Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Mutational status of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP): molecular analysis should be performed for NIFTPs with nuclear score 3
- Ayaka Sako, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Michiko Matsuse, Miyoko Higuchi, Akira Miyauchi, Takashi Akamizu, Atsushi Kawakami, Norisato Mitsutake
- Received October 14, 2025 Accepted December 6, 2025 Published online February 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.12.06 [Epub ahead of print]
- 268 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The classification of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) was introduced to prevent the overtreatment of indolent tumors that were formerly diagnosed as non-invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas (NIEFV-PTCs). Although NIFTP was initially estimated to account for 10%–20% of papillary thyroid carcinomas in Western populations, its incidence is substantially lower in Asian cohorts. However, a multi-institutional Japanese study revealed that 31.0% of tumors previously diagnosed as follicular adenomas (FAs) were reclassified as NIFTPs. NIFTP diagnosis requires a nuclear score (NS) of 2–3, and according to the recent World Health Organization criteria, molecular analysis is recommended, but not mandatory, to exclude high-risk subtypes, namely cases with the BRAFV600E mutation, particularly for NS3 tumors. Methods: We performed genetic analysis on 92 archival thyroid tumor samples, including 69 previously diagnosed as FA, of which 34 remained as FA upon re-evaluation (group A) and 35 were reclassified as NIFTP with NS2 (group B). Additional 23 tumors previously diagnosed as NIEFV-PTC were reclassified as NIFTP with NS3 (group C). Results: RAS mutations were detected in 8.8%, 34.3%, and 21.7% of the tumor samples in groups A, B, and C, respectively, whereas BRAF mutations were present in 43.5% of the tumor samples in group C only. Conclusions: These findings suggest the presence of two distinct tumor subsets within NIFTP-NS3, underscoring the need for routine molecular diagnostics in NIFTP-NS3 to facilitate appropriate clinical management.
- Solitary fibrous tumor: an updated review
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):20-46. Published online December 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.08
- 1,748 View
- 140 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a fibroblastic neoplasm characterized by a branching, thin-walled dilated staghorn-shaped (hemangiopericytoma-like) vasculature and a NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion. SFTs can occur in almost any anatomical location, including superficial and deep soft tissues, visceral organs, and bone. They most commonly occur in extrapleural locations, equally affect both sexes, and are typically present in adults. Although metastasis is rare, SFTs frequently show local recurrence. The diagnosis of SFTs is difficult because of their broad histological and morphological overlap with other neoplasms. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding disease management and prognosis. Despite advances in molecular diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, the biological complexity and unpredictable clinical behavior of SFTs present significant challenges. This review provides an updated overview of SFT, with a focus on its molecular genetics, histopathological features, and diagnostic considerations.
- Categorizing high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma into clinically relevant subgroups using deep learning–based histomic clusters
- Byungsoo Ahn, Eunhyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):91-104. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.23
- 5,367 View
- 254 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSC) exhibits significant heterogeneity, posing challenges for effective clinical categorization. Understanding the histomorphological diversity within HGSC could lead to improved prognostic stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Methods: We applied the Histomic Atlases of Variation Of Cancers model to whole slide images from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for ovarian cancer. Histologically distinct tumor clones were grouped into common histomic clusters. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering classified HGSC samples into three groups: highly differentiated (HD), intermediately differentiated (ID), and lowly differentiated (LD). Results: HD tumors showed diverse patterns, lower densities, and stronger eosin staining. ID tumors had intermediate densities and balanced staining, while LD tumors were dense, patternless, and strongly hematoxylin-stained. RNA sequencing revealed distinct patterns in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and energy metabolism, with upregulation in the HD, downregulation in the LD, and the ID positioned in between. Survival analysis showed significantly lower overall survival for the LD compared to the HD and ID, underscoring the critical role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in HGSC progression. Conclusions: Deep learning-based histologic analysis effectively stratifies HGSC into clinically relevant prognostic groups, highlighting the role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in disease progression. This method offers a novel approach to HGSC categorization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Syed Mohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, Ahmad H. Alhowail, Syed Imam Rabbani, Naira Nayeem, Syed Mohammed Emaduddin Asdaq, Faiqa Nausheen
SAGE Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
- Primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a female patient: case report
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):84-90. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.30
- 5,158 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BCOR-rearranged sarcoma was classified by the World Health Organization in 2020 as a new subgroup of undifferentiated small round-cell sarcoma. It is known to occur very rarely in the kidney. This report presents the first case of a primary renal BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma in a 22-year-old woman. An 8-cm cystic mass was identified in the left kidney by abdominal pelvic computed tomography. Histopathologic examination revealed the mass to be composed of small round to oval or spindle cells with fibrous septa and a delicate vascular network. A BCOR::CCNB3 fusion was detected by next-generation sequencing–based molecular testing. BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma presents diagnostic difficulties, highlighting the importance of recognizing its histological features. Immunohistochemical markers are helpful for diagnosis, but genetic molecular testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis. These tumors have a very poor and aggressive prognosis, and an optimal therapeutic regimen has not yet been defined. Therefore, further studies are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
Jungo Imanishi, Kenji Sato, Yoshinao Kikuchi, Asako Yamamoto, Shiori Watabe, Taisuke Matsuyama, Chiaki Sato, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Hirotaka Kawano
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology.2025; 55(10): 1097. CrossRef
- Update on the management of BCOR::CCNB3 sarcoma
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):39-49. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
- 4,482 View
- 329 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Methods
We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
Results
We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
Shuo Lv, Jinbao Wang, Guohao Chen, Yongshun Wang, Naiqing Liu
Frontiers in Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in immunotherapy for thyroid malignancies: from molecular targets to clinical outcomes
- Revisiting the utility of identifying nuclear grooves as unique nuclear changes by an object detector model
- Pedro R. F. Rende, Joel Machado Pires, Kátia Sakimi Nakadaira, Sara Lopes, João Vale, Fabio Hecht, Fabyan E. L. Beltrão, Gabriel J. R. Machado, Edna T. Kimura, Catarina Eloy, Helton E. Ramos
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):117-126. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.07
- 5,200 View
- 273 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Among other structures, nuclear grooves are vastly found in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Considering that the application of artificial intelligence in thyroid cytology has potential for diagnostic routine, our goal was to develop a new supervised convolutional neural network capable of identifying nuclear grooves in Diff-Quik stained whole-slide images (WSI) obtained from thyroid fineneedle aspiration.
Methods
We selected 22 Diff-Quik stained cytological slides with cytological diagnosis of PTC and concordant histological diagnosis. Each of the slides was scanned, forming a WSI. Images that contained the region of interest were obtained, followed by pre-formatting, annotation of the nuclear grooves and data augmentation techniques. The final dataset was divided into training and validation groups in a 7:3 ratio.
Results
This is the first artificial intelligence model based on object detection applied to nuclear structures in thyroid cytopathology. A total of 7,255 images were obtained from 22 WSI, totaling 7,242 annotated nuclear grooves. The best model was obtained after it was submitted 15 times with the train dataset (14th epoch), with 67% true positives, 49.8% for sensitivity and 43.1% for predictive positive value.
Conclusions
The model was able to develop a structure predictor rule, indicating that the application of an artificial intelligence model based on object detection in the identification of nuclear grooves is feasible. Associated with a reduction in interobserver variability and in time per slide, this demonstrates that nuclear evaluation constitutes one of the possibilities for refining the diagnosis through computational models.
- EWSR1 rearranged primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma: a diagnostic conundrum
- Nilay Nishith, Zachariah Chowdhury
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):284-288. Published online September 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.08.08
- 4,335 View
- 213 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary renal myoepithelial carcinoma is an exceedingly rare neoplasm with an aggressive phenotype and Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) rearrangement in a small fraction of cases. In addition to its rarity, the diagnosis can be challenging for the pathologist due to morphologic heterogeneity, particularly on the biopsy specimen. At times, immunohistochemistry may be indecisive; therefore, molecular studies should be undertaken for clinching the diagnosis. We aim to illustrate a case of primary myoepithelial carcinoma of the kidney with EWSR1-rearrangement in a 67-year-old male patient who presented with right supraclavicular mass, which was clinically diagnosed as carcinoma of an unknown primary. An elaborate immunohistochemical work-up aided by fluorescent in-situ hybridization allowed us to reach a conclusive diagnosis. This unusual case report advocates that one should be aware of the histological mimickers and begin with broad differential diagnoses alongside sporadic ones and then narrow them down with appropriate ancillary studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney
João Lobo, Huiying He, Raheel Ahmed, Bassel Zein-Sabatto, Thomas Winokur, Shi Wei, Shuko Harada, Jesse K. McKenney, Jonathan L. Myles, Jane K. Nguyen, Christopher G. Przybycin, Sean R. Williamson, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Reza Alaghehbandan
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 49(10): 1078. CrossRef
- Primary Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney
- Loss of aquaporin-1 expression is associated with worse clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study
- Seokhyeon Lee, Bohyun Kim, Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):232-237. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.17
- 4,908 View
- 171 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aquaporin (AQP) expression has been investigated in various malignant neoplasms, and the overexpression of AQP is related to poor prognosis in some malignancies. However, the expression of AQP protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has not been extensively investigated by immunohistochemistry with large sample size.
Methods
We evaluated the AQP expression in 827 ccRCC with immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarray blocks and classified the cases into two categories, high and low expression.
Results
High expression of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) was found in 320 cases (38.7%), but aquaporin-3 was not expressed in ccRCC. High AQP1 expression was significantly related to younger age, low TNM stage, low World Health Organization/International Society of Urologic Pathology nuclear grade, and absence of distant metastasis. Furthermore, high AQP1 expression was also significantly associated with longer overall survival (OS; p<.001) and progression-specific survival (PFS; p<.001) and was an independent predictor of OS and PFS in ccRCC.
Conclusions
Our study revealed the prognostic significance of AQP1 protein expression in ccRCC. These findings could be applied to predict the prognosis of ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
César I. Gaspari, Carine Beaupere, Seth Richard, Estanislao Peixoto, Bouchra Lekbaby, Mirko Minini, Branko Dubravcic, Javier Vaquero, Marie Vallette, Ander Arbelaiz, Marion Janona, Corentin Louis, Pauline Le Gall, Cédric Coulouarn, Julieta Marrone, Juan E
The American Journal of Pathology.2026; 196(2): 428. CrossRef - Construction and validation of renal cell carcinoma tumor cell differentiation-related prognostic classification (RCC-TCDC): an integrated bioinformatic analysis and clinical study
Yifan Liu, Keqin Dong, Yuntao Yao, Bingnan Lu, Lei Wang, Guo Ji, Haoyu Zhang, Zihui Zhao, Xinyue Yang, Runzhi Huang, Wang Zhou, Xiuwu Pan, Xingang Cui
Annals of Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Assessment of Aquaporins in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: An In Silico Analysis
Vignesh Krishnasamy, Lalhmingliana, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Current Biotechnology.2025; 14(2): 130. CrossRef - Targeting PLOD2 induces epithelioid differentiation and improves therapeutic response in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma
Xiangyu Chen, Dongkui Xu, Yu Ji, Xichen Dong, Xiaomei Dong, Zihan Li, Jingyu Tan, Qianqian Sun, Huixian Xin, Ziwei Liu, Qing Deng, Tao Wen, Yanjun Jia, Xuhui Zhu, Jian Liu
Journal of Advanced Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Exosomal MiR-874 as a Potential Biomarker for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Amal F. Gharib, Saad S. Al-Shehri, Abdulraheem Almalki, Ayman Alhazmi, Mamdouh Allahyani, Ahmed Alghamdi, Amani A. Alrehaili, Maha M. Bakhuraysah, Althobaiti Naif Saad M., Weal H. Elsawy
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Loss of Aquaporin-1 in Tumor Cells Fosters Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Progression
- Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
- Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):319-325. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.29
- 9,747 View
- 315 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Due to the extremely indolent behavior, a subset of noninvasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas has been classified as “noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP)” since 2016 and is no longer considered carcinoma. Since the introduction of this new terminology, changes and refinements have been made in diagnostic criteria. Initially, the incidence of NIFTP was estimated substantial. However, the reported incidence of NIFTP varies greatly among studies and regions, with higher incidence in North American and European countries than in Asian countries. Thus, the changes in the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) differ inevitably among regions. Because more conservative surgery is recommended for NIFTPs, distinguishing NIFTPs from papillary thyroid carcinomas in preoperative fine-needle aspiration cytology became one of the major concerns. This review will provide comprehensive overview of updates on diagnostic criteria, actual incidence and preoperative cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP, and its impact on the ROM in TBSRTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Papillae, psammoma bodies, and/or many nuclear pseudoinclusions are helpful criteria but should not be required for a definitive cytologic diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma: An institutional experience of 207 cases with surgical follow up
Tarik M. Elsheikh, Matthew Thomas, Jennifer Brainard, Jessica Di Marco, Erica Manosky, Bridgette Springer, Dawn Underwood, Deborah J. Chute
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(6): 348. CrossRef - ThyroSeq overview on indeterminate thyroid nodules: An institutional experience
Sam Sirotnikov, Christopher C. Griffith, Daniel Lubin, Chao Zhang, Nabil F. Saba, Dehong Li, Amanda Kornfield, Amy Chen, Qiuying Shi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(7): 353. CrossRef - Oncocytic Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Case Report
Kaveripakam Ajay Joseph, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S4): 606. CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Preoperative evaluation of thyroid nodules – Diagnosis and management strategies
Tapoi Dana Antonia, Lambrescu Ioana Maria, Gheorghisan-Galateanu Ancuta-Augustina
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 246: 154516. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - Strategies for Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
Deepika Yadav, Pramod Kumar Sharma, Rishabha Malviya, Prem Shankar Mishra
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(5): 406. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
- Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):354-360. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.05
- 8,672 View
- 154 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Detection of glandular abnormalities in Papanicolaou (Pap) tests is challenging. This study aimed to review our institute’s experience interpreting such abnormalities, assess cytohistologic concordance, and identify cytomorphologic features associated with malignancy in follow-up histology.
Methods
Patients with cytologically-detected glandular lesions identified in our pathology records from 1995 to 2020 were included in this study.
Results
Of the 683,197 Pap tests performed, 985 (0.144%) exhibited glandular abnormalities, 657 of which had tissue follow-up available. One hundred eighty-eight cases were cytologically interpreted as adenocarcinoma and histologically diagnosed as malignant tumors of various origins. There were 213 cases reported as atypical glandular cells (AGC) and nine cases as adenocarcinoma in cytology, yet they were found to be benign in follow-up histology. In addition, 48 cases diagnosed with AGC and six with adenocarcinoma cytology were found to have cervical squamous lesions in follow-up histology, including four squamous cell carcinomas. Among the cytomorphological features examined, nuclear membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and presence of mitoses were associated with malignant histology in follow-up.
Conclusions
This study showed our institute’s experience detecting glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology over a 25-year period, revealing the difficulty of this task. Nonetheless, the present study indicates that several cytological findings such as membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and evidence of proliferation could help distinguishing malignancy from a benign lesion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
Havva Gokce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 71. CrossRef - Expertise in Gynecological Pathology Impacts Diagnosis of Atypical Glandular Cell Category in Cervical Cytology
Havva Gökce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease.2025; 29(4): 297. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytological and/or Histopathological Results of Patients with Single and Multiple HPV Positivity
Fatih Mehmet Kaya, Şafak Ersöz, Cihan Comba, Ömer Demir
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analysis of atypical glandular cells in ThinPrep Pap smear and follow-up histopathology
Tengfei Wang, Yinan Hua, Lina Liu, Bing Leng
Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings.2024; 37(3): 403. CrossRef
- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
- Cytopathologic features of human papillomavirus–independent, gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Min-Kyung Yeo, Go Eun Bae, Dong-Hyun Kim, In-Ock Seong, Kwang-Sun Suh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):260-269. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.07.05
- 6,317 View
- 165 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (GEA) is unrelated to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and is clinically aggressive compared with HPV-associated usual-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (UEA). The cytological diagnosis falls short of a definitive diagnosis of GEA and is often categorized as atypical glandular cells (AGCs). To improve cytologic recognition, cytological findings of HPV-independent GEA were analyzed and the results compared with HPV-associated UEA.
Methods
Cervical Papanicolaou (Pap) smears from eight patients with a histopathologic diagnosis of GEA and 12 control cases of UEA were reviewed. All slides were conventionally prepared and/or liquid-based prepared (ThinPrep) and stained following the Pap method. A mucinous background, architectural, nuclear, and cytoplasmic features were analyzed and compared with UEA.
Results
Preoperative cytologic diagnoses of the eight GEA cases were AGCs, favor neoplastic in three cases, adenocarcinoma in situ in one case, and adenocarcinoma in four cases. Cytologically, monolayered honeycomb-like sheets (p = .002) of atypical endocervical cells with vacuolar granular cytoplasm (p = .001) were extensive in GEA, and three-dimensional clusters (p = .010) were extensive in UEA. Although the differences were not statistically significant, background mucin (p = .058), vesicular nuclei (p = .057), and golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin (p = .089) were also discriminatory findings for GEA versus UEA.
Conclusions
Although GEA is difficult to diagnose on cytologic screening, GEA can be recognized based on cytologic features of monolayered honeycomb sheets of atypical endocervical cells with abundant vacuolar cytoplasm and some golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin. UEA cases are characterized by three-dimensional clusters. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Features, Molecular Landscape, and Therapeutic Challenges
Hiroshi Yoshida, Daiki Higuchi, Waku Takigawa, Nao Kikkawa, Taro Yamanaka, Ayaka Nagao, Mayumi Kobayashi-Kato, Masaya Uno, Mitsuya Ishikawa, Kouya Shiraishi
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2026; 16(2): 72. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of Usual- and Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma in a Japanese Population Reveals Distinct Clinicopathological and Molecular Features with Prognostic and Therapeutic Insights
Umme Farzana Zahan, Hasibul Islam Sohel, Kentaro Nakayama, Masako Ishikawa, Mamiko Nagase, Sultana Razia, Kosuke Kanno, Hitomi Yamashita, Shahataj Begum Sonia, Satoru Kyo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7469. CrossRef - Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Y
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 444. CrossRef - Risk Factors Affecting Clinical Outcomes of Low-risk Early-stage Human Papillomavirus–Associated Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Treated by Surgery Alone: Application of Silva Pattern
Bong Kyung Bae, Hyunsik Bae, Won Kyung Cho, Byoung-Gie Kim, Chel Hun Choi, Tae-Joong Kim, Yoo-Young Lee, Jeong-Won Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim, Won Park
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(5): 447. CrossRef - Tall‐columnar glandular cells in SurePath™ liquid‐based cytology Pap sample: Learning from mimics/pitfalls
Nalini Gupta, Vanita Jain, Radhika Srinivasan, Tulika Singh
Cytopathology.2024; 35(4): 510. CrossRef
- Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Features, Molecular Landscape, and Therapeutic Challenges
- Deep learning for computer-assisted diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
- Sean A. Rasmussen, Thomas Arnason, Weei-Yuarn Huang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(2):118-124. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.12.22
- 5,433 View
- 134 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Patients with hereditary diffuse gastric cancer often undergo prophylactic gastrectomy to minimize cancer risk. Because intramucosal poorly cohesive carcinomas in this setting are typically not grossly visible, many pathologists assess the entire gastrectomy specimen microscopically. With 150 or more slides per case, this is a major time burden for pathologists. This study utilizes deep learning methods to analyze digitized slides and detect regions of carcinoma.
Methods
Prophylactic gastrectomy specimens from seven patients with germline CDH1 mutations were analyzed (five for training/validation and two for testing, with a total of 133 tumor foci). All hematoxylin and eosin slides containing cancer foci were digitally scanned, and patches of size 256×256 pixels were randomly extracted from regions of cancer as well as from regions of normal background tissue, resulting in 15,851 images for training/validation and 970 images for testing. A model with DenseNet-169 architecture was trained for 150 epochs, then evaluated on images from the test set. External validation was conducted on 814 images scanned at an outside institution.
Results
On individual patches, the trained model achieved a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) of 0.9986. This enabled it to maintain a sensitivity of 90% with a false-positive rate of less than 0.1%. On the external validation dataset, the model achieved a similar ROC AUC of 0.9984. On whole slide images, the network detected 100% of tumor foci and correctly eliminated an average of 99.9% of the non-cancer slide area from consideration.
Conclusions
Overall, our model shows encouraging progress towards computer-assisted diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Now and future of artificial intelligence-based signet ring cell diagnosis: A survey
Zhu Meng, Junhao Dong, Limei Guo, Fei Su, Jiaxuan Liu, Guangxi Wang, Zhicheng Zhao
Expert Systems with Applications.2026; 296: 129188. CrossRef - Development and application of deep learning-based diagnostics for pathologic diagnosis of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection specimens
Soomin Ahn, Yiyu Hong, Sujin Park, Yunjoo Cho, Inwoo Hwang, Ji Min Na, Hyuk Lee, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Jae J. Kim, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Gastric Cancer.2025; 28(4): 609. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Literature Review of the CDH1 Mutation and Its Role in Gastric Cancer
Malik Samardali, Jehad Samardaly, Ibrahim Shanti
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning for multiclass tumor cell detection in histopathology slides of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
Robin Lomans, Valentina Angerilli, Joey Spronck, Liudmila L. Kodach, Irene Gullo, Fátima Carneiro, Rachel S. van der Post, Francesco Ciompi
iScience.2025; 28(8): 113064. CrossRef - Non-endoscopic Applications of Machine Learning in Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review
Marianne Linley L. Sy-Janairo, Jose Isagani B. Janairo
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2024; 55(1): 47. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence applicated in gastric cancer: A bibliometric and visual analysis via CiteSpace
Guoyang Zhang, Jingjing Song, Zongfeng Feng, Wentao Zhao, Pan Huang, Li Liu, Yang Zhang, Xufeng Su, Yukang Wu, Yi Cao, Zhengrong Li, Zhigang Jie
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning of endoscopic features for the assessment of neoadjuvant therapy response in locally advanced rectal cancer
Anqi Wang, Jieli Zhou, Gang Wang, Beibei Zhang, Hongyi Xin, Haiyang Zhou
Asian Journal of Surgery.2023; 46(9): 3568. CrossRef - Preparing Data for Artificial Intelligence in Pathology with Clinical-Grade Performance
Yuanqing Yang, Kai Sun, Yanhua Gao, Kuansong Wang, Gang Yu
Diagnostics.2023; 13(19): 3115. CrossRef - Using Deep Learning to Predict Final HER2 Status in Invasive Breast Cancers That are Equivocal (2+) by Immunohistochemistry
Sean A. Rasmussen, Valerie J. Taylor, Alexi P. Surette, Penny J. Barnes, Gillian C. Bethune
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(10): 668. CrossRef
- Now and future of artificial intelligence-based signet ring cell diagnosis: A survey
- A machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosis prediction of lymphoid neoplasms using a probabilistic decision-tree algorithm and immunohistochemistry profile database
- Yosep Chong, Ji Young Lee, Yejin Kim, Jingyun Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Gyeongsin Park, Mee Yon Cho, Nishant Thakur
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(6):462-470. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.11
- 7,361 View
- 132 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) has played an essential role in the diagnosis of hematolymphoid neoplasms. However, IHC interpretations can be challenging in daily practice, and exponentially expanding volumes of IHC data are making the task increasingly difficult. We therefore developed a machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosing lymphoid neoplasms.
Methods
A probabilistic decision-tree algorithm based on the Bayesian theorem was used to develop mobile application software for iOS and Android platforms. We tested the software with real data from 602 training and 392 validation cases of lymphoid neoplasms and compared the precision hit rates between the training and validation datasets.
Results
IHC expression data for 150 lymphoid neoplasms and 584 antibodies was gathered. The precision hit rates of 94.7% in the training data and 95.7% in the validation data for lymphomas were not statistically significant. Results in most B-cell lymphomas were excellent, and generally equivalent performance was seen in T-cell lymphomas. The primary reasons for lack of precision were atypical IHC profiles for certain cases (e.g., CD15-negative Hodgkin lymphoma), a lack of disease-specific markers, and overlapping IHC profiles of similar diseases.
