Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Variation in mitotic counting and risk classification practices for gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a survey of pathologists in South Korea
- In Hye Song, Soomin Ahn, Jeong-Hyeon Jo, Young Soo Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):348-352. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.14
- 2,042 View
- 29 Download
- Interpretation of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: summary of a consensus meeting of Korean gastrointestinal pathologists
- Soomin Ahn, Yoonjin Kwak, Gui Young Kwon, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Hyunki Kim, Young Soo Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Kyoungyul Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Hye Seung Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):103-116. Published online April 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.15
- 20,702 View
- 692 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Nivolumab plus chemotherapy in the first-line setting has demonstrated clinical efficacy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, and is currently indicated as a standard treatment. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression is an important biomarker for predicting response to anti–programmed death 1/PD-L1 agents in several solid tumors, including gastric cancer. In the CheckMate-649 trial, significant clinical improvements were observed in patients with PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS) ≥ 5, determined using the 28-8 pharmDx assay. Accordingly, an accurate interpretation of PD-L1 CPS, especially at a cutoff of 5, is important. The CPS method evaluates both immune and tumor cells and provides a comprehensive assessment of PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. However, CPS evaluation has several limitations, one of which is poor interobserver concordance among pathologists. Despite these limitations, clinical indications relying on PD-L1 CPS are increasing. In response, Korean gastrointestinal pathologists held a consensus meeting for the interpretation of PD-L1 CPS in gastric cancer. Eleven pathologists reviewed 20 PD-L1 slides with a CPS cutoff close to 5, stained with the 28-8 pharmDx assay, and determined the consensus scores. The issues observed in discrepant cases were discussed. In this review, we present cases of gastric cancer with consensus PD-L1 CPS. In addition, we briefly touch upon current practices and clinical issues associated with assays used for the assessment of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
Winta Mehtsun, Lola Van Doosselaere, Ugwuji N. Maduekwe
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Learning Analysis Based on Dual-energy CT-Derived Iodine Map for Predicting PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Study
Lihong Chen, Yuncong Zhao, Xiaomin Tian, Deye Zeng, Yongxiu Tong, Haiping Xu, Yaru You, Caiming Weng, Sen Lin, Keru Chen, Yilin Chen, Yunjing Xue
Academic Radiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjuvant immunotherapy in patients with resected gastric and oesophagogastric junction cancer following preoperative chemotherapy with high risk for recurrence (ypN+ and/or R1): European Organisation of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 1707 VESTIG
F. Lordick, M.E. Mauer, G. Stocker, C.A. Cella, I. Ben-Aharon, G. Piessen, L. Wyrwicz, G. Al-Haidari, T. Fleitas-Kanonnikoff, V. Boige, R. Lordick Obermannová, U.M. Martens, C. Gomez-Martin, P. Thuss-Patience, V. Arrazubi, A. Avallone, K.K. Shiu, P. Artru
Annals of Oncology.2025; 36(2): 197. CrossRef - PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy
Yunjoo Cho, Soomin Ahn, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 177. CrossRef - PD-L1 importance in malignancies comprehensive insights into the role of PD-L1 in malignancies: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities
Mojdeh Soltani, Mohammad Abbaszadeh, Hamed Fouladseresht, Mark J. M. Sullman, Nahid Eskandari
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - CLDN18.2 expression in gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: prevalence, heterogeneity, and prognostic implications in Spanish patients
Carolina Martinez-Ciarpaglini, María Ortega, Sandra Pérez-Buira, Aitana Bolea, Beatriz Casado Guerra, Carmen Herencia Bellido, Paula Tornero Piñero, Dolores Naranjo-Hans, Brenda Palomar, Hernán Quiceno, Amanda Sardón Fernández, Ariadna Torner Calvo, Feder
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(6): 1337. CrossRef - Distinct clinicopathological and survival profiles of CLDN18.2 and PD-L1 expression in advanced gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
D.R. Castillo, M. Guo, P. Shah, M. Hazeltin, D. Tai, F. Al-Manaseer, S. Mlamba, D. Perez, S. Yeremian, S. Guzman, R. Mannan, C. Crook, C. Lau, N. Tawar, G. Brar, M. Raoof, Y. Woo, S.P. Wu, D. Li
ESMO Gastrointestinal Oncology.2025; 10: 100261. CrossRef - Best Practice PD-L1 Staining and Interpretation in Gastric Cancer Using PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 22C3 and PD-L1 IHC PharmDx 28-8 Assays, with Reference to Common Issues and Solutions
Soomin Ahn, Inwoo Hwang, Yuyeon Kim, Somin Lee, Yunjoo Cho, So Young Kang, Deok Geun Kim, Jeeyun Lee, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Biomedicines.2025; 13(11): 2824. CrossRef - Intraperitoneal immune microenvironment and efficacy of intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancer and peritoneal metastasis
Tomoya Nakanishi, Motohiro Imano, Masashi Kohda, Hiroaki Kato, Naoko Kounami, Atsushi Yamada, Masuhiro Terada, Yoko Hiraki, Osamu Shiraishi, Atsushi Yasuda, Masayuki Shinkai, Takushi Yasuda
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - PD-L1 thresholds predict efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition in first-line treatment of advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis of seven phase III randomized trials
V. Formica, C. Morelli, L. Fornaro, S. Riondino, M. Rofei, E. Fontana, E.C. Smyth, M. Roselli, H.-T. Arkenau
ESMO Open.2024; 9(11): 103967. CrossRef
- Organ Preservation for Gastroesophageal Junction and Gastric Cancers: Ready for Primetime?
- A standardized pathology report for gastric cancer: 2nd edition
- Young Soo Park, Myeong-Cherl Kook, Baek-hui Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Dong-Wook Kang, Mi-Jin Gu, Ok Ran Shin, Younghee Choi, Wonae Lee, Hyunki Kim, In Hye Song, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Hee Sung Kim, Guhyun Kang, Do Youn Park, So-Young Jin, Joon Mee Kim, Yoon Jung Choi, Hee Kyung Chang, Soomin Ahn, Mee Soo Chang, Song-Hee Han, Yoonjin Kwak, An Na Seo, Sung Hak Lee, Mee-Yon Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(1):1-27. Published online January 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.12.23
- 34,619 View
- 1,532 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The first edition of ‘A Standardized Pathology Report for Gastric Cancer’ was initiated by the Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists and published 17 years ago. Since then, significant advances have been made in the pathologic diagnosis, molecular genetics, and management of gastric cancer (GC). To reflect those changes, a committee for publishing a second edition of the report was formed within the Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. This second edition consists of two parts: standard data elements and conditional data elements. The standard data elements contain the basic pathologic findings and items necessary to predict the prognosis of GC patients, and they are adequate for routine surgical pathology service. Other diagnostic and prognostic factors relevant to adjuvant therapy, including molecular biomarkers, are classified as conditional data elements to allow each pathologist to selectively choose items appropriate to the environment in their institution. We trust that the standardized pathology report will be helpful for GC diagnosis and facilitate large-scale multidisciplinary collaborative studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spatial and Temporal Tumor Heterogeneity in Gastric Cancer: Discordance of Predictive Biomarkers
Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 192. CrossRef - PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Gastric Cancer Immunotherapy
Yunjoo Cho, Soomin Ahn, Kyoung-Mee Kim
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 177. CrossRef - Korean Gastric Cancer Association-Led Nationwide Survey on Surgically Treated Gastric Cancers in 2023
Dong Jin Kim, Jeong Ho Song, Ji-Hyeon Park, Sojung Kim, Sin Hye Park, Cheol Min Shin, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyunghye Bang, Chung-sik Gong, Sung Eun Oh, Yoo Min Kim, Young Suk Park, Jeesun Kim, Ji Eun Jung, Mi Ran Jung, Bang Wool Eom, Ki Bum Park, Jae Hun Chung, S
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 115. CrossRef - A Comprehensive and Comparative Review of Global Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines: 2024 Update
Sang Soo Eom, Keun Won Ryu, Hye Sook Han, Seong-Ho Kong
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2025; 25(1): 153. CrossRef - Korea, Japan, Europe, and the United States: Why are guidelines for gastric cancer different?
Emily E. Stroobant, Seong-Ho Kong, Maria Bencivenga, Takahiro Kinoshita, Tae-Han Kim, Takeshi Sano, Giovanni de Manzoni, Han-Kwang Yang, Yuko Kitagawa, Vivian E. Strong
Gastric Cancer.2025; 28(4): 559. CrossRef - Can the Japanese guidelines for endoscopic submucosal dissection be safely applied to Korean gastric cancer patients? A multicenter retrospective study based on the Korean Gastric Cancer Association nationwide survey
Hayemin Lee, Mi Ryeong Park, Junhyun Lee
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2025; 109(2): 81. CrossRef - Double optimal transport for differential gene regulatory network inference with unpaired samples
Mengyu Li, Bencong Zhu, Cheng Meng, Xiaodan Fan, Laura Cantini
Bioinformatics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Effect of Fibrin Glue on Bleeding after Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Tae-Se Kim, Tae-Jun Kim, Yang Won Min, Hyuk Lee, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Poong-Lyul Rhee, Jae J. Kim
Gut and Liver.2025; 19(5): 677. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of stereomicroscopy assessment of invasion depth in ex vivo specimens of early gastric cancer
Jing Wang, Lin Chang, Dong-Feng Niu, Yan Yan, Chang-Qi Cao, Shi-Jie Li, Qi Wu
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - SMMILe enables accurate spatial quantification in digital pathology using multiple-instance learning
Zeyu Gao, Anyu Mao, Yuxing Dong, Hannah Clayton, Jialun Wu, Jiashuai Liu, ChunBao Wang, Kai He, Tieliang Gong, Chen Li, Mireia Crispin-Ortuzar
Nature Cancer.2025; 6(12): 2025. CrossRef - Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of Gastric Cancer with Bone Metastasis
Sujin Oh, Soo Kyung Nam, Keun-Wook Lee, Hye Seung Lee, Yujun Park, Yoonjin Kwak, Kyu Sang Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Jin Won Kim, Minsu Kang, Young Suk Park, Sang-Hoon Ahn, Yun-Suhk Suh, Do Joong Park, Hyung Ho Kim
Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 56(1): 219. CrossRef - Microscopic tumor mapping of post-neoadjuvant therapy pancreatic cancer specimens to predict post-surgical recurrence: A prospective cohort study
Yeshong Park, Yeon Bi Han, Jinju Kim, MeeYoung Kang, Boram Lee, Eun Sung Ahn, Saemi Han, Haeryoung Kim, Hee-Young Na, Ho-Seong Han, Yoo-Seok Yoon
Pancreatology.2024; 24(4): 562. CrossRef - Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Resectable Gastric Cancer: Analysis from a Western Academic Center
Elliott J. Yee, Danielle Gilbert, Jeffrey Kaplan, Sachin Wani, Sunnie S. Kim, Martin D. McCarter, Camille L. Stewart
Cancers.2024; 16(7): 1428. CrossRef - Interpretation of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: summary of a consensus meeting of Korean gastrointestinal pathologists
Soomin Ahn, Yoonjin Kwak, Gui Young Kwon, Kyoung-Mee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Hyunki Kim, Young Soo Park, Hyeon Jeong Oh, Kyoungyul Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Hye Seung Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(3): 103. CrossRef - Expression of claudin 18.2 in poorly cohesive carcinoma and its association with clinicopathologic parameters in East Asian patients
Moonsik Kim, Byung Woog Kang, Jihyun Park, Jin Ho Baek, Jong Gwang Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 263: 155628. CrossRef - Clinicopathological analysis of claudin 18.2 focusing on intratumoral heterogeneity and survival in patients with metastatic or unresectable gastric cancer
T.-Y. Kim, Y. Kwak, S.K. Nam, D. Han, D.-Y. Oh, S.-A. Im, H.S. Lee
ESMO Open.2024; 9(12): 104000. CrossRef - Pathological Interpretation of Gastric Tumors in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Jung Yeon Kim
Journal of Digestive Cancer Research.2023; 11(1): 15. CrossRef - Histopathology of Gastric Cancer
Baek-hui Kim, Sung Hak Lee
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2023; 23(2): 143. CrossRef - Endoscopic submucosal dissection hands-on training with artificial mucosal layer EndoGEL
Tae-Se Kim, Jun Haeng Lee
Journal of Innovative Medical Technology.2023; 1(1): 5. CrossRef
- Spatial and Temporal Tumor Heterogeneity in Gastric Cancer: Discordance of Predictive Biomarkers
- HER2 status in breast cancer: changes in guidelines and complicating factors for interpretation
- Soomin Ahn, Ji Won Woo, Kyoungyul Lee, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):34-44. Published online November 6, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.03
- 38,128 View
- 1,323 Download
- 190 Web of Science
- 187 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein overexpression and/or HER2 gene amplification is found in about 20% of invasive breast cancers. It is a sole predictive marker for treatment benefits from HER2 targeted therapy and thus, HER2 testing is a routine practice for newly diagnosed breast cancer in pathology. Currently, HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) is used for a screening test, and in situ hybridization is used as a confirmation test for HER2 IHC equivocal cases. Since the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)/College of American Pathologists (CAP) guidelines on HER2 testing was first released in 2007, it has been updated to provide clear instructions for HER2 testing and accurate determination of HER2 status in breast cancer. During HER2 interpretation, some pitfalls such as intratumoral HER2 heterogeneity and increase in chromosome enumeration probe 17 signals may lead to inaccurate assessment of HER2 status. Moreover, HER2 status can be altered after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or during metastatic progression, due to biologic or methodologic issues. This review addresses recent updates of ASCO/CAP guidelines and factors complicating in the interpretation of HER2 status in breast cancers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Model Outperformed the Single Radiomics Model in Noninvasively Predicting the HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Cancer
