Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- PSMA expression in hepatic colorectal cancer metastasis
- Eundong Park, Michel Kmeid, Xin Wang, Haiyan Qiu, Clifton G. Fulmer, Marcello P. Toscano, Nusret Bekir Subasi, Maciej Gracz, Hwajeong Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):107-123. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.20
- 349 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is expressed in the neovasculature of various malignancies, such as colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, PSMA expression in hepatic CRC metastasis has not been studied in detail. Methods: The PSMA expression in primary CRC and corresponding hepatic metastasis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in a metastatic CRC cohort (n = 56), which was divided into subgroups according to treatment history and timing of metastasis. Demographic and histological characteristics of primary CRC were collected and their relationships with PSMA expression were examined. Additionally, the PSMA expression in resected HCC (n = 76) was compared with that of hepatic CRC metastasis. Results: In primary CRC, PSMA level showed a positive association with tumor size. Lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis was associated with higher primary CRC grade, advanced pTNM stage at the time of CRC resection, presence of tumor deposit, and unresectability of metastatic lesion. PSMA expression in primary CRC correlated with that in hepatic metastasis only in concurrent and untreated metastasis subgroup. PSMA expression in primary CRC and hepatic metastasis, regardless of treatment history and timing of metastasis, was not significantly different from that of HCC. Conclusions: Several adverse pathological features of primary CRC were associated with a lower PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis. PSMA expression in hepatic metastasis correlated with that of primary CRC only in concurrent and untreated subgroup. Primary HCC and hepatic CRC metastasis show comparable levels of PSMA expression.
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,157 View
- 240 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 13,760 View
- 593 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
- Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as a primary thyroid tumor
- Jai-Hyang Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):242-245. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.16
- 4,415 View
- 117 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma is rare. To date, only six cases have been reported in the literature. This case was unusual and presented with thyromegaly before the diagnosis of the primary tumor. A 55-year-old male patient was suspected to have a primary thyroid tumor with nodal metastasis. The thyroid gland was diffusely enlarged, with no discernible mass. Histologically, the thyroid parenchyma revealed extensive endolymphatic tumor emboli, which were positive for p40 and p16 in a background of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed hypermetabolic activity in the right tonsillar region. Tonsillar biopsy revealed human papillomavirus–positive squamous cell carcinoma. The present case is the first reported case of intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma with an initial clinical presentation of thyroid enlargement before the primary tumor of tonsillar cancer was diagnosed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
Avneet Kaur, Rohit Nayyar, Harit Kumar Chaturvedi, Akshat Malik
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025; 16(1): 122. CrossRef - Metastatic oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma to the thyroid: A case report and review of literature
Hannah Walker, Jed Speers, Milena Fabry, Sameep Kadakia
American Journal of Otolaryngology.2024; 45(4): 104306. CrossRef
- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
- Metastatic choroidal melanoma in the breast: a case report and review of the literature
- Loay Abudalu, Vinisha Malhotra, Nabila Nasir, Sami Titi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):238-241. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.07
- 4,983 View
- 128 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The breast is an unusual site for metastases, accounting for less than 2% of malignant breast lesions but include those from malignant melanomas, carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas from various organs. We diagnosed a very rare case of metastatic choroidal melanoma for a 67-year-old female who presented with a right breast lump and who had been previously diagnosed with choroidal melanoma-monosomy 3 in 2017. To the best of our knowledge, only five such cases have been published so far, with one in a male patient.
- Clinicopathologic characterization of cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor: a multicenter study in Korea
- Miseon Lee, Uiree Jo, Joon Seon Song, Youn Soo Lee, Chang Gok Woo, Dong-Hoon Kim, Jung Yeon Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):166-177. Published online May 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.04.12
- 6,145 View
- 171 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Research regarding cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor (CUP) according to human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status in Korea has been sporadic and small-scale. This study aims to analyze and understand the characteristics of CUP in Korea according to viral and p16 and p53 status through a multicenter study.
Methods
Ninety-five cases of CUP retrieved from six hospitals in Korea between January 2006 and December 2016 were subjected to high-risk HPV detection (DNA in situ hybridization [ISH] or real-time polymerase chain reaction), EBV detection (ISH), and immunohistochemistry for p16 and p53.
Results
CUP was HPV-related in 37 cases (38.9%), EBV-related in five cases (5.3%), and unrelated to HPV or EBV in 46 cases (48.4%). HPV-related CUP cases had the best overall survival (OS) (p = .004). According to the multivariate analysis, virus-unrelated disease (p = .023) and longer smoking duration (p < .005) were prognostic factors for poor OS. Cystic change (p = .016) and basaloid pattern (p < .001) were more frequent in HPV-related cases, and lymphoepithelial lesion was frequent in EBV-related cases (p = .010). There was no significant association between viral status and p53 positivity (p = .341), smoking status (p = .728), or smoking duration (p = .187). Korean data differ from Western data in the absence of an association among HPV, p53 positivity, and smoking history.
Conclusions
Virus-unrelated CUP in Korea had the highest frequency among all CUP cases. HPV-related CUP is similar to HPV-mediated oropharyngeal cancer and EBVrelated CUP is similar to nasopharyngeal cancer in terms of characteristics, respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differenzierung von benignen und malignen Halszysten – eine diagnostische Herausforderung
Christina Sauter, Matthias Sand, Karim Plath, Michaela Maria Plath
Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie.2025; 104(05): 296. CrossRef - Unlocking the Hidden: Advancing Imaging Techniques in Diagnosing Cancers of Unknown Primary in the Head and Neck Region
Daniela Messineo, Filippo Valentini, Giovanni Francesco Niccolini, Federica Zoccali, Francesca Ripari, Enrico Marotta, Marcello Caratozzolo, Pasquale Frisina
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(4): 2194. CrossRef - Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 361. CrossRef - Management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: current evidence-based diagnostic and treatment strategies
Marcel Kloppenburg, Matthias Santer, Lukas Schmutzler, Felix Johnson, Benedikt Hofauer, Teresa Steinbichler
memo - Magazine of European Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to assess the potential of adoptive cell therapy
Sangjoon Choi, Mofazzal Hossain, Hyun Lee, Jina Baek, Hye Seon Park, Chae-Lyul Lim, DoYeon Han, Taehyun Park, Jong Hyeok Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Mi-Na Kweon, Hee Jin Lee
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Differenzierung von benignen und malignen Halszysten – eine diagnostische Herausforderung
- Correlation between myoferlin expression and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Ji Min Na, Dong Chul Kim, Dae Hyun Song, Hyo Jung An, Hyun Min Koh, Jeong-Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):199-204. Published online May 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.03.19
- 4,940 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Myoferlin is a multifunctional protein expressed in various normal and cancer cells, with novel oncogenic roles being newly discovered. Recently, correlations have been found between myoferlin expression and unfavorable prognosis in various carcinomas. This study investigated the prognostic role of myoferlin expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), specifically that associated with nodal metastasis.
Methods
We collected clinicopathological data and PTC tissues from 116 patients who had been admitted to Gyeongsang National University Hospital in 2010. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on surgical specimen-derived tissue microarray blocks. Myoferlin expression was graded, and the relationship between expression level and pathological features of tumors based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system was evaluated.
Results
Of the 116 patient samples, 100 cases exhibited positive myoferlin expression. Higher grade of myoferlin expression was correlated with lower T category group (p = .010). Presence of lymph node metastasis was determined to be significantly correlated with low-grade myoferlin expression (p = .019), with no significant difference between pN1a and pN1b tumors.
Conclusions
Our study revealed an adverse correlation between myoferlin expression and pathological features of PTC, evidence of the potential prognostic role of myoferlin in PTC lymph node metastasis.
- Clinicopathologic features of cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies
- Hyeong Mok Kwon, Gyu Yeong Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Young Kyung Bae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(4):289-297. Published online July 7, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.05.24
- 7,622 View
- 186 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Cutaneous metastasis (CM) is the spread of cancer cells from a primary site to the skin and is rarely the first sign of silent cancer. We investigated the clinicopathological characteristics of CM from internal malignancies in Korean patients treated at our institution over 20 years.
Methods
The clinicopathological findings of 112 patients (62 females, 50 males) with CM diagnosed at Yeungnam University Hospital between 2000 and 2020 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
Mean patient age was 58.6 years (range, 26 to 87 years), and the most common primary cancer site was breast (74.2%) in women and lung (36.0%) in men. Ninety-six patients (85.7%) presented with CM after primary tumor diagnosis. CM from the lung or biliary tract usually occurred within 2 years of primary tumor diagnosis, whereas metastases from the breast and kidney occurred several years later. The chest, abdomen, and scalp were common sites of CM. Breast cancer usually metastasized to chest skin, while gastrointestinal tract cancers commonly metastasized to the abdomen. The scalp was a common location for CM from various tumors. The most common dermatologic presentations were nodules and masses. Immunohistochemical studies helped identify underlying malignancies when primary tumors were unknown.
Conclusions
The relative frequency of CM parallels the overall incidence of primary malignant tumors, and CMs usually occur at anatomic sites close to the primary tumor. CM can be diagnosed based on clinical, radiological, and histological features; however, immunohistochemical study is required in some cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cutaneous Metastases—Histological Particularities of Multifaceted Entities
Andreea Cătălina Tinca, Bianca Andreea Lazar, Andreea Raluca Cozac-Szőke, Georgian Nicolae Radu, Simina Petra Simion, Diana Maria Chiorean, Irina Bianca Kosovski, Adrian Horațiu Sabău, Raluca Niculescu, Iuliu Gabriel Cocuz, Raluca-Diana Hagău, Emoke Andre
Dermatopathology.2025; 12(2): 14. CrossRef - Cutaneous metastases of carcinomas originating from visceral organs - a contribution to the issue and description of particular cases
Vladimír Bartoš, Michal Urda
Onkologie.2025; 19(3): 160. CrossRef - A Mirror of Metastatic Destiny – A Case Series of Cutaneous Metastases
Rochelle Monteiro, Monisha Madhumita, Hemanth Kumar, Jacintha Martis
Clinical Dermatology Review.2024; 8(1): 58. CrossRef - Nonbrain metastases seen on magnetic resonance imaging during metastatic brain tumor screening
Mio Sakai, Nobuo Kashiwagi, Katsuyuki Nakanishi, Noboru Maeda, Yasuhiro Nakaya, Junichiro Tanaka, Shinichiro Watanabe, Hidenari Hongyo, Yu Tanaka, Sawaka Yamada, Atsushi Kawata, Sou Toda, Koji Takano, Hideyuki Arita, Noriyuki Tomiyama
Japanese Journal of Radiology.2023; 41(4): 367. CrossRef - Cutaneous Metastasis as a Diagnostic Prelude in a 48-year-old Female
Nagatoshi M. Ebisawa, Isabel G. Palabyab-Imperial, Leilani R. Senador, Luella Joy A. Escueta-Alcos
Journal of the Philippine Dermatological Society.2023; 32(2): 107. CrossRef - Pigmented epidermotropic breast cancer metastases: A rare variant with a particularly unusual feature
Juan Torre‐Castro, Cristina Moya‐Martínez, Lara Haya‐Martínez, María Dolores Mendoza‐Cembranos, Itziar Eraña‐Tomás, Luis Requena
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2022; 49(1): 99. CrossRef - Skin metastases in the clinical and dermoscopic aspects
Grazyna Kamińska-Winciorek, Aleksandra Pilśniak, Wojciech Piskorski, Jerzy Wydmański
Seminars in Oncology.2022; 49(2): 160. CrossRef - Dermoscopy and novel non invasive imaging of Cutaneous Metastases
Dimitrios Alexandris, Nektarios Alevizopoulos, Leonidas Marinos, Charikleia Gakiopoulou
Advances in Cancer Biology - Metastasis.2022; 6: 100078. CrossRef
- Cutaneous Metastases—Histological Particularities of Multifaceted Entities
- Potential of AKT2 expression as a predictor of lymph-node metastasis in invasive breast carcinoma of no special type
- Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Kristina Anna Bethania, Kusmardi Kusmardi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(4):271-278. Published online June 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.04.26
- 5,997 View
- 154 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST) is the most common type of breast cancer and mainly causes regional lymph-node metastasis (LNM). We investigated the potential for AKT2 expression as a predictive biomarker for LNM in IBC-NST.
Methods
Forty-eight paraffin blocks containing IBC-NST primary tumors were divided into two groups based on presence or absence of LNM. Age, tumor grade, tumor size, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), and AKT expression were assessed. AKT2 expression was assessed based on immunohistochemical staining, while other data were collected from archives.
Results
Multiple logistic regression results showed that AKT2 expression and LVI were significantly associated with LNM (odds ratio [OR], 5.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.42 to 19.93 and OR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.17 to 16.97, respectively). AKT2 expression was able to discriminate against LNM (area under the receiver operating characteristic, 0.799 ± 0.063; 95% CI, 0.676 to 0.921) at an H-score cutoff of 104.62 (83.3% sensitivity, 62.5% specificity).
Conclusions
AKT2 expression has potential as a predictor of LNM in IBC-NST. The H-score cutoff for AKT2 expression can be used as a classification guide in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Src with Nottingham Prognostic Index in Breast Cancer: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognostication
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2024; 7(2): 90. CrossRef - CD4+ Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy-treated Invasive Breast Cancer of No Special Type
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Meike Pramono, Sinta Chaira Maulanisa
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2024; 7(3): 179. CrossRef - Potential of AKNA as a Predictive Biomarker for Ovarian Cancer and Its Relationship to Tumor Grading
P Rustamadji, E Wiyarta, M Miftahuzzakiyah, D Sukmawati, DA Suryandari, R Kodariah
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(9): 1089. CrossRef - Exploring the Expression of Survivin on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Ineke Anggreani
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(B): 1440. CrossRef - Effect of Omega-3-Rich Fish Oil on TNF- Expression in Mice's Colonic Tissue Induced with Azoxymethane (AOM) and Dextran Sodium Sulphate (DSS)
Elvan Wiyarta, Kusmardi Kusmardi, Yurnadi Hanafi Midoen
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 3179. CrossRef - The potential of lunasin extract for the prevention of breast cancer progression by upregulating E-Cadherin and inhibiting ICAM-1
Kusmardi Kusmardi, Elvan Wiyarta, Numlil Khaira Rusdi, Andi Muh. Maulana, Ari Estuningtyas, Hadi Sunaryo
F1000Research.2021; 10: 902. CrossRef - CD44 Variant Exon 6 Isoform Expression as a Potential Predictor of Lymph Node Metastasis in Invasive Breast Carcinoma of No Special Type
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Elvan Wiyarta, Kristina A. Bethania, Rakesh Sathish Nair
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Correlation between CD 34 and CD 68 expression in placental malaria with maternal anemia
Primariadewi Rustamadji, Muhammad Takbir, Puspita Eka Wuyung, Kusmardi Kusmardi, Elvan Wiyarta
Tropical Parasitology.2021; 11(2): 92. CrossRef
- Association of Src with Nottingham Prognostic Index in Breast Cancer: Implications for Breast Cancer Prognostication
- Histologically confirmed distant metastatic urothelial carcinoma from the urinary bladder: a retrospective review of one institution’s 20-year experience
- Youngeun Yoo, Junghye Lee, Heae Surng Park, Min-Sun Cho, Sun Hee Sung, Sanghui Park, Euno Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):94-101. Published online December 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.10.19
- 6,245 View
- 155 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) accounts for roughly 90% of bladder cancer, and has a high propensity for diverse differentiation. Recently, certain histologic variants of UC have been recognized to be associated with unfavorable clinical outcomes. Several UC studies have also suggested that tumor budding is a poor prognostic marker. Distant metastasis of UC after radical cystectomy is not uncommon. However, these metastatic lesions are not routinely confirmed with histology.
Methods
We investigated the histopathologic features of 13 cases of UC with biopsy-proven distant metastases, with a special emphasis on histologic variants and tumor budding.
Results
Lymph nodes (6/13, 46%) were the most common metastatic sites, followed by the lung (4/13, 31%), liver (4/13, 31%), and the adrenal gland (2/13, 15%). The histologic variants including squamous (n=1), micropapillary (n=4), and plasmacytoid (n=1) variants in five cases of UC. Most histologic variants (4/5, 80%) of primary UCs appeared in the metastatic lesions. In contrast, high-grade tumor budding was detected in six cases (46%), including one case of non-muscle invasive UC. Our study demonstrates that histologic variants are not uncommonly detected in distant metastatic UCs. Most histologic variants seen in primary UCs persist in the distant metastatic lesions. In addition, high-grade tumor budding, which occurs frequently in primary tumors, may contribute to the development of distant metastasis.
Conclusions
Therefore, assessing the presence or absence of histologic variants and tumor budding in UCs of the urinary bladder, even in non-muscle invasive UCs, may be useful to predict distant metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do Histology and Primary Tumor Location Influence Metastatic Patterns in Bladder Cancer?
Hyung Kyu Park
Current Oncology.2023; 30(10): 9078. CrossRef
- Do Histology and Primary Tumor Location Influence Metastatic Patterns in Bladder Cancer?
- Lymph node size and its association with nodal metastasis in ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
- Jaehoon Shin, Seungbeom Shin, Jae Hoon Lee, Ki Byung Song, Dae Wook Hwang, Hyoung Jung Kim, Jae Ho Byun, HyungJun Cho, Song Cheol Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):387-395. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.23
- 11,580 View
- 130 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although lymph node metastasis is a poor prognostic factor in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), our understanding of lymph node size in association with PDAC is limited. Increased nodal size in preoperative imaging has been used to detect node metastasis. We evaluated whether lymph node size can be used as a surrogate preoperative marker of lymph node metastasis.
Methods
We assessed nodal size and compared it to the nodal metastatic status of 200 patients with surgically resected PDAC. The size of all lymph nodes and metastatic nodal foci were measured along the long and short axis, and the relationships between nodal size and metastatic status were compared at six cutoff points.
Results
A total of 4,525 lymph nodes were examined, 9.1% of which were metastatic. The mean size of the metastatic nodes (long axis, 6.9±5.0 mm; short axis, 4.3±3.1 mm) was significantly larger than that of the non-metastatic nodes (long axis, 5.0±4.0 mm; short axis, 3.0±2.0 mm; all p<.001). Using a 10 mm cutoff, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, overall accuracy, and area under curve was 24.8%, 88.0%, 17.1%, 82.3%, and 0.60 for the long axis and 7.0%, 99.0%, 40.3%, 90.6%, and 0.61 for the short axis, respectively.