Conclusions
Application of the machine-learning algorithm to diagnosis precision produced acceptable hit rates in training and validation datasets. Because of the lack of origin- or disease- specific markers in differential diagnosis, contextual information such as clinical and histological features should be taken into account to make proper use of this system in the pathologic decision-making process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discovery of Marker Genes in Adult T Cell Leukemia (ATL) Pathogenesis with Machine Learning Models and Performance Comparison
Sabire Kiliçarslan, Sait Can Yücebaş
Karadeniz Fen Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 15(3): 1046. CrossRef - Revolutionizing Pathology with Artificial Intelligence: Innovations in Immunohistochemistry
Diana Gina Poalelungi, Anca Iulia Neagu, Ana Fulga, Marius Neagu, Dana Tutunaru, Aurel Nechita, Iuliu Fulga
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(7): 693. CrossRef - Enhanced Immunohistochemistry Interpretation with a Machine Learning-Based Expert System
Anca Iulia Neagu, Diana Gina Poalelungi, Ana Fulga, Marius Neagu, Iuliu Fulga, Aurel Nechita
Diagnostics.2024; 14(17): 1853. CrossRef - Optimization of diagnosis and treatment of hematological diseases via artificial intelligence
Shi-Xuan Wang, Zou-Fang Huang, Jing Li, Yin Wu, Jun Du, Ting Li
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in lymphoma histopathology: a systematic review (Preprint)
Yao Fu, Zongyao Huang, Xudong Deng, Linna Xu, Yang Liu, Mingxing Zhang, Jinyi Liu, Bin Huang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-Life Barriers to Diagnosis of Early Mycosis Fungoides: An International Expert Panel Discussion
Emmilia Hodak, Larisa Geskin, Emmanuella Guenova, Pablo L. Ortiz-Romero, Rein Willemze, Jie Zheng, Richard Cowan, Francine Foss, Cristina Mangas, Christiane Querfeld
American Journal of Clinical Dermatology.2023; 24(1): 5. CrossRef - Validation of a Machine Learning Expert Supporting System, ImmunoGenius, Using Immunohistochemistry Results of 3000 Patients with Lymphoid Neoplasms
Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kyung Jin Seo, Hye-Ra Jung, Gyeongsin Park, Seung-Sook Lee, Yosep Chong
Diagnostics.2023; 13(7): 1308. CrossRef - Clinical approaches for integrating machine learning for patients with lymphoma: Current strategies and future perspectives
Dai Chihara, Loretta J. Nastoupil, Christopher R. Flowers
British Journal of Haematology.2023; 202(2): 219. CrossRef - Current Trend of Artificial Intelligence Patents in Digital Pathology: A Systematic Evaluation of the Patent Landscape
Muhammad Joan Ailia, Nishant Thakur, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Chan Kwon Jung, Kwangil Yim, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2400. CrossRef - Recent Application of Artificial Intelligence in Non-Gynecological Cancer Cytopathology: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(14): 3529. CrossRef - Diagnosis prediction of tumours of unknown origin using ImmunoGenius, a machine learning-based expert system for immunohistochemistry profile interpretation
Yosep Chong, Nishant Thakur, Ji Young Lee, Gyoyeon Hwang, Myungjin Choi, Yejin Kim, Hwanjo Yu, Mee Yon Cho
Diagnostic Pathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Discovery of Marker Genes in Adult T Cell Leukemia (ATL) Pathogenesis with Machine Learning Models and Performance Comparison
- Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology
- Soojeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(2):125-134. Published online February 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.12.31
- 21,578 View
- 651 Download
- 86 Web of Science
- 90 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Digital pathology (DP) is no longer an unfamiliar term for pathologists, but it is still difficult for many pathologists to understand the engineering and mathematics concepts involved in DP. Computer-aided pathology (CAP) aids pathologists in diagnosis. However, some consider CAP a threat to the existence of pathologists and are skeptical of its clinical utility. Implementation of DP is very burdensome for pathologists because technical factors, impact on workflow, and information technology infrastructure must be considered. In this paper, various terms related to DP and computer-aided pathologic diagnosis are defined, current applications of DP are discussed, and various issues related to implementation of DP are outlined. The development of computer-aided pathologic diagnostic tools and their limitations are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Deep learning model to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis from haematoxylin/eosin-stained myocardial tissue
Takeshi Tohyama, Takeshi Iwasaki, Masataka Ikeda, Masato Katsuki, Tatsuya Watanabe, Kayo Misumi, Keisuke Shinohara, Takeo Fujino, Toru Hashimoto, Shouji Matsushima, Tomomi Ide, Junji Kishimoto, Koji Todaka, Yoshinao Oda, Kohtaro Abe
European Heart Journal - Imaging Methods and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The current landscape of artificial intelligence in oral and maxillofacial surgery– a narrative review
Rushil Rajiv Dang, Balram Kadaikal, Sam El Abbadi, Branden R. Brar, Amit Sethi, Radhika Chigurupati
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the quality of whole slide images in cytology from nuclei features
Paul Barthe, Romain Brixtel, Yann Caillot, Benoît Lemoine, Arnaud Renouf, Vianney Thurotte, Ouarda Beniken, Sébastien Bougleux, Olivier Lézoray
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 17: 100420. CrossRef - An update on applications of digital pathology: primary diagnosis; telepathology, education and research
Shamail Zia, Isil Z. Yildiz-Aktas, Fazail Zia, Anil V. Parwani
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence–driven digital pathology in urological cancers: current trends and future directions
Inyoung Paik, Geongyu Lee, Joonho Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hong Koo Ha
Prostate International.2025; 13(4): 181. CrossRef - Label-free optical microscopy with artificial intelligence: a new paradigm in pathology
Chiho Yoon, Eunwoo Park, Donggyu Kim, Byullee Park, Chulhong Kim
Biophotonics Discovery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - EPIIC: Edge-Preserving Method Increasing Nuclei Clarity for Compression Artifacts Removal in Whole-Slide Histopathological Images
Julia Merta, Michal Marczyk
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(8): 4450. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of a 5G campus network and existing networks for real-time consultation in remote pathology
Ilgar I. Guseinov, Arnab Bhowmik, Somaia AbuBaker, Anna E. Schmaus-Klughammer, Thomas Spittler
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 18: 100444. CrossRef - The Evolution of Digital Pathology in Infrastructure, Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Impact
Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 6. CrossRef - Role of Telepathology, Artificial Intelligence, and Emerging Technologies in Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
Yugeshwari R. Tiwade, Obaid Noman, Pratibha Dawande, Nandkishor J Bankar, Sweta Bahadure, Praful Patil
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2025; 8(2): 115. CrossRef - Analysis of system and scanner downtime in a digital pathology–predominant institution: A 6-year experience
Ryan Reagans, Lokman Cevik, Himani Kumar, David Kellough, Abberly Lott Limbach, Giovanni Lujan, Anil Parwani, Hamza N Gokozan
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(4): 634. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; 70(1): 126. CrossRef - Telepathology for Consultation in the Military Health System: An Evaluation of Pathologists’ Impressions of Facilitators and Barriers Prior to Implementation
Victoria Mahar, Zachary Colburn, Joshua Sakai
Laboratory Investigation.2025; 105(11): 104236. CrossRef - Online histostereometric analysis in digital forensic pathology: a technical report
Vladimir G. Nedugov, Anna V. Zhukova, German V. Nedugov
Russian Journal of Forensic Medicine.2025; 11(2): 145. CrossRef - Latent representation of H&E images retains biological information in a breast cancer cohort
Chloé Benmussa, Esther Sanfeliu, Anabel Martínez-Romero, Blanca González-Farré, Tomás Pascual, Joaquín Gavilá, Alona Levy-Jurgenson, Ariel Shamir, Fara Brasó-Maristany, Aleix Prat, Zohar Yakhini, Amgad Muneer
PLOS One.2025; 20(9): e0329221. CrossRef - Modernizing Colorectal Cancer Care With Artificial Intelligence: Real-Time Detection, Radiomics, and Digital Pathology
Elmoatazbellah Nasr, Zaid Al-Hamid, Mina H Younan, Mohamed Omran, Maan Sarsam, Mohamed Abdellatif
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A multi-task learning model for evaluating non-tumor gastric diseases indicators in whole slide images
Mingxi Fu, Liming Liu, Fanglei Fu, Jingli Ouyang, Xueying Shi, Song Duan, Tian Guan, Yonghong He, Zhiqiang Cheng, Lianghui Zhu
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance Evaluation of MambaVision in Breast Cancer Detection from Histopathology Images
Hasan Zan
Dicle Üniversitesi Mühendislik Fakültesi Mühendislik Dergisi.2025; 16(4): 879. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence for automatic detection of basal cell carcinoma from frozen tissue tangential biopsies
Dennis H Murphree, Yong-hun Kim, Kirk A Sidey, Nneka I Comfere, Nahid Y Vidal
Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.2024; 49(7): 719. CrossRef - Performance of externally validated machine learning models based on histopathology images for the diagnosis, classification, prognosis, or treatment outcome prediction in female breast cancer: A systematic review
Ricardo Gonzalez, Peyman Nejat, Ashirbani Saha, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Andrew P. Norgan, Cynthia Lokker
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100348. CrossRef - Invisible for a few but essential for many: the role of Histotechnologists in the establishment of digital pathology
Gisela Magalhães, Rita Calisto, Catarina Freire, Regina Silva, Diana Montezuma, Sule Canberk, Fernando Schmitt
Journal of Histotechnology.2024; 47(1): 39. CrossRef - Using digital pathology to analyze the murine cerebrovasculature
Dana M Niedowicz, Jenna L Gollihue, Erica M Weekman, Panhavuth Phe, Donna M Wilcock, Christopher M Norris, Peter T Nelson
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism.2024; 44(4): 595. CrossRef - PATrans: Pixel-Adaptive Transformer for edge segmentation of cervical nuclei on small-scale datasets
Hexuan Hu, Jianyu Zhang, Tianjin Yang, Qiang Hu, Yufeng Yu, Qian Huang
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2024; 168: 107823. CrossRef - CNAC-Seg: Effective segmentation for cervical nuclei in adherent cells and clusters via exploring gaps of receptive fields
Hexuan Hu, Jianyu Zhang, Tianjin Yang, Qiang Hu, Yufeng Yu, Qian Huang
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2024; 90: 105833. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: Current State and Future Implications
Swati Satturwar, Anil V. Parwani
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2024; 31(2): 136. CrossRef - Ensemble Deep Learning Model to Predict Lymphovascular Invasion in Gastric Cancer
Jonghyun Lee, Seunghyun Cha, Jiwon Kim, Jung Joo Kim, Namkug Kim, Seong Gyu Jae Gal, Ju Han Kim, Jeong Hoon Lee, Yoo-Duk Choi, Sae-Ryung Kang, Ga-Young Song, Deok-Hwan Yang, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee, Sangjeong Ahn, Kyoung Min Moon, Myung-Giun Noh
Cancers.2024; 16(2): 430. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence’s impact on breast cancer pathology: a literature review
Amr Soliman, Zaibo Li, Anil V. Parwani
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated Analysis of Nuclear Parameters in Oral Exfoliative Cytology Using Machine Learning
Shubhangi Mhaske, Karthikeyan Ramalingam, Preeti Nair, Shubham Patel, Arathi Menon P, Nida Malik, Sumedh Mhaske
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing AI Research for Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Datasets
Alessio Fiorin, Carlos López Pablo, Marylène Lejeune, Ameer Hamza Siraj, Vincenzo Della Mea
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine.2024; 37(6): 2996. CrossRef - Current Developments in Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Tumors: From Structure to Artificial Intelligence
Alexandra Corina Faur, Roxana Buzaș, Adrian Emil Lăzărescu, Laura Andreea Ghenciu
Life.2024; 14(6): 727. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN) diagnosis in rat kidneys using an artificial intelligence deep learning model
Yeji Bae, Jongsu Byun, Hangyu Lee, Beomseok Han
Toxicological Research.2024; 40(4): 551. CrossRef - A Pan-Cancer Patient-Derived Xenograft Histology Image Repository with Genomic and Pathologic Annotations Enables Deep Learning Analysis
Brian S. White, Xing Yi Woo, Soner Koc, Todd Sheridan, Steven B. Neuhauser, Shidan Wang, Yvonne A. Evrard, Li Chen, Ali Foroughi pour, John D. Landua, R. Jay Mashl, Sherri R. Davies, Bingliang Fang, Maria Gabriela Raso, Kurt W. Evans, Matthew H. Bailey, Y
Cancer Research.2024; 84(13): 2060. CrossRef - Non-contrasted computed tomography (NCCT) based chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) automatic diagnosis using cascaded network with multiple instance learning
Mayang Zhao, Liming Song, Jiarui Zhu, Ta Zhou, Yuanpeng Zhang, Shu-Cheng Chen, Haojiang Li, Di Cao, Yi-Quan Jiang, Waiyin Ho, Jing Cai, Ge Ren
Physics in Medicine & Biology.2024; 69(18): 185011. CrossRef - MR_NET: A Method for Breast Cancer Detection and Localization from Histological Images Through Explainable Convolutional Neural Networks
Rachele Catalano, Myriam Giusy Tibaldi, Lucia Lombardi, Antonella Santone, Mario Cesarelli, Francesco Mercaldo
Sensors.2024; 24(21): 7022. CrossRef - Advances in AI-Enhanced Biomedical Imaging for Cancer Immunology
Willa Wen-You Yim, Felicia Wee, Zheng Yi Ho, Xinyun Feng, Marcia Zhang, Samuel Lee, Inti Zlobec, Joe Yeong, Mai Chan Lau
World Scientific Annual Review of Cancer Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Blockchain: A safe digital technology to share cancer diagnostic results in pandemic times—Challenges and legacy for the future
Bruno Natan Santana Lima, Lucas Alves da Mota Santana, Rani Iani Costa Gonçalo, Carla Samily de Oliveira Costa, Daniel Pitanga de Sousa Nogueira, Cleverson Luciano Trento, Wilton Mitsunari Takeshita
Oral Surgery.2023; 16(3): 300. CrossRef - Pathologists’ acceptance of telepathology in the Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Hospitals in Saudi Arabia: A survey study
Raneem Alawashiz, Sharifah Abdullah AlDossary
DIGITAL HEALTH.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An Atrous Convolved Hybrid Seg-Net Model with residual and attention mechanism for gland detection and segmentation in histopathological images
Manju Dabass, Jyoti Dabass
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2023; 155: 106690. CrossRef - Validation of a Machine Learning Expert Supporting System, ImmunoGenius, Using Immunohistochemistry Results of 3000 Patients with Lymphoid Neoplasms
Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kyung Jin Seo, Hye-Ra Jung, Gyeongsin Park, Seung-Sook Lee, Yosep Chong
Diagnostics.2023; 13(7): 1308. CrossRef - Diagnosing Infectious Diseases in Poultry Requires a Holistic Approach: A Review
Dieter Liebhart, Ivana Bilic, Beatrice Grafl, Claudia Hess, Michael Hess
Poultry.2023; 2(2): 252. CrossRef - Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Kyung Jin Seo, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Canine Mammary Tumor Histopathological Image Classification via Computer-Aided Pathology: An Available Dataset for Imaging Analysis
Giovanni P. Burrai, Andrea Gabrieli, Marta Polinas, Claudio Murgia, Maria Paola Becchere, Pierfranco Demontis, Elisabetta Antuofermo
Animals.2023; 13(9): 1563. CrossRef - Rapid digital pathology of H&E-stained fresh human brain specimens as an alternative to frozen biopsy
Bhaskar Jyoti Borah, Yao-Chen Tseng, Kuo-Chuan Wang, Huan-Chih Wang, Hsin-Yi Huang, Koping Chang, Jhih Rong Lin, Yi-Hua Liao, Chi-Kuang Sun
Communications Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Applied machine learning in hematopathology
Taher Dehkharghanian, Youqing Mu, Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Clinton J. V. Campbell
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2023; 45(S2): 87. CrossRef - Automated diagnosis of 7 canine skin tumors using machine learning on H&E-stained whole slide images
Marco Fragoso-Garcia, Frauke Wilm, Christof A. Bertram, Sophie Merz, Anja Schmidt, Taryn Donovan, Andrea Fuchs-Baumgartinger, Alexander Bartel, Christian Marzahl, Laura Diehl, Chloe Puget, Andreas Maier, Marc Aubreville, Katharina Breininger, Robert Klopf
Veterinary Pathology.2023; 60(6): 865. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in the Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Sangjoon Choi, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 410. CrossRef - Efficient Convolution Network to Assist Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Target Therapy
Ching-Wei Wang, Kai-Lin Chu, Hikam Muzakky, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
Cancers.2023; 15(15): 3991. CrossRef - Multi-Configuration Analysis of DenseNet Architecture for Whole Slide Image Scoring of ER-IHC
Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Md Jahid Hasan, Zaka Ur Rehman, Jenny Tung Hiong Lee, See Yee Khor, Lai-Meng Looi, Fazly Salleh Abas, Afzan Adam, Elaine Wan Ling Chan, Sei-Ichiro Kamata
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 79911. CrossRef - Digitization of Pathology Labs: A Review of Lessons Learned
Lars Ole Schwen, Tim-Rasmus Kiehl, Rita Carvalho, Norman Zerbe, André Homeyer
Laboratory Investigation.2023; 103(11): 100244. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration/Biopsy (EUS-FNA/B) for Solid Pancreatic Lesions: Opportunities and Challenges
Xianzheng Qin, Taojing Ran, Yifei Chen, Yao Zhang, Dong Wang, Chunhua Zhou, Duowu Zou
Diagnostics.2023; 13(19): 3054. CrossRef - Deep Learning for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cholangiocarcinoma, and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Hyun-Jong Jang, Jai-Hyang Go, Younghoon Kim, Sung Hak Lee
Cancers.2023; 15(22): 5389. CrossRef - AIR-UNet++: a deep learning framework for histopathology image segmentation and detection
Anusree Kanadath, J. Angel Arul Jothi, Siddhaling Urolagin
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2023; 83(19): 57449. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Dermatological Condition Detection: A Systematic Review With Recent Methods, Datasets, Challenges, and Future Directions
Stephanie S. Noronha, Mayuri A. Mehta, Dweepna Garg, Ketan Kotecha, Ajith Abraham
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 140348. CrossRef - Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice
Vipul Baxi, Robin Edwards, Michael Montalto, Saurabh Saha
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(1): 23. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Toxicological Pathology: Quantitative Evaluation of Compound-Induced Follicular Cell Hypertrophy in Rat Thyroid Gland Using Deep Learning Models
Valeria Bertani, Olivier Blanck, Davy Guignard, Frederic Schorsch, Hannah Pischon
Toxicologic Pathology.2022; 50(1): 23. CrossRef - Investigating the genealogy of the literature on digital pathology: a two-dimensional bibliometric approach
Dayu Hu, Chengyuan Wang, Song Zheng, Xiaoyu Cui
Scientometrics.2022; 127(2): 785. CrossRef - Digital Dermatopathology and Its Application to Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Yeongjoo Oh, Hye Min Kim, Soon Won Hong, Eunah Shin, Jihee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(Suppl): S112. CrossRef - Assessment of parathyroid gland cellularity by digital slide analysis
Rotem Sagiv, Bertha Delgado, Oleg Lavon, Vladislav Osipov, Re'em Sade, Sagi Shashar, Ksenia M. Yegodayev, Moshe Elkabets, Ben-Zion Joshua
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 58: 151907. CrossRef - PancreaSys: An Automated Cloud-Based Pancreatic Cancer Grading System
Muhammad Nurmahir Mohamad Sehmi, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Elaine Wan Ling Chan
Frontiers in Signal Processing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Classification of Mouse Lung Metastatic Tumor with Deep Learning
Ha Neul Lee, Hong-Deok Seo, Eui-Myoung Kim, Beom Seok Han, Jin Seok Kang
Biomolecules & Therapeutics.2022; 30(2): 179. CrossRef - Techniques for digital histological morphometry of the pineal gland
Bogdan-Alexandru Gheban, Horaţiu Alexandru Colosi, Ioana-Andreea Gheban-Roșca, Carmen Georgiu, Dan Gheban, Doiniţa Crişan, Maria Crişan
Acta Histochemica.2022; 124(4): 151897. CrossRef - Current Trend of Artificial Intelligence Patents in Digital Pathology: A Systematic Evaluation of the Patent Landscape
Muhammad Joan Ailia, Nishant Thakur, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Chan Kwon Jung, Kwangil Yim, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2400. CrossRef - Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence from Histopathologic Image-Based Prediction of Microsatellite Instability in Solid Cancers: A Systematic Review
Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Jamshid Abdul-Ghafar, Kwangil Yim, Nishant Thakur, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2022; 14(11): 2590. CrossRef - Development of a prognostic prediction support system for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia using artificial intelligence-based diagnosis
Takayuki Takahashi, Hikaru Matsuoka, Rieko Sakurai, Jun Akatsuka, Yusuke Kobayashi, Masaru Nakamura, Takashi Iwata, Kouji Banno, Motomichi Matsuzaki, Jun Takayama, Daisuke Aoki, Yoichiro Yamamoto, Gen Tamiya
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Applications in Pathology
Heounjeong Go
Brain Tumor Research and Treatment.2022; 10(2): 76. CrossRef - Mass spectrometry imaging to explore molecular heterogeneity in cell culture
Tanja Bien, Krischan Koerfer, Jan Schwenzfeier, Klaus Dreisewerd, Jens Soltwisch
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrating artificial intelligence in pathology: a qualitative interview study of users' experiences and expectations
Jojanneke Drogt, Megan Milota, Shoko Vos, Annelien Bredenoord, Karin Jongsma
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1540. CrossRef - Deep Learning on Basal Cell Carcinoma In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy Data
Veronika Shavlokhova, Michael Vollmer, Patrick Gholam, Babak Saravi, Andreas Vollmer, Jürgen Hoffmann, Michael Engel, Christian Freudlsperger
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1471. CrossRef - Deep Learning-Based Classification of Uterine Cervical and Endometrial Cancer Subtypes from Whole-Slide Histopathology Images
JaeYen Song, Soyoung Im, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2623. CrossRef - A self-supervised contrastive learning approach for whole slide image representation in digital pathology
Parsa Ashrafi Fashi, Sobhan Hemati, Morteza Babaie, Ricardo Gonzalez, H.R. Tizhoosh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2022; 13: 100133. CrossRef - A Matched-Pair Analysis of Nuclear Morphologic Features Between Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Specimen in Thyroid Tumors Using a Deep Learning Model
Faridul Haq, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(4): 472. CrossRef - Development of quality assurance program for digital pathology by the Korean Society of Pathologists
Yosep Chong, Jeong Mo Bae, Dong Wook Kang, Gwangil Kim, Hye Seung Han
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 370. CrossRef - Machine learning in renal pathology
Matthew Nicholas Basso, Moumita Barua, Julien Meyer, Rohan John, April Khademi
Frontiers in Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole Slide Image Quality in Digital Pathology: Review and Perspectives
Romain Brixtel, Sebastien Bougleux, Olivier Lezoray, Yann Caillot, Benoit Lemoine, Mathieu Fontaine, Dalal Nebati, Arnaud Renouf
IEEE Access.2022; 10: 131005. CrossRef - Generalizability of Deep Learning System for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Various Cancers
Hyun-Jong Jang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 808. CrossRef - Recent advances in the use of stimulated Raman scattering in histopathology
Martin Lee, C. Simon Herrington, Manasa Ravindra, Kristel Sepp, Amy Davies, Alison N. Hulme, Valerie G. Brunton
The Analyst.2021; 146(3): 789. CrossRef - Preference and Demand for Digital Pathology and Computer-Aided Diagnosis among Korean Pathologists: A Survey Study Focused on Prostate Needle Biopsy
Soo Jeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(16): 7380. CrossRef - An SVM approach towards breast cancer classification from H&E-stained histopathology images based on integrated features
M. A. Aswathy, M. Jagannath
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2021; 59(9): 1773. CrossRef - Diagnosis prediction of tumours of unknown origin using ImmunoGenius, a machine learning-based expert system for immunohistochemistry profile interpretation
Yosep Chong, Nishant Thakur, Ji Young Lee, Gyoyeon Hwang, Myungjin Choi, Yejin Kim, Hwanjo Yu, Mee Yon Cho
Diagnostic Pathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning for Automatic Subclassification of Gastric Carcinoma Using Whole-Slide Histopathology Images
Hyun-Jong Jang, In-Hye Song, Sung-Hak Lee
Cancers.2021; 13(15): 3811. CrossRef - A novel evaluation method for Ki-67 immunostaining in paraffin-embedded tissues
Eliane Pedra Dias, Nathália Silva Carlos Oliveira, Amanda Oliveira Serra-Campos, Anna Karoline Fausto da Silva, Licínio Esmeraldo da Silva, Karin Soares Cunha
Virchows Archiv.2021; 479(1): 121. CrossRef - Assessment of Digital Pathology Imaging Biomarkers Associated with Breast Cancer Histologic Grade
Andrew Lagree, Audrey Shiner, Marie Angeli Alera, Lauren Fleshner, Ethan Law, Brianna Law, Fang-I Lu, David Dodington, Sonal Gandhi, Elzbieta A. Slodkowska, Alex Shenfield, Katarzyna J. Jerzak, Ali Sadeghi-Naini, William T. Tran
Current Oncology.2021; 28(6): 4298. CrossRef - Prediction of genetic alterations from gastric cancer histopathology images using a fully automated deep learning approach
Hyun-Jong Jang, Ahwon Lee, Jun Kang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(44): 7687. CrossRef - Clustered nuclei splitting based on recurrent distance transform in digital pathology images
Lukasz Roszkowiak, Anna Korzynska, Dorota Pijanowska, Ramon Bosch, Marylene Lejeune, Carlos Lopez
EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Trends of Artificial Intelligence for Colorectal Cancer Pathology Image Analysis: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Hongjun Yoon, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1884. CrossRef - A bird’s-eye view of deep learning in bioimage analysis
Erik Meijering
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2020; 18: 2312. CrossRef - Pathomics in urology
Victor M. Schuettfort, Benjamin Pradere, Michael Rink, Eva Comperat, Shahrokh F. Shariat
Current Opinion in Urology.2020; 30(6): 823. CrossRef - Model Fooling Attacks Against Medical Imaging: A Short Survey
Tuomo Sipola, Samir Puuska, Tero Kokkonen
Information & Security: An International Journal.2020; 46(2): 215. CrossRef - Recommendations for pathologic practice using digital pathology: consensus report of the Korean Society of Pathologists
Yosep Chong, Dae Cheol Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong-chul Kim, Sang Yong Song, Hee Jae Joo, Sang-Yeop Yi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 437. CrossRef - A machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosis prediction of lymphoid neoplasms using a probabilistic decision-tree algorithm and immunohistochemistry profile database
Yosep Chong, Ji Young Lee, Yejin Kim, Jingyun Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Gyeongsin Park, Mee Yon Cho, Nishant Thakur
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(6): 462. CrossRef
- Deep learning model to diagnose cardiac amyloidosis from haematoxylin/eosin-stained myocardial tissue
- Comparison of papanicolaou smear and human papillomavirus (HPV) test as cervical screening tools: can we rely on HPV test alone as a screening method? An 11-year retrospective experience at a single institution
- Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Jungsuk An, Sangho Lee, Jae Yeon Seok, Juhyeon Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):112-118. Published online January 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.29
- 14,533 View
- 267 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The decrease in incidence of cervical dysplasia and carcinoma has not been as dramatic as expected with the development of improved research tools and test methods. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test alone has been suggested for screening in some countries. The National Cancer Screening Project in Korea has applied Papanicolaou smears (Pap smears) as the screening method for cervical dysplasia and carcinoma. We evaluated the value of Pap smear and HPV testing as diagnostic screening tools in a single institution.
Methods
Patients co-tested with HPV test and Pap smear simultaneously or within one month of each other were included in this study. Patients with only punch biopsy results were excluded because of sampling errors. A total of 999 cases were included, and the collected reports encompassed results of smear cytology, HPV subtypes, and histologic examinations.
Results
Sensitivity and specificity of detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were higher for Pap smears than for HPV tests (sensitivity, 97.14%; specificity, 85.58% for Pap smears; sensitivity, 88.32%; specificity, 54.92% for HPV tests). HPV tests and Pap smears did not differ greatly in detection of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (85.35% for HPV test, 80.31% for Pap smears). When atypical glandular cells were noted on Pap smears, the likelihood for histologic diagnosis of adenocarcinoma following Pap smear was higher than that of high-risk HPV test results (18.8 and 1.53, respectively).
Conclusions
Pap smears were more useful than HPV tests in the diagnosis of HSIL, SCC, and glandular lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
Mohammad Panji, Mohammad Hossein Modarresi, Zahra Azizi, Moloud Absalan, Elahe Motevaseli
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of cervical precancerous lesions and cancer by small-scale RT-qPCR analysis of oppositely deregulated mRNAs pairs in cytological smears
Anastasia A. Artyukh, Mikhail K. Ivanov, Sergei E. Titov, Victoria V. Dzyubenko, Sergey E. Krasilnikov, Anastasia O. Shumeikina, Nikita A. Afanasev, Anastasia V. Malek, Sergei A. Glushkov, Eduard F. Agletdinov
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High burden of abnormal cervical smears in South African primary health care: health programmes implications
Olufemi B Omole, Joel M Francis, John M Musonda, Pumla P Sodo, Elizabeth Reji, Nyundu S J Phukuta, Honey L M Mabuza, Joyce S Musonda, Jimmy Akii, John V Ndimande, Olalekan A Ayo-Yusuf
Health Promotion International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis: a study of the microenvironment in cervical cancer (2000-2024)
Yun-Tao Zhang, Yan-Ni Wei, Chen-Chen Liu, Mai-Qing Yang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy biomarkers in cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Isaac Kinyua Njangiru, Bizhar Ahmed Tayeb, Hazhmat Ali, Rafl M. Kamil
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 10: 100328. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Human Papilloma Virus Testing in Comparison with Pap Cytology and Histopathology in Unvaccinated Women with Cervical High-Grade Dysplasia and Carcinoma in Botswana
Patricia Setsile Rantshabeng, Nametso Dire, Andrew Khulekani Ndlovu, Ishmael Kasvosve
Venereology.2025; 4(4): 15. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagmosis of cervical pathologies
D. Y. Chernov, O. A. Tikhonovskaya, S. V. Logvinov, I. A. Petrov, Y. S. Yuriev, A. A. Zhdankina, A. V. Gerasimov, I. V. Zingalyuk, G. A. Mikheenko
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 201. CrossRef - “Barriers and Advantages of Self-Sampling Tests, for HPV Diagnosis: A Qualitative Field Experience Before Implementation in a Rural Community in Ecuador”
Bernardo Vega-Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Ruth Maldonado - Rengel, Diana López, Dayanara Delgado-López, Gabriela Guerra Astudillo, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 947. CrossRef - Cervical Human Papillomavirus Testing
Carol N. Rizkalla, Eric C. Huang
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2024; 17(3): 431. CrossRef - Segmentation of Overlapping Cells in Cervical Cytology Images: A Survey
E Chen, Hua-Nong Ting, Joon Huang Chuah, Jun Zhao
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 114170. CrossRef - Knowledge and awareness regarding pap test and HPV typing for cervical cancer screening in Edo North, Nigeria
Amina Momodu, Johnsolomon Eghosa Ohenhen, Godfrey Innocent Iyare, Musa Abidemi Muhibi, Godwin Avwioro
Discover Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Colposcopy Value in Young Child-bearing Women: Is New Recommendations Necessary?