Weimin Liu, Yiqing Yang, Xiaohong Wang, Chao Li, Chen Liu, Xiaolei Li, Junzhe Wen, Xue Lin, Jie Qin
Academic Radiology.2025; 32(1): 24. CrossRef - Multiparametric MRI Radiomics With Machine Learning for Differentiating HER2-Zero, -Low, and -Positive Breast Cancer: Model Development, Testing, and Interpretability Analysis
Yongxin Chen, Siyi Chen, Wenjie Tang, Qingcong Kong, Zhidan Zhong, Xiaomeng Yu, Yi Sui, Wenke Hu, Xinqing Jiang, Yuan Guo
American Journal of Roentgenology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Unknown Origin and Remote Primary at a Tertiary Cancer Centre in North India: Case Series with Review of Literature
Kriti Grover, Siddharth Arora, Mansi Dey, Deepti Awasthi, Harshad Sharma, Bibhu Prasad Mishra, Nitesh Mohan, Cheena Garg, Arjun Agarwal
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2025; 77(1): 424. CrossRef - Pooled clinical trial analyses evaluating outcomes of HER2-low vs HER2-0 expression in patients with metastatic breast cancer following chemotherapy
Elizabeth B. Lamont, Emily Stein, Paolo Tarantino, Sara M. Tolaney, Corinne Ahlberg, Krishna Chinnathambu, Jiezhi Qi, Jackie Bilan, Ruthie Davi, Lisa Ensign
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 210(1): 11. CrossRef - Insights into AI advances in immunohistochemistry for effective breast cancer treatment: a literature review of ER, PR, and HER2 scoring
Genevieve Chyrmang, Kangkana Bora, Anup Kr. Das, Gazi N. Ahmed, Lopamudra Kakoti
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2025; 41(1): 115. CrossRef - Prediction of Lung Adenocarcinoma Driver Genes Through Protein–Protein Interaction Networks Utilizing GenePlexus
Fei Yuan, Yu‐Hang Zhang, FeiMing Huang, Xiaoyu Cao, Lei Chen, JiaBo Li, WenFeng Shen, KaiYan Feng, YuSheng Bao, Tao Huang, Yu‐Dong Cai
PROTEOMICS.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative expression of estrogen, progesterone and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 and their correlation with immunohistochemistry in breast cancer at Uganda Cancer Institute
Henry Wannume, Nixon Niyonzima, Sam Kalungi, Julius Boniface Okuni, Tonny Okecha, Edward Kakungulu, Steven Mpungu Kiwuwa, Geoffrey Waiswa, Sylvester Kadhumbula, Monica Namayanja, Martin Nabwana, Jackson Orem, Kenji Fujiwara
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(1): e0311185. CrossRef - Automated Quantification of HER2 Amplification Levels Using Deep Learning
Ching-Wei Wang, Kai-Lin Chu, Ting-Sheng Su, Keng-Wei Liu, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2025; 29(1): 333. CrossRef - CAR-macrophage therapy for HER2-overexpressing advanced solid tumors: a phase 1 trial
Kim A. Reiss, Mathew G. Angelos, E. Claire Dees, Yuan Yuan, Naoto T. Ueno, Paula R. Pohlmann, Melissa L. Johnson, Joseph Chao, Olga Shestova, Jonathan S. Serody, Maggie Schmierer, Madison Kremp, Michael Ball, Rehman Qureshi, Benjamin H. Schott, Poonam Son
Nature Medicine.2025; 31(4): 1171. CrossRef - Human Cytomegalovirus Infection and Breast Cancer: A Literature Review of Clinical and Experimental Data
Rancés Blanco, Juan P. Muñoz
Biology.2025; 14(2): 174. CrossRef - An antibody-photosensitiser bioconjugate overcomes trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer
Mireia Jordà-Redondo, Ana Piqueras, Ana Castillo, Pedro Luis Fernández, Roger Bresolí-Obach, Lidia Blay, Joan Francesc Julián Ibáñez, Santi Nonell
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 290: 117511. CrossRef - Dynamic HER2-low status among patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and the impact of repeat biopsies
Yael Bar, Geoffrey Fell, Aylin Dedeoglu, Natalie Moffett, Neelima Vidula, Laura Spring, Seth A. Wander, Aditya Bardia, Naomi Ko, Beverly Moy, Leif W. Ellisen, Steven J. Isakoff
npj Breast Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical significances of RPL15 gene expression in circulating tumor cells of patients with breast cancer
Ying Zhuang, Keli Su, Shushu Liu, Wei Fan, Huijuan Lv, Wei Zhong
Biomedical Reports.2025; 22(5): 1. CrossRef - Advancing Breast Cancer Treatment: The Role of Immunotherapy and Cancer Vaccines in Overcoming Therapeutic Challenges
Marco Palma
Vaccines.2025; 13(4): 344. CrossRef - Complete preclinical evaluation of the novel antibody mimetic Nanofitin-IRDye800CW for diverse non-invasive diagnostic applications in the management of HER-2 positive tumors
Margherita Iaboni, Federico Crivellin, Francesca Arena, Francesca La Cava, Alessia Cordaro, Francesco Stummo, Daniele Faletto, Simon Huet, Leo Candela, Jessy Pedrault, Eugenia R. Zanella, Andrea Bertotti, Francesco Blasi, Alessandro Maiocchi, Luisa Poggi,
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - New insights on Galectin-9 expression in cancer prognosis: An updated systemic review and meta-analysis
Chun Yan So, Yusong Li, Kwan Ting Chow, Xiaosheng Tan
PLOS ONE.2025; 20(3): e0320441. CrossRef - Role of artificial intelligence –based machine learning model in predicting HER2/neu gene status in breast cancer
Ghada Mohamed, Omar Hamdy, Anwar Alkallas, Youssef Tahoun, Mohammed Mohammed Gomaa, Inas Moaz, Ahmed Orabi, Yasmine Hany elzohery, AL-Shimaa Zakaria, Mahitab Ibrahim Eltohamy
Pathology - Research and Practice.2025; 270: 155927. CrossRef - HER2 mRNA Score From Quantitative ERBB2 mRNA Expression of Oncotype Dx
Hyunwoo Lee, Jai Min Ryu, Se Kyung Lee, Byung Joo Chae, Jonghan Yu, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Won Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Yoon Ah Cho, Eun Yoon Cho
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2025; 49(8): 807. CrossRef - Neratinib and metformin: A novel therapeutic approach against HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Hadeel Kheraldine, Arij Fouzat Hassan, Sumayyah Saeed, Maysaloun Merhi, Jericha Miles Mateo, Monika Ulamec, Melita Peric-Balja, Semir Vranic, Hamda Al-Thawadi, Ala-Eddin Al Moustafa
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2025; 187: 118034. CrossRef - Machine learning prediction of HER2-low expression in breast cancers based on hematoxylin–eosin-stained slides
Jun Du, Jun Shi, Dongdong Sun, Yifei Wang, Guanfeng Liu, Jingru Chen, Wei Wang, Wenchao Zhou, Yushan Zheng, Haibo Wu
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting sentinel lymph node metastatic burden with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in clinical early-stage breast cancer patients
Mingli Jin, Fang Xiao, Qi Zhao, Ying Jiang, Zhihua Pan, Zhicai Duan, Juxi Jiang, Miaoqi Zhang, Jian Shu
Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2025; 121: 110397. CrossRef - HbA1c levels and breast cancer prognosis in women without diabetes
Jonas Busk Holm, Jens Meldgaard Bruun, Peer Christiansen, Reimar Wernich Thomsen, Jan Frystyk, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Signe Borgquist
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes in Early-Stage HER2-Low and HER2-Zero Breast Cancer: Single-Center Experience
Jamshid Hamdard, Mehmet Haluk Yücel, Harun Muğlu, Özgür Açıkgöz, Aslı Çakır, Ahmet Bilici, Ömer Fatih Ölmez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(9): 2937. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanism of Breast Cancer and Predisposition of Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus Propagation Cycle
Arya Ghosh, Subash C.B. Gopinath
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 32(12): 2330. CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF RECEPTOR CONVERSION ROLE FOR ADVANCED BREAST CANCER ON THE CHEMORESISTANCE OCCURRENCE
Oleksii V. Movchan, Ivan I. Smolanka, Andriy O. Lyashenko, Anton D. Loboda, Iryna V. Dosenko, Oksana M. Ivankova
Clinical and Preventive Medicine.2025; (3): 56. CrossRef - Combining conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) parameters with clinicopathologic data for differentiation of the three-tiered human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer
W. Liu, C. Liu, Y. Yang, Y. Chen, A. Muhetaier, Z. Lin, Z. Weng, X. Wang, P. Zhang, J. Qin
Clinical Radiology.2025; 86: 106955. CrossRef - IN SILICO STUDY: THE POTENTIAL OF KILEMO (Litsea cubeba) ENDEMIC PLANT FROM KALIMANTAN AS ANTI-BREAST CANCER THROUGH HER2 INHIBITION
Dwi Utami, Tarisha Elmaningtyas Zahro, Khairun Nisa, Muhammad Farid
JIIS (Jurnal Ilmiah Ibnu Sina): Ilmu Farmasi dan Kesehatan.2025; 10(1): 166. CrossRef - Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Metastatic Breast Cancer: Real-World Multicentric Study in the Portuguese Population
Luísa Soares Miranda, Maria João Sousa, Miguel Martins Braga, Marisa Couto, Isabel Vieira Fernandes, Francisca Abreu, Inês Eiriz, Catarina Lopes Fernandes, Alice Fonseca Marques, Maria Teresa Marques, Raquel Romão, Fernando Gonçalves, Joana Simões, Antóni
Cancers.2025; 17(12): 1911. CrossRef - Factors influencing pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in resectable breast cancer: A retrospective study
Jian Kang, Huifen Xiong, Xiaoliu Jiang, Zhaohui Huang, Yonghong Guo, Yali Cao, Jingxian Ding
Oncology Letters.2025; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Association of HER2-low with clinicopathological features in patients with early invasive lobular breast cancer: an international multicentric study
Karen Van Baelen, Ha-Linh Nguyen, François Richard, Gitte Zels, Maria Margarete Karsten, Guilherme Nader-Marta, Peter Vermeulen, Luc Dirix, Adam David Dordevic, Evandro de Azambuja, Denis Larsimont, Marion Maetens, Elia Biganzoli, Hans Wildiers, Ann Smeet
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Collagenase type IV improves the quality of HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization for breast cancers
Shang-En Lee, Sheng-Chi Hsu, Tsai-Hsien Hung, Kwai-Fong Ng, Tse-Ching Chen
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(3): 342. CrossRef - Resonant multi-focal scanning super-resolution microscopy with extended depth and field-of-view
Kidan Tadesse, Keyi Han, Wenhao Liu, Oliver S. Lee, Shu Jia
Cell Reports Physical Science.2025; 6(7): 102680. CrossRef - Scalable Nuclei Detection in HER2-SISH Whole Slide Images via Fine-Tuned Stardist with Expert-Annotated Regions of Interest
Zaka Ur Rehman, Mohammad Faizal Ahmad Fauzi, Wan Siti Halimatul Munirah Wan Ahmad, Fazly Salleh Abas, Phaik-Leng Cheah, Seow-Fan Chiew, Lai-Meng Looi
Diagnostics.2025; 15(13): 1584. CrossRef - Molecular landscape of HER2-mutated non-small cell lung cancer in Northeastern Brazil: Clinical, histopathological, and genomic insights
Cleto Dantas Nogueira, Samuel Frota, Huylmer Lucena Chaves, Juliana Cordeiro de Sousa, Guilherme de Sousa Veloso, Francisco Jonathan dos Santos Araujo, Gabriel Barbosa Silva, Samuel Silva Ferreira, Marclesson Santos Alves, Fabio Nasser, Ezequiel Rangel, F
Oncotarget.2025; 16(1): 467. CrossRef - Correlation between CTMP expression levels and resistance to trastuzumab in HER2 + metastatic breast cancer
Mania Makhoul, Maher Saifo, Fariz Ahmad, Jumana Saleh
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between body mass index and neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in patients with breast cancer
Jonas Busk Holm, Stine Blaabjerg Skovbjerg, Hanne Melgaard Nielsen, Peer Christiansen, Jens Meldgaard Bruun, Jan Alsner, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Signe Borgquist
Breast Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - An immunohistochemical characterization of basal cell carcinoma in patients below 40 years of age
Vincent Waller, Myriam Boeschen, Thomas Lingscheidt, Mathias Stiller, Lena Eickenscheidt, Thomas Wilhelm, Sonja Grunewald, Mirjana Ziemer, Jan‐Christoph Simon, Hendrik Bläker, Maximilian von Laffert
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2025; 23(11): 1414. CrossRef - Clinical Relationship Between Serum ApoB, HER2, and Myocardial Ischemia Risk in Breast Cancer Patients
Yeyan Lei, Dongmei Li, Shuang Bai, Xing Zeng, Rongyuan Yang, Qing Liu
Cancer Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual-targeting and steric hindrance resolution in HER2 IHC: a novel approach to improve diagnostic sensitivity
Li Luo, Xi Zhang, Linqiong Chen, Zhuohan Chen, Yuchen Wang, Kaihao Huang, Xiaoyun Lin, Hongxiang Zhu, Wangqi Du
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Time‐Dependent Diffusion MRI‐Based Microstructural Mapping for Characterizing HER2‐Zero, ‐Low, ‐Ultra‐Low, and ‐Positive Breast Cancer
Xiaoxia Wang, Yao Huang, Ying Cao, Huifang Chen, Xueqin Gong, Xiaosong Lan, Jiuquan Zhang, Zhaoxiang Ye
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2025; 62(6): 1754. CrossRef - Digital pathology enabling lean management of HER2/neu testing in breast Cancer
Aishwarya Sharma, Prarthna Shah, Manali Ranade, Trupti Pai, Ayushi Sahay, Asawari Patil, Tanuja Shet, Heena Gupta, Devika Chauhan, Puneet Somal, Sankalp Sancheti, Sangeeta Desai
Journal of Pathology Informatics.2025; 19: 100515. CrossRef - Enhancing HER2-low breast cancer detection with quantitative transcriptomics
Maria-Anna Misiakou, Maj-Britt Jensen, Maj-Lis Talman, Bent Ejlertsen, Maria Rossing
npj Breast Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Caracterización inmunohistoquímica del cáncer de mama correlacionado con histopatología,estudio realizado en un hospital de Ecuador
María Fernanda Calderón León, Diego Mauricio Cabrera Moyano, Jorge Daniel Cárdenas Rodríguez, Paula Andrea Vásquez Jaramillo, Andrea Alexandra Saltos Román, Maryoli González Sánchez
Journal of the Selva Andina Research Society.2025; 16(2): 116. CrossRef - Relationship of vitamin D receptor expression with hormone receptors and other clinicopathological features in primary breast carcinomas: A retrospective cross-sectional study
Yaşar Ünlü, Ethem Ömeroğlu, Abdülhalim Serden Ay, Meryem İlkay Eren Karanis, Kilinç Ayşe Nur Uğur, Esra Yilmaz
Medicine.2025; 104(35): e44222. CrossRef - Improving HER2 Diagnostics with Digital Real‐Time PCR for Ultrafast, Precise Prediction of Anti‐HER2 Therapy Response in Patients with Breast Cancer
Hee‐Joo Choi, Soo Young Park, Minsik Song, Jinhyuk Chang, YoonSik Kim, Hosub Park, Chihwan David Cha, Sohyeon Yang, Nam Hun Heo, Min Ji Song, Da Sol Kim, Hayeon Kim, Minuk Kim, Jae Eun Park, Yesung Lee, EunChae Ji, Heekyoung Chung, Ilecheon Jeong, Mineui
Small Methods.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Unveiling Metabolic Signatures as Potential Biomarkers in Common Cancers: Insights from Lung, Breast, Colorectal, Liver, and Gastric Tumours
Kha Wai Hon, Rakesh Naidu
Biomolecules.2025; 15(10): 1376. CrossRef - Validation of ancillary procedures on formalin liquid fixed aspiration cytologic samples: from minimum to maximum
Orsolya Rideg, Tímea Dergez, Arnold Tóth, Tamás Tornóczky, Gábor Pavlovics, Endre Kálmán
American Journal of Clinical Pathology.2025; 164(6): 924. CrossRef - Challenges & recommendations for identification of human epidermal growth factor receptor -2 (HER2)-low metastatic breast cancer in India: Expert opinion statement
Neeraj Arora, Jyoti Bajpai, Amanjit Bal, Atul Batra, Anurag Gupta, Deepak Kumar Mishra, Geetashree Mukherjee, Trupti Pai, Mayur Parihar, Geeta V. Patil Okaly, Shilpa Prabhudesai, Milap Shah, Somashekhar S.P.
