We analyzed the cytopathological findings of 15 cases of endobronchial ultrasound guided aspiration and a case of bronchial washing. These cases were selected based on the histomorphology of
ALK -rearranged lung adenocarcinoma.Results Cytology showed mucinous (81.3%) and hemorrhagic (50%) backgrounds. The cells were arranged in tubulopapillary or tubulocribriform patterns (93.8%), and clusters (56.3%) admixed with signet ring cell features (87.5%). The tumor cells were monotonous and uniform with vesicular nuclei and a small nucleolus.
Conclusions The characteristic findings were sheets showing a tubulopapillary or tubulocribriform appearance, with vesicular nuclei and a bland chromatin pattern (p<0.001). Scattered signet ring cells were helpful in suggesting
ALK -positive adenocarcinoma (p<0.001).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytomorphological and histomorphological features of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangement
Nikola Gardić, Aleksandra Lovrenski, Vanesa Sekeruš, Svetlana Lečić, Milorad Bijelović, Tanja Lakić, Aleksandra Ilić, Bojan Zarić, Sofija Glumac
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine learning‐based gene alteration prediction model for primary lung cancer using cytologic images
Shuhei Ishii, Manabu Takamatsu, Hironori Ninomiya, Kentaro Inamura, Takeshi Horai, Akira Iyoda, Naoko Honma, Rira Hoshi, Yuko Sugiyama, Noriko Yanagitani, Mingyon Mun, Hitoshi Abe, Tetuo Mikami, Kengo Takeuchi
Cancer Cytopathology.2022; 130(10): 812. CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration cytology of non‐small cell lung carcinoma: A paradigm shift
Pranab Dey, Ratan Kumar Ghosh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(4): 351. CrossRef - Qualitative and quantitative cytomorphological features of primary anaplastic lymphoma kinase‐positive lung cancer
Ryuko Tsukamoto, Hiroyuki Ohsaki, Sho Hosokawa, Yasunori Tokuhara, Shingo Kamoshida, Toshiko Sakuma, Tomoo Itoh, Chiho Ohbayashi
Cytopathology.2019; 30(3): 295. CrossRef - Primary signet-ring adenocarcinoma of the lung: A rare lung tumor
Varun Rajpal, Rahul Kumar Sharma, Charul Dabral, Deepak Talwar
South Asian Journal of Cancer.2019; 08(04): 257. CrossRef - Cytological features in eight patients with ALK‐rearranged lung cancer
Naoto Kuroda, Masahiko Ohara, Yukari Wada, Kaori Yasuoka, Keiko Mizuno, Kenji Yorita, Chiho Obayashi, Kengo Takeuchi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(6): 516. CrossRef - Cytological markers for predicting ALK‐positive pulmonary adenocarcinoma
K. Miyata, S. Morita, H. Dejima, N. Seki, N. Matsutani, M. Mieno, F. Kondo, Y. Soejima, F. Tanaka, M. Sawabe
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2017; 45(11): 963. CrossRef - ALK-rearranged adenocarcinoma with extensive mucin production can mimic mucinous adenocarcinoma: clinicopathological analysis and comprehensive histological comparison with KRAS-mutated mucinous adenocarcinoma
Yoon Jin Cha, Joungho Han, Soo Hyun Hwang, Tae Bum Lee, Hojoong Kim, Jea Ill Zo
Pathology.2016; 48(4): 325. CrossRef - Cytomorphological identification of advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma harboring KRAS mutation in lymph node fine‐needle aspiration specimens: Comparative investigation of adenocarcinoma with KRAS and EGFR mutations
Dae Hyun Song, Boram Lee, Yooju Shin, In Ho Choi, Sang Yun Ha, Jae Jun Lee, Min Eui Hong, Yoon‐La Choi, Joungho Han, Sang‐Won Um
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2015; 43(7): 539. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of RET and ROS1 rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma
Seung Eun Lee, Boram Lee, Mineui Hong, Ji-Young Song, Kyungsoo Jung, Maruja E Lira, Mao Mao, Joungho Han, Jhingook Kim, Yoon-La Choi
Modern Pathology.2015; 28(4): 468. CrossRef
- Cytomorphological and histomorphological features of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangement
- EBV-Positive T/NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of Childhood
- Mineui Hong, Young Hyeh Ko, Keon Hee Yoo, Hong Hoe Koo, Seok Jin Kim, Won Seog Kim, Heejung Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):137-147. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.137
- 16,289 View
- 122 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), EBV-positive systemic T-cell lymphoproliferative disease (STLPD) of childhood, and chronic active EBV (CAEBV) infection may develop after primary EBV infection. This study reviewed the clinicopathological spectrum of EBV-associated T- and natural killer (NK)-cell LPD, including STLPD and CAEBV infection, with an analysis of T-cell clonality.