Fahimeh Sabet, Avishan Aminizad, Fariba Behnamfar, Tajossadat Allameh, Seyedeh Ghazal Shahrokh, Rostami Koushan, Amirmohammad Taravati, Leila Mousavi Seresht
Advanced Biomedical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Selection of endogenous control and identification of significant microRNA deregulations in cervical cancer
T. Stverakova, I. Baranova, P. Mikyskova, B. Gajdosova, H. Vosmikova, J. Laco, V. Palicka, H. Parova
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology Versus Molecular Diagnosis of HPV for Cervical Cancer Screening. Comparison of the Diagnostic Properties of Four Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Rocío Murillo, Cristina Ochoa Avilés
ESPOCH Congresses: The Ecuadorian Journal of S.T.E.A.M..2023; 3(1): 139. CrossRef - Attitudes towards prevention of cervical cancer and early diagnosis among female academicians
Nurhan Doğan, Gamze Fışkın
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(6): 1433. CrossRef - Role of Self-Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: Diagnostic Test Properties of Three Tests for the Diagnosis of HPV in Rural Communities of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz Segarra, Ruth Maldonado Rengel, Diana López, María Paz Orellana, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4619. CrossRef - Utility of Scoring System for Screening and Early Warning of Cervical Cancer Based on Big Data Analysis
Dan Hou, Binjie Yang, Yangdan Li, Ming Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine and Vaginal Self-Sampling versus Clinician-Based Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: A Field Comparison of the Acceptability of Three Sampling Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz S, Ruth Maldonado-Rengel, Diana López, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1614. CrossRef - Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 354. CrossRef - Primary screening of cervical cancer by Pap smear in women of reproductive age group
Ruchi Mishra, Dakshina Bisht, Manisha Gupta
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2022; 11(9): 5327. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Investigating host-virus interaction mechanism and phylogenetic analysis of viral proteins involved in the pathogenesis
Ahmad Abu Turab Naqvi, Farah Anjum, Alaa Shafie, Sufian Badar, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Timir Tripathi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(12): e0261497. CrossRef - Utility of Human Papillomavirus Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Mee-seon Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Moon-il Park, Jae Seok Lee, Kisu Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Hyoun Wook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(5): 1726. CrossRef
- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
- A Multi-institutional Study of Prevalence and Clinicopathologic Features of Non-invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP) in Korea
- Ja Yeong Seo, Ji Hyun Park, Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoon Jin Cha, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong Eun Song, Jeong Ja Kwak, So Yeon Park, Hee Young Na, Jang-Hee Kim, Jae Yeon Seok, Hee Sung Kim, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):378-385. Published online October 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.18
- 8,913 View
- 344 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the present multi-institutional study, the prevalence and clinicopathologic characteristics of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) were evaluated among Korean patients who underwent thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Methods
Data from 18,819 patients with PTC from eight university hospitals between January 2012 and February 2018 were retrospectively evaluated. Pathology reports of all PTCs and slides of potential NIFTP cases were reviewed. The strict criterion of no papillae was applied for the diagnosis of NIFTP. Due to assumptions regarding misclassification of NIFTP as non-PTC tumors, the lower boundary of NIFTP prevalence among PTCs was estimated. Mutational analysis for BRAF and three RAS isoforms was performed in 27 randomly selected NIFTP cases.
Results
The prevalence of NIFTP was 1.3% (238/18,819) of all PTCs when the same histologic criteria were applied for NIFTP regardless of the tumor size but decreased to 0.8% (152/18,819) when tumors ≥1 cm in size were included. The mean follow-up was 37.7 months and no patient with NIFTP had evidence of lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, or disease recurrence during the follow-up period. A difference in prevalence of NIFTP before and after NIFTP introduction was not observed. BRAFV600E mutation was not found in NIFTP. The mutation rate for the three RAS genes was 55.6% (15/27).
Conclusions
The low prevalence and indolent clinical outcome of NIFTP in Korea was confirmed using the largest number of cases to date. The introduction of NIFTP may have a small overall impact in Korean practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case report & review: Bilateral NIFTP harboring concomitant HRAS and KRAS mutation: Report of an unusual case and literature review
Marianna Rita Brogna, Francesca Collina, Maria Grazia Chiofalo, Debora De Bartolo, Angela Montone, Maria Rosaria Schiano, Michele Del Sesto, Nubia Pizza, Gerardo Ferrara
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2024; 63(12): 2273. CrossRef - Non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP): what do we need to know?
Andrés Coca-Pelaz, Juan P. Rodrigo, Abbas Agaimy, Dana M. Hartl, Göran Stenman, Vincent Vander Poorten, Antti A. Mäkitie, Mark Zafereo, Karthik N. Rao, Gregory W. Randolph, Alessandra Rinaldo, Alfio Ferlito
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(6): 977. CrossRef - Study of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm: A borderline entity
Rupali Bavikar, Ruchi S. Randive, Anubhaw Verma, Madhuri Singh, Vidya Viswanathan, Arpana Dharwadkar
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2024; 20(5): 1365. CrossRef - Analysis of a pre-2017 follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma cohort reclassified as noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like features (NIFTP): an 11-year retrospective single institution experience
Shaham Beg, Sana Irfan Khan, Isabella Cui, Theresa Scognamiglio, Rema Rao
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(2): 112. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm With Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: What a Surgeon Should Know
Jabir Alharbi, Thamer Alraddadi, Haneen Sebeih, Mohammad A Alessa, Haddad H Alkaf, Ahmed Bahaj, Sherif K Abdelmonim
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - NTRK Fusion in a Cohort of BRAF p. V600E Wild-Type Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Seung Eun Lee, Mi-Sook Lee, Heejin Bang, Mi Young Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Young Lyun Oh
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(8): 100180. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Study on the Diagnosis and Management of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features
Bayan A. Alzumaili, Lauren N. Krumeich, Reagan Collins, Timothy Kravchenko, Emad I. Ababneh, Adam S. Fisch, William C. Faquin, Vania Nosé, Maria Martinez-Lage, Gregory W. Randolph, Rajshri M. Gartland, Carrie C. Lubitz, Peter M. Sadow
Thyroid.2023; 33(5): 566. CrossRef - Clinical-Pathological and Molecular Evaluation of 451 NIFTP Patients from a Single Referral Center
Paola Vignali, Agnese Proietti, Elisabetta Macerola, Anello Marcello Poma, Liborio Torregrossa, Clara Ugolini, Alessio Basolo, Antonio Matrone, Teresa Rago, Ferruccio Santini, Rossella Elisei, Gabriele Materazzi, Fulvio Basolo
Cancers.2022; 14(2): 420. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 Consensus on the management of thyroid nodules : Follow-up: How and how long?
Sophie Leboulleux, Livia Lamartina, Emmanuelle Lecornet Sokol, Fabrice Menegaux, Laurence Leenhardt, Gilles Russ
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2022; 83(6): 407. CrossRef - Different Threshold of Malignancy for RAS-like Thyroid Tumors Causes Significant Differences in Thyroid Nodule Practice
Kennichi Kakudo
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 812. CrossRef - Clinicopathological parameters for predicting non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary features (NIFTP)
Eunju Jang, Kwangsoon Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Incidence of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Meta-Analysis Assessing Worldwide Impact of the Reclassification
Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Thu Quynh Nguyen, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Chan Kwon Jung, Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov
Thyroid.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Genomic Landscape of Thyroid Cancer Tumourigenesis and Implications for Immunotherapy
Amandeep Singh, Jeehoon Ham, Joseph William Po, Navin Niles, Tara Roberts, Cheok Soon Lee
Cells.2021; 10(5): 1082. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) is rare, benign lesion using modified stringent diagnostic criteria: Reclassification and outcome study
David Cubero Rego, Hwajeong Lee, Anne Boguniewicz, Timothy A. Jennings
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 44: 151439. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: From Echography to Genetic Profile
Francesca Maletta, Enrico Costantino Falco, Alessandro Gambella, Jasna Metovic, Mauro Papotti
The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.2020; 252(3): 209. CrossRef
- Case report & review: Bilateral NIFTP harboring concomitant HRAS and KRAS mutation: Report of an unusual case and literature review
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- Hye Yoon Chang, Chan Kwon Jung, Junwoo Isaac Woo, Sanghun Lee, Joonyoung Cho, Sun Woo Kim, Tae-Yeong Kwak
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):1-12. Published online December 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.12.16
- 33,522 View
- 1,289 Download
- 128 Web of Science
- 142 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As in other domains, artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important in medicine. In particular,deep learning-based pattern recognition methods can advance the field of pathology byincorporating clinical, radiologic, and genomic data to accurately diagnose diseases and predictpatient prognoses. In this review, we present an overview of artificial intelligence, the brief historyof artificial intelligence in the medical domain, recent advances in artificial intelligence applied topathology, and future prospects of pathology driven by artificial intelligence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
Shuangshuang Li, Kaiwen Zhao, Wen Li, Qingsheng Lu, Jian Zhou, Jia He
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2026; 122: 895. CrossRef - An automatic, rapid and accurate method for the annotation of tumor components on whole slide images
Hong Tang, Xiaodong Wang, Xiaolin Zhang, Xiaojun Wu, Xinyue Tang, Yaqiong Ma, Ying Chen, Guanzhen Yu
Journal of Histotechnology.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Exploring the status of artificial intelligence for healthcare research in Africa: a bibliometric and thematic analysis
Tabu S. Kondo, Salim A. Diwani, Ally S. Nyamawe, Mohamed M. Mjahidi
AI and Ethics.2025; 5(1): 117. CrossRef - Prioritize Threat Alerts Based on False Positives Qualifiers Provided by Multiple AI Models Using Evolutionary Computation and Reinforcement Learning
Anup Sharma, V. G. Kiran Kumar, Asmita Poojari
Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B.2025; 106(4): 1305. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence versus human analysis: Interpreting data in elderly fat reduction study
Piotr Sporek, Mariusz Konieczny
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2025; 12(1): 13. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare applications targeting cancer diagnosis—part I: data structure, preprocessing and data organization
Anna Luíza Damaceno Araújo, Marcelo Sperandio, Giovanna Calabrese, Sarah S. Faria, Diego Armando Cardona Cardenas, Manoela Domingues Martins, Cristina Saldivia-Siracusa, Daniela Giraldo-Roldán, Caique Mariano Pedroso, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2025; 140(1): 79. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence–driven digital pathology in urological cancers: current trends and future directions
Inyoung Paik, Geongyu Lee, Joonho Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Hong Koo Ha
Prostate International.2025; 13(4): 181. CrossRef - Optimizing deep learning for accurate blood cell classification: A study on stain normalization and fine-tuning techniques
Mohammed Tareq Mutar, Jaffar Nouri Alalsaidissa, Mustafa Majid Hameed, Ali Almothaffar
Iraqi Journal of Hematology.2025; 14(1): 60. CrossRef - Structural imbalance of medical resources amid population mobility and digital empowerment: a study of national and port-developed provinces in China
Haiwei Fu, Junjie Lu
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the evolution of artificial intelligence in pathology: a bibliometric and network analysis
Burcu Sanal Yılmaz
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2025; 6(3): 224. CrossRef - ШТУЧНИЙ ІНТЕЛЕКТ У СУЧАСНІЙ СТОМАТОЛОГІЇ
О. І. Бульбук, О. В. Бульбук, О. В. Шутак, Ю. І. Сухоребський
Art of Medicine.2025; : 101. CrossRef - Natural language processing in veterinary pathology: A review
Lev Stimmer, Raoul V. Kuiper, Laura Polledo, Lorenzo Ressel, Josep M. Monné Rodriguez, Inês B. Veiga, Jonathan Williams, Vanessa Herder
Veterinary Pathology.2025; 62(6): 829. CrossRef - Impact of Magnification, Image Type, and Number on Convolutional Neural Network Performance in Differentiating Canine Large Cell Lymphoma From Non‐Lymphoma via Lymph Node Cytology
Christina Pacholec, Hehuang Xie, Julianne Curnin, Amy Lin, Kurt Zimmerman
Veterinary Clinical Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology image-based predictive model for individual survival time of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma patients
Vi Thi-Tuong Vo, Hyung-Jeong Yang, Taebum Lee, Soo-Hyung Kim
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Artificial Intelligence's Potential to Enhance Conventional Anticancer Drug Development
Sorin‐Ștefan Bobolea, Miruna‐Ioana Hinoveanu, Andreea Dimitriu, Miruna‐Andrada Brașoveanu, Cristian‐Nicolae Iliescu, Cristina‐Elena Dinu‐Pîrvu, Mihaela Violeta Ghica, Valentina Anuța, Lăcrămioara Popa, Răzvan Mihai Prisada
Drug Development Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicability of PD-L1 expression in cancer cells based solely on H&E-stained sections
Gavino Faa, Matteo Fraschini, Pina Ziranu, Andrea Pretta, Giuseppe Porcu, Luca Saba, Mario Scartozzi, Nazar Shokun, Massimo Rugge
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 19: 100524. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
Umur Karan, Osman Elbek
Thoracic Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Whole Slide Imaging Technology and Its Applications: Current and Emerging Perspectives
Ekta Jain, Ankush Patel, Anil V. Parwani, Saba Shafi, Zoya Brar, Shivani Sharma, Sambit K. Mohanty
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(3): 433. CrossRef - ChatGPT as an aid for pathological diagnosis of cancer
Shaivy Malik, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 154989. CrossRef - Computational pathology: A survey review and the way forward
Mahdi S. Hosseini, Babak Ehteshami Bejnordi, Vincent Quoc-Huy Trinh, Lyndon Chan, Danial Hasan, Xingwen Li, Stephen Yang, Taehyo Kim, Haochen Zhang, Theodore Wu, Kajanan Chinniah, Sina Maghsoudlou, Ryan Zhang, Jiadai Zhu, Samir Khaki, Andrei Buin, Fatemeh
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2024; 15: 100357. CrossRef - Applications of artificial intelligence in the field of oral and maxillofacial pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Nishath Sayed Abdul, Ganiga Channaiah Shivakumar, Sunila Bukanakere Sangappa, Marco Di Blasio, Salvatore Crimi, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine-learning models are superior to severity scoring systems for the prediction of the mortality of critically ill patients in a tertiary medical center
Ruey-Hsing Chou, Benny Wei-Yun Hsu, Chun-Lin Yu, Tai-Yuan Chen, Shuo-Ming Ou, Kuo-Hua Lee, Vincent S. Tseng, Po-Hsun Huang, Der-Cherng Tarng
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2024; 87(4): 369. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Technology for the Differentiation of Fresh Human Blood Cells From Other Species Blood in the Investigation of Crime Scenes
Syed Sajid Hussain Shah, Ekramy Elmorsy, Rashad Qasem Ali Othman, Asmara Syed, Syed Umar Armaghan, Syed Usama Khalid Bokhari, Mahmoud E Elmorsy, Abdulhakim Bawadekji
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of Diagnostic and Immunohistochemical Workup and Literature Review Capabilities of Online Artificial Intelligence Assistance Models in Pathology
Johnika Dougan, Netra Patel, Svetoslav Bardarov
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - ChatENT: Augmented Large Language Model for Expert Knowledge Retrieval in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery
Cai Long, Deepak Subburam, Kayle Lowe, André dos Santos, Jessica Zhang, Sang Hwang, Neil Saduka, Yoav Horev, Tao Su, David W.J. Côté, Erin D. Wright
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2024; 171(4): 1042. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in forensic medicine and related sciences – selected issues = Sztuczna inteligencja w medycynie sądowej i naukach pokrewnych – wybrane zagadnienia
Michał Szeremeta, Julia Janica, Anna Niemcunowicz-Janica
Archives of Forensic Medicine and Criminology.2024; 74(1): 64. CrossRef - Unveiling the landscape of pathomics in personalized immunotherapy for lung cancer: a bibliometric analysis
Lei Yuan, Zhiming Shen, Yibo Shan, Jianwei Zhu, Qi Wang, Yi Lu, Hongcan Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PathEX: Make good choice for whole slide image extraction
Xinda Yang, Ranze Zhang, Yuan Yang, Yu Zhang, Kai Chen, Alberto Marchisio
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0304702. CrossRef - Automatic point detection on cephalograms using convolutional neural networks: A two-step method
Miki HORI, Makoto JINCHO, Tadasuke HORI, Hironao SEKINE, Akiko KATO, Ken MIYAZAWA, Tatsushi KAWAI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 701. CrossRef - The use of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in teaching and assessment of postgraduate students in pathology and microbiology
Dipmala Das, Asitava Deb Roy, Subhayan Dasgupta, Rohon Das Roy
Indian Journal of Microbiology Research.2024; 11(3): 140. CrossRef - Inteligencia artificial: desafíos éticos y futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence: ethical and future challenges
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inteligência artificial: desafios éticos e futuros
Jhadson Silva Leonel, Camila Ferreira Silva Leonel, Jonas Byk, Silvania da Conceição Furtado
Revista Bioética.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Constrained-Disorder Principle Assists in Overcoming Significant Challenges in Digital Health: Moving from “Nice to Have” to Mandatory Systems
Noa Hurvitz, Yaron Ilan
Clinics and Practice.2023; 13(4): 994. CrossRef - Building a nonclinical pathology laboratory of the future for pharmaceutical research excellence
D.G. Rudmann, L. Bertrand, A. Zuraw, J. Deiters, M. Staup, Y. Rivenson, J. Kuklyte
Drug Discovery Today.2023; 28(10): 103747. CrossRef - Automated image analysis of keratin 7 staining can predict disease outcome in primary sclerosing cholangitis
Nelli Sjöblom, Sonja Boyd, Anniina Manninen, Sami Blom, Anna Knuuttila, Martti Färkkilä, Johanna Arola
Hepatology Research.2023; 53(4): 322. CrossRef - Application of convolutional neural network for analyzing hepatic fibrosis in mice
Hyun-Ji Kim, Eun Bok Baek, Ji-Hee Hwang, Minyoung Lim, Won Hoon Jung, Myung Ae Bae, Hwa-Young Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Toxicologic Pathology.2023; 36(1): 21. CrossRef - Machine Learning Techniques for Prognosis Estimation and Knowledge Discovery From Lab Test Results With Application to the COVID-19 Emergency
Alfonso Emilio Gerevini, Roberto Maroldi, Matteo Olivato, Luca Putelli, Ivan Serina
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 83905. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in dentistry—A review
Hao Ding, Jiamin Wu, Wuyuan Zhao, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Michael F. Burrow, James K. H. Tsoi
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dental Age Estimation Using the Demirjian Method: Statistical Analysis Using Neural Networks
Byung-Yoon Roh, Jong-Seok Lee, Sang-Beom Lim, Hye-Won Ryu, Su-Jeong Jeon, Ju-Heon Lee, Yo-Seob Seo, Ji-Won Ryu, Jong-Mo Ahn
Korean Journal of Legal Medicine.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence in health care. Problems of identification of patients' conditions in the processes of detailing the diagnosis
Mintser O
Artificial Intelligence.2023; 28(AI.2023.28): 8. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Data Augmentation for Mature White Blood Cell Image Classification in Deep Learning — Selection of an Optimal Technique for Hematological Morphology Recognition —
Hiroyuki NOZAKA, Kosuke KAMATA, Kazufumi YAMAGATA
IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems.2023; E106.D(5): 707. CrossRef - Rectal Cancer Stages T2 and T3 Identification Based on Asymptotic Hybrid Feature Maps
Shujing Sun, Jiale Wu, Jian Yao, Yang Cheng, Xin Zhang, Zhihua Lu, Pengjiang Qian
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences.2023; 137(1): 923. CrossRef - How to use AI in pathology
Peter Schüffler, Katja Steiger, Wilko Weichert
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2023; 62(9): 564. CrossRef - Cutting-Edge Technologies for Digital Therapeutics: A Review and Architecture Proposals for Future Directions
Joo Hun Yoo, Harim Jeong, Tai-Myoung Chung
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(12): 6929. CrossRef - A convolutional neural network STIFMap reveals associations between stromal stiffness and EMT in breast cancer
Connor Stashko, Mary-Kate Hayward, Jason J. Northey, Neil Pearson, Alastair J. Ironside, Johnathon N. Lakins, Roger Oria, Marie-Anne Goyette, Lakyn Mayo, Hege G. Russnes, E. Shelley Hwang, Matthew L. Kutys, Kornelia Polyak, Valerie M. Weaver
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based PTEN Loss Assessment as an Early Predictor of Prostate Cancer Metastasis After Surgery: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Palak Patel, Stephanie Harmon, Rachael Iseman, Olga Ludkowski, Heidi Auman, Sarah Hawley, Lisa F. Newcomb, Daniel W. Lin, Peter S. Nelson, Ziding Feng, Hilary D. Boyer, Maria S. Tretiakova, Larry D. True, Funda Vakar-Lopez, Peter R. Carroll, Matthew R. Co
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(10): 100241. CrossRef - Minimum resolution requirements of digital pathology images for accurate classification
Lydia Neary-Zajiczek, Linas Beresna, Benjamin Razavi, Vijay Pawar, Michael Shaw, Danail Stoyanov
Medical Image Analysis.2023; 89: 102891. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in the Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Sangjoon Choi, Seokhwi Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2023; 23(3): 410. CrossRef - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Based Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms
Jin-Seok Park, Seok Jeong
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2023; 28(3): 53. CrossRef - Framework for Classifying Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Algorithms in Clinical Medicine
Thomas Gniadek, Jason Kang, Talent Theparee, Jacob Krive
Online Journal of Public Health Informatics.2023; 15: e50934. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Future of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Oral Pathology, and Oral Surgery in the Hands of Technology
Ishita Singhal, Geetpriya Kaur, Dirk Neefs, Aparna Pathak
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - AI-Powered Biomolecular-Specific and Label-Free Multispectral Imaging Rapidly Detects Malignant Neoplasm in Surgically Excised Breast Tissue Specimens
Rishikesh Pandey, David Fournier, Gary Root, Machele Riccio, Aditya Shirvalkar, Gianfranco Zamora, Noel Daigneault, Michael Sapack, Minghao Zhong, Malini Harigopal
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(11): 1298. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence for patient scheduling in the real-world health care setting: A metanarrative review
Dacre R.T. Knight, Christopher A. Aakre, Christopher V. Anstine, Bala Munipalli, Parisa Biazar, Ghada Mitri, Jose Raul Valery, Tara Brigham, Shehzad K. Niazi, Adam I. Perlman, John D. Halamka, Abd Moain Abu Dabrh
Health Policy and Technology.2023; 12(4): 100824. CrossRef - Towards Autonomous Healthcare: Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Personalized Medicine and Disease Prediction
Nitin Rane, Saurabh Choudhary, Jayesh Rane
SSRN Electronic Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical imaging and multimodal artificial intelligence models for streamlining and enhancing cancer care: opportunities and challenges
Kevin Pierre, Manas Gupta, Abheek Raviprasad, Seyedeh Mehrsa Sadat Razavi, Anjali Patel, Keith Peters, Bruno Hochhegger, Anthony Mancuso, Reza Forghani
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2023; 23(12): 1265. CrossRef - Automated differential diagnostics of respiratory diseases using an electronic stethoscope
Diana Arhypenko, Denis Panaskin, Dmytro Babko
Polish Journal of Medical Physics and Engineering.2023; 29(4): 208. CrossRef - Application of machine learning in identification of pathogenic microbes
Lakshmi Venkata S Kutikuppala, Kanishk K Adhit, Reewen George D Silva
Digital Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Beginning of a New Era
C Nandini, Shaik Basha, Aarchi Agarawal, R Parikh Neelampari, Krishna P Miyapuram, R Jadeja Nileshwariba
Advances in Human Biology.2023; 13(1): 4. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Respiratory Medicine
K Kalaiyarasan, R Sridhar
Journal of Association of Pulmonologist of Tamil Nadu.2023; 6(2): 53. CrossRef - Automated abstraction of myocardial perfusion imaging reports using natural language processing
Parija Sharedalal, Ajay Singh, Neal Shah, Diwakar Jain
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.2022; 29(3): 1188. CrossRef - Polyploid giant cancer cell characterization: New frontiers in predicting response to chemotherapy in breast cancer
Geetanjali Saini, Shriya Joshi, Chakravarthy Garlapati, Hongxiao Li, Jun Kong, Jayashree Krishnamurthy, Michelle D. Reid, Ritu Aneja
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 81: 220. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of Markov Random Field and Conditional Random Field Approaches in Pathology Image Analysis
Yixin Li, Chen Li, Xiaoyan Li, Kai Wang, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Changhao Sun, Hao Chen, Xinran Wu, Hong Zhang, Qian Wang
Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering.2022; 29(1): 609. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology: From bench to clinic
Jamal Elkhader, Olivier Elemento
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 84: 113. CrossRef - Yeast‐like organisms phagocytosed by circulating neutrophils: Evidence of disseminated histoplasmosis
Yue Zhao, Jenna McCracken, Endi Wang
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology.2022; 44(1): 51. CrossRef - Whole-slide imaging, tissue image analysis, and artificial intelligence in veterinary pathology: An updated introduction and review
Aleksandra Zuraw, Famke Aeffner
Veterinary Pathology.2022; 59(1): 6. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of computer-aided whole-slide image analysis: from datasets to feature extraction, segmentation, classification and detection approaches
Xintong Li, Chen Li, Md Mamunur Rahaman, Hongzan Sun, Xiaoqi Li, Jian Wu, Yudong Yao, Marcin Grzegorzek
Artificial Intelligence Review.2022; 55(6): 4809. CrossRef - Liquid Biopsy and Artificial Intelligence as Tools to Detect Signatures of Colorectal Malignancies: A Modern Approach in Patient’s Stratification
Octav Ginghina, Ariana Hudita, Marius Zamfir, Andrada Spanu, Mara Mardare, Irina Bondoc, Laura Buburuzan, Sergiu Emil Georgescu, Marieta Costache, Carolina Negrei, Cornelia Nitipir, Bianca Galateanu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Automated bone marrow cytology using deep learning to generate a histogram of cell types
Rohollah Moosavi Tayebi, Youqing Mu, Taher Dehkharghanian, Catherine Ross, Monalisa Sur, Ronan Foley, Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Clinton J. V. Campbell
Communications Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risultati di esami di laboratorio per intelligenza artificiale e "machine learning"
Marco PRADELLA
La Rivista Italiana della Medicina di Laboratorio.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Deception of Certainty: how Non-Interpretable Machine Learning Outcomes Challenge the Epistemic Authority of Physicians. A deliberative-relational Approach
Florian Funer
Medicine, Health Care and Philosophy.2022; 25(2): 167. CrossRef - Deep discriminative learning model with calibrated attention map for the automated diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Sautami Basu, Ravinder Agarwal, Vishal Srivastava
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2022; 76: 103728. CrossRef - Question and Answer Techniques for Financial Audits in Universities Based on Deep Learning
Qiang Li, Hangjun Che
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Noninvasive Screening Tool for Hyperkalemia Using a Single-Lead Electrocardiogram and Deep Learning: Development and Usability Study
Erdenebayar Urtnasan, Jung Hun Lee, Byungjin Moon, Hee Young Lee, Kyuhee Lee, Hyun Youk
JMIR Medical Informatics.2022; 10(6): e34724. CrossRef - Impact of artificial intelligence on pathologists’ decisions: an experiment
Julien Meyer, April Khademi, Bernard Têtu, Wencui Han, Pria Nippak, David Remisch
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2022; 29(10): 1688. CrossRef - Rapid Screening Using Pathomorphologic Interpretation to Detect BRAFV600E Mutation and Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer
Satoshi Fujii, Daisuke Kotani, Masahiro Hattori, Masato Nishihara, Toshihide Shikanai, Junji Hashimoto, Yuki Hama, Takuya Nishino, Mizuto Suzuki, Ayatoshi Yoshidumi, Makoto Ueno, Yoshito Komatsu, Toshiki Masuishi, Hiroki Hara, Taito Esaki, Yoshiaki Nakamu
Clinical Cancer Research.2022; 28(12): 2623. CrossRef - Using Deep Learning to Predict Final HER2 Status in Invasive Breast Cancers That are Equivocal (2+) by Immunohistochemistry
Sean A. Rasmussen, Valerie J. Taylor, Alexi P. Surette, Penny J. Barnes, Gillian C. Bethune
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(10): 668. CrossRef - Deep Neural Network for the Prediction of KRAS Genotype in Rectal Cancer
Waleed M Ghareeb, Eman Draz, Khaled Madbouly, Ahmed H Hussein, Mohammed Faisal, Wagdi Elkashef, Mona Hany Emile, Marcus Edelhamre, Seon Hahn Kim, Sameh Hany Emile
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2022; 235(3): 482. CrossRef - Next Generation Digital Pathology: Emerging Trends and Measurement Challenges for Molecular Pathology
Alex Dexter, Dimitrios Tsikritsis, Natalie A. Belsey, Spencer A. Thomas, Jenny Venton, Josephine Bunch, Marina Romanchikova
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2022; 3(3): 168. CrossRef - Animation Design of Multisensor Data Fusion Based on Optimized AVOD Algorithm
Li Ding, Guobing Wei, Kai Zhang, Gengxin Sun
Journal of Sensors.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Study on Machine Translation Teaching Model Based on Translation Parallel Corpus and Exploitation for Multimedia Asian Information Processing
Yan Gong
ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis and Estimation of Pathological Data and Findings with Deep Learning Methods
Ahmet Anıl ŞAKIR, Ali Hakan IŞIK, Özlem ÖZMEN, Volkan İPEK
Veterinary Journal of Mehmet Akif Ersoy University.2022; 7(3): 175. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Pathology: Friend or Enemy?
