Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The significance of papillary architecture in the follow-up biopsies of patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia
- Wangpan J. Shi, Oluwole Fadare
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2026;60(1):58-68. Published online January 8, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.09.12
- 1,458 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Follow-up biopsies in patients with progestin-treated atypical endometrial hyperplasia/endometrioid intraepithelial neoplasia (AH/EIN) may show papillary structures, the significance of which is unclear. Methods: The authors reviewed 253 serial specimens of 84 consecutive patients diagnosed with AH/EIN, inclusive of each patient's pre-progestin treatment sample and all post-treatment specimens. We assessed the predictive relationship between papillary architecture in a post-treatment biopsy and two study outcomes: AH/EIN or carcinoma in at least one sample subsequent to the one in which papillae were identified, and/or the last specimen received for that patient. Results: Papillae were identified in only 51.5% of pre-treatment samples but were present in at least one subsequent post-treatment sample for all patients. Post-treatment samples that exhibited papillae and no glandular crowding were associated with AH/EIN in at least one subsequent specimen in 39.7% (29/73) of cases, compared to 24.0% (6/25) in samples with neither papillae nor glandular crowding (p = .227) and 64.0% (16/25) in samples with concurrent gland crowding and papillae (p = .048). Univariate logistic regression analyses showed that the presence of papillae was not associated with study outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 0.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.49 to 1.99; p = .985), as compared with gland crowding (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.04 to 2.27; p = .031), or concurrent papillae and gland crowding (OR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.01 to 5.52; p = .048). Conclusions: In post-treatment samples of progestin-treated AH/EIN, the presence of papillary architecture was not demonstrably associated with study outcomes independent of gland crowding, although the concurrent presence of both features may be significantly predictive.
- Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
- Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Young Sub Lee, Sang-Ryung Lee, Myunghee Kang, Young Jin Seo, Seung-Sook Lee, Yoon-Jung Hwang, Hyun-Jung Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(6):444-452. Published online November 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2025.10.21
- 3,625 View
- 136 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) independent cervical malignancies (HPV-IDCMs) have recently been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) 5th edition. These malignancies have historically received limited attention due to their rarity and the potential for evasion of HPV-based screening.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 5,854 biopsy-confirmed cervical malignancies from 22 institutions over 3 years (July 2020–June 2023). Histologic classification followed the WHO guidelines. HPV independence was confirmed by dual negativity for p16 and HPV; discordant cases (p16-positive/HPV-negative) underwent additional HPV testing using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cytological results were matched sequentially to histological confirmation.
Results
The prevalence of HPV-IDCM was 4.4% (257/5,854) overall and was 3.6% (208/5,805 cases) among primary cervical malignancy. Patient age of HPV-IDCM was 29 to 89 years (median, 57.79). Its histologic subtypes included primary adenocarcinoma (n = 116), endometrial adenocarcinoma (n = 35), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 72), metastatic carcinoma (n = 14), carcinoma, not otherwise specified (n = 10), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 3), and others (n = 7). Among 155 cytology-histological matched cases, the overall and primary Pap test detection rates were 85.2% (132/155) and 83.2% (104/125), respectively. The interval between cytology and histologic confirmation extended up to 38 months.
Conclusions
HPV-IDCMs comprised 3.6% of primary cervical malignancies with a high detection rate via cytology (83.2%). These findings affirm the value of cytological screening, particularly in patients with limited screening history or at risk for HPV-independent lesions, and may guide future screening protocols.
- Low Ki-67 labeling index is a clinically useful predictive factor for recurrence-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Takashi Masui, Katsunari Yane, Ichiro Ota, Kennichi Kakudo, Tomoko Wakasa, Satoru Koike, Hirotaka Kinugawa, Ryuji Yasumatsu, Tadashi Kitahara
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2025;59(2):115-124. Published online February 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.08
- 5,596 View
- 248 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We report a new risk stratification of invasive stage papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) by combining invasive status, using extrathyroid invasion (Ex) status, and tumor growth speed using the Ki-67 labeling index (LI). Methods: We examined tumor recurrence in 167 patients with PTC who were surgically treated at the Kindai University Nara Hospital between 2010 and 2022. The patients were classified according to the degree of invasion [negative (Ex0) or positive (Ex1, Ex2, and Ex3)] and tumor growth speed expressed with Ki-67 LI, as low (<5%) or high (>5%). This study confirmed previous findings that the disease-free survival (DFS) rate in PTCs significantly differed between patients with a high and low Ki-67 index. Results: When combining Ex status (negative or positive) and Ki-67 proliferation status (low or high), the DFS rate of invasion in the negative, low Ki-67 LI group was only 1.1%, while that of invasion in the positive, high Ki-67 LI was 44.1%. This study reports for the first time that recurrence risks can be stratified accurately when combining carcinoma’s essential two features of extrathyroid invasion status and tumor growth speed. Conclusions: We believe the evidence for low tumor recurrence risk may contribute to use of more conservative treatment options for invasive-stage PTCs and help alleviate patient anxiety about tumor recurrence and death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
锦容 马
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(09): 326. CrossRef - Immunophenotypic Panel for Comprehensive Characterization of Aggressive Thyroid Carcinomas
Mihail Ceausu, Mihai Alin Publik, Dana Terzea, Carmen Adina Cristea, Dumitru Ioachim, Dana Manda, Sorina Schipor
Cells.2025; 14(19): 1554. CrossRef - High Ki-67 labeling index correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective study
Defi Nurlia Erdian, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Agnes Stephanie Harahap
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress on the Correlation between Three Biomarkers, Ki-67, CAIX and VEGF and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cytology in pregnancy
- Ji-Young Kim, Jeong Yun Shim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):283-290. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.17
- 10,928 View
- 451 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer screening during pregnancy presents unique challenges for cytologic interpretation. This review focuses on pregnancy-associated cytomorphological changes and their impact on diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer. Pregnancy-induced alterations include navicular cells, hyperplastic endocervical cells, immature metaplastic cells, and occasional decidual cells or trophoblasts. These changes can mimic abnormalities such as koilocytosis, adenocarcinoma in situ, and high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions, potentially leading to misdiagnosis. Careful attention to nuclear features and awareness of pregnancy-related changes are crucial for correct interpretation. The natural history of CIN during pregnancy shows higher regression rates, particularly for CIN 2, with minimal risk of progression. Management of abnormal cytology follows modified risk-based guidelines to avoid invasive procedures, with treatment typically deferred until postpartum. The findings reported in this review emphasize the importance of considering pregnancy status in cytological interpretation, highlight potential problems, and provide guidance on differentiating benign pregnancy-related changes from true abnormalities. Understanding these nuances is essential for accurate diagnosis and proper management of cervical abnormalities in pregnant women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Xue Mi, Maharjan Rashmi, Zangyu Pan, Di Wu, Jinwei Miao
Frontiers in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncologic and pregnancy outcomes of cervical high-grade intraepithelial lesions and delivery mode
Olga P. Matylevich, Ilya A. Tarasau, Sviatlana Y. Shelkovich, Aliaksandr F. Martsinkevich
Academia Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The significance of biological samples from pregnant women in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
- Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):265-282. Published online November 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.10.11
- 15,769 View
- 625 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common thyroid malignancy, characterized by a range of subtypes that differ in their cytologic features, clinical behavior, and prognosis. Accurate cytologic evaluation of PTC using fine-needle aspiration is essential but can be challenging due to the morphologic diversity among subtypes. This review focuses on the distinct cytologic characteristics of various PTC subtypes, including the classic type, follicular variant, tall cell, columnar cell, hobnail, diffuse sclerosing, Warthin-like, solid/trabecular, and oncocytic PTCs. Each subtype demonstrates unique nuclear features, architectural patterns, and background elements essential for diagnosis and differentiation from other thyroid lesions. Recognizing these distinct cytologic patterns is essential for identifying aggressive subtypes like tall cell, hobnail, and columnar cell PTCs, which have a higher risk of recurrence, metastasis, and poorer clinical outcomes. Additionally, rare subtypes such as diffuse sclerosing and Warthin-like PTCs present unique cytologic profiles that must be carefully interpreted to avoid diagnostic errors. The review also highlights the cytologic indicators of lymph node metastasis and high-grade features, such as differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma. The integration of molecular testing can further refine subtype diagnosis by identifying specific genetic mutations. A thorough understanding of these subtype-specific cytologic features and molecular profiles is vital for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized management of PTC patients. Future improvements in diagnostic techniques and standardization are needed to enhance cytologic evaluation and clinical decision-making in thyroid cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
Adeel M. Ashraf, Faisal Hassan, Adrian A. Dawkins, Julie C. Dueber, Derek B. Allison, Thèrése J. Bocklage
Cytopathology.2026; 37(1): 108. CrossRef - Using a new type of visible light-based emission fluorescence microscope to identify the benign and malignant nature of thyroid tissue during the surgical process: Analysis of diagnostic results
Yu Miao, Liu Xiaowei, Li Muyang, Gao Jian, Chen Lu
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2026; 57: 105324. CrossRef - Clinical Behavior of Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective Case–Control Study
Jovan Ilic, Nikola Slijepcevic, Katarina Tausanovic, Bozidar Odalovic, Goran Zoric, Marija Milinkovic, Branislav Rovcanin, Milan Jovanovic, Matija Buzejic, Duska Vucen, Boban Stepanovic, Sara Ivanis, Milan Parezanovic, Milan Marinkovic, Vladan Zivaljevic
Cancers.2026; 18(2): 345. CrossRef - Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - Structure-based molecular screening and dynamic simulation of phytocompounds targeting VEGFR-2: a novel therapeutic approach for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Shuai Wang, Lingqian Zhang, Wenjun Zhang, Xiong Zeng, Jie Mei, Weidong Xiao, Lijie Yang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Propensity score-matched analysis of the ‘2+2’ parathyroid strategy in total thyroidectomy with central neck dissection
Hao Gong, Simei Yao, Tianyuchen Jiang, Yi Yang, Yuhan Jiang, Zhujuan Wu, Anping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Findings in Pediatric Thoracic Tumors: A Review of Diagnostic Insights and Pitfalls
Parikshaa Gupta, Pranab Dey
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef
- Oncocytic Thyroid Tumours With Pathogenic FLCN Mutations Mimic Oncocytic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Fine‐Needle Aspiration
- TERT mutations and aggressive histopathologic characteristics of radioiodine-refractory papillary thyroid cancer
- Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoon Jin Cha, SoonWon Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):310-320. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.29
- 5,094 View
- 344 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Radioiodine (RI) ablation following thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression is an effective treatment for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), typically leading to favorable outcomes. However, RI-refractory tumors exhibit aggressive behavior and poor prognoses. Recent studies highlight the role of genetic abnormalities in PTC signaling pathways, including the activation of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), and the correlation of mutations with adverse outcomes.
Methods
This study analyzed mutations in BRAF V600E and the TERT-promoter genes, comparing clinicopathological features between RI-refractory and RI-responsive PTCs. Among 82 RI-refractory patients, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues from initial surgeries were available for 26. Another 89 without distant metastasis over 5 years formed a matched RI-responsive control group.
Results
Histopathologically, RI-refractory PTCs showed increased frequencies of small tumor clusters without fibrovascular cores, hobnail features, and a high height-to-width ratio of tumor cells. These tumors were more likely to exhibit necrosis, mitosis, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension, and involvement of resection margins. TERT-promoter mutations were statistically significantly associated with these aggressive clinicopathologic features. Immunohistochemically, decreased expression of sodium iodide symporter and thyroglobulin stimulating hormone receptor proteins was common in RI-refractory PTCs, along with lower levels of oncogenic proteins such as vascular endothelial cell growth factor, vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 2, and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. Total loss of PTEN expression was occasionally observed. In contrast, all cases tested positive for cytoplasmic β-catenin.
Conclusions
RI-refractory PTCs are linked to TERT mutations and exhibit specific aggressive histopathologic features, particularly in tumor centers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
Myoung Ju Koh, Songmi Noh, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2026; 80: 152578. CrossRef - Insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction in thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer
Stefano Iuliano, Maria Mirabelli, Stefania Giuliano, Antonio Brunetti
Current Opinion in Oncology.2026; 38(1): 1. CrossRef - Differentiated high-grade thyroid carcinoma (DHGTC): clinicopathological analysis of a new entity in a chilean center
Marlín Solórzano, Ignacio Fuentes, José Miguel González, Nicole Lustig, Lorena Mosso, Joel Falcón, Catalina Ruiz, Joaquín Viñambres, Rodolfo Cabello, Hernán González, Pablo H Montero, Francisco Cruz, Rodrigo Jaimovich, Juan Carlos Quintana, Antonieta Sola
Endocrine.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics and outcome of pediatric and adult differentiated thyroid cancer with distant metastases
Ali S. Alzahrani, Lulu Alobaid, Eman Albasri, Afnan Hadadi, Abdulrhman Hakami, Fayha Abothenain, Deema Alturki, Najla Ewain, Ali Howaidi, Hindi Alhindi, Ghada Alskait, Yasser Aljufan, Shatha Alghaihb, Azzam Alkhalifah, Leenah AlAyoubi, Amani Abualnaja
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The ability of anexelekto (AXL) expression and TERT promoter mutation to predict radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Hasrayati Agustina, Tutik Nur Ayni, Yohana Azhar, Erwin Affandi Soeriadi, Bethy Suryawathy Hernowo
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of papillary thyroid carcinoma, tall cell subtype and subtype with tall cell features, an institutional experience
Xueting Jin, Shunsuke Koga, Xiao Zhou, Niaz Z. Khan, Zubair W. Baloch
Human Pathology.2025; 161: 105867. CrossRef - Calcifying nested stromal-epithelial tumor of the liver: Report of two cases revealing novel WT1 mutation and distinct epigenetic features
Andrea Strakova-Peterikova, Franco Fedeli, Boris Rychly, Jiri Soukup, Michael Michal, Petr Martinek, Marian Grendar, Elaheh Mosaieby, Nikola Ptakova, Maryna Slisarenko, Michal Michal, Kvetoslava Michalova
Virchows Archiv.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Characterizing thyroid carcinomas in the elderly: Histological subtypes and TERT promoter mutation analysis based on the latest WHO classification
- Diagnostic challenges in the assessment of thyroid neoplasms using nuclear features and vascular and capsular invasion: a multi-center interobserver agreement study
- Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Maria Francisca Ham, Dina Khoirunnisa, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Husni Cangara, Aswiyanti Asri, Diah Prabawati Retnani, Fairuz Quzwain, Hasrayati Agustina, Hermawan Istiadi, Indri Windarti, Krisna Murti, Muhammad Takbir, Ni Made Mahastuti, Nila Kurniasari, Nungki Anggorowati, Pamela Abineno, Yulita Pundewi Setyorini, Kennichi Kakudo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2024;58(6):299-309. Published online September 12, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.07.25
- Correction in: J Pathol Transl Med 2025;59(3):201
- 5,440 View
- 412 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms necessitates the identification of distinct histological features. Various education/hospital centers located in cities across Indonesia likely result in discordances among pathologists when diagnosing thyroid neoplasms.
Methods
This study examined the concordance among Indonesian pathologists in assessing nuclear features and capsular and vascular invasion of thyroid tumors. Fifteen pathologists from different centers independently assessed the same 14 digital slides of thyroid tumor specimens. All the specimens were thyroid neoplasms with known BRAFV600E and RAS mutational status, from a single center. We evaluated the pre- and post-training agreement using the Fleiss kappa. The significance of the training was evaluated using a paired T-test.
Results
Baseline agreement on nuclear features was slight to fair based on a 3-point scoring system (k = 0.14 to 0.28) and poor to fair based on an eight-point system (k = –0.02 to 0.24). Agreements on vascular (κ = 0.35) and capsular invasion (κ = 0.27) were fair, whereas the estimated molecular type showed substantial agreement (κ = 0.74). Following the training, agreement using the eight-point system significantly improved (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The level of concordance among Indonesian pathologists in diagnosing thyroid neoplasm was relatively poor. Consensus in pathology assessment requires ongoing collaboration and education to refine diagnostic criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Dina Khoirunnisa, Salinah, Maria Francisca Ham
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2025; 75: 152434. CrossRef
- Nuclear pseudoinclusion is associated with BRAFV600E mutation: Analysis of nuclear features in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Clinicopathologic characterization of cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor: a multicenter study in Korea
- Miseon Lee, Uiree Jo, Joon Seon Song, Youn Soo Lee, Chang Gok Woo, Dong-Hoon Kim, Jung Yeon Kim, Sun Och Yoon, Kyung-Ja Cho
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2023;57(3):166-177. Published online May 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2023.04.12
- 6,528 View
- 171 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Research regarding cervical metastasis from an unknown primary tumor (CUP) according to human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status in Korea has been sporadic and small-scale. This study aims to analyze and understand the characteristics of CUP in Korea according to viral and p16 and p53 status through a multicenter study.
Methods
Ninety-five cases of CUP retrieved from six hospitals in Korea between January 2006 and December 2016 were subjected to high-risk HPV detection (DNA in situ hybridization [ISH] or real-time polymerase chain reaction), EBV detection (ISH), and immunohistochemistry for p16 and p53.
Results
CUP was HPV-related in 37 cases (38.9%), EBV-related in five cases (5.3%), and unrelated to HPV or EBV in 46 cases (48.4%). HPV-related CUP cases had the best overall survival (OS) (p = .004). According to the multivariate analysis, virus-unrelated disease (p = .023) and longer smoking duration (p < .005) were prognostic factors for poor OS. Cystic change (p = .016) and basaloid pattern (p < .001) were more frequent in HPV-related cases, and lymphoepithelial lesion was frequent in EBV-related cases (p = .010). There was no significant association between viral status and p53 positivity (p = .341), smoking status (p = .728), or smoking duration (p = .187). Korean data differ from Western data in the absence of an association among HPV, p53 positivity, and smoking history.
Conclusions
Virus-unrelated CUP in Korea had the highest frequency among all CUP cases. HPV-related CUP is similar to HPV-mediated oropharyngeal cancer and EBVrelated CUP is similar to nasopharyngeal cancer in terms of characteristics, respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: current evidence-based diagnostic and treatment strategies
Marcel Kloppenburg, Matthias Santer, Lukas Schmutzler, Felix Johnson, Benedikt Hofauer, Teresa Steinbichler
memo - Magazine of European Medical Oncology.2026; 19(1): 45. CrossRef - Differenzierung von benignen und malignen Halszysten – eine diagnostische Herausforderung
Christina Sauter, Matthias Sand, Karim Plath, Michaela Maria Plath
Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie.2025; 104(05): 296. CrossRef - Unlocking the Hidden: Advancing Imaging Techniques in Diagnosing Cancers of Unknown Primary in the Head and Neck Region
Daniela Messineo, Filippo Valentini, Giovanni Francesco Niccolini, Federica Zoccali, Francesca Ripari, Enrico Marotta, Marcello Caratozzolo, Pasquale Frisina
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(4): 2194. CrossRef - Characterization of undifferentiated carcinoma of the salivary gland: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analyses in comparison with lymphoepithelial carcinoma
Sangjoon Choi, Gyuheon Choi, Hee Jin Lee, Joon Seon Song, Yoon Se Lee, Seung-Ho Choi, Kyung-Ja Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 361. CrossRef - Expansion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to assess the potential of adoptive cell therapy
Sangjoon Choi, Mofazzal Hossain, Hyun Lee, Jina Baek, Hye Seon Park, Chae-Lyul Lim, DoYeon Han, Taehyun Park, Jong Hyeok Kim, Gyungyub Gong, Mi-Na Kweon, Hee Jin Lee
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Management of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary in the head and neck: current evidence-based diagnostic and treatment strategies
- Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
- Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):319-325. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.29
- 9,770 View
- 315 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Due to the extremely indolent behavior, a subset of noninvasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinomas has been classified as “noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP)” since 2016 and is no longer considered carcinoma. Since the introduction of this new terminology, changes and refinements have been made in diagnostic criteria. Initially, the incidence of NIFTP was estimated substantial. However, the reported incidence of NIFTP varies greatly among studies and regions, with higher incidence in North American and European countries than in Asian countries. Thus, the changes in the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) differ inevitably among regions. Because more conservative surgery is recommended for NIFTPs, distinguishing NIFTPs from papillary thyroid carcinomas in preoperative fine-needle aspiration cytology became one of the major concerns. This review will provide comprehensive overview of updates on diagnostic criteria, actual incidence and preoperative cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP, and its impact on the ROM in TBSRTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Minh-Khang Le, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Shanop Shuangshoti, Nakarin Kitkumthorn, Somboon Keelawat
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(1): 39. CrossRef - Papillae, psammoma bodies, and/or many nuclear pseudoinclusions are helpful criteria but should not be required for a definitive cytologic diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma: An institutional experience of 207 cases with surgical follow up
Tarik M. Elsheikh, Matthew Thomas, Jennifer Brainard, Jessica Di Marco, Erica Manosky, Bridgette Springer, Dawn Underwood, Deborah J. Chute
Cancer Cytopathology.2024; 132(6): 348. CrossRef - ThyroSeq overview on indeterminate thyroid nodules: An institutional experience
Sam Sirotnikov, Christopher C. Griffith, Daniel Lubin, Chao Zhang, Nabil F. Saba, Dehong Li, Amanda Kornfield, Amy Chen, Qiuying Shi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(7): 353. CrossRef - Oncocytic Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Case Report
Kaveripakam Ajay Joseph, Sana Ahuja, Sufian Zaheer
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S4): 606. CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Preoperative evaluation of thyroid nodules – Diagnosis and management strategies
Tapoi Dana Antonia, Lambrescu Ioana Maria, Gheorghisan-Galateanu Ancuta-Augustina
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 246: 154516. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - Strategies for Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
Deepika Yadav, Pramod Kumar Sharma, Rishabha Malviya, Prem Shankar Mishra
Current Drug Targets.2023; 24(5): 406. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef
- Diagnosis of invasive encapsulated follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma by protein-based machine learning
- Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
- Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(6):354-360. Published online November 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.09.05
- 8,732 View
- 154 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Detection of glandular abnormalities in Papanicolaou (Pap) tests is challenging. This study aimed to review our institute’s experience interpreting such abnormalities, assess cytohistologic concordance, and identify cytomorphologic features associated with malignancy in follow-up histology.
Methods
Patients with cytologically-detected glandular lesions identified in our pathology records from 1995 to 2020 were included in this study.
Results
Of the 683,197 Pap tests performed, 985 (0.144%) exhibited glandular abnormalities, 657 of which had tissue follow-up available. One hundred eighty-eight cases were cytologically interpreted as adenocarcinoma and histologically diagnosed as malignant tumors of various origins. There were 213 cases reported as atypical glandular cells (AGC) and nine cases as adenocarcinoma in cytology, yet they were found to be benign in follow-up histology. In addition, 48 cases diagnosed with AGC and six with adenocarcinoma cytology were found to have cervical squamous lesions in follow-up histology, including four squamous cell carcinomas. Among the cytomorphological features examined, nuclear membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and presence of mitoses were associated with malignant histology in follow-up.
Conclusions
This study showed our institute’s experience detecting glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology over a 25-year period, revealing the difficulty of this task. Nonetheless, the present study indicates that several cytological findings such as membrane irregularity, three-dimensional clusters, single-cell pattern, and evidence of proliferation could help distinguishing malignancy from a benign lesion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
Havva Gokce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 71. CrossRef - Expertise in Gynecological Pathology Impacts Diagnosis of Atypical Glandular Cell Category in Cervical Cytology
Havva Gökce Terzioglu, Alessa Aragao, Julieta E. Barroeta
Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease.2025; 29(4): 297. CrossRef - Comparison of Cytological and/or Histopathological Results of Patients with Single and Multiple HPV Positivity
Fatih Mehmet Kaya, Şafak Ersöz, Cihan Comba, Ömer Demir
Acta Cytologica.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Analysis of atypical glandular cells in ThinPrep Pap smear and follow-up histopathology
Tengfei Wang, Yinan Hua, Lina Liu, Bing Leng
Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings.2024; 37(3): 403. CrossRef
- “Atypical Glandular Cells” on Cervical Cytology: Correlation Between Glandular Cell Component Volume and Histological Follow‐Up
- Papillary and medullary thyroid carcinomas coexisting in the same lobe, first suspected based on fine-needle aspiration cytology: a case report
- Hyun Hee Koh, Young Lyun Oh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):301-308. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.03
- 6,426 View
- 117 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Because different types of thyroid malignancies have distinct embryological origins, coexisting tumors are rarely observed. We describe a coexisting papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) first suspected by fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). A 57-year-old female presented with an irregular mass in the right thyroid lobe. The cytopathologic findings of fine-needle aspiration showed two components: a papillary-like arrangement consisting of cells with pale enlarged nuclei indicative of PTC and loose clusters comprised of oval cells with granular chromatin indicative of MTC. The diagnosis of a coexisting PTC and MTC was initially confirmed by calcitonin immunocytochemistry and later after total thyroidectomy. Although some surgical case reports of PTC and MTC coexisting in either the same or different lobes have been documented, a case suspected by FNAC before the surgery has rarely been reported. Because appropriate treatment and prognosis of PTC and MTC are different, cytopathologists should be aware of this rare entity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Fine‐Needle Aspiration Cytology—Based on a Single Tertiary Centre Experience
Si‐Yi Chen, Dong‐Mei Gu
Cytopathology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Synchronous papillary and medullary thyroid carcinoma with distinct genetic mutations: A case report
Huanyu Jiang, Lijuan Zhou, Gang Zou, Haidong Zhang, Zhenkun Yu
Oral Oncology.2025; 161: 107191. CrossRef - Coexisting papillary and medullary thyroid carcinomas in a 60 year old male: a case report
Allahdad Khan, Anam Malik, Abdul Ahad Riaz, Muhammad Hussnain Sadiq, Muhammad Shahzaib Arshad, Alka Rani, Ibrahim Nagmeldin Hassan
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2025; 87(10): 6740. CrossRef - Dedifferentiated Leiomyosarcoma of the Uterine Corpus with Heterologous Component: Clinicopathological Analysis of Five Consecutive Cases from a Single Institution and Comprehensive Literature Review
Suyeon Kim, Hyunsik Bae, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2024; 14(2): 160. CrossRef - Coexisting Medullary and Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas: A Case of Dual Neoplasia With a High Risk of Misdiagnosis
Santiago Sierra Castillo, Maria A Henao Rincón, David Aristizabal Colorado, David Alexander Vernaza Trujillo, Alin Abreu Lomba
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Fine‐Needle Aspiration Cytology—Based on a Single Tertiary Centre Experience
- Evaluation of the characteristics of multiple human papillomavirus (HPV) infections identified using the BD Onclarity HPV assay and comparison with those of single HPV infection
- Jinhee Kim, Moonsik Kim, Ji Young Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):289-293. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.08.02
- 8,186 View
- 139 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a major cause of cervical cancer and associated precursor lesions. Multiple HPV genotype infections have been reported. However, their clinicopathological characteristics still remain elusive.