The Indian Journal of Medical Research.2025; 162: 279. CrossRef - Eine immunhistologische Charakterisierung des Basalzellkarzinoms bei Patienten unter 40 Jahren
Vincent Waller, Myriam Boeschen, Thomas Lingscheidt, Mathias Stiller, Lena Eickenscheidt, Thomas Wilhelm, Sonja Grunewald, Mirjana Ziemer, Jan‐Christoph Simon, Hendrik Bläker, Maximilian von Laffert
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2025; 23(11): 1414. CrossRef - Comparison of Immunohistochemical 2 (+) HER2 Gene Status with SISH in Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Alper Sayiner, Hatice Karaman, Fatma Şenel, Arzu Tasdemir, Merve Doğan, İpek Özer
Sakarya Medical Journal.2025; 15(4): 338. CrossRef - Concurrent genomic assessment of circulating tumour cells and ctDNA to guide therapy in metastatic breast cancer
Rebecca C. Allsopp, Karen Page, Evie Wren, Georgios Nteliopoulos, Kelly L. T. Gleason, Gurdeep Matharu Lall, Shradha Bhagani, Emmanuel Acheampong, Marc K. Wadsley, Raoul Charles Coombes, Jacqueline A. Shaw
BMC Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management Strategies and Outcomes in HR+/HER2− Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving CDK4/6 Inhibitors and Subsequent Therapies
Katarzyna Pogoda, Hubert Pawlik, Anna Balata, Magdalena Czopowicz, Agata Bak, Iwona Twardowska, Malgorzata Meluch, Maria Wojda, Agnieszka Mlodzinska, Ewa Szombara, Renata Sienkiewicz, Aleksandra Konieczna, Elzbieta Brewczynska, Izabela Lemanska, Anna Majs
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2025; Volume 17: 1307. CrossRef - Identification of novel chemical scaffolds against kinase domain of cancer causing human epidermal growth factor receptor 2: a systemic chemoinformatic approach
Faris Alrumaihi
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; 42(12): 6269. CrossRef - Standardized pathology report for HER2 testing in compliance with 2023 ASCO/CAP updates and 2023 ESMO consensus statements on HER2-low breast cancer
Mariia Ivanova, Francesca Maria Porta, Marianna D’Ercole, Carlo Pescia, Elham Sajjadi, Giulia Cursano, Elisa De Camilli, Oriana Pala, Giovanni Mazzarol, Konstantinos Venetis, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Giuseppe Curigliano, Giuseppe Viale, Nicola Fusco
Virchows Archiv.2024; 484(1): 3. CrossRef - Analytical Performance Evaluation of a 523-Gene Circulating Tumor DNA Assay for Next-Generation Sequencing–Based Comprehensive Tumor Profiling in Liquid Biopsy Samples
Johannes Harter, Eleonora Buth, Janina Johaenning, Florian Battke, Maria Kopp, Henning Zelba, Martin Schulze, Jiri Koedding, Saskia Biskup
The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics.2024; 26(1): 61. CrossRef - Are There More HER2 FISH in the Sea? An Institution’s Experience in Identifying HER2 Positivity Using Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization in Patients with HER2 Negative Immunohistochemistry
Camille Suydam, Fairouz Chibane, Nicole Brown, Madeleine Schlafly, Alicia H. Arnold, Intisar Ghleilib, Melissa Easley, Joseph White
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 376. CrossRef - HER2 copy number determination in breast cancer using the highly sensitive droplet digital PCR method
Beate Alinger-Scharinger, Cornelia Kronberger, Georg Hutarew, Wolfgang Hitzl, Roland Reitsamer, Klaassen-Federspiel Frederike, Martina Hager, Thorsten Fischer, Karl Sotlar, Heidi Jaksch-Bogensperger
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(1): 53. CrossRef - Impact of HER2-low status for patients with early-stage breast cancer and non-pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a National Cancer Database Analysis
Huiyue Li, Jennifer K. Plichta, Kan Li, Yizi Jin, Samantha M. Thomas, Fei Ma, Li Tang, Qingyi Wei, You-Wen He, Qichen Chen, Yuanyuan Guo, Yueping Liu, Jian Zhang, Sheng Luo
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 204(1): 89. CrossRef - Qualification of a multiplexed tissue imaging assay and detection of novel patterns of HER2 heterogeneity in breast cancer
Jennifer L. Guerriero, Jia-Ren Lin, Ricardo G. Pastorello, Ziming Du, Yu-An Chen, Madeline G. Townsend, Kenichi Shimada, Melissa E. Hughes, Siyang Ren, Nabihah Tayob, Kelly Zheng, Shaolin Mei, Alyssa Patterson, Krishan L. Taneja, Otto Metzger, Sara M. Tol
npj Breast Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Utility and Benefits of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Cancer
Melissa Yuwono Tjota, Jeremy P Segal, Peng Wang
The Journal of Applied Laboratory Medicine.2024; 9(1): 76. CrossRef - High contrast breast cancer biomarker semi-quantification and immunohistochemistry imaging using upconverting nanoparticles
Sanathana Konugolu Venkata Sekar, Hui Ma, Katarzyna Komolibus, Gokhan Dumlupinar, Matthias J. Mickert, Krzysztof Krawczyk, Stefan Andersson-Engels
Biomedical Optics Express.2024; 15(2): 900. CrossRef - HER2-low breast cancer and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a population-based cohort study
Ximena Baez-Navarro, Mieke R. van Bockstal, Agnes Jager, Carolien H.M. van Deurzen
Pathology.2024; 56(3): 334. CrossRef - Fast-tracking drug development with biomarkers and companion diagnostics
Noreen McBrearty, Devika Bahal, Suso Platero
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging Landscape of Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancers With Low Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Protein Expression
Gary Tozbikian, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Marilyn M. Bui, Michael Feldman, David G. Hicks, Shabnam Jaffer, Thaer Khoury, Shi Wei, Hannah Wen, Paula Pohlmann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(2): 242. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns and Health Outcomes among Patients with HER2 IHC0/-Low Metastatic or Recurrent Breast Cancer
Eliya Farah, Chantelle Carbonell, Devon J. Boyne, Darren R. Brenner, Jan-Willem Henning, Daniel Moldaver, Simran Shokar, Winson Y. Cheung
Cancers.2024; 16(3): 518. CrossRef - Clinical Internal Dosimetry and Biodistribution of 177Lu-DOTA-Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Metastatic and Locally Advanced Breast Carcinoma
Yoga S. Narwadkar, Rahul V. Parghane, Sudeep Sahu, Sangita Lad, Kamal Deep, Gaurav Wanage, Tejal Suralkar, Sharmila Banerjee, Sudeep Gupta, Sandip Basu, Rajendra A. Badwe
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2024; 49(4): e149. CrossRef - Molecular Classifications in Gastric Cancer: A Call for Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Cristina Díaz del Arco, María Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Luis Ortega Medina
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2649. CrossRef - The combined immunohistochemical expression of AMBRA1 and SQSTM1 identifies patients with poorly differentiated cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at risk of metastasis: A proof of concept study
Michael H. Alexander, William J. Cousins, Tom Ewen, Andrew P. South, Penny Lovat, Niki Stefanos
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2024; 51(6): 450. CrossRef - Concordance between pathologists and between specimen types in detection of HER2-low breast carcinoma by immunohistochemistry
Jing Wang, Esther Yoon, Savitri Krishnamurthy
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2024; 70: 152288. CrossRef - Detection of HER2 expression using 99mTc-NM-02 nanobody in patients with breast cancer: a non-randomized, non-blinded clinical trial
Lingzhou Zhao, Yan Xing, Changcun Liu, Shaofei Ma, Wenhua Huang, Zhen Cheng, Jinhua Zhao
Breast Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pyrotinib and Trastuzumab Plus Chemotherapy Serve as an Acceptable Neoadjuvant Regimen Exhibiting Good Efficacy and Tolerance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients
Yibo Chen, Tianyi Zhang, Rui Zhang, Xuchen Cao
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2024; 39(6): 435. CrossRef - Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of VEGF, PDGF-B, and HER2/neu expression in gallbladder cancer
Pooja Shukla, Kumudesh Mishra, Ratnakar Shukla, Ruchira Vishwakarma, Niraj Kumari, Narendra Krishnani, Anu Behari, Vinay K. Kapoor
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2024; 20(1): 349. CrossRef - Open questions, current challenges, and future perspectives in targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-low breast cancer
G. Curigliano, R. Dent, H. Earle, S. Modi, P. Tarantino, G. Viale, S.M. Tolaney
ESMO Open.2024; 9(4): 102989. CrossRef - Concordance of HER2 status between core needle biopsy and surgical resection specimens of breast cancer: an analysis focusing on the HER2-low status
Sei Na, Milim Kim, Yujun Park, Hyun Jung Kwon, Hee-Chul Shin, Eun-Kyu Kim, Mijung Jang, Sun Mi Kim, So Yeon Park
Breast Cancer.2024; 31(4): 705. CrossRef - Impact of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) on Biomarker Expression in Breast Cancer
Suji Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, So Jeong Lee, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Kyung Bin Kim, Jung Hee Lee, Dong Hoon Shin, Kyung Un Choi, Chang Hun Lee, Gi Yeong Huh, Ahrong Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(5): 737. CrossRef - Clinical Use of Molecular Biomarkers in Canine and Feline Oncology: Current and Future
Heike Aupperle-Lellbach, Alexandra Kehl, Simone de Brot, Louise van der Weyden
Veterinary Sciences.2024; 11(5): 199. CrossRef - Clinical Validation of Artificial Intelligence–Powered PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score Interpretation for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response Prediction in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
Hyojin Kim, Seokhwi Kim, Sangjoon Choi, Changhee Park, Seonwook Park, Sergio Pereira, Minuk Ma, Donggeun Yoo, Kyunghyun Paeng, Wonkyung Jung, Sehhoon Park, Chan-Young Ock, Se-Hoon Lee, Yoon-La Choi, Jin-Haeng Chung
JCO Precision Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor amplification correlates with adverse pathological features and poor clinical outcome in colorectal cancer
Qiu-Xiao Yu, Ping-Ying Fu, Chi Zhang, Li Li, Wen-Ting Huang
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2024; 16(5): 1395. CrossRef - Lipid nanoparticles-based RNA therapies for breast cancer treatment
Luigia Serpico, Yuewen Zhu, Renata Faria Maia, Sumedha Sumedha, Mohammad-Ali Shahbazi, Hélder A. Santos
Drug Delivery and Translational Research.2024; 14(10): 2823. CrossRef - Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status in breast cancer: practice points and challenges
Natthawadee Laokulrath, Mihir Gudi, Syed Ahmed Salahuddin, Angela Phek Yoon Chong, Cristine Ding, Jabed Iqbal, Wei Qiang Leow, Benjamin Yongcheng Tan, Gary Tse, Emad Rakha, Puay Hoon Tan
Histopathology.2024; 85(3): 371. CrossRef - Comprehensive Immunohistochemical Analysis of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Biomarkers in the Invasive Micropapillary Cancer of the Breast
Ozden Oz, Funda Alkan Tasli, Resmiye Irmak Yuzuguldu, Baha Zengel, Demet Kocatepe Cavdar, Merih Guray Durak, Raika Durusoy, Pranshu Sahgal
International Journal of Breast Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancing HER2-low breast cancer management: enhancing diagnosis and treatment strategies
Simona Borstnar, Ivana Bozovic-Spasojevic, Ana Cvetanovic, Natalija Dedic Plavetic, Assia Konsoulova, Erika Matos, Lazar Popovic, Savelina Popovska, Snjezana Tomic, Eduard Vrdoljak
Radiology and Oncology.2024; 58(2): 258. CrossRef - Peer‐to‐peer validation of Ki‐67 scoring in a pathology quality circle as a tool to assess interobserver variability: are we better than we thought?
Marit Bernhardt, Leonie Weinhold, Christine Sanders, Oliver Hommerding, Jan‐Frederic Lau, Marieta Toma, Verena Tischler, Matthias Schmid, Tomasz Zienkiewicz, Ralf Hildenbrand, Peter Gerlach, Hui Zhou, Martin Braun, Gunnar Müller, Erich Sieber, Christian M
APMIS.2024; 132(10): 718. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Expression of Cyclin D1 and p16 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Association with Clinicopathological Parameters
Shaivy Malik, Shakthivel V., Sana Ahuja, Charanjeet Ahluwalia
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(4): 864. CrossRef - Novel engineered HER2 specific recombinant protein nanocages for targeted drug delivery
Javad Kheshti, Mohammad Ahmadyousefi, Meysam Soleimani
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating C-reactive protein levels as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer across body mass index groups
J. B. Holm, E. Baggesen, D. Cronin-Fenton, J. Frystyk, J. M. Bruun, P. Christiansen, S. Borgquist
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Standardized molecular pathology workflow for ctDNA-based ESR1 testing in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer
Elena Guerini-Rocco, Konstantinos Venetis, Giulia Cursano, Eltjona Mane, Chiara Frascarelli, Francesco Pepe, Mariachiara Negrelli, Edoardo Olmeda, Davide Vacirca, Alberto Ranghiero, Dario Trapani, Carmen Criscitiello, Giuseppe Curigliano, Christian Rolfo,
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2024; 201: 104427. CrossRef - The differences between pure and mixed invasive micropapillary breast cancer: the epithelial–mesenchymal transition molecules and prognosis
Ozden Oz, Resmiye Irmak Yuzuguldu, Ayse Yazici, Demet Kocatepe Cavdar, Cengiz Yilmaz, Mucteba Ozturk, Hilal Duzel, Duygu Gurel
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2024; 208(1): 41. CrossRef - Best practices for achieving consensus in HER2‐low expression in breast cancer: current perspectives from practising pathologists
Gary Tozbikian, Marilyn M. Bui, David G Hicks, Shabnam Jaffer, Thaer Khoury, Hannah Y Wen, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Shi Wei
Histopathology.2024; 85(3): 489. CrossRef - Consensus Guidelines on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-Low Testing in Breast Cancer in Malaysia
Pathmanathan Rajadurai, Sarala Ravindran, Bang Rom Lee, Suria Hayati Md Pauzi, Seow Fan Chiew, Kean Hooi Teoh, Navarasi S. Raja Gopal, Mastura Md Yusof, Cheng Har Yip
Cancers.2024; 16(13): 2325. CrossRef - Revolutionizing Pathology with Artificial Intelligence: Innovations in Immunohistochemistry
Diana Gina Poalelungi, Anca Iulia Neagu, Ana Fulga, Marius Neagu, Dana Tutunaru, Aurel Nechita, Iuliu Fulga
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(7): 693. CrossRef - Interobserver Variability in HER‐2 Immunostaining Interpretation of Metastatic HER2 Low Breast Cancers in Cytology Specimens
Niyati Desai, Courtney F. Connelly, Simon Sung, Adela Cimic, Swikrity U. Baskota
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(12): 722. CrossRef - Weakly-supervised deep learning models enable HER2-low prediction from H &E stained slides
Renan Valieris, Luan Martins, Alexandre Defelicibus, Adriana Passos Bueno, Cynthia Aparecida Bueno de Toledo Osorio, Dirce Carraro, Emmanuel Dias-Neto, Rafael A. Rosales, Jose Marcio Barros de Figueiredo, Israel Tojal da Silva
Breast Cancer Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the spectrum of HER2 status in breast cancer: From HER2-positive to ultra-low HER2
Sana Ahuja, Adil Aziz Khan, Sufian Zaheer
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 262: 155550. CrossRef - Systematic review of added immunotherapy in traditional treatment for HER2 positive breast cancer patients
Rohan Choudhari
Innovative Practice in Breast Health.2024; 3-4: 100013. CrossRef - Detecting early-stage breast cancer with GATA3-positive circulating tumor cells
Chun-Hsin Hsieh, Ya-Herng Chang, Pei-Ying Ling, Ying-Tai Jin, Pei-Hsuan Lo, Hei-Jen Jou
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2024; 63(5): 745. CrossRef - First-in-human study of DP303c, a HER2-targeted antibody-drug conjugate in patients with HER2 positive solid tumors
Jian Zhang, Yiqun Du, Yanchun Meng, Xiaojun Liu, Yuxin Mu, Yunpeng Liu, Yehui Shi, Jufeng Wang, Aimin Zang, Shanzhi Gu, Tianshu Liu, Huan Zhou, Hongqian Guo, Silong Xiang, Xialu Zhang, Suqiong Wu, Huanhuan Qi, Mengke Li, Xichun Hu
npj Precision Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting CD276 for T cell-based immunotherapy of breast cancer
Ilona Hagelstein, Laura Wessling, Alexander Rochwarger, Latifa Zekri, Boris Klimovich, Christian M. Tegeler, Gundram Jung, Christian M. Schürch, Helmut R. Salih, Martina S. Lutz
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Androgen Receptor Expression With Ki67 Proliferative Index and Other Clinicopathological Characteristics in Invasive Mammary Carcinomas
D Keerthana Devi, V Pavithra, Leena D Joseph, Chithra Bhanu Challa
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CD81-guided heterologous EVs present heterogeneous interactions with breast cancer cells
Elena Gurrieri, Giulia Carradori, Michela Roccuzzo, Michael Pancher, Daniele Peroni, Romina Belli, Caterina Trevisan, Michela Notarangelo, Wen-Qiu Huang, Agata S. A. Carreira, Alessandro Quattrone, Guido Jenster, Timo L. M. Ten Hagen, Vito Giuseppe D’Agos
Journal of Biomedical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Deciphering HER2-low breast cancer (BC): insights from real-world data in early stage breast cancer
Anna Pous, Adrià Bernat-Peguera, Assumpció López-Paradís, Beatriz Cirauqui, Vanesa Quiroga, Iris Teruel, Eudald Felip, Angelica Ferrando-Díez, Milana Bergamino, Laia Boronat, Margarita Romeo, Gemma Soler, Christian Mariño, Paula Rodríguez-Martínez, Laura
Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy-based technologies: a promising tool for biomarker identification in her2-low breast cancer patients for improved therapeutic outcomes
Aldo D’Alessandro, Anca Florentina Deaconu, Sandro Mandolesi, Federico Pio Fabrizio, Massimo Lombardi, Giovanna Liguori, Giovanni Pepe, Nicola Marino, Aureliano Stingi, Alessandro D’Alessandro, Antonio Giordano
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - SPP1 mRNA Expression Is Associated with M2 Macrophage Infiltration and Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Yu-Chia Chen, Chia-Ching Chen, Rong-Fu Chen, Hsin-Hung Chen, Po-Ming Chen
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2024; 46(12): 13499. CrossRef - MicroRNAs and their role in breast cancer metabolism (Review)
Wen Lee, Bann Yeo, Rozi Mahmud, Geok Tan, Mohamed Wahid, Yoke Cheah
International Journal of Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - CDH1 methylation and expression of E-cadherin and other markers in breast cancer
Luiz Fernando de Queiroz, Marcelo Soares da Mota e Silva, Fernando Colonna Rosman, Siane Lopes Bittencourt Rosas, Heitor Siffert Pereira de Souza, Maria da Glória da Costa Carvalho
Mastology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical Management of the Axilla in HR+/HER2– Breast Cancer in the Z1071 Era: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of the National Cancer Database
Vayda R. Barker, Samer A. Naffouje, Melissa A. Mallory, Susan A. Hoover, Christine Laronga
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(13): 8371. CrossRef - Noninvasive identification of HER2-low-positive status by MRI-based deep learning radiomics predicts the disease-free survival of patients with breast cancer
Yuan Guo, Xiaotong Xie, Wenjie Tang, Siyi Chen, Mingyu Wang, Yaheng Fan, Chuxuan Lin, Wenke Hu, Jing Yang, Jialin Xiang, Kuiming Jiang, Xinhua Wei, Bingsheng Huang, Xinqing Jiang
European Radiology.2023; 34(2): 899. CrossRef - Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
Lan Deng, Le Zhao, Lifen Liu, Haomin Huang
Open Life Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HER2-low expression in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors
B. Uzunparmak, C. Haymaker, G. Raso, S. Masciari, L. Wang, H. Lin, A. Gorur, B. Kirby, A.-M. Cimo, A. Kennon, Q. Ding, G. Urschel, Y. Yuan, G. Feng, Y. Rizvi, A. Hussain, C. Zhu, P. Kim, G. Abbadessa, V. Subbiah, T.A. Yap, J. Rodon, S.A. Piha-Paul, F. Mer
Annals of Oncology.2023; 34(11): 1035. CrossRef - Data on 2D culture characterisation of potential markers in human HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines
Son H. Pham, Lyn R. Griffiths, Rachel K. Okolicsanyi, Larisa M. Haupt
Data in Brief.2023; 46: 108880. CrossRef - Determining HER2 Status by Artificial Intelligence: An Investigation of Primary, Metastatic, and HER2 Low Breast Tumors
Christiane Palm, Catherine E. Connolly, Regina Masser, Barbara Padberg Sgier, Eva Karamitopoulou, Quentin Simon, Beata Bode, Marianne Tinguely
Diagnostics.2023; 13(1): 168. CrossRef - Gene amplification mutations originate prior to selective stress in Acinetobacter baylyi
Jennifer A Herrmann, Agata Koprowska, Tesa J Winters, Nancy Villanueva, Victoria D Nikityuk, Feini Pek, Elizabeth M Reis, Constancia Z Dominguez, Daniel Davis, Eric McPherson, Staci R Rocco, Cynthia Recendez, Shyla M Difuntorum, Kelly Faeth, Mario D Lopez
G3.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Flow Rate-Independent Multiscale Liquid Biopsy for Precision Oncology
Jie Wang, Robert Dallmann, Renquan Lu, Jing Yan, Jérôme Charmet
ACS Sensors.2023; 8(3): 1200. CrossRef - Single-cell HER2 quantification via instant signal amplification in microdroplets
Xiaoxian Liu, Yifan Zhu, Caoxin Li, Yanyun Fang, Jinna Chen, Fei Xu, Yanqing Lu, Perry Ping Shum, Ying Liu, Guanghui Wang
Analytica Chimica Acta.2023; 1251: 340976. CrossRef - Molecular imaging of HER2 receptor: Targeting HER2 for imaging and therapy in nuclear medicine
Daniela Miladinova
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CORRELATION BETWEEN DIFFERENT CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF FEMALE BREAST CARCINOMA IN SOUTH REGION OF IRAQ
Yassir Alaa Muhammed Hassan Shubbar
Wiadomości Lekarskie.2023; 76(1): 97. CrossRef - Pathological identification of HER2-low breast cancer: Tips, tricks, and troubleshooting for the optimal test
Elham Sajjadi, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Elisa De Camilli, Oriana Pala, Giovanni Mazzarol, Konstantinos Venetis, Mariia Ivanova, Nicola Fusco
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective Effect of HER2 Gene Polymorphism rs24537331 in the Outcome of Canine Mammary Tumors
Ana Canadas-Sousa, Marta Santos, Patrícia Dias-Pereira
Animals.2023; 13(8): 1384. CrossRef - Can Patients with HER2-Low Breast Cancer Benefit from Anti-HER2 Therapies? A Review
Jin Wang, Dongying Liao, Xuemin Zhang, Changhong Miao, Kuang Chen
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 281. CrossRef - HER2 Low Breast Cancer: A New Subtype or a Trojan for Cytotoxic Drug Delivery?