Selim Sevim, Ezgi Dicle Serbes, Murat Bahadır, Mustafa Said Kartal, Serpil Dizbay Sak
Journal of Ankara University Faculty of Medicine.2022; 75(1): 13. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding artificial intelligence in histopathology: A cross-sectional study among oral pathologists in India
M. Indu, Vidya Gurram Shankar, Latha Mary Cherian, Revathi Krishna, Sabu Paul, Pradeesh Sathyan
Saudi Journal of Oral Sciences.2022; 9(3): 157. CrossRef - Evaluation Challenges in the Validation of B7-H3 as Oral Tongue Cancer Prognosticator
Meri Sieviläinen, Anna Maria Wirsing, Aini Hyytiäinen, Rabeia Almahmoudi, Priscila Rodrigues, Inger-Heidi Bjerkli, Pirjo Åström, Sanna Toppila-Salmi, Timo Paavonen, Ricardo D. Coletta, Elin Hadler-Olsen, Tuula Salo, Ahmed Al-Samadi
Head and Neck Pathology.2021; 15(2): 469. CrossRef - Amsterdam International Consensus Meeting: tumor response scoring in the pathology assessment of resected pancreatic cancer after neoadjuvant therapy
Boris V. Janssen, Faik Tutucu, Stijn van Roessel, Volkan Adsay, Olca Basturk, Fiona Campbell, Claudio Doglioni, Irene Esposito, Roger Feakins, Noriyoshi Fukushima, Anthony J. Gill, Ralph H. Hruban, Jeffrey Kaplan, Bas Groot Koerkamp, Seung-Mo Hong, Alyssa
Modern Pathology.2021; 34(1): 4. CrossRef - Fabrication of ultra-thin 2D covalent organic framework nanosheets and their application in functional electronic devices
Weikang Wang, Weiwei Zhao, Haotian Xu, Shujuan Liu, Wei Huang, Qiang Zhao
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2021; 429: 213616. CrossRef - Generalizability of Deep Learning System for the Pathologic Diagnosis of Various Cancers
Hyun-Jong Jang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(2): 808. CrossRef - Integrated digital pathology at scale: A solution for clinical diagnostics and cancer research at a large academic medical center
Peter J Schüffler, Luke Geneslaw, D Vijay K Yarlagadda, Matthew G Hanna, Jennifer Samboy, Evangelos Stamelos, Chad Vanderbilt, John Philip, Marc-Henri Jean, Lorraine Corsale, Allyne Manzo, Neeraj H G Paramasivam, John S Ziegler, Jianjiong Gao, Juan C Peri
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.2021; 28(9): 1874. CrossRef - Translational Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Diagnostic Pathology in Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Comprehensive and Evolutive Analysis
Julia Moran-Sanchez, Antonio Santisteban-Espejo, Miguel Angel Martin-Piedra, Jose Perez-Requena, Marcial Garcia-Rojo
Biomolecules.2021; 11(6): 793. CrossRef - Development and operation of a digital platform for sharing pathology image data
Yunsook Kang, Yoo Jung Kim, Seongkeun Park, Gun Ro, Choyeon Hong, Hyungjoon Jang, Sungduk Cho, Won Jae Hong, Dong Un Kang, Jonghoon Chun, Kyoungbun Lee, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Kyoung Chul Moon, Gheeyoung Choe, Kyu Sang Lee, Jeong Hwan Park, Won-Ki Jeong, Se Yo
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sliding window based deep ensemble system for breast cancer classification
Amin Alqudah, Ali Mohammad Alqudah
Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology.2021; 45(4): 313. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and computational pathology
Miao Cui, David Y. Zhang
Laboratory Investigation.2021; 101(4): 412. CrossRef - Effects of Image Quantity and Image Source Variation on Machine Learning Histology Differential Diagnosis Models
Elham Vali-Betts, Kevin J. Krause, Alanna Dubrovsky, Kristin Olson, John Paul Graff, Anupam Mitra, Ananya Datta-Mitra, Kenneth Beck, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Cynthia Loomis, Antonio Galvao Neto, Esther Adler, Hooman H. Rashidi
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 5. CrossRef - Feasibility of deep learning‐based fully automated classification of microsatellite instability in tissue slides of colorectal cancer
Sung Hak Lee, In Hye Song, Hyun‐Jong Jang
International Journal of Cancer.2021; 149(3): 728. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare
Yamini D Shah, Shailvi M Soni, Manish P Patel
Indian Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2021; 8(2): 102. CrossRef - Proof of Concept for a Deep Learning Algorithm for Identification and Quantification of Key Microscopic Features in the Murine Model of DSS-Induced Colitis
Agathe Bédard, Thomas Westerling-Bui, Aleksandra Zuraw
Toxicologic Pathology.2021; 49(4): 897. CrossRef - An empirical analysis of machine learning frameworks for digital pathology in medical science
S.K.B. Sangeetha, R Dhaya, Dhruv T Shah, R Dharanidharan, K. Praneeth Sai Reddy
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2021; 1767(1): 012031. CrossRef - Application of Single-Cell Approaches to Study Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Biology
Daniel Royston, Adam J. Mead, Bethan Psaila
Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America.2021; 35(2): 279. CrossRef - Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) and Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI): Diagnostic Algorithm Based on the Quantitative Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM)
Rolf Teschke, Gaby Danan
Diagnostics.2021; 11(3): 458. CrossRef - Searching Images for Consensus
Hamid R. Tizhoosh, Phedias Diamandis, Clinton J.V. Campbell, Amir Safarpoor, Shivam Kalra, Danial Maleki, Abtin Riasatian, Morteza Babaie
The American Journal of Pathology.2021; 191(10): 1702. CrossRef - Automated Classification and Segmentation in Colorectal Images Based on Self‐Paced Transfer Network
Yao Yao, Shuiping Gou, Ru Tian, Xiangrong Zhang, Shuixiang He, Zhiguo Zhou
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and sleep: Advancing sleep medicine
Nathaniel F. Watson, Christopher R. Fernandez
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2021; 59: 101512. CrossRef - Prospective Of Artificial Intelligence: Emerging Trends In Modern Biosciences Research
Pradeep Kumar, Ajit Kumar Singh Yadav, Abhishek Singh
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2021; 1020(1): 012008. CrossRef - Use and Control of Artificial Intelligence in Patients Across the Medical Workflow: Single-Center Questionnaire Study of Patient Perspectives
Simon Lennartz, Thomas Dratsch, David Zopfs, Thorsten Persigehl, David Maintz, Nils Große Hokamp, Daniel Pinto dos Santos
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(2): e24221. CrossRef - HEAL: an automated deep learning framework for cancer histopathology image analysis
Yanan Wang, Nicolas Coudray, Yun Zhao, Fuyi Li, Changyuan Hu, Yao-Zhong Zhang, Seiya Imoto, Aristotelis Tsirigos, Geoffrey I Webb, Roger J Daly, Jiangning Song, Zhiyong Lu
Bioinformatics.2021; 37(22): 4291. CrossRef - A Review of Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Gastroenterology
Khalid Nawab, Ravi Athwani, Awais Naeem, Muhammad Hamayun, Momna Wazir
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Cancer-Related Biomarkers Based on Pathological Images: A Systematic Review
Xiaoliang Xie, Xulin Wang, Yuebin Liang, Jingya Yang, Yan Wu, Li Li, Xin Sun, Pingping Bing, Binsheng He, Geng Tian, Xiaoli Shi
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based histopathological segmentation for whole slide images of colorectal cancer in a compressed domain
Hyeongsub Kim, Hongjoon Yoon, Nishant Thakur, Gyoyeon Hwang, Eun Jung Lee, Chulhong Kim, Yosep Chong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Ex Vivo Fluorescent Confocal Microscopy Data: A Feasibility Study
Veronika Shavlokhova, Sameena Sandhu, Christa Flechtenmacher, Istvan Koveshazi, Florian Neumeier, Víctor Padrón-Laso, Žan Jonke, Babak Saravi, Michael Vollmer, Andreas Vollmer, Jürgen Hoffmann, Michael Engel, Oliver Ristow, Christian Freudlsperger
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(22): 5326. CrossRef - A Pathologist-Annotated Dataset for Validating Artificial Intelligence: A Project Description and Pilot Study
Sarah N. Dudgeon, Si Wen, Matthew G. Hanna, Rajarsi Gupta, Mohamed Amgad, Manasi Sheth, Hetal Marble, Richard Huang, Markus D. Herrmann, Clifford H. Szu, Darick Tong, Bruce Werness, Evan Szu, Denis Larsimont, Anant Madabhushi, Evangelos Hytopoulos, Weijie
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2021; 12(1): 45. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: A Multinational Multi-Center Survey on the Medical and Dental Students' Perception
Sotirios Bisdas, Constantin-Cristian Topriceanu, Zosia Zakrzewska, Alexandra-Valentina Irimia, Loizos Shakallis, Jithu Subhash, Maria-Madalina Casapu, Jose Leon-Rojas, Daniel Pinto dos Santos, Dilys Miriam Andrews, Claudia Zeicu, Ahmad Mohammad Bouhuwaish
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital/Computational Technology for Molecular Cytology Testing: A Short Technical Note with Literature Review
Robert Y. Osamura, Naruaki Matsui, Masato Kawashima, Hiroyasu Saiga, Maki Ogura, Tomoharu Kiyuna
Acta Cytologica.2021; 65(4): 342. CrossRef - Advances in Digital Pathology: From Artificial Intelligence to Label-Free Imaging
Frederik Großerueschkamp, Hendrik Jütte, Klaus Gerwert, Andrea Tannapfel
Visceral Medicine.2021; 37(6): 482. CrossRef - Feasibility of fully automated classification of whole slide images based on deep learning
Kyung-Ok Cho, Sung Hak Lee, Hyun-Jong Jang
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2020; 24(1): 89. CrossRef - Same same but different: A Web‐based deep learning application revealed classifying features for the histopathologic distinction of cortical malformations
Joshua Kubach, Angelika Muhlebner‐Fahrngruber, Figen Soylemezoglu, Hajime Miyata, Pitt Niehusmann, Mrinalini Honavar, Fabio Rogerio, Se‐Hoon Kim, Eleonora Aronica, Rita Garbelli, Samuel Vilz, Alexander Popp, Stefan Walcher, Christoph Neuner, Michael Schol
Epilepsia.2020; 61(3): 421. CrossRef - Segmentation and Classification in Digital Pathology for Glioma Research: Challenges and Deep Learning Approaches
Tahsin Kurc, Spyridon Bakas, Xuhua Ren, Aditya Bagari, Alexandre Momeni, Yue Huang, Lichi Zhang, Ashish Kumar, Marc Thibault, Qi Qi, Qian Wang, Avinash Kori, Olivier Gevaert, Yunlong Zhang, Dinggang Shen, Mahendra Khened, Xinghao Ding, Ganapathy Krishnamu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology
B. Acs, M. Rantalainen, J. Hartman
Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 288(1): 62. CrossRef - Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology
Soojeong Nam, Yosep Chong, Chan Kwon Jung, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Ji Youl Lee, Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Heounjeong Go
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(2): 125. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence with multi-functional machine learning platform development for better healthcare and precision medicine
Zeeshan Ahmed, Khalid Mohamed, Saman Zeeshan, XinQi Dong
Database.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Scoring pleurisy in slaughtered pigs using convolutional neural networks
Abigail R. Trachtman, Luca Bergamini, Andrea Palazzi, Angelo Porrello, Andrea Capobianco Dondona, Ercole Del Negro, Andrea Paolini, Giorgio Vignola, Simone Calderara, Giuseppe Marruchella
Veterinary Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status of Computational Intelligence Applications in Dermatological Clinical Practice
Carmen Rodríguez-Cerdeira, José Luís González-Cespón, Roberto Arenas
The Open Dermatology Journal.2020; 14(1): 6. CrossRef - New unified insights on deep learning in radiological and pathological images: Beyond quantitative performances to qualitative interpretation
Yoichi Hayashi
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2020; 19: 100329. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology: Present and Future
Francisco Lopez-Jimenez, Zachi Attia, Adelaide M. Arruda-Olson, Rickey Carter, Panithaya Chareonthaitawee, Hayan Jouni, Suraj Kapa, Amir Lerman, Christina Luong, Jose R. Medina-Inojosa, Peter A. Noseworthy, Patricia A. Pellikka, Margaret M. Redfield, Vero
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(5): 1015. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in oncology
Hideyuki Shimizu, Keiichi I. Nakayama
Cancer Science.2020; 111(5): 1452. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence and the future of global health
Nina Schwalbe, Brian Wahl
The Lancet.2020; 395(10236): 1579. CrossRef - The future of pathology is digital
J.D. Pallua, A. Brunner, B. Zelger, M. Schirmer, J. Haybaeck
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153040. CrossRef - Weakly-supervised learning for lung carcinoma classification using deep learning
Fahdi Kanavati, Gouji Toyokawa, Seiya Momosaki, Michael Rambeau, Yuka Kozuma, Fumihiro Shoji, Koji Yamazaki, Sadanori Takeo, Osamu Iizuka, Masayuki Tsuneki
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The use of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in oncologic histopathology
Ahmed S. Sultan, Mohamed A. Elgharib, Tiffany Tavares, Maryam Jessri, John R. Basile
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2020; 49(9): 849. CrossRef - Convergence of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence Tools in Anatomic Pathology Practice: Current Landscape and Future Directions
Anil V. Parwani, Mahul B. Amin
Advances in Anatomic Pathology.2020; 27(4): 221. CrossRef - Advances in tissue-based imaging: impact on oncology research and clinical practice
Arman Rahman, Chowdhury Jahangir, Seodhna M. Lynch, Nebras Alattar, Claudia Aura, Niamh Russell, Fiona Lanigan, William M. Gallagher
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2020; 20(10): 1027. CrossRef - Current Trends of Artificial Intelligence for Colorectal Cancer Pathology Image Analysis: A Systematic Review
Nishant Thakur, Hongjun Yoon, Yosep Chong
Cancers.2020; 12(7): 1884. CrossRef - Explainable Machine Learning Model for Predicting GI Bleed Mortality in the Intensive Care Unit
Farah Deshmukh, Shamel S. Merchant
American Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 115(10): 1657. CrossRef - Prediction of clinically actionable genetic alterations from colorectal cancer histopathology images using deep learning
Hyun-Jong Jang, Ahwon Lee, J Kang, In Hye Song, Sung Hak Lee
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 26(40): 6207. CrossRef - Application of system analysis methods for modeling the development of hand-arm vibration syndrome: problems and approaches to solution
M P Diakovich, M V Krivov
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1661(1): 012029. CrossRef - Histo-ELISA technique for quantification and localization of tissue components
Zhongmin Li, Silvia Goebel, Andreas Reimann, Martin Ungerer
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of artificial intelligence in diagnostic oral pathology-A modern approach
Ayinampudi Bhargavi Krishna, Azra Tanveer, Pancha Venkat Bhagirath, Ashalata Gannepalli
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2020; 24(1): 152. CrossRef - Applications of deep learning for the analysis of medical data
Hyun-Jong Jang, Kyung-Ok Cho
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2019; 42(6): 492. CrossRef - PROMISE CLIP Project: A Retrospective, Multicenter Study for Prostate Cancer that Integrates Clinical, Imaging and Pathology Data
Jihwan Park, Mi Jung Rho, Yong Hyun Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Yosep Chong, Choung-Soo Kim, Heounjeong Go, Seong Soo Jeon, Minyong Kang, Hak Jong Lee, Sung Il Hwang, Ji Youl Lee
Applied Sciences.2019; 9(15): 2982. CrossRef - Key challenges for delivering clinical impact with artificial intelligence
Christopher J. Kelly, Alan Karthikesalingam, Mustafa Suleyman, Greg Corrado, Dominic King
BMC Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning for Whole Slide Image Analysis: An Overview
Neofytos Dimitriou, Ognjen Arandjelović, Peter D. Caie
Frontiers in Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Barriers to Artificial Intelligence Adoption in Healthcare Management: A Systematic Review
Mir Mohammed Assadullah
SSRN Electronic Journal .2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interpretable Machine Learning Approaches for Identification of Acute Aortic Dissection in Chest Pain Patients
- Quilty Lesions in the Endomyocardial Biopsies after Heart Transplantation
- Haeyon Cho, Jin-Oh Choi, Eun-Seok Jeon, Jung-Sun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(1):50-56. Published online December 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.11.30
- 8,504 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical significance of Quilty lesions in endomyocardial biopsies (EMBs) of cardiac transplantation patients.
Methods
A total of 1190EMBs from 117 cardiac transplantation patients were evaluated histologically for Quilty lesions,acute cellular rejection, and antibody-mediated rejection. Cardiac allograft vasculopathy wasdiagnosed by computed tomography coronary angiography. Clinical information, including thepatients’ survival was retrieved by a review of medical records.
Results
Eighty-eight patients(75.2%) were diagnosed with Quilty lesions, which were significantly associated with acute cellularrejection, but not with acute cellular rejection ≥ 2R or antibody-mediated rejection. In patientsdiagnosed with both Quilty lesions and acute cellular rejection, the time-to-onset of Quilty lesionsfrom transplantation was longer than that of acute cellular rejections. We found a significant associationbetween Quilty lesions and cardiac allograft vasculopathy. No significant relationship wasfound between Quilty lesions and the patients’ survival.
Conclusions
Quilty lesion may be an indicator of previous acute cellular rejection rather than a predictor for future acute cellular rejection. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
Andrea Fernandez Valledor, Cathrine M. Moeller, Adi Hertz, Daniel Oren, Ilan Richter, Boaz Elad, Julia Baranowska, Salwa Rahman, Carolyn Hennecken, Afsana Rahman, Dor Lotan, David Bae, Adil Yunis, Justin A. Fried, Ersilia M. DeFilippis, David T Majure, Ja
The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of tertiary lymphoid structures in orchestrating immune responses in peripheral organs
Keisuke Taniguchi, Takahisa Yoshikawa, Motoko Yanagita
Inflammation and Regeneration.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The human myocardium harbors a population of naive B-cells with a distinctive gene expression signature conserved across species
Kevin C. Bermea, Nicolas Kostelecky, Sylvie T. Rousseau, Chieh-Yu Lin, Luigi Adamo
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Examination of tracheal allografts after long-term survival in dogs
Tao Lu, Yiwei Huang, Yulei Qiao, Yongxing Zhang, Yu Liu
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.2021; 59(1): 155. CrossRef - Essentials in the diagnosis of postoperative myocardial lesions similar to or unrelated to rejection in heart transplant
Costel Dumitru, Ancuta Zazgyva, Adriana Habor, Ovidiu Cotoi, Horațiu Suciu, Carmen Cotrutz, Bogdan Grecu, Ileana Anca Sin
Revista Romana de Medicina de Laborator.2021; 29(3): 307. CrossRef - Clinical outcome of donor heart with prolonged cold ischemic time: A single‐center study
Fazal Shafiq, Yixuan Wang, Geng Li, Zongtao Liu, Fei Li, Ying Zhou, Li Xu, Xingjian Hu, Nianguo Dong
Journal of Cardiac Surgery.2020; 35(2): 397. CrossRef - The XVth Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology the Banff Workshop Heart Report: Improving the diagnostic yield from endomyocardial biopsies and Quilty effect revisited
Jean-Paul Duong Van Huyen, Marny Fedrigo, Gregory A. Fishbein, Ornella Leone, Desley Neil, Charles Marboe, Eliot Peyster, Jan von der Thüsen, Alexandre Loupy, Michael Mengel, Monica P. Revelo, Benjamin Adam, Patrick Bruneval, Annalisa Angelini, Dylan V. M
American Journal of Transplantation.2020; 20(12): 3308. CrossRef
- A Molecular Reappraisal of Quilty Lesions: Insights from Tissue and Circulating Biomarkers in Heart Transplantation
- Loss of Nuclear BAP1 Expression Is Associated with High WHO/ISUP Grade in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Young Chan Wi, Ahrim Moon, Min Jung Jung, Yeseul Kim, Seong Sik Bang, Kiseok Jang, Seung Sam Paik, Su-Jin Shin
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(6):378-385. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.09.21
- 10,995 View
- 228 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) mutations are frequently reported in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); however, very few studies have evaluated the role of these mutations in other renal cell carcinoma (RCC) subtypes. Therefore, we analyzed BAP1 protein expression using immunohistochemistry in several RCC subtypes and assessed its relationship with clinicopathological characteristics of patients.
Methods
BAP1 expression was immunohistochemically evaluated in tissue microarray blocks constructed from 371 samples of RCC collected from two medical institutions. BAP1 expression was evaluated based on the extent of nuclear staining in tumor cells, and no expression or expression in < 10% of tumor cells was defined as negative.
Results
Loss of BAP1 expression was observed in ccRCC (56/300, 18.7%), chromophobe RCC (6/26, 23.1%), and clear cell papillary RCC (1/4, 25%), while we failed to detect BAP1 expression loss in papillary RCC, acquired cystic disease-associated RCC, or collecting duct carcinoma. In ccRCC, loss of BAP1 expression was significantly associated with high World Health Organization (WHO)/International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grade (p = .002); however, no significant correlation was observed between loss of BAP1 expression and survival in ccRCC. Loss of BAP1 expression showed no association with prognostic factors in chromophobe RCC.
Conclusions
Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in both ccRCC and chromophobe RCC. In addition, BAP1 expression loss was associated with poor prognostic factors such as high WHO/ISUP grade in ccRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) in Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): Biology, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Opportunities
Alberto Bongiovanni, Pierfranco Conte, Vincenza Conteduca, Matteo Landriscina, Giuseppe Di Lorenzo, Francesco Cognetti
Current Oncology.2025; 32(12): 690. CrossRef - Clinical and Genomic Features of Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: Analysis of a Multi-Institutional Database
Corbin J. Eule, Junxiao Hu, Dale Hedges, Alkesh Jani, Thomas Pshak, Brandon J. Manley, Alejandro Sanchez, Robert Dreicer, Zin W. Myint, Yousef Zakharia, Elaine T. Lam
Cancers.2024; 16(10): 1920. CrossRef - Immune regulation and prognosis indicating ability of a newly constructed multi-genes containing signature in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Ziwei Gui, Juan Du, Nan Wu, Ningning Shen, Zhiqing Yang, Huijun Yang, Xuzhi Wang, Na Zhao, Zixin Zeng, Rong Wei, Wenxia Ma, Chen Wang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiogenomic Associations Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: An Exploratory Study
Derek H Liu, Komal A Dani, Sharath S Reddy, Xiaomeng Lei, Natalie L Demirjian, Darryl H Hwang, Bino A Varghese, Suhn Kyong Rhie, Felix Y. Yap, David I. Quinn, Imran Siddiqi, Manju Aron, Ulka Vaishampayan, Haris Zahoor, Steven Y Cen, Inderbir S Gill, Vinay
Oncology.2023; 101(6): 375. CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of renal epithelial neoplasms
Mahmut Akgul, Sean R Williamson
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - BRCA1-Associated Protein 1 (BAP-1) as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review
Shuchi Gulati, Melissa Previtera, Primo N. Lara
Kidney Cancer.2022; 6(1): 23. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Review and Update
Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Luan D. Truong
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 657. CrossRef - CD117, BAP1, MTAP, and TdT Is a Useful Immunohistochemical Panel to Distinguish Thymoma from Thymic Carcinoma
Mounika Angirekula, Sindy Y Chang, Sarah M. Jenkins, Patricia T. Greipp, William R. Sukov, Randolph S. Marks, Kenneth R. Olivier, Stephen D. Cassivi, Anja C Roden
Cancers.2022; 14(9): 2299. CrossRef - BAP1 in cancer: epigenetic stability and genome integrity
Sabrina Caporali, Alessio Butera, Ivano Amelio
Discover Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioinformatic analysis identifying FGF1 gene as a new prognostic indicator in clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Xiaoqin Zhang, Ziyue Wang, Zixin Zeng, Ningning Shen, Bin Wang, Yaping Zhang, Honghong Shen, Wei Lu, Rong Wei, Wenxia Ma, Chen Wang
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of Four Pathological Stage‐Relevant Genes in Association with Progression and Prognosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
Dengyong Xu, Yuzi Xu, Yiming Lv, Fei Wu, Yunlong Liu, Ming Zhu, Dake Chen, Bingjun Bai, Rui Liu
BioMed Research International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Functional characterisation guides classification of novel BAP1 germline variants
Jing Han Hong, Siao Ting Chong, Po-Hsien Lee, Jing Tan, Hong Lee Heng, Nur Diana Binte Ishak, Sock Hoai Chan, Bin Tean Teh, Joanne Ngeow
npj Genomic Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Tissue-Based Immunohistochemical Markers for Diagnosis and Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Liang G Qu, Vaisnavi Thirugnanasundralingam, Damien Bolton, Antonio Finelli, Nathan Lawrentschuk
Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal.2020; 1(1): 68. CrossRef - Radiogenomics: bridging imaging and genomics
Zuhir Bodalal, Stefano Trebeschi, Thi Dan Linh Nguyen-Kim, Winnie Schats, Regina Beets-Tan
Abdominal Radiology.2019; 44(6): 1960. CrossRef
- The Role of Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) in Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): Biology, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Opportunities
- Let Archived Paraffin Blocks Be Utilized for Research with Waiver of Informed Consent
- Yong-Jin Kim, Jeong Sik Park, Karam Ko, Chang Rok Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):141-147. Published online April 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.02.07
- 10,754 View
- 142 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Advances in biomedical and genetic research have contributed to more effective public health improvement via bench-to-bed research and the emergence of personalized medicine. This has certainly showcased the importance of archived human tissues, especially paraffin-embedded blocks in pathology. Currently in Korea, undue legislative regulations of the Bioethics and Safety Act suspend and at times discourage studies from taking place. In this paper, the authors underline the value of paraffin blocks in the era of personalized and translational medicine. We discuss detailed clauses regarding the applicability of paraffin blocks from a legal perspective and compare Korea’s regulations with those of other countries. The necessity for allowing waived consent and Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval will be argued throughout. The authors suggest that researchers declare the following to obtain IRB approval and waiver of informed consents: research could not be practically carried out without a waiver of consent; the proposed research presents no more than minimal risk of harm to subjects, and the waiver of consent will not adversely affect the rights and welfare of subjects; and research will not utilize a tissue block if only 1 is available for each subject, to allow future clinical use such as re-evaluation or further studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating GILZ and SGK-1 in Oral Lesions: Biomarker Potential in Malignant Transformation
Soo Min Lee, Nur S. Ismail, Dina M. Saleh
Journal of Current Research in Oral Surgery.2025; 5(1): 70. CrossRef - NaV1.7 channels are expressed in the lower airways of the human respiratory tract
Everardo Hernández-Plata, Ana Alfaro Cruz, Carina Becerril
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.2023; 311: 104034. CrossRef - Expression Profiles of GILZ and SGK-1 in Potentially Malignant and Malignant Human Oral Lesions
Mahmood S. Mozaffari, Rafik Abdelsayed
Frontiers in Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - IRB review points for studies utilizing paraffin blocks archived in the pathology laboratory
Yong-Jin Kim, Chang Rok Jeong, Jeong Sik Park
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2018; 35(1): 36. CrossRef
- Investigating GILZ and SGK-1 in Oral Lesions: Biomarker Potential in Malignant Transformation
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features and Its Impact on the Risk of Malignancy in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: An Institutional Experience
- Milim Kim, Joung Eun Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Yoonjin Kwak, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):171-178. Published online April 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.03
- 11,682 View
- 205 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study was performed to analyze cytologic diagnosis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) and its impact on the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC).
