Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- E-cadherin expression and tumor-stroma ratio as prognostic biomarkers of peritoneal recurrence in advanced gastric cancer: a digital image analysis-based stratification study
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):408-420. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.27
- 2,512 View
- 111 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric cancer remains a significant global health burden, with a high peritoneal recurrence rates after curative surgery. E-cadherin and the tumor-stroma ratio (TSR) have been proposed as prognostic indicators, but their combined prognostic utility remains unclear. Methods: This retrospective study included 130 patients with T3/T4a gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy at Ulsan University Hospital between 2014 and 2019. Immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin and Vimentin was performed. Digital image analysis using QuPath’s object classifier quantified E-cadherin expression and TSR. Results: Low E-cadherin expression was associated with diffuse-type histology and advanced T stage. Low TSR was linked to younger age, female sex, and XELOX treatment. In Kaplan-Meier analysis, low TSR showed a non-significant trend toward higher peritoneal recurrence (p = .054), while low E-cadherin expression was significantly associated with increased peritoneal recurrence (p = .002). Combined biomarker analysis also revealed a significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) among the four groups (p = .005); patients with both high TSR and high E-cadherin expression experienced the most favorable RFS. In multivariable analysis, E-cadherin expression remained the only independent predictor of peritoneal recurrence (high vs. low; hazard ratio, 0.348; 95% confidence interval, 0.149 to 0.816; p = .015). Conclusions: E-cadherin and TSR reflect distinct tumor biology such as epithelial integrity and stromal composition, and their combined evaluation improves prognostic stratification. Digital image analysis enhances reproducibility and objectivity, supporting their integration into clinical workflows.
- Spectrum of thyroiditis types: clinical, cytomorphological, and radiological findings
- Anam Singh, Indrajeet Kundu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):421-433. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.13
- 3,102 View
- 174 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Thyroiditis encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions affecting the thyroid gland. Lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT) is a common form of thyroiditis, with acute suppuration of the thyroid, while tuberculous thyroiditis is relatively rare. Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) remains a safe and cost-effective tool for diagnosing thyroid-related diseases, especially when paired with ultrasound (US) and clinical examination. Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 21 cases. The cases were reported as thyroiditis on US and FNAC, and the findings were correlated with patient clinical history, symptoms during presentation, and serological profiles. Results: The cases of thyroiditis encompassed the more common forms, LT and subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), as well as relatively rare forms like tuberculous thyroiditis and thyroid abscess. Cases of follicular neoplasms (FN) arising in the context of LT also are included in this study. The case of tuberculous thyroiditis presented as a bulky thyroid gland that appeared heterogeneous on US with extensive necrosis on FNAC. The cases of thyroid abscess and SAT presented with painful neck swellings, with granulomas in the latter cases. US features of LT showed an array of appearances ranging from pseudonodular to an atrophic thyroid gland. All cases of FN showed a lymphocytic background. Conclusions: Thyroiditis is a commonly encountered condition that needs to be sub-categorized accurately into acute, subacute, and chronic types for appropriate clinical management, as they can sometimes show overlapping features. Though rare, acute suppurative and tuberculous thyroiditis are often encountered and warrant immediate care and treatment.
Review Article
- Recent topics on thyroid cytopathology: reporting systems and ancillary studies
- Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):214-224. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.18
- 4,117 View
- 294 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As fine-needle aspiration techniques and diagnostic methodologies for thyroid nodules have continued to evolve and reporting systems have been updated accordingly, we need to be up to date with the latest information to achieve accurate diagnoses. However, the diagnostic approaches and therapeutic strategies for thyroid nodules vary across laboratories and institutions. Several differences exist between Western and Eastern practices regarding thyroid fine-needle aspiration. This review describes the reporting systems for thyroid cytopathology and ancillary studies. Updated reporting systems enhance the accuracy, consistency, and clarity of cytology reporting, leading to improved patient outcomes and management strategies. Although a single global reporting system is optimal, reporting systems tailored to each country is acceptable. In such cases, compatibility must be ensured to facilitate data sharing. Ancillary methods include liquid-based cytology, immunocytochemistry, biochemical measurements, flow cytometry, molecular testing, and artificial intelligence, all of which improve diagnostic accuracy. These methods continue to evolve, and cytopathologists should actively adopt the latest methods and information to achieve more accurate diagnoses. We believe this review will be useful to practitioners of routine thyroid cytology.
Reviews
- Breast fine-needle aspiration cytology in the era of core-needle biopsy: what is its role?
- Ahrong Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Jee Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):26-38. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.01
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(2):147
- 13,693 View
- 457 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) has long been recognized as a minimally invasive, cost-effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for breast lesions. However, with the advent of core-needle biopsy (CNB), the role of FNAC has diminished in some clinical settings. This review aims to re-evaluate the diagnostic value of FNAC in the current era, focusing on its complementary use alongside CNB, the adoption of new approaches such as the International Academy of Cytology Yokohama System, and the implementation of rapid on-site evaluation to reduce inadequate sample rates. Advances in liquid-based cytology, receptor expression testing, molecular diagnostics, and artificial intelligence are discussed, highlighting their potential to enhance the diagnostic accuracy of FNAC. Despite challenges, FNAC remains a valuable diagnostic method, particularly in low-resource settings and specific clinical scenarios, and its role continues to evolve with technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
Manish Jaiswal, Anurag Gupta, Tripti Verma, Pradyumn Singh, Rita Yadav, Akash Agarwal, Ashish Singhal, Nuzhat Husain, Shamrendra Narayan, Neha Singh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(3): 184. CrossRef - Personalizing therapies over the course of hormone receptor‐positive/HER2‐negative metastatic breast cancer
Akshara Singareeka Raghavendra, Senthil Damodaran, Carlos H. Barcenas, Suzanne A. Fuqua, Rachel M. Layman, Debu Tripathy
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Bulk-lysis protocols as a sensitive method for investigation of circulating CK19 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry
Daniella Serafin Couto Vieira, Laura Otto Walter, Maria Eduarda Cunha da Silva, Lisandra de Oliveira Silva, Heloísa Zorzi Costa, Chandra Chiappin Cardoso, Fernando Carlos de Lander Schmitt, Maria Cláudia Santos-Silva
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(23): 4771. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Breast Lesions on Cytology Using International Academy of Cytology Yokohama Standardized Reporting System
- Next step of molecular pathology: next-generation sequencing in cytology
- Ricella Souza da Silva, Fernando Schmitt
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):291-298. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.22
- 6,687 View
- 381 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The evolving landscape of precision oncology underscores the pivotal shift from morphological diagnosis to treatment decisions driven by molecular profiling. Recent guidelines from the European Society for Medical Oncology recomend the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) across a broader range of cancers, reflecting its superior efficiency and clinical value. NGS not only updates oncology testing by offering quicker, sample-friendly, and sensitive analysis but also reduces the need for multiple individual tests. Cytology samples, often obtained through less invasive methods, can yield high-quality genetic material suitable for molecular analysis. This article focuses on optimizing the use of cytology samples in NGS, and outlines their potential benefits in identifying actionable molecular alterations for targeted therapies across various solid tumors. It also addresses the need for validation studies and the strategies to incorporate or combine different types of samples into routine clinical practice. Integrating cytological and liquid biopsies into routine clinical practice, alongside conventional tissue biopsies, offers a comprehensive approach to tumor genotyping, early disease detection, and monitoring of therapeutic responses across various solid tumor types. For comprehensive biomarker characterization, all patient specimens, although limited, is always valuable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Immacolata Cozzolino, Mats Ehinger, Maria Calaminici, Andrea Ronchi, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi, Helena Barroca, Beata Bode-Lesniewska, David F. Chhieng, Ruth L. Katz, Oscar Lin, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Martha Bishop Pitman, Arvind Rajwanshi, Fernando C. Schmitt, Ph
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The impact of cytological preparation techniques on RNA quality: A comparative study on smear samples
Cisel Aydin Mericoz, Gulsum Caylak, Elif Sevin Sanioglu, Zeynep Seçil Satilmis, Ayse Humeyra Dur Karasayar, Ibrahim Kulac
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reimagining cytopathology in the molecular era: Integration or fragmentation?
Sumanta Das, R. Naveen Kumar, Biswajit Dey, Pranjal Kalita
Cytojournal.2025; 22: 94. CrossRef
- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Original Articles
- The combination of CDX2 expression status and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density as a prognostic factor in adjuvant FOLFOX-treated patients with stage III colorectal cancers
- Ji-Ae Lee, Hye Eun Park, Hye-Yeong Jin, Lingyan Jin, Seung Yeon Yoo, Nam-Yun Cho, Jeong Mo Bae, Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):50-59. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.26
- 3,914 View
- 283 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX2) loss are recognized to pursue an aggressive behavior but tend to be accompanied by a high density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). However, little is known about whether there is an interplay between CDX2 loss and TIL density in the survival of patients with CRC.
Methods
Stage III CRC tissues were assessed for CDX2 loss using immunohistochemistry and analyzed for their densities of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial (iTILs) and stromal areas using a machine learning-based analytic method.
Results
CDX2 loss was significantly associated with a higher density of CD8 TILs in both intraepithelial and stromal areas. Both CDX2 loss and a high CD8 iTIL density were found to be prognostic parameters and showed hazard ratios of 2.314 (1.050–5.100) and 0.378 (0.175–0.817), respectively, for cancer-specific survival. A subset of CRCs with retained CDX2 expression and a high density of CD8 iTILs showed the best clinical outcome (hazard ratio of 0.138 [0.023–0.826]), whereas a subset with CDX2 loss and a high density of CD8 iTILs exhibited the worst clinical outcome (15.781 [3.939–63.230]).
Conclusions
Altogether, a high density of CD8 iTILs did not make a difference in the survival of patients with CRC with CDX2 loss. The combination of CDX2 expression and intraepithelial CD8 TIL density was an independent prognostic marker in adjuvant chemotherapy-treated patients with stage III CRC.
- International Academy of Cytology standardized reporting of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology with cyto-histopathological correlation of breast carcinoma
- Shweta Pai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):241-248. Published online September 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.14
- 8,517 View
- 442 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Academy of Cytology (IAC) has developed a standardized approach for reporting the findings of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Accordingly, there are five chief categories of breast lesions, C1 (insufficient material), C2 (benign), C3 (atypical), C4 (suspicious), and C5 (malignant). The prognostication and management of breast carcinoma can be performed readily on the basis of this classification system. The aim of this study was to classify various breast lesions into one of the above-named categories and to further grade the C5 lesions specifically using the Robinson system. The latter grades were then correlated with modified Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grades.
Methods
This retrospective study was undertaken in the pathology department of a hospital located in the urban part of the city of Bangalore. All FNAC procedures performed on breast lumps spanning the year 2020 were included in the study.
Results
A total of 205 breast lesions was classified according to the IAC guidelines into C1 (6 cases, 2.9%), C2 (151 cases, 73.7%), C3 (13 cases, 6.3%), C4 (5 cases, 2.5%), and C5 (30 cases, 14.6%) groups. The C5 cases were further graded using Robinson’s system. The latter showed a significant correlation with the SBR system (concordance=83.3%, Spearman correlation=0.746, Kendall’s tau-b=0.736, kappa=0.661, standard error=0.095, p≤.001).
Conclusions
A standardized approach for FNAC reporting of breast lesions, as advocated for by the IAC, improves the quality and clarity of the reports and assures diagnostic reproducibility on a global scale. Further, the cytological grading of C5 lesions provides reliable cyto-prognostic scores that can help assess a tumor’s aggressiveness and predict its histological grade.
Case Study
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and ALK and cytokeratin expression: a case report
- Hyeong Rok An, Kyung-Ja Cho, Sang Woo Song, Ji Eun Park, Joon Seon Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):255-260. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.15
- 4,511 View
- 219 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) comprises of heterogeneous group of neoplasms that occasionally express epithelial markers on immunohistochemistry (IHC). We herein report the case of a patient who developed RMS of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and cytokeratin expression as cytomorphologic features. A 40-year-old man presented with a mass in his forehead. Surgical resection was performed, during which intraoperative frozen specimens were obtained. Squash cytology showed scattered or clustered spindle and epithelioid cells. IHC revealed that the resected tumor cells were positive for desmin, MyoD1, cytokeratin AE1/ AE3, and ALK. Although EWSR1 rearrangement was identified on fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK, and TFCP2 rearrangement were not noted. Despite providing adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, the patient died of tumor progression 10 months after diagnosis. We emphasize that a subset of RMS can express cytokeratin and show characteristic histomorphology, implying the need for specific molecular examination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Ahmed Shah, Andrew L. Folpe
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(3): 503. CrossRef - Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions
Erkan Gökçe, Murat Beyhan
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Morphology of Telangiectatic Osteosarcoma Associated With Сystic Content: A Case Report
David Makaridze, Armaz Mariamidze, Tamuna Gvianishvili, Giulia Ottaviani , Liana Gogiashvili
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Original Article
- Paricalcitol prevents MAPK pathway activation and inflammation in adriamycin-induced kidney injury in rats
- Amanda Lima Deluque, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Beatriz Magalhães Oliveira, Cláudia Silva Souza, Ana Lívia Dias Maciel, Heloísa Della Coletta Francescato, Cleonice Giovanini, Roberto Silva Costa, Terezila Machado Coimbra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):219-228. Published online August 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.12
- 3,961 View
- 222 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway induces uncontrolled cell proliferation in response to inflammatory stimuli. Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (ADRN) in rats triggers MAPK activation and pro-inflammatory mechanisms by increasing cytokine secretion, similar to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) plays a crucial role in suppressing the expression of inflammatory markers in the kidney and may contribute to reducing cellular proliferation. This study evaluated the effect of pre-treatment with paricalcitol on ADRN in renal inflammation mechanisms.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an osmotic minipump containing activated vitamin D (paricalcitol, Zemplar, 6 ng/day) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%). Two days after implantation, ADR (Fauldoxo, 3.5 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) was injected. The rats were divided into four experimental groups: control, n = 6; paricalcitol, n = 6; ADR, n = 7 and, ADR + paricalcitol, n = 7.
Results
VDR activation was demonstrated by increased CYP24A1 in renal tissue. Paricalcitol prevented macrophage infiltration in the glomeruli, cortex, and outer medulla, prevented secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, increased arginase I and decreased arginase II tissue expressions, effects associated with attenuation of MAPK pathways, increased zonula occludens-1, and reduced cell proliferation associated with proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Paricalcitol treatment decreased the stromal cell-derived factor 1α/chemokine C-X-C receptor type 4/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions
Paricalcitol plays a renoprotective role by modulating renal inflammation and cell proliferation. These results highlight potential targets for treating CKD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Ana Checa-Ros, Antonella Locascio, Owahabanun-Joshua Okojie, Pablo Abellán-Galiana, Luis D’Marco
BMC Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating amiodarone-induced lung toxicity by the vitamin D receptor activator paricalcitol in rats: targeting TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Aamal G. El-Waseif, Mahmoud Elshal, Dalia H. El-Kashef, Nashwa M. Abu-Elsaad
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Review
- Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
- Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):165-173. Published online July 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.11
- 4,672 View
- 279 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review addresses new reporting systems for lung and pancreatobiliary cytopathology as well as the most recent edition of The Bethesda Reporting System for Thyroid Cytopathology. The review spans past, present, and future aspects within the context of the intricate interplay between traditional morphological assessments and cutting-edge molecular diagnostics. For lung and pancreas, the authors discuss the evolution of reporting systems, emphasizing the bridge between past directives and more recent collaborative efforts of the International Academy of Cytology and the World Health Organization in shaping universal reporting systems. The review offers a brief overview of the structure of these novel systems, highlighting their strengths and pinpointing areas that require further refinement. For thyroid, the authors primarily focus on the third edition of The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology, also considering the two preceding editions. This review serves as an invaluable resource for cytopathologists, offering a panoramic view of the evolving landscape of cytopathology reporting and pointing out the integrative role of the cytopathologist in an era of rapid diagnostic and therapeutic advancements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Zahra Maleki, Sule Canberk, Andrew Field
Cytopathology.2025; 36(5): 434. CrossRef - Reproducibility of the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology (TBSRTC): An observational study of 100 patients
Kishori Moni Panda, Reena Naik, Mohd Ghouse Mohiddin
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2024; 11(4): 385. CrossRef
- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Case Study
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,904 View
- 211 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
Original Articles
- The importance of histomorphological features and ERG expression in the diagnosis of malignancy in cases with atypical small acinar proliferation
- Gizem Teoman, Ayten Livaoglu, Hatice Kucuk, Afs ¸ın Rahman Murtezaoglu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):134-140. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.18
- 4,359 View
- 234 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Atypical small acinar proliferation (ASAP) cases typically require rebiopsy, which are invasive and associated with increased risk of complications. Our aim in this study was to determine the importance of laboratory and histological findings and E-26 transformation-specific-related gene (ERG) expression in the diagnosis of malignancy.
Methods
Between March 2016 and March 2022, 84 patients who were diagnosed with ASAP on biopsy or rebiopsy were included in the study. Clinical-laboratory features of age, serum prostate-specific antigen level, and histopathological features were compared and included multifocality, number of suspicious acini, nuclear enlargement, nucleolar prominence, hyperchromasia, cytoplasmic amphophilia, luminal amorphous acellular secretion, crystalloid presence, infiltrative appearance, inflammation, atrophy, α-methyl acyl-CoA racemase, p63, and/or high molecular weight cytokeratin were analyzed. In addition, ERG expression was evaluated immunohistochemically.
Results
Statistically significant correlation was found between nucleolar prominence, nuclear hyperchromasia, crystalloid presence, infiltrative pattern, and prostate cancer (p < .001). In 19 of 84 cases (22.6%) ERG was positive in the nucleus. Prostate cancer was diagnosed at rebiopsy in 15 of the 19 ERG-positive cases (78.9%). A statistically significant correlation was found between ERG positivity and prostate cancer (p= .002).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that evaluation of these markers during initial transrectal ultrasound biopsies may decrease and prevent unnecessary prostate rebiopsy.
- Revisiting the utility of identifying nuclear grooves as unique nuclear changes by an object detector model
- Pedro R. F. Rende, Joel Machado Pires, Kátia Sakimi Nakadaira, Sara Lopes, João Vale, Fabio Hecht, Fabyan E. L. Beltrão, Gabriel J. R. Machado, Edna T. Kimura, Catarina Eloy, Helton E. Ramos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):117-126. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.07
- 5,192 View
- 273 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Among other structures, nuclear grooves are vastly found in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Considering that the application of artificial intelligence in thyroid cytology has potential for diagnostic routine, our goal was to develop a new supervised convolutional neural network capable of identifying nuclear grooves in Diff-Quik stained whole-slide images (WSI) obtained from thyroid fineneedle aspiration.
Methods
We selected 22 Diff-Quik stained cytological slides with cytological diagnosis of PTC and concordant histological diagnosis. Each of the slides was scanned, forming a WSI. Images that contained the region of interest were obtained, followed by pre-formatting, annotation of the nuclear grooves and data augmentation techniques. The final dataset was divided into training and validation groups in a 7:3 ratio.
Results
This is the first artificial intelligence model based on object detection applied to nuclear structures in thyroid cytopathology. A total of 7,255 images were obtained from 22 WSI, totaling 7,242 annotated nuclear grooves. The best model was obtained after it was submitted 15 times with the train dataset (14th epoch), with 67% true positives, 49.8% for sensitivity and 43.1% for predictive positive value.
Conclusions
The model was able to develop a structure predictor rule, indicating that the application of an artificial intelligence model based on object detection in the identification of nuclear grooves is feasible. Associated with a reduction in interobserver variability and in time per slide, this demonstrates that nuclear evaluation constitutes one of the possibilities for refining the diagnosis through computational models.
- Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes evaluated using digital image analysis predict the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Yunjoo Cho, Jiyeon Lee, Bogyeong Han, Sang Eun Yoon, Seok Jin Kim, Won Seog Kim, Junhun Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):12-21. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.02
- 5,397 View
- 271 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The implication of the presence of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TIL-T) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is yet to be elucidated. We aimed to investigate the effect of TIL-T levels on the prognosis of patients with DLBCL.
Methods
Ninety-six patients with DLBCL were enrolled in the study. The TIL-T ratio was measured using QuPath, a digital pathology software package. The TIL-T ratio was investigated in three foci (highest, intermediate, and lowest) for each case, resulting in TIL-T–Max, TIL-T–Intermediate, and TIL-T–Min. The relationship between the TIL-T ratios and prognosis was investigated.
Results
When 19% was used as the cutoff value for TIL-T–Max, 72 (75.0%) and 24 (25.0%) patients had high and low TIL-T–Max, respectively. A high TIL-T–Max was significantly associated with lower serum lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < .001), with patient group who achieved complete remission after RCHOP therapy (p < .001), and a low-risk revised International Prognostic Index score (p < .001). Univariate analysis showed that patients with a low TIL-T–Max had a significantly worse prognosis in overall survival compared to those with a high TIL-T–Max (p < .001); this difference remained significant in a multivariate analysis with Cox proportional hazards (hazard ratio, 7.55; 95% confidence interval, 2.54 to 22.42; p < .001).
Conclusions
Patients with DLBCL with a high TIL-T–Max showed significantly better prognosis than those with a low TIL-T–Max, and the TIL-T–Max was an independent indicator of overall survival. These results suggest that evaluating TIL-T ratios using a digital pathology system is useful in predicting the prognosis of patients with DLBCL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
Valerie J. Poirier, Valeria Meier, Michelle Turek, Neil Christensen, Jacqueline Bowal, Matthew D. Ponzini, Stefan M. Keller
Veterinary and Comparative Oncology.2025; 23(1): 82. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment and PD-L1 Expression Associations with Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Yun-Li Xie, Long-Feng Ke, Wen-Wen Zhang, Fu Kang, Shu-Yi Lu, Chen-Yu Wu, Huan-Huan Zhu, Jian-Chao Wang, Gang Chen, Yan-Ping Chen
Blood and Lymphatic Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 15: 167. CrossRef - Metabolic-immune axis in the tumor microenvironment: a new strategy for prognostic assessment and precision therapy in DLBCL and FL
Chengqian Chen, Wei Guo, Haotian Wang, Luming Cao, Ou Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrative analysis of a novel immunogenic PANoptosis‑related gene signature in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma for prognostication and therapeutic decision-making
Ming Xu, Ming Ruan, Wenhua Zhu, Jiayue Xu, Ling Lin, Weili Li, Weirong Zhu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Do Pre‐Treatment Biopsy Characteristics Predict Early Tumour Progression in Feline Diffuse Large B Cell Nasal Lymphoma Treated With Radiotherapy?