Conclusions
The metastatic nodes are larger than the non-metastatic nodes in PDAC patients. However, the difference in nodal size was too small to be identified with preoperative imaging. The performance of preoperative radiologic imaging to predict lymph nodal metastasis was not good. Therefore, nodal size cannot be used a surrogate preoperative marker of lymph node metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Radiomics for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
炜枫 潘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(07): 432. CrossRef - Preoperative MRI and CA19-9 for predicting occult lymph node metastasis in small pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (≤ 2 cm)
Qiying Tang, Lei Li, Zhiwei Pan, Jianbo Li, Xiaolan Huang, Mengsu Zeng, Haitao Sun, Jianjun Zhou
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual-tracer fluorescence imaging and surgical resection of metastatic lymph nodes in breast cancer: sensitivity, specificity, and first-in-human results
Ziyang Wang, Bo Dai, Jian Zhang, Yang Wu, Yunlong Li, Ying Cao, Qi You, Wei Wang, Sunil Singhal, Shuming Nie, Christopher J. Butch, Huiming Cai, Yiqing Wang
Med-X.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological Features of Cervical Lymphadenopathy of Children Less Than 15 Years Old: A Hospital-based Study
Ali Kosari, Shokouh Taghipour Zahir, Saadat Eslami
Journal of Head & Neck Physicians and Surgeons.2025; 13(2): 180. CrossRef - Long‐term outcomes of neoadjuvant gemcitabine, nab‐paclitaxel, and S1 (GAS) in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer with arterial contact: Results from a phase II trial
Kenichiro Uemura, Naru Kondo, Takeshi Sudo, Tatsuaki Sumiyoshi, Ryuta Shintakuya, Kenjiro Okada, Kenta Baba, Takumi Harada, Yoshiaki Murakami, Shinya Takahashi
Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sciences.2024; 31(5): 351. CrossRef - Comparison of MRI and CT-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Piaoe Zeng, Chao Qu, Jianfang Liu, Jingjing Cui, Xiaoming Liu, Dianrong Xiu, Huishu Yuan
Acta Radiologica.2023; 64(7): 2221. CrossRef - Prevalence of Adenopathy at Chest Computed Tomography After Vaccination for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Georgeann McGuinness, Jeffrey B. Alpert, Geraldine Brusca-Augello, Lea Azour, Jane P. Ko, Farah Tamizuddin, Elliott K. Gozansky, William H. Moore
Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography.2023; 47(1): 50. CrossRef - Predictive role of radiomics features extracted from preoperative cross-sectional imaging of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in detecting lymph node metastasis: a systemic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, Seyedeh Panid Madani, Haneyeh Shahbazian, Golnoosh Ansari, Alireza Mohseni, Ali Borhani, Shadi Afyouni, Ihab R. Kamel
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 48(8): 2570. CrossRef - Regional lymph node metastasis detected on preoperative CT and/or FDG-PET may predict early recurrence of pancreatic adenocarcinoma after curative resection
Ja Kyung Yoon, Mi-Suk Park, Seung-Seob Kim, Kyunghwa Han, Hee Seung Lee, Seungmin Bang, Ho Kyoung Hwang, Sang Hyun Hwang, Mijin Yun, Myeong-Jin Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of CA 19.9 in the Management of Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: State of the Art and Future Perspectives
Alessandro Coppola, Vincenzo La Vaccara, Tommaso Farolfi, Michele Fiore, Roberto Cammarata, Sara Ramella, Roberto Coppola, Damiano Caputo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(9): 2091. CrossRef - Evaluation of the 8th Edition AJCC Staging System for the Clinical Staging of Pancreatic Cancer
Huapyong Kang, Seung-seob Kim, Min Je Sung, Jung Hyun Jo, Hee Seung Lee, Moon Jae Chung, Jeong Youp Park, Seung Woo Park, Si Young Song, Mi-Suk Park, Seungmin Bang
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4672. CrossRef - Does direct invasion of peripancreatic lymph nodes impact survival in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma? A retrospective dual-center study
Daisuke Hashimoto, Sohei Satoi, Mitsuaki Ishida, Kenji Nakagawa, Masaya Kotsuka, Tadataka Takagi, Hironori Ryota, Taichi Terai, Tatsuma Sakaguchi, Minako Nagai, So Yamaki, Takahiro Akahori, Tomohisa Yamamoto, Mitsugu Sekimoto, Masayuki Sho
Pancreatology.2021; 21(5): 884. CrossRef - CA19.9 Serum Level Predicts Lymph-Nodes Status in Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis
Alessandro Coppola, Vincenzo La Vaccara, Michele Fiore, Tommaso Farolfi, Sara Ramella, Silvia Angeletti, Roberto Coppola, Damiano Caputo
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in Radiomics for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- Sarcoma metastasis to the pancreas: experience at a single institution
- Miseon Lee, Joon Seon Song, Seung-Mo Hong, Se Jin Jang, Jihun Kim, Ki Byung Song, Jae Hoon Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):220-227. Published online April 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.03.04
- 8,654 View
- 167 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Reports of metastatic sarcoma to the pancreas are limited. We reviewed the clinicopathologic characteristics of such cases.
Methods
We reviewed 124 cases of metastatic tumors to the pancreas diagnosed at Asan Medical Center between 2000 and 2017.
Results
Metastatic tumors to the pancreas consisted of 111 carcinomas (89.5%), 12 sarcomas (9.6%), and one melanoma (0.8%). Primary sarcoma sites were bone (n = 4); brain, lung, and soft tissue (n = 2 for each); and the uterus and pulmonary vein (n = 1 for each). Pathologically, the 12 sarcomas comprised 2 World Health Organization grade III solitary fibrous tumors/hemangiopericytomas, and one case each of synovial sarcoma, malignant solitary fibrous tumor, undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma, osteosarcoma, mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, intimal sarcoma, myxofibrosarcoma, myxoid liposarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, subtype uncertain, and high-grade spindle-cell sarcoma of uncertain type. The median interval between primary cancer diagnosis and pancreatic metastasis was 28.5 months. One case manifested as a solitary pancreatic osteosarcoma metastasis 15 months prior to detection of osteosarcoma in the femur and was initially misdiagnosed as sarcomatoid carcinoma of the pancreas.
Conclusions
The metastatic sarcoma should remain a differential diagnosis when spindle-cell malignancy is found in the pancreas, even for solitary lesions or in patients without prior history. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic synovial sarcoma masquerading as primary neuroendocrine tumor of pancreas: a diagnostic conundrum
Sherrin Jacob, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Rajni Yadav, Anany Gupta, Samagra Agarwal, Shamim A. Shamim, Sameer Rastogi, Adarsh Barwad, Deepali Jain
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2025; 18(3): 499. CrossRef - Metastatic tumors to the pancreas: An institutional experience
Matthew Romanish, Rana Naous
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 79: 152528. CrossRef - Visceral Metastases of Osteosarcoma in the Hepatopancreatobiliary System
Anna Hohensteiner, Lars Kowalscheck, Kevin Döring, Gerhard Martin Hobusch, Raphael Johannes Tanios, Oliver Strobel, Reinhard Windhager, Philipp Theodor Funovics
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8702. CrossRef - Metastatic clear cell sarcoma of the pancreas: A sporadic cancer
Vittorio Gebbia, Carlo Carnaghi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(18): 3291. CrossRef - Metastatic clear cell sarcoma of the pancreas: An overview
Rachid Ait Addi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(29): 6262. CrossRef - Myxofibrosarcoma with pancreatic metastasis, a case report and literature reviews
Kodai ABE, Yasutomo SEKIDO, Yasuo KABESHIMA
Suizo.2024; 39(5): 334. CrossRef - Metástasis pancreática de sarcoma, un hallazgo infrecuente
Daniel Aparicio-López, Jorge Chóliz-Ezquerro, Carlos Hörndler-Algárate, Mario Serradilla-Martín
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2023; 46(5): 376. CrossRef - Pancreatic metastasis from sarcoma, an infrequent finding
Daniel Aparicio-López, Jorge Chóliz-Ezquerro, Carlos Hörndler-Algárate, Mario Serradilla-Martín
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2023; 46(5): 376. CrossRef - Acute pancreatitis secondary to osteosarcoma metastasis
Pablo Salmón Olavarría, Ana Gordo Ortega, Maren Eizagirre Ubegun, Verónica Ubieto Capella, Elena Carracedo Vega, Juan Carrascosa Gil, David Ruiz-Clavijo García
Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - First Recurrence of Synovial Sarcoma Presenting With Solitary Pancreatic Mass
Raja R Narayan, Greg W Charville, Daniel Delitto, Kristen N Ganjoo
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intravenous Leiomyosarcoma of the Lower Extremity: As Peripheral as It Gets
Levent F Umur, Selami Cakmak, Mehmet Isyar, Hamdi Tokoz
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Could the burden of pancreatic cancer originate in childhood?
Smaranda Diaconescu, Georgiana Emmanuela Gîlcă-Blanariu, Silvia Poamaneagra, Otilia Marginean, Gabriela Paduraru, Gabriela Stefanescu
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(32): 5322. CrossRef - Staged Surgical Resection of Primary Pulmonary Synovial Sarcoma with Synchronous Multiple Pancreatic Metastases: Report of a Rare Case and Review of the Literature
Panagiotis Dorovinis, Nikolaos Machairas, Stylianos Kykalos, Paraskevas Stamopoulos, George Agrogiannis, Nikolaos Nikiteas, Georgios C. Sotiropoulos
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2021; 52(3): 1151. CrossRef
- Metastatic synovial sarcoma masquerading as primary neuroendocrine tumor of pancreas: a diagnostic conundrum
- Prognostic Role of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungseek Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):331-338. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.07
- 9,174 View
- 131 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study is to elucidate the clinicopathological significances, including the prognostic role, of metastatic lymph node ratio (mLNR) and tumor deposit diameter in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) through a retrospective review and meta-analysis.
Methods
We categorized the cases into high (≥ 0.44) and low mLNR (< 0.44) and investigated the correlations with clinicopathological parameters in 64 PTCs with neck level VI lymph node (LN) metastasis. In addition, meta-analysis of seven eligible studies was used to investigate the correlation between mLNR and survival.
Results
Among 64 PTCs with neck level VI LN metastasis, high mLNR was found in 34 PTCs (53.1%). High mLNR was significantly correlated with macrometastasis (tumor deposit diameter ≥ 0.2 cm), extracapsular spread, and number of metastatic LNs. Based on linear regression test, mLNR was significantly increased by the largest LN size but not the largest metastatic LN (mLN) size. High mLNR was not correlated with nuclear factor κB or cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression, Ki-67 labeling index, or other pathological parameters of primary tumor. Based on meta-analysis, high mLNR significantly correlated with worse disease-free survival at the 5-year and 10-year follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 4.866; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.527 to 6.714 and HR, 5.769; 95% CI, 2.951 to 11.275, respectively).
Conclusions
Our data showed that high mLNR significantly correlated with worse survival, macrometastasis, and extracapsular spread of mLNs. Further cumulative studies for more detailed criteria of mLNR are needed before application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Chang Liu, Shangjie Yang, Tian Xue, Qian Zhang, Yanjing Zhang, Yufang Zhao, Guolin Yin, Xiaohui Yan, Ping Liang, Liping Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of a Nomogram Based on Ultrasound Radiomics, Clinical Factors, and Enhanced Ultrasound Features for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Lei Gao, Xiuli Wen, Guanghui Yue, Hui Wang, Ziqing Lu, Beibei Wu, Zhihong Liu, Yuming Wu, Dongmei Lin, Shijian Yi, Wei Jiang, Yi Hao
Ultrasonic Imaging.2025; 47(2): 93. CrossRef - Lymph Node Metastasis Ratio: Prognostic Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ana Rita Ferreira, Diogo Ramalho, Daniela Martins, Andreia Amado, Susana Graça, Carlos Soares, Bela Pereira, Maria João Oliveira, Manuel Oliveira, Antónia Póvoa
Indian Journal of Surgery.2025; 87(6): 1047. CrossRef - CD105 (Endoglin) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
İlker Çordan, Tuğba Günler
Clinical Endocrinology.2025; 103(4): 596. CrossRef - Application and subgroup analysis of competing risks model based on different lymph node staging systems in differentiated thyroid cancer
Zhe Xu Cao, Jiang Sheng Huang, Ming Ming Wang
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(5): 1927. CrossRef - Цитологічне прогнозування агресії раку щитоподібної залози як новий перспективний напрямок у клінічній тиреоїдології
H.V. Zelinska
Endokrynologia.2024; 29(4): 363. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin expression, Ki-67 index, and lymph node ratio in the prognostic assessment of papillary thyroid cancer
Helene Lindfors, Marie Karlsen, Ellinor Karlton, Jan Zedenius, Catharina Larsson, Catharina Ihre Lundgren, C. Christofer Juhlin, Ivan Shabo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Node Metastasis as an Independent Factor of Worse Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Renan Aguera Pinheiro, Ana Kober Leite, Beatriz Godoi Cavalheiro, Evandro Sobroza de Mello, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Leandro Luongo Matos
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 943. CrossRef - A High-Quality Nomogram for Predicting Lung Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study
WenYi Wang, JiaJing Liu, XiaoFan Xu, LiQun Huo, XuLin Wang, Jun Gu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Low Lymph Node Yield
Il Ku Kang, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 2947. CrossRef - Superiority of metastatic lymph node ratio over number of node metastases and TNM/AJCC N classification in predicting cancer‐specific survival in medullary thyroid cancer
Andreas Machens, Kerstin Lorenz, Frank Weber, Henning Dralle
Head & Neck.2022; 44(12): 2717. CrossRef - Value of Combining Clinical Factors, Conventional Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features in Preoperative Prediction of Central Lymph Node Metastases of Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Yanfang Wang, Fang Nie, Guojuan Wang, Ting Liu, Tiantian Dong, Yamin Sun
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3403. CrossRef - Atypical Histiocytoid Cells and Multinucleated Giant Cells in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid Predict Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Ji Eun Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 816. CrossRef - Patients Aged ≥55 Years With Stage T1-2N1M1 Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Should Be Downstaged in the Eighth Edition AJCC/TNM Cancer Staging System
Zeming Liu, Sichao Chen, Yihui Huang, Di Hu, Min Wang, Wei Wei, Chao Zhang, Wen Zeng, Liang Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Colorectal Cancers: Comparison Depending on Tumor Location
Jung-Soo Pyo, Young-Min Shin, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1812. CrossRef
- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Malignant Pleural Effusion from Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Report with Unusual Cytologic Findings
- Jinyoung Jeon, Tae-Jung Kim, Hong Sik Park, Kyo-Young Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):257-261. Published online June 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.05.08
- 11,309 View
- 132 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We present a case of 55-year-old man who complained of dyspnea and sputum for a month. He was an ex-smoker with a history of prostate cancer and pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest radiographs revealed bilateral pleural effusions of a small to moderate amount. Pigtail catheters were inserted for drainage. The pleural fluid consisted of large clusters and tightly cohesive groups of malignant cells, which however could not be ascribed to prostate cancer with certainty. We performed immunocytochemical panel studies to determine the origin of cancer metastasis. The immunostaining results were positive for prostate-specific antigen, alpha-methylacyl-coenzyme A racemase, and Nkx 3.1, consistent with prostate cancer. Pleural effusion associated with prostate cancer is rare. To our knowledge, this is the first case report in Korea to describe cytologic features of malignant pleural effusion associated with prostate cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pleural Metastasis as an Initial Presentation of Prostate Cancer: Case Report and Literature Review
Katarzyna Skrobisz, Kevin Miszewski, Laura Miszewska, Michał Bieńkowski, Marcin Matuszewski, Michał Studniarek
Diagnostics.2025; 15(6): 666. CrossRef - EBUS-TBNA pleural biopsy reveals prostate cancer metastasis: A rare case report and review of the literature
Fotios Sampsonas, Dimitrios Komninos, Vasilina Sotiropoulou, Matthaios Katsaras, Dimitra Gkanetsou, Ourania Papaioannou, Panagiota Tsiri, Vasiliki Tzelepi, Argyrios Tzouvelekis
Pneumon.2024; 37(2): 1. CrossRef - Cytopathological Features of Extensive Bilateral Pleural Effusions in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Report of a Rare Case
Hehua Huang, Caroline Yap
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bilateral pleural effusion: etiology, diagnostics
N. A. Stogova
PULMONOLOGIYA.2022; 32(6): 885. CrossRef - Rare Metastatic Prostate Cancer Mimicking Lymphoma with Malignant Pleural Effusion
Tung Liu, En Meng, Yu-Chun Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao, Yi-Ming Chang
Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 42(1): 46. CrossRef
- Pleural Metastasis as an Initial Presentation of Prostate Cancer: Case Report and Literature Review
- Prognostic Utility of Histological Growth Patterns of Colorectal Lung Oligometastasis
- Son Jae Yeong, Min Gyoung Pak, Hyoun Wook Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):98-104. Published online February 12, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.12.27
- 7,857 View
- 127 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Patients with resectable colorectal lung oligometastasis (CLOM) demonstrate a heterogeneous oncological outcome. However, the parameters for predicting tumor aggressiveness have not yet been fully investigated in CLOM. This study was performed to determine the prognostic value of histological growth patterns in patients who underwent surgery for CLOM.
Methods
The study included 92 patients who were diagnosed with CLOM among the first resection cases. CLOMs grow according to three histological patterns: aerogenous, pushing, and desmoplastic patterns. The growth patterns were evaluated on archival hematoxylin and eosin–stained tissue sections.
Results
The aerogenous pattern was found in 29.4% (n=27) of patients, the pushing pattern in 34.7% (n=32), the desmoplastic pattern in 6.5% (n=6), and a mix of two growth patterns in 29.4% (n=27). The size of the aerogenous pattern was significantly smaller than that of metastases with other patterns (p=.033). Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that patients showing an aerogenous pattern appeared to have a poorer prognosis, which was calculated from the time of diagnosis of the CLOM (p=.044). The 5-year survival rate from the diagnosis of colorectal cancer tended to be lower in patients with an aerogenous pattern than in those who had a non-aerogenous pattern; however, the difference was marginally significant (p=.051). In the multivariate Cox analysis, the aerogenous pattern appeared as an independent predictor of poor overall survival (hazard ratio, 3.122; 95% confidence interval, 1.196 to 8.145; p=.020).