Methods Clinicopathological features of seven patients with EBV-associated HLH or STLPD and 12 patients with CAEBV infection were reviewed. Immunohistochemical staining and a T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement study were performed.
Results STLPD and EBV-positive HLH showed significantly overlapping clinicopathological findings. One patient with STLPD and one patient with EBV-positive HLH demonstrated moderate to severe atypia of the infiltrating lymphocytes, whereas the remaining patients lacked significant atypia. Twelve patients had CAEBV infection, four of whom suffered mosquito-bite hypersensitivity, five showed NK lymphocytosis, and one suffered hydroa vacciniforme. Infiltrating lymphocytes were predominantly small and devoid of atypia. Hemophagocytic histiocytosis was found in seven of 11 patients. Monoclonality was detected in three (50%) of the six patients with successful TCR gene analysis.
Conclusions EBV-positive HLH and STLPD share similar clinicopathological findings and may constitute a continuous spectrum of acute EBV-associated T- or NK-cell proliferative disorders. The distinction of EBV-positive T-cell LPD from EBV-positive HLH may be difficult during routine diagnoses because of the technical limitations of clonality assessment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histopathological characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated encephalitis and colitis in chronic active EBV infection
Betty A Kasimo, James J Yahaya, Sun Och Yoon, Se Hoon Kim, Minsun Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(3): 188. CrossRef - Die fünfte Auflage der WHO‐Klassifikation – Was ist neu für kutane Lymphome?
Susanne Melchers, Jana D. Albrecht, Werner Kempf, Jan P. Nicolay
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2024; 22(9): 1254. CrossRef - Fifth Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: Mature T-Cell, NK-Cell, and Stroma-Derived Neoplasms of Lymphoid Tissues
Roberto N. Miranda, Catalina Amador, John K.C. Chan, Joan Guitart, Karen L. Rech, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Kikkeri N. Naresh
Modern Pathology.2024; 37(8): 100512. CrossRef - Clinical epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders (EBV-LPDs) in hospitalized children: A six-year multi-institutional study in China
Dilara Dilmurat, Xinyu Wang, Liwei Gao, Jiao Tian, Junhong Ai, Linlin Zhang, Mengjia Liu, Guoshuang Feng, Yueping Zeng, Ran Wang, Zhengde Xie
Italian Journal of Pediatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The fifth edition of the WHO‐Classification – what is new for cutaneous lymphomas?
Susanne Melchers, Jana D. Albrecht, Werner Kempf, Jan P. Nicolay
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2024; 22(9): 1254. CrossRef - An update on Epstein-Barr virus–and human T-lymphotropic virus type-1–induced cutaneous manifestations. CME Part II
Alejandro A. Gru, Jose A. Plaza, Jose A. Sanches, Denis Miyashiro, Omar P. Sangueza, Francisco Bravo Puccio, Sonia Toussaint, J. Martin Sangueza
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.2023; 88(5): 983. CrossRef - The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms
Rita Alaggio, Catalina Amador, Ioannis Anagnostopoulos, Ayoma D. Attygalle, Iguaracyra Barreto de Oliveira Araujo, Emilio Berti, Govind Bhagat, Anita Maria Borges, Daniel Boyer, Mariarita Calaminici, Amy Chadburn, John K. C. Chan, Wah Cheuk, Wee-Joo Chng,
Leukemia.2022; 36(7): 1720. CrossRef - Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus enteritis: A literature review
Yang Shen, Yu Fang Wang
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2022; 23(5-6): 248. CrossRef - EBV-Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Young Hyeh Ko
Clinical Pediatric Hematology-Oncology.2021; 28(1): 14. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic findings of chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection in adults: A single-center retrospective study in China
Jing Lin, Haicong Wu, Lei Gu, Xia Wu, Miaofang Su, Haiyan Lin, Bang Liu, Jiaolong Zheng, Xuan Mei, Dongliang Li
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2021; 21(3): 369. CrossRef - Outcome of L-DEP regimen for treatment of pediatric chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection
Honghao Ma, Liping Zhang, Ang Wei, Jun Yang, Dong Wang, Qing Zhang, Yunze Zhao, Sitong Chen, Hongyun Lian, Li Zhang, Chunju Zhou, Maoquan Qin, Zhigang Li, Tianyou Wang, Rui Zhang
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epstein-Barr virus NK and T cell lymphoproliferative disease: report of a 2018 international meeting
Jeffrey I. Cohen, Keiji Iwatsuki, Young-Hyeh Ko, Hiroshi Kimura, Irini Manoli, Koichi Ohshima, Stefania Pittaluga, Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez, Elaine S. Jaffe