Reviews
- Clinical practice recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing in patients with solid cancer: a joint report from KSMO and KSP
- Miso Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Sheehyun Kim, In Hee Lee, Jihun Kim, Shinkyo Yoon, Hyung-Don Kim, Inkeun Park, Jae Ho Jeong, Changhoon Yoo, Jaekyung Cheon, In-Ho Kim, Jieun Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Sehhoon Park, Hyun Ae Jung, Jin Won Kim, Han Jo Kim, Yongjun Cha, Sun Min Lim, Han Sang Kim, Choong-Kun Lee, Jee Hung Kim, Sang Hoon Chun, Jina Yun, So Yeon Park, Hye Seung Lee, Yong Mee Cho, Soo Jeong Nam, Kiyong Na, Sun Och Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Kee-Taek Jang, Hongseok Yun, Sungyoung Lee, Jee Hyun Kim, Wan-Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):147-164. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.01
- 9,423 View
- 496 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years, next-generation sequencing (NGS)–based genetic testing has become crucial in cancer care. While its primary objective is to identify actionable genetic alterations to guide treatment decisions, its scope has broadened to encompass aiding in pathological diagnosis and exploring resistance mechanisms. With the ongoing expansion in NGS application and reliance, a compelling necessity arises for expert consensus on its application in solid cancers. To address this demand, the forthcoming recommendations not only provide pragmatic guidance for the clinical use of NGS but also systematically classify actionable genes based on specific cancer types. Additionally, these recommendations will incorporate expert perspectives on crucial biomarkers, ensuring informed decisions regarding circulating tumor DNA panel testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Étienne Rouleau, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Dominique Galibert, Alexandre Harlé, Isabelle Soubeyran
Revue Francophone des Laboratoires.2025; 2025(568): 67. CrossRef - The Redox–Adhesion–Exosome (RAX) Hub in Cancer: Lipid Peroxidation-Driven EMT Plasticity and Ferroptosis Defense with HNE/MDA Signaling and Lipidomic Perspectives
Moon Nyeo Park, Jinwon Choi, Rosy Iara Maciel de Azambuja Ribeiro, Domenico V. Delfino, Seong-Gyu Ko, Bonglee Kim
Antioxidants.2025; 14(12): 1474. CrossRef
- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
- The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
- Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(6):289-304. Published online November 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.04
- 9,463 View
- 305 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The Asian Thyroid Working Group was founded in 2017 at the 12th Asia Oceania Thyroid Association (AOTA) Congress in Busan, Korea. This group activity aims to characterize Asian thyroid nodule practice and establish strict diagnostic criteria for thyroid carcinomas, a reporting system for thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology without the aid of gene panel tests, and new clinical guidelines appropriate to conservative Asian thyroid nodule practice based on scientific evidence obtained from Asian patient cohorts. Asian thyroid nodule practice is usually designed for patient-centered clinical practice, which is based on the Hippocratic Oath, “First do not harm patients,” and an oriental filial piety “Do not harm one’s own body because it is a precious gift from parents,” which is remote from defensive medical practice in the West where physicians, including pathologists, suffer from severe malpractice climate. Furthermore, Asian practice emphasizes the importance of resource management in navigating the overdiagnosis of low-risk thyroid carcinomas. This article summarizes the Asian Thyroid Working Group activities in the past 7 years, from 2017 to 2023, highlighting the diversity of thyroid nodule practice between Asia and the West and the background reasons why Asian clinicians and pathologists modified Western systems significantly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Performance of Two‐Tiered Subclassification of Atypia of Undetermined Significance in Thyroid Fine‐Needle Aspiration Without Routine Molecular Testing
Pocholo D. Santos, Chiung‐Ru Lai, Jen‐Fan Hang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 78. CrossRef - Risk of Infertility in Reproductive-Age Patients With Thyroid Cancer Receiving or Not Receiving 131I Treatment
Chun-Yi Lin, Cheng-Li Lin, Chia-Hung Kao
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2025; 50(3): 201. CrossRef - Association Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Thyroid Cancer
Sang Yi Moon, Minkook Son, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Ji Min Han, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh
Thyroid®.2025; 35(1): 79. CrossRef - Letter: “High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis” by Fung et al
Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov, Jen-Fan Hang, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Somboon Keelawat, Zhiyan Liu, Radhika Srinivasan, Chan Kwon Jung
Thyroid®.2025; 35(5): 595. CrossRef - Thyroid Nodules with Nuclear Atypia of Undetermined Significance (AUS-Nuclear) Hold a Two-Times-Higher Risk of Malignancy than AUS-Other Nodules Regardless of EU-TIRADS Class of the Nodule or Borderline Tumor Interpretation
Dorota Słowińska-Klencka, Bożena Popowicz, Joanna Duda-Szymańska, Mariusz Klencki
Cancers.2025; 17(8): 1365. CrossRef - Response to Kakudo et al.: “High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis”
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(5): 597. CrossRef - Molecular Testing Could Drive Smarter Decision-Marking for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodule if the Price was Right
Sarah C. Brennan, Matti L. Gild, Venessa Tsang
Clinical Thyroidology®.2025; 37(5): 165. CrossRef - Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(4): 165. CrossRef - Are we ready to bridge classification systems? A comprehensive review of different reporting systems in thyroid cytology
Esther Diana Rossi, Liron Pantanowitz
Cytopathology.2024; 35(6): 674. CrossRef - Aggressive Types of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms
Maria Boudina, Eleana Zisimopoulou, Persefoni Xirou, Alexandra Chrisoulidou
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(20): 6119. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnoses of follicular thyroid carcinoma: results from a multicenter study in Asia
Hee Young Na, Miyoko Higuchi, Shinya Satoh, Kaori Kameyama, Chan Kwon Jung, Su-Jin Shin, Shipra Agarwal, Jen-Fan Hang, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 331. CrossRef
- Performance of Two‐Tiered Subclassification of Atypia of Undetermined Significance in Thyroid Fine‐Needle Aspiration Without Routine Molecular Testing
Case Study
- Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as a primary thyroid tumor
- Jai-Hyang Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):242-245. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.16
- 4,634 View
- 117 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma is rare. To date, only six cases have been reported in the literature. This case was unusual and presented with thyromegaly before the diagnosis of the primary tumor. A 55-year-old male patient was suspected to have a primary thyroid tumor with nodal metastasis. The thyroid gland was diffusely enlarged, with no discernible mass. Histologically, the thyroid parenchyma revealed extensive endolymphatic tumor emboli, which were positive for p40 and p16 in a background of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed hypermetabolic activity in the right tonsillar region. Tonsillar biopsy revealed human papillomavirus–positive squamous cell carcinoma. The present case is the first reported case of intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma with an initial clinical presentation of thyroid enlargement before the primary tumor of tonsillar cancer was diagnosed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
Avneet Kaur, Rohit Nayyar, Harit Kumar Chaturvedi, Akshat Malik
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025; 16(1): 122. CrossRef - Metastatic oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma to the thyroid: A case report and review of literature
Hannah Walker, Jed Speers, Milena Fabry, Sameep Kadakia
American Journal of Otolaryngology.2024; 45(4): 104306. CrossRef
- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
Review
- A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes
- Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):196-207. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.12
- 48,668 View
- 2,341 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The cytological diagnosis of lymph node lesions is extremely challenging because of the diverse diseases that cause lymph node enlargement, including both benign and malignant or metastatic lymphoid lesions. Furthermore, the cytological findings of different lesions often resemble one another. A stepwise diagnostic approach is essential for a comprehensive diagnosis that combines: clinical findings, including age, sex, site, multiplicity, and ultrasonography findings; low-power reactive, metastatic, and lymphoma patterns; high-power population patterns, including two populations of continuous range, small monotonous pattern and large monotonous pattern; and disease-specific diagnostic clues including granulomas and lymphoglandular granules. It is also important to remember the histological features of each diagnostic category that are common in lymph node cytology and to compare them with cytological findings. It is also essential to identify a few categories of diagnostic pitfalls that often resemble lymphomas and easily lead to misdiagnosis, particularly in malignant small round cell tumors, poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinomas, and nasopharyngeal undifferentiated carcinoma. Herein, we review a stepwise approach for fine needle aspiration cytology of lymphoid diseases and suggest a diagnostic algorithm that uses this approach and the Sydney classification system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Critical Role of Ancillary Testing in Fine-Needle Aspiration of Lymph Nodes, Thymus, and Spleen
Diana A. Baptista, Helena Barroca, Fernando C. Schmitt
Acta Cytologica.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Explainable Artificial Intelligence System for Automatic Diagnosis of Cervical Lymphadenopathy From Ultrasound Images
Ming Xu, Yubiao Yue, Zhenzhang Li, Yinhong Li, Guoying Li, Haihua Liang, Di Liu, Xiaohong Xu, Mohamadreza (Mohammad) Khosravi
International Journal of Intelligent Systems.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of the Sydney system for classification and reporting lymph node cytopathology: a retrospective analysis at a tertiary centre
Ashok Teja Kummari, Pramod Kumar Pamu, Krishna Kiran Ganna, Param Jyothi, Sadashivudu
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic approach to FNA biopsy of cystic lesions of the head and neck
Stefen Andrianus, Olivia Leung, Zubair Baloch
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Applicability of Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Lymph Nodes Using WHO Reporting System: Comparison between Pediatric and Adult Brazilian Populations
Leonardo Fávaro Ficoto, Deolino João Camilo Júnior, Gustavo Resende Nora, Vitor Bonetti Valente, Daniel Galera Bernabé, José Cândido Caldeira Xavier-Júnior
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Intraoperative cytological assessment of sentinel lymph nodes in gynecologic cancer: diagnostic accuracy and limitations
O. V. Pankova, S. V. Vtorushin, M. V. Klimova, D. S. Pismenny, M. O. Ochirov, L. A. Kolomiets, V. M. Perelmuter
Siberian journal of oncology.2025; 24(5): 72. CrossRef - From smear to diagnosis: the impact of ancillary techniques in lymph node fine-needle cytology
Elisabetta Maffei, Giuseppe Di Motta, Angela D’Ardia, Riccardo Ruotolo, Valentina Giudice, Alessandro Caputo, Pio Zeppa
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Non-Neoplastic Inflammatory Disorders of Lymphoid Organs
Joy M. Hoang, Havva Gokce Terzioglu, Matthew L. Kleinjan, Tatjana Antic, Nalini Gupta, Manish Rohilla, Radhika Srinivasan, Arvind Rajwanshi, Eva M. Wojcik, Güliz A. Barkan, Mark A. Russell, Swati Mehrotra
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Immunocytochemical markers, molecular testing and digital cytopathology for aspiration cytology of metastatic breast carcinoma
Joshua J. X. Li, Gary M. Tse
Cytopathology.2024; 35(2): 218. CrossRef - Response to comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 43. CrossRef - Comment on “A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes”
Elisabetta Maffei, Valeria Ciliberti, Pio Zeppa, Alessandro Caputo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(1): 40. CrossRef - The Incidence of Thyroid Cancer in Bethesda III Thyroid Nodules: A Retrospective Analysis at a Single Endocrine Surgery Center
Iyad Hassan, Lina Hassan, Nahed Balalaa, Mohamad Askar, Hussa Alshehhi, Mohamad Almarzooqi
Diagnostics.2024; 14(10): 1026. CrossRef - Efficiency of Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) in Relation to Tru-Cut Biopsy of Lateral Neck Swellings
Mohammed S Al Olaimat, Fahad S Al Qooz, Zaid R Alzoubi, Elham M Alsharaiah, Ali S Al Murdif, Mohammad O Alanazi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls in the Cytological Diagnosis of Nodal Hodgkin Lymphoma
Uma Handa, Rasheeda Mohamedali, Rajpal Singh Punia, Simrandeep Singh, Ranjeev Bhagat, Phiza Aggarwal, Manveen Kaur
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(12): 715. CrossRef - Rapid 3D imaging at cellular resolution for digital cytopathology with a multi-camera array scanner (MCAS)
Kanghyun Kim, Amey Chaware, Clare B. Cook, Shiqi Xu, Monica Abdelmalak, Colin Cooke, Kevin C. Zhou, Mark Harfouche, Paul Reamey, Veton Saliu, Jed Doman, Clay Dugo, Gregor Horstmeyer, Richard Davis, Ian Taylor-Cho, Wen-Chi Foo, Lucas Kreiss, Xiaoyin Sara J
npj Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Critical Role of Ancillary Testing in Fine-Needle Aspiration of Lymph Nodes, Thymus, and Spleen
Original Article
- Significance of tumor-associated neutrophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-invasive and invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Wael Abdo Hassan, Ahmed Kamal ElBanna, Noha Noufal, Mohamed El-Assmy, Hany Lotfy, Rehab Ibrahim Ali
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):88-94. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.06
- 7,790 View
- 326 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and lymphocytes play essential roles in promoting or combating various neoplasms. This study aimed to investigate the association between tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and lymphocytes and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the progression of urothelial carcinoma.
Methods
A total of 106 patients diagnosed with urothelial carcinoma were was. Pathological examination for tumor grade and stage and for tumor-infiltrating neutrophils, both CD4 and CD8+ T lymphocytes, as well as the neutrophil- to-lymphocyte ratio were evaluated.
Results
The presence of neutrophils and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio correlated with high-grade urothelial neoplasms. In both low- and high-grade tumors, the lymphocytes increased during progression from a non-invasive neoplasm to an early-invasive neoplasm. CD8+ T lymphocytes increased in low-grade non–muscle-invasive tumors compared to non-invasive tumors. Additionally, there was a significant decrease in CD8+ T lymphocytes during progression to muscle-invasive tumors.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and CD8+ T lymphocytes have a significant effect on tumor grade and progression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic role of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in high‐risk BCG‐naïve non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical gemcitabine/docetaxel
Mohamad Abou Chakra, Riitta Lassila, Nancy El Beayni, Sarah L. Mott, Michael A. O'Donnell
BJU International.2025; 135(1): 125. CrossRef - Understanding the Dual Role of Macrophages in Tumor Growth and Therapy: A Mechanistic Review
Muhammad Summer, Saima Riaz, Shaukat Ali, Qudsia Noor, Rimsha Ashraf, Rana Rashad Mahmood Khan
Chemistry & Biodiversity.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-Talk Between Cancer and Its Cellular Environment—A Role in Cancer Progression
Eliza Turlej, Aleksandra Domaradzka, Justyna Radzka, Dominika Drulis-Fajdasz, Julita Kulbacka, Agnieszka Gizak
Cells.2025; 14(6): 403. CrossRef - Global trends in tumor-associated neutrophil research: a bibliometric and visual analysis
Shaodong Li, Peng Dong, Xueliang Wu, Zhenhua Kang, Guoqiang Yan
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor-associated neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in lung cancer: antitumor/protumor insights and therapeutic implications
Milad Sheervalilou, Mostafa Ghanei, Masoud Arabfard
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction of a column-line graphical model of poor outcome of neoadjuvant regimens for muscle-invasive bladder cancer based on NLR, dNLR and SII indicators
Bo Hu, Longsheng Wang, Shanna Qu, Tao Zhang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning of Urine Cytology Highlights Increased Neutrophil Count in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma
Moe Kameda, Sayaka Kobayashi, Yoshimi Nishijima, Ryosuke Akuzawa, Rio Kaneko, Rio Shibanuma, Seiji Arai, Hayato Ikota, Kazuhiro Suzuki, Hideaki Yokoo, Masanao Saio
Journal of Cytology.2025; 42(3): 124. CrossRef - Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Prognostic Implications, Predictive Value, and Future Perspectives
Roberta Mazzucchelli, Angelo Cormio, Magda Zanelli, Maurizio Zizzo, Andrea Palicelli, Andrea Benedetto Galosi, Francesca Sanguedolce
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(22): 12032. CrossRef - Immune cell networking in solid tumors: focus on macrophages and neutrophils
Irene Di Ceglie, Silvia Carnevale, Anna Rigatelli, Giovanna Grieco, Piera Molisso, Sebastien Jaillon
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry assessment of tissue neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts outcomes in melanoma patients treated with anti-programmed cell death 1 therapy
Renan J. Teixeira, Vinícius G. de Souza, Bruna P. Sorroche, Victor G. Paes, Fabiana A. Zambuzi-Roberto, Caio A.D. Pereira, Vinicius L. Vazquez, Lidia M.R.B. Arantes
Melanoma Research.2024; 34(3): 234. CrossRef - Association between alteration of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, cancer antigen-125 and surgical outcomes in advanced stage ovarian cancer patient who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ponganun Tuntinarawat, Ratnapat Tangmanomana, Thannaporn Kittisiam
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2024; 52: 101347. CrossRef - Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer with intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiaguo Huang, Li Lin, Dikai Mao, Runmiao Hua, Feifei Guan
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on the Mechanism of Action of Intravesical BCG Therapy to Treat Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Mohamad Abou Chakra, Yi Luo, Igor Duquesne, Michael A O'Donnell
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Significant association between high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunhua Xu, Fenfang Wu, Lailing Du, Yeping Dong, Shan Lin
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitinase 3-like-1 Expression in the Microenvironment Is Associated with Neutrophil Infiltration in Bladder Cancer
Ling-Yi Xiao, Yu-Li Su, Shih-Yu Huang, Yi-Hua Chen, Po-Ren Hsueh
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15990. CrossRef
- Prognostic role of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in high‐risk BCG‐naïve non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical gemcitabine/docetaxel
Reviews
- Inflammatory bowel disease–associated intestinal fibrosis
- Ji Min Park, Jeongseok Kim, Yoo Jin Lee, Sung Uk Bae, Hye Won Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):60-66. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.02
- 20,458 View
- 468 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrosis is characterized by a proliferation of fibroblasts and excessive extracellular matrix following chronic inflammation, and this replacement of organ tissue with fibrotic tissue causes a loss of function. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, and intestinal fibrosis is common in IBD patients, resulting in several complications that require surgery, such as a stricture or penetration. This review describes the pathogenesis and various factors involved in intestinal fibrosis in IBD, including cytokines, growth factors, epithelial-mesenchymal and endothelial-mesenchymal transitions, and gut microbiota. Furthermore, histopathologic findings and scoring systems used for stenosis in IBD are discussed, and differences in the fibrosis patterns of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are compared. Biomarkers and therapeutic agents targeting intestinal fibrosis are briefly mentioned at the end.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Short-Chain Fatty Acids Elicit Differential Expression of Growth Factors and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Immortalized Rat Enteric Glial Cells
Michelle M. Beltran, Danielle M. Defries
Nutrients.2026; 18(3): 436. CrossRef - Leveraging Organ‐on‐Chip Models to Investigate Host–Microbiota Dynamics and Targeted Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tim Kaden, Raquel Alonso‐Román, Johannes Stallhofer, Mark S. Gresnigt, Bernhard Hube, Alexander S. Mosig
Advanced Healthcare Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prominence of Microbiota to Predict Fibrous Stenosis in Crohn’s Disease
Xue Yang, Yan Pan, Cai-Ping Gao, Hang Li, Ying-Hui Zhang, Chun-Li Huang, Lu Cao, Shi-Yu Xiao, Zhou Zhou
Journal of Inflammation Research.2025; Volume 18: 1413. CrossRef - Fibrosierende Erkrankungen im Gastrointestinaltrakt
Elke Roeb
Die Innere Medizin.2025; 66(7): 695. CrossRef - Roles of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and IBD-associated fibrosis
Takayoshi Ito, Hisako Kayama
International Immunology.2025; 37(7): 379. CrossRef - Disease Clearance in Ulcerative Colitis: A Narrative Review
Silvio Danese, Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet, Vipul Jairath, Ferdinando D'Amico, Shashi Adsul, Christian Agboton, Fernando Magro
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(6): 902. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota as a Mediator Between Intestinal Fibrosis and Creeping Fat in Crohn's Disease
Caiguang Liu, Rongchang Li, Jing Nie, Jinshen He, Zihao Lin, Xiaomin Wu, Jinyu Tan, Zishan Liu, Longyuan Zhou, Xiaozhi Li, Zhirong Zeng, Minhu Chen, Shixian Hu, Yijun Zhu, Ren Mao
United European Gastroenterology Journal.2025; 13(7): 1092. CrossRef - Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): immunotoxicity at the primary sites of exposure
Emma Arnesdotter, Charlotte B. A. Stoffels, Wiebke Alker, Arno C. Gutleb, Tommaso Serchi
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2025; 55(4): 484. CrossRef - Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis
Harshal Sawant, Alip Borthakur
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(12): 5713. CrossRef - Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Thomas Grewal, Hauke Christian Tews, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(13): 6101. CrossRef - Revealing Fibrosis Genes as Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis: A Bioinformatics Study Based on ScRNA and Bulk RNA Datasets
Yandong Wang, Li Liu, Weihao Wang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2025; 25(9): 710. CrossRef - Fibrosis in Immune-Mediated and Autoimmune Disorders
Magdalena Żurawek, Iwona Ziółkowska-Suchanek, Katarzyna Iżykowska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6636. CrossRef - Plasma-activated media inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorates intestinal fibrosis through the PPARγ/TGF-β1/SMAD3 pathway
Yi You, Yaping Shen, Yan Yang, Xiaoyang Wei, Yuheng Zhou, Foxing Tan, Longcheng Deng, Haolin Du, Sen Wang, Cheng Wang, Yan Huang, Vinay Kumar,
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0335225. CrossRef - (R)-Bambuterol attenuates DSS-induced chronic colitis by suppressing inflammation, repairing intestinal barrier, and modulating gut microbiota and serum metabolomic profile
Liangjun Deng, Le Tian, Dan Su, Jiukun Xie, Yuer Qian, Yipeng Li, Shidong Zhang, Shanping Wang, Zhihua Liu
European Journal of Pharmacology.2025; 1008: 178346. CrossRef - Beyond inflammation: what drives the self-perpetuating cycle of fibrosis in IBD?
Yutong Wei, Zhou Zhou, Shiyu Xiao
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Neurokinin-1 Receptor Regulation of Fibroblast Phenotype and Function
Scott P. Levick
Receptors.2025; 4(4): 23. CrossRef - Tumor Development in Ulcerative Colitis: Perspectives From Biomechanical Characteristics
Hirotaka Tao
Development, Growth & Differentiation.2025; 67(9): 487. CrossRef - Effects of maternal overnutrition and metabolic challenge in adult life on the histological integrity of the liver and intestinal epithelium in rabbits
Lucía Carolina Cano, Erika Navarrete, Pedro Medina, Juan Pablo Ochoa-Romo, Georgina Díaz, Rodrigo Montúfar-Chaveznava, Rosa María Vigueras-Villaseñor, Ivette Caldelas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Full-Thickness Resection of a Non-Lifting Adenoma in an Ulcerative Colitis Patient Using OVESCO: A Case Report
Fei Yang Pan, Rupert Leong, Saurabh Gupta, Talia Fuchs, Viraj Kariyawasam
Case Reports in Gastroenterology.2025; 19(1): 682. CrossRef - Resistance to apoptosis in complicated Crohn's disease: Relevance in ileal fibrosis
M. Seco-Cervera, D. Ortiz-Masiá, D.C. Macias-Ceja, S. Coll, L. Gisbert-Ferrándiz, J. Cosín-Roger, C. Bauset, M. Ortega, B. Heras-Morán, F. Navarro-Vicente, M. Millán, J.V. Esplugues, S. Calatayud, M.D. Barrachina
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(2): 166966. CrossRef - Characterization of patient-derived intestinal organoids for modelling fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ilaria Laudadio, Claudia Carissimi, Noemi Scafa, Alex Bastianelli, Valerio Fulci, Alessandra Renzini, Giusy Russo, Salvatore Oliva, Roberta Vitali, Francesca Palone, Salvatore Cucchiara, Laura Stronati
Inflammation Research.2024; 73(8): 1359. CrossRef - Food additives impair gut microbiota from healthy individuals and IBD patients in a colonic in vitro fermentation model
Irma Gonza, Elizabeth Goya-Jorge, Caroline Douny, Samiha Boutaleb, Bernard Taminiau, Georges Daube, Marie–Louise Scippo, Edouard Louis, Véronique Delcenserie
Food Research International.2024; 182: 114157. CrossRef - Epigenetic Regulation of EMP/EMT-Dependent Fibrosis
Margherita Sisto, Sabrina Lisi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2775. CrossRef - Mechanisms and therapeutic research progress in intestinal fibrosis
Yanjiang Liu, Tao Zhang, Kejian Pan, He Wei
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Disease clearance in ulcerative colitis: A new therapeutic target for the future
Syed Adeel Hassan, Neeraj Kapur, Fahad Sheikh, Anam Fahad, Somia Jamal
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(13): 1801. CrossRef - Urinary Hydroxyproline as an Inflammation-Independent Biomarker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Muriel Huss, Tanja Elger, Johanna Loibl, Arne Kandulski, Benedicta Binder, Petra Stoeckert, Patricia Mester, Martina Müller, Christa Buechler, Hauke Christian Tews
Gastroenterology Insights.2024; 15(2): 486. CrossRef - Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Immune Function, Tissue Fibrosis and Current Therapies
Jesús Cosín-Roger
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(12): 6416. CrossRef - The Diagnosis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease—Present and Future
Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Jolanta Gruszecka, Rafał Filip
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(13): 6935. CrossRef - Role of gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis: Insights from fecal microbiota transplantation in mouse model
Qiang Wu, Lian-Wen Yuan, Li-Chao Yang, Ya-Wei Zhang, Heng-Chang Yao, Liang-Xin Peng, Bao-Jia Yao, Zhi-Xian Jiang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(31): 3689. CrossRef - Ultrasound of the bowel with a focus on IBD: the new best practice
Christina Merrill, Stephanie R. Wilson
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 50(2): 555. CrossRef - Unveiling the anti-inflammatory potential of 11β,13-dihydrolactucin for application in inflammatory bowel disease management
Melanie S. Matos, María Ángeles Ávila-Gálvez, Antonio González-Sarrías, Nuno-Valério Silva, Carolina Lage Crespo, António Jacinto, Ana Teresa Serra, Ana A. Matias, Cláudia Nunes dos Santos
Food & Function.2024; 15(18): 9254. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and mesenteric adipose tissue interactions in shaping phenotypes and treatment strategies for Crohn’s disease
Anis Hasnaoui, Racem Trigui, Mario Giuffrida
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(46): 4969. CrossRef - Pathways Affected by Falcarinol-Type Polyacetylenes and Implications for Their Anti-Inflammatory Function and Potential in Cancer Chemoprevention
Ruyuf Alfurayhi, Lei Huang, Kirsten Brandt
Foods.2023; 12(6): 1192. CrossRef - Time to eRAASe chronic inflammation: current advances and future perspectives on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system and chronic intestinal inflammation in dogs and humans
Romy M. Heilmann, Georg Csukovich, Iwan A. Burgener, Franziska Dengler
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the epithelial barrier in intestinal fibrosis associated with inflammatory bowel disease: relevance of the epithelial-to mesenchymal transition
Dulce C. Macias-Ceja, M. Teresa Mendoza-Ballesteros, María Ortega-Albiach, M. Dolores Barrachina, Dolores Ortiz-Masià
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids Elicit Differential Expression of Growth Factors and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Immortalized Rat Enteric Glial Cells
- Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
- Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):319-325. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.29
- 9,731 View
- 315 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Due to the extremely indolent behavior, a subset of noninvasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas has been classified as “noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP)” since 2016 and is no longer considered carcinoma. Since the introduction of this new terminology, changes and refinements have been made in diagnostic criteria. Initially, the incidence of NIFTP was estimated substantial. However, the reported incidence of NIFTP varies greatly among studies and regions, with higher incidence in North American and European countries than in Asian countries. Thus, the changes in the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) differ inevitably among regions. Because more conservative surgery is recommended for NIFTPs, distinguishing NIFTPs from papillary thyroid carcinomas in preoperative fine-needle aspiration cytology became one of the major concerns. This review will provide comprehensive overview of updates on diagnostic criteria, actual incidence and preoperative cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP, and its impact on the ROM in TBSRTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Papillae, psammoma bodies, and/or many nuclear pseudoinclusions are helpful criteria but should not be required for a definitive cytologic diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma: An institutional experience of 207 cases with surgical follow up
Tarik M. Elsheikh, Matthew Thomas, Jennifer Brainard, Jessica Di Marco, Erica Manosky, Bridgette Springer, Dawn Underwood, Deborah J. Chute
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(6): 348. CrossRef - ThyroSeq overview on indeterminate thyroid nodules: An institutional experience
Sam Sirotnikov, Christopher C. Griffith, Daniel Lubin, Chao Zhang, Nabil F. Saba, Dehong Li, Amanda Kornfield, Amy Chen, Qiuying Shi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(7): 353. CrossRef - Oncocytic Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Case Report
Kaveripakam Ajay Joseph, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S4): 606. CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Preoperative evaluation of thyroid nodules – Diagnosis and management strategies
Tapoi Dana Antonia, Lambrescu Ioana Maria, Gheorghisan-Galateanu Ancuta-Augustina
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 246: 154516. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - Strategies for Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
Deepika Yadav, Pramod Kumar Sharma, Rishabha Malviya, Prem Shankar Mishra
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(5): 406. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- The application of high-throughput proteomics in cytopathology
- Ilias P. Nikas, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):309-318. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.30
- 7,452 View
- 154 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-throughput genomics and transcriptomics are often applied in routine pathology practice to facilitate cancer diagnosis, assess prognosis, and predict response to therapy. However, the proteins rather than nucleic acids are the functional molecules defining the cellular phenotype in health and disease, whereas genomic profiling cannot evaluate processes such as the RNA splicing or posttranslational modifications and gene expression does not necessarily correlate with protein expression. Proteomic applications have recently advanced, overcoming the issue of low depth, inconsistency, and suboptimal accuracy, also enabling the use of minimal patient-derived specimens. This review aims to present the recent evidence regarding the use of high-throughput proteomics in both exfoliative and fine-needle aspiration cytology. Most studies used mass spectrometry, as this is associated with high depth, sensitivity, and specificity, and aimed to complement the traditional cytomorphologic diagnosis, in addition to identify novel cancer biomarkers. Examples of diagnostic dilemmas subjected to proteomic analysis included the evaluation of indeterminate thyroid nodules or prediction of lymph node metastasis from thyroid cancer, also the differentiation between benign and malignant serous effusions, pancreatic cancer from autoimmune pancreatitis, non-neoplastic from malignant biliary strictures, and benign from malignant salivary gland tumors. A few cancer biomarkers—related to diverse cancers involving the breast, thyroid, bladder, lung, serous cavities, salivary glands, and bone marrow—were also discovered. Notably, residual liquid-based cytology samples were suitable for satisfactory and reproducible proteomic analysis. Proteomics could become another routine pathology platform in the near future, potentially by using validated multi-omics protocols.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mass spectrometry-based proteomics of FFPE tissues: progress, limitations, and clinical translation barriers
Sara Abdulmohsen AlHammadi, Lamar Nabil Nagshabandi, Huzaifa Muhammad, Hatouf H. Sukkarieh, Ahmad Aljada
Clinical Proteomics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef
- Mass spectrometry-based proteomics of FFPE tissues: progress, limitations, and clinical translation barriers
Case Study
- Papillary and medullary thyroid carcinomas coexisting in the same lobe, first suspected based on fine-needle aspiration cytology: a case report
- Hyun Hee Koh, Young Lyun Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):301-308. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.03
- 6,404 View
- 117 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Because different types of thyroid malignancies have distinct embryological origins, coexisting tumors are rarely observed. We describe a coexisting papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) first suspected by fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). A 57-year-old female presented with an irregular mass in the right thyroid lobe. The cytopathologic findings of fine-needle aspiration showed two components: a papillary-like arrangement consisting of cells with pale enlarged nuclei indicative of PTC and loose clusters comprised of oval cells with granular chromatin indicative of MTC. The diagnosis of a coexisting PTC and MTC was initially confirmed by calcitonin immunocytochemistry and later after total thyroidectomy. Although some surgical case reports of PTC and MTC coexisting in either the same or different lobes have been documented, a case suspected by FNAC before the surgery has rarely been reported. Because appropriate treatment and prognosis of PTC and MTC are different, cytopathologists should be aware of this rare entity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Fine‐Needle Aspiration Cytology—Based on a Single Tertiary Centre Experience
Si‐Yi Chen, Dong‐Mei Gu
Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Synchronous papillary and medullary thyroid carcinoma with distinct genetic mutations: A case report
Huanyu Jiang, Lijuan Zhou, Gang Zou, Haidong Zhang, Zhenkun Yu
Oral Oncology.2025; 161: 107191. CrossRef - Coexisting papillary and medullary thyroid carcinomas in a 60 year old male: a case report
Allahdad Khan, Anam Malik, Abdul Ahad Riaz, Muhammad Hussnain Sadiq, Muhammad Shahzaib Arshad, Alka Rani, Ibrahim Nagmeldin Hassan
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2025; 87(10): 6740. CrossRef - Dedifferentiated Leiomyosarcoma of the Uterine Corpus with Heterologous Component: Clinicopathological Analysis of Five Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution and Comprehensive Literature Review
Suyeon Kim, Hyunsik Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2024; 14(2): 160. CrossRef - Coexisting Medullary and Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas: A Case of Dual Neoplasia With a High Risk of Misdiagnosis
Santiago Sierra Castillo, Maria A Henao Rincón, David Aristizabal Colorado, David Alexander Vernaza Trujillo, Alin Abreu Lomba
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Fine‐Needle Aspiration Cytology—Based on a Single Tertiary Centre Experience
Review
- Lymphoproliferative disorder involving body fluid: diagnostic approaches and roles of ancillary studies
- Jiwon Koh, Sun Ah Shin, Ji Ae Lee, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):173-186. Published online July 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.05.16
- 11,372 View
- 323 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lymphocyte-rich effusions represent benign reactive process or neoplastic condition. Involvement of lymphoproliferative disease in body cavity is not uncommon, and it often causes diagnostic challenge. In this review, we suggest a practical diagnostic approach toward lymphocyte-rich effusions, share representative cases, and discuss the utility of ancillary tests. Cytomorphologic features favoring neoplastic condition include high cellularity, cellular atypia/pleomorphism, monomorphic cell population, and frequent apoptosis, whereas lack of atypia, polymorphic cell population, and predominance of small T cells usually represent benign reactive process. Involvement of non-hematolymphoid malignant cells in body fluid should be ruled out first, followed by categorization of the samples into either small/medium-sized cell dominant or large-sized cell dominant fluid. Small/medium-sized cell dominant effusions require ancillary tests when either cellular atypia or history/clinical suspicion of lymphoproliferative disease is present. Large-sized cell dominant effusions usually suggest neoplastic condition, however, in the settings of initial presentation or low overall cellularity, ancillary studies are helpful for more clarification. Ancillary tests including immunocytochemistry, in situ hybridization, clonality test, and next-generation sequencing can be performed using cytologic preparations. Throughout the diagnostic process, proper review of clinical history, cytomorphologic examination, and application of adequate ancillary tests are key elements for successful diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fluid Overload-Associated Large B-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Isolated Pleural Effusion
Kevin Leeper, Lauren Borecky, Mojtaba Akhtari, Jun Wang
Hematology Reports.2026; 18(1): 13. CrossRef - The case of the sneaky lymphoma: solved by flow cytometry
Renu Singh, Md Ali Osama, Rachana Meena, Shailaja Shukla, Jagdish Chandra
Indian Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2025; 41(9): 1258. CrossRef - The urgency of Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis in fluid cytology—A tertiary care experience
Soundarya Ravi, Anu K. Devi, Prabhu Manivannan, Debasis Gochhait, Rakhee Kar, Neelaiah Siddaraju
Cytopathology.2024; 35(2): 275. CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry on frozen-embedded cell block for the diagnosis of hematolymphoid cytology specimen: a straightforward alternative to the conventional cell block
Youjeong Seo, Sanzida Alam Prome, Lucia Kim, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Suk Jin Choi
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Lymphoma presenting as the first finding in pleural fluid cytology: A rare cytologic presentation
Kafil Akhtar, Gowthami Nagendhran, Anjum Ara, Masheera Akhtar
IP Archives of Cytology and Histopathology Research.2024; 8(4): 250. CrossRef
- Fluid Overload-Associated Large B-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as Isolated Pleural Effusion
Original Articles
- Blocking Toll-like receptor 9 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury
- Badr Alzahrani, Mohamed M. S. Gaballa, Ahmed A. Tantawy, Maha A. Moussa, Salma A. Shoulah, Said M. Elshafae
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(2):81-91. Published online March 2, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.12.27
- 7,998 View
- 150 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is one of the most common complications in coronavirus disease 2019 patients suffering from acute lung injury (ALI). In ARDS, marked distortion of pulmonary architecture has been reported. The pulmonary lesions in ARDS include hemodynamic derangements (such as alveolar edema and hemorrhage), vascular and bronchiolar damage, interstitial inflammatory cellular aggregations, and eventually fibrosis. Bleomycin induces ARDS-representative pulmonary damage in mice and rats; therefore, we used bleomycin model mice in our study. Recently, Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) was implicated in the development of ARDS and ALI.
