Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Significance of KM55 immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis and prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Hoe In Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Minsun Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):69-82. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.17
- 591 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Galactose-deficient IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a crucial role in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). The monoclonal antibody KM55 has emerged as a simplified method for detecting Gd-IgA1; however, the clinicopathological significance of immunohistochemistry for Gd-IgA1 remains underexplored. This study evaluated the prognostic and clinicopathological significance of KM55 immunohistochemistry in IgAN. Methods: A total of 114 native kidney biopsies showing at least mild mesangial IgA positivity on immunofluorescence were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were categorized as having IgAN or non-IgAN diseases. The KM55 immunohistochemical staining was graded as 0, 1+, 2+, 3, or 4+. Data on Oxford classification, laboratory parameters, and renal outcomes were collected. Results: The IgAN group showed significantly higher KM55 scores than the non-IgAN group (median: 3 vs. 1; p < .001). IgAN cases were further stratified into KM55-high (≥3+, n = 38) and -low groups (≤2+, n = 37). The KM55-high group had significantly higher diastolic blood pressure, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine protein/creatinine ratio, and Oxford mesangial hypercellularity scores, along with lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum albumin. Cox analysis revealed significantly poorer outcomes in the KM55-high group for chronic kidney disease stage 4 (p = .015), end-stage renal disease (p = .024), and 75% eGFR decline (p = .016). Conclusions: Mesangial Gd-IgA1 deposition graded by KM55 immunohistochemistry may be a useful adjunct for IgAN diagnosis and a potential prognostic biomarker.
- The significance of papillary architecture in the follow-up biopsies of patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia
- Wangpan J. Shi, Oluwole Fadare
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):58-68. Published online January 8, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.12
- 377 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follow-up biopsies in patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia/endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasia (AH/EIN) may show papillary structures, the significance of which is unclear. Methods: The authors reviewed 253 serial specimens of 84 consecutive patients diagnosed with AH/EIN, inclusive of each patient's pre-progestin treatment sample and all post-treatment specimens. We assessed the predictive relationship between papillary architecture in a post-treatment biopsy and two study outcomes: AH/EIN or carcinoma in at least one sample subsequent to the one in which papillae were identified, and/or the last specimen received for that patient. Results: Papillae were identified in only 51.5% of pre-treatment samples but were present in at least one subsequent post-treatment sample for all patients. Post-treatment samples that exhibited papillae and no glandular crowding were associated with AH/EIN in at least one subsequent specimen in 39.7% (29/73) of cases, compared to 24.0% (6/25) in samples with neither papillae nor glandular crowding (p = .227) and 64.0% (16/25) in samples with concurrent gland crowding and papillae (p = .048). Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that the presence of papillae was not associated with study outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 0.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 1.99; p = .985), as compared with gland crowding (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04 to 2.27; p = .031), or concurrent papillae and gland crowding (OR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.01 to 5.52; p = .048). Conclusions: In post-treatment samples of progestin-treated AH/EIN, the presence of papillary architecture was not demonstrably associated with study outcomes independent of gland crowding, although the concurrent presence of both features may be significantly predictive.
Review Article
- Solitary fibrous tumor: an updated review
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):20-46. Published online December 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.08
- 541 View
- 69 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a fibroblastic neoplasm characterized by a branching, thin-walled dilated staghorn-shaped (hemangiopericytoma-like) vasculature and a NAB2::STAT6 gene fusion. SFTs can occur in almost any anatomical location, including superficial and deep soft tissues, visceral organs, and bone. They most commonly occur in extrapleural locations, equally affect both sexes, and are typically present in adults. Although metastasis is rare, SFTs frequently show local recurrence. The diagnosis of SFTs is difficult because of their broad histological and morphological overlap with other neoplasms. An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding disease management and prognosis. Despite advances in molecular diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, the biological complexity and unpredictable clinical behavior of SFTs present significant challenges. This review provides an updated overview of SFT, with a focus on its molecular genetics, histopathological features, and diagnostic considerations.
Original Articles
- Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
- Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Young Sub Lee, Sang-Ryung Lee, Myunghee Kang, Young Jin Seo, Seung-Sook Lee, Yoon-Jung Hwang, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):444-452. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.21
- 2,497 View
- 120 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) independent cervical malignancies (HPV-IDCMs) have recently been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) 5th edition. These malignancies have historically received limited attention due to their rarity and the potential for evasion of HPV-based screening.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 5,854 biopsy-confirmed cervical malignancies from 22 institutions over 3 years (July 2020–June 2023). Histologic classification followed the WHO guidelines. HPV independence was confirmed by dual negativity for p16 and HPV; discordant cases (p16-positive/HPV-negative) underwent additional HPV testing using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytological results were matched sequentially to histological confirmation.
Results
The prevalence of HPV-IDCM was 4.4% (257/5,854) overall and was 3.6% (208/5,805 cases) among primary cervical malignancy. Patient age of HPV-IDCM was 29 to 89 years (median, 57.79). Its histologic subtypes included primary adenocarcinoma (n = 116), endometrial adenocarcinoma (n = 35), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 72), metastatic carcinoma (n = 14), carcinoma, not otherwise specified (n = 10), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 3), and others (n = 7). Among 155 cytology-histological matched cases, the overall and primary Pap test detection rates were 85.2% (132/155) and 83.2% (104/125), respectively. The interval between cytology and histologic confirmation extended up to 38 months.
Conclusions
HPV-IDCMs comprised 3.6% of primary cervical malignancies with a high detection rate via cytology (83.2%). These findings affirm the value of cytological screening, particularly in patients with limited screening history or at risk for HPV-independent lesions, and may guide future screening protocols.
- E-cadherin expression and tumor-stroma ratio as prognostic biomarkers of peritoneal recurrence in advanced gastric cancer: a digital image analysis-based stratification study
- Somang Lee, Binnari Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):408-420. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.27
- 1,828 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric cancer remains a significant global health burden, with a high peritoneal recurrence rates after curative surgery. E-cadherin and the tumor-stroma ratio (TSR) have been proposed as prognostic indicators, but their combined prognostic utility remains unclear. Methods: This retrospective study included 130 patients with T3/T4a gastric cancer who underwent curative gastrectomy at Ulsan University Hospital between 2014 and 2019. Immunohistochemistry for E-cadherin and Vimentin was performed. Digital image analysis using QuPath’s object classifier quantified E-cadherin expression and TSR. Results: Low E-cadherin expression was associated with diffuse-type histology and advanced T stage. Low TSR was linked to younger age, female sex, and XELOX treatment. In Kaplan-Meier analysis, low TSR showed a non-significant trend toward higher peritoneal recurrence (p = .054), while low E-cadherin expression was significantly associated with increased peritoneal recurrence (p = .002). Combined biomarker analysis also revealed a significant difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS) among the four groups (p = .005); patients with both high TSR and high E-cadherin expression experienced the most favorable RFS. In multivariable analysis, E-cadherin expression remained the only independent predictor of peritoneal recurrence (high vs. low; hazard ratio, 0.348; 95% confidence interval, 0.149 to 0.816; p = .015). Conclusions: E-cadherin and TSR reflect distinct tumor biology such as epithelial integrity and stromal composition, and their combined evaluation improves prognostic stratification. Digital image analysis enhances reproducibility and objectivity, supporting their integration into clinical workflows.
- Spectrum of thyroiditis types: clinical, cytomorphological, and radiological findings
- Anam Singh, Indrajeet Kundu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):421-433. Published online November 6, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.13
- 2,255 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Thyroiditis encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions affecting the thyroid gland. Lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT) is a common form of thyroiditis, with acute suppuration of the thyroid, while tuberculous thyroiditis is relatively rare. Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) remains a safe and cost-effective tool for diagnosing thyroid-related diseases, especially when paired with ultrasound (US) and clinical examination. Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 21 cases. The cases were reported as thyroiditis on US and FNAC, and the findings were correlated with patient clinical history, symptoms during presentation, and serological profiles. Results: The cases of thyroiditis encompassed the more common forms, LT and subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (SAT), as well as relatively rare forms like tuberculous thyroiditis and thyroid abscess. Cases of follicular neoplasms (FN) arising in the context of LT also are included in this study. The case of tuberculous thyroiditis presented as a bulky thyroid gland that appeared heterogeneous on US with extensive necrosis on FNAC. The cases of thyroid abscess and SAT presented with painful neck swellings, with granulomas in the latter cases. US features of LT showed an array of appearances ranging from pseudonodular to an atrophic thyroid gland. All cases of FN showed a lymphocytic background. Conclusions: Thyroiditis is a commonly encountered condition that needs to be sub-categorized accurately into acute, subacute, and chronic types for appropriate clinical management, as they can sometimes show overlapping features. Though rare, acute suppurative and tuberculous thyroiditis are often encountered and warrant immediate care and treatment.
Review Article
- Breast schwannoma: review of entity and differential diagnosis
- Sandra Ixchel Sanchez, Ashley Cimino-Mathews
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):353-360. Published online November 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.12
- 2,294 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Schwannomas are benign peripheral nerve sheath tumors composed of Schwann cells, which uncommonly involve the breast. Most breast schwannomas are clinically present as a superficial palpable breast mass but may also be detected on screening mammography. Excision is the preferred treatment if symptomatic, and these are not known to recur. Histomorphology is similar to other anatomic sites: bland spindle cells with wavy nuclei, nuclear palisading (Verocay bodies), variably hypercellular (Antoni A) and hypocellular (Antoni B) areas, myxoid stroma, hyalinized vessels and variable cystic degeneration. Classic immunohistochemistry is diffuse and strong labeling for S100 and Sox10. Notable diagnostic pitfalls specific to the breast include myofibroblastoma, particularly the palisaded variant, and fascicular pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia.
Case Study
- Clinicopathological characteristics of digestive system angioleiomyomas: case report and literature review
- Georgios Kalliopitsas, Christos Topalidis, Constantine Halkias, Theodora Gkeka, Konstantinos Sapalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):453-459. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.04
- 1,840 View
- 101 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Angioleiomyomas are benign soft tissue tumors originating from the vascular wall. Although angioleiomyomas mainly occur in extremities, followed by head, neck, and trunk, they can also be found throughout the digestive system and especially in the oral cavity. Herein, the fourth case of a rectal angioleiomyoma in the English literature is reported and the clinicopathological features of digestive system angioleiomyomas were investigated. In contrast to their soft tissue counterparts, digestive system angioleiomyomas mainly affect males at a slightly younger age. Angioleiomyomas are mainly asymptomatic and only rarely elicit pain. Clinicians consider angioleiomyomas infrequently and instead include more common soft tissue or epithelial tumors in their differential diagnosis. To prevent angiomyolipoma misdiagnosis, pathologists should exercise caution when examining an angioleiomyoma composed of adipose tissue, smooth muscle, and blood vessels. Pathologists, radiologists, and surgeons should be aware that angioleiomyomas can occur in the digestive system.
Original Article
- Clinicopathological implications of miR-3127 in melanoma
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Chau M. Bui, Vuong Gia Huy
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):371-381. Published online October 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.08
- 2,976 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Cutaneous melanoma is the most lethal of all skin cancers. Recent studies suggested that miR-3127 is dysregulated in multiple tumor types and has important roles in tumorigenesis and cancer progression, giving it potential as a prognostic biomarker. The aim of this study was to use bioinformatic analysis to assess miR-3127 expression and correlate expression patterns with disease course in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Methods: miRNA, mRNA sequencing, DNA methylation data, and clinical information of cutaneous melanoma cases were downloaded from the Human Cancer Atlas – Skin Cutaneous Melanoma (TCGA-SKCM). miR-3127 expression was classified into miR-3127–low and miR-3127–high clusters using maximally selected rank statistics. Results: Clustering analysis showed that high expression of miR-3127 (≥20.3 reads per million) was associated with worse progression-free (p < .001) and overall (p = .011) survival compared to low miR-3127 expression. More than five thousand differentially expressed genes between the two miR-3127 sample groups encoded cell differentiation markers, cytokines, growth factors, translocated cancer genes, and oncogenes. Pathway analysis revealed that miR-3127–high samples related to activity of proliferation, DNA repair, and ultraviolet response. Conclusions: The expression level of miR-3127 could act as a prognostic indicator for patients with melanoma.
Case Study
- Cytological characteristics of Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterine corpus: a case report and literature review
- Junko Kuramoto, Chihiro Matsubara, Yasuko Sasamoto, Hitomi Tsukada, Shigemichi Hirose
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):340-347. Published online September 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.08.11
- 2,577 View
- 78 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Müllerian adenosarcoma of the uterus is a rare morphological variant of uterine sarcoma. Müllerian adenosarcoma has been described histologically, though it is rare in the cytological literature. This report describes the cytological findings of a case of adenosarcoma arising from the endometrium. The patient was a Japanese woman in her 40s. Endometrial cytological and histological findings were observed for 5 years, from the appearance of a polypoid lesion until adenosarcoma was suspected, and then hysterectomy was performed. Based on these longitudinal cytological and histological observations, it was possible to identify the cytological characteristics of adenosarcoma: decrease in the glandular-to-stromal ratio; increase in stromal cell density; and progression of stromal cell atypia. This case stresses the importance and usefulness of endometrial cytology in the identification of the sarcomatous component in adenosarcoma.
Original Articles
- Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):361-370. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.07
- 2,753 View
- 254 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to reclassify a subset of poorly differentiated salivary gland carcinoma that do not conform to any entities of the current World Health Organization (WHO) classification into the category of undifferentiated carcinoma (UDC) because they lack specific histologic differentiation or immunophenotype. Methods: Cases of salivary gland carcinomas from Asan Medical Center (2002–2020) that did not fit any existing WHO classification criteria and were diagnosed as poorly differentiated carcinoma, high-grade carcinoma, or UDC, were retrospectively reviewed. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for p40, neuroendocrine markers, androgen receptor (AR), and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed. Clinical data were collected from the electronic medical records. Results: Six salivary gland carcinomas did not align with any specific entities and lacked distinct differentiation. Two of six cases displayed lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC)-like morphology but were negative or showed negligible immunoreactivity for p40 and EBV ISH, distinguishing them from LEC of the salivary gland. Two cases showed strong AR positivity, suggesting a potential overlap with salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) but lacked classic SDC morphologies and GCDFP-15 expression. No cases expressed neuroendocrine markers. Conclusions: This study proposes reclassifying these poorly differentiated or high-grade salivary gland carcinomas as UDC based on their indeterminate differentiation and IHC profiles. This may lead to a clearer diagnostic category and enhance our understanding of these high-grade tumors.
- Evaluation of potential prognostic significance of JUNB in human prostate cancer: a bioinformatic and histopathological study
- Noha R. Noufal, Einas M. Yousef, Mohamed Taha
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):291-305. Published online September 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.06.06
- 1,409 View
- 113 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in males worldwide. Serum prostate-specific antigen is a frequently employed biomarker in the diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer; however, it is known for its low predictive accuracy for disease progression. New prognostic biomarkers are needed to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer from low-risk disease. This study aimed to identify and validate potential prognostic biomarkers of prostate cancer. Methods: Two prostate cancer datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes between benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatic carcinoma. Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the JUNB proto-oncogene, a subunit of the AP-1 transcription factor (JUNB), in 70 prostate cancer patients and 10 BPH samples. Results: Our findings showed that JUNB was significantly enriched in prostate cancer-related pathways and biological processes. JUNB expression was considerably higher in prostatic adenocarcinoma patients than in BPH patients. Regarding JUNB expression in prostate cancer cases, lower levels of JUNB expression were associated with higher grades of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Lower JUNB expression was associated with a higher risk of prostatic adenocarcinoma progression and shorter overall survival. Conclusions: These results suggest that JUNB is a promising prognostic biomarker and a potential tumor suppressor in prostate cancer.