Conclusions
These results suggest that the growth patterns may play a part as a histology-based prognostic parameter for patients with CLOM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predicting liver metastases growth patterns: Current status and future possibilities
Rui Caetano Oliveira, Henrique Alexandrino, Maria Augusta Cipriano, Filipe Caseiro Alves, José Guilherme Tralhão
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2021; 71: 42. CrossRef - Histological growth patterns and molecular analysis of resected colorectal lung metastases
Emanuela Pilozzi, Damiano Fedele, Andrea Montori, Laura Lorenzon, Valentina Peritore, Giorgia Mannocchi, Nikta Bagheri, Chiara Leone, Antonio Palumbo, Michela Roberto, Giulio Ranazzi, Erino Rendina, Genoveffa Balducci, Mohsen Ibrahim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153414. CrossRef
- Predicting liver metastases growth patterns: Current status and future possibilities
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to Pleural Fluid: A Case Report
- Ye-Young Rhee, Soo Hee Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):206-209. Published online November 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.11.10
- 8,133 View
- 130 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare aggressive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin that shows locoregional or distant metastasis. Metastasis of MCC to body cavity effusion is extremely rare; only three cases have been reported so far. Metastatic MCC in effusion cytology shows small blue round cells with fine stippled chromatin like other small blue round cell tumors such as small cell lung carcinoma or lymphoma. The diagnosis of metastatic MCC can grant patients good chances at recently advanced therapeutic options. Here, we present a case of metastatic MCC to pleural effusion with characteristic single file-like pattern.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pleural Metastasis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Sina Maghsoudlou, Marc Pusztaszeri, Mauro Saieg
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(6): 308. CrossRef - Merkel cell carcinoma presenting as a malignant pleural effusion post‐COVID‐19 hospitalization: A case report and literature review
Joel Lanceta, Mesut Toprak, Oana C. Rosca
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology coupled with immunocytochemistry identifies Merkel cell carcinoma: A rare intruder in the cerebrospinal fluid
Reetu Kundu, Brijdeep Singh, Pranab Dey
Cytopathology.2022; 33(4): 530. CrossRef - Derrame pleural por carcinoma de células de Merkel
María J. Soler-Sempere, María O. Alvárez-Fernández, Isabel Padilla-Navas, María Cabezas-Macián, Jose F. Sánchez-Hernández, Eduardo García-Pachón
Archivos de Bronconeumología.2021; 57(11): 715. CrossRef - A rare case of pleural localisation of both metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
Elise Kaspi, Shirley Fritz, Julien Colle, Florent Amatore, Diane Frankel, Patrice Roll
Cytopathology.2021; 32(3): 367. CrossRef - Merkel cell carcinoma with pleural effusion
María J. Soler-Sempere, María O. Alvárez-Fernández, Isabel Padilla-Navas, María Cabezas-Macián, Jose F. Sánchez-Hernández, Eduardo García-Pachón
Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition).2021; 57(11): 715. CrossRef
- Pleural Metastasis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Aggressive Supratentorial Ependymoma, RELA Fusion-Positive with Extracranial Metastasis: A Case Report
- Seong-Ik Kim, Yoojin Lee, Seung Ki Kim, Hyoung Jin Kang, Sung-Hye Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(6):588-593. Published online November 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.10
- 12,455 View
- 231 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ependymoma is the third most common pediatric primary brain tumor. Ependymomas are categorized according to their locations and genetic abnormalities, and these two parameters are important prognostic factors for patient outcome. For supratentorial (ST) ependymomas, RELA fusion-positive ependymomas show a more aggressive behavior than YAP1 fusion-positive ependymomas. Extracranial metastases of intra-axial neuroepithelial tumors are extremely rare. In this paper, we report a case of aggressive anaplastic ependymoma arising in the right frontoparietal lobe, which had genetically 1q25 gain, CDKN2A homozygous deletion, and L1CAM overexpression. The patient was a 10-year-old boy who underwent four times of tumor removal and seven times of gamma knife surgery. Metastatic loci were scalp and temporalis muscle overlying primary operation site, lung, liver, buttock, bone, and mediastinal lymph nodes. He had the malignancy for 10 years and died. This tumor is a representative case of RELA fusion-positive ST ependymoma, showing aggressive behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic Supratentorial Ependymoma: A Case Presentation and Systematic Review of the Literature
Khanh Tan Tran, József Virga, Nour Kurdi, Krisztina Ajna Chalupa, Bernadett Szűcs, Álmos Klekner, Attila Mokanszki, Judit Bedekovics
Neuropathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Polymorphous low-grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young and supratentorial ependymoma diagnosed in an adult male
Cynthia Y. Xu, Craig A. Beers, Jian-Qiang Lu, Crystal L. Hann, Ronald C. Ramos
Frontiers in Neurology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Pediatric Case of Extraneural Subcutaneous Metastasis of Ependymoma
Chika Ueno, Masayuki Tanaka, Ayako Yamazaki, Shuichi Yamamoto
Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.2023; 45(8): e1025. CrossRef - Patterns of Extraneural Metastases in Children With Ependymoma
Priya P. Chan, Nicholas S. Whipple, Biswarathan Ramani, David A. Solomon, Holly Zhou, Luke L. Linscott, John R.W. Kestle, Carol S. Bruggers
Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.2023; 45(2): e272. CrossRef - Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features of Zinc Finger Translocation Associated-RELA Fusion Ependymoma Compared to Its Wild-Type Counterpart
Hanbing Shao, Ni Chen, Xiaorui Su, Linmao Zheng, Xibiao Yang, Xinyue Wan, Simin Zhang, Qiaoyue Tan, Shuang Li, Qiyong Gong, Qiang Yue
World Neurosurgery.2023; 175: e1283. CrossRef - A clinicopathological analysis of supratentorial ependymoma, ZFTA fusion-positive: utility of immunohistochemical detection of CDKN2A alterations and characteristics of the immune microenvironment
Naohito Hashimoto, Tomonari Suzuki, Keisuke Ishizawa, Sumihito Nobusawa, Hideaki Yokoo, Ryo Nishikawa, Masanori Yasuda, Atsushi Sasaki
Brain Tumor Pathology.2023; 40(3): 163. CrossRef - Recurrent intracranial anaplastic ependymoma with late‐onset giant scalp metastasis
Gianluca Scalia, Gianluca Ferini, Bipin Chaurasia, Francesca Graziano, Stefano Priola, Paolo Amico, Giuseppe Emmanuele Umana
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Extra-Neural Metastases From Primary Intracranial Ependymomas: A Systematic Review
Paolo Palmisciano, Gianluca Ferini, Fabio Barone, Vishal Chavda, Fabrizio Romano, Paolo Amico, Donatella Emmanuele, Giovanni F. Nicoletti, Gianluca Pompili, Giuseppe Roberto Giammalva, Rosario Maugeri, Domenico Gerardo Iacopino, Lidia Strigari, Tseng T. Y
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes to pediatric brain tumors in 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system
Murat Alp Oztek, Sakura M. Noda, Erin K. Romberg, Bonnie L. Cole, Jason N. Wright, Gisele E. Ishak, Francisco A. Perez
Pediatric Radiology.2022; 53(3): 523. CrossRef - Delineation of molecular characteristics in pediatric PFA ependymoma involving rare osseous and pulmonary metastases: A case report and literature review
Mading Zhou, Leiming Wang, Peng Sun, Yutong Liu, Ge Chen, Gao Zeng
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SeekFusion - A Clinically Validated Fusion Transcript Detection Pipeline for PCR-Based Next-Generation Sequencing of RNA
Jagadheshwar Balan, Garrett Jenkinson, Asha Nair, Neiladri Saha, Tejaswi Koganti, Jesse Voss, Christopher Zysk, Emily G. Barr Fritcher, Christian A. Ross, Caterina Giannini, Aditya Raghunathan, Benjamin R. Kipp, Robert Jenkins, Cris Ida, Kevin C. Halling,
Frontiers in Genetics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology of Extraneural Metastases of Nonhematolymphoid Primary Central Nervous System Tumors: Six Cases with Histopathological Correlation and Literature Update
Joerg Schwock, Lorna Mirham, Zeina Ghorab
Acta Cytologica.2021; 65(6): 529. CrossRef - Mutation profiling of anaplastic ependymoma grade III by Ion Proton next generation DNA sequencing
Ejaz Butt, Sabra Alyami, Tahani Nageeti, Muhammad Saeed, Khalid AlQuthami, Abdellatif Bouazzaoui, Mohammad Athar, Zainularifeen Abduljaleel, Faisal Al-Allaf, Mohiuddin Taher
F1000Research.2020; 8: 613. CrossRef - Cortically based cystic supratentorial RELA fusion-positive ependymoma: a case report with unusual presentation and appearance and review of literature
Yasmine T. Sallam, Qi Zhang, Sachin K. Pandey
Radiology Case Reports.2020; 15(12): 2495. CrossRef - Mutation profiling of anaplastic ependymoma grade III by Ion Proton next generation DNA sequencing
Muhammad Butt, Sabra Alyami, Tahani Nageeti, Muhammad Saeed, Khalid AlQuthami, Abdellatif Bouazzaoui, Mohammad Athar, Zainularifeen Abduljaleel, Faisal Al-Allaf, Mohiuddin Taher
F1000Research.2019; 8: 613. CrossRef - Extraneural metastatic anaplastic ependymoma: a systematic review and a report of metastases to bilateral parotid glands
Gray Umbach, Tarek Y El Ahmadieh, Aaron R Plitt, Salah G Aoun, Om J Neeley, Kristopher A Lyon, Ekokobe Fonkem, Jack M Raisanen, Justin A Bishop, Zabi Wardak, Toral R Patel, Larry Myers, Bruce E Mickey
Neuro-Oncology Practice.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - RELA Fusion in Supratentorial Extraventricular Ependymomas: A Morphologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Study of 43 Cases
Leiming Wang, Lina Liu, Hainan Li, PeiPei Wang, Zeliang Hu, Yukui Wei, Ming Zhang, Wenjuan Wen, Zhi Li, Li Liu, Lihong Zhao, Dehong Lu, Lianghong Teng
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 43(12): 1674. CrossRef - Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition–related transcription factors are up-regulated in ependymomas and correlate with a poor prognosis
Prit Benny Malgulwar, Aruna Nambirajan, Pankaj Pathak, Madhu Rajeshwari, Vaishali Suri, Chitra Sarkar, Manmohan Singh, Mehar Chand Sharma
Human Pathology.2018; 82: 149. CrossRef
- Metastatic Supratentorial Ependymoma: A Case Presentation and Systematic Review of the Literature
- Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression and Its Correlation with Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyo Jung An, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jeong-Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Dong Chul Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim, Jin Pyeong Kim, Eun Jung Jung, Dae Hyun Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):9-13. Published online October 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.07.26
- 10,635 View
- 282 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The immunotherapeutic role of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in life expectancy in many cancers has been highlighted. However, data regarding PD-L1 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) are limited. In this study, we describe the PD-L1 and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) expressions in PTC and analyze their correlation with lymph node (LN) metastasis.
Methods
Clinicopathological data were obtained from 116 patients with PTC who were treated in Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea in 2009. Tissue microarray blocks were made using representative paraffin blocks of classical PTCs excluding follicular variants. Two pathologists graded the proportion and intensity of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression in both tumor and inflammatory cells. According to their proportions, positive PTC cells were scored as negative (0%), grade 1 (1%–50%), and grade 2 (51%–100%). Similarly, positive inflammatory cells were graded as negative (0%), grade 1 (1%–10%), and grade 2 (11%–20%). The intensity of each protein expression was simplified as positive or negative.
Results
A statistically significant correlation exists between the proportions of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression both in papillary carcinoma (p=.001) and peritumoral lymphoid cells in the thyroid (p<.001). In addition, the proportion of PD-L1 expression in PTC cells was closely related to metastatic LNs (p=.036).
Conclusions
PD-L1 is a valuable predictive marker for LN metastasis in PTC. Immunomodulating therapies that inhibit PD-L1 might be an option for patients with LN metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study of PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Correlation to the Clinicopathologic Characteristics
Asmaa Gamal Mohamed El Sayed, Dina Ragab Diab Ibrahim, Mahmoud Mahmoud El-Leithy, Mai Mohamed Ali Ezz El Din, Hoda Hassan Abou Gabal, Reham Mohamed Faheim
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Xiaoteng Sun, Zhengyan He, Weijie Yu, Baoyuan Li, Xinmiao Xu, Xiaoqin Zhang, Minglong Yin
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunotyping of thyroid cancer for clinical outcomes and implications
Jin Xu, Zhen Luo, Dayong Xu, Mujing Ke, Cheng Tan
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of PD-L1, TERT promoter mutations, and BRAFV600E mutation in poorly differentiated, differentiated high grade thyroid carcinoma and anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid: our institutional experience
Alessia Piermattei, Giuseppe Migliara, Angela Feraco, Carmine Bruno, Luisa Cioni, Qianqian Zhang, Belen Padial-Urtueta, Elisabetta Merenda, Guido Fadda, Marco Raffaelli, Luigi Maria Larocca, Antonino Mule, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Esther Diana Rossi
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(3): 605. CrossRef - Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis with Oncocytic Metaplasia Influences PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Vitor Barreto Santana, Vitória Machado Krüger, Maria Cristina Yunes Abrahão, Pietru Lentz Martins Cantú, Rosicler Luzia Brackmann, Gisele Moroni Pandolfi, Liane Scheffler Marisco, Gabriela Remonatto, Luciana Adolfo Ferreira, Marcia Silveira Graudenz
Head and Neck Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring markers of immunoresponsiveness in papillary thyroid carcinoma and future treatment strategies
Atish Mohanty, Michelle Afkhami, Amanda Reyes, Rebecca Pharaon, Holly Yin, Haiqing Li, Dana Do, Diana Bell, Arin Nam, Sue Chang, Thomas Gernon, Robert Kang, Arya Amini, Sagus Sampath, Prakash Kulkarni, Raju Pillai, Vicky Villaflor, Ravi Salgia, Ellie Magh
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2024; 12(7): e008505. CrossRef - Update regarding the role of PD-L1 in oncocytic thyroid lesions on cytological samples
Marco Dell'Aquila, Pietro Tralongo, Alessia Granitto, Maurizio Martini, Sara Capodimonti, Mariangela Curatolo, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Guido Fadda, Celestino Pio Lombardi, Maco Raffaelli, Liron Pantanowitz, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Dia
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2023; 76(10): 671. CrossRef - Analysis of anti‐apoptotic PVT1 oncogene and apoptosis‐related proteins (p53, Bcl2, PD‐1, and PD‐L1) expression in thyroid carcinoma
Afaf T. Ibrahiem, Amin K. Makhdoom, Khalid S. Alanazi, Abdulaziz M. Alanazi, Abdulaziz M. Mukhlef, Saad H. Elshafey, Eman A. Toraih, Manal S. Fawzy
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - EphA10 drives tumor progression and immune evasion by regulating the MAPK/ERK cascade in lung adenocarcinoma
Wenyue Zhao, Lu Liu, Xuehao Li, Shun Xu
International Immunopharmacology.2022; 110: 109031. CrossRef - Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Minimizes Lymph Node Metastasis in BRAF Mutant Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Peter P. Issa, Mahmoud Omar, Yusef Buti, Chad P. Issa, Bert Chabot, Christopher J. Carnabatu, Ruhul Munshi, Mohammad Hussein, Mohamed Aboueisha, Mohamed Shama, Ralph L. Corsetti, Eman Toraih, Emad Kandil
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 2051. CrossRef - Expression of β-Catenin in Thyroid Neoplasms (Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study)
Mohamed Sherif Ismail, Amr Mousa Abdel Gawad Mousa, Mohammed Faisal Darwish, M. Mostafa Salem, Randa Said
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 1565. CrossRef - Identification and validation of an immune-related prognostic signature and key gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Rujia Qin, Chunyan Li, Xuemin Wang, Zhaoming Zhong, Chuanzheng Sun
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - PD‐L1 and thyroid cytology: A possible diagnostic and prognostic marker
Marco Dell’Aquila, Alessia Granitto, Maurizio Martini, Sara Capodimonti, Alessandra Cocomazzi, Teresa Musarra, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Celestino Pio Lombardi, Guido Fadda, Liron Pantanowitz, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Diana Rossi
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(3): 177. CrossRef - Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Is a Potential Biomarker of Disease-Free Survival in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of PD-L1 Immunoexpression in Follicular Epithelial Derived Thyroid Carcinoma
Ilaria Girolami, Liron Pantanowitz, Ozgur Mete, Matteo Brunelli, Stefano Marletta, Chiara Colato, Pierpaolo Trimboli, Anna Crescenzi, Massimo Bongiovanni, Mattia Barbareschi, Albino Eccher
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(3): 291. CrossRef - Regression of Papillary Thyroid Cancer during Nivolumab for Renal Cell Cancer
Andrea Palermo, Andrea Napolitano, Daria Maggi, Anda Mihaela Naciu, Gaia Tabacco, Silvia Manfrini, Anna Crescenzi, Chiara Taffon, Francesco Pantano, Bruno Vincenzi, Guiseppe Tonini, Daniele Santini
European Thyroid Journal.2020; 9(3): 157. CrossRef - A potential biomarker hsa-miR-200a-5p distinguishing between benign thyroid tumors with papillary hyperplasia and papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xian Wang, Shan Huang, Xiaocan Li, Dongrui Jiang, Hongzhen Yu, Qiang Wu, Chaobing Gao, Zhengsheng Wu, Yi-Hsien Hsieh
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(7): e0200290. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Emerging from Hashimoto Thyroiditis Demonstrates Increased PD-L1 Expression, Which Persists with Metastasis
Daniel Lubin, Ezra Baraban, Amanda Lisby, Sahar Jalali-Farahani, Paul Zhang, Virginia Livolsi
Endocrine Pathology.2018; 29(4): 317. CrossRef - Chemotherapeutic Treatments Increase PD-L1 Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma through EGFR/ERK Activation
Hoi Yan Ng, Jian Li, Lihua Tao, Alfred King-Yin Lam, Kwok Wah Chan, Josephine Mun Yee Ko, Valen Zhuoyou Yu, Michael Wong, Benjamin Li, Maria Li Lung
Translational Oncology.2018; 11(6): 1323. CrossRef
- Study of PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Correlation to the Clinicopathologic Characteristics
- A Rare Case of Aggressive Melanotic Schwannoma Occurred in Spinal Nerve of a 59-Year-Old Male
- Sung-eun Choi, Yoon Jin Cha, Jisup Kim, Hyunseo Cha, Jayeong Seo, Sung-Uk Kuh, Sung-Jun Kim, Se Hoon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(5):505-508. Published online April 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.01.04
- 14,741 View
- 221 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Melanotic schwannoma (MS) is a rare variant of nerve sheath neoplasm that shows ultrastructural and immunophenotypical features of Schwann cells but also has cytoplasmic melanosomes and is reactive for melanocytic markers as well. Unlike conventional schwannoma, which is totally benign, MS has an unpredictable prognosis and is thought to have low-malignant potential. Herein, we present a rare case of recurrent MS in lumbar spine of a 59-year-old male.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The “Pigmented Side” of Nerve Sheaths: Malignant Melanotic Nerve Sheath Tumor
Raduan Ahmed Franca, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Lorenzo Ugga, Rosa Della Monica, Elena D'Avella
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 33(4): 1068. CrossRef - Case Report: Cutaneous melanocytic schwannoma with concomitant melanocytoma in a canine
Olwam H. Monakali, Nicolize O'Dell, Louise van der Weyden
Wellcome Open Research.2024; 8: 364. CrossRef - Intradural Melanotic Schwannoma of the Sacral Spine: An Illustrated Case Report of Diagnostic Conundrum
Jiunn-Kai Chong, Navneet Kumar Dubey, Wen-Cheng Lo
Reports.2024; 7(3): 56. CrossRef - Rare giant retroperitoneal melanotic schwannoma: a case report and literature review
Pan Chen, Junfeng Cheng, Lin Zhang
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Case of Melanotic Schwannoma Occurred Intraosseous of Sacrum: A Literature Review
Xiaobo Yan, Keyi Wang, Nong Lin, Xin Huang, YanBiao Fu, Zhaoming Ye
Orthopaedic Surgery.2023; 15(2): 655. CrossRef - Sporadic spinal psammomatous malignant melanotic nerve sheath tumor: A case report and literature review
Giulio Bonomo, Alessandro Gans, Elio Mazzapicchi, Emanuele Rubiu, Paolo Alimonti, Marica Eoli, Rosina Paterra, Bianca Pollo, Guglielmo Iess, Francesco Restelli, Jacopo Falco, Francesco Acerbi, Marco Paolo Schiariti, Paolo Ferroli, Morgan Broggi
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Case Report: Cutaneous melanocytic schwannoma with concomitant melanocytoma in a canine
Olwam H. Monakali, Nicolize O'Dell, Louise van der Weyden
Wellcome Open Research.2023; 8: 364. CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration cytology of melanotic schwannoma in the submandibular gland
Yu‐Hua Huang, Ying‐Chou Lu, Hsuan‐Ying Huang, Chien‐Chin Chen
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(1): 142. CrossRef - Checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy in refractory malignant melanocytic schwannoma with Carney complex: first evidence of efficacy
Jyoti Bajpai, Akhil Kapoor, Rakesh Jalali, Mrinal M Gounder
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(5): e240296. CrossRef - 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for aggressive melanotic schwannoma of the L3 spinal root
Xun-Ze Shen, Wei Wang, Zhou-Ye Luo
Medicine.2021; 100(8): e24803. CrossRef - Hemorrhagic spinal melanotic schwannoma presenting as acute chest pain: A case report and literature review
Dallas J. Soyland, Dylan R. Goehner, Kayla M. Hoerschgen, Troy D. Gust, Shawn M. Vuong
Surgical Neurology International.2021; 12: 164. CrossRef - Retroperitoneal Recurrence of Melanotic Schwannoma on 18F-FDG PET/CT
Xiangliu OuYang, Lichun Zheng, Xiaoming Zhang
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2021; 46(12): 991. CrossRef - Schwannoma originating from the common iliac artery: a case report
Seung-Myoung Son, Chang Gok Woo
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Intraosseous Melanotic Schwannoma in the Sacrum Mimicking Primary Bone Tumor
Yoshitaka Nagashima, Yusuke Nishimura, Kaoru Eguchi, Takayuki Awaya, Satoshi Yoshikawa, Shoichi Haimoto, Toshihiko Wakabayashi, Masahito Hara
NMC Case Report Journal.2020; 7(3): 107. CrossRef - Extramedullary melanotic schwannoma recurrence in the cervical vertebral arch: a case report and review of the literature
Zongbin Hou, Teng Shi, Guangrun Li, Lin Tian, Xinna Li, Xiaoyang Liu
Journal of International Medical Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Extramedullary malignant melanotic schwannoma of the spine: Case report and an up to date systematic review of the literature
Georgios Solomou, Adikarige Haritha Dulanka Silva, Adrianna Wong, Ute Pohl, Nikolaos Tzerakis
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2020; 59: 217. CrossRef - Melanotic Schwannoma of the Vagina: A Report of a Very Rare Tumor and Review of the Literature
Kofi Effah, Stefan Seidl, Edith Gorges, Patrick Kafui Akakpo
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Melanotic Schwannomas Are Rarely Seen Pigmented Tumors with Unpredictable Prognosis and Challenging Diagnosis
Elif Keskin, Sumeyye Ekmekci, Ozgur Oztekin, Gulden Diniz
Case Reports in Pathology.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- The “Pigmented Side” of Nerve Sheaths: Malignant Melanotic Nerve Sheath Tumor
- Do Helper T Cell Subtypes in Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Play a Role in the Antitumor Effect?
