Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification
- Hye Ju Kang, Sun Young Kwon, Ahrong Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Soo Kee Min, So Young Park, Sun Hee Sung, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Hyang Im Lee, Ho Chang Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Sun Young Jun, Min Jung Jung, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Hye Jeong Choi, So Yeon Park, Jee Yeon Kim, In Ae Park, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):380-387. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
- 7,163 View
- 226 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
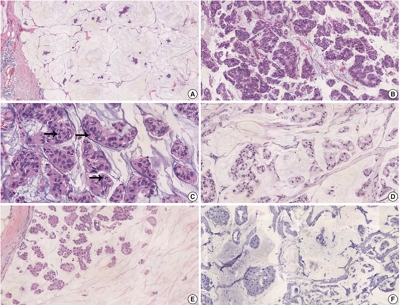
Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
Methods
Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
Results
On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
Conclusions
Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
- Standardized pathology report for breast cancer
- Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(1):1-15. Published online January 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.11.20
- 15,843 View
- 724 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Given the recent advances in management and understanding of breast cancer, a standardized pathology report reflecting these changes is critical. To meet this need, the Breast Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists has developed a standardized pathology reporting format for breast cancer, consisting of ‘standard data elements,’ ‘conditional data elements,’ and a biomarker report form. The ‘standard data elements’ consist of the basic pathologic features used for prognostication, while other factors related to prognosis or diagnosis are described in the ‘conditional data elements.’ In addition to standard data elements, all recommended issues are also presented. We expect that this standardized pathology report for breast cancer will improve diagnostic concordance and communication between pathologists and clinicians, as well as between pathologists inter-institutionally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Breast Associated With an Incidental Radial Scar: A Cyto‐Histopathology Correlation
Rallapalli Rajyalakshmi, Valasapalli Rajani, Tanuku Sreedhar, Kollabathula Arpitha
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating discrepancies: The assessment of residual lymphovascular invasion in breast carcinoma after neoadjuvant treatment
Anikó Kovács, Åsa Rundgren-Sellei, Gunilla Rask, Annette Bauer, Anna Bodén, Johannes van Brakel, Eugenia Colón-Cervantes, Anna Ehinger, Johan Hartman, Balazs Acs
The Breast.2025; 82: 104519. CrossRef - Residual pure intralymphatic carcinoma component only (lymphovascular tumor emboli without invasive carcinoma) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with poor outcome: Not pathologic complete response
Hyunwoo Lee, Yunjeong Jang, Yoon Ah Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
Human Pathology.2024; 145: 1. CrossRef - Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with ductal carcinomain situ: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Colm O’Flaherty, Eoin F. Cleere, Aoife Nohilly, James Phelan, Evan Ronane, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of Breast Associated With an Incidental Radial Scar: A Cyto‐Histopathology Correlation
- Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
- Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):95-102. Published online November 13, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.10.24
- 10,690 View
- 293 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pure mucinous carcinoma (PMC) is a rare type of breast cancer, estimated to represent 2% of invasive breast cancer. PMC is typically positive for estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR) and negative for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive PMC have not been investigated.
Methods
Pathology archives were searched for PMC diagnosed from January 1999 to April 2018. Clinicopathologic data and microscopic findings were reviewed and compared between HER2-positive PMC and HER2-negative PMC. We also analyzed the differences in disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival according to clinicopathologic parameters including HER2 status in overall PMC cases.
Results
There were 21 HER2-positive cases (4.8%) in 438 PMCs. The average tumor size of HER2-positive PMC was 32.21 mm (± 26.55). Lymph node metastasis was present in seven cases. Compared to HER2-negative PMC, HER2-positive PMC presented with a more advanced T category (p < .001), more frequent lymph node metastasis (p = .009), and a higher nuclear and histologic grade (p < .001). Microscopically, signet ring cells were frequently observed in HER2-positive PMC (p < .001), whereas a micropapillary pattern was more frequent in HER2-negative PMC (p = .012). HER2-positive PMC was more frequently negative for ER (33.3% vs. 1.2%) and PR (28.6% vs. 7.2%) than HER2-negative PMC and showed a high Ki-67 labeling index. During follow-up, distant metastasis and recurrence developed in three HER2-positive PMC patients. Multivariate analysis revealed that only HER2-positivity and lymph node status were significantly associated with DFS.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that HER2-positive PMC is a more aggressive subgroup of PMC. HER2 positivity should be considered for adequate management of PMC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
Sunayana Misra, Mihir Gudi, Kimberly H Allison, Edi Brogi, Cecily Quinn, Hannah Y Wen, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of a 6-years study from national cancer center in Vietnam
Thi Huyen Phung, Thanh Tung Pham, Huu Thang Nguyen, Dinh Thach Nguyen, Thanh Long Nguyen, Thi Hoai Hoang
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(3): 667. CrossRef - Poor response of HER2-positive mucinous carcinomas of breast to neoadjuvant HER2-targeted therapy: A study of four cases
Min Han, Daniel Schmolze, Javier A. Arias-Stella, Christina H. Wei, Joanne Mortimer, Fang Fan
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 74: 152396. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Mesonephric Marker Expression in Low-grade Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma
Yurimi Lee, Sangjoon Choi, Hyun-Soo Kim
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(3): 221. CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of circ-FOXO3 and miR-23a in radiosensitivity of breast cancer
Elahe Abdollahi, Hossein Mozdarani, Behrooz Z. Alizadeh
Breast Cancer.2023; 30(5): 714. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Spectrum of Mucin-containing Lesions of the Breast: Multimodality Imaging Review with Pathologic Correlation
Janice N. Thai, Melinda F. Lerwill, Shinn-Huey S. Chou
RadioGraphics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Ovary: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Hyun Hee Koh, Eunhyang Park, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 326. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Metastasis of the Mucionous adenocarcinoma of breast to the mandibular gingiva: Rare case report
Ivana Mijatov, Aleksandra Fejsa Levakov, Aleksandar Spasić, Jelena Nikolić, Saša Mijatov
Medicine.2022; 101(38): e30732. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Carcinoma mucosecretor de mama HER2-positivo, un caso clínico
A.M. González Aranda, E. Martínez Gómez, A. Santana Costa, F. Arnanz Velasco, M.H. González de Diego, A. Zapico Goñi
Clínica e Investigación en Ginecología y Obstetricia.2021; 48(4): 100685. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic features of unexpectedly HER2 positive breast carcinomas: An institutional experience
Carissa LaBoy, Kalliopi P. Siziopikou, Lauren Rosen, Luis Z. Blanco, Jennifer L. Pincus
Pathology - Research and Practice.2021; 222: 153441. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef
- Mucin‐producing breast lesions: a practical approach to diagnosis
- The Prognostic Impact of Synchronous Ipsilateral Multiple Breast Cancer: Survival Outcomes according to the Eighth American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging and Molecular Subtype
- Jinah Chu, Hyunsik Bae, Youjeong Seo, Soo Youn Cho, Seok-Hyung Kim, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):396-403. Published online October 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.10.03
- 8,140 View
- 102 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the current American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system of breast cancer, only tumor size determines T-category regardless of whether the tumor is single or multiple. This study evaluated if tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and can be used to subclassify breast cancer.