Review Article
- Central nervous system tumors with BCOR internal tandem duplications: a systematic review of clinical, radiological, and pathological features in 69 cases
- Ji Young Lee, Sung Sun Kim, Hee Jo Baek, Tae-Young Jung, Kyung-Sub Moon, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Kyung-Hwa Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(5):273-280. Published online September 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.07.23
- 3,222 View
- 174 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Central nervous system tumors with BCL6 corepressor (BCOR) internal tandem duplications (ITDs) constitute a rare, recently characterized pediatric neoplasm with distinct molecular and histopathological features. To date, 69 cases have been documented in the literature, including our institutional case. These neoplasms predominantly occur in young children, with the cerebellum representing the most frequent anatomical location. Radiologically, these tumors present as large, well-circumscribed masses frequently demonstrating necrosis, hemorrhage, and heterogeneous enhancement. Histologically, they are characterized by a monomorphic cellular population featuring ependymoma-like perivascular pseudorosettes, myxoid stroma, and elevated mitotic activity. Immunohistochemically, these tumors exhibit sparse glial fibrillary acidic protein expression while consistently demonstrating positive staining for vimentin and CD56. The defining molecular hallmark is a heterozygous ITD within exon 15 of the BCOR gene, with insertions ranging from 9 to 42 amino acids in length. BCOR immunohistochemistry reveals nuclear positivity in 97.9% of examined cases, although this finding is not pathognomonic for BCOR ITDs. This comprehensive review synthesizes data from all published cases of this novel tumor entity, providing a detailed analysis of clinical presentation, neuroimaging findings, histopathological features with differential diagnostic considerations, therapeutic approaches, and prognostic outcomes.
Original Article
- AMACR is a highly sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing prostate cancer on biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Johannes Cansius Prihadi, Stevan Kristian Lionardi, Nicolas Daniel Widjanarko, Steven Alvianto, Fransiskus Xaverius Rinaldi, Archie Fontana Iskandar
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):235-248. Published online July 3, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.16
- 6,241 View
- 205 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is the preferred biomarker for distinguishing malignant from benign glands in prostate biopsies, showing high sensitivity and specificity for prostate cancer. A meta-analysis of immunohistochemistry (IHC) for AMACR is essential to further assess its diagnostic accuracy across diverse sample sources. Methods: A systematic search of databases including MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, ProQuest, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library was performed, focusing on studies of AMACR to diagnose prostate cancer, particularly in biopsy samples analyzed through IHC over the last 20 years. Quality of studies was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 tool, followed by a meta-analysis of regions and subgroups to calculate summary estimates of diagnostic test accuracy. Results: In the final analysis, 37 studies, with a pooled size of 5,898 samples, were included from the examination of 94 full-text papers. Among them, 27 studies with similar sample sources and testing methodologies underwent meta-analysis, yielding a combined sensitivity estimate of 0.90 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.86 to 0.93) and specificity of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95), both with significant heterogeneity (p < .01). The region beneath the hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), positive likelihood ratio was 9.6 (95% CI, 5.3 to 17.4), negative likelihood ratio was 0.11 (95% CI, 0.08 to 0.15), and diagnostic odds ratio was 88 (95% CI, 42 to 181). Conclusions: Our meta-analysis findings substantiate AMACR as a highly accurate tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, specifically in biopsy samples, via immunohistochemical staining. Further studies involving diverse samples are needed to enhance our understanding of the AMACR diagnostic accuracy in a range of clinical settings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Jessica M. Logan, Victoria Malone, John J. O’Leary, Doug A. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11786. CrossRef
- Pathogenesis-Guided Biomarker Assessment: A Shift in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
Case Studies
- Acquired aberrant partial CD3 expression in recurrent Epstein-Barr virus–negative solitary plasmacytoma of tonsil
- Chenchen Niu, Dong Ren, Truc Tran, Ashley Gamayo, Sherif Rezk, Xiaohui Zhao
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(4):262-268. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.17
- 2,633 View
- 127 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The aberrant expression of specific T-cell maker CD3 in B-cell neoplasms can be a potential diagnostic pitfall leading to a misclassification of cell lineage. Here, we report a case of recurrent solitary plasmacytoma with new aberrant expression of CD3. The neoplastic plasma cells of the recurrent tumor were kappa restricted, positive for CD138, MUM1, negative for CD20, cyclin D1, and Epstein-Barr virus. CD79a was positive in majority of the tumor cells, except for a small focus which was strongly positive for CD3, but negative for other T-cell markers (CD2, CD5, CD7, CD4, and CD8) and CD56. The neoplastic plasma cells of the original tumor were negative for CD3. To the best of our knowledge, only one case of recurrent plasmacytoma with aberrant expression of CD3 has been published, which revealed disease progression in the recurrence. However, we did not observe morphologic evidence of disease progression in our case.
- Cytological features of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung: a case report
- Misa Takahashi, Seiya Homma, Chisato Setoguchi, Yoko Umezawa, Atsuhiko Sakamoto
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):195-200. Published online May 9, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.04.09
- 3,938 View
- 128 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) and adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) are generally treated as different lesions, depending on the differences in lesion size and histological findings. However, these differences are not absolute; thus, AAH and AIS are often difficult to distinguish. Moreover, whether AAH and AIS can be regarded as different lesions remains unknown because cytological specimens, especially those of AAH, are rare. In this study, we examined these uncommon cytological specimens and compared the cytological findings between AAH and AIS. We observed many common cytological features with no obvious differences between AAH and AIS. These findings suggest that these two distinct lesions can be grouped into a single category. Therefore, we propose creating a new cytological category.
Original Articles
- Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: a clinicopathologic study of four cases with a review of literature
- Gyuheon Choi, Joon Seon Song, Hee Jin Lee, Gi Hwan Kim, Young Ho Jung, Yoon Se Lee, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(3):171-179. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.03.25
- 3,566 View
- 153 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland is currently not listed in the World Health Organization classification. However, cases of Merkel cell type neuroendocrine carcinomas of the salivary gland with perinuclear cytokeratin 20 positivity have been intermittently reported. We here investigated the clinicopathologic features of additional cases.
Methods
Data of four cases of Merkel cell type small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the salivary gland were retrieved. To confirm the tumors’ primary nature, clinical records and pathologic materials were reviewed. Optimal immunohistochemical staining was performed to support the diagnosis.
Results
All tumors were located in the parotid gland. Possibilities of metastasis were excluded in all cases through a meticulous clinicopathological review. Tumor histology was consistent with the diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Tumors’ immunohistochemical phenotypes were consistent with Merkel cell carcinoma, including Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen positivity in two of the four cases.
Conclusions
Merkel cell carcinomas can originate in salivary glands and are partly associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus infection as in cutaneous Merkel cell carcinomas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report
Tong Gao, Dengshun Wang, Hongwei Yu, Yu’e Wang, Haibin Lu
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Parotid intranodal metastasis of Merkel cell carcinoma: a rare case report
- Association study of TYMS gene expression with TYMS and ENOSF1 genetic variants in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response of gastric cancer
- Khadijeh Arjmandi, Iman Salahshourifar, Shiva Irani, Fereshteh Ameli, Mohsen Esfandbod
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):105-114. Published online February 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.05
- 3,178 View
- 141 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The present research was designed to study the associations between genetic variants of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes with TYMS and ENOSF1 gene expression in neoadjuvant chemotherapy response among patients with gastric cancer. Methods: Formalin-embedded and paraffin-fixed matched tumor and normal gastric cancer tissue samples from patients who received neoadjuvant 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) treatment were obtained. DNA and RNA were extracted for all samples. A 28-bp variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) at the 5' untranslated region of TYMS gene and rs2612091 and rs2741171 variants in the ENOSF1 gene were genotyped for normal tissue samples. The real-time polymerase chain reaction method was used to study the expression of ENOSF1 and TYMS genes in both normal and tumor tissues. Data were analyzed using REST 2000 and SPSS ver. 26.0 software programs. Results: A significant association between TYMS 2R3R VNTR genotypes and 5-FU therapy was found (p = .032). The 3R3R and 2R2R genotypes were significantly associated with increased and decreased survival time, respectively (p = .003). The 3R3R genotype was significantly associated with TYMS overexpression (p < .001). Moreover, a significant association was found between the rs2612091 genotype and treatment outcome (p = .017). Conclusions: This study highlights the impact of TYMS and ENOSF1 genes as predictive indicators for survival and response to 5-FU–based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Innovative biomaterial strategies for mitigating radiotherapy toxicity: multidimensional mechanistic interventions of nano-microscale materials and hydrogels
Yifan Liu, Fengdi Jiang, Jie Song, Huaijin Qiao, Junlong Dai, Hao Bai, Shuyu Zhang
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2026; 549: 217313. CrossRef
- Innovative biomaterial strategies for mitigating radiotherapy toxicity: multidimensional mechanistic interventions of nano-microscale materials and hydrogels
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,159 View
- 240 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Categorizing high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma into clinically relevant subgroups using deep learning–based histomic clusters
- Byungsoo Ahn, Eunhyang Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):91-104. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.23
- 5,031 View
- 248 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSC) exhibits significant heterogeneity, posing challenges for effective clinical categorization. Understanding the histomorphological diversity within HGSC could lead to improved prognostic stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Methods: We applied the Histomic Atlases of Variation Of Cancers model to whole slide images from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for ovarian cancer. Histologically distinct tumor clones were grouped into common histomic clusters. Principal component analysis and K-means clustering classified HGSC samples into three groups: highly differentiated (HD), intermediately differentiated (ID), and lowly differentiated (LD). Results: HD tumors showed diverse patterns, lower densities, and stronger eosin staining. ID tumors had intermediate densities and balanced staining, while LD tumors were dense, patternless, and strongly hematoxylin-stained. RNA sequencing revealed distinct patterns in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and energy metabolism, with upregulation in the HD, downregulation in the LD, and the ID positioned in between. Survival analysis showed significantly lower overall survival for the LD compared to the HD and ID, underscoring the critical role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in HGSC progression. Conclusions: Deep learning-based histologic analysis effectively stratifies HGSC into clinically relevant prognostic groups, highlighting the role of mitochondrial dynamics and energy metabolism in disease progression. This method offers a novel approach to HGSC categorization. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Syed Mohammed Basheeruddin Asdaq, Ahmad H. Alhowail, Syed Imam Rabbani, Naira Nayeem, Syed Mohammed Emaduddin Asdaq, Faiqa Nausheen
SAGE Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century: Integrating Neuroscience, Education, and Technology for Better Outcomes
Review
- Post-transplant liver biopsies: a concise and practical approach for beginners
- Mohamad Besher Ourfali, David Hirsch, Marianna Scranton, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):1-10. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.15
- 4,489 View
- 381 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Exposure to post-transplant liver biopsies varies among pathology residencies and largely depends on the institution's training program, particularly if the hospital has a liver transplant program. The interpretation of biopsies from transplanted livers presents its own set of challenges, even for those with a solid understanding of non-transplant medical liver biopsies. In this review, we aim to provide a succinct, step-by-step approach to help you interpret liver transplant biopsies. This article may be beneficial for residents interested in liver pathology, gastrointestinal and liver pathology fellows in the early stages of training, clinical gastroenterology and hepatology fellows, hepatologists and general pathologists who are curious about this niche.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7729. CrossRef
- Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Original Article
- Comparison of tissue-based and plasma-based testing for EGFR mutation in non–small cell lung cancer patients
- Yoon Kyung Kang, Dong Hoon Shin, Joon Young Park, Chung Su Hwang, Hyun Jung Lee, Jung Hee Lee, Jee Yeon Kim, JooYoung Na
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):60-67. Published online January 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.01
- 4,684 View
- 197 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutation testing is crucial for the administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors to treat non–small cell lung cancer. In addition to traditional tissue-based tests, liquid biopsies using plasma are increasingly utilized, particularly for detecting T790M mutations. This study compared tissue- and plasma-based EGFR testing methods.
Methods
A total of 248 patients were tested for EGFR mutations using tissue and plasma samples from 2018 to 2023 at Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital. Tissue tests were performed using PANAmutyper, and plasma tests were performed using the Cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2.
Results
All 248 patients underwent tissue-based EGFR testing, and 245 (98.8%) showed positive results. Of the 408 plasma tests, 237 (58.1%) were positive. For the T790M mutation, tissue biopsies were performed 87 times in 69 patients, and 30 positive cases (38.6%) were detected. Plasma testing for the T790M mutation was conducted 333 times in 207 patients, yielding 62 positive results (18.6%). Of these, 57 (27.5%) were confirmed to have the mutation via plasma testing. Combined tissue and plasma tests for the T790M mutation were positive in nine patients (13.4%), while 17 (25.4%) were positive in tissue only and 12 (17.9%) in plasma only. This mutation was not detected in 28 patients (43.3%).
Conclusions
Although the tissue- and plasma-based tests showed a sensitivity of 37.3% and 32.8%, respectively, combined testing increased the detection rate to 56.7%. Thus, neither test demonstrated superiority, rather, they were complementary.
Reviews
- Next step of molecular pathology: next-generation sequencing in cytology
- Ricella Souza da Silva, Fernando Schmitt
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):291-298. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.22
- 6,003 View
- 366 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The evolving landscape of precision oncology underscores the pivotal shift from morphological diagnosis to treatment decisions driven by molecular profiling. Recent guidelines from the European Society for Medical Oncology recomend the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) across a broader range of cancers, reflecting its superior efficiency and clinical value. NGS not only updates oncology testing by offering quicker, sample-friendly, and sensitive analysis but also reduces the need for multiple individual tests. Cytology samples, often obtained through less invasive methods, can yield high-quality genetic material suitable for molecular analysis. This article focuses on optimizing the use of cytology samples in NGS, and outlines their potential benefits in identifying actionable molecular alterations for targeted therapies across various solid tumors. It also addresses the need for validation studies and the strategies to incorporate or combine different types of samples into routine clinical practice. Integrating cytological and liquid biopsies into routine clinical practice, alongside conventional tissue biopsies, offers a comprehensive approach to tumor genotyping, early disease detection, and monitoring of therapeutic responses across various solid tumor types. For comprehensive biomarker characterization, all patient specimens, although limited, is always valuable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
Immacolata Cozzolino, Mats Ehinger, Maria Calaminici, Andrea Ronchi, Mousa A. Al-Abbadi, Helena Barroca, Beata Bode-Lesniewska, David F. Chhieng, Ruth L. Katz, Oscar Lin, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, Martha Bishop Pitman, Arvind Rajwanshi, Fernando C. Schmitt, Ph
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - The impact of cytological preparation techniques on RNA quality: A comparative study on smear samples
Cisel Aydin Mericoz, Gulsum Caylak, Elif Sevin Sanioglu, Zeynep Seçil Satilmis, Ayse Humeyra Dur Karasayar, Ibrahim Kulac
Cancer Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reimagining cytopathology in the molecular era: Integration or fragmentation?