Methods
For this study, 814 consecutive patients who had undergone colposcopy and HPV genotyping test using BD Onclarity HPV assay were retrospectively selected. Clinicopathological parameters of multiple HPV infections were compared with those of single HPV infection.
Results
Multiple HPV infections were found in 110 out of 814 cases (13.5%). Multiple HPV infections were associated with a significantly higher incidence of high-grade intraepithelial lesions (HSILs) compared with single HPV infection. Other high-risk HPV genotypes, in addition to HPV 16, were found more frequently in the multiple HPV infections group; these included HPV 51, 52, 33/58, 56/59/66, and 35/39/68. No specific coinfection pattern was not identified. Additionally, the number of HPV genotypes in multiple HPV infections was not associated with the progression to HSIL or squamous cell carcinoma.
Conclusions
Multiple HPV infections have distinct clinicopathological characteristics (compared with single HPV infection). As their biological behavior is uncertain, close and frequent follow-up is warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Prevalence of Multi-Type Infections Among Human Papillomavirus Types in Korean Women
Jang Mook Kim, Hee Seung Song, Jieun Hwang, Jae Kyung Kim
Pathogens.2025; 14(4): 369. CrossRef - Multiple high-risk human papillomavirus infections exacerbate cervical lesion risk: epidemiological evidence from suining, Sichuan
Yaling Jing, Jianhui Chen, Fang Lin, Xiaonan Huang, Yulin Liu, Mingcai Zhao, Chuan Ye, Lianfang Zhao, Xiaofang Liu, Jiayan Yang
Virology Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The cervical cancer related distribution, coinfection and risk of 15 HPV types in Baoan, Shenzhen, in 2017–2023
Rukai Li, Weiwei Meng, Yunhai Zuo, Yanli Xu, Shaonan Wu
Virology Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular findings and virological assessment of bladder papillomavirus infection in cattle
Francesca De Falco, Anna Cutarelli, Francesca Luisa Fedele, Cornel Catoi, Sante Roperto
Veterinary Quarterly.2024; 44(1): 1. CrossRef - Patterns of single and multiple HPV infections in female: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Dan Zhou, Jing Xue, Yaqiong Sun, Liling Zhu, Ming Zhao, Meimei Cui, Min Zhang, Jingjing Jia, Limei Luo
Heliyon.2024; 10(17): e35736. CrossRef - Age distribution of patients with multiple High-Risk Human Papilloma Virus (HR-HPV) genotypes and HPV vaccine recommendations by age
Gülçin Çetin Uysal, Nil Tekin
Family Practice and Palliative Care.2024; 9(3): 80. CrossRef - Relative distribution of HPV genotypes in histological cervical samples and associated grade lesion in a women population over the last 16 years in Burgundy, France
Christelle Auvray, Serge Douvier, Odile Caritey, Jean-Baptiste Bour, Catherine Manoha
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiologic characteristics of high-risk HPV and the correlation between multiple infections and cervical lesions
Qinli Luo, Xianghua Zeng, Hanyi Luo, Ling Pan, Ying Huang, Haiyan Zhang, Na Han
BMC Infectious Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Prevalence of Multi-Type Infections Among Human Papillomavirus Types in Korean Women
- Cytopathologic features of human papillomavirus–independent, gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma
- Min-Kyung Yeo, Go Eun Bae, Dong-Hyun Kim, In-Ock Seong, Kwang-Sun Suh
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(5):260-269. Published online September 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.07.05
- 6,327 View
- 165 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (GEA) is unrelated to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and is clinically aggressive compared with HPV-associated usual-type endocervical adenocarcinoma (UEA). The cytological diagnosis falls short of a definitive diagnosis of GEA and is often categorized as atypical glandular cells (AGCs). To improve cytologic recognition, cytological findings of HPV-independent GEA were analyzed and the results compared with HPV-associated UEA.
Methods
Cervical Papanicolaou (Pap) smears from eight patients with a histopathologic diagnosis of GEA and 12 control cases of UEA were reviewed. All slides were conventionally prepared and/or liquid-based prepared (ThinPrep) and stained following the Pap method. A mucinous background, architectural, nuclear, and cytoplasmic features were analyzed and compared with UEA.
Results
Preoperative cytologic diagnoses of the eight GEA cases were AGCs, favor neoplastic in three cases, adenocarcinoma in situ in one case, and adenocarcinoma in four cases. Cytologically, monolayered honeycomb-like sheets (p = .002) of atypical endocervical cells with vacuolar granular cytoplasm (p = .001) were extensive in GEA, and three-dimensional clusters (p = .010) were extensive in UEA. Although the differences were not statistically significant, background mucin (p = .058), vesicular nuclei (p = .057), and golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin (p = .089) were also discriminatory findings for GEA versus UEA.
Conclusions
Although GEA is difficult to diagnose on cytologic screening, GEA can be recognized based on cytologic features of monolayered honeycomb sheets of atypical endocervical cells with abundant vacuolar cytoplasm and some golden-brown intracytoplasmic mucin. UEA cases are characterized by three-dimensional clusters. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Features, Molecular Landscape, and Therapeutic Challenges
Hiroshi Yoshida, Daiki Higuchi, Waku Takigawa, Nao Kikkawa, Taro Yamanaka, Ayaka Nagao, Mayumi Kobayashi-Kato, Masaya Uno, Mitsuya Ishikawa, Kouya Shiraishi
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2026; 16(2): 72. CrossRef - A Comparative Analysis of Usual- and Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma in a Japanese Population Reveals Distinct Clinicopathological and Molecular Features with Prognostic and Therapeutic Insights
Umme Farzana Zahan, Hasibul Islam Sohel, Kentaro Nakayama, Masako Ishikawa, Mamiko Nagase, Sultana Razia, Kosuke Kanno, Hitomi Yamashita, Shahataj Begum Sonia, Satoru Kyo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(15): 7469. CrossRef - Diagnostic value of cytology in detecting human papillomavirus–independent cervical malignancies: a nation-wide study in Korea
Hye-Ra Jung, Junyoung Shin, Chong Woo Yoo, Eun Na Kim, Cheol Lee, Kyeongmin Kim, Ho-chang Lee, Yonghee Lee, Ji Hye Kim, Soo Jin Jung, Yumin Chung, Joo Yeon Kim, Hye Eun Park, Tae Hoen Kim, Wonae Lee, Min-Sun Cho, Ran Hong, Yoon Jung Choi, Younghee Choi, Y
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2025; 59(6): 444. CrossRef - Risk Factors Affecting Clinical Outcomes of Low-risk Early-stage Human Papillomavirus–Associated Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Treated by Surgery Alone: Application of Silva Pattern
Bong Kyung Bae, Hyunsik Bae, Won Kyung Cho, Byoung-Gie Kim, Chel Hun Choi, Tae-Joong Kim, Yoo-Young Lee, Jeong-Won Lee, Hyun-Soo Kim, Won Park
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2024; 43(5): 447. CrossRef - Tall‐columnar glandular cells in SurePath™ liquid‐based cytology Pap sample: Learning from mimics/pitfalls
Nalini Gupta, Vanita Jain, Radhika Srinivasan, Tulika Singh
Cytopathology.2024; 35(4): 510. CrossRef
- Gastric-Type Cervical Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Features, Molecular Landscape, and Therapeutic Challenges
- Correlation between myoferlin expression and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Ji Min Na, Dong Chul Kim, Dae Hyun Song, Hyo Jung An, Hyun Min Koh, Jeong-Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2022;56(4):199-204. Published online May 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2022.03.19
- 5,111 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Myoferlin is a multifunctional protein expressed in various normal and cancer cells, with novel oncogenic roles being newly discovered. Recently, correlations have been found between myoferlin expression and unfavorable prognosis in various carcinomas. This study investigated the prognostic role of myoferlin expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), specifically that associated with nodal metastasis.
Methods
We collected clinicopathological data and PTC tissues from 116 patients who had been admitted to Gyeongsang National University Hospital in 2010. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on surgical specimen-derived tissue microarray blocks. Myoferlin expression was graded, and the relationship between expression level and pathological features of tumors based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system was evaluated.
Results
Of the 116 patient samples, 100 cases exhibited positive myoferlin expression. Higher grade of myoferlin expression was correlated with lower T category group (p = .010). Presence of lymph node metastasis was determined to be significantly correlated with low-grade myoferlin expression (p = .019), with no significant difference between pN1a and pN1b tumors.
Conclusions
Our study revealed an adverse correlation between myoferlin expression and pathological features of PTC, evidence of the potential prognostic role of myoferlin in PTC lymph node metastasis.
- A multicenter study of interobserver variability in pathologic diagnosis of papillary breast lesions on core needle biopsy with WHO classification
- Hye Ju Kang, Sun Young Kwon, Ahrong Kim, Woo Gyeong Kim, Eun Kyung Kim, Ae Ree Kim, Chungyeul Kim, Soo Kee Min, So Young Park, Sun Hee Sung, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Ahwon Lee, Ji Shin Lee, Hyang Im Lee, Ho Chang Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Sun Young Jun, Min Jung Jung, Chang Won Jung, Soo Youn Cho, Eun Yoon Cho, Hye Jeong Choi, So Yeon Park, Jee Yeon Kim, In Ae Park, Youngmee Kwon
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(6):380-387. Published online October 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.07.29
- 7,417 View
- 226 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Papillary breast lesions (PBLs) comprise diverse entities from benign and atypical lesions to malignant tumors. Although PBLs are characterized by a papillary growth pattern, it is challenging to achieve high diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility. Thus, we investigated the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs in core needle biopsy (CNB) specimens with World Health Organization (WHO) classification.
Methods
Diagnostic reproducibility was assessed using interobserver variability (kappa value, κ) and agreement rate in the pathologic diagnosis of 60 PBL cases on CNB among 20 breast pathologists affiliated with 20 medical institutions in Korea. This analysis was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for cytokeratin 5 (CK5) and p63. The pathologic diagnosis of PBLs was based on WHO classification, which was used to establish simple classifications (4-tier, 3-tier, and 2-tier).
Results
On WHO classification, H&E staining exhibited ‘fair agreement’ (κ = 0.21) with a 47.0% agreement rate. Simple classifications presented improvement in interobserver variability and agreement rate. IHC staining increased the kappa value and agreement rate in all the classifications. Despite IHC staining, the encapsulated/solid papillary carcinoma (EPC/SPC) subgroup (κ = 0.16) exhibited lower agreement compared to the non-EPC/SPC subgroup (κ = 0.35) with WHO classification, which was similar to the results of any other classification systems.
Conclusions
Although the use of IHC staining for CK5 and p63 increased the diagnostic agreement of PBLs in CNB specimens, WHO classification exhibited a higher discordance rate compared to any other classifications. Therefore, this result warrants further intensive consensus studies to improve the diagnostic reproducibility of PBLs with WHO classification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
Arslan Ahmad, Muhammad Ammar, Muhammad Hasnain Saleem Choudary, Muhammad Nouman Sadiq, Rana Uzair Ahmad, Nouman Aziz
Radiology Case Reports.2025; 20(5): 2500. CrossRef - Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast
Shijing Wang, Qingfu Zhang, Xiaoyun Mao
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recommendations for Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning in Pathology: A Concept Paper From the College of American Pathologists
Matthew G. Hanna, Niels H. Olson, Mark Zarella, Rajesh C. Dash, Markus D. Herrmann, Larissa V. Furtado, Michelle N. Stram, Patricia M. Raciti, Lewis Hassell, Alex Mays, Liron Pantanowitz, Joseph S. Sirintrapun, Savitri Krishnamurthy, Anil Parwani, Giovann
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2024; 148(10): e335. CrossRef - Encapsulated papillary carcinoma of the breast: A single institution experience
Liang Xu, Qixin Mao, Qiuming Liu, Yufeng Gao, Lihua Luo, Chungen Guo, Wei Qu, Ningning Yan, Yali Cao
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High-risk and selected benign breast lesions diagnosed on core needle biopsy: Evidence for and against immediate surgical excision
Aparna Harbhajanka, Hannah L. Gilmore, Benjamin C. Calhoun
Modern Pathology.2022; 35(11): 1500. CrossRef
- Beyond the benign: A rare case report of myxoid pleomorphic liposarcoma
- Proto-oncogene Pokemon in thyroid cancer: a potential promoter of tumorigenesis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Kyungseek Chang, Sung-Im Do, Kyungeun Kim, Seoung Wan Chae, In-gu Do, Hyun Joo Lee, Dong Hoon Kim, Jin Hee Sohn
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(5):317-323. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.06.28
- 6,004 View
- 131 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Pokemon is an oncogenic transcription regulator that plays a critical role in cellular differentiation. Although it has been found to be overexpressed in several types of cancer involving different organs, its role in thyroid gland has yet to be reported. The objective of this study was to evaluate the expression of Pokemon in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) based on clinicopathological parameters.
Methods
Tissue microarray samples derived from patients with PTC or benign thyroid disease were used to evaluate Pokemon expression based on immunohistochemical analysis. Correlations of its expression with various clinicopathological parameters were then analyzed.
Results
Pokemon expression was observed in 22.0% of thyroid follicular cells from the normal group, 44.0% from the group with benign thyroid diseases, and 92.1% from the group with PTC (p < .001). The intensity of Pokemon expression was markedly higher in the PTC group. Pokemon expression level and PTC tumor size showed an inverse correlation. T1a tumors showed strong expression levels of Pokemon. However, larger tumors showed weak expression (p = .006).
Conclusions
Pokemon expression is associated with tumorigenesis of PTC, with expression showing an inverse correlation with PTC tumor size. This might be related to the negative regulation of aerobic glycolysis by Pokemon. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Systems biology approach delineates critical pathways associated with papillary thyroid cancer: a multi-omics data analysis
Febby Payva, Santhy K. S., Remya James, Amrisa Pavithra E, Venketesh Sivaramakrishnan
Thyroid Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the dysregulation of PURPL, a novel long intergenic noncoding RNA, in thyroid cancer progression
Mina Kazemzadeh, Reza Safaralizadeh, Amir Ali Mokhtarzadeh, Mohammad Ali Hosseinpour Feizi
Human Gene.2025; 46: 201499. CrossRef - ZBTB7A as a therapeutic target for cancer
Ying Zhou, Xisha Chen, Xuyu Zu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2024; 736: 150888. CrossRef - Knockdown of FBI-1 Inhibits the Warburg Effect and Enhances the Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Molecular Targeted Agents via miR-3692/HIF-1α
Juan Liu, Chao Yang, Xiao-Mei Huang, Pan-Pan Lv, Ya-Kun Yang, Jin-Na Zhao, Si-Yuan Zhao, Wan-Jun Sun
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Systems biology approach delineates critical pathways associated with papillary thyroid cancer: a multi-omics data analysis
- Evaluation of human papillomavirus (HPV) prediction using the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification system, compared to p16 immunohistochemistry and HPV RNA in-situ hybridization
- Hezhen Ren, Jennifer Pors, Christine Chow, Monica Ta, Simona Stolnicu, Robert Soslow, David Huntsman, Lynn Hoang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(6):480-488. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.18
- 8,647 View
- 175 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC) separated endocervical adenocarcinomas into human papillomavirus (HPV) associated (HPVA) and non–HPV-associated (NHPVA) categories by morphology alone. Our primary objective was to assess the accuracy of HPV prediction by the IECC system compared to p16 immunohistochemistry and HPV RNA in-situ hybridization (RISH). Our secondary goal was to directly compare p16 and HPV RISH concordance.
Methods
Cases were classified by IECC and stained for p16 and HPV RISH on tissue microarray, with discordant p16/HPV RISH cases re-stained on whole tissue sections. Remaining discordant cases (p16/HPV, IECC/p16, IECC/HPV discordances) were re-reviewed by the original pathologists (n = 3) and external expert pathologists (n = 2) blinded to the p16 and HPV RISH results. Final IECC diagnosis was assigned upon independent agreement between all reviewers.
Results
One hundred and eleven endocervical adenocarcinomas were classified originally into 94 HPVA and 17 NHPVA cases. p16 and HPV RISH was concordant in 108/111 cases (97%) independent of the IECC. HPV RISH and p16 was concordant with IECC in 103/111 (93%) and 106/111 (95%), respectively. After expert review, concordance improved to 107/111 (96%) for HPV RISH. After review of the eight discordant cases, one remained as HPVA, four were reclassified to NHPVA from HPVA, two were unclassifiable, and one possibly represented a mixed usual and gastric-type adenocarcinoma.
Conclusions
p16 and HPV RISH have excellent concordance in endocervical adenocarcinomas, and IECC can predict HPV status in most cases. Focal apical mitoses and apoptotic debris on original review led to the misclassification of several NHPVA as HPVA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of human papillomavirus status in the classification, diagnosis, and prognosis of malignant cervical epithelial tumors and precursor lesions
Simona Stolnicu
Die Pathologie.2026; 47(S1): 97. CrossRef - EdgeNeXt-SEDP for cervical adenocarcinoma HPV-associated and non-HPV-associated diagnosis and decision support
Qi Chen, Hao Wang, Hao Zhang, Zhenkun Zhu, Xi Wei
Life Sciences.2025; 380: 123931. CrossRef - Cytology and histology of endocervical glandular lesions: a review with emphasis on recent developments
Natalie Banet, Karen L. Talia
Pathology.2025; 57(7): 817. CrossRef - Joint detection of multiple HPV-testing technologies and evaluation of clinicopathological characteristics discriminate between HPV-independent and low-copy HPV-associated cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) -an analysis of 3869 cases
Linghui Lu, Tianqi Liu, Shunni Wang, Jing Li, Feiran Zhang, Yan Ning, Yiqin Wang
Gynecologic Oncology.2023; 170: 59. CrossRef - Incidence and Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Human Papillomavirus–independent Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Cervix
Simona Stolnicu, Douglas Allison, Aaron M. Praiss, Basile Tessier-Cloutier, Amir Momeni Boroujeni, Jessica Flynn, Alexia Iasonos, Rene Serrette, Lien Hoang, Andrei Patrichi, Cristina Terinte, Anna Pesci, Claudia Mateoiu, Ricardo R. Lastra, Takako Kiyokawa
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 47(12): 1376. CrossRef - Testing Algorithms for the Diagnosis of Malignant Glandular Tumors of the Uterine Cervix Histotyped per the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC) System
Máire A. Duggan, Qiuli Duan, Ruth M. Pfeiffer, Mary Anne Brett, Sandra Lee, Mustapha Abubakar, Martin Köbel, Monica Rodriguez, Aylin Sar
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2022; 30(2): 91. CrossRef - Local and Metastatic Relapses in a Young Woman with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 599. CrossRef - Clinical correlation of lymphovascular invasion and Silva pattern of invasion in early-stage endocervical adenocarcinoma: proposed binary Silva classification system
Simona Stolnicu, Lien Hoang, Noorah Almadani, Louise De Brot, Glauco Baiocchi, Graziele Bovolim, Maria Jose Brito, Georgia Karpathiou, Antonio Ieni, Esther Guerra, Takako Kiyokawa, Pavel Dundr, Carlos Parra-Herran, Sofia Lérias, Ana Felix, Andres Roma, An
Pathology.2022; 54(5): 548. CrossRef - Reproducibility of Morphologic Parameters of the International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification System and Correlation With Clinicopathologic Parameters: A Multi-Institutional Study
Pinar Bulutay, Nihan Haberal, Özlem Özen, Özlem Erdem, Emine H. Zeren, İbrahim Kulac, Çagatay Taskiran, Dogan Vatansever, Ali Ayhan, Nilgün Kapucuoğlu
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2022; 41(5): 447. CrossRef - HPV-Negative Cervical Cancer: A Narrative Review
Francesca Arezzo, Gennaro Cormio, Vera Loizzi, Gerardo Cazzato, Viviana Cataldo, Claudio Lombardi, Giuseppe Ingravallo, Leonardo Resta, Ettore Cicinelli
Diagnostics.2021; 11(6): 952. CrossRef - International Endocervical Adenocarcinoma Criteria and Classification (IECC): An Independent Cohort With Clinical and Molecular Findings
Hezhen Ren, Noorah Almadani, Jennifer Pors, Samuel Leung, Julie Ho, Christine Chow, Monica Ta, Kay J. Park, Simona Stolnicu, Robert Soslow, David Huntsman, Blake C. Gilks, Lynn Hoang
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology.2021; 40(6): 533. CrossRef
- Role of human papillomavirus status in the classification, diagnosis, and prognosis of malignant cervical epithelial tumors and precursor lesions
- Prevalence of high-risk human papillomavirus and its genotype distribution in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- Yuil Kim, Young-Hoon Joo, Min-Sik Kim, Youn Soo Lee
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(5):411-418. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.06.22
- 12,612 View
- 188 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
High-risk (HR) human papillomavirus (HPV) is found in a subset of head and neck (HN) squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs). For oropharyngeal SCCs, HR HPV positivity is known to be associated with good prognosis, and a separate staging system for HPV-associated carcinomas using p16 immunohistochemistry (IHC) as a surrogate test has been adopted in the 8th American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. We examined the HR HPV status and the genotype distribution in five HN subsites.
Methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections were used for p16 IHC and DNA extraction. HPV DNA detection and genotyping were done employing either a DNA chip-based or real-time polymerase chain reaction–based method.
Results
During 2011–2019, a total of 466 SCCs were tested for HPV DNA with 34.1% positivity for HR HPV. Among HN subsites, the oropharynx showed the highest HR HPV prevalence (149/205, 75.1%), followed by the sinonasal tract (3/14, 21.4%), larynx (5/43, 11.6%), hypopharynx (1/38, 2.6%), and oral cavity (1/166, 0.6%). The most common HPV genotype was HPV16 (84.3%) followed by HPV35 (6.9%) and HPV33 (4.4%). Compared with HR HPV status, the sensitivity and specificity of p16 IHC were 98.6% and 94.3% for the oropharynx, and 99.2% and 93.8% for the tonsil, respectively.