Methods
We included 5,758 patients with invasive breast cancer who underwent surgery at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, from 1995 to 2012.
Results
Patients were divided into two groups according to multiplicity (single, n = 4,744; multiple, n = 1,014). Statistically significant differences in lymph node involvement and lymphatic invasion were found between the two groups (p < .001). Patients with multiple masses tended to have luminal A molecular subtype (p < .001). On Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, patients with multiple masses had significantly poorer disease-free survival (DFS) (p = .016). The prognostic significance of multiplicity was seen in patients with anatomic staging group I and prognostic staging group IA (p = .019 and p = .032, respectively). When targeting patients with T1-2 N0 M0, hormone receptor–positive, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)–negative cancer, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis also revealed significantly reduced DFS with multiple cancer (p = .031). The multivariate analysis indicated that multiplicity was independently correlated with worse DFS (hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.03 to 1.47; p = .025). The results of this study indicate that tumor multiplicity is frequently found in luminal A subtype, is associated with frequent lymph node metastasis, and is correlated with worse DFS.
Conclusions
Tumor multiplicity has prognostic value and could be used to subclassify invasive breast cancer at early stages. Adjuvant chemotherapy would be necessary for multiple masses of T1–2 N0 M0, hormone-receptor-positive, and HER2-negative cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
Neyaz Ahmad, Khushboo Rani, Zenith Kerketta, Krishna Murari, Anish Baxla, Ujala Murmu, Amit Nishant, Shreya .
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Large Format Histology in Diagnosis of Breast Carcinoma
Hari Shankar Pandey, Sanya Bhasin, Suman Kumari Pandey
NMO Journal.2025; 19(2): 189. CrossRef - Prognostic Impact of Multiple Synchronous T1 Breast Cancer
Hongki Gwak, Sung Hoo Jung, Young Jin Suh, Seok Jin Nam, Jai Hong Han, Se Jeong Oh, Eun Hwa Park, Seong Hwan Kim
Cancers.2024; 16(23): 4019. CrossRef - Deep learning-based system for automatic prediction of triple-negative breast cancer from ultrasound images
Alexandre Boulenger, Yanwen Luo, Chenhui Zhang, Chenyang Zhao, Yuanjing Gao, Mengsu Xiao, Qingli Zhu, Jie Tang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2023; 61(2): 567. CrossRef - Multicentre prospective cohort study of unmet supportive care needs among patients with breast cancer throughout their cancer treatment trajectory in Penang: a PenBCNeeds Study protocol
Noorsuzana Mohd Shariff, Nizuwan Azman, Rohayu Hami, Noor Mastura Mohd Mujar, Mohammad Farris Iman Leong Bin Abdullah
BMJ Open.2021; 11(3): e044746. CrossRef - The subgross morphology of breast carcinomas: a single-institution series of 2033 consecutive cases documented in large-format histology slides
Tibor Tot, Maria Gere, Syster Hofmeyer, Annette Bauer, Ulrika Pellas
Virchows Archiv.2020; 476(3): 373. CrossRef - Editorial for “Synchronous Breast Cancer: Phenotypic Similarities on MRI”
Uma Sharma
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2020; 52(1): 309. CrossRef - Synchronous Multiple Breast Cancers—Do We Need to Reshape Staging?
Minodora Onisâi, Adrian Dumitru, Iuliana Iordan, Cătălin Aliuș, Oana Teodor, Adrian Alexandru, Daniela Gheorghiță, Iulian Antoniac, Adriana Nica, Alexandra-Ana Mihăilescu, Sebastian Grădinaru
Medicina.2020; 56(5): 230. CrossRef - Molecular mechanism of triple‑negative breast cancer‑associated BRCA1 and the identification of signaling pathways
Feng Qi, Wen‑Xing Qin, Yuan‑Sheng Zang
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Role of Serum Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (β-hCG) in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions at a Tertiary Care Center in Jharkhand
- TFE3-Expressing Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of the Breast
- Hyunjin Kim, Jimin Kim, Se Kyung Lee, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):62-65. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.30
- 9,312 View
- 157 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) is a very rare mesenchymal tumor with a distinctive morphology and immunophenotype. PEComas usually harbor TSC2 alterations, although TFE3 translocations, which occur in MiT family translocation renal cell carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma, are also possible. We recently experienced a case of PEComa with TFE3 expression arising in the breast. An 18-year-old female patient presented with a right breast mass. Histologically, the tumor consisted of epithelioid cells with alveolar structure and showed a diffuse strong expression of HMB45 and TFE3. TSC2 was preserved. Melan A and smooth muscle actin were negative. To our knowledge, this is the first Korean case of PEComa of the breast that intriguingly presented with TFE3 expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
Anuradha Sharma, Reetika Sharma, Jyoti Bala, Monika Sharma
Journal of Mid-life Health.2025; 16(1): 107. CrossRef - Malignant lung PEComa (clear cell tumor): rare case report and literature review
Marcos Adriano Garcia Campos, Lucas Fernandes Vasques, Rafael Goulart de Medeiros, Érico Murilo Monteiro Cutrim, Ana Júlia Favarin, Sarah Rebecca Machado Silva, Gyl Eanes Barros Silva, Marcelo Padovani de Toledo Moraes, Mariana Lopes Zanatta, Diego Aparec
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cathepsin K: A Versatile Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Various Cancers
Die Qian, Lisha He, Qing Zhang, Wenqing Li, Dandan Tang, Chunjie Wu, Fei Yang, Ke Li, Hong Zhang
Current Oncology.2022; 29(8): 5963. CrossRef - Endometrioid Carcinomas of the Ovaries and Endometrium Involving Endocervical Polyps: Comprehensive Clinicopathological Analyses
Jihee Sohn, Yurimi Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2339. CrossRef - Serous Carcinoma of the Endometrium with Mesonephric-Like Differentiation Initially Misdiagnosed as Uterine Mesonephric-Like Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report with Emphasis on the Immunostaining and the Identification of Splice Site TP53 Mutation
Sangjoon Choi, Yoon Yang Jung, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(4): 717. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Differentiation of Endometrial Endometrioid Carcinoma: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics Distinct from Those of Uterine Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma
Sujin Park, Go Eun Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(8): 1450. CrossRef - Mesonephric-like Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Corpus: Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analyses Using Markers for Mesonephric, Endometrioid and Serous Tumors
Hyunjin Kim, Kiyong Na, Go Eun Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2042. CrossRef - Invasive Lobular Carcinoma With Extensive Clear Cells: A Pitfall in Diagnosis
Mark H. Kavesh, Daniel Sanchez, Jaya Ruth Asirvatham
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2020; 28(2): 169. CrossRef - Glycogen-rich Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review
Semir Vranic, Faruk Skenderi, Vanesa Beslagic, Zoran Gatalica
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2020; 28(9): 655. CrossRef - TFE3-expressing primary perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the Lymph node mimicking nodal relapse of rectal cancer
Jongmin Park, An Na Seo
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2019; 59(C): 46. CrossRef
- Malignant Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor of Ovary: A Rare Case Report
- Secretory Carcinoma Arising in a Fibroadenoma: A Brief Case Report
- Sharon Lim, Min Keun Shim, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):198-201. Published online October 4, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.01
- 7,339 View
- 118 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Breast Carcinoma within Fibroadenoma: A Systematic Review
Abdulwahid M. Salih, Lana R.A. Pshtiwan, Mohammed Gh. Hamasaeed, Sami S. Omar, Shaban Latif, Shadi H. Sidiq, Bushra O. Hussein, Hunar A. Hassan, Diyar A. Omar, Sarhang S. Abdalla, Hemn A. Hassan, Yousif M. Mahmood, Marwan N. Hassan, Dahat A.