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2020; 61(4): 808. CrossRef - EBV-positive T/NK-associated lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood: A complete autopsy report
JonathanY Keow, WilliamM Stecho, AaronR Haig, NikhilA Sangle
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2020; 63(1): 78. CrossRef - Chronic active Epstein‐Barr virus infection: A heterogeneous entity requiring a high index of suspicion for diagnosis
Sarah L. Ondrejka, Eric D. Hsi
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2020; 42(S1): 99. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated T and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases
Wook Youn Kim, Ivonne A. Montes-Mojarro, Falko Fend, Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A clinicopathologic study of the spectrum of systemic forms of EBV‐associated T‐cell lymphoproliferative disorders of childhood: A single tertiary care pediatric institution experience in North America
Amy M. Coffey, Annisa Lewis, Andrea N. Marcogliese, M. Tarek Elghetany, Jyotinder N. Punia, Chung‐Che Chang, Carl E. Allen, Kenneth L. McClain, Amos S. Gaikwad, Nader Kim El‐Mallawany, Choladda V. Curry
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Unusual lymphoid malignancy and treatment response in two children with Down syndrome
Ashley Geerlinks, Jennifer Keis, Bo Ngan, Amer Shammas, Reza Vali, Johann Hitzler
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - EBV-Positive Lymphoproliferations of B- T- and NK-Cell Derivation in Non-Immunocompromised Hosts
Stefan Dojcinov, Falko Fend, Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
Pathogens.2018; 7(1): 28. CrossRef - Cutaneous Hematolymphoid and Histiocytic Proliferations in Children
Alejandro A Gru, Louis P Dehner
Pediatric and Developmental Pathology.2018; 21(2): 208. CrossRef - Clinicopathological categorization of Epstein–Barr virus-positive T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disease: an analysis of 42 cases with an emphasis on prognostic implications
Jin Ho Paik, Ji-Young Choe, Hyojin Kim, Jeong-Ok Lee, Hyoung Jin Kang, Hee Young Shin, Dong Soon Lee, Dae Seog Heo, Chul-Woo Kim, Kwang-Hyun Cho, Tae Min Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2017; 58(1): 53. CrossRef - Cutaneous EBV-related lymphoproliferative disorders
Alejandro A. Gru, Elaine S. Jaffe
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2017; 34(1): 60. CrossRef - T- and NK-Cell Lymphomas and Systemic Lymphoproliferative Disorders and the Immunodeficiency Setting
Dita Gratzinger, Daphne de Jong, Elaine S. Jaffe, Amy Chadburn, John K. C. Chan, John R. Goodlad, Jonathan Said, Yasodha Natkunam
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2017; 147(2): 188. CrossRef - Systemic Epstein-Barr Virus-positive T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of Childhood With Good Response to Steroid Therapy
Do-Hoon Kim, Myungshin Kim, Yonggoo Kim, Kyungja Han, Eunhee Han, Jae Wook Lee, Nack-Gyun Chung, Bin Cho
Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.2017; 39(8): e497. CrossRef - Recent advances in the risk factors, diagnosis and management of Epstein-Barr virus post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease
Paibel Aguayo-Hiraldo, Reuben Arasaratnam, Rayne H. Rouce
Boletín Médico del Hospital Infantil de México.2016; 73(1): 31. CrossRef - Severe Epstein–Barr virus infection in primary immunodeficiency and the normal host
Austen J. J. Worth, Charlotte J. Houldcroft, Claire Booth
British Journal of Haematology.2016; 175(4): 559. CrossRef - Recent advances in the risk factors, diagnosis and management of Epstein-Barr virus post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease
Paibel Aguayo-Hiraldo, Reuben Arasaratnam, Rayne H. Rouce
Boletín Médico Del Hospital Infantil de México (English Edition).2016; 73(1): 31. CrossRef - Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Lymphomas
Ewelina Grywalska, Jacek Rolinski
Seminars in Oncology.2015; 42(2): 291. CrossRef - Epstein–Barr virus-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder in children and young adults has similar molecular signature to extranodal nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma but shows distinctive stem cell-like phenotype
Siok-Bian Ng, Koichi Ohshima, Viknesvaran Selvarajan, Gaofeng Huang, Shoa-Nian Choo, Hiroaki Miyoshi, Norio Shimizu, Renji Reghunathan, Hsin-Chieh Chua, Allen Eng-Juh Yeoh, Thuan-Chong Quah, Liang-Piu Koh, Poh-Lin Tan, Wee-Joo Chng
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2015; 56(8): 2408. CrossRef - An uncommon presentation of EBV-driven HLH. Primary or secondary? An ongoing dilemma