Conclusions
Using a Korean dataset, we confirmed that HR HPV is most frequently detected in oropharyngeal SCCs. p16 positivity showed a good concordance with HR HPV DNA for oropharyngeal and especially tonsillar carcinomas. The use of p16 IHC may further be extended to predict HR HPV positivity in sinonasal tract SCCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of histopathological parameters in prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
R. P. Ekanayaka, W. M. Tilakaratne
Oral Diseases.2025; 31(5): 1420. CrossRef - Prevalence of human papilloma virus in head and neck mucous squamous cell carcinoma and genotypes by location: an observational study
Emilie Uhlrich, Jerzy Klijanienko, Joey Martin, Emmanuelle Jeannot, Anne Vincent-Salomon, Paul Freneaux, Christophe Le Tourneau, Olivier Choussy, Antoine Dubray-Vautrin
European Journal of Cancer Prevention.2025; 34(5): 426. CrossRef - Risk factors for cervical lymph node metastasis in oropharyngeal cancer and its impact on prognosis
Li Zhang, Zhilin Li, Jing Wang, Chen Wang, Shuxin Wen
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2025; 91(2): 101520. CrossRef - Co-infection of human papillomavirus genotypes and Epstein-Barr virus in tumors of the oral cavity and oropharynx: a retrospective study in Northeastern Mexico
Gerardo del Carmen Palacios-Saucedo, Jose Manuel Vazquez-Guillen, Alondra Yamileth Alanis-Valdez, Leticia Lizeth Valdez-Treviño, Luis Roberto Galindo-Mendez, Angel Zavala-Pompa, Lydia Guadalupe Rivera-Morales, Ana Carolina Martinez-Torres, Roberto Lopez-V
IJID Regions.2025; 14: 100555. CrossRef - Rates of p16 and p53 expression in head and neck cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma vary according to human papillomavirus status
Rachid Ait Addi
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The epidemiological trends and survival of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer other than tonsils and base of tongue − a systematic review and meta-analysis
Anas Mohammad Al Fadel, Kathrine Kronberg Jakobsen, Lasse Holmgaard Jensen, Amanda-Louise Fenger Carlander, Christian Grønhøj, Christian von Buchwald
Oral Oncology.2025; 165: 107311. CrossRef - Oropharyngeal Helicobacter pylori colonization increases risk and worsens prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Xianyao Jiang, Yongjin Huang, Changwu Li, Hongyan Jiang
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of human papillomavirus infection among oropharyngeal cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Meimei Cui, Jinling Cheng, Huijuan Cheng, Ming Zhao, Dan Zhou, Min Zhang, Jingjing Jia, Limei Luo
Archives of Oral Biology.2024; 157: 105830. CrossRef - Longitudinal Screening for Oral High-Risk Non-HPV16 and Non-HPV18 Strains of Human Papillomavirus Reveals Increasing Prevalence among Adult and Pediatric Biorepository Samples: A Pilot Study
Jordan Jacobs, Eugene Chon, Karl Kingsley
Vaccines.2024; 12(8): 895. CrossRef - Position Statement about Gender-Neutral HPV Vaccination in Korea
Kyung-Jin Min, Yung-Taek Ouh, Sangrak Bae, Yong-Bae Ji, Jae-Kwan Lee, Jae-Weon Kim, Kwang-Jae Cho, Dong-Hun Im
Vaccines.2024; 12(10): 1110. CrossRef - High-risk HPV Does not Appear to be an Important Risk Factor for Sinonasal Carcinomas in Turkish Population: A Tertiary Center Experience
Evsen Apaydin Arikan, Levent Aydemir, Murat Ulusan, Dilek Yilmazbayhan, Yasemin Ozluk
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(2): 124. CrossRef - Practical Application of Circulating Tumor-Related DNA of Human Papillomavirus in Liquid Biopsy to Evaluate the Molecular Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer
Agnieszka M. Mazurek, Tomasz W. Rutkowski
Cancers.2023; 15(4): 1047. CrossRef - The Prevalence of HPV in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Seyed Keybud Katirachi, Mathias Peter Grønlund, Kathrine Kronberg Jakobsen, Christian Grønhøj, Christian von Buchwald
Viruses.2023; 15(2): 451. CrossRef - The Protective Role of Cranberries and Blueberries in Oral Cancer
César Esquivel-Chirino, Mario Augusto Bolaños-Carrillo, Daniela Carmona-Ruiz, Ambar Lopéz-Macay, Fernando Hernández-Sánchez, Delina Montés-Sánchez, Montserrat Escuadra-Landeros, Luis Alberto Gaitán-Cepeda, Silvia Maldonado-Frías, Beatriz Raquel Yáñez-Ocam
Plants.2023; 12(12): 2330. CrossRef - Unusual cases of sinonasal malignancies: a letter to the editor on HPV-positive sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas
Benedicte Bitsch Lauritzen, Sannia Sjöstedt, Jakob Myllerup Jensen, Katalin Kiss, Christian von Buchwald
Acta Oncologica.2023; 62(6): 608. CrossRef - Prevalence of human Papillomavirus associated oropharyngeal and oral squamous cell carcinoma in Asian countries: A systematic review and large-scale meta-analysis
Yy Jean Tan, Ken Wong Siong Hou, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Jasmine Lim Suk Wun, Wan Nor Amira Wan Ahmad Abdul Nasir, Lynn Wei Linn Ko
Acta Marisiensis - Seria Medica.2023; 69(2): 77. CrossRef - Top 100 most cited articles on human papillomavirus-induced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A bibliographic review
Rahul Mohandas, Subhashree Mohapatra, Mary Oshin, ShubhangiSambhaji Hajare
Journal of International Oral Health.2023; 15(3): 219. CrossRef - Intracellular Toll-Like Receptors Modulate Adaptive Immune Responses in Head and Neck Cancer
Sangeetha K. Nayanar, Deepak Roshan V.G., Shruthi Surendran, Göran Kjeller, Bengt Hasséus, Daniel Giglio
Viral Immunology.2023; 36(10): 659. CrossRef - Positive Rate of Human Papillomavirus and Its Trend in Head and Neck Cancer in South Korea
Hyun Woong Jun, Yong Bae Ji, Chang Myeon Song, Jae Kyung Myung, Hae Jin Park, Kyung Tae
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptionally active HPV in OPMD and OSCC: A systematic review following the CAP/ASCO guidelines
Laura Borges Kirschnick, Lauren Frenzel Schuch, Maria Eduarda Pérez‐de‐Oliveira, Ana Gabriela Costa Normando, Bruno Augusto Linhares Almeida Mariz, Eliete Neves Silva Guerra, Felipe Martins Silveira, Ana Carolina Uchoa Vasconcelos, Luciana Estevam Simonat
Oral Diseases.2022; 28(8): 2309. CrossRef - Effect of National Oral Health Screening Program on the Risk of Head and Neck Cancer: A Korean National Population-Based
Chan Woo Wee, Hyo-Jung Lee, Jae-Ryun Lee, Hyejin Lee, Min-Jeong Kwoen, Woo-Jin Jeong, Keun-Yong Eom
Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 54(3): 709. CrossRef - Expression of p16, p53, and TLR9 in HPV-Associated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Clinicopathological Correlations and Potential Prognostic Significance
Shu Wang, Xibing Zhuang, Caixia Gao, Tiankui Qiao
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 867. CrossRef - The Role of Human Papilloma Virus in Dictating Outcomes in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Shane Brennan, Anne-Marie Baird, Esther O’Regan, Orla Sheils
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Contemporary Systematic Review on Repartition of HPV-Positivity in Oropharyngeal Cancer Worldwide
Amanda F. Carlander, Kathrine K. Jakobsen, Simone K. Bendtsen, Martin Garset-Zamani, Charlotte D. Lynggaard, Jakob Schmidt Jensen, Christian Grønhøj, Christian von Buchwald
Viruses.2021; 13(7): 1326. CrossRef - The Prevalence of High- and Low-Risk Types of HPV in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Patients with Chronic Tonsillitis, and Healthy Individuals Living in Poland
Joanna Katarzyna Strzelczyk, Krzysztof Biernacki, Jadwiga Gaździcka, Elżbieta Chełmecka, Katarzyna Miśkiewicz-Orczyk, Natalia Zięba, Janusz Strzelczyk, Maciej Misiołek
Diagnostics.2021; 11(12): 2180. CrossRef
- Impact of histopathological parameters in prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Highly prevalent BRAF V600E and low-frequency TERT promoter mutations underlie papillary thyroid carcinoma in Koreans
- Sue Youn Kim, Taeeun Kim, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(4):310-317. Published online June 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.05.12
- 11,626 View
- 199 Download
- 29 Web of Science
- 32 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The presence of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations have been associated with a poor prognosis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTC). The frequency of TERT promoter mutations varies widely depending on the population and the nature of the study.
Methods
Data were prospectively collected in 724 consecutive patients who underwent thyroidectomy for PTC from 2018 to 2019. Molecular testing for BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations was performed in all cases.
Results
TERT promoter alterations in two hotspots (C228T and C250T) and C216T were found in 16 (2.2%) and 4 (0.6%) of all PTCs, respectively. The hotspot mutations were significantly associated with older age at diagnosis, larger tumor size, extrathyroidal extension, higher pathologic T category, lateral lymph node metastasis, and higher American Thyroid Association recurrence risk. The patients with C216T variant were younger and had a lower American Thyroid Association recurrence risk than those with hotspot mutations. Concurrent BRAF V600E was found in 19 of 20 cases with TERT promoter mutations. Of 518 microcarcinomas measuring ≤1.0 cm in size, hotspot mutations and C216T variants were detected in five (1.0%) and three (0.6%) cases, respectively.
Conclusions
Our study indicates a low frequency of TERT promoter mutations in Korean patients with PTC and supports previous findings that TERT promoter mutations are more common in older patients with unfavorable clinicopathologic features and BRAF V600E. TERT promoter mutations in patients with microcarcinoma are uncommon and may have a limited role in risk stratification. The C216T variant seems to have no clinicopathologic effect on PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Xiaoteng Sun, Zhengyan He, Weijie Yu, Baoyuan Li, Xinmiao Xu, Xiaoqin Zhang, Minglong Yin
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of C216T and hot spot mutations of the TERT promoter on the clinicopathologic characteristics and S100A10 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a comparative study
Ping Li, Chuqiang Huang, Xiaoling Liu, Huihui Gui, Jian Li
Diagnostic Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Refining NTRK Fusion Detection in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry and Histopathologic Features
Hyun Lee, Sue Youn Kim, Ji Min Park, Seung-Hyun Jung, Ozgur Mete, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validation of Diagnostic Utility of Washout CYFRA 21-1 in Lymph Node Metastasis of Thyroid Cancer
Jeongmin Lee, Yuri Shin, Jeongun Kwak, Hye Lim Park, Sohee Lee, Mee Kyung Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Chan Kwon Jung, So Lyung Jung, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Dong-Jun Lim
Clinical Cancer Research.2025; 31(10): 1922. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shin Je Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2025; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - 2025 Korean Thyroid Association Clinical Management Guideline on Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Eun Kyung Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seung Heon Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ji-hoon Kim, Shinje Moon, Kyorim Back, Young Shin Song, Jong-hyuk Ahn, Hwa Young Ahn, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Kyon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 307. CrossRef - Evaluation of BRAF V600E and TERT mutation analysis in differential thyroid cancers
Nigar Aktash, Ahmet Cem Dural, Husnu Aydin, Nuri Alper Sahbaz, Deniz Guzey, Serdar Altınay, Cevher Akarsu, Yasir Musa Kesgin, Sezer Bulut, Mehmet Karabulut
Updates in Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Active surveillance for adult low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma—a review focused on the 30-year experience of Kuma Hospital—
Yasuhiro Ito, Akira Miyauchi, Makoto Fujishima, Masashi Yamamoto, Takahiro Sasaki
Endocrine Journal.2024; 71(1): 7. CrossRef - Diagnostic utilities of washout CYFRA 21-1 combined with washout thyroglobulin for metastatic lymph nodes in thyroid cancer: a prospective study
Joonseon Park, Solji An, Kwangsoon Kim, Jeong Soo Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Part I. Initial Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers - Chapter 5. Evaluation of Recurrence Risk Postoperatively and Initial Risk Stratification in Different
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Shin Je Moon, Dong-Jun Lim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Yun Jae Chung, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 68. CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules 2024
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Su Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung,
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 208. CrossRef - PD-L1 Expression and Its Modulating Factors in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
Shipra Agarwal, Chan Kwon Jung, Pranitha Gaddam, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Takuya Higashiyama, Jen-Fan Hang, Wei-An Lai, Somboon Keelawat, Zhiyan Liu, Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park, Junya Fukuoka, Shinya Satoh, Zhanna Mussazhanova, Masahiro Nakashima, Kennichi Ka
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2024; 48(10): 1233. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors for occult lesions in low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma patients with tumor characteristics appropriate for thermal ablation: A retrospective study
Langping Jin, Kaijun Zhu, Changliang Xu, Jiaying Lu, Liming Huang
Medicine.2023; 102(38): e34938. CrossRef - Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors
So-Yeon Lee, Jong-Lyul Park, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jae-Yoon Kim, Seon-Young Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(3): 311. CrossRef - Risk factors and predictive model for recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a single-center retrospective cohort study based on 955 cases
Yin Li, Jiahe Tian, Ke Jiang, Zhongyu Wang, Songbo Gao, Keyang Wei, Ankui Yang, Qiuli Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BRAFV600E Positivity-Dependent Effect of Age on Papillary Thyroid Cancer Recurrence Risk
Joonseon Park, Solji An, Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(22): 5395. CrossRef - BRAFV600E mutation test on fine‐needle aspiration specimens of thyroid nodules: Clinical correlations for 4600 patients
Huang Chen, Aiping Song, Ye Wang, Yifan He, Jie Tong, Jinxi Di, Chun Li, Zhongren Zhou, Xiaopin Cai, Dingrong Zhong, Jiping Da
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(1): 40. CrossRef - Clinicopathological indicators for TERT promoter mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Hee Young Na, Hyeong Won Yu, Woochul Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Il Choi, Yeo Koon Kim, June Young Choi, So Yeon Park
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 97(1): 106. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta‐analysis on the Occurrence of Biomarker Mutation in Colorectal Cancer among the Asian Population
Hafeez Afolabi, Salzihan Md Salleh, Zaidi Zakaria, Ch’ng Ewe Seng, Siti Norasikin Binti Mohd Nafil, Ahmad Aizat Bin Abdul Aziz, Yusuf Wada, Ahmad Irekeola, Syed Sameer Aga
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Significance of Concomitant BRAFV600E and TERT Mutations in Polish Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on 430 Cases
Artur Kuchareczko, Janusz Kopczyński, Artur Kowalik, Kinga Hińcza-Nowak, Agnieszka Walczyk, Iwona Pałyga, Tomasz Trybek, Monika Szymonek, Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Klaudia Gadawska-Juszczyk, Estera Mikina, Izabela Płachta, Agnieszka Suligowska, Agnieszka Płu
Thyroid.2022; 32(11): 1372. CrossRef - Machine learning for identifying benign and malignant of thyroid tumors: A retrospective study of 2,423 patients
Yuan-yuan Guo, Zhi-jie Li, Chao Du, Jun Gong, Pu Liao, Jia-xing Zhang, Cong Shao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - TERT Promoter and BRAF V600E Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience in Korea
Min Jhi Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Woong Youn Chung, Daham Kim, Kee-Hyun Nam
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4928. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Sue Youn Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 947. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Hyunju Park, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 949. CrossRef - Molecular Pathology of Non-familial Follicular Epithelial–Derived Thyroid Cancer in Adults: From RAS/BRAF-like Tumor Designations to Molecular Risk Stratification
Paula Soares, Antónia Afonso Póvoa, Miguel Melo, João Vinagre, Valdemar Máximo, Catarina Eloy, José Manuel Cameselle-Teijeiro, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões
Endocrine Pathology.2021; 32(1): 44. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study
Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Hwa Young Ahn, Hee Sung Kim, Yong Joon Suh, Dughyun Choi, Bu Kyung Kim, Go Eun Yang, Il-Seok Park, Ka Hee Yi, Chan Kwon Jung, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 619. CrossRef - Clinical Application of TERT Promoter Mutations in Urothelial Carcinoma
Yujiro Hayashi, Kazutoshi Fujita, George J. Netto, Norio Nonomura
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA Profile for Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Seon-Kyu Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan-Kwon Jung, Yong-Sung Kim
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 632. CrossRef - Prospective Analysis of TERT Promoter Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma at a Single Institution
Yun-Suk Choi, Seong-Woon Choi, Jin-Wook Yi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(10): 2179. CrossRef - Significance of telomerase reverse-transcriptase promoter mutations in differentiated thyroid cancer
Hung-Fei Lai, Chi-Yu Kuo, Shih-Ping Cheng
Formosan Journal of Surgery.2021; 54(5): 171. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer Results Rather in Overtreatment Than a Better Survival
Jolanta Krajewska, Aleksandra Kukulska, Malgorzata Oczko-Wojciechowska, Agnieszka Kotecka-Blicharz, Katarzyna Drosik-Rutowicz, Malgorzata Haras-Gil, Barbara Jarzab, Daria Handkiewicz-Junak
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
- Clinical management of abnormal Pap tests: differences between US and Korean guidelines
- Seyeon Won, Mi Kyoung Kim, Seok Ju Seong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(3):213-219. Published online April 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.03.11
- 14,796 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cervical cancer has been the most common gynecological cancer in Korea but has become a preventable disease with regular screening and proper vaccination. If regular screening is provided, cervical cancer does not progress to more than carcinoma in situ, due to its comparatively long precancerous duration (years to decades). In 2012, the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology published guidelines to aid clinicians in managing women with abnormal Papanicolaou (Pap) tests, and they soon became the standard in the United States. Not long thereafter, the Korean Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the Korean Society for Cytopathology published practical guidelines to reflect the specific situation in Korea. The detailed screening guidelines and management options in the case of abnormal Pap test results are sometimes the same and sometimes different in the United States and Korean guidelines. In this article, we summarize the differences between the United States and Korean guidelines in order to facilitate physicians’ proper management of abnormal Pap test results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of HR-HPV Infection Concordance Rates in Cervical and Urine Specimens; Proposal of Additional Cervical Screening Process for Women Who Refuse Invasive Cervical Sampling
Dong Hyeok Kim, Hyunwoo Jin, Kyung Eun Lee
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(12): 1949. CrossRef - Analysis of HR-HPV Prevalence among Unvaccinated Busan Women
Dong Hyeok Kim, Kyung Eun Lee
Biomedical Science Letters.2022; 28(4): 229. CrossRef
- Analysis of HR-HPV Infection Concordance Rates in Cervical and Urine Specimens; Proposal of Additional Cervical Screening Process for Women Who Refuse Invasive Cervical Sampling
- Comparison of papanicolaou smear and human papillomavirus (HPV) test as cervical screening tools: can we rely on HPV test alone as a screening method? An 11-year retrospective experience at a single institution
- Myunghee Kang, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Na Rae Kim, Jungsuk An, Sangho Lee, Jae Yeon Seok, Juhyeon Jeong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2020;54(1):112-118. Published online January 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.11.29
- 14,592 View
- 268 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The decrease in incidence of cervical dysplasia and carcinoma has not been as dramatic as expected with the development of improved research tools and test methods. The human papillomavirus (HPV) test alone has been suggested for screening in some countries. The National Cancer Screening Project in Korea has applied Papanicolaou smears (Pap smears) as the screening method for cervical dysplasia and carcinoma. We evaluated the value of Pap smear and HPV testing as diagnostic screening tools in a single institution.
Methods
Patients co-tested with HPV test and Pap smear simultaneously or within one month of each other were included in this study. Patients with only punch biopsy results were excluded because of sampling errors. A total of 999 cases were included, and the collected reports encompassed results of smear cytology, HPV subtypes, and histologic examinations.
Results
Sensitivity and specificity of detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were higher for Pap smears than for HPV tests (sensitivity, 97.14%; specificity, 85.58% for Pap smears; sensitivity, 88.32%; specificity, 54.92% for HPV tests). HPV tests and Pap smears did not differ greatly in detection of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (85.35% for HPV test, 80.31% for Pap smears). When atypical glandular cells were noted on Pap smears, the likelihood for histologic diagnosis of adenocarcinoma following Pap smear was higher than that of high-risk HPV test results (18.8 and 1.53, respectively).
Conclusions
Pap smears were more useful than HPV tests in the diagnosis of HSIL, SCC, and glandular lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
Mohammad Panji, Mohammad Hossein Modarresi, Zahra Azizi, Moloud Absalan, Elahe Motevaseli
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of cervical precancerous lesions and cancer by small-scale RT-qPCR analysis of oppositely deregulated mRNAs pairs in cytological smears
Anastasia A. Artyukh, Mikhail K. Ivanov, Sergei E. Titov, Victoria V. Dzyubenko, Sergey E. Krasilnikov, Anastasia O. Shumeikina, Nikita A. Afanasev, Anastasia V. Malek, Sergei A. Glushkov, Eduard F. Agletdinov
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - High burden of abnormal cervical smears in South African primary health care: health programmes implications
Olufemi B Omole, Joel M Francis, John M Musonda, Pumla P Sodo, Elizabeth Reji, Nyundu S J Phukuta, Honey L M Mabuza, Joyce S Musonda, Jimmy Akii, John V Ndimande, Olalekan A Ayo-Yusuf
Health Promotion International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis: a study of the microenvironment in cervical cancer (2000-2024)
Yun-Tao Zhang, Yan-Ni Wei, Chen-Chen Liu, Mai-Qing Yang
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Liquid biopsy biomarkers in cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Isaac Kinyua Njangiru, Bizhar Ahmed Tayeb, Hazhmat Ali, Rafl M. Kamil
The Journal of Liquid Biopsy.2025; 10: 100328. CrossRef - Diagnostic Utility of Human Papilloma Virus Testing in Comparison with Pap Cytology and Histopathology in Unvaccinated Women with Cervical High-Grade Dysplasia and Carcinoma in Botswana
Patricia Setsile Rantshabeng, Nametso Dire, Andrew Khulekani Ndlovu, Ishmael Kasvosve
Venereology.2025; 4(4): 15. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagmosis of cervical pathologies
D. Y. Chernov, O. A. Tikhonovskaya, S. V. Logvinov, I. A. Petrov, Y. S. Yuriev, A. A. Zhdankina, A. V. Gerasimov, I. V. Zingalyuk, G. A. Mikheenko
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 201. CrossRef - “Barriers and Advantages of Self-Sampling Tests, for HPV Diagnosis: A Qualitative Field Experience Before Implementation in a Rural Community in Ecuador”
Bernardo Vega-Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Ruth Maldonado - Rengel, Diana López, Dayanara Delgado-López, Gabriela Guerra Astudillo, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Women's Health.2024; Volume 16: 947. CrossRef - Cervical Human Papillomavirus Testing
Carol N. Rizkalla, Eric C. Huang
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2024; 17(3): 431. CrossRef - Segmentation of Overlapping Cells in Cervical Cytology Images: A Survey
E Chen, Hua-Nong Ting, Joon Huang Chuah, Jun Zhao
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 114170. CrossRef - Knowledge and awareness regarding pap test and HPV typing for cervical cancer screening in Edo North, Nigeria
Amina Momodu, Johnsolomon Eghosa Ohenhen, Godfrey Innocent Iyare, Musa Abidemi Muhibi, Godwin Avwioro
Discover Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Colposcopy Value in Young Child-bearing Women: Is New Recommendations Necessary?
Fahimeh Sabet, Avishan Aminizad, Fariba Behnamfar, Tajossadat Allameh, Seyedeh Ghazal Shahrokh, Rostami Koushan, Amirmohammad Taravati, Leila Mousavi Seresht
Advanced Biomedical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Selection of endogenous control and identification of significant microRNA deregulations in cervical cancer
T. Stverakova, I. Baranova, P. Mikyskova, B. Gajdosova, H. Vosmikova, J. Laco, V. Palicka, H. Parova
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytology Versus Molecular Diagnosis of HPV for Cervical Cancer Screening. Comparison of the Diagnostic Properties of Four Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, Rocío Murillo, Cristina Ochoa Avilés
ESPOCH Congresses: The Ecuadorian Journal of S.T.E.A.M..2023; 3(1): 139. CrossRef - Attitudes towards prevention of cervical cancer and early diagnosis among female academicians
Nurhan Doğan, Gamze Fışkın
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2022; 48(6): 1433. CrossRef - Role of Self-Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: Diagnostic Test Properties of Three Tests for the Diagnosis of HPV in Rural Communities of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz Segarra, Ruth Maldonado Rengel, Diana López, María Paz Orellana, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(8): 4619. CrossRef - Utility of Scoring System for Screening and Early Warning of Cervical Cancer Based on Big Data Analysis
Dan Hou, Binjie Yang, Yangdan Li, Ming Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Urine and Vaginal Self-Sampling versus Clinician-Based Sampling for Cervical Cancer Screening: A Field Comparison of the Acceptability of Three Sampling Tests in a Rural Community of Cuenca, Ecuador
Bernardo Vega Crespo, Vivian Alejandra Neira, José Ortíz S, Ruth Maldonado-Rengel, Diana López, Andrea Gómez, María José Vicuña, Jorge Mejía, Ina Benoy, Tesifón Parrón Carreño, Veronique Verhoeven
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1614. CrossRef - Diagnostic distribution and pitfalls of glandular abnormalities in cervical cytology: a 25-year single-center study
Jung-A Sung, Ilias P. Nikas, Haeryoung Kim, Han Suk Ryu, Cheol Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 354. CrossRef - Primary screening of cervical cancer by Pap smear in women of reproductive age group
Ruchi Mishra, Dakshina Bisht, Manisha Gupta
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2022; 11(9): 5327. CrossRef - Comparison of Learning Transfer Using Simulation Problem-Based Learning and Demonstration: An Application of Papanicolaou Smear Nursing Education
Jeongim Lee, Hae Kyoung Son
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(4): 1765. CrossRef - Investigating host-virus interaction mechanism and phylogenetic analysis of viral proteins involved in the pathogenesis
Ahmad Abu Turab Naqvi, Farah Anjum, Alaa Shafie, Sufian Badar, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Timir Tripathi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(12): e0261497. CrossRef - Utility of Human Papillomavirus Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Mee-seon Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Moon-il Park, Jae Seok Lee, Kisu Kim, Mee Sook Roh, Hyoun Wook Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(5): 1726. CrossRef
- Development of a Nano-Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Kit for Detection and Genotyping of High-Risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Strains Using Dedicated TaqMan Probes
- A Multi-institutional Study of Prevalence and Clinicopathologic Features of Non-invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP) in Korea
- Ja Yeong Seo, Ji Hyun Park, Ju Yeon Pyo, Yoon Jin Cha, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong Eun Song, Jeong Ja Kwak, So Yeon Park, Hee Young Na, Jang-Hee Kim, Jae Yeon Seok, Hee Sung Kim, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(6):378-385. Published online October 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.09.18
- 8,922 View
- 344 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the present multi-institutional study, the prevalence and clinicopathologic characteristics of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) were evaluated among Korean patients who underwent thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Methods
Data from 18,819 patients with PTC from eight university hospitals between January 2012 and February 2018 were retrospectively evaluated. Pathology reports of all PTCs and slides of potential NIFTP cases were reviewed. The strict criterion of no papillae was applied for the diagnosis of NIFTP. Due to assumptions regarding misclassification of NIFTP as non-PTC tumors, the lower boundary of NIFTP prevalence among PTCs was estimated. Mutational analysis for BRAF and three RAS isoforms was performed in 27 randomly selected NIFTP cases.