Methods
Five thousand five hundred and forty-nine cases of thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) diagnosed between 2012 and 2014 were included in this study. Diagnostic categories based on TBSRTC were compared with final surgical diagnoses, and the ROM in each category was calculated both when NIFTP was included in malignant lesions and when excluded from malignant lesions.
Results
Of the 5,549 thyroid FNAC cases, 1,891 cases underwent surgical resection. In final diagnosis, 1,700 cases were revealed as papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), and 25 cases were reclassified as NIFTP. The cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP were non-diagnostic in one, benign in five, atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) in 14, follicular neoplasm in two, and suspicious for malignancy in three cases. Collectively, NIFTP/encapsulated follicular variant of PTC (EFVPTC) were more frequently classified as benign, AUS, or follicular neoplasm and less frequently categorized as malignant compared to conventional PTCs. Exclusion of NIFTP from malignant diagnoses resulted in a slight decrease in malignancy rates in non-diagnostic, benign, AUS, follicular neoplasm, and suspicious for malignancy categories without any statistical significance.
Conclusions
The decrease in the ROM was not significant when NIFTP was excluded from malignant lesions. In thyroid FNACs, NIFTP/EFVPTCs were mostly classified into indeterminate categories. Therefore, it might be feasible to separate NIFTP/EFVPTC from conventional PTC on FNAC to guide clinicians to conservative management for patients with NIFTP/EFVPTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Spatial transcriptomics reveals prognosis‐associated cellular heterogeneity in the papillary thyroid carcinoma microenvironment
Kai Yan, Qing‐Zhi Liu, Rong‐Rong Huang, Yi‐Hua Jiang, Zhen‐Hua Bian, Si‐Jin Li, Liang Li, Fei Shen, Koichi Tsuneyama, Qing‐Ling Zhang, Zhe‐Xiong Lian, Haixia Guan, Bo Xu
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Features of “Non-invasive Follicular Tumour with Papillary Like Nuclear Features” – A Single Institutional Experience in India
K Amita, HB Rakshitha, M Sanjay, Prashantha Kalappa
Journal of Cytology.2023; 40(1): 28. CrossRef - Detailed fine needle aspiration cytopathology findings of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features with nuclear grading correlated to that of biopsy and Bethesda category and systematic review
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2023; 51(12): 758. CrossRef - Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features Is Not a Cytological Diagnosis, but It Influences Cytological Diagnosis Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elina Haaga, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvíková, Ivana Kholová
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(2): 85. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - Comprehensive DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Sora Jeon, Eun-Hye Seo, Dong Hyuck Bae, Young Mun Jeong, Yourha Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Seon-Kyu Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Yong Sung Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(2): 192. CrossRef - Differences in surgical resection rate and risk of malignancy in thyroid cytopathology practice between Western and Asian countries: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Hanh Thi Tuyet Ngo, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung, Trang Huyen Vu, Kim Bach Lu, Kennichi Kakudo, Tetsuo Kondo
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(4): 238. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular neoplasm with papillary like nuclear features: A comprehensive analysis with a diagnostic algorithm
Chanchal Rana, Shreyamsa Manjunath, Pooja Ramakant, Kulranjan Singh, Suresh Babu, Anand Mishra
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(4): 330. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features and the risk of malignancy in The Bethesda System for the Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology
Danielle Elliott Range, Xiaoyin “Sara” Jiang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(6): 531. CrossRef - Did Introducing a New Category of Thyroid Tumors (Non-invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features) Decrease the Risk of Malignancy for the Diagnostic Categories in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology?
Janusz Kopczyński, Agnieszka Suligowska, Kornelia Niemyska, Iwona Pałyga, Agnieszka Walczyk, Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Artur Kowalik, Kinga Hińcza, Ryszard Mężyk, Stanisław Góźdź, Aldona Kowalska
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - High risk of malignancy in cases with atypia of undetermined significance on fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules even after exclusion of NIFTP
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Büşra Yaprak Bayrak, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(11): 986. CrossRef - The importance of risk of neoplasm as an outcome in cytologic‐histologic correlation studies on thyroid fine needle aspiration
Yu‐Hsin Chen, Kristen L. Partyka, Rae Dougherty, Harvey M. Cramer, Howard H. Wu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(12): 1237. CrossRef - Preoperative diagnostic categories of fine needle aspiration cytology for histologically proven thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma, and Hurthle cell adenoma and carcinoma: Analysis of cause of under- or misdiagnoses
Hee Young Na, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241597. CrossRef - How is noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) shaping the way we interpret thyroid cytology?
Michiya Nishino
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2019; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Cytological Diagnoses Associated with Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasms with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features According to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Massimo Bongiovanni, Luca Giovanella, Francesco Romanelli, Pierpaolo Trimboli
Thyroid.2019; 29(2): 222. CrossRef - Preoperative Diagnostic Categories of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features in Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy and Its Impact on Risk of Malignancy
Hee Young Na, Ji Won Woo, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(4): 329. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Reclassification to Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): a Retrospective Clinicopathologic Study
Khurram Shafique, Virginia A. LiVolsi, Kathleen Montone, Zubair W. Baloch
Endocrine Pathology.2018; 29(4): 339. CrossRef
- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
- Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):359-364. Published online June 13, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.16
- 9,362 View
- 168 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) is presumed to be associated with adipogenic differentiation. Histone modification is known to be important for adipogenesis, and the function of histone demethylase plant homeodomain finger 2 (PHF2) has been noted. In addition, PHF2 may act as a tumor suppressor via epigenetic regulation of p53 and is reported to be reduced in colon cancer and stomach cancer tissues. In this study, we examined PHF2 expression in CCRCC specimens by immunohistochemistry.
Methods
We studied 254 CCRCCs and 56 non-neoplastic renal tissues from patients who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy between 2000 and 2003 at the Seoul National University Hospital. Tissue microarray blocks were prepared, and immunohistochemical staining for PHF2 was performed.
Results
Among 254 CCRCC cases, 150 cases (59.1%) showed high expression and 104 cases (40.1%) showed low expression. High expression of PHF2 was significantly correlated with a low Fuhrman nuclear grade (p < .001), smaller tumor size (p < .001), low overall stage (p = .003), longer cancer-specific survival (p = .002), and progression-free survival (p < .001) of the patients. However, it was not an independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis adjusted for Fuhrman nuclear grade and overall stage.
Conclusions
Our study showed that low expression of PHF2 is associated with aggressiveness and poor prognosis of CCRCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
Dexter Kai Hao Thng, Lissa Hooi, Wai Khang Yong, Dennis Kappei, Tan Boon Toh, Edward Kai-Hua Chow
Oncogenesis.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Phosphoproteomics identifies determinants of PAK inhibitor sensitivity in leukaemia cells
Pedro Casado, Santiago Marfa, Marym M. Hadi, Henry Gerdes, Sandra M. Martin-Guerrero, Farideh Miraki-Moud, Vinothini Rajeeve, Pedro R. Cutillas
Cell Communication and Signaling.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of histone methylation in renal cell cancer: an update
Yanguang Hou, Yan Yuan, Yanze Li, Lei Wang, Juncheng Hu, Xiuheng Liu
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(3): 2735. CrossRef - Phosphorylation of PHF2 by AMPK releases the repressive H3K9me2 and inhibits cancer metastasis
Ying Dong, Hao Hu, Xuan Zhang, Yunkai Zhang, Xin Sun, Hanlin Wang, Weijuan Kan, Min-jia Tan, Hong Shi, Yi Zang, Jia Li
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HIF-1α-mediated augmentation of miRNA-18b-5p facilitates proliferation and metastasis in osteosarcoma through attenuation PHF2
Peng Luo, Yan-dong Zhang, Feng He, Chang-jun Tong, Kai Liu, He Liu, Shi-zhuang Zhu, Jian-zhou Luo, Bing Yuan
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integration of meta-analysis and supervised machine learning for pattern recognition in breast cancer using epigenetic data
Reza Panahi, Esmaeil Ebrahimie, Ali Niazi, Alireza Afsharifar
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2021; 24: 100629. CrossRef - PHF2 regulates homology-directed DNA repair by controlling the resection of DNA double strand breaks
Ignacio Alonso-de Vega, Maria Cristina Paz-Cabrera, Magdalena B Rother, Wouter W Wiegant, Cintia Checa-Rodríguez, Juan Ramón Hernández-Fernaud, Pablo Huertas, Raimundo Freire, Haico van Attikum, Veronique A J Smits
Nucleic Acids Research.2020; 48(9): 4915. CrossRef - Emerging of lysine demethylases (KDMs): From pathophysiological insights to novel therapeutic opportunities
Sarder Arifuzzaman, Mst Reshma Khatun, Rabeya Khatun
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 129: 110392. CrossRef - Biology and targeting of the Jumonji-domain histone demethylase family in childhood neoplasia: a preclinical overview
Tyler S. McCann, Lays M. Sobral, Chelsea Self, Joseph Hsieh, Marybeth Sechler, Paul Jedlicka
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2019; 23(4): 267. CrossRef - MiR-221 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Migration via Targeting PHF2
Yi Fu, Mingyan Liu, Fengxia Li, Li Qian, Ping Zhang, Fengwei Lv, Wenting Cheng, Ruixing Hou
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - PHF2 histone demethylase prevents DNA damage and genome instability by controlling cell cycle progression of neural progenitors
Stella Pappa, Natalia Padilla, Simona Iacobucci, Marta Vicioso, Elena Álvarez de la Campa, Claudia Navarro, Elia Marcos, Xavier de la Cruz, Marian A. Martínez-Balbás
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2019; 116(39): 19464. CrossRef - Plant homeodomain finger protein 2 as a novel IKAROS target in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Zheng Ge, Yan Gu, Qi Han, Justin Sloane, Qinyu Ge, Goufeng Gao, Jinlong Ma, Huihui Song, Jiaojiao Hu, Baoan Chen, Sinisa Dovat, Chunhua Song
Epigenomics.2018; 10(1): 59. CrossRef
- The role of histone demethylase PHF2 as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SRXN1
- Morphological Features and Immunohistochemical Expression of p57Kip2 in Early Molar Pregnancies and Their Relations to the Progression to Persistent Trophoblastic Disease
- Marwa Khashaba, Mohammad Arafa, Eman Elsalkh, Reda Hemida, Wagiha Kandil
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):381-387. Published online June 12, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.04.28
- 16,326 View
- 246 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Although the morphological features characteristic of products of conception specimens including molar pregnancies are well described, substantial histopathological similarities are observed between the different entities, especially in cases of early pregnancies. Furthermore, there are no current solid criteria that could predict cases with progression to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease. In this study, we aimed to determine the most specific histopathological and immunohistochemical features required for accurate diagnosis that can reliably predict the clinical behavior.
Methods
Sixty-five cases of products of conception were reviewed clinically and pathologically, and any progression to persistent gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), if present, was noted. Pathological assessment of the archival material included re-cut sections of 5 μm in thickness, routine staining with hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining of p57Kip2.
Results
Certain histopathological criteria were found to be significant in differentiation between complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and partial hydatidiform mole including villous shape and outline, villous trophoblast hyperplasia, and atypia in extravillous trophoblasts. There were no significant differences in any morphological or immunohistochemical features between cases with or without subsequent development of GTD.
Conclusions
Histopathological diagnosis of molar pregnancy remains problematic especially in early gestation. Their diagnosis should be stated after a constellation of specific histopathological criteria in order not to miss CHM. p57Kip2 immunohistochemistry is of great value in diagnosis of cases that had equivocal morphology by histopathological examination. However, there were no significant features to predict cases that subsequently developed persistent GTD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Basis of Hydatidiform Moles—A Systematic Review
Shadha Nasser Mohammed Bahutair, Rajani Dube, Manjunatha Goud Bellary Kuruba, Rasha Aziz Attia Salama, Mohamed Anas Mohamed Faruk Patni, Subhranshu Sekhar Kar, Rakhee Kar
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(16): 8739. CrossRef - Diagnosis of hydatidiform moles using p57 immunohistochemistry and chromogenic insitu hybridization: A retrospective study
Mojgan Akbarzadeh-Jahromi, Tara Taheri, Fatemeh Sari Aslani, Akbar Safaei, Fatemeh Pouraminaee, Marjan Zare
International Journal of Reproductive BioMedicine (IJRM).2024; 22(9): 727. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical expression of BCL-2 in hydatidiform moles: a tissue microarray study
Muna Al-Jabri, Suaad Al-Badi, Hunaina Al-Kindi, Mohammad Arafa
Pathologica.2023; 115(3): 148. CrossRef - Persistent gestational trophoblastic disease following ectopic molar pregnancy
I.N. Voloshchuk, I.V. Barinova, S.N. Buyanova, S.A. Petrakova, N.A. Shchukina, M.V. Mgeliashvili
Arkhiv patologii.2021; 83(1): 44. CrossRef - P57 and Ki-67 expression in hydropic abortion and molar pregnancy
Sylvia A. Ashamallah, Mie A. Mohamed, Hany O. Habashy
Egyptian Journal of Pathology.2017; 37(2): 393. CrossRef
- Molecular Basis of Hydatidiform Moles—A Systematic Review
- Comparison of Unsatisfactory Samples from Conventional Smear versus Liquid-Based Cytology in Uterine Cervical Cancer Screening Test
- Hoiseon Jeong, Sung Ran Hong, Seoung-Wan Chae, So-Young Jin, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Juhie Lee, Eun Kyung Kim, Sook Tai Ha, Sung Nam Kim, Eun-Jung Park, Jong Jae Jung, Sun Hee Sung, Sung-chul Lim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):314-319. Published online April 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.17
- 14,648 View
- 334 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cervical cytology for uterine cervical cancer screening has transitioned from conventional smear (CS) to liquid-based cytology (LBC), which has many advantages. The aim of this study was to compare the proportion of unsatisfactory specimens from CS versus LBC at multiple institutions including general hospitals and commercial laboratories.
Methods
Each participating institution provided a minimum of 500 Papanicolaou (Pap) test results for analysis. Pap tests were classified according to the participating institution (commercial laboratory or general hospital) and the processing method (CS, ThinPrep, SurePath, or CellPrep). The causes of unsatisfactory results were classified as technical problems, scant cellularity, or complete obscuring factors.
Results
A total of 38,956 Pap test results from eight general hospitals and three commercial laboratories were analyzed. The mean unsatisfactory rate of LBC was significantly lower than that of CS (1.26% and 3.31%, p = .018). In the LBC method, samples from general hospitals had lower unsatisfactory rates than those from commercial laboratories (0.65% vs 2.89%, p = .006). The reasons for unsatisfactory results were heterogeneous in CS. On the other hand, 66.2% of unsatisfactory results in LBC were due to the scant cellularity.
Conclusions
Unsatisfactory rate of cervical cancer screening test results varies according to the institution and the processing method. LBC has a significantly lower unsatisfactory rate than CS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Poor Performance of Applicator Tampon‐Based Self‐Collection for Liquid‐Based Cytology Among Women Attending a Tertiary Hospital in South Africa
Teboho Amelia Tiiti, Varsetile Varster Nkwinika, Tebogo Loraine Mashishi, Kgotlaethata Aaron Molefi, Thembeni Lucia Msibi, Moshawa Khaba, Johannes Bogers, Ramokone Lisbeth Lebelo
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(4): 150. CrossRef - The state of cervical cancer screening in Vanuatu: A retrospective analysis (2015–2020)
Emma R. Allanson, Vera Velanova, Boniface Damutalau, Harriet Obed, Geetha Warrier, Ian H. Frazer, Margaret McAdam
Malignancy Spectrum.2025; 2(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluation of a New Ethanol-Based Preservative Medium for Liquid-Based Cervical Cytology: A Performance Pilot Study for Molecular Applications
Floriana Conticelli, Pasquale Pisapia, Antonino Iaccarino, Maria Salatiello, Alessandro Venuta, Gianluca Gragnano, Luca Vallefuoco, Rosanna Sorrentino, Giuseppe Portella, Nadia Casatta, Carmelo Lupo, Dario Bruzzese, Giancarlo Troncone, Caterina De Luca
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2025; 6(3): 22. CrossRef - Comparison of Conventional Pap Smear and Liquid-Based Cytology in the detection of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical Cancer
Rachita Garg, Krishna Agarwal, Niharika Dhiman, Gauri Gandhi, Meeta Singh
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The current status of liquid-based cytology (LBC) in oral cytology
Kayo Kuyama
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of conventional Pap smear and liquid-based cytology in detecting cervical abnormalities
Đelila Šečerović
Sanamed.2024; 19(2): 227. CrossRef - The possibilities of adapting the re-processing protocol in the practice of the ThinPrep Pap test usage
Artem K. Aksamentov, Nadezhda V. Melnikova, Eugenia V. Moshnina, Nadezhda A. Kolyshkina, Olga N. Kucherova, Vladimir P. Baklaushev
Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 14(1): 108. CrossRef - The Role of p16/Ki67 Dual Staining in Cervical Cancer Screening
Andraž Dovnik, Alenka Repše Fokter
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2023; 45(10): 8476. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Novel Fixative Solution for Liquid-Based Cytology in Diagnostic Cytopathology
Nadia Casatta, Alessia Poli, Sara Bassani, Gianna Veronesi, Giulio Rossi, Clarissa Ferrari, Carmelo Lupo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(24): 3601. CrossRef - Liquid-Based Cytology in the Detection of Premalignant Lesions in Patients with “Atypia in Squamous Cells” in Conventional Cytology
Lia Barrios, Yoled Vizcaíno, Ines Benedetti
Journal of Cytology.2022; 39(4): 148. CrossRef - Meeting the challenges of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination in the UK
Roxanne Westwood, Joanna Lavery
Primary Health Care.2022; 32(01): 22. CrossRef - Method for preservation of DNA stability of liquid-based cytology specimens from a lung adenocarcinoma cell line
Yukiko Matsuo, Kazuya Yamashita, Tsutomu Yoshida, Yukitoshi Satoh
Virchows Archiv.2021; 478(3): 507. CrossRef - High-risk human papillomavirus test in anal smears: can it optimize the screening for anal cancer?
Cintia M.S. Kimura, Caio S.R. Nahas, Edésio V. Silva-Filho, Vinícius L. Ribeiro, Aluisio C. Segurado, Flávio F.P. Alcântara, Ivan Cecconello, Sergio C. Nahas
AIDS.2021; 35(5): 737. CrossRef - Automatic model for cervical cancer screening based on convolutional neural network: a retrospective, multicohort, multicenter study
Xiangyu Tan, Kexin Li, Jiucheng Zhang, Wenzhe Wang, Bian Wu, Jian Wu, Xiaoping Li, Xiaoyuan Huang
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The cytological component of cervical cancer screening: causes of false negative and false positive results, and ways to avoid them
O.A. Burka, N.F. Lygyrda, V.V. Kutsovol, A.V. Svintsitska
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (57): 61. CrossRef - Comparison of liquid-based cytology with conventional smear cytology for EUS-guided FNA of solid pancreatic masses: a prospective randomized noninferiority study
Jung Won Chun, Kyoungbun Lee, Sang Hyub Lee, Haeryoung Kim, Min Su You, Yoon Jung Hwang, Woo Hyun Paik, Ji Kon Ryu, Yong-Tae Kim
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2020; 91(4): 837. CrossRef - Effective reduction in inadequate Pap smears by using a saline-lubricated speculum and two glass slides
Chi-Jui Chen, Mun-Kun Hong, Dah-Ching Ding
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2020; 59(6): 906. CrossRef - Characterizing the Effect of Automated Cell Sorting Solutions on Cytomorphological Changes
Katsuhide Ikeda, Shouichi Sato, Hiroshi Chigira, Yasuo Shibuki, Nobuyoshi Hiraoka
Acta Cytologica.2020; 64(3): 232. CrossRef - Comparison between Conventional Cytology and Liquid-Based Cytology in the Tertiary Brazilian Navy Hospital in Rio de Janeiro
Antônio Carlos Almeida de Oliveira, Miguel Fontes Domingues, Paulo Murilo Neufeld, Marcos Fleury, José Firmino Nogueira Neto
Acta Cytologica.2020; 64(6): 539. CrossRef - Follow‐up with histopathology and HPV testing on LSIL cytology in China’s largest academic woman’s hospital
Xiang Tao, Huina Zhang, Hao Zhang, Jianan Xiao, Juan Li, Xianrong Zhou, Li Wang, Chengquan Zhao
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(4): 258. CrossRef - Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(4): 210. CrossRef - Reducing DNA damage by formaldehyde in liquid‐based cytology preservation solutions to enable the molecular testing of lung cancer specimens
Yukiko Matsuo, Tsutomu Yoshida, Kazuya Yamashita, Yukitoshi Satoh
Cancer Cytopathology.2018; 126(12): 1011. CrossRef - Cervical Cancer Screening Programs in Europe: The Transition Towards HPV Vaccination and Population-Based HPV Testing
Andreas C. Chrysostomou, Dora C. Stylianou, Anastasia Constantinidou, Leondios G. Kostrikis
Viruses.2018; 10(12): 729. CrossRef
- Poor Performance of Applicator Tampon‐Based Self‐Collection for Liquid‐Based Cytology Among Women Attending a Tertiary Hospital in South Africa
- Nodular Fasciitis of External Auditory Canal
- Jihyun Ahn, Sunyoung Kim, Youngsil Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):394-396. Published online June 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.11
- 10,138 View
- 80 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nodular fasciitis is a pseudosarcomatous reactive process composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, and it is most common in the upper extremities. Nodular fasciitis of the external auditory canal is rare. To the best of our knowledge, less than 20 cases have been reported to date. We present a case of nodular fasciitis arising in the cartilaginous part of the external auditory canal. A 19-year-old man complained of an auricular mass with pruritus. Computed tomography showed a 1.7 cm sized soft tissue mass in the right external auditory canal, and total excision was performed. Histologic examination revealed spindle or stellate cells proliferation in a fascicular and storiform pattern. Lymphoid cells and erythrocytes were intermixed with tumor cells. The stroma was myxoid to hyalinized with a few microcysts. The tumor cells were immunoreactive for smooth muscle actin, but not for desmin, caldesmon, CD34, S-100, anaplastic lymphoma kinase, and cytokeratin. The patient has been doing well during the 1 year follow-up period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nodular Fasciitis of the Nose and External Auditory Canal: Two Rare Case Reports
Wanjie Luo, Tianyu Ma, Siqi Wang, Xiaowei Qin, Li Jiang, Yuyao Wang, Tianhong Zhang
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathology Clinic: Nodular Fasciitis Involving the External Ear
Christina M. Yver, Michael A. Husson, Oren Friedman
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2023; 102(5): NP203. CrossRef - Nodular fasciitis of the external auditory canal: Clinical case report and review of the literature
Adrien Philippart, Jean-Christophe Degols, Jacques Vilain
Journal of Otology.2023; 18(4): 240. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Nodular Fasciitis of Ear Region in Children: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Antonio Della Volpe, Paola Festa, Alfonso Maria Varricchio, Carmela Russo, Eugenio Maria Covelli, Delfina Bifano, Piera Piroli, Antonietta De Lucia, Arianna Di Stadio, Franco Ionna
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 1962. CrossRef - A Case of Recurred Nodular Fasciitis in Supraauricular
Region
Dong-Jo Kim, Seong-Wook Choi, Chung-Su Hwang, Hyun-Min Lee
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2022; 33(4): 203. CrossRef
- Nodular Fasciitis of the Nose and External Auditory Canal: Two Rare Case Reports
- Molecular Dimensions of Gastric Cancer: Translational and Clinical Perspectives
- Yoon Young Choi, Sung Hoon Noh, Jae-Ho Cheong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(1):1-9. Published online October 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.09.10
- 15,327 View
- 157 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gastric cancer is a global health burden and has the highest incidence in East Asia. This disease is complex in nature because it arises from multiple interactions of genetic, local environmental, and host factors, resulting in biological heterogeneity. This genetic intricacy converges on molecular characteristics reflecting the pathophysiology, tumor biology, and clinical outcome. Therefore, understanding the molecular characteristics at a genomic level is pivotal to improving the clinical care of patients with gastric cancer. A recent landmark study, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project, showed the molecular landscape of gastric cancer through a comprehensive molecular evaluation of 295 primary gastric cancers. The proposed molecular classification divided gastric cancer into four subtypes: Epstein-Barr virus–positive, microsatellite unstable, genomic stable, and chromosomal instability. This information will be taken into account in future clinical trials and will be translated into clinical therapeutic decisions. To fully realize the clinical benefit, many challenges must be overcome. Rapid growth of high-throughput biology and functional validation of molecular targets will further deepen our knowledge of molecular dimensions of this cancer, allowing for personalized precision medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishment and characterization of a new mouse gastric carcinoma cell line, MCC
Yushen Wang, Xianju Li, Yi Wang, Jun Qin
Cancer Cell International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements and challenges in gastric cancer: epidemiology, biomarkers, and therapeutic strategies
Marina Nishimuni, Laura Carolina Lopez Claro, Maria Ignez Freitas Melro Braghiroli
Surgical and Experimental Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Tissue Biomarkers in Gastric Cancer Treatment: Present and Future
Giulia Airò, Virginia Agnetti, Fabiana Pratticò, Marianna Peroni, Simona Bui, Giovanni Mura, Maria Urbanowicz-Nijaki, Eleonora Lai, Marco Puzzoni, Fabiana Contu, Nerina Denaro, Mario Scartozzi, Cinzia Solinas, Chiara Tommasi
International Journal of Translational Medicine.2024; 4(4): 640. CrossRef - Research Progress of MSI Gastric Cancer Subtypes
成菊 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(07): 6719. CrossRef - OCT4-mediated transcription confers oncogenic advantage for a subset of gastric tumors with poor clinical outcome
Jaishree Pandian, Ponmathi Panneerpandian, Balaji T. Sekar, Karthikeyan Selvarasu, Kumaresan Ganesan
Functional & Integrative Genomics.2022; 22(6): 1345. CrossRef - Secondary Primary Cancer after Primary Gastric Cancer: Literature Review and Big Data Analysis Using the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) Database of Republic of Korea
Jeong Ho Song, Yeonkyoung Lee, Jaesung Heo, Sang-Yong Son, Hoon Hur, Sang-Uk Han
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6165. CrossRef - Microsatellite instability: a review of what the oncologist should know
Kai Li, Haiqing Luo, Lianfang Huang, Hui Luo, Xiao Zhu
Cancer Cell International.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Single Patient Classifier Assay, Microsatellite Instability, and Epstein-Barr Virus Status Predict Clinical Outcomes in Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: Results from CLASSIC Trial
Chul Kyu Roh, Yoon Young Choi, Seohee Choi, Won Jun Seo, Minah Cho, Eunji Jang, Taeil Son, Hyoung-Il Kim, Hyeseon Kim, Woo Jin Hyung, Yong-Min Huh, Sung Hoon Noh, Jae-Ho Cheong
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(2): 132. CrossRef - Ten Thousand Consecutive Gastrectomies for Gastric Cancer: Perspectives of a Master Surgeon
Yoon Young Choi, Minah Cho, In Gyu Kwon, Taeil Son, Hyoung-Il Kim, Seung Ho Choi, Jae-Ho Cheong, Woo Jin Hyung
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(3): 235. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic significance of human leukocyte antigen class I expression in patients with stage II and III gastric cancer
Yujun Park, Jiwon Koh, Yoonjin Kwak, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2019; 68(11): 1779. CrossRef - Phosphoproteomics Enables Molecular Subtyping and Nomination of Kinase Candidates for Individual Patients of Diffuse-Type Gastric Cancer
Mengsha Tong, Chunyu Yu, Jinwen Shi, Wenwen Huang, Sai Ge, Mingwei Liu, Lei Song, Dongdong Zhan, Xia Xia, Wanlin Liu, Jinwen Feng, Wenhao Shi, Jiafu Ji, Jing Gao, Tieliu Shi, Weimin Zhu, Chen Ding, Yi Wang, Fuchu He, Lin Shen, Tingting Li, Jun Qin
iScience.2019; 22: 44. CrossRef - Trastuzumab Specific Epitope Evaluation as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Patients
Jiwon Koh, Soo Kyung Nam, Youn Woo Lee, Jin Won Kim, Keun-Wook Lee, Chan-Young Ock, Do-Youn Oh, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Hyung-Ho Kim, Keon-Wook Kang, Woo Ho Kim, Ho-Young Lee, Hye Seung Lee
Biomolecules.2019; 9(12): 782. CrossRef - Targeted drug delivery of capecitabine to mice xenograft gastric cancer by PAMAM dendrimer nanocarrier
Sharareh Jafari, Fatemeh Nabavizadeh, Jalal Vahedian, Mehdi Shafie Ardestani, Hedayat Samandari, Ali Zare Mehrjerdi
african journal of gastroenterology and hepatology.2019; 2(1): 28. CrossRef - New therapeutic options opened by the molecular classification of gastric cancer
Mihaela Chivu-Economescu, Lilia Matei, Laura G Necula, Denisa L Dragu, Coralia Bleotu, Carmen C Diaconu
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 24(18): 1942. CrossRef - Proposed Molecular and miRNA Classification of Gastric Cancer
Lara Alessandrini, Melissa Manchi, Valli De Re, Riccardo Dolcetti, Vincenzo Canzonieri
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(6): 1683. CrossRef - High serum MMP-14 predicts worse survival in gastric cancer
Aaro Kasurinen, Taina Tervahartiala, Alli Laitinen, Arto Kokkola, Timo Sorsa, Camilla Böckelman, Caj Haglund, Dajun Deng
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(12): e0208800. CrossRef - miR-30 functions as an oncomiR in gastric cancer cells through regulation of P53-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
Jianjun Wang, Yang Jiao, Lunmeng Cui, Lili Jiang
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry.2017; 81(1): 119. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic implication of meticulous pathologic examination of regional lymph nodes in gastric cancer patients
Jiwon Koh, Hee Eun Lee, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Ju-Seog Lee
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(3): e0174814. CrossRef - Perioperative chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer – what is the evidence?
