Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Clinicopathologic significance of the delta-like ligand 4, vascular endothelial growth factor, and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in gallbladder cancer
- Sujin Park, Junsik Kim, Woncheol Jang, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Kee-Taek Jang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):113-122. Published online March 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.02.01
- 5,487 View
- 112 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is usually detected in advanced stages with a low 5-year survival rate. Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha (HIF2α) have been studied for their role in tumorigenesis and potential for therapeutic target, and multiple clinical trials of the agents targeting them are ongoing. We investigated the expression of these markers in surgically resected GBC and tried to reveal their association with the clinicopathologic features, mutual correlation of their expression, and prognosis of the GBC patients by their expression.
Methods
We constructed the tissue microarray blocks of 99 surgically resected GBC specimens and performed immunohistochemistry of DLL4, VEGF, and HIF2α. We used the quantitative digital image analysis to evaluate DLL4 and VEGF expression, while the expression of HIF2α was scored manually.
Results
The expression of VEGF and HIF2α showed a significant trend with tumor differentiation (p= .028 and p= .006, respectively). We found that the high DLL4 and VEGF expression were significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis (p= .047, both). The expression of VEGF and HIF2α were significantly correlated (p < .001). The GBC patients with low HIF2α expression showed shorter recurrence-free survival than those with high HIF2α expression.
Conclusions
This study suggested the possibility of the usage of DLL4 and VEGF to predict the lymph node metastasis and the possibility of VEGF and HIF2α to predict the expression level mutually. Further studies may be needed to validate our study results and eventually accelerate the introduction of the targeted therapy in GBC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dedifferentiated Leiomyosarcoma of the Uterine Corpus with Heterologous Component: Clinicopathological Analysis of Five Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution and Comprehensive Literature Review
Suyeon Kim, Hyunsik Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2024; 14(2): 160. CrossRef - Identification of Key Immune Infiltration Related Genes Involved in Aortic Dissection Using Bioinformatic Analyses and Experimental Verification
Lin Zheng, Yusi Yang, Jie Liu, Tianliang Zhao, Xin Zhang, Lihua Chen
Journal of Inflammation Research.2024; Volume 17: 2119. CrossRef
- Dedifferentiated Leiomyosarcoma of the Uterine Corpus with Heterologous Component: Clinicopathological Analysis of Five Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution and Comprehensive Literature Review
- Significance of tumor-associated neutrophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-invasive and invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Wael Abdo Hassan, Ahmed Kamal ElBanna, Noha Noufal, Mohamed El-Assmy, Hany Lotfy, Rehab Ibrahim Ali
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(2):88-94. Published online January 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.11.06
- 7,472 View
- 325 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and lymphocytes play essential roles in promoting or combating various neoplasms. This study aimed to investigate the association between tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and lymphocytes and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in the progression of urothelial carcinoma.
Methods
A total of 106 patients diagnosed with urothelial carcinoma were was. Pathological examination for tumor grade and stage and for tumor-infiltrating neutrophils, both CD4 and CD8+ T lymphocytes, as well as the neutrophil- to-lymphocyte ratio were evaluated.
Results
The presence of neutrophils and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio correlated with high-grade urothelial neoplasms. In both low- and high-grade tumors, the lymphocytes increased during progression from a non-invasive neoplasm to an early-invasive neoplasm. CD8+ T lymphocytes increased in low-grade non–muscle-invasive tumors compared to non-invasive tumors. Additionally, there was a significant decrease in CD8+ T lymphocytes during progression to muscle-invasive tumors.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that tumor-infiltrating neutrophils and CD8+ T lymphocytes have a significant effect on tumor grade and progression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic role of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in high‐risk BCG‐naïve non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical gemcitabine/docetaxel
Mohamad Abou Chakra, Riitta Lassila, Nancy El Beayni, Sarah L. Mott, Michael A. O'Donnell
BJU International.2025; 135(1): 125. CrossRef - Understanding the Dual Role of Macrophages in Tumor Growth and Therapy: A Mechanistic Review
Muhammad Summer, Saima Riaz, Shaukat Ali, Qudsia Noor, Rimsha Ashraf, Rana Rashad Mahmood Khan
Chemistry & Biodiversity.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-Talk Between Cancer and Its Cellular Environment—A Role in Cancer Progression
Eliza Turlej, Aleksandra Domaradzka, Justyna Radzka, Dominika Drulis-Fajdasz, Julita Kulbacka, Agnieszka Gizak
Cells.2025; 14(6): 403. CrossRef - Global trends in tumor-associated neutrophil research: a bibliometric and visual analysis
Shaodong Li, Peng Dong, Xueliang Wu, Zhenhua Kang, Guoqiang Yan
Frontiers in Immunology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Tumor-associated neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in lung cancer: antitumor/protumor insights and therapeutic implications
Milad Sheervalilou, Mostafa Ghanei, Masoud Arabfard
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction of a column-line graphical model of poor outcome of neoadjuvant regimens for muscle-invasive bladder cancer based on NLR, dNLR and SII indicators
Bo Hu, Longsheng Wang, Shanna Qu, Tao Zhang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning of Urine Cytology Highlights Increased Neutrophil Count in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma
Moe Kameda, Sayaka Kobayashi, Yoshimi Nishijima, Ryosuke Akuzawa, Rio Kaneko, Rio Shibanuma, Seiji Arai, Hayato Ikota, Kazuhiro Suzuki, Hideaki Yokoo, Masanao Saio
Journal of Cytology.2025; 42(3): 124. CrossRef - Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Prognostic Implications, Predictive Value, and Future Perspectives
Roberta Mazzucchelli, Angelo Cormio, Magda Zanelli, Maurizio Zizzo, Andrea Palicelli, Andrea Benedetto Galosi, Francesca Sanguedolce
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(22): 12032. CrossRef - Immune cell networking in solid tumors: focus on macrophages and neutrophils
Irene Di Ceglie, Silvia Carnevale, Anna Rigatelli, Giovanna Grieco, Piera Molisso, Sebastien Jaillon
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry assessment of tissue neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts outcomes in melanoma patients treated with anti-programmed cell death 1 therapy
Renan J. Teixeira, Vinícius G. de Souza, Bruna P. Sorroche, Victor G. Paes, Fabiana A. Zambuzi-Roberto, Caio A.D. Pereira, Vinicius L. Vazquez, Lidia M.R.B. Arantes
Melanoma Research.2024; 34(3): 234. CrossRef - Association between alteration of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, cancer antigen-125 and surgical outcomes in advanced stage ovarian cancer patient who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Ponganun Tuntinarawat, Ratnapat Tangmanomana, Thannaporn Kittisiam
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2024; 52: 101347. CrossRef - Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer with intravesical Bacillus Calmette–Guérin immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jiaguo Huang, Li Lin, Dikai Mao, Runmiao Hua, Feifei Guan
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on the Mechanism of Action of Intravesical BCG Therapy to Treat Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
Mohamad Abou Chakra, Yi Luo, Igor Duquesne, Michael A O'Donnell
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Significant association between high neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Chunhua Xu, Fenfang Wu, Lailing Du, Yeping Dong, Shan Lin
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chitinase 3-like-1 Expression in the Microenvironment Is Associated with Neutrophil Infiltration in Bladder Cancer
Ling-Yi Xiao, Yu-Li Su, Shih-Yu Huang, Yi-Hua Chen, Po-Ren Hsueh
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15990. CrossRef
- Prognostic role of the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in high‐risk BCG‐naïve non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer treated with intravesical gemcitabine/docetaxel
- The proteomic landscape shows oncologic relevance in cystitis glandularis
- Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):67-74. Published online December 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.10.24
- 5,359 View
- 177 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The relationship between cystitis glandularis (CG) and bladder malignancy remains unclear.
Methods
We identified the oncologic significance of CG at the molecular level using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of 10 CG, 12 urothelial carcinoma (UC), and nine normal urothelium (NU) specimens. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were identified based on an analysis of variance false discovery rate < 0.05, and their functional enrichment was analyzed using a network model, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, and Gene Ontology annotation.
Results
We identified 9,890 proteins across all samples and 1,139 DEPs among the three entities. A substantial number of DEPs overlapped in CG/NU, distinct from UC. Interestingly, we found that a subset of DEP clusters (n = 53, 5%) was differentially expressed in NU but similarly between CG and UC. This “UC-like signature” was enriched for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and energy metabolism, growth and DNA repair, transport, motility, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and cell survival. Using the top 10 shortlisted DEPs, including SOD2, PRKCD, CYCS, and HCLS1, we identified functional elements related to ROS metabolism, development, and transport using network analysis. The abundance of these four molecules in UC/CG than in NU was consistent with the oncologic functions in CG.
Conclusions
Using a proteomic approach, we identified a predominantly non-neoplastic landscape of CG, which was closer to NU than to UC. We also confirmed a small subset of common DEPs in UC and CG, suggesting that altered ROS metabolism might imply potential cancerous risks in CG. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma
Jun Yong Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Dohyun Han, Ilias P. Nikas, Hyeyoon Kim, Minsun Jung, Han Suk Ryu
Heliyon.2024; 10(15): e35475. CrossRef - KRT18 as a Novel Biomarker of Urothelial Papilloma while Evaluating Low-Grade Papillary Urothelial Neoplasms: Bi-Center Analysis
Minsun Jung, Bohyun Kim, Jae Seok Lee, Jun Yong Kim, Dohyun Han, Kwangsoo Kim, Sunah Yang, Eun Na Kim, Hyeyooon Kim, Ilias P. Nikas, Sohyeon Yang, Kyung Chul Moon, Hyebin Lee, Han Suk Ryu
Pathobiology.2024; : 1. CrossRef
- Quantitative proteomics and immunohistochemistry uncover NT5DC2 as a diagnostic biomarker for papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Clinically undetected plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder with non-mass-forming metastases in multiple organs: an autopsy case
- Yuya Asano, Kosuke Miyai, Shinya Yoshimatsu, Makoto Sasaki, Katsunori Ikewaki, Susumu Matsukuma
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):217-224. Published online May 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.03.15
- 8,522 View
- 167 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This case report outlines a clinically undetected urinary bladder plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma (PUC) with multiple metastases detected at autopsy. An 89-year-old man presented with edema in the lower limbs. Pleural fluid cytology revealed discohesive carcinomatous cells, although imaging studies failed to identify the primary site of tumor. The patient died of respiratory failure. Autopsy disclosed a prostate tumor and diffusely thickened urinary bladder and rectum without distinct tumorous lesions. Histologically, the tumor consisted of acinar-type prostate adenocarcinoma with no signs of metastasis. Additionally, small, plasmacytoid tumor cells were observed in the urinary bladder/rectum as isolated or small clustering fashions. These metastasized to the lungs, intestine, generalized lymph nodes in a non-mass-forming manner. Combined with immunohistochemical studies, these tumor cells were diagnosed PUC derived from the urinary bladder. Both clinicians and pathologists should recognize PUC as an aggressive histological variant, which can represent a rapid systemic progression without mass-forming lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Severe Rectal Stenosis as the First Clinical Appearance of a Metastasis Originating from the Bladder: A Case Report and Literature Review
Claudiu Daha, Eugen Brătucu, Ioan Burlănescu, Virgiliu-Mihail Prunoiu, Hortensia-Alina Moisă, Ștefania Ariana Neicu, Laurențiu Simion
Life.2025; 15(5): 682. CrossRef - Carcinomatous Meningitis and Hydrocephalus in Plasmacytoid Urothelial Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder With Extremely Elevated CA19-9 Levels
Fumiaki Henmi, Kayako Ukai, Atsuhito Nakayama, Yutaka Takazawa, Yoshikazu Uesaka
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Advances in the Management of Nonurothelial Subtypes of Bladder Cancer
Evangelia Vlachou, Burles Avner Johnson, Ezra Baraban, Rosa Nadal, Jean Hoffman-Censits
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasmacytoid urothelial carcinoma: a multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and management
Marcus Zorovich, Jude Khatib, Aysha Mubeen, Katie Gardner, Nayana Patel
Abdominal Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Divergent Histology in Bladder Cancer: What We Need to Know?