- Seok Woo Yang, Seong-Ho Kang, Kyung Rae Kim, In Hong Choi, Hang Seok Chang, Young Lyun Oh, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):377-384. Published online September 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.25
- 9,994 View
- 108 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is frequently accompanied by lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT). Some reports claim that Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (the clinical form of LT) enhances the likelihood of PTC; however, others suggest that LT has antitumor activity. This study was aimed to find out the relationship between the patterns of helper T cell (Th) cytokines in thyroid tissue of PTC with or without LT and the clinicopathological manifestation of PTC.
Methods
Fresh surgical samples of PTC with (13 cases) or without (10 cases) LT were used. The prognostic parameters (tumor size, extra-thyroidal extension of PTC, and lymph node metastasis) were analyzed. The mRNA levels of two subtypes of Th cytokines, Th1 (tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α], interferon γ [IFN-γ ], and interleukin [IL] 2) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-10), were analyzed. Because most PTC cases were microcarcinomas and recent cases without clinical follow-up, negative or faint p27 immunoreactivity was used as a surrogate marker for lymph node metastasis.
Results
PTC with LT cases showed significantly higher expression of TNF-α (p = .043), IFN-γ (p < .010), IL-4 (p = .015) than those without LT cases. Although the data were not statistically significant, all analyzed cytokines (except for IL-4) were highly expressed in the cases with higher expression of p27 surrogate marker.
Conclusions
These results indicate that mixed Th1 (TNF-α, IFN-γ , and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-10) immunity might play a role in the antitumor effect in terms of lymph node metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: impact and correlation
Shengpeng Yao, Hong Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Fabiana Franchini, Giuseppe Palatucci, Annamaria Colao, Paola Ungaro, Paolo Emidio Macchia, Immacolata Cristina Nettore
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(3): 1116. CrossRef - Association between Hashimoto thyroiditis and clinical outcomes of papillary thyroid carcinoma: A meta-analysis
Qizhi Tang, Weiyu Pan, Liangyue Peng, Francis Moore
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269995. CrossRef - The Heat Shock Protein Story—From Taking mTORC1,2 and Heat Shock Protein Inhibitors as Therapeutic Measures for Treating Cancers to Development of Cancer Vaccines
Peter Chin Wan Fung, Regina Kit Chee Kong
Journal of Cancer Therapy.2017; 08(11): 962. CrossRef
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: impact and correlation
- A Rare Case of Recurrent Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
- Hye Seung Lee, Han Kyeom Kim, Bong Kyung Shin, Jin Hyuk Choi, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):87-91. Published online August 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.16
- 12,516 View
- 234 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 61-year-old woman visited our hospital for bilateral multiple lung nodules and a mass in her thorax. She had a long history of multiple metastatic recurrences of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN); 24 years previously, the patient had undergone pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for a 9.9 × 8.6 cm mass in the pancreatic head. The tumor was diagnosed as an SPN. Nine years later, metastatic nodules were found on computed tomography in the patient’s liver and peritoneum and were excised. She subsequently underwent an additional eight metastatectomy procedures in diverse organs. For the presented event, the lung nodules were removed. The prevalence of malignant SPN in the general population is 5%–15%. However, multiple metastatic recurrence of malignant SPN is rare; the lung is a particularly rare site of metastasis, found in only three cases in the literature. Here, we describe this exceptional case and provide a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
Jun Hyung Kim, Hyung Sun Kim, Jung Min Lee, Ji Hae Nahm, Joon Seong Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2025; 29(1): 83. CrossRef - Curative Resection for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of Pancreas—a Case Series
Aparna M. Jagannathan, Manbha L. Rymbai, Abhilasha Anand, Anoop Paul, Borna Das, Thomas Alex Kodiatte, Frederick L. Vyas, Ravish Sanghi Raju, Philip Joseph
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S2): 232. CrossRef - Malignant Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: An Orthogonal Analysis
Andrew M. Fleming, Leah E. Hendrick, Danny Yakoub, Hafeez Abdelhafeez, Jeremiah L. Deneve, Max R. Langham, Evan S. Glazer, Andrew M. Davidoff, Nipun B. Merchant, Paxton V. Dickson, Andrew J. Murphy
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 475. CrossRef - A Unique Presentation of Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas Requiring Pancreaticoduodenectomy Without Pancreatojejunostomy: A Case Report and Literature Review
Alexis L Carmona, Sameh A Fayek
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Clinical analysis and literature review of five cases of metastatic solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas
Run Hu, Renjie Gui, Xi Nie, Huaxin Duan
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case of Treatment of Solid Pseudopapillary Pancreatic Tumor
F. S. Rakhimova, N. D. Mamashev, O. A. Shimkina, B. Kh. Bebezov
Creative surgery and oncology.2023; 13(2): 178. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: A report of 18 cases
Ayiguzaili Maimaijiang, Haiyun Wang, Wanfu Li, Yaqi Wang
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Large tumor size, lymphovascular invasion, and synchronous metastasis are associated with the recurrence of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas
Goeun Lee, You-Na Sung, Sung Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Lee, Ki-Byung Song, Dae Wook Hwang, Jihun Kim, Sang Soo Lee, Song Cheol Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
HPB.2021; 23(2): 220. CrossRef - Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A 63-Case Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Features and Risk Factors of Malignancy
Hongchun Chen, Yuchen Huang, Ningning Yang, Wentian Yan, Ruxue Yang, Shan Zhang, Panpan Yang, Nan Li, Zhenzhong Feng
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3335. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Approach for Pancreatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm and Initially Undiagnosed Slowly Progressing Liver Tumor
Shohei Takaichi, Yoshifumi Iwagami, Shogo Kobayashi, Yoshito Tomimaru, Hirofumi Akita, Tadafumi Asaoka, Takehiro Noda, Kunihito Gotoh, Masaki Mori, Yuichiro Doki, Hidetoshi Eguchi
Pancreas.2020; 49(8): e70. CrossRef - Rare Solid Tumor of the Exocrine Pancreas: A Pictorial Review
Marco Dioguardi Burgio, Maxime Ronot, Valérie Vilgrain
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2019; 40(6): 483. CrossRef - The Stomach: a Rare Site for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
Prajwala S. Prakash, Dexter Yak Seng Chan, Krishnakumar Madhavan
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2018; 22(4): 759. CrossRef - European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms
Gut.2018; 67(5): 789. CrossRef
- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
- Stromal Expression of MicroRNA-21 in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients with Distant Metastases
- Kyu Sang Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Jiwon Koh, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Gheeyoung Choe, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):270-277. Published online May 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.19
- 10,621 View
- 99 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study was to determine the regional heterogeneity and clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 (miR-21) in advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with distant metastasis.
Methods
miR-21 expression was investigated by using locked nucleic acid– fluorescence in situ hybridization in the center and periphery of the primary cancer and in distant metastasis from 170 patients with advanced CRC. In addition, α-smooth muscle actin and desmin were evaluated to identify cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by using immunohistochemistry.
Results
The miR-21 signal was observed in the cancer stroma. The expression of miR-21 (a score of 1–4) in the center and periphery of the primary cancer and in distant metastasis was observed in specimens from 133 (78.2%), 105 (61.8%), and 91 (53.5%) patients, respectively. miR-21 expression was heterogeneous in advanced CRC. Discordance between miR-21 expression in the center of the primary cancer and either the periphery of the primary cancer or distant metastasis was 31.7% or 44.7%, respectively. miR-21 stromal expression in the periphery of the primary cancer was significantly associated with a better prognosis (p=.004). miR-21 expression was significantly associated with CAFs in the center of the primary cancer (p=.001) and distant metastases (p=.041).
Conclusions
miR-21 expression is observed in cancer stroma related to the CAF quantity and frequently presents regional heterogeneity in CRC. Our findings indicate that the role of miR-21 in predicting prognosis may be controversial but provide a new perspective of miR-21 level measurement in cancer specimens. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity of primary and metastatic CAFs: From differential treatment outcomes to treatment opportunities (Review)
Zixing Kou, Cun Liu, Wenfeng Zhang, Changgang Sun, Lijuan Liu, Qiming Zhang
International Journal of Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of Selected miRNAs in Normal and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and in BxPc3 and MIA PaCa-2 Cell Lines of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Václav Mandys, Alexey Popov, Robert Gürlich, Jan Havránek, Lucie Pfeiferová, Michal Kolář, Jana Vránová, Karel Smetana, Lukáš Lacina, Pavol Szabo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3617. CrossRef - MicroRNAs and colorectal cancer: clinical potential and regulatory networks
George Yiadom Osei, Joseph Adu-Amankwaah, Selina Koomson, Solomon Beletaa, Emmanuel Akomanin Asiamah, Cecilia Smith-Togobo, Siti Razila Abdul Razak
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(11): 9575. CrossRef - MicroRNA-552 expression in colorectal cancer and its clinicopathological significance
Joon Im, Soo Kyung Nam, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(2): 125. CrossRef - Postoperative changes in plasma miR21‐5p as a novel biomarker for colorectal cancer recurrence: A prospective study
Masahiro Fukada, Nobuhisa Matsuhashi, Takao Takahashi, Nobuhiko Sugito, Kazuki Heishima, Kazuhiro Yoshida, Yukihiro Akao
Cancer Science.2021; 112(10): 4270. CrossRef - Differential expression of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: Different patterns between isolated cancer gland and stromal cells
Ayaka Sato, Yasuko Fujita, Koki Otsuka, Akira Sasaki, Hiromu Suzuki, Takayuki Matsumoto, Tamotsu Sugai
Pathology International.2020; 70(1): 21. CrossRef - High-Throughput Multiplex Immunohistochemical Imaging of the Tumor and Its Microenvironment
Jiwon Koh, Yoonjin Kwak, Jin Kim, Woo Ho Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2020; 52(1): 98. CrossRef - Tumor Tissue MIR92a and Plasma MIRs21 and 29a as Predictive Biomarkers Associated with Clinicopathological Features and Surgical Resection in a Prospective Study on Colorectal Cancer Patients
Masahiro Fukada, Nobuhisa Matsuhashi, Takao Takahashi, Nobuhiko Sugito, Kazuki Heishima, Yukihiro Akao, Kazuhiro Yoshida
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(8): 2509. CrossRef - The promising role of noncoding RNAs in cancer-associated fibroblasts: an overview of current status and future perspectives
Zengli Fang, Jin Xu, Bo Zhang, Wei Wang, Jiang Liu, Chen Liang, Jie Hua, Qingcai Meng, Xianjun Yu, Si Shi
Journal of Hematology & Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Altered miR-21, miRNA-148a Expression in Relation to KRAS Mutation Status as Indicator of Adenoma-Carcinoma Transitional Pattern in Colorectal Adenoma and Carcinoma Lesions
Somayeh Igder, Javad Mohammadiasl, Pooneh Mokarram
Biochemical Genetics.2019; 57(6): 767. CrossRef - Development and Validation of an Easy-to-Implement, Practical Algorithm for the Identification of Molecular Subtypes of Gastric Cancer: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications
Jiwon Koh, Keun-Wook Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, An Na Seo, Ji-Won Kim, Jin Won Kim, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
The Oncologist.2019; 24(12): e1321. CrossRef - Prognostic Utility of Histological Growth Patterns of Colorectal Lung Oligometastasis
Son Jae Yeong, Min Gyoung Pak, Hyoun Wook Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2018; 52(2): 98. CrossRef - Effect of dietary components on miRNA and colorectal carcinogenesis
Adewale Oluwaseun Fadaka, Babajide A. Ojo, Olusola Bolaji Adewale, Temitope Esho, Ashley Pretorius
Cancer Cell International.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Ligand-Independent Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Overexpression Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer
Sumi Yun, Yoonjin Kwak, Soo Kyung Nam, An Na Seo, Heung-Kwon Oh, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang, Hye Seung Lee
Cancer Research and Treatment.2018; 50(4): 1351. CrossRef - Mutation analysis of CTNNB1 gene and the ras pathway genes KRAS , NRAS , BRAF , and PIK3CA in eyelid sebaceous carcinomas
Mi Jung Kwon, Eun Sook Nam, Seong Jin Cho, Hye-Rim Park, Soo Kee Min, Jinwon Seo, Ji-Young Choe
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(6): 654. CrossRef - Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts
Fengming Yang, Zhiqiang Ning, Ling Ma, Weitao Liu, Chuchu Shao, Yongqian Shu, Hua Shen
Molecular Cancer.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic implications of immune classification by PD-L1 expression and CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in stage II and III gastric cancer patients
Jiwon Koh, Chan-Young Ock, Jin Won Kim, Soo Kyung Nam, Yoonjin Kwak, Sumi Yun, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(16): 26356. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity of primary and metastatic CAFs: From differential treatment outcomes to treatment opportunities (Review)
- Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer: Review Article from a Pathologist’s Point of View
- Sophia K. Apple
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):83-95. Published online January 12, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.11.23
- 25,911 View
- 493 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Breast cancer staging, in particular N-stage changed most significantly due to the advanced technique of sentinel lymph node biopsy two decades ago. Pathologists have more thoroughly examined and scrutinized sentinel lymph node and found increased number of small volume metastases. While pathologists use the strict criteria from the Tumor Lymph Node Metastasis (TNM) Classification, studies have shown poor reproducibility in the application of American Joint Committee on Cancer and International Union Against Cancer/TNM guidelines for sentinel lymph node classification in breast cancer. In this review article, a brief history of TNM with a focus on N-stage is described, followed by innate problems with the guidelines, and why pathologists may have difficulties in assessing lymph node metastases uniformly. Finally, clinical significance of isolated tumor cells, micrometastasis, and macrometastasis is described by reviewing historical retrospective data and significant prospective clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Out-of-distribution generalization for segmentation of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
Yiannis Varnava, Kiran Jakate, Richard Garnett, Dimitrios Androutsos, Pascal N. Tyrrell, April Khademi
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen section analysis in community settings: Diagnostic challenges and key considerations
Rashna Meunier, Kisong Kim, Noureldien Darwish, Syed M. Gilani
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 42(3): 150903. CrossRef - Axillary lymph node dissection offers no survival benefit in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node micrometastases after neoadjuvant therapy
Jianing Zhang, Yudong Zhou, Lizhe Zhu, Jiaqi Zhang, Chenglong Duan, Jinsui Du, Yi Pan, Yalong Wang, Danni Li, Yu Ren, Bin Wang
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between postoperative pathological results and non-sentinel nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node-positive breast cancer
Lingguang Dong, Suosu Wei, Zhen Huang, Fei Liu, Yujie Xie, Jing Wei, Chongde Mo, Shengpeng Qin, Quanqing Zou, Jianrong Yang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clonal dominance defines metastatic dissemination in pancreatic cancer
I-Lin Ho, Chieh-Yuan Li, Fuchenchu Wang, Li Zhao, Jingjing Liu, Er-Yen Yen, Charles A. Dyke, Rutvi Shah, Zhaoliang Liu, Ali Osman Çetin, Yanshuo Chu, Francesca Citron, Sergio Attanasio, Denise Corti, Faezeh Darbaniyan, Edoardo Del Poggetto, Sara Loponte,
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognosis of isolated tumor cells and use of molecular classification in early stage endometrioid endometrial cancer
Eric Rios-Doria, Nadeem R Abu-Rustum, Kaled M Alektiar, Vicky Makker, Ying L Liu, Dmitriy Zamarin, Claire F Friedman, Carol Aghajanian, Lora H Ellenson, Sarah Chiang, Britta Weigelt, Jennifer J Mueller, Mario M Leitao
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2024; 34(9): 1373. CrossRef - Predictive factors for dissection-free sentinel node micrometastases in early oral squamous cell carcinoma
Takashi Matsuzuka, Kiyoaki Tsukahara, Seiichi Yoshimoto, Kazuaki Chikamatsu, Akihiro Shiotani, Isao Oze, Yoshiko Murakami, Takeshi Shinozaki, Yuichiro Enoki, Shinichi Ohba, Daisuke Kawakita, Nobuhiro Hanai, Yusuke Koide, Michi Sawabe, Yusuke Nakata, Yujir
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Nodes and Nodal Assessment in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prediction in ER+, Node-Positive Breast Cancer
Charlene Kay, Carlos Martinez-Perez, J. Michael Dixon, Arran K. Turnbull
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(10): 1476. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Personalized Medicine
Jong Seok Ahn, Sangwon Shin, Su-A Yang, Eun Kyung Park, Ki Hwan Kim, Soo Ick Cho, Chan-Young Ock, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Breast Cancer.2023; 26(5): 405. CrossRef - Clinicopathological predictors of finding additional inguinal lymph node metastases in penile cancer patients after positive dynamic sentinel node biopsy: a European multicentre evaluation
Hielke M. de Vries, Hack Jae Lee, Wayne Lam, Rosa S. Djajadiningrat, Sarah R. Ottenhof, Eduard Roussel, Bin Klaas Kroon, Igle Jan de Jong, Pedro Oliveira, Hussain M. Alnajjar, Maarten Albersen, Asif Muneer, Vijay Sangar, Arie Parnham, Benjamin Ayres, Nick
BJU International.2022; 130(1): 126. CrossRef - Fast Segmentation of Metastatic Foci in H&E Whole-Slide Images for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Muhammad-Adil Khalil, Yu-Ching Lee, Huang-Chun Lien, Yung-Ming Jeng, Ching-Wei Wang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 990. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Postoperative Complications of Sentinel Node Identification Using the SentiMag® Method and the Use of a Radiotracer in Patients with Breast Cancer
Andrzej Lorek, Katarzyna Steinhof-Radwańska, Wojciech Zarębski, Joanna Lorek, Zoran Stojčev, Jacek Zych, Aleksandra Syrkiewicz, Paweł Niemiec, Karol Szyluk
Current Oncology.2022; 29(5): 2887. CrossRef - Improving Cancer Metastasis Detection via Effective Contrastive Learning
Haixia Zheng, Yu Zhou, Xin Huang
Mathematics.2022; 10(14): 2404. CrossRef - Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images
Haixia Zheng, Yu Zhou, Xin Huang
Mathematics.2022; 10(15): 2657. CrossRef - Independent assessment of a deep learning system for lymph node metastasis detection on the Augmented Reality Microscope
David Jin, Joseph H. Rosenthal, Elaine E. Thompson, Jared Dunnmon, Arash Mohtashamian, Daniel Ward, Ryan Austin, Hassan Tetteh, Niels H. Olson
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2022; 13: 100142. CrossRef - Generalization of Deep Learning in Digital Pathology: Experience in Breast Cancer Metastasis Detection
Sofia Jarkman, Micael Karlberg, Milda Pocevičiūtė, Anna Bodén, Péter Bándi, Geert Litjens, Claes Lundström, Darren Treanor, Jeroen van der Laak
Cancers.2022; 14(21): 5424. CrossRef - Assessment of cellular and humoral immunity in sentinel lymph node in breast cancer
A. D. Neryakhin, A. U. Gallyamov, D. N. Kamilianov, E. H. Sunagatullina, R. U. Kamalov, L. A. Sharafutdinova
Ural Medical Journal.2022; 21(6): 13. CrossRef - Lessons Learned from Designing an AI-Enabled Diagnosis Tool for Pathologists
Hongyan Gu, Jingbin Huang, Lauren Hung, Xiang 'Anthony' Chen
Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction.2021; 5(CSCW1): 1. CrossRef - Deep Regional Metastases Segmentation for Patient-Level Lymph Node Status Classification
Lu Wang, Tian Song, Takafumi Katayama, Xiantao Jiang, Takashi Shimamoto, Jenq-Shiou Leu
IEEE Access.2021; 9: 129293. CrossRef - Isolated tumor cells in the regional lymph nodes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus are rarely observed but often represent part of a true metastasis
Dea Natalie Munch Jepsen, Anne-Marie Kanstrup Fiehn, Bonnie Svendsen, Michael Patrick Achiam, Birgitte Federspiel
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 45: 151478. CrossRef - Independent risk factors for axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with one or two positive sentinel lymph nodes
Wei Zhang, Jing Xu, Ke Wang, Xiao-Jiang Tang, Hua Liang, Jian-Jun He
BMC Women's Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The spectrum of pathological diagnoses in non-sentinel axillary lymph node biopsy: A single institution's experience
Wei Huang, Xiaoyu Tang, Jozef Malysz, Bing Han, Zhaohai Yang
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 49: 151646. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic Algorithm for the Assessment of Sentinel Lymph Nodes That Drain the Mammary Carcinomas in Female Dogs
Florin Stan, Alexandru Gudea, Aurel Damian, Adrian Florin Gal, Ionel Papuc, Alexandru Raul Pop, Cristian Martonos
Animals.2020; 10(12): 2366. CrossRef - Prognostic Value of EndoPredict in Women with Hormone Receptor–Positive, HER2-Negative Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer
Ivana Sestak, Martin Filipits, Richard Buus, Margaretha Rudas, Marija Balic, Michael Knauer, Ralf Kronenwett, Florian Fitzal, Jack Cuzick, Michael Gnant, Richard Greil, Mitch Dowsett, Peter Dubsky
Clinical Cancer Research.2020; 26(17): 4682. CrossRef - Performance of Molecular Lymphosonography for Detection and Quantification of Metastatic Involvement in Sentinel Lymph Nodes
Kibo Nam, Robert Stapp, Ji‐Bin Liu, Maria Stanczak, Flemming Forsberg, Patrick L. O'Kane, Zhou Lin, Ziyin Zhu, Jingzhi Li, Charalambos C. Solomides, John R. Eisenbrey, Andrej Lyshchik
Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2019; 38(8): 2103. CrossRef - Application of Circulation Tumor Cells Detection in Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Tumors
Fengfeng Cai, Chunmei Cen, Lu Cai, Manuel Antonio Falar Luis, Ewelina Biskup
Rejuvenation Research.2019; 22(6): 498. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence–Based Breast Cancer Nodal Metastasis Detection: Insights Into the Black Box for Pathologists
Yun Liu, Timo Kohlberger, Mohammad Norouzi, George E. Dahl, Jenny L. Smith, Arash Mohtashamian, Niels Olson, Lily H. Peng, Jason D. Hipp, Martin C. Stumpe
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(7): 859. CrossRef - Isolated tumor cells in regional lymph nodes in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction might represent part of true metastases
Anne-Marie Kanstrup Fiehn, Dea Natalie Munch Jepsen, Michael Patrick Achiam, Heidi Ugleholdt, Birgitte Federspiel
Human Pathology.2019; 93: 90. CrossRef - Impact of Deep Learning Assistance on the Histopathologic Review of Lymph Nodes for Metastatic Breast Cancer
David F. Steiner, Robert MacDonald, Yun Liu, Peter Truszkowski, Jason D. Hipp, Christopher Gammage, Florence Thng, Lily Peng, Martin C. Stumpe
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 42(12): 1636. CrossRef - One-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA): where do we go with it?