Results
The prevalence of NIFTP was 1.3% (238/18,819) of all PTCs when the same histologic criteria were applied for NIFTP regardless of the tumor size but decreased to 0.8% (152/18,819) when tumors ≥1 cm in size were included. The mean follow-up was 37.7 months and no patient with NIFTP had evidence of lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, or disease recurrence during the follow-up period. A difference in prevalence of NIFTP before and after NIFTP introduction was not observed. BRAFV600E mutation was not found in NIFTP. The mutation rate for the three RAS genes was 55.6% (15/27).
Conclusions
The low prevalence and indolent clinical outcome of NIFTP in Korea was confirmed using the largest number of cases to date. The introduction of NIFTP may have a small overall impact in Korean practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case report & review: Bilateral NIFTP harboring concomitant HRAS and KRAS mutation: Report of an unusual case and literature review
Marianna Rita Brogna, Francesca Collina, Maria Grazia Chiofalo, Debora De Bartolo, Angela Montone, Maria Rosaria Schiano, Michele Del Sesto, Nubia Pizza, Gerardo Ferrara
Molecular Carcinogenesis.2024; 63(12): 2273. CrossRef - Non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP): what do we need to know?
Andrés Coca-Pelaz, Juan P. Rodrigo, Abbas Agaimy, Dana M. Hartl, Göran Stenman, Vincent Vander Poorten, Antti A. Mäkitie, Mark Zafereo, Karthik N. Rao, Gregory W. Randolph, Alessandra Rinaldo, Alfio Ferlito
Virchows Archiv.2024; 485(6): 977. CrossRef - Study of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm: A borderline entity
Rupali Bavikar, Ruchi S. Randive, Anubhaw Verma, Madhuri Singh, Vidya Viswanathan, Arpana Dharwadkar
Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics.2024; 20(5): 1365. CrossRef - Analysis of a pre-2017 follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma cohort reclassified as noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like features (NIFTP): an 11-year retrospective single institution experience
Shaham Beg, Sana Irfan Khan, Isabella Cui, Theresa Scognamiglio, Rema Rao
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(2): 112. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm With Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: What a Surgeon Should Know
Jabir Alharbi, Thamer Alraddadi, Haneen Sebeih, Mohammad A Alessa, Haddad H Alkaf, Ahmed Bahaj, Sherif K Abdelmonim
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - NTRK Fusion in a Cohort of BRAF p. V600E Wild-Type Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Seung Eun Lee, Mi-Sook Lee, Heejin Bang, Mi Young Kim, Yoon-La Choi, Young Lyun Oh
Modern Pathology.2023; 36(8): 100180. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Study on the Diagnosis and Management of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features
Bayan A. Alzumaili, Lauren N. Krumeich, Reagan Collins, Timothy Kravchenko, Emad I. Ababneh, Adam S. Fisch, William C. Faquin, Vania Nosé, Maria Martinez-Lage, Gregory W. Randolph, Rajshri M. Gartland, Carrie C. Lubitz, Peter M. Sadow
Thyroid.2023; 33(5): 566. CrossRef - Clinical-Pathological and Molecular Evaluation of 451 NIFTP Patients from a Single Referral Center
Paola Vignali, Agnese Proietti, Elisabetta Macerola, Anello Marcello Poma, Liborio Torregrossa, Clara Ugolini, Alessio Basolo, Antonio Matrone, Teresa Rago, Ferruccio Santini, Rossella Elisei, Gabriele Materazzi, Fulvio Basolo
Cancers.2022; 14(2): 420. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 Consensus on the management of thyroid nodules : Follow-up: How and how long?
Sophie Leboulleux, Livia Lamartina, Emmanuelle Lecornet Sokol, Fabrice Menegaux, Laurence Leenhardt, Gilles Russ
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2022; 83(6): 407. CrossRef - Different Threshold of Malignancy for RAS-like Thyroid Tumors Causes Significant Differences in Thyroid Nodule Practice
Kennichi Kakudo
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 812. CrossRef - Clinicopathological parameters for predicting non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary features (NIFTP)
Eunju Jang, Kwangsoon Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Incidence of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Meta-Analysis Assessing Worldwide Impact of the Reclassification
Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Thu Quynh Nguyen, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Chan Kwon Jung, Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov
Thyroid.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Genomic Landscape of Thyroid Cancer Tumourigenesis and Implications for Immunotherapy
Amandeep Singh, Jeehoon Ham, Joseph William Po, Navin Niles, Tara Roberts, Cheok Soon Lee
Cells.2021; 10(5): 1082. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) is rare, benign lesion using modified stringent diagnostic criteria: Reclassification and outcome study
David Cubero Rego, Hwajeong Lee, Anne Boguniewicz, Timothy A. Jennings
Annals of Diagnostic Pathology.2020; 44: 151439. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: From Echography to Genetic Profile
Francesca Maletta, Enrico Costantino Falco, Alessandro Gambella, Jasna Metovic, Mauro Papotti
The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.2020; 252(3): 209. CrossRef
- Case report & review: Bilateral NIFTP harboring concomitant HRAS and KRAS mutation: Report of an unusual case and literature review
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
- Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2019;53(4):210-216. Published online May 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.04.11
- 14,227 View
- 278 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the introduction of the Papanicolaou (Pap) smear system in 1943, cervicovaginal cytology has been used as a standard screening test for cervical cancer. The dissemination of this test contributed to reductions of the incidence and mortality of cervical cancer worldwide. In Korea, regular health check-ups for industrial workers and their family members were introduced in 1988 and were performed as part of the National Cancer Screening Program in 1999. As a result, the incidence of cervical cancer in Korea has been steadily decreasing. However, about 800 cases of cervical cancer-related deaths are reported each year due to false-negative test results. Hence, new screening methods have been proposed. Liquid-based cytology (LBC) was introduced in 1996 to overcome the limitations of conventional Pap smears. Since then, other LBC methods have been developed and utilized, including the human papilloma virus test—a method with higher sensitivity that requires fewer screenings. In this study, we review current issues and future perspectives related to cervical cancer screening in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
Yosep Chong, Ran Hong, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Haeryoung Kim, Lucia Kim, Soon Jae Kim, Yoon Jung Choi
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2026; 54(2): 146. CrossRef - A Study on the Workload of Cytotechnologists: Focus on Commercial Laboratories
Eun-Suk PARK
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2025; 57(2): 228. CrossRef - Metastatic Cervical Cancer in the Asia-Pacific Region: Current Treatment Landscape and Barriers
Jeffrey Chee-Hong Goh, Chyong-Huey Lai, Efren Javier Domingo, Jae Hoon Kim, Carmel Spiteri, Danny Hsu, Soo Yeon Ihm, Peng Peng
Cancer Research Communications.2025; 5(8): 1429. CrossRef - Mathematical Assessment of the Roles of Vaccination and Pap Screening on the Burden of HPV and Related Cancers in Korea
Soyoung Park, Hyunah Lim, Abba B. Gumel
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A questionnaire study on disparity of cervical cancer prevention programs in Asia‐Oceania
Ka Yu Tse, Kimio Ushijima, Ai Ling Tan, Perapong Intasorn, Jitendra Pariyar, Chih‐Long Chang, Efren J. Domingo, Hiralal Konar, Suresh Kumarasamy, Brahmana Askandar Tjokroprawiro, Sarikapan Wilailak
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2023; 49(4): 1230. CrossRef - Current state of cytopathology residency training: a Korean national survey of pathologists
Uiju Cho, Tae Jung Kim, Wan Seop Kim, Kyo Young Lee, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Hyun Joo Choi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(2): 95. CrossRef - Meeting the challenges of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination in the UK
Roxanne Westwood, Joanna Lavery
Primary Health Care.2022; 32(01): 22. CrossRef - Local and Metastatic Relapses in a Young Woman with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
Ha Young Woo, Hyun-Soo Kim
Diagnostics.2022; 12(3): 599. CrossRef - Serum Human Epididymis Protein 4 as a Prognostic Marker in Cervical Cancer
Woo Yeon Hwang, Dong Hoon Suh, Kidong Kim, Yong Beom Kim, Jae Hong No
Cancer Control.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HPV detection and/or cytological diagnostics
Sanja Milenković
Glasnik javnog zdravlja.2022; 96(3): 313. CrossRef - Clinical management of abnormal Pap tests: differences between US and Korean guidelines
Seyeon Won, Mi Kyoung Kim, Seok Ju Seong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(3): 213. CrossRef - Current status of cytopathology practices in Korea: annual report on the Continuous Quality Improvement program of the Korean Society for Cytopathology for 2018
Yosep Chong, Haeyoen Jung, Jung-Soo Pyo, Soon Won Hong, Hoon Kyu Oh
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(4): 318. CrossRef - Cytomorphological Features of Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups in Liquid-Based Cervicovaginal Cytology: A Single Institutional Experience
Youngeun Lee, Cheol Lee, In Ae Park, Hyoung Jin An, Haeryoung Kim
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(6): 393. CrossRef
- Practice of Cytopathology in Korea: A 40‐Year Evolution Through Standardization, Digital Transformation, and Global Partnership
- Prognostic Role of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Kyungseek Chang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(5):331-338. Published online August 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.08.07
- 9,586 View
- 131 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study is to elucidate the clinicopathological significances, including the prognostic role, of metastatic lymph node ratio (mLNR) and tumor deposit diameter in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) through a retrospective review and meta-analysis.
Methods
We categorized the cases into high (≥ 0.44) and low mLNR (< 0.44) and investigated the correlations with clinicopathological parameters in 64 PTCs with neck level VI lymph node (LN) metastasis. In addition, meta-analysis of seven eligible studies was used to investigate the correlation between mLNR and survival.
Results
Among 64 PTCs with neck level VI LN metastasis, high mLNR was found in 34 PTCs (53.1%). High mLNR was significantly correlated with macrometastasis (tumor deposit diameter ≥ 0.2 cm), extracapsular spread, and number of metastatic LNs. Based on linear regression test, mLNR was significantly increased by the largest LN size but not the largest metastatic LN (mLN) size. High mLNR was not correlated with nuclear factor κB or cyclin D1 immunohistochemical expression, Ki-67 labeling index, or other pathological parameters of primary tumor. Based on meta-analysis, high mLNR significantly correlated with worse disease-free survival at the 5-year and 10-year follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 4.866; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.527 to 6.714 and HR, 5.769; 95% CI, 2.951 to 11.275, respectively).
Conclusions
Our data showed that high mLNR significantly correlated with worse survival, macrometastasis, and extracapsular spread of mLNs. Further cumulative studies for more detailed criteria of mLNR are needed before application in daily practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Chang Liu, Shangjie Yang, Tian Xue, Qian Zhang, Yanjing Zhang, Yufang Zhao, Guolin Yin, Xiaohui Yan, Ping Liang, Liping Liu
Frontiers in Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Predictive Value of a Nomogram Based on Ultrasound Radiomics, Clinical Factors, and Enhanced Ultrasound Features for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Lei Gao, Xiuli Wen, Guanghui Yue, Hui Wang, Ziqing Lu, Beibei Wu, Zhihong Liu, Yuming Wu, Dongmei Lin, Shijian Yi, Wei Jiang, Yi Hao
Ultrasonic Imaging.2025; 47(2): 93. CrossRef - Lymph Node Metastasis Ratio: Prognostic Significance in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Ana Rita Ferreira, Diogo Ramalho, Daniela Martins, Andreia Amado, Susana Graça, Carlos Soares, Bela Pereira, Maria João Oliveira, Manuel Oliveira, Antónia Póvoa
Indian Journal of Surgery.2025; 87(6): 1047. CrossRef - CD105 (Endoglin) Expression as a Prognostic Marker in Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
İlker Çordan, Tuğba Günler
Clinical Endocrinology.2025; 103(4): 596. CrossRef - Application and subgroup analysis of competing risks model based on different lymph node staging systems in differentiated thyroid cancer
Zhe Xu Cao, Jiang Sheng Huang, Ming Ming Wang
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(5): 1927. CrossRef - Цитологічне прогнозування агресії раку щитоподібної залози як новий перспективний напрямок у клінічній тиреоїдології
H.V. Zelinska
Endokrynologia.2024; 29(4): 363. CrossRef - Thyroglobulin expression, Ki-67 index, and lymph node ratio in the prognostic assessment of papillary thyroid cancer
Helene Lindfors, Marie Karlsen, Ellinor Karlton, Jan Zedenius, Catharina Larsson, Catharina Ihre Lundgren, C. Christofer Juhlin, Ivan Shabo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidental Node Metastasis as an Independent Factor of Worse Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Renan Aguera Pinheiro, Ana Kober Leite, Beatriz Godoi Cavalheiro, Evandro Sobroza de Mello, Luiz Paulo Kowalski, Leandro Luongo Matos
Cancers.2023; 15(3): 943. CrossRef - A High-Quality Nomogram for Predicting Lung Metastasis in Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Study
WenYi Wang, JiaJing Liu, XiaoFan Xu, LiQun Huo, XuLin Wang, Jun Gu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lymph Node Ratio Predicts Recurrence in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Low Lymph Node Yield
Il Ku Kang, Joonseon Park, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Kwangsoon Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(11): 2947. CrossRef - Superiority of metastatic lymph node ratio over number of node metastases and TNM/AJCC N classification in predicting cancer‐specific survival in medullary thyroid cancer
Andreas Machens, Kerstin Lorenz, Frank Weber, Henning Dralle
Head & Neck.2022; 44(12): 2717. CrossRef - Value of Combining Clinical Factors, Conventional Ultrasound, and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Features in Preoperative Prediction of Central Lymph Node Metastases of Different Sized Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Yanfang Wang, Fang Nie, Guojuan Wang, Ting Liu, Tiantian Dong, Yamin Sun
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3403. CrossRef - Atypical Histiocytoid Cells and Multinucleated Giant Cells in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of the Thyroid Predict Lymph Node Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Ji Eun Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Dong-Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Cancers.2019; 11(6): 816. CrossRef - Patients Aged ≥55 Years With Stage T1-2N1M1 Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Should Be Downstaged in the Eighth Edition AJCC/TNM Cancer Staging System
Zeming Liu, Sichao Chen, Yihui Huang, Di Hu, Min Wang, Wei Wei, Chao Zhang, Wen Zeng, Liang Guo
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Implication of Metastatic Lymph Node Ratio in Colorectal Cancers: Comparison Depending on Tumor Location
Jung-Soo Pyo, Young-Min Shin, Dong-Wook Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 1812. CrossRef
- The application of a clinical-multimodal ultrasound radiomics model for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Cytologic Diagnosis of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features and Its Impact on the Risk of Malignancy in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: An Institutional Experience
- Milim Kim, Joung Eun Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Yul Ri Chung, Yoonjin Kwak, So Yeon Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):171-178. Published online April 3, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.04.03
- 11,688 View
- 205 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study was performed to analyze cytologic diagnosis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) and its impact on the risk of malignancy (ROM) in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC).
Methods
Five thousand five hundred and forty-nine cases of thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) diagnosed between 2012 and 2014 were included in this study. Diagnostic categories based on TBSRTC were compared with final surgical diagnoses, and the ROM in each category was calculated both when NIFTP was included in malignant lesions and when excluded from malignant lesions.
Results
Of the 5,549 thyroid FNAC cases, 1,891 cases underwent surgical resection. In final diagnosis, 1,700 cases were revealed as papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), and 25 cases were reclassified as NIFTP. The cytologic diagnoses of NIFTP were non-diagnostic in one, benign in five, atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) in 14, follicular neoplasm in two, and suspicious for malignancy in three cases. Collectively, NIFTP/encapsulated follicular variant of PTC (EFVPTC) were more frequently classified as benign, AUS, or follicular neoplasm and less frequently categorized as malignant compared to conventional PTCs. Exclusion of NIFTP from malignant diagnoses resulted in a slight decrease in malignancy rates in non-diagnostic, benign, AUS, follicular neoplasm, and suspicious for malignancy categories without any statistical significance.
Conclusions
The decrease in the ROM was not significant when NIFTP was excluded from malignant lesions. In thyroid FNACs, NIFTP/EFVPTCs were mostly classified into indeterminate categories. Therefore, it might be feasible to separate NIFTP/EFVPTC from conventional PTC on FNAC to guide clinicians to conservative management for patients with NIFTP/EFVPTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
Man Him Matrix Fung, Ching Tang, Gin Wai Kwok, Tin Ho Chan, Yan Luk, David Tak Wai Lui, Carlos King Ho Wong, Brian Hung Hin Lang
Thyroid®.2025; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Spatial transcriptomics reveals prognosis‐associated cellular heterogeneity in the papillary thyroid carcinoma microenvironment
Kai Yan, Qing‐Zhi Liu, Rong‐Rong Huang, Yi‐Hua Jiang, Zhen‐Hua Bian, Si‐Jin Li, Liang Li, Fei Shen, Koichi Tsuneyama, Qing‐Ling Zhang, Zhe‐Xiong Lian, Haixia Guan, Bo Xu
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytological Features of “Non-invasive Follicular Tumour with Papillary Like Nuclear Features” – A Single Institutional Experience in India
K Amita, HB Rakshitha, M Sanjay, Prashantha Kalappa
Journal of Cytology.2023; 40(1): 28. CrossRef - Detailed fine needle aspiration cytopathology findings of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features with nuclear grading correlated to that of biopsy and Bethesda category and systematic review
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2023; 51(12): 758. CrossRef - Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features Is Not a Cytological Diagnosis, but It Influences Cytological Diagnosis Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Elina Haaga, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvíková, Ivana Kholová
Acta Cytologica.2022; 66(2): 85. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features: its updated diagnostic criteria, preoperative cytologic diagnoses and impact on the risk of malignancy
Hee Young Na, So Yeon Park
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2022; 56(6): 319. CrossRef - Usage and Diagnostic Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology and Core Needle Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Literature Published by Korean Authors
Soon-Hyun Ahn
Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology.2021; 14(1): 116. CrossRef - Comprehensive DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Thyroid Cancer
Jong-Lyul Park, Sora Jeon, Eun-Hye Seo, Dong Hyuck Bae, Young Mun Jeong, Yourha Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Seon-Kyu Kim, Chan Kwon Jung, Yong Sung Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(2): 192. CrossRef - Differences in surgical resection rate and risk of malignancy in thyroid cytopathology practice between Western and Asian countries: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Hanh Thi Tuyet Ngo, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung, Trang Huyen Vu, Kim Bach Lu, Kennichi Kakudo, Tetsuo Kondo
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(4): 238. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular neoplasm with papillary like nuclear features: A comprehensive analysis with a diagnostic algorithm
Chanchal Rana, Shreyamsa Manjunath, Pooja Ramakant, Kulranjan Singh, Suresh Babu, Anand Mishra
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(4): 330. CrossRef - Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary‐like nuclear features and the risk of malignancy in The Bethesda System for the Reporting of Thyroid Cytopathology
Danielle Elliott Range, Xiaoyin “Sara” Jiang
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(6): 531. CrossRef - Did Introducing a New Category of Thyroid Tumors (Non-invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features) Decrease the Risk of Malignancy for the Diagnostic Categories in the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology?
Janusz Kopczyński, Agnieszka Suligowska, Kornelia Niemyska, Iwona Pałyga, Agnieszka Walczyk, Danuta Gąsior-Perczak, Artur Kowalik, Kinga Hińcza, Ryszard Mężyk, Stanisław Góźdź, Aldona Kowalska
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(2): 143. CrossRef - High risk of malignancy in cases with atypia of undetermined significance on fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules even after exclusion of NIFTP
Sevgiye Kaçar Özkara, Büşra Yaprak Bayrak, Gupse Turan
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(11): 986. CrossRef - The importance of risk of neoplasm as an outcome in cytologic‐histologic correlation studies on thyroid fine needle aspiration
Yu‐Hsin Chen, Kristen L. Partyka, Rae Dougherty, Harvey M. Cramer, Howard H. Wu
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2020; 48(12): 1237. CrossRef - Preoperative diagnostic categories of fine needle aspiration cytology for histologically proven thyroid follicular adenoma and carcinoma, and Hurthle cell adenoma and carcinoma: Analysis of cause of under- or misdiagnoses
Hee Young Na, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park, Paula Soares
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241597. CrossRef - How is noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP) shaping the way we interpret thyroid cytology?
Michiya Nishino
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2019; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - Cytological Diagnoses Associated with Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasms with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features According to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Massimo Bongiovanni, Luca Giovanella, Francesco Romanelli, Pierpaolo Trimboli
Thyroid.2019; 29(2): 222. CrossRef - Preoperative Diagnostic Categories of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features in Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy and Its Impact on Risk of Malignancy
Hee Young Na, Ji Won Woo, Jae Hoon Moon, June Young Choi, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yeo Koon Kim, Ji-Young Choe, So Yeon Park
Endocrine Pathology.2019; 30(4): 329. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Reclassification to Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): a Retrospective Clinicopathologic Study
Khurram Shafique, Virginia A. LiVolsi, Kathleen Montone, Zubair W. Baloch
Endocrine Pathology.2018; 29(4): 339. CrossRef
- High Rates of Unnecessary Surgery for Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules in the Absence of Molecular Test and the Cost-Effectiveness of Utilizing Molecular Test in an Asian Population: A Decision Analysis
- Preoperative Cytologic Diagnosis of Warthin-like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jisup Kim, Beom Jin Lim, Soon Won Hong, Ju Yeon Pyo
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(2):105-109. Published online February 12, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.12.26
- 9,348 View
- 154 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (WLV-PTC) is a relatively rare variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma with favorable prognosis. However, preoperative diagnosis using fine-needle aspiration (FNA) specimens is challenging especially with lymphocytic thyroiditis characterized by Hürthle cells and lymphocytic background. To determine a helpful cytological differential point, we compared WLV-PTC FNA findings with conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymphocytic thyroiditis (PTC-LT) and conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma without lymphocytic thyroiditis (PTC) regarding infiltrating inflammatory cells and their distribution. Preoperative diagnosis or potential for WLV-PTC will be helpful for surgeons to decide the scope of operation.
Methods
Of the 8,179 patients treated for papillary thyroid carcinoma between January 2007 and December 2012, 16 patients (0.2%) were pathologically confirmed as WLV-PTC and four cases were available for cytologic review. For comparison, we randomly selected six PTC-LT cases and five PTC cases during the same period. The number of intratumoral and background lymphocytes, histiocytes, neutrophils, and the presence of giant cells were evaluated and compared using conventional smear and ThinPrep preparations.
Results
WLV-PTC showed extensive lymphocytic smear with incorporation of thyroid follicular tumor cell clusters and frequent histiocytes. WLV-PTC was associated with higher intratumoral and background lymphocytes and histiocytes compared with PTC-LT or PTC. The difference was more distinct in liquid-based cytology.
Conclusions
The lymphocytic smear pattern and the number of inflammatory cells of WLV-PTC are different from those of PTC-LT or PTC and will be helpful for the differential diagnosis of WLV-PTC in preoperative FNA. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Algorithmic Approach to Defining Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Accuracy of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
Neha Nigam, Neha Kumari, Rishabh Sahai, Nandita Chaudhary, Sabaretnam Mayilvaganan, Pallavi Prasad, Prabhakar Mishra
Journal of Cytology.2025; 42(1): 27. CrossRef - A Case of Warthin-Like Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Amy Chow, Israa Laklouk
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a rare case report
Rafif E Mattar, Osama Almubadel, Areej Bokhari
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastases: a case report and review of the literature
Andrii Hryshchyshyn, Andrii Bahrii, Pavlina Botsun, Volodymyr Chuba
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytologic hallmarks and differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma subtypes
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2024; 58(6): 265. CrossRef - Warthin-like papillary thyroid carcinoma: a case report and comprehensive review of the literature
Abdel Mouhaymen Missaoui, Fatma Hamza, Wafa Belabed, Manel Mellouli, Mohamed Maaloul, Slim Charfi, Issam Jardak, Tahya Sellami-Boudawara, Nabila Rekik, Mohamed Abid
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinomas: a clinicopathologic analysis report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Yijia Zhang, Pengyu Hao, Mingzhen Zhao, Xingbin Shen
Oncologie.2023; 25(5): 581. CrossRef - Challenges in Cytology Specimens With Hürthle Cells
Eleni Thodou, Sule Canberk, Fernando Schmitt
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Warthin-like variant of Papillary thyroid carcinoma—Case report of an uncommon tumour with review of literature
Pradyumna Kumar Sahoo, Rashmi Patnayak, Perwez Alam Khan, Amitabh Jena
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 77(C): 9. CrossRef
- An Algorithmic Approach to Defining Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Accuracy of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- The Significance of TROP2 Expression in Predicting BRAF Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Joon Seog Kong, Hyeon Jin Kim, Min-Jung Kim, Areumnuri Kim, Dalnim Lee, Kanghee Han, Sunhoo Park, Jae Soo Koh, Jae Kyung Myung
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):14-20. Published online December 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.10.17
- 10,834 View
- 249 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Trophoblast antigen 2 (TROP2) is a human trophoblast cell-surface glycoprotein that is overexpressed in several types of epithelial cancers, and is suggested to be associated with an unfavorable prognosis. BRAF mutations are the most common genetic alteration in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). We evaluated the correlation between TROP2 expression and BRAF mutation in PTC.
Methods
First, we carried out pyrosequencing for BRAF mutations and immunohistochemistry for TROP2 expression with a tissue microarray consisting of 52 PTC cases. Membranous staining in at least 5% of tumor cells was designated as positive staining and we analyzed the relationship between TROP2 expression and diverse clinicopathological factors, including BRAF mutation. Second, we tested TROP2 mRNA expression in three thyroid cancer cell lines with BRAF mutations (BCPAP, SNU790, and 8505C) and a normal thyroid cell line. Additionally, we checked TROP2 protein levels in a normal thyroid cell line after introduction of the BRAF V600E mutation.