Shashank Agrawal, Arun Ramdas Menon, Ginil Kumar Pooleri
UroCancer Clinics of India.2024; 2(2): 100. CrossRef
- Severe Rectal Stenosis as the First Clinical Appearance of a Metastasis Originating from the Bladder: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Histologically confirmed distant metastatic urothelial carcinoma from the urinary bladder: a retrospective review of one institution’s 20-year experience
- Youngeun Yoo, Junghye Lee, Heae Surng Park, Min-Sun Cho, Sun Hee Sung, Sanghui Park, Euno Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):94-101. Published online December 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.10.19
- 6,282 View
- 155 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) accounts for roughly 90% of bladder cancer, and has a high propensity for diverse differentiation. Recently, certain histologic variants of UC have been recognized to be associated with unfavorable clinical outcomes. Several UC studies have also suggested that tumor budding is a poor prognostic marker. Distant metastasis of UC after radical cystectomy is not uncommon. However, these metastatic lesions are not routinely confirmed with histology.
Methods
We investigated the histopathologic features of 13 cases of UC with biopsy-proven distant metastases, with a special emphasis on histologic variants and tumor budding.
Results
Lymph nodes (6/13, 46%) were the most common metastatic sites, followed by the lung (4/13, 31%), liver (4/13, 31%), and the adrenal gland (2/13, 15%). The histologic variants including squamous (n=1), micropapillary (n=4), and plasmacytoid (n=1) variants in five cases of UC. Most histologic variants (4/5, 80%) of primary UCs appeared in the metastatic lesions. In contrast, high-grade tumor budding was detected in six cases (46%), including one case of non-muscle invasive UC. Our study demonstrates that histologic variants are not uncommonly detected in distant metastatic UCs. Most histologic variants seen in primary UCs persist in the distant metastatic lesions. In addition, high-grade tumor budding, which occurs frequently in primary tumors, may contribute to the development of distant metastasis.
Conclusions
Therefore, assessing the presence or absence of histologic variants and tumor budding in UCs of the urinary bladder, even in non-muscle invasive UCs, may be useful to predict distant metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Do Histology and Primary Tumor Location Influence Metastatic Patterns in Bladder Cancer?
Hyung Kyu Park
Current Oncology.2023; 30(10): 9078. CrossRef
- Do Histology and Primary Tumor Location Influence Metastatic Patterns in Bladder Cancer?
- Programmed death-ligand 1 expression and its correlation with clinicopathological parameters in gallbladder cancer
- Ji Hye Kim, Kyungbin Kim, Misung Kim, Young Min Kim, Jae Hee Suh, Hee Jeong Cha, Hye Jeong Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):154-164. Published online February 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.13
- 9,627 View
- 172 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Immunomodulatory therapies targeting the interaction between programmed cell death protein 1 and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) have become increasingly important in anticancer treatment. Previous research on the subject of this immune response has established an association with tumor aggressiveness and a poor prognosis in certain cancers. Currently, scant information is available on the relationship between PD-L1 expression and gallbladder cancer (GBC).
Methods
We investigated the expression of PD-L1 in 101 primary GBC cases to determine the potential association with prognostic impact. PD-L1 expression was immunohistochemically assessed using a single PD-L1 antibody (clone SP263). Correlations with clinicopathological parameters, overall survival (OS), or progression- free survival (PFS) were analyzed.
Results
PD-L1 expression in tumor cells at cutoff levels of 1%, 10%, and 50% was present in 18.8%, 13.8%, and 7.9% of cases. Our study showed that positive PD-L1 expression at any cutoff was significantly correlated with poorly differentiated histologic grade and the presence of lymphovascular invasion (p < .05). PD-L1 expression at cutoff levels of 10% and 50% was significantly positive in patients with perineural invasion, higher T categories, and higher pathologic stages (p < .05). Additionally, there was a significant association noted between PD-L1 expression at a cutoff level of 50% and worse OS or PFS (p = .049 for OS, p = .028 for PFS). Other poor prognostic factors included histologic grade, T category, N category, pathologic stage, lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, growth pattern, and margin of resection (p < .05).
Conclusions
The expression of PD-L1 in GBC varies according to cutoff level but is valuably associated with poor prognostic parameters and survival. Our study indicates that the overexpression of PD-L1 in GBC had a negative prognostic impact. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PD-L1 Expression in Biliary Tract Cancer: Comparison Across Antibody Clones and Role as a Predictor of Response to Chemoimmunotherapy: A Meta-Analysis
Juan J. Juarez-Vignon Whaley, Soravis Osataphan, Ben Ponvilawan, Nipith Charoenngam, Mary Linton Peters
JCO Precision Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An MRI-based model for preoperative prediction of tertiary lymphoid structures in patients with gallbladder cancer
Ying Xu, Zhuo Li, Weihua Zhi, Yi Yang, Jingzhong Ouyang, Yanzhao Zhou, Zeliang Ma, Sicong Wang, Lizhi Xie, Jianming Ying, Jinxue Zhou, Xinming Zhao, Feng Ye
Insights into Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Lacking Immunotherapy Biomarkers for Biliary Tract Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Giorgio Frega, Fernando P. Cossio, Jesus M. Banales, Vincenzo Cardinale, Rocio I. R. Macias, Chiara Braconi, Angela Lamarca
Cells.2023; 12(16): 2098. CrossRef - Gallbladder carcinomas: review and updates on morphology, immunohistochemistry, and staging
Whayoung Lee, Vishal S. Chandan
Human Pathology.2023; 132: 149. CrossRef - Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions
Neetu Rawal, Supriya Awasthi, Nihar Ranjan Dash, Sunil Kumar, Prasenjit Das, Amar Ranjan, Anita Chopra, Maroof Ahmad Khan, Sundeep Saluja, Showket Hussain, Pranay Tanwar
Current Oncology.2023; 30(2): 1571. CrossRef - Identification of genes associated with gall bladder cell carcinogenesis: Implications in targeted therapy of gall bladder cancer
Ishita Ghosh, Ruma Dey Ghosh, Soma Mukhopadhyay
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2023; 15(12): 2053. CrossRef - CD73 and PD-L1 as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Gallbladder Cancer
Lu Cao, Kim R. Bridle, Ritu Shrestha, Prashanth Prithviraj, Darrell H. G. Crawford, Aparna Jayachandran
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1565. CrossRef - Evolving Role of Immunotherapy in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancers
Sandra Kang, Bassel F. El-Rayes, Mehmet Akce
Cancers.2022; 14(7): 1748. CrossRef - Novel immune scoring dynamic nomograms based on B7-H3, B7-H4, and HHLA2: Potential prediction in survival and immunotherapeutic efficacy for gallbladder cancer
Chao Lv, Shukun Han, Baokang Wu, Zhiyun Liang, Yang Li, Yizhou Zhang, Qi Lang, Chongli Zhong, Lei Fu, Yang Yu, Feng Xu, Yu Tian
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-1 inhibitors plus nab-paclitaxel-containing chemotherapy for advanced gallbladder cancer in a second-line setting: A retrospective analysis of a case series
Sirui Tan, Jing Yu, Qiyue Huang, Nan Zhou, Hongfeng Gou
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of HER2 and Mismatch Repair Proteins in Surgically Resected Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma
You-Na Sung, Sung Joo Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Changhoon Yoo, Kyu-Pyo Kim, Jae Hoon Lee, Dae Wook Hwang, Shin Hwang, Sang Soo Lee, Seung-Mo Hong
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Programmed Death Ligand-1 (PD-L1) Is an Independent Negative Prognosticator in Western-World Gallbladder Cancer
Thomas Albrecht, Fritz Brinkmann, Michael Albrecht, Anke S. Lonsdorf, Arianeb Mehrabi, Katrin Hoffmann, Yakup Kulu, Alphonse Charbel, Monika N. Vogel, Christian Rupp, Bruno Köhler, Christoph Springfeld, Peter Schirmacher, Stephanie Roessler, Benjamin Goep
Cancers.2021; 13(7): 1682. CrossRef - Immune Microenvironment in Gallbladder Adenocarcinomas
Pallavi A. Patil, Kara Lombardo, Weibiao Cao
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2021; 29(8): 557. CrossRef - Molecular Targets and Emerging Therapies for Advanced Gallbladder Cancer
Matteo Canale, Manlio Monti, Ilario Giovanni Rapposelli, Paola Ulivi, Francesco Giulio Sullo, Giulia Bartolini, Elisa Tiberi, Giovanni Luca Frassineti
Cancers.2021; 13(22): 5671. CrossRef - Overview of current targeted therapy in gallbladder cancer
Xiaoling Song, Yunping Hu, Yongsheng Li, Rong Shao, Fatao Liu, Yingbin Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- PD-L1 Expression in Biliary Tract Cancer: Comparison Across Antibody Clones and Role as a Predictor of Response to Chemoimmunotherapy: A Meta-Analysis
- Combined Adenosquamous and Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
- Jiyoon Jung, Yang-Seok Chae, Chul Hwan Kim, Youngseok Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Dong-Sik Kim, Young-Dong Yu, Joo Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):121-125. Published online October 5, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.08.20
- 8,882 View
- 155 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) of the gallbladder is extremely rare and usually combined with other type of malignancy, mostly adenocarcinoma. We report an unusual case of combined adenosquamous carcinoma and LCNEC of the gallbladder in a 54-year-old woman. A radical cholecystectomy specimen revealed a 4.3×4.0 cm polypoid mass in the fundus with infiltration of adjacent liver parenchyma. Microscopically, the tumor consisted of two distinct components. Adenosquamous carcinoma was predominant and abrupt transition from adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma was observed. LCNEC showed round cells with large, vesicular nuclei, abundant mitotic figures, and occasional pseudorosette formation. The patient received adjuvant chemotherapy. However, multiple liver metastases were identified at 3-month follow-up. Metastatic nodules were composed of LCNEC and squamous cell carcinoma components. Detecting LCNEC component is important in gallbladder cancer, because the tumor may require a different chemotherapy regimen and show early metastasis and poor prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postoperative gastric cancer accompanied by large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report
Zhiqin Chen, Jiang Liu, Jin Liu, Yinhang Wu, Jian Liu
Medicine.2025; 104(41): e44367. CrossRef - Does the size of the neuroendocrine-carcinoma component determine the prognosis of gallbladder cancer?
Ya-Fei Hu, Jun-Ke Wang, Wen-Jie Ma, Hai-Jie Hu, Han-Fei Gu, Fei Liu, Tian-Run Lv, Si-Qi Yang, Yu-Shi Dai, Rui-Qi Zou, Yan-Wen Jin, Fu-Yu Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Az epehólyag adenosquamosus daganata
Fanni Hegedűs, Anita Sejben
Orvosi Hetilap.2024; 165(49): 1945. CrossRef - Comparison of Metastatic Patterns Among Neuroendocrine Tumors, Neuroendocrine Carcinomas, and Nonneuroendocrine Carcinomas of Various Primary Organs
Hyung Kyu Park, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical features and outcomes analysis of Gallbladder neuroendocrine carcinoma
Man Jiang, Yijing Zhang
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2023; 19(4): 910. CrossRef - Primary mixed large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder: A case report and literature review
Tingting Yu, Shike Li, Zhuo Zhang
Asian Journal of Surgery.2022; 45(11): 2336. CrossRef - Mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasm of the gallbladder: case report and literature review
Xu Ren, Hong Jiang, Kan Sun, Xufu Qin, Yongping Qu, Tian Xia, Yan Chen
Diagnostic Pathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Gallbladder: A Clinicopathological Analysis of 13 Patients and a Review of the Literature
Pengyan Wang, Jingci Chen, Ying Jiang, Congwei Jia, Junyi Pang, Shan Wang, Xiaoyan Chang, Oronzo Brunetti
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Gallbladder Mixed Neuroendocrine-Non-neuroendocrine Neoplasm (MiNEN) Arising in Intracholecystic Papillary Neoplasm: Clinicopathologic and Molecular Analysis of a Case and Review of the Literature
Amedeo Sciarra, Edoardo Missiaglia, Mounir Trimech, Emmanuel Melloul, Jean-Philippe Brouland, Christine Sempoux, Stefano La Rosa
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(1): 84. CrossRef - Mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine carcinoma of gallbladder: case report
Adam Skalický, Lucie Vištejnová, Magdaléna Dubová, Tomáš Malkus, Tomáš Skalický, Ondřej Troup
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Postoperative gastric cancer accompanied by large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report
- Differential Immunohistochemical Profiles for Distinguishing Prostate Carcinoma and Urothelial Carcinoma
- Woo Jin Oh, Arthur Minwoo Chung, Jee Soon Kim, Ji Heun Han, Sung Hoo Hong, Ji Yeol Lee, Yeong Jin Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):345-354. Published online August 7, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.14
- 15,062 View
- 351 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The pathologic distinction between high-grade prostate adenocarcinoma (PAC) involving the urinary bladder and high-grade urothelial carcinoma (UC) infiltrating the prostate can be difficult. However, making this distinction is clinically important because of the different treatment modalities for these two entities.