Sumanta Das, R. Naveen Kumar, Biswajit Dey, Pranjal Kalita
Cytojournal.2025; 22: 94. CrossRef
- The World Health Organization Reporting System for Lymph Node, Spleen, and Thymus Cytopathology: Part 1 – Lymph Node
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cytology in pregnancy
- Ji-Young Kim, Jeong Yun Shim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):283-290. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.17
- 10,185 View
- 439 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer screening during pregnancy presents unique challenges for cytologic interpretation. This review focuses on pregnancy-associated cytomorphological changes and their impact on diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer. Pregnancy-induced alterations include navicular cells, hyperplastic endocervical cells, immature metaplastic cells, and occasional decidual cells or trophoblasts. These changes can mimic abnormalities such as koilocytosis, adenocarcinoma in situ, and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. Careful attention to nuclear features and awareness of pregnancy-related changes are crucial for correct interpretation. The natural history of CIN during pregnancy shows higher regression rates, particularly for CIN 2, with minimal risk of progression. Management of abnormal cytology follows modified risk-based guidelines to avoid invasive procedures, with treatment typically deferred until postpartum. The findings reported in this review emphasize the importance of considering pregnancy status in cytological interpretation, highlight potential problems, and provide guidance on differentiating benign pregnancy-related changes from true abnormalities. Understanding these nuances is essential for accurate diagnosis and proper management of cervical abnormalities in pregnant women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Xue Mi, Maharjan Rashmi, Zangyu Pan, Di Wu, Jinwei Miao
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncologic and pregnancy outcomes of cervical high-grade intraepithelial lesions and delivery mode
Olga P. Matylevich, Ilya A. Tarasau, Sviatlana Y. Shelkovich, Aliaksandr F. Martsinkevich
Academia Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 13,766 View
- 593 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Original Articles
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(1):39-49. Published online October 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.09.14
- 4,151 View
- 322 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although the criteria for follicular-pattern thyroid tumors are well-established, diagnosing these lesions remains challenging in some cases. In the recent World Health Organization Classification of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumors (5th edition), the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was reclassified as its own entity. It is crucial to differentiate this variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from low-risk follicular pattern tumors due to their shared morphological characteristics. Proteomics holds significant promise for detecting and quantifying protein biomarkers. We investigated the potential value of a protein biomarker panel defined by machine learning for identifying the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma, initially using formalin- fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Methods
We developed a supervised machine-learning model and tested its performance using proteomics data from 46 thyroid tissue samples.
Results
We applied a random forest classifier utilizing five protein biomarkers (ZEB1, NUP98, C2C2L, NPAP1, and KCNJ3). This classifier achieved areas under the curve (AUCs) of 1.00 and accuracy rates of 1.00 in training samples for distinguishing the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from non-malignant samples. Additionally, we analyzed the performance of single-protein/gene receiver operating characteristic in differentiating the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from others within The Cancer Genome Atlas projects, which yielded an AUC >0.5.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that integration of high-throughput proteomics with machine learning can effectively differentiate the invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma from other follicular pattern thyroid tumors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
Kai-Li Yang, Heng-Tong Han, Shou-Hua Li, Xiao-Xiao Li, Ze Yang, Li-Bin Ma, Yong-Xun Zhao
Discover Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Misdiagnosed follicular adenoma with 11 year postoperative liver and lung metastases a case report and literature review
- International Academy of Cytology standardized reporting of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology with cyto-histopathological correlation of breast carcinoma
- Shweta Pai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):241-248. Published online September 13, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.14
- 7,728 View
- 407 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Academy of Cytology (IAC) has developed a standardized approach for reporting the findings of breast fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). Accordingly, there are five chief categories of breast lesions, C1 (insufficient material), C2 (benign), C3 (atypical), C4 (suspicious), and C5 (malignant). The prognostication and management of breast carcinoma can be performed readily on the basis of this classification system. The aim of this study was to classify various breast lesions into one of the above-named categories and to further grade the C5 lesions specifically using the Robinson system. The latter grades were then correlated with modified Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grades.
Methods
This retrospective study was undertaken in the pathology department of a hospital located in the urban part of the city of Bangalore. All FNAC procedures performed on breast lumps spanning the year 2020 were included in the study.
Results
A total of 205 breast lesions was classified according to the IAC guidelines into C1 (6 cases, 2.9%), C2 (151 cases, 73.7%), C3 (13 cases, 6.3%), C4 (5 cases, 2.5%), and C5 (30 cases, 14.6%) groups. The C5 cases were further graded using Robinson’s system. The latter showed a significant correlation with the SBR system (concordance=83.3%, Spearman correlation=0.746, Kendall’s tau-b=0.736, kappa=0.661, standard error=0.095, p≤.001).
Conclusions
A standardized approach for FNAC reporting of breast lesions, as advocated for by the IAC, improves the quality and clarity of the reports and assures diagnostic reproducibility on a global scale. Further, the cytological grading of C5 lesions provides reliable cyto-prognostic scores that can help assess a tumor’s aggressiveness and predict its histological grade.
- TERT mutations and aggressive histopathologic characteristics of radioiodine-refractory papillary thyroid cancer
- Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoon Jin Cha, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):310-320. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.29
- 4,723 View
- 342 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Radioiodine (RI) ablation following thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression is an effective treatment for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), typically leading to favorable outcomes. However, RI-refractory tumors exhibit aggressive behavior and poor prognoses. Recent studies highlight the role of genetic abnormalities in PTC signaling pathways, including the activation of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), and the correlation of mutations with adverse outcomes.
Methods
This study analyzed mutations in BRAF V600E and the TERT-promoter genes, comparing clinicopathological features between RI-refractory and RI-responsive PTCs. Among 82 RI-refractory patients, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues from initial surgeries were available for 26. Another 89 without distant metastasis over 5 years formed a matched RI-responsive control group.
Results
Histopathologically, RI-refractory PTCs showed increased frequencies of small tumor clusters without fibrovascular cores, hobnail features, and a high height-to-width ratio of tumor cells. These tumors were more likely to exhibit necrosis, mitosis, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension, and involvement of resection margins. TERT-promoter mutations were statistically significantly associated with these aggressive clinicopathologic features. Immunohistochemically, decreased expression of sodium iodide symporter and thyroglobulin stimulating hormone receptor proteins was common in RI-refractory PTCs, along with lower levels of oncogenic proteins such as vascular endothelial cell growth factor, vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 2, and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. Total loss of PTEN expression was occasionally observed. In contrast, all cases tested positive for cytoplasmic β-catenin.
Conclusions
RI-refractory PTCs are linked to TERT mutations and exhibit specific aggressive histopathologic features, particularly in tumor centers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
Myoung Ju Koh, Songmi Noh, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152578. CrossRef - The ability of anexelekto (AXL) expression and TERT promoter mutation to predict radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Hasrayati Agustina, Tutik Nur Ayni, Yohana Azhar, Erwin Affandi Soeriadi, Bethy Suryawathy Hernowo
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma, tall cell subtype and subtype with tall cell features, an institutional experience
Xueting Jin, Shunsuke Koga, Xiao Zhou, Niaz Z. Khan, Zubair W. Baloch
Human Pathology.2025; 161: 105867. CrossRef - Calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumor of the liver: Report of two cases revealing novel WT1 mutation and distinct epigenetic features
Andrea Strakova-Peterikova, Franco Fedeli, Boris Rychly, Jiri Soukup, Michael Michal, Petr Martinek, Marian Grendar, Elaheh Mosaieby, Nikola Ptakova, Maryna Slisarenko, Michal Michal, Kvetoslava Michalova
Virchows Archiv.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction in thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer
Stefano Iuliano, Maria Mirabelli, Stefania Giuliano, Antonio Brunetti
Current Opinion in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
- Diagnostic challenges in the assessment of thyroid neoplasms using nuclear features and vascular and capsular invasion: a multi-center interobserver agreement study
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Husni Cangara, Aswiyanti Asri, Diah Prabawati Retnani, Fairuz Quzwain, Hasrayati Agustina, Hermawan Istiadi, Indri Windarti, Krisna Murti, Muhammad Takbir, Ni Made Mahastuti, Nila Kurniasari, Nungki Anggorowati, Pamela Abineno, Yulita Pundewi Setyorini, Kennichi Kakudo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):299-309. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.25
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(3):201
- 5,015 View
- 405 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms necessitates the identification of distinct histological features. Various education/hospital centers located in cities across Indonesia likely result in discordances among pathologists when diagnosing thyroid neoplasms.
Methods
This study examined the concordance among Indonesian pathologists in assessing nuclear features and capsular and vascular invasion of thyroid tumors. Fifteen pathologists from different centers independently assessed the same 14 digital slides of thyroid tumor specimens. All the specimens were thyroid neoplasms with known BRAFV600E and RAS mutational status, from a single center. We evaluated the pre- and post-training agreement using the Fleiss kappa. The significance of the training was evaluated using a paired T-test.
Results
Baseline agreement on nuclear features was slight to fair based on a 3-point scoring system (k = 0.14 to 0.28) and poor to fair based on an eight-point system (k = –0.02 to 0.24). Agreements on vascular (κ = 0.35) and capsular invasion (κ = 0.27) were fair, whereas the estimated molecular type showed substantial agreement (κ = 0.74). Following the training, agreement using the eight-point system significantly improved (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The level of concordance among Indonesian pathologists in diagnosing thyroid neoplasm was relatively poor. Consensus in pathology assessment requires ongoing collaboration and education to refine diagnostic criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef
- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Case Studies
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and ALK and cytokeratin expression: a case report
- Hyeong Rok An, Kyung-Ja Cho, Sang Woo Song, Ji Eun Park, Joon Seon Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):255-260. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.15
- 4,208 View
- 217 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) comprises of heterogeneous group of neoplasms that occasionally express epithelial markers on immunohistochemistry (IHC). We herein report the case of a patient who developed RMS of the skull with EWSR1 fusion and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and cytokeratin expression as cytomorphologic features. A 40-year-old man presented with a mass in his forehead. Surgical resection was performed, during which intraoperative frozen specimens were obtained. Squash cytology showed scattered or clustered spindle and epithelioid cells. IHC revealed that the resected tumor cells were positive for desmin, MyoD1, cytokeratin AE1/ AE3, and ALK. Although EWSR1 rearrangement was identified on fluorescence in situ hybridization, ALK, and TFCP2 rearrangement were not noted. Despite providing adjuvant chemoradiation therapy, the patient died of tumor progression 10 months after diagnosis. We emphasize that a subset of RMS can express cytokeratin and show characteristic histomorphology, implying the need for specific molecular examination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
Ahmed Shah, Andrew L. Folpe
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2025; 18(3): 503. CrossRef - Review of imaging modalities and radiological findings of calvarial lesions
Erkan Gökçe, Murat Beyhan
World Journal of Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Morphology of Telangiectatic Osteosarcoma Associated With Сystic Content: A Case Report
David Makaridze, Armaz Mariamidze, Tamuna Gvianishvili, Giulia Ottaviani , Liana Gogiashvili
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rhabdomyosarcomas of Bone
- Colorectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variant inherited paternally: a case report
- Kyoung Min Kim, Min Ro Lee, Ae Ri Ahn, Myoung Ja Chung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):341-345. Published online September 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.08.14
- 6,730 View
- 305 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BRCA genes have well-known associations with breast and ovarian cancers. However, variations in the BRCA gene, especially germline variations, have also been reported in colorectal cancer (CRC). We present the case of a rectal cancer with a germline BRCA1 variation inherited from the paternal side. A 39-year-old male was admitted with rectal cancer. The patient underwent surgical resection and the pathologic diagnosis was adenocarcinoma. Next-generation sequencing was performed and a BRCA1 variant was detected. Reviewing the public database and considering the young age of the patient, the variant was suggested to be germline. The patient’s father had had prostate cancer and next-generation sequencing testing revealed an identical BRCA1 variant. In the BRCA cancer group, there is relatively little attention paid to male cancers. The accumulation of male CRC cases linked to BRCA variations may help clarify the potential pathological relationship between the two.
Original Article
- Paricalcitol prevents MAPK pathway activation and inflammation in adriamycin-induced kidney injury in rats
- Amanda Lima Deluque, Lucas Ferreira de Almeida, Beatriz Magalhães Oliveira, Cláudia Silva Souza, Ana Lívia Dias Maciel, Heloísa Della Coletta Francescato, Cleonice Giovanini, Roberto Silva Costa, Terezila Machado Coimbra
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):219-228. Published online August 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.12
- 3,719 View
- 221 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway induces uncontrolled cell proliferation in response to inflammatory stimuli. Adriamycin (ADR)-induced nephropathy (ADRN) in rats triggers MAPK activation and pro-inflammatory mechanisms by increasing cytokine secretion, similar to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) plays a crucial role in suppressing the expression of inflammatory markers in the kidney and may contribute to reducing cellular proliferation. This study evaluated the effect of pre-treatment with paricalcitol on ADRN in renal inflammation mechanisms.
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with an osmotic minipump containing activated vitamin D (paricalcitol, Zemplar, 6 ng/day) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%). Two days after implantation, ADR (Fauldoxo, 3.5 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) was injected. The rats were divided into four experimental groups: control, n = 6; paricalcitol, n = 6; ADR, n = 7 and, ADR + paricalcitol, n = 7.
Results
VDR activation was demonstrated by increased CYP24A1 in renal tissue. Paricalcitol prevented macrophage infiltration in the glomeruli, cortex, and outer medulla, prevented secretion of tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin-1β, increased arginase I and decreased arginase II tissue expressions, effects associated with attenuation of MAPK pathways, increased zonula occludens-1, and reduced cell proliferation associated with proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression. Paricalcitol treatment decreased the stromal cell-derived factor 1α/chemokine C-X-C receptor type 4/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusions
Paricalcitol plays a renoprotective role by modulating renal inflammation and cell proliferation. These results highlight potential targets for treating CKD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Ana Checa-Ros, Antonella Locascio, Owahabanun-Joshua Okojie, Pablo Abellán-Galiana, Luis D’Marco
BMC Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Attenuating amiodarone-induced lung toxicity by the vitamin D receptor activator paricalcitol in rats: targeting TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways
Aamal G. El-Waseif, Mahmoud Elshal, Dalia H. El-Kashef, Nashwa M. Abu-Elsaad
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Perirenal fat differs in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving different vitamin D-based treatments: a preliminary study
Review
- Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
- Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):165-173. Published online July 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.06.11
- 4,133 View
- 276 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review addresses new reporting systems for lung and pancreatobiliary cytopathology as well as the most recent edition of The Bethesda Reporting System for Thyroid Cytopathology. The review spans past, present, and future aspects within the context of the intricate interplay between traditional morphological assessments and cutting-edge molecular diagnostics. For lung and pancreas, the authors discuss the evolution of reporting systems, emphasizing the bridge between past directives and more recent collaborative efforts of the International Academy of Cytology and the World Health Organization in shaping universal reporting systems. The review offers a brief overview of the structure of these novel systems, highlighting their strengths and pinpointing areas that require further refinement. For thyroid, the authors primarily focus on the third edition of The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology, also considering the two preceding editions. This review serves as an invaluable resource for cytopathologists, offering a panoramic view of the evolving landscape of cytopathology reporting and pointing out the integrative role of the cytopathologist in an era of rapid diagnostic and therapeutic advancements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Zahra Maleki, Sule Canberk, Andrew Field
Cytopathology.2025; 36(5): 434. CrossRef - Reproducibility of the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology (TBSRTC): An observational study of 100 patients
Kishori Moni Panda, Reena Naik, Mohd Ghouse Mohiddin
Indian Journal of Pathology and Oncology.2024; 11(4): 385. CrossRef
- WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non‐Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
Original Article
- Single umbilical artery and associated birth defects in perinatal autopsies: prenatal diagnosis and management
- Manushree Saxena, Bhagyashri Hungund
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):214-218. Published online July 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.03
- 14,378 View
- 425 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The umbilical cord forms the connection between the fetus and the placenta at the feto-maternal interface and normally comprises two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. In some cases, only a single umbilical artery (SUA) is present. This study was conducted to evaluate associations between SUA and other congenital malformations discovered in perinatal autopsies and to ascertain the existence of preferential associations between SUA and certain anomalies.