Marina Popović, Tajana Silovski, Marija Križić, Natalija Dedić Plavetić
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 8206. CrossRef - HER2-Low Breast Cancer—Diagnostic Challenges and Opportunities for Insights from Ongoing Studies: A Podcast
Aditya Bardia, Giuseppe Viale
Targeted Oncology.2023; 18(3): 313. CrossRef - Histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of predictive and prognostic markers in spontaneous canine mammary cancer
Vladimír Tancoš, Marcel Kovalik, Martin Levkut, Martina Bobrovská, Petra Kolenčíková, Ľubomír Straka, Zuzana Ševčíková, Ondřej Škor, Martina Antošová, Lukáš Plank, Keith L. Thoday
Acta Veterinaria Brno.2023; 92(2): 143. CrossRef - Dissecting sources of variability in patient response to targeted therapy: anti-HER2 therapies as a case study
Timothy Qi, Yanguang Cao
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 186: 106467. CrossRef - The Effect of HER2-Low Status on Pathological Complete Response and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yakup Ergun, Baran Akagunduz, Cengiz Karacin, Sema Turker, Gokhan Ucar
Clinical Breast Cancer.2023; 23(6): 567. CrossRef - Efficacy, toxicity and prognostic factors of pyrotinib‑involved neoadjuvant therapy in HER2‑positive breast cancer: A retrospective study
Hao Wang, Hailing Cao, Zhiyun Guo
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer
Feng Ye, Saikat Dewanjee, Yuehua Li, Niraj Kumar Jha, Zhe-Sheng Chen, Ankush Kumar, Vishakha, Tapan Behl, Saurabh Kumar Jha, Hailin Tang
Molecular Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weakly supervised bilayer convolutional network in segmentation of HER2 related cells to guide HER2 targeted therapies
Ching-Wei Wang, Kun-Lin Lin, Hikam Muzakky, Yi-Jia Lin, Tai-Kuang Chao
Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics.2023; 108: 102270. CrossRef - Immune Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving the Predictivity of Current Testing Methods
Francesca Maria Porta, Elham Sajjadi, Konstantinos Venetis, Chiara Frascarelli, Giulia Cursano, Elena Guerini-Rocco, Nicola Fusco, Mariia Ivanova
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(7): 1176. CrossRef - HER2 Equivocal (Score = 2+) Breast Carcinoma Cases Identified by Immunohistochemistry at a South African Hospital. What is the Impact of Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Testing?
Reena Dhansukh Mohanlal, Nikki Bouwer, Pascale Willem
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2023; 31(8): 555. CrossRef - Discordance of HER2 Expression and/or Amplification on Repeat Testing
Timothy P. DiPeri, Kathleen Kong, Kaushik Varadarajan, Daniel D. Karp, Jaffer A. Ajani, Shubham Pant, Michael F. Press, Sarina A. Piha-Paul, Ecaterina E. Dumbrava, Funda Meric-Bernstam
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2023; 22(8): 976. CrossRef - Low and Ultra-Low HER2 in Human Breast Cancer: An Effort to Define New Neoplastic Subtypes
Mariausilia Franchina, Cristina Pizzimenti, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Maurizio Martini, Giuseppina Rosaria Rita Ricciardi, Nicola Silvestris, Antonio Ieni, Giovanni Tuccari
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12795. CrossRef - Genetic analysis of oligo-recurrence breast cancer: correlation with clinical outcomes
Kuikui Jiang, Danyang Zhou, Fei Xu, Wen Xia, Qiufan Zheng, Qianyi Lu, Rongzhen Luo, Ruoxi Hong, Shusen Wang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single domain antibodies specific for HER2 dimerization domain effectively disrupts HER2 dimerization
Ahmad Najafi, Reza Valadan, Hossein Asgarian-Omran, Alireza Rafiei, Mohsen Tehrani
International Immunopharmacology.2023; 124: 110999. CrossRef - Récepteur du facteur de croissance épidermique HER2, tests utilisés pour rechercher son amplification dans le cancer du sein : principes et limites
Imane Eliahiai, Mohammed Eljiar, Sanae Chaib, Jinane KHarmoum, Mariame Chraïbi
Bulletin du Cancer.2023; 110(12): 1301. CrossRef - Integrated Molecular Characterization of HER2-Low Breast Cancer Using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Jean-Louis Merlin, Marie Husson, Nassim Sahki, Pauline Gilson, Vincent Massard, Alexandre Harlé, Agnès Leroux
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3164. CrossRef - GLUCOSE LEVELS OF PLEURAL EFFUSION FLUID AND HER2 STATUS IN PLEURAL-METASTATIC BREAST CANCER
Muhammad Dhanny Irawan, Desak Gede Agung Suprabawati, Heru Purwanto
Majalah Biomorfologi.2023; 33(2): 75. CrossRef - Design of a Ratiometric Plasmonic Biosensor for Herceptin Detection in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Neda Shahbazi, Rouholah Zare-Dorabei, Seyed Morteza Naghib
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2022; 8(2): 871. CrossRef - A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
Mahdi Sadeghi, Soheila Kashanian, Seyed Morteza Naghib, Esfandyar Askari, Fateme Haghiralsadat, Davood Tofighi
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 793. CrossRef - Anti-HER2 therapy in metastatic breast cancer: many choices and future directions
Carrie S. Wynn, Shou-Ching Tang
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2022; 41(1): 193. CrossRef - Electroanalytical overview: screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms for the detection of vital cardiac, cancer and inflammatory biomarkers
Robert D. Crapnell, Alejandro Garcia-Miranda Ferrari, Nina C. Dempsey, Craig E. Banks
Sensors & Diagnostics.2022; 1(3): 405. CrossRef - FTO genotype was associated with breast cancer in HER2 negative patients
Fateme Montazeri, Hossein Hatami, Soroor Fathi, Naeemeh Hasanpour Ardekanizadeh, Fatemeh Bourbour, Samira Rastgoo, Fatemeh Shafiee, Mohammad Esmail Akbari, Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Seyed Alireza Mosavi Jarrahi, Saeid Doaei
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 49: 495. CrossRef - Breast Cancer Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 mRNA Molecular Testing Compared to Immunohistochemistry with Correlation to Neoadjuvant Therapy Response
Mahmoud Behairy, Samia Mohamed Gabal, Mohamed Sherif Negm
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 352. CrossRef - Validity and utility of HER2/ERBB2 copy number variation assessed in liquid biopsies from breast cancer patients: A systematic review
Noortje Verschoor, Teoman Deger, Agnes Jager, Stefan Sleijfer, Saskia M. Wilting, John W.M. Martens
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2022; 106: 102384. CrossRef - RETRACTED: Longitude Variation of the microRNA-497/FGF-23 Axis during Treatment and Its Linkage with Neoadjuvant/Adjuvant Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiotoxicity in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients
Hui Liu, Xiaoyan Hu, Lingyun Wang, Tao Du, Jing Feng, Ming Li, Lei Liu, Xiaofang Liu
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of Radionuclide-Based Imaging Methods in Breast Cancer
Betül Altunay, Agnieszka Morgenroth, Felix M. Mottaghy
Seminars in Nuclear Medicine.2022; 52(5): 561. CrossRef - Functional regulations between genetic alteration-driven genes and drug target genes acting as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
Li Wang, Lei Yu, Jian Shi, Feng Li, Caiyu Zhang, Haotian Xu, Xiangzhe Yin, Lixia Wang, Shihua Lin, Anastasiia Litvinova, Yanyan Ping, Shangwei Ning, Hongying Zhao
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 and endocrine resistance in hormone-dependent breast cancer
Anastasia Alataki, Mitch Dowsett
Endocrine-Related Cancer.2022; 29(8): R105. CrossRef - The Evolution of Targeted Radionuclide Diagnosis of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Olga D. Bragina, Sergei M. Deyev, Vladimir I. Chernov, Vladimir M. Tolmachev
Acta Naturae.2022; 14(2): 4. CrossRef - Deriving tumor purity from cancer next generation sequencing data: applications for quantitative ERBB2 (HER2) copy number analysis and germline inference of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
Stephanie E. Siegmund, Danielle K. Manning, Phani K. Davineni, Fei Dong
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(10): 1458. CrossRef - Current challenges and unmet needs in treating patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive advanced breast cancer
Matti Aapro, Fatima Cardoso, Giuseppe Curigliano, Alexandru Eniu, Joseph Gligorov, Nadia Harbeck, Andreas Mueller, Olivia Pagani, Shani Paluch-Shimon, Elzbieta Senkus, Beat Thürlimann, Khalil Zaman
The Breast.2022; 66: 145. CrossRef - [Retracted] Application of Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Assisted by Fluorescence Microscope in Detection of Her2 Gene in Breast Cancer Patients
Fang Lu, Tingting Zhou, Yan Liu, Liying Song, Bin Zhang, Yuyan Li, Sorayouth Chumnanvej
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High sensitivity label-free detection of HER2 using an Al–GaN/GaN high electron mobility transistor-based biosensor
Shivanshu Mishra, Pharyanshu Kachhawa, Amber Kumar Jain, Rajiv Ranjan Thakur, Nidhi Chaturvedi
Lab on a Chip.2022; 22(21): 4129. CrossRef - Indian Data on HER2 Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in Invasive Breast Cancer with Immunohistochemically Equivocal Results As Per 2018 ASCO/CAP Guidelines
B. R. Nagarjun, Biren Parikh, Manaswi Nareshkumar Patel, Pina J. Trivedi, Dharmesh M. Patel
South Asian Journal of Cancer.2022; 11(04): 281. CrossRef - S‑phase fraction, lymph node status and disease staging as the main prognostic factors to differentiate between young and older patients with invasive breast carcinoma
António Pinto, João Matos, Teresa Pereira, Giovani Silva, Saudade André
Oncology Letters.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inferring tumor-specific cancer dependencies through integrating ex vivo drug response assays and drug-protein profiling
Alina Batzilla, Junyan Lu, Jarno Kivioja, Kerstin Putzker, Joe Lewis, Thorsten Zenz, Wolfgang Huber, James Gallo
PLOS Computational Biology.2022; 18(8): e1010438. CrossRef - Clinical possibilities of HER2-positive breast cancer diagnosis using alternative scaffold proteins
O. D. Bragina, V. I. Chernov, S. M. Deyev, V. M. Tolmachev
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2022; 21(3): 132. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Gastric Cancer
Moonsik Kim, An Na Seo
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2022; 22(4): 264. CrossRef - Loss of NECTIN1 triggers melanoma dissemination upon local IGF1 depletion
Julien Ablain, Amira Al Mahi, Harriet Rothschild, Meera Prasad, Sophie Aires, Song Yang, Maxim E. Dokukin, Shuyun Xu, Michelle Dang, Igor Sokolov, Christine G. Lian, Leonard I. Zon
Nature Genetics.2022; 54(12): 1839. CrossRef - Advanced diagnosis technologies for HER2 breast cancer markers
Mengxue Zhang
Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology.2022; 14: 44. CrossRef - An Overview of Clinical Development of Agents for Metastatic or Advanced Breast Cancer Without ERBB2 Amplification (HER2-Low)
Aleix Prat, Aditya Bardia, Giuseppe Curigliano, M. Elizabeth H. Hammond, Sibylle Loibl, Sara M. Tolaney, Giuseppe Viale
JAMA Oncology.2022; 8(11): 1676. CrossRef - Development of T-cell engagers selective for cells co-expressing two antigens
Danielle M. Dicara, Sunil Bhakta, Mary Ann Go, James Ziai, Ron Firestein, Bill Forrest, Chen Gu, Steven R. Leong, Genee Lee, Shang-Fan Yu, Andrew G. Polson, Nicholas J. Agard
mAbs.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The clinical significance of HER2 expression in DCIS
Ioanna Akrida, Francesk Mulita
Medical Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Breast Cancer: Spotlight on HER2
Rachel Occhiogrosso Abelman, Arielle Medford, Laura Spring, Aditya Bardia
The Cancer Journal.2022; 28(6): 423. CrossRef - The Clinical Utility of Droplet Digital PCR for Profiling Circulating Tumor DNA in Breast Cancer Patients
Ugur Gezer, Abel J. Bronkhorst, Stefan Holdenrieder
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3042. CrossRef - Lapatinib and lapatinib plus trastuzumab therapy versus trastuzumab therapy for HER2 positive breast cancer patients: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Ye Yuan, Xumei Liu, Yi Cai, Wenyuan Li
Systematic Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactions dietary components with expression level of breast cancer-related genes
Fatemeh Bourbour, Azam Pourtaheri, Khadijeh Abbasi, Naeemeh Hasanpour Ardekanizadeh, Maryam Gholamalizadeh, Azadeh Hajipour, Sepideh Abdollahi, Seyedeh Elaheh Bagheri, Mina Ahmadzadeh, Saeid Doaei, Arezoo Haghighian
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HER2-directed antibodies, affibodies and nanobodies as drug-delivery vehicles in breast cancer with a specific focus on radioimmunotherapy and radioimmunoimaging
Betül Altunay, Agnieszka Morgenroth, Mohsen Beheshti, Andreas Vogg, Nicholas C. L. Wong, Hong Hoi Ting, Hans-Jürgen Biersack, Elmar Stickeler, Felix M. Mottaghy
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2021; 48(5): 1371. CrossRef - Risk-based decision-making in the treatment of HER2-positive early breast cancer: Recommendations based on the current state of knowledge
Christian Jackisch, Patricia Cortazar, Charles E. Geyer, Luca Gianni, Joseph Gligorov, Zuzana Machackova, Edith A. Perez, Andreas Schneeweiss, Sara M. Tolaney, Michael Untch, Andrew Wardley, Martine Piccart
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2021; 99: 102229. CrossRef - Histologic Patterns of Cutaneous Metastases of Breast Carcinoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 232 Cases
Shira Ronen, David Suster, Wei-Shen Chen, Natali Ronen, Sri Krishna C. Arudra, Celestine Trinidad, Doina Ivan, Victor G. Prieto, Saul Suster
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2021; 43(6): 401. CrossRef - Standardized pathology report for breast cancer
Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(1): 1. CrossRef - The impact of oral contraceptive use on breast cancer risk: State of the art and future perspectives in the era of 4P medicine
R. Bonfiglio, M.L. Di Pietro
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2021; 72: 11. CrossRef - The Co-Expression of Melanoma-Antigen Family a Proteins and New York Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma-1 in Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study
Yu-Xin Wang, Feng-Lian Li, Li-Xin Du, Jun-Fang Liu, Li-Gang Huo, Shu-Qing Li, Bin Tian
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 6123. CrossRef - Targeting HER2 protein in individual cells using ICP-MS detection and its potential as prognostic and predictive breast cancer biomarker
A. Fernández Asensio, M. Corte-Rodríguez, J. Bettmer, L.M. Sierra, M. Montes-Bayón, E. Blanco- González
Talanta.2021; 235: 122773. CrossRef - Development of a 99mTc-Labeled Single-Domain Antibody for SPECT/CT Assessment of HER2 Expression in Breast Cancer
Lingzhou Zhao, Changcun Liu, Yan Xing, Jin He, Jim O’Doherty, Wenhua Huang, Jinhua Zhao
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2021; 18(9): 3616. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Nouvelles stratégies thérapeutiques dans les cancers du sein HER2-surexprimé
Benoîte Mery, Philippe Toussaint, Pierre-Etienne Heudel, Armelle Dufresne, Mélodie Carbonnaux, Hélène Vanacker, Thomas Bachelot, Olivier Trédan
Bulletin du Cancer.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective observational study of HER2 immunohistochemistry in borderline breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy, with an emphasis on Group 2 (HER2/CEP17 ratio ≥2.0, HER2 copy number <4.0 signals/cell) cases
Emad A. Rakha, Islam M. Miligy, Cecily M. Quinn, Elena Provenzano, Abeer M. Shaaban, Caterina Marchiò, Michael S. Toss, Grace Gallagy, Ciara Murray, Janice Walshe, Ayaka Katayama, Karim Eldib, Nahla Badr, Bruce Tanchel, Rebecca Millican-Slater, Colin Purd
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 124(11): 1836. CrossRef - Loss of HER2‐positivity following neoadjuvant targeted therapy for breast cancer is not associated with inferior oncologic outcomes
Catherine L. Wetzel, Thomas L. Sutton, Stuart Gardiner, Maryam Farinola, Nathalie Johnson, Jennifer R. Garreau
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2021; 124(8): 1224. CrossRef - Clinical and Genetic Predictive Models for the Prediction of Pathological Complete Response to Optimize the Effectiveness for Trastuzumab Based Chemotherapy
Lun Li, Min Chen, Shuyue Zheng, Hanlu Li, Weiru Chi, Bingqiu Xiu, Qi Zhang, Jianjing Hou, Jia Wang, Jiong Wu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - tRNA‐derived fragments: tRF‐Gly‐CCC‐046, tRF‐Tyr‐GTA‐010 and tRF‐Pro‐TGG‐001 as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer
Yue Zhang, Zhao Bi, Xiaohan Dong, Miao Yu, Kangyu Wang, Xingguo Song, Li Xie, Xianrang Song
Thoracic Cancer.2021; 12(17): 2314. CrossRef - Detection of secondary metastatic breast cancer by measurement of plasma CA 15.3
L. De Cock, J. Heylen, A. Wildiers, K. Punie, A. Smeets, C. Weltens, P. Neven, J. Billen, A. Laenen, H. Wildiers
ESMO Open.2021; 6(4): 100203. CrossRef - Standardized Pathology Report for Breast Cancer
Soo Youn Cho, So Yeon Park, Young Kyung Bae, Jee Yeon Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Youngmee Kwon, Ahwon Lee, Hee Jin Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Jee Young Park, Gyungyub Gong, Hye Kyoung Yoon
Journal of Breast Cancer.2021; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Circular RNA circ-ERBB2 promotes HER2-positive breast cancer progression and metastasis via sponging miR-136-5p and miR-198
Jin-xiu Zhong, Yun-yuan Kong, Rong-guang Luo, Guo-jin Xia, Wen-xing He, Xue-zhong Chen, Wei-wei Tan, Qing-jie Chen, Yu-yin Huang, Yan-xing Guan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nouvelles stratégies thérapeutiques dans les cancers du sein HER2-surexprimé
Benoîte Mery, Philippe Toussaint, Pierre-Etienne Heudel, Armelle Dufresne, Mélodie Carbonnaux, Hélène Vanacker, Thomas Bachelot, Olivier Trédan
Bulletin du Cancer.2021; 108(11): 11S8. CrossRef - Association of Estrogen and Progesterone Receptors with Clinicopathological Prognostic Factors in Breast Cancer
Ali Abdul Hadi Abdul-Kareem, Qahtan A. Mahdi
Medical Journal of Babylon.2021; 18(2): 111. CrossRef - HER2 alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer – Druggable or undruggable?