Methods
A total of 249 patient cases (PAC, 111 cases; UC, 138 cases) collected between June 1995 and July 2009 at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital were studied. An immunohistochemical evaluation of prostatic markers (prostate-specific antigen [PSA], prostate-specific membrane antigen [PSMA], prostate acid phosphatase [PAP], P501s, NKX3.1, and α-methylacyl coenzyme A racemase [AMACR]) and urothelial markers (CK34βE12, p63, thrombomodulin, S100P, and GATA binding protein 3 [GATA3]) was performed using tissue microarrays from each tumor.
Results
The sensitivities of prostatic markers in PAC were 100% for PSA, 83.8% for PSMA, 91.9% for PAP, 93.7% for P501s, 88.3% for NKX 3.1, and 66.7% for AMACR. However, the urothelial markers CK34βE12, p63, thrombomodulin, S100P, and GATA3 were also positive in 1.8%, 0%, 0%, 3.6%, and 0% of PAC, respectively. The sensitivities of urothelial markers in UC were 75.4% for CK34βE12, 73.9% for p63, 45.7% for thrombomodulin, 22.5% for S100P, and 84.8% for GATA3. Conversely, the prostatic markers PSA, PSMA, PAP, P501s, NKX3.1, and AMACR were also positive in 9.4%, 0.7%, 18.8%, 0.7%, 0%, and 8.7% of UCs, respectively.
Conclusions
Prostatic and urothelial markers, including PSA, NKX3.1, p63, thrombomodulin, and GATA3 are very useful for differentiating PAC from UC. The optimal combination of prostatic and urothelial markers could improve the ability to differentiate PAC from UC pathologically. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative histologic survey and transcriptomic investigation into canine prostate carcinoma
Nathan K. Hoggard, Said M. Elshafae, Nigel A. Daniels, Jonathan A. Young, Chris Premanandan, John B. Echols, Darshan S. Chandrashekar, Blake E. Hildreth, Michael C. Haffner, Thomas J. Rosol
Research in Veterinary Science.2026; 198: 105981. CrossRef - Impact of hormone sensitivity status on aberrant expression of CK7, CK20, CDX2, GATA3 and TTF1 in prostate cancer
Qing Yin Wang, Nazim Benzerdjeb, Samuel Jaquet, Andreea Stepanov, Mame-Kany Diop, Mirela Birlea, Fred Saad, Dominique Trudel
Human Pathology.2025; 163: 105877. CrossRef - Unusual Perineal Metastasis in a Case of Prostate Cancer on 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT
Ritanshu Solanki, Bhagwant Rai Mittal, Rajender Kumar, Aravindh Sekar, Narender Kumar
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2024; 49(2): e73. CrossRef - NKX3.1 Expression in Non-Prostatic Tumors and Characterizing its Expression in Esophageal/Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma
Ansa Mehreen, Kiran G. Manjee, Divyangi Paralkar, Gladell P. Paner, Thanh Lan
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2024; 31(3): 202. CrossRef - Clinical Management of Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate
Gabriel Wasinger, Olivier Cussenot, Eva Compérat
Cancers.2024; 16(9): 1650. CrossRef - Adenocarcinomas of the Gynecologic Tract Involving the Urinary Bladder: A Series of 16 Cases Potentially Mimicking Urothelial Malignancy
Daniel H. Russell, Jonathan I. Epstein, Oleksandr N. Kryvenko, Matthew Schlumbrecht, Merce Jorda, Andre Pinto
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(6): 705. CrossRef - Assessing the diagnostic impact of P63, PSA and BCL-2 proteins in premalignant and malignant prostate tissues
Aderonke C. Ogunlayi, Victor O. Ekundina, Adedapo O. Kehinde, Linus A. Enye, Adegoke O. Aremu
International Journal of Scientific Reports.2024; 10(6): 188. CrossRef - Concurrent occurrence of adenocarcinoma and urothelial carcinoma of the prostate gland: A case report
Jhe Yuan Hsu, Yi Sheng Lin, Li Hua Huang, Tang Yi Tsao, Chao Yu Hsu, Yen Chuan Ou, Min Che Tung
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(26): 5952. CrossRef - Metastatic prostate cancer presenting as a posterior mediastinal mass: A rare presentation
Muhammad Haider, Arun Umesh Mahtani, Bachar Botrus, Foma Munoh Kenne, Madiha Fatima Master
Clinical Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic and Prognostic Roles of GATA3 Immunohistochemistry in Urothelial Carcinoma
Daeseon Yoo, Kyueng-Whan Min, Jung-Soo Pyo, Nae Yu Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(8): 1452. CrossRef - Primary high-grade urothelial carcinoma of prostate with prostatic hyperplasia: a rare case report and review of the literature
Liang Liu, Fu-zhen Sun, Pan-ying Zhang, Yu Xiao, Xiao Yue, Dong-Ming Wang, Qiang Wang
The Aging Male.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Expression of Gata Binding Protein 3 as a Prognostic Factor in Urogenital Lesions and Its Association With Morphology
T Govardhan, Debahuti Mohapatra, Sujata Naik, Prateek Das, Pranita Mohanty, Ankita Pal
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Histological and immunohistochemical investigation of canine prostate carcinoma with identification of common intraductal carcinoma component
Simone de Brot, Jennifer Lothion‐Roy, Llorenç Grau‐Roma, Emily White, Franco Guscetti, Mark A. Rubin, Nigel P. Mongan
Veterinary and Comparative Oncology.2022; 20(1): 38. CrossRef - Urothelial Carcinoma and Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen: Cellular, Imaging, and Prognostic Implications
Arsalan Tariq, Amy E. McCart Reed, Andrew Morton, Sima Porten, Ian Vela, Elizabeth D. Williams, John W. Yaxley, Peter C. Black, Matthew J. Roberts
European Urology Focus.2022; 8(5): 1256. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Reactivity of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen in Salivary Gland Tumors
Haruto Nishida, Yoshihiko Kondo, Takahiro Kusaba, Hiroko Kadowaki, Tsutomu Daa
Head and Neck Pathology.2022; 16(2): 427. CrossRef - Weak NKX3.1 expression in a urothelial carcinoma: A diagnostic pitfall
Maryam Abdo, Robert Hoyt, Ashley Highfill, Daniel Mettman
Human Pathology Reports.2022; 27: 300599. CrossRef - Gene of the month: NKX3.1
Jon Griffin, Yuqing Chen, James W F Catto, Sherif El-Khamisy
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2022; 75(6): 361. CrossRef - Diagnostic Value of GATA3 and Uroplakin 3 in Differentiating Urothelial Carcinoma from Prostatic and Colorectal Carcinoma
Maha Salama, Dina A. Khairy
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 514. CrossRef - Diagnostic challenges for the distinction of high-grade prostatic adenocarcinoma and high-grade urothelial carcinoma of simultaneous occurrences - A literature review
Shreyas Bhushan Jayade, Manana Jikurashvili
GEORGIAN SCIENTISTS.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytomorphology, immunoprofile, and clinicopathologic correlation of metastatic prostatic carcinoma
Xiaoqi Lin, Qiuying Shi, Ximing J. Yang
Human Pathology.2022; 130: 36. CrossRef - Cutaneous Metastasis of Prostate Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Presentation of a Common Disease
Alexander Dills, Okechukwu Obi, Kevin Bustos, Jesse Jiang, Shweta Gupta
Journal of Investigative Medicine High Impact Case Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mining The Cancer Genome Atlas gene expression data for lineage markers in distinguishing bladder urothelial carcinoma and prostate adenocarcinoma
Ewe Seng Ch’ng
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical analysis of thrombomodulin expression in myocardial tissue from autopsy cases of ischemic heart disease
Takeshi Kondo, Motonori Takahashi, Gentaro Yamasaki, Marie Sugimoto, Azumi Kuse, Mai Morichika, Kanako Nakagawa, Makoto Sakurada, Migiwa Asano, Yasuhiro Ueno
Legal Medicine.2021; 51: 101897. CrossRef - Application and Pitfalls of Immunohistochemistry in Diagnosis of Challenging Genitourinary Cases
Jenny Ross, Guangyuan Li, Ximing J. Yang
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2020; 144(3): 290. CrossRef - New Screening Test Improves Detection of Prostate Cancer Using Circulating Tumor Cells and Prostate-Specific Markers
Karin Ried, Tasnuva Tamanna, Sonja Matthews, Peter Eng, Avni Sali
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - An Unlikely Culprit: Gastric Metastasis from Primary Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Eric Omar Then, Spoorthi Nutakki, Andrew Ofosu, Saad Saleem, Vijay Gayam, Tagore Sunkara, Vinaya Gaduputi
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(3): 1081. CrossRef - MRI of prostatic urethral mucinous urothelial carcinoma: Expanding the differential diagnosis for T2 hyperintense prostatic masses
Neel Patel, Bryan R. Foster, Elena K. Korngold, Kyle Jensen, Kevin R. Turner, Fergus V. Coakley
Clinical Imaging.2020; 68: 68. CrossRef - Morphological and Immunohistochemical Biomarkers in Distinguishing Prostate Carcinoma and Urothelial Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
Francesca Sanguedolce, Davide Russo, Vito Mancini, Oscar Selvaggio, Beppe Calò, Giuseppe Carrieri, Luigi Cormio
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2019; 27(2): 120. CrossRef - A Case of Metastatic Prostate Cancer to the Urethra That Resolved After Androgen Deprivation Therapy
Darren J. Bryk, Kenneth W. Angermeier, Eric A. Klein
Urology.2019; 129: e4. CrossRef - The Homeodomain Transcription Factor NKX3.1 Modulates Bladder Outlet Obstruction Induced Fibrosis in Mice
Mehul S. Patel, Diana K. Bowen, Nicholas M. Tassone, Andrew D. Gould, Kirsten S. Kochan, Paula R. Firmiss, Natalie A. Kukulka, Megan Y. Devine, Belinda Li, Edward M. Gong, Robert W. Dettman
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer of unknown primary: Ancillary testing of cytologic and small biopsy specimens in the era of targeted therapy
Morgan L. Cowan, Christopher J. VandenBussche
Cancer Cytopathology.2018; 126(S8): 724. CrossRef - Glandular Tumors of the Urachus and Urinary Bladder: A Practical Overview of a Broad Differential Diagnosis
Alexander S. Taylor, Rohit Mehra, Aaron M. Udager
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(10): 1164. CrossRef - S100P as a Marker for Urothelial Histogenesis: A Critical Review and Comparison With Novel and Traditional Urothelial Immunohistochemical Markers
Moushumi Suryavanshi, Julian Sanz-Ortega, Deepika Sirohi, Mukul K. Divatia, Chisato Ohe, Claudia Zampini, Daniel Luthringer, Steven C. Smith, Mahul B. Amin
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2017; 24(3): 151. CrossRef
- Comparative histologic survey and transcriptomic investigation into canine prostate carcinoma
- A Different Perspective on Macroscopic Sampling of Cholecystectomy Specimens
- Asuman Argon, Ayşe Yağcı, Funda Taşlı, Tulu Kebat, Senem Deniz, Nazif Erkan, Gül Kitapçıoğlu, Enver Vardar
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):519-525. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.519
- 9,367 View
- 72 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Because there may be interdepartmental differences in macroscopic sampling of cholecystectomy specimens, we aimed to investigate differences between the longitudinal sampling technique and our classical sampling technique in cholecystectomy specimens in which there was no obvious malignancy.