Yasuhiro Tamaki
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 22(1): 3. CrossRef
- Out-of-distribution generalization for segmentation of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
- Tumor Sprouting in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Is Correlated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence
- Eunjung Lee, Wonkyung Jung, Jeong-Soo Woo, Jae Bok Lee, Bong Kyung Shin, Han Kyeom Kim, Aeree Kim, Baek-hui Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):117-125. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.117
- 13,070 View
- 68 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Identification of poor prognostic factors in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients is important for the patients' care and follow-up. We can sometimes see small tumor clusters without desmoplasia and no evidence of lymphatic emboli around the main tumor mass of PTC. We termed this form of tumor clustering, 'tumor sprouting,' and determined whether these tumors correlate with lymphovascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, and recurrence.
Methods We analyzed a total of 204 cases of papillary thyroid macrocarcinoma. Number, size and distance from the main tumor of the tumor sprouting were observed and analyzed with clinicopathologic characteristics.
Results Tumor sprouting was observed in 101 patients. Presence of tumor sprouting was significantly associated with positive resection margin (p=.002), lymphovascular invasion (p=.001), lymph node metastasis (p<.001), and recurrence (p=.004). Univariate analysis of recurrence-free survival revealed that tumor multiplicity (p=.037), positive resection margin (p=.007), lymphovascular invasion (p=.004), lymph node metastasis (p<.001), and tumor sprouting (p=.004) were poor prognostic factors. In multivariate analysis, positive resection margin was an independent poor prognostic factor of recurrence.
Conclusions In conclusion, tumor sprouting is significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and recurrence. Evaluation of tumor sprouting in PTC patients could be helpful in predicting tumor recurrence or lymph node metastasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Initial Risk Stratification System for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Key Updates in the 2024 Korean Thyroid Association Guideline
Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 357. CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Part I. Initial Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers - Chapter 5. Evaluation of Recurrence Risk Postoperatively and Initial Risk Stratification in Different
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Shin Je Moon, Dong-Jun Lim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Yun Jae Chung, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 68. CrossRef - Significance of Lymphovascular Invasion as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ho-Ryun Won, Bon Seok Koo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(2): 157. CrossRef - Peripheral Versus Intraparenchymal Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Different Morphologies and PD-L1 Expression
Bozidar Kovacevic, Dragana Vucevic, Snezana Cerovic, Catarina Eloy
Head and Neck Pathology.2022; 16(1): 200. CrossRef - Lymphovascular invasion and risk of recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Katy Wagner, Earl Abraham, Bryan Tran, David Roshan, James Wykes, Peter Campbell, Ardalan Ebrahimi
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2020; 90(9): 1727. CrossRef - The Predictors of Multicentricity in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Mohamed Hegazi, Waleed El Nahas, Mohamed Elmetwally, Amr Hassan, Waleed Gado , Islam Abdou, Ahmed Senbel, Mohamed Samir Abou-Sheishaa
Journal of Analytical Oncology.2018; 7(4): 65. CrossRef - Prognostic impact of vascular invasion in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Tetsuo Kondo, Uyen N P Duong, Thong Quang Pham, Naoki Oishi, Kunio Mochizuki, Tadao Nakazawa, Lewis Hassell, Ryohei Katoh
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 177(2): 207. CrossRef - Detection of Tumor Multifocality Is Important for Prediction of Tumor Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis
Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(4): 278. CrossRef
- The Initial Risk Stratification System for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Key Updates in the 2024 Korean Thyroid Association Guideline
- IMP3, a Promising Prognostic Marker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Ji Young Park, Misun Choe, Yuna Kang, Sang Sook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):108-116. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.108
- 9,106 View
- 45 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3) has been reported as a prognostic biomarker in various cancers. To validate IMP3 as a prognostic biomarker in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), we investigated the expression of IMP3, p53, and Ki-67, and their associations with clinicopathologic outcomes.
Methods We studied 148 clear cell RCCs (CCRCCs) from patients who underwent radical nephrectomy. The expression levels of IMP3, p53, and Ki-67 were assessed by immunohistochemical staining and the clinical and pathologic parameters were retrospectively reviewed.
Results Twenty-nine percent of CCRCCs expressed IMP3. Forty-one percent of IMP3-immunopositive tumors developed metastases, while only 11.4% of IMP3-negative tumors developed metastases (p<.001). A Kaplan-Meier curve showed that patients with IMP3-immunopositive tumors had lower metastasis-free survival and cancer-specific survival than did those with IMP3-immunonegative tumors (p<.001 and p<.001, respectively). Expression of high Ki-67 proliferation index was also associated with a higher metastatic rate. In the multivariate Cox regression analysis, pT stage and IMP3-positivity were independently associated with disease-specific survival.
Conclusions IMP3 is an independent prognostic biomarker for patients with CCRCC to predict metastasis and poor outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- IMP3 Immunohistochemical Expression Is Related with Progression and Metastases in Xenografted and Cutaneous Melanomas
Natividad Martin-Morales, Miguel Padial-Molina, Isabel Tovar, Virginea De Araujo Farias, Pedro Hernández-Cortés, Esperanza Ramirez-Moreno, Mercedes Caba-Molina, Justin Davis, Alejandro Carrero Castaño, Jose Mariano Ruiz de Almodovar, Pablo Galindo-Moreno,
Pathobiology.2024; 91(2): 132. CrossRef - circRARS synergises with IGF2BP3 to regulate RNA methylation recognition to promote tumour progression in renal cell carcinoma
Yuenan Liu, Kailei Chen, Yi Shou, Sen Li, Jun Wang, Qingyang Zhang, Ziwei Huang, Jiaju Xu, Mingfeng Li, Di Liu, Huageng Liang, Hongmei Yang, Xiaoping Zhang
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of insulin‑like growth factor 2 mRNA‑binding protein 3 and vascular endothelial growth factor‑A in patients with primary non‑small‑cell lung cancer
Jiannan Liu, Ying Liu, Wenjing Gong, Xiangshuo Kong, Congcong Wang, Shuhua Wang, Aina Liu
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelial‑mesenchymal transition in colorectal carcinoma cells is mediated by DEK/IMP3
Shuping You, Yun Guan, Weihong Li
Molecular Medicine Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- IMP3 Immunohistochemical Expression Is Related with Progression and Metastases in Xenografted and Cutaneous Melanomas
- Primary Sigmoid Adenocarcinoma Metastasis to the Breast in a 28-Year-Old Female: A Case Study and a Review of Literature
- Amna Ahmad, Kweku Baiden-Amissah, Adegoke Oyegade, Mohammed Absar, Kate Swainson, Sami Titi
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):58-61. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.58
- 9,336 View
- 52 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metastasis to the breast from colorectal carcinoma is rare, only a few cases have been reported in the literature, and no cases have been reported in a young, 28-year-old patient. This report confirms the occurrence of the disease in a younger age group. The patient was referred to the Breast Clinic with a history of a gradually increasing lump in her right breast for two weeks' duration. On clinical examination, a 2-cm firm lump was noted in the upper inner quadrant of the right breast, which was clinically benign; however, histological examination of the breast core biopsy together with immunohistochemistry confirmed metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma. The primary colorectal carcinoma was later confirmed to be a stage pT4N2M1 tumor, and the Duke stage was C1. Histology with immunohistochemistry is very important in the diagnosis of cases of this nature, but the clinical correlation should be taken into consideration at multidisciplinary team meetings to decide the final management of the patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Breast mass as the first sign of metastasis from rectal carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
Jiawei Xu, Chao Liu, Chengdong Yu, Tenghua Yu, Fan Fan, Xiaofang Zhang, Chuansheng Huang, Wen Chen, Zhengkui Sun, Meng Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A case report of multiple bilateral breast metastases after colorectal cancer
Khaled Arnaout, Nouran Hawa, Sarab Agha, Lama Kadoura, Marwa Aloulou, Kusay Ayoub
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2021; 81: 105759. CrossRef - Metastatic Breast Signet-Ring Cell Carcinoma from a Colonic Primary: Review of a Rare Case Report
Ghazaleh Shaker, Hayedeh Haeri, Behnaz Jahanbin
International Journal of Cancer Management.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast metastasis from rectal cancer with BRAF V600E mutation: a case report with a review of the literature
Hiroko Hasegawa, Yoko Nagata, Yuko Sakakibara, Masakazu Miyake, Kiyoshi Mori, Norikazu Masuda, Masayuki Mano, Shoichi Nakazuru, Hisashi Ishida, Eiji Mita
Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 13(2): 153. CrossRef - Colonic mucinous adenocarcinoma with secondary in the breast: A case report and literature review
Ameera Balhareth, Abdullah A. AlQatari, Fozan Aldulaijan, Amani Joudeh
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 76: 364. CrossRef - Breast metastasis from colorectal cancer treated by multimodal therapy
Tien-Chan Hsieh, Chao-Wen Hsu
Medicine.2019; 98(51): e18016. CrossRef - A case series of metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies
Tanvi Vaidya, Subhash Ramani, Ashita Rastogi
Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging.2018; 28(04): 470. CrossRef - Metástasis mamaria de un adenocarcinoma mucinoso de colon: descripción de un caso y revisión de la literatura
Marta Seoane Vigo, María Berdeal Díaz, Lourdes Galán Raposo, Fabio Ares Farpón, Alejandro García Varona, Luis González Crespo
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2017; 30(1): 28. CrossRef - Metastases of transverse colon cancer to bilateral ovaries (Krukenberg tumor) and the left breast: A case report
Xin-Yu Luo, Jue Wang, Jia Zhao, Rui Chen, Xiao-Ming Zha
Oncology Letters.2017; 14(1): 31. CrossRef - Metastasis of rectal signet ring adenocarcinoma to the breast in a young woman after 10 years, a rare case report and review of the literature
Bita Geramizadeh, Ali Mohammad Bananzadeh, Mohammad Reza Sasani, Asieh Khorshidi, Mahsa Marzban
Cancer Treatment Communications.2016; 7: 58. CrossRef - Metastatic Colonic Adenocarcinoma in Breast: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature
Jiten P. Kothadia, Rezina Arju, Monica Kaminski, Arvind Ankireddypalli, Sushil Duddempudi, Jonathan Chow, Shah Giashuddin
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef
- Breast mass as the first sign of metastasis from rectal carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature
- Diagnostic Accuracy of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology in Metastatic Tumors: An Analysis of Consecutive CSF Samples
- Yoon Sung Bae, June-Won Cheong, Won Seok Chang, Sewha Kim, Eun Ji Oh, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):563-568. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.563
- 9,848 View
- 69 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination can be used to verify the presence of primary malignancies as well as cases of central nervous system (CNS) metastasis. Because of its importance, there have been several studies concerning the sensitivity of CSF cytology. To determine the practical use and reproducibility of diagnoses based on CSF cytology, we evaluated this test by analyzing cytology results from consecutive CSF samples.
Methods Between July 2010 and June 2013, 385 CSF cytology samples from 42 patients were collected. The samples were gathered using a ventricular catheter and reservoir. CSF cytology of all patients was examined more than two times with immunocytochemistry for cytokeratin.
Results Primary neoplastic sites and histologic types of patients' metastatic cancer were diverse. The overall sensitivity for detecting malignancy was 41.3%. Even within short-term intervals, diagnoses frequently changed.
Conclusions Our results were inconsistent, with low sensitivity, when compared to the results of previous studies. However, CSF evaluation can still provide valuable diagnostic and prognostic information because adjuvant treatments are now routinely performed in patients with CNS metastasis. Negative CSF cytology results should not be ignored, and continuous CSF follow-up is essential for following the clinical course of patients with metastatic cancer involving the CNS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analytical validation of the Belay Vantage™ assay for evaluation of MGMT promoter methylation using enzymatically converted tumorDNA from cerebrospinal fluid
Kala F Schilter, Qian Nie, Jennifer N Adams, Rakshitha Jagadish, Anthony Acevedo, Alexandra Larson, Samantha A Vo, Brett A Domagala, Kyle M Hernandez, Christopher Douville, Yuxuan Wang, Brian Coe, Chetan Bettegowda, Honey V Reddi
Cancer Genetics.2025; 294-295: 94. CrossRef - Analytical Validation and Clinical Sensitivity of the Belay Summit Assay for the Detection of DNA Variants in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Primary and Metastatic Central Nervous System Cancer
Qian Nie, Kala F. Schilter, Kyle M. Hernandez, Jennifer N. Adams, Rakshitha Jagadish, Anthony Acevedo, Alexandra Larson, Brett A. Domagala, Samantha A. Vo, Sakshi Khurana, Kathleen Mitchell, Dean Ellis, Baymuhammet Muhammedov, Yuxuan Wang, Christopher Dou
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2025; 27(7): 615. CrossRef - Demonstrating the clinical utility of genomic profiling using cerebrospinal fluid to inform management of central nervous system tumors – a meta analysis of the literature
Sakshi Khurana, Qian Nie, Kala F. Schilter, Honey V. Reddi
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 9: 100317. CrossRef - Application of the International System for Serous Fluid Cytopathology in Cerebrospinal Fluid Cytology
Ioannina Vidali, Konstantinos Christofidis, Georgia Bairaktari, Maria Sevastiadou, Alexandros Pergaris, Aglaia Dimitrakopoulou, Panagiota Keramari, Panagiota Mikou
Cytopathology.2025; 36(6): 589. CrossRef - The Spectrum of Malignant Diagnoses in Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cytology in Both Pediatric and Adult Populations: A Single‐Institutional Retrospective Review
Nida Babar, Asif Loya, Sajid Mushtaq, Maryam Hameed, Usman Hassan, Mudassar Hussain
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(12): 620. CrossRef - Molecular Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Tumor-Derived DNA to Aid in the Diagnosis and Targeted Treatment of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis
Michael Youssef, Alexandra Larson, Vindhya Udhane, Viriya Keo, Kala F. Schilter, Qian Nie, Honey V. Reddi
Diseases.2025; 13(10): 336. CrossRef - Numb cheek syndrome in breast cancer: a case report
Zhibin Tan, Si Ying Tan
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility and performance of cell blocks in cerebrospinal fluid cytology: Experience at two teaching hospitals
Hyeji Yoon, Constance V. Chen, Vimal Krishnan, Jill Grochowski, Gioia Iezza, Poonam Vohra, Ronald Balassanian, Nancy Y. Greenland
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(10): 621. CrossRef - Liquid biopsy for evaluating mutations and chromosomal aberrations in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with primary or metastatic CNS tumors
Ahmad Charifa, Sally Agersborg, Arash Mohtashamian, Andrew Ip, Andre Goy, Maher Albitar
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2024; 6: 100281. CrossRef - Body fluids
Shyam H. Nemade, Meherbano M. Kamal
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2023; 66(1): 75. CrossRef - Standardizing a volume benchmark for cerebrospinal fluids for optimal diagnostic accuracy
David Kim, Susan A. Alperstein, Momin T. Siddiqui
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(2): 258. CrossRef - Evaluating Infectious, Neoplastic, Immunological, and Degenerative Diseases of the Central Nervous System with Cerebrospinal Fluid-Based Next-Generation Sequencing
Konstantinos I. Tsamis, Hercules Sakkas, Alexandros Giannakis, Han Suk Ryu, Constantina Gartzonika, Ilias P. Nikas
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2021; 25(2): 207. CrossRef - Imaging of Intraspinal Tumors
Luke N. Ledbetter, John D. Leever
Radiologic Clinics of North America.2019; 57(2): 341. CrossRef - Isolated leptomeningeal carcinomatosis and possible fungal meningitis as late sequelae of oesophageal adenocarcinoma
Richard Dumbill, Sanja Thompson, Heiko Peschl, GDH Turner, Charles Woodrow
BMJ Case Reports.2019; 12(11): e230117. CrossRef - Cytomorphological and immunocytochemical examinations of cerebrospinal fluid in primary and metastatic brain lesions
M. V. Savostikova, L. Ya. Fomina, E. S. Fedoseeva, E. Yu. Furminskaya
Onkologiya. Zhurnal imeni P.A.Gertsena.2018; 7(1): 28. CrossRef - Metastatic Breast Carcinoma in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Cytopathological Review of 15 Cases
Rema Rao, Syed A. Hoda, Alan Marcus, Rana S. Hoda
The Breast Journal.2017; 23(4): 456. CrossRef - Clinicocytological analysis of cases with positive cerebrospinal fluid in our hospital
Nozomi IWAMOTO, Mitsuaki ISHIDA, Akiko KAGOTANI, Nozomi KASUGA, Muneo IWAI, Yuji HAYASHI, Namie ARITA, Yoshimitsu MIYAHIRA, Ryoji KUSHIMA
The Journal of the Japanese Society of Clinical Cytology.2016; 55(5): 291. CrossRef
- Analytical validation of the Belay Vantage™ assay for evaluation of MGMT promoter methylation using enzymatically converted tumorDNA from cerebrospinal fluid
- Morphologic Alteration of Metastatic Neuroblastic Tumor in Bone Marrow after Chemotherapy
- Go Eun Bae, Yeon-Lim Suh, Ki Woong Sung, Jung-Sun Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):433-442. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.433
- 8,748 View
- 49 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The aim of this study is to evaluate the histologic features of metastatic neuroblastic tumors (NTs) in bone marrow (BM) before and after chemotherapy in comparison with those of primary NTs.