Barw Medical Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Breast Carcinoma within Fibroadenoma: A Systematic Review
- Evaluation of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Experience in a Single Institution over a 10-Year Period
- Misun Choi, Yeon Hee Park, Jin Seok Ahn, Young-Hyuck Im, Seok Jin Nam, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):69-78. Published online December 25, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.10.05
- 12,874 View
- 268 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has been associated with favorable clinical outcome in breast cancer patients. However, the possibility that the prognostic significance of pCR differs among various definitions has not been established. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated the pathologic response after NAC in 353 breast cancer patients and compared the prognoses after applying the following different definitions of pCR: ypT0/is, ypT0, ypT0/is ypN0, and ypT0 ypN0. Results: pCR was significantly associated with improved distant disease-free survival (DDFS) regardless of the definition (ypT0/is, p = .002; ypT0, p = .008; ypT0/is ypN0, p < .001; ypT0 ypN0, p = .003). Presence of tumor deposits of any size in the lymph nodes (LNs; ypN ≥ 0(i+)) was associated with worse DDFS (ypT0 ypN0 vs ypT0 ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .036 and ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN ≥ 0(i+), p = .015), and presence of isolated tumor cells was associated with decreased overall survival (OS; ypT0/is ypN0 vs ypT0/is ypN0(i+), p = .013). Residual ductal carcinoma in situ regardless of LN status showed no significant difference in DDFS or OS (DDFS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .373 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .462; OS: ypT0 vs ypTis, p = .441 and ypT0 ypN0 vs ypTis ypN0, p = .758). In subsequent analysis using ypT0/is ypN0, pCR was associated with improved DDFS and OS in triple-negative tumors (p < .001 and p = .003, respectively). Conclusions: Based on our study results, the prognosis and rate of pCR differ according to the definition of pCR and ypT0/is ypN0 might be considered a more preferable definition of pCR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
Christine Hong Ngoc Che Thai, Selena J. An, Conner R. Haase, Julia M. Selfridge, Chris B. Agala, Philip M. Spanheimer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 209(2): 315. CrossRef - Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Study on Response Rate and Toxicity
Matt Galloway, Paula Barlow, Jody Jordan, Edward Lo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(20): 7362. CrossRef - Association of residual ductal carcinoma in situ with breast cancer treatment outcomes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy according to hormone receptor status
Eunju Shin, Tae-Kyung Yoo, Jisun Kim, Il Yong Chung, Beom Seok Ko, Hee Jeong Kim, Jong Won Lee, Byung Ho Son, Sae Byul Lee
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Mammographic Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Detection in Predicting Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Ga Eun Park, Bong Joo Kang, Sung Hun Kim, Han Song Mun
Life.2024; 14(11): 1449. CrossRef - Pathology after neoadjuvant treatment – How to assess residual disease
Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
The Breast.2022; 62: S25. CrossRef - Pathological examination of breast cancer samples before and after neoadjuvant therapy: recommendations from the Italian Group for the Study of Breast Pathology - Italian Society of Pathology (GIPaM-SIAPeC)
Nicola Fusco, Antonio Rizzo, Leopoldo Costarelli, Alfredo Santinelli, Bruna Cerbelli, Cristian Scatena, Ettore Macrì, Francesca Pietribiasi, Giulia d’Amati, Anna Sapino, Isabella Castellano
Pathologica.2022; 114(2): 104. CrossRef - Pathological complete response as a surrogate to improved survival in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Matthew G. Davey, Ferdia Browne, Nicola Miller, Aoife J. Lowery, Michael J. Kerin
BJS Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neoadjuvant therapy with doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide followed by weekly paclitaxel in early breast cancer: a retrospective analysis of 200 consecutive patients treated in a single center with a median follow-up of 9.5 years
Lisi M. Dredze, Michael Friger, Samuel Ariad, Michael Koretz, Bertha Delgado, Ruthy Shaco-Levy, Margarita Tokar, Michael Bayme, Ravit Agassi, Maia Rosenthal, Victor Dyomin, Olga Belochitski, Shai Libson, Tamar Mizrahi, David B. Geffen
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 193(3): 597. CrossRef - “No Ink on Tumor” in Breast-Conserving Surgery after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Giulia Atzori, Marco Gipponi, Chiara Cornacchia, Raquel Diaz, Marco Sparavigna, Maurizio Gallo, Tommaso Ruelle, Federica Murelli, Simonetta Franchelli, Francesca Depaoli, Daniele Friedman, Piero Fregatti
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1031. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models and Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Carmen Herrero Vicent, Xavier Tudela, Paula Moreno Ruiz, Víctor Pedralva, Ana Jiménez Pastor, Daniel Ahicart, Silvia Rubio Novella, Isabel Meneu, Ángela Montes Albuixech, Miguel Ángel Santamaria, María Fonfria, Almudena Fuster-Matanzo, Santiago Olmos Antó
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3508. CrossRef - Applying artificial intelligence technology to assist with breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction
Meredith A. Jones, Warid Islam, Rozwat Faiz, Xuxin Chen, Bin Zheng
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemotherapy response score as a prognostic tool in patients with advanced stage endometrial carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ina Jani, Ricardo R Lastra, Katherine S Brito, Chuanhong Liao, Isabel Lazo, Nita Karnik Lee, S Diane Yamada, Katherine C Kurnit
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2021; 31(6): 852. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with anlotinib in occult breast cancer: A case report and review of literature
Yu Zhang, Di Wu, Bo Zhao, Xue-Liang Tian, Tian-Cheng Yao, Feng Li, Wei-Fang Liu, Ai-Ping Shi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(4): 919. CrossRef - Pathologic Complete Response and Its Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Patient’s Survival after Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Hui Liu, Liqiong Lv, Hui Gao, Ming Cheng, Tao Huang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Impact of Surgical Margins in Breast Cancer After Preoperative Systemic Chemotherapy on Local Recurrence and Survival
K. Wimmer, M. Bolliger, Z. Bago-Horvath, G. Steger, D. Kauer-Dorner, R. Helfgott, C. Gruber, F. Moinfar, M. Mittlböck, F. Fitzal
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2020; 27(5): 1700. CrossRef - Predictive factors for omitting lymphadenectomy in patients with node‐positive breast cancer treated with neo‐adjuvant systemic therapy
Sergi Fernandez‐Gonzalez, Catalina Falo, Maria J. Pla, Paula Verdaguer, Diana Nuñez, Anna Guma, Teresa Soler, Andrea Vethencourt, Silvia Vázquez, Maria Eulalia Fernandez‐Montoli, Miriam Campos, Sonia Pernas, Miguel Gil, Jordi Ponce, Amparo Garcia‐Tejedor
The Breast Journal.2020; 26(5): 888. CrossRef - Is There a Role for Post-Mastectomy Radiotherapy for T1-2N1 Breast Cancers With Node-Positive Pathology After Patients Become Node-Negative Pathology Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?