Erling A Bringeland, Hans H Wasmuth, Jon E Grønbech
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 52(6-7): 647. CrossRef - Molecular classifications of gastric cancers: Novel insights and possible future applications
Silvio Ken Garattini, Debora Basile, Monica Cattaneo, Valentina Fanotto, Elena Ongaro, Marta Bonotto, Francesca V Negri, Rosa Berenato, Paola Ermacora, Giovanni Gerardo Cardellino, Mariella Giovannoni, Nicoletta Pella, Mario Scartozzi, Lorenzo Antonuzzo,
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2017; 9(5): 194. CrossRef - GRAM domain-containing protein 1B (GRAMD1B), a novel component of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, functions in gastric carcinogenesis
Puja Khanna, Pei Jou Chua, Belinda Shu Ee Wong, Changhong Yin, Aye Aye Thike, Wei Keat Wan, Puay Hoon Tan, Gyeong Hun Baeg
Oncotarget.2017; 8(70): 115370. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic implications of immune classification by PD-L1 expression and CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in stage II and III gastric cancer patients
Jiwon Koh, Chan-Young Ock, Jin Won Kim, Soo Kyung Nam, Yoonjin Kwak, Sumi Yun, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Do Joong Park, Hyung-Ho Kim, Woo Ho Kim, Hye Seung Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(16): 26356. CrossRef
- Establishment and characterization of a new mouse gastric carcinoma cell line, MCC
- Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma Arising from Adenofibroma in a Patient with Endometriosis of the Ovary
- Inju Cho, Sung-Chul Lim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):155-159. Published online October 26, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.08.07
- 11,507 View
- 134 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ovarian clear cell adenocarcinomas (CCACs) are frequently associated with endometriosis and, less often with clear cell adenofibromas (CCAFs). We encountered a case of ovarian CCAC arising from benign and borderline adenofibromas of the clear cell and endometrioid types with endometriosis in a 53-year-old woman. Regions of the adenofibromas showed transformation to CCAC and regions of the endometriosis showed atypical endometriotic cysts. This case demonstrates that CCAC can arise from CCAF or endometriosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pure non-gestational ovarian choriocarcinoma in a postmenopausal woman coexisting with a clear cell adenofibroma and endometriosis foci: A case report and review of the literature
Ainhoa Ordoñez Arrillaga, Miguel Ángel Resano Abarzuza, Marta Rezola Bajineta, Begoña Aguiar Losada, Yessica P. Rodríguez-Velandia, Manuel Moreno Valladares, Iraide Bernal Simón, Ibon Jaunarena Marín, Irune Ruiz Díaz
Revista Española de Patología.2026; 59(1): 100856. CrossRef - Ovarian Clear Cell Adenofibroma of Low Malignant Potential Developing Into Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
Zhiwei Yin, Stephen Peters, Ravi Chokshi, Debra Heller
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2018; 26(6): 578. CrossRef - Origins based clinical and molecular complexities of epithelial ovarian cancer
Thingreila Muinao, Mintu Pal, Hari Prasanna Deka Boruah
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2018; 118: 1326. CrossRef
- Pure non-gestational ovarian choriocarcinoma in a postmenopausal woman coexisting with a clear cell adenofibroma and endometriosis foci: A case report and review of the literature
- Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix
- Juhyeon Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Jungsuk An
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):396-402. Published online August 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.08
- 11,244 View
- 97 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) and adenoid basal carcinoma (ABC) are rare in the uterine cervix. ACC is more aggressive than ABC, thus accurate differential diagnosis is important. In this study, we identified cytologic features useful in distinguishing these two tumors for diagnosis. Methods: Three cases of ACC and five cases of ABC were selected for this study. Cervicovaginal smear slides were reviewed retrospectively, and the area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis of nuclei were measured using an image analyzer. Results: ACC displayed three-dimensional clusters with a small acini pattern. ABC displayed peripheral palisading without an acini pattern. The nuclei of ACC were more irregular and angulated than those of ABC, and the former showed a coarsely granular chromatin pattern. The nucleic area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis were 18.556±8.665 µm2, 23.320±11.412 µm, 5.664±1.537 µm, and 4.127±1.107 µm in ACC and 11.017±4.440 µm2, 15.920±5.664 µm, 4.612±1.025 µm, and 3.088±0.762 µm in the cases of ABC. All measured values showed statistically significant difference (p < .001). Conclusions: Although the nuclei of both of these tumor types were oval shaped, inferred from the ratio of minor axis to major axis (0.728 in ACC and 0.669 in ABC), the area of nuclei was approximately 1.7 times larger in ACC than in ABC. Distinguishing nucleic features, including area, morphology, and chromatin pattern, may be helpful in making a correct diagnosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix
Anas Mohamed, Tesfalem Korga, Ahlam Ali, Javier Laurini
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2025; : 101873. CrossRef - Adenoid Basal Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report
Tatsuya Kanuma, Keiko Kigure, Tosio Nishimura, Yuji Ibuki, Shigeru Tsuchida, Harumi Kamiyama, Misa Iijima, Kazuto Nakamura
The KITAKANTO Medical Journal.2016; 66(1): 11. CrossRef
- Adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix
- The Limitations of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma: A Brief Case Report
- Heae Surng Park, Sun Och Yoon, Beom Jin Lim, Joo Hee Kim, Soon Won Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):405-408. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.405
- 8,487 View
- 63 Download
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus Type 39 in a Seborrheic Inclusion Cyst of the Buttock
- Dae Hyun Song, Sang-Guk Lee, Dong Chul Kim, Jeong Hee Lee, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jong Sil Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):398-400. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.398
- 8,233 View
- 49 Download
- Papillary Cystadenoma of the Fallopian Tube Not Associated with von Hippel-Lindau Disease: A Case Report
- Jae Yeon Seok, Myunghee Kang, Jungsuk An, Hyunchul Kim, Kwang-Beom Lee, Hyun Yee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):382-386. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.382
- 8,892 View
- 70 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Retrospective Study on the Occurrence and Prevalence of Ovarian Masses in the Patients of Rajkot District, Gujarat
Kirtan M Vyas, Avni P Patel, Ashita K Vyas, Hardik Gohel
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(3): 375. CrossRef - Clear Cell Papillary Cystadenoma of the Ovary Masquerading as Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Aarti E. Sharma, Farid Saei Hamedani, Julieta E. Barroeta, Peter Pytel, Jennifer A. Bennett, Ricardo R. Lastra
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2021; 40(3): 290. CrossRef - Mesonephric (Wolffian) Pseudoendometrioid Carcinoma of the Broad Ligament, Arising From a Papillary Cystadenoma
Philippe Moerman, Frederic Amant, Ignace Vergote
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 24(7): 635. CrossRef
- A Retrospective Study on the Occurrence and Prevalence of Ovarian Masses in the Patients of Rajkot District, Gujarat
- Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hyun Ju Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):361-365. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.361
- 10,333 View
- 64 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) of the uterine cervix is a rare malignancy, and 21 cases have been reported the literature from every language (including our case). Herein, we describe a 17-yearold female patient who presented with active vaginal bleeding. Pelvic examination revealed a 1.6 ×1.0×0.5-cm-sized soft mass protruding from the uterine cervix. The final pathological diagnosis was ASPS of the uterine cervix. Immunohistochemically, tumor cells were strongly nuclear positive for transcription factor E3. The patient remained disease free for 24 months without adjuvant therapy. The prognosis of ASPS in the cervix is considerably better than that of ASPS in soft tissues due to early clinical detection, small size, and resectability. ASPS should be considered in the differential diagnosis of an unusual epithelioid neoplasm showing organoid appearance with mild cytologic atypia and no/rare mitotic figures, particularly in young women. Pathologists should be aware of those unusual locations where ASPS may originate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of Alveolar Soft-Part Sarcoma in the Uterine cervix
Mei Du, Yanli Li, Xiaorong Fan, Han Gao, Jie Shi, Shiyu Cheng, Tingzhu Meng
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Uterine Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma in a Postmenopausal Woman: Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of a Rare Case
Anjali Gupta, Parikshaa Gupta, Amarjot Kaur, Snigdha Kumari, Gupta Nalini, Shalini Gainder
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 32(6): 1165. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma in the Female Genital Tract: Case Series with Literature Review and SEER Database Analysis
Xingtao Long, Qingming Jiang, Rengui Li, Dong Wang, Dongling Zou
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 17. CrossRef - Alveolar soft part sarcoma: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of 26 cases emphasizing risk factors and prognosis
Yi Zhang, Yuchen Huang, Yanzi Qin, Ningning Yang, Panpan Yang, Nan Li, Zhenzhong Feng
Diagnostic Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epithelioid and clear‐cell variant of Kaposi sarcoma: A rare histopathologic subtype
Kaitlyn M. Yim, Tom Liang, Esteban Gnass, Brittney DeClerck
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2022; 49(4): 381. CrossRef - A Case of TFE3-positive Non-neoplastic Pseudodecidualized Endometrium Presenting as a Cervical Mass
Serenella Serinelli, Dana Hariri, Gustavo de la Roza, Daniel J. Zaccarini
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(6): e50. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Uterus: Clinicopathological and Molecular Characteristics
Yurimi Lee, Kiyong Na, Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(5): 1102. CrossRef - Alveolar soft part sarcoma in childhood and adolescence: Report of three cases and review of literature
Yudi Zhang, Ying Wang, Hao Wang, Chuan Wen, Xiaochuan Wu
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the Histogenesis and Diagnostic Strategy Using Immunoassay and RT-PCR in Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma
Xinxin Ju, Kunming Sun, Ruixue Liu, Shugang Li, Gulinaer Abulajiang, Hong Zou, Jiaojiao Lan, Yan Ren, Jinfang Jiang, Weihua Liang, Lijuan Pang, Feng Li
Pathology & Oncology Research.2018; 24(3): 593. CrossRef - Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma of the Female Genital Tract
J. Kenneth Schoolmeester, Joseph Carlson, Gary L. Keeney, Karen J. Fritchie, Esther Oliva, Robert H. Young, Marisa R. Nucci
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2017; 41(5): 622. CrossRef - Recurrent alveolar soft part sarcoma of the uterine cervix
Aeli Ryu, Seong Taek Mun, Hyun Ju Lee, Nan-Seol Kim
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2017; 37(8): 1099. CrossRef
- A rare case of Alveolar Soft-Part Sarcoma in the Uterine cervix
- Mdm2 and p53 Expression in Radiation-Induced Sarcomas of the Head and Neck: Comparison with De Novo Sarcomas
- Min Jeong Song, Joon Seon Song, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim, Sung Bae Kim, Sang-wook Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):346-350. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.346
- 13,104 View
- 55 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background: The pathogenesis of radiation-induced sarcomas (RISs) is not well known. In RIS, TP53 mutations are frequent, but little is known about Mdm2-p53 interaction, which is a recent therapeutic target of sarcomas. Methods: We studied the immunohistochemical expression of Mdm2 and p53 of 8 RISs. The intervals between radiation therapy and diagnosis of secondary sarcomas ranged from 3 to 17 years. Results: Mdm2 expression was more common in de novo sarcomas than RISs (75% vs 37.5%), and p53 expression was more common in RISs than in de novo cases (75% vs 37.5%). While half of the RISs were Mdm2(–)/p53(+), none of de novo cases showed such combination; while half of de novo sarcomas were Mdm2(+)/p53(–), which are a candidate group of Mdm2 inhibitors, only 1 RIS showed such a combination. Variable immunoprofiles observed in both groups did not correlate with tumor types, except that all of 2 myxofibrosarcomas were Mdm2(+)/p53(+). Conclusions: In conclusion, we speculated that both radiation- induced and de novo sarcomagenesis are not due to a unique genetic mechanism. Mdm2- expression without p53 overexpression in 1 case of RIS decreases the future possibility of applying Mdm2 inhibitors on a subset of these difficult tumors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiation-induced osteosarcoma in the head and neck region: Case report and literature review
Iara Vieira Ferreira, Marcelo Elias Schempf Cattan, Carlos Takahiro Chone, Arthur Antolini, Erika Said Abu Egal, Albina Altemani, Fernanda Viviane Mariano
Oral Oncology.2025; 162: 107216. CrossRef - Radiation-Induced Sarcomas of the Head and Neck: A Systematic Review
Andrés Coca-Pelaz, Antti A. Mäkitie, Primož Strojan, June Corry, Avraham Eisbruch, Jonathan J. Beitler, Sandra Nuyts, Robert Smee, Johannes A. Langendijk, William M. Mendenhall, Cesare Piazza, Alessandra Rinaldo, Alfio Ferlito
Advances in Therapy.2021; 38(1): 90. CrossRef - Genomic Characterization of Radiation-Induced Intracranial Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma
Christopher S. Hong, Edwin Partovi, James Clune, Anita Huttner, Henry S. Park, Sacit Bulent Omay, Balraj Mittal
Case Reports in Genetics.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Radiation-Induced Sarcoma of the Head and Neck: A Review of the Literature
Lorenzo Giannini, Fabiola Incandela, Marco Fiore, Alessandro Gronchi, Silvia Stacchiotti, Claudia Sangalli, Cesare Piazza
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Radiation-induced osteosarcoma in the head and neck region: Case report and literature review
- Guideline Recommendations for Testing of
ALK Gene Rearrangement in Lung Cancer: A Proposal of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group - Hyojin Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Lucia Kim, Tae-Jung Kim, Kun Young Kwon, Geon Kook Lee, Jin-Haeng Chung
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):1-9. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.1
- 16,534 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rearrangement of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (
ALK ) gene is the best predictor of response to crizotinib, an ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor. However, the prevalence of theALK fusion is low, so accurate patient identification is crucial for successful treatment using ALK inhibitors. Furthermore, most patients with lung cancer present with advanced-stage disease at the time of diagnosis, so it is important for pathologists to detectALK -rearranged patients while effectively maximizing small biopsy or cytology specimens. In this review, we propose a guideline recommendation for ALK testing approved by the Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Characteristics of Radon Associated Lung Cancer Highlights MET Alterations
Gabriele Gamerith, Marcel Kloppenburg, Finn Mildner, Arno Amann, Sabine Merkelbach-Bruse, Carina Heydt, Janna Siemanowski, Reinhard Buettner, Michael Fiegl, Claudia Manzl, Georg Pall
Cancers.2022; 14(20): 5113. CrossRef -
ALK Translocation in ALK-Positive Mesenchymal Tumors: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Insights
Minsun Jung, Kyung Chul Moon, Jeongmo Bae, Tae Min Kim, Miso Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Cheol Lee
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2022; 146(12): 1460. CrossRef - Molecular biomarker testing for non–small cell lung cancer: consensus statement of the Korean Cardiopulmonary Pathology Study Group
Sunhee Chang, Hyo Sup Shim, Tae Jung Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Wan Seop Kim, Dong Hoon Shin, Lucia Kim, Heae Surng Park, Geon Kook Lee, Chang Hun Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(3): 181. CrossRef - Testing for EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Considerations for Countries in Emerging Markets
Mercedes L Dalurzo, Alejandro Avilés-Salas, Fernando Augusto Soares, Yingyong Hou, Yuan Li, Anna Stroganova, Büge Öz, Arif Abdillah, Hui Wan, Yoon-La Choi
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4671. CrossRef - Molecular testing for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Malaysia: Consensus statement from the College of Pathologists, Academy of Medicine Malaysia, the Malaysian Thoracic Society, and the Malaysian Oncological Society
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Phaik Leng Cheah, Soon Hin How, Chong Kin Liam, Muhammad Azrif Ahmad Annuar, Norhayati Omar, Noriah Othman, Nurhayati Mohd Marzuki, Yong Kek Pang, Ros Suzanna Ahmad Bustamam, Lye Mun Tho
Lung Cancer.2019; 136: 65. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2018; 13(3): 323. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H. Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benj
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2018; 20(2): 129. CrossRef - Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the
Neal I. Lindeman, Philip T. Cagle, Dara L. Aisner, Maria E. Arcila, Mary Beth Beasley, Eric H Bernicker, Carol Colasacco, Sanja Dacic, Fred R. Hirsch, Keith Kerr, David J. Kwiatkowski, Marc Ladanyi, Jan A. Nowak, Lynette Sholl, Robyn Temple-Smolkin, Benja
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2018; 142(3): 321. CrossRef - 5′/ 3′ imbalance strategy to detect ALK fusion genes in circulating tumor RNA from patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Yongqing Tong, Zhijun Zhao, Bei Liu, Anyu Bao, Hongyun Zheng, Jian Gu, Mary McGrath, Ying Xia, Bihua Tan, Chunhua Song, Yan Li
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular testing and treatment patterns for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: PIvOTAL observational study
Dae Ho Lee, Ming-Sound Tsao, Karl-Otto Kambartel, Hiroshi Isobe, Ming-Shyan Huang, Carlos H. Barrios, Adnan Khattak, Filippo de Marinis, Smita Kothari, Ashwini Arunachalam, Xiting Cao, Thomas Burke, Amparo Valladares, Javier de Castro, Aamir Ahmad
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0202865. CrossRef - Microfluidics-based immunofluorescence for fast staining of ALK in lung adenocarcinoma
Saška Brajkovic, Benjamin Pelz, Maria-Giuseppina Procopio, Anne-Laure Leblond, Grégoire Repond, Ariane Schaub-Clerigué, Diego G Dupouy, Alex Soltermann
Diagnostic Pathology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Expanded Circulating Tumor Cells from a Patient with ALK- Positive Lung Cancer Present with EML4-ALK Rearrangement Along with Resistance Mutation and Enable Drug Sensitivity Testing: A Case Study
Zhuo Zhang, Hiroe Shiratsuchi, Nallasivam Palanisamy, Sunitha Nagrath, Nithya Ramnath
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2017; 12(2): 397. CrossRef - Molecular Testing of Lung Cancers
Hyo Sup Shim, Yoon-La Choi, Lucia Kim, Sunhee Chang, Wan-Seop Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Tae-Jung Kim, Seung Yeon Ha, Jin-Haeng Chung, Se Jin Jang, Geon Kook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(3): 242. CrossRef - Novel ALK fusion partners in lung cancer
Aglaya G. Iyevleva, Grigory A. Raskin, Vladislav I. Tiurin, Anna P. Sokolenko, Natalia V. Mitiushkina, Svetlana N. Aleksakhina, Aigul R. Garifullina, Tatiana N. Strelkova, Valery O. Merkulov, Alexandr O. Ivantsov, Ekatherina Sh. Kuligina, Kazimir M. Pozha
Cancer Letters.2015; 362(1): 116. CrossRef - Strategic management of transthoracic needle aspirates for histological subtyping and EGFR testing in patients with peripheral lung cancer: An institutional experience
Choonhee Son, Eun‐Ju Kang, Mee Sook Roh
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2015; 43(7): 532. CrossRef - Current and future molecular diagnostics in non-small-cell lung cancer
Chun Man Li, Wing Ying Chu, Di Lun Wong, Hin Fung Tsang, Nancy Bo Yin Tsui, Charles Ming Lok Chan, Vivian Wei Wen Xue, Parco Ming Fai Siu, Benjamin Yat Ming Yung, Lawrence Wing Chi Chan, Sze Chuen Cesar Wong
Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics.2015; 15(8): 1061. CrossRef - Role of biopsy sampling for diagnosis of early and progressed hepatocellular carcinoma
Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology.2014; 28(5): 813. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions
Mee Sook Roh
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2014; 77(2): 49. CrossRef - Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangements in lung cancer with nodular ground-glass opacity
Sung-Jun Ko, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park, Young-Jae Cho, Ho Il Yoon, Jin-Haeng Chung, Tae Jung Kim, Kyung Won Lee, Kwhanmien Kim, Sanghoon Jheon, Hyojin Kim, Jae Ho Lee, Choon-Taek Lee
BMC Cancer.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular Characteristics of Radon Associated Lung Cancer Highlights MET Alterations
- Diagnostic Utility of a Clonality Test for Lymphoproliferative Diseases in Koreans Using the BIOMED-2 PCR Assay
- Young Kim, Yoo Duk Choi, Chan Choi, Jong-Hee Nam
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):458-465. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.458
- 12,613 View
- 102 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background A clonality test for immunoglobulin (IG) and T cell receptor (TCR) is a useful adjunctive method for the diagnosis of lymphoproliferative diseases (LPDs). Recently, the BIOMED-2 multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay has been established as a standard method for assessing the clonality of LPDs. We tested clonality in LPDs in Koreans using the BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR and compared the results with those obtained in European, Taiwanese, and Thai participants. We also evaluated the usefulness of the test as an ancillary method for diagnosing LPDs.
Methods Two hundred and nineteen specimens embedded in paraffin, including 78 B cell lymphomas, 80 T cell lymphomas and 61 cases of reactive lymphadenitis, were used for the clonality test.
Results Mature B cell malignancies showed 95.7% clonality for IG, 2.9% co-existing clonality, and 4.3% polyclonality. Mature T cell malignancies exhibited 83.8% clonality for TCR, 8.1% co-existing clonality, and 16.2% polyclonality. Reactive lymphadenitis showed 93.4% polyclonality for IG and TCR. The majority of our results were similar to those obtained in Europeans. However, the clonality for IGK of B cell malignancies and TCRG of T cell malignancies was lower in Koreans than Europeans.
Conclusions The BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR assay was a useful adjunctive method for diagnosing LPDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infectious mononucleosis complicated by transitory Epstein-Barr virus infection of T and natural killer cells
Yanlin Zhang, JianLan Xie, Yuanyuan Zheng, XiaoGe Zhou
Journal of Hematopathology.2024; 17(3): 129. CrossRef - Experiencia en el uso de protocolos Biomed-2 para el estudio de reordenamientos de TCR e inmunoglobulinas en proliferaciones linfoides en el Instituto Nacional de Cancerología, Colombia
Nicolás Villamizar-Rivera, Natalia Olaya
Biomédica.2022; 42(Sp. 1): 64. CrossRef - Enhancing diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma using non-recombined T-cell receptor sequences
Yi-Lin Chen, Chung-Liang Ho, Chen-Yan Hung, Wan-Li Chen, Chen Chang, Yi-Hsin Hou, Jian-Rong Chen, Pin-Jun Chen, Nan-Haw Chow, Wenya Huang, Ya-Ting Hsu, Tsai-Yun Chen, Tsunglin Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The utility and limitations of B- and T-cell gene rearrangement studies in evaluating lymphoproliferative disorders
Hadrian Mendoza, Christopher A. Tormey, Henry M. Rinder, John G. Howe, Alexa J. Siddon
Pathology.2021; 53(2): 157. CrossRef - Combined detection of lymphocyte clonality and MALT1 translocations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosing pulmonary lymphomas
Takashi Kido, Hiroshi Ishimoto, Hiroshi Ishii, Kanako Hara, Mutsumi Ozasa, Hiroki Kawabata, Toshinori Kawanami, Yu Suzuki, Hiroki Yoshikawa, Atsuko Hara, Noriho Sakamoto, Nobuhiro Matsumoto, Chiharu Yoshii, Junya Fukuoka, Masaki Fujita, Masamitsu Nakazato
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiation of lymphocytic-plasmacytic enteropathy and small cell lymphoma in cats using histology-guided mass spectrometry
Sina Marsilio, Shelley J. Newman, James Scot Estep, Paula R. Giaretta, Jonathan A. Lidbury, Emma Warry, Andi Flory, Paul S. Morley, Katy Smoot, Erin H. Seeley, Matthew J. Powell, Jan S. Suchodolski, Jörg M. Steiner
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2020; 34(2): 669. CrossRef - T-Cell Receptor Rearrangements Determined Using Fragment Analysis in Patients With T-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Hyerim Kim, In-Suk Kim, Chulhun L. Chang, Sun-Young Kong, Young Tak Lim, Seom Gim Kong, Eun Hae Cho, Eun-Yup Lee, Ho-Jin Shin, Hyeon Jin Park, Hyeon-Seok Eom, Hyewon Lee
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2019; 39(2): 125. CrossRef - Monitoring immunoglobulin heavy chain and T‑cell receptor gene rearrangement in cfDNA as minimal residual disease detection for patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Ling Zhong, Jiao Chen, Xiaobing Huang, Yanxing Li, Tao Jiang
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular pathology diagnosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma using BIOMED-2 clonal gene rearrangements
Saeid Ghorbian
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2017; 29: 28. CrossRef - Improved clonality detection in B‐cell lymphoma using a semi‐nested modification of the BIOMED‐2 PCR assay for IGH rearrangement: A paraffin‐embedded tissue study
Yuma Sakamoto, Ayako Masaki, Satsuki Aoyama, Shusen Han, Kosuke Saida, Kana Fujii, Hisashi Takino, Takayuki Murase, Shinsuke Iida, Hiroshi Inagaki
Pathology International.2017; 67(9): 453. CrossRef - The prognostic significance of monoclonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in conjunction with histologic B‐cell aggregates in the bone marrow of patients with diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma
Yoon Ah Cho, Woo Ick Yang, Jae‐Woo Song, Yoo Hong Min, Sun Och Yoon
Cancer Medicine.2016; 5(6): 1066. CrossRef - Nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphomas are more frequently T rather than NK lineage based on T-cell receptor gene, RNA, and protein studies: lineage does not predict clinical behavior
Mineui Hong, Taehee Lee, So Young Kang, Suk-Jin Kim, Wonseog Kim, Young-Hyeh Ko
Modern Pathology.2016; 29(5): 430. CrossRef - Long-term Tumor-free Survival With Untreated Primary Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma of the Tonsil
Xiaojing Zhang, Yuanyuan Zheng, Jianlan Xie, Jun Zhu, Yuqin Song, Xiaojing Teng, Wei Liu, Yi Ding, Yuhua Huang, Xiaoge Zhou
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(11): 1493. CrossRef - Evaluation diagnostic usefulness of immunoglobulin light chains (Igκ, Igλ) and incomplete IGH D-J clonal gene rearrangements in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas using BIOMED-2 protocol
S. Ghorbian, I. Jahanzad, G. R. Javadi, E. Sakhinia
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2014; 16(11): 1006. CrossRef
- Infectious mononucleosis complicated by transitory Epstein-Barr virus infection of T and natural killer cells
- Histologic Variations and Immunohistochemical Features of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Han Nam, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):426-432. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.426
- 13,280 View
- 90 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Due to advancements in treatment of metastatic and advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), it has become increasingly important to diagnose metastatic RCC and the specific subtype. In this study, we investigated the diverse histologic features of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cases in comparison with corresponding primary lesions.