Results
In this study, 21 of 26 cases with BRAF mutation showed TROP2 immunoreactivity, whereas all 26 cases without BRAF mutation showed no immunoreactivity for TROP2 with a statistically significant difference (p<.001). Upregulation of TROP2 mRNA was observed in all three thyroid cancer cell lines, but not in the normal thyroid cell line. Interestingly, however, the TROP2 expression was increased in the normal thyroid cell line after introduction of the BRAF V600E mutation.
Conclusions
Based on these results, we concluded that TROP2 expression is significantly associated with BRAF mutation and that TROP2 immunohistochemistry could be used for predicting BRAF mutations or diagnosing papillary thyroid carcinoma. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trop2-Targeted [18F]AlF-RESCA-RT4 ImmunoPET/CT in Guiding Clinical Surgeries of Thyroid Cancers: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Xinlu Yin, Wenzhi Jia, Le Xu, Wenjie Zheng, Yiqing Gao, Linglin Tang, You Zhang, Qianyun Wu, Dongsheng Xu, Shuxian An, Weijun Wei, Jianjun Liu, Qinyi Zhou, Jialin Feng, Jun Chen
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evolution of TROP2: Biological insights and clinical applications
Xinyue Zhang, Hong Xiao, Fangjian Na, Jingqi Sun, Qi Guan, Ruotong Liu, Lutong Cai, Heming Li, Mingfang Zhao
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2025; 296: 117863. CrossRef - Diagnostic and prognostic utility of TROP-2, SLP-2, and CXCL12 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Amany Selim Attia, Samia Hussein, Hend Sameh, Amr Khalil, Ahmad Barakat Waley, Ihab Matar, Reham Sameh
Cancer Biomarkers.2024; 39(3): 211. CrossRef - BRAF mutation, selected miRNAs and genes expression in primary papillary thyroid carcinomas and local lymph node metastases
David Kalfert, Marie Ludvikova, Martin Pesta, Tommi Hakala, Lucie Dostalova, Hana Grundmannova, Jindra Windrichova, Katerina Houfkova, Tereza Knizkova, Jaroslav Ludvik, Jiri Polivka, Ivana Kholova
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 258: 155319. CrossRef - Unveiling the placental secrets: Exploring histopathological changes and TROP2 expression in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Cezmi Baran Ozalp, Sozdar Akdogan, Dilan Cetinavci, Melike Nur Akin, Hulya Elbe, Burcu Kasap
Placenta.2024; 154: 201. CrossRef - Trop2-Targeted Molecular Imaging in Solid Tumors: Current Advances and Future Outlook
Yongshun Liu, Wenpeng Huang, Rachel J. Saladin, Jessica C. Hsu, Weibo Cai, Lei Kang
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2024; 21(12): 5909. CrossRef - TROP2 is a Good Indicator for Infiltrative Nature of Carcinoma Rather than Diagnosing Malignancy in Thyroid
E. Kılınc, P. Gunes, A. Doganer
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2022; 74(S2): 2560. CrossRef - Advances in Trop2-targeted therapy: Novel agents and opportunities beyond breast cancer
Xinlin Liu, Junwen Deng, Yang Yuan, Wujun Chen, Wenshe Sun, Yanhong Wang, Haiming Huang, Bing Liang, Tao Ming, Jialian Wen, Binghuan Huang, Dongming Xing
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 239: 108296. CrossRef - Knockdown of Trop2 inhibits proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis of endometrial cancer cells via AKT/β‐catenin pathway
Xiaotong Sun, Guangyang Xing, Cui Zhang, Kun Lu, Yuqiong Wang, Xiyan He
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2020; 38(2): 141. CrossRef - Can TROP2 be used as a prognostic marker in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma?
SerkanY Celik, Özgürİlhan Çelik
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2020; 63(3): 418. CrossRef - Diagnostic Value of TROP-2 and CK19 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in Both Surgical and Cytological Specimens
Asmaa Gaber Abdou, Mohammed Shabaan, Rania Abdallha, Nehal Nabil
Clinical Pathology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Diagnostic Utility of Immunohistochemistry Markers of TROP-2 and HBME-1 in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Carcinoma
Nooshin Zargari, Maral Mokhtari
European Thyroid Journal.2019; 8(1): 1. CrossRef - The diagnostic value of TROP-2, SLP-2 and CD56 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xueyang Yang, Yifang Hu, He Shi, Chengzhou Zhang, Zhixiao Wang, Xiaoyun Liu, Huanhuan Chen, Lijuan Zhang, Dai Cui
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2018; 275(8): 2127. CrossRef - TROP2 promotes cell proliferation and migration in osteosarcoma through PI3K/AKT signaling
Qing‑Zhi Gu, Abulimiti Nijiati, Xing Gao, Kai‑Liang Tao, Cheng‑Duo Li, Xue‑Peng Fan, Zheng Tian
Molecular Medicine Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Trop2-Targeted [18F]AlF-RESCA-RT4 ImmunoPET/CT in Guiding Clinical Surgeries of Thyroid Cancers: A Proof-of-Concept Study
- Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression and Its Correlation with Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyo Jung An, Gyung Hyuck Ko, Jeong-Hee Lee, Jong Sil Lee, Dong Chul Kim, Jung Wook Yang, Min Hye Kim, Jin Pyeong Kim, Eun Jung Jung, Dae Hyun Song
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(1):9-13. Published online October 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.07.26
- 10,893 View
- 283 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The immunotherapeutic role of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in life expectancy in many cancers has been highlighted. However, data regarding PD-L1 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) are limited. In this study, we describe the PD-L1 and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) expressions in PTC and analyze their correlation with lymph node (LN) metastasis.
Methods
Clinicopathological data were obtained from 116 patients with PTC who were treated in Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea in 2009. Tissue microarray blocks were made using representative paraffin blocks of classical PTCs excluding follicular variants. Two pathologists graded the proportion and intensity of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression in both tumor and inflammatory cells. According to their proportions, positive PTC cells were scored as negative (0%), grade 1 (1%–50%), and grade 2 (51%–100%). Similarly, positive inflammatory cells were graded as negative (0%), grade 1 (1%–10%), and grade 2 (11%–20%). The intensity of each protein expression was simplified as positive or negative.
Results
A statistically significant correlation exists between the proportions of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression both in papillary carcinoma (p=.001) and peritumoral lymphoid cells in the thyroid (p<.001). In addition, the proportion of PD-L1 expression in PTC cells was closely related to metastatic LNs (p=.036).
Conclusions
PD-L1 is a valuable predictive marker for LN metastasis in PTC. Immunomodulating therapies that inhibit PD-L1 might be an option for patients with LN metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study of PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Correlation to the Clinicopathologic Characteristics
Asmaa Gamal Mohamed El Sayed, Dina Ragab Diab Ibrahim, Mahmoud Mahmoud El-Leithy, Mai Mohamed Ali Ezz El Din, Hoda Hassan Abou Gabal, Reham Mohamed Faheim
Indian Journal of Medical and Paediatric Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Summary and Analysis of Molecular Biological Changes, PD-L1 Immune Status and Clinicopathological Features of 78 Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (<1 cm in Diameter) Combined With Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis
Xiaoteng Sun, Zhengyan He, Weijie Yu, Baoyuan Li, Xinmiao Xu, Xiaoqin Zhang, Minglong Yin
Applied Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunotyping of thyroid cancer for clinical outcomes and implications
Jin Xu, Zhen Luo, Dayong Xu, Mujing Ke, Cheng Tan
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of PD-L1, TERT promoter mutations, and BRAFV600E mutation in poorly differentiated, differentiated high grade thyroid carcinoma and anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid: our institutional experience
Alessia Piermattei, Giuseppe Migliara, Angela Feraco, Carmine Bruno, Luisa Cioni, Qianqian Zhang, Belen Padial-Urtueta, Elisabetta Merenda, Guido Fadda, Marco Raffaelli, Luigi Maria Larocca, Antonino Mule, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Esther Diana Rossi
Virchows Archiv.2025; 487(3): 605. CrossRef - Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis with Oncocytic Metaplasia Influences PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Vitor Barreto Santana, Vitória Machado Krüger, Maria Cristina Yunes Abrahão, Pietru Lentz Martins Cantú, Rosicler Luzia Brackmann, Gisele Moroni Pandolfi, Liane Scheffler Marisco, Gabriela Remonatto, Luciana Adolfo Ferreira, Marcia Silveira Graudenz
Head and Neck Pathology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring markers of immunoresponsiveness in papillary thyroid carcinoma and future treatment strategies
Atish Mohanty, Michelle Afkhami, Amanda Reyes, Rebecca Pharaon, Holly Yin, Haiqing Li, Dana Do, Diana Bell, Arin Nam, Sue Chang, Thomas Gernon, Robert Kang, Arya Amini, Sagus Sampath, Prakash Kulkarni, Raju Pillai, Vicky Villaflor, Ravi Salgia, Ellie Magh
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2024; 12(7): e008505. CrossRef - Update regarding the role of PD-L1 in oncocytic thyroid lesions on cytological samples
Marco Dell'Aquila, Pietro Tralongo, Alessia Granitto, Maurizio Martini, Sara Capodimonti, Mariangela Curatolo, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Guido Fadda, Celestino Pio Lombardi, Maco Raffaelli, Liron Pantanowitz, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Dia
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2023; 76(10): 671. CrossRef - Analysis of anti‐apoptotic PVT1 oncogene and apoptosis‐related proteins (p53, Bcl2, PD‐1, and PD‐L1) expression in thyroid carcinoma
Afaf T. Ibrahiem, Amin K. Makhdoom, Khalid S. Alanazi, Abdulaziz M. Alanazi, Abdulaziz M. Mukhlef, Saad H. Elshafey, Eman A. Toraih, Manal S. Fawzy
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - EphA10 drives tumor progression and immune evasion by regulating the MAPK/ERK cascade in lung adenocarcinoma
Wenyue Zhao, Lu Liu, Xuehao Li, Shun Xu
International Immunopharmacology.2022; 110: 109031. CrossRef - Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Minimizes Lymph Node Metastasis in BRAF Mutant Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Peter P. Issa, Mahmoud Omar, Yusef Buti, Chad P. Issa, Bert Chabot, Christopher J. Carnabatu, Ruhul Munshi, Mohammad Hussein, Mohamed Aboueisha, Mohamed Shama, Ralph L. Corsetti, Eman Toraih, Emad Kandil
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 2051. CrossRef - Expression of β-Catenin in Thyroid Neoplasms (Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study)
Mohamed Sherif Ismail, Amr Mousa Abdel Gawad Mousa, Mohammed Faisal Darwish, M. Mostafa Salem, Randa Said
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(A): 1565. CrossRef - Identification and validation of an immune-related prognostic signature and key gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Rujia Qin, Chunyan Li, Xuemin Wang, Zhaoming Zhong, Chuanzheng Sun
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - PD‐L1 and thyroid cytology: A possible diagnostic and prognostic marker
Marco Dell’Aquila, Alessia Granitto, Maurizio Martini, Sara Capodimonti, Alessandra Cocomazzi, Teresa Musarra, Vincenzo Fiorentino, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Celestino Pio Lombardi, Guido Fadda, Liron Pantanowitz, Luigi Maria Larocca, Esther Diana Rossi
Cancer Cytopathology.2020; 128(3): 177. CrossRef - Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Is a Potential Biomarker of Disease-Free Survival in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of PD-L1 Immunoexpression in Follicular Epithelial Derived Thyroid Carcinoma
Ilaria Girolami, Liron Pantanowitz, Ozgur Mete, Matteo Brunelli, Stefano Marletta, Chiara Colato, Pierpaolo Trimboli, Anna Crescenzi, Massimo Bongiovanni, Mattia Barbareschi, Albino Eccher
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(3): 291. CrossRef - Regression of Papillary Thyroid Cancer during Nivolumab for Renal Cell Cancer
Andrea Palermo, Andrea Napolitano, Daria Maggi, Anda Mihaela Naciu, Gaia Tabacco, Silvia Manfrini, Anna Crescenzi, Chiara Taffon, Francesco Pantano, Bruno Vincenzi, Guiseppe Tonini, Daniele Santini
European Thyroid Journal.2020; 9(3): 157. CrossRef - A potential biomarker hsa-miR-200a-5p distinguishing between benign thyroid tumors with papillary hyperplasia and papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xian Wang, Shan Huang, Xiaocan Li, Dongrui Jiang, Hongzhen Yu, Qiang Wu, Chaobing Gao, Zhengsheng Wu, Yi-Hsien Hsieh
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(7): e0200290. CrossRef - Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Emerging from Hashimoto Thyroiditis Demonstrates Increased PD-L1 Expression, Which Persists with Metastasis
Daniel Lubin, Ezra Baraban, Amanda Lisby, Sahar Jalali-Farahani, Paul Zhang, Virginia Livolsi
Endocrine Pathology.2018; 29(4): 317. CrossRef - Chemotherapeutic Treatments Increase PD-L1 Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma through EGFR/ERK Activation
Hoi Yan Ng, Jian Li, Lihua Tao, Alfred King-Yin Lam, Kwok Wah Chan, Josephine Mun Yee Ko, Valen Zhuoyou Yu, Michael Wong, Benjamin Li, Maria Li Lung
Translational Oncology.2018; 11(6): 1323. CrossRef
- Study of PD-L1 Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Correlation to the Clinicopathologic Characteristics
- Prognostic Significance of a Micropapillary Pattern in Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Comparative Analysis with Micropapillary Carcinoma
- Hyun-Jung Kim, Kyeongmee Park, Jung Yeon Kim, Guhyun Kang, Geumhee Gwak, Inseok Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):403-409. Published online June 9, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.18
- 9,547 View
- 201 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast is an indolent tumors with a favorable prognosis; however, micropapillary features tend to lead to aggressive behavior. Thus, mucinous carcinoma and micropapillary carcinoma exhibit contrasting biologic behaviors. Here, we review invasive mucinous carcinoma with a focus on micropapillary features and correlations with clinicopathological factors.
Methods
A total of 64 patients with invasive breast cancer with mucinous or micropapillary features were enrolled in the study. Of 36 pure mucinous carcinomas, 17 (47.2%) had micropapillary features and were termed mucinous carcinoma with micropapillary features (MUMPC), and 19 (52.8%) had no micropapillary features and were termed mucinous carcinoma without micropapillary features. MUMPC were compared with 15 invasive micropapillary carcinomas (IMPC) and 13 invasive ductal and micropapillary carcinomas (IDMPC).
Results
The clinicopathological factors of pure mucinous carcinoma and MUMPC were not significantly different. In contrast to IMPC and IDMPC, MUMPC had a low nuclear grade, lower mitotic rate, higher expression of hormone receptors, negative human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status, lower Ki-67 proliferating index, and less frequent lymph node metastasis (p < .05). According to univariate analyses, progesterone receptor, HER2, T-stage, and lymph node metastasis were significant risk factors for overall survival; however, only T-stage remained significant in a multivariate analysis (p < .05).
Conclusions
In contrast to IMPC and IDMPC, the micropapillary pattern in mucinous carcinoma does not contribute to aggressive behavior. However, further analysis of a larger series of patients is required to clarify the prognostic significance of micropapillary patterns in mucinous carcinoma of the breast. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pure mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast with the rare lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: A case report with review of literature
Yash Hasmukhbhai Prajapati, Vishal Bhabhor, Kahan Samirkumar Mehta, Mithoon Barot, Husen Boriwala, Mohamed Omar
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma with a micropapillary structure
Beibei Yang, Menglu Shen, Bo Sun, Jing Zhao, Meng Wang
Thoracic Cancer.2024; 15(36): 2530. CrossRef - Expression of autocrine motility factor receptor (AMFR) in human breast and lung invasive micropapillary carcinomas
Jing Xu, Hongfei Ma, Qi Wang, Hui Zhang
International Journal of Experimental Pathology.2023; 104(1): 43. CrossRef - The Spectrum of Mucinous Lesions of the Breast
Upasana Joneja, Juan Palazzo
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2023; 147(1): 19. CrossRef - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
Cherie M Kuzmiak, Benjamin C Calhoun
Journal of Breast Imaging.2023; 5(2): 180. CrossRef - On Ultrasonographic Features of Mucinous Carcinoma with Micropapillary Pattern
Wei-Sen Yang, Yang Li, Ya Gao
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2023; Volume 15: 473. CrossRef - Micropapillary Breast Carcinoma: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Prognosis
Georgios-Ioannis Verras, Levan Tchabashvili, Francesk Mulita, Ioanna Maria Grypari, Sofia Sourouni, Evangelia Panagodimou, Maria-Ioanna Argentou
Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 14: 41. CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: distinctive histopathologic and genetic characteristics
Minjung Jung
Kosin Medical Journal.2022; 37(3): 176. CrossRef - Triple-Positive Breast Carcinoma: Histopathologic Features and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Jennifer Zeng, Marcia Edelweiss, Dara S. Ross, Bin Xu, Tracy-Ann Moo, Edi Brogi, Timothy M. D'Alfonso
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2021; 145(6): 728. CrossRef - HER2 positive mucinous carcinoma of breast with micropapillary features: Report of a case and review of literature
Dinesh Chandra Doval, Rupal Tripathi, Sunil Pasricha, Pankaj Goyal, Chaturbhuj Agrawal, Anurag Mehta
Human Pathology: Case Reports.2021; 25: 200531. CrossRef - Sonographic Features of Pure Mucinous Breast Carcinoma With Micropapillary Pattern
Wu Zhou, Yong-Zhong Li, Li-Min Gao, Di-Ming Cai
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathologic characteristics of HER2-positive pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Yunjeong Jang, Hera Jung, Han-Na Kim, Youjeong Seo, Emad Alsharif, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Yeon Hee Park, Eun Yoon Cho, Soo Youn Cho
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2020; 54(1): 95. CrossRef - Mucinous carcinoma with micropapillary features is morphologically, clinically and genetically distinct from pure mucinous carcinoma of breast
Peng Sun, Zaixuan Zhong, Qianyi Lu, Mei Li, Xue Chao, Dan Chen, Wenyan Hu, Rongzhen Luo, Jiehua He
Modern Pathology.2020; 33(10): 1945. CrossRef - Micropapillary pattern in pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast – does it matter or not?
Xiaoli Xu, Rui Bi, Ruohong Shui, Baohua Yu, Yufan Cheng, Xiaoyu Tu, Wentao Yang
Histopathology.2019; 74(2): 248. CrossRef - An Update of Mucinous Lesions of the Breast
Beth T. Harrison, Deborah A. Dillon
Surgical Pathology Clinics.2018; 11(1): 61. CrossRef - The clinicopathological significance of micropapillary pattern in colorectal cancers
Jung-Soo Pyo, Mee Ja Park, Dong-Wook Kang
Human Pathology.2018; 77: 159. CrossRef - The sonographic findings of micropapillary pattern in pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast
Heqing Zhang, Li Qiu, Yulan Peng
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic dilemma of micropapillary variant of mucinous breast cancer
Geok Hoon Lim, Zhiyan Yan, Mihir Gudi
BMJ Case Reports.2018; 2018: bcr-2018-225775. CrossRef
- Pure mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast with the rare lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: A case report with review of literature
- Comparison of Unsatisfactory Samples from Conventional Smear versus Liquid-Based Cytology in Uterine Cervical Cancer Screening Test
- Hoiseon Jeong, Sung Ran Hong, Seoung-Wan Chae, So-Young Jin, Hye Kyoung Yoon, Juhie Lee, Eun Kyung Kim, Sook Tai Ha, Sung Nam Kim, Eun-Jung Park, Jong Jae Jung, Sun Hee Sung, Sung-chul Lim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(3):314-319. Published online April 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.03.17
- 14,665 View
- 335 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cervical cytology for uterine cervical cancer screening has transitioned from conventional smear (CS) to liquid-based cytology (LBC), which has many advantages. The aim of this study was to compare the proportion of unsatisfactory specimens from CS versus LBC at multiple institutions including general hospitals and commercial laboratories.
Methods
Each participating institution provided a minimum of 500 Papanicolaou (Pap) test results for analysis. Pap tests were classified according to the participating institution (commercial laboratory or general hospital) and the processing method (CS, ThinPrep, SurePath, or CellPrep). The causes of unsatisfactory results were classified as technical problems, scant cellularity, or complete obscuring factors.
Results
A total of 38,956 Pap test results from eight general hospitals and three commercial laboratories were analyzed. The mean unsatisfactory rate of LBC was significantly lower than that of CS (1.26% and 3.31%, p = .018). In the LBC method, samples from general hospitals had lower unsatisfactory rates than those from commercial laboratories (0.65% vs 2.89%, p = .006). The reasons for unsatisfactory results were heterogeneous in CS. On the other hand, 66.2% of unsatisfactory results in LBC were due to the scant cellularity.
Conclusions
Unsatisfactory rate of cervical cancer screening test results varies according to the institution and the processing method. LBC has a significantly lower unsatisfactory rate than CS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Poor Performance of Applicator Tampon‐Based Self‐Collection for Liquid‐Based Cytology Among Women Attending a Tertiary Hospital in South Africa
Teboho Amelia Tiiti, Varsetile Varster Nkwinika, Tebogo Loraine Mashishi, Kgotlaethata Aaron Molefi, Thembeni Lucia Msibi, Moshawa Khaba, Johannes Bogers, Ramokone Lisbeth Lebelo
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2025; 53(4): 150. CrossRef - The state of cervical cancer screening in Vanuatu: A retrospective analysis (2015–2020)
Emma R. Allanson, Vera Velanova, Boniface Damutalau, Harriet Obed, Geetha Warrier, Ian H. Frazer, Margaret McAdam
Malignancy Spectrum.2025; 2(1): 46. CrossRef - Evaluation of a New Ethanol-Based Preservative Medium for Liquid-Based Cervical Cytology: A Performance Pilot Study for Molecular Applications
Floriana Conticelli, Pasquale Pisapia, Antonino Iaccarino, Maria Salatiello, Alessandro Venuta, Gianluca Gragnano, Luca Vallefuoco, Rosanna Sorrentino, Giuseppe Portella, Nadia Casatta, Carmelo Lupo, Dario Bruzzese, Giancarlo Troncone, Caterina De Luca
Journal of Molecular Pathology.2025; 6(3): 22. CrossRef - Comparison of Conventional Pap Smear and Liquid-Based Cytology in the detection of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical Cancer
Rachita Garg, Krishna Agarwal, Niharika Dhiman, Gauri Gandhi, Meeta Singh
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The current status of liquid-based cytology (LBC) in oral cytology
Kayo Kuyama
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Medicine, and Pathology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of conventional Pap smear and liquid-based cytology in detecting cervical abnormalities
Đelila Šečerović
Sanamed.2024; 19(2): 227. CrossRef - The possibilities of adapting the re-processing protocol in the practice of the ThinPrep Pap test usage
Artem K. Aksamentov, Nadezhda V. Melnikova, Eugenia V. Moshnina, Nadezhda A. Kolyshkina, Olga N. Kucherova, Vladimir P. Baklaushev
Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 14(1): 108. CrossRef - The Role of p16/Ki67 Dual Staining in Cervical Cancer Screening
Andraž Dovnik, Alenka Repše Fokter
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2023; 45(10): 8476. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Novel Fixative Solution for Liquid-Based Cytology in Diagnostic Cytopathology
Nadia Casatta, Alessia Poli, Sara Bassani, Gianna Veronesi, Giulio Rossi, Clarissa Ferrari, Carmelo Lupo
Diagnostics.2023; 13(24): 3601. CrossRef - Liquid-Based Cytology in the Detection of Premalignant Lesions in Patients with “Atypia in Squamous Cells” in Conventional Cytology
Lia Barrios, Yoled Vizcaíno, Ines Benedetti
Journal of Cytology.2022; 39(4): 148. CrossRef - Meeting the challenges of cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination in the UK
Roxanne Westwood, Joanna Lavery
Primary Health Care.2022; 32(01): 22. CrossRef - Method for preservation of DNA stability of liquid-based cytology specimens from a lung adenocarcinoma cell line
Yukiko Matsuo, Kazuya Yamashita, Tsutomu Yoshida, Yukitoshi Satoh
Virchows Archiv.2021; 478(3): 507. CrossRef - High-risk human papillomavirus test in anal smears: can it optimize the screening for anal cancer?