Methods
We evaluated records of all fetuses sent for autopsy to the Department of Pathology during the 10-year period from 2013 through 2022 (n = 1,277). The data were obtained from the hospital’s pathology laboratory records. The congenital anomalies were grouped by organ or system for analysis and included cardiovascular, urinary tract, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal, and lung anomalies.
Results
A SUA was present in 8.61% of the autopsies. The gestational age of the affected fetuses ranged between 13 to 40 weeks. An SUA presented as an isolated single anomaly in 44 cases (3.4%). Of the 110 SUA cases, 60% had other congenital anomalies. There was a significant association between birth defects and SUAs (p < .001). Strong associations between SUA and urinary tract, lung, and musculoskeletal anomalies were observed.
Conclusions
A SUA is usually seen in association with other congenital malformations rather than as an isolated defect. Therefore, examination for associated anomalies when an SUA is detected either antenatally or postnatally is imperative. The findings of this study should be helpful in counseling expectant mothers and their families in cases of SUA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Amulya Choudary Kotapati, Bhargavi Khandru, Vijayasree M.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2025; : 10. CrossRef - Epidemiological and Histopathological Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Disorders: A Study in Greece
Despoina Nteli, Maria Nteli, Konstantinos Konstantinidis, Maria Ouzounidou, Paschalis Theotokis, Maria-Eleni Manthou, Iasonas Dermitzakis, Xeni Miliara, Chrysoula Gouta, Stamatia Angelidou, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Soultana Meditskou
Biology.2025; 14(6): 626. CrossRef
- Single Umbilical Artery with Symmetrical IUGR and Multiple Fetal Anomalies - An Interesting Case Report
Case Studies
- Intravascular schwannoma as an extremely unusual cause of vein obstruction: a case report
- Luis Miguel Chinchilla-Tábora, Beatriz Segovia Blázquez, José María Sayagués, Marta Rodríguez González, Joaquín González-Rivero, José Antonio Muñoz León, Andrea Beatriz Jiménez Pérez, Idalia González Morais, Diego Bueno-Sacristán, María Dolores Ludeña
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(5):249-254. Published online July 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.05.15
- 4,149 View
- 282 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The blood vessel lumen is an extremely rare location for a benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor like schwannoma. Less than 10 cases have been previously reported. In this report, we present a case of a 68-year-old woman who had a soft tissue nodule at the posterior calf of her left leg during a physical examination. Pathological examination was performed after complete surgical excision. The patient underwent follow-up for 12 months after surgery without evidence of recurrence or any other complication. This is the first case of intravascular schwannoma reported as a cause of vein obstruction. Microscopically, the tumor was composed of Schwann spindle cells that were immunoreactive for S100 protein and SOX10. This tumor was surrounded by a well-defined vascular smooth muscle wall. Prospective series are required to improve the knowledge on the underlying mechanisms of intravascular schwannoma development.
- Primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain with EML4::ALK fusion mimicking intra-axial glioma: a case report and brief literature review
- Eric Eunshik Kim, Chul-Kee Park, Koung Mi Kang, Yoonjin Kwak, Sung-Hye Park, Jae-Kyung Won
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):141-145. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.04.12
- 4,531 View
- 210 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An aggressive subtype of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma occurs primarily inside the abdominal cavity, followed by a pulmonary localization. Most harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements, with RANBP2 and RRBP1 among the well-documented fusion partners. We report the second case of primary epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma of the brain, with a well-known EML4::ALK fusion. The case is notable for its intra-axial presentation that clinico-radiologically mimicked glioma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
Original Articles
- The importance of histomorphological features and ERG expression in the diagnosis of malignancy in cases with atypical small acinar proliferation
- Gizem Teoman, Ayten Livaoglu, Hatice Kucuk, Afs ¸ın Rahman Murtezaoglu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):134-140. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.18
- 4,133 View
- 232 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Atypical small acinar proliferation (ASAP) cases typically require rebiopsy, which are invasive and associated with increased risk of complications. Our aim in this study was to determine the importance of laboratory and histological findings and E-26 transformation-specific-related gene (ERG) expression in the diagnosis of malignancy.
Methods
Between March 2016 and March 2022, 84 patients who were diagnosed with ASAP on biopsy or rebiopsy were included in the study. Clinical-laboratory features of age, serum prostate-specific antigen level, and histopathological features were compared and included multifocality, number of suspicious acini, nuclear enlargement, nucleolar prominence, hyperchromasia, cytoplasmic amphophilia, luminal amorphous acellular secretion, crystalloid presence, infiltrative appearance, inflammation, atrophy, α-methyl acyl-CoA racemase, p63, and/or high molecular weight cytokeratin were analyzed. In addition, ERG expression was evaluated immunohistochemically.
Results
Statistically significant correlation was found between nucleolar prominence, nuclear hyperchromasia, crystalloid presence, infiltrative pattern, and prostate cancer (p < .001). In 19 of 84 cases (22.6%) ERG was positive in the nucleus. Prostate cancer was diagnosed at rebiopsy in 15 of the 19 ERG-positive cases (78.9%). A statistically significant correlation was found between ERG positivity and prostate cancer (p= .002).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that evaluation of these markers during initial transrectal ultrasound biopsies may decrease and prevent unnecessary prostate rebiopsy.
- The spectrum of microvascular patterns in adult diffuse glioma and their correlation with tumor grade
- Soni , Vaishali Walke, Deepti Joshi, Tanya Sharma, Adesh Shrivastava, Amit Agrawal
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(3):127-133. Published online May 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.03.11
- 6,760 View
- 347 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Primary brain tumors constitute the leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Among them, adult diffuse gliomas are the most common type, affecting the cerebral hemispheres and displaying a diffuse infiltrative pattern of growth in the surrounding neuropil that accounts for about 80% of all primary intracranial tumors. The hallmark feature of gliomas is blood vessel proliferation, which plays an important role in tumor growth, tumor biological behavior, and disease outcome. High-grade gliomas exhibit increased vascularity, the worst prognosis, and lower survival rates. Several angiogenic receptors and factors are upregulated in glioblastomas and stimulate angiogenesis signaling pathways by means of activating oncogenes and/or down-regulating tumor-suppressor genes. Existing literature has emphasized that different microvascular patterns (MVPs) are displayed in different subtypes of adult diffuse gliomas.
Methods
We examined the distribution and biological characteristics of different MVPs in 50 patients with adult diffuse gliomas. Haematoxylin and eosin staining results, along with periodic acid–Schiff and CD34 dual-stained sections, were examined to assess the vascular patterns and correlate with different grades of diffuse glioma.
Results
The present observational study on adult diffuse glioma evaluated tumor grade and MVPs. Microvascular sprouting was the most common pattern, while a bizarre pattern (type 2) was associated with the presence of a high-grade glioma. Vascular mimicry was observed in 6% of cases, all of which were grade 4 gliomas.
Conclusions
This study supplements the role of neo-angiogenesis and aberrant vasculature patterns in the grading and progression of adult diffuse gliomas, which can be future targets for planning treatment strategies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
Sujitha Jayaprakash, Hiu Yan Lam, Ravichandran Vishwa, Bandari BharathwajChetty, Kenneth C-H Yap, Mohammed S. Alqahtani, Mohamed Abbas, Gautam Sethi, Alan Prem Kumar, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara
Chinese Medical Journal.2025; 138(21): 2722. CrossRef - Uptake patterns of Adult-type Non-Enhanced diffuse gliomas on [11C] methionine positron emission tomography
Shoji Yasuda, Naoya Imai, Hirohito Yano, Yuka Ikegame, Soko Ikuta, Takashi Maruyama, Noriyuki Nakayama, Morio Kumagai, Yoshihiro Muragaki, Jun Shinoda, Tsuyoshi Izumo
Neuroradiology.2025; 67(10): 2611. CrossRef - Loss of Fibronectin Fiber Tension in Glioblastoma is Associated with Microvascular Proliferations and Immune Cell Infiltration
Michele Crestani, Isabel Gerber, Arnaud Mieville, Katrin Frauenknecht, Theoni Maragkou, Tibor Hortobagyi, Viola Vogel
Advanced Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High ORC6 expression is a prognostic indicator of poor survival in glioma patients
Mengjie Wang, Song Feng, Chen Zhang, Feng Jin
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Consequences of Hypoxic Events, Necrosis, and Microvascular Density, in Astrocytoma IDH-Mutant, CNS WHO Grade 4
Cristian Ionut Orasanu, Madalina Bosoteanu, Sorin Vamesu, Raluca Ioana Voda, Anamaria Sincu, Mariana Deacu
Medical Sciences.2025; 14(1): 6. CrossRef
- Unlocking therapeutic potential: Exploring nuclear receptors in brain cancer treatment
Review
- Exploring histological predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy response in non–small cell lung cancer
- Uiju Cho, Soyoung Im, Hyung Soon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):49-58. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.31
- 9,356 View
- 344 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Treatment challenges persist in advanced lung cancer despite the development of therapies beyond the traditional platinum-based chemotherapy. The early 2000s marked a shift to tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting epidermal growth factor receptor, ushering in personalized genetic-based treatment. A further significant advance was the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), especially for non–small cell lung cancer. These target programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, which enhanced the immune response against tumor cells. However, not all patients respond, and immune-related toxicities arise. This review emphasizes identifying biomarkers for ICI response prediction. While PD-L1 is a widely used, validated biomarker, its predictive accuracy is imperfect. Investigating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tertiary lymphoid structure, and emerging biomarkers such as high endothelial venule, Human leukocyte antigen class I, T-cell immunoreceptors with Ig and ITIM domains, and lymphocyte activation gene-3 counts is promising. Understanding and exploring additional predictive biomarkers for ICI response are crucial for enhancing patient stratification and overall care in lung cancer treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Daisuke Komura, Mieko Ochi, Shumpei Ishikawa
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2025; 27: 383. CrossRef - Beyond single biomarkers: multi-omics strategies to predict immunotherapy outcomes in blood cancers
Mohammad Pirouzbakht, Soroosh Hamzeh, Hamed Soleimani Samarkhazan
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal changes in tongue color during immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective observational study using digital tongue diagnosis
Eunbyul Cho, Woosu Choi, Jun Hyeok Lim, Ji Woong Son, Seung Hun Jang, Seung Hyeun Lee, Jong Gwon Choi, In-Jae Oh, Tae-Won Jang, Seong Hoon Yoon, Seung Joon Kim, Chang-Min Choi, Sung Yong Lee, Mi Mi Ko, Mi-Kyung Jeong
Oncology Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis: Updates in 2024
Original Articles
- TRPS1 expression in non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasms: an immunohistochemical analysis of 200 cases
- Yi A. Liu, Phyu P. Aung, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Jonathan L. Curry, Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, Doina Ivan, Victor G. Prieto, Qingqing Ding, Woo Cheal Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):72-80. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.23
- 6,971 View
- 389 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) was initially thought to be highly sensitive and specific for carcinomas and mesenchymal tumors of mammary origin, more recent data suggest its expression is not limited to breast neoplasms but also can be seen in other cutaneous neoplasms, such as extramammary Paget disease and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ.
Methods
Two-hundred cases of non-melanocytic cutaneous neoplasm, including basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) (n = 41), SCCs (n = 35), Merkel cell carcinomas (MCCs) (n = 25), and adnexal neoplasms (n = 99), were tested for TRPS1 expression using a monoclonal anti- TRPS1 rabbit anti-human antibody.
Results
TRPS1 expression was present in almost all cases of SCC (94%), with a median H-score of 200, while it was either absent or only focally present in most BCCs (90%), with a median H-score of 5. The difference between BCCs and SCCs in H-score was significant (p < .001). All MCCs (100%) lacked TRPS1 expression. TRPS1 expression was frequently seen in most adnexal neoplasms, benign and malignant, in variable intensity and proportion but was consistently absent in apocrine carcinomas. All endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinomas (EMPSGCs) (100%, 6/6) showed diffuse and strong TRPS1 immunoreactivity, with a median H-score of 300, which was significantly different (p < .001) than that of BCCs.
Conclusions
Our study shows that TRPS1 may be an effective discriminatory marker for BCCs and SCCs. It also has a role in distinguishing BCCs from EMPSGCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Thiri Htoo Aung, Neha Seth, Anam Khan, Kasturi Das
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1 (TRPS1) in breast pathology: diagnostic utility and pitfalls
Atif Ali Hashmi, Edi Brogi, Hannah Y. Wen
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Refining NTRK Fusion Detection in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry and Histopathologic Features
Hyun Lee, Sue Youn Kim, Ji Min Park, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ozgur Mete, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma: Case report and literature review
Nan Guo, Zhenlin Fan, Yitong Chen, Qian Li, Limin Guo
European Journal of Ophthalmology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Updates on utility of immunohistochemistry in diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer
Hongxia Sun, Aysegul A. Sahin, Qingqing Ding
Human Pathology.2025; 162: 105821. CrossRef - Primary Cutaneous NUT Adnexal Carcinoma With BRD4::NUTM1 Fusion: A 19-Year Follow-Up
Elsayed Ibrahim, Richard K. Yang, Maria A. Gubbiotti, Victor G. Prieto, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2025; 47(9): 731. CrossRef - Primary mucinous carcinoma of the skin with co-expression of TRPS1 and GATA3: a case report
Liling Song, Ning Zhu, Lei Jiang, Dong Gao, Guohua Yu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Algorithm for Secondary Extramammary Paget Disease from Institutional Cases and Literature Review
Salin Kiratikanon, Ayaka Fukui, Masahiro Hirata, Jakob M. T. Moran, Masakazu Fujimoto, Mai P. Hoang
Cancers.2025; 17(24): 4014. CrossRef - TRPS1 Expression Is Frequently Seen in a Subset of Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms and Tumors of Uncertain Differentiation: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
Moon Joo Kim, Yi A. Liu, Yunyi Wang, Jing Ning, Woo Cheal Cho
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(3): 200. CrossRef - TRPS1 expression in MPNST is correlated with PRC2 inactivation and loss of H3K27me3
Rossana Lazcano, Davis R. Ingram, Gauri Panse, Alexander J. Lazar, Wei-Lien Wang, Jeffrey M. Cloutier
Human Pathology.2024; 151: 105632. CrossRef - Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum-Like Features in Poroma: An Unusual Morphologic Pattern of Poroma or True Synchronous Occurrence of 2 Distinct Neoplasms?