Tânia Serrão, Alexandra Dias, Pedro Nunes, António Figueiredo
BMJ Case Reports.2015; 2015: bcr2015209615. CrossRef - Hemophagocytic syndromes — An update
Gritta E. Janka, Kai Lehmberg
Blood Reviews.2014; 28(4): 135. CrossRef - Epstein–Barr virus‐associated T/natural killer‐cell lymphoproliferative disorders
Sanghui Park, Young H. Ko
The Journal of Dermatology.2014; 41(1): 29. CrossRef
- Histopathological characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–associated encephalitis and colitis in chronic active EBV infection
- Cervical Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma after Dapsone-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome
- Min Young Rim, Junshik Hong, Inku Yo, Hyeonsu Park, Dong Hae Chung, Jeong Yeal Ahn, Sanghui Park, Jinny Park, Yun Soo Kim, Jae Hoon Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):606-610. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.606
- 10,479 View
- 62 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A 36-year-old woman presented with erythematous confluent macules on her whole body with fever and chills associated with jaundice after 8 months of dapsone therapy. Her symptoms had developed progressively, and a physical examination revealed bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. Excisional biopsy of a cervical lymph node showed effacement of the normal architecture with atypical lymphoid hyperplasia and proliferation of high endothelial venules compatible with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. However, it was assumed that the cervical lymphadenopathy was a clinical manifestation of a systemic hypersensitivity reaction because her clinical course was reminiscent of dapsone-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. A liver biopsy revealed drug-induced hepatitis with no evidence of lymphomatous involvement. Intravenous glucocorticoid was immediately initiated and her symptoms and clinical disease dramatically improved. The authors present an unusual case of cervical lymphadenopathy mimicking angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma as an adverse reaction to dapsone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-leprosy related dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome: A case report and literature review
Hang-Qi Zhu, Si-Hua Jiang, Guo-Lin Song
Medicine.2025; 104(27): e43073. CrossRef - Morphologic Spectrum of Lymphadenopathy in Drug Reaction With Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome
Hui-Chun Chen, Ren Ching Wang, Huey-Pin Tsai, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Kung-Chao Chang
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2022; 146(9): 1084. CrossRef - Antibacterial antibiotic-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome: a literature review
Shiva Sharifzadeh, Amir Hooshang Mohammadpour, Ashraf Tavanaee, Sepideh Elyasi
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2021; 77(3): 275. CrossRef - Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity Syndrome: A Clinical, Radiologic, and Histologic Mimic of Lymphoma
Faaria Gowani, Bradley Gehrs, Teresa Scordino
Case Reports in Hematology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - In vitrotesting for diagnosis of idiosyncratic adverse drug reactions: Implications for pathophysiology
Abdelbaset A. Elzagallaai, Michael J. Rieder
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2015; 80(4): 889. CrossRef - Dapsone-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome, misdiagnosed as lymphoma
Bomi Shin, So Young Park, Sun-Young Yoon, Eun-Hye Shin, Young-Joo Yang, Hyung-Jin Cho, Il-Young Jang, Dong-Uk Kang, Tae-Bum Kim, You Sook Cho, Hee-Bom Moon, Hyouk-Soo Kwon
Allergy, Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2013; 1(4): 400. CrossRef - T-cell lymphoma presenting as drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome
Mi-Ae Kim, Hye-Soo Yoo, Sun Hyuk Hwang, Yoo Seob Shin, Dong-Ho Nahm, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2013; 1(3): 280. CrossRef
- Non-leprosy related dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Expression of HAT1 and HDAC1, 2, 3 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas, Peripheral T-Cell Lymphomas, and NK/T-Cell Lymphomas
- Soo Kee Min, Young Ho Koh, Yunwoong Park, Hyo Jung Kim, Jinwon Seo, Hye-Rim Park, Seong Jin Cho, In Sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):142-150. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.142
- 9,316 View
- 72 Download
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background It has generally been proven that histone acetylation and deacetylation are involved in the malignant transformation. To date, however, this has rarely been studied in cases of malignant lymphoma.