Methods Six hundred eight cholecystectomy specimens that were collected between 2011 and 2012 were included in this study. The first group included 273 specimens for which one sample was taken from each of the fundus, body, and neck regions (our classical technique). The second group included 335 specimens for which samples taken from the neck region and lengthwise from the fundus toward the neck were placed together in one cassette (longitudinal sampling). The Pearson chi-square, Fisher exact, and ANOVA tests were used and differences were considered significant at p<.05.
Results In the statistical analysis, although gallbladders in the first group were bigger, the average length of the samples taken in the second group was greater. Inflammatory cells, pyloric metaplasia, intestinal metaplasia, low grade dysplasia, and invasive carcinoma were seen more often in the second group.
Conclusions In our study, the use of a longitudinal sampling technique enabled us to examine a longer mucosa and to detect more mucosal lesions than did our classical technique. Thus, longitudinal sampling can be an effective technique in detecting preinvasive lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differentiating Neoplastic From Non-neoplastic Gallbladder Lesions Using MUC1 and MUC5AC: An Immunohistochemical Analysis
Umika Gupta, Vijai Singh, Sanjeev Yadav
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cholecystectomy in children: indications, clinical, laboratory and histopathological findings and cost analysis
Aysel Ünlüsoy Aksu, Nebiyye Genel, Gülseren Şahin, Ferda Özbay Hoşnut, Ayşegül Tok, Ayşe Karaman
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics.2024; 66(4): 473. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic features of gallbladder wall thickening in dogs with hypoalbuminemia
Masahiro Murakami, Hock Gan Heng, Sarah Steinbach, Mario Sola
Veterinary Quarterly.2023; 43(1): 1. CrossRef - Can the sampling method affect the detection of incidental gallbladder carcinoma? Comparative analysis of two sampling methods
Ezgi Hacihasanoglu, Esra Pasaoglu, Merve Cin, Enver Yarikkaya, Nevra Dursun, Sevim Baykal Koca
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2023; 67: 152187. CrossRef - Current management of incidental gallbladder cancer: A review
Claudio F. Feo, Giorgio C. Ginesu, Alessandro Fancellu, Teresa Perra, Chiara Ninniri, Giulia Deiana, Antonio M. Scanu, Alberto Porcu
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 98: 106234. CrossRef - Accuracy of Right Upper Quadrant Ultrasound in Estimating Gallbladder Wall Thickness
Lindsay Cefalu, Robert McMurray, Grant Sizemore, Gerald Bieniek, Michael Lustik, Christopher Yheulon
Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques.2019; 29(1): 26. CrossRef - Optimal block sampling of routine, non‐tumorous gallbladders
Newton A C S Wong
Histopathology.2017; 71(1): 162. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Intracholecystic Papillary-Tubular Neoplasms and Invasive Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Asuman Argon, Funda Yılmaz Barbet, Deniz Nart
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 24(6): 504. CrossRef
- Differentiating Neoplastic From Non-neoplastic Gallbladder Lesions Using MUC1 and MUC5AC: An Immunohistochemical Analysis
- Expression of MUC1 and MUC4 in Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma
- Su-Mi Kim, Sun-Ju Oh, Bang Hur
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):429-435. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.429
- 10,007 View
- 68 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Recent reports have indicated that overexpression of mucin (MUC) 1 and/or MUC4 correlates with the occurrence and progression of extra-hepatobiliary malignancy. In this study, we investigated the expression of MUC1 and MUC4 and their prognostic significance in gallbladder adenocarcinoma.
Methods We examined 54 surgical gallbladder adenocarcinoma samples by immunohistochemistry for MUC1 and MUC4 expression. Staining was evaluated as a sum score of extent and intensity, dividing the samples into low and high expression groups.
Results The low expression group for both MUC1 and MUC4 was 10 samples (18.5%), and the high expression group was 44 samples (81.5%). High MUC1 expression was significantly correlated with more differentiated tumors (p=0.033), whereas high expression of MUC4 correlated with negative nodal status (p=0.012). Other pathological features were not correlated with MUC expression. Multivariate cox regression analysis showed that neither MUC1 nor MUC4 expression correlated with survival.
Conclusions Although there were some correlations found, a prognostic role for either MUC1 or MUC4 expression in gallbladder carcinoma was not identified in this study. Further investigation is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differentiating Neoplastic From Non-neoplastic Gallbladder Lesions Using MUC1 and MUC5AC: An Immunohistochemical Analysis
Umika Gupta, Vijai Singh, Sanjeev Yadav
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Environmental and Metabolic Risk Factors Linked to Gallbladder Dysplasia
Andrei Bojan, Catalin Pricop, Manuela Ciocoiu, Maria Cristina Vladeanu, Iris Bararu Bojan, Oana Viola Badulescu, Minerva Codruta Badescu, Carmen Elena Plesoianu, Dan Iliescu Halitchi, Liliana Georgeta Foia
Metabolites.2024; 14(5): 273. CrossRef - Expression of Mucoproteins in Gallbladder Cancer
Puneet Kumar, Priyesh Shukla, Soni Kumari, Ruhi Dixit, Gopeshwar Narayan, V. K. Dixit, A. K. Khanna
Indian Journal of Surgery.2022; 84(3): 456. CrossRef - Prognostic and clinicopathological value of MUC1 expression in colorectal cancer
Chao Li, Tao Liu, Libin Yin, Didi Zuo, Yuyang Lin, Lei Wang
Medicine.2019; 98(9): e14659. CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of Mucin Antigen MUC1 in Various Human Epithelial Cancers
Feng Xu, Fuquan Liu, Hongwei Zhao, Guangyu An, Guosheng Feng
Medicine.2015; 94(50): e2286. CrossRef - Increased Expression of CCN2, Epithelial Membrane Antigen, and Fibroblast Activation Protein in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Fibrous Stroma Showing Aggressive Behavior
Gi Jeong Kim, Hyungjin Rhee, Jeong Eun Yoo, Jung Eun Ko, Jee San Lee, Hyunki Kim, Jin Sub Choi, Young Nyun Park, Philip C. Trackman
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(8): e105094. CrossRef - State-of-the-art in the management of locally advanced and metastatic gallbladder cancer
Mairéad G. McNamara, Cristiane Metran-Nascente, Jennifer J. Knox
Current Opinion in Oncology.2013; 25(4): 425. CrossRef - Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of MUC-2, MUC-4 and MUC-5AC Expression in Japanese Gastric Carcinomas
Li-Jun Xiao, Shuang Zhao, En-Hong Zhao, Xin Zheng, Wen-Feng Gou, Ya-Nan Xing, Yasuo Takano, Hua-Chuan Zheng
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2012; 13(12): 6447. CrossRef
- Differentiating Neoplastic From Non-neoplastic Gallbladder Lesions Using MUC1 and MUC5AC: An Immunohistochemical Analysis
- The Expression of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma
- Tae Jung Jang, Sung Woo Kim, Kyung Seop Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):261-265. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.261
- 7,696 View
- 24 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is an anti-angiogenic factor. The purpose of this study is to examine the involvement of PEDF in the angiogenesis and biological behavior of bladder transitional cell carcinoma (TCC).
Methods We examined the expression of PEDF in 99 bladder TCCs and ten non-neoplastic tissues, and evaluated microvessel density (MVD).
Results The positive immunoreactivity for PEDF was seen in normal urothelium in 60% (6/10) and TCC in 13% (13/99). The PEDF expression had a significant correlation with MVD, i.e., a low MVD in 42% (5/12), a middle MVD in 11% (8/76) and a high MVD 0% (0/11) of tumors. The PEDF expression was not significantly correlated with the differentiation and invasion of TCC, but the degree of MVD was significantly higher in both high grade TCC and the pT2 tumors.
Conclusions The degree of PEDF expression is significantly higher in normal bladder urothelium than bladder TCC; it is inversely correlated with the angiogenesis; and it is not related to the differentiation and progression of TCC. It can therefore be concluded that bladder TCC would initially occur if there is a lack of the PEDF expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of pigment epithelium derived factor expression with cancer progression and prognosis: a meta-analysis study
Guo Cheng, Crystal Song
Discover Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Level of mitoses in non-muscle invasive papillary urothelial carcinomas (pTa and pT1) at initial bladder biopsy is a simple and powerful predictor of clinical outcome: a multi-center study in South Korea
Ji Eun Kwon, Nam Hoon Cho, Yeong-Jin Choi, So Dug Lim, Yong Mee Cho, Sun Young Jun, Sanghui Park, Young A. Kim, Sung-Sun Kim, Mi Sun Choe, Jung-dong Lee, Dae Yong Kang, Jae Y. Ro, Hyun-Jung Kim
Diagnostic Pathology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Endogenous Gastric-Resident Mesenchymal Stem Cells Contribute to Formation of Cancer Stroma and Progression of Gastric Cancer
Eun-Kyung Kim, Hye-Jung Kim, Young-Il Yang, Jong Tae Kim, Min-Young Choi, Chang Soo Choi, Kwang-Hee Kim, Jeong-Han Lee, Won-Hee Jang, Soon-Ho Cheong
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(6): 507. CrossRef
- Association of pigment epithelium derived factor expression with cancer progression and prognosis: a meta-analysis study
- Evaluation of Urine Cytology in Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Comparison of CellprepPlus® Liquid-Based Cytology and Conventional Smear
- Seung-Myoung Son, Ji Hae Koo, Song-Yi Choi, Ho-Chang Lee, Yong-Moon Lee, Hyung Geun Song, Hae-Kyung Hwang, Hye-Suk Han, Seok-Joong Yun, Wun-Jae Kim, Eun-Joong Kim, Ok-Jun Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):68-74. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.68
- 12,705 View
- 96 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Urine cytology is an important test in the screening of urothlelial neoplasms. The conventional smear (CS) method of testing urine samples has a low sensitivity, approximately 50% result accuracy for detecting urothelial carcinomas, while liquid-based cytology (LBC) has much improved diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. The aim of this study was to compare the morphologic features and diagnostic efficacy of CellprepPlus® LBC with those of CS for urine cytology.
Methods A total of 713 cases of urine specimens collected from November 2009 to September 2010 were included. All specimens were divided equally for the preparation of CellprepPlus® LBC and CS for each case.
Results CellprepPlus® revealed more cellularity, a cleaner background and better cytomorphologic features, but it showed a less intact architectural pattern compared to that of CS. Of the 88 histologically confirmed cases, the diagnostic sensitivity for CellprepPlus® was 50% and higher than the 37.5% for CS. The specificity of both preparations was 100%.