Qian Wang, Jingjing Zhao, Xiaowei Han, Puchun Er, Xiangying Meng, Jinyan Shi, Huiru Sun, Jingyang Zhu, Li Zhu, Shikai Wu, Wencheng Zhang, Bing Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic role of microRNA 182 and microRNA 18a in locally advanced triple negative breast cancer
Rajat Bajaj, Rupal Tripathi, T. S. Sridhar, Aruna Korlimarla, Kumardeep Dutta Choudhury, Moushumi Suryavanshi, Anurag Mehta, Dinesh Chandra Doval, Elda Tagliabue
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242190. CrossRef - Association of Pathologic Complete Response with Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Min Huang, Joyce O'Shaughnessy, Jing Zhao, Amin Haiderali, Javier Cortés, Scott D. Ramsey, Andrew Briggs, Peter Hu, Vassiliki Karantza, Gursel Aktan, Cynthia Z. Qi, Chenyang Gu, Jipan Xie, Muhan Yuan, John Cook, Michael Untch, Peter Schmid, Peter A. Fasch
Cancer Research.2020; 80(24): 5427. CrossRef - Multiparametric MR imaging to assess response following neoadjuvant systemic treatment in various breast cancer subtypes: Comparison between different definitions of pathologic complete response
G Santamaría, X Bargalló, S Ganau, I Alonso, M Muñoz, M Mollà, PL Fernández, A Prat
European Journal of Radiology.2019; 117: 132. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of residual nodal burden using lymph node ratio in locally advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Reshu Agarwal, Arun Philip, Keechilat Pavithran, Anupama Rajanbabu, Gaurav Goel, DK Vijaykumar
Indian Journal of Cancer.2019; 56(3): 228. CrossRef - Application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in occult breast cancer
Haisong Yang, Ling Li, Mengmeng Zhang, Shiyong Zhang, Shu Xu, Xiaoxia Ma
Medicine.2017; 96(40): e8200. CrossRef - Wnt7a Deficiency Could Predict Worse Disease-Free and Overall Survival in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Kijong Yi, Kyueng-Whan Min, Young Chan Wi, Yeseul Kim, Su-Jin Shin, Min Sung Chung, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik
Journal of Breast Cancer.2017; 20(4): 361. CrossRef
- Differential prognostic value of residual nodal burden in breast cancer subtypes
- A Rare Case of Thymic Gangliocytic Paraganglioma
- Jung Wook Yang, Joungho Han, Hyun Woo Lee, Soo Youn Cho, Hong Kwan Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):165-167. Published online October 8, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.15
- 9,651 View
- 56 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Composite gangliocytoma/neuroma and neuroendocrine tumour: a contemporary analysis of 71 cases shows risk factors for metastasis
Luiz M Nova‐Camacho, Changqing Ma, Ibrahim Abukhiran, Nuha Shaker, M‐Nasan Abdul Baki, Katrina Collins, Iván González, Timothy Chao, Zhaohai Yang, Monika Vyas, Michael Feely, Andrew M Bellizzi, Diana Agostini‐Vulaj, Aaron R Huber, Alexandros D Polydorides
Histopathology.2025; 87(6): 933. CrossRef - Primary gangliocytic paraganglioma of the lung
Yee Sing Lin, Christopher Cao, Wendy A. Cooper, Veronica Ka-Yan Cheung
Pathology.2024; 56(3): 423. CrossRef - Pulmonary gangliocytic paraganglioma: An under-recognized mimic of carcinoid tumor
Julia R. Naso, Diping Wang, Arthur O. Romero, Timothy Leclair, Peter Smit, Jennifer M. Boland, Andrew L. Folpe, Melanie C. Bois
Human Pathology.2024; 146: 23. CrossRef - Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Paragangliomas and Pheochromocytomas
Ozgur Mete, Sylvia L. Asa, Anthony J. Gill, Noriko Kimura, Ronald R. de Krijger, Arthur Tischler
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(1): 90. CrossRef - The Rarest of Rare Thymic Lesions: A 10-Year Surgical Pathology Experience
Fiorella Calabrese, Francesco Fortarezza, Federica Pezzuto, Francesca Lunardi, Giovanni Comacchio, Marta Sbaraglia, Giulia Pasello, Giuseppe Marulli, Angelo Paolo Dei Tos, Federico Rea
Cancers.2021; 13(16): 4056. CrossRef - Gangliocytic Paraganglioma of the Minor Papilla of the Duodenum
Hiroyuki Matsubayashi, Hirotoshi Ishiwatari, Toru Matsui, Shinya Fujie, Katsuhiko Uesaka, Teiichi Sugiura, Yukiyasu Okamura, Yusuke Yamamoto, Ryo Ashida, Takaaki Ito, Keiko Sasaki, Hiroyuki Ono
Internal Medicine.2017; 56(9): 1029. CrossRef - Endoscopic resection of a periampullary gangliocytic paraganglioma of the duodenum
Christoph Paasch, Michael Hünerbein, Franz Theissig
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2016; 29(C): 39. CrossRef - Duodenal Rare Neuroendocrine Tumor: Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients with Gangliocytic Paraganglioma
Yoichiro Okubo, Tomoyuki Yokose, Osamu Motohashi, Yohei Miyagi, Emi Yoshioka, Masaki Suzuki, Kota Washimi, Kae Kawachi, Madoka Nito, Tetsuo Nemoto, Kazutoshi Shibuya, Yoichi Kameda
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- Composite gangliocytoma/neuroma and neuroendocrine tumour: a contemporary analysis of 71 cases shows risk factors for metastasis