Suresh Kumar Bondili, Ravindra Nandhana, Vanita Noronha, Swayamprabha Pawar, Nandini Menon, Omshree Shetty, Anuradha Chougule, Abhishek Mahajan, Rajiv Kumar, Vijay M. Patil, Amit Joshi, Kumar Prabhash
Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment.2021; 4(2): 374. CrossRef - UCNP-based Photoluminescent Nanomedicines for Targeted Imaging and Theranostics of Cancer
Evgenii L. Guryev, Anita S. Smyshlyaeva, Natalia Y. Shilyagina, Evgeniya A. Sokolova, Samah Shanwar, Alexey B. Kostyuk, Alexander V. Lyubeshkin, Alexey A. Schulga, Elena V. Konovalova, Quan Lin, Indrajit Roy, Irina V. Balalaeva, Sergey M. Deyev, Andrei V.
Molecules.2020; 25(18): 4302. CrossRef - Impact of the Updated Guidelines on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) Testing in Breast Cancer
Min Chong Kim, Su Hwan Kang, Jung Eun Choi, Young Kyung Bae
Journal of Breast Cancer.2020; 23(5): 484. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Model Outperformed the Single Radiomics Model in Noninvasively Predicting the HER2 Status in Patients with Breast Cancer
- Combined Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Neuroendocrine Carcinoma with Ectopic Secretion of Parathyroid Hormone: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Hyun Jung Kwon, Ji-Won Kim, Haeryoung Kim, YoungRok Choi, Soomin Ahn
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(4):232-237. Published online May 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.05.17
- 8,726 View
- 159 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary combined hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and neuroendocrine carcinoma is a rare entity, and so is hypercalcemia due to ectopic parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion by tumor. A 44-year old man with hepatitis B virus associated chronic liver disease presented with a hepatic mass. Hemihepatectomy discovered the mass as combined HCC and poorly differentiated cholangiocarcinoma. During adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, he presented with nausea, and multiple systemic metastases were found. Laboratory tests revealed hypercalcemia with markedly elevated PTH and neuron specific enolase. Parathyroid scan showed normal uptake in parathyroid glands, suggestive of ectopic PTH secretion. Subsequently, immunohistochemistry of neuroendocrine marker was performed on the primary lesion, and confirmed the neuroendocrine differentiation in non-HCC component. The patient died 71 days after surgery. This report may suggest the possibility of ectopic PTH secretion by neuroendocrine carcinoma of hepatic origin causing hypercalcemia. Caution for neuroendocrine differentiation should be exercised when diagnosing poorly differentiated HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mixed glandular neuroendocrine carcinoma of the endometrium with hypercalcemic crisis
Mei Luo, Xiaoxia Yu, Zhongpei Chen, Zhenhan Li
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2025; 369(2): 281. CrossRef - Combined Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma of the Liver: Systematic Literature Review Suggests Implementing Biological Characterization to Optimize Therapeutic Strategy
Daniela Sambataro, Sandro Bellavia, Paolo Di Mattia, Danilo Centonze, Carmela Emmanuele, Annalisa Bonasera, Giuseppe Caputo, Andrea Maria Onofrio Quattrocchi, Ernesto Vinci, Vittorio Gebbia, Maria Rosaria Valerio
Cancers.2025; 17(7): 1074. CrossRef - Surgical Resection of Primary Hepatic Mixed Neuroendocrine-Non-Neuroendocrine Neoplasm: A Report of Three Cases
Ryosuke Toyonaka, Osamu Aramaki, Nao Yoshida, Yusuke Mitsuka, Masanori Nakamura, Shu Inagaki, Kaiki Murai, Toshiyuki Ishige, Ryusuke Tsujimura, Sumie Ohni, Shinobu Masuda, Hiroharu Yamashita, Yukiyasu Okamura
The Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery.2025; 58(6): 331. CrossRef - Case report: mixed large-cell neuroendocrine and hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver
Xin Gao, Heng Wang, Zheyu Niu, Meng Liu, Xiaohan Kong, Hongrui Sun, Chaoqun Ma, Huaqiang Zhu, Jun Lu, Xu Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mixed Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Hepatic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Woo Young Shin, Keon Young Lee, Kyeong Deok Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(2): 418. CrossRef - Comparison of Metastatic Patterns Among Neuroendocrine Tumors, Neuroendocrine Carcinomas, and Nonneuroendocrine Carcinomas of Various Primary Organs
Hyung Kyu Park, Ghee Young Kwon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical characterization of a steroid-secreting oncocytic adrenal carcinoma responsible for paraneoplastic hyperparathyroidism
Magalie Haissaguerre, Estelle Louiset, Christofer C Juhlin, Adam Stenman, Christophe Laurent, Hélène Trouette, Hervé Lefebvre, Antoine Tabarin
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 188(4): K11. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the biliary tree, liver and pancreas: a pathological approach
Claudio Luchini, Giuseppe Pelosi, Aldo Scarpa, Paola Mattiolo, Deborah Marchiori, Roberta Maragliano, Fausto Sessa, Silvia Uccella
Pathologica.2021; 113(1): 28. CrossRef - Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Findings of Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Case Report
Hong Wang, Dan Yang, Zhenru Wu, Yan Luo, Wenwu Ling
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma: case report and literature review
Akira Nakano, Kenichi Hirabayashi, Hiroshi Yamamuro, Taro Mashiko, Yoshihito Masuoka, Seiichiro Yamamoto, Soji Ozawa, Toshio Nakagohri
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with renal dysfunction: Pathophysiology, prognosis, and treatment challenges
Hsuan Yeh, Chung-Cheng Chiang, Tzung-Hai Yen
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(26): 4104. CrossRef - Severe hypercalcaemia from ectopic intact parathyroid hormone secretion treated with continuous renal replacement therapy in a patient with two malignancies
Nathaniel Hocker, Maria Story, Alysa Lerud, Sarat Kuppachi
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(6): e242172. CrossRef - Parathyroid Carcinoma and Ectopic Secretion of Parathyroid hormone
Filomena Cetani, Elena Pardi, Claudio Marcocci
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2021; 50(4): 683. CrossRef - Primary hepatic neuroendocrine cancer coexisted with hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Chikara Ebisutani, Seitetsu Yoon, Toshiki Hyodo, Takafumi Watanabe, Hirofumi Okada, Yutaka Shirakawa, Yoshio Sakamoto, Shigeya Hirohata
Kanzo.2020; 61(3): 122. CrossRef - Two-in-one: A pooled analysis of primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma combined/collided with hepatocellular carcinoma
Jia-Xi Mao, Fei Teng, Ke-Yan Sun, Cong Liu, Guo-Shan Ding, Wen-Yuan Guo
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2020; 19(4): 399. CrossRef - Primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma coexisting with distal cholangiocarcinoma
Qi Xin, Rong Lv, Cheng Lou, Zhe Ma, Gui-Qiu Liu, Qin Zhang, Hai-Bo Yu, Chuan-Shan Zhang
Medicine.2020; 99(26): e20854. CrossRef - Mixed hepatocellular carcinoma-neuroendocrine carcinoma—A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge
Nusrat Jahan, Irfan Warraich, Edwin Onkendi, Sanjay Awasthi
Current Problems in Cancer: Case Reports.2020; 1: 100020. CrossRef
- Mixed glandular neuroendocrine carcinoma of the endometrium with hypercalcemic crisis
- The Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of the Gross Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Yangkyu Lee, Hyunjin Park, Hyejung Lee, Jai Young Cho, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Young-Rok Choi, Ho-Seong Han, Eun Sun Jang, Jin-Wook Kim, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Soomin Ahn, Haeryoung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):85-92. Published online November 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.11.13
- 14,741 View
- 389 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We aimed to determine the clinicopathological significance of the gross classification of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) according to the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) guidelines.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was performed on 242 cases of consecutively resected solitary primary HCC between 2003 and 2012 at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. The gross classification (vaguely nodular [VN], expanding nodular [EN], multinodular confluent [MC], nodular with perinodular extension [NP], and infiltrative [INF]) was reviewed for all cases, and were correlated with various clinicopathological features and the expression status of “stemness”-related (cytokeratin 19 [CK19], epithelial cell adhesion molecule [EpCAM]), and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)–related (urokinase plasminogen activator receptor [uPAR] and Ezrin) markers.
Results
Significant differences were seen in overall survival (p=.015) and disease-free survival (p = .034) according to the gross classification; INF type showed the worst prognosis while VN and EN types were more favorable. When the gross types were simplified into two groups, type 2 HCCs (MC/NP/INF) were more frequently larger and poorly differentiated, and showed more frequent microvascular and portal venous invasion, intratumoral fibrous stroma and higher pT stages compared to type 1 HCCs (EN/VN) (p<.05, all). CK19, EpCAM, uPAR, and ezrin expression was more frequently seen in type 2 HCCs (p<.05, all). Gross classification was an independent predictor of both overall and disease-free survival by multivariate analysis (overall survival: p=.030; hazard ratio, 4.118; 95% confidence interval, 1.142 to 14.844; disease-free survival: p=.016; hazard ratio, 1.617; 95% confidence interval, 1.092 to 2.394).
Conclusions
The gross classification of HCC had significant prognostic value and type 2 HCCs were associated with clinicopathological features of aggressive behavior, increased expression of “stemness”- and EMT-related markers, and decreased survival. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-Term Outcomes of Transarterial Chemoembolization plus Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Patients with Large BCLC Stage A/B HCC
Ying-Wen Hou, Tian-Qi Zhang, Li-Di Ma, Yi-Quan Jiang, Xue Han, Tian Di, Lu Tang, Rong-Ping Guo, Min-Shan Chen, Jin-Xin Zhang, Zhi-Mei Huang, Jin-Hua Huang
Academic Radiology.2025; 32(7): 3960. CrossRef - Membranous Overexpression of Fibronectin Predicts Microvascular Invasion and Poor Survival Outcomes in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Yoon Jung Hwang, Hyejung Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Su Jong Yu, Haeryoung Kim
Gut and Liver.2025; 19(2): 275. CrossRef - Association between tumor morphology and efficacy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Nobuaki Ishihara, Shohei Komatsu, Keitaro Sofue, Eisuke Ueshima, Yoshihiko Yano, Yoshimi Fujishima, Jun Ishida, Masahiro Kido, Hidetoshi Gon, Kenji Fukushima, Takeshi Urade, Hiroaki Yanagimoto, Hirochika Toyama, Yoshihide Ueda, Yuzo Kodama, Takamichi Mura
Hepatology Research.2024; 54(8): 773. CrossRef - Macroscopic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Underexploited Source of Prognostic Factors
Stéphanie Gonvers, Sebastiao Martins-Filho, André Hirayama, Julien Calderaro, Rebecca Phillips, Emilie Uldry, Nicolas Demartines, Emmanuel Melloul, Young Nyun Park, Valérie Paradis, Swan Thung, Venancio Alves, Christine Sempoux, Ismail Labgaa
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2024; Volume 11: 707. CrossRef - Serum Total Superoxide Dismutase Activity as a Predictive Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Yanqiu Xu, Bin Liu, Shiqing Cheng, Junguo Zhang, Xiue Cao, Yong Wang, Fang Luan
Hepatitis Monthly.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic value of expressions of cancer stem cell markers for adverse outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma and their associations with prognosis: A Bayesian network meta‑analysis
Zhengrong Ou, Shoushuo Fu, Jian Yi, Jingxuan Huang, Weidong Zhu
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease versus hepatitis B infection
Jungnam Lee, Jong-In Chang, Young-Joo Jin, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Ju Yeon Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Soon Sun Kim, Hyun Woong Lee, Sun Hong Yoo, Jung Hwan Yu, Jin-Woo Lee
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 35(4): 431. CrossRef - Comprehensive investigating of MMR gene in hepatocellular carcinoma with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Han Chinese population
Ning Ma, Ao Jin, Yitong Sun, Yiyao Jin, Yucheng Sun, Qian Xiao, XuanYi Sha, Fengxue Yu, Lei Yang, Wenxuan Liu, Xia Gao, Xiaolin Zhang, Lu Li
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - LI-RADS Morphological Type Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Radical Resection
Chunhui Zhang, Rui Yang, Xinxin Wang, Yuqing Tao, Shuli Tang, Zhennan Tian, Yang Zhou
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(8): 4876. CrossRef - From clinical variables to multiomics analysis: a margin morphology-based gross classification system for hepatocellular carcinoma stratification
Zhongqi Fan, Meishan Jin, Lei Zhang, Nanya Wang, Mingyue Li, Chuanlei Wang, Feng Wei, Ping Zhang, Xiaohong Du, Xiaodong Sun, Wei Qiu, Meng Wang, Hongbin Wang, Xiaoju Shi, Junfeng Ye, Chao Jiang, Jianpeng Zhou, Wengang Chai, Jun Qi, Ting Li, Ruoyan Zhang,
Gut.2023; 72(11): 2149. CrossRef - A clinical and pathological update on hepatocellular carcinoma
Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Luca Di Tommaso
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 14. CrossRef - An approach to grossing of hepatectomy specimens
Archana Rastogi
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2021; 64(5): 121. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma: a clinical and pathological overview
Salvatore Lorenzo Renne, Samantha Sarcognato, Diana Sacchi, Maria Guido, Massimo Roncalli, Luigi Terracciano, Luca Di Tommaso
Pathologica.2021; 113(3): 203. CrossRef - The Clinicopathological Significance of YAP/TAZ Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Relation to Hypoxia and Stemness
Hyunjin Park, Yangkyu Lee, Kiryang Lee, Hyejung Lee, Jeong Eun Yoo, Soomin Ahn, Young Nyun Park, Haeryoung Kim
Pathology and Oncology Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Adjuvant versus Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Clinical and Immunologic Perspectives
Yung-Yeh Su, Chia-Chen Li, Yih-Jyh Lin, Chiun Hsu
Seminars in Liver Disease.2021; 41(03): 263. CrossRef - Prognostic significance of viable tumor size measurement in hepatocellular carcinomas after preoperative locoregional treatment
Yoon Jung Hwang, Youngeun Lee, Hyunjin Park, Yangkyu Lee, Kyoungbun Lee, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2021; 55(5): 338. CrossRef - Survival according to recurrence patterns after resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma in HBV endemic area: Appraisal of liver transplantation strategy
Chung Gyo Seo, Sun Young Yim, Soon Ho Um, Yoo Ra Lee, Yoo Jin Lee, Tae Hyung Kim, Hyun Gil Goh, Young Sun Lee, Sang Jun Suh, Na Yeon Han, Hyuk Soon Choi, Eun Sun Kim, Bora Keum, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyung Joon Yim, Ji Hoon Kim, Dong Sik Kim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Hoon
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2020; 44(4): 532. CrossRef - A radiomics-based biomarker for cytokeratin 19 status of hepatocellular carcinoma with gadoxetic acid–enhanced MRI
Wentao Wang, Dongsheng Gu, Jingwei Wei, Ying Ding, Li Yang, Kai Zhu, Rongkui Luo, Sheng-Xiang Rao, Jie Tian, Mengsu Zeng
European Radiology.2020; 30(5): 3004. CrossRef Paeonol Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion and Induces Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating miR-21-5p/KLF6 Axis
Miaoguo Cai, Wei Shao, Huijun Yu, Ye Hong, Lili Shi
Cancer Management and Research.2020; Volume 12: 5931. CrossRef- Update on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Brief Review from Pathologist Standpoint
Nese Karadag Soylu
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer.2020; 51(4): 1176. CrossRef - Clinico-Radio-Pathological and Molecular Features of Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Keratin 19 Expression
Hyungjin Rhee, Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
Liver Cancer.2020; 9(6): 663. CrossRef - Histopathological characteristics of needle core biopsy and surgical specimens from patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Ju-Shan Wu, Ji-Liang Feng, Rui-Dong Zhu, San-Guang Liu, Da-Wei Zhao, Ning Li
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology.2019; 11(5): 404. CrossRef - The strengths and weaknesses of gross and histopathological evaluation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a brief review
Sebastião N. Martins-Filho, Venâncio Avancini Ferreira Alves
Surgical and Experimental Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Changing role of histopathology in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Archana Rastogi
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 24(35): 4000. CrossRef
- Long-Term Outcomes of Transarterial Chemoembolization plus Ablation versus Surgical Resection in Patients with Large BCLC Stage A/B HCC
- Transformation to Small Cell Lung Cancer of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Analysis of Six Cases
- Soomin Ahn, Soo Hyun Hwang, Joungho Han, Yoon-La Choi, Se-Hoon Lee, Jin Seok Ahn, Keunchil Park, Myung-Ju Ahn, Woong-Yang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):258-263. Published online May 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.04.19
- 14,146 View
- 253 Download
- 54 Web of Science
- 49 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are considered the first line treatment for a subset of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Although transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is one of the known mechanisms of resistance to EGFR TKIs, it is not certain whether transformation to SCLC is exclusively found as a mechanism of TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant tumors.