Conclusions The CellprepPlus® showed an improved quality of slides and provided better diagnostic accuracy, thus CellprepPlus® could be a first-line screening tool in urinary tract cytology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Conventional Sediment Smears and Liquid‐Based Cytology and Utility of Cell Block Preparation in Urinary Cytology
Jagriti Singh Fartiyal, Meenakshi Rao, Poonam Abhay Elhence, Aasma Nalwa, Divya Aggarwal, Taruna Yadav, Gautam Ram Choudhary
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of Diagnostic Performance and Cytomorphologic Features Between Newly Developed WellPrep® and SurePath™ in Serous Effusion Cytology
Ji Eun Choi, Min-Sun Jin, Da Sol Kim, Ilias P. Nikas, Han Suk Ryu
Journal of Cytology.2025; 42(3): 142. CrossRef - Advances in diagnostic liquid‐based cytology
Hideyuki Abe, Akihiko Kawahara, Jun Akiba, Rin Yamaguchi
Cytopathology.2024; 35(6): 682. CrossRef - Impact of implementing the first edition of the Paris system for reporting: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sahar J. Farahani, Joshua Li, Beatrice Minder, Philippe Vielh, Marija Glisic, Taulant Muka
Cytopathology.2024; 35(5): 616. CrossRef - Body fluids
Shyam H. Nemade, Meherbano M. Kamal
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2023; 66(1): 75. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Screening of Urothelial Carcinoma in Whole Slide Images of Liquid-Based Cytology Urine Specimens
Masayuki Tsuneki, Makoto Abe, Fahdi Kanavati
Cancers.2022; 15(1): 226. CrossRef - Diagnostic efficacy of smear plus liquid-based cytology for EUS-FNA of solid pancreatic lesions
Masahiro Itonaga, Shin-Ichi Murata, Keiichi Hatamaru, Takashi Tamura, Junya Nuta, Yuki Kawaji, Takao Maekita, Mikitaka Iguchi, Jun Kato, Fumiyoshi Kojima, Hiroki Yamaue, Manabu Kawai, Ken-Ichi Okada, Seiko Hirono, Toshio Shimokawa, Kensuke Tanioka, Masayu
Medicine.2019; 98(19): e15575. CrossRef - Evaluation and application of Cellprep for cervical cytology
Rinko OZEKI, Keiichi IWAYA, Yuko UMAYAHARA, Yuka MORITA, Mie ARAI, Yukari TAKASUGI, Ryoko KIKUCHI, Kiyohiko MIYAKE, Atsuhiko SAKAMOTO, Masaru SAKAMOTO
The Journal of the Japanese Society of Clinical Cytology.2018; 57(3): 159. CrossRef - Quantitative Proteomic Analysis Identifies AHNAK (Neuroblast Differentiation-associated Protein AHNAK) as a Novel Candidate Biomarker for Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnosis by Liquid-based Cytology
Hyebin Lee, Kwangsoo Kim, Jongmin Woo, Joonho Park, Hyeyoon Kim, Kyung Eun Lee, Hyeyeon Kim, Youngsoo Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Ji Young Kim, In Ae Park, Bo Bae Shim, Ji Hye Moon, Dohyun Han, Han Suk Ryu
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.2018; 17(9): 1788. CrossRef - Reliability of Estrogen Receptor and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Expression on Breast Cancer Cells Stored in Cellprep® Vials
Ayumi Ryu, Jyun-ichi Ashimura, Takahiro Nakayama, Yasuhiro Tamaki, Shin-ichi Nakatsuka, Yasuhiko Tomita
Acta Cytologica.2018; 62(5-6): 360. CrossRef - Current status of urine cytology: what should the urologist know?
Kristýna Pivovarčíková, Tomáš Pitra, Milan Hora, Marián Švajdler, Ondřej Hes
Czech Urology.2018; 22(4): 242. CrossRef - Morphologic Analysis of Cytomegalovirus Infected Cells in Bronchial Washing Cytology: Comparison of Liquid-Based Preparation and Conventional Smear
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Seung Yeon Ha, Dong Hae Chung, Sangho Lee, Hyunchul Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(2): 147. CrossRef - Romanowsky staining using liquid‐based cytology: A pilot study using Cytolyt®/HESPANDER® processing solution for ThinPrep® preparations
Yuichi Kinoshita, Takashi Yuri, Katsuhiko Yoshizawa, Kosho Takasu, Yuko Emoto, Airo Tsubura, Nobuaki Shikata
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2015; 43(12): 960. CrossRef - Diagnostic Value of Liquid-Based Cytology in Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
You Luo, Dong-Li She, Hu Xiong, Li Yang, Sheng-Jun Fu, Francisco X. Real
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(8): e0134940. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef - Diagnostic Efficacy of Cell Block Immunohistochemistry, Smear Cytology, and Liquid-Based Cytology in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration of Pancreatic Lesions: A Single-Institution Experience
Shan-yu Qin, You Zhou, Ping Li, Hai-xing Jiang, Robert L. Schmidt
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(9): e108762. CrossRef
- Comparison of Conventional Sediment Smears and Liquid‐Based Cytology and Utility of Cell Block Preparation in Urinary Cytology
- Carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder in bladder washing cytology.
- Doo Hyun Chung, In Ae Park, Eui Keun Ham
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1991;2(1):51-55.
- 2,112 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of urinary bladder is difficult in that the symptoms and cystoscopic findings are nonspecific. The cytology of urine could be helpful for diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of urinary bladder. We present a case of bladder washing cytology of carcinoma in situ. A 54 year old man presented with dysuria for 1 year. Cystoscopic findings revealed multifocal reddish trabeculated lesions. The bladder washing cytology revealed rather uniform tumor cells which were singly scattered or forming syncytium in the clean background. The nuclei were round to oval with inconspicious nucleoli. The cystoscopic biopsy revealed typical histologic features of carcinoma in situ of urinary bladder.
- Mixed Endocrine-Exocrine Carcinoma of Gallbladder Derived from Dysplasia.
- Min Jin Lhee, Ji Young Woo
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(5):537-541.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.5.537
- 3,455 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A rare case of multiple mixed endocrine-exocrine carcinoma (MEEC) of gallbladder in a 68-year-old man is described. The lesions were two separate nodules (17x13x7 mm and 17 mm in length) on the mucosa, which were composed of predominant neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) infiltrating into the adventitia and minor portion of adenocarcinoma (AC) or high grade dysplasia (HGD) on the surface. Surrounding mucosa showed areas of low grade dysplasia (LGD). Two nodal metastases out of 16 nodes were found containing NEC component. By immunohistochemistry, human mutL homolog 1 (hMLH1), p53, human mutS homolog 2 (hMSH2) and human mutS homolog 6 (hMSH6) showed diffuse strong positive reaction in HGD, AC and NEC, contrasting with weak positive reaction in LGD. On genetic analysis, all lesions of HGD, AC, and NEC except for LGD showed positive loss of heterozygosity in D5S346 locus. For microsatellite instability and K-ras mutation tests, all lesions showed negative results. Common immunophenotypes and molecular results among HGD, AC, and NEC suggested that NEC of this MEEC was derived from the dysplasia-AC sequence.
- Sarcomatoid Carcinoma of the Gallbladder with Pure Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Brief Case Report.
- Seungkoo Lee, Song Yi Kim, Seong Kweon Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(2):209-211.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.2.209
- 4,265 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report here on a rare case of sarcomatoid carcinoma that contained an epithelial component of squamous cell carcinoma. A 77-year-old woman was found to have a gallbladder mass. The gallbladder showed a diffuse infiltrative wall mass with a polypoid lesion, and the mass measured 8x7x3 cm. There were no gallstones. Histologically, the tumor was composed of two components of squamous cell carcinoma and spindle cell malignancy. The tumor extended to the perimuscular connective tissue and one regional lymph node. The postoperative course was uneventful and the patient was well without tumor recurrence at one and a half months after surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carcinosarcoma of gallbladder: A world review
Thomas Zheng Jie Teng, Branden Qi Yu Chua, Vishal G Shelat
World Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 12(12): 1244. CrossRef
- Carcinosarcoma of gallbladder: A world review
- The Expression Pattern of Annexin A1 in Urinary Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma and Its Clinicopathologic Significance.
- Hojung Lee, Seung Kyu Choi, Young Ok Hong, Won Mi Lee, Sook Kyung Ko, Eun Kyung Kim, Jong Eun Joo
- Korean J Pathol. 2011;45(1):62-68.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2011.45.1.62
- 3,598 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Annexin A1 (ANXA1) is known to be involved in the progression and differentiation of various tumors. However, its significance and role in bladder carcinogenesis has not been fully elucidated. To determine the role ANXA1 plays in urothelial carcinoma (UC), we investigated the expression of ANXA1 protein in normal urothelial tissue, carcinoma in situ (CIS), and UC of the urinary bladder.
METHODS
Protein expression level of ANXA1 and its subcellular localization were analyzed in 88 cases of UCs and corresponding 24 normal tissues and 24 CISs by immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
ANXA1 was significantly down-regulated at all subcellular localization in CIS and in the cytoplasm and membrane of cells of UC, compared to normal tissues. No significant correlation between ANXA1 expression level and tumor depth (pT), growth pattern, and recurrence was found. However, cytoplasmic and membranous ANXA1 were significantly up-regulated in high grade than in low grade UC (p=0.02 in cytoplasm and p=0.03 in membrane).
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest that ANXA1 dysregulation is involved in urothelial carcinogenesis and ANXA1 is potentially a marker for the pathologic differentiation of UC.
- Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Sung Hak Lee, Eun Deok Chang, Eun Jung Lee, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(2):216-219.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.2.216
- 4,258 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary malignant melanoma in the bladder is very rare, with only 18 cases having been currently reported. A 65-year-old male patient presented with a 5-month history of gross hematuria. On ultrasonography, an 8.1 x 6.1 cm mass was revealed on the bladder wall. A partial cystectomy was performed. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of atypical, pigmented melanocytes that were positive for S-100 protein and they were negative for human melanoma black-45. Although he underwent supportive therapy, an 8.7 x 5.9 cm mass occupying the prevesical space was noted on a follow-up computed tomography scan 4 months later. Two nodules of the left lower lung and multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the left external iliac chain were also revealed. The patient declined any further treatment. The histogenesis of primary bladder melanoma is uncertain, but an origin from neural crest cells has been proposed. The prognosis for patients with this tumor is still poor despite the availability of several therapeutic options.
- Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision-Like Protein HuR in Gallbladder Carcinoma.
- Sung Im Do, Gou Young Kim, Sung Jig Lim, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2010;44(1):42-47.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.42
- 4,071 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is an enzyme that promotes proliferation of tumor cells. HuR is a member of the family of embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like proteins. Recent studies show that cytoplasmic HuR stabilizes the mRNA of COX-2 and regulates the expression of COX-2. Moreover, cytoplasmic HuR expression is associated with a poorer prognosis for patients with some cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate the expression patterns of and the relationship between COX-2 and HuR in gallbladder carcinoma.
METHODS
We analyzed COX-2 and HuR expression by immunohistochemical staining of 108 gallbladder carcinomas.
RESULTS
COX-2 expression and nuclear and cytoplasmic HuR expression were seen in, respectively, 61 (56.5%), 77 (71.3%), and 4 (3.7%) cases. COX-2 and nuclear HuR were simultaneously expressed in 44 of the 108 samples without any quantitative association between the levels of each. COX-2 expression correlated with tumor stage, differentiation (based on histology), lymph node metastasis, perineural invasion, and survival. Nuclear and cytological expression of HuR did not correlate with any clinical parameters.
CONCLUSIONS
COX-2 expression but not HuR may play an important role in the prognosis of patients with gallbladder carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic Molecular Markers in Resected Extrahepatic Biliary Tract Cancers; A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Immunohistochemically Detected Biomarkers
Robert P Jones, Nicholas TE Bird, Richard A Smith, Daniel H Palmer, Steven W Fenwick, Graeme J Poston, Hassan Z Malik
Biomarkers in Medicine.2015; 9(8): 763. CrossRef
- Prognostic Molecular Markers in Resected Extrahepatic Biliary Tract Cancers; A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Immunohistochemically Detected Biomarkers
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of an Ileal Neobladder: A Case Report.
- Ran Hong, Dong Youl Choi, Dae Eun Shin, Hyung Yoon Moon, Keun Hong Kee
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(5):467-470.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.5.467
- 3,917 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bladder reconstruction using bowel segments, especially the ileum, has become a realistic option for urinary diversion. There is only one prior case of squamous cell carcinoma of the ileal neobladder that has been reported in the clinical literature. Here we report a patient with a spectrum of squamous cell lesions, including squamous cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid carcinoma, squamous papilloma and squamous metaplasia that developed in the ileal neobladder. A 46-year-old woman underwent a hysterectomy, cystectomy and ileocystoplasty for tuberculosis 25 years previously complained of urinary frequency and gross hematuria for one week. A pelvic CT revealed a 6.3 cm mass in the neobladder. The histopathological examination showed an 11x8 cm polypoid fragile mass with a microscopically well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, squamous papilloma and non-tumor squamous metaplasia.