- Biliary Granular Cell Tumor
- Changwon Jung, Ilyeong Heo, Sang Bum Kim, Sunhoo Park, Soo Youn Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(1):89-91. Published online January 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.07
- 9,587 View
- 65 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Hybrid Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (Granular Cell Tumor + Schwannoma) of Cystic Duct Origin, Presenting with Gallbladder Enlargement and Abdominal Pain
Akira Imoto, Masahiro Yamamura, Atsushi Okuda, Nao Kawaguchi, Koji Komeda, Shigeru Kawabata, Emi Yasuda, Yoshitaka Kurisu, Takeshi Ogura, Sang-Woong Lee, Yoshinobu Hirose, Hiroki Nishikawa
Internal Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A rare case of granular cell tumor of gall bladder
Sunil Dhakal, Sapana Bhandari, Avinam H Kandangwa
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Granular cell tumor of the gallbladder: case report and review of the literature
Walid E Abdelrahim, Salwa O Mekki, Fatima M A Ali, Sarra Ahmed H Mukhtar, Kamal E Elssidig, Elthir A G Khalil, Omer Alfarog
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Malignant Granular Cell Tumor of the Bile Duct
Patrick L. Quinn, Eihab Abdelfatah, Mark A. Galan, Sushil K. Ahlawat, Ravi J. Chokshi
ACG Case Reports Journal.2019; 6(8): e00193. CrossRef - Multifocal granular cell tumour of the biliary tree
Felip Vilardell, Marina Pardina, Jorge Juan Olsina, Xavier Matias-Guiu
BMJ Case Reports.2018; 11(1): e226352. CrossRef - Solitary, multiple, benign, atypical, or malignant: the “Granular Cell Tumor” puzzle
Isidro Machado, Julia Cruz, Javier Lavernia, Antonio Llombart-Bosch
Virchows Archiv.2016; 468(5): 527. CrossRef
- A Hybrid Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (Granular Cell Tumor + Schwannoma) of Cystic Duct Origin, Presenting with Gallbladder Enlargement and Abdominal Pain
- Primary Myxoid Leiomyoma of the Liver
- Hee Seung Choi, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Sang Bum Kim, Sunhoo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):54-57. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.54
- 9,815 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Herein, we report a case of primary myxoid leiomyoma of the liver. A 60-year-old woman complained of upper abdominal fullness. Computed tomography showed a solid tumor (8 cm) in the liver. The patient underwent right hepatectomy and histological findings from the resected specimen revealed scattered bland spindle cells in a background of exuberant myxoid material. The tumor cells were immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin and desmin. No other lesions were found elsewhere in the body. Thus, the tumor was diagnosed as a primary myxoid leiomyoma of the liver.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatic Myxoid Leiomyoma: A Very Rare Tumor
João Fraga, Rui Caetano Oliveira, Luigi Terracciano, Mário Rui Silva, Maria Augusta Cipriano
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 27(5): 352. CrossRef - A Firm Hepatic Mass Cannot Be Penetrated by US-Guided Needle Biopsy
Suk Hyun Jang, Sun Moon Kim, Jang Sihn Sohn, Ki Hyun Ryu, Hyung Bin Yuk
Clinical Ultrasound.2016; 1(2): 126. CrossRef
- Hepatic Myxoid Leiomyoma: A Very Rare Tumor
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Parathyroid Lesions
- Ilyeong Heo, Sunhoo Park, Chang Won Jung, Jae Soo Koh, Seung-Sook Lee, Hyesil Seol, Hee Seung Choi, Soo Youn Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):466-471. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.466
- 11,985 View
- 123 Download
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background There has been an increase in the use of fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) for the diagnosis of parathyroid lesions (PLs). Differentiation between a thyroid lesion and a PL is not easy because of their similar features. We reviewed parathyroid aspirates in our institution and aimed to uncover trends in diagnostic criteria.
Methods We selected 25 parathyroid aspirates (from 6 men and 19 women) confirmed surgically or immunohistochemically from 2006 to 2011.
Results Major architectural findings of PLs include scattered naked nuclei, loose clusters, a papillary pattern with a fibrovascular core, tight clusters, and a follicular pattern. These architectures were commonly admixed with one another. Cytological features included anisokaryosis, stippled chromatin, a well-defined cell border, and oxyphilic cytoplasm. Eighteen of the 25 patients were diagnosed with PL using FNAC. Seven patients had been misdiagnosed with atypical cells (n=2), benign follicular cells (n=2), adenomatous goiter (n=2) and metastatic carcinoma (n=1) in FNAC. Using clinicoradiologic data, the sensitivity of the cytological diagnosis was 86.7%. The cytological sensitivity decreased to 50% without this information.