Methods
In this study, we evaluated the efficiency of a TLR9 blocker (ODN2088) on bleomycin-induced pulmonary damage. We measured the apoptosis rate, inflammatory reaction, and fibroplasia in bleomycin- and bleomycin + ODN2088-treated mice.
Results
Our results showed a significant amelioration in bleomycin-induced damage to pulmonary architecture following ODN2088 treatment. A marked decrease in pulmonary epithelial and endothelial apoptosis rate as measured by cleaved caspase-3 expression, inflammatory reaction as indicated by tumor necrosis factor α expression, and pulmonary fibrosis as demonstrated by Van Gieson staining and α-smooth muscle actin immunohistochemistry were observed following ODN2088 treatment.
Conclusions
All these findings indicate that blocking downstream TLR9 signaling could be beneficial in prevention or mitigation of ARDS through hemodynamic derangements, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A novel mouse model of myositis-associated interstitial lung disease was established by using TLR9 agonist combined with muscle homogenate
Ling Bai, Jiarui Zhu, Wenlan Ma, Peipei Zhao, Feifei Li, Cen Zhang, Sigong Zhang
Clinical and Experimental Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Toll-like Receptor 9 Inhibition Mitigates Fibroproliferative Responses in Translational Models of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Glenda Trujillo, Alicia Regueiro-Ren, Chunjian Liu, Buqu Hu, Ying Sun, Farida Ahangari, Vitoria Fiorini, Genta Ishikawa, Karam Al Jumaily, Johad Khoury, John McGovern, Chris J. Lee, Xue Yan Peng, Taylor Pivarnik, Huanxing Sun, Anjali Walia, Samuel Woo, Sh
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.2025; 211(1): 91. CrossRef - CD103+ dendritic cell–fibroblast crosstalk via TLR9, TDO2, and AHR signaling drives lung fibrogenesis
Hannah Carter, Rita Medina Costa, Taylor S. Adams, Talon M. Gilchrist, Claire E. Emch, Monica Bame, Justin M. Oldham, Steven K. Huang, Angela L. Linderholm, Imre Noth, Naftali Kaminski, Bethany B. Moore, Stephen J. Gurczynski
JCI Insight.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mitigated Effect of the Combination of Metformin and Stearic Acid to Ameliorate Bleomycin‐Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats via Inhibiting Gal‐3/Smad3/α‐SMA and TNF‐α/NF‐κβ Signaling Pathways
Maha M. Salem, Nermin S. Youssef, Mai El Keiy, Abeer A. Khamis
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling the Interactive Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Promoting Macrophage Polarization in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Jiajia Zou, Junling Jian, Dehua Ge, Bin Zhou, Jiaxiang Zhang
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms underlying dose-limiting toxicities of conventional chemotherapeutic agents
Mohammad Amin Manavi, Mohammad Hosein Fathian Nasab, Razieh Mohammad Jafari, Ahmad Reza Dehpour
Journal of Chemotherapy.2024; 36(8): 623. CrossRef - Innate Immune Response-Mediated Inflammation in Viral Pneumonia
Weiwei Ni, Xin Wei, Rui Wu
Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2024; 19(03): 140. CrossRef - Combination of losartan with pirfenidone: a protective anti-fibrotic against pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in rats
Arian Amirkhosravi, Maryamossadat Mirtajaddini Goki, Mahmoud Reza Heidari, Somayyeh Karami-Mohajeri, Maryam Iranpour, Maryam Torshabi, Mitra Mehrabani, Ali Mandegary, Mehrnaz Mehrabani
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Suppression of miR-17 Alleviates Acute Respiratory Distress-associated Lung Fibrosis by Regulating Mfn2
Mei-xia Xu, Tao Xu, Ning An
Current Medical Science.2024; 44(5): 964. CrossRef - Study of Recombinant Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Compositions Biological Activity After Injection and Inhalation in Mouse Model of Pulmonary Inflammation
Alexander M. Ischenko, Ksenia A. Nekrasova, Denis S. Laptev, Dmitry V. Bobkov, Alexander A. Kolobov, Andrey S. Simbirtsev
Cytokines and inflammation.2024; 21(3): 153. CrossRef - TLR9: A friend or a foe
Mona M. Saber, Nada Monir, Azza S. Awad, Marwa E. Elsherbiny, Hala F. Zaki
Life Sciences.2022; 307: 120874. CrossRef
- A novel mouse model of myositis-associated interstitial lung disease was established by using TLR9 agonist combined with muscle homogenate
- Immunohistochemical expression of programmed death-ligand 1 and CD8 in glioblastomas
- Dina Mohamed El Samman, Manal Mohamed El Mahdy, Hala Sobhy Cousha, Zeinab Abd El Rahman Kamar, Khaled Abdel Karim Mohamed, Hoda Hassan Abou Gabal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):388-397. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.04
- 6,926 View
- 195 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive primary malignant brain tumor in adults and is characterized by poor prognosis. Immune evasion occurs via programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1)/programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) interaction. Some malignant tumors have responded to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade treatment strategies, and PD-L1 has been described as a potential predictive biomarker. This study discussed the expression of PD-L1 and CD8 in glioblastomas.
Methods
Thirty cases of glioblastoma were stained immunohistochemically for PD-L1 and CD8, where PD-L1 expression in glioblastoma tumor tissue above 1% is considered positive and CD-8 is expressed in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. The expression of each marker was correlated with clinicopathologic parameters. Survival analysis was conducted to correlate progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) with PD-L1 and CD8 expression.
Results
Diffuse/fibrillary PD-L1 was expressed in all cases (mean expression, 57.6%), whereas membranous PD-L1 was expressed in six of 30 cases. CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD8+ TILs) had a median expression of 10%. PD-L1 and CD8 were positively correlated (p = .001). High PD-L1 expression was associated with worse PFS and OS (p = .026 and p = .001, respectively). Correlation of CD8+ TILs percentage with age, sex, tumor site, laterality, and outcomes were statistically insignificant. Multivariate analysis revealed that PD-L1 was the only independent factor that affected prognosis.
Conclusions
PD-L1 expression in patients with glioblastoma is robust; higher PD-L1 expression is associated with lower CD8+ TIL expression and worse prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dual biomarker role of PD-L1 and LC3B in glioblastoma: prognostic and therapeutic potential
Rana Fathy Torky, Rania Makboul, Dalia M. Badary, Wael M. A. El-Ghani, Ahmed El-Hakeem, Rabab M. H. El Ghorori
Neurosurgical Review.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathological diagnosis of central nervous system tumours in adults: what's new?
Evert-Jan Kooi, Lukas Marcelis, Pieter Wesseling
Pathology.2025; 57(2): 144. CrossRef - Expression of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Astrocytic Tumors and Its Correlation With Histopathological Grade and Proliferative Index (Ki-67): A Cross-Sectional Study
Namita Singh, Ranjana Giri, Prita Pradhan, Diptiranjan Satapathy, Ipsita Debata
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune intrinsic escape signature stratifies prognosis, characterizes the tumor immune microenvironment, and identifies tumorigenic PPP1R8 in glioblastoma multiforme patients
Ran Du, Lijun Jing, Denggang Fu
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 Clones and Their Relevance in Glioblastoma, IDH-Wildtype: A Comparative Analysis
Michal Hendrych, Frantisek Vana, Marketa Hermanova, Radek Lakomy, Tomas Kazda, Kvetoslava Matulova, Alena Kopkova, Martina Jelinkova, Radim Jancalek, Martin Smrcka, Vaclav Vybihal, Jiri Sana
Bratislava Medical Journal.2025; 126(9): 2233. CrossRef - Tumor-associated microenvironment, PD-L1 expression and their relationship with immunotherapy in glioblastoma, IDH-wild type: A comprehensive review with emphasis on the implications for neuropathologists
Giuseppe Broggi, Giuseppe Angelico, Jessica Farina, Giordana Tinnirello, Valeria Barresi, Magda Zanelli, Andrea Palicelli, Francesco Certo, Giuseppe Barbagallo, Gaetano Magro, Rosario Caltabiano
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 254: 155144. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Profile of Adult Glioblastoma IDH-Wildtype Microenvironment: A Cohort Study
Sofia Asioli, Lidia Gatto, Uri Vardy, Claudio Agostinelli, Vincenzo Di Nunno, Simona Righi, Alicia Tosoni, Francesca Ambrosi, Stefania Bartolini, Caterina Giannini, Enrico Franceschi
Cancers.2024; 16(22): 3859. CrossRef - Analysis of PD-L1 and CD3 Expression in Glioblastoma Patients and Correlation with Outcome: A Single Center Report
Navid Sobhani, Victoria Bouchè, Giovanni Aldegheri, Andrea Rocca, Alberto D’Angelo, Fabiola Giudici, Cristina Bottin, Carmine Antonio Donofrio, Maurizio Pinamonti, Benvenuto Ferrari, Stefano Panni, Marika Cominetti, Jahard Aliaga, Marco Ungari, Antonio Fi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 311. CrossRef - Immuno-PET Imaging of Tumour PD-L1 Expression in Glioblastoma
Gitanjali Sharma, Marta C. Braga, Chiara Da Pieve, Wojciech Szopa, Tatjana Starzetz, Karl H. Plate, Wojciech Kaspera, Gabriela Kramer-Marek
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3131. CrossRef
- Dual biomarker role of PD-L1 and LC3B in glioblastoma: prognostic and therapeutic potential
- Post-mortem assessment of vimentin expression as a biomarker for renal tubular regeneration following acute kidney injury
- Juan Carlos Alvarez Moreno, Hisham F. Bahmad, Christopher A. Febres-Aldana, Andrés Pirela, Andres Azuero, Ali Salami, Robert Poppiti
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):369-379. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.03
- 7,438 View
- 150 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality. It mainly targets the renal tubular epithelium with pathological changes, referred to as acute tubular injury. The latter is followed by a regenerative response that is difficult to visualize on routine hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains. In this study, we examined the regenerative capacity of renal tubules by correlating vimentin (VIM) immunohistochemical (IHC) expression and pathological findings of AKI and renal tubular regeneration (RTR) on H&E.
Methods
We reviewed 23 autopsies performed in the clinical setting of AKI and RTR. VIM expression was scored in the renal cortical tubular epithelium using a statistical cutoff ≥ 3% for high expression and < 3% for low expression.
Results
Of the 23 kidney tissues examined, seven (30.4%) had low VIM expression, and 16 (69.6%) had high VIM expression. Kidney tissues with evidence of AKI and RTR had significantly higher VIM expression. Renal peritubular microenvironment features showing regenerative changes on H&E were associated with high VIM expression. In the univariate model, kidney tissues with RTR were 18-fold more likely to have high VIM expression.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings suggest that VIM could serve as an IHC marker for RTR following AKI. However, correlation with H&E findings remains critical to excluding chronic tubular damage. Collectively, our preliminary results pave the way for future studies including a larger sample size to validate the use of VIM as a reliable biomarker for RTR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Myocardial Infarction Injury Is Exacerbated by Nicotine in Vape Aerosol Exposure
Clarissa Savko, Carolina Esquer, Claudia Molinaro, Sophie Rokaw, Abraham G. Shain, Faid Jaafar, Morgan K. Wright, Joy A. Phillips, Tyler Hopkins, Sama Mikhail, Abigail Rieder, Ariana Mardani, Barbara Bailey, Mark A. Sussman
Journal of the American Heart Association.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatio-temporal transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct nephrotoxicity, DNA damage, and regeneration response after cisplatin
Lukas S. Wijaya, Steven J. Kunnen, Panuwat Trairatphisan, Ciarán P. Fisher, Meredith E. Crosby, Kai Schaefer, Karen Bodié, Erin E. Vaughan, Laura Breidenbach, Thomas Reich, Diana Clausznitzer, Sylvestre Bonnet, Sipeng Zheng, Chantal Pont, James L. Stevens
Cell Biology and Toxicology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization of macrophages in ischemia–reperfusion injury-induced acute kidney injury based on single-cell RNA-Seq and bulk RNA-Seq analysis
Qin Wang, Yuxing Liu, Yan Zhang, Siyuan Zhang, Meifang Zhao, Zhangzhe Peng, Hui Xu, Hao Huang
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 130: 111754. CrossRef - Renal tubular necrosis associated with anagrelide administration: a case report
Atsushi Sawase, Mineaki Kitamura, Misato Morimoto, Haruka Fukuda, Tadashi Uramatsu, Eisuke Katafuchi, Hiroshi Yamashita, Toshiyuki Nakayama, Hiroshi Mukae, Tomoya Nishino
CEN Case Reports.2024; 13(6): 510. CrossRef - Morin attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by regulating inflammatory responses, oxidative stress and tubular regeneration (morin and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury)
Aya M. Shehata, Nagui H. Fares, Basma H. Amin, Asmaa A. Mahmoud, Yomna I. Mahmoud
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2024; 111: 104543. CrossRef
- Myocardial Infarction Injury Is Exacerbated by Nicotine in Vape Aerosol Exposure
- Programmed death-ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters
- Gaurav Garg, Kuruswamy Thurai Prasad, Navneet Singh, Parul Gupta, Valliappan Muthu, Ashim Das, Amanjit Bal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):398-405. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.08.08
- 5,647 View
- 167 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Data on the prevalence of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and their clinical significance in Indian patients are limited.
Methods
Newly diagnosed NSCLC cases (adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma [SqCC] histology) were included in the present study. The TILs were evaluated based on morphology on hematoxylin and eosin–stained slides. PD-L1 expression in tumors was assessed using immunohistochemistry with rabbit monoclonal antibody (SP263) on the Ventana automated immunostainer. Tumors with PD-L1 expression > 50% on tumor cells were considered PD-L1–positive. Tumors in which TILs occupy > 25% of stroma were considered to have high TILs. The association of PD-L1 expression and TILs with various clinical parameters including overall survival (OS) was investigated.
Results
The present study included 128 cases of NSCLC (67 adenocarcinoma, 61 SqCC). PD-L1 positivity was observed in 17.2% of the patients with NSCLC. Baseline characteristics of PD-L1–positive subjects were similar to PD-L1–negative subjects except for a higher prevalence of liver metastasis (18.2% vs. 2.8%; p = .018) and a higher probability of diagnosis from extrapulmonary biopsies. High TILs were observed in 26.6% of the subjects. However, PD-L1 expression and high TIL did not affect OS.
Conclusions
PD-L1 positivity and high TILs were observed in 20% and 25% of the patients with NSCLC, respectively, however, neither were predictors of survival in SqCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PDL1 and IDO‐2 Immunohistochemistry in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Versus Bronchoscopic Biopsy of Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer
Menna Allah Hesham Mohammed Fekry, Yosria Mohammed El‐Gohary, Hesham Radwan Abd‐Elaziz, Tarek Hamdy Hassan, Mona Mostafa Ahmed
Cytopathology.2026; 37(2): 151. CrossRef - Multiplex plasma protein assays as a diagnostic tool for lung cancer
Mohammad Tanvir Ahamed, Jenny Forshed, Adrian Levitsky, Janne Lehtiö, Amanj Bajalan, Maria Pernemalm, Lars E. Eriksson, Björn Andersson
Cancer Science.2024; 115(10): 3439. CrossRef - Real-world prevalence of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: an Australia-wide multi-centre retrospective observational study
Prudence A. Russell, Alexandra L. Farrall, Sarita Prabhakaran, Khashayar Asadi, Wade Barrett, Caroline Cooper, Wendy Cooper, Samuel Cotton, Edwina Duhig, Matthew Egan, Stephen Fox, David Godbolt, Shilpa Gupta, Aniza Hassan, Connull Leslie, Trishe Leong, D
Pathology.2023; 55(7): 922. CrossRef
- PDL1 and IDO‐2 Immunohistochemistry in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Versus Bronchoscopic Biopsy of Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification
- Hye Ju Kang, Sun Young Kwon, Ahrong Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Soo Kee Min, So Young Park, Sun Hee Sung, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Hyang Im Lee, Ho Chang Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Sun Young Jun, Min Jung Jung, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Hye Jeong Choi, So Yeon Park, Jee Yeon Kim, In Ae Park, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):380-387. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
- 7,405 View
- 226 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
Methods
Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
Results
On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
Conclusions
Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Case Study
- A case of concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration against a mutated EGFR background in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
- Ki-Chang Lee, Jiwon Koh, Doo Hyun Chung, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):139-144. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.12.16
- 5,397 View
- 111 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rare cases of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) with concomitant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) translocation have been reported. However, their clonal and evolutional relationship remains unclear. We report a case of early-stage EGFR-mutated LUAD with a focal concomitant EGFR/ALK alteration. A 63-year-old male underwent lobectomy to remove a 1.9-cm-sized lung nodule, which was diagnosed with EGFR-mutated LUAD. ALK immunohistochemistry (IHC) showed focal positivity within the part of the tumor characterized by lepidic pattern, also confirmed by fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH). Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed separately on the ALK IHC/FISH-positive and -negative areas. EGFR L833V/L858R mutations were detected in both areas, whereas EML4 (echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4)-ALK translocations was confirmed only in the ALK IHC/FISH-positive area, suggesting the divergence of an EGFR/ALK co-altered subclone from the original EGFR-mutant clone. Our study suggests that concurrent alterations of EGFR and ALK can arise via divergent tumor evolution, even in the relatively early phases of tumorigenesis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Machine learning-based characterization of a PANoptosis-associated model for enhancing prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Ziqiao Fu, Jia Zeng, Xiaomin Xiong, Weimin Zhong
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of molecular subtype and prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma based on neutrophil extracellular traps
Yanhua Zuo, Guangyi Leng, Ping Leng
Pathology and Oncology Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning-Based Integration Develops a Macrophage-Related Index for Predicting Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Zuwei Li, Minzhang Guo, Wanli Lin, Peiyuan Huang
Archives of Medical Research.2023; 54(7): 102897. CrossRef - Big data analysis identified a telomere-related signature predicting the prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
Weiyi Zhang
Medicine.2023; 102(46): e35526. CrossRef
- Machine learning-based characterization of a PANoptosis-associated model for enhancing prognosis and immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma patients
Original Article
- Causes of necrotic features in fine-needle aspirates from cervical lymph nodes
- Young Jin Seo, Hyeongchan Shin, Hye Won Lee, Hye Ra Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):60-67. Published online November 27, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.09.28
- 17,959 View
- 206 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Lymph node fine-needle aspiration (LN FNA) cytology indicates necrosis in various diseases. Dominant necrotic features make the diagnosis of underlying conditions very difficult.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 460 patients who underwent cervical LN aspiration cytology that revealed necrotic findings at Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital in Daegu, Korea, from 2003–2017. Each specimen was evaluated and analyzed in association with the clinical findings, biopsy findings, and/or other ancillary tests, including acid-fast bacilli staining and molecular testing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Results
When necrotic features were noted upon cervical LN FNA cytology, the most common pathologic LN FNA category was necrosis alone (31.5%). The second most common category was granulomatous inflammation (31.3%), followed by Kikuchi disease (20.0%) and malignant neoplasm (8.7%). In cases where the cervical LN FNA revealed necrosis alone, the most common final diagnosis was tuberculosis. In young patients, Kikuchi disease should be considered as one cervical LN FNA category, while metastatic carcinoma should be suspected in older patients.