Mouaz Alsawas, Fiorinda F. Muhaj, Phyu P. Aung, Priyadharsini Nagarajan, Woo Cheal Cho
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2024; 46(12): 871. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review of TRPS1 as a Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Marker for Primary Breast Carcinoma: Latest Insights and Diagnostic Pitfalls
Antonia-Carmen Georgescu, Tiberiu-Augustin Georgescu, Simona-Alina Duca-Barbu, Lucian Gheorghe Pop, Daniela Oana Toader, Nicolae Suciu, Dragos Cretoiu
Cancers.2024; 16(21): 3568. CrossRef - Expression of TRPS1 in Metastatic Tumors of the Skin: An Immunohistochemical Study of 72 Cases
Kassiani Boulogeorgou, Christos Topalidis, Triantafyllia Koletsa, Georgia Karayannopoulou, Jean Kanitakis
Dermatopathology.2024; 11(4): 293. CrossRef
- Metastatic Vulvar Paget's Disease Presenting in a Supraclavicular Lymph Node: A Diagnostic Challenge on Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Clinicopathological implications of immunohistochemical expression of TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, CCR4, and TCF1 in nodal follicular helper T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified
- Bogyeong Han, Sojung Lim, Jeemin Yim, Young Keun Song, Jiwon Koh, Sehui Kim, Cheol Lee, Young A Kim, Yoon Kyung Jeon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(2):59-71. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.01.04
- 7,603 View
- 373 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The classification of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) has evolved according to histology, cell-of-origin, and genetic alterations. However, the comprehensive expression pattern of follicular helper T-cell (Tfh) markers, T-cell factor-1 (TCF1), and Th1- and Th2-like molecules in nodal PTCL is unclear.
Methods
Eighty-two cases of nodal PTCL were classified into 53 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas (AITLs)/nodal T-follicular helper cell lymphoma (nTFHL)-AI, 18 PTCLs-Tfh/nTFHL–not otherwise specified (NOS), and 11 PTCLs-NOS according to the revised 4th/5th World Health Organization classifications. Immunohistochemistry for TCF1, TBX21, CXCR3, GATA3, and CCR4 was performed.
Results
TCF1 was highly expressed in up to 68% of patients with nTFHL but also in 44% of patients with PTCL-NOS (p > .05). CXCR3 expression was higher in AITLs than in non-AITLs (p = .035), whereas GATA3 expression was higher in non-AITL than in AITL (p = .007) and in PTCL-Tfh compared to AITL (p = .010). Of the cases, 70% of AITL, 44% of PTCLTfh/ nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the TBX21 subtype; and 15% of AITL, 38% of PTCL-Tfh/nTFHL-NOS, and 36% of PTCL-NOS were subclassified as the GATA3 subtype. The others were an unclassified subtype. CCR4 expression was associated with poor progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with PTCL-Tfh (p < .001) and nTFHL (p = .023). The GATA3 subtype showed poor overall survival in PTCL-NOS compared to TBX21 (p = .046) and tended to be associated with poor PFS in patients with non-AITL (p = .054).
Conclusions
The TBX21 subtype was more prevalent than the GATA3 subtype in AITL. The GATA3 subtype was associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-AITL and PTCL-NOS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- CXCR Family and Hematologic Malignancies in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Yanquan Liu, Huanwen Tang
Biomolecules.2025; 15(5): 716. CrossRef - Diagnostic and therapeutic pathways for lymphoma patients: expert consensus through Nominal Group Technique and Delphi methodology
Attilio Guarini, Valentina Bozzoli, Sabino Ciavarella, Michele Cimminiello, Francesca Donatelli, Angelo Fama, Vincenza Fernanda Fesce, Vincenzo Fraticelli, Francesco Gaudio, Giuseppina Greco, Augusto Martellini, Francesca Merchionne, Rosanna Maria Miccoli
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Significance of TBX21 and GATA3 Subtype Classification in Indolent Adult T‐Cell Leukemia‐Lymphoma With Cutaneous Lesions
Kazuhiro Kawai, Youhei Uchida, Takuro Kanekura
The Journal of Dermatology.2025; 52(11): 1674. CrossRef
- CXCR Family and Hematologic Malignancies in the Bone Marrow Microenvironment
Reviews
- Diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases: from Averill A. Liebow to artificial intelligence
- Eunhee S. Yi, Paul Wawryko, Jay H. Ryu
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(1):1-11. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.17
- 7,387 View
- 430 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Histopathologic criteria of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) were defined over the years and endorsed by leading organizations decades after Dr. Averill A. Liebow first coined the term UIP in the 1960s as a distinct pathologic pattern of fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Novel technology and recent research on interstitial lung diseases with genetic component shed light on molecular pathogenesis of UIP/IPF. Two antifibrotic agents introduced in the mid-2010s opened a new era of therapeutic approaches to UIP/IPF, albeit contentious issues regarding their efficacy, side effects, and costs. Recently, the concept of progressive pulmonary fibrosis was introduced to acknowledge additional types of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases with the clinical and pathologic phenotypes comparable to those of UIP/IPF. Likewise, some authors have proposed a paradigm shift by considering UIP as a stand-alone diagnostic entity to encompass other fibrosing interstitial lung diseases that manifest a relentless progression as in IPF. These trends signal a pendulum moving toward the tendency of lumping diagnoses, which poses a risk of obscuring potentially important information crucial to both clinical and research purposes. Recent advances in whole slide imaging for digital pathology and artificial intelligence technology could offer an unprecedented opportunity to enhance histopathologic evaluation of interstitial lung diseases. However, current clinical practice trends of moving away from surgical lung biopsies in interstitial lung disease patients may become a limiting factor in this endeavor as it would be difficult to build a large histopathologic database with correlative clinical data required for artificial intelligence models.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
Nathan Hennion, Corentin Bedart, Léonie Vandomber, Frédéric Gottrand, Sarah Humez, Cécile Chenivesse, Jean-Luc Desseyn, Valérie Gouyer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Insights into UIP Pattern: A Comparison Between IPF and Non-IPF Patients
Stefano Palmucci, Miriam Adorna, Angelica Rapisarda, Alessandro Libra, Sefora Fischetti, Gianluca Sambataro, Letizia Antonella Mauro, Emanuele David, Pietro Valerio Foti, Claudia Mattina, Corrado Spatola, Carlo Vancheri, Antonio Basile
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4162. CrossRef
- Identification of early genes in the pathophysiology of fibrotic interstitial lung disease in a new model of pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical practice recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing in patients with solid cancer: a joint report from KSMO and KSP
- Miso Kim, Hyo Sup Shim, Sheehyun Kim, In Hee Lee, Jihun Kim, Shinkyo Yoon, Hyung-Don Kim, Inkeun Park, Jae Ho Jeong, Changhoon Yoo, Jaekyung Cheon, In-Ho Kim, Jieun Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Sehhoon Park, Hyun Ae Jung, Jin Won Kim, Han Jo Kim, Yongjun Cha, Sun Min Lim, Han Sang Kim, Choong-Kun Lee, Jee Hung Kim, Sang Hoon Chun, Jina Yun, So Yeon Park, Hye Seung Lee, Yong Mee Cho, Soo Jeong Nam, Kiyong Na, Sun Och Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Kee-Taek Jang, Hongseok Yun, Sungyoung Lee, Jee Hyun Kim, Wan-Seop Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(4):147-164. Published online January 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.11.01
- 8,504 View
- 493 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years, next-generation sequencing (NGS)–based genetic testing has become crucial in cancer care. While its primary objective is to identify actionable genetic alterations to guide treatment decisions, its scope has broadened to encompass aiding in pathological diagnosis and exploring resistance mechanisms. With the ongoing expansion in NGS application and reliance, a compelling necessity arises for expert consensus on its application in solid cancers. To address this demand, the forthcoming recommendations not only provide pragmatic guidance for the clinical use of NGS but also systematically classify actionable genes based on specific cancer types. Additionally, these recommendations will incorporate expert perspectives on crucial biomarkers, ensuring informed decisions regarding circulating tumor DNA panel testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Étienne Rouleau, Lucie Karayan-Tapon, Marie-Dominique Galibert, Alexandre Harlé, Isabelle Soubeyran
Revue Francophone des Laboratoires.2025; 2025(568): 67. CrossRef - The Redox–Adhesion–Exosome (RAX) Hub in Cancer: Lipid Peroxidation-Driven EMT Plasticity and Ferroptosis Defense with HNE/MDA Signaling and Lipidomic Perspectives
Moon Nyeo Park, Jinwon Choi, Rosy Iara Maciel de Azambuja Ribeiro, Domenico V. Delfino, Seong-Gyu Ko, Bonglee Kim
Antioxidants.2025; 14(12): 1474. CrossRef
- Apport de la génomique dans la prise en charge des cancers
Original Article
- BRCA-mutated gastric adenocarcinomas are associated with chromosomal instability and responsiveness to platinum-based chemotherapy
- Ji Hyun Oh, Chang Ohk Sung, Hyung-Don Kim, Sung-Min Chun, Jihun Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(6):323-331. Published online November 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.22
- 6,383 View
- 265 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Homologous recombination defect is an important biomarker of chemotherapy in certain tumor types, and the presence of pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations involving BRCA1 or BRCA2 (p-BRCA) mutations is the most well-established marker for the homologous recombination defect. Gastric cancer, one of the most prevalent tumor types in Asia, also harbors p-BRCA mutations.
Methods
To investigate the clinical significance of p-BRCA mutations, we analyzed 366 gastric cancer cases through next-generation sequencing. We determined the zygosity of p-BRCA mutations based on the calculated tumor purity through variant allelic fraction patterns and investigated whether the presence of p-BRCA mutations is associated with platinum-based chemotherapy and a certain molecular subtype.
Results
Biallelic p-BRCA mutation was associated with better response to platinum-based chemotherapy than heterozygous p-BRCA mutation or wild type BRCA genes. The biallelic p-BRCA mutations was observed only in the chromosomal instability subtype, while all p-BRCA mutations were heterozygous in microsatellite instability subtype.
Conclusions
In conclusion, patients with gastric cancer harboring biallelic p-BRCA mutations were associated with a good initial response to platinum-based chemotherapy and those tumors were exclusively chromosomal instability subtype. Further investigation for potential association with homologous recombination defect is warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk prediction criteria for the primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumour family, including angiomyolipoma: analysis of 132 cases with a literature review
Youngeun Yoo, Jihun Kim, In Hye Song
Histopathology.2025; 86(6): 979. CrossRef - Presence of RB1 or Absence of LRP1B Mutation Predicts Poor Overall Survival in Patients with Gastric Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma
In Hye Song, Bokyung Ahn, Young Soo Park, Deok Hoon Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
Cancer Research and Treatment.2025; 57(2): 492. CrossRef - Predictive value of homologous recombination-related gene mutations in survival outcomes of first-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy for gastric cancer
Yuna Lee, Hyung-Don Kim, Sun Young Lee, Hyungeun Lee, Jaewon Hyung, Meesun Moon, Jinho Shin, Young Soo Park, Tae Won Kim, Min-Hee Ryu
Gastric Cancer.2025; 28(6): 1158. CrossRef - Association of RAD51 expression with response to neoadjuvant treatment and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer
Serhat Sekmek, Serhat Ozan, Fahriye Tugba Kos, Hayriye Tatli Dogan, Mehmet Akif Parlar, Didem Sener Dede
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2025; 25(12): 1433. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence algorithm for neoplastic cell percentage estimation and its application to copy number variation in urinary tract cancer
Jinahn Jeong, Deokhoon Kim, Yeon-Mi Ryu, Ja-Min Park, Sun Young Yoon, Bokyung Ahn, Gi Hwan Kim, Se Un Jeong, Hyun-Jung Sung, Yong Il Lee, Sang-Yeob Kim, Yong Mee Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(5): 229. CrossRef
- Risk prediction criteria for the primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumour family, including angiomyolipoma: analysis of 132 cases with a literature review
Review
- The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
- Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(6):289-304. Published online November 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.10.04
- 8,718 View
- 304 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The Asian Thyroid Working Group was founded in 2017 at the 12th Asia Oceania Thyroid Association (AOTA) Congress in Busan, Korea. This group activity aims to characterize Asian thyroid nodule practice and establish strict diagnostic criteria for thyroid carcinomas, a reporting system for thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology without the aid of gene panel tests, and new clinical guidelines appropriate to conservative Asian thyroid nodule practice based on scientific evidence obtained from Asian patient cohorts. Asian thyroid nodule practice is usually designed for patient-centered clinical practice, which is based on the Hippocratic Oath, “First do not harm patients,” and an oriental filial piety “Do not harm one’s own body because it is a precious gift from parents,” which is remote from defensive medical practice in the West where physicians, including pathologists, suffer from severe malpractice climate. Furthermore, Asian practice emphasizes the importance of resource management in navigating the overdiagnosis of low-risk thyroid carcinomas. This article summarizes the Asian Thyroid Working Group activities in the past 7 years, from 2017 to 2023, highlighting the diversity of thyroid nodule practice between Asia and the West and the background reasons why Asian clinicians and pathologists modified Western systems significantly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Performance of Two‐Tiered Subclassification of Atypia of Undetermined Significance in Thyroid Fine‐Needle Aspiration Without Routine Molecular Testing
Pocholo D. Santos, Chiung‐Ru Lai, Jen‐Fan Hang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 78. CrossRef - Risk of Infertility in Reproductive-Age Patients With Thyroid Cancer Receiving or Not Receiving 131I Treatment
Chun-Yi Lin, Cheng-Li Lin, Chia-Hung Kao
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2025; 50(3): 201. CrossRef - Association Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Thyroid Cancer
Sang Yi Moon, Minkook Son, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Ji Min Han, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh
Thyroid®.2025; 35(1): 79. CrossRef - Letter: “High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis” by Fung et al
Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov, Jen-Fan Hang, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Somboon Keelawat, Zhiyan Liu, Radhika Srinivasan, Chan Kwon Jung
Thyroid®.2025; 35(5): 595. CrossRef - Thyroid Nodules with Nuclear Atypia of Undetermined Significance (AUS-Nuclear) Hold a Two-Times-Higher Risk of Malignancy than AUS-Other Nodules Regardless of EU-TIRADS Class of the Nodule or Borderline Tumor Interpretation
Dorota Słowińska-Klencka, Bożena Popowicz, Joanna Duda-Szymańska, Mariusz Klencki
Cancers.2025; 17(8): 1365. CrossRef - Response to Kakudo et al.: “High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis”
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(5): 597. CrossRef - Molecular Testing Could Drive Smarter Decision-Marking for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodule if the Price was Right
Sarah C. Brennan, Matti L. Gild, Venessa Tsang
Clinical Thyroidology®.2025; 37(5): 165. CrossRef - Welcoming the new, revisiting the old: a brief glance at cytopathology reporting systems for lung, pancreas, and thyroid
Rita Luis, Balamurugan Thirunavukkarasu, Deepali Jain, Sule Canberk
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(4): 165. CrossRef - Are we ready to bridge classification systems? A comprehensive review of different reporting systems in thyroid cytology
Esther Diana Rossi, Liron Pantanowitz
Cytopathology.2024; 35(6): 674. CrossRef - Aggressive Types of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms
Maria Boudina, Eleana Zisimopoulou, Persefoni Xirou, Alexandra Chrisoulidou
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(20): 6119. CrossRef - Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnoses of follicular thyroid carcinoma: results from a multicenter study in Asia
Hee Young Na, Miyoko Higuchi, Shinya Satoh, Kaori Kameyama, Chan Kwon Jung, Su-Jin Shin, Shipra Agarwal, Jen-Fan Hang, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 331. CrossRef
- Performance of Two‐Tiered Subclassification of Atypia of Undetermined Significance in Thyroid Fine‐Needle Aspiration Without Routine Molecular Testing
Original Article
- Diagnostic proficiency test using digital cytopathology and comparative assessment of whole slide images of cytologic samples for quality assurance program in Korea
- Yosep Chong, Soon Auck Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh, Soo Jin Jung, Bo-Sung Kim, Ji Yun Jeong, Ho-Chang Lee, Gyungyub Gong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):251-264. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.07.17
- 7,662 View
- 339 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The Korean Society for Cytopathology introduced a digital proficiency test (PT) in 2021. However, many doubtful opinions remain on whether digitally scanned images can satisfactorily present subtle differences in the nuclear features and chromatin patterns of cytological samples.