Conclusions FNAC of PL is easily confused with thyroid lesions. A combination of cytological parameters and clinical data will be required to improve the diagnostic sensitivity of PLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic approach to FNA biopsy of cystic lesions of the head and neck
Stefen Andrianus, Olivia Leung, Zubair Baloch
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Sonographic Features of Atypical and Initially Missed Parathyroid Adenomas: Lessons Learned From a Single-Center Cohort
Seyfettin Ilgan, Berna İmge Aydoğan, Özdeş Emer, Cüneyd Anıl, Alptekin Gürsoy, Mustafa Cesur, Banu Bilezikçi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): 439. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration biopsy of parathyroid; is it meaningful? A cytologic study of 81 cases with histological and clinical correlations
Elwira Bakuła‐Zalewska, Joanna Długosińska, Agata Stanek‐Widera, Piotr Góralski, Jacek Gałczyński, Agnieszka Żyłka, Monika Durzyńska, Marek Dedecjus
Cytopathology.2024; 35(3): 362. CrossRef - Primary hyperparathyroidism with intrathyroidal location of parathyroid adenoma
M. I. Fadeeva, L. Z. Vasifova, E. A. Savelyeva, L. S. Urusova, A. K. Eremkina, N. G. Mokrysheva
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2024; (16): 230. CrossRef - Diagnosis of parathyroid incidentaloma detected on thyroid ultrasonography: the role of fine-needle aspiration cytology and washout parathyroid hormone measurements
Boeun Lee, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hwan Baek
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(1): 129. CrossRef - Intrathyroidal parathyroid adenomas: Scoping review on clinical presentation, preoperative localization, and surgical treatment
Shravan V. Gowrishankar, Rohan Bidaye, Tilak Das, Veronika Majcher, Brian Fish, Ruth Casey, Liam Masterson
Head & Neck.2023; 45(3): 706. CrossRef - A stepwise approach to fine needle aspiration cytology of lymph nodes
Yosep Chong, Gyeongsin Park, Hee Jeong Cha, Hyun-Jung Kim, Chang Suk Kang, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 196. CrossRef - The Utility of Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Mediastinal Lesions
Uma Kundu, Qiong Gan, Deepak Donthi, Nour Sneige
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2400. CrossRef - Case presentation of the smallest non-functional parathyroid carcinoma and review of the literature
S. Ivaniš, M. Jovanović, D. Dunđerović, G. Zorić, B. Odalović, N. Slijepčević, K. Taušanović, B. Rovčanin, M. Buzejić, D. Vučen, B. Stepanović, J. Ilić, M. Parezanović, M. Marinković, M. Stojanović, A. Tošković, I. Mojsić, V. Živaljević
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2023; 280(12): 5637. CrossRef - Utility of parathyroid hormone immunocytochemistry in fine needle aspiration diagnosis of parathyroid tissue
Ruhani Sardana, Rita Abi‐Raad, Adebowale J. Adeniran, Guoping Cai
Cytopathology.2023; 34(6): 597. CrossRef - Parathyroid carcinoma: impact of preoperative diagnosis on the choice of surgical procedure
Yoshitaka Kawai, Yo Kishimoto, Hisanobu Tamaki, Takashi Fujiwara, Ryo Asato, Koji Ushiro, Shogo Shinohara, Shinpei Kada, Shinji Takebayashi, Tsuyoshi Kojima, Shuya Otsuki, Masakazu Miyazaki, Yohei Kumabe, Koichi Omori
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(10): 969. CrossRef - The Value of Preoperative and Intraoperative Ultrasound in the Localization of Intrathyroidal Parathyroid Adenomas
Wei Zhao, Ruigang Lu, Li Yin, Bojun Wei, Mulan Jin, Chun Zhang, Ruijun Guo, Xiuzhang Lv
Journal of Investigative Surgery.2022; 35(4): 752. CrossRef - Cyto‐morphological features of parathyroid lesions: Fine‐needle aspiration cytology series from an endocrine tumor referral center
Sanna Steen, Martin Hysek, Jan Zedenius, Henrik Falhammar, Carl Christofer Juhlin
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022; 50(2): 75. CrossRef - Non‐secreting parathyroid carcinoma in a dog
Giovanni Tremolada, Paula Schaffer, Kathryne Pitt
Veterinary Record Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration of an intrathyroidal parathyroid carcinoma mimicking a primary thyroid anaplastic carcinoma: A case report with review of the literature
Fatima Mir, Prih Rohra, Nfn Aakash, Karina Furlan, Ritu Ghai, Vijaya Reddy, Lin Cheng, Paolo Gattuso
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Fine‐needle aspiration of parathyroid adenomas: Indications as a diagnostic approach
Ayana Suzuki, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Risa Kanematsu, Aki Tanaka, Naoki Yamao, Miyoko Higuchi, Toshitetsu Hayashi, Seiji Kuma, Akihiro Miya, Akira Miyauchi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2021; 49(1): 70. CrossRef - Two-year changes of biochemical profiles and bone mineral density after percutaneous ultrasound-guided microwave ablation for primary hyperparathyroidism
Wenjun Wu, Qi Zhou, Shihao Xu, Siqin An, Feixia Shen, Huanbin Li, Xiaohua Gong, Xiaojun Chen
Endocrine.2021; 71(2): 476. CrossRef - Multimodal imaging of thyroid cancer
Katrin Brauckhoff, Martin Biermann
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2020; 27(5): 335. CrossRef - Major Clues and Pitfalls in the Differential Diagnosis of Parathyroid and Thyroid Lesions Using Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Hwa Jeong Ha, Eun Ju Kim, Jung-Soon Kim, Myung-Soon Shin, Insup Noh, Sunhoo Park, Jae Soo Koh, Seung-Sook Lee
Medicina.2020; 56(11): 558. CrossRef - Comparison of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation and parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism
Fangyi Liu, Xiaoling Yu, Zhoulu Liu, Zhi Qiao, Jianping Dou, Zhigang Cheng, Zhiyu Han, Jie Yu, Ping Liang
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2019; 36(1): 834. CrossRef - Giant parathyroid adenoma: a case report and review of the literature
Mohamed S. Al-Hassan, Menatalla Mekhaimar, Walid El Ansari, Adham Darweesh, Abdelrahman Abdelaal
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Water Clear Cell Parathyroid Adenoma: A Report of Two Cases
Abdelrahman M. Radaideh, Hisham Alkhalidi, Mohamad Nusier, Mohammad Alqudah
Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research.2019; : 33. CrossRef - Cytological challenges in the diagnosis of intrathyroidal parathyroid carcinoma: A case report and review of literature
Meera Balakrishnan, Smiley Annie George, Sayed Hashim Rajab, Issam M Francis, Kusum Kapila
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(1): 47. CrossRef - Association of parathyroid carcinoma and thyroid disorders: A clinical review
Alfredo Campennì, Salvatore Giovinazzo, Salvatore Antonio Pignata, Francesca Di Mauro, Domenico Santoro, Lorenzo Curtò, Francesco Trimarchi, Rosaria Maddalena Ruggeri, Sergio Baldari
Endocrine.2017; 56(1): 19. CrossRef - Fine needle cytology pre‐surgical differentiation of parathyroid neoplasms: Is it reliable?