Conclusions
Even when necrosis alone is observed in LN FNA cytology, it is important to determine the cause through further evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Potential Use of Peptides in the Fight against Chagas Disease and Leishmaniasis
Hayelom Berhe, Mahesh Kumar Cinthakunta Sridhar, Mulate Zerihun, Nir Qvit
Pharmaceutics.2024; 16(2): 227. CrossRef - Tips and tricks for a proper radiological assessment of abdominal and pelvic lymph nodes
Ana Laura Lopes Potente, Cynthia Lopes Pereira de Borborema, Iza Campos Pedra Vieira, Aley Talans, Eduardo Oliveira Pacheco, Lucas Rios Torres, Serli Kiyomi Nakao Ueda, Fernanda Lopez Mazzucato, Andrei Saraiva Purysko, Daniel Lahan Martins, Ulysses Santos
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(11): 4057. CrossRef - Does the Necrotic Portion of Metastatic Lymphadenopathy from Squamous Cell Carcinoma Still Have Tumoral Oncologic Information? Differential Diagnosis of Benign Necrotic Lymphadenopathy Using microRNA
Eun Shin, Seung Hoon Han, Il-Seok Park, Jee Hye Wee, Joong Seob Lee, Heejin Kim
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2407. CrossRef - Impact of HPV status in T1–2 oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma with bulky N3 nodes: a multicenter GETTEC study
Charles Hurel, Florent Carsuzaa, Julia Salleron, Philippe Gorphe, Christian Righini, Maximilien Rogé, Erwan de Mones, Sylvain Morinière, Sébastien Vergez, Juliette Thariat, Xavier Dufour
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2023; 280(2): 847. CrossRef - Lymph nodes in health and disease – A pathologist's perspective
N S Priya
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2023; 27(1): 6. CrossRef
- The Potential Use of Peptides in the Fight against Chagas Disease and Leishmaniasis
Reviews
- DNA-protein biomarkers for immunotherapy in the era of precision oncology
- Binnari Kim, So Young Kang, Kyoung-Mee Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):26-32. Published online November 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.09.23
- 7,053 View
- 186 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The use of biomarkers to guide patient and therapy selection has gained much attention to increase the scope and complexity of targeted therapy options and immunotherapy. Clinical trials provide a basis for discovery of biomarkers, which can then aid in development of new drugs. To that end, samples from cancer patients, including DNA, RNA, protein, and the metabolome isolated from cancer tissues and blood or urine, are analyzed in various ways to identify relevant biomarkers. In conjunction with nucleotide-based, high-throughput, next-generation sequencing techniques, therapy-guided biomarker assays relying on protein-based immunohistochemistry play a pivotal role in cancer care. In this review, we discuss the current knowledge regarding DNA and protein biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment Selection for Patients with HER2-Negative Metastatic Gastric Cancer Expressing Claudin 18.2 and PD-L1
Yusuke Miyajima, Takeshi Kawakami
Cancers.2025; 17(7): 1120. CrossRef - NCKAP1 as a prognostic and immunological biomarker: pan-cancer analysis and validation in renal clear cell carcinoma
Xiao Liang
American Journal of Translational Research.2024; 16(8): 4083. CrossRef - Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Personalized Immunotherapy in Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, An Na Seo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2782. CrossRef
- Treatment Selection for Patients with HER2-Negative Metastatic Gastric Cancer Expressing Claudin 18.2 and PD-L1
- Pathologic interpretation of endoscopic ultrasound–guided fine needle aspiration cytology/biopsy for pancreatic lesions
- Haeryoung Kim, Kee-Taek Jang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):367-377. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.21
- 9,343 View
- 224 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pathologic interpretation of endoscopic ultrasound–guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) cytology/biopsy specimens is one of the most challenging tasks in cytology and surgical pathology practice, as the procedure often yields minimal amounts of diagnostic material and contains contaminants, such as blood cells and normal intestinal mucosa. EUS-FNA cytology/biopsy will nevertheless become a more popular procedure for evaluation of various pancreatic lesions because they are difficult to approach with conventional endoscopic procedures. Pathologists should understand the structural differences and limitations of EUS-FNA that make pathologic diagnosis difficult. Ancillary tests are available for differential diagnosis of EUS-FNA for various pancreatic lesions. Immunostains are the most commonly used ancillary tests, and pathologists should able to choose the necessary panel for differential diagnosis. Pathologists should review clinical history and radiologic and/or EUS findings before selecting an immunostain panel and making a pathologic diagnosis. In addition, one’s threshold of malignancy should be adjusted according to the appropriate clinical setting to avoid under-evaluation of pathologic diagnoses. Clinico-pathologic correlation is essential in pathologic evaluation of EUS-FNA for pancreatic lesions. Pathologists can reduce errors by correlating clinical and radiologic findings when evaluating EUS-FNA. Some molecular tests can be applied in differential diagnosis of pancreatic neoplastic and cystic lesions. Molecular data should be used as supportive evidence of a specific disease entity, rather than direct evidence, and should be correlated with clinico-pathologic findings to avoid errors in pathologic diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic Performance of EUS‐FNA for Pancreatic Lesions at Tertiary Centers in Iran Without Rapid On‐Site Evaluation
Maryam Bazmandegan, Gholam Reza Sivandzadeh, Kamran Bagheri Lankarani, Zahra Beyzaei, Bita Geramizadeh
Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatic Tissue Sampling: Lesion Assessment, Needles, and Techniques
Jahnvi Dhar, Jayanta Samanta, Zaheer Nabi, Manik Aggarwal, Maria Cristina Conti Bellocchi, Antonio Facciorusso, Luca Frulloni, Stefano Francesco Crinò
Medicina.2024; 60(12): 2021. CrossRef - A prospective randomized noninferiority trial comparing conventional smears and SurePathTM liquid-based cytology in endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of esophageal, gastric, and duodenal lesions
Jae Chang Jun, Sang Hyub Lee, Han Myung Lee, Sang Gyun Kim, Hyunsoo Chung, Joo Seong Kim, Namyoung Park, Jin Ho Choi, Yoonjin Kwak, Soo-Jeong Cho
Medicine.2023; 102(29): e34321. CrossRef - Double Ki-67 and synaptophysin labeling in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor biopsies
Bokyung Ahn, Jin Kying Jung, HaeSung Jung, Yeon-Mi Ryu, Yeon Wook Kim, Tae Jun Song, Do Hyun Park, Dae wook Hwang, HyungJun Cho, Sang-Yeob Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
Pancreatology.2022; 22(3): 427. CrossRef - Comparison of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration with 19-Gauge and 22-Gauge Needles for Solid Pancreatic Lesions
Changjuan Li, Jianwei Mi, Fulai Gao, Xinying Zhu, Miao Su, Xiaoli Xie, Dongqiang Zhao
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 10439. CrossRef
- Diagnostic Performance of EUS‐FNA for Pancreatic Lesions at Tertiary Centers in Iran Without Rapid On‐Site Evaluation
- Thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology in Taiwan: a nationwide survey and literature update
- Chien-Chin Chen, Jen-Fan Hang, Chih-Yi Liu, Yeh-Han Wang, Chiung-Ru Lai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):361-366. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.17
- 6,917 View
- 158 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In Taiwan, thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology is easily accessible and reliable for evaluating thyroid nodules. The sonographic pattern plays a major role and is the deciding factor for aspiration. We conducted a nationwide survey in 2017 and it revealed that 31% of laboratories had adopted The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. There was a relatively high unsatisfactory rate (24.04%) and low rates of indeterminate diagnoses, including atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesions of undetermined significance: 4.87%, and follicular neoplasm/suspicious for a follicular neoplasm: 0.35%. Moreover, the risks of malignancy in benign, atypia of undetermined significance, and suspicious for a follicular neoplasm were relatively high. These may reflect strict diagnostic criteria for indeterminate categories and better patient selection for surgery. Improvements in specimen sampling and continuing education programs are crucial. Newly-developed thyroid cytology technologies, such as immunocytochemistry, molecular testing, and computerized cytomorphometry, may further facilitate cytology diagnoses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytopathology in Taiwan: Historical Perspectives, Current Practices, and Future Directions
Yeh‐Han Wang, Wen‐Ying Lee, Jen‐Fan Hang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(1): 54. CrossRef - Diagnostic values of SurePath liquid‐based cytology versus conventional smear in thyroid aspiration samples: A 13‐year experience at a single institution
Wen‐Ying Lee, Hsiu‐Chu Wang, Lee‐E Huang, Min‐Hui Tseng, Shu‐Hui Chiang, Ching‐Chien Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(7): 369. CrossRef - Comparison of fine-needle aspiration with fine-needle capillary cytology in thyroid nodules
H Hatami, M Samsami, S Movahedinia, B Salehi, M Movahedinia, M Ardeshir
The Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England.2023; 105(2): 162. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - Thyroid malignancy rates according to the Bethesda reporting system in Israel - A multicenter study
Ory Madgar, Galit Avior, Isaac Shochat, Ben-Zion Joshua, Lior Baraf, Yuval Avidor, Avi khafif, Niddal Assadi, Eran E. Alon
European Journal of Surgical Oncology.2021; 47(6): 1370. CrossRef
- Cytopathology in Taiwan: Historical Perspectives, Current Practices, and Future Directions
Original Articles
- A retrospective cytohistological correlation of fine-needle aspiration cytology with classification by the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology
- Ji Hyun Park, Yoon Jin Cha, Ja Yeong Seo, Jae Yol Lim, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):419-425. Published online July 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.09
- 7,245 View
- 204 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Before publication of the new classification system named the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology (MSRSGC) in 2018, there was no standard classification for salivary gland lesions obtained by fine-needle aspiration (FNA). We therefore aimed to evaluate the diagnostic utility of this system by retrospectively reviewing FNA samples using the MSRSGC and to determine their risk of developing into neoplasms and becoming malignant.
Methods
Retrospective slide review and classification of salivary gland FNAs obtained over a 6-year period (2013–2018) at a single center were performed by two pathologists. The risks of neoplasm and malignancy for each category also were calculated.
Results
This study surveyed 374 FNAs (371 patients) performed over a six-year period and selected 148 cases that included documented surgical follow-up (39.6%). Among the surgically treated cases, the distributions of FNA categories were as follows: non-diagnostic (ND; 16.9%), non-neoplastic (NN; 2.7%), atypia of undetermined significance (AUS; 3.4%), benign (BN; 54.7%), salivary gland neoplasm of uncertain malignant potential (SUMP; 10.1%), suspicious for malignancy (SM; 6.8%), and malignant (M; 5.4%). The risk of malignancy (ROM) was 24.0% for ND, 0% for NN, 40.0% for AUS, 2.5% for BN, 46.7% for SUMP, 100% for SM, and 87.5% for M. The overall diagnostic accuracy was 95.9% (142/148 cases).
Conclusions
The newly proposed MSRSGC appears to be a reliable system for classification of salivary gland lesions according to the associated ROM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Lesion-Specific and Sampling-Related Factors on Success of Salivary Gland Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
Marcel Mayer, Mohammad Marwan Alfarra, Kathrin Möllenhoff, Marianne Engels, Christoph Arolt, Alexander Quaas, Philipp Wolber, Louis Jansen, Lisa Nachtsheim, Maria Grosheva, Jens Peter Klussmann, Sami Shabli
Head and Neck Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Myriad Spectrum of Salivary Gland Lesions: Cytohistological Correlation on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology, Core Needle Biopsy, and Resections in a 5‐Year Single Institutional Experience of North India
Zachariah Chowdhury, Pallavi Majumdar, Sumeet Narain, Komal Lamba
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(8): 391. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology and a Proposed Algorithm for Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Salivary Gland Lesions
Norihide Mochizuki, Hirotaka Fujita, Takuma Tajiri, Masataka Ueda, Makiko Kurata, Chie Inomoto, Tomoko Sugiyama, Daisuke Maki, Shuichi Shiraishi, Tomohisa Machida, Hitoshi Ito, Yohei Masugi, Naoya Nakamura
Acta Cytologica.2025; 69(4): 324. CrossRef - A study of fine needle aspiration cytology and histopathology correlation of salivary gland neoplasms in a tertiary care hospital: an observational study
Asima Malik, Ahlam Mushtaq, Salma Bhat, Suhail Naik
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics.2025; 13(1): 23. CrossRef - The Milan system for reporting salivary gland cytopathology – Assessment of utility and the risk of malignancy
Annu E. Prakash, Renu Sukumaran, Nileena Nayak, K. Lakshmi, Anitha Mathews, Jayasree Kattoor
Indian Journal of Cancer.2024; 61(3): 575. CrossRef - Salivary gland fine-needle aspiration biopsy: quality assurance results from a tertiary cancer center
Fanni Ratzon, Dominique L. Feliciano, Nora Katabi, Bin Xu, Oscar Lin, Xiao-Jun Wei
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(3): 206. CrossRef - Cytohistological correlation and risk stratification of salivary gland lesions using the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology: A tertiary care centre experience
Tarun Kumar, Prerna Tewari, Jitendra Singh Nigam, Shreekant Bharti, Surabhi, Ruchi Sinha, Punam Prasad Bhadani
Cytopathology.2023; 34(3): 225. CrossRef - Assessment of Risk of Malignancy of Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology in Salivary Gland Lesions Using the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology Categorization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Amit Kumar, Subhash Chandra, Bishnupati Singh, Swati Sharma, Ankita Tandon, Ajoy Kumar Shahi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2023; 23(10): 1039. CrossRef - Milan Sınıflandırma Sistemi’ne Göre Değerlendirilen Tükürük Bezi İnce İğne Aspirasyon Sitolojilerinin Histopatolojik Tanı Uyumu
Özlem SARAYDAROĞLU, Selin YİRMİBEŞ
Uludağ Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 49(3): 285. CrossRef - Milan system for reporting salivary gland cytopathology: Adoption and outcomes in a community setting
Samih J. Nassif, Ali R. Sasani, Garrey T. Faller, Jennifer L. Harb, Jagdish K. Dhingra
Head & Neck.2022; 44(6): 1462. CrossRef - Nondiagnostic salivary gland FNAs are associated with decreased risk of malignancy compared with “all‐comer” patients: Analysis of the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology with a focus on Milan I: Nondiagnostic
Shu K. Lui, Troy Tenney, Patrick C. Mullane, Kartik Viswanathan, Daniel J. Lubin
Cancer Cytopathology.2022; 130(10): 800. CrossRef - Application of the Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Zhaoyang Wang, Huan Zhao, Huiqin Guo, Changming An
Cancer Cytopathology.2022; 130(11): 849. CrossRef - Multiplexed single‐cell analysis of FNA allows accurate diagnosis of salivary gland tumors
Juhyun Oh, Tae Yeon Yoo, Talia M. Saal, Lisa Tsay, William C. Faquin, Jonathan C.T. Carlson, Daniel G. Deschler, Sara I. Pai, Ralph Weissleder
Cancer Cytopathology.2022; 130(8): 581. CrossRef - Cytologic analysis of vitreous fluids: A retrospective review of our 24 years of experience
Gabriel L. Collins, Elizabeth W. Hubbard, Christopher T. Clark, Lisa D. Duncan, Laurentia Nodit
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(10): 1122. CrossRef
- The Impact of Lesion-Specific and Sampling-Related Factors on Success of Salivary Gland Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Prediction of TP53 mutations by p53 immunohistochemistry and their prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Hye Jung Hwang, Soo Kyung Nam, Hyunjin Park, Yujun Park, Jiwon Koh, Hee Young Na, Yoonjin Kwak, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):378-386. Published online July 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.01
- 13,154 View
- 287 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Recently, molecular classifications of gastric cancer (GC) have been proposed that include TP53 mutations and their functional activity. We aimed to demonstrate the correlation between p53 immunohistochemistry (IHC) and TP53 mutations as well as their clinicopathological significance in GC.
Methods
Deep targeted sequencing was performed using surgical or biopsy specimens from 120 patients with GC. IHC for p53 was performed and interpreted as strong, weak, or negative expression. In 18 cases (15.0%) with discrepant TP53 mutation and p53 IHC results, p53 IHC was repeated.
Results
Strong expression of p53 was associated with TP53 missense mutations, negative expression with other types of mutations, and weak expression with wild-type TP53 (p<.001). The sensitivity for each category was 90.9%, 79.0%, and 80.9%, and the specificity was 95.4%, 88.1%, and 92.3%, respectively. The TNM stage at initial diagnosis exhibited a significant correlation with both TP53 mutation type (p=.004) and p53 expression status (p=.029). The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for 109 stage II and III GC cases showed that patients with TP53 missense mutations had worse overall survival than those in the wild-type and other mutation groups (p=.028). Strong expression of p53 was also associated with worse overall survival in comparison to negative and weak expression (p=.035).
Conclusions
Results of IHC of the p53 protein may be used as a simple surrogate marker of TP53 mutations. However, negative expression of p53 and other types of mutations of TP53 should be carefully interpreted because of its lower sensitivity and different prognostic implications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The future is now: advancing p53 immunohistochemistry in Barrett's oesophagus and its implication for the everyday pathologist
Yevgen Chornenkyy, Monika Vyas, Vikram Deshpande
Histopathology.2026; 88(2): 380. CrossRef - Advancement in preclinical development of cancer treatment agents through modulation of Rac1: From EHop-016 to natural products
Yingyi Liu, Sze-Nga Wong, Aiping Lyu, Joshua Ka-Shun Ko
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer.2026; 1881(1): 189522. CrossRef - Tumor-Associated Macrophage Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer According to a Modified TCGA-Based Classification
Boram Song, Dong-Hoe Koo, Eo Jin Kim, In-Gu Do, Jinah Chu, Kyungeun Kim, Hyebin Lee, Min-Jung Kwon, Jung Ho Park, Byung Ho Son, Chang Hak Yoo, Seoung Wan Chae
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor microenvironment dynamics in gastric cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic resistance
Zhenhua Lu, Qinnan Zhang, Jing Han, Jiafu Ji, Xiaofang Xing
Molecular Cancer.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Linking p53 immunostaining to TP53 mutation status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Taeyeong Kim, Suyeon Kim, Sangjin Lee, Soohyun Hwang, Joungho Han, Hoyeon Jeong, Yoon-La Choi
Pathology.2025; 57(7): 881. CrossRef - Correlation of TP53 Genetic Alterations with p53 Immunohistochemical Expression and Their Prognostic Significance in DLBCL
Chen Chen, Zijuan Hu, Min Ren, Longlong Bao, Ran Wei, Tian Tian, Xiaoli Zhu, Qianming Bai, Baohua Yu, Xiaoqiu Li, Xiaoyan Zhou
Current Oncology.2025; 32(9): 488. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - Multiple approaches revealed MGc80‐3 as a somatic hybrid with HeLa cells rather than a gastric cancer cell line
Fang Cao, Hao Sun, Zhenli Yang, Yanhua Bai, Xiao Hu, Yuhong Hou, Xiaocui Bian, Yuqin Liu
International Journal of Cancer.2024; 154(1): 155. CrossRef - In Response to p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and TP53 Gene Mutations in Endometrial Cancer: Does Null Pattern Correlate With Prognosis?