- The Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Survivin in Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma.
- Tae Jung Jang, Kyung Seob Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2009;43(3):206-211.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.206
- 4,510 View
- 29 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to investigate the expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and survivin in bladder transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) that has different clinicopathologic characteristics, and we also wanted to determine if a relation exists between the COX-2 and survivin expressions.
METHODS
The expressions of COX-2 and survivin were investigated in 80 bladder TCCs by performing immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS
The normal bladder mucosa did not express COX-2 and survivin. COX-2 immunopositivity and cytoplasmic survivin immunopositivity were seen in 48% and 30% of bladder tumors, respectively. The expressions of COX-2 and survivin were closely related to the differentiation, depth and recurrence of bladder TCC, and there was a significant correlation in topographic distribution of COX-2 and survivin immunopositivity. In addition, COX-2 and survivin were predominantly expressed at the invasive front of tumors.
CONCLUSIONS
This data suggest that COX-2 and survivin may be involved in the progression of bladder TCC, and there is a close correlation between the expressions of COX-2 and survivin. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of survivin and p27 expression as potential prognostic markers in urothelial cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in Egyptian patients
Noha Said Helal, Zeinab Omran, Mona Moussa
African Journal of Urology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma and its Association with Clinicopathological Characteristics
Hedieh Moradi Tabriz, Golrokh Olfati, Seyed Ali Ahmadi, Sudabeh Yusefnia
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2013; 14(8): 4539. CrossRef - High survivin expression in premalignant and malignant kidney lesions
Tahany M. Shams, Samaka M. Rehab, Mokhtar Metawea
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2012; 32(1): 21. CrossRef - Reciprocal correlation between the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and E-cadherin in human bladder transitional cell carcinomas
Tae Jung Jang, Woo Heon Cha, Kyung Seob Lee
Virchows Archiv.2010; 457(3): 319. CrossRef
- Assessment of survivin and p27 expression as potential prognostic markers in urothelial cell carcinoma of urinary bladder in Egyptian patients
- Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Jong Sil Lee, Jeong Seok Hwa, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jeong Hee Lee, Hwal Woong Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(2):129-131.
- 1,975 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) most commonly affects the pleura and these tumors have been recently reported to be found in unusual locations. We describe here a solitary fibrous tumor of the urinary bladder that was removed from a 79-year-old man having a history of gross hematuria and dysuria. Transabdominal ultrasonography showed a huge soft tissue mass in the urinary bladder. The cut surface of the tumor showed a grayish-white, hemorrhagic and gelatinous appearance. Necrosis was not found. Microscopically, the tumor showed a proliferation of spindle or ovoid cells that were intervened by a collagenous stroma. A variety of growth patterns was identified but the so-called patternless pattern was the predominant one. The spindle cells had almost no mitotic figures, and there was very little or no nuclear atypia. Immunohistochemical stains showed a strong reactivity for CD34 and a focal reactivity for bcl-2. The ultrastructure of the tumor cells showed mesenchymal-myofibroblastic traits.
- Collision Tumor Composed of Papillary Transitional Cell Carcinoma, and Osteosarcoma in Urinary Bladder: A cases report.
- Nam Hoon Cho, Chanil Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(3):374-377.
- 1,973 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This is to report a case of collision tumor of the urinary bladder, which was composed of papillary transitional cell carcinoma(PTCC) and osteosarcoma. Grossly the tumor was located at left antero-lateral wall and was a fungating, gray yellow, bony hard mass with papillary configuration of the luminal surface. Histologically the tumor was composed of PTCC confined to the mucosa and sarcomatous component not intermixed with the overlying PTCC. The sarcomatous area had features of classic osteosarcoma with anaplastic tumor cells and haphazardly arranged osteoid matrix, and was positive for osteonectin but entirely negative for cytokeratin or epithelial membrane antigen. Ultrastructural study demonstrated the tumor cells to be osteoblast which had rich rERs and a few lipid vesicles in plump cytoplasm without any evidence of epithelial ongin. The case is thought to be an example of collision tumor because there was no evidence of transition between PTCC and osteosarcoma.
- Urinary Cytologic Findings of Plasmacytoid Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report .
- Mi Ok Park, Yong Jin Kim, Jae Bok Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1999;10(1):67-71.
- 1,888 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of 53-year-old man with plasmacytoid transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder, which may be confused with plasmacytoma. The patient initially presented with gross hematuria and dysuria for two months. Cystoscopy and radiologic studies revealed multiple intraluminal protruding masses on the urinary bladder invading perivesical fat tissue. After urinary cytologic examination and cystoscopic biopsy, radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissections were done. Urine cytology showed single cells and poorly cohesive cells with round eccentric nuclei, bi-or multi-nucleation, indistinct nucleoli, coarse chromatin, and abundant basophilic cytoplasm within relatively clear background. The cytologic findings of tumor cells were similar to the plasma cells seen in plasmacytoma. The tumor of the bladder was composed of discohesive, individual cancer cells with diffuse pattern that simulated lymphoma or plasmacytoma. Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies clearly established the epithelial nature of the neoplasm. Recognition of this plasmacytoid type of transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder can avoid the misdiagnosis.
- Localized Amyloidosis of the Ureter: A Report of Two Cases.
- Ho Jung Lee, Dong Eun Song, Jong Eun Joo, Won Mi Lee, Dong Hoon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Jae Y Ro
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(3):184-187.
- 2,220 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report on two cases of localized amyloidosis involving the ureter. The patients were a 64-year-old woman with right upper quadrant pain (case 1) and a 36-year-old woman suffering from left flank pain and intermittent gross hematuria (case 2). An intravenous pyelography of case 1 revealed multiple filling defects in the entire right ureter, whereas retrograde pyelography in case 2 showed diffuse narrowing in the mid and lower portions of the left ureter. Localized amyloidosis of the ureter was diagnosed in the two cases, and both had amyloid deposit in the renal pelvis and the urinary bladder in case 1, and in the contralateral ureter and the renal pelvis in case 2. Right nephroureterectomy was performed in case 1, but a segmental resection of the ureter with preservation of the kidney was administered in case 2. These two cases demonstrate that ureteral amyloidosis can be associated with amyloid deposition in the renal pelvis and the urinary bladder. Although ureteral amyloidosis is a rare occurrence, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of ureteral obstruction to avoid unnecessary radical surgery.
- Necrotizing Vasculitis of the Gallbladder: A case report.
- Ah Won Lee, Youn Soo Lee, Seok Jin Kang, Byung Kee Kim, Sang In Shim
- Korean J Pathol. 1999;33(4):292-294.
- 2,295 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report a case of necrotizing arteritis involving the gallbladder. This case was clinically diagnosed as cholelithiasis with cholecystitis, and necrotizing arteritis was found in the surgically resected specimen. Vascular changes were similar to those seen in classic polyarteritis nodosa, involving medium-sized muscular arteries and characterized by fibrinoid necrosis and panarterial and periarterial inflammation varying from active to resolving stages. Acute cholecystitis is a rare initial clinical manifestation of the systemic vasculitis. If acute cholecystitis is found in the absence of obvious cause, careful examination is essential. Since steroid therapy improves the prognosis in the systemic vasculitis, clinicians and pathologists should be aware of this unusual lesion.
- Urachal Adenocarcinoma with a Concomitant Urachal Remnant: A Case Report.
- Tae Hoon Kim, Mee Joo, Min Kyung Kim, Hanseong Kim, Je G Chi, Jae Y Ro
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(4):280-283.
- 2,139 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Urachal adenocarcinoma is a rare tumor, and it has similarities with nonurachal adenocarcinoma; therefore, it is sometimes difficult to make a diagnosis. We present a typical case of urachal adenocarcinoma that had all the diagnostic criteria including the presence of an urachal remnant. A 65-year-old woman presented with complaints of a painless gross hematuria. Pelvic CT and cystoscopy showed an intraluminal protruding mass centered in the bladder wall. When diagnosed as adenocarcinoma with a signet ring cell component being noted by frozen biopsy, partial cystectomy with resection of the median umbilical ligament and peritoneum was carried out for a suspected urachal adenocarcinoma. The tumor morphology showed as typical mucinous adenocarcinoma. Characteristic tubular structures showing the typical histology of an urachal remnant was found in the perivesical fat. On immunohistochemical staining, the urachal adenocarcinoma showed a pattern similar to colonic adenocarcinoma, while the urachal remnant showed strong positivity for CK7 and Chromogranin A.
- Hyperplasia, Metaplasia, and Dysplasia of the Gallbladder Correlation to Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma.
- Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(6):527-537.
- 2,999 View
- 66 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The correlation of metaplasia to dysplasia and carcinoma in the gallbladder has attracted the attention of many investigators. We mapped and examined a total of 263 cholecystectomized gallbladders to analyze the mucosal changes in the carcinogenesis of the gallbladder. Stones were present in 59.7%, hyperplasia in 28.5%, metaplasia in 55.5% (gastric 37.6%, intestinal 17.9%), dysplasia in 17.1% (low grade 9.1%, high grade 8%) and carcinoma in 7.6%. Metaplasia was more frequently identified in the stone-positive group (62.4%) than in the stone-negative group (45.3%) (P<0.05). Especially, the incidence of intestinal metaplasia was significantly higher in the stone-positive group. Dysplasia and carcinoma were more frequent in the metaplasia-positive group (dysplasia 26.7%, carcinoma 11%) than in the metaplasia-negative group (dysplasia 5.1%, carcinoma 3.4%) (P<0.05). Their incidences were significantly higher in the intestinal metaplasia than in the gastric metaplasia. Forty four percent of the dysplasia-positive cases were associated with carcinoma in the adjacent mucosa but carcinoma was absent in the dysplasia-negative cases. Hyperplasia did not reveal any significant correlation with metaplasia, dysplasia and carcinoma. These results suggest that gallstone is causally related to the metaplasia in the gallbladder and the metaplasia-dysplasia- carcinoma sequence exists in the gallbladder.
- Radiation-Induced Epithelial Proliferation Mimicking Invasive Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Report of 2 Cases.
- Ok Jun Lee, Kyu Rae Kim, Dae Woon Eom, Hyun Jung Kim, Na Hye Myong, Jae Y Ro
- Korean J Pathol. 2004;38(5):341-344.
- 2,260 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Radiation-induced epithelial proliferation in the urinary bladder mimicking urothelial carcinoma has received only a little attention in the literature. Herein, we describe two cases of radiation-induced epithelial proliferative changes, which mimicked invasive urothelial carcinoma. Cystoscopy revealed bullous or edematous mucosal changes with multiple hemorrhagic foci. Microscopically, we observed inverted epithelial proliferation, forming nests and cords extending into the lamina propria. The epithelial cells in these nests and cords exhibited enlarged, hyperchromatic and pleomorphic nuclei, closely mimicking the infiltrative growth of urothelial carcinoma. However, the presence of radiation-induced changes was validated by the observation of abundant vacuolated cytoplasm, normal or slightly increased nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios, the absence of mitotic activity, dilated blood vessels containing frequent fibrin thrombi, scattered atypical fibroblasts, and the patients' previous history of radiation treatment. Radiation-induced changes should be always included in differential diagnoses of proliferative epithelial lesions in the urinary bladder and a pertinent clinical history of radiotherapy should be searched.
- Hamartoma Arising in the Urinary Bladder: A case report.
- Young Bae Kim, Tae Sook Hwang, Byung Gon Park, Jin Sook Jeong, Sook Hee Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 1993;27(3):283-286.