Methods
We identified six patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma that showed transformation to SCLC on second biopsy (n = 401) during a 6-year period. Clinicopathologic information was analyzed and EGFR mutation results were compared between initial and second biopsy samples.
Results
Six patients showed transformation from adenocarcinoma to SCLC, of which four were pure SCLCs and two were combined adenocarcinoma and SCLCs. Clinically, four cases were EGFR-mutant tumors from non-smoking females who underwent TKI treatment, and the EGFR mutation was retained in the transformed SCLC tumors. The remaining two adenocarcinomas were EGFR wild-type, and one of these patients received EGFR TKI treatment.
Conclusions
NSCLC can acquire a neuroendocrine phenotype with or without EGFR TKI treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patients outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma transforming to small-cell lung cancer after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy
Shuai Wang, Yongsen Wang, Xuan Wu, Li Yang, Xiaoju Zhang
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline retinoblastoma transcriptional corepressor 1 (Rb1) functional inactivation is a pre-requisite but not sufficient for small-cell histological transformation in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant lung adenocarcinomas post-tyrosine kinas
Aruna Nambirajan, Amber Rathor, Hemavathi Baskarane, Anju GS, Sachin Khurana, Somagattu Sushmitha, Aparna Sharma, Prabhat Singh Malik, Deepali Jain
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(3): 639. CrossRef - Case Report: Transforming small cell lung cancer: two cases report and literature review
Jinlong Liu, Jing Ai, Lize Zhao, Yimeng Qian, Qingxin Zhao, Chunling Ma, Yu Zhao, Jing Zhao
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploration of CT-based discrimination and diagnosis of various pathological types of ground glass nodules in the lungs
Haihui Wu, Xiong Zhang, Zheng Zhong
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between treatments and outcomes of patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer that transitioned into small-cell lung cancer: an international retrospective study
C. Catania, S.V. Liu, M. Garassino, A. Delmonte, V. Scotti, F. Cappuzzo, C. Genova, A. Russo, M. Russano, C. Bennati, I. Colantonio, S. Martini, M. Pino, F. Conforti, L. Pala, G. Minuti, F. Citarella, E. Olmetto, A. Esposito, P. Cascetta, A. Di Lello, T.
ESMO Open.2025; 10(7): 105326. CrossRef - TPM3–NTRK1 fusion confers resistance to osimertinib in lung adenocarcinoma: a model in a continuous cell line
Fang Cao, Jiayin Dai, Kun Dong, Zhenli Yang, Yanli Zhu, Changsong Qi, Dongmei Lin, Xiaocui Bian, Yuqin Liu
Human Cell.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Small cell lung cancer transdifferentiation: not a negligible phenomenon
Lilla Horvath, Kristiina Boettiger, Zsolt Megyesfalvi, Balázs Döme, Clemens Aigner, Anita Horváth-Rózsás, Judit Berta
Current Opinion in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Transformation to small cell lung cancer is irrespective of EGFR and accelerated by SMAD4-mediated ASCL1 transcription independently of RB1 in non-small cell lung cancer
Xi Ding, Min-xing Shi, Di Liu, Jing-xue Cao, Kai-xuan Zhang, Run-dong Zhang, Li-ping Zhang, Kai-xing Ai, Bo Su, Jie Zhang
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The study of primary and acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib to improve the outcome of EGFR-mutated advanced Non-small cell lung cancer patients: the challenge is open for new therapeutic strategies
Alessandra Ferro, Gian Marco Marinato, Cristiana Mulargiu, Monica Marino, Giulia Pasello, Valentina Guarneri, Laura Bonanno
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2024; 196: 104295. CrossRef - Comprehensive molecular and clinical insights into non-small cell lung cancer transformation to small cell lung cancer with an illustrative case report
Kresimir Tomic, Kristina Krpina, Lara Baticic, Miroslav Samarzija, Semir Vranic
Journal of Drug Targeting.2024; 32(5): 499. CrossRef - Transcriptomic Heterogeneity of EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Evolution Toward Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Songji Oh, Jaemoon Koh, Tae Min Kim, Soyeon Kim, Jeonghwan Youk, Miso Kim, Bhumsuk Keam, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Ja-Lok Ku, Dong-Wan Kim, Doo Hyun Chung, Dae Seog Heo
Clinical Cancer Research.2024; 30(20): 4729. CrossRef - Transformation of lung adenocarcinoma into small cell lung cancer after treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Linwu Kuang, Yangkai Li
Oncology and Translational Medicine.2024; 10(6): 286. CrossRef - Exon-18-EGFR Mutated Transformed Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review
Nunzio Digiacomo, Tommaso De Pas, Giovanna Rossi, Paola Bossi, Erika Stucchi, Fabio Conforti, Emilia Cocorocchio, Daniele Laszlo, Laura Pala, Emma Zattarin, Chiara Catania
Current Oncology.2023; 30(3): 3494. CrossRef - Current knowledge of small cell lung cancer transformation from non-small cell lung cancer
Giuseppe Giaccone, Yongfeng He
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2023; 94: 1. CrossRef - Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy: What’s new in 2023?
Sushanta Halder, Soumi Basu, Shobhit P. Lall, Apar K. Ganti, Surinder K. Batra, Parthasarathy Seshacharyulu
Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets.2023; 27(4-5): 305. CrossRef - Outcomes in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinoma With Transformation to Small Cell Lung Cancer After EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Resistance: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis
Jinhe Xu, Lihuan Xu, Baoshan Wang, Wencui Kong, Ying Chen, Zongyang Yu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Small cell lung cancer transformation: From pathogenesis to treatment
Xiaomeng Yin, Yueyi Li, Hang Wang, Tingting Jia, Enli Wang, Yuling Luo, Yuhao Wei, Zeyi Qin, Xuelei Ma
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 86: 595. CrossRef - Small Cell Lung Cancer Transformation following Treatment in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Isa Mambetsariev, Leonidas Arvanitis, Jeremy Fricke, Rebecca Pharaon, Angel R. Baroz, Michelle Afkhami, Marianna Koczywas, Erminia Massarelli, Ravi Salgia
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(5): 1429. CrossRef - Morphologic-Molecular Transformation of Oncogene Addicted Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Fiorella Calabrese, Federica Pezzuto, Francesca Lunardi, Francesco Fortarezza, Sofia-Eleni Tzorakoleftheraki, Maria Vittoria Resi, Mariaenrica Tiné, Giulia Pasello, Paul Hofman
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4164. CrossRef - Genomic and Gene Expression Studies Helped to Define the Heterogeneity of Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Other Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors and to Identify New Therapeutic Targets
Ugo Testa, Elvira Pelosi, Germana Castelli
Onco.2022; 2(3): 186. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine transformation from EGFR/ALK-wild type or TKI-naïve non-small cell lung cancer: An under-recognized phenomenon
Xiao Chu, Yuyin Xu, Ye Li, Yue Zhou, Li Chu, Xi Yang, Jianjiao Ni, Yida Li, Tiantian Guo, Zhiqin Zheng, Qiang Zheng, Qianlan Yao, Yuan Li, Xiaoyan Zhou, Zhengfei Zhu
Lung Cancer.2022; 169: 22. CrossRef - Three Third-Generation Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Similarities and Differences
Ling Chen, Yangqingqing Zhou, Chaosheng Gan, XiaoLi Wang, Yihui Liu, Chunhui Dong, Ruiyuan He, Jin Yang
Cancer Investigation.2022; 40(7): 590. CrossRef - Histomorphological transformation from non-small cell lung carcinoma to small cell lung carcinoma after targeted therapy or immunotherapy: A report of two cases
Hao Liu, Li-Hong Chen, Zhi-Hui Zhang, Ning Wang, Si-Hui Zhuang, Hao Chen, Jin Du, Li-Juan Pang, Yan Qi
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impressive response to dabrafenib, trametinib, and osimertinib in a metastatic EGFR-mutant/BRAF V600E lung adenocarcinoma patient
Maurício Fernando Silva Almeida Ribeiro, Franciele Hinterholz Knebel, Fabiana Bettoni, Rodrigo Saddi, Karina Perez Sacardo, Felipe Sales Nogueira Amorim Canedo, João Victor Machado Alessi, Andrea Kazumi Shimada, José Flávio Gomes Marin, Anamaria Aranha Ca
npj Precision Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Histological transformation of non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical analysis of nine cases
Cai-Bao Jin, Ling Yang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(18): 4617. CrossRef - Lamellarin 14, a derivative of marine alkaloids, inhibits the T790M/C797S mutant epidermal growth factor receptor
Naoyuki Nishiya, Yusuke Oku, Chie Ishikawa, Tsutomu Fukuda, Shingo Dan, Tetsuo Mashima, Masaru Ushijima, Yoko Furukawa, Yuka Sasaki, Keishi Otsu, Tomoko Sakyo, Masanori Abe, Honami Yonezawa, Fumito Ishibashi, Masaaki Matsuura, Akihiro Tomida, Hiroyuki Sei
Cancer Science.2021; 112(5): 1963. CrossRef - Case Report: Transformation From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to Small Cell Lung Cancer During Anti-PD-1 Therapy: A Report of Two Cases
Qian Shen, Jingjing Qu, Lingyan Sheng, Qiqi Gao, Jianying Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the resistance mechanisms of second-line osimertinib and their prognostic implications using next-generation sequencing in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
Kyoungmin Lee, Deokhoon Kim, Shinkyo Yoon, Dae Ho Lee, Sang-We Kim
European Journal of Cancer.2021; 148: 202. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of treatment modes and clinical outcomes of small cell lung cancer transformed from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma
Shouzheng Wang, Tongji Xie, Xuezhi Hao, Yan Wang, Xingsheng Hu, Lin Wang, Yan Li, Junling Li, Puyuan Xing
Thoracic Cancer.2021; 12(19): 2585. CrossRef - EGFR-Mutant SCLC Exhibits Heterogeneous Phenotypes and Resistance to Common Antineoplastic Drugs
Chih-An Lin, Sung-Liang Yu, Hsuan-Yu Chen, Huei-Wen Chen, Shr-Uen Lin, Chia-Ching Chang, Chong-Jen Yu, Pan-Chyr Yang, Chao-Chi Ho
Journal of Thoracic Oncology.2019; 14(3): 513. CrossRef - The clinicopathologic of pulmonary adenocarcinoma transformation to small cell lung cancer
Haiyan Yang, Li Liu, Chunhua Zhou, Yi Xiong, Yijuan Hu, Nong Yang, Jingjing Qu
Medicine.2019; 98(12): e14893. CrossRef - Chemistry and pharmacological diversity of quinoxaline motifs as anticancer agents
Olayinka O. Ajani, Martins T. Nlebemuo, Joseph A. Adekoya, Kehinde O. Ogunniran, Tolutope O. Siyanbola, Christiana O. Ajanaku
Acta Pharmaceutica.2019; 69(2): 177. CrossRef - Resistance to EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical management and future perspectives
Chiara Tomasello, Cinzia Baldessari, Martina Napolitano, Giulia Orsi, Giulia Grizzi, Federica Bertolini, Fausto Barbieri, Stefano Cascinu
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2018; 123: 149. CrossRef - Small cell lung cancer transformation from EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma: A case report and literatures review
Yangyang Liu
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2018; 19(6): 445. CrossRef - Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-expressing Lung Adenocarcinoma with Combined Neuroendocrine Component or Neuroendocrine Transformation: Implications for Neuroendocrine Transformation and Response to ALK-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Jongmin Sim, Hyunjin Kim, Jiyeon Hyeon, Yoon-La Choi, Joungho Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients WithEGFRT790M–Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib
Geoffrey R. Oxnard, Yuebi Hu, Kathryn F. Mileham, Hatim Husain, Daniel B. Costa, Philip Tracy, Nora Feeney, Lynette M. Sholl, Suzanne E. Dahlberg, Amanda J. Redig, David J. Kwiatkowski, Michael S. Rabin, Cloud P. Paweletz, Kenneth S. Thress, Pasi A. Jänne
JAMA Oncology.2018; 4(11): 1527. CrossRef - Clinicopathological and genomic comparisons between different histologic components in combined small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer
Mong-Wei Lin, Kang-Yi Su, Te-Jen Su, Chia-Ching Chang, Jing-Wei Lin, Yi-Hsuan Lee, Sung-Liang Yu, Jin-Shing Chen, Min-Shu Hsieh
Lung Cancer.2018; 125: 282. CrossRef - Transformation to small‑cell lung cancer following treatment with icotinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma
Hongyang Lu, Bo Chen, Jing Qin, Fajun Xie, Na Han, Zhiyu Huang
Oncology Letters.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Histological transformation of adenocarcinoma to small cell carcinoma lung as a rare mechanism of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Report of a case with review of literature
Monalisa Hui, ShantveerG Uppin, BalaJoseph Stalin, G Sadashivudu
Lung India.2018; 35(2): 160. CrossRef - A rare case of squamous cell carcinoma lung with multiple locoregional recurrences and histological transformation
Ram Niwas, Shibdas Chakrabarti, Viswesvaran Balasubramanian, ManasKamal Sen, JagdishChander Suri
Lung India.2018; 35(6): 511. CrossRef - Small cell lung cancer transformation during immunotherapy with nivolumab: A case report
Takuma Imakita, Kohei Fujita, Osamu Kanai, Tsuyoshi Terashima, Tadashi Mio
Respiratory Medicine Case Reports.2017; 21: 52. CrossRef - Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor in a female wolf (Canis lupus lupus)
Ayako SHIRAKI, Toshinori YOSHIDA, Masahi KAWASHIMA, Hirotada MURAYAMA, Rei NAGAHARA, Nanao ITO, Makoto SHIBUTANI
Journal of Veterinary Medical Science.2017; 79(3): 588. CrossRef - Secondary biopsy of non‐oncogenic‐driven lung cancer may reveal a clinically sensible histologic change. A brief report of two paradigmatic cases
Maria C. Mengoli, Giulia Orsi, Filippo Lococo, Giulia Grizzi, Fausto Barbieri, Federica Bertolini, Giulio Rossi, Silvia Novello
Thoracic Cancer.2017; 8(4): 359. CrossRef - Small-cell lung cancer in never smokers: The clinicopathological features including the prognosis
Masahiro Yamasaki, Naomi Saito, Wakako Daido, Sayaka Ishiyama, Naoko Deguchi, Masaya Taniwaki, Akio Sakatani, Megumu Fujihara, Nobuyuki Ohashi, Ken-ichi Arita
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2017; 12: 1. CrossRef - Clonal History and Genetic Predictors of Transformation Into Small-Cell Carcinomas From Lung Adenocarcinomas
June-Koo Lee, Junehawk Lee, Sehui Kim, Soyeon Kim, Jeonghwan Youk, Seongyeol Park, Yohan An, Bhumsuk Keam, Dong-Wan Kim, Dae Seog Heo, Young Tae Kim, Jin-Soo Kim, Se Hyun Kim, Jong Seok Lee, Se-Hoon Lee, Keunchil Park, Ja-Lok Ku, Yoon Kyung Jeon, Doo Hyun
Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 35(26): 3065. CrossRef - Australian recommendations for EGFR T790M testing in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Thomas John, Jeffrey J Bowden, Stephen Clarke, Stephen B Fox, Kerryn Garrett, Keith Horwood, Christos S Karapetis
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2017; 13(4): 296. CrossRef - Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Lung Adenocarcinoma after Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
Hyung Kyu Park, Youjeong Seo, Yoon-La Choi, Myung-Ju Ahn, Joungho Han
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(4): 441. CrossRef - Sequential occurrence of small cell and non-small lung cancer in a male patient: Is it a transformation?