Methods A total of 294 biopsies from 48 children diagnosed with NTs with BM metastasis were examined. There were 48 primary neoplasm biopsies, 48 BM biopsies before chemotherapy, 36 primary neoplasm excisional biopsies after chemotherapy, and 162 BM biopsies after chemotherapy.
Results Metastatic NTs in BM before chemotherapy were composed of undifferentiated and/or differentiating neuroblasts, but had neither ganglion cells nor Schwannian stroma. Metastatic foci of BM after chemotherapy were found to have differentiated into ganglion cells or Schwannian stroma, which became more prominent after further cycles of chemotherapy. Persistence of NTs or tumor cell types in BM after treatment did not show statistically significant correlation to patients' outcome. However, three out of five patients who newly developed poorly differentiated neuroblasts in BM after treatment expired due to disease progression.
Conclusions Metastatic NTs in BM initially consist of undifferentiated or differentiating neuroblasts regardless of the primary tumor subtype, and become differentiated after chemotherapy. Newly appearing poorly differentiated neuroblasts after treatment might be an indicator for poor prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postchemotherapy gross residual tumor in non‐high‐risk neuroblastoma: Clinical significance and the role of adjuvant therapy
Eun Seop Seo, Hana Lim, Hee Won Cho, Hee Young Ju, Ji Won Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Sanghoon Lee, Do Hoon Lim, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Postchemotherapy gross residual tumor in non‐high‐risk neuroblastoma: Clinical significance and the role of adjuvant therapy
- Histologic Variations and Immunohistochemical Features of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):426-432. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.426
- 12,872 View
- 89 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Due to advancements in treatment of metastatic and advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), it has become increasingly important to diagnose metastatic RCC and the specific subtype. In this study, we investigated the diverse histologic features of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cases in comparison with corresponding primary lesions.
Methods We identified 119 metastatic CCRCC cases from 81 corresponding primary lesions diagnosed between 1995 and 2010 and evaluated the diverse histologic and immunohistochemical features of these lesions.
Results A total of 44 primary lesions (54.3%) had a non-clear cell component in addition to a typical clear cell component. Of the 119 metastatic lesions, 63 lesions (52.9%) contained a non-clear cell component, and 29 metastatic lesions were composed of a non-clear cell component only. Rhabdoid features were the most frequent non-clear cell histology among the metastatic lesions. Metastatic CCRCCs mainly showed positive CD10 and epithelial membrane antigen staining and negative cytokeratin 7 staining.
Conclusions Metastatic CCRCC commonly showed a variety of histologic features. If there is a difficulty to diagnose metastatic CCRCC due to a variety of histologic features or small biopsy specimen, histologic review of the primary lesion and immunohistochemical analysis can help determine the correct diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
Adebowale J. Adeniran, Brian Shuch, Peter A. Humphrey
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(7): e65. CrossRef - Emerging Antibody-Drug Conjugate Therapies and Targets for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Harrison C. Gottlich, Reza Nabavizadeh, Mihai Dumbrava, Rodrigo Rodrigues Pessoa, Ahmed M. Mahmoud, Ishita Garg, Jacob Orme, Brian A. Costello, John Cheville, Fabrice Lucien
Kidney Cancer.2023; 7(1): 161. CrossRef - Painful, bleeding fingertip papule
Jane Gay, Sarah Simpson, Patrick Rush, Alex Holliday
JAAD Case Reports.2022; 21: 130. CrossRef - Development and initial clinical testing of a multiplexed circulating tumor cell assay in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Rory M. Bade, Jennifer L. Schehr, Hamid Emamekhoo, Benjamin K. Gibbs, Tamara S. Rodems, Matthew C. Mannino, Joshua A. Desotelle, Erika Heninger, Charlotte N. Stahlfeld, Jamie M. Sperger, Anupama Singh, Serena K. Wolfe, David J. Niles, Waddah Arafat, John
Molecular Oncology.2021; 15(9): 2330. CrossRef - Laparoscopic cytoreductive nephrectomy and adrenalectomy for metachronous RCC metastases—Case report
Bogdan Petrut, Cristina Eliza Bujoreanu, Vasile Vlad Hardo, Adrian Barbos, Bogdan Fetica
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 74: 268. CrossRef - Does CARMENA mark the end of cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Steven L. Chang, Toni K. Choueiri, Lauren C. Harshman
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2019; 37(8): 525. CrossRef - Metastatic TFE3-overexpressing renal clear cell carcinoma with dense granules: a histological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study
Shoujun Chen, Elba A. Turbat-Herrera, Guillermo A. Herrera, Meghna Chadha, Rodney E. Shackelford, Eric X. Wei
Ultrastructural Pathology.2018; 42(4): 369. CrossRef - The Clinical Activity of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Metastatic Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Rana R. McKay, Dominick Bossé, Wanling Xie, Stephanie A.M. Wankowicz, Abdallah Flaifel, Raphael Brandao, Aly-Khan A. Lalani, Dylan J. Martini, Xiao X. Wei, David A. Braun, Eliezer Van Allen, Daniel Castellano, Guillermo De Velasco, J. Connor Wells, Daniel
Cancer Immunology Research.2018; 6(7): 758. CrossRef - Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 359. CrossRef - Pulmonary metastasectomy from renal cell carcinoma including 3 cases with sarcomatoid component
Tsuyoshi Ueno, Motohiro Yamashita, Shigeki Sawada, Ryujiro Sugimoto, Noriko Nishijima, Yoshifumi Sugawara, Iku Ninomiya
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2016; 64(3): 149. CrossRef - Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer?
Aleksandra Semeniuk-Wojtaś, Rafał Stec, Cezary Szczylik
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2016; 34(5): 215. CrossRef - Concordance of Pathologic Features Between Metastatic Sites and the Primary Tumor in Surgically Resected Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sarah P. Psutka, John C. Cheville, Brian A. Costello, Suzanne B. Stewart-Merrill, Christine M. Lohse, Bradley C. Leibovich, Stephen A. Boorjian, R. Houston Thompson
Urology.2016; 96: 106. CrossRef - The Correlation of Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Lesions: A Tissue Microarray Study
Sung Han Kim, Weon Seo Park, Eun Young Park, Boram Park, Jungnam Joo, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
The Korean Journal of Urological Oncology.2016; 14(3): 152. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up and clinical course of a rare case of von Hippel-Lindau disease: A case report and review of the literature
YU ZOU, JINGJING XU, MINMING ZHANG
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(5): 3273. CrossRef - Genetic alterations in renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation
Carmen M. Perrino, Vishwanathan Hucthagowder, Michael Evenson, Shashikant Kulkarni, Peter A. Humphrey
Human Pathology.2015; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - High expression of APRIL correlates with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
Pathology - Research and Practice.2015; 211(11): 824. CrossRef - A Case of Cutaneous Metastasis from a Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with an Eosinophilic Cell Component to the Submandibular Region
Yusuke Amano, Sumie Ohni, Toshiyuki Ishige, Taku Homma, Tsutomu Yamada, Nobuyuki Nishimori, Norimichi Nemoto
Journal of Nihon University Medical Association.2015; 74(2): 73. CrossRef
- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Histopathologic Predictors of Lymph Node Metastasis and Prognosis in Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Dong Jin Lee, Mi Jung Kwon, Eun Sook Nam, Ji Hyun Kwon, Jin Hwan Kim, Young-Soo Rho, Hyung Sik Shin, Seong Jin Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):203-210. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.203
- 11,359 View
- 67 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) need to be established to determine the degree of surgery required to achieve high curative rates. However, little is known currently about the histopathological features predicting prognosis, specifically in TSCC.
Methods This study included 53 patients who underwent surgical resection with neck dissection. Clinicopathological factors investigated included age, gender, alcohol use, tobacco consumption, tumor stage, adjacent structure involvement, cell differentiation, squamous dysplasia,
in situ carcinoma associated with primary invasive cancer, carcinomain situ skip lesions, necrosis, invasive front, depth of invasion, and lymphatic, muscle, or perineural invasion.Results Contralateral cervical metastasis was associated with higher T stages and soft palate invasion. Lymphatic and muscle invasion were associated with ipsilateral cervical metastasis. Advanced T stage, invasion to the base of tongue, and skip lesions were associated with decreased disease-free survival. Advanced T stage and skip lesions were associated with worse overall survival.
Conclusions Advanced T stage and soft palate invasion may predict a high risk of contralateral nodal metastasis. T stage and skip lesion are worse prognostic factors in TSCC and should be commented in pathology reports.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Systematic Review of Occult Contralateral Neck Metastasis in Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Nihal Punjabi, Arjun Sharma, Jamie Park, Kari Kennedy, Jared C. Inman
The Laryngoscope.2025; 135(1): 27. CrossRef - OpenAi’s ChatGPT-4, BARD and YOU.com (AI) and the Cancer Patient, for Now, Caveat Emptor, but Stay Tuned
Glenn Tisman, Raju Seetharam
Digital Medicine and Healthcare Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Distinct Gene Expression Patterns of Tumor Microenvironment in HPV-Associated and HPV-Non Associated Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Reham M. Alahmadi, Najat Marraiki, Mohammed Alswayyed, Hatim A. Khoja, Abdullah E. Al-Anazi, Rawan M. Alahmadi, Meshael M. Alkusayer, Bandar Alosaimi, Maaweya Awadalla
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5548. CrossRef - Predictors of contralateral‐bilateral nodal disease in oropharyngeal cancer: A National Cancer Data Base Study
Masanari G. Kato, Mark A. Ellis, Shaun A. Nguyen, Terry A. Day
Head & Neck.2018; 40(2): 338. CrossRef - Clinical implication of programmed cell death-1 ligand-1 expression in tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma in association with intratumoral heterogeneity, human papillomavirus, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Mi Jung Kwon, Young-Soo Rho, Eun Sook Nam, Seong Jin Cho, Hye-Rim Park, Soo Kee Min, Jinwon Seo, Ji-Young Choe, Eun Soo Kim, Bumjung Park, Mineui Hong, Kyueng-Whan Min
Human Pathology.2018; 80: 28. CrossRef - Comparison of the eighth version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer manual to the seventh version for colorectal cancer: A retrospective review of our data
Guo-Jun Tong, Gui-Yang Zhang, Jian Liu, Zhao-Zheng Zheng, Yan Chen, Ping-Ping Niu, Xu-Ting Xu
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2018; 9(7): 148. CrossRef - HIPK2 Overexpression and Its Prognostic Role in Human Papillomavirus-Positive Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Mi Jung Kwon, So Young Kang, Eun Sook Nam, Seong Jin Cho, Young-Soo Rho
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Frequent hepatocyte growth factor overexpression and low frequency of c-Met gene amplification in human papillomavirus–negative tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma and their prognostic significances
Mi Jung Kwon, Dong Hoon Kim, Hye-Rim Park, Hyung Sik Shin, Ji Hyun Kwon, Dong Jin Lee, Jin Hwan Kim, Seong Jin Cho, Eun Sook Nam
Human Pathology.2014; 45(7): 1327. CrossRef - CT and MR imaging findings of palatal tumors
Hiroki Kato, Masayuki Kanematsu, Hiroki Makita, Keizo Kato, Daijiro Hatakeyama, Toshiyuki Shibata, Keisuke Mizuta, Mitsuhiro Aoki
European Journal of Radiology.2014; 83(3): e137. CrossRef
- A Systematic Review of Occult Contralateral Neck Metastasis in Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid Metastatic to Adenocarcinoma
In Situ of Lung: Report of an Unusual Case - Kyoung Min Kim, Yo Na Kim, Hyun Hee Chu, Heung Yong Jin, Min Ho Kim, Myoung Ja Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):282-286. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.282
- 9,243 View
- 53 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The tumor-to-tumor metastasis is a rare event. The lung tumors are the most common donor tumors in tumor-to-tumor metastasis, but are exceedingly rare as a recipient. Here, we report a case of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) metastasizing to adenocarcinoma
in situ (AIS, formerly bronchioloalveolar carcinoma) of the lung in a 44-year-old woman who underwent total thyroidectomy for PTC 8 years ago. To the best of our knowledge, the present case is the first case reporting on PTC metastasized to AIS. A review of the relevant literature is presented.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of colorectal cancer with intratumoral metastasis to primary lung cancer
Yasushi Cho, Mitsuhito Kaji, Shunsuke Nomura, Yusuke Motohashi, Masaaki Sato, Motoya Takeuchi
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2021; 35(5): 576. CrossRef - Tumor-to-tumor metastasis: metastatic invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast within adenocarcinoma of the lung
Myoung Jae Kang, Ae Ri An, Myoung Ja Chung, Kyoung Min Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(2): 188. CrossRef - Metastatic Renal Cell Neoplasm Within a Papillary Thyroid
Carcinoma as Incidental Finding in an Asymptomatic Patient: a Case Report
Maria-Rosa Bella-Cueto, Mireia Pascua-Solé, Albert Cano-Palomares, M. Àngels Cabezuelo-Hernandez, Maria-Rosa Escoda-Giralt, Santiago Barcons-Vilaplana, Paula Serret-Miralles, Carmen Caral-Vanaclocha, Xavier Guirao-Garriga, Joan Prats-Lopez, Meritxell Meda
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2020; 2(7): 978. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Tumor-to-Tumor Metastasis of Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma within a Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma
Taebum Lee, Yoon Jin Cha, Sangjeong Ahn, Joungho Han, Young Mog Shim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2015; 49(1): 78. CrossRef - Tumour-to-tumour metastasis from papillary thyroid carcinoma withBRAFmutation to lung adenocarcinoma withEGFRmutation: the utility of mutation-specific antibodies
Yuki Katsuya, Akihiko Yoshida, Shun-ichi Watanabe, Koji Tsuta
Histopathology.2015; 67(2): 262. CrossRef - Pulmonary metastasis of a papillary thyroid carcinoma and primary lung adenocarcinoma: two coincident carcinomas at the same location
Liyan Xue, Zhonghua Luan, Ying Liu, Shuangmei Zou, Jun Jiang, Ning Wu, Ning Lu, Dongmei Lin
Diagnostic Pathology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- A case of colorectal cancer with intratumoral metastasis to primary lung cancer
- Metastatic Carcinomas to the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
- Su-Jin Shin, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim, Sung Bae Kim, Sang-wook Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):266-271. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.266
- 12,092 View
- 109 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Metastases to the oral/oropharynx are very rare and their diagnosis is challenging.
Methods We reviewed pathologic data for malignant tumors of the oral/oropharynx that were diagnosed at the Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea from 1995 until 2010.
Results Twenty-nine cases of oral/oropharyngeal metastases were retrieved, comprising 2.0% of 1,445 malignancies. The most common primary sites were the liver and lung, followed by the stomach, colon, breast, prostate, and kidney. The gingiva was the most common metastatic site, followed by the tonsil/pillar, mandible, tongue, tongue base, palate mucosa, mouth floor, and buccal mucosa. Intervals between detection of primary tumors and metastases were variable, from -1 month to 104 months. Ten patients with lung (7 cases), liver, stomach, and kidney carcinomas manifested with oral/oropharyngeal metastases as the first sign of systemic metastases. The majority of patients had died within one year of the onset of an oral/oropharyngeal metastasis, but exceptionally long-lived cases were also present. The survival periods of patients with lung cancers were longer than those of patients with non-pulmonary tumors.
Conclusions An awareness of the incidence, common primary sites, metastatic subsites, and metastatic courses or patterns of oral/oropharyngeal metastases is helpful in the diagnosis of metastatic carcinomas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastasis of leiomyosarcoma to the sublingual region
Seiji Baba, Kyoko Ishimaru, Eiji Ito, Saki Goto, Keizo Kato, Yoichi Yamada
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2024; 36(1): 95. CrossRef - A Case of Oropharyngeal Carcinoma Accompanying a Presacral Malignant Epidermoid Cyst
Daiki Kitano, Yuki Komatsu, Makoto Omori
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mandibular metastasis of follicular thyroid carcinoma: A case report along with the concise review of literature
MK Jawanda, R Narula, S Gupta, P Gupta
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2022; 26(1): 133. CrossRef - Gingival metastasis from primary hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Yuan Huang, Yanqiu Bao, Dongyuan Xu, Lan Liu
Journal of International Medical Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mandibular metastasis of follicular thyroid carcinoma
Manveen Kaur Jawanda, Sonia Gupta, Priya Gupta, Ravi Narula
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2022; 26(2): 283. CrossRef - Lung carcinoma presenting as bilateral metastases in the mandibular gingivae: a case report and literature review
Nusaybah Elsherif, Predrag Jeremic, Tim Blackburn
Dental Update.2021; 48(10): 846. CrossRef - Recurrent clear cell carcinoma of the tongue base with high grade transformation in a pregnant patient
Emad M. Al Haj Ali, Ahmed M. Ibrahim, Tamer A. Ghanem, Christian E. Keller
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2020; 32(2): 104. CrossRef - Primary Lingual Colonic-Type Adenocarcinoma: A Rare and Emerging Distinct Entity!
Stephen M. Smith, Matthew Old, O. Hans Iwenofu
Head and Neck Pathology.2017; 11(2): 234. CrossRef - Rare Gingival Metastasis by Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Li-Jun Xue, Xiao-Bei Mao, Jian Geng, Ya-Nan Chen, Qian Wang, Xiao-Yuan Chu
Case Reports in Medicine.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung metastasizing to the tonsil
Luca Valle, Joel Thomas, Chul Kim, Eva Szabo, G. Thomas Brown, Deborah Citrin, Arun Rajan
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2017; 6(5): 705. CrossRef - Epulis-Like Presentation of Gingival Renal Cancer Metastasis
Gianfilippo Nifosì, Hubert Bressand, Antonio Fabrizio Nifosì, Lorenzo Nifosì, Pierre Damseaux
Case Reports in Oncology.2017; 10(2): 758. CrossRef - A Case of Oral Metastasis From Hepatocellular Carcinoma Displayed on 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging
Lei Jiang, Taoying Gu, Fang Liu, Lijuan Luan, Hongcheng Shi
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2016; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - A case of renal cell carcinoma diagnosed in association with a palatal mucosa mass
Masaharu NOI, Yoshizou TSUDA, Shota SAITO, Takeshi ADACHI, Tomoki HIGO, Gaku YAMAMOTO
Japanese Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2016; 62(2): 62. CrossRef - Unusual Presentation of an Adenocarcinoma of the Lung Metastasizing to the Mandible, Including Molecular Analysis and a Review of the Literature
Sibel Elif Gultekin, Burcu Senguven, Ipek Isik Gonul, Begum Okur, Reinhard Buettner
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2016; 74(10): 2007.e1. CrossRef - A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Presenting as a Gingival Mass
Min Jung Kwon, Soo Hyung Ryu, Soo Yeon Jo, Chul Hoon Kwak, Won Jae Yoon, Jeong Seop Moon, Hye Kyung Lee
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 68(6): 321. CrossRef - Mandibular metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma: A case report
Tae Min You, Kee-Deog Kim, Ho-Gul Jeong, Wonse Park
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2015; 45(4): 247. CrossRef - Oral Floor and Gingival Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Yukihiro Nakanishi, Bo Xu, Charles LeVea
Case Reports in Pathology.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung Leading to Metastatic Jaw Tumor
Chintamaneni Raja Lakshmi, M. Sudhakara Rao, Sujana Mulk Bhavana, Sivan Sathish
Case Reports in Pulmonology.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - A Case of Gingival Metastasis from Rectal Cancer in Which Immunohistochemistry and PET-CT Were Useful for the Diagnostic Procedure
Masami Yamauchi, Katsunori Shinozaki, Mihoko Doi, Tomoko Nitta, Takashi Nishisaka
Case Reports in Oncology.2014; 7(1): 246. CrossRef
- Metastasis of leiomyosarcoma to the sublingual region
- Chemotherapy-Associated Hepatopathy in Korean Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Patients: Oxaliplatin-Based Chemotherapy and Sinusoidal Injury
- Soo Jeong Nam, Jai Young Cho, Hye Seung Lee, Gheeyoung Choe, Ja June Jang, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Ho-Seong Han, Haeryoung Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):22-29. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.22
- 10,069 View
- 71 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Although chemotherapy-related hepatic injury has been reported in colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) patients, the morphologic changes caused by chemotherapeutic agents and the effect of chemotherapy on postoperative outcome remain ill-defined. A comprehensive review of the morphologic changes in the post-chemotherapy non-neoplastic liver was performed and the clinical effect of preoperative chemotherapy in CRLM patients was analyzed.