Ikuko Sakamoto, Keiko Kagami, Takahiro Nozaki, Yosuke Hirotsu, Kenji Amemiya, Toshio Oyama, Masao Omata
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(3): 374. CrossRef - CHEK2 germline variants identified in familial nonmedullary thyroid cancer lead to impaired protein structure and function
Carolina Pires, Inês J. Marques, Mariana Valério, Ana Saramago, Paulo E. Santo, Sandra Santos, Margarida Silva, Margarida M. Moura, João Matos, Teresa Pereira, Rafael Cabrera, Diana Lousa, Valeriano Leite, Tiago M. Bandeiras, João B. Vicente, Branca M. Ca
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2024; 300(3): 105767. CrossRef - The spectrum of TP53 mutations in Rwandan patients with gastric cancer
Augustin Nzitakera, Jean Bosco Surwumwe, Ella Larissa Ndoricyimpaye, Schifra Uwamungu, Delphine Uwamariya, Felix Manirakiza, Marie Claire Ndayisaba, Gervais Ntakirutimana, Benoit Seminega, Vincent Dusabejambo, Eric Rutaganda, Placide Kamali, François Ngab
Genes and Environment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gastric cancer molecular classification based on immunohistochemistry and in‐situ hybridisation and mortality
Maarit Eskuri, Eva‐Maria Birkman, Joonas H Kauppila
Histopathology.2024; 85(2): 327. CrossRef - Redefining aberrant P53 expression of gastric cancer and its distinct clinical significance among molecular-histologic subtypes
Shih-Chiang Huang, Ian Yi-Feng Chang, Tse-Ching Chen, Hsiao-Ching Lin, Chun-Yi Tsai, Jun-Te Hsu, Chun-Nan Yeh, Shih-Cheng Chang, Ta-Sen Yeh
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(11): 4699. CrossRef - Assessment of TP53 and CDKN2A status as predictive markers of malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma
Soohyeon Kwon, Jeong-Whun Kim, Eun Sun Kim, Jin Ho Paik, Jin-Haeng Chung, Sung-Woo Cho, Tae-Bin Won, Chae-Seo Rhee, Jee Hye Wee, Hyojin Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implementing an integrated molecular classification for gastric cancer from endoscopic biopsies using on-slide tests
Simona Costache, Adelina Baltan , Sofia Diaz McLinn , Mattia Pegoraro , Rebecca de Havilland , Matthew Porter , Ana Lerga , Teresa Thomas , Alina Elena Chefani
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology.2024; 65(2): 257. CrossRef - Application of NGS molecular classification in the diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma: A supplement to traditional pathological diagnosis
Qunxian Rao, Jianwei Liao, Yangyang Li, Xin Zhang, Guocai Xu, Changbin Zhu, Shengya Tian, Qiuhong Chen, Hui Zhou, Bingzhong Zhang
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(5): 5409. CrossRef - Predictive value of p53 and AXL immunostaining for the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor-based therapy after osimertinib treatment in patients with epidermal growth factor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
Kenji Morimoto, Tadaaki Yamada, Ryo Sawada, Koichi Azuma, Yasuhiro Goto, Taishi Harada, Shinsuke Shiotsu, Nobuyo Tamiya, Yusuke Chihara, Takayuki Takeda, Osamu Hiranuma, Isao Hasegawa, Satomi Tanaka, Akihiro Yoshimura, Masahiro Iwasaku, Shinsaku Tokuda, Y
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2023; 72(6): 1699. CrossRef - Validation of p53 Immunohistochemistry (PAb240 Clone) in Canine Tumors with Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis
Barbara Brunetti, Dario de Biase, Giulia Dellapina, Luisa Vera Muscatello, Francesco Ingravalle, Giorgia Tura, Barbara Bacci
Animals.2023; 13(5): 899. CrossRef - Mesonephric‐like adenocarcinoma of the female genital tract: novel observations and detailed molecular characterisation of mixed tumours and mesonephric‐like carcinosarcomas
Jelena Mirkovic, Ekaterina Olkhov‐Mitsel, Yutaka Amemiya, Maysa Al‐Hussaini, Sharon Nofech‐Mozes, Bojana Djordjevic, Rachel Kupets, Arun Seth, W Glenn McCluggage
Histopathology.2023; 82(7): 978. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characterization of cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor: a multicenter study in Korea
Miseon Lee, Uiree Jo, Joon Seon Song, Youn Soo Lee, Chang Gok Woo, Dong-Hoon Kim, Jung Yeon Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Kyung-Ja Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(3): 166. CrossRef - P53 in Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Pattern-Based Immunohistochemical Framework with Molecular Correlation
Isabel Trias, Adela Saco, Lorena Marimon, Ricardo López del Campo, Carolina Manzotti, Oriol Ordi, Marta del Pino, Francisco M. Pérez, Naiara Vega, Silvia Alós, Antonio Martínez, Leonardo Rodriguez-Carunchio, Oscar Reig, Pedro Jares, Cristina Teixido, Tare
Cancers.2023; 15(10): 2719. CrossRef - p53/TP53 Status Assessment in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma
Elisa Boldrin, Maria Assunta Piano, Francesco Bernaudo, Rita Alfieri, Maria Raffaella Biasin, Isabella Monia Montagner, Alice Volpato, Genny Mattara, Francesco Lamacchia, Giovanna Magni, Antonio Rosato, Antonio Scapinello, Pierluigi Pilati, Matteo Curtare
Cancers.2023; 15(10): 2783. CrossRef - Genomic profiling of dedifferentiated endometrial carcinomas arising in the background of high‐grade carcinoma: a targeted next‐generation sequencing study
Ekaterina Olkhov‐Mitsel, Aurelia Busca, Carlos Parra‐Herran, Yutaka Amemiya, Sharon Nofech‐Mozes, Bojana Djordjevic, Marisa R Nucci, Arun Seth, Jelena Mirkovic
Histopathology.2023; 83(3): 366. CrossRef -
Clinicopathologic Features and Prognostic Significance of Immunohistochemistry and In Situ Hybridization Based Molecular Classification in Gastric Carcinoma
Gizem Issin, İlyas Sayar, Fatih Demir, İrem Güvendir Bakkaloğlu, Mehmet Gamsizkan, Zeliha Yildiz, Ismail Yilmaz, Sevilay Akalp Özmen, Diren Vuslat Çağatay, Itır Ebru Zemheri, Murat Demiriz, Armağan Günal
Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology.2023; 42(4): 1. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and Molecular Characterization of Anorectal Neuroendocrine Carcinomas Reveals Human Papillomavirus, p53, and c-Myc as Alternative Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis
Allison J. Cox, William E. Crowe, Qi Yang, Bin Zhang, Zoltán N. Oltvai, Xiaoyan Liao
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(11): 100295. CrossRef - Dedifferentiated Endometrial Carcinoma: A Rare Aggressive Neoplasm-Clinical, Morphological and Immunohistochemical Features
Giovanna Giordano, Elena Ferioli, Debora Guareschi, Alessandro Tafuni
Cancers.2023; 15(21): 5155. CrossRef - Characterization on the oncogenic effect of the missense mutations of p53 via machine learning
Qisheng Pan, Stephanie Portelli, Thanh Binh Nguyen, David B Ascher
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adrenal Nodules Detected at Staging CT in Patients with Resectable Gastric Cancers Have a Low Incidence of Malignancy
Hae Young Kim, Won Chang, Yoon Jin Lee, Ji Hoon Park, Jungheum Cho, Hee Young Na, Hyungwoo Ahn, Sung Il Hwang, Hak Jong Lee, Young Hoon Kim, Kyoung Ho Lee
Radiology.2022; 302(1): 129. CrossRef - Intestinal-type gastric dysplasia in Helicobacter pylori-naïve patients
Kotaro Shibagaki, Ayako Itawaki, Yoichi Miyaoka, Kenichi Kishimoto, Yusuke Takahashi, Satoshi Kotani, Tsuyoshi Mishiro, Naoki Oshima, Kousaku Kawashima, Norihisa Ishimura, Hideyuki Onuma, Makoto Nagasaki, Mamiko Nagase, Asuka Araki, Kyuichi Kadota, Ryoji
Virchows Archiv.2022; 480(4): 783. CrossRef - Dedifferentiation-like tubular and solid carcinoma of the stomach shows phenotypic divergence and association with deficient SWI/SNF complex
Shih-Chiang Huang, Kuang-Hua Chen, Kwai-Fong Ng, I-Chieh Lin, Yi-Chun Chao, Ta-Sen Yeh, Huei-Chieh Chuang, Tse-Ching Chen
Virchows Archiv.2022; 480(4): 771. CrossRef - Distinct molecular phenotype and the potential prognostic value of immune prognostic index and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach
Muxing Kang, Xiaojing Ma, Jifei Shi, Guofeng Chen, Xiaoli Jin, Jun Wang, Lele Lin, Zhiwei Wu, Kaibo Chen, Jinghong Xu, Pintong Huang, Jian Chen
Translational Oncology.2022; 19: 101380. CrossRef - Evaluation of Tumor DNA Sequencing Results in Patients with Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma Stratified by TP53 Mutation Status
Anthony C Wood, Yonghong Zhang, Qianxing Mo, Ling Cen, Jacques Fontaine, Sarah E Hoffe, Jessica Frakes, Sean P Dineen, Jose M Pimiento, Christine M Walko, Rutika Mehta
The Oncologist.2022; 27(4): 307. CrossRef - Comprehensive Clinical Analysis of Gallbladder Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Large-Volume Multicenter Study During One Decade
Yangyang Wang, Bingfeng Huang, Qihan Fu, Jianing Wang, Mao Ye, Manyi Hu, Kai Qu, Kai Liu, Xiao Hu, Shumei Wei, Ke Sun, Wenbo Xiao, Bo Zhang, Haijun Li, Jingsong Li, Qi Zhang, Tingbo Liang
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2022; 29(12): 7619. CrossRef - Expression of SASP, DNA Damage Response, and Cell Proliferation Factors in Early Gastric Neoplastic Lesions: Correlations and Clinical Significance
Li Liang, Yijie Chai, Fei Chai, Haijing Liu, Ningning Ma, Hong Zhang, Shuang Zhang, Lin Nong, Ting Li, Bo Zhang
Pathology and Oncology Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Systems biology and OMIC data integration to understand gastrointestinal cancers
Iasmin Moreira Costa Bispo, Henry Paul Granger, Palloma Porto Almeida, Patricia Belini Nishiyama, Leandro Martins de Freitas
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 13(10): 762. CrossRef - MicroRNA-552 expression in colorectal cancer and its clinicopathological significance
Joon Im, Soo Kyung Nam, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(2): 125. CrossRef - Different effects of p53 protein overexpression on the survival of gastric cancer patients according to Lauren histologic classification: a retrospective study
Ki Wook Kim, Nayoung Kim, Yonghoon Choi, Won Seok Kim, Hyuk Yoon, Cheol Min Shin, Young Soo Park, Dong Ho Lee, Young Suk Park, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Jin Won Kim, Keun-Wook Lee, Won Chang, Ji Hoon Park, Yoon
Gastric Cancer.2021; 24(4): 844. CrossRef - The association between the expression of nuclear Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and p53 protein expression profile in breast cancer patients
Yoon Jin Cha, Dooreh Kim, Soong June Bae, Sung Gwe Ahn, Joon Jeong, Min Kyung Cho, Pill Sun Paik, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Woo-Chan Park, Chang Ik Yoon, Elda Tagliabue
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0250986. CrossRef
- The future is now: advancing p53 immunohistochemistry in Barrett's oesophagus and its implication for the everyday pathologist
Review
- Evolving pathologic concepts of serrated lesions of the colorectum
- Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):276-289. Published online June 26, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.04.15
- 18,659 View
- 847 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Here, we provide an up-to-date review of the histopathology and molecular pathology of serrated colorectal lesions. First, we introduce the updated contents of the 2019 World Health Organization classification for serrated lesions. The sessile serrated lesion (SSL) is a new diagnostic terminology that replaces sessile serrated adenoma and sessile serrated polyp. The diagnostic criteria for SSL were revised to require only one unequivocal distorted serrated crypt, which is sufficient for diagnosis. Unclassified serrated adenomas have been included as a new category of serrated lesions. Second, we review ongoing issues concerning the morphology of serrated lesions. Minor morphologic variants with distinct molecular features were recently defined, including serrated tubulovillous adenoma, mucin-rich variant of traditional serrated adenoma (TSA), and superficially serrated adenoma. In addition to intestinal dysplasia and serrated dysplasia, minimal deviation dysplasia and not otherwise specified dysplasia were newly suggested as dysplasia subtypes of SSLs. Third, we summarize the molecular features of serrated lesions. The critical determinant of CpG island methylation development in SSLs is patient age. Interestingly, there may be ethnic differences in BRAF/KRAS mutation frequencies in SSLs. The molecular pathogenesis of TSAs is divided into KRAS and BRAF mutation pathways. SSLs with MLH1 methylation can progress into favorable prognostic microsatellite instability-positive (MSI+)/CpG island methylator phenotype-positive (CIMP+) carcinomas, whereas MLH1-unmethylated SSLs and BRAF-mutated TSAs can be precursors of poor-prognostic MSI−/CIMP+ carcinomas. Finally, based on our recent data, we propose an algorithm for stratifying risk subgroups of non-dysplastic SSLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predominant Serrated Molecular Signature in Postcolonoscopy Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jen-Hao Yeh, Sin-Hua Moi, Chia-Chi Chen, Chao-Wen Hsu, Wen-Shuo Yeh, Tzu-Ning Tseng, Chuan-Pin Lin, Yu-Peng Liu, Jaw-Yuan Wang
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2026; 121(1): 122. CrossRef - Re-evaluating post-polypectomy surveillance: The role of non-invasive modalities in colorectal cancer prevention
Ethna McFerran, Damian McKay, Maurice B. Loughrey, Mark Lawler, Stephen T. McSorley
Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology.2026; 80: 102092. CrossRef - Clinical and endoscopic characteristics of colorectal traditional serrated adenomas with dysplasia/adenocarcinoma in a Korean population
Ki-Hyun Kim, Eun Myung, Hyung Hoon Oh, Chan-Muk Im, Young-Eun Seo, Je-Seong Kim, Chae-June Lim, Ga-Ram You, Sung-Bum Cho, Wan-Sik Lee, Myung-Giun Noh, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Young-Eun Joo
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA: role in macrophage polarisation and colorectal cancer pathogenesis
Haihong Lin, Jun Zhou, Ying He, Yifan Zhu, Puwen Chen, Hongwei Yan, Junyun Huang, Ersheng Gong, Xiaoling Wang
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Submucosal fibrosis in large colorectal serrated lesions in cases receiving endoscopic submucosal dissection
Erik Manriquez-Alegria, Naohisa Yoshida, Reo Kobayashi, Naoto Iwai, Ken Inoue, Osamu Dohi, Lucas Cardoso, Hideyuki Konishi
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating the Colorectal Cancer Maze: Unveiling Pathways To Diagnosis, Management, Pathophysiology and Prevention
Khalid Ali Mohammed Al Kamzari, Constantina Constantinou
Current Oncology Reports.2025; 27(10): 1115. CrossRef - Fosl1 is a transcriptional effector of BRAFV600E-driven intestinal tumorigenesis
Zakia Alam, Rebecca Nightingale, Analia Lesmana, Cheng Liu, Laura J. Jenkins, Mark F. Richardson, Lawrence Croft, Ian Y. Luk, Camilla M. Reehorst, Fiona Chionh, Natalia Vukelic, Faiza Basheer, Eugene Tulchinsky, Joshua Badshah, Troy Dumenil, Latifa Bakiri
iScience.2025; 28(11): 113875. CrossRef - Sessile Serrated Lesions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Hidden Players in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer?
Roberto de Sire, Diletta De Deo, Miriana Mercurio, Gianluca Franchellucci, Giulio Calabrese, Livio Bonacci, Mauro Sollai Pinna, Cristina Bezzio, Alessandro Armuzzi, Cesare Hassan, Alessandro Repici, Fabiana Castiglione, Sandro Ardizzone, Roberta Maselli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(22): 8042. CrossRef - Histologic Reappraisal and Evaluation of MLH1 Protein Expression in Sessile Serrated Lesions of the Proximal Colon
Priscilla de Sene Portel Oliveira, Miriam Aparecida da Silva Trevisan, Rita Barbosa de Carvalho, Rita de Cássia Perina Martins, João José Fagundes, Claudio Saddy Rodrigues Coy, Ashwini Esnakula
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Superiority of excellent over good bowel preparation for proximal serrated polyp detection in a fecal immunochemical test-based screening cohort
Stefano Fantasia, Stefano Kayali, Pablo Cortegoso Valdivia, Stefano Andreotti, Daniele Macchi, Giorgio Nervi, Nico Pagano, Luigi Laghi
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of AI-aided colonoscopy in clinical practice: a prospective randomised controlled trial
Johanna Schöler, Marko Alavanja, Thomas de Lange, Shunsuke Yamamoto, Per Hedenström, Jonas Varkey
BMJ Open Gastroenterology.2024; 11(1): e001247. CrossRef - The histologic features, molecular features, detection and management of serrated polyps: a review
Jin-Dong Wang, Guo-Shuai Xu, Xin-Long Hu, Wen-Qiang Li, Nan Yao, Fu-Zhou Han, Yin Zhang, Jun Qu
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serrated polyps <10 mm cannot reliably be characterized by i-Scan without magnification at routine colonoscopy
Sabrina G.G. TESTONI, Chiara NOTARISTEFANO, Giuliano F. BONURA, Maria NAPOLITANO, Dario ESPOSITO, Edi VIALE, Lorella FANTI, Francesco AZZOLINI, Giulia M. CAVESTRO, PierAlberto TESTONI
Minerva Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interobserver variability in the histopathological classification and grading of dysplasia in elevated colon lesions in the city of Lima
Guido Gallegos-Serruto, Aldo Gutiérrez, César Chian García, Isthvan Torres Perez
Revista de Gastroenterología del Perú.2024; 44(3): 239. CrossRef - Comparison of adenoma detection rate and proximal serrated polyp detection rate and their effect on post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer mortality in screening patients
Jasmin Zessner-Spitzenberg, Elisabeth Waldmann, Lena Jiricka, Lisa-Maria Rockenbauer, Anna Hinterberger, Jeremy Cook, Arno Asaturi, Aleksandra Szymanska, Barbara Majcher, Michael Trauner, Monika Ferlitsch
Endoscopy.2023; 55(05): 434. CrossRef - The yield of dysplasia and serrated lesions in a single-centre tertiary inflammatory bowel disease cohort
Fiona Yeaman, Lena Thin
Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef -
The BEETS (JACCRO CC-18) Trial: An Observational and Translational Study of
BRAF
-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Chiaki Inagaki, Ryo Matoba, Satoshi Yuki, Manabu Shiozawa, Akihito Tsuji, Eisuke Inoue, Kei Muro, Wataru Ichikawa, Masashi Fujii, Yu Sunakawa
Future Oncology.2023; 19(17): 1165. CrossRef - A retrospective analysis of the histology of resected polyps and colonoscopy quality parameters in Belgium
E Macken, S Van Dongen, G Van Hal
Acta Gastro Enterologica Belgica.2023; 86(2): 277. CrossRef - Prognostic Biomarkers of Cell Proliferation in Colorectal Cancer (CRC): From Immunohistochemistry to Molecular Biology Techniques
Aldona Kasprzak
Cancers.2023; 15(18): 4570. CrossRef - Assimilating Epigenetics and Transcriptomics for the Identification
of Prognostic Novel Biomarkers and Imminent Targets in
Colorectal Carcinoma with Therapeutic Potential
Suman Kumar Ray, Sukhes Mukherjee
Current Molecular Medicine.2023; 23(8): 784. CrossRef - Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening
Erica K. Barnell, Elizabeth M. Wurtzler, Julie La Rocca, Thomas Fitzgerald, Jessica Petrone, Yansheng Hao, Yiming Kang, Faith L. Holmes, David A. Lieberman
JAMA.2023; 330(18): 1760. CrossRef - Microbiome in Colonic Carcinogenesis
Jun Sun, Yinglin Xia
Comprehensive Physiology.2023; 13(3): 4685. CrossRef - Impact of comprehensive optical diagnosis training using Workgroup serrAted polypS and Polyposis classification on detection of adenoma and sessile serrated lesion
Jooyoung Lee, Jung Ho Bae, Su Jin Chung, Hae Yeon Kang, Seung Joo Kang, Min‐Sun Kwak, Ji Yeon Seo, Ji Hyun Song, Sun Young Yang, Jong In Yang, Seon Hee Lim, Jeong Yoon Yim, Joo Hyun Lim, Goh Eun Chung, Eun Hyo Jin, Ji Min Choi, Yoo Min Han, Joo Sung Kim
Digestive Endoscopy.2022; 34(1): 180. CrossRef - Clinicopathological and molecular analyses of hyperplastic lesions including microvesicular variant and goblet cell rich variant hyperplastic polyps and hyperplastic nodules—Hyperplastic nodule is an independent histological entity
Noriyuki Uesugi, Yoichi Ajioka, Tomio Arai, Yoshihito Tanaka, Tamotsu Sugai
Pathology International.2022; 72(2): 128. CrossRef - Comprehensive clinicopathologic, molecular, and immunologic characterization of colorectal carcinomas with loss of three intestinal markers, CDX2, SATB2, and KRT20
Ji Ae Lee, Mi-Kyoung Seo, Seung-Yeon Yoo, Nam-Yun Cho, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyoungbun Lee, Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
Virchows Archiv.2022; 480(3): 543. CrossRef - Serrated Colorectal Lesions: An Up-to-Date Review from Histological Pattern to Molecular Pathogenesis
Martino Mezzapesa, Giuseppe Losurdo, Francesca Celiberto, Salvatore Rizzi, Antonio d’Amati, Domenico Piscitelli, Enzo Ierardi, Alfredo Di Leo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4461. CrossRef - Arterial stiffness is associated with high-risk colorectal adenomas and serrated lesions: A cross-sectional study in a Taiwanese population
Hung-Yu Chen, Wen-Huang Lee, Hung-Lung Hsu, Yu-Tsung Chou, Fei-Lin Su, I-Hsuan Wu, Ting-Hsing Chao
Journal of Cardiology.2022; 80(2): 139. CrossRef - Morphological and molecular characterization of colorectal sessile serrated lesions with dysplasia
Filippo Cappello, Valentina Angerilli, Luca Dal Santo, Giada Munari, Marianna Sabbadin, Marcello Lo Mele, Gianmaria Pennelli, Claudio Luchini, Paola Parente, Stefano Lazzi, Matteo Fassan
Pathology - Research and Practice.2022; 240: 154214. CrossRef - Serrated polyposis: an overview
Jonathan Fawkes
Gastrointestinal Nursing.2022; 20(9): 24. CrossRef - Sessile serrated lesion presenting as large pedunculated polyp in the rectum: A case report
Shin Ju Oh, Jung-Wook Kim, Chi Hyuk Oh
Medicine.2022; 101(51): e32287. CrossRef - WHICH LESIONS ARE AT HIGHER RISK OF DEVELOPING COLORECTAL CARCINOMAS: SUPERFICIALLY ELEVATED SERRATED LESIONS OR DEPRESSED LESIONS?
Artur Adolfo PARADA, Filadelfio Euclydes VENCO, Miguel Reynaldo VARCA-NETO, Roberto EL IBRAHIM, Paula Bechara POLETTI, Helcio Pedrosa BRITO, Heloisa de Fátima SARE, Osvaldo MALAFAIA
ABCD. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva (São Paulo).2022;[Epub] CrossRef - WNT5a in Colorectal Cancer: Research Progress and Challenges
Guangshun Sun, Liangliang Wu, Guoqiang Sun, Xuesong Shi, Hongyong Cao, Weiwei Tang
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 2483. CrossRef - Endoscopic diagnosis for colorectal sessile serrated lesions
Toshihiro Nishizawa, Shuntaro Yoshida, Akira Toyoshima, Tomoharu Yamada, Yoshiki Sakaguchi, Taiga Irako, Hirotoshi Ebinuma, Takanori Kanai, Kazuhiko Koike, Osamu Toyoshima
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(13): 1321. CrossRef - NTRK oncogenic fusions are exclusively associated with the serrated neoplasia pathway in the colorectum and begin to occur in sessile serrated lesions
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Hoon Hong, Yoon‐La Choi, Ji Ae Lee, Mi‐kyoung Seo, Mi‐Sook Lee, Sung Bin An, Min Jung Sung, Nam‐Yun Cho, Sung‐Su Kim, Young Kee Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
The Journal of Pathology.2021; 255(4): 399. CrossRef - Differential pre-malignant programs and microenvironment chart distinct paths to malignancy in human colorectal polyps
Bob Chen, Cherie’ R. Scurrah, Eliot T. McKinley, Alan J. Simmons, Marisol A. Ramirez-Solano, Xiangzhu Zhu, Nicholas O. Markham, Cody N. Heiser, Paige N. Vega, Andrea Rolong, Hyeyon Kim, Quanhu Sheng, Julia L. Drewes, Yuan Zhou, Austin N. Southard-Smith, Y
Cell.2021; 184(26): 6262. CrossRef - Molecular Insights Into Colorectal Carcinoma
Domenika Ortiz Requena, Monica Garcia-Buitrago
Archives of Medical Research.2020; 51(8): 839. CrossRef
- Predominant Serrated Molecular Signature in Postcolonoscopy Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Original Articles
- Peripheral type squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: clinicopathologic characteristics in comparison to the central type
- Yeoun Eun Sung, Uiju Cho, Kyo Young Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):290-299. Published online June 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.05.04
- 11,205 View
- 209 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Squamous cell carcinomas (SqCCs) of the lung are known to arise more often in a central area but reports of peripheral SqCCs have increased, with a pathogenesis that is obscured. In this study, the clinicopathologic characteristics of peripheral lung SqCCs were studied and compared with those of the central type.
Methods
This study included 63 peripheral lung SqCCs and 48 randomly selected central cases; hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides of surgically resected specimens were reviewed in conjunction with radiologic images and clinical history. Cytokeratin-7 immunohistochemical staining of key slides and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/KRAS mutations tested by DNA sequencing were also included.
Results
Stages of peripheral SqCCs were significantly lower than central SqCCs (p=.016). Cystic change of the mass (p=.007), presence of interstitial fibrosis (p=0.007), and anthracosis (p=.049) in the background lung were significantly associated with the peripheral type. Cytokeratin-7 positivity was also higher in peripheral SqCCs with cutoffs of both 10% and 50% (p=.011). Pathogenic mutations in EGFR and KRAS were observed in only one case out of the 72 evaluated. The Cox proportional hazard model indicated a significantly better disease-free survival (p=.009) and the tendency of better overall survival (p=.106) in the peripheral type.
Conclusions
In peripheral type, lower stage is a favorable factor for survival but more frequent interstitial fibrosis and older age are unfavorable factors. Multivariate Cox analysis revealed that peripheral type is associated with better disease-free survival. The pathogenesis of peripheral lung SqCCs needs further investigation, together with consideration of the background lung conditions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing the performance of chest x‐ray screening in detecting early‐stage lung cancer in the general population
Choy‐Lye Chei, Sho Nakamura, Kaname Watanabe, Takashi Mizutani, Hiroto Narimatsu
International Journal of Cancer.2025; 156(11): 2127. CrossRef - Whole lung radiomic features are associated with overall survival in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiotherapy
Meng Yan, Zhen Zhang, Jia Tian, Jiaqi Yu, Andre Dekker, Dirk de Ruysscher, Leonard Wee, Lujun Zhao
Radiation Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging appearances, CT evolution patterns, and surgical prognosis of stage I lung squamous cell carcinoma
Wei-hua Zhao, Tian-you Luo, Fa-jin Lv, Qi Li
Cancer Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma and lymphoepithelial carcinoma – morphology, molecular characteristics and differential diagnosis
Sabina Berezowska, Marie Maillard, Mark Keyter, Bettina Bisig
Histopathology.2024; 84(1): 32. CrossRef - Assessment of seasonal variability of PM, BC and UFP levels at a highway toll stations and their associated health risks
Nazneen, Aditya Kumar Patra, Soma Sekhara Rao Kolluru, Abhishek Penchala, Sachidanand Kumar, Namrata Mishra, Naragam Bhanu Sree, Samrat Santra, Ravish Dubey
Environmental Research.2024; 245: 118028. CrossRef - Association between Airport Ultrafine Particles and Lung Cancer Risk: The Multiethnic Cohort Study
Arthur Bookstein, Justine Po, Chiuchen Tseng, Timothy V. Larson, Juan Yang, Sung-shim L. Park, Jun Wu, Salma Shariff-Marco, Pushkar P. Inamdar, Ugonna Ihenacho, Veronica W. Setiawan, Mindy C. DeRouen, Loïc Le Marchand, Daniel O. Stram, Jonathan Samet, Bea
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2024; 33(5): 703. CrossRef - Clinical and Bronchoscopy Assessment in Diagnosing the Histopathology Type of Primary Central Lung Tumors
Mia Elhidsi, Jamal Zaini, Lisnawati Rachmadi, Asmarinah Asmarinah, Aria Kekalih, Noni Soeroso, Menaldi Rasmin
The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Possible thoracic metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma of the external auditory canal: A case report
Hiroshi Takehara, Ken Kodama, Toru Momozane, Masashi Takeda, Kaichi Shigetsu, Hiroki Kishima
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological precursor lesions of lung squamous cell carcinoma: Early progression patterns and divergent volume doubling time between hilar and peripheral zones
Haruto Sugawara, Yasushi Yatabe, Hirokazu Watanabe, Hiroyuki Akai, Osamu Abe, Shun-ichi Watanabe, Masahiko Kusumoto
Lung Cancer.2023; 176: 31. CrossRef - Loss of GSTO2 contributes to cell growth and mitochondria function via the p38 signaling in lung squamous cell carcinoma
Ryusuke Sumiya, Masayoshi Terayama, Teruki Hagiwara, Kazuaki Nakata, Keigo Sekihara, Satoshi Nagasaka, Hideki Miyazaki, Toru Igari, Kazuhiko Yamada, Yuki I. Kawamura
Cancer Science.2022; 113(1): 195. CrossRef - Primary tumor location in lung cancer: the evaluation and administration
Xueqi Xie, Xiaolin Li, Wenjie Tang, Peng Xie, Xuefen Tan
Chinese Medical Journal.2022; 135(2): 127. CrossRef - Pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma with a lepidic-pagetoid growth pattern
Claudio Guerrieri, Mark Lindner, Joanna Sesti, Abhishek Chakraborti, Rachel Hudacko
Pathologica.2022; 114(4): 304. CrossRef - Deposition modeling of ambient particulate matter in the human respiratory tract
Salman Khan, Bhola Ram Gurjar, Veerendra Sahu
Atmospheric Pollution Research.2022; 13(10): 101565. CrossRef - Selection of the surgical approach for patients with cStage IA lung squamous cell carcinoma: A population-based propensity score matching analysis
Shengteng Shao, Guisong Song, Yuanyong Wang, Tengfei Yi, Shuo Li, Fuhui Chen, Yang Li, Xiaotong Liu, Bin Han, Yuhong Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Virus Nanoparticles & Different Nanoparticles Affect Lung Cancer- A New Approach
Ranajit Nath, Ratna Roy, Soubhik bhattacharyya, Sourav Datta
International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology.2021; : 867. CrossRef
- Assessing the performance of chest x‐ray screening in detecting early‐stage lung cancer in the general population
- Highly prevalent BRAF V600E and low-frequency TERT promoter mutations underlie papillary thyroid carcinoma in Koreans
- Sue Youn Kim, Taeeun Kim, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):310-317. Published online June 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.05.12
- 11,591 View
- 199 Download
- 29 Web of Science
- 32 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The presence of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations have been associated with a poor prognosis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTC). The frequency of TERT promoter mutations varies widely depending on the population and the nature of the study.
Methods
Data were prospectively collected in 724 consecutive patients who underwent thyroidectomy for PTC from 2018 to 2019. Molecular testing for BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations was performed in all cases.
Results
TERT promoter alterations in two hotspots (C228T and C250T) and C216T were found in 16 (2.2%) and 4 (0.6%) of all PTCs, respectively. The hotspot mutations were significantly associated with older age at diagnosis, larger tumor size, extrathyroidal extension, higher pathologic T category, lateral lymph node metastasis, and higher American Thyroid Association recurrence risk. The patients with C216T variant were younger and had a lower American Thyroid Association recurrence risk than those with hotspot mutations. Concurrent BRAF V600E was found in 19 of 20 cases with TERT promoter mutations. Of 518 microcarcinomas measuring ≤1.0 cm in size, hotspot mutations and C216T variants were detected in five (1.0%) and three (0.6%) cases, respectively.