Methods We studied nine cases of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, 78 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), 13 cases of peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), and 13 cases of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (NKTCL). Thus, we attempted to elucidate the associations of the degree of the expression of histone acetyltransferase 1 (HAT1), histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1, HDAC2, and HDAC3 with the clinical behaviors of above malignant lymphomas using the immunohistochemistry and a western blot analysis.
Results The degree of the expression of HAT1 was higher in cases of DLBCL, PTCL-NOS or NKTCL as compared with reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (p<0.05). The degree of the expression of HAT1 was correlated with that of HDAC1 in cases of DLBCL or NKTCL (p<0.05). The degree of the expression of HAT1 and HDAC1 was correlated with a poor survival in cases of DLBCL or PTCL-NOS (p>0.05).
Conclusions HAT1, HDAC1, and HDAC2 play a critical role in the development of malignant lymphomas. Both HAT1 and HDAC1 might be indicators for a poor prognosis in cases of DLBCL as cooperating factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Advancements in the Development of HDAC/Tubulin Dual-Targeting Inhibitors
Christine Tran, Abdallah Hamze
Pharmaceuticals.2025; 18(3): 341. CrossRef - Management of T‐cell malignancies: Bench‐to‐bedside targeting of epigenetic biology
Ariana Sabzevari, Johnson Ung, Jeffrey W. Craig, Kallesh D. Jayappa, Ipsita Pal, David J. Feith, Thomas P. Loughran, Owen A. O’Connor
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2025; 75(4): 282. CrossRef - Chidamide and orelabrutinib synergistically induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
Chunyan Wu, Shilv Chen, Zhimin Wu, Jiao Xue, Wen Zhang, Shan Wang, Xindong Zhao, Shaoling Wu
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting HDACs for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma therapy
Chunyan Wu, Qiao Song, Sophie Gao, Shaoling Wu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in epigenetic therapies for B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma
Weiwen Hu, Lanlan Zang, Xiaoxi Feng, Shuhui Zhuang, Liudi Chang, Yongjing Liu, Jinyan Huang, Yuanyuan Zhang
Annals of Hematology.2024; 103(12): 5085. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation in hematopoiesis and its implications in the targeted therapy of hematologic malignancies
Ailin Zhao, Hui Zhou, Jinrong Yang, Meng Li, Ting Niu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding HAT1: A Comprehensive Review of Noncanonical Roles and Connection with Disease
Miguel A. Ortega, Diego De Leon-Oliva, Cielo Garcia-Montero, Oscar Fraile-Martinez, Diego Liviu Boaru, María del Val Toledo Lobo, Ignacio García-Tuñón, Mar Royuela, Natalio García-Honduvilla, Julia Bujan, Luis G. Guijarro, Melchor Alvarez-Mon, Miguel Ánge
Genes.2023; 14(4): 915. CrossRef - HAT1: Landscape of Biological Function and Role in Cancer
Vincenza Capone, Laura Della Torre, Daniela Carannante, Mehrad Babaei, Lucia Altucci, Rosaria Benedetti, Vincenzo Carafa
Cells.2023; 12(7): 1075. CrossRef - Recent advancement of HDAC inhibitors against breast cancer
Syed Abdulla Mehmood, Kantrol Kumar Sahu, Sounok Sengupta, Sangh Partap, Rajshekhar Karpoormath, Brajesh Kumar, Deepak Kumar
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Noncoding rules of survival: epigenetic regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis
LaShanale Wallace, Esther A. Obeng
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Therapeutic Use of Aptamers against HAT1 in Lung Cancer
José Ignacio Klett-Mingo, Celia Pinto-Díez, Julio Cambronero-Plaza, Rebeca Carrión-Marchante, Miriam Barragán-Usero, María Isabel Pérez-Morgado, Eulalia Rodríguez-Martín, Mª Val Toledo-Lobo, Víctor M González, M. Elena Martín
Cancers.2022; 15(1): 227. CrossRef - Modulation of serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) complexes: A promising approach in cancer treatment
Bárbara Matos, John Howl, Carmen Jerónimo, Margarida Fardilha
Drug Discovery Today.2021; 26(11): 2680. CrossRef - Histone acetyltransferase 1 promotes gemcitabine resistance by regulating the PVT1/EZH2 complex in pancreatic cancer
Yan Sun, Dianyun Ren, Yingke Zhou, Jian Shen, Heshui Wu, Xin Jin