Ahsan Wahab, Kavitha Kesari, Siddique Chaudhary, Mahin Khan, Hafiz Khan, Susan Smith, Yanis Boumber
Cancer Biology & Therapy.2017; 18(12): 940. CrossRef - The expression of S100B protein in serum of patients with brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer and its clinical significance
Shanling Mu, Hong Ma, Jun Shi, Dezhi Zhen
Oncology Letters.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Patients outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma transforming to small-cell lung cancer after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy
- Pulmonary Arteriovenous Fistula: Clinical and Histologic Spectrum of Four Cases
- Soomin Ahn, Joungho Han, Hong Kwan Kim, Tae Sung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):390-393. Published online May 9, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.04.18
- 11,814 View
- 211 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula (PAVF) is abnormally dilated vessels that provide a right-to-left shunt between pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein and is clinically divided into simple and complex type. Here, we report four cases of surgically resected sporadic PAVFs presenting various clinical and histologic spectrums. Cases 1 (a 57-old-female) and 2 (a 54-old-female) presented as incidentally identified single aneurysmal fistulas and the lesions were surgically removed without complication. On the other hand, case 3 (an 11-old-male) showed diffuse dilated vascular sacs involving both lungs and caused severe hemodynamic and pulmonary dysfunction. Embolization and surgical resection of the main lesion failed to relieve the symptoms. Case 4 (a 36-old-male) had a localized multiloculated cyst clinically mimicking congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Microscopically, the lesion consisted of dilated thick vessels, consistent with the diagnosis of fistulous arteriovenous malformation/hemangioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Shunt of It
Brittany M. Scarpato, Jamie McDonald, Pinar Bayrak-Toydemir, C. Gregory Elliott, Barbara C. Cahill, Lyska L. Emerson, Lynn M. Keenan
Chest.2023; 163(5): e201. CrossRef - Malformations artérioveineuses pulmonaires : diagnostic et étiologies
M.-F. Carette, R. Epaud, M. Nouri Neuville, M. Barral, A. Parrot, A. Khalil
EMC - Radiologie et imagerie médicale - Cardiovasculaire - Thoracique - Cervicale.2021; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Pyogenic Brain Abscesses in a Patient With Digital Clubbing
Vimal Kumar Paliwal, Sucharita Anand, Vivek Singh
JAMA Neurology.2020; 77(1): 129. CrossRef - Recurrent hemoptysis caused by arteriovenous malformation
Ivana Meta-Jevtović, Romana Suša, Bojan Đokić
Medicinski casopis.2020; 54(3): 120. CrossRef - A 10-year-old boy with dyspnea and hypoxia: abernathy malformation masquerading as pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
Lijian Xie, Yun Li, Xunwei Jiang, Jian Zhao, Tingting Xiao
BMC Pediatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics and analysis of right-to-left shunt-related dizziness in patients without hypoxemia
Liming Cao
Journal of International Medical Research.2019; 47(7): 2921. CrossRef - A ruptured pulmonary arteriovenous fistula after laparoscopic operation
Hong-Wei Shang, Sheng-Bin Sun, Guang-Yao Ma, Xing-Ming Mei, Chao Li, Kang Yang
Chinese Journal of Traumatology.2017; 20(6): 359. CrossRef
- The Shunt of It
- A Rare Case of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Hemangioma Presenting as a Peribronchial Mass
- Soomin Ahn, Sejin Jung, Jong Ho Cho, Tae Sung Kim, Joungho Han
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(3):243-245. Published online November 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.15
- 9,695 View
- 62 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of systemic pulmonary collaterals in a Doberman Pinscher with dilated cardiomyopathy phenotype
Tatiana Vladimirovna Sereda, Vladislava Konstantinovna Illarionova, Dmitrii Evgenievich Mitrushkin, Klavdiia Nikolaevna Naletova, Ramil Rafikovich Kadyrov, Aleksei Alekseevich Gazin, Sergei Konstantinovich Shebeko, Alexey Mikhailovich Ermakov
Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Pathology.2025; 18: e018013. CrossRef - Incidental discovery of a large complicated arteriovenous haemangioma
Alberto Anthony Goizueta, Peter Libbey, Anthony Moulton, Rabih El-Bizri
BMJ Case Reports.2017; 2017: bcr-2016-218759. CrossRef - Pulmonary Arteriovenous Fistula: Clinical and Histologic Spectrum of Four Cases
Soomin Ahn, Joungho Han, Hong Kwan Kim, Tae Sung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(5): 390. CrossRef
- A case of systemic pulmonary collaterals in a Doberman Pinscher with dilated cardiomyopathy phenotype
- Pleural Mesothelioma: An Institutional Experience of 66 Cases
- Soomin Ahn, In Ho Choi, Joungho Han, Jhingook Kim, Myung-Ju Ahn
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):91-99. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.91
- 10,896 View
- 94 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Malignant mesothelioma of the pleura is an aggressive tumor known to be associated with asbestos. Histological diagnosis of mesothelioma is challenging and is usually aided by immunohistochemical markers.
Methods During an 18-year period (1995-2012), 66 patients with pleural mesothelioma were diagnosed at the Samsung Medical Center in Seoul. We reviewed hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical slides of pleural mesothelioma and evaluated their pathological and clinical features.
Results The male-to-female ratio was 1.75:1, and age of patients ranged from 28 to 80 years with an average age of 56.84 years. Twenty-two out of 66 patients underwent curative pneumonectomy. Follow-up data was available in 60 patients (90.9%), and 50 of them (83.3%) died from the disease. The average overall survival was 15.39 months. Histologically, the epithelioid type was the most common, followed by the sarcomatoid and the biphasic types. Epidemiologic information was not available in most cases, and only one patient was confirmed to have a history of asbestos exposure.
Conclusions Malignant mesothelioma of the pleura is a fatal tumor, and the therapeutic benefit of pneumonectomy remains unproven. The combination of calretinin, Wilms tumor 1, HMBE-1, and thyroid transcription factor-1 may provide high diagnostic accuracy in diagnosing mesothelioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression of V-set immunoregulatory receptor in malignant mesothelioma
Yeon Seung Chung, Moonsik Kim, Yoon Jin Cha, Kyung A Kim, Hyo Sup Shim
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(2): 263. CrossRef - Is the pathology related to the amount of pleural thickening measured by thorax CT?
özgür katrancıoğlu, Tuba Sahinoglu, Kayhan Karakus, Ozan Kandemir, Semiha Urvay, Esra Aydın Karakaya, Nurkay Katrancioglu
Cumhuriyet Medical Journal.2018; 40(2): 157. CrossRef
- Expression of V-set immunoregulatory receptor in malignant mesothelioma
- Comparison of Three
BRAF Mutation Tests in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Clinical Samples - Soomin Ahn, Jeeyun Lee, Ji-Youn Sung, So Young Kang, Sang Yun Ha, Kee-Taek Jang, Yoon-La Choi, Jung-Sun Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Kyoung-Mee Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(4):348-354. Published online August 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.348
- 9,873 View
- 60 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Recently,
BRAF inhibitors showed dramatic treatment outcomes inBRAF V600 mutant melanoma. Therefore, the accuracy ofBRAF mutation test is critical.Methods BRAF mutations were tested by dual-priming oligonucleotide-polymerase chain reaction (DPO-PCR), direct sequencing and subsequently retested with a real-time PCR assay, cobas 4800 V600 mutation test. In total, 64 tumors including 34 malignant melanomas and 16 papillary thyroid carcinomas were analyzed. DNA was extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue samples and the results of cobas test were directly compared with those of DPO-PCR and direct sequencing.Results BRAF mutations were found in 23 of 64 (35.9%) tumors. There was 9.4% discordance among 3 methods. Out of 6 discordant cases, 4 cases were melanomas; 3 cases wereBRAF V600E detected only by cobas test, but were not detected by DPO-PCR and direct sequencing. One melanoma patient withBRAF mutation detected only by cobas test has been on vemurafenib treatment for 6 months and showed a dramatic response to vemurafenib. DPO-PCR failed to detect V600K mutation in one case identified by both direct sequencing and cobas test.Conclusions In direct comparison of the currently available DPO-PCR, direct sequencing and real-time cobas test for
BRAF mutation, real-time PCR assay is the most sensitive method.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative BRAFV600E mutation detection in thyroid carcinoma by immunocytochemistry
Kristine Zøylner Swan, Stine Horskær Madsen, Steen Joop Bonnema, Viveque Egsgaard Nielsen, Marie Louise Jespersen
APMIS.2022; 130(11): 627. CrossRef - Strategy to reduce unnecessary surgeries in thyroid nodules with cytology of Bethesda category III (AUS/FLUS): a retrospective analysis of 667 patients diagnosed by surgery
Yong Joon Suh, Yeon Ju Choi
Endocrine.2020; 69(3): 578. CrossRef - A new primer construction technique that effectively increases amplification of rare mutant templates in samples
Jr-Kai Huang, Ling Fan, Tao-Yeuan Wang, Pao-Shu Wu
BMC Biotechnology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - BRAF and NRAS mutations and antitumor immunity in Korean malignant melanomas and their prognostic relevance: Gene set enrichment analysis and CIBERSORT analysis
Kyueng-Whan Min, Ji-Young Choe, Mi Jung Kwon, Hye Kyung Lee, Ho Suk Kang, Eun Sook Nam, Seong Jin Cho, Hye-Rim Park, Soo Kee Min, Jinwon Seo, Yun Joong Kim, Nan Young Kim, Ho Young Kim
Pathology - Research and Practice.2019; 215(12): 152671. CrossRef - The association between dermoscopic features and BRAF mutational status in cutaneous melanoma: Significance of the blue-white veil
Miquel Armengot-Carbó, Eduardo Nagore, Zaida García-Casado, Rafael Botella-Estrada
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.2018; 78(5): 920. CrossRef - Comparison of Five Different Assays for the Detection of BRAF Mutations in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues of Patients with Metastatic Melanoma
Claire Franczak, Julia Salleron, Cindy Dubois, Pierre Filhine-Trésarrieu, Agnès Leroux, Jean-Louis Merlin, Alexandre Harlé
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy.2017; 21(2): 209. CrossRef - Validation of an NGS mutation detection panel for melanoma
Anne Reiman, Hugh Kikuchi, Daniela Scocchia, Peter Smith, Yee Wah Tsang, David Snead, Ian A Cree
BMC Cancer.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Transformation to Small Cell Lung Cancer of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Analysis of Six Cases
Soomin Ahn, Soo Hyun Hwang, Joungho Han, Yoon-La Choi, Se-Hoon Lee, Jin Seok Ahn, Keunchil Park, Myung-Ju Ahn, Woong-Yang Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(4): 258. CrossRef - Immunohistochemistry with the anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) antibody: impact of pre-analytical conditions and concordance with DNA sequencing in colorectal and papillary thyroid carcinoma
Katerina Dvorak, Birte Aggeler, John Palting, Penny McKelvie, Andrew Ruszkiewicz, Paul Waring
Pathology.2014; 46(6): 509. CrossRef
- Preoperative BRAFV600E mutation detection in thyroid carcinoma by immunocytochemistry
- Prognostic Significance of BCL9 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jiyeon Hyeon, Soomin Ahn, Jae Jun Lee, Dae Hyun Song, Cheol-Keun Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(2):130-136. Published online April 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.130
- 9,479 View
- 71 Download
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background BCL9 enhances β-catenin-mediated transcriptional activity regardless of the mutational status of the Wnt signaling components and increases the cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and metastatic potential of tumor cells. The goal of this study was to elucidate the prognostic significance of BCL9 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients.
Methods We evaluated BCL9 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in tumor tissue from 288 primary HCC patients who underwent curative hepatectomy. The impact of BCL9 expression on the survival of the patients was analyzed. The median follow-up period was 97.1 months.
Results Nuclear BCL9 protein expression was observed in 74 (25.7%) of the 288 HCCs. BCL9 expression was significantly associated with younger age (p=0.038), higher Edmondson grade (p=0.001), microvascular invasion (p=0.013), and intrahepatic metastasis (p=0.017). Based on univariate analyses, BCL9 expression showed an unfavorable influence on both disease-free survival (DFS, p=0.012) and disease-specific survival (DSS, p=0.032). Multivariate analyses revealed that higher Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage was an independent predictor of both shorter DFS (p<0.001) and shorter DSS (p<0.001). BCL9 expression tended to be an independent predictor of shorter DFS (p=0.078).
Conclusions BCL9 protein expression might be a marker of shorter DFS in HCC patients after curative hepatectomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- BCL9 as a Key Player in Wnt/β-catenin Signaling: Implications for Osteogenesis, Tissue Repair, and Oncology
Yupeng Nie, Rixu Liu, Haoyang Sun, Yongchang Yao
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Wnt-dependent and Wnt-independent functions of BCL9 in development, tumorigenesis, and immunity: Implications in therapeutic opportunities
Minjie Wu, Heng Dong, Chao Xu, Mengqing Sun, Haojin Gao, Fangtian Bu, Jianxiang Chen
Genes & Diseases.2024; 11(2): 701. CrossRef - The role of BCL9 genetic variation as a biomarker for hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients
Eman Abd El Razek Abbas, Ahmed Barakat Barakat, Mohamed Hassany, Samar Samir Youssef
Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology.2022; 20(1): 4. CrossRef - Molecular Targets and Signaling Pathways of microRNA-122 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Kwang-Hoon Chun
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(7): 1380. CrossRef - Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling and Its Cofactor BCL9L Have an Oncogenic Effect in Bladder Cancer Cells
Roland Kotolloshi, Mieczyslaw Gajda, Marc-Oliver Grimm, Daniel Steinbach
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5319. CrossRef - Bcl9 Depletion Modulates Endothelial Cell in Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer Tumor
Zhuang Wei, Mei Feng, Zhongen Wu, Shuru Shen, Di Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Wnt Signaling Pathway Is among the Drivers of Liver Metastasis
Ivana Samaržija
Livers.2021; 1(4): 180. CrossRef - Nuclear Expression of Pygo2 Correlates with Poorly Differentiated State Involving c-Myc, PCNA and Bcl9 in Myanmar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Myo Win Htun, Yasuaki Shibata, Kyaw Soe, Takehiko Koji
ACTA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOCHEMICA.2021; 54(6): 195. CrossRef - Wnt status-dependent oncogenic role of BCL9 and BCL9L in hepatocellular carcinoma
Nicole Huge, Maria Sandbothe, Anna K. Schröder, Amelie Stalke, Marlies Eilers, Vera Schäffer, Brigitte Schlegelberger, Thomas Illig, Beate Vajen, Britta Skawran
Hepatology International.2020; 14(3): 373. CrossRef - Structure and function of Pygo in organ development dependent and independent Wnt signalling
Yan Shi, Xiushan Wu, Shuoji Zhu, Huanlei Huang, Jian Zhuang, Haiyun Yuan, Wuzhou Yuan, Ping Zhu
Biochemical Society Transactions.2020; 48(4): 1781. CrossRef - BCL9/BCL9L in hepatocellular carcinoma: will it or Wnt it be the next therapeutic target?
Akshata Moghe, Satdarshan P. Monga
Hepatology International.2020; 14(4): 460. CrossRef - Loss of BCL9/9l suppresses Wnt driven tumourigenesis in models that recapitulate human cancer
David M. Gay, Rachel A. Ridgway, Miryam Müller, Michael C. Hodder, Ann Hedley, William Clark, Joshua D. Leach, Rene Jackstadt, Colin Nixon, David J. Huels, Andrew D. Campbell, Thomas G. Bird, Owen J. Sansom
Nature Communications.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Mapping of Bcl9 Using Two Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes Is Useful to Characterize Juvenile Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Myanmar
Myat Thu Soe, Yasuaki Shibata, Myo Win Htun, Kuniko Abe, Kyaw Soe, Nay Win Than, Thann Lwin, Myat Phone Kyaw, Takehiko Koji
ACTA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOCHEMICA.2019; 52(1): 9. CrossRef - Low BCL9 expression inhibited ovarian epithelial malignant tumor progression by decreasing proliferation, migration, and increasing apoptosis to cancer cells
Jing Wang, Mingjun Zheng, Liancheng Zhu, Lu Deng, Xiao Li, Linging Gao, Caixia Wang, Huimin Wang, Juanjuan Liu, Bei Lin
Cancer Cell International.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - SOX7 Suppresses Wnt Signaling by Disrupting β-Catenin/BCL9 Interaction
Rong Fan, HaiYan He, Wang Yao, YanFeng Zhu, XunJie Zhou, MingTai Gui, Jing Lu, Hao Xi, ZhongLong Deng, Min Fan
DNA and Cell Biology.2018; 37(2): 126. CrossRef - Hypoxia activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating the expression of BCL9 in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Wei Xu, Wang Zhou, Mo Cheng, Jing Wang, Zhian Liu, Shaohui He, Xiangji Luo, Wending Huang, Tianrui Chen, Wangjun Yan, Jianru Xiao
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma biology predicts survival outcome after liver transplantation in the USA
Mohamed Abd El-Fattah
Indian Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 36(2): 117. CrossRef - miR-30a acts as a tumor suppressor by double-targeting COX-2 and BCL9 in H. pylori gastric cancer models
Xuan Liu, Qing Ji, Chengcheng Zhang, Xiaowei Liu, Yanna Liu, Ningning Liu, Hua Sui, Lihong Zhou, Songpo Wang, Qi Li
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - BCL9, a coactivator for Wnt/β-catenin transcription, is targeted by miR-30c and is associated with prostate cancer progression
XIAO-HUI LING, ZHI-YUN CHEN, HONG-WEI LUO, ZE-ZHEN LIU, YING-KE LIANG, GUAN-XING CHEN, FU-NENG JIANG, WEI-DE ZHONG
Oncology Letters.2016; 11(3): 2001. CrossRef
- BCL9 as a Key Player in Wnt/β-catenin Signaling: Implications for Osteogenesis, Tissue Repair, and Oncology
- CHD1L Is a Marker for Poor Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Surgical Resection
- Jiyeon Hyeon, Soomin Ahn, Cheol-Keun Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(1):9-15. Published online February 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.1.9
- 9,304 View
- 71 Download
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background The gene for chromodomain helicase/ATPase DNA binding protein 1-like (
CHD1L ) was recently identified as a target oncogene within the 1q21 amplicon, which occurs in 46% to 86% of primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases. However, the prognostic significance of CHD1L in HCC remains uncertain. In this study, we investigated the roles of CHD1L in the prognosis of HCC.Methods We investigated the expressions of CHD1L in tumor tissue microarrays of 281 primary HCC patients who underwent surgical resection using immunohistochemistry. Prognostic factors of HCC were examined by univariate and multivariate analyses. The median follow-up period was 75.6 months.
Results CHD1L expression was observed in 48 of the 281 HCCs (17.1%). CHD1L expression was associated with a younger age (p=0.033), higher Edmondson grade (p=0.019), microvascular invasion (p<0.001), major portal vein invasion (p=0.037), higher American Joint Committee on Cancer T stage (p=0.001), lower albumin level (p=0.047), and higher α-fetoprotein level (p=0.002). Multivariate analyses revealed that CHD1L expression (p=0.027), Edmondson grade III (p=0.034), and higher Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage (p<0.001) were independent predictors of shorter disease-free survival.