A. Caleo, M. Vitale, L. Valvano, M. Siano, B. Angrisani, M. Forlenza, A. Massari, A. Puzziello, F. Salzano, P. Zeppa
Cytopathology.2017; 28(4): 273. CrossRef - Identification of parathyroid tissue in thyroid fine‐needle aspiration: A combined approach using cytology, immunohistochemical, and molecular methods
Robert P. Domingo, Lorna L. Ogden, Laura C. Been, Giulia C. Kennedy, S. Thomas Traweek
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2017; 45(6): 526. CrossRef - Cytomorphologic features distinguishing Bethesda category IV thyroid lesions from parathyroid
Simon Sung, Anjali Saqi, Elizabeth M. Margolskee, John P. Crapanzano
CytoJournal.2017; 14: 10. CrossRef - Core-needle biopsy for the preoperative diagnosis of follicular neoplasm in thyroid nodule screening: A validation study
Sung Hak Lee, Gyeong Sin Park, So Lyung Jung, Min-Hee Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Dong Jun Lim, Chan Kwon Jung
Pathology - Research and Practice.2016; 212(1): 44. CrossRef - Parathyroid lesions: Difficult diagnosis on cytology
Charu Agarwal, Manju Kaushal
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2016; 44(8): 704. CrossRef - Intrathyroidal parathyroid adenoma: Diagnostic pitfalls on fine‐needle aspiration: Two case reports and literature review
Chang Shi, Hongwei Guan, Wenjing Qi, Jialin Ji, Jialing Wu, Feng Yan, Huali Wang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2016; 44(11): 921. CrossRef - Diagnostic value of GATA-3 in cytological identification of parathyroid tissues
Nami Takada, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ayana Suzuki, Miyoko Higuchi, Seiji Kuma, Akira Miyauchi
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(7): 621. CrossRef - PARATHYROID CYTOLOGY: A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA
Naval Kishore Bajaj, Shrinivas Somalwar, Akhtar Mohammad, Ezhil Arasi Nagamuthu
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2016; 3(71): 3849. CrossRef - Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Parathyroid Lesions
Teklu Legesse, Paul N. Staats
Pathology Case Reviews.2015; 20(5): 227. CrossRef - A nonfunctioning parathyroid carcinoma misdiagnosed as a follicular thyroid nodule
Filomena Cetani, Gianluca Frustaci, Liborio Torregrossa, Silvia Magno, Fulvio Basolo, Alberto Campomori, Paolo Miccoli, Claudio Marcocci
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diagnostic approach to FNA biopsy of cystic lesions of the head and neck
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Pleomorphic Carcinomas of the Lung
- Hee Seung Choi, Hyesil Seol, Il Yeong Heo, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Sunhoo Park, Jae Soo Koh, Seung-Sook Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):576-582. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.576
- 9,117 View
- 42 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Pleomorphic carcinoma (PC) is a rare pulmonary malignancy. Because of its rarity and histological heterogeneity, cytopathologists might suspect PC only rarely on the basis of its cytological specimen. In addition, cytological findings from fine needle aspiration (FNA) specimens have rarely been described. Hence, we investigated the cytological features of FNA in the cases of PC.
Methods We reviewed 7 FNA specimens of PC. The patients had undergone surgical resection at the Korea Cancer Center Hospital between 2007 and 2011. The cytological features of PC were assessed and compared with the histopathological features of the corresponding surgical specimen. Immunocytochemical analysis with cytokeratin and vimentin was performed on the cell blocks.
Results The tumor cells were either dispersed or arranged in loose aggregates, and generally lacked any glandular or squamous differentiation. Pleomorphic or spindle shape tumor cells were observed, and mono-, bi-, or multi-nucleated giant cells were frequently observed. The background showed necrosis and contained numerous lymphocytes and neutrophils. Immunocytochemically, the tumor cells were positive for cytokeratin and vimentin.
Conclusions PC displays characteristic cytological features. It might therefore be possible to make an accurate diagnosis of PC by assessing the degree of nuclear atypia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcomatoid carcinoma in cytology: Report of a rare entity presenting in pleural and pericardial fluid preparations
Atreyee Basu, Andre L. Moreira, Anthony Simms, Tamar C. Brandler
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(8): 813. CrossRef - Cytological Evaluation of Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung
Kevin Kuan, Samer N. Khader, Siba El Hussein
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2019; 47(9): 961. CrossRef - Combined small cell carcinoma with giant cell carcinoma component of the lung: A case successfully diagnosed by computed tomography‑guided fine‑needle aspiration cytology
Yusuke Ebisu, Mitsuaki Ishida, Tomohito Saito, Tomohiro Murakawa, Yoshiko Uemura, Koji Tsuta
Oncology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary Pleomorphic Carcinoma Detected as a Result of Pneumothorax and the Subsequent Occurrence of Multiple Cystic Metastases
Hideaki Yamakawa, Masahiro Yoshida, Masami Yabe, Yuri Baba, Emiri Baba, Hiroaki Katagi, Takeo Ishikawa, Masamichi Takagi, Takeo Nakada, Tadashi Akiba, Kazuyoshi Kuwano
Case Reports in Medicine.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma with multiple metastases to the right posterior knee complicated by paraneoplastic hypercalcemia
PENG-FEI LI, CHENG-HSIANG LO, SHAN-HAN YANG, PING-YING CHUNG, CHING-LIANG HO
Oncology Letters.2014; 7(2): 452. CrossRef
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma in cytology: Report of a rare entity presenting in pleural and pericardial fluid preparations
- Primary Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma Arising in the Mesentery: Case Report of an Extremely Rare Mesenteric Sarcoma Confirmed by Molecular Detection of a
SYT-SSX2 Fusion Transcript - Han Suk Ryu, Ilyeong Heo, Jae Soo Koh, Sung-Ho Jin, Hye Jin Kang, Soo Youn Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):187-191. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.187
- 7,806 View
- 42 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Synovial sarcoma arises in the para-articular tissues, and it can also occur in various unexpected sites. We report a rare case of primary monophasic synovial sarcoma (MSS) arising in the mesentery. A 59-year-old man presented with a palpable abdominal mass. On microscopic examination, the entire tumor comprised a dense proliferation of the spindle cells without epithelial components. The tumor cells were positive for transducin-like enhancer of split 1, bcl-2, epithelial membrane antigen and CD99 but negative for CD34, CD117, alpha-smooth muscle actin, cytokeratin, and calretinin on immunohistochemistry. The reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction revealed a single 151-bp fragment representing the
SYT-SSX2 fusion transcript. Because mesenteric MSS is extremely rare and many cases display histologic findings that overlap with those of more frequently involved tumors such as hemangiopericytoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor, there is a chance of making an incorrect diagnosis that can result in an inappropriate treatment.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of primary mesenteric synovial sarcoma: a challenging presentation
Nihed Abdessayed, Malek Barka, Samiha Mabrouk, Zeineb Nfikha, Zeineb Maatoug, Yosra Fejji, Mohamed Salah Jarrar, Sabri Youssef, Moncef Mokni
Surgical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Giant solitary fibrous tumor of the pelvis: A case report and review of literature
Gerardo Palmieri, Carmine Grassi, Luigi Conti, Filippo Banchini, Maria Diletta Daccò, Gaetano M. Cattaneo, Patrizio Capelli
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 77: S52. CrossRef - Tumeur neuroectodermique gastro-intestinale (GNET) : à propos d’un cas de tumeur du grêle avec métastases hépatiques
Thibault Kervarrec, Claire Lecointre, Rémy Kerdraon, Guido Bens, Arnaud Piquard, Patrick Michenet
Annales de Pathologie.2015; 35(6): 506. CrossRef
- A case of primary mesenteric synovial sarcoma: a challenging presentation
- Comparison of the Expression of Variants of CD44 between Node-positive and Node-negative Breast Carcinomas.