Conclusions
Our study indicates a low frequency of TERT promoter mutations in Korean patients with PTC and supports previous findings that TERT promoter mutations are more common in older patients with unfavorable clinicopathologic features and BRAF V600E. TERT promoter mutations in patients with microcarcinoma are uncommon and may have a limited role in risk stratification. The C216T variant seems to have no clinicopathologic effect on PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Xiaoteng Sun, Zhengyan He, Weijie Yu, Baoyuan Li, Xinmiao Xu, Xiaoqin Zhang, Minglong Yin
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of C216T and hot spot mutations of the TERT promoter on the clinicopathologic characteristics and S100A10 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a comparative study
Ping Li, Chuqiang Huang, Xiaoling Liu, Huihui Gui, Jian Li
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Refining NTRK Fusion Detection in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry and Histopathologic Features
Hyun Lee, Sue Youn Kim, Ji Min Park, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ozgur Mete, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of Diagnostic Utility of Washout CYFRA 21-1 in Lymph Node Metastasis of Thyroid Cancer
Jeongmin Lee, Yuri Shin, Jeongun Kwak, Hye Lim Park, Sohee Lee, Mee Kyung Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Chan Kwon Jung, So Lyung Jung, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Dong-Jun Lim
Clinical Cancer Research.2025; 31(10): 1922. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - Evaluation of BRAF V600E and TERT mutation analysis in differential thyroid cancers
Nigar Aktash, Ahmet Cem Dural, Husnu Aydin, Nuri Alper Sahbaz, Deniz Guzey, Serdar Altınay, Cevher Akarsu, Yasir Musa Kesgin, Sezer Bulut, Mehmet Karabulut
Updates in Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Active surveillance for adult low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma—a review focused on the 30-year experience of Kuma Hospital—
Yasuhiro Ito, Akira Miyauchi, Makoto Fujishima, Masashi Yamamoto, Takahiro Sasaki
Endocrine Journal.2024; 71(1): 7. CrossRef - Diagnostic utilities of washout CYFRA 21-1 combined with washout thyroglobulin for metastatic lymph nodes in thyroid cancer: a prospective study
Joonseon Park, Solji An, Kwangsoon Kim, Jeong Soo Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Part I. Initial Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers - Chapter 5. Evaluation of Recurrence Risk Postoperatively and Initial Risk Stratification in Different
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Shin Je Moon, Dong-Jun Lim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Yun Jae Chung, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 68. CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules 2024
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Su Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung,
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 208. CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression and Its Modulating Factors in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
Shipra Agarwal, Chan Kwon Jung, Pranitha Gaddam, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Takuya Higashiyama, Jen-Fan Hang, Wei-An Lai, Somboon Keelawat, Zhiyan Liu, Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park, Junya Fukuoka, Shinya Satoh, Zhanna Mussazhanova, Masahiro Nakashima, Kennichi Ka
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(10): 1233. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors for occult lesions in low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma patients with tumor characteristics appropriate for thermal ablation: A retrospective study
Langping Jin, Kaijun Zhu, Changliang Xu, Jiaying Lu, Liming Huang
Medicine.2023; 102(38): e34938. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef - Risk factors and predictive model for recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a single-center retrospective cohort study based on 955 cases
Yin Li, Jiahe Tian, Ke Jiang, Zhongyu Wang, Songbo Gao, Keyang Wei, Ankui Yang, Qiuli Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BRAFV600E Positivity-Dependent Effect of Age on Papillary Thyroid Cancer Recurrence Risk
Joonseon Park, Solji An, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(22): 5395. CrossRef - BRAFV600E mutation test on fine‐needle aspiration specimens of thyroid nodules: Clinical correlations for 4600 patients
Huang Chen, Aiping Song, Ye Wang, Yifan He, Jie Tong, Jinxi Di, Chun Li, Zhongren Zhou, Xiaopin Cai, Dingrong Zhong, Jiping Da
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(1): 40. CrossRef - Clinicopathological indicators for TERT promoter mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Hee Young Na, Hyeong Won Yu, Woochul Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Il Choi, Yeo Koon Kim, June Young Choi, So Yeon Park
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 97(1): 106. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta‐analysis on the Occurrence of Biomarker Mutation in Colorectal Cancer among the Asian Population
Hafeez Afolabi, Salzihan Md Salleh, Zaidi Zakaria, Ch’ng Ewe Seng, Siti Norasikin Binti Mohd Nafil, Ahmad Aizat Bin Abdul Aziz, Yusuf Wada, Ahmad Irekeola, Syed Sameer Aga
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Significance of Concomitant BRAFV600E and TERT Mutations in Polish Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on 430 Cases
Artur Kuchareczko, Janusz Kopczyński, Artur Kowalik, Kinga Hińcza-Nowak, Agnieszka Walczyk, Iwona Pałyga, Tomasz Trybek, Monika Szymonek, Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Klaudia Gadawska-Juszczyk, Estera Mikina, Izabela Płachta, Agnieszka Suligowska, Agnieszka Płu
Thyroid.2022; 32(11): 1372. CrossRef - Machine learning for identifying benign and malignant of thyroid tumors: A retrospective study of 2,423 patients
Yuan-yuan Guo, Zhi-jie Li, Chao Du, Jun Gong, Pu Liao, Jia-xing Zhang, Cong Shao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - TERT Promoter and BRAF V600E Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience in Korea
Min Jhi Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Woong Youn Chung, Daham Kim, Kee-Hyun Nam
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4928. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Sue Youn Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 947. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Hyunju Park, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 949. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Non-familial Follicular Epithelial–Derived Thyroid Cancer in Adults: From RAS/BRAF-like Tumor Designations to Molecular Risk Stratification
Paula Soares, Antónia Afonso Póvoa, Miguel Melo, João Vinagre, Valdemar Máximo, Catarina Eloy, José Manuel Cameselle-Teijeiro, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões
Endocrine Pathology.2021; 32(1): 44. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study
Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Hwa Young Ahn, Hee Sung Kim, Yong Joon Suh, Dughyun Choi, Bu Kyung Kim, Go Eun Yang, Il-Seok Park, Ka Hee Yi, Chan Kwon Jung, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 619. CrossRef - Clinical Application of TERT Promoter Mutations in Urothelial Carcinoma
Yujiro Hayashi, Kazutoshi Fujita, George J. Netto, Norio Nonomura
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA Profile for Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Seon-Kyu Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan-Kwon Jung, Yong-Sung Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 632. CrossRef - Prospective Analysis of TERT Promoter Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma at a Single Institution
Yun-Suk Choi, Seong-Woon Choi, Jin-Wook Yi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(10): 2179. CrossRef - Significance of telomerase reverse-transcriptase promoter mutations in differentiated thyroid cancer
Hung-Fei Lai, Chi-Yu Kuo, Shih-Ping Cheng
Formosan Journal of Surgery.2021; 54(5): 171. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer Results Rather in Overtreatment Than a Better Survival
Jolanta Krajewska, Aleksandra Kukulska, Malgorzata Oczko-Wojciechowska, Agnieszka Kotecka-Blicharz, Katarzyna Drosik-Rutowicz, Malgorzata Haras-Gil, Barbara Jarzab, Daria Handkiewicz-Junak
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
- Double cocktail immunostains with high molecular weight cytokeratin and GATA-3: useful stain to discriminate in situ involvement of prostatic ducts or acini from stromal invasion by urothelial carcinoma in the prostate
- Junghye Lee, Youngeun Yoo, Sanghui Park, Min-Sun Cho, Sun Hee Sung, Jae Y. Ro
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):146-153. Published online February 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.12
- 8,654 View
- 136 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Distinguishing prostatic stromal invasion (PSI) by urothelial carcinoma (UC) from in situ UC involving prostatic ducts or acini with no stromal invasion (in situ involvement) may be challenging on hematoxylin and eosin stained sections. However, the distinction between them is important because cases with PSI show worse prognosis. This study was performed to assess the utility of double cocktail immunostains with high molecular weight cytokeratin (HMWCK) and GATA-3 to discriminate PSI by UC from in situ UC involvement of prostatic ducts or acini in the prostate.
Methods
Among 117 radical cystoprostatectomy specimens for bladder UCs, 25 cases showed secondary involvement of bladder UC in prostatic ducts/acini only or associated stromal invasion and of these 25 cases, seven cases revealed equivocal PSI. In these seven cases with equivocal PSI, HMWCK, and GATA-3 double immunohistochemical stains were performed to identify whether this cocktail stain is useful to identify the stromal invasion.
Results
In all cases, basal cells of prostate glands showed strong cytoplasmic staining for HMWCK and UC cells showed strong nuclear staining for GATA-3. In cases with stromal invasion of UC, GATA-3-positive tumor cells in the prostatic stroma without surrounding HMWCK-positive basal cells were highlighted and easily recognized. Among seven equivocal cases, two cases showed PSI and five in situ UC in the prostate. In two cases, the original diagnoses were revised.
Conclusions
Our study suggested that HMWCK and GATA-3 double stains could be utilized as an adjunct method in the distinction between PSI by UC from in situ UC involving prostatic ducts or acini. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aberrant expression of GATA3 in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate: an important pitfall
João Lobo, Nazario P Tenace, Sofia Cañete‐Portillo, Isa Carneiro, Rui Henrique, Roberta Lucianò, Lara R Harik, Cristina Magi‐Galluzzi
Histopathology.2024; 84(3): 507. CrossRef - Utility of D2-40, Cytokeratin 5/6, and High–Molecular-weight Cytokeratin (Clone 34βE12) in Distinguishing Intraductal Spread of Urothelial Carcinoma From Prostatic Stromal Invasion
Oleksii A. Iakymenko, Laurence M. Briski, Katiana S. Delma, Merce Jorda, Oleksandr N. Kryvenko
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 46(4): 454. CrossRef
- Aberrant expression of GATA3 in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate: an important pitfall
Review
- Tumor immune response and immunotherapy in gastric cancer
- Yoonjin Kwak, An Na Seo, Hee Eun Lee, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):20-33. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.08
- 18,702 View
- 748 Download
- 73 Web of Science
- 68 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Remarkable developments in immuno-oncology have changed the landscape of gastric cancer (GC) treatment. Because immunotherapy intervenes with tumor immune response rather than directly targeting tumor cells, it is important to develop a greater understanding of tumor immunity. This review paper summarizes the tumor immune reaction and immune escape mechanisms while focusing on the role of T cells and their co-inhibitory signals, such as the immune checkpoint molecules programmed death-1 and programmed deathligand 1 (PD-L1). This paper also describes past clinical trials of immunotherapy for patients with GC and details their clinical implications. Strong predictive markers are essential to improve response to immunotherapy. Microsatellite instability, Epstein-Barr virus, PD-L1 expression, and tumor mutational burden are now regarded as potent predictive markers for immunotherapy in patients with GC. Novel immunotherapy and combination therapy targeting new immune checkpoint molecules such as lymphocyte-activation gene 3, T cell immunoglobulin, and mucin domain containing-3, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase have been suggested, and trials are ongoing to evaluate their safety and efficacy. Immunotherapy is an important treatment option for patients with GC and has great potential for improving patient outcome, and further research in immuno-oncology should be carried out.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using glucocorticoid receptor-related genes to create and validate a survival model predicting gastric cancer
Ke Guo, Ping Huang, Jiasheng Zhang, Bo Zhang, Linyang Li, Jiaxin Li
Computational Biology and Chemistry.2026; 120: 108726. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming Regulating Immunosuppression in the Gastric Cancer Tumor Microenvironment
Wenting Dong, Xuepeng Qian, Honglin Liu, Jinhai Huo, Weiming Wang
Biomolecules.2026; 16(1): 160. CrossRef - Perineural invasion in digestive tract tumors: Immune system interactions and therapeutic strategies
Jia-Yu Pang, Rong-Yao Jin, Han-Xiao Zhang, Ying-Hua Zhang, Xin-Yue Wei, Wen-Bo Cao, Yi-Xiao Chen, Jun-Ling Wang, Sai-Jun Mo
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - FOXP3+/CD8+ ratio associated with aggressive behavior in RUNX3‐methylated diffuse esophagogastric junction tumor
Suguru Maruyama, Yu Imamura, Tasuku Toihata, Ikumi Haraguchi, Manabu Takamatsu, Makiko Yamashita, Yuichiro Nakashima, Eiji Oki, Kenichi Taguchi, Manabu Yamamoto, Shinji Mine, Akihiko Okamura, Jun Kanamori, Souya Nunobe, Takeshi Sano, Shigehisa Kitano, Tet
Cancer Science.2025; 116(1): 178. CrossRef - Immune biomarkers and predictive signatures in gastric cancer: Optimizing immunotherapy responses
Sundaram Vickram, Shofia Saghya Infant, S. Manikandan, D. Jenila Rani, C.M. Mathan Muthu, Hitesh Chopra
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 265: 155743. CrossRef - Korean Practice Guidelines for Gastric Cancer 2024: An Evidence-based, Multidisciplinary Approach (Update of 2022 Guideline)
In-Ho Kim, Seung Joo Kang, Wonyoung Choi, An Na Seo, Bang Wool Eom, Beodeul Kang, Bum Jun Kim, Byung-Hoon Min, Chung Hyun Tae, Chang In Choi, Choong-kun Lee, Ho Jung An, Hwa Kyung Byun, Hyeon-Su Im, Hyung-Don Kim, Jang Ho Cho, Kyoungjune Pak, Jae-Joon Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 5. CrossRef - Targeted therapy and immunotherapy for gastric cancer: rational strategies, novel advancements, challenges, and future perspectives
Dong Luo, Yunmei Liu, Zhengmao Lu, Lei Huang
Molecular Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of the triglyceride-glucose index in gastric cancer
Tugce Eskazan, Suat Saribas, Bekir Kocazeybek
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering the dual role of autophagy in gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction cancer: from tumor suppression to cancer progression
Lili Lei, Junling Zhang, Ran Wei, Bingqi Dong, Xin Wang, Ying Zhou
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of clinicopathological parameters with the presence of Epstein–Barr virus and the absence of DNA mismatch repair proteins in gastric adenocarcinomas
Özge Eyeoğlu, Serra Kayaçetin
Asian Biomedicine.2025; 19(2): 86. CrossRef - The impact of combined immunotherapy on the cellular composition of the tumor microenvironment in patients with gastric carcinoma
L.A. Tashireva, A.Yu. Kalinchuk, D.M. Loos, E.A. Tsarenkova, A.V. Avgustinovich, S.G. Afanas’ev, S.V. Vtorushin
Russian Journal of Archive of Pathology.2025; 87(4): 24. CrossRef - Immunotherapy in gastric adenocarcinoma – a rapidly evolving treatment landscape
Yang Wang, Geoffrey Chong
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2025; 216: 104941. CrossRef - Ubiquilin-4 induces immune escape in gastric cancer by activating the notch signaling pathway
Quan Jiang, Hao Chen, Shixin Zhou, Tao Zhu, Wenshuai Liu, Hao Wu, Yong Zhang, Fenglin Liu, Yihong Sun
Cellular Oncology.2024; 47(1): 303. CrossRef - Expression and prognostic value of APOBEC2 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its association with tumor-infiltrating immune cells
Lipan Wei, Xiuqian Wu, Lan Wang, Ling Chen, Xuejun Wu, Tiantian Song, Yuanyuan Wang, Wenjun Chang, Aizhen Guo, Yongdong Niu, Haihua Huang
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and characterization of CLEC11A and its derived immune signature in gastric cancer
Qing Zheng, Zhenqi Gong, Baizhi Li, Runzi Cheng, Weican Luo, Cong Huang, Huaiming Wang
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical cancer subtype identification and model building based on lipid metabolism and post-infection microenvironment immune landscape
Yongzhi Chen, Rongjie Cui, Dun Xiong, Yuan Zhao, Jianyu Pang, Samina Gul, Qi Qi, Yuheng Tang, Xuhong Zhou, Wenru Tang
Heliyon.2024; 10(9): e30746. CrossRef - Systematic Analysis of Tumor Stem Cell-related Gene Characteristics
to Predict the PD-L1 Immunotherapy and Prognosis of Gastric
Cancer
Chenchen Wang, Ying Chen, Ru Zhou, Ya’nan Yang, Yantian Fang
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 31(17): 2467. CrossRef - Comprehensive landscape of m6A regulator-related gene patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer
Bin Peng, Yinglin Lin, Gao Yi, Mingzhen Lin, Yao Xiao, Yezhenghong Qiu, Wenxia Yao, Xinke Zhou, Zhaoyu Liu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Distinctive Phenotypic and Microenvironmental Characteristics of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma Components in Gastric Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
Yoonjin Kwak, Soo Kyung Nam, Yujun Park, Yun-Suhk Suh, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Seong-Ho Kong, Do Joong Park, Hyuk-Joon Lee, Hyung-Ho Kim, Han-Kwang Yang, Hye Seung Lee
Modern Pathology.2024; 37(10): 100568. CrossRef - Computed tomography-detected extramural venous invasion-related gene signature: a potential negative biomarker of immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in patients with gastric cancer
Hao Yang, Xinyi Gou, Caizhen Feng, Yinli Zhang, Fan Chai, Nan Hong, Yingjiang Ye, Yi Wang, Bo Gao, Jin Cheng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A standardized pathology report for gastric cancer: 2nd edition
Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi,
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(1): 1. CrossRef - A Standardized Pathology Report for Gastric Cancer: 2nd Edition
Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi,
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(1): 107. CrossRef - Korean Practice Guidelines for Gastric Cancer 2022: An Evidence-based, Multidisciplinary Approach
Tae-Han Kim, In-Ho Kim, Seung Joo Kang, Miyoung Choi, Baek-Hui Kim, Bang Wool Eom, Bum Jun Kim, Byung-Hoon Min, Chang In Choi, Cheol Min Shin, Chung Hyun Tae, Chung sik Gong, Dong Jin Kim, Arthur Eung-Hyuck Cho, Eun Jeong Gong, Geum Jong Song, Hyeon-Su Im
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Could Toll-like Receptor 2 Serve as Biomarker to Detect Advanced Gastric Cancer?
Marek Majewski, Kamil Torres, Paulina Mertowska, Sebastian Mertowski, Izabela Korona-Głowniak, Jan Korulczyk, Witold Zgodziński, Ewelina Grywalska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 5824. CrossRef - Research Progress of Immunotherapy for Gastric Cancer
Zhipeng Zhang, Ningning Liu, Mingyu Sun
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Case Report: A rare synchronous multiple gastric carcinoma achieved progression-free disease through NGS-guided serial treatment
Xinyi Shao, Jin Yin, Di Wang, Erjiong Huang, Yini Zhang, Jiani C. Yin, Chen Huang, Hao Wu, Xiaoli Wu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Gastric Cancer Interpretations
Mustafa Yousif, Liron Pantanowitz
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2023; 16(4): 673. CrossRef - The Optimal Tumor Mutational Burden Cutoff Value as a Novel Marker for Predicting the Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced Gastric Cancer
Jae Yeon Jang, Youngkyung Jeon, Sun Young Jeong, Sung Hee Lim, Won Ki Kang, Jeeyun Lee, Seung Tae Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 476. CrossRef - Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Personalized Immunotherapy in Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, An Na Seo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2782. CrossRef - The Prognostic Value of the Prognostic Nutritional Index in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Gastric Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy
Yuting Pan, Yue Ma, Guanghai Dai
Nutrients.2023; 15(19): 4290. CrossRef - Molecular classification of gastric cancer predicts survival in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy based on project HOPE
Kenichiro Furukawa, Keiichi Hatakeyama, Masanori Terashima, Takeshi Nagashima, Kenichi Urakami, Keiichi Ohshima, Akifumi Notsu, Takashi Sugino, Taisuke Yagi, Keiichi Fujiya, Satoshi Kamiya, Makoto Hikage, Yutaka Tanizawa, Etsuro Bando, Yae Kanai, Yasuto A
Gastric Cancer.2022; 25(1): 138. CrossRef - Immunotherapy for Gastric Cancer: A 2021 Update
Christo Kole, Nikolaos Charalampakis, Sergios Tsakatikas, Nikolaos-Iasonas Kouris, George Papaxoinis, Michalis V Karamouzis, Anna Koumarianou, Dimitrios Schizas
Immunotherapy.2022; 14(1): 41. CrossRef - The immune microenvironment in gastric adenocarcinoma
Yana Zavros, Juanita L. Merchant
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 19(7): 451. CrossRef - Immunomodulation by Gut Microbiome on Gastrointestinal Cancers: Focusing on Colorectal Cancer
Raghad Khalid AL-Ishaq, Lenka Koklesova, Peter Kubatka, Dietrich Büsselberg
Cancers.2022; 14(9): 2140. CrossRef - An Immunity-Associated lncRNA Signature for Predicting Prognosis in Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Xiaowen Zhao, Pingfan Wu, Dongling Liu, Changtian Li, Ling Xue, Zhe Liu, Meng Zhu, Jie Yang, Ziyi Chen, Yaling Li, Yali She, Kathiravan Srinivasan
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - RNA modification writers influence tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer and prospects of targeted drug therapy
Peng Song, Sheng Zhou, Xiaoyang Qi, Yuwen Jiao, Yu Gong, Jie Zhao, Haojun Yang, Zhifen Qian, Jun Qian, Liming Tang
Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the three subtypes and the prognostic characteristics of stomach adenocarcinoma: analysis of the hypoxia-related long non-coding RNAs
Zehua Fan, Yanqun Wang, Rong Niu
Functional & Integrative Genomics.2022; 22(5): 919. CrossRef - Complete Response of High Microsatellite Instability Gastric Cancer and Synchronous Microsatellite Stability Rectal Cancer
Zachary E Hunzeker, Pooja Bhakta, Sindusha R Gudipally, Sri Bharathi Kavuri, Rohit Venkatesan, Chukwuyejulumafor Nwanze
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Profiling in Gastric Cancer Reveals the Dynamic Landscape of Immune Signature Underlying Tumor Progression
Yuhan Wei, Jianwei Zhang, Xueke Fan, Zhi Zheng, Xiaoyue Jiang, Dexi Chen, Yuting Lu, Yingrui Li, Miao Wang, Min Hu, Qi Du, Liuting Yang, Hongzhong Li, Yi Xiao, Yongfu Li, Jiangtao Jin, Deying Wang, Xiangliang Yuan, Qin Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor vessel normalization and immunotherapy in gastric cancer
Xianzhe Yu, Shan He, Jian Shen, Qiushi Huang, Peng Yang, Lin Huang, Dan Pu, Li Wang, Lu Li, Jinghua Liu, Zelong Liu, Lingling Zhu
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - FN1 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric cancers
Han Wang, Junchang Zhang, Huan Li, Hong Yu, Songyao Chen, Shuhao Liu, Changhua Zhang, Yulong He
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, An Na Seo
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2022; 22(4): 264. CrossRef - Bioinformatics Analysis and Structure of Gastric Cancer Prognosis Model Based on Lipid Metabolism and Immune Microenvironment
Yongzhi Chen, Hongjun Yuan, Qian Yu, Jianyu Pang, Miaomiao Sheng, Wenru Tang
Genes.2022; 13(9): 1581. CrossRef - Clinical implications of interleukins-31, 32, and 33 in gastric cancer
Qing-Hua Liu, Ji-Wei Zhang, Lei Xia, Steven G Wise, Brett David Hambly, Kun Tao, Shi-San Bao
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2022; 14(9): 1808. CrossRef - Microbiota and the Immune System—Actors in the Gastric Cancer Story
Marek Majewski, Paulina Mertowska, Sebastian Mertowski, Konrad Smolak, Ewelina Grywalska, Kamil Torres
Cancers.2022; 14(15): 3832. CrossRef - Bioinformatics and Experimental Analyses Reveal MAP4K4 as a Potential Marker for Gastric Cancer
Junping Zhang, Xiaoping Cai, Weifeng Cui, Zheng Wei
Genes.2022; 13(10): 1786. CrossRef - Common strategies for effective immunotherapy of gastroesophageal cancers using immune checkpoint inhibitors
Shuang Ma, Fei Chen
Pathology - Research and Practice.2022; 238: 154110. CrossRef - High-level of intratumoral GITR+ CD4 T cells associate with poor prognosis in gastric cancer
Shouyu Ke, Feng Xie, Yixian Guo, Jieqiong Chen, Zeyu Wang, Yimeng Yu, Haigang Geng, Danhua Xu, Xu Liu, Xiang Xia, Fengrong Yu, Chunchao Zhu, Zizhen Zhang, Gang Zhao, Bin Li, Wenyi Zhao
iScience.2022; 25(12): 105529. CrossRef - Characteristics of Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA editing-based subtypes and novel risk score for the prognosis and drug sensitivity in stomach adenocarcinoma
Jingjing Pan, Xinyuan Gu, Jing Luo, Xinye Qian, Qiang Gao, Tianjie Li, Longying Ye, Chenlu Li
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of NF‐κB is required for oleanolic acid to downregulate PD‐L1 by promoting DNA demethylation in gastric cancer cells
Xirong Lu, Yuyi Li, Wei Yang, Minghao Tao, Yanmiao Dai, Jinkang Xu, Qianfei Xu
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Value of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Liang Yue, Yi Lu, Yulin Li, Yilin Wang
Nutrition and Cancer.2021; 73(10): 1864. CrossRef - Immunogenic characteristics of microsatellite instability‐low esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma based on clinicopathological, molecular, immunological and survival analyses
Yu Imamura, Tasuku Toihata, Ikumi Haraguchi, Yoko Ogata, Manabu Takamatsu, Aya Kuchiba, Norio Tanaka, Osamu Gotoh, Seiichi Mori, Yuichiro Nakashima, Eiji Oki, Masaki Mori, Yoshinao Oda, Kenichi Taguchi, Manabu Yamamoto, Masaru Morita, Naoya Yoshida, Hideo
International Journal of Cancer.2021; 148(5): 1260. CrossRef - Two Similar Signatures for Predicting the Prognosis and Immunotherapy Efficacy of Stomach Adenocarcinoma Patients
Taohua Yue, Shuai Zuo, Jing Zhu, Shihao Guo, Zhihao Huang, Jichang Li, Xin Wang, Yucun Liu, Shanwen Chen, Pengyuan Wang
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor microenvironment characterization in stage IV gastric cancer
Feng Yang, Zhenbao Wang, Xianxue Zhang
Bioscience Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - E2F2 inhibition induces autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer
Hui Li, Shufen Zhao, Liwei Shen, Peige Wang, Shihai Liu, Yingji Ma, Zhiwei Liang, Gongjun Wang, Jing Lv, Wensheng Qiu
Aging.2021; 13(10): 13626. CrossRef - Chemoradiation induces upregulation of immunogenic cell death-related molecules together with increased expression of PD-L1 and galectin-9 in gastric cancer
S. H. Petersen, L. F. Kua, S. Nakajima, W. P. Yong, K. Kono
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of an Immune Cell Infiltration Score to Help Predict the Prognosis and Chemotherapy Responsiveness of Gastric Cancer Patients
Quan Jiang, Jie Sun, Hao Chen, Chen Ding, Zhaoqing Tang, Yuanyuan Ruan, Fenglin Liu, Yihong Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Microsatellite instability in Gastric Cancer: Between lights and shadows
Elisabetta Puliga, Simona Corso, Filippo Pietrantonio, Silvia Giordano
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2021; 95: 102175. CrossRef - Survival-associated alternative splicing events interact with the immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma
Zai-Sheng Ye, Miao Zheng, Qin-Ying Liu, Yi Zeng, Sheng-Hong Wei, Yi Wang, Zhi-Tao Lin, Chen Shu, Qiu-Hong Zheng, Lu-Chuan Chen
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(21): 2871. CrossRef - Immunotherapy of gastric cancer: Past, future perspective and challenges
Jun Xie, Liping Fu, Li Jin
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 218: 153322. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic and Prognostic Association of GRP94 Expression in Colorectal Cancer with Synchronous and Metachronous Metastases
Sumi Yun, Sukmook Lee, Ho-Young Lee, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Yoonjin Kwak, Hye Seung Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(13): 7042. CrossRef - Injectable shear-thinning polylysine hydrogels for localized immunotherapy of gastric cancer through repolarization of tumor-associated macrophages
Yan Yang, Yang Yang, Meili Chen, Jianquan Chen, Jinyan Wang, Yajun Ma, Hanqing Qian
Biomaterials Science.2021; 9(19): 6597. CrossRef - Correlation between LRP1B Mutations and Tumor Mutation Burden in Gastric Cancer
Sizhe Hu, Xiaokang Zhao, Feng Qian, Cancan Jin, Kaishun Hou, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis to Identify MAGEA3 Expression Correlated With Immune Infiltrates and Lymph Node Metastasis in Gastric Cancer
Jinji Jin, Jianxin Tu, Jiahuan Ren, Yiqi Cai, Wenjing Chen, Lifang Zhang, Qiyu Zhang, Guanbao Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of P2X7 receptor on tumorigenesis and its pharmacological properties
Wen-jun Zhang, Ce-gui Hu, Zheng-ming Zhu, Hong-liang Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 125: 109844. CrossRef - Current status and future potential of predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitors in gastric cancer
Byung Woog Kang, Ian Chau
ESMO Open.2020; 5(4): e000791. CrossRef - Is Ramucirumab Still the Only Second-Line Treatment in Metastatic Gastric Cancer?