Methods
We prepared 30 whole-slide images (WSIs) from the conventional PT archive by a selection process for digital PT. Digital and conventional PT were performed in parallel for volunteer institutes, and the results were compared using feedback. To assess the quality of cytological assessment WSIs, 12 slides were collected and scanned using five different scanners, with four cytopathologists evaluating image quality through a questionnaire.
Results
Among the 215 institutes, 108 and 107 participated in glass and digital PT, respectively. No significant difference was noted in category C (major discordance), although the number of discordant cases was slightly higher in the digital PT group. Leica, 3DHistech Pannoramic 250 Flash, and Hamamatsu NanoZoomer 360 systems showed comparable results in terms of image quality, feature presentation, and error rates for most cytological samples. Overall satisfaction was observed with the general convenience and image quality of digital PT.
Conclusions
As three-dimensional clusters are common and nuclear/chromatin features are critical for cytological interpretation, careful selection of scanners and optimal conditions are mandatory for the successful establishment of digital quality assurance programs in cytology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Chang Gok Woo, Seung‐Myoung Son, Hye‐Kyung Hwang, Jung‐Sil Bae, Ok‐Jun Lee, Ho‐Chang Lee
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(1): 35. CrossRef - Integration of AI‐Assisted in Digital Cervical Cytology Training: A Comparative Study
Yihui Yang, Dongyi Xian, Lihua Yu, Yanqing Kong, Huaisheng Lv, Liujing Huang, Kai Liu, Hao Zhang, Weiwei Wei, Hongping Tang
Cytopathology.2025; 36(2): 156. CrossRef - National quality assurance program using digital cytopathology: a 5-year digital transformation experience by the Korean Society for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Soon Auck Hong, Sung Soon Kim, Bo-Sung Kim, Younghee Choi, Yoon Jung Choi, Jung-Soo Pyo, Ji Yun Jeong, Soo Jin Jung, Hoon Kyu Oh, Seung-Sook Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(5): 320. CrossRef - Integration of Digital Cytology in Quality Assurance Programs for Cytopathology
Yosep Chong, Maria Jesús Fernández Aceñero, Zaibo Li, Andrey Bychkov
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Focus Quality in Whole-Slide Imaging of Thyroid Liquid-Based Cytology Using Laplacian Variance
Chan Kwon Jung, Chankyung Kim, Sora Jeon, Andrey Bychkov
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of digital image slides for diagnosis in cervico-vaginal cytology
Francisco Tresserra, Gemma Fabra, Olga Luque, Miriam Castélla, Carla Gómez, Carmen Fernández-Cid, Ignacio Rodríguez
Revista Española de Patología.2024; 57(3): 182. CrossRef - Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology with Artificial Intelligence Technology
Yujin Lee, Mohammad Rizwan Alam, Hongsik Park, Kwangil Yim, Kyung Jin Seo, Gisu Hwang, Dahyeon Kim, Yeonsoo Chung, Gyungyub Gong, Nam Hoon Cho, Chong Woo Yoo, Yosep Chong, Hyun Joo Choi
Thyroid®.2024; 34(6): 723. CrossRef
- Sensitivity, Specificity, and Cost–Benefit Effect Between Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing, Primary Liquid‐Based Cytology, and Co‐Testing Algorithms for Cervical Lesions
Case Studies
- Hepatic small vessel neoplasm: not totally benign, not yet malignant
- Madison Miranda, David Howell, Tony El Jabbour
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(5):273-277. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.19
- 6,711 View
- 280 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatic small vessel neoplasm (HSVN) is a rare vascular tumor with few reports in the literature. While imaging findings may show characteristic enhancement patterns, limited available literature may not reveal the full potential for image-based diagnosis. Histologically, HSVN mimics other entities, though certain morphologic and immunohistochemical findings provide clues for diagnosis. However, HSVN still provides diagnostic challenges, especially on core biopsies with limited material for morphologic and molecular evaluation. While current recommendations are surgical resection and close observation, the long-term course of the tumor is unknown. We report a case of HSVN in a liver with additional feature of organized lymphoid aggregates necessitating additional hematopathology consultation and workup to rule out concurrent entities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
Joon Hyuk Choi, Swan N. Thung
Biomedicines.2025; 13(2): 479. CrossRef - Revisiting Hepatic Small Vessel Neoplasms and Anastomosing Hemangiomas as a Unique Capillary Liver Neoplasm: A 25-Case Series With Pathomolecular Correlations
Aurélie Beaufrère, Astrid Laurent-Bellue, Antoinette Lemoine, Agnès Bourillon, Nathalie Sturm, Pierre Gosset, Virginie Cahn, Valérie Vilgrain, Maité Lewin, Valérie Paradis, Catherine Guettier
Modern Pathology.2025; 38(10): 100835. CrossRef - Imaging features of recently identified low-grade vascular neoplasia of the liver: hepatic small vessel neoplasm and anastomosing hemangioma
Maïté Lewin, Rauda Aldhaheri, Aurélie Beaufrère, Christophe Desterke, Anita Paisant, Ivan Bricault, Paul Borde, Gabriel Simon, Mickaël Lesurtel, Daniel Cherqui, Clara Prud’Homme, Valérie Vilgrain, Astrid Laurent-Bellue
European Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mesenchymal Tumors of the Liver: An Update Review
- Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma masquerading as a primary thyroid tumor
- Jai-Hyang Go
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):242-245. Published online July 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.06.16
- 4,417 View
- 117 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma is rare. To date, only six cases have been reported in the literature. This case was unusual and presented with thyromegaly before the diagnosis of the primary tumor. A 55-year-old male patient was suspected to have a primary thyroid tumor with nodal metastasis. The thyroid gland was diffusely enlarged, with no discernible mass. Histologically, the thyroid parenchyma revealed extensive endolymphatic tumor emboli, which were positive for p40 and p16 in a background of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed hypermetabolic activity in the right tonsillar region. Tonsillar biopsy revealed human papillomavirus–positive squamous cell carcinoma. The present case is the first reported case of intrathyroidal metastasis of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma with an initial clinical presentation of thyroid enlargement before the primary tumor of tonsillar cancer was diagnosed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
Avneet Kaur, Rohit Nayyar, Harit Kumar Chaturvedi, Akshat Malik