Conclusions CHD1L expression might be a prognostic marker of shorter disease-free survival in HCC patients after surgical resection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Expression of CHD1L, a Potent Oncogene Is Associated With Aggressive Head and Neck Cancer and Poor Survival Outcome
Aishvarya Rukmani Panayappan, Chandra Pandi, Vijayashree Priyadharshini Jayaseelan, Paramasivam Arumugam
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted Inhibition of CHD1L by OTI-611 Reprograms Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Suppresses Proliferation to Produce Synergistic Antitumor Effects in Breast and Colorectal Cancer
Hector Esquer, Qiong Zhou, Daniel V. LaBarbera
Cells.2025; 14(5): 318. CrossRef - CHD1L in cancer and beyond: structure, oncogenic functions, and therapeutic potential
Sophia Clune, Paul Awolade, Hector Esquer, Qiong Zhou, Daniel V. LaBarbera
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The validation of new CHD1L inhibitors as a therapeutic strategy for cancer
Sophia Clune, Paul Awolade, Qiong Zhou, Hector Esquer, Brock Matter, Jeffrey T. Kearns, Timothy Kellett, Damilola Caleb Akintayo, Uday B. Kompella, Daniel V. LaBarbera
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 170: 116037. CrossRef - Role of pelitinib in the regulation of migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of Twist1
Sewoong Lee, Eunjeong Kang, Unju Lee, Sayeon Cho
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of the First Inhibitors of Oncogenic CHD1L
Brett J. Prigaro, Hector Esquer, Qiong Zhou, Laura A. Pike, Paul Awolade, Xin-He Lai, Adedoyin D. Abraham, Joshua M. Abbott, Brock Matter, Uday B. Kompella, Wells A. Messersmith, Daniel L. Gustafson, Daniel V. LaBarbera
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 65(5): 3943. CrossRef - Diversity roles of CHD1L in normal cell function and tumorigenesis
Xifeng Xiong, Xudong Lai, Aiguo Li, Zhihe Liu, Ningfang Ma
Biomarker Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein levels are associated with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hong-Lin Chen, Yu-Hua Chen, Lin Du, Yi-Ping Song, Bin Zhu
Arab Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 22(1): 12. CrossRef - Genome-wide scanning for CHD1L gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Y. Y. Kang, J. J. Li, J. X. Sun, J. X. Wei, C. Ding, C. L. Shi, G. Wu, K. Li, Y. F. Ma, Y. Sun, H. Qiao
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2021; 23(12): 2536. CrossRef - The high expression of CHD1L and its clinical significance in human solid tumors
Long Zhang, Yufen Jiang, Panpan Jiao, Xiaohong Deng, Yuancai Xie
Medicine.2021; 100(10): e24851. CrossRef - Clinical Significance of Trk Receptor Expression as a New Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sangjoon Choi, Sujin Park, Yoon Ah Cho, Cheol-Keun Park, Sang Yun Ha
Pathology & Oncology Research.2020; 26(4): 2587. CrossRef - Hepatocyte ploidy and pathological mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma: impact on oncogenesis and therapeutics
Taiji Yamazoe, Taizo Mori, Sachiyo Yoshio, Tatsuya Kanto
Global Health & Medicine.2020; 2(5): 273. CrossRef - First-in-Class Inhibitors of Oncogenic CHD1L with Preclinical Activity against Colorectal Cancer
Joshua M. Abbott, Qiong Zhou, Hector Esquer, Laura Pike, Travis P. Broneske, Sébastien Rinaldetti, Adedoyin D. Abraham, Dominique A. Ramirez, Paul J. Lunghofer, Todd M. Pitts, Daniel P. Regan, Aik Choon Tan, Daniel L. Gustafson, Wells A. Messersmith, Dani
Molecular Cancer Therapeutics.2020; 19(8): 1598. CrossRef - Prognostic role of chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1-like protein in human solid cancers
Wanwei Liu, Jiwei Xu, Caiyun Zhang
Medicine.2018; 97(29): e11522. CrossRef - CHD1L Expression Increases Tumor Progression and Acts as a Predictive Biomarker for Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer
Chuan Liu, Xiaowei Fu, Zhiwei Zhong, Jing Zhang, Haiyan Mou, Qiong Wu, Tianle Sheng, Bo Huang, Yeqing Zou
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2017; 62(9): 2376. CrossRef - Overexpression of CHD1L is associated with poor survival and aggressive tumor biology in esophageal carcinoma
Ze-Han Liu, Qi Zhang, Yi-Jie Ding, Ying-Hui Ren, Hui-Peng Yang, Qing Xi, Ying-Nan Cheng, Guo-Lin Miao, Hong-Kun Liu, Cai-Xia Li, Wen-Qiang Yan, Yan Li, Zhenyi Xue, Lijuan Zhang, Xin-Ye Li, Chen-Long Zhao, Yurong Da, Xian-Zhong Wu, Jun-Qiang Chen, Rongxin
Oncotarget.2017; 8(43): 74178. CrossRef - CHD1L Regulates Cell Cycle, Apoptosis, and Migration in Glioma
Jie Sun, Li Zhang, Hongyu Zhao, Xiaojun Qiu, Wenjuan Chen, Donglin Wang, Na Ban, Shaochen Fan, Chaoyan Shen, Xiaojie Xia, Bin Ji, Yuchan Wang
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology.2016; 36(4): 565. CrossRef - Expression of DBC1 is associated with poor prognosis in hepatitis virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Sang Yun Ha, Jeong Hoon Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Hyunsik Bae, Hae Yon Cho, Cheol-Keun Park
Pathology - Research and Practice.2016; 212(7): 616. CrossRef - The Overexpression of CCAR1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associates with Poor Prognosis
Sang Yun Ha, Jeong Hoon Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Jimin Kim, Binnari Kim, Cheol-Keun Park
Cancer Research and Treatment.2016; 48(3): 1065. CrossRef - Genetic alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update
Zhao-Shan Niu, Xiao-Jun Niu, Wen-Hong Wang
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(41): 9069. CrossRef - CHD1L is a novel independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer
Z. Su, J. Zhao, G. Xian, W. Geng, Z. Rong, Y. Wu, C. Qin
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2014; 16(8): 702. CrossRef - Presence of CHD1L Over-Expression Is Associated with Aggressive Tumor Biology and Is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker for Patient Survival in Human Breast Cancer
Jiayi Wu, Yu Zong, Xiaochun Fei, Xiaosong Chen, Ou Huang, Jianrong He, Weiguo Chen, Yafen Li, Kunwei Shen, Li Zhu, Xin-Yuan Guan
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(8): e98673. CrossRef - CHD1L: a novel oncogene
Wen Cheng, Yun Su, Feng Xu
Molecular Cancer.2013; 12(1): 170. CrossRef - Expression of CHD1L in bladder cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
Feng Tian, Feng Xu, Zheng-Yu Zhang, Jing-Ping Ge, Zhi-Feng Wei, Xiao-Feng Xu, Wen Cheng
Tumor Biology.2013; 34(6): 3687. CrossRef
- High Expression of CHD1L, a Potent Oncogene Is Associated With Aggressive Head and Neck Cancer and Poor Survival Outcome
- Clinicopathological Analysis of 21 Thymic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Soomin Ahn, Jae Jun Lee, Sang Yun Ha, Chang Ohk Sung, Jhingook Kim, Joungho Han
- Korean J Pathol. 2012;46(3):221-225. Published online June 22, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.221
- 10,904 View
- 95 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Thymic neuroendocrine carcinomas (NECs) are uncommon, for which there is no established information available because of a limited number of epidemiological study in Asia.
Methods We reviewed 21 cases of surgically resected thymic NECs, and evaluated their pathological and clinical features.
Results It showed male predominance (male/female ratio, 15/6) with wide age range from 20 to 72 years (mean age, 49 years). All 21 cases were divided into two types according to the World Health Organization criteria: atypical carcinoid (n=18) and large cell NEC (n=3). Three cases of atypical carcinoid (AC) were associated with ectopic Cushing's syndrome. All the patients (3/3) with large cell NEC (3/3) and 16.7% (3/18) of those with AC died of tumor progression. Common sites of metastasis included lung, lymph node, brain, lumbar spine, mediastinum, bone, and liver.
Conclusions In conclusion, thymic neuroendocrine tumors carry a poor prognosis. Regarding the tumor classification, our results showed that a vast majority of carcinoids in the thymus correspond to ACs. In addition, our results also indicate that typical carcinoid is a very rare entity. Some cases of AC exhibited a large size, solid pattern and they showed aggressive clinical behavior, which highlights the spectrum of histologic appearances of thymic NECs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Stage IV Thymic Typical Carcinoid with Multiple Bone Metastases
Hisaya Chikaraishi, Tomohiro Maniwa, Hironobu Samejima, Masao Kobayashi, Julian Horiguchi, Ryu Kanzaki, Hidetoshi Satomi, Keiichiro Honma, Jiro Okami
Haigan.2025; 65(4): 286. CrossRef - Pathology, molecular biology, medical oncology, and radiotherapy implications of lung neuroendocrine neoplasm classification: a multidisciplinary perspective
Giuseppe Pelosi, Alice Laffi, Gianpiero Catalano, Antonino Bruno, Mauro Papotti, Barbara Bassani, Fabrizio Bianchi, Eleonora Duregon, Tommaso Martino De Pas, Chiara Catania, Riccardo Ricotta, Riccardo Papa, Sergio Harari, Angelica Sonzogni, Ilaria Guerrie
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the thymus
Paul D. Barone, Chen Zhang
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymic neuroendocrine tumours
Jan von der Thüsen
Diagnostic Histopathology.2023; 29(2): 114. CrossRef - The Utility of Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy in the Diagnosis of Mediastinal Lesions
Uma Kundu, Qiong Gan, Deepak Donthi, Nour Sneige
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2400. CrossRef - Paediatric and adolescent ectopic Cushing's syndrome: systematic review
Chethan Yami Channaiah, Manjiri Karlekar, Vijaya Sarathi, Anurag Ranjan Lila, Shruthi Ravindra, Padma Vikram Badhe, Gaurav Malhotra, Saba Samad Memon, Virendra Ashokrao Patil, C S Pramesh, Tushar Bandgar
European Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 189(4): S75. CrossRef - Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1) and neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs)
Grigoris Effraimidis, Ulrich Knigge, Maria Rossing, Peter Oturai, Åse Krogh Rasmussen, Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 79: 141. CrossRef - Multiple electrolyte disturbances as the presenting feature of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1)
Adrian Po Zhu Li, Sheela Sathyanarayan, Salvador Diaz-Cano, Sobia Arshad, Eftychia E Drakou, Royce P Vincent, Ashley B Grossman, Simon J B Aylwin, Georgios K Dimitriadis
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metastatic Thymic Carcinoid: Does Surgeon Have a Primary Role?
Kumud Gupta, Ravindra K. Dewan, Vinitha Viswambharan Nair, Rajat Saxena, Shaleen Prasad
The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases and Allied Sciences.2022; 56(4): 255. CrossRef - A resected case of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the thymus
Masashi Umeda, Takahiko Misao, Tomoya Senoh, Yoshinobu Shikatani, Motoi Aoe
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2022; 36(7): 766. CrossRef - Treatment strategy and prognostic analysis of spinal metastases from thymomas: A retrospective study from a single center
Shuzhong Liu, Xi Zhou, An Song, Zhen Huo, Siyuan Yao, Yipeng Wang, Yong Liu
Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery.2020; 196: 106056. CrossRef - Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Mediastinum Successfully Treated with Systemic Chemotherapy after Palliative Radiotherapy
Takeaki Hidaka, Saki Okuzumi, Ako Matsuhashi, Hidenori Takahashi, Kazunori Hata, Seiichiro Shimizu, Yoshinobu Iwasaki
Internal Medicine.2019; 58(4): 563. CrossRef - Surgical management of spinal metastases of thymic carcinoma
Shuzhong Liu, Xi Zhou, An Song, Zhen Huo, William A. Li, Radhika Rastogi, Yipeng Wang, Yong Liu
Medicine.2019; 98(3): e14198. CrossRef - Resected thymic large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
Shogo Ogata, Ryo Maeda, Masaki Tomita, Yuichiro Sato, Takanori Ayabe, Kunihide Nakamura
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2019; 60(C): 53. CrossRef - Metastatic or locally advanced mediastinal neuroendocrine tumours
Aadil Adnan, Shreyas Kudachi, Sudha Ramesh, Kumar Prabhash, Sandip Basu
Nuclear Medicine Communications.2019; 40(9): 947. CrossRef - Results of treatment for thymic neuroendocrine tumours: multicentre clinicopathological study†
Naoko Ose, Hajime Maeda, Masayoshi Inoue, Eiichi Morii, Yasushi Shintani, Hiroshi Matsui, Hirohito Tada, Tositeru Tokunaga, Kenji Kimura, Yasushi Sakamaki, Yukiyasu Takeuchi, Kenjiro Fukuhara, Hiroshi Katsura, Teruo Iwasaki, Meinoshin Okumura
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2018; 26(1): 18. CrossRef - Patterns of Failure Following Postoperative Radiation Therapy Based on “Tumor Bed With Margin” for Stage II to IV Type C Thymic Epithelial Tumor
Kyung Hwa Lee, Jae Myoung Noh, Yong Chan Ahn, Dongryul Oh, Jhingook Kim, Young Mog Shim, Jung-ho Han
International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics.2018; 102(5): 1505. CrossRef - Resected thymic large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: report of a case
Hiromitsu Domen, Yasuhiro Hida, Masaaki Sato, Haruka Takahashi, Tatsuru Ishikawa, Yosuke Shionoya, Midori Hashimoto, Kaoru Nishiyama, Yuma Aoki, Kazuho Inoko, Syotaro Furukawa, Kazuomi Ichinokawa, Hidehisa Yamada
Surgical Case Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful treatment of malignant thymoma with sacrum metastases
Shuzhong Liu, Xi Zhou, An Song, Zhen Huo, William A. Li, Radhika Rastogi, Yipeng Wang, Yong Liu
Medicine.2018; 97(51): e13796. CrossRef - Incidental metastatic mediastinal atypical carcinoid in a patient with parathyroid adenoma: a case report
Zareen Kiran, Asma Ahmed, Owais Rashid, Saira Fatima, Faizan Malik, Saulat Fatimi, Mubassher Ikram
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Thymus neuroendocrine tumors with CTNNB1 gene mutations, disarrayed ß-catenin expression, and dual intra-tumor Ki-67 labeling index compartmentalization challenge the concept of secondary high-grade neuroendocrine tumor: a paradigm shift
Alessandra Fabbri, Mara Cossa, Angelica Sonzogni, Paolo Bidoli, Stefania Canova, Diego Cortinovis, Maria Ida Abbate, Fiorella Calabrese, Nazarena Nannini, Francesca Lunardi, Giulio Rossi, Stefano La Rosa, Carlo Capella, Elena Tamborini, Federica Perrone,
Virchows Archiv.2017; 471(1): 31. CrossRef - Thymic large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma – a rare and aggressive tumor: a case report
Efared Boubacar, Gabrielle Atsame-Ebang, Sani Rabiou, Ammor Fatimazahra, Asmae Mazti, Ibrahim S. Sidibé, Layla Tahiri, Nawal Hammas, Ouadnouni Yassine, Smahi Mohamed, Chbani Laila, El Fatemi Hinde
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological features of neoplasms with neuroendocrine differentiation occurring in the liver
Yoriko Nomura, Osamu Nakashima, Jun Akiba, Sachiko Ogasawara, Shogo Fukutomi, Rin Yamaguchi, Hironori Kusano, Masayoshi Kage, Koji Okuda, Hirohisa Yano
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2017; 70(7): 563. CrossRef - Retrosternal goiter and thymic carcinoid: A rare co-existence
Abdulsalam Yaseen Taha, Nezar A. Almahfooz, Hassanain H. Khudair
Journal of the Egyptian Society of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.2017; 25(4): 369. CrossRef - A case of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the thymus involving a patient with long-term survival after surgery
Qiuming Kan, Kohei Tagawa, Teruaki Ishida, Mitsuyo Nishimura, Katsuhiko Aoyama
The Journal of the Japanese Association for Chest Surgery.2017; 31(7): 927. CrossRef - Neuroendokrine Neoplasien des Mediastinums
L. Brcic, M. Heidinger, H. Popper
Der Pathologe.2016; 37(5): 434. CrossRef - Outcome of primary neuroendocrine tumors of the thymus: A joint analysis of the International Thymic Malignancy Interest Group and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons databases
Pier Luigi Filosso, Xiaopan Yao, Usman Ahmad, Yilei Zhan, James Huang, Enrico Ruffini, William Travis, Marco Lucchi, Andreas Rimner, Alberto Antonicelli, Francesco Guerrera, Frank Detterbeck
The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.2015; 149(1): 103. CrossRef - Clinical Significance of Persistent Tumor in Bone Marrow during Treatment of High-risk Neuroblastoma
Young Bae Choi, Go Eun Bae, Na Hee Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Soo Hyun Lee, Keon Hee Yoo, Ki Woong Sung, Hong Hoe Koo
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(8): 1062. CrossRef - Tumor genetics and survival of thymic neuroendocrine neoplasms: A multi‐institutional clinicopathologic study
Philipp Ströbel, Andreas Zettl, Konstantin Shilo, Wen‐Yu Chuang, Andrew G. Nicholson, Yoshihiro Matsuno, Anthony Gal, Rolf Hubert Laeng, Peter Engel, Carlo Capella, Mirella Marino, John Kwok-Cheung Chan, Andreas Rosenwald, William Travis, Teri J. Franks,
Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer.2014; 53(9): 738. CrossRef - Disseminated large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma associated with ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion
A Van der Walt, K Huddle, S Pather, A Korb
Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa.2014; 19(1): 40. CrossRef - Morphologic Alteration of Metastatic Neuroblastic Tumor in Bone Marrow after Chemotherapy
Go Eun Bae, Yeon-Lim Suh, Ki Woong Sung, Jung-Sun Kim
Korean Journal of Pathology.2013; 47(5): 433. CrossRef
- A Case of Stage IV Thymic Typical Carcinoid with Multiple Bone Metastases

 E-submission
E-submission



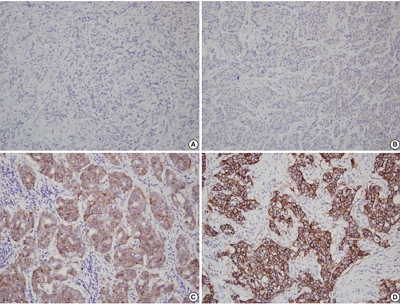
 First
First Prev
Prev