Cintia M.S. Kimura, Caio S.R. Nahas, Edésio V. Silva-Filho, Vinícius L. Ribeiro, Aluisio C. Segurado, Flávio F.P. Alcântara, Ivan Cecconello, Sergio C. Nahas
AIDS.2021; 35(5): 737. CrossRef - Automatic model for cervical cancer screening based on convolutional neural network: a retrospective, multicohort, multicenter study
Xiangyu Tan, Kexin Li, Jiucheng Zhang, Wenzhe Wang, Bian Wu, Jian Wu, Xiaoping Li, Xiaoyuan Huang
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The cytological component of cervical cancer screening: causes of false negative and false positive results, and ways to avoid them
O.A. Burka, N.F. Lygyrda, V.V. Kutsovol, A.V. Svintsitska
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (57): 61. CrossRef - Comparison of liquid-based cytology with conventional smear cytology for EUS-guided FNA of solid pancreatic masses: a prospective randomized noninferiority study
Jung Won Chun, Kyoungbun Lee, Sang Hyub Lee, Haeryoung Kim, Min Su You, Yoon Jung Hwang, Woo Hyun Paik, Ji Kon Ryu, Yong-Tae Kim
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.2020; 91(4): 837. CrossRef - Effective reduction in inadequate Pap smears by using a saline-lubricated speculum and two glass slides
Chi-Jui Chen, Mun-Kun Hong, Dah-Ching Ding
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2020; 59(6): 906. CrossRef - Characterizing the Effect of Automated Cell Sorting Solutions on Cytomorphological Changes
Katsuhide Ikeda, Shouichi Sato, Hiroshi Chigira, Yasuo Shibuki, Nobuyoshi Hiraoka
Acta Cytologica.2020; 64(3): 232. CrossRef - Comparison between Conventional Cytology and Liquid-Based Cytology in the Tertiary Brazilian Navy Hospital in Rio de Janeiro
Antônio Carlos Almeida de Oliveira, Miguel Fontes Domingues, Paulo Murilo Neufeld, Marcos Fleury, José Firmino Nogueira Neto
Acta Cytologica.2020; 64(6): 539. CrossRef - Follow‐up with histopathology and HPV testing on LSIL cytology in China’s largest academic woman’s hospital
Xiang Tao, Huina Zhang, Hao Zhang, Jianan Xiao, Juan Li, Xianrong Zhou, Li Wang, Chengquan Zhao
Cancer Cytopathology.2019; 127(4): 258. CrossRef - Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea
Sung-Chul Lim, Chong Woo Yoo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2019; 53(4): 210. CrossRef - Reducing DNA damage by formaldehyde in liquid‐based cytology preservation solutions to enable the molecular testing of lung cancer specimens
Yukiko Matsuo, Tsutomu Yoshida, Kazuya Yamashita, Yukitoshi Satoh
Cancer Cytopathology.2018; 126(12): 1011. CrossRef - Cervical Cancer Screening Programs in Europe: The Transition Towards HPV Vaccination and Population-Based HPV Testing
Andreas C. Chrysostomou, Dora C. Stylianou, Anastasia Constantinidou, Leondios G. Kostrikis
Viruses.2018; 10(12): 729. CrossRef
- Poor Performance of Applicator Tampon‐Based Self‐Collection for Liquid‐Based Cytology Among Women Attending a Tertiary Hospital in South Africa
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Korean Breast Cancer Patients by Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction and Meta-Analysis of Human Papillomavirus and Breast Cancer
- Jinhyuk Choi, Chungyeul Kim, Hye Seung Lee, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim, Jinhwan Lee, Hyeyoon Chang, Aeree Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(6):442-450. Published online October 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.08
- 14,389 View
- 225 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a well-established oncogenic virus of cervical, anogenital, and oropharyngeal cancer. Various subtypes of HPV have been detected in 0% to 60% of breast cancers. The roles of HPV in the carcinogenesis of breast cancer remain controversial. This study was performed to determine the prevalence of HPV-positive breast cancer in Korean patients and to evaluate the possibility of carcinogenic effect of HPV on breast.
Methods
Meta-analysis was performed in 22 case-control studies for HPV infection in breast cancer. A total of 123 breast cancers, nine intraductal papillomas and 13 nipple tissues of patients with proven cervical HPV infection were tested by real-time polymerase chain reaction to detect 28 subtypes of HPV. Breast cancers were composed of 106 formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) breast cancer samples and 17 touch imprint cytology samples of breast cancers.
Results
The overall odds ratio between breast cancer and HPV infection was 5.43 (95% confidence interval, 3.24 to 9.12) with I2 = 34.5% in meta-analysis of published studies with case-control setting and it was statistically significant. HPV was detected in 22 cases of breast cancers (17.9%) and two cases of intaductal papillomas (22.2%). However, these cases had weak positivity.
Conclusions
These results failed to serve as significant evidence to support the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. Further study with larger epidemiologic population is merited to determine the relationship between HPV and breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
Zhi-yong Liu, Ran Chen
Frontiers in Oncology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in human papillomavirus detection for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis: challenges of conventional methods and opportunities for emergent tools
O. Fashedemi, Okoroike C. Ozoemena, Siwaphiwe Peteni, Aderemi B. Haruna, Leshweni J. Shai, Aicheng Chen, Frankie Rawson, Maggie E. Cruickshank, David Grant, Oluwafunmilola Ola, Kenneth I. Ozoemena
Analytical Methods.2025; 17(7): 1428. CrossRef - Bacterial-Viral Interactions in Human Orodigestive and Female Genital Tract Cancers: A Summary of Epidemiologic and Laboratory Evidence
Ikuko Kato, Jilei Zhang, Jun Sun
Cancers.2022; 14(2): 425. CrossRef - Breast cancer association with oncogenic papillomaviruses: papillomaviral DNA detection in breast cancer cells
G. M. Volgareva
Advances in Molecular Oncology.2022; 9(2): 10. CrossRef - Presence of Human Papillomavirus DNA in Malignant Neoplasia and Non-Malignant Breast Disease
Erika Maldonado-Rodríguez, Marisa Hernández-Barrales, Adrián Reyes-López, Susana Godina-González, Perla I. Gallegos-Flores, Edgar L. Esparza-Ibarra, Irma E. González-Curiel, Jesús Aguayo-Rojas, Adrián López-Saucedo, Gretel Mendoza-Almanza, Jorge L. Ayala-
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3648. CrossRef - Risk Role of Breast Cancer in Association with Human Papilloma Virus among Female Population in Taiwan: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Chia-Hsin Liu, Chi-You Liao, Ming-Hsin Yeh, James Cheng-Chung Wei
Healthcare.2022; 10(11): 2235. CrossRef - HPV-Associated Breast Cancer: Myth or Fact?
Erik Kudela, Eva Kudelova, Erik Kozubík, Tomas Rokos, Terezia Pribulova, Veronika Holubekova, Kamil Biringer
Pathogens.2022; 11(12): 1510. CrossRef - Assessment of Human Papillomavirus Infection and Risk Factors in Egyptian Women With Breast Cancer
Nabila El-Sheikh, Nahla O Mousa, Amany M Tawfeik, Alaa M Saleh, Iman Elshikh, Mohamed Deyab, Faten Ragheb, Manar M Moneer, Ahmed Kawashti, Ahmed Osman, Mohamed Elrefaei
Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Detection by Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (CISH) and p16 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) in Breast Intraductal Papilloma and Breast Carcinoma
Hua Guo, Juan P. Idrovo, Jin Cao, Sudarshana Roychoudhury, Pooja Navale, Louis J. Auguste, Tawfiqul Bhuiya, Silvat Sheikh-Fayyaz
Clinical Breast Cancer.2021; 21(6): e638. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus in Breast Carcinogenesis: A Passenger, a Cofactor, or a Causal Agent?
Rancés Blanco, Diego Carrillo-Beltrán, Juan P. Muñoz, Alejandro H. Corvalán, Gloria M. Calaf, Francisco Aguayo
Biology.2021; 10(8): 804. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of the papillomavirus prevalence in breast cancer fresh tissues
Geilson Gomes de Oliveira, Ana Katherine Gonçalves, José Eleutério, Luiz Gonzaga Porto Pinheiro
Breast Disease.2021; 41(1): 123. CrossRef - Is human papillomavirus associated with breast cancer or papilloma presenting with pathologic nipple discharge?
Fatih Levent Balci, Cihan Uras, Sheldon Marc Feldman
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2019; 19: 100122. CrossRef - Is the HPV virus responsible for the development of breast cancer?
Erik Kudela, Marcela Nachajova, Jan Danko
The Breast Journal.2019; 25(5): 1053. CrossRef - Absence of Human Papillomavirus in Benign and Malignant Breast Tissue
Maryam Kazemi Aghdam, Seyed Alireza Nadji, Azadeh Alvandimanesh, Maliheh Khoddami, Yassaman Khademi
Iranian Journal of Pathology.2019; 14(4): 279. CrossRef - Oncogenic Viruses and Breast Cancer: Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus (MMTV), Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), and Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)
James S. Lawson, Brian Salmons, Wendy K. Glenn
Frontiers in Oncology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Viral infections and breast cancer – A current perspective
O.M. Gannon, A. Antonsson, I.C. Bennett, N.A. Saunders
Cancer Letters.2018; 420: 182. CrossRef - Prevalence of EBV, HPV and MMTV in Pakistani breast cancer patients: A possible etiological role of viruses in breast cancer
Wasifa Naushad, Orooj Surriya, Hajra Sadia
Infection, Genetics and Evolution.2017; 54: 230. CrossRef
- HPV, APOBEC3B, and the origins of breast cancer: a narrative review and perspectives on novel mechanisms
- Do Helper T Cell Subtypes in Lymphocytic Thyroiditis Play a Role in the Antitumor Effect?
- Seok Woo Yang, Seong-Ho Kang, Kyung Rae Kim, In Hong Choi, Hang Seok Chang, Young Lyun Oh, Soon Won Hong
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):377-384. Published online September 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.07.25
- 10,206 View
- 108 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is frequently accompanied by lymphocytic thyroiditis (LT). Some reports claim that Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (the clinical form of LT) enhances the likelihood of PTC; however, others suggest that LT has antitumor activity. This study was aimed to find out the relationship between the patterns of helper T cell (Th) cytokines in thyroid tissue of PTC with or without LT and the clinicopathological manifestation of PTC.
Methods
Fresh surgical samples of PTC with (13 cases) or without (10 cases) LT were used. The prognostic parameters (tumor size, extra-thyroidal extension of PTC, and lymph node metastasis) were analyzed. The mRNA levels of two subtypes of Th cytokines, Th1 (tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α], interferon γ [IFN-γ ], and interleukin [IL] 2) and Th2 (IL-4 and IL-10), were analyzed. Because most PTC cases were microcarcinomas and recent cases without clinical follow-up, negative or faint p27 immunoreactivity was used as a surrogate marker for lymph node metastasis.
Results
PTC with LT cases showed significantly higher expression of TNF-α (p = .043), IFN-γ (p < .010), IL-4 (p = .015) than those without LT cases. Although the data were not statistically significant, all analyzed cytokines (except for IL-4) were highly expressed in the cases with higher expression of p27 surrogate marker.
Conclusions
These results indicate that mixed Th1 (TNF-α, IFN-γ , and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-10) immunity might play a role in the antitumor effect in terms of lymph node metastasis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: impact and correlation
Shengpeng Yao, Hong Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Fabiana Franchini, Giuseppe Palatucci, Annamaria Colao, Paola Ungaro, Paolo Emidio Macchia, Immacolata Cristina Nettore
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(3): 1116. CrossRef - Association between Hashimoto thyroiditis and clinical outcomes of papillary thyroid carcinoma: A meta-analysis
Qizhi Tang, Weiyu Pan, Liangyue Peng, Francis Moore
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269995. CrossRef - The Heat Shock Protein Story—From Taking mTORC1,2 and Heat Shock Protein Inhibitors as Therapeutic Measures for Treating Cancers to Development of Cancer Vaccines
Peter Chin Wan Fung, Regina Kit Chee Kong
Journal of Cancer Therapy.2017; 08(11): 962. CrossRef
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: impact and correlation
- Difference of the Nuclear Green Light Intensity between Papillary Carcinoma Cells Showing Clear Nuclei and Non-neoplastic Follicular Epithelia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyekyung Lee, Tae Hwa Baek, Meeja Park, Seung Yun Lee, Hyun Jin Son, Dong Wook Kang, Joo Heon Kim, Soo Young Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(5):355-360. Published online August 22, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.05.19
- 8,480 View
- 90 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
There is subjective disagreement regarding nuclear clearing in papillary thyroid carcinoma. In this study, using digital instruments, we were able to quantify many ambiguous pathologic features and use numeric data to express our findings.
Methods
We examined 30 papillary thyroid carcinomas. For each case, we selected representative cancer cells showing clear nuclei and surrounding non-neoplastic follicular epithelial cells and evaluated objective values of green light intensity (GLI) for quantitative analysis of nuclear clearing in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Results
From 16,274 GLI values from 600 cancer cell nuclei and 13,752 GLI values from 596 non-neoplastic follicular epithelial nuclei, we found a high correlation of 94.9% between GLI and clear nuclei. GLI between the cancer group showing clear nuclei and non-neoplastic follicular epithelia was statistically significant. The overall average level of GLI in the cancer group was over two times higher than the non-neoplastic group despite a wide range of GLI. On a polygonal line graph, there was a fluctuating unique difference between both the cancer and non-neoplastic groups in each patient, which was comparable to the microscopic findings.
Conclusions
Nuclear GLI could be a useful factor for discriminating between carcinoma cells showing clear nuclei and non-neoplastic follicular epithelia in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
- A Rare Case of Recurrent Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
- Hye Seung Lee, Han Kyeom Kim, Bong Kyung Shin, Jin Hyuk Choi, Yoo Jin Choi, Ha Yeon Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(1):87-91. Published online August 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.06.16
- 12,737 View
- 234 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 61-year-old woman visited our hospital for bilateral multiple lung nodules and a mass in her thorax. She had a long history of multiple metastatic recurrences of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN); 24 years previously, the patient had undergone pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for a 9.9 × 8.6 cm mass in the pancreatic head. The tumor was diagnosed as an SPN. Nine years later, metastatic nodules were found on computed tomography in the patient’s liver and peritoneum and were excised. She subsequently underwent an additional eight metastatectomy procedures in diverse organs. For the presented event, the lung nodules were removed. The prevalence of malignant SPN in the general population is 5%–15%. However, multiple metastatic recurrence of malignant SPN is rare; the lung is a particularly rare site of metastasis, found in only three cases in the literature. Here, we describe this exceptional case and provide a literature review.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
Jun Hyung Kim, Hyung Sun Kim, Jung Min Lee, Ji Hae Nahm, Joon Seong Park
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2025; 29(1): 83. CrossRef - Curative Resection for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of Pancreas—a Case Series
Aparna M. Jagannathan, Manbha L. Rymbai, Abhilasha Anand, Anoop Paul, Borna Das, Thomas Alex Kodiatte, Frederick L. Vyas, Ravish Sanghi Raju, Philip Joseph
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2024; 15(S2): 232. CrossRef - Malignant Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: An Orthogonal Analysis
Andrew M. Fleming, Leah E. Hendrick, Danny Yakoub, Hafeez Abdelhafeez, Jeremiah L. Deneve, Max R. Langham, Evan S. Glazer, Andrew M. Davidoff, Nipun B. Merchant, Paxton V. Dickson, Andrew J. Murphy
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2024; 31(1): 475. CrossRef - A Unique Presentation of Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas Requiring Pancreaticoduodenectomy Without Pancreatojejunostomy: A Case Report and Literature Review
Alexis L Carmona, Sameh A Fayek
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Clinical analysis and literature review of five cases of metastatic solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas
Run Hu, Renjie Gui, Xi Nie, Huaxin Duan
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case of Treatment of Solid Pseudopapillary Pancreatic Tumor
F. S. Rakhimova, N. D. Mamashev, O. A. Shimkina, B. Kh. Bebezov
Creative surgery and oncology.2023; 13(2): 178. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: A report of 18 cases
Ayiguzaili Maimaijiang, Haiyun Wang, Wanfu Li, Yaqi Wang
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Large tumor size, lymphovascular invasion, and synchronous metastasis are associated with the recurrence of solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas
Goeun Lee, You-Na Sung, Sung Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Lee, Ki-Byung Song, Dae Wook Hwang, Jihun Kim, Sang Soo Lee, Song Cheol Kim, Seung-Mo Hong
HPB.2021; 23(2): 220. CrossRef - Solid-Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas: A 63-Case Analysis of Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Features and Risk Factors of Malignancy
Hongchun Chen, Yuchen Huang, Ningning Yang, Wentian Yan, Ruxue Yang, Shan Zhang, Panpan Yang, Nan Li, Zhenzhong Feng
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 3335. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Approach for Pancreatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm and Initially Undiagnosed Slowly Progressing Liver Tumor
Shohei Takaichi, Yoshifumi Iwagami, Shogo Kobayashi, Yoshito Tomimaru, Hirofumi Akita, Tadafumi Asaoka, Takehiro Noda, Kunihito Gotoh, Masaki Mori, Yuichiro Doki, Hidetoshi Eguchi
Pancreas.2020; 49(8): e70. CrossRef - Rare Solid Tumor of the Exocrine Pancreas: A Pictorial Review
Marco Dioguardi Burgio, Maxime Ronot, Valérie Vilgrain
Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI.2019; 40(6): 483. CrossRef - The Stomach: a Rare Site for Metastatic Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas
Prajwala S. Prakash, Dexter Yak Seng Chan, Krishnakumar Madhavan
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2018; 22(4): 759. CrossRef - European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms
Gut.2018; 67(5): 789. CrossRef
- A rare case of a large solid pseudopapillary neoplasm with extensive liver metastasis
- Clinical Significance of an HPV DNA Chip Test with Emphasis on HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 Detection in Korean Gynecological Patients
- Min-Kyung Yeo, Ahwon Lee, Soo Young Hur, Jong Sup Park
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):294-299. Published online June 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.05.09
- 10,780 View
- 80 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a major risk factor for cervical cancer.
Methods
We evaluated the clinical significance of the HPV DNA chip genotyping assay (MyHPV chip, Mygene Co.) compared with the Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2) chemiluminescent nucleic acid hybridization kit (Digene Corp.) in 867 patients.
Results
The concordance rate between the MyHPV chip and HC2 was 79.4% (kappa coefficient, κ = 0.55). The sensitivity and specificity of both HPV tests were very similar (approximately 85% and 50%, respectively). The addition of HPV result (either MyHPV chip or HC2) to cytology improved the sensitivity (95%, each) but reduced the specificity (approximately 30%, each) compared with the HPV test or cytology alone. Based on the MyHPV chip results, the odds ratio (OR) for ≥ high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSILs) was 9.9 in the HPV-16/18 (+) group and 3.7 in the non-16/18 high-risk (HR)-HPV (+) group. Based on the HC2 results, the OR for ≥ HSILs was 5.9 in the HR-HPV (+) group. When considering only patients with cytological diagnoses of “negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy” and “atypical squamous cell or atypical glandular cell,” based on the MyHPV chip results, the ORs for ≥ HSILs were 6.8 and 11.7, respectively, in the HPV-16/18 (+) group.
Conclusions
The sensitivity and specificity of the MyHPV chip test are similar to the HC2. Detecting HPV-16/18 with an HPV DNA chip test, which is commonly used in many Asian countries, is useful in assessing the risk of high-grade cervical lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Human papilloma virus identification in ocular surface squamous neoplasia by p16 immunohistochemistry and DNA chip test
Tina Shrestha, Won Choi, Ga Eon Kim, Jee Myung Yang, Kyung Chul Yoon
Medicine.2019; 98(2): e13944. CrossRef - Comparison of the PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip Test with the Cobas 4800 HPV and Hybrid Capture 2 Tests for Detection of HPV in ASCUS Women
Eun Young Ki, Yoon Kyung Lee, Ahwon Lee, Jong Sup Park
Yonsei Medical Journal.2018; 59(5): 662. CrossRef
- Human papilloma virus identification in ocular surface squamous neoplasia by p16 immunohistochemistry and DNA chip test
- Detection of Tumor Multifocality Is Important for Prediction of Tumor Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis
- Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(4):278-286. Published online June 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.03.29
- 12,230 View
- 111 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The clinicopathological characteristics and conclusive treatment modality for multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (mPTMC) have not been fully established.
Methods
A retrospective study, systematic review, and meta-analysis were conducted to elucidate the clinicopathological significance of mPTMC. We investigated the multiplicity of 383 classical papillary thyroid microcarcinomas (PTMCs) and the clinicopathological significance of incidental mPTMCs. Correlation between tumor recurrence and multifocality in PTMCs was evaluated through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Results
Tumor multifocality was identified in 103 of 383 PTMCs (26.9%). On linear regression analysis, primary tumor diameter was significantly correlated with tumor number (R2=0.014, p=.021) and supplemental tumor diameter (R2=0.117, p=.023). Of 103 mPTMCs, 61 (59.2%) were non-incidental, with tumor detected on preoperative ultrasonography, and 42 (40.8%) were diagnosed (incidental mPTMCs) on pathological examination. Lymph node metastasis and higher tumor stage were significantly correlated with tumor multifocality. However, there was no difference in nodal metastasis or tumor stage between incidental and non-incidental mPTMCs. On meta-analysis, tumor multifocality was significantly correlated with tumor recurrence in PTMCs (odds ratio, 2.002; 95% confidence interval, 1.475 to 2.719, p<.001).