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2025; 16(1): 122. CrossRef - Metastatic oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma to the thyroid: A case report and review of literature
Hannah Walker, Jed Speers, Milena Fabry, Sameep Kadakia
American Journal of Otolaryngology.2024; 45(4): 104306. CrossRef
- Metastasis to Thyroid from Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Series and Review of Literature
Reviews
- A review of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis regression
- Michael J. Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(4):189-195. Published online June 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.05.24
- 28,874 View
- 872 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cirrhosis has traditionally been considered an irreversible process of end-stage liver disease. With new treatments for chronic liver disease, there is regression of fibrosis and cirrhosis, improvement in clinical parameters (i.e. liver function and hemodynamic markers, hepatic venous pressure gradient), and survival rates, demonstrating that fibrosis and fibrolysis are a dynamic process moving in two directions. Microscopically, hepatocytes push into thinning fibrous septa with eventual perforation leaving behind delicate periportal spikes in the portal tracts and loss of portal veins. Obliterated portal veins during progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis due to parenchymal extinction, vascular remodeling and thrombosis often leave behind a bile duct and hepatic artery within the portal tract. Traditional staging classification systems focused on a linear, progressive process; however, the Beijing classification system incorporates both the bidirectional nature for the progression and regression of fibrosis. However, even with regression, vascular lesions/remodeling, parenchymal extinction and a cumulative mutational burden place patients at an increased risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma and should continue to undergo active clinical surveillance. It is more appropriate to consider cirrhosis as another stage in the evolution of chronic liver disease as a bidirectional process rather than an end-stage, irreversible state.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular and cellular secrets revealed: How umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells can target hepatocellular carcinoma
Mohammad Sadegh Izadi, Reza Arefnezhad, Amirmasoud Asadi, Aryan Rezaee, Leila Kalantari, Farzad Nasrpour Tahouneh, Mohammad Mehdi Shadravan, Seyyed Taher Seyyed Mahmoudi, Zahra GhaniBeygi, Fatemeh Rostamnezhad, Armin Razman, Fardad Ejtehadi, Fatemeh Rezae
Tissue and Cell.2026; 98: 103200. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values of Spleen and Liver in Assessment of Severity of Portal Hypertension and Liver Cirrhosis
Kommuri Siddhardha, S. Jalaludheen, Senthil Kumar Aiyappan
Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal.2026; 33(1): 118. CrossRef - Head to head: should portal inflammation be part of grading necroinflammatory activity in metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease?
Daniela Allende, Alastair D Burt
Histopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of deep learning-enhanced MRI techniques for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammadreza Elhaie, Abolfazl Koozari, Iraj Abedi
Egyptian Liver Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical Activity and Liver Fibrosis: A Stratified Analysis by Obesity and Diabetes Status
Junghwan Cho, Sunghwan Suh, Ji Min Han, Hye In Kim, Hanaro Park, Hye Rang Bak, Ji Cheol Bae
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2026; 15(2): 757. CrossRef - Serum Kallistatin level as a biomarker for evaluation of liver function status in cirrhotic patients
Mahmoud Rizk, F. M. Khalil, Mohamed El-Assal, Hussien Ali, Ahmed R. Mohamed, Samer S. Zekry, Abeer Mahmoud El-Bahy, Amira Kamal ElDin Mohammed ElAlfy
Egyptian Liver Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The Dual-Faceted Role of Metal-Based Nanomaterials in Hepatic Fibrosis Therapy
Yinqing Mao, Yankai Gong, Xue Bai
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2026; Volume 21: 1. CrossRef - Reply to the Letter on “Clinical implications of fibrosis marker dynamics after hepatitis C cure: insights from paired biopsies”
Hung-Wei Wang, Cheng-Yuan Peng
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation: a Shared Mechanism for Chronic Diseases
Mariana Cifuentes, Hugo E. Verdejo, Pablo F. Castro, Alejandro H. Corvalan, Catterina Ferreccio, Andrew F. G. Quest, Marcelo J. Kogan, Sergio Lavandero
Physiology.2025; 40(1): 4. CrossRef - Natural History of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Metabolic Syndrome to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Melchor Alpízar Salazar, Samantha Estefanía Olguín Reyes, Andrea Medina Estévez, Julieta Alejandra Saturno Lobos, Jesús Manuel De Aldecoa Castillo, Juan Carlos Carrera Aguas, Samary Alaniz Monreal, José Antonio Navarro Rodríguez, Dulce María Fernanda Alpí
Medicina.2025; 61(1): 88. CrossRef - Unveiling the Link between Albumin-Bilirubin Grade and Liver Fibrosis in Patients with a History of Gallstone and Gallbladder Surgery: A Focus on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis
Mohammadjavad Sotoudeheian
The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract.2025; 30(1): 10. CrossRef - Impact of Weight Loss on Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Fibrosis
Marina W. Takawy, Manal F. Abdelmalek
Current Diabetes Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticle-based therapeutic strategies for chronic liver diseases: Advances and insights
Sathiyamoorthy Padmanaban, Ji-Won Baek, Sai Sahithya Chamarthy, Saipriya Chandrasekaran, Antony V Samrot, Vijayakumar Gosu, In-Kyu Park, Kamalakannan Radhakrishnan, Don-Kyu Kim
Liver Research.2025; 9(2): 104. CrossRef - Innovative Strategies in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis and Associated Syndromes
Ashok Kumar Sah, Mohd Afzal, Rabab H. Elshaikh, Anass M. Abbas, Manar G. Shalabi, Pranav Kumar Prabhakar, Asaad M. A. Babker, Fariza Tursunbaevna Khalimova, Velilyaeva Aliya Sabrievna, Ranjay Kumar Choudhary
Life.2025; 15(5): 779. CrossRef - Poly(I:C)-Stimulated Exosomes Mitigate Cholesterol-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis by Modulating the TGF-β/Smad3 Signal Transduction Pathway
Shahla Asadizadeh, Parichehreh Yaghmaei, Nasim Hayati Roodbari, Azam Khedri
Hepatitis Monthly.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The postbiotic ReFerm® versus standard nutritional support in advanced alcohol-related liver disease (GALA-POSTBIO): a randomized controlled phase 2 trial