- In Ae Park, Ho Chang Lee, Soo Youn Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(3):172-180.
- 2,023 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study is to determine the value of CD44 and its splice variants as markers for the metastatic potential of infiltrating ductal carcinomas of the breast.
METHODS
Tissue samples of infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast were examined for the expression of standard CD44 (CD44H) and s CD44 isoforms, v3, v4-5 and v6 in 41 node-positive and 31 node-negative cases. The immunohistochemistry results were correlated with other clinicopathologic parameters, and these results were correlated with accompanying high grade and non-high grade DCIS areas of the tumors in both node-positive and node-negative cases.
RESULTS
The expression of CD44 in the invasive tumor areas and in the metastatic foci of the lymph nodes showed a statistically significant correlation. The expression of CD44H in the invasive tumor areas and the DCIS area showed a statistically significant correlation in the lymph node (-) group. There was statistical significance between the CD44 H and CD44v3 expressions and the histologic grade of the invasive tumor in the cases with positive lymph nodes. There was no statistical significance between CD44 expression and lymph node metastasis, tumor size and type of tumor margin.
CONCLUSIONS
We conclude that changes in the CD44 expression in breast cancer occur early in breast carcinogenesis, and this is involved in tumor differentiation, but we could not establish any correlation between the expression of the CD44 variant isoforms and the metastasis of breast cancer.
- Differential Diagnosis between Small Cell Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma of Lung in Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology.
- Young Hee Choi, Jae Soo Koh, Sunhoo Park, Min Suk Kim, Soo Youn Cho, Jung Soon Kim, Hwa Jung Ha, Seung Sook Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(2):120-125.
- 2,801 View
- 71 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distinguishing small cell carcinoma from other lung malignancies is of great clinico-therapeutic significance. Small cell carcinoma is an aggressive tumor with a tendency to metastasize early. Survival time if untreated is low but this tumor is highly responsive to chemotherapy. We have occasionally experienced difficulties in differentiation between adenocarcinoma and small cell carcinoma of the lung in fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). The aim of this study was to investigate the possibility of distinguishing small cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma of the lung in FNAC. We evaluated cytomorphological features of FNAC specimens from 62 small cell carcinomas and 57 adenocarcinomas from the lung that were confirmed by biopsy and/or immunohistochemistry on cell block. Cytomorphological details of the two tumors were compared. Nuclear smearing and nearly absent cytoplasm were the most distinct findings in small cell carcinoma compared to adenocarcinoma (p<0.05). Necrotic background, architecture and chromatin pattern, nuclear molding and nucleoli were significantly different (p<0.05). Nuclear size, nuclear membrane nature and nuclear size variation however were not helpful in distinguishing the two tumors. Combining several features described above, small cell carcinoma can be properly differentiated from adenocarcinoma on FNAC. FNAC is proposed as a diagnostic tool of small cell carcinoma of the lung in the case of inaccessibility to biopsy, and so may allow the proper therapeutic strategies to be determined in such cases.
- Cytomorphologic Comparison of Hodgkin Lymphoma and Anaplastic Large cell Lymphoma in Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology.
- Seung Sook Lee, Jae Soo Koh, Sunhoo Park, Min Suk Kim, Soo Youn Cho, Soo Young Chung, Han Suk Ryu, Jung Soon Kim, Hwa Jung Ha, Baek Youl Ryoo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(2):126-135.
- 2,936 View
- 62 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To study the differentiating cytomorphological features of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) using fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), cytomorphological features of 16 patients with HL (n=8) or ALCL (n=8) were analyzed. In the initial cytological diagnosis prior to biopsy, HLs were properly diagnosed in 4 out of 8 cases (4 HL, 2 atypical, 2 benign), whereas all ALCL were diagnosed as malignancies. However, correct diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) was made in only two ALCL patients (2 NHL, 1 HL, 1 sarcoma, 4 malignancy without specific type). Overall, the percentage of large abnormal cells ranged from 30% to 90% in ALCL except for one case, whereas it was less than 5% in all 8 HL. A spectrum of atypical cells was more characteristic of ALCL. In contrast, HL showed an sharp difference between reactive lymphoid cells and neoplastic ones (bimorphic pattern). Moreover, the emergence of kidney-shaped abnormal cells or wreath-like multinucleated cells was helpful in diagnosing ALCL. The combination of thesefeatures would be useful in differentiating HL and ALCL. Nevertheless, these two types of lymphomas cannot be definitely distinguished based on cytomorphological features alone. Therefore, the aim of FNAC would be to suggest a specific diagnosis and indicate the need for a biopsy.
- Bilateral Mammary Metastasis of Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma: A Case Report.
- Soo Youn Cho, Ho Chang Lee, Chong Jai Kim, Min Suk Kim, Sun Hoo Park, Eui Keun Ham, In Ae Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(5):365-368.
- 2,190 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An alveolar soft part sarcoma(ASPS) is a rare malignant soft tissue tumor, which metastasizes to the lung, bone and brain. Recently, we encountered an unusual case of a metastatic ASPS to the bilateral breasts in a 27-year-old woman. She had undergone surgery for an ASPS in her right thigh two years ago, which metastasized to the breast on three occasions, 15 months, 20 months and two years after surgery.
- Endometrial Mucinous Adenocarcinoma with Extensive Squamous Differentiation: A Case Report.
- Ho chang Lee, Pil Gyu Hwang, Soo Youn Cho, Young S Park, In Ae Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2003;37(6):438-441.
- 2,389 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Endometrial mucinous adenocarcinoma occurs in 1-9% of endometrial adenocarcinomas and adenocarcinoma with squamous differentiation in approximately 25%. We report a rare case of mucinous adenocarcinoma with squamous differentiation in a 53-year-old woman. Curetting biopsies of the endometrial lesion were taken twice after hormone replacement therapy, which lasted for four months. Because the squamous differentiation was so extensive, the initial diagnosis based on each curetting specimen was squamous papilloma. A total hysterectomy was performed and the tumor was revealed to be a mucinous adenocarcinoma with squamous differentiation. We subsequently discussed the pathogenesis and prognosis of this type of tumor.

 E-submission
E-submission



 First
First Prev
Prev