- 2,503 View
- 57 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hamartoma of the bladder is quite a rare entity which is composed of a disorderly admixture of mature cellular elements normally present in the urinary bladder. There is a great controversy regarding the pathogenesis of this lesion. Whether it is a true hamartomatous lesion or metaplastic lesion developed secondary to the inflammatory process. Similar or identical lesions has often been given by other names such as florid examples of cystitis glandularis. We prefer to cell florid examples of cystitis glandularis rather than hamartoma when it was occurred in an old age higher then 50th decade. Here we report a case of hamartoma of the urinary bladder in 44 years old man. Cystoscopic examination revealed a papillary polypoid mass which was attached to the fundus of bladder by long stalk. The mass measured 1.5 cm in greatest diameter. It was composed of epithelial nests resembling von Brunn's nest, cystitis glandularis or cystitis cystica dispersed in a stroma rich in smooth muscle and fibrous tissue.
- Pathologic Analysis of Gallbladder Cancer by the Stage and Intestinal Metaplasia with the Diagnostic Significance of CEA and p53.
- Hee Jin Chang, Jung Il Suh
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(7):599-607.
- 2,059 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty cases of gallbladder cancers were examined using 5 mm stepwise tissue sections. We analyzed the clinicopathologic findings of the early (stage 1, II) and advanced carcinoma (stage III, IV, V) and those of carcinoma with or without metaplasia in the tumor. We also performed CEA and p53 immunohistochemical staining and compared their findings with those of normal mucosa and preneoplastic lesions. The results were as follow: 1) All of the early carcinomas (n=5) were incidentally diagnosed after the resection for the gallstone. They were compared to advanced carcinoma (n=15) in the absence of the lymphatic or angioinvasion, recurrence, metastasis and death. 2) Metaplastic and non-metaplastic carcinoma did not reveal any difference of the clinicopathologic findings except age distribution. 3) CEA and p53 were positive in preneoplastic and malignant lesions. The extent of staining was related to the degree of the atypia. From the above results, an early detection of gallbladder cancer is very important for the prognosis of the patients. Since preoperative diagnosis is difficult, thorough pathologic examination of routinely resected gallbladder is necessary for the early diagnosis. CEA and p53 immunohistochemical staining may be helpful in the differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic and neoplastic lesion of the gallbladder.
- Immunohistochemical Study for p53 and hsc70 in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: Correlation with Histologic Grade, Clinical Stage and DNA Ploidy Pattern.
- Hyuni Cho, Sung Jin Cho, Han Kyeom Kim, Yang Seok Chae
- Korean J Pathol. 1995;29(6):766-775.
- 1,982 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is the most common cancer of the genitourinary tract in Korea and its prognosis is determined by the histologic grade and clinical stage present at initial diagnosis. Recently, an extensive search for a more objective and reproducible method to evaluate the proliferation activity of cancer cells has been done. The p53 gene is located on the short arm of the chromosome 17 and acts as a cancer suppressor gene. Mutant p53 gene induces malignant transformation. Recent studies reveal that the level of mutant p53 protein is elevated in some human tumor and many diverse transformed cell lines. Heat shock proteins(HSPs) are present constitutively in normal cells, where they play an important role in normal cell metabolism. In mammalian cells, they are induced by a variety of physical and chemical stimuli. A protein that belongs to the hsp70 family, called hsc70, is only slightly heat inducible and is found at a higher level in growing cells than in the resting cells. The mutant p53 protein binds with hsc70 and the p53-hsc70 complex has functional significance in the transforming capacity of the mutant p53. We investigated the correlation between the p53 and hsc70 by immunohistochemical methods and with better defined prognostic indicators such as histologic grade, clinical stage, and DNA ploidy pattern in 42 transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder. The results are summarized as follows. p53 expression rate was higher in the DNA aneuploid group than in the DNA diploid group(p=0.061), but there was no significant difference in the histologic grade(p=0.861) or clinical stage(p=0.154). The higher the hsc70 expression rate was, the poorer the tumor differentiation(p=0.000) and the deeper the invasion(p=0.001). The aneuploid group showed a higher hsc70 expression rate than the diploid group(p=0.017). 27 of 42(64.3%) carcinomas showed positivity of both p53 and hsc70. Though statistically insignificant, their correlation showed a relatively low correlation coefficient (P=0.059). In conclusion, we suspect that p53 and hsc70 are closely correlated to each other by comparing the results of this immunohistochemical study, and hsc70 will be a useful prognostic marker in transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder after sufficient follow up studies are performed.
- Cytologic Findings of Primary Small Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A case report.
- Mi Seon Kwon, Geung Hwan Ahn, Jin Haeng Chung, Seung Sook Lee, Jae Soo Koh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2001;12(2):121-126.
- 2,247 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare malignant tumor. A more rapidly fatal course may be seen in advanced stages of small cell carcinoma as compared to similar stages of urothelial carcinoma. It is very important to recognize this distinct form of bladder cancer by urinary cytology. The differential diagnosis of small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder includes metastatic small cell carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma, and primary or secondary malignant lymphoma. This article highlights the urinary cytologic diagnosis of a case of primary small cell carcinoma. A 59-year-old male presented with gross hematuria for five months. Urinary cytology showed high cellularity consisting of tiny monotonous tumor cells in the necrotic background. The tumor cells occurred predominantly singly, but a few in clusters. The cytoplasm was so scanty that only a very narrow rim of it was seen. The nuclei were oval or round and had finely stippled chromatin. Rarely, the nuclei contain visible nucleoli. Frequently cell molding was noted in clusters. Many single cells demonstrated nuclear pyknosis or karyorrhexis. The histologic findings of transurethral resection and partial cystectomy specimen were those of small cell carcinoma. Cytologic distinction may be very difficult but careful attention to clinical features and cellualr details can classify these neoplasms correctly.
- Ectopic Liver Associated with the Gallbladder: A Brief Case Report.
- Hee Eun Kyeong, Younghee Park, Sanghui Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(2):128-130.
- 2,052 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ectopic liver is a rare entity that has been previously identified during abdominal exploration for other surgery and this has usually been described in the vicinity of the liver such as on the gallbladder, hepatic ligaments, diaphragm, thoracic cavity, adrenal glands, pancreas, omentum, spleen, esophagus and umbilical cord. Most cases of ectopic liver reported in the literature were located in the gallbladder. We report here on a case of ectopic liver related to the gallbladder, and this was encountered during an elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
- Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Gallbladder Arising as Double Tumor.
- Dae Hyun Baek, Seong Ki Min, Jin Man Kim, Kwang Sun Suh, Dae Young Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 1990;24(3):299-303.
- 2,005 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pleomorphic (undifferentated) carcinoma is a rare histologic type of carcinomas of the gallbladder and an atypical carcinoid is thought to be an intermediated type between carcinoid tumor and small cell carcinoma. Dense core "neurosecretory" granules can be found in the above mentioned tumors. We experienced a case of a double tumor of the gallbladder in a 51-year old male patient. Grossly, a large solid mass, about 5.0 cm in diameter, was found in the fundic portion and the neck portion also had a small 1.5 cm-sized polypoid mass. Microscopically, these lesions had features of pleomorphic carcinoma and atypical carcinoid, respectively. Immunohistochemically, they manifested reactivity for neuron specific enolase. Ultrastructural study revealed neurosecretory granules in the cytoplasms of tumor cells of the fundic and neck masses. Although light microscopic features of these tumor masses are quite different, we consider that these tumors represent a spectrum of neuroendocrine differentiation.
- Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Gallbladder.
- Dae Woon Eom, Gil Hyun Kang, Hyuk Jai Gang
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(3):162-164.
- 2,510 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Micropapillary carcinoma (MPC) is a rare variant of carcinoma, and it is composed of small papillary neoplastic cell clusters lying within clear lacunar spaces that simulate lymphovascular channels. This tumor has been described in the several organs such as the breast, lung, urinary bladder and salivary gland and it is known to be frequently associated with a high incidence of lymphatic invasion and metastasis in lymph nodes, resulting in poor clinical outcome. We present here a case of MPC in the gall bladder, and this type of case has not been previously described. Histologically, the tumor was composed of micropapillary carcinoma with tight clusters of micropapillary aggregates in the background of tubular adenoma. Focal invasive micropapillary components were also noted in the submuscular connective tissue. A metastatic lesion in a regional lymph node also showed an entirely micropapillary pattern.
- Florid von Brunn Nests of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Han Seong Kim, Ji Eun Kwak, Sang Hwa Shim, Mee Joo, Sun Hee Chang, Je G Chi, In Rae Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(3):169-171.
- 4,409 View
- 161 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Among benign proliferations of the urinary bladder, von Brunn nests and cystitis cystica et glandularis are common. Sometimes florid proliferation of von Brunn nests makes an intravesical mass, which mimics tumorous lesions. We report here on a case of florid von Brunn nests, occurred in the 34-year-old man with hematuria. Radiological and cystoscopic examinations reveal a polypoid-papillary lesion and transurethral resection was then performed. Pathologically, prominent proliferations of urothelial cell nests were found deep in the lamina propria. Neither significant cytologic atypia nor muscle invasion was noted. Florid von Brunn nests should be considered both clinically and pathologically in the differential diagnosis of a intravesical mass.
- Urinary Cytologic Findings of Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Case Report.
- Dong Hoon Kim, Dong Wook Kang, Kyung Hee Kim, Ju Heon Kim, Mee Ja Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2002;13(2):78-83.
- 2,006 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We report the cytologic features of a case of primary small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder with high grade transitional cell and signet ring cell carcinomatous components. A 64-year-old male presented with gross hematuria for one week. Computed tomography revealed an ill-defined mass in the left lateral wall of the urinary bladder. Urinary cytology showed hypercellularity with predominantly isolated single cells and clustered cells. They have scanty cytoplasm and naked hyperchromatic nuclei with finely granular nuclear chromatin and rare nucleoli. The tumor cells occurred predominantly singe cells, but a few in clusters. Nuclear molding was prominent. No glandular formation or nesting was noted. The second tumor cells had high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, irregular nuclear membrane, and coarse granular chromatin. The background was inflamed and necrotic. The histologic findings of transurethral resection were mainly composed of small cell carcinoma, and partly transitional cell and signet ring cell carcinomatous components. Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma have distinctive cytologic features to make a proper diagnosis.
- Expression of p16, Rb and FHIT Proteins in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder.
- Sun Hee Han, Ju Han Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Jungsuk An, Eung Seok Lee, Young Sik Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2008;42(5):294-298.
- 2,445 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The goal of this study was to investigate the expression of p16, retinoblastoma (Rb) and fragile histidine triad (FHIT) proteins in urothelial carcinomas of the urinary bladder, and to evaluate the relationship between clinicopathlogic parameters and each protein expression level. METHODS: The expression of p16, Rb, and FHIT proteins were studied in 176 patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder by immunohistochemistry. RESULTS: The diffuse positive expression of the p16 protein was significantly associated with high grade and advanced tumor depth (p=0.007 and p=0.020). The loss of the Rb protein was significantly associated with old age and disease recurrence (p=0.020 and 0.037). The loss of the FHIT protein was significantly associated with advanced tumor depth (p=0.002). CONCLUSION: Our data suggest that p16 and FHIT proteins may be involved in the progression of urothelial carcinoma. In addition, p16 may be a useful prognostic marker for individual urothelial carcinoma patients.
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma of Urinary Bladder Diagnosed by Urine Cytology: A Case Report.
- Joo Heon Kim, Ho Lee, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Sang Ho Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(1):71-73.
- 1,987 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcomas are found mainly in young patients, but rare in adults. A correlated cytological and histologic study of one case of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is presented. The cytologic appearance of the urine smear corresponded well with the histologic findings. Cytologically, two main cell types were distinguished; a predominant primitive, small round cell with scant cytoplasm and a large cell with abundant cytoplasm. The cytologic feature proving rhabdomyoblastic differenti-ation, such as cross-striation, was absent.
- Study on Creating A Classifier for Grading of Bladder Carcinoma Based on Computerized Method.
- Hyun Ju Choi, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Heung Kook Choi
- Korean J Pathol. 2002;36(3):154-162.