Methods Hematoxylin-eosin, Masson's trichrome and reticulin-stained slides from non-neoplastic livers obtained from 89 CRLM patients were analyzed, and the clinicopathologic features were correlated with the status of chemotherapy exposure.
Results Histopathologic features of sinusoidal injury (sinusoidal dilatation, centrilobular perivenular fibrosis, parenchymal extinction lesions, small vessel obliteration, and hepatocyte plate disruption) were significantly more frequent in oxaliplatin-exposed livers (p<0.05). The extent of sinusoidal dilatation was positively correlated with increasing numbers of chemotherapy cycles (p=0.022). Abnormal preoperative liver function tests were more frequently seen (p<0.05) and postoperative total bilirubin was higher in the chemotherapy group (p=0.008). Postoperative morbidity was more common in the chemotherapy group (p=0.044).
Conclusions Sinusoidal injury is frequently seen in oxaliplatin-treated livers, and its presence, especially when extensive, should be documented in surgical pathology practice. The recognition of sinusoidal injury may provide helpful guidelines for surgeons in deciding the extent of hepatic resection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Model establishment and microarray analysis of mice with oxaliplatin‑induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
Chen Zhu, Xinwei Cheng, Ping Gao, Qianyan Gao, Ximin Wang, Dong Liu, Xiuhua Ren, Chengliang Zhang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxaliplatin-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
Chen Zhu, Xiuhua Ren, Dong Liu, Chengliang Zhang
Toxicology.2021; 460: 152882. CrossRef - Hepatic steatosis in patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases: A target for prehabilitation? A narrative review
D.T. Doherty, P.O. Coe, L. Rimmer, S. Lapsia, A. Krige, D.A. Subar
Surgical Oncology.2019; 30: 147. CrossRef - Protective effect of Korean red ginseng on oxaliplatin-mediated splenomegaly in colon cancer
Jeonghyun Kang, Joon Seong Park, Sung Gwe Ahn, Jin Hong Lim, Seung Hyuk Baik, Dong Sup Yoon, Kang Young Lee, Joon Jeong
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2018; 95(3): 161. CrossRef - Use of Imaging to Predict Complete Response of Colorectal Liver Metastases after Chemotherapy: MR Imaging versus CT Imaging
Min Jung Park, Nurhee Hong, Kyunghwa Han, Min Ju Kim, Yoon Jin Lee, Yang Shin Park, Sung Eun Rha, Sumi Park, Won Jae Lee, Seong Ho Park, Chang Hee Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Chansik An, Hye Jin Kim, Honsoul Kim, Mi-Suk Park
Radiology.2017; 284(2): 423. CrossRef - Systematic review of the influence of chemotherapy-associated liver injury on outcome after partial hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases
J Zhao, K M C van Mierlo, J Gómez-Ramírez, H Kim, C H C Pilgrim, P Pessaux, S S Rensen, E P van der Stok, F G Schaap, O Soubrane, T Takamoto, L Viganò, B Winkens, C H C Dejong, S W M Olde Damink, I García Sanz, E Martín Pérez, J Y Cho, Y R Choi, W Phillip
British Journal of Surgery.2017; 104(8): 990. CrossRef - Hepatic Lesions that Mimic Metastasis on Radiological Imaging during Chemotherapy for Gastrointestinal Malignancy: Recent Updates
Sung-Hye You, Beom Jin Park, Yeul Hong Kim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2017; 18(3): 413. CrossRef - Changes in Noninvasive Liver Fibrosis Indices and Spleen Size During Chemotherapy
Sehhoon Park, Hwi Young Kim, Haeryoung Kim, Jin Hyun Park, Jung Ho Kim, Ki Hwan Kim, Won Kim, In Sil Choi, Yong Jin Jung, Jin-Soo Kim
Medicine.2016; 95(2): e2454. CrossRef - Genetic predisposition resulting in sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a patient with resected sigmoid cancer on adjuvant oxaliplatin
Si Xuan Koo, Sock Hoai Chan, Joanne Ngeow
BMJ Case Reports.2016; 2016: bcr2015212978. CrossRef - Hepar lobatum carcinomatosum associated with liver metastases from breast cancer: Report of five cases
N. Alberti, D. Bechade, F. Dupuis, A. Crombe, A. Neuville, M. Debled, J. Palussiere, X. Buy, J.-T. Perez, M. Desjardin, N. Frulio, M. Kind
Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging.2015; 96(1): 73. CrossRef - Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy
An Na Seo, Haeryoung Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced Focal Hepatopathy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Malignancy: Gadoxetic Acid–enhanced and Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging with Clinical-Pathologic Correlation
Na Yeon Han, Beom Jin Park, Deuk Jae Sung, Min Ju Kim, Sung Bum Cho, Chang Hee Lee, Yun-Jin Jang, So Yeon Kim, Dong Sik Kim, Soon Ho Um, Nam Hee Won, Kyung Sook Yang
Radiology.2014; 271(2): 416. CrossRef - Histopathologic Manifestations of Drug-induced Hepatotoxicity
Xuchen Zhang, Jie Ouyang, Swan N. Thung
Clinics in Liver Disease.2013; 17(4): 547. CrossRef
- Model establishment and microarray analysis of mice with oxaliplatin‑induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Gingiva from the Lung: A Case Report
- Tack Kune You, So Ri Kim, Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, Woo Sung Moon, Myoung Ja Chung, Dong Geun Lee, Myoung Jae Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):101-104. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.101
- 8,461 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metastases of malignant tumors to the oral region from distant sites are uncommon. A 45-year-old man with painless gingival swelling was diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the lung. On cytology, clusters of tumor cells on mucous background revealed enlarged nuclei, indistinct cell borders, and irregular nuclear membranes. Some cells showed nuclear inclusions, nuclear grooves and small nucleoli. These findings are indicative of metastatic adenocarcinoma. We present a case of gingival metastasis from a lung adenocarcinoma.
- Value of Additional Immunocytochemical Stain for Cytokeratin in the Diagnosis of Leptomeningeal Involvement of Metastatic Carcinoma.
- Junjeong Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):516-519.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.516
- 3,647 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to describe potential pitfalls in the diagnosis of metastatic adenocarcinoma in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and to suggest additional work in association with cytokeratin immunocytochemistry for the proper diagnosis, especially in the specimens with low cellularity.
METHODS
We collected 267 cytologic specimens of CSF from patients, who were diagnosed over a 9-month period. Each of the individual samples were divided into half the sample size and processed via both, ThinPrep (TP) with Papanicolau stain and cytocentrifugation-based preparation (cytospin, CP) with immunocytochemical stain for cytokeratin.
RESULTS
Amongst the 267 cases, 45 cases from 22 patients were diagnosed to be positive for metastasis adenocarcinoma in CSF. TP with Papanicolau stain showed satisfactory cytomorphology when compared with specimen of CP preparation and cytokeratin immunocytochemical staining. All the TP processed cases belonged to satisfactory/superior categories based on the assessment of technical artifact, which potentially helps in decreasing diagnositc errors. However, in 10 out of 45 cases, diagnostic atypical cells were present only in one of the two slides.
CONCLUSIONS
Immunocytochemical stain for cytokeratin along with TP processed specimen helps in decreasing potential diagnostic errors in the cytological diagnosis of metastatic carcinoma in CSF specimen.
- Prognostic Significance and Nature of Rhabdoid Features in Renal Cell Carcinoma.
- Misun Choe, Ji Young Park, Ilseon Hwang, Sang Pyo Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(4):371-378.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.4.371
- 4,732 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Recent reports have indicated that renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with rhabdoid features follows an aggressive clinical course. We investigated the prognostic significance and nature of the rhabdoid component.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed the incidence and clinicopathologic characteristics of RCC with rhabdoid features in 174 radical nephrectomy cases. The specimens were examined histologically and immunohistochemically.
RESULTS
Twelve of the 174 RCC cases (6.9%) showed rhabdoid features. Histologically, all the tumors with rhabdoid features were of the clear cell type. The presence of rhabdoid features was significantly associated with higher Fuhrman's nuclear grade and higher pathologic tumor stage at presentation. Among the 12 patients who showed the rhabdoid component, nine (75%) developed metastasis and seven (58.3%) died of disease-related causes. The presence of rhabdoid features was independently associated with metastasis and disease-related mortality. The rhabdoid cells were positive for vimentin; variably positive for pan-cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen, and CD10; and negative for cytokeratin 7, smooth muscle actin, desmin, E-cadherin, and c-Kit. No case showed loss of integrase interactor-1; one was p53 positive, and five were insulin-like growth factor mRNA binding protein 3 positive. The Ki-67 labeling index was 1-25% (mean, 5.5%).
CONCLUSIONS
The rhabdoid component is an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of RCC; therefore, identification of this component is critical.
- A Metastatic Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Producing Sarcomatoid Carcinoma of the Lung Causing Jejunal Intussusception: Report of a Case.
- Min Eui Hong, Soon Auck Hong, Gui Young Kwon, Tae Jin Lee, Eon Sub Park, Sung Jae Cha, Jae Hyuk Do, Jae Hyung Yoo
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):205-208.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.205
- 3,548 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 75-year-old man was referred to our hospital with intestinal obstruction caused by intussusception. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed seven polypoid masses in the small intestine, while chest CT revealed a mass in the right lower lobe. Preoperative laboratory tests showed white blood cell (WBC) and neutrophil differential counts of 63,630/mm3 and 95%, respectively. The serum granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) was 114 pg/mL, which was elevated (normal range, <18.1 pg/mL). After resection of the small bowel, the WBC count decreased to 20,510/mm3. The pathology showed a poorly differentiated carcinoma with sarcomatous components confirmed by positive immunostaining of cytokeratin (AE1/AE3) and vimentin in the small intestine. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry with specific monoclonal antibodies against G-CSF was positive. A lung biopsy revealed the same histological findings as the small intestine lesion. Therefore, the patient was diagnosed as having a G-CSF producing sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung with metastasis to the small intestine.
- Cytologic Findings of Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma Presenting with Multiple Pulmonary Masses: A Case Report with Review of Literature.
- Na Rae Kim, Jae Y Ro, Eun Kyung Cho, Mi Jin Kim, Jungsuk An, Seung Yeon Ha
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):119-124.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.119
- 3,663 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is a rare malignant soft tissue tumor of uncertain origin, and it has a strong propensity for metastasis to the lungs, bones and brain. We report upon an unusual case of ASPS, presenting as multiple lung nodules with no other detectable primary site, in a 44-year-old man. A fine needle aspiration of the nodules yielded scattered, discohesive cells, each containing an eccentrically displaced nucleus and prominent nucleolus, on a granular background. Tumor cells with numerous bared nuclei, and occasional sheets of epithelioid cells were also found. Under the cytological diagnosis of an unclassified epithelioid malignant tumor, resection of the lung nodules was performed. The histologic findings were consistent with ASPS, showing positive TFE3-nuclear immunoreactivity. There is limited literature concerning cytological findings associated with pulmonary ASPS: especially in cases where the primary site is unknown. Here, we present a cytological review of pulmonary ASPS, investigating the significance of TFE3 staining in the diagnosis of ASPS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alveolar soft part sarcoma: A case report with emphasis on some unusual cytological features
Neelam Sood, Minakshi Gulia
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(2): 170. CrossRef
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma: A case report with emphasis on some unusual cytological features
- The Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of a Metastatic Pulmonary Adrenocortical Carcinoma Mimicking Primary Large Cell Carcinoma of the Lung.
- Na Rae Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Ik Lee, Seung Yeon Ha
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(5):558-563.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.5.558
- 3,258 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare neoplasm and it has an invariably lethal prognosis. We report here on the fine needle aspiration cytologic findings of a solitary metastatic pulmonary adrenocortical carcinoma in a 24-year-old woman. The aspirate smears were very cellular and they were composed of a monomorphic population of large polyhedral cells with abundant granular or vacuolated cytoplasm, and the cells were predominantly singly scattered in a necrotic background. Multinucleated pleomorphic tumor cells were also found. Pleomorphic nuclei with thickened nuclear membranes were impinging on the cell membranes. Mitotic activity was occasionally seen. The cytologic findings of pleomorphic cells with microvacuolated cytoplasm and the presence of vague gland-like sheets, as well as the patient's history of undergoing adrenalectomy for primary adrenocortical carcinoma helped the pathologist reach the diagnosis of metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma. Here, we focus on the cytologic differential points of metastastic pulmonary adrenocortical carcinoma and primary pulmonary carcinoma, especially large cell carcinoma.
- Metastases from Rectum and Thyroid Cancers in Same Cervical Lymph Node: A Case Report.
- Bulent Yildiz, Abdulkadir Reis, Evren Fidan, Feyyaz Ozdemir, Halil Kavgaci, Fazil Aydin
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(5):551-553.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.5.551
- 3,505 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An excisional biopsy targeting a cervical lymph node was performed on a 49-year-old female patient with metastatic rectal cancer. The biopsy revealed rectal and papillary thyroid cancer metastasis in the same lymph node. A thin-needle thyroid aspiration biopsy was performed, and the result was papillary thyroid carcinoma. The patient, who received chemotherapy for the metastatic rectal cancer, died due to disease progression about 5 months after a secondary primary tumor was detected. Metastasis of multiple malignancies in the same lymph node is extremely rare. A metastases of rectal and thyroid cancers to the same lymph node has not been reported until now. Our patient is the first case in the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tumor-to-tumor metastases: systematic review and meta-analysis of 685 reported cases
Michał Kunc, Paulina Skrzypkowska, Rafał Pęksa, Wojciech Biernat
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Tumor-to-tumor metastases: systematic review and meta-analysis of 685 reported cases
- Expression of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Correlates with Histologic Grade and Metastasis in Osteosarcoma.
- Hye Rim Park, Jinwon Seo, Patrizia Bacchini, Franco Bertoni, Yong Koo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(4):384-389.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.4.384
- 3,564 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) is reportedly overexpressed in several types of carcinomas, but little is known about the expression pattern of CA9 in osteosarcoma. We aimed to assess the prevalence of CA9 expression and its prognostic implications in osteosarcoma patients.
METHODS
We compared immunohistochemical expression of CA9 between conventional, high-grade and low-grade, central osteosarcomas. Specimens were obtained before chemotherapy and stained with anti-human CA9 antibody. We also evaluated the histologic grade, presence of metastasis, and patient prognosis.
RESULTS
Among 38 samples of conventional high-grade osteosarcoma, 22 (57.9%) tumors displayed CA9 overexpression. Twenty-five cases of low-grade central osteosarcomas were all negative (p < 0.0001). CA9 expression was significantly associated with the presence of metastasis (p = 0.0010). The overall survival rate was significantly reduced with increased CA9 expression (p = 0.0012), higher histologic grade (p < 0.0001), and younger age (p = 0.0140). However, the overall survival rate was not significantly correlated with gender, tumor size, or American Joint Committee on Cancer stage.
CONCLUSIONS
CA9 expression is a frequent and tumor-specific event in osteosarcoma. CA9 expression is associated with higher grade tumors, metastasis and poor prognosis for the osteosarcoma patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The reducing effect of TNF-α on carbonic anhydrase III gene expression in colon carcinoma and osteosarcoma cells
Sümeyye Aydoğan Türkoğlu, Derya Okuyan, Feray Köçkar
Cytotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The reducing effect of TNF-α on carbonic anhydrase III gene expression in colon carcinoma and osteosarcoma cells
- Metastatic Carcinomas to the Sinonasal Tract.
- Eun Ju Kim, Bong Jae Lee, Kyung Ja Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):302-307.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.302
- 4,954 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metastases to the sinonasal tract are rare but occur for many malignancies. The demographics of sinonasal metastases in Korea aren't well known.
METHODS
Nine cases of metastases to the sinonasal tract identified at Asan Medical Center from January, 1995 to December, 2007 were reviewed.
RESULTS
Metastatic carcinomas accounted for 2.4% of sinonasal malignancies and 4.7% of carcinomas. Six kinds of cancer metastasized to the sinonasal tract. They included hepatocellular carcinomas (nasal cavity and maxillary sinus), colonic adenocarcinomas (sphenoid sinus and maxillary sinus), clear cell renal cell carcinoma (nasal cavity), pulmonary small cell carcinoma (nasal cavity), follicular carcinoma of thyroid (sphenoid sinus), and breast ductal carcinoma (maxillary sinus). Primary sites had been known in 7 cases, but follicular carcinoma and one adenocarcinoma were diagnosed after sinus metastases. Histologically, they had ill-defined borders and involved both mucosae and bones. Microscopic findings were not different from those for the primary tumors.
CONCLUSIONS
The pattern of sinonasal metastases in Korea are different from western data regarding incidence, site, and type, with hepatocellular carcinoma and the nasal cavity being the most common type and site, respectively. Awareness of the possibility of metastases and their pattern is encouraged when examining sinonasal tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic Carcinomas to the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
Su-Jin Shin, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim, Sung Bae Kim, Sang-wook Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(3): 266. CrossRef
- Metastatic Carcinomas to the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
- Expression of Raf-1 Kinase Inhibitory Protein in Extrahepatic Bile Duct Carcinoma.
- Hyun Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):234-242.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.234
- 4,601 View
- 21 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) recently has been identified as a metastasis suppressor in a variety of human carcinomas. The prognostic significance of RKIP expression in extrahepatic bile duct (EBD) carcinoma has not been studied. The aims of the current study were to evaluate RKIP expression and to determine the prognostic significance of RKIP expression in EBD carcinoma.
METHODS
Immunohistochemical staining for RKIP was performed for 131 cases of EBD carcinoma. The associations of RKIP expression with clinicopathologic parameters and patient outcomes were examined. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent predictive parameters for lymphovascular invasion and nodal and distant metastases.
RESULTS
Loss of RKIP expression was observed in 55.0% (72/131) of cases. EBD carcinoma had significantly lower RKIP immunoreactivity than normal EBD (p < 0.001). Loss of RKIP expression was significantly associated with lymphatic invasion (p = 0.030) and nodal metastasis (p = 0.036), but it was not found to be a significant prognostic predictor for overall, disease-free or distant metastasis-free survival. In addition, loss of RKIP expression was an independent predictor for lymphatic invasion (p = 0.027).