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering genes associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with lymphomatous effusions: A mutational accumulation scoring approach
Sina Abdollahi, Seyedeh Zahra Dehghanian, Liang-Yi Hung, Shiang-Jie Yang, Dao-Peng Chen, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Jung-Hsien Chiang, Kung-Chao Chang
Biomarker Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The contributory roles of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in hematopoiesis regulation and possibilities for pharmacologic interventions in hematologic malignancies
Mahdieh Mehrpouri, Atieh Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, Davood Bashash
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 100: 108114. CrossRef - Emerging role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Mingyang Wang, Xiaosheng Fang, Xin Wang
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2020; 61(4): 763. CrossRef Effective Treatment with PD-1 Antibody, Chidamide, Etoposide, and Thalidomide (PCET) for Relapsed/Refractory Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Report of Three Cases
Lijun Du, Lei Zhang, Ling Li, Xin Li, Jiaqin Yan, Xinhua Wang, Xiaorui Fu, Zhenchang Sun, Xudong Zhang, Zhaoming Li, Jingjing Wu, Hui Yu, Yu Chang, Zhiyuan Zhou, Feifei Nan, Xiaolong Wu, Li Tian, Mingzhi Zhang
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 7189. CrossRef- Overexpressed histone acetyltransferase 1 regulates cancer immunity by increasing programmed death-ligand 1 expression in pancreatic cancer
Ping Fan, Jingyuan Zhao, Zibo Meng, Heyu Wu, Bo Wang, Heshui Wu, Xin Jin
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone modifications: A review about the presence of this epigenetic phenomenon in carcinogenesis
Emanuely Silva Chrun, Filipe Modolo, Filipe Ivan Daniel
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(11): 1329. CrossRef - Histone Acetyltransferase 1 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Induces Cisplatin Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Xin Jin, Shenghua Tian, Pingping Li
Oncology Research Featuring Preclinical and Clinical Cancer Therapeutics.2017; 25(6): 939. CrossRef - HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy
Yixuan Li, Edward Seto
Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine.2016; 6(10): a026831. CrossRef - Histone deacetylase inhibitors and epigenetic regulation in lymphoid malignancies
Diana Markozashvili, Vincent Ribrag, Yegor S. Vassetzky
Investigational New Drugs.2015; 33(6): 1280. CrossRef - Genome-Wide Association Study of Event-Free Survival in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Immunochemotherapy
Hervé Ghesquieres, Susan L. Slager, Fabrice Jardin, Amelie S. Veron, Yan W. Asmann, Matthew J. Maurer, Thierry Fest, Thomas M. Habermann, Marie C. Bene, Anne J. Novak, Sylvain Mareschal, Corinne Haioun, Thierry Lamy, Stephen M. Ansell, Herve Tilly, Thomas
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2015; 33(33): 3930. CrossRef - Histone deacetylase 2 controls p53 and is a critical factor in tumorigenesis
Tobias Wagner, Peter Brand, Thorsten Heinzel, Oliver H. Krämer
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2014; 1846(2): 524. CrossRef - Targetome profiling and functional genetics implicate miR-618 in lymphomagenesis
Alan Fu, Aaron E Hoffman, Ran Liu, Daniel I Jacobs, Tongzhang Zheng, Yong Zhu
Epigenetics.2014; 9(5): 730. CrossRef - Expression of Histone Deacetylases HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, and HDAC6 in Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
Jinwon Seo, Soo Kee Min, Hye-Rim Park, Dong Hoon Kim, Mi Jung Kwon, Lee Su Kim, Young-Su Ju
Journal of Breast Cancer.2014; 17(4): 323. CrossRef - Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Maurizio Martelli, Andrés J.M. Ferreri, Claudio Agostinelli, Alice Di Rocco, Michael Pfreundschuh, Stefano A. Pileri
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2013; 87(2): 146. CrossRef - Histone deacetylase inhibitors activate CIITA and MHC class II antigen expression in diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma
Kelly A. Cycon, Kathleen Mulvaney, Lisa M. Rimsza, Daniel Persky, Shawn P. Murphy
Immunology.2013; 140(2): 259. CrossRef
- Recent Advancements in the Development of HDAC/Tubulin Dual-Targeting Inhibitors
- Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma Accompanied by Heavy Eosinophilic Infiltration and Peripheral Blood Eosinophilia, Involving Skeletal Muscles.