- 1,899 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We have described an objective and reproducible classification method for grading malignancy in the Feulgen stained bladder carcinoma. To create an optimized classifier for malignancy grading of histological bladder carcinoma cell images, it is necessary to extract the features that accurately describle the order/disorder of the nuclear variation and to evaluate the significance of the features. Above all, features selection considered about the correlation of features is very important, because the performance of the classification method depends on the selected features.
METHODS
First, we acquired 40 representative histological bladder carcinoma cell images from each of four groups (Grade 1, Grade 2A, Grade 2B, Grade 3) and extracted morphology features, texture features and the texture features of wavelet transformed images. Second, we evaluated the significance of the extracted features using variance analysis. Third, we created classifiers for each selected feature and its combination set using discriminant analysis. Finally, we compared and analyzed the correct classification rate of each classifer.
RESULTS
The optimized classifier was created from the combination of morphology features, texture features and the texture features of wavelet transformed images.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that the correlation of features is more important than one feature's great significance in grading the malignancy of bladder carcinoma, and we have confirmed that the correct classification rate is determined by feature extractin, feature evaluation and feature selection.
- Leiomyoma of the Urinary Bladder.
- Kye Weon Kwon, Hee Jung Ahn, Yoon Jung Choi, Young Kwon Hong, Jae Seop Shin
- Korean J Pathol. 1997;31(12):1320-1323.
- 2,150 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Leiomyoma is commonly found in the female genital tract, but occurrence in the urinary bladder is very rare with only 235 cases reported in the literature. These tumors have been classified as intravesical (63%), intramural (7%) and extravesical (30%) depending on the direction of the growth. We report a case of intravesical leiomyoma of the urinary bladder in a 36 year-old woman who exhibited dysuria and urinary retention. The gross and microscopical findings of leiomyoma of the bladder are similar to those of the uterus. Immunohistochemical stains for estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) revealed diffuse nuclear staining in smooth muscle cells, supporting the hypothesis of hormonal influence in tumorigenesis.
- Cytodiagnosis of Primary Small Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report.
- Hye Sun Kim, Aee Ree Kim, Chul Hwan Kim, Yang Seok Chae, Nam Hee Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1994;5(2):167-171.
- 1,834 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Samll cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is a rare tumor which occurs in about 0.48% of all bladder tumors. We report cytologic features of small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder in a 66-year-old man who had painless total gross hematuria, which was confirmed by partial cystectomy. In urine cytology, abundant tumor cells appeared in scattered and clustered forms in a bloody background. The tumor cells were small and uniform in size with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. The nuclei of the tumor cells were hyperchromatic, characteristically molded and showed inconspicuous nucleoli. The cytoplasms were scanty and plae blue.
- A Case of Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Urinary Biadder.
- Hye Rim Park, Min Chul Lee, Nack Kyu Choi, Young Euy Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1991;25(3):256-262.
- 2,727 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder is a proliferative spindle cell lesion that microscopically may suggest a sarcoma but that are benign without a recent history of an operation. The first such case was reported by Roth, in 1980, and thereafter about seven more cases were reported in medical literatures. We reported a case of inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder mimicking leiomyosarcoma. Patient was a 36-year-old woman with complaint of painless total and gross hematuria for 3 weeks. Partial cystectomy specimen showed a well-demarcated nodular mass of yellow white color, involving the submucosal and muscular layers. Microscopic examination revealed proliferating bundles of spindle cells interspersed with infiltration of many inflammatory cells including eosinophils. Spindle cells were positive for vimentin on immunohistochemistry and corresponding to myofibroblasts on the electron microscopic examination.
- Inflammatory Pseudotumor of the Urinary Bladder: An Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study.
- Seung Sam Paik, Joo Seob Keum, Moon Hyang Park, Jung Dal Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):447-452.
- 2,072 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Inflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder is an unusual, benign mesenchymal proliferative lesion of the submucosal stroma easily mistaken for a malignant neoplasm clinically and histologically. We present a case and describe the clinical presentation and radiologic, histologic, histochemical, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural findings. A 23-year old patient presented with sudden onset of gross painless hematuria for 3 months. There was no previous instrumentation or surgery involving the genitourinary tract. Cystoscopy revealed a large polypoid and ulcerated bladder mass. The lesion consisted of plump spindle shaped, fibroblast-like cells embedded in a myxoid stroma. Mitotic figures were negligible and the lesion showed encroachment on the superficial muscle bundles. The spindle cells were immunoreactive for vimentin and muscle specific actin. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural findings revealed the fibroblastic-myofibroblastic nature of this lesion. Complete surgical excision by partial cystectomy was successful in eradicating the lesion. The findings are described with a discussion of the pathogenesis and review of the literature.
- Alpha-Fetoprotein-Producing Carcinoma of the Gallbladder.
- Young Ha Oh, Haeng Ji Kang, Hyoung Guen Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Yong Il Kim, Jung Dal Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 1996;30(5):453-456.
- 2,366 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a well-known tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatoblastoma, and yolk sac tumors. There are several studies on AFP-producing tumors that arose from the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, lung, kidney, and urachal tract. AFP-producing carcinoma of the gallbladder is extremely rare. We report a case of AFP-producing carcinoma of the gallbladder without liver involvement in a 58-year-old man with a gallstone, on which clinical, morphologic, and immunohistochemical studies were performed.
- Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Related Protein in Gallbladder Cancer: An Association with p53 Mutation.
- Ho Sung Park, Kyu Yun Jang, Kyung Ryoul Kim, Hak Yong Lee, Andrzej S Tarnawski, Adhip P N Majumdar, Myoung Jae Kang, Dong Geun Lee, Woo Sung Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2005;39(6):385-390.
- 2,362 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It has been well demonstrated that the overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with numerous gastrointestinal malignancies, including gallbladder carcinoma. However, the cellular events that regulate EGFR in cancer cells have not been fully elucidated. A novel negative regulator of EGFR that is referred to as EGFR related protein (ERRP) has recently been identified. The aim of this study was to investigate the expression and localization of ERRP in gallbladder carcinoma and to examine a possible role for ERRP.
METHODS
We examined the immunohistochemical expressions of ERRP, p53 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen labeling index (PCNA-LI) in formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded specimens of 43 cases of gallbladder carcinoma, 7 cases of adenoma and 3 cases of dysplasia.
RESULTS
In the normal mucosa, ERRP immunoreactivity was positive in over 64% of specimens. In contrast, the ERRP staining was positive in only 46% of the cancer specimens. The expression of ERRP in cancer cells was inversely correlated with tumor cell proliferation. The loss of ERRP expression correlated with the p53 overexpression.
CONCLUSIONS
Our data indicate that the down-regulation or loss of ERRP could play an important role in the progression of gallbladder carcinoma. The inverse relationship between the ERRP expression and PCNA-LI suggests that ERRP may play a role in the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation in gallbladder cancer.
- Pedunculated Gallbladder Encircled by Accessory Liver: A case report.
- Woo Ho Kim, Cheol Keun Park, Kyung Hyuck Ko
- Korean J Pathol. 1987;21(4):274-277.
- 2,047 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors presented a case of gastroschisis with a pedunculated gallbladder embedded in hepatic tissue. The patient was born after fullterm gestation. Due to extensive abdominal wall defect, she succumbed 3 days after birth. There was a pedunculated mass measuring 2.5x1.5x1.5 cm between the liver and distended stomach without any attachment to the liver. The pedicle of the mass was connected to the common bile duct. Cut surface revealed that the mass was an accessory hepatic lobe encircling the gallbladder. The histologic feature of both accessory liver and gallbladder was markedly altered probably due to vascular obstruction. We could find only a single similar case in literlature. That case was associated with Beckwith syndrome and ours was associated with large atrial spetal defect, large patent ductus arteriosus, accessory spleen as well as gastroschisis. The common feature of abdominal wall defect might be a predisposing factor.
- New Techniques for the Detection of the Malignant Cells in Urine Cytology.
- Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(1):18-26.
- 2,410 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is common in the genitourinary tract. The gold standard for the diagnosis of bladder cancer has been cystoscopy, along with urine cytology. Cystoscopy is an invasive and relatively expensive technique. By comparison, urine cytology is easy to perform and specific for a diagnosis of bladder cancer, although less sensitive, especially in low-grade tumors. For this reason, there has been a need for superior noninvasive technology to increase our confidence in being able to detect bladder cancer. There are many reports of the various urinary tests that are available to facilitate the diagnosis. In this article, I reviewed the literature on urinary markers and tests that may be clinically useful, including fluorescence in situ hybridization, uCyt+/Immunocyte, the BTA(R) test, the NMP 22TM, the FDP(R) test, the telomerase activity test, the HA and HAse tests, and flow cytometry. Most of these tests have a higher sensitivity and specificity than cytology. However, urine cytology has the highest specificity, especially in individuals with a high-grade tumor. We conclude that no urinary markers or tests can replace the role of cystoscopy along with cytology in the diagnosis of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. However, some markers could be used adjunctively to increase the diagnostic accuracy during screening or during the postoperative follow-up examination of patients with bladder cancer.
- Prognostic Value of the PCNA Index in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder.
- Sang Yeop Yi, Young Nyun Park, Chan Il Park
- Korean J Pathol. 1994;28(3):282-287.
- 1,877 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- It is well known that histologic grade and tumor stage are important prognostic factors, and that the monoclonal antibody to proliferating cell nuclear antigen(PCNA) can recognize S-phase cells. The PCNA index of 53 transitional cell carcinomas(TCCs) of the urinary bladder was studied to evaluate its prognostic validity. The PCNA indices of TCCs ranged from 38 to 92, whih were quite different from that of normal transitional epithelium(9.4). The PCNA indices were significantly higher in tumors of the higher histologic grade and/or tumor stage(correlation coefficient 0.64 and 0.43; P=0.00). The PCNA index was particularly valuable in discriminating the superficial TCCs from the deeply invasive TCCs(67.1+/-15.46 and 79.9+/-9.70; P=0.000). Among TCCs of the same tumor stage, the histologic grade affected the PCNA index. However, TCCs of the same histologic grade revealed similar PCNA indices regardless of tumor stage. These results indicate that the PCNA index is an objective and reliable prognostic factor in TCCs, which is superior to the conventional histologic grade.
- Micropapillary Variant of Urothelial Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder: Report of a Case with Cytologic Diagnosis in Urine Specimen.
- Young Seok Lee, Hyunjoo Lee, Jung Woo Choi, Bongkyung Shin, Hankyem Kim, Insun Kim, Aeree Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2006;17(1):46-50.
- 2,201 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A micropapillary variant of urothelial carcinoma (MPC) is a distinct entity with an aggressive clinical course. It has a micropapillary configuration resembling that of ovarian papillary serous carcinoma. Its cytologic features have rarely been reported. We report a case of MPC detected by urine cytology. A woman aged 93 years presented with a chief complaint of macroscopic hematuria. Cytology of her voided urine showed clusters of malignant cells in a micropapillary configuration. Each tumor cell had a vacuolated cytoplasm, a high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio, and irregular hyperchromatic nuclei. An ureteroscopic examination revealed exophytic sessile papillary masses extending from the left lateral wall to the anterolateral wall of the urinary bladder. A transurethral resection of the tumor was carried out. The tumor was characterized by delicate papillae with a thin, well-developed fibrovascular stromal core and numerous secondary micropapillae lined with small cuboidal cells containing uniform low- to intermediate-grade nuclei and occasional intracytoplasmic mucinous inclusions. These tumor cells infiltrated the muscle layers of the bladder, and lymphatic tumor emboli were frequently seen. Recognizing that the presence of MPC components in urinary cytology is important for distinguishing this lesion from low-grade papillary lesions and high-grade urothelial carcinomas can result in early detection and earlier treatment for an improved treatment outcome.

 E-submission
E-submission






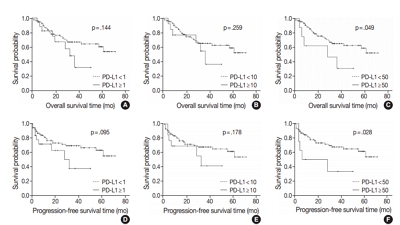
 First
First Prev
Prev