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that RKIP may play a role in the suppression of lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis in EBD carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Down-regulation of osteoprotegerin expression as a novel biomarker for colorectal carcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gun Yoon, Sung-Im Do, Sung-Joo Kim, Youn-Wha Kim
Oncotarget.2016; 7(12): 15187. CrossRef - Expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase at the invasive front of hepatic colorectal metastasis
HYUN-SOO KIM, SUNG-IM DO, BYEONG-JOO NOH, YOUNG IN JEONG, SUN JIN PARK, YOUN WHA KIM
Oncology Letters.2015; 9(3): 1261. CrossRef - Reduced expression of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein predicts regional lymph node metastasis and shorter survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Kyu Yeoun Won, Gou Young Kim, Soo Cheol Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Youn Wha Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2012; 208(5): 292. CrossRef - Expression of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein in carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater
Hyun-Soo Kim, Sun Ho Lee, Kyu Yeoun Won, Gou Young Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Youn Wha Kim
Virchows Archiv.2012; 460(1): 61. CrossRef - Raf-1 Kinase Inhibitory Protein Expression in Thyroid Carcinomas
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung-Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
Endocrine Pathology.2010; 21(4): 253. CrossRef - Loss of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Hyun-Soo Kim, Gou Young Kim, Sung-Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
Pathology.2010; 42(7): 655. CrossRef
- Down-regulation of osteoprotegerin expression as a novel biomarker for colorectal carcinoma
- Validation of Gene Expression Changes of Osteopontin and MMP-1 in Primary and Metastatic Colorectal Carcinomas.
- Junjeong Choi, Sangkyum Kim, Jeon Han Park, Nam Kyu Kim, Hoguen Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(3):225-233.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.3.225
- 4,607 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metastasis is one of the most important characteristics of cancer in terms of its impact on patient survival. Unfortunately, identification of altered genes during tumor metastasis is limited.
METHODS
Using high-throughput microarrays containing 19K spotted human oligonucleotides, gene expression of primary and matched metastatic colon cancer were compared in previous study. Although DNA microarray analysis did not demonstrate complete classification of primary and metastatic carcinoma, 80 differentially expressed genes were identified. Among these, expression of osteopontin, matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and serpin A1 was assessed using immunohistochemistry in a validation set containing 43 pairs from tissue microarrays.
RESULTS
The expression of osteopontin was significantly higher in metastatic carcinoma than in primary carcinoma, as indicated by mRNA expression. The expression of MMP-1 was significantly lower in metastatic carcinoma. Expression of serpin A1 was not correlated with the microarray results.
CONCLUSIONS
Osteopontin and MMP-1 expression successfully classified primary and metastatic colorectal carcinomas and further studies on their clinical application is encouraged.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of a Myxoid Leiomyosarcoma with Epithelioid Features and It Metastasized to the Abdominal Wall: A Case Report.
- Lee So Maeng, Hiun Suk Chae, Anhi Lee, Yongan Chung, Kyo Young Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):220-224.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.220
- 3,341 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We present the cytologic findings observed in a fine needle aspiration biopsy specimen of a rare myxoid variant of leiomyosarcoma with epithelioid features and the tumor had metastasized to the abdominal wall. The aspirate showed hypercellularity in a hemorrhagic background. Some large 3-dimensional aggregates of spindle cells were observed. Each cell had a solitary ovoid-to-elongated nucleus with finely granulated chromatin, one or two small distinct nucleoli and an irregular nuclear membrane. There were irregular fascicles of spindle cells with cigar-shaped, blunt-ended nuclei admixed with inflammatory cells. Epithelioid cells with a rather narrow, dense cytoplasmic rim and a well-defined cell border were embedded in a myxoid matrix in a cord-like and cluster arrangement. The matrix appeared as a pale green substance with sharply defined edges. There were very few mitoses. These cytologic features were the same as those of a uterine myxoid leiomyosarcoma that was surgically excised 7 years ago, and immunohistochemical staining revealed the smooth muscle origin of the tumor.
- Metastatic Tumors to the Breast from Extramammary Malignancies.
- Bong Hee Park, Yonghee Lee, Sei Hyun Ahn, Hak Hee Kim, Sung Bae Kim, Gyungyub Gong
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):70-76.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.70
- 3,968 View
- 49 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies are very rare. We describe here the clinicopathologic features of the metastatic breast tumors that were identified in Korean patients at a single institute.
METHODS
We analyzed the clinicopathologic data of the patients who were diagnosed between January 1989 and April 2009 at Asan Medical Center.
RESULTS
Only 31 (0.21%) patients with metastases to the breast from extramammary malignancies were diagnosed over a 20-year period, and 29 of them had available data. The mean time to the diagnosis of metastasis after the diagnosis of the primary malignancy was 21 months (range, 0 to 102 months). The most common primary site was the stomach, followed by the uterus and lung. The most common histologic type was adenocarcinoma. A common clinical presentation was a unilateral palpable mass. Most metastatic tumors had morphological features that were similar to those of their respective primary tumors. However, in situ carcinoma, microcalcification and desmoplastic reactions were rarely observed.
CONCLUSIONS
Metastatic breast lesions from extramammary sites are extremely rare, and the stomach, uterus and lung could be considered as the common primary sites in Korean patients. The clinical history and comparing the morphology of the primary tumor with the morphology of the metastatic tumor are important for achieving the proper diagnosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histological clues to the diagnosis of metastasis to the breast from extramammary malignancies
Andrew H S Lee, Zsolt Hodi, Irshad Soomro, Vishakha Sovani, Areeg Abbas, Emad Rakha, Ian O Ellis
Histopathology.2020; 77(2): 303. CrossRef
- Histological clues to the diagnosis of metastasis to the breast from extramammary malignancies
- Clinicopathologic Significances of EGFR Expression at Invasive Front of Colorectal Cancer.
- Yeo Ju Kang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yeong Jin Choi, Kyo Young Lee, Hyung Jin Kim, Won Kyung Kang, Seong Taek Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):16-21.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.16
- 4,220 View
- 41 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is frequently expressed in the invasive front of colorectal cancer (CRC), but its clinicopathologic significance remains unclear. We investigated the clinical value of the EGFR expression at the invasive front of CRC.
METHODS
We performed an immunohistochemical analysis in order to examine the expression and distribution of EGFR in 214 cases of CRC. The EGFR status was considered positive when > or =1% of the tumor cells had membranous staining.
RESULTS
Overall, an EGFR expression was observed in 144 (67%) cases and it had no significant relationship with the clinicopathologic parameters. However, an EGFR expression at the invasive front was correlated with lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis and a high level of serum carcinoembryonic antigen (p = 0.028, p = 0.043, and p = 0.045, respectively). For the budding-positive CRCs liver metastases were found in the cases with an EGFR expression at the budding, but no liver metastasis occurred in the EGFR negative cases at the budding (p = 0.030).
CONCLUSIONS
An EGFR expression at the invasive front has clinicopathologic significances in patients with CRC. An EGFR expression at tumor cell budding is a pathologic marker that suggests the high potential for liver metastasis in CRC.
- Metastatic Osteosarcoma to the Prostate: A Case Report.
- Hyoung Yeon Seo, Jae Hyuk Lee, Chang Soo Park, Jin Gyoon Park, Sung Taek Jung
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(5):475-477.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.5.475
- 4,639 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The most common site for the metastasis of osteosarcoma is the lung, and other sites of metastases include the bone, lymph node, pleura and liver. Although unusual extrapulmonary metastases have been reported with the improvement of the therapeutic results for the primary lesions, they are exceptionally rare. We report here on a case of prostatic metastasis of an osteosarcoma of the proximal tibia, and this developed seven years after successful resection, and four years after resection of a pulmonary metastasis. Radical prostatectomy was performed, and histological examination demonstrated metastatic osteosarcoma. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of prostatic metastasis of osteosarcoma in the medical literature.
- Comparison of Cytologic Evaluation between Conventional Method and CellprepPlus(R) Liquid-Based Cytology in Body Fluid.
- Ji Hae Koo, Ho Chang Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Hye Suk Han, Ki Hyeong Lee, Kang Hyeon Choe, Ki Man Lee, Ok Jun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(5):448-452.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.5.448
- 5,855 View
- 127 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Assessment of body fluid cytology is a useful means of evaluating a metastatic tumor. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) has been developed as a replacement for the conventional Papanicolaou (CP) test. This study was performed to compare CellprepPlus(R) LBC with CP in cytologic diagnosis. METHODS: Body fluid samples (n=188, including 72 peritoneal fluid and 116 pleural fluid samples) were divided equally and analyzed by both CellprepPlus(R) and CP.
RESULTS
CellprepPlus(R) revealed distributed thin layers of non-overlapping cells. All CellprepPlus(R) preparations were adequate, while 18 (9.57%) CP preparations were inadequate. The respective diagnostic rates of CellprepPlus(R) and CP were 75.0% and 76.1% negative, 10.6% and 6.38% atypical, 5.85% and 2.66% suspicious, and 8.51% and 5.32% malignant. Of the 58 confirmed cases, the sensitivity of CellprepPlus(R) and CP was 94.4% and 73.3%, respectively, and the negative predictive value was 97.2% and 87.9%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
CellprepPlus(R) LBC has better sensitivity and negative predictive value, and produces higher quality slide preparations than than CP, making it suitable as in screening of body fluid as a cytologic diagnostic tool. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CYTOLOGIC EVALUATION BETWEEN CONVENTIONAL METHOD & LIQUID BASED CYTOLOGY IN PLEURAL, PERICARDIAL & PERITONEAL FLUIDS
R. P. Siddiqui, Mohd. Jafar Memon, Shraddha Sahu
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Comparison of liquid-based cytology (CellPrepPlus) and conventional smears in pancreaticobiliary disease
Myeong Ho Yeon, Hee Seok Jeong, Hee Seung Lee, Jong Soon Jang, Seungho Lee, Soon Man Yoon, Hee Bok Chae, Seon Mee Park, Sei Jin Youn, Joung-Ho Han, Hye-Suk Han, Ho Chang Lee
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(5): 883. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine Cytology in Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Comparison of CellprepPlus® Liquid-Based Cytology and Conventional Smear
Seung-Myoung Son, Ji Hae Koo, Song-Yi Choi, Ho-Chang Lee, Yong-Moon Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Hae-Kyung Hwang, Hye-Suk Han, Seok-Joong Yun, Wun-Jae Kim, Eun-Joong Kim, Ok-Jun Lee
Korean Journal of Pathology.2012; 46(1): 68. CrossRef - CellprepPlus® Liquid-based Smear in Sono-guided Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration: A Comparison of Conventional Method and CellprepPlus® Liquid-based Cytology
Ji Hae Koo, Seung Young Lee, Ho-chang Lee, Jin-Woo Park, Sung Soo Koong, Tae Keun Oh, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Eun-Joong Kim, Ok-Jun Lee
The Korean Journal of Pathology.2011; 45(2): 182. CrossRef
- A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CYTOLOGIC EVALUATION BETWEEN CONVENTIONAL METHOD & LIQUID BASED CYTOLOGY IN PLEURAL, PERICARDIAL & PERITONEAL FLUIDS
- Morphological Features of Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors after Gleevec Treatment: Two Cases Report.
- Joon Hyuk Choi, Young Kyung Bae, Sun Kyo Song, Hong Jin Kim, Min Chul Shim, Kyung Hee Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(4):368-373.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.4.368
- 3,578 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report two patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) with a focus on the morphological features related to Gleevec treatment. In case 1, a 50-year-old woman presented with a 1.8 cm metastatic GIST in the liver after resection of a gastric GIST. Majority of the metastatic tumor showed fibrosis and hyalinization after 8 weeks of Gleevec treatment. CD117-positive cells were present in approximately 1% of the overall tumor. In case 2, a 2 cm and 14 cm metastatic liver masses were found in a 54-year-old man who had a rectal GIST. After 4 weeks of Gleevec treatment, metastatic tumors showed a decrease in size on CT scan. The metastatic tumors showed a decrease in number of tumor cells. The hemorrhage, cystic changes, necrosis, and fibrosis made up approximately 90% of the tumor. The morphological features related to Gleevec treatment are important for correct diagnosis and evaluation of tumor response and prognosis.

 E-submission
E-submission
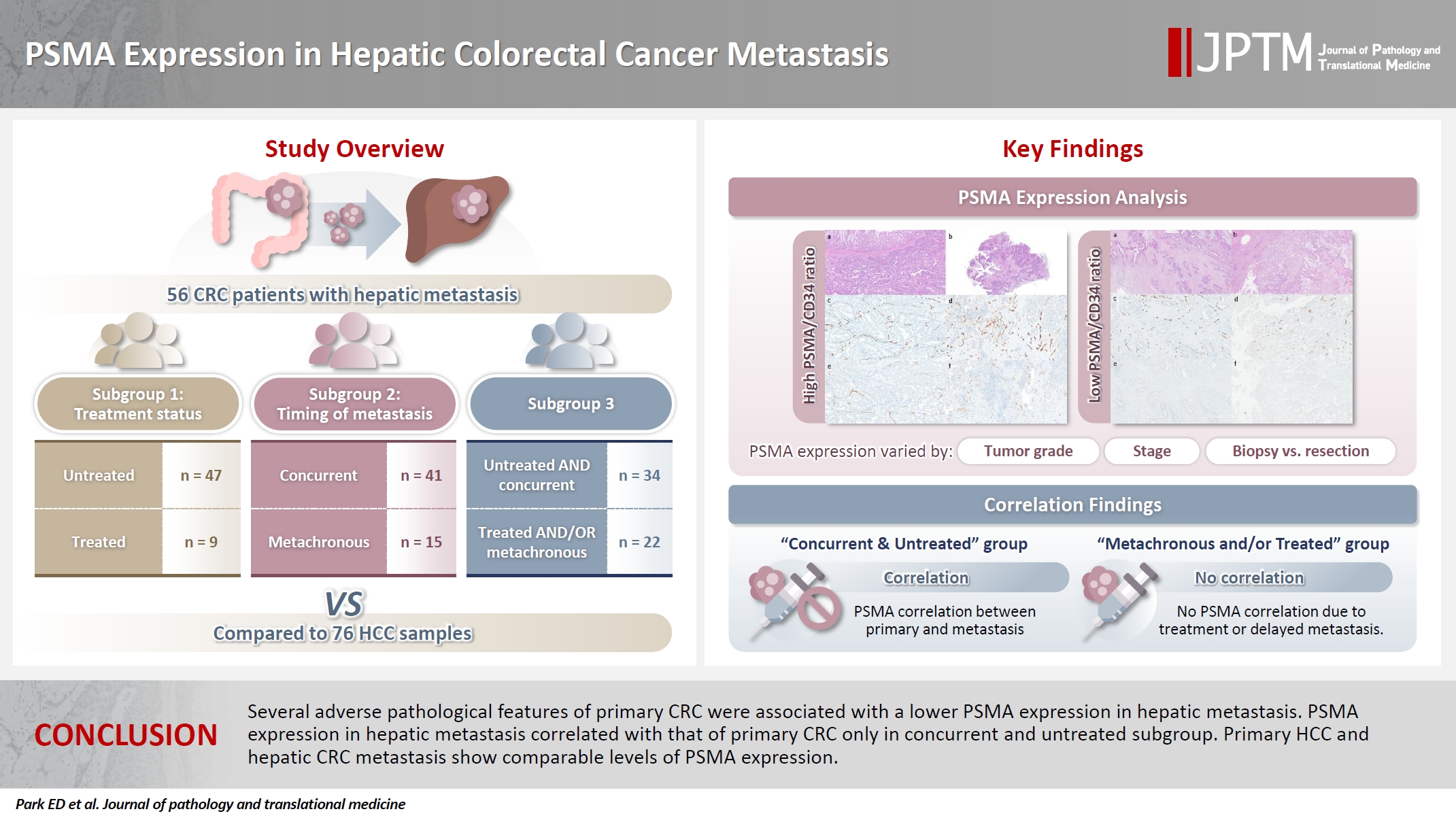
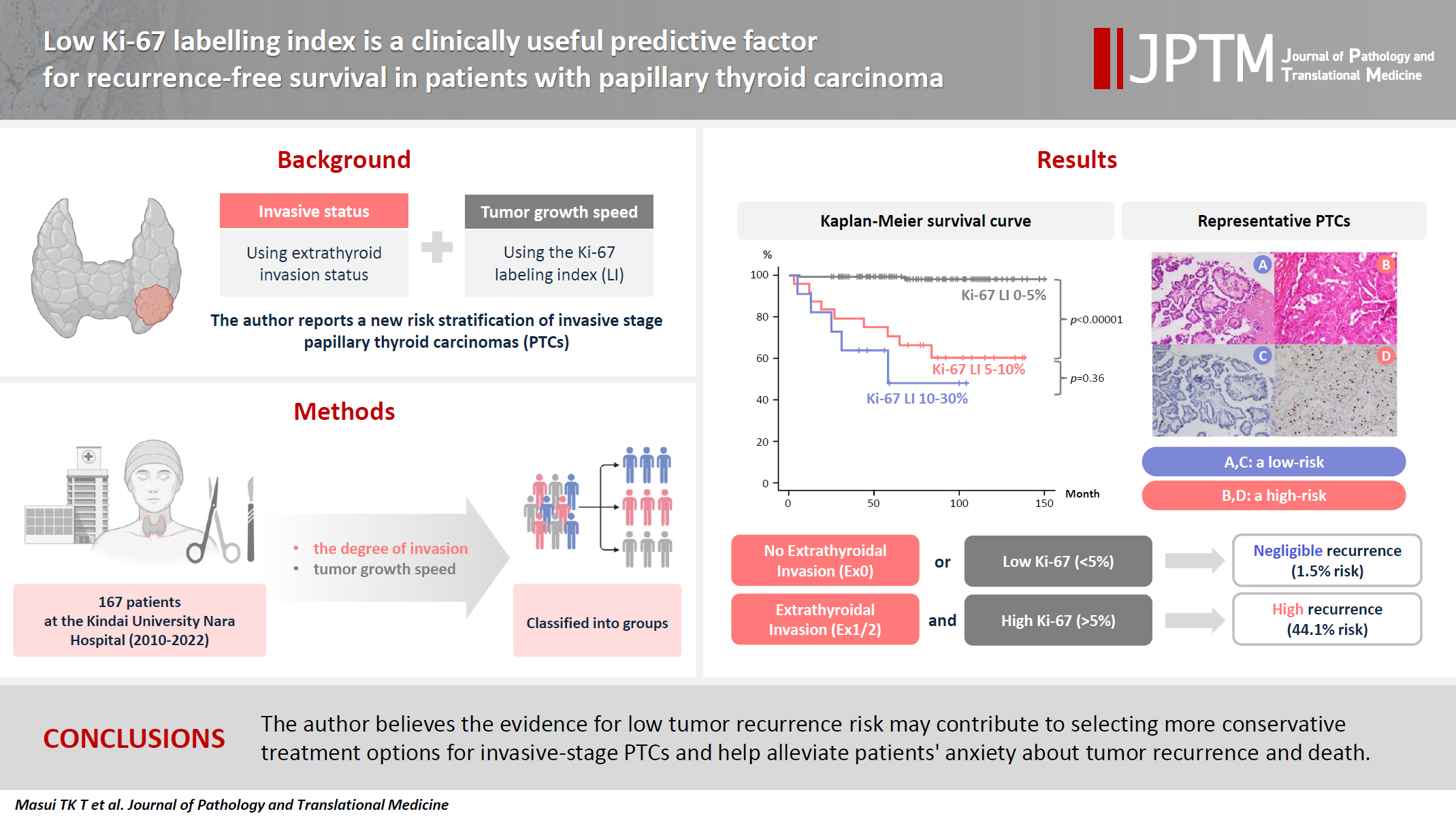










 First
First Prev
Prev