Johanne K. Hansen, Mads Israelsen, Suguru Nishijima, Sara E. Stinson, Peter Andersen, Stine Johansen, Camilla D. Hansen, Maximilian Joseph Brol, Sabine Klein, Robert Schierwagen, Frank Erhard Uschner, Karolina Sulek, Ida F. Villesen, Katrine P. Lindvig, K
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ADVANCING CURCUMIN APPLICATIONS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA: INSIGHTS INTO PHARMACOKINETICS, PHARMACODYNAMICS AND NANODELIVERY SYSTEMS
RESHMA T. MATE, ANURADHA N. CHIVATE, NAMDEO R. JADHAV, NIRANJAN D. CHIVATE
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics.2025; : 19. CrossRef - Genetic Determinants of Apoptosis Regulate Liver Cirrhosis Risk: The FAS/FASL Polymorphism Connection in Iraqi Population
Wisam Hindawi Hoidy, Ahmed Ghdhban Al-Ziaydi
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Histological and Molecular Evaluation of Liver Biopsies: A Practical and Updated Review
Joon Hyuk Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(16): 7729. CrossRef - Resolving fibrosis by stimulating HSC-dependent extracellular matrix degradation
Sachin Sharma, Vijaya Prathigudupu, Carson Cable, Lia R. Serrano, Srilaxmi Nerella, Alina Chen, Ghmkin Hassan, Johnathon Lakins, Carlos Lizama Valenzuela, Tatsuya Tsukui, Roopa Ramamoorthi, Jae-Jun Kim, Holger Willenbring, Aras N. Mattis, Regan F. Volk, B
Science Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ANGPT2 and NOS3 Gene Variants With Esophageal Variceal Progression in HCV‐Induced Cirrhosis
Omnia S. Nabih, Mohamed Abdel‐Samiee, Marwa A. Tahoon, Elaf Abozeid, Heba Demerdash, Fatma Omar Khalil, Randa M. Seddik, Marwa L. Helal, Gamalat A. El Gedawy, HalaA E. Khalil, Badawy W AboBakr. Yossef, Ahmed B. Zaid, Mai I. Elashmawy
Journal of Medical Virology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging advanced approaches for diagnosis and inhibition of liver fibrogenesis
Tamer A. Addissouky, Majeed M. A. Ali, Ibrahim El Tantawy El Sayed, Yuliang Wang
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation by nutraceuticals: an emphasis on mechanisms of action
Vasudevan Sekar, Venkateish VP, Vani Vijay, Annapoorna BR, Nivya Vijayan, Madan Kumar Perumal
Journal of Food Science and Technology.2024; 61(11): 2046. CrossRef - The Role of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor in TAA-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice: Modulatory Effects of Betaine
Tatjana Radosavljevic, Dusan Vukicevic, Jasmina Djuretić, Kristina Gopcevic, Milica Labudovic Borovic, Sanja Stankovic, Janko Samardzic, Milica Radosavljevic, Danijela Vucevic, Vladimir Jakovljevic
Biomedicines.2024; 12(6): 1337. CrossRef - Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis: Role of Gene-Environment Interactions in Liver Disease Progression
Anindita Banerjee, Patrizia Farci
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(16): 8641. CrossRef - Multiomic predictors for regression of cirrhosis: Clinical implications and future directions
Binghua Li, Decai Yu
iLIVER.2024; 3(4): 100116. CrossRef - Commonly encountered symptoms and their management in patients with cirrhosis
Cyriac Abby Philips
Frontiers in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant Potential of Xanthohumol in Disease Prevention: Evidence from Human and Animal Studies
Jakub Piekara, Dorota Piasecka-Kwiatkowska
Antioxidants.2024; 13(12): 1559. CrossRef - AdhMMP8 Vector Administration in Muscle: An Alternate Strategy to Regress Hepatic Fibrosis
Jesús García-Bañuelos, Edén Oceguera-Contreras, Ana Sandoval-Rodríguez, Blanca Estela Bastidas-Ramírez, Silvia Lucano-Landeros, Daniela Gordillo-Bastidas, Belinda C. Gómez-Meda, Arturo Santos, Eira Cerda-Reyes, Juan Armendariz-Borunda
Cells.2023; 12(17): 2127. CrossRef - Nutritional deficiency in patients with liver cirrhosis
Maria S. Zhigalova, Vladimir V. Kiselev, Alla A. Ryk, Petr A. Yartsev
Clinical nutrition and metabolism.2023; 4(4): 265. CrossRef
- Molecular and cellular secrets revealed: How umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells can target hepatocellular carcinoma
- Trouble-makers in cytologic interpretation of the uterine cervix
- Eunah Shin, Jaeeun Yu, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):139-146. Published online May 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.04.25
- 10,980 View
- 466 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development and standardization of cytologic screening of the uterine cervix has dramatically decreased the prevalence of squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Advances in the understanding of biology of human papillomavirus have contributed to upgrading the histologic diagnosis of the uterine cervix; however, cytologic screening that should triage those that need further management still poses several difficulties in interpretation. Cytologic features of high grade intraepithelial squamous lesion (HSIL) mimics including atrophy, immature metaplasia, and transitional metaplasia, and glandular lesion masquerades including tubal metaplasia and HSIL with glandular involvement are described with accentuation mainly on the differential points. When the cytologic features lie in a gray zone between the differentials, the most important key to the more accurate interpretation is sticking to the very basics of cytology; screening the background and cellular architecture, and then scrutinizing the nuclear and cytoplasmic details.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of cervical stenosis after cervical excision in postmenopausal patients
Eva Hauge, Line Winther Gustafson, Mette Tranberg, Pinar Bor
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2025; 308: 208. CrossRef - Pitfalls in Gynecological Cytology: Review of the Common and Less Frequent Entities in Pap Test
Danijela Vrdoljak-Mozetič, Snježana Štemberger-Papić, Damjana Verša Ostojić, Roberta Rubeša, Marko Klarić, Senija Eminović
Acta Cytologica.2024; 68(3): 281. CrossRef - Cytological features of human papillomavirus‐infected immature squamous metaplastic cells from cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2
Mitsuaki Okodo, Kaori Okayama, Koji Teruya, Ruku Shinohara, Shuichi Mizuno, Rei Settsu, Yasuyoshi Ishii, Masahiko Fujii, Hirokazu Kimura, Mizue Oda
Journal of Medical Virology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Risk of cervical stenosis after cervical excision in postmenopausal patients

 E-submission
E-submission
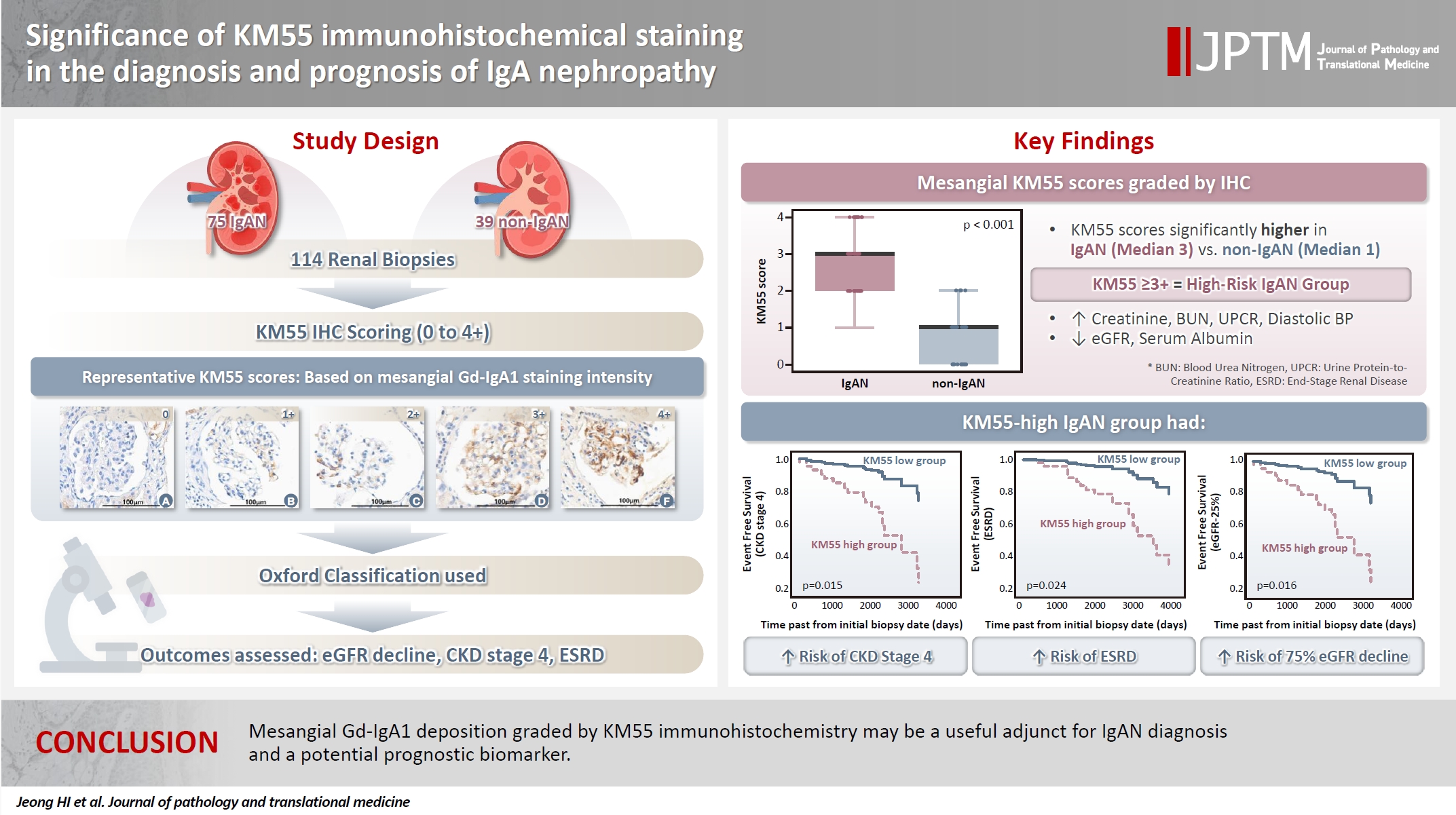




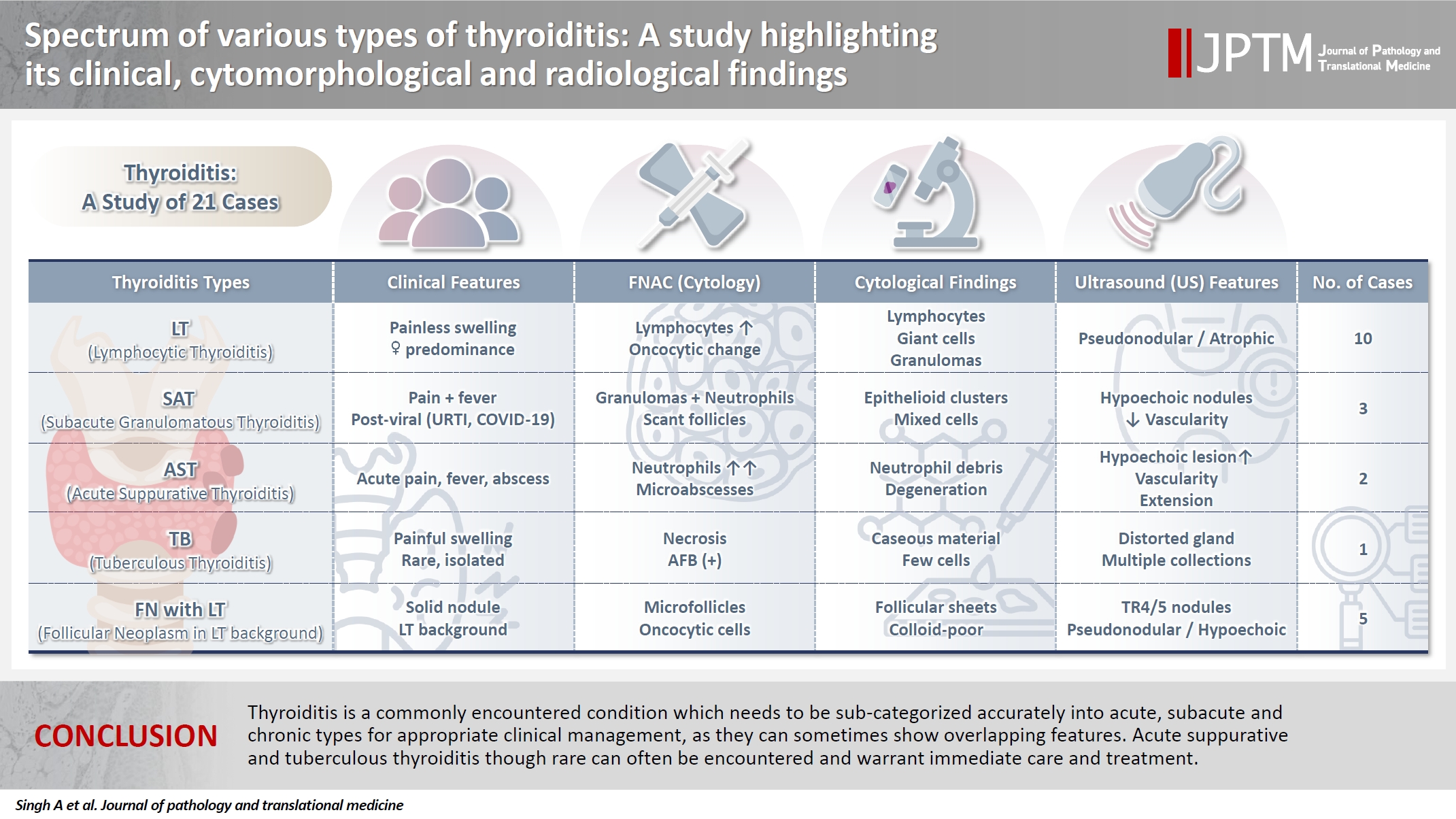
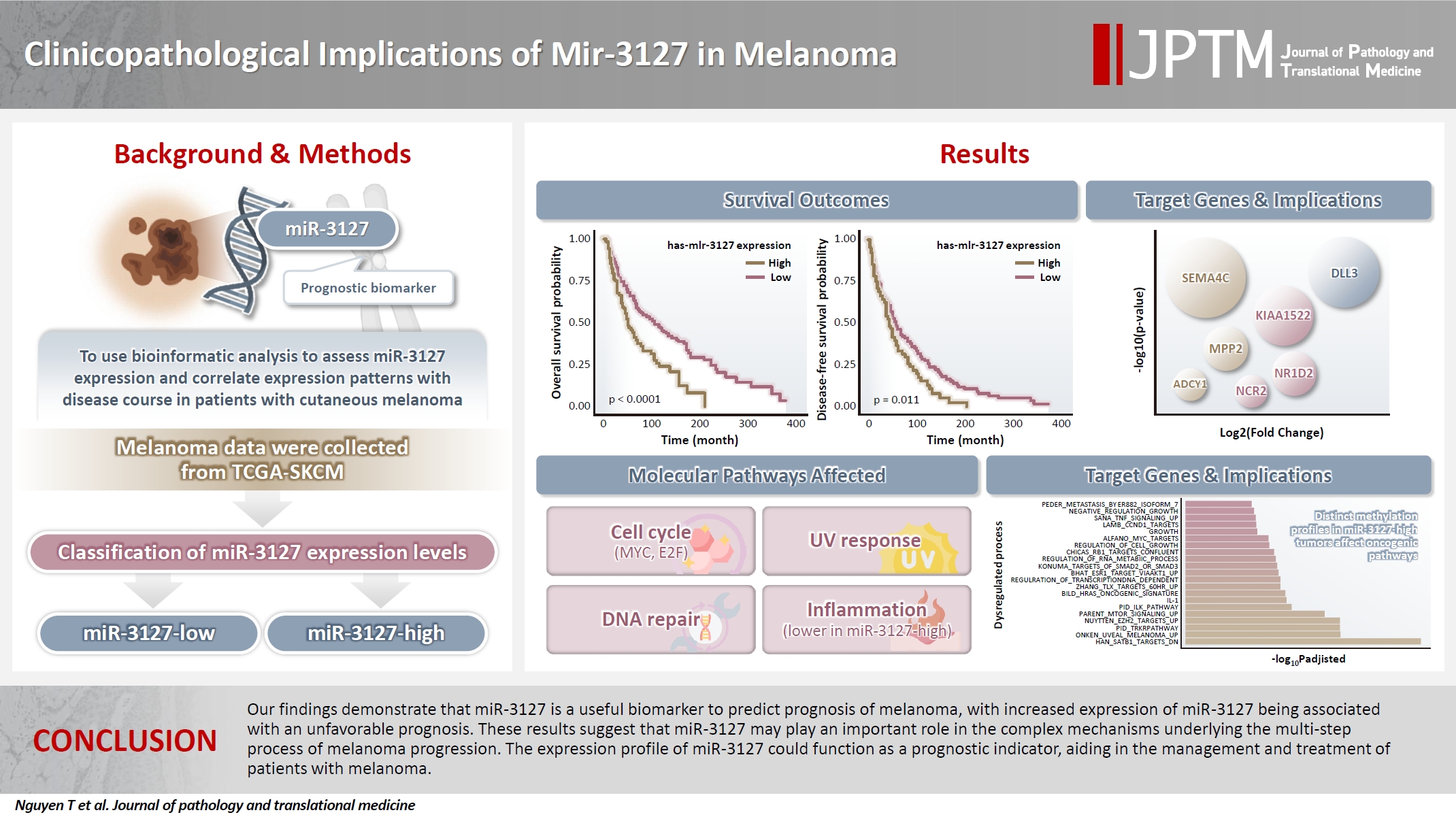
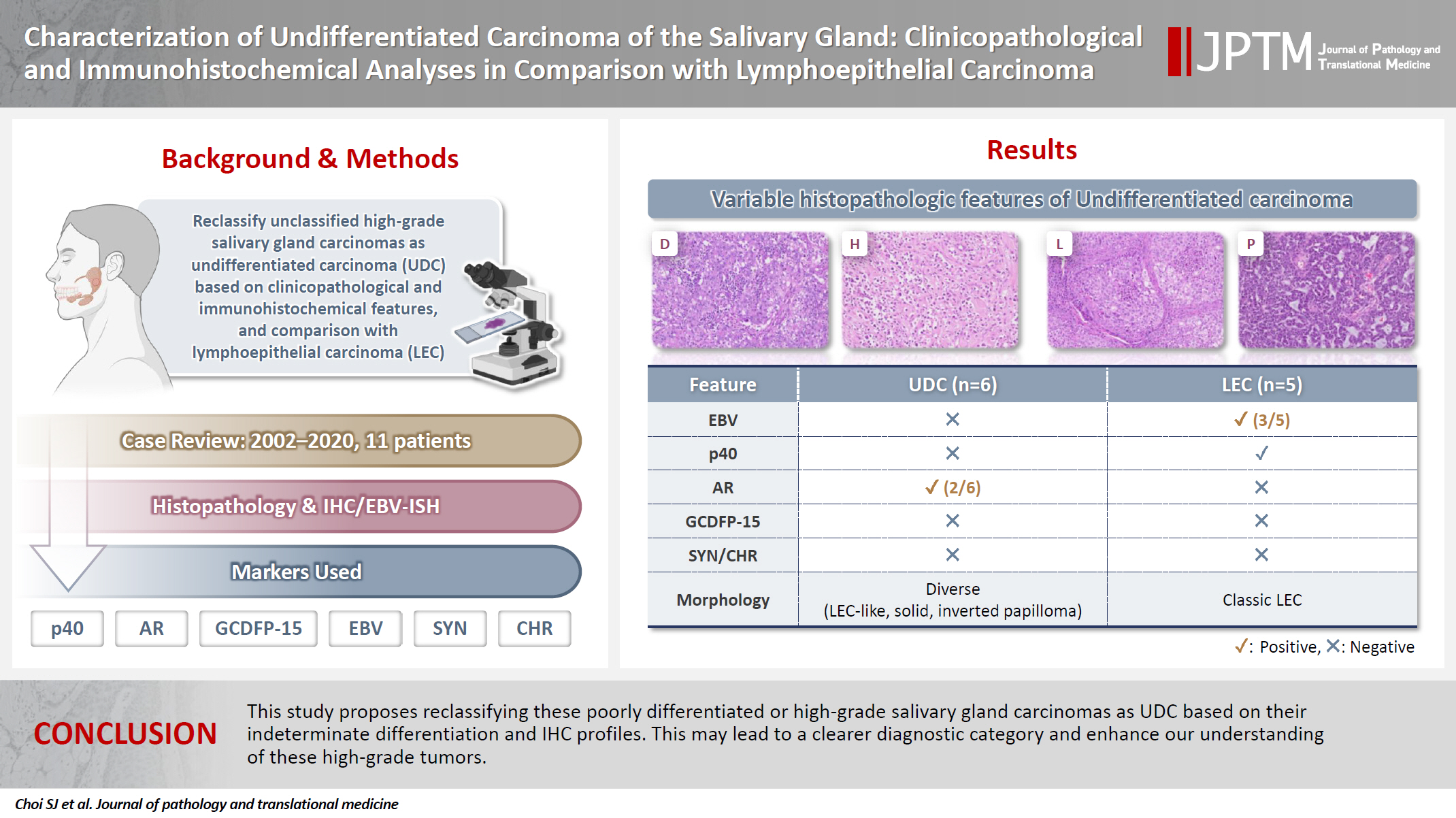
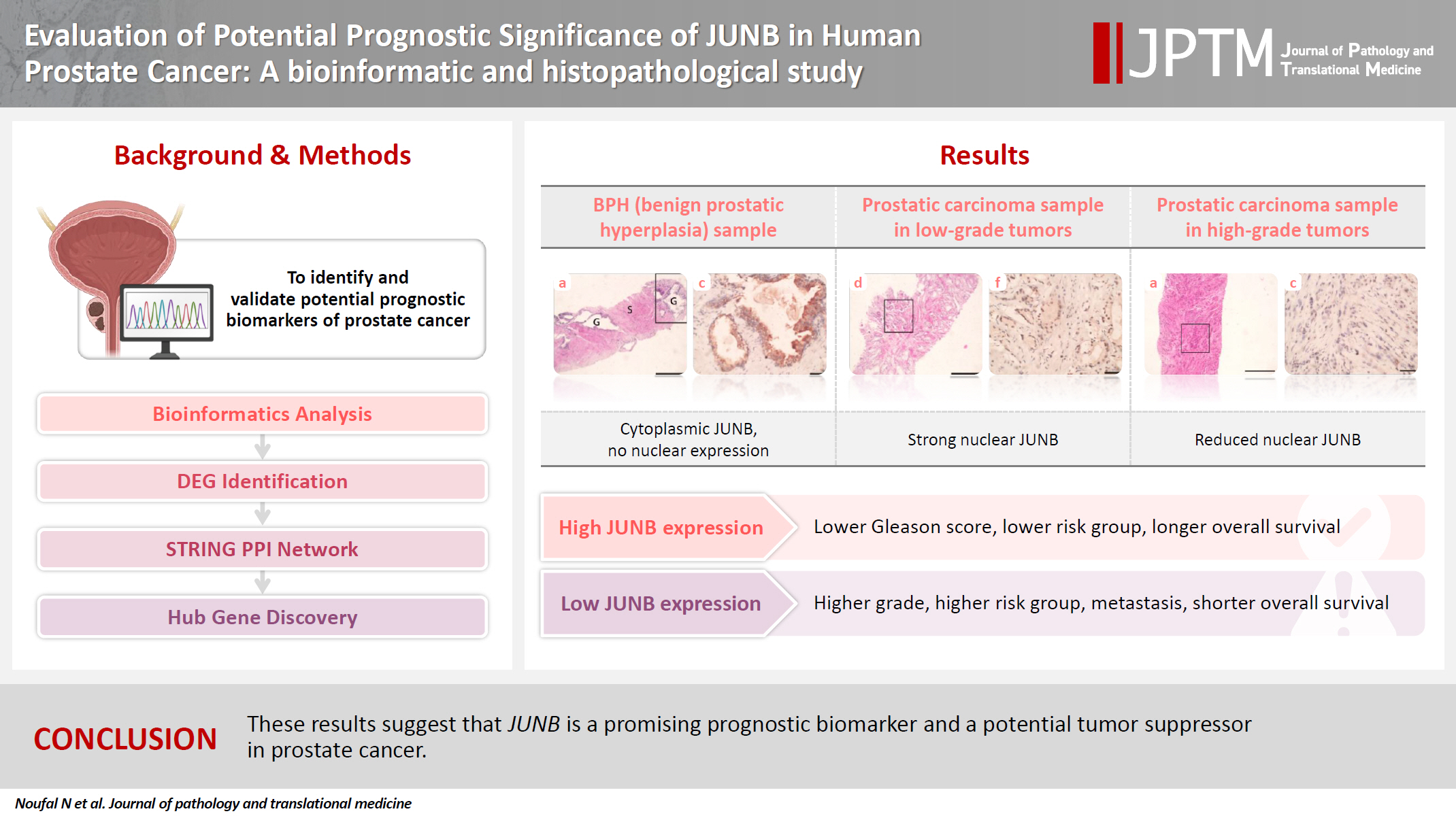







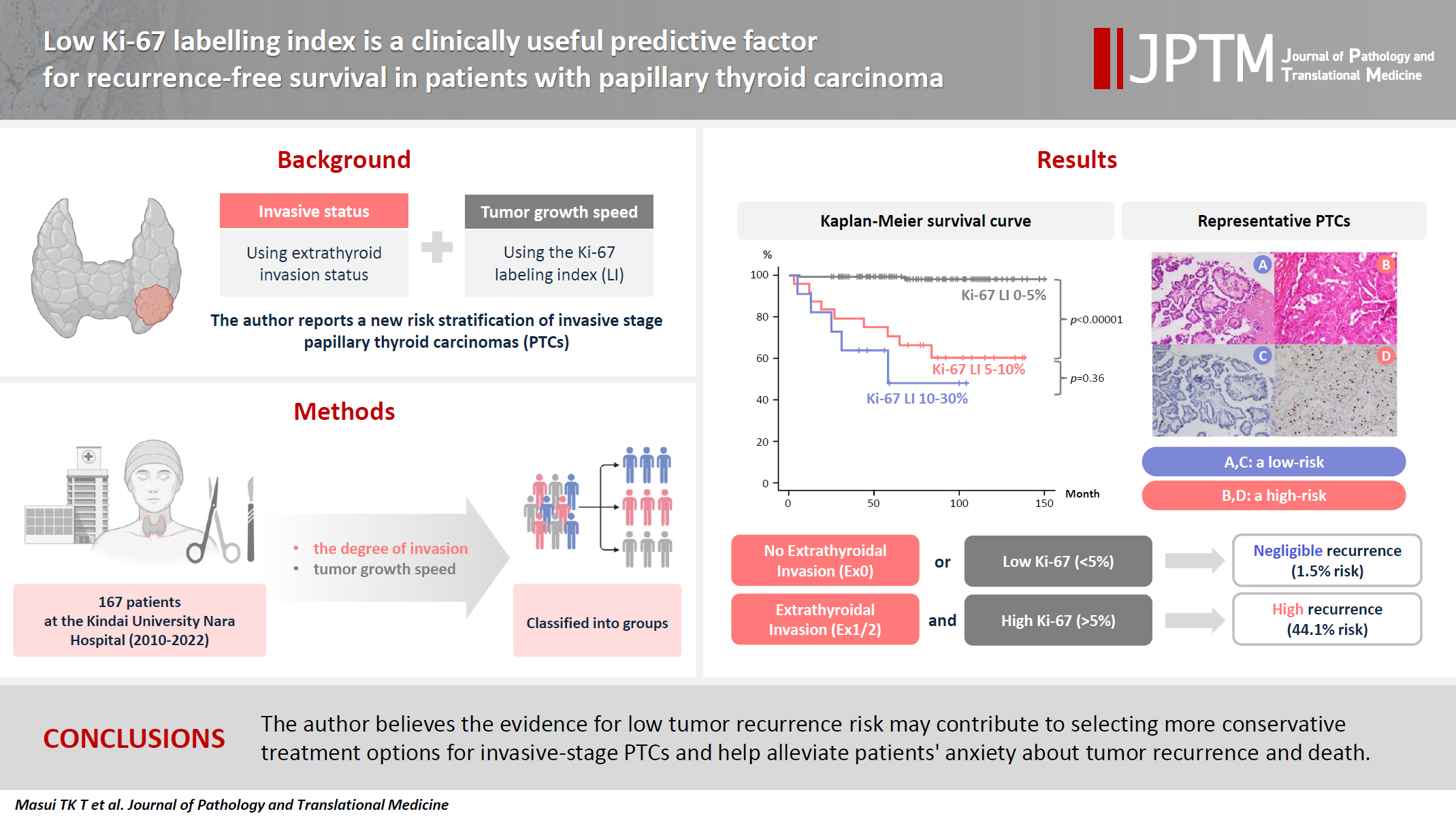
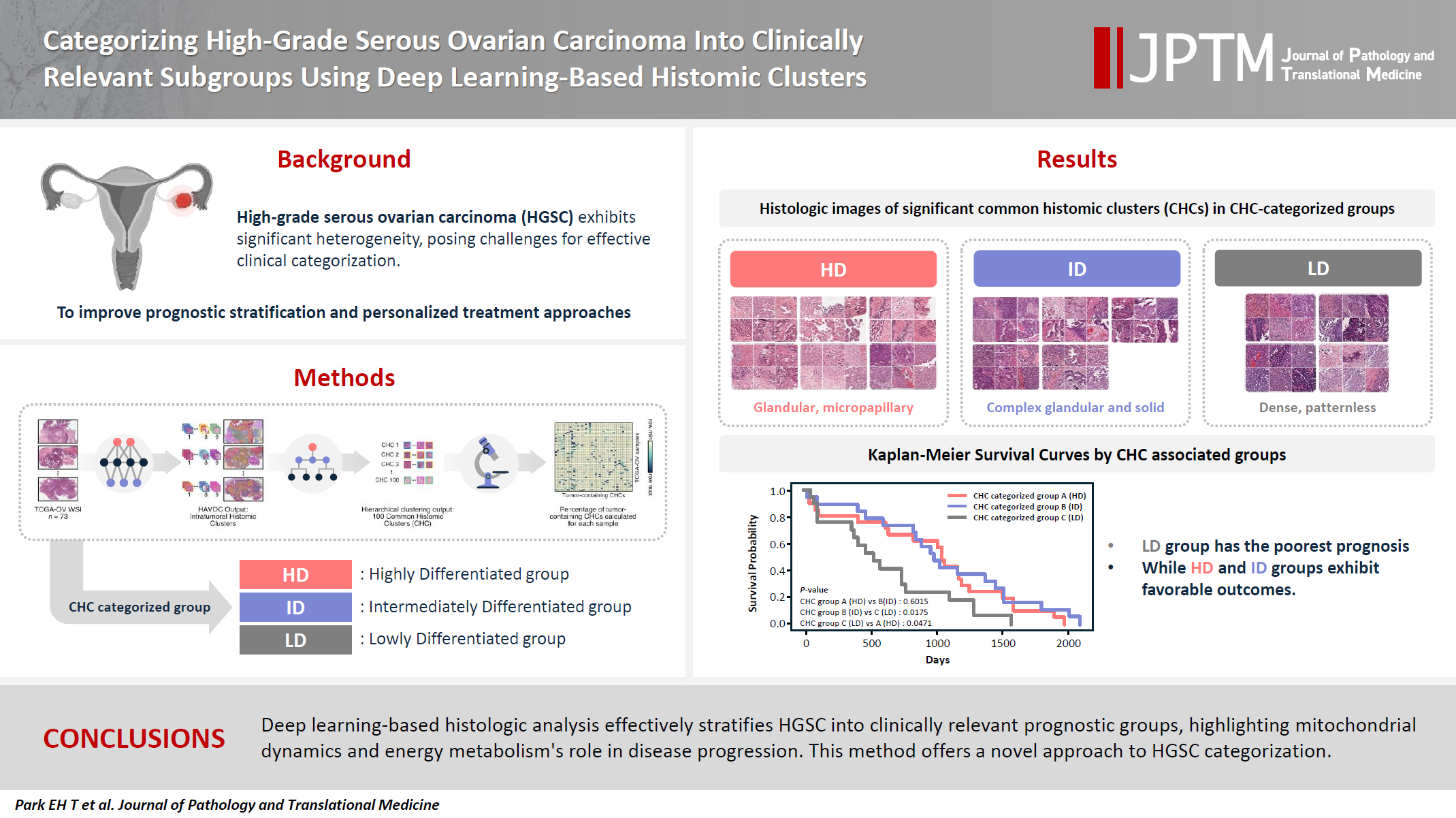





























 First
First Prev
Prev