- Jin Ho Paik, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Heounjeong Go, Chul Woo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S70-S74.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S70
- 4,746 View
- 42 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The patient was a 52-year-old female with swelling in both lower legs and peripheral blood eosinophilia. Biopsy specimen revealed the heavy infiltration of eosinophils with sparse small lymphocytes showing mild atypia. The diagnosis was Kimura disease. The symptoms including eosinophilia were relieved by steroid treatment. At 17 months from initial biopsy, the patient developed swelling of the buttock. At 25 months, fever and dyspnea with multiple lung nodules developed. Wedge resection revealed multiple aggregates of CD3(+), CD56(+), Epstein-Barr virus(+) large atypical lymphocytes with necrosis. The patient was finally diagnosed with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma (NKTL). Epstein-Barr virus in situ hybridization retrospectively performed on the previous biopsies demonstrated Epstein-Barr virus infection in small CD3(+) lymphocytes. The patient expired after 26 months despite chemotherapy. Blood eosinophilia correlated well with disease activity during the clinical course. This case shows not only unusual histologic features, which hampered the correct diagnosis, but also a unique clinical manifestation of NKTL.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma suspected to be focal myositis of the masseter muscle
Junya YAMASHITA, Daisuke TAKEDA, Tatsuya SHIRAI, Kaito URYU, Nanae YATAGAI, Masaya AKASHI
Japanese Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025; 71(1): 33. CrossRef - Muscular involvement of extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as polymyositis: A case report and review of literature
Li-Hui Liu, Qing Huang, Yun-Hai Liu, Jie Yang, Han Fu, Lin Jin
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(5): 963. CrossRef - Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma with paraneoplastic eosinophilic myositis
Jayati Mallick, Jasmine Zain, Dennis D. Weisenburger
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2020; 21: 200391. CrossRef - Extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma Mimicking Granulomatous Myositis
Norihiko Kawaguchi, Rumiko Izumi, Masahiro Kobayashi, Maki Tateyama, Naoki Suzuki, Fumiyoshi Fujishima, Juichi Fujimori, Masashi Aoki, Ichiro Nakashima
Internal Medicine.2019; 58(2): 277. CrossRef - Uveitis and Myositis as Immune Complications in Chemorefractory NK/T-Cell Nasal-Type Lymphoma Successfully Treated with Allogeneic Stem-Cell Transplant
Maria José Gómez-Crespo, Aránzazu García-Raso, Jose Luis López-Lorenzo, Teresa Villaescusa, María Rodríguez-Pinilla, José Fortes, Cristina Serrano, Salma Machan, Pilar Llamas, Raúl Córdoba
Case Reports in Hematology.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Prognostic implications of CD30 expression in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma according to treatment modalities
Wook Youn Kim, Soo Jeong Nam, Sehui Kim, Tae Min Kim, Dae Seog Heo, Chul-Woo Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Leukemia & Lymphoma.2015; 56(6): 1778. CrossRef - Unusual case of metachronous EBV‐associated B‐cell and NK/T‐cell lymphoma mimicking polymyositis‐diagnostic challenges and pitfalls
Esther H.L. Chan, Suat‐Jin Lu, Fredrik Petersson, Kong‐Bing Tan, Wee‐Joo Chng, Siok‐Bian Ng
American Journal of Hematology.2014; 89(1): 110. CrossRef - CD30+ extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma mimicking phlegmonous myositis: A case report
YAN-JIA YANG, YA-XIN LI, YAN-BIN LIU, MEI YANG, KAI LIU
Oncology Letters.2014; 7(5): 1419. CrossRef
- A case of extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma suspected to be focal myositis of the masseter muscle
- In Situ Follicular Lymphoma Developed after Hodgkin Lymphoma.
- Ho Sung Park, Sang Jae Noh, Jae Yong Kwak, Eun Kee Song, Myung Hee Sohn, Ho Lee, Woo Sung Moon, Kyu Yun Jang
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45:S53-S57.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.S1.S53
- 3,871 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In situ follicular lymphoma is a newly defined entity among the lymphoid neoplasms and is defined as architecturally normal-appearing lymph nodes and other lymphoid tissues that have one or more follicles that demonstrate bcl-2 overexpressing centrocytes and centroblasts, with or without a monomorphic cytologic appearance suggestive of follicular lymphoma. Here we present a case of in situ follicular lymphoma diagnosed during the follow-up after a complete response to the treatment of lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin's lymphoma. In our case, because only a few germinal centers contained bcl-2 overexpressing cells, we missed the diagnosis of in situ follicular lymphoma in the initial histological examination. We could establish the diagnosis only after performing bcl-2 immunostaining in the sequential biopsy. Therefore, we recommend that careful histological examination along with bcl-2 immunostaining is needed in patients with suspicious clinical findings.