Conclusions
Our results show that tumor multifocality in PTMC, regardless of manner of detection, is significantly correlated with aggressive tumor behavior. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
Chih-Chieh Hsu, Chun-Yi Tsai, Li-Ching Lin, Shang-Yu Wang, Chun-Nan Yeh, Miaw-Jene Liou, Szu-Tah Chen
Cancer Management and Research.2026; Volume 18: 1. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Multifocality and Bilaterality on Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Merima Goran, Marko Buta, Srdjan Nikolic, Nada Santrac, Nikola Jeftic, Nevena Savkovic, Jovan Raketic, Zoran Kozomara, Natasa Medic-Milijic, Ana Cvetkovic, Saska Pavlovic, Ivan Markovic
Diagnostics.2026; 16(2): 208. CrossRef - A machine learning model utilizing Delphian lymph node characteristics to predict contralateral central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a prospective multicenter study
Jia-ling He, Yu-zhao Yan, Yan Zhang, Jin-sui Li, Fei Wang, Yi You, Wei Liu, Ying Hu, Ming-Hao Wang, Qing-wen Pan, Yan Liang, Ming-shijing Ren, Zi-wei Wu, Kai You, Yi Zhang, Jun Jiang, Peng Tang
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(1): 360. CrossRef - Individual risk factors for recurrence after hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in the presence of autoimmune thyroiditis
E.V. Ryabchenko
P.A. Herzen Journal of Oncology.2023; 12(3): 20. CrossRef - The value of total tumor diameter in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis
Zhu-juan Wu, Bao-ying Xia, Zi-wei Chen, Hao Gong, Munire Abuduwaili, Zhi-chao Xing, An-ping Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Negative Histopathological Prognostic Factors Affecting Morbidity in T1 Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Mine Araz, Elgin Özkan, Pınar Gunduz, Cigdem Soydal, N. Özlem Küçük, K. Metin Kır
Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals.2022; 37(1): 56. CrossRef - Total tumor diameter is a better indicator of multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis
Ke-cheng Jiang, Bei Lin, Yu Zhang, Ling-qian Zhao, Ding-cun Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective comparison of individual risk factors hemithyroidectomy and thyroidectomy in patients with papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland in combination with autoimmune thyroiditis
E. V. Ryabchenko
Head and neck tumors (HNT).2022; 12(4): 71. CrossRef - The relationship between lipotoxicity and risk of extrathyroidal extension in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Changlin Li, Haixia Guan, Qiao He, Yishen Zhao, Nan liang, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Hui Sun
Endocrine.2021; 74(3): 646. CrossRef - Multifocality and Progression of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma During Active Surveillance
Ryuta Nagaoka, Aya Ebina, Kazuhisa Toda, Tomoo Jikuzono, Marie Saitou, Masaomi Sen, Hiroko Kazusaka, Mami Matsui, Keiko Yamada, Hiroki Mitani, Iwao Sugitani
World Journal of Surgery.2021; 45(9): 2769. CrossRef - Correlation of ThyroSeq Results with Surgical Histopathology in Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
Patrick D. Chin, Catherine Y. Zhu, Dipti P. Sajed, Gregory A. Fishbein, Michael W. Yeh, Angela M. Leung, Masha J. Livhits
Endocrine Pathology.2020; 31(4): 377. CrossRef - Application of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Management of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Huang, MD Kun, Liu, MD Ji-Bin
ADVANCED ULTRASOUND IN DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY.2020; 4(4): 284. CrossRef - Analysis of Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms with a Striking Rise of Papillary Microcarcinoma in an Endemic Goiter Region
Alka Mary Mathai, K. Preetha, S. Valsala Devi, Sam Vicliph, Raja Pradeep, Aqib Shaick
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery.2019; 71(S1): 121. CrossRef - The first postoperative-stimulated serum thyroglobulin is a prognostic factor for thyroid microcarcinomas
Isabela de Oliveira Amui, José Vicente Tagliarini, Emanuel C. Castilho, Mariângela de Alencar Marques, Yoshio Kiy, José Eduardo Corrente, Gláucia M.F.S. Mazeto
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2019; 85(1): 37. CrossRef - Surgical management of follicular thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents: A study of 30 cases
Claudio Spinelli, Leonardo Rallo, Riccardo Morganti, Valentina Mazzotti, Alessandro Inserra, Giovanni Cecchetto, Maura Massimino, Paola Collini, Silvia Strambi
Journal of Pediatric Surgery.2019; 54(3): 521. CrossRef - The role of prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in elderly patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a multicentric study
Claudio Gambardella, Renato Patrone, Francesco Di Capua, Chiara Offi, Claudio Mauriello, Guglielmo Clarizia, Claudia Andretta, Andrea Polistena, Alessandro Sanguinetti, Pietrogiorgio Calò, Giovanni Docimo, Nicola Avenia, Giovanni Conzo
BMC Surgery.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Cervical Lymph Node Metastases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, in the Central and Lateral Compartments, in Children and Adolescents: Predictive Factors
C. Spinelli, F. Tognetti, S. Strambi, R. Morganti, M. Massimino, P. Collini
World Journal of Surgery.2018; 42(8): 2444. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Challenges and Prospects
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Zachary A. Hurst, Yi Seok Chang, Guang Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of lobectomy and total thyroidectomy in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective individual risk factor-matched cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 176(4): 371. CrossRef - Total thyroidectomy may be more reasonable as initial surgery in unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a single-center experience
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Lack of Efficacy of Radioiodine Remnant Ablation for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Verification Using Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting
Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Minkyu Han, Dong Eun Song, Tae-Yon Sung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jin-Sook Ryu, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2017; 24(9): 2596. CrossRef - Radioactive Iodine Ablation Decrease Recurrences in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma with Lateral Lymph Node Metastasis in Chinese Patients
Shuai Xue, Peisong Wang, Jia Liu, Guang Chen
World Journal of Surgery.2017; 41(12): 3139. CrossRef - The Prognostic Value of Tumor Multifocality in Clinical Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Fei Wang, Xiaolong Yu, Xiaopei Shen, Guangwu Zhu, Yueye Huang, Rengyun Liu, David Viola, Rossella Elisei, Efisio Puxeddu, Laura Fugazzola, Carla Colombo, Barbara Jarzab, Agnieszka Czarniecka, Alfred K Lam, Caterina Mian, Federica Vianello, Linwah Yip, Gar
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(9): 3241. CrossRef - Evaluation of surgical results of micropapillary thyroid cancers according to tumor size and focality
Bekir Uçan, Muhammed Erkam Sencar, Muhammed Kızılgül, Mustafa Özbek, İlknur Öztürk Ünsal, Erman Çakal
Ortadoğu Tıp Dergisi.2017; 9(3): 123. CrossRef - Contrastive study of two screening criteria for active surveillance in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 1001 patients
Kai Qian, Kai Guo, Xiaoke Zheng, Tuanqi Sun, Duanshu Li, Yi Wu, Qinghai Ji, Zhuoying Wang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(39): 65836. CrossRef - 10.1016/j.bjorlp.2018.01.005
CrossRef Listing of Deleted DOIs.2000;[Epub] CrossRef
- Risk Stratification in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Clinical Features Predicting Multifocality, Lymph Node Metastasis, and Recurrence – A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Comparison of Analytical and Clinical Performance of HPV 9G DNA Chip, PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip, and Hybrid-Capture II Assay in Cervicovaginal Swabs
- Ho Young Jung, Hye Seung Han, Hyo Bin Kim, Seo Young Oh, Sun-Joo Lee, Wook Youn Kim
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(2):138-146. Published online January 13, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.10.21
- 10,406 View
- 68 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection can be detected by using several molecular methods, including Hybrid-Capture II (HC2) assay and variable HPV DNA chip tests, although each method has different sensitivities and specificities. Methods: We performed HPV 9G DNA Chip (9G) and PANArray HPV Genotyping Chip (PANArray) tests on 118 cervicovaginal swabs and compared the results with HC2, cytology, histology, and direct sequencing results. Results: The overall and high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) positivity rates were 62.7% and 44.9% using 9G, and 61.0% and 30.5% using PANArray, respectively. The positivity rates for HR-HPV with these two chips were significantly lower than 55.1% when HC2 was used. The sensitivity of overall HPV positivity in detecting histologically confirmed low-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions or higher was 88.7% for all three tests. The specificity was 58.5% for 9G and 61.5% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 72.3% for HC2. With the HR-HPV+ genotype threshold, the sensitivity decreased to 75.5% for 9G and 52.8% for PANArray, which was significantly lower than the 88.7% for HC2. Comparison of the two chips showed concordant results in 55.1% of the samples, compatible results in 16.9%, and discordant results in 28.0%, exhibiting poor agreement in detecting certain HPV genotypes. Compared with direct sequencing, 9G yielded no discordant results, whereas PANArray yielded 31 discordant results (26.7%). Conclusions: Compared with HC2, the HPV genotyping tests showed lower sensitivity in histologic correlation. When the two chips were compared, the 9G was more sensitive and accurate for detecting HR-HPV than the PANArray. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
Habtamu Biazin
Journal of Virological Methods.2022; 301: 114435. CrossRef - The clinical performance of human papillomavirus genotyping using PANArray HPV chip: Comparison to ThinPrep cytology alone and co-testing
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Lee-So Maeng
Pathology - Research and Practice.2020; 216(9): 153121. CrossRef - Analytic performance of PANArray HPV and HPV 9G DNA chip tests for genotyping of high-risk human papillomavirus in cervical ThinPrep PreservCyt samples
Jiyoung Kim, Sun-Young Jun, Magdalena Grce
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0224483. CrossRef
- Concordance of Anyplex™ II HPV HR assays with reference HPV assays in cervical cancer screening: Systematic review
- Parafibromin Staining Characteristics in Urothelial Carcinomas and Relationship with Prognostic Parameters
- Serap Karaarslan, Banu Yaman, Hakan Ozturk, Banu Sarsik Kumbaraci
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):389-395. Published online September 15, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.08.10
- 9,088 View
- 47 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Parafibromin is a recently defined tumor suppressor gene. The aim of our study was to determine the relationships of parafibromin expression in urothelial carcinomas (UCs) with prognostic parameters and to evaluate the use of parafibromin as a potential marker of UC. Methods: Parafibromin expression was assessed in 49 UC specimens using immunohistochemistry. The correlations between parafibromin expression and clinical and pathologic parameters were investigated. Results: Of the patients, 42 (85.7%) were male, and the mean age was 69.6 ± 8.2 years (range, 54 to 88 years). Morphologically, the UCs were divided into two groups: papillary (n = 27) and non-papillary (n = 22). There were seven low-grade (14.3%) and 42 high-grade (85.7%) tumors. Parafibromin was negative in 13 tumors (26.5%), partially positive in 19 tumors (38.8%), and positive in 17 tumors (34.7%). Parafibromin expression was more negative in UCs from upper urinary locations (n=17) and with muscularis propria invasion (n=28), which was statistically significant (p = .009 and p = .007, respectively). There was no statistically significant relationship between parafibromin expression and gender, age, tumor grade, survival, or disease-free survival. Conclusions: We found that UC cases with parafibromin positivity had less of a tendency to show muscularis propria invasion and were more commonly located in the lower urinary system. These results need to be confirmed with studies based on larger case series. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The roles of the tumor suppressor parafibromin in cancer
Hua-chuan Zheng, Hang Xue, Cong-yu Zhang
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic role of parafibromin staining and CDC73 mutation in patients with parathyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta‐analysis based on individual patient data
Ruizhe Zhu, Zixing Wang, Ya Hu
Clinical Endocrinology.2020; 92(4): 295. CrossRef - Thein vitroandin vivoeffects of nuclear and cytosolic parafibromin expression on the aggressive phenotypes of colorectal cancer cells: a search of potential gene therapy target
Hua-chuan Zheng, Jia-jie Liu, Jing Li, Ji-cheng Wu, Lei Yang, Gui-feng Zhao, Xin Zhao, Hua-mao Jiang, Ke-qiang Huang, Zhi-jie Li
Oncotarget.2017; 8(14): 23603. CrossRef - The clinicopathological and prognostic significances ofCDC73expression in cancers: a bioinformatics analysis
Hua-Chuan Zheng, Bao-Cheng Gong, Shuang Zhao
Oncotarget.2017; 8(56): 95270. CrossRef - Significance of Parafibromin Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Inju Cho, Mija Lee, Sharon Lim, Ran Hong
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(4): 264. CrossRef
- The roles of the tumor suppressor parafibromin in cancer
- Comparison of Cytologic Characteristics between Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma and Adenoid Basal Carcinoma in the Uterine Cervix
- Juhyeon Jeong, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho, Dong Hae Chung, Jungsuk An
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(5):396-402. Published online August 17, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.07.08
- 11,256 View
- 97 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) and adenoid basal carcinoma (ABC) are rare in the uterine cervix. ACC is more aggressive than ABC, thus accurate differential diagnosis is important. In this study, we identified cytologic features useful in distinguishing these two tumors for diagnosis. Methods: Three cases of ACC and five cases of ABC were selected for this study. Cervicovaginal smear slides were reviewed retrospectively, and the area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis of nuclei were measured using an image analyzer. Results: ACC displayed three-dimensional clusters with a small acini pattern. ABC displayed peripheral palisading without an acini pattern. The nuclei of ACC were more irregular and angulated than those of ABC, and the former showed a coarsely granular chromatin pattern. The nucleic area, circumference, major axis, and minor axis were 18.556±8.665 µm2, 23.320±11.412 µm, 5.664±1.537 µm, and 4.127±1.107 µm in ACC and 11.017±4.440 µm2, 15.920±5.664 µm, 4.612±1.025 µm, and 3.088±0.762 µm in the cases of ABC. All measured values showed statistically significant difference (p < .001). Conclusions: Although the nuclei of both of these tumor types were oval shaped, inferred from the ratio of minor axis to major axis (0.728 in ACC and 0.669 in ABC), the area of nuclei was approximately 1.7 times larger in ACC than in ABC. Distinguishing nucleic features, including area, morphology, and chromatin pattern, may be helpful in making a correct diagnosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix
Anas Mohamed, Tesfalem Korga, Ahlam Ali, Javier Laurini
International Journal of Gynecological Cancer.2025; : 101873. CrossRef - Adenoid Basal Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report
Tatsuya Kanuma, Keiko Kigure, Tosio Nishimura, Yuji Ibuki, Shigeru Tsuchida, Harumi Kamiyama, Misa Iijima, Kazuto Nakamura
The KITAKANTO Medical Journal.2016; 66(1): 11. CrossRef
- Adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix
- Fallopian Metaplastic Papillary Tumour: An Atypical Transdifferentiation of the Tubal Epithelium?
- Miguel Fdo. Salazar, Isaías Estrada Moscoso, Lorena Troncoso Vázquez, Nubia Leticia López García, Paola Andrea Escalante Abril
- J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49(2):148-155. Published online March 12, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2014.10.15
- 10,453 View
- 60 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A metaplastic papillary tumor of the Fallopian tube is an extremely uncommon condition, with odd and confusing features that make it difficult to categorize as benign or borderline. Here, we summarize all the published cases to date and document the case of a 41-year-old woman diagnosed with this alteration after her last childbirth and ensuing tubal ligation. One of the tubes was bulky and filled with a caramel-like substance encircling a blurry spot. Light microscopy detailed a slender stalk covered by eosinophilic, columnar plump cells, showing atypical nuclei and focal budding. Mitotic figures were absent. The immunohistochemistry panel was positive for pan-cytokeratin, epithelial membrane antigen, cyclin D1, and hormone receptors. Additionally, a proliferation index of less than 5% was rated using Ki-67. The true nature of this tumor (reactive vs neoplastic) is uncertain. Nonetheless, its association with pregnancy suggests an adaptive change, likely similar to the atypical transdifferentiation proposed for Arias-Stella reaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ungewöhnliche Proliferation des Eileiters
Angelina Vlaški, Vanessa Neukunft, Andrea Maria Gassel, Frederick Klauschen, Doris Mayr
Die Pathologie.2025; 46(1): 56. CrossRef - Fallopian tube papilloma
Shashank Mishra, Prerna Guleria
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2021; 64(3): 608. CrossRef - Metaplastic papillary tumour of the fallopian tube, a rare entity, analysed by next‐generation sequencing
Sandra Sunitsch, Julia Reisinger, Luca Abete, Karl Kashofer, Peter Regitnig
Histopathology.2020; 76(6): 923. CrossRef
- Ungewöhnliche Proliferation des Eileiters
- The Limitations of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma: A Brief Case Report
- Heae Surng Park, Sun Och Yoon, Beom Jin Lim, Joo Hee Kim, Soon Won Hong
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):405-408. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.405
- 8,493 View
- 63 Download
- Pulmonary Hodgkin Lymphoma in a Patient with Crohn’s Disease
- Jae-Young Park, Juhie Lee
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(5):387-389. Published online October 27, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.5.387
- 7,939 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Complex Relationship between Mechanisms Underlying Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Its Treatment, and the Risk of Lymphomas: A Comprehensive Review
Katarzyna Stasik, Rafał Filip
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4241. CrossRef - Extra-intestinal malignancies in inflammatory bowel diseases: An update with emphasis on MDCT and MR imaging features
A. Dohan, S.A. Faraoun, M. Barral, Y. Guerrache, M. Boudiaf, X. Dray, C. Hoeffel, M. Allez, O. Farges, L. Beaugerie, T. Aparicio, P. Marteau, E.K. Fishman, O. Lucidarme, C. Eveno, M. Pocard, R. Dautry, P. Soyer
Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging.2015; 96(9): 871. CrossRef
- The Complex Relationship between Mechanisms Underlying Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Its Treatment, and the Risk of Lymphomas: A Comprehensive Review
- Recurrent Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma in Children Under Ten Years Old: Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
- Byeong-Joo Noh, Ji-Youn Sung, Youn-Wha Kim, Yong-Koo Park
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(4):297-301. Published online August 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.4.297
- 9,076 View
- 50 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) in children under ten years old is very rare. To date, 18 cases of PTC in children under ten years old (including our two cases) have been reported in Korea. Here, we describe two cases of recurrent PTC with follicular variant and conventional type in an 8-year-old boy and a 7-year-old boy, respectively, and discuss clinicopathologic and molecular characteristics that differ in pediatric patients from adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely Well-Differentiated Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Resembling Adenomatous Hyperplasia Can Metastasize to the Skull: A Case Report
Ju Yeon Pyo, Jisup Kim, Sung-eun Choi, Eunah Shin, Seok-Woo Yang, Cheong Soo Park, Seok-Mo Kim, SoonWon Hong
Yonsei Medical Journal.2017; 58(1): 255. CrossRef
- Extremely Well-Differentiated Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Resembling Adenomatous Hyperplasia Can Metastasize to the Skull: A Case Report
- Well-Differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis: A Case Study and Review of the Literature
- Seyda Erdogan, Arbil Acikalin, Handan Zeren, Gulfılız Gonlusen, Suzan Zorludemir, Volkan Izol
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(3):225-228. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.3.225
- 10,416 View
- 72 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma is an uncommon tumor of the testes that usually presents as a hydrocele. Here, we present the case of one patient who did not have a history of asbestos exposure. The tumor was localized in the tunica vaginalis and was composed of three pedunculated masses macroscopically. Microscopically, branching papillary structures with focal coagulative necrosis were present. In addition to immunohistochemistry, simian virus 40 DNA was also tested by polymerase chain reaction. This report presents one case of this rare entity, its clinical and macroscopic features, and follow-up results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors predictive of progression in lesions categorised as well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the pleura, tunica vaginalis and peritoneum: a scoping review
Sarita Prabhakaran, Harry James Gaffney, Yazad Irani, Ashleigh J. Hocking, David Roder, Sonja Klebe
Cancer Treatment and Research Communications.2026; 47: 101137. CrossRef - Testicular/paratesticular mesothelial tumours: Uncommon histopathologic entities in a very complex anatomical site
Francesca Pagliuca, Stefano Lucà, Marco De Sio, Davide Arcaniolo, Gaetano Facchini, Marco De Martino, Francesco Esposito, Ferdinando DE Vita, Paolo Chieffi, Renato Franco
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; 253: 155069. CrossRef - Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelial Tumour of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis – A Rare Lesion, but one Pathologists Should Know About Two Patient Reports and a Review of the Literature
Johannes Kläger, Felicitas Oberndorfer, Cristophe Brunel, Julian Veser, Eva Compérat
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(6): 1126. CrossRef - A diagnostic approach to paratesticular lesions with tubulopapillary architecture: a series of 16 serous borderline tumors/low-grade serous carcinoma and 14 well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumors and mesothelioma
Rabia Zafar, Lacey J. Schrader, John C. Cheville, J. Kenneth Schoolmeester, Anja C. Roden, Marie-Christine Aubry, Eunhee S. Yi, Aditya Raghunathan, Loren Herrera-Hernandez, R. Houston Thompson, Stephen A. Boorjian, Bradley C. Leibovich, Gary L. Keeney, Ra
Human Pathology.2022; 128: 31. CrossRef - Mesothelioma subtypes of the tunica vaginalis: a rare case report and review of histological criteria
Cutts Rebecca, Martin J Connor, Luxi Sun, Thomas Johnston, Rachel Gooch, John McLoughlin
Journal of Surgical Case Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Well‐differentiated papillary mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis testis of unknown malignant potential: Sonographic appearance
K.W.S. Ko, K.S. Tse, K.W. Shek, M.N. Hau, S.H. Ting
Journal of Clinical Ultrasound.2018; 46(5): 364. CrossRef - Tunica Vaginalis Thickening, Hemorrhagic Infiltration and Inflammatory Changes in 8 Children with Primary Hydrocele; Reactive Mesothelial Hyperplasia? A Prospective Clinical Study
Ioannis Patoulias, Evangelia Rachmani, Maria Kalogirou, Kyriakos Chatzopoulos, Dimitrios Patoulias
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2018; 61(2): 41. CrossRef - A 45-year-old man presenting with chest pain
Sheetu Singh, Arpita Jindal
Lung India.2018; 35(2): 171. CrossRef - Two Case Reports of Benign Testicular Mesothelioma and Review of the Literature
Cristobal Ramirez Sevilla, Carme Admella Salvador, Josep Feliu Canaleta, Juan Llopis Manzanera, Miguel Angel Barranco Sanz, Juan Antoni Romero Martin, Sergi Bernal Salguero, Francesco A. Mauri
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Well-differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis
Wei Keith Tan, Mae-Yen Tan, Hui Meng Tan, Rajadurai Pathmanathan, Wei Phin Tan
Urology.2016; 90: e7. CrossRef - Well-Differentiated Papillary Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis: Case Report and Systematic Review of Literature
Wei Keith Tan, Mae-Yen Tan, Wei Shen Tan, Soon Ching Gan, Rajadurai Pathmanathan, Hui Meng Tan, Wei Phin Tan
Clinical Genitourinary Cancer.2016; 14(4): e435. CrossRef - The legacy of the F344 rat as a cancer bioassay model (a retrospective summary of three common F344 rat neoplasms)
Robert R. Maronpot, Abraham Nyska, Jennifer E. Foreman, Yuval Ramot
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2016; 46(8): 641. CrossRef - Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis: A Rare Neoplasm—Case Report and Literature Review
Manuel Segura-González, Jorge Urias-Rocha, Jorge Castelán-Pedraza
Clinical Genitourinary Cancer.2015; 13(6): e401. CrossRef - In vivo Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging of the Mesothelium Using Developed Window Models
Yeh-Chan Ahn, Yu-Gyeong Chae, Sang Seok Hwang, Bong-Kwon Chun, Maan Hong Jung, Sung Jin Nam, Hae-Young Lee, Jae Min Chung, Chulho Oak, Eun-Kee Park
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea.2015; 19(1): 69. CrossRef
- Factors predictive of progression in lesions categorised as well-differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour of the pleura, tunica vaginalis and peritoneum: a scoping review
- Tumor Sprouting in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Is Correlated with Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence
- Eunjung Lee, Wonkyung Jung, Jeong-Soo Woo, Jae Bok Lee, Bong Kyung Shin, Han Kyeom Kim, Aeree Kim, Baek-hui Kim
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(2):117-125. Published online April 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.2.117
- 13,388 View
- 68 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Identification of poor prognostic factors in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) patients is important for the patients' care and follow-up. We can sometimes see small tumor clusters without desmoplasia and no evidence of lymphatic emboli around the main tumor mass of PTC. We termed this form of tumor clustering, 'tumor sprouting,' and determined whether these tumors correlate with lymphovascular invasion, lymph node metastasis, and recurrence.
Methods We analyzed a total of 204 cases of papillary thyroid macrocarcinoma. Number, size and distance from the main tumor of the tumor sprouting were observed and analyzed with clinicopathologic characteristics.
Results Tumor sprouting was observed in 101 patients. Presence of tumor sprouting was significantly associated with positive resection margin (p=.002), lymphovascular invasion (p=.001), lymph node metastasis (p<.001), and recurrence (p=.004). Univariate analysis of recurrence-free survival revealed that tumor multiplicity (p=.037), positive resection margin (p=.007), lymphovascular invasion (p=.004), lymph node metastasis (p<.001), and tumor sprouting (p=.004) were poor prognostic factors. In multivariate analysis, positive resection margin was an independent poor prognostic factor of recurrence.
Conclusions In conclusion, tumor sprouting is significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and recurrence. Evaluation of tumor sprouting in PTC patients could be helpful in predicting tumor recurrence or lymph node metastasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Initial Risk Stratification System for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Key Updates in the 2024 Korean Thyroid Association Guideline
Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2025; 40(3): 357. CrossRef - Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines on the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers; Part I. Initial Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers - Chapter 5. Evaluation of Recurrence Risk Postoperatively and Initial Risk Stratification in Different
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Shin Je Moon, Dong-Jun Lim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Yun Jae Chung, Chan Kwon Jung, Young Joo Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2024; 17(1): 68. CrossRef - Significance of Lymphovascular Invasion as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ho-Ryun Won, Bon Seok Koo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(2): 157. CrossRef - Peripheral Versus Intraparenchymal Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Different Morphologies and PD-L1 Expression
Bozidar Kovacevic, Dragana Vucevic, Snezana Cerovic, Catarina Eloy
Head and Neck Pathology.2022; 16(1): 200. CrossRef - Lymphovascular invasion and risk of recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Katy Wagner, Earl Abraham, Bryan Tran, David Roshan, James Wykes, Peter Campbell, Ardalan Ebrahimi
ANZ Journal of Surgery.2020; 90(9): 1727. CrossRef - The Predictors of Multicentricity in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Mohamed Hegazi, Waleed El Nahas, Mohamed Elmetwally, Amr Hassan, Waleed Gado , Islam Abdou, Ahmed Senbel, Mohamed Samir Abou-Sheishaa
Journal of Analytical Oncology.2018; 7(4): 65. CrossRef - Prognostic impact of vascular invasion in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Huy Gia Vuong, Tetsuo Kondo, Uyen N P Duong, Thong Quang Pham, Naoki Oishi, Kunio Mochizuki, Tadao Nakazawa, Lewis Hassell, Ryohei Katoh
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 177(2): 207. CrossRef - Detection of Tumor Multifocality Is Important for Prediction of Tumor Recurrence in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis
Jung-Soo Pyo, Jin Hee Sohn, Guhyun Kang
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2016; 50(4): 278. CrossRef
- The Initial Risk Stratification System for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Key Updates in the 2024 Korean Thyroid Association Guideline
- Uncommon and Rare Human Papillomavirus Genotypes Relating to Cervical Carcinomas
- Na Rae Kim, Myunghee Kang, Soon Pyo Lee, Hyunchul Kim, Jungsuk An, Dong Hae Chung, Seung Yeon Ha, Hyun Yee Cho
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):43-49. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.43
- 10,619 View
- 56 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an oncogenic virus in cervical cancer and most invasive carcinomas (ICs) are caused by HPV16 and 18. However, the roles and contributions of other uncommon and rare genotypes remain uncertain.
Methods HPV genotypes were retrospectively assessed using an HPV DNA chip that can specify up to 32 HPV genotypes. We arbitrarily regarded genotypes accounting for less than 6% of the total as uncommon and rare genotypes.
Results A total of 3,164 HPV-positive cases were enrolled. In groups 2A, 2B, 3, and unclassified HPV genotypes, 2.4% of cases with uncommon HPV genotypes (68, 26, 34, 53, 66, 69, 70, 73, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 55, 61, 62, 6, and 11) showed high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and ICs. There were no HPV32- and 57-infected cases.