Khalil El Gharib, Hampig Raphael Kourie
Pharmacogenomics.2020; 21(17): 1203. CrossRef - Deep Learning Predicts Underlying Features on Pathology Images with Therapeutic Relevance for Breast and Gastric Cancer
Renan Valieris, Lucas Amaro, Cynthia Aparecida Bueno de Toledo Osório, Adriana Passos Bueno, Rafael Andres Rosales Mitrowsky, Dirce Maria Carraro, Diana Noronha Nunes, Emmanuel Dias-Neto, Israel Tojal da Silva
Cancers.2020; 12(12): 3687. CrossRef
- Using glucocorticoid receptor-related genes to create and validate a survival model predicting gastric cancer
Case Study
- Morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma associated with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: two case reports with targeted next-generation sequencing analysis
- Yoo Jin Lee, Harim Oh, Eojin Kim, Bokyung Ahn, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Youngseok Lee, Yang Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):119-122. Published online November 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.30
- 6,703 View
- 138 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Morules, or morule-like features, can be identified in benign and malignant lesions in various organs. Morular features are unusual in pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with only 26 cases reported to date. Here, we describe two cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma with morule-like features in Korean women. One patient had a non-mucinous-type adenocarcinoma in situ and the other had an acinarpredominant adenocarcinoma with a micropapillary component. Both patients showed multiple intra-alveolar, nodular, whorled proliferative foci composed of atypical spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Targeted next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of the tumors. Results showed unusual epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, which are associated with drug resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, revealing the importance of identifying morule-like features in pulmonary adenocarcinoma and the need for additional study, since there are few reported cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Mitsuteru Yosida, Mitsuru Tomita, Naoya Kawakita, Teruki Shimizu, Ryou Yamada, Hiromitsu Takizawa, Hisanori Uehara
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2024; 48: 102008. CrossRef - Clinicopathological, Radiological, and Molecular Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma with Morule-Like Components
Li-Li Wang, Li Ding, Peng Zhao, Jing-Jing Guan, Xiao-Bin Ji, Xiao-Li Zhou, Shi-Hong Shao, Yu-Wei Zou, Wei-Wei Fu, Dong-Liang Lin, Dong Pan
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Pulmonary adenocarcinoma in situ with morule - like components: A surgical case report
Original Articles
- Reclassification of Mongolian Diffuse Gliomas According to the Revised 2016 World Health Organization Central Nervous System Tumor Classification
- Enkhee Ochirjav, Bayarmaa Enkhbat, Tuul Baldandorj, Gheeyoung Choe
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(5):298-307. Published online August 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.07.15
- 7,680 View
- 110 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of central nervous system (CNS) tumors has been modified to incorporate the IDH mutation and 1p/19q co-deletion in the diagnosis of diffuse gliomas. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the feasibility and prognostic significance of the revised 2016 WHO classification of CNS tumors in Mongolian patients with diffuse gliomas.
Methods
A total of 124 cases of diffuse gliomas were collected, and tissue microarray blocks were made. IDH1 mutation was tested using immunohistochemistry, and 1p/19q co-deletion status was examined using fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis.
Results
According to the 2016 WHO classification, 124 cases of diffuse brain glioma were reclassified as follows: 10 oligodendroglioma, IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted; three anaplastic oligodendroglioma, IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted; 35 diffuse astrocytoma, IDHmut, 11 diffuse astrocytoma, IDHwt, not otherwise specified (NOS); 22 anaplastic astrocytoma, IDHmut, eight anaplastic astrocytoma, IDHwt, NOS; and 35 glioblastoma, IDHwt, NOS, respectively. The 2016 WHO classification presented better prognostic value for overall survival in patients with grade II tumors than traditional histological classification. Among patients with grade II tumors, those with oligodendroglioma IDHmut and 1p/19q co-deleted and diffuse astrocytoma IDHmut showed significantly higher survival than those with diffuse astrocytoma IDHwt, NOS (p<.01).
Conclusions
Mongolian diffuse gliomas could be reclassified according to the new 2016 WHO classification. Reclassification revealed substantial changes in diagnosis of both oligodendroglial and astrocytic entities. We have confirmed that the revised 2016 WHO CNS tumor classification has prognostic significance in Mongolian patients with diffuse gliomas, especially those with grade II tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeted next‐generation sequencing of adult gliomas for retrospective prognostic evaluation and up‐front diagnostics
J. K. Petersen, H. B. Boldt, M. D. Sørensen, S. Blach, R. H. Dahlrot, S. Hansen, M. Burton, M. Thomassen, T. Kruse, F. R. Poulsen, L. Andreasen, H. Hager, B. P. Ulhøi, S. Lukacova, G. Reifenberger, B. W. Kristensen
Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.2021; 47(1): 108. CrossRef
- Targeted next‐generation sequencing of adult gliomas for retrospective prognostic evaluation and up‐front diagnostics
- CpG Island Methylation in Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyp of the Colorectum: Implications for Differential Diagnosis of Molecularly High-Risk Lesions among Non-dysplastic Sessile Serrated Adenomas/Polyps
- Ji Ae Lee, Hye Eun Park, Seung-Yeon Yoo, Seorin Jeong, Nam-Yun Cho, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Jung Ho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):225-235. Published online March 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.03.12
- 9,846 View
- 246 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although colorectal sessile serrated adenomas/polyps (SSA/Ps) with morphologic dysplasia are regarded as definite high-risk premalignant lesions, no reliable grading or risk-stratifying system exists for non-dysplastic SSA/Ps. The accumulation of CpG island methylation is a molecular hallmark of progression of SSA/Ps. Thus, we decided to classify non-dysplastic SSA/Ps into risk subgroups based on the extent of CpG island methylation.
Methods
The CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) status of 132 non-dysplastic SSA/Ps was determined using eight CIMP-specific promoter markers. SSA/Ps with CIMP-high and/or MLH1 promoter methylation were regarded as a high-risk subgroup.
Results
Based on the CIMP analysis results, methylation frequency of each CIMP marker suggested a sequential pattern of CpG island methylation during progression of SSA/P, indicating MLH1 as a late-methylated marker. Among the 132 non-dysplastic SSA/Ps, 34 (26%) were determined to be high-risk lesions (33 CIMP-high and 8 MLH1-methylated cases; seven cases overlapped). All 34 high-risk SSA/Ps were located exclusively in the proximal colon (100%, p = .001) and were significantly associated with older age (≥ 50 years, 100%; p = .003) and a larger histologically measured lesion size (> 5 mm, 100%; p = .004). In addition, the high-risk SSA/Ps were characterized by a relatively higher number of typical base-dilated serrated crypts.
Conclusions
Both CIMP-high and MLH1 methylation are late-step molecular events during progression of SSA/Ps and rarely occur in SSA/Ps of young patients. Comprehensive consideration of age (≥ 50), location (proximal colon), and histologic size (> 5 mm) may be important for the prediction of high-risk lesions among non-dysplastic SSA/Ps. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MLH1 Methylation Status and Microsatellite Instability in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Manuel Alejandro Rico-Méndez, Miguel Angel Trujillo-Rojas, María de la Luz Ayala-Madrigal, Jesús Arturo Hernández-Sandoval, Anahí González-Mercado, Melva Gutiérrez-Angulo, José Geovanni Romero-Quintana, Jesús Alonso Valenzuela-Pérez, Ruth Ramírez-Ramírez,
Genes.2025; 16(2): 182. CrossRef - Histologic Reappraisal and Evaluation of MLH1 Protein Expression in Sessile Serrated Lesions of the Proximal Colon
Priscilla de Sene Portel Oliveira, Miriam Aparecida da Silva Trevisan, Rita Barbosa de Carvalho, Rita de Cássia Perina Martins, João José Fagundes, Claudio Saddy Rodrigues Coy, Ashwini Esnakula
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune microenvironmental heterogeneity according to tumor DNA methylation phenotypes in microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancers
Jung Ho Kim, Jiyun Hong, Ji Ae Lee, Minsun Jung, Eunwoo Choi, Nam-Yun Cho, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Sangwoo Kim
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How to "pick up" colorectal serrated lesions and polyps in daily histopathology practice: From terminologies to diagnostic pitfalls
Thai H Tran, Vinh H Nguyen, Diem TN Vo
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2024; 15(9): 1157. CrossRef - Serrated Colorectal Lesions: An Up-to-Date Review from Histological Pattern to Molecular Pathogenesis
Martino Mezzapesa, Giuseppe Losurdo, Francesca Celiberto, Salvatore Rizzi, Antonio d’Amati, Domenico Piscitelli, Enzo Ierardi, Alfredo Di Leo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4461. CrossRef - NTRK oncogenic fusions are exclusively associated with the serrated neoplasia pathway in the colorectum and begin to occur in sessile serrated lesions
Jung Ho Kim, Jeong Hoon Hong, Yoon‐La Choi, Ji Ae Lee, Mi‐kyoung Seo, Mi‐Sook Lee, Sung Bin An, Min Jung Sung, Nam‐Yun Cho, Sung‐Su Kim, Young Kee Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
The Journal of Pathology.2021; 255(4): 399. CrossRef - Evolving pathologic concepts of serrated lesions of the colorectum
Jung Ho Kim, Gyeong Hoon Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 276. CrossRef
- MLH1 Methylation Status and Microsatellite Instability in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
- Association between p53 Expression and Amount of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Miseon Lee, In Ah Park, Sun-Hee Heo, Young-Ae Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Hee Jin Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(3):180-187. Published online March 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.02.08
- 9,995 View
- 205 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Most triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) have a high histologic grade, are associated with high endoplasmic stress, and possess a high frequency of TP53 mutations. TP53 missense mutations lead to the production of mutant p53 protein and usually show high levels of p53 protein expression. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) accumulate as part of the anti-tumor immune response and have a strong prognostic and predictive significance in TNBC. We aimed to elucidate the association between p53 expression and the amount of TILs in TNBC.
Methods
In 678 TNBC patients, we evaluated TIL levels and expression of endoplasmic stress molecules. Immunohistochemical examination of p53 protein expression was categorized into three groups: no, low, and high expression.
Results
No, low, and high p53 expression was identified in 44.1% (n = 299), 20.1% (n = 136), and 35.8% (n = 243) of patients, respectively. Patients with high p53 expression showed high histologic grade (p < .001), high TIL levels (p = .009), and high expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated molecules (p-eIF2a, p = .013; XBP1, p = .007), compared to patients with low p53 expression. There was no significant difference in disease-free (p = .406) or overall survival rates (p = .444) among the three p53 expression groups.
Conclusions
High p53 expression is associated with increased expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress molecules and TIL influx. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparative analysis of mutational profiles between triple-negative breast cancer and non-triple-negative breast cancer
Wanlin Li, Chenchen Feng, Shunheng Zhou
Discover Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The search for a TNBC vaccine: the guardian vaccine
Cory Fines, Helen McCarthy, Niamh Buckley
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlating p53 immunostaining patterns with somatic TP53 mutation and functional properties of mutant p53 in triple‐negative breast cancer
Meejeong Kim, Miseon Lee, Ahwon Lee, Byung‐Ock Choi, Woo‐Chan Park, Sung Hun Kim, Jieun Lee, Jun Kang
Histopathology.2025; 87(2): 299. CrossRef - GD3 synthase drives resistance to p53-induced apoptosis in breast cancer by modulating mitochondrial function
Vivek Anand, Fouad El-Dana, Natalia Baran, Jenny Borgman, Zheng Yin, Hong Zhao, Stephen T. Wong, Michael Andreeff, V. Lokesh Battula
Oncogene.2025; 44(30): 2646. CrossRef - Topoisomerase Inhibitor Resistance in Breast Cancer: Exploring Alterations in Cellular Metabolism and Properties Driving Drug Insensitivity
Juhong Lee, Youngjoo Kwon
Drug Targets and Therapeutics.2025; 4(2): 185. CrossRef - Updated Austrian treatment algorithm for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
Rupert Bartsch, Gabriel Rinnerthaler, Edgar Petru, Daniel Egle, Michael Gnant, Marija Balic, Thamer Sliwa, Christian Singer
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2024; 136(11-12): 347. CrossRef - Triple negative breast cancer: Immunogenicity, tumor microenvironment, and immunotherapy
Sotiris Loizides, Anastasia Constantinidou
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic benefit of TILs independent of clinicopathological and molecular factors
Koen Brummel, Anneke L. Eerkens, Marco de Bruyn, Hans W. Nijman
British Journal of Cancer.2023; 129(5): 737. CrossRef - Dihydroartemisinin-Transferrin Adducts Enhance TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in a P53-Independent and ROS-Dependent Manner
Xinyu Zhou, Abel Soto-Gamez, Fleur Nijdam, Rita Setroikromo, Wim J. Quax
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Challenges in the Differential Diagnosis of High-Grade Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Serous Carcinoma
Andrii Puzyrenko, Chandler S Cortina, Julie M Jorns
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2022; 30(7): 728. CrossRef - Prognostic analysis of cuproptosis-related gene in triple-negative breast cancer
Shengnan Sha, Luyi Si, Xinrui Wu, Yuanbiao Chen, Hui Xiong, Ying Xu, Wangrui Liu, Haijun Mei, Tao Wang, Mei Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - p53 Missense Mutation is Associated with Immune Cell PD-L1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Ai-Yan Xing, Long Liu, Ke Liang, Bin Wang
Cancer Investigation.2022; 40(10): 879. CrossRef - Crosstalk between Immune Checkpoint Modulators, Metabolic Reprogramming and Cellular Plasticity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Arpita Poddar, Sushma R. Rao, Prashanth Prithviraj, George Kannourakis, Aparna Jayachandran
Current Oncology.2022; 29(10): 6847. CrossRef - The tumor microenvironment and triple-negative breast cancer aggressiveness: shedding light on mechanisms and targeting
Natsuki Furukawa, Vered Stearns, Cesar A. Santa-Maria, Aleksander S. Popel
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2022; 26(12): 1041. CrossRef - Intracellular partners of fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 - implications for functions
Katarzyna Dominika Sluzalska, Jakub Slawski, Martyna Sochacka, Agata Lampart, Jacek Otlewski, Malgorzata Zakrzewska
Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews.2021; 57: 93. CrossRef - Targeted Chinese Medicine Delivery by A New Family of Biodegradable Pseudo-Protein Nanoparticles for Treating Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Hiu Yee Kwan, Qinghua Xu, Ruihong Gong, Zhaoxiang Bian, Chih-Chang Chu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptomic Properties of HER2+ Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Associate with Absence of Immune Cells
Marie Colombe Agahozo, Marcel Smid, Ronald van Marion, Dora Hammerl, Thierry P. P. van den Bosch, Mieke A. M. Timmermans, Chayenne J. Heijerman, Pieter J. Westenend, Reno Debets, John W. M. Martens, Carolien H. M. van Deurzen
Biology.2021; 10(8): 768. CrossRef - With Our Powers Combined
Lawrence Kasherman, Katherine Karakasis, Amit M. Oza
The Cancer Journal.2021; 27(6): 511. CrossRef The Research Progress on the Prognostic Value of the Common Hematological Parameters in Peripheral Venous Blood in Breast Cancer
Li Chen, Xiangyi Kong, Chengrui Yan, Yi Fang, Jing Wang
OncoTargets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1397. CrossRefBiomolecular Factors Represented by Bcl-2, p53, and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Predict Response for Adjuvant Anthracycline Chemotherapy in Patients with Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Xenia Elena Bacinschi, Anca Zgura, Inga Safta, Rodica Anghel
Cancer Management and Research.2020; Volume 12: 11965. CrossRef
- A comparative analysis of mutational profiles between triple-negative breast cancer and non-triple-negative breast cancer
- Quilty Lesions in the Endomyocardial Biopsies after Heart Transplantation
- Haeyon Cho, Jin-Oh Choi, Eun-Seok Jeon, Jung-Sun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):50-56. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.11.30
- 8,501 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical significance of Quilty lesions in endomyocardial biopsies (EMBs) of cardiac transplantation patients.
Methods
A total of 1190EMBs from 117 cardiac transplantation patients were evaluated histologically for Quilty lesions,acute cellular rejection, and antibody-mediated rejection. Cardiac allograft vasculopathy wasdiagnosed by computed tomography coronary angiography. Clinical information, including thepatients’ survival was retrieved by a review of medical records.
Results
Eighty-eight patients(75.2%) were diagnosed with Quilty lesions, which were significantly associated with acute cellularrejection, but not with acute cellular rejection ≥ 2R or antibody-mediated rejection. In patientsdiagnosed with both Quilty lesions and acute cellular rejection, the time-to-onset of Quilty lesionsfrom transplantation was longer than that of acute cellular rejections. We found a significant associationbetween Quilty lesions and cardiac allograft vasculopathy. No significant relationship wasfound between Quilty lesions and the patients’ survival.
Conclusions
Quilty lesion may be an indicator of previous acute cellular rejection rather than a predictor for future acute cellular rejection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
Andrea Fernandez Valledor, Cathrine M. Moeller, Adi Hertz, Daniel Oren, Ilan Richter, Boaz Elad, Julia Baranowska, Salwa Rahman, Carolyn Hennecken, Afsana Rahman, Dor Lotan, David Bae, Adil Yunis, Justin A. Fried, Ersilia M. DeFilippis, David T Majure, Ja
The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of tertiary lymphoid structures in orchestrating immune responses in peripheral organs
Keisuke Taniguchi, Takahisa Yoshikawa, Motoko Yanagita
Inflammation and Regeneration.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The human myocardium harbors a population of naive B-cells with a distinctive gene expression signature conserved across species
Kevin C. Bermea, Nicolas Kostelecky, Sylvie T. Rousseau, Chieh-Yu Lin, Luigi Adamo
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of tracheal allografts after long-term survival in dogs
Tao Lu, Yiwei Huang, Yulei Qiao, Yongxing Zhang, Yu Liu
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.2021; 59(1): 155. CrossRef - Essentials in the diagnosis of postoperative myocardial lesions similar to or unrelated to rejection in heart transplant
Costel Dumitru, Ancuta Zazgyva, Adriana Habor, Ovidiu Cotoi, Horațiu Suciu, Carmen Cotrutz, Bogdan Grecu, Ileana Anca Sin
Revista Romana de Medicina de Laborator.2021; 29(3): 307. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of donor heart with prolonged cold ischemic time: A single‐center study
Fazal Shafiq, Yixuan Wang, Geng Li, Zongtao Liu, Fei Li, Ying Zhou, Li Xu, Xingjian Hu, Nianguo Dong
Journal of Cardiac Surgery.2020; 35(2): 397. CrossRef - The XVth Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology the Banff Workshop Heart Report: Improving the diagnostic yield from endomyocardial biopsies and Quilty effect revisited
Jean-Paul Duong Van Huyen, Marny Fedrigo, Gregory A. Fishbein, Ornella Leone, Desley Neil, Charles Marboe, Eliot Peyster, Jan von der Thüsen, Alexandre Loupy, Michael Mengel, Monica P. Revelo, Benjamin Adam, Patrick Bruneval, Annalisa Angelini, Dylan V. M
American Journal of Transplantation.2020; 20(12): 3308. CrossRef
- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
- Loss of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer
- Hong Sik Park, Uiju Cho, So Young Im, Chang Young Yoo, Ji Han Jung, Young Jin Suh, Hyun Joo Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(2):75-85. Published online November 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.11
- 9,507 View
- 191 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) molecules play important roles in regulating immune responses. Loss or reduction of HLA-I expression has been shown to be associated with prognosis in several cancers. Regulatory T-cells (Tregs) also play critical functions in immune response regulation. Evaluation of HLA-I expression status by the EMR8-5 antibody and its clinical impact in breast cancer have not been well studied, and its relationship with Tregs remains unclear.
Methods
We evaluated HLA-I expression and Treg infiltration by immunohistochemistry in 465 surgically resected breast cancer samples. We examined the correlation between HLA-I expression and Treg infiltration and clinicopathologic characteristics and survival analyses were performed.