Methods We identified 119 metastatic CCRCC cases from 81 corresponding primary lesions diagnosed between 1995 and 2010 and evaluated the diverse histologic and immunohistochemical features of these lesions.
Results A total of 44 primary lesions (54.3%) had a non-clear cell component in addition to a typical clear cell component. Of the 119 metastatic lesions, 63 lesions (52.9%) contained a non-clear cell component, and 29 metastatic lesions were composed of a non-clear cell component only. Rhabdoid features were the most frequent non-clear cell histology among the metastatic lesions. Metastatic CCRCCs mainly showed positive CD10 and epithelial membrane antigen staining and negative cytokeratin 7 staining.
Conclusions Metastatic CCRCC commonly showed a variety of histologic features. If there is a difficulty to diagnose metastatic CCRCC due to a variety of histologic features or small biopsy specimen, histologic review of the primary lesion and immunohistochemical analysis can help determine the correct diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
Adebowale J. Adeniran, Brian Shuch, Peter A. Humphrey
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(7): e65. CrossRef - Emerging Antibody-Drug Conjugate Therapies and Targets for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Harrison C. Gottlich, Reza Nabavizadeh, Mihai Dumbrava, Rodrigo Rodrigues Pessoa, Ahmed M. Mahmoud, Ishita Garg, Jacob Orme, Brian A. Costello, John Cheville, Fabrice Lucien
Kidney Cancer.2023; 7(1): 161. CrossRef - Painful, bleeding fingertip papule
Jane Gay, Sarah Simpson, Patrick Rush, Alex Holliday
JAAD Case Reports.2022; 21: 130. CrossRef - Development and initial clinical testing of a multiplexed circulating tumor cell assay in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Rory M. Bade, Jennifer L. Schehr, Hamid Emamekhoo, Benjamin K. Gibbs, Tamara S. Rodems, Matthew C. Mannino, Joshua A. Desotelle, Erika Heninger, Charlotte N. Stahlfeld, Jamie M. Sperger, Anupama Singh, Serena K. Wolfe, David J. Niles, Waddah Arafat, John
Molecular Oncology.2021; 15(9): 2330. CrossRef - Laparoscopic cytoreductive nephrectomy and adrenalectomy for metachronous RCC metastases—Case report
Bogdan Petrut, Cristina Eliza Bujoreanu, Vasile Vlad Hardo, Adrian Barbos, Bogdan Fetica
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 74(C): 268. CrossRef - Does CARMENA mark the end of cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Steven L. Chang, Toni K. Choueiri, Lauren C. Harshman
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2019; 37(8): 525. CrossRef - Metastatic TFE3-overexpressing renal clear cell carcinoma with dense granules: a histological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study
Shoujun Chen, Elba A. Turbat-Herrera, Guillermo A. Herrera, Meghna Chadha, Rodney E. Shackelford, Eric X. Wei
Ultrastructural Pathology.2018; 42(4): 369. CrossRef - The Clinical Activity of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Metastatic Non–Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Rana R. McKay, Dominick Bossé, Wanling Xie, Stephanie A.M. Wankowicz, Abdallah Flaifel, Raphael Brandao, Aly-Khan A. Lalani, Dylan J. Martini, Xiao X. Wei, David A. Braun, Eliezer Van Allen, Daniel Castellano, Guillermo De Velasco, J. Connor Wells, Daniel
Cancer Immunology Research.2018; 6(7): 758. CrossRef - Implication of PHF2 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Bohyun Kim, Boram Song, Kyung Chul Moon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 359. CrossRef - Pulmonary metastasectomy from renal cell carcinoma including 3 cases with sarcomatoid component
Tsuyoshi Ueno, Motohiro Yamashita, Shigeki Sawada, Ryujiro Sugimoto, Noriko Nishijima, Yoshifumi Sugawara, Iku Ninomiya
General Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2016; 64(3): 149. CrossRef - Are primary renal cell carcinoma and metastases of renal cell carcinoma the same cancer?
Aleksandra Semeniuk-Wojtaś, Rafał Stec, Cezary Szczylik
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2016; 34(5): 215. CrossRef - Concordance of Pathologic Features Between Metastatic Sites and the Primary Tumor in Surgically Resected Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Sarah P. Psutka, John C. Cheville, Brian A. Costello, Suzanne B. Stewart-Merrill, Christine M. Lohse, Bradley C. Leibovich, Stephen A. Boorjian, R. Houston Thompson
Urology.2016; 96: 106. CrossRef - The Correlation of Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Lesions: A Tissue Microarray Study
Sung Han Kim, Weon Seo Park, Eun Young Park, Boram Park, Jungnam Joo, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
The Korean Journal of Urological Oncology.2016; 14(3): 152. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up and clinical course of a rare case of von Hippel-Lindau disease: A case report and review of the literature
YU ZOU, JINGJING XU, MINMING ZHANG
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(5): 3273. CrossRef - Genetic alterations in renal cell carcinoma with rhabdoid differentiation
Carmen M. Perrino, Vishwanathan Hucthagowder, Michael Evenson, Shashikant Kulkarni, Peter A. Humphrey
Human Pathology.2015; 46(1): 9. CrossRef - High expression of APRIL correlates with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cheol Lee, Jeong-Whan Park, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
Pathology - Research and Practice.2015; 211(11): 824. CrossRef - A Case of Cutaneous Metastasis from a Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with an Eosinophilic Cell Component to the Submandibular Region
Yusuke Amano, Sumie Ohni, Toshiyuki Ishige, Taku Homma, Tsutomu Yamada, Nobuyuki Nishimori, Norimichi Nemoto
Journal of Nihon University Medical Association.2015; 74(2): 73. CrossRef
- Sarcomatoid and Rhabdoid Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Clinicopathological Analysis of Hepatocellular Adenoma According to New Bordeaux Classification: Report of Eight Korean Cases
- Hyunchul Kim, Ja-June Jang, Dong-Sik Kim, Beom Woo Yeom, Nam Hee Won
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(5):411-417. Published online October 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.5.411
- 10,142 View
- 49 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Hepatocellular adenoma (HCA) is a rare benign tumor of the liver. A subtype classification of HCA (hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α [HNF1α]-mutated, β-catenin-mutated HCA, inflammatory HCA, and unclassified HCA) has recently been established based on a single institutional review of a HCA series by the Bordeaux group.
Methods We used histologic and immunohistochemical parameters to classify and evaluate eight cases from our institution. We evaluated the new classification method and analyzed correlations between our results and those of other reports.
Results Seven of our eight cases showed histologic and immunohistochemical results consistent with previous reports. However, one case showed overlapping histologic features, as previously described by the Bordeaux group. Four cases showed glutamine synthetase immunohistochemical staining inconsistent with their classification, indicating that glutamine synthetase staining may not be diagnostic for β-catenin-mutated HCA. HNF1α-mutated HCA may be indicated by the absence of liver fatty acid binding protein expression. Detection of amyloid A may indicate inflammatory HCA. HCA with no mutation in the HNF1α or β-catenin genes and no inflammatory protein expression is categorized as unclassified HCA.
Conclusions Although the new classification is now generally accepted, validation through follow-up studies is necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perinatal Management of Hepatic Adenomas
Megan A. Nocita, Carla W. Brady, Jeffrey A. Kuller, Luke A. Gatta
Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey.2024; 79(12): 735. CrossRef - Relevance of morphological features for hepatocellular adenoma classification in pathology practice
Carla Henriques Agostini, Osmar Damasceno Ribeiro, Arlete Fernandes, Adriana Caroli-Bottino, Vera Lucia Pannain
Surgical and Experimental Pathology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The molecular functions of hepatocyte nuclear factors – In and beyond the liver
Hwee Hui Lau, Natasha Hui Jin Ng, Larry Sai Weng Loo, Joanita Binte Jasmen, Adrian Kee Keong Teo
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1033. CrossRef - Hepatocellular adenoma: Classification, variants and clinical relevance
Paulette Bioulac-Sage, Christine Sempoux, Charles Balabaud
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2017; 34(2): 112. CrossRef - A Limited Immunohistochemical Panel Can Subtype Hepatocellular Adenomas for Routine Practice
Brent K. Larson, Maha Guindi
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2017; 147(6): 557. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Neoplasms Arising in Association With Androgen Use
Sounak Gupta, Bita V. Naini, Richard Munoz, Rondell P. Graham, Benjamin R. Kipp, Michael S. Torbenson, Taofic Mounajjed
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(4): 454. CrossRef - Pigmented hepatocellular adenomas have a high risk of atypia and malignancy
Taofic Mounajjed, Saba Yasir, Patrice A Aleff, Michael S Torbenson
Modern Pathology.2015; 28(9): 1265. CrossRef
- Perinatal Management of Hepatic Adenomas
- Cytological Evaluation and REBA HPV-ID HPV Testing of Newly Developed Liquid-Based Cytology, EASYPREP: Comparison with SurePath
- Youn Soo Lee, Gyungyub Gong, Jin Hee Sohn, Ki Sung Ryu, Jung Hun Lee, Shin Kwang Khang, Kyung-Ja Cho, Yong-Man Kim, Chang Suk Kang
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):265-274. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.265
- 12,078 View
- 98 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The objective of this study was to evaluate a newly-developed EASYPREP liquid-based cytology method in cervicovaginal specimens and compare it with SurePath.
Methods Cervicovaginal specimens were prospectively collected from 1,000 patients with EASYPREP and SurePath. The specimens were first collected by brushing for SurePath and second for EASYPREP. The specimens of both methods were diagnosed according to the Bethesda System. Additionally, we performed to REBA HPV-ID genotyping and sequencing analysis for human papillomavirus (HPV) on 249 specimens.
Results EASYPREP and SurePath showed even distribution of cells and were equal in cellularity and staining quality. The diagnostic agreement between the two methods was 96.5%. Based on the standard of SurePath, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of EASYPREP were 90.7%, 99.2%, 94.8%, and 98.5%, respectively. The positivity of REBA HPV-ID was 49.4% and 95.1% in normal and abnormal cytological samples, respectively. The result of REBA HPV-ID had high concordance with sequencing analysis.
Conclusions EASYPREP provided comparable results to SurePath in the diagnosis and staining quality of cytology examinations and in HPV testing with REBA HPV-ID. EASYPREP could be another LBC method choice for the cervicovaginal specimens. Additionally, REBA HPV-ID may be a useful method for HPV genotyping.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Virome capture sequencing for comprehensive HPV genotyping in cervical samples
Thanayod Sasivimolrattana, Sasiprapa Liewchalermwong, Wasun Chantratita, Insee Sensorn, Arkom Chaiwongkot, Parvapan Bhattarakosol
Science Progress.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High-Risk Human Papillomavirus Detection via Cobas® 4800 and REBA HPV-ID® Assays
Sasiprapa Liewchalermwong, Shina Oranratanaphan, Wichai Termrungruanglert, Surang Triratanachat, Patou Tantbirojn, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Parvapan Bhattarakosol, Arkom Chaiwongkot
Viruses.2022; 14(12): 2713. CrossRef - Evaluation of nuclear chromatin using grayscale intensity and thresholded percentage area in liquid‐based cervical cytology
Hyekyung Lee, Myungein Han, Taejo Yoo, Chanho Jung, Hyun‐Jin Son, Migyung Cho
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2018; 46(5): 384. CrossRef - Comparison of EASYPREP® and SurePath® in thyroid fine‐needle aspiration
Yosep Chong, Ki Hyun Baek, Jee Young Kim, Tae‐Jung Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Chang Suk Kang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2016; 44(4): 283. CrossRef
- Virome capture sequencing for comprehensive HPV genotyping in cervical samples
- In-house Manual Construction of High-Density and High-Quality Tissue Microarrays by Using Homemade Recipient Agarose-Paraffin Blocks
- Kyu Ho Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Yeon Il Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):238-244. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.238
- 11,840 View
- 94 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Self-made tissue punches can be effectively used to punch holes in blank recipient paraffin blocks and extract tissue cores from the donor paraffin blocks for the low-cost construction of tissue microarrays (TMAs). However, variable degrees of section distortion and loss of the tissue cores can occurs during cutting of the TMAs, posing technical problems for in-house manual construction of high-density TMAs. We aimed to update the method for in-house manual TMA construction to improve the quality of high-density TMAs.
Methods Blocks of agarose gel were subjected to the standard tissue processing and embedding procedure to prepare recipient agarose-paraffin blocks. The self-made tissue punches and recipient agarose-paraffin blocks were used to construct TMAs, which were completely melted and re-embedded in paraffin to make finished TMA blocks.
Results The donor tissue cores were completely integrated into the surrounding paraffin of the recipient blocks. This method enabled us to construct high-density TMAs with significantly less section distortion or loss of tissue cores during microtomy.
Conclusions Simple and inexpensive construction of high-density and high-quality TMAs can be warranted by using paraffinized agarose gels as recipient blocks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using Quality Function Deployment to Design an Image-Guided, Multibiopsy Tool for Neurosurgical Applications
Kaytlin Andrews, Hunter Dejean, Cameron MacLeod, Kate Prieditis, Heidi-Lynn Ploeg, James Purzner, Teresa Purzner
Operative Neurosurgery.2026; 30(3): 422. CrossRef - An introduction of an easy-operating and economical technique for tissue microarray preparation
Yi-Jing Chen, Chun-Mei Yang, Jiang-Sheng Huang, Ping Wang, Yan-Hua Lv, Cheng Tang, Wei Deng
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2020; 73(7): 403. CrossRef - Optimization of Tissue Microarrays from Banked Human Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues in the Cancer Research Setting
Tammy Sexton, Gregory L. Kucera, Edward A. Levine, Kounosuke Watabe, Stacey S. O'Neill
Biopreservation and Biobanking.2019; 17(5): 452. CrossRef - Monocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 are independent prognostic biomarkers for the survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and those receiving therapy targeting angiogenesis
Yan-Wei Cao, Yong Liu, Zhen Dong, Lei Guo, En-Hao Kang, Yong-Hua Wang, Wei Zhang, Hai-Tao Niu
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2018; 36(6): 311.e15. CrossRef - Platelet-derived growth factor receptor α in hepatocellular carcinoma is a prognostic marker independent of underlying liver cirrhosis
Jung-Hwan Yu, Joon Mee Kim, Ja Kyung Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Kwan Sik Lee, Jin-Woo Lee, Hye Young Chang, Jung Il Lee
Oncotarget.2017; 8(24): 39534. CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Semi-quantitative Immunohistochemical Assessment of CD20 Expression in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Chang Hwan Choi, Young Hoon Park, Joo Han Lim, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(2): 96. CrossRef - High Quality Tissue Miniarray Technique Using a Conventional TV/Radio Telescopic Antenna
Mohamed A. Elkablawy, Abdulkader M. Albasri
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(3): 1129. CrossRef
- Using Quality Function Deployment to Design an Image-Guided, Multibiopsy Tool for Neurosurgical Applications
- Prognostic Significance of Heat Shock Protein 70 Expression in Early Gastric Carcinoma
- Youngran Kang, Woon Yong Jung, Hyunjoo Lee, Wonkyung Jung, Eunjung Lee, Bong Kyung Shin, Aeree Kim, Han Kyeom Kim, Baek-hui Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):219-226. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.219
- 9,674 View
- 36 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Overexpression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) has been observed in many types of cancer including gastric adenocarcinomas, although the exact role of HSP70 in carcinogenesis remains unclear.
Methods The study analyzed a total of 458 radical gastrectomy specimens which were immunohistochemically stained with HSP70, p53, and Ki-67 antibodies.
Results The study determined that the expression of HSP70 was significantly increased in early gastric cancer (EGC) compared to advanced gastric cancer (p<0.001). The HSP70 expression was correlated with well-differentiated tumor type, intestinal type of Lauren classification and the lower pT and pN stage. Negative expression of Ki-67 and p53 expression was associated with poor prognosis. The study did not find any correlation between HSP70 and p53 expression. The study determined that HSP70 expression in the EGC subgroup was associated with a poor prognosis (p=0.009), as well as negative Ki-67 expression (p=0.006), but was not associated with p53. Based on multivariate analysis, HSP70 expression (p=0.024), negative expression of Ki-67, invasion depth and lymph node metastasis were determined to be independent prognostic markers.
Conclusions HSP70 is expressed in the early stages of gastric adenocarcinoma. In EGC, HSP70 is a poor independent prognostic marker and is correlated with a low proliferation index.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Prognostic Importance of Ki-67 in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas: A Meta-analysis and Multi-omics Approach
Mahdieh Razmi, Fatemeh Tajik, Farideh Hashemi, Ayna Yazdanpanah, Fatemeh Hashemi-Niasari, Adeleh Divsalar
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2024; 55(2): 599. CrossRef - Clinicopathological significance of HSP70 expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaolu Wang, Li Xie, Lijing Zhu
BMC Gastroenterology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta-sheet-specific interactions with heat shock proteins define a mechanism of delayed tumor cell death in response to HAMLET
Aftab Nadeem, James C.S. Ho, Tuan Hiep Tran, Sanchari Paul, Victoria Granqvist, Nadege Despretz, Catharina Svanborg
Journal of Molecular Biology.2019; 431(14): 2612. CrossRef - Evolving paradigms on the interplay of mitochondrial Hsp70 chaperone system in cell survival and senescence
Shubhi Srivastava, Vinaya Vishwanathan, Abhijit Birje, Devanjan Sinha, Patrick D’Silva
Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2019; 54(6): 517. CrossRef - Clinicopathologic significance and prognostic value of Ki-67 expression in patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
Guanying Luo, Yunzhao Hu, Zhiqiao Zhang, Peng Wang, Zhaowen Luo, Jinxin Lin, Canchang Cheng, You Yang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(30): 50273. CrossRef - Extracellular HSP70-peptide complexes promote the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via TLR2/4/JNK1/2MAPK pathway
Yi Zhe, Yan Li, Dan Liu, Dong-Ming Su, Jin-Gang Liu, Hang-Yu Li
Tumor Biology.2016; 37(10): 13951. CrossRef - The cytomegalovirus protein UL138 induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by binding to heat shock protein 70
Wenjing Chen, Kezhi Lin, Liang Zhang, Gangqiang Guo, Xiangwei Sun, Jing Chen, Lulu Ye, Sisi Ye, Chenchen Mao, Jianfeng Xu, Lifang Zhang, Lubin Jiang, Xian Shen, Xiangyang Xue
Oncotarget.2016; 7(5): 5630. CrossRef - Targeting the hsp70 gene delays mammary tumor initiation and inhibits tumor cell metastasis
J Gong, D Weng, T Eguchi, A Murshid, M Y Sherman, B Song, S K Calderwood
Oncogene.2015; 34(43): 5460. CrossRef
- The Prognostic Importance of Ki-67 in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas: A Meta-analysis and Multi-omics Approach
- Construction of High-Density Tissue Microarrays at Low Cost by Using Self-Made Manual Microarray Kits and Recipient Paraffin Blocks
- Chang Hwan Choi, Kyu Ho Kim, Ju Young Song, Suk Jin Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):562-568. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.562
- 12,283 View
- 109 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Advances of tissue microarray (TMA) technology have enabled simultaneous
in situ analysis of biomarker expression in a large number of archived pathology specimens. However, the relatively high cost of TMA construction may hamper many researchers from using this essential tool of modern pathology research. We discuss methods for making TMA kits and recipient blocks for manual construction of high-density TMAs at low cost.Methods Ordinary cannula piercing needles, hypodermic needles, bone marrow biopsy needles, metallic ink cartridges of ballpoint pens, and disposable skin biopsy punches were used to construct self-made manual TMA kits. The recipient blocks were manufactured by boring holes in the conventional bare paraffin blocks. A mini electric hand drill and a microcompound table assembled on a drill stand were used to maximize the capacity of the recipient blocks.
Results By using TMA kits made from cannula piercing needles (16- and 18-gauge), it was possible to construct TMAs with 1 mm×140 cores, 0.6 mm×320 cores, 2 mm×70 cores, 3 mm×35 cores, and 5 mm×12 cores. The capacity of the recipient blocks could be dramatically increased by drilling holes.
Conclusions Construction of TMAs using self-made TMA kits is an inexpensive alternative to construction of TMAs using commercial devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic Potential of CD44, CD133, and VDR in Epithelial Ovarian Tumors: Association with Histopathology Parameters
Ljubiša Jovanović, Branka Šošić-Jurjević, Anđa Ćirković, Sandra Dragičević, Branko Filipović, Svetlana Milenković, Stefan Dugalić, Miroslava Gojnić-Dugalić, Aleksandra Nikolić
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(8): 3729. CrossRef - Comparison of programmed death-1 (PD-1)-positive T-cells with known prognostic indicators in breast cancer
Ankit Kaushik, Anamika Jaiswal, B Priya, Ashish Jain, Sonal Sharma
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2025; 14(11): 4631. CrossRef - Constructing high-density tissue microarrays with a novel method and a self-made tissue-arraying instrument
Ping Qin, Liu Li, Li Zhao, Piaopiao Bian, Zhongtang Xiong
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 245: 154430. CrossRef - The correlation of PD-L1 expression in cytological and histological material of serous high-grade ovarian cancer
Ljubiša Jovanović, Anđa Ćirković, Ljubinka Nikolić, Milena Jović, Darko Mikić, Svetlana Milenković, Radmila Janković
Srpski medicinski casopis Lekarske komore.2023; 4(3): 246. CrossRef - Expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors, HER2 protein and Ki-67 proliferation index in breast carcinoma in both tumor tissue and tissue microarray
UP Hacısalihoğlu, MA Dogan
Biotechnic & Histochemistry.2022; 97(4): 298. CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression in High-Grade Serous and Clear Cell Ovarian Cancer
Ljubiša Jovanović, Andja Ćirković, Milena Jović, Radmila Janković
Indian Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression in Different Segments and Histological Types of Ovarian Cancer According to Lymphocytic Infiltrate
Ljubiša Jovanović, Radmila Janković, Andja Ćirković, Milena Jović, Tijana Janjić, Slaviša Djuričić, Svetlana Milenković
Medicina.2021; 57(12): 1309. CrossRef - Optimization of Tissue Microarrays from Banked Human Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues in the Cancer Research Setting
Tammy Sexton, Gregory L. Kucera, Edward A. Levine, Kounosuke Watabe, Stacey S. O'Neill
Biopreservation and Biobanking.2019; 17(5): 452. CrossRef - Peripheral nerve sheath tumor invading the nasal cavities of a 6-year-old female Pointer dog
Alessandra Sfacteria, Laura Perillo, Francesco Macrì, Giovanni Lanteri, Claudia Rifici, Giuseppe Mazzullo
Veterinary Quarterly.2015; 35(3): 170. CrossRef - High Quality Tissue Miniarray Technique Using a Conventional TV/Radio Telescopic Antenna
Mohamed A. Elkablawy, Abdulkader M. Albasri
Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.2015; 16(3): 1129. CrossRef - Overview on Techniques to Construct Tissue Arrays with Special Emphasis on Tissue Microarrays
Ulrich Vogel
Microarrays.2014; 3(2): 103. CrossRef - Tissue Microarray
Kathleen Barrette, Joost J. van den Oord, Marjan Garmyn
Journal of Investigative Dermatology.2014; 134(9): 1. CrossRef - Altered Expression of PTEN and Its Major Regulator MicroRNA-21 in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
Hyoun Wook Lee, Seung Yeon Ha, Mee Sook Roh
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(1): 17. CrossRef - Optimizing tissue microarray construction procedure to improve quality of sections
Hua Chang, Diane Peluso, Sadiq Hussain, Michail Shipitsin, Peter Blume-Jensen
Journal of Histotechnology.2014; 37(3): 95. CrossRef - In-house Manual Construction of High-Density and High-Quality Tissue Microarrays by Using Homemade Recipient Agarose-Paraffin Blocks
Kyu Ho Kim, Suk Jin Choi, Yeon Il Choi, Lucia Kim, In Suh Park, Jee Young Han, Joon Mee Kim, Young Chae Chu
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(3): 238. CrossRef
- Diagnostic Potential of CD44, CD133, and VDR in Epithelial Ovarian Tumors: Association with Histopathology Parameters
- Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report of 15 Cases Including Three Cases of Concurrent Other-Type Renal Cell Carcinomas
- Jeong Hwan Park, Cheol Lee, Ja Hee Suh, Kyung Chul Moon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(6):541-547. Published online December 26, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.541
- 10,064 View
- 65 Download
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma (CCPRCC) is a recently established subtype of renal epithelial tumor. The aim of this study was to identify the diagnostic criteria of CCPRCC with an emphasis on immunohistochemical studies, and to report three cases with concurrent other-type renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods A total of 515 RCC patients that consecutively underwent surgical resection at Seoul National University Hospital from 1 January 2010 to 31 December 2011 were screened. Each case was reviewed based on the histologic features and was evaluated immunohistochemically.
Results A total of 15 CCPRCCs were identified, which composed 2.9% of the total RCCs. The mean age was 52 years, and the average tumor size was 1.65 cm. All 15 cases showed low nuclear grade, no lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. The CCPRCCs showed variable architectural patterns including cystic, trabecular, papillary, and acinar. All of the cases showed moderate to intense immunoreactivity for cytokeratin 7 (CK7). CD10 was negative or showed focal weak positivity. Three cases had concurrent other-type RCC, including a clear cell RCC and an acquired cystic disease-associated RCC.