Conclusions We found that the uncommon and rare HPV genotypes may provide incremental etiologic contributions in cervical carcinogenesis, especially HPV68, 70, and 53. Further studies on these uncommon and rare HPV genotypes will be of importance in establishing the significance of genotypes in different regions, especially in planning a strategy for further vaccine development as well as follow-up on the effectiveness of the currently used vaccines.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-risk human papillomavirus diversity among indigenous women of western Botswana with normal cervical cytology and dysplasia
Patricia S. Rantshabeng, Billy M. Tsima, Andrew K. Ndlovu, Keneilwe Motlhatlhedi, Kirthana Sharma, Carol B. Masole, Natasha O. Moraka, Kesego Motsumi, Angela K. T. Maoto-Mokote, Alemayehu B. Eshetu, Leabaneng Tawe, Tendani Gaolathe, Sikhulile Moyo, Lynnet
BMC Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus (HPV69/HPV73) Coinfection associated with Simultaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Anus and Presumed Lung Metastasis
Stephanie Shea, Marina Muñoz, Stephen C. Ward, Mary B. Beasley, Melissa R Gitman, Michael D Nowak, Jane Houldsworth, Emilia Mia Sordillo, Juan David Ramirez, Alberto E. Paniz Mondolfi
Viruses.2020; 12(3): 349. CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus Selected Properties and Related Cervical Cancer Prevention Issues
Saule Balmagambetova, Andrea Tinelli, Ospan A. Mynbaev, Arip Koyshybaev, Olzhas Urazayev, Nurgul Kereyeva, Elnara Ismagulova
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(18): 2073. CrossRef - Periungual Bowen's disease with a narrow longitudinal melanonychia mimicking periungual warts
Taiyo HITAKA, Michiko HASEGAWA, Akira SHIMIZU, Yuko KURIYAMA, Atsushi TAMURA
Skin Cancer.2019; 33(3): 211. CrossRef - Detection of HPV RNA molecules in stratified mucin-producing intraepithelial lesion (SMILE) with concurrent cervical intraepithelial lesion: a case report
Shiho Fukui, Kazunori Nagasaka, Naoko Iimura, Ranka Kanda, Takayuki Ichinose, Takeru Sugihara, Haruko Hiraike, Shunsuke Nakagawa, Yuko Sasajima, Takuya Ayabe
Virology Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls of commercially available HPV tests in HPV68a detection
Hana Jaworek, Katerina Kubanova, Vladimira Koudelakova, Rastislav Slavkovsky, Jiri Drabek, Marian Hajduch, Craig Meyers
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220373. CrossRef - Overall accuracy of cervical cytology and clinicopathological significance of LSIL cells in ASC‐H cytology
S. H. Kim, J. M. Lee, H. G. Yun, U. S. Park, S. U. Hwang, J.‐S. Pyo, J. H. Sohn
Cytopathology.2017; 28(1): 16. CrossRef - Human papillomavirus genotyping by Linear Array and Next-Generation Sequencing in cervical samples from Western Mexico
María Guadalupe Flores-Miramontes, Luis Alberto Torres-Reyes, Liliana Alvarado-Ruíz, Salvador Angel Romero-Martínez, Verenice Ramírez-Rodríguez, Luz María Adriana Balderas-Peña, Verónica Vallejo-Ruíz, Patricia Piña-Sánchez, Elva Irene Cortés-Gutiérrez, Lu
Virology Journal.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of human papillomavirus coinfections on the risk of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion and cervical cancer
Adela Carrillo-García, Sergio Ponce-de-León-Rosales, David Cantú-de-León, Verónica Fragoso-Ontiveros, Imelda Martínez-Ramírez, Asunción Orozco-Colín, Alejandro Mohar, Marcela Lizano
Gynecologic Oncology.2014; 134(3): 534. CrossRef - Human papillomavirus 66‐associated subungual squamous cell carcinoma
Jin Hee Kang, Hwa young Ahn, Miri Kim, Shin Taek Oh, Baik Kee Cho, Hyun Jeong Park
The Journal of Dermatology.2014; 41(12): 1119. CrossRef
- High-risk human papillomavirus diversity among indigenous women of western Botswana with normal cervical cytology and dysplasia
- P2X7 Receptor Expression in Coexistence of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Ji Hyun Kwon, Eun Sook Nam, Hyung Sik Shin, Seong Jin Cho, Hye Rim Park, Mi Jung Kwon
- Korean J Pathol. 2014;48(1):30-35. Published online February 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2014.48.1.30
- 11,315 View
- 56 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background This study was aimed at investigating the relation of P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) expression with the clinicopathological features of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) coexisting with Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT).
Methods We examined 170 patients (84, PTC with HT; 86, PTC without HT). P2X7R expression was examined by immunohistochemical methods. The staining intensity and patterns were evaluated and scored using a semi-quantitative method.
Results The PTC with HT group was more likely to contain women and had less extrathyroid extension, lymph node (LN) metastasis, lymphovascular invasion, and recurrence than the PTC without HT group. Patients positive for P2X7R had significantly higher frequencies of lymphovascular invasion, extrathyroid extension, LN metastasis, and absence of HT. As shown by multivariate analysis, the expression of P2X7R was significantly higher if HT was absent and extrathyroid extension was present. In the PTC with HT group, the expression of P2X7R was significantly higher in patients with tumor multifocality, lymphovascular invasion, and extrathyroid extension. In the PTC without HT group, the expression of P2X7R was significantly higher in women and those having tumor multifocality.
Conclusions Coexistence of PTC with HT is associated with good prognostic factors, and P2X7R expression in PTC was correlated with poor prognostic factors and the absence of HT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress in the Relationship Between P2X7R and Cervical Cancer
Yiqing Tang, Cuicui Qiao, Qianqian Li, Xiaodi Zhu, Ronglan Zhao, Xiaoxiang Peng
Reproductive Sciences.2023; 30(3): 823. CrossRef - Warthin-like papillary thyroid carcinoma: a case report and comprehensive review of the literature
Abdel Mouhaymen Missaoui, Fatma Hamza, Wafa Belabed, Manel Mellouli, Mohamed Maaloul, Slim Charfi, Issam Jardak, Tahya Sellami-Boudawara, Nabila Rekik, Mohamed Abid
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mapping the path towards novel treatment strategies: a bibliometric analysis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis research from 1990 to 2023
Manping Guo, Qingna Li, Xingfang Liu, Yiming Wang, Qiaoning Yang, Rui Li, Yang Zhao, Chenfei Li, Song Sheng, Hangkun Ma, Zhenghong Li, Rui Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Hashimoto thyroiditis and clinical outcomes of papillary thyroid carcinoma: A meta-analysis
Qizhi Tang, Weiyu Pan, Liangyue Peng, Francis Moore
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269995. CrossRef - Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Minimizes Lymph Node Metastasis in BRAF Mutant Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas
Peter P. Issa, Mahmoud Omar, Yusef Buti, Chad P. Issa, Bert Chabot, Christopher J. Carnabatu, Ruhul Munshi, Mohammad Hussein, Mohamed Aboueisha, Mohamed Shama, Ralph L. Corsetti, Eman Toraih, Emad Kandil
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 2051. CrossRef - Overexpression of PD-L1 in Papillary Carcinoma and Its Association with Clinicopathological Variables
Servet KOCAÖZ, Gülay TURAN
Düzce Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; 23(3): 252. CrossRef - Effect of P2X7 receptor on tumorigenesis and its pharmacological properties
Wen-jun Zhang, Ce-gui Hu, Zheng-ming Zhu, Hong-liang Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 125: 109844. CrossRef - P2X7 in Cancer: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutics
Romain Lara, Elena Adinolfi, Catherine A. Harwood, Mike Philpott, Julian A. Barden, Francesco Di Virgilio, Shaun McNulty
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The P2X7 Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: Angel or Demon?
Luiz E. B. Savio, Paola de Andrade Mello, Cleide Gonçalves da Silva, Robson Coutinho-Silva
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Patients with Oncocytic Variant Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Have a Similar Prognosis to Matched Classical Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Controls
Azadeh A. Carr, Tina W.F. Yen, Diana I. Ortiz, Bryan C. Hunt, Gilbert Fareau, Becky L. Massey, Bruce H. Campbell, Kara L. Doffek, Douglas B. Evans, Tracy S. Wang
Thyroid.2018; 28(11): 1462. CrossRef - Extracellular purines, purinergic receptors and tumor growth
F Di Virgilio, E Adinolfi
Oncogene.2017; 36(3): 293. CrossRef - Multifaceted Effects of Extracellular Adenosine Triphosphate and Adenosine in the Tumor–Host Interaction and Therapeutic Perspectives
Paola de Andrade Mello, Robson Coutinho-Silva, Luiz Eduardo Baggio Savio
Frontiers in Immunology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential role of P2X7R in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation
André A Santos, Angélica R Cappellari, Fernanda O de Marchi, Marina P Gehring, Aline Zaparte, Caroline A Brandão, Tiago Giuliani Lopes, Vinicius D da Silva, Luis Felipe Ribeiro Pinto, Luiz Eduardo Baggio Savio, Aline Cristina Abreu Moreira-Souza, Robson C
Purinergic Signalling.2017; 13(3): 279. CrossRef - Potential relationship between Hashimoto's thyroiditis and BRAFV600E mutation status in papillary thyroid cancer
Rui‐chao Zeng, Lang‐ping Jin, En‐dong Chen, Si‐yang Dong, Ye‐feng Cai, Guan‐li Huang, Quan Li, Chun Jin, Xiao‐hua Zhang, Ou‐chen Wang
Head & Neck.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis as an incidental finding
Al Mogrampi Saad, A. Krexi, N. Papoulidis, M. Verroiotou, D. Michalakis, I. Fardellas
Hellenic Journal of Surgery.2016; 88(1): 47. CrossRef - Association of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and thyroid cancer
Salem I. Noureldine, Ralph P. Tufano
Current Opinion in Oncology.2015; 27(1): 21. CrossRef - Cribriform-morular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a study of 3 cases featuring the PIK3CA mutation
Mi Jung Kwon, Young-Soo Rho, Jin Cheol Jeong, Hyung Sik Shin, Jong Seok Lee, Seong Jin Cho, Eun Sook Nam
Human Pathology.2015; 46(8): 1180. CrossRef - Understanding the roles of the P2X7 receptor in solid tumour progression and therapeutic perspectives
Sébastien Roger, Bilel Jelassi, Isabelle Couillin, Pablo Pelegrin, Pierre Besson, Lin-Hua Jiang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes.2015; 1848(10): 2584. CrossRef - Purinergic signaling pathways in endocrine system
Ivana Bjelobaba, Marija M. Janjic, Stanko S. Stojilkovic
Autonomic Neuroscience.2015; 191: 102. CrossRef - P2X7 receptor stimulates breast cancer cell invasion and migration via the AKT pathway
JIYI XIA, XIAOLAN YU, LI TANG, GANG LI, TAO HE
Oncology Reports.2015; 34(1): 103. CrossRef - Regulation of the P2X7R by microRNA-216b in human breast cancer
Luming Zheng, Xukui Zhang, Feng Yang, Jian Zhu, Peng Zhou, Fang Yu, Lei Hou, Lei Xiao, Qingqing He, Baocheng Wang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2014; 452(1): 197. CrossRef
- Research Progress in the Relationship Between P2X7R and Cervical Cancer
- Development of Six Tumors in a Sebaceus Nevus of Jadassohn: Report of a Case
- Serap Gozel, Melahat Donmez, Noyan Can Akdur, Hulya Yikilkan
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(6):569-574. Published online December 24, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.6.569
- 10,938 View
- 95 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn is a congenital cutaneous hamartoma comprised of multiple skin structures. It has the potential to develop into variety of neoplasms of various epidermal adnexal origins. While multiple tumors may occasionally arise, it is unusual for more than four tumors to arise simultaneously within a single sebaceus nevus. Here in, we report a case of a 70-year-old woman with six neoplastic proliferations including a syringocystadenoma papilliferum, pigmented trichoblastoma, tubular apocrine adenoma, sebaceoma, tumors of follicular infundibulum and superficial epithelioma with sebaceus differentiation arising in a long standing nevus sebaceus on the scalp. Our case is extraordinary because a single nevus sebaceus contained six neoplastic proliferations with differentiation toward the folliculosebaceous-apocrine unit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Melanotrichoblastoma Arising on Nevus Sebaceous: A Rare Occurence
Apaopa J. Thekho, Deepika Uikey, Shanta Passi, V. Ramesh
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2025; 70(2): 105. CrossRef - Co-occurrence of Tubular Apocrine Adenoma and Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum over the Hypogastrium: A Rare Case Report
R Raghunatha Reddy, Mukunda Ranga Swaroop, Yogesh Devaraj, Greeshma Jagadish, Namratha Govindaraju
Clinical Dermatology Review.2025; 9(1): 69. CrossRef - Tumor of follicular infundibulum – reappraisal in a series of 28 patients with critical review of the literature
Michael Wilk, Bettina G. Zelger, Bernhard Zelger
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2024; 22(2): 223. CrossRef - Tumor des follikulären Infundibulums – Neubewertung in einer Serie von 28 Patienten mit kritischer Analyse der Literatur
Michael Wilk, Bettina G. Zelger, Bernhard Zelger
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2024; 22(2): 223. CrossRef - Adnexal neoplasms of the eye
Roman Drozdowski, Jane M. Grant-Kels, Madina Falcone, Campbell L. Stewart
Clinics in Dermatology.2024; 42(4): 321. CrossRef - Melanotrichoblastoma: sixth case report in the literature
Juliana Polizel Ocanha-Xavier, José Cândido Caldeira Xavier-Júnior
Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia.2023; 98(6): 871. CrossRef - Multiple secondary neoplasms in nevus sebaceus excision
Travis S. Dowdle, David A. Mehegran, Dylan Maldonado, Cort D. McCaughey
Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings.2022; 35(2): 241. CrossRef - Congenital tumors arising from nevus sebaceous in 2 neonates
Lynette Wei Yi Wee, Bori Born, Sharon Mun Yee Wong, Hui-Ling Chia, Sithach Mey, Suresh Chandran, Mark Jean Aan Koh
JAAD Case Reports.2022; 21: 70. CrossRef - Development of seven secondary neoplasms in a nevus sebaceous: a case report and literature review
Yi-Wen Kuo, Jung-Chia Lin, Wei-Hsuan Tsai
Archives of Craniofacial Surgery.2022; 23(2): 83. CrossRef - Multiple rare neoplasms arising from the nevus sebaceous of the scalp: A case report
Deepthi Shetty, Anilkumar Desai, Niranjan Kumar, Dinesh U.S., Aditya Agnihotri, Saurav Bhaduri
Gulhane Medical Journal.2022; 64(2): 197. CrossRef - Syringocystadenoma Papilliferum and Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising in Nevus Sebaceous
Jingjing Jiang, Yujuan Chen, Qi He, Jiao Yang, Zhengzhong Zhang, Hao Yang, Huan Zhang, Chuan Yang
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology.2022; Volume 15: 2021. CrossRef - Eyelid trichoblastoma – A case series
Gunja Chowdhury, Meghana Tanwar, Usha Kim, Shanthi R. Krishnan
Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology and Research.2021; 9(3): 123. CrossRef - Trilogy Revisited
Anand Bardia, Debajyoti Chatterjee, Keshavamurthy Vinay
Indian Dermatology Online Journal.2021; 12(4): 577. CrossRef - Trichilemmoma coexisting with sebaceous nevus
AngooriG Rao, VangaliS Reddy, M Tejal, M Divya
Indian Dermatology Online Journal.2020; 11(2): 253. CrossRef - Syndromic sebaceous nevus: current findings
Oumama El Ezzi, Anthony S. de Buys Roessingh, Michèle Bigorre, Guillaume Captier
International Journal of Dermatology.2018; 57(5): 599. CrossRef - Syringocystadenoma papilliferum and trichoblastoma arising in the nevus sebaceous
Feifei Wang, Yatong Wu, Zhancai Zheng, Yanping Bai
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2018; 61(1): 106. CrossRef - Dermoscopic Analysis of Nevus Sebaceus of Jadassohn: A Study of 13 Cases
Awatef Kelati, Hanane Baybay, Salim Gallouj, Fatima Zahra Mernissi
Skin Appendage Disorders.2017; 3(2): 83. CrossRef - Secondary neoplasms arising from nevus sebaceus: A retrospective study of 450 cases in Taiwan
Ming‐Chun Hsu, Jau‐Yu Liau, Jin‐Liern Hong, Yin Cheng, Yi‐Hua Liao, Jau‐Shiuh Chen, Yi‐Shuan Sheen, Jin‐Bon Hong
The Journal of Dermatology.2016; 43(2): 175. CrossRef - A Histological Snapshot of Hypothetical Multistep Progression From Nevus Sebaceus to Invasive Syringocystadenocarcinoma Papilliferum
Vishwas Parekh, Cesar E. Guerrero, Charles F. Knapp, Craig A. Elmets, Kristopher M. McKay
The American Journal of Dermatopathology.2016; 38(1): 56. CrossRef - Trichoblastoma, syringocystadenoma papilliferum, desmoplastic trichilemmoma and tumor of the follicular infundibulum with signet‐ring cells, all arising in nevus sebaceus
Emilie Dore, Megan H. Noe, Brian L. Swick
Journal of Cutaneous Pathology.2015; 42(9): 645. CrossRef - Ceruminous adenoma (ceruminoma) arising in a nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn within the external auditory canal of a 3 year-old boy – A case report
Elżbieta Niemczyk, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Jadwiga Małdyk, Lidia Zawadzka-Głos
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology.2015; 79(11): 1932. CrossRef - Fehlbildungen und Nävi des behaarten Kopfes
V. Behle, H. Hamm
Der Hautarzt.2014; 65(12): 1022. CrossRef
- Melanotrichoblastoma Arising on Nevus Sebaceous: A Rare Occurence
- Cytological Findings of the Micropapillary Variant of Urothelial Carcinoma: A Comparison with Typical High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma
- Kyu-Ho Kim, Chang-Hwan Choi, Jee-Young Han, Lucia Kim, Suk-Jin Choi, In-Suh Park, Joon-Mee Kim, Young-Chae Chu
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(4):365-371. Published online August 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.365
- 8,524 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Background Micropapillary variant of urothelial carcinoma (MPUC) showed distinct pathologic features and aggressive behavior. The cytologic findings of MPUC are still indistinct. In this study, we evaluated the cytological findings of MPUC compared with those of high-grade urothelial carcinoma (HGUC).
Methods The voided urine cytology of 8 cases of MPUC and 8 cases of HGUC was reviewed. Following cytological parameters were evaluated: cellularity, background, number of small, tight papillary clusters, small acinar structure, scattered single cells, cytoplasmic features, nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, nuclear pleomorphism, nuclear membrane irregularity, hyperchromasia, chromatin pattern and nucleoli.
Results Compared to that of HGUC, cytology of MPUC showed large numbers of small, tight papillary clusters, small acinar structure, few numbers of single cells, and hyperchromatic nuclei. Other parameters were similar between the two groups; both groups showed similar cellularity, dense or vacuolated cytoplasm, moderate to severe nuclear pleomorphism, irregular nuclear membrane, coarse granular chromatin, and small and prominent nucleoli.
Conclusions The urine cytology of MPUCs showed smaller and tighter papillary cell clusters, more small acinar structures, fewer numbers of scattered single cells, and more hyperchromatic nuclei than that of HGUC. These features can help to distinguish MPUC and HGUC and offer an early cytological diagnosis of MPUC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytologic features of micropapillary variant urothelial carcinoma in urinary tract cytology: Case series and review of literature
Nancy Y. Greenland, Yue Peng, Poonam Vohra, Z. Laura Tabatabai
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyto-histo correlations of plasmacytoid and micropapillary variants of high-grade urothelial carcinoma: do they fit well in The Paris System for reporting urinary cytology?
Liye Suo, Ivonne Vega, Michael Thrall
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2021; 10(1): 20. CrossRef - A case report of urothelial carcinoma with combined micropapillary and plasmacytoid morphology in the urinary bladder
Sanghui Park, Min‐Sun Cho, Kwang Hyun Kim
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2016; 44(2): 124. CrossRef - Two cases with the micropapillary variant of urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder
Akiko KAGOTANI, Mitsuaki ISHIDA, Muneo IWAI, Nozomi IWAMOTO, Nozomi KASUGA, Yuji HAYASHI, Yoshimitsu MIYAHIRA, Ryoji KUSHIMA
The Journal of the Japanese Society of Clinical Cytology.2016; 55(3): 165. CrossRef
- Cytologic features of micropapillary variant urothelial carcinoma in urinary tract cytology: Case series and review of literature
- A Case of Multifocal Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Consisting of One Encapsulated Follicular Variant with
BRAF K601E Mutation and Three Conventional Types withBRAF V600E Mutation - Wook Youn Kim, Young Sin Ko, Tae Sook Hwang, Hye Seung Han, So Dug Lim, Wan Seop Kim, Seo Young Oh
- Korean J Pathol. 2013;47(3):293-298. Published online June 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.3.293
- 10,510 View
- 51 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Multifocal papillary thyroid carcinoma (mPTC) comprises about 20-30% of PTC. In mPTC, individual tumor foci can be identical or frequently composed of different histological types including follicular, solid, tall-cell or conventional patterns. We report a case of mPTC consisting of one encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma (FVPTC) and three conventional PTCs in a 44-year-old woman. This case genetically demonstrates unique features including the simultaneous presence of the
BRAF V600E (T1799A) mutation and theBRAF K601E (A1801G) mutation in conventional PTC and FVPTC, respectively.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- BRAF K601E Mutation in Oncocytic Carcinoma of the Thyroid: A Case Report and Literature Review
Antonio Matrone, Fabrizia Citro, Carla Gambale, Alessandro Prete, Elisa Minaldi, Raffaele Ciampi, Teresa Ramone, Gabriele Materazzi, Liborio Torregrossa, Rossella Elisei
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(22): 6970. CrossRef - Case of aggressive metastatic follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma with BRAF K601E and BCORL1 mutations
Doaa Attia, Alexander Lurie, Qihui Zhai, Thomas Mesko, Robert Smallridge
BMJ Case Reports.2020; 13(6): e234208. CrossRef - BRAF gene: From human cancers to developmental syndromes
Muhammad Ramzan Manwar Hussain, Mukhtiar Baig, Hussein Sheik Ali Mohamoud, Zaheer Ulhaq, Daniel C. Hoessli, Ghaidaa Siraj Khogeer, Ranem Radwan Al-Sayed, Jumana Yousuf Al-Aama
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2015; 22(4): 359. CrossRef - Clinical significance of BRAF V600E mutation in 154 patients with thyroid nodules
LINGYING YU, LIZHEN MA, QIAOFENG TU, YI ZHANG, YUEMING CHEN, DAOJUN YU, SHAOYU YANG
Oncology Letters.2015; 9(6): 2633. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Features of Rare BRAF Mutations in Korean Thyroid Cancer Patients
Uiju Cho, Woo Jin Oh, Ja Seong Bae, Sohee Lee, Young Sub Lee, Gyeong Sin Park, Youn Soo Lee, Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(8): 1054. CrossRef - Recurrent Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma in Children Under Ten Years Old: Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Byeong-Joo Noh, Ji-Youn Sung, Youn-Wha Kim, Yong-Koo Park
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(4): 297. CrossRef - Anaplastic Transformation of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in a Young Man: A Case Study with Immunohistochemical andBRAFAnalysis
Ji Hye Park, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Cheong Soo Park, SoonWon Hong
Korean Journal of Pathology.2014; 48(3): 234. CrossRef
- BRAF K601E Mutation in Oncocytic Carcinoma of the Thyroid: A Case Report and Literature Review

 E-submission
E-submission


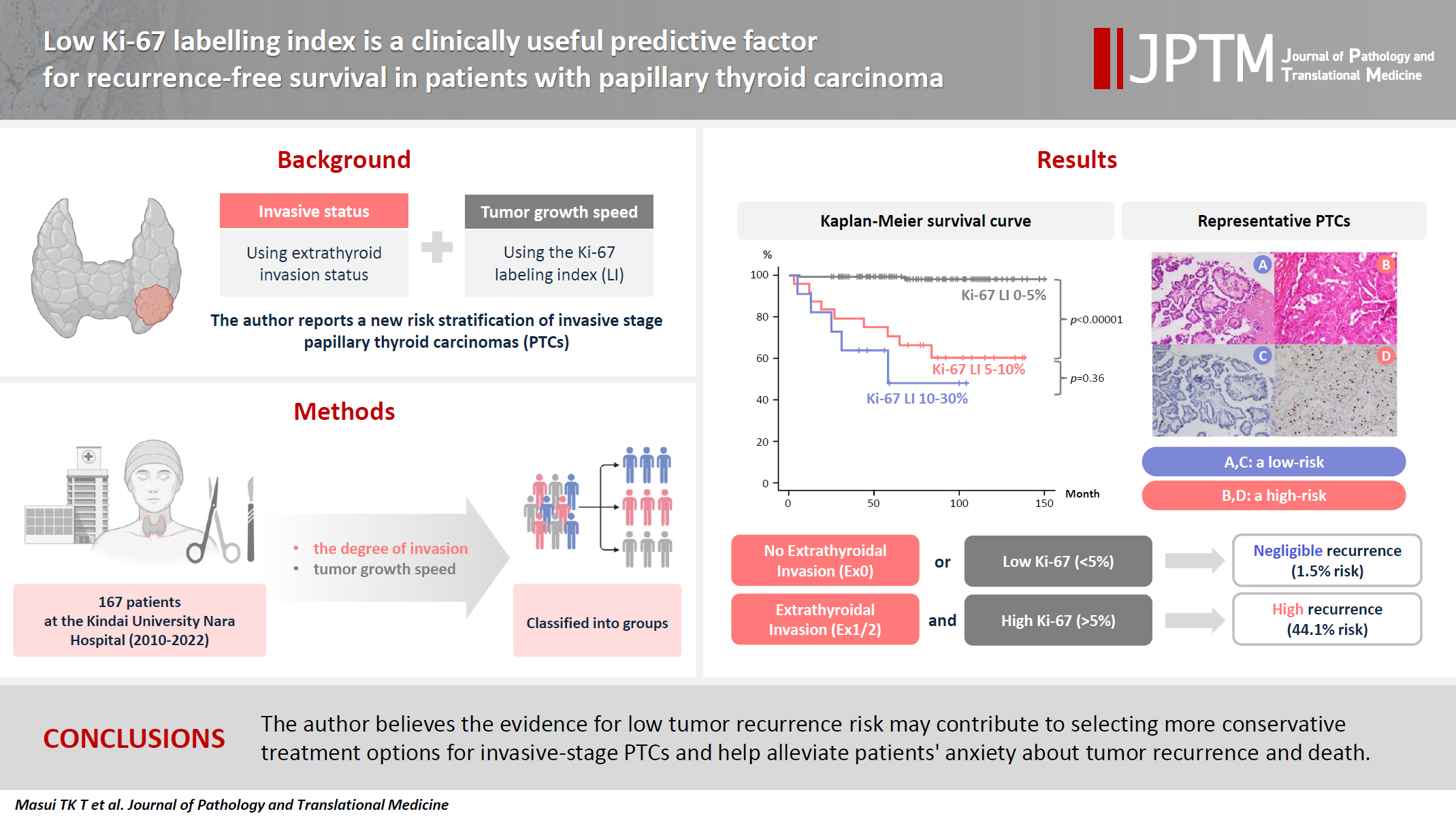

















 First
First Prev
Prev