Results
Total loss of HLA-I expression was found in 84 breast cancer samples (18.1%). Univariate survival analysis revealed that loss of HLA-I expression was significantly associated with worse disease-specific survival (DSS) (p = .029). HLA-I was not an independent prognostic factor in the entire patient group, but it was an adverse independent prognostic factor for DSS in patients with advanced disease (stage II–IV) (p = .031). Treg numbers were significantly higher in the intratumoral stroma of HLA-I–positive tumors than in HLA-I–negative tumors (median 6.3 cells/high power field vs 2.1 cells/high power field, p < .001). However, Tregs were not an independent prognostic factor in our cohort.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that the loss of HLA-I expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients, highlighting the role of HLA-I alterations in immune evasion mechanisms of breast cancer. HLA-I could be a promising marker that enables the application of more effective and precise immunotherapies for patients with advanced breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estrogen Signaling in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Impact on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
Chiara Corti, Busem Binboğa Kurt, Beyza Koca, Tasnim Rahman, Fabio Conforti, Laura Pala, Giampaolo Bianchini, Carmen Criscitiello, Giuseppe Curigliano, Ana C. Garrido-Castro, Sheheryar K. Kabraji, Adrienne G. Waks, Elizabeth A. Mittendorf, Sara M. Tolaney
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2025; 132: 102852. CrossRef - MHC-I upregulation by macbecin II in the solid tumors potentiates the effect of active immunotherapy
Ravindra Pramod Deshpande, Kerui Wu, Shih-Ying Wu, Abhishek Tyagi, Eleanor C Smith, Jee-Won Kim, Kounosuke Watabe
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2025; 17(4): 797. CrossRef - Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) and major Histocompatibility Complex Class I (MHC Class I) Expression Patterns and Their Pathologic Associations in triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Ponkrit Kaewkedsri, Piyapharom Intarawichian, Sirawich Jessadapattarakul, Waritta Kunprom, Supinda Koonmee, Malinee Thanee, Ongart Somintara, Anongporn Wongbuddha, Payia Chadbunchachai, Supajit Nawapun, Chaiwat Aphivatanasiri
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 17: 123. CrossRef - Comment on “Prognostic and Clinical Significance of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression in Breast Cancer: A Meta‑Analysis”
Wei Han, Li-zhou Shi, Yu-wei Zhang, Hao-nan Wang
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2024; 28(2): 237. CrossRef - Immunotherapy resistance in solid tumors: mechanisms and potential solutions
Daniel S. Lefler, Steven A. Manobianco, Babar Bashir
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of cancer cell‐expressed HLA class I molecules and their immunopathological implications
Terufumi Kubo, Shiori Asano, Kenta Sasaki, Kenji Murata, Takayuki Kanaseki, Tomohide Tsukahara, Yoshihiko Hirohashi, Toshihiko Torigoe
HLA.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression and Natural Killer Cell Infiltration and Its Correlation with Prognostic Features in Luminal Breast Cancers
Maria Vernet-Tomas, Ivonne Vazquez, Francesc Olivares, David Lopez, Jose Yelamos, Laura Comerma
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2024; Volume 16: 657. CrossRef - Upregulation of MHC I antigen processing machinery gene expression in breast cancer cells by Trichostatin A
A. H. Murtadha, N. A. Sharudin, I. I.M. Azahar, A. T. Che Has, N. F. Mokhtar
Молекулярная биология.2024; 58(1): 121. CrossRef - HLA-I and breast cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Francisco Cezar Aquino de Moraes, Jorge Henrique Cavalcanti Orestes Cardoso, Francinny Alves Kelly, Michele Kreuz, Lilianne Rodrigues Fernandes, Maria Cristina Figueroa Magalhães, Rommel Mario Rodríguez Burbano
Human Immunology.2024; 85(6): 111148. CrossRef - Cancer Immunology: Immune Escape of Tumors—Expression and Regulation of HLA Class I Molecules and Its Role in Immunotherapies
Yuan Wang, Simon Jasinski-Bergner, Claudia Wickenhauser, Barbara Seliger
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2023; 30(3): 148. CrossRef - In Silico Pipeline to Identify Tumor-Specific Antigens for Cancer Immunotherapy Using Exome Sequencing Data
Diego Morazán-Fernández, Javier Mora, Jose Arturo Molina-Mora
Phenomics.2023; 3(2): 130. CrossRef - HLA and tumour immunology: immune escape, immunotherapy and immune-related adverse events
Ning Jiang, Yue Yu, Dawei Wu, Shuhang Wang, Yuan Fang, Huilei Miao, Peiwen Ma, Huiyao Huang, Min Zhang, Yu Zhang, Yu Tang, Ning Li
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2023; 149(2): 737. CrossRef - Relationship between Systemic Inflammatory Markers, GLUT1 Expression, and Maximum 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Their Prognostic Significance
Sonya Youngju Park, Deog-Gon Cho, Byoung-Yong Shim, Uiju Cho
Diagnostics.2023; 13(6): 1013. CrossRef - Prognostic and Clinical Significance of Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Expression in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Weiqiang Qiao, Zhiqiang Jia, Wanying Guo, Qipeng Liu, Xiao Guo, Miao Deng
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2023; 27(5): 573. CrossRef - Challenges and solutions for therapeuticTCR‐based agents
Manish Malviya, Zita E. H. Aretz, Zaki Molvi, Jayop Lee, Stephanie Pierre, Patrick Wallisch, Tao Dao, David A. Scheinberg
Immunological Reviews.2023; 320(1): 58. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of impaired antigenic presentation as a cause of tumor escape from immune surveillance
A.A. Korotaeva, A.A. Borunova, A.Yu. Kuzevanova, T.N. Zabotina, A.A. Alimov
Russian Journal of Archive of Pathology.2023; 85(6): 76. CrossRef - Immune Escape Mechanism of Cancer
Ayse Caner
Current Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 10(1): 9. CrossRef - Upregulation of MHC I Antigen Processing Machinery Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Cells by Trichostatin A
A. H. Murtadha, N. A. Sharudin, I. I. M. Azahar, A. T. Che Has, N. F. Mokhtar
Molecular Biology.2023; 57(6): 1212. CrossRef - Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I Antigen-Processing Machinery Upregulation by Anticancer Therapies in the Era of Checkpoint Inhibitors
Ananthan Sadagopan, Theodoros Michelakos, Gabriella Boyiadzis, Cristina Ferrone, Soldano Ferrone
JAMA Oncology.2022; 8(3): 462. CrossRef - Mechanisms of MHC-I Downregulation and Role in Immunotherapy Response
Brandie C. Taylor, Justin M. Balko
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: Resistance Mechanisms and Future Perspectives
Ioannis A. Vathiotis, Ioannis Trontzas, Niki Gavrielatou, Georgia Gomatou, Nikolaos K. Syrigos, Elias A. Kotteas
Clinical Breast Cancer.2022; 22(7): 642. CrossRef - Aberrant synaptophysin expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Soyoung Im, Jeong-A. Kim, Gyeongsin Park, Uiju Cho
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of HLA class I is associated with immune cell infiltration and patient outcome in breast cancer
Song-Hee Han, Milim Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Ji Won Woo, Hye Yeon Choi, So Yeon Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune landscape and therapeutic strategies: new insights into PD-L1 in tumors
Yuan Wei, Xiao Xiao, Xiang-Ming Lao, Limin Zheng, Dong-Ming Kuang
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2021; 78(3): 867. CrossRef - Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immunotherapy for the treatment of breast cancer
Leisha A Emens, Sylvia Adams, Ashley Cimino-Mathews, Mary L Disis, Margaret E Gatti-Mays, Alice Y Ho, Kevin Kalinsky, Heather L McArthur, Elizabeth A Mittendorf, Rita Nanda, David B Page, Hope S Rugo, Krista M Rubin, Hatem Soliman, Patricia A Spears, Sara
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2021; 9(8): e002597. CrossRef - Resistance mechanisms to checkpoint inhibitors
Sarah A Weiss, Mario Sznol
Current Opinion in Immunology.2021; 69: 47. CrossRef - The Immunology of Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Jonathan Goldberg, Ricardo G. Pastorello, Tuulia Vallius, Janae Davis, Yvonne Xiaoyong Cui, Judith Agudo, Adrienne G. Waks, Tanya Keenan, Sandra S. McAllister, Sara M. Tolaney, Elizabeth A. Mittendorf, Jennifer L. Guerriero
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - B4GALNT2 Gene Promotes Proliferation, and Invasiveness and Migration Abilities of Model Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cells by Interacting With HLA-B Protein
Pu Yu, Lili Zhu, Kang Cui, Yabing Du, Chaojie Zhang, Wang Ma, Jia Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Recurrence biomarkers of triple negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and anti-EGFR antibodies
Nina Radosevic-Robin, Pier Selenica, Yingjie Zhu, Helen H. Won, Michael F. Berger, Lorenzo Ferrando, Emiliano Cocco, Maud Privat, Flora Ponelle-Chachuat, Catherine Abrial, Jean-Marc Nabholtz, Frederique Penault-Llorca, Jorge S. Reis-Filho, Maurizio Scaltr
npj Breast Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Beyond an era of chemoradiation?
Liam Masterson, James Howard, Jazmina Gonzalez‐Cruz, Christopher Jackson, Catherine Barnett, Lewis Overton, Howard Liu, Rahul Ladwa, Fiona Simpson, Margie McGrath, Ben Wallwork, Terry Jones, Christian Ottensmeier, Melvin L.K. Chua, Chris Perry, Rajiv Khan
International Journal of Cancer.2020; 146(8): 2305. CrossRef - Co-expression of HLA-I loci improved prognostication in HER2+ breast cancers
Julia Y. Tsang, Chun-Sing Ho, Yun-Bi Ni, Yan Shao, Ivan K. Poon, Siu-Ki Chan, Sai-Yin Cheung, Ka-Ho Shea, Monalyn Marabi, Gary M. Tse
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2020; 69(5): 799. CrossRef - Breast cancer patients overall survival depends on a combination of the polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor gene and HLA-haplotypes
T.F. Malivanova, E.V. Alferova, A.S. Ostashkin, T.A. Astrelina, N.N. Mazurenko
Molecular Genetics Microbiology and Virology (Russian version).2020; 38(1): 40. CrossRef - The Overall Survival of Breast Cancer Patients Depends on a Combination of Polymorphisms of Tumor Necrosis Factor Gene and HLA Haplotypes
T. F. Malivanova, E. V. Alferova, A. S. Ostashkin, T. A. Astrelina, N. N. Mazurenko
Molecular Genetics, Microbiology and Virology.2020; 35(1): 38. CrossRef - The Emergence of Natural Killer Cells as a Major Target in Cancer Immunotherapy
Fernando Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes, Joseph Cursons, Nicholas D. Huntington
Trends in Immunology.2019; 40(2): 142. CrossRef
- Estrogen Signaling in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Impact on Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
- The Usefulness of Immunocytochemistry of CD56 in Determining Malignancy from Indeterminate Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Hyunseo Cha, Ju Yeon Pyo, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):404-410. Published online October 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.20
- 9,614 View
- 175 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Fine-needle aspiration cytology serves as a safe, economical tool in evaluating thyroid nodules. However, about 30% of the samples are categorized as indeterminate. Hence, many immunocytochemistry markers have been studied, but there has not been a single outstanding marker. We studied the efficacy of CD56 with human bone marrow endothelial cell marker-1 (HBME-1) in diagnosis in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) category III.
Methods
We reviewed ThinPrep liquid-based cytology (LBC) samples with Papanicolaou stain from July 1 to December 31, 2016 (2,195 cases) and selected TBSRTC category III cases (n = 363). Twenty-six cases were histologically confirmed as benign (six cases, 23%) or malignant (20 cases, 77%); we stained 26 LBC slides with HBME-1 and CD56 through the cell transfer method. For evaluation of reactivity of immunocytochemistry, we chose atypical follicular cell clusters.
Results
CD56 was not reactive in 18 of 20 cases (90%) of malignant nodules and showed cytoplasmic positivity in five of six cases (83%) of benign nodules. CD56 showed high sensitivity (90.0%) and relatively low specificity (83.3%) in detecting malignancy (p = .004). HBME-1 was reactive in 17 of 20 cases (85%) of malignant nodules and was not reactive in five of six cases (83%) of benign nodules. HBME-1 showed slightly lower sensitivity (85.0%) than CD56. The specificity in detecting malignancy by HBME-1 was similar to that of CD56 (83.3%, p = .008). CD56 and HBME-1 tests combined showed lower sensitivity (75.0% vs 90%) and higher specificity (93.8% vs 83.3%) in detecting malignancy compared to using CD56 alone.
Conclusions
Using CD56 alone showed relatively low specificity despite high sensitivity for detecting malignancy. Combining CD56 with HBME-1 could increase the specificity. Thus, we suggest that CD56 could be a useful preoperative marker for differential diagnosis of TBSRTC category III samples. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Immunocytochemistry on Diagnostic Accuracy in Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Retrospective Study
Ali Mızrak, Cansu Benli Işık, Esen Gül Uzuner, Saime Gül Barut
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2025; 15(3): 531. CrossRef - Preoperative evaluation of thyroid nodules – Diagnosis and management strategies
Tapoi Dana Antonia, Lambrescu Ioana Maria, Gheorghisan-Galateanu Ancuta-Augustina
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 246: 154516. CrossRef - Immunocytochemistry in thyroid cytology and its multiple roles: a systematic review
Federica Policardo, Pietro Tralongo, Angela Feraco, Federica Vegni, Angela Carlino, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Celestino Pio Lombardi, Marco Raffaelli, Francesco Pierconti, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Diana Rossi
Diagnostic Histopathology.2023; 29(8): 386. CrossRef - Paving the path toward multi-omics approaches in the diagnostic challenges faced in thyroid pathology
Isabella Piga, Vincenzo L’Imperio, Giulia Capitoli, Vanna Denti, Andrew Smith, Fulvio Magni, Fabio Pagni
Expert Review of Proteomics.2023; 20(12): 419. CrossRef - CD56 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Is Highly Dependent on the Histologic Subtype: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
Uiju Cho, Yourha Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(5): 389. CrossRef
- The Effects of Immunocytochemistry on Diagnostic Accuracy in Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Retrospective Study
- Prognostic Role of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungseek Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):331-338. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.07
- 9,503 View
- 131 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study is to elucidate the clinicopathological significances, including the prognostic role, of metastatic lymph node ratio (mLNR) and tumor deposit diameter in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) through a retrospective review and meta-analysis.
Methods
We categorized the cases into high (≥ 0.44) and low mLNR (< 0.44) and investigated the correlations with clinicopathological parameters in 64 PTCs with neck level VI lymph node (LN) metastasis. In addition, meta-analysis of seven eligible studies was used to investigate the correlation between mLNR and survival.
Results
Among 64 PTCs with neck level VI LN metastasis, high mLNR was found in 34 PTCs (53.1%). High mLNR was significantly correlated with macrometastasis (tumor deposit diameter ≥ 0.2 cm), extracapsular spread, and number of metastatic LNs. Based on linear regression test, mLNR was significantly increased by the largest LN size but not the largest metastatic LN (mLN) size. High mLNR was not correlated with nuclear factor κB or cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression, Ki-67 labeling index, or other pathological parameters of primary tumor. Based on meta-analysis, high mLNR significantly correlated with worse disease-free survival at the 5-year and 10-year follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 4.866; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.527 to 6.714 and HR, 5.769; 95% CI, 2.951 to 11.275, respectively).
Conclusions
Our data showed that high mLNR significantly correlated with worse survival, macrometastasis, and extracapsular spread of mLNs. Further cumulative studies for more detailed criteria of mLNR are needed before application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Chang Liu, Shangjie Yang, Tian Xue, Qian Zhang, Yanjing Zhang, Yufang Zhao, Guolin Yin, Xiaohui Yan, Ping Liang, Liping Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of a Nomogram Based on Ultrasound Radiomics, Clinical Factors, and Enhanced Ultrasound Features for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Lei Gao, Xiuli Wen, Guanghui Yue, Hui Wang, Ziqing Lu, Beibei Wu, Zhihong Liu, Yuming Wu, Dongmei Lin, Shijian Yi, Wei Jiang, Yi Hao
Ultrasonic Imaging.2025; 47(2): 93. CrossRef - Lymph Node Metastasis Ratio: Prognostic Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ana Rita Ferreira, Diogo Ramalho, Daniela Martins, Andreia Amado, Susana Graça, Carlos Soares, Bela Pereira, Maria João Oliveira, Manuel Oliveira, Antónia Póvoa
Indian Journal of Surgery.2025; 87(6): 1047. CrossRef - CD105 (Endoglin) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
İlker Çordan, Tuğba Günler
Clinical Endocrinology.2025; 103(4): 596. CrossRef - Application and subgroup analysis of competing risks model based on different lymph node staging systems in differentiated thyroid cancer
Zhe Xu Cao, Jiang Sheng Huang, Ming Ming Wang
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(5): 1927. CrossRef - Цитологічне прогнозування агресії раку щитоподібної залози як новий перспективний напрямок у клінічній тиреоїдології
H.V. Zelinska
Endokrynologia.2024; 29(4): 363. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin expression, Ki-67 index, and lymph node ratio in the prognostic assessment of papillary thyroid cancer
Helene Lindfors, Marie Karlsen, Ellinor Karlton, Jan Zedenius, Catharina Larsson, Catharina Ihre Lundgren, C. Christofer Juhlin, Ivan Shabo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Node Metastasis as an Independent Factor of Worse Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Renan Aguera Pinheiro, Ana Kober Leite, Beatriz Godoi Cavalheiro, Evandro Sobroza de Mello, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Leandro Luongo Matos
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 943. CrossRef - A High-Quality Nomogram for Predicting Lung Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study
WenYi Wang, JiaJing Liu, XiaoFan Xu, LiQun Huo, XuLin Wang, Jun Gu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Low Lymph Node Yield
Il Ku Kang, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 2947. CrossRef - Superiority of metastatic lymph node ratio over number of node metastases and TNM/AJCC N classification in predicting cancer‐specific survival in medullary thyroid cancer
Andreas Machens, Kerstin Lorenz, Frank Weber, Henning Dralle
Head & Neck.2022; 44(12): 2717. CrossRef - Value of Combining Clinical Factors, Conventional Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features in Preoperative Prediction of Central Lymph Node Metastases of Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Yanfang Wang, Fang Nie, Guojuan Wang, Ting Liu, Tiantian Dong, Yamin Sun
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3403. CrossRef - Atypical Histiocytoid Cells and Multinucleated Giant Cells in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid Predict Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Ji Eun Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 816. CrossRef - Patients Aged ≥55 Years With Stage T1-2N1M1 Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Should Be Downstaged in the Eighth Edition AJCC/TNM Cancer Staging System
Zeming Liu, Sichao Chen, Yihui Huang, Di Hu, Min Wang, Wei Wei, Chao Zhang, Wen Zeng, Liang Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Colorectal Cancers: Comparison Depending on Tumor Location
Jung-Soo Pyo, Young-Min Shin, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1812. CrossRef
- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features and Its Impact on the Risk of Malignancy in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: An Institutional Experience
- Milim Kim, Joung Eun Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Yoonjin Kwak, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):171-178. Published online April 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.03
- 11,671 View
- 205 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study was performed to analyze cytologic diagnosis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) and its impact on the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC).
Methods
Five thousand five hundred and forty-nine cases of thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) diagnosed between 2012 and 2014 were included in this study. Diagnostic categories based on TBSRTC were compared with final surgical diagnoses, and the ROM in each category was calculated both when NIFTP was included in malignant lesions and when excluded from malignant lesions.
Results
Of the 5,549 thyroid FNAC cases, 1,891 cases underwent surgical resection. In final diagnosis, 1,700 cases were revealed as papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), and 25 cases were reclassified as NIFTP. The cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP were non-diagnostic in one, benign in five, atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) in 14, follicular neoplasm in two, and suspicious for malignancy in three cases. Collectively, NIFTP/encapsulated follicular variant of PTC (EFVPTC) were more frequently classified as benign, AUS, or follicular neoplasm and less frequently categorized as malignant compared to conventional PTCs. Exclusion of NIFTP from malignant diagnoses resulted in a slight decrease in malignancy rates in non-diagnostic, benign, AUS, follicular neoplasm, and suspicious for malignancy categories without any statistical significance.
Conclusions
The decrease in the ROM was not significant when NIFTP was excluded from malignant lesions. In thyroid FNACs, NIFTP/EFVPTCs were mostly classified into indeterminate categories. Therefore, it might be feasible to separate NIFTP/EFVPTC from conventional PTC on FNAC to guide clinicians to conservative management for patients with NIFTP/EFVPTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Spatial transcriptomics reveals prognosis‐associated cellular heterogeneity in the papillary thyroid carcinoma microenvironment
Kai Yan, Qing‐Zhi Liu, Rong‐Rong Huang, Yi‐Hua Jiang, Zhen‐Hua Bian, Si‐Jin Li, Liang Li, Fei Shen, Koichi Tsuneyama, Qing‐Ling Zhang, Zhe‐Xiong Lian, Haixia Guan, Bo Xu
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Features of “Non-invasive Follicular Tumour with Papillary Like Nuclear Features” – A Single Institutional Experience in India
K Amita, HB Rakshitha, M Sanjay, Prashantha Kalappa
Journal of Cytology.2023; 40(1): 28. CrossRef - Detailed fine needle aspiration cytopathology findings of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features with nuclear grading correlated to that of biopsy and Bethesda category and systematic review
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2023; 51(12): 758. CrossRef - Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features Is Not a Cytological Diagnosis, but It Influences Cytological Diagnosis Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elina Haaga, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvíková, Ivana Kholová
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(2): 85. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - Comprehensive DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Sora Jeon, Eun-Hye Seo, Dong Hyuck Bae, Young Mun Jeong, Yourha Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Seon-Kyu Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Yong Sung Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(2): 192. CrossRef - Differences in surgical resection rate and risk of malignancy in thyroid cytopathology practice between Western and Asian countries: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Hanh Thi Tuyet Ngo, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung, Trang Huyen Vu, Kim Bach Lu, Kennichi Kakudo, Tetsuo Kondo
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(4): 238. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular neoplasm with papillary like nuclear features: A comprehensive analysis with a diagnostic algorithm
Chanchal Rana, Shreyamsa Manjunath, Pooja Ramakant, Kulranjan Singh, Suresh Babu, Anand Mishra
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(4): 330. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features and the risk of malignancy in The Bethesda System for the Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology
Danielle Elliott Range, Xiaoyin “Sara” Jiang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(6): 531. CrossRef - Did Introducing a New Category of Thyroid Tumors (Non-invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features) Decrease the Risk of Malignancy for the Diagnostic Categories in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology?
Janusz Kopczyński, Agnieszka Suligowska, Kornelia Niemyska, Iwona Pałyga, Agnieszka Walczyk, Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Artur Kowalik, Kinga Hińcza, Ryszard Mężyk, Stanisław Góźdź, Aldona Kowalska
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - High risk of malignancy in cases with atypia of undetermined significance on fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules even after exclusion of NIFTP
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Büşra Yaprak Bayrak, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(11): 986. CrossRef - The importance of risk of neoplasm as an outcome in cytologic‐histologic correlation studies on thyroid fine needle aspiration
Yu‐Hsin Chen, Kristen L. Partyka, Rae Dougherty, Harvey M. Cramer, Howard H. Wu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(12): 1237. CrossRef - Preoperative diagnostic categories of fine needle aspiration cytology for histologically proven thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma, and Hurthle cell adenoma and carcinoma: Analysis of cause of under- or misdiagnoses
Hee Young Na, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241597. CrossRef - How is noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) shaping the way we interpret thyroid cytology?
Michiya Nishino
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2019; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Cytological Diagnoses Associated with Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasms with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features According to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Massimo Bongiovanni, Luca Giovanella, Francesco Romanelli, Pierpaolo Trimboli
Thyroid.2019; 29(2): 222. CrossRef - Preoperative Diagnostic Categories of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features in Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy and Its Impact on Risk of Malignancy
Hee Young Na, Ji Won Woo, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(4): 329. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Reclassification to Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): a Retrospective Clinicopathologic Study
Khurram Shafique, Virginia A. LiVolsi, Kathleen Montone, Zubair W. Baloch
Endocrine Pathology.2018; 29(4): 339. CrossRef
- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis

 E-submission
E-submission

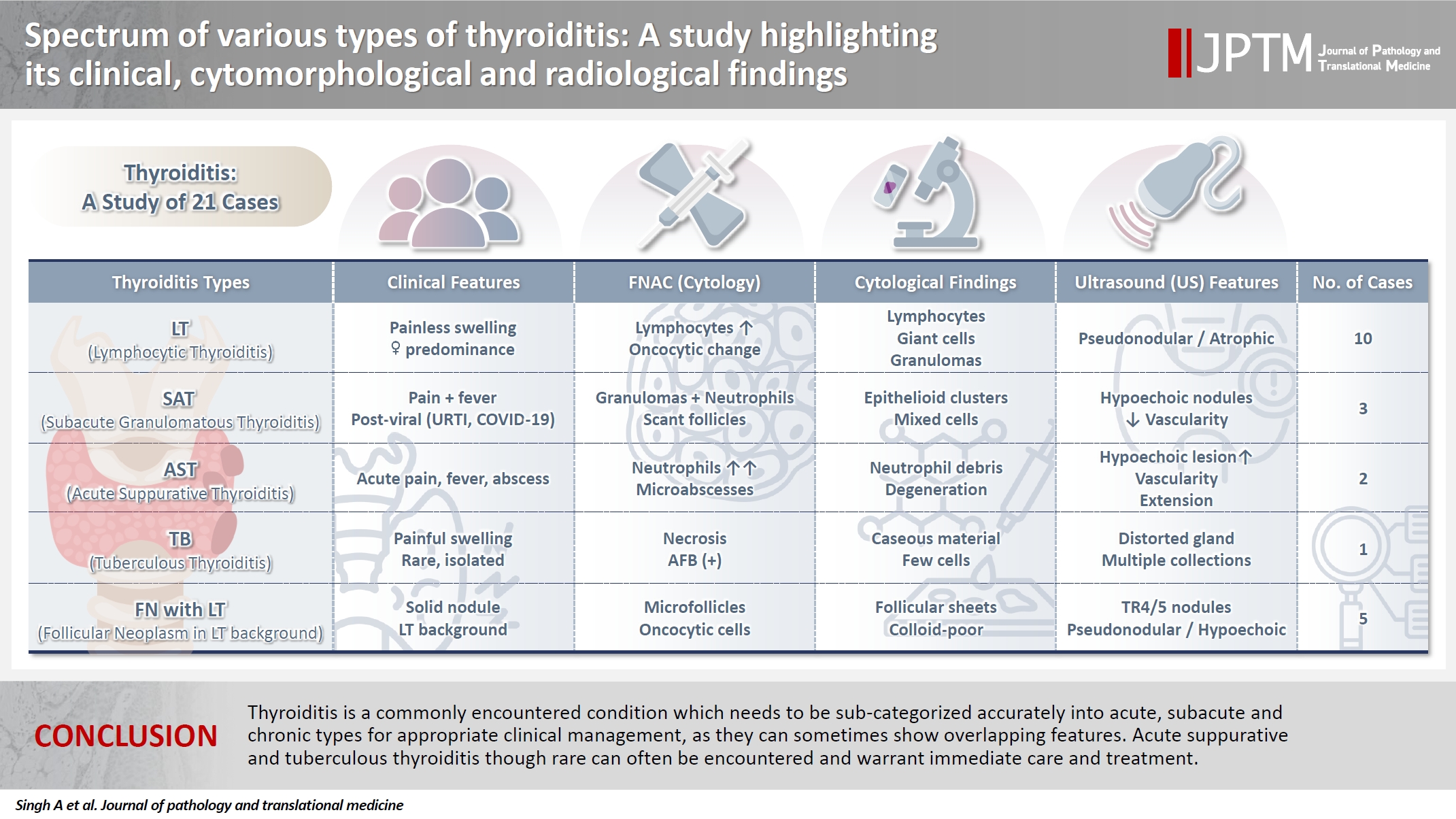





























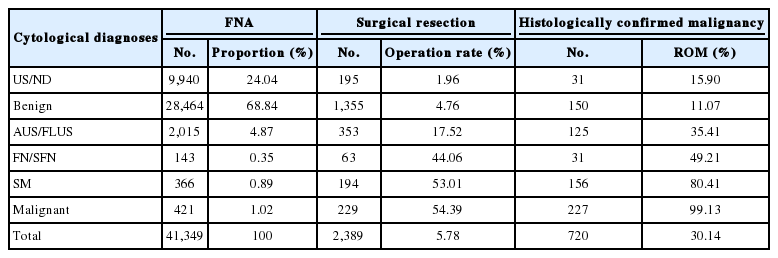







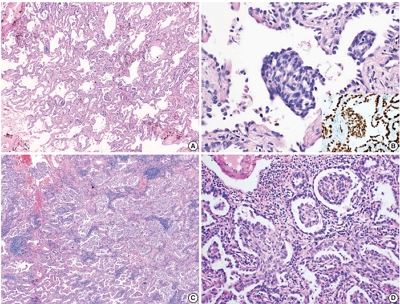
 First
First Prev
Prev