- CD44s and CD44v6 Are Predominantly Expressed in the Non-germinal Center B-Cell-like Type of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas.
- Kyueng Whan Min, Young Ha Oh, Chan Kum Park, So Dug Lim, Wan Seop Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):589-595.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.589
- 4,136 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
CD44 protein is known as a homing cellular adhesion molecule that is linked to diverse cellular functions such as adhesion, migration and invasion, which are all important in cancer progression and metastasis. The expression of CD44 standard and variant isoforms (CD44 standard isoform [CD44s] and CD44 splice variants containing exon v6 [CD44v6], respectively) is associated with an unfavorable clinical outcome in various neoplasms.
METHODS
Forty patients who were diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) through biopsy at Hanyang University Hospital between 1996 and 2003 were included in this study. CD44 proteins expression was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining on a tissue microarray and the correlation of CD44 with the types of DLBCL and clinical parameters, including the factors defined by the International Prognostic Index, was evaluated.
RESULTS
A high CD44s and intermediate to strong CD44v6 expression, including cytoplasmic membranous staining patterns, was present in 35% (14/40) and 25% (10/40) of DLBCL patients, respectively. High CD44s expression was correlated significantly with non-germinal center B-cell-like types (non-GCB, p=0.004) and patients with old age (p=0.041).
CONCLUSIONS
High CD44s expression may be significantly associated with the non-GCB type compared to the GCB type and may be essential to the prediction of disease outcome in tumor stage III in DLBCL patients.
- Prognostic Implication of Programmed Death-1-Positive Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.
- Young Sin Ko, Young Ha Oh, Chan Kum Park, Wook Youn Kim, Hye Seung Han, So Dug Lim, Tae Sook Hwang, Wan Seop Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(6):573-581.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.6.573
- 4,466 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is physiologically expressed by germinal center-associated helper T-cells and has an inhibitory effect on T-cell activity.
METHODS
We examined 63 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and determined the number of PD-1-positive helper T-cells in a representative tumor area after immunohistochemical staining using a monoclonal antibody against PD-1. The PD-1-positive cells were counted in 3 high-power fields (HPFs; 400x).
RESULTS
Patients were divided into 2 groups: one with a high number of PD-1-positive cells (>20/HPF, n=33) and one with a low number of PD-1-positive cells (< or =20/HPF, n=30). The former group showed decreased overall survival, but at a statistically non-significant level (p=0.073). A high number of PD-1-positive cells was more common in patients at an advanced clinical stage and with high international prognostic index score (p=0.025 and p=0.026, respectively). The number of extranodal sites also somewhat correlated with the PD-1 staining status (p=0.071). However, the number of PD-1-positive cells was not associated with patient age, serum lactate dehydrogenase level, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score.
CONCLUSIONS
The high number of PD-1-positive cells might be associated with an unfavorable outcome in DLBCL patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and prognostic relevance in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a summary of immunohistochemical studies
Pauline Gravelle, Barbara Burroni, Sarah Péricart, Cédric Rossi, Christine Bezombes, Marie Tosolini, Diane Damotte, Pierre Brousset, Jean-Jacques Fournié, Camille Laurent
Oncotarget.2017; 8(27): 44960. CrossRef - Expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in advanced stage EBV-associated extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma is associated with better prognosis
Wook Youn Kim, Ho Young Jung, Soo Jeong Nam, Tae Min Kim, Dae Seog Heo, Chul-Woo Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
Virchows Archiv.2016; 469(5): 581. CrossRef
- Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and prognostic relevance in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a summary of immunohistochemical studies

 E-submission
E-submission


















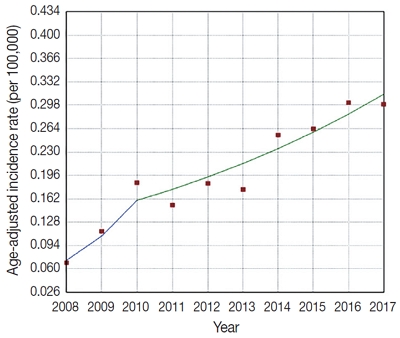





 First
First Prev
Prev