Conclusions The strong CK7 and negative or focal weak CD10 expression will be useful for the diagnosis of CCPRCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
Ankur R Sangoi, Harrison Tsai, Lara Harik, Jonathan Mahlow, Maria Tretiakova, Sean R Williamson, Michelle S Hirsch
Histopathology.2024; 84(7): 1167. CrossRef - Clinical features and Surgical Outcome of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Tumor: result from a prospective cohort
Si Hyun Kim, Jang Hee Han, Seung-hwan Jeong, Hyeong Dong Yuk, Ja Hyeon Ku, Cheol Kwak, Hyeon Hoe Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Chang Wook Jeong
BMC Urology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of multiple clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma with renal oncocytoma: a case report
Amine Hermi, Ahmed Saadi, Seif Mokadem, Ahlem Blel, Marouene Chakroun, Mohamed Riadh Ben Slama
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 2017. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in End-Stage Renal Disease: A Review and Update
Ziad M. El-Zaatari, Luan D. Truong
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 657. CrossRef - The Clinicopathologic and Molecular Landscape of Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications in Diagnosis and Management
Stanley Weng, Renzo G. DiNatale, Andrew Silagy, Roy Mano, Kyrollis Attalla, Mahyar Kashani, Kate Weiss, Nicole E. Benfante, Andrew G. Winer, Jonathan A. Coleman, Victor E. Reuter, Paul Russo, Ed Reznik, Satish K. Tickoo, A. Ari Hakimi
European Urology.2021; 79(4): 468. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Characteristics and survival outcomes from a large single institutional series
James E. Steward, Sean Q. Kern, Liang Cheng, Ronald S. Boris, Yan Tong, Clint D. Bahler, Timothy A. Masterson, K. Clint Cary, Hristos Kaimakliotis, Thomas Gardner, Chandru P. Sundaram
Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations.2021; 39(6): 370.e21. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: an update after 15 years
Sean R. Williamson
Pathology.2021; 53(1): 109. CrossRef - Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Jianping Zhao, Eduardo Eyzaguirre
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(9): 1154. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma – An indolent subtype of renal tumor
Wei-Jen Chen, Chin-Chen Pan, Shu-Huei Shen, Hsiao-Jen Chung, Chih-Chieh Lin, Alex T.L. Lin, Yen-Hwa Chang
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2018; 81(10): 878. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature
Sung Han Kim, Whi-An Kwon, Jae Young Joung, Ho Kyung Seo, Kang Hyun Lee, Jinsoo Chung
World Journal of Nephrology.2018; 7(8): 155. CrossRef - Clinical features and survival analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: A 10‑year retrospective study from two institutions
Yiqiu Wang, Ying Ding, Jian Wang, Min Gu, Zengjun Wang, Chao Qin, Conghui Han, Hongxia Li, Xia Liu, Pengfei Wu, Guangchao Li
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A contemporary series of renal masses with emphasis on recently recognized entities and tumors of low malignant potential: A report based on 624 consecutive tumors from a single tertiary center
Maria Rosaria Raspollini, Ilaria Montagnani, Rodolfo Montironi, Liang Cheng, Guido Martignoni, Andrea Minervini, Sergio Serni, Giulio Nicita, Marco Carini, Antonio Lopez-Beltran
Pathology - Research and Practice.2017; 213(7): 804. CrossRef - Renal Neoplasms With Overlapping Features of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma and Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Hari P. Dhakal, Jesse K. McKenney, Li Yan Khor, Jordan P. Reynolds, Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, Christopher G. Przybycin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2016; 40(2): 141. CrossRef - New and emerging renal tumour entities
Naoto Kuroda, Ondřej Hess, Ming Zhou
Diagnostic Histopathology.2016; 22(2): 47. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Panel for Differentiating Renal Cell Carcinoma with Clear and Papillary Features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Pathology & Oncology Research.2015; 21(4): 893. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical panel for differentiating renal cell carcinoma with clear and papillary features
Hanan AlSaeid Alshenawy
Journal of Microscopy and Ultrastructure.2015; 3(2): 68. CrossRef - Clear Cell-Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Kidney Not Associated With End-stage Renal Disease
Manju Aron, Elena Chang, Loren Herrera, Ondrej Hes, Michelle S. Hirsch, Eva Comperat, Philippe Camparo, Priya Rao, Maria Picken, Michal Michal, Rodolfo Montironi, Pheroze Tamboli, Federico Monzon, Mahul B. Amin
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(7): 873. CrossRef - Papillary or pseudopapillary tumors of the kidney
Fang-Ming Deng, Max X. Kong, Ming Zhou
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology.2015; 32(2): 124. CrossRef - Do Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinomas Have Malignant Potential?
Mairo L. Diolombi, Liang Cheng, Pedram Argani, Jonathan I. Epstein
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2015; 39(12): 1621. CrossRef - Targeted next‐generation sequencing and non‐coding RNA expression analysis of clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma suggests distinct pathological mechanisms from other renal tumour subtypes
Charles H Lawrie, Erika Larrea, Gorka Larrinaga, Ibai Goicoechea, María Arestin, Marta Fernandez‐Mercado, Ondrej Hes, Francisco Cáceres, Lorea Manterola, José I López
The Journal of Pathology.2014; 232(1): 32. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma is the fourth most common histologic type of renal cell carcinoma in 290 consecutive nephrectomies for renal cell carcinoma
Haijun Zhou, Shaojiang Zheng, Luan D. Truong, Jae Y. Ro, Alberto G. Ayala, Steven S. Shen
Human Pathology.2014; 45(1): 59. CrossRef - Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Incidence, morphological features, immunohistochemical profile, and biologic behavior: A single institution study
Borislav A. Alexiev, Cinthia B. Drachenberg
Pathology - Research and Practice.2014; 210(4): 234. CrossRef - MRI Phenotype in Renal Cancer
Naomi Campbell, Andrew B. Rosenkrantz, Ivan Pedrosa
Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2014; 23(2): 95. CrossRef
- Vascular, adipose tissue, and/or calyceal invasion in clear cell tubulopapillary renal cell tumour: potentially problematic diagnostic scenarios
- Cytologic Features of Giant Cell Ependymoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Myoung Ju Koh, Sun Och Yoon, Hyae Min Jeon, Hyeon Joo Jeong, Soon Won Hong, Se Hoon Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(5):507-513. Published online October 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.507
- 10,495 View
- 71 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Here, we present a case of anaplastic giant cell ependymoma (GCE) occurring in a 15-year-old woman. Squash smear slides for intraoperative frozen section diagnosis revealed oval to round cell clusters with a papillary structure in a fibrillary background. This was occasionally accompanied by the presence of bizarre pleomorphic giant cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and prominent intranuclear inclusions. These intranuclear inclusions were a key clue to diagnosis of ependymoma. Histologic analysis revealed features of a high-grade tumor with perivascular pseudorosettes and bizarre pleomorphic giant cells, which established the diagnosis of GCE. We performed a review of literatures about the cytologic features of GCE, including our case, thus proposing that intraoperative frozen diagnosis of GCE would be established by squash smear preparations featuring the mitosis and necrosis, as well as the high cellularity, and the presence of giant cells showing hyperchromatic nuclei with eosinophilic cytoplasm and intranuclear inclusions/pseudoinclusions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of myxopapillary ependymoma with predominant giant cell morphology: A rare entity with comprehensive genomic profiling and review of literature
Bryan Morales‐Vargas, Hassan Saad, Daniel Refai, Matthew Schniederjan, Zied Abdullaev, Kenneth Aldape, Malak Abedalthagafi
Neuropathology.2025; 45(1): 13. CrossRef - Report of a case of giant cell ependymoma with unusual clinical and pathological presentation
Mónica B. Mezmezian, Victor Del Caño, Liliana G. Olvi
Neuropathology.2019; 39(4): 313. CrossRef - Giant Cell Ependymoma of Cervicomedullary Junction: A Case Report of a Long-Term Survivor and Literature Review
Martina Cappelletti, Andrea G. Ruggeri, Giorgia Iacopino, Roberto Delfini
World Neurosurgery.2018; 116: 121. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical features of giant cell ependymoma of the filum terminale with unusual clinical and radiological presentation
Fernando Candanedo-Gonzalez, Cindy Sharon Ortiz-Arce, Samuel Rosales-Perez, Ana Lilia Remirez-Castellanos, Candelaria Cordova-Uscanga, Armando Gamboa-Dominguez
Diagnostic Pathology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Giant Cell Ependymoma of Lateral Ventricle: Case Report, Literature Review, and Analysis of Prognostic Factors and Genetic Profile
Hirokazu Takami, Christopher S. Graffeo, Avital Perry, Aditya Raghunathan, Robert B. Jenkins, Caterina Giannini, Terry C. Burns
World Neurosurgery.2017; 108: 997.e9. CrossRef
- A case of myxopapillary ependymoma with predominant giant cell morphology: A rare entity with comprehensive genomic profiling and review of literature
- Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma of Different Histological Subtypes in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Ki Yong Na, Hyun-Soo Kim, Yong-Koo Park, Sung-Goo Chang, Youn Wha Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):382-386. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.382
- 10,741 View
- 77 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney (ADPKD) is rare. To date, 54 cases of RCC in ADPKD have been reported. Among these, only 2 cases have different histologic types of RCC. Here we describe a 45-year-old man who received radical nephrectomy for multifocal RCC with synchronous papillary and clear cell histology in ADPKD and chronic renal failure under regular hemodialysis. The case reported herein is another example of the rare pathological finding of RCC arising in a patient with ADPKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
Consolato M. Sergi, Luis Guerra, Josef Hager
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(9): 3965. CrossRef - Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Patients Requiring Nephrectomy: Characteristics and Surgical Considerations
Joel Ern Zher Chan, Kate S. Olakkengil, Shantanu Bhattacharjya, Santosh Antony Olakkengil
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2025; 95(7-8): 1605. CrossRef - Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Background of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
Poorva Vias, Shikha Goyal, Renu Madan, Nandita Kakkar, Ridhi Sood, Kannan Periasamy, Rajender Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2024; 45(02): 188. CrossRef - Detection of two synchronous histologically different renal cell carcinoma subtypes in the same kidney: a case report and review of the literature
Mohamed Sakr, Merhan Badran, Sarah Ahmed Hassan, Mohamed Elsaqa, Mohamed Anwar Elwany, Nevine M. F. El Deeb, Mohamed Sharafeldeen
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Importance of Genetic Testing in the Differential Diagnosis of Atypical TSC2-PKD1 Contiguous Gene Syndrome—Case Series
Petronella Orosz, Zita Kollák, Ákos Pethő, András Fogarasi, György Reusz, Kinga Hadzsiev, Tamás Szabó
Children.2023; 10(3): 420. CrossRef - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease coming up with an unusual presentation of renal cell carcinoma on its first encounter
Asma Shoukat Masumdar, Anitha Padmanabhan, Nitin Gadgil, Gargi Padalkar
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2023; 10(4): 417. CrossRef - Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review
Yuji Hakozaki, Kiyotaka Uchiyama, Akane Yanai, Daisuke Yamada, Yuka Kamijo, Yoshitaka Ishibashi
CEN Case Reports.2021; 10(2): 199. CrossRef - CT and MRI findings of cystic renal cell carcinoma: comparison with cystic collecting duct carcinoma
Qingqiang Zhu, Jun Ling, Jing Ye, Wenrong Zhu, Jingtao Wu, Wenxin Chen
Cancer Imaging.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental occurrence of papillary renal cell carcinoma in the native kidney with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease after renal transplantation: A case report
Mahmoud Abbas, Melanie Pätzel, Angelika Thurn, Olaf Brinkmann, Olaf Bettendorf
Molecular and Clinical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patient with preserved renal function
Hyuk Huh, Hyung Ah Jo, YongJin Yi, Seung Hyup Kim, Kyung Chul Moon, Curie Ahn, Hayne Cho Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 1108. CrossRef - The Association between Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and Renal Cell Carcinoma
Chase C. Hansen, Michael Derrick, Irfan Warriach, James Thomas Cammack, James Thomas Cammack, Werner de Riese
Open Journal of Urology.2015; 05(06): 84. CrossRef - The MSCT and MRI findings of collecting duct carcinoma
Q. Zhu, J. Wu, Z. Wang, W. Zhu, W. Chen, S. Wang
Clinical Radiology.2013; 68(10): 1002. CrossRef - Thyroid-like follicular carcinoma of the kidney in a patient with nephrolithiasis and polycystic kidney disease: a case report
Metka Volavšek, Margareta Strojan-Fležar, Gregor Mikuz
Diagnostic Pathology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef
- Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review
- Comparison of Diagnostic Cytomorphology of Atypical Squamous Cells in Liquid-Based Preparations and Conventional Smears
- Jung Dal Lee, Young-Ha Oh, Seong Ok Lee, Jong Yull Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(4):365-369. Published online August 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.4.365
- 12,904 View
- 85 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The aims of this study were to compare the cytomorphologic features diagnostic of atypical squamous cells (ASC) in liquid-based preparations (LBPs) and conventional Pap (CP) smears and to cytomorphologically assess the performance of the Cell Scan 1500™ in cervical cytology practice.
Methods Cervicovaginal smears were obtained from 938 women. Two smears were obtained simultaneously from each individual, one for an LBP and the other for a CP smear; the smears were independently examined. ASC was diagnosed in 24 patients, and their samples were cytomorphologically and semiquantitatively analyzed.
Results A total of 24 of the 938 women (2.6%) were diagnosed with ASC by one or both methods. Results from LBPs and CP smears were in agreement in 13 of 24 cases of ASC diagnosis (absolute direct agreement, 54.2%; k<0.20; p-value from chi-square test=0.085). Diagnostic features of ASC in the LBPs included squamous cell atypia and atypical squamous metaplasia.
Conclusions The cellular features diagnostic of ASC present in one preparation can manifest themselves differently in the other. Changes in individual cells, particularly nuclear changes, are the most reliable features for diagnosing ASC. The Cell Scan 1500™ processor is more effective at detecting ASC than are CP smears.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risikobewertung von Zytologiebefunden im Zervixkarzinom-Screening
Katrin Marquardt, Peter Ziemke, Konrad Neumann, Wolfgang Kühn
Der Gynäkologe.2019; 52(12): 937. CrossRef - Nationwide cervical cancer screening in Korea: data from the National Health Insurance Service Cancer Screening Program and National Cancer Screening Program, 2009–2014
Seung-Hyuk Shim, Hyeongsu Kim, In-Sook Sohn, Han-Sung Hwang, Han-Sung Kwon, Sun Joo Lee, Ji Young Lee, Soo-Nyung Kim, Kunsei Lee, Sounghoon Chang
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Morphologic Analysis of Cytomegalovirus Infected Cells in Bronchial Washing Cytology: Comparison of Liquid-Based Preparation and Conventional Smear
Jae Yeon Seok, Jungsuk An, Seung Yeon Ha, Dong Hae Chung, Sangho Lee, Hyunchul Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(2): 147. CrossRef
- Risikobewertung von Zytologiebefunden im Zervixkarzinom-Screening
- Tumor Budding and Recurrence in Submucosal Invasive Colorectal Cancers of Favorable Histology: Case Reports of Two Early Colorectal Cancers with Advanced Recurrences
- Heae Surng Park, Hee Jin Chang, Ji Won Park, Byung Chang Kim, Dae Kyung Sohn, Chang Won Hong, Ji-Yeon Baek, Sun Young Kim, Hyo Seong Choi, Jae Hwan Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):272-277. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.272
- 10,138 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Complete resection of submucosal invasive colorectal cancer (SICC) showing favorable histology is regarded as curative. We report on two cases of SICC showing recurrence within 5 years despite complete resection. The first patient was a 68-year-old woman with well differentiated rectal adenocarcinoma invading the superficial submucosa, which recurred after 4.7 years. The second patient was a 53-year-old man with pT1N0 moderately differentiated colonic adenocarcinoma. He developed widespread tumor recurrence after 3.9 years. Retrospective pathologic review of the original tumors showed multiple foci of tumor budding at the invasive front. Immunohistochemical staining for D2-40 of deeper levels of the paraffin blocks showed rare foci of small lymphatic invasion. Tumor budding at the invasive front may be an important indicator for SICC aggressiveness or may reflect early lymphatic invasion. More aggressive pathologic examination and follow-up is required for patients with SICC showing tumor budding, even in the absence of unfavorable histologic findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estudio de factores histológicos predictivos de metástasis ganglionar locorregional en adenocarcinoma colorrectal mínimamente invasivo pT1
Isidro Machado, Miriam Valera-Alberni, Fernando Martínez de Juan, José A. López-Guerrero, Alfonso García Fadrique, Julia Cruz, Carmen Martínez Lapiedra, Fernanda Maia de Alcantara, Ricardo Yaya, Jorge Campos, Carlos Fernández-Martos, Rafael Estevan
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2016; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Histological factors predicting loco-regional lymph node metastasis in early invasive colorectal adenocarcinoma pT1
Isidro Machado, Miriam Valera-Alberni, Fernando Martínez de Juan, José A. López-Guerrero, Alfonso García Fadrique, Julia Cruz, Carmen Martínez Lapiedra, Fernanda Maia de Alcantara, Ricardo Yaya, Jorge Campos, Carlos Fernández-Martos, Rafael Estevan
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2016; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Tumor budding in the clinical management of colon and rectal cancer
Viktor H Koelzer, Inti Zlobec, Alessandro Lugli
Colorectal Cancer.2014; 3(4): 387. CrossRef
- Estudio de factores histológicos predictivos de metástasis ganglionar locorregional en adenocarcinoma colorrectal mínimamente invasivo pT1
- Cytologic Findings of Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Urethra: A Case Report
- Jee-Young Han, Kyu-Ho Kim, Lucia Kim, Suk-Jin Choi, In-Suh Park, Joon-Mee Kim, Young-Chae Chu, Sang-Min Yoon
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(2):210-214. Published online April 25, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.2.210
- 10,094 View
- 59 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the urethra is a rare disease entity with an uncertain histogenesis. Here, we present a case of primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the female urethra with its cytological findings. A 54-year-old woman presented with a painless gross hematuria lasting 3 months. On vaginal sonography, there was a sausage-like, elongated mass in the urethra, measuring 3.8×4.3 cm. The voided urine cytology revealed small clusters of rounded or papillary cells. The necrotic debris and inflammatory cells were present within some clusters of tumor cells. These tumor cells were enlarged and had abundant clear or granular cytoplasm with cytoplasmic vacuoles. The nucleus was granular and contained vesicular chromatin with prominent nucleoli. The hobnail cells and hyaline globules were also present as in a histologic section. The histologic findings were compatible with clear cell adenocarcinoma. The tumor showed distinctive cytological features. Cytologically, however, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis from other adenocarcinoma or high-grade urothelial carcinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytological and histological findings of upper tract mucinous urothelial carcinoma with clear cell component: A case report and review of literature
Go Kobayashi, Naohiro Uraoka, Kazuhiro Sentani, Jun Shibata, Ryosuke Nobuhiro, Yoichi Saito, Daiki Taniyama, Masanori Hanamoto, Hiroyuki Nose, Naohide Oue
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Presentación de reporte de caso: adenocarcinoma de célula clara de uretra
Nataly González, Yuly Ramirez, Jose Szelezsán, Daniel Rojas
Revista Urología Colombiana / Colombian Urology Journal.2018; 27(02): 191. CrossRef - Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Urethra: Review of the Literature
Anthony Kodzo-Grey Venyo
International Journal of Surgical Oncology.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef
- Cytological and histological findings of upper tract mucinous urothelial carcinoma with clear cell component: A case report and review of literature
- Nuclear Image Analysis Study of Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Meeja Park, Taehwa Baek, Jongho Baek, Hyunjin Son, Dongwook Kang, Jooheon Kim, Hyekyung Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(1):38-41. Published online February 23, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.38
- 8,339 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background There is a subjective disagreement about nuclear chromatin in the field of pathology. Objective values of red, green, and blue (RGB) light intensities for nuclear chromatin can be obtained through a quantitative analysis using digital images.
Methods We examined 10 cases of well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the rectum, small cell lung carcinomas, and moderately differentiated squamous cell lung carcinomas respectively. For each case, we selected 30 representative cells and captured typical microscopic findings. Using an image analyzer, we determined the longest nuclear line profiles and obtained graph files and Excel data on RGB light intensities. We assessed the meaningful differences in graph files and Excel data among the three different tumors.
Results The nucleus of hematoxylin and eosin-stained tumor cells was expressed as a combination of RGB light sources. The highest intensity was from blue, whereas the lowest intensity was from green. According to the graph files, green showed the most noticeable change in the light intensity, which is consistent with the difference in standard deviations.
Conclusions The change in the light intensity for green has an important implication for differentiating between tumors. Specific features of the nucleus can be expressed in specific values of RGB light intensities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hyekyung Lee, Tae Hwa Baek, Meeja Park, Seung Yun Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Dong Wook Kang, Joo Heon Kim, Soo Young Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(5): 355. CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus® and ThinPrep® liquid‐based preparations in effusion cytology
Yong‐Moon Lee, Ji‐Yong Hwang, Seung‐Myoung Son, Song‐Yi Choi, Ho‐Chang Lee, Eun‐Joong Kim, Hye‐Suk Han, Jin young An, Joung‐Ho Han, Ok‐Jun Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2014; 42(5): 384. CrossRef
- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Cytologic Diagnosis of hepatocellular Carcinoma by Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy.
- Ki Kwon Kim, Eun Sook Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1990;1(1):18-26.
- 2,016 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - CT guided percutaneous fine-needle aspiration(FNA) of the liver for both cytologic and histologic examination has great value in diagnosing liver malignancy. From March, 1986 to April, 1990, 62 patients with the clinical impression of liver malignancy underwent CT guided percutaneous FNA biopsy. Of these, 43 cases were reviewed for this study, 19 were reported to be liver cell carcinoma, 2 were adenocarcinoma, 11 were reported as anaplastic cell present, and the rest (11 cases) were negative (9) or necrotic (2). Among the 11 cases of the last group, 9 were diagnosed as liver cell carcinoma and 2 were necrotic histologically. Retrospective review, in order to clarify the casuse of cytologic diagnostic error, of both cytologic and histologic slides of all cases showed discordance of 23% between these diagnoses and sensitivity is 93.9% and specificity is 90.9%. The reasons were as follows :1) the lack of awareness of tumor cells of well differentiated liver cell carcinoma (4 cases), 2) missed tumor cells due to too scanty cellularity (1 case), 3) improper smear (2 cases) and no tumor cell in the cytologic smears (3 cases). In such cases, at the initiation of FNA, a correct diagnosis of liver malignancy could only be made by a combination of cytologic and histologic examinations. However after three years' experience we can conclude that cytomorphologic features of liver cell carcinoma are sufficiently distinctive from other liver malignancies to be diagnostic
- Cytologic Study of Thymoma.
- Gu Kong, Se Jin Jang, Jung Dal Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 1990;1(1):36-42.
- 2,050 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The fluoroscopy-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy has been gaining widespread acceptance as a rapid and effective method to make a pre-operative diagnosis of mediastinal tumors including thymoma, malignant lymphoma, and metastatic carcinoma. Although thymoma is a most common tumor of the superior mediastinum, most cytopathologists are not experted in cytologic diagnosis of this tumor because of limited experience. In order to define the diagnostic cytologic features of thymoma, we have retrospectively reviewed imprinting smears and corresponding tissue sections from four cases of this tumor. All cases revealed an apparent biphasic pattern of epithelial cell clusters and lymphocytes with occasional branching capillary fronds extending from three dimensional epithelial cell clusters. Epithelial cell clusters predominated in one case and lymphocytes in two cases. Mixed epithelial cell and lymphocyte type represented in one of four cases. In the lymphocyte predominant type, the presence of epithelial cell clusters and small mature lymphocytes are helpful features to differentiate from a malignent lymphoma.

 E-submission
E-submission

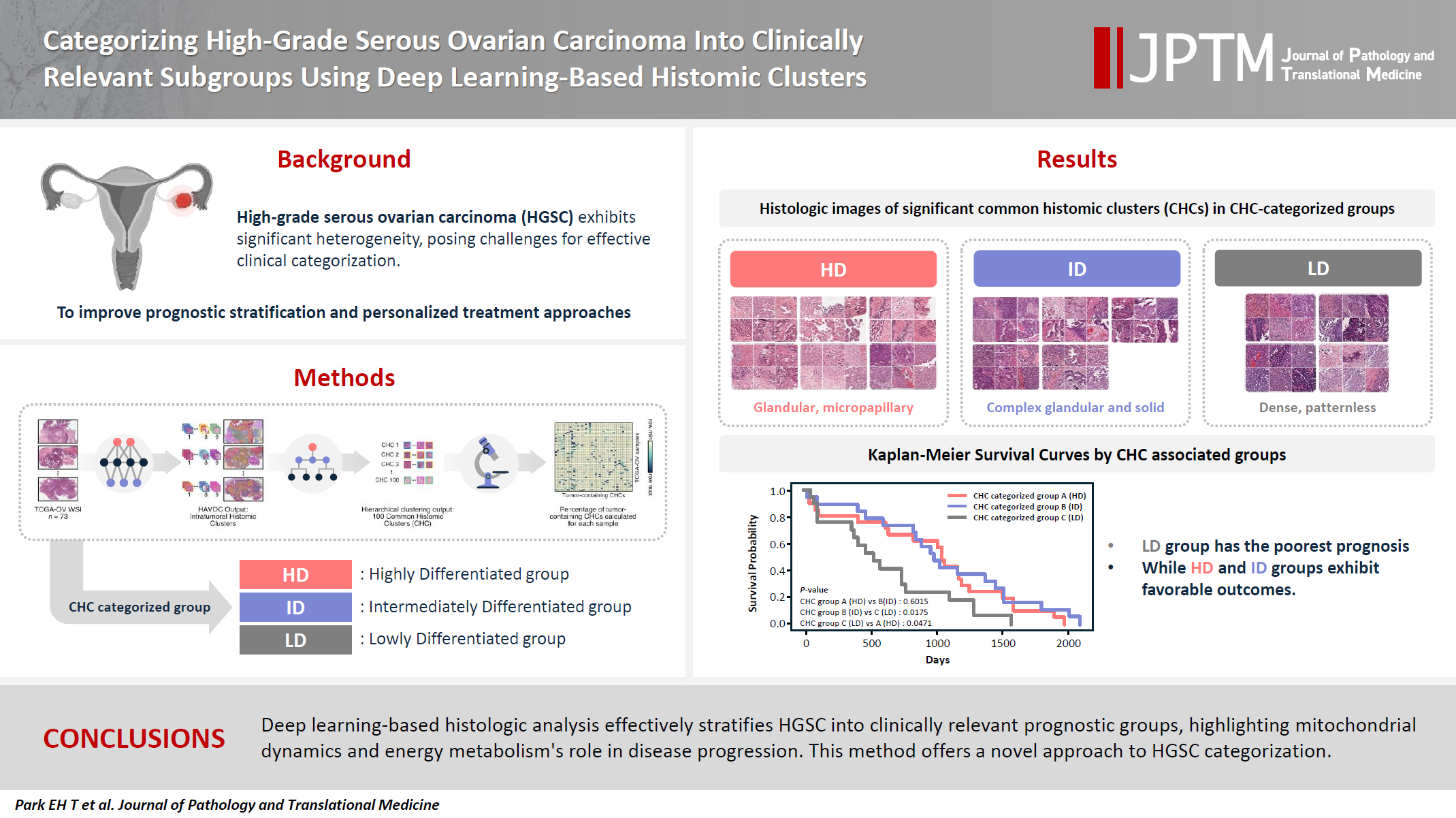









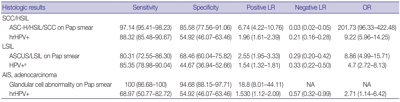

 First
First Prev
Prev



